- 1Department of Nursing, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 2Department of Medical Oncology, Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Intervention, Ministry of Education, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 3Zhejiang Provincial Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Hangzhou, China
- 4Cancer Center of Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
- 5Center for Medical Research and Innovation in Digestive System Tumors, Ministry of Education, Hangzhou, China
- 6School of Renji Medical Sciences, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have revolutionized cancer therapy, but immune-related hypersensitivity reactions remain a clinical concern. Cadonilimab, a novel PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody, has demonstrated encouraging antitumor efficacy across various solid tumors; however, hypersensitivity or infusion-related reactions may occasionally occur.
Methods: We herein report five cases of cadonilimab-induced allergic or infusion-related reactions in patients with different advanced solid tumors. Clinical manifestations ranged from mild skin rash to severe anaphylaxis with hypotension. All patients were managed promptly with individualized anti-allergic interventions, and some were able to safely continue therapy with modified infusion protocols.
Results: The series emphasizes the importance of early identification and tailored management of hypersensitivity reactions during cadonilimab treatment. Additionally, a comprehensive literature review was conducted summarizing current clinical trials, case reports, and real-world evidence regarding cadonilimab’s efficacy and safety across multiple cancer types.
Conclusion: Our findings highlight both the potential risks and manageable nature of cadonilimab-induced hypersensitivity, supporting its continued clinical application with appropriate monitoring and management strategies.
Introduction
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 pathways have dramatically improved clinical outcomes across a variety of malignancies (1–4). Cadonilimab (AK104), a novel bispecific antibody simultaneously targeting PD-1 and CTLA-4, has received regulatory approval in China for the treatment of several advanced solid tumors (5). While cadonilimab is generally well tolerated, infusion-related hypersensitivity or anaphylactic reactions may occur in some patients, presenting unique clinical management challenges (6).
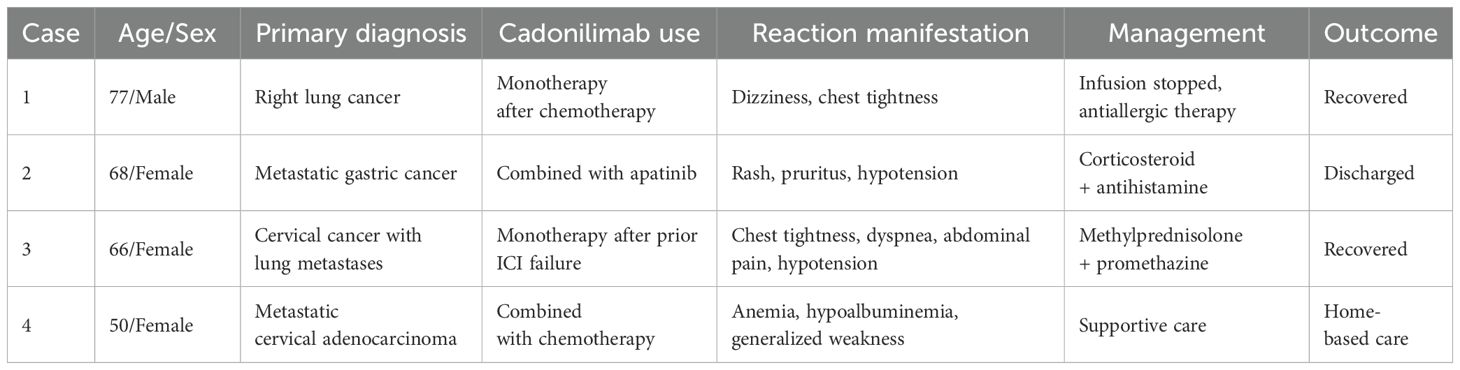
In this study, we report a series of four patients who experienced infusion-related hypersensitivity reactions following cadonilimab administration across different tumor types (Table 1). We systematically summarize the clinical presentations, management strategies, and outcomes of these cases. Additionally, we provide a comprehensive literature review of cadonilimab’s clinical development, encompassing published clinical trials, case reports, and real-world studies to offer further context on the safety profile and clinical efficacy of this novel bispecific antibody.
Case presentations
Case 1
A 77-year-old male was diagnosed with right lung cancer (cT3NxM1) in November 2021. He underwent two courses of six-cycle chemotherapy with stable disease (SD) initially and progressive disease (PD) subsequently. In November 2022, cadonilimab was introduced every three weeks. After receiving three cycles, the patient reported intolerance and switched to serplulimab therapy. Additionally, radioactive seed implantation was performed once. On June 26, 2023, during the cadonilimab infusion period, the patient experienced dizziness and chest tightness suggestive of an infusion reaction. The infusion was discontinued, antiallergic management was initiated, and the patient recovered promptly.
