- 1Saha Cardiovascular Research Center, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, United States
- 2Lexington VA Healthcare System, Lexington, KY, United States
- 3Department of Physiology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, United States
According to the Surviving Sepsis Campaign, 50.3% of septic shock patients received steroid/glucocorticoid (GC) therapy. However, whether GC therapy is beneficial and who might benefit from it are hotly debated. Initial guidelines recommended GC therapy for septic patients with adrenal insufficiency, but this has since been retracted. Recent studies using animal models of adrenal insufficiency have shed light on the mechanisms, demonstrating that the adrenal stress response is a part of the host response that is essential for control inflammatory response in sepsis and the adrenal insufficiency is a risk factor for sepsis. This perspective review explores the limitations of GC therapy through the lens of GC biology, with a particular focus on the role of scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI) in mediating the adrenal stress response. We highlight the mechanisms of how SR-BI-mediated adrenal stress response contributes to the regulation of hyperinflammation and innate immune responses. By integrating mechanistic insights with the limitations of GC therapy, we advocate for a precision medicine approach to GC therapy in sepsis– selectively applying GC therapy for patients with adrenal insufficiency, not without.
Background
Sepsis is a major cause of mortality and morbidity, affecting 49 million people annually (1). It is caused a dysregulated host response to infection (2). When an infection happens, immune cells recognize the invading microorganism using pattern recognition receptors. This triggers the innate immune system, releasing cytokines, chemokines and nitric oxide, to fight infection. However, hyper activation of the host response causes organ injury, leading to organ dysfunction and death (3, 4).
Despite the significant role of inflammation in organ injury, many trials targeting inflammatory signaling have had little impact on patient survival (5). One potential limitation is that these therapies were applied nonselectively to all septic patients. In reality, septic patients have heterogeneous subtypes; some exhibit a hyperinflammatory response while other show a hypoinflammatory response. Anti-inflammation therapy may benefit those with a hyperinflammatory response but could harm those with a hypoinflammatory response. Additionally, the inflammatory response can shift from hyperinflammation to hypoinflammation depending on the stage of sepsis, requiring timely targeting of the inflammatory response (6). Given the complexity of sepsis, there is a growing call for an endotype-based precision medicine approach for sepsis therapy (7–11). In this translational review, we discuss the potential limitations of steroid/glucocorticoid (GC) therapy for sepsis regarding the target and timing of GC therapy, review the role of scavenger receptor BI (SR-BI)-mediated adrenal stress response in sepsis. By integrating mechanistic insights with the limitations of GC therapy, we advocate for a precision medicine approach to GC therapy in sepsis– selectively applying GC therapy for patients with adrenal insufficiency, not without.
Glucocorticoid, inducible glucocorticoid and adrenal insufficiency in sepsis
GC is produced in adrenal gland and presents in circulation at 20–200 ng/ml at physiological conditions (12). GC has potent activity in regulation of inflammatory response (please refer to review article for mechanism of GC regulation of inflammatory signaling (13)). A lack of physiological levels of GC is lethal without treatment, as shown in patients with Addison’s disease and in mice undergoing adrenalectomy (14). GC acts through its receptor, glucocorticoid receptor (GR) (15). Mice lacking GR in macrophage, endothelial, dendritic, or T cells are susceptible to sepsis (16–19). These early studies clearly demonstrated critical protective roles of GC-GR signaling in sepsis.
A striking feature of GC in sepsis is its inducible nature. GC production is rapidly upregulated by 5-10-fold in response to septic stress (20). We call this inducible or induced GC (iGC) (8, 9, 21). Importantly, iGC is closely related to a common condition/phenotype in septic patients, called relative adrenal insufficiency (RAI). Patients with RAI have insufficient iGC production in response to stress, which is diagnosed by a delta total cortisol of < 9µg/dL post-ACTH stimulation (22). 25-60% of septic patients develop RAI (15, 22–24). Numerous clinical studies showed that RAI is associated with a poor prognosis of sepsis (22, 25), but some studies failed to find such correlation (26). Nevertheless, the contribution of RAI, the major type of adrenal insufficiency, to sepsis and the pathogenesis caused by RAI are largely unknown.
In 2008, the term “RAI” was replaced by “critical illness-related corticosteroid insufficiency” (CIRCI) (27). CIRCI is defined by inadequate cellular corticosteroid activity for the severity of the patient’s critical illness. It includes all types of adrenal insufficiency: absolute adrenal insufficiency, RAI and GC resistance. It is diagnosed when a seriously ill patient has very low cortisol levels (less than 10 μg/dl) or a delta cortisol < 9 g/dl upon ACTH stimulation test. Despite some disagreement, the ACTH test is commonly used to diagnose CIRCI (28).
The absolute adrenal insufficiency refers to low plasma cortisol level and is uncommon. GC resistance refers to impaired cellular GC-GR signaling. An early study by Liberty’s group reported genome-wide GC resistance in sepsis (29). In their study, mice were subjected to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) or sham surgery, followed by dexamethasone (DEX) treatment six hours later. RNA sequencing was performed two hours post-treatment to assess gene expression changes. The authors observed no significant gene induction following DEX administration in septic mice and concluded that sepsis induces genome-wide GC resistance. However, several issues in the experimental design and interpretation of the data may undermine this conclusion. At 8 hours post-CLP, mice were under significant septic stress, and endogenous GC levels had already peaked. According to Figure S2 of RNA-seq data, 60% of genes upregulated by DEX in sham mice were also upregulated by CLP alone (227/376 genes), and 68% of genes downregulated by DEX in sham mice were similarly downregulated by CLP alone (113/165 genes). These findings show that GC/GR signaling remains active at this time point, challenging the assertion of genome-wide GC resistance. GC resistance is typically defined as impaired GR signaling despite the presence of GCs. In this context, the relevance of additional GR activation by exogenous DEX, when endogenous GC levels are already maximal, is unclear. To test the hypothesis that early GR activation leads to exhaustion, the authors performed adrenalectomy (ADX) and found that septic ADX mice failed to respond to DEX (Figure S2C). They interpreted this as evidence to support the hypothesis that early HPA axis activation causes GC resistance. However, this experiment is problematic: 90% of ADX mice died within 10 hours post-CLP as indicated in Figure S1C of the article, raising concerns about the validity of RNA-seq data collected just 2 hours before death. Moreover, DEX supplementation rescued septic ADX mice (Figure S1K), which is inconsistent with the presence of functional GR resistance. Another earlier study has also shown that GC supplementation as late as 18 hours post-CLP rescues mice with adrenal insufficiency (30). Given these inconsistencies, the data presented in the article does not convincingly support the conclusion of genome-wide GR resistance in sepsis. While GC resistance has been extensively studied in chronic diseases, it remains an underexplored area in the context of sepsis/critical illness.
As the absolute adrenal insufficiency is less common and no method to diagnose GC resistance in septic patients, we focus on RAI/CIRCI in this review.
GC therapy for sepsis is highly controversial