Case 2
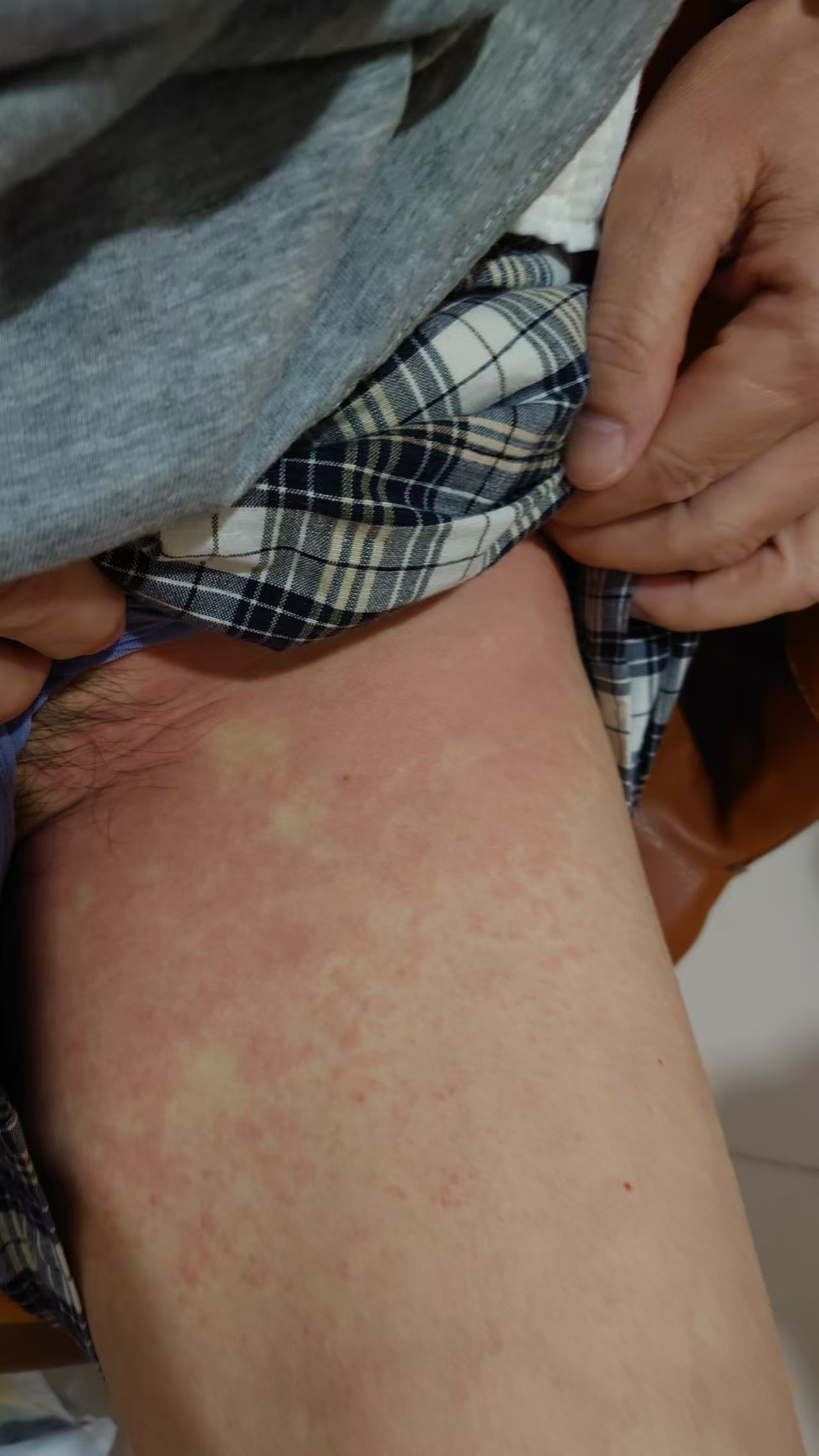
A 68-year-old female presented with gastric cardia adenocarcinoma with extensive metastases to the bone, liver, lymph nodes, and pelvic muscles. Initial treatment included six cycles of oxaliplatin (150 mg on day 1), S-1 (40 mg), and nivolumab (340 mg on day 1 every 3 weeks [d1 q3w]), resulting in partial response (PR). Subsequent progression occurred in June 2023 after 11 months of progression-free survival. On July 28, 2023, she initiated capecitabine (0.5 g once daily [qd] + 1 g once daily [qd] on days 1–14) combined with cadonilimab (375 mg on day 1 every 3 weeks [d1 q3w]) and apatinib. During the second cycle on September 11, 2023, she developed diffuse rash, pruritus, and hypotension (Figures 1, 2), with a significant drop in blood pressure. Immediate management included dexamethasone 10 mg intravenous (IV), methylprednisolone 40 mg intravenous (IV), intravenous fluids, and supportive therapy. Her condition stabilized, and she was discharged in stable condition.
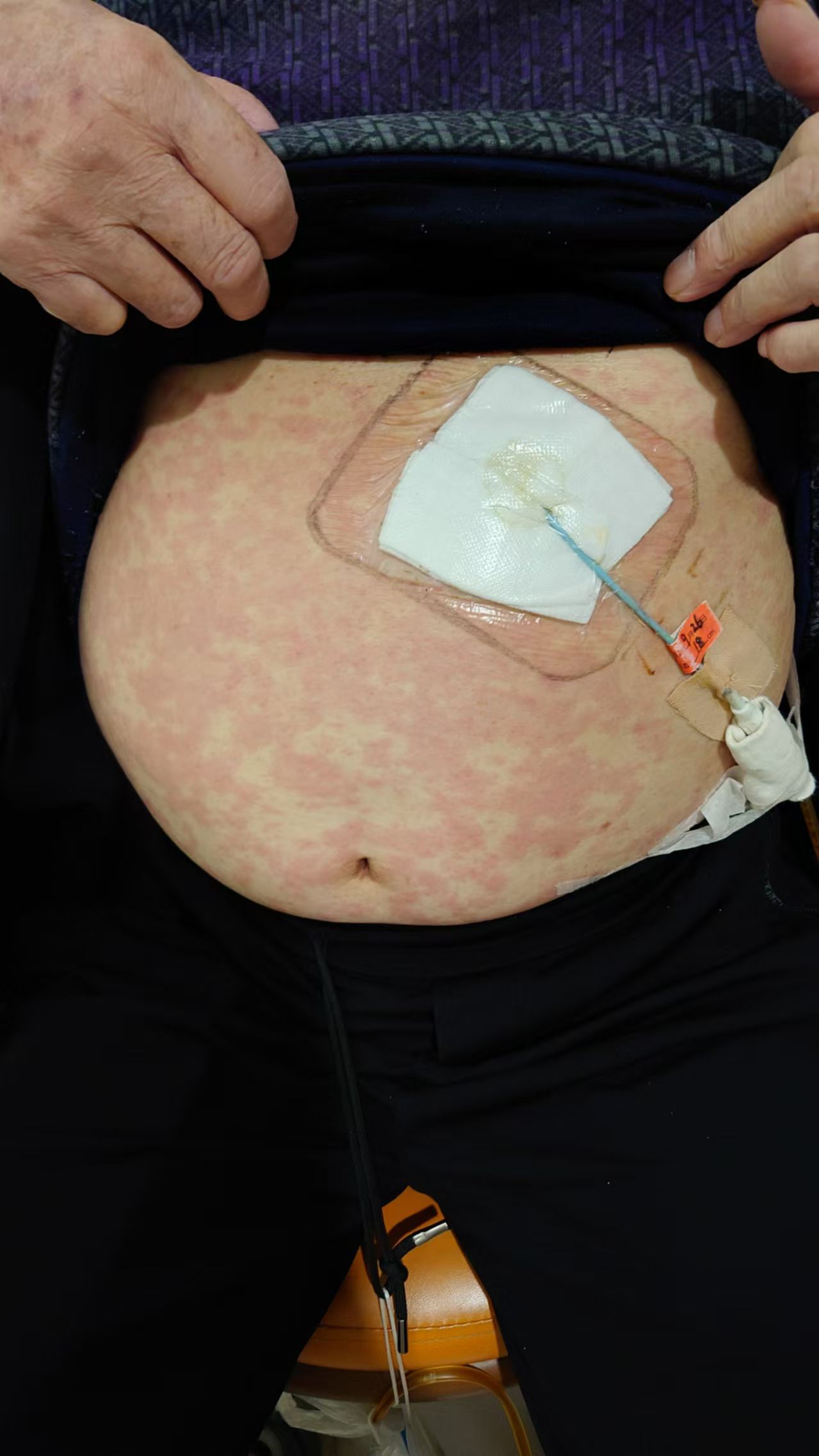
Figure 2. Skin reaction with erythema and pruritus at the infusion site during cadonilimab treatment.
Case 3
A 66-year-old female with cervical squamous carcinoma and lung metastases had previously received multiple treatment regimens, including paclitaxel, carboplatin, pembrolizumab, and anlotinib. Following disease progression, cadonilimab 250 mg was initiated. On September 26, 2023, during the infusion, she developed chest tightness, dyspnea, abdominal pain, and hypotension. Emergency management included methylprednisolone 40 mg intravenous (IV), promethazine 12.5 mg intramuscular (IM), dexamethasone 5 mg IV, and fluid resuscitation. The patient recovered promptly and remained clinically stable thereafter.
Case 4
A female patient diagnosed with metastatic cervical adenocarcinoma in 2024 received on March 22, 2025 paclitaxel 240 mg IV over 1 h (premedication: dexamethasone 10 mg IV, diphenhydramine 25 mg IV, famotidine 50 mg IV), followed by carboplatin 550 mg IV over 30 min and cadonilimab 480 mg IV over 1 h. Approximately five minutes into the cadonilimab infusion, she developed facial and generalized erythema with pruritus and hypotension (blood pressure fell from 120/80 mmHg to 85/55 mmHg); post-infusion labs revealed anemia (Hb 61 g/L), elevated inflammatory markers, hypoalbuminemia, and systemic weakness. Rescue treatment with dexamethasone 10 mg IV, methylprednisolone 40 mg IV, promethazine 25 mg IM and intravenous fluids led to rapid symptom resolution. Having tolerated three prior cycles of paclitaxel-based chemotherapy with identical premedication without hypersensitivity—and with this reaction occurring exclusively during cadonilimab infusion—cadonilimab is strongly implicated as the likely trigger. The patient stabilized after treatment but opted for home-based care per personal preference.
Literature review
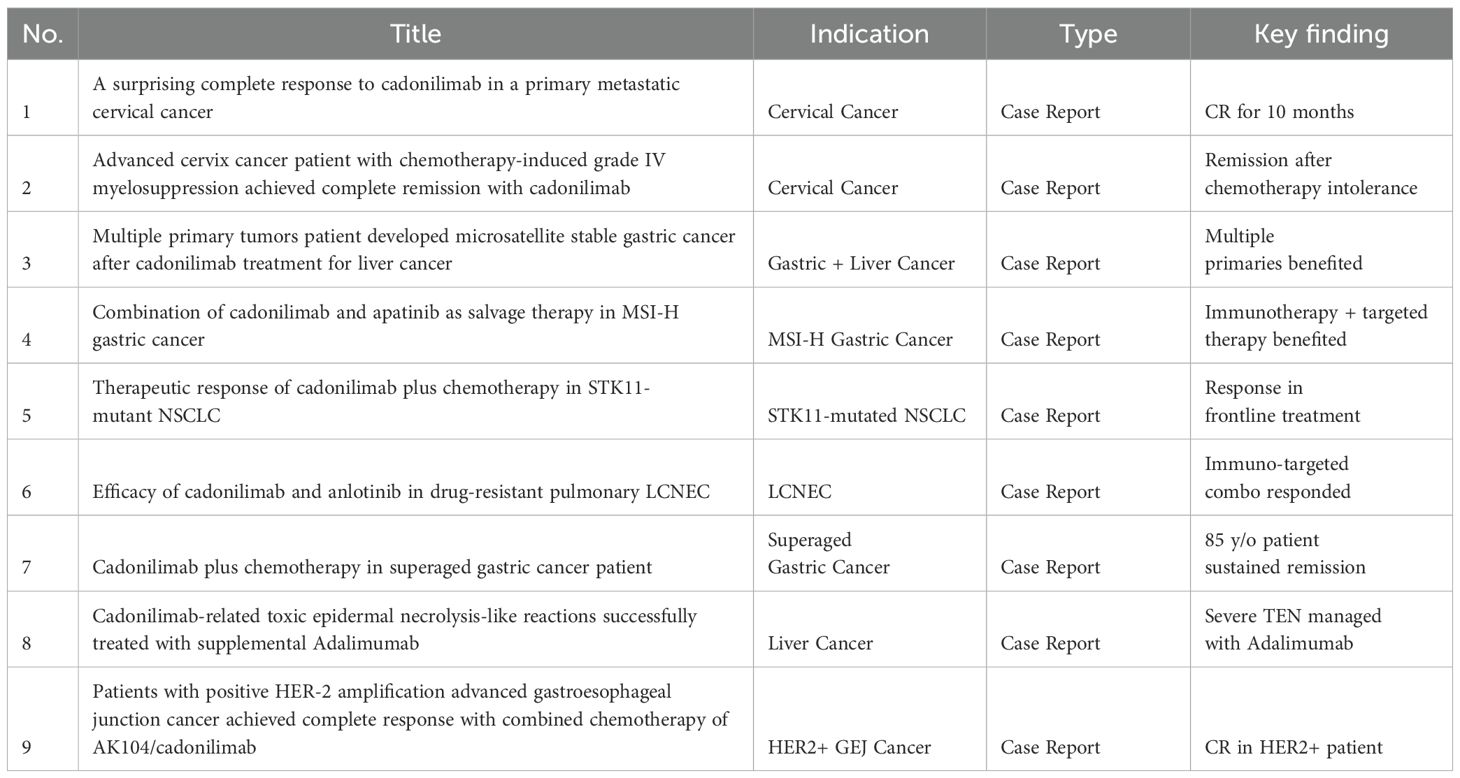
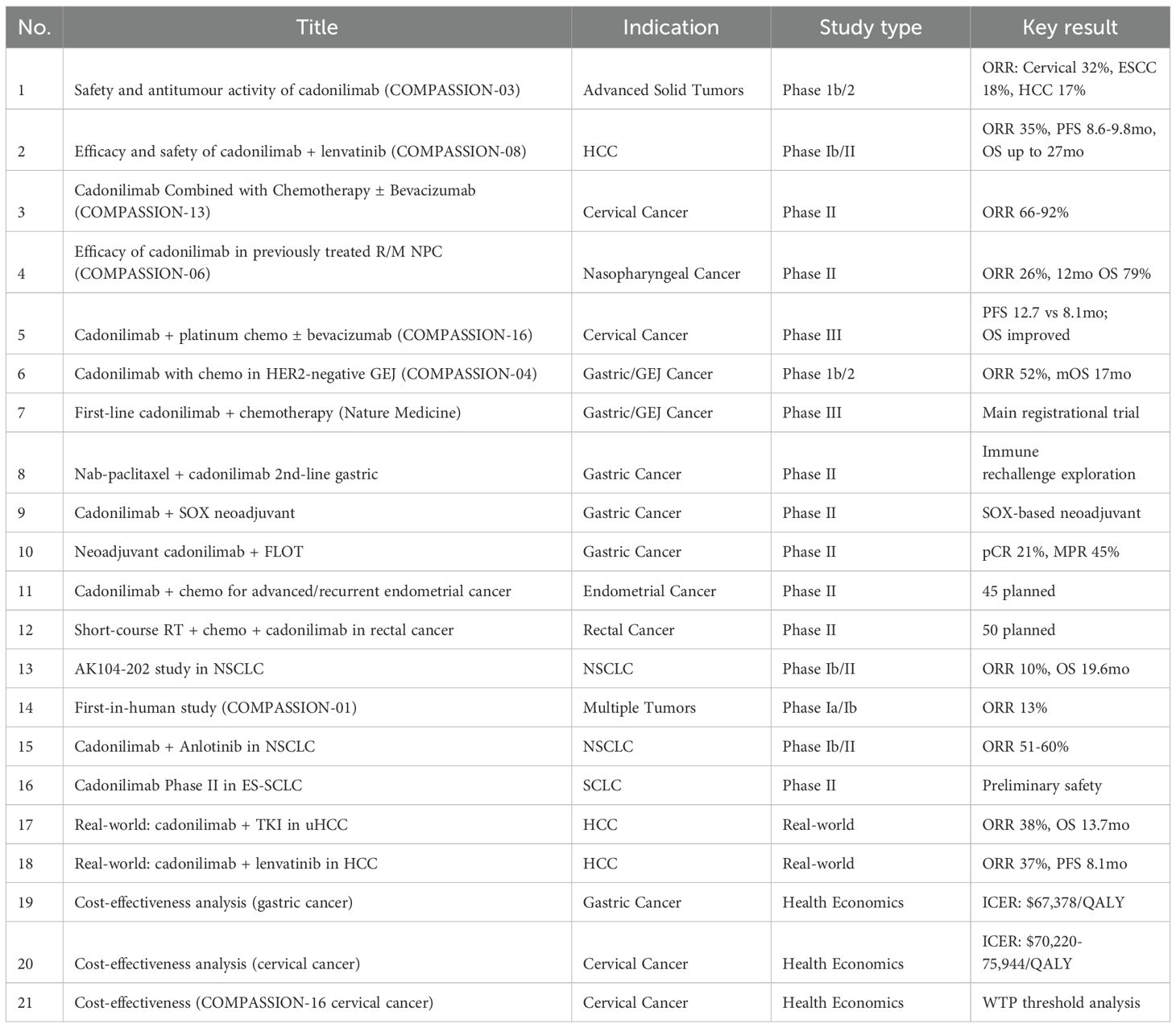
As of June 1, 2025, a search using the keyword “Cadonilimab[Title]” on PubMed yielded 43 publications. Based on this, we systematically reviewed and summarized all available clinical trials and case reports related to cadonilimab (AK104), organizing the data into a comprehensive tabular format (Table 2, Table 3).
Cadonilimab, a first-in-class bispecific antibody targeting both programmed death-1 (PD-1) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4), has undergone extensive clinical development in a wide range of solid tumors, demonstrating broad-spectrum antitumor activity and manageable safety profiles (7–9).
Currently, based on published clinical studies and case reports, cadonilimab has been explored across multiple tumor types, including gastric/gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer, cervical cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), small cell lung cancer (SCLC), large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC), nasopharyngeal carcinoma, endometrial cancer, and rectal cancer. The available evidence spans phase I to phase III clinical trials, real-world studies, and health economics analyses (data source: systematic literature integration, N=30) (10–13).
In registrational trials, the phase III COMPASSION-16 study established the survival benefit of cadonilimab combined with chemotherapy (± bevacizumab) for patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer, with a progression-free survival (PFS) improvement to 12.7 months (HR = 0.62; NCT04982237) (12, 14). In HER2-negative advanced gastric cancer, the phase 1b/2 COMPASSION-04 trial demonstrated an objective response rate (ORR) of 52.1% and a median overall survival (OS) of 17.5 months (CTR20182027). Additionally, in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, the phase Ib/II COMPASSION-08 trial of cadonilimab combined with lenvatinib achieved an ORR of 35% and a median PFS of 8.6–9.8 months (15).
Real-world evidence and case reports further expanded the application spectrum of cadonilimab in various special patient subgroups (10). Successful treatment outcomes have been reported in patients with MSI-H gastric cancer, HER2-amplified gastric cancer, STK11-mutant NSCLC, PD-1-resistant nasopharyngeal carcinoma, multiple primary malignancies, and super-aged populations. Furthermore, several severe immune-related adverse events (irAEs), such as toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN-like reactions), immune hepatitis, and immune pneumonitis, have also been documented, and most were successfully managed with corticosteroids and biological agents (13).
In summary, cadonilimab demonstrates promising potential for multi-indication development through combination strategies with chemotherapy and targeted agents. Particularly, cadonilimab offers new therapeutic opportunities in traditionally immunotherapy-resistant populations (e.g., HER2-positive, STK11-mutated, and microsatellite stable gastric cancer). Its bispecific structure design may also reduce the incidence of severe immune-related toxicity compared to conventional PD-1 plus CTLA-4 combinations, positioning cadonilimab as a next-generation platform in immune-oncology development.
Discussion
Cadonilimab, a novel PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody, has demonstrated promising antitumor efficacy across multiple solid tumors, including cervical cancer, gastric cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and non-small cell lung cancer. However, as with other immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), cadonilimab carries the risk of immune-related adverse events (irAEs), including rare but potentially life-threatening hypersensitivity or infusion-related reactions. Owing to its bispecific structure, cadonilimab may theoretically exhibit more complex immune activation and hypersensitivity profiles compared to monospecific PD-1 or CTLA-4 inhibitors (5, 16, 17).
Furthermore, although we initially considered the delayed onset of infusion reactions after the second or third dose to be inconsistent with a true allergic mechanism, this interpretation may be oversimplified. Indeed, a true IgE-mediated or T-cell–mediated allergic response can manifest with rapid symptoms after the second or subsequent exposures, as prior sensitization may prime the adaptive immune response. Therefore, the occurrence of rapid-onset hypersensitivity reactions after multiple infusions of cadonilimab in our series could still be compatible with a true allergic mechanism, and warrants further immunological investigation.
In addition, an alternative mechanism involving MRGPRX2-mediated mast cell activation has been proposed for monoclonal antibody–related reactions. This pathway can trigger non–IgE-mediated anaphylactoid responses; however, such reactions are typically more pronounced during the first administration. Since our cases experienced hypersensitivity reactions after several treatment cycles, the role of MRGPRX2 alone may be less likely (18–20). Future in vitro testing of cadonilimab on mast cell degranulation models could help to further clarify its involvement.
Finally, it is important to note that cadonilimab has an Fc-null engineered backbone, which reduces Fc receptor–dependent immune activation and potentially lowers certain immune-related adverse events (16). Nevertheless, this modification does not eliminate the risk of all hypersensitivity or immune-mediated reactions. Therefore, these explanations remain speculative, and caution is warranted in interpreting the comparatively favorable safety profile of cadonilimab without further immunologic confirmation. The occurrence of severe reactions in our patients suggests that other pathways—beyond Fc engagement—may contribute to these infusion-related events, highlighting the need for close monitoring and mechanistic research.
Although paclitaxel is a recognized cause of infusion-related hypersensitivity, several lines of evidence in this patient argue against it being the culprit. First, the paclitaxel infusion (preceded by standard dexamethasone, diphenhydramine, and famotidine premedication) was completed uneventfully, and the acute reaction began only after cadonilimab infusion commenced. Second, the patient had previously tolerated three cycles of paclitaxel-based chemotherapy with identical premedication without any hypersensitivity. Third, the rapid onset of rash, pruritus, and hypotension—within 5 minutes of starting cadonilimab—is more consistent with reactions reported for PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibodies than with classical paclitaxel reactions (21). Taken together, these observations strongly implicate cadonilimab rather than paclitaxel as the primary trigger in Case 4.
The clinical spectrum of hypersensitivity reactions in our patients was heterogeneous, ranging from mild cutaneous manifestations (rash, pruritus) to more severe systemic symptoms, including hypotension, dyspnea, and gastrointestinal discomfort (Table 4). Notably, one patient experienced hypotension without loss of consciousness, while others displayed combinations of multisystem involvement. This variability underscores the importance of early recognition and prompt intervention. In all cases, immediate interruption of infusion and initiation of anti-allergic therapy successfully stabilized patients, preventing further clinical deterioration (22, 23).
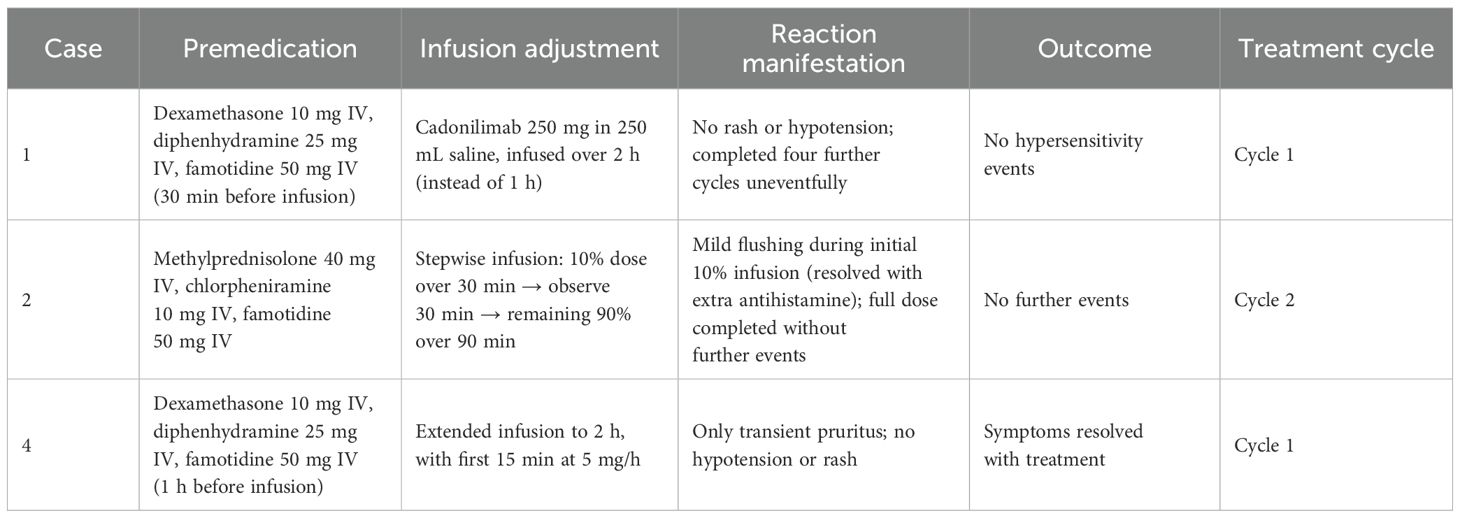
Table 4. Premedication, infusion adjustments, and outcomes of cadonilimab rechallenge in hypersensitivity cases.
Importantly, three patients in our series were able to resume cadonilimab therapy following the initial hypersensitivity event. Reintroduction was achieved either through reduced infusion rates, corticosteroid and antihistamine premedication, or modified dosing schedules. This experience aligns with previously reported desensitization and rechallenge strategies for other ICIs, suggesting that hypersensitivity events do not invariably necessitate permanent discontinuation of therapy, particularly when clinical benefit remains substantial.
In addition to the infusion-related hypersensitivity reactions observed in our reported cases, severe immune-related adverse events (irAEs) associated with cadonilimab have also been documented in the literature (24). For example, a recently published case reported toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)-like reactions induced by cadonilimab in a hepatocellular carcinoma patient receiving combination therapy, which were successfully managed with supplemental adalimumab. This case highlights that although cadonilimab’s Fc-null structure is designed to reduce immune activation, significant irAEs can still occur and warrant careful monitoring and prompt intervention. Our case series, together with these reports, suggests that both immediate-type hypersensitivity reactions and delayed immune-related toxicities should be considered as part of the safety profile of cadonilimab. Further pharmacovigilance and mechanistic studies are needed to elucidate risk factors and optimal management strategies for these events.
As cadonilimab continues to expand its clinical indications across diverse tumor types and treatment settings, hypersensitivity reactions warrant heightened clinical awareness. Proactive risk stratification, early symptom recognition, and well-prepared management protocols are critical to ensuring both patient safety and therapeutic continuity (3, 25). Moreover, larger prospective studies are needed to elucidate the underlying immunopathogenesis of cadonilimab-induced hypersensitivity and to establish evidence-based desensitization or prophylactic algorithms for high-risk patients.
Conclusion
Cadonilimab-induced hypersensitivity reactions present clinical challenges requiring multidisciplinary management. With increasing clinical application, heightened vigilance, prompt intervention, and individualized rechallenge strategies may allow continued benefit from immunotherapy in select patients.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the ethics committee of The Second Affiliated Hospital ZheJiang University School of Medicine. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
PS: Methodology, Data curation, Validation, Writing – original draft. YJ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Data curation. LF: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. FY: Resources, Writing – review & editing. YT: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Supervision, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82102708 and 82373415), Zhejiang Provincial Clinical Research Center for Cancer (2022E50008, 2024ZY01056), Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation (Grant No. Y-tongshu2021/ms-0003), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LQ22H160045), National College Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (202410343036), and two projects from the National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, Hospital Management Research Institute (DSZ20251002 and DSZ20251073).
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients for their participation and consent.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Generative AI Statement The author(s) confirm that generative AI tools were used solely to assist in language editing, grammar checking, and stylistic refinement during manuscript preparation. No AI tools were used for data analysis, scientific reasoning, study design, interpretation of results, or drawing conclusions. All AI-assisted content was carefully reviewed, verified, and approved by the authors, who take full responsibility for the integrity, accuracy, and originality of the manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Subbiah V, Gouda MA, Ryll B, Burris HA, and Kurzrock R. The evolving landscape of tissue-agnostic therapies in precision oncology. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:433–52. doi: 10.3322/caac.21844
2. Chen QY, Guo SS, Luo Y, Qu S, Wu DH, Chen XZ, et al. Efficacy and safety of cadonilimab in previously treated recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma(COMPASSION-06): A phase II multicenter study. Oral Oncol. (2024) 151:106723. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2024.106723
3. Zhou Y, Tao L, Qiu J, Xu J, Yang X, Zhang Y, et al. Tumor biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis and targeted therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:132. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01823-2
4. Noori M, Jafari-Raddani F, Davoodi-Moghaddam Z, Delshad M, Safiri S, and Bashash D. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in gastrointestinal Malignancies: An umbrella review. Cancer Cell Int. (2024) 24:10. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03183-3
6. Li H, Zhao W, Li C, Shen H, Li M, Wang C, et al. The efficacy and safety of a novel PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody cadonilimab (AK104) in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A multicenter retrospective observational study. Thorac Cancer. (2024) 15:2327–38. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15455
7. Zhao J, Li X, Sun X, Xiao R, Xue J, Sui K, et al. Combination of cadonilimab (PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody) and apatinib as salvage therapy achieves partial response in MSI-H advanced gastric cancer: A case report. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1533700. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1533700
8. Yu H, Lin J, Chen J, Chen L, Zou J, Liu B, et al. A surprising complete response to cadonilimab in a primary metastatic cervical cancer: A case report. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1494138. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1494138
9. Wang X, Yang K, Yang Y, Wang X, and Yuan K. Immunotherapy rechallenge of advanced lung adenocarcinoma with cadonilimab (PD-1/CTLA-4 bi-specific antibody): A case report. Anti Cancer Drugs. (2024) 35:288–91. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001557
10. Yuan G, Chen Y, Zhu P, Deng Q, Su K, Liu J, et al. Cadonilimab (PD-1/CTLA-4) in combination with lenvatinib in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): A retrospective real-world study. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e37616. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37616
11. Zhou Z, Yang Y, Chen S, and You M. Cost-effectiveness analysis of first-line cadonilimab plus chemotherapy in HER2-negative advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1575627. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1575627
12. Zhou N, Yang L, and Wei W. Vogt-koyanagi-harada-like syndrome after cadonilimab (PD-1/CTLA-4 inhibition) for metastatic uveal melanoma. Ophthalmol Retina. (2024) 8:e48. doi: 10.1016/j.oret.2024.01.015
13. Xiang Z, Li Z, Chen X, and Fu Y. Cadonilimab plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for persistent, recurrent, or metastatic cervical cancer: A cost-effectiveness analysis. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1562875. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1562875
14. Ding Y, Wang C, Shu Y, Wang J, and Zhang Q. Cost-effectiveness analysis of a first-line treatment with cadonilimab plus platinum-based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for persistent, recurrent, or metastatic cervical cancer in China: COMPASSION-16 trial. J Pharm Policy Pract. (2025) 18:2464781. doi: 10.1080/20523211.2025.2464781
15. Qiao Q, Han C, Ye S, Li J, Shao G, Bai Y, et al. The efficacy and safety of cadonilimab combined with lenvatinib for first-line treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (COMPASSION-08): A phase ib/II single-arm clinical trial. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1238667. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1238667
16. Pang X, Huang Z, Zhong T, Zhang P, Wang ZM, Xia M, et al. Cadonilimab, a tetravalent PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody with trans-binding and enhanced target binding avidity. Mabs. (2023) 15:2180794. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2023.2180794
17. Kaplon H, Crescioli S, Chenoweth A, Visweswaraiah J, and Reichert JM. Antibodies to watch in 2023. Mabs. (2023) 15:2153410. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2022.2153410
18. Worrall WPM and Reber LL. Current and future therapeutics targeting mast cells in disease. Pharmacol Ther. (2025), 108892. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2025.108892
19. Ye D, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Zhou H, Guo J, Yang M, et al. MRGPRX2 gain-of-function mutation drives enhanced mast cell reactivity in chronic spontaneous urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2025) S0091-6749(25)305-7. 21. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2025.03.007
20. Bawazir M, Sutradhar S, Roy S, and Ali H. MRGPRX2 facilitates IgE-mediated systemic anaphylaxis in a newly established knock-in mouse model. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2025) 155(3). doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2024.11.021
21. Hellmann MD, Paz-Ares L, Caro RB, Zurawski B, Kim SW, Costa EC, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. (2019). doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910231
22. Muraro A, Worm M, Alviani C, Cardona V, DunnGalvin A, Garvey LH, et al. EAACI guidelines: Anaphylaxis (2021 update). Allergy. (2022) 77:357–77. doi: 10.1111/all.15032
23. Bruhns P and Chollet-Martin S. Mechanisms of human drug-induced anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2021) 147:1133–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.02.013
24. Chen P-Y, Li Z-Y, and Cai S-Q. Case report: Cadonilimab-related toxic epidermal necrolysis-like reactions successfully treated with supplemental adalimumab. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1188523. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1188523
Keywords: cadonilimab, hypersensitivity reaction, infusion-related reaction, immune checkpoint inhibitor, case report, literature review
Citation: Song P, Jin Y, Fu L, Yang F and Tan Y (2025) Case Report: When dual immune checkpoint blockade strikes back: cadonilimab-induced hypersensitivity in solid tumors — a case series and review. Front. Immunol. 16:1643279. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1643279
Received: 08 June 2025; Accepted: 14 July 2025;
Published: 11 August 2025.
Edited by:
Miroslawa Puskulluoglu, Maria Sklodowska-Curie National Research Institute of Oncology, PolandCopyright © 2025 Song, Jin, Fu, Yang and Tan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yinuo Tan, dGFuMHlpMG51b0B6anUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Ping Song
Ping Song Yuqi Jin
Yuqi Jin Linglin Fu6†
Linglin Fu6† Yinuo Tan
Yinuo Tan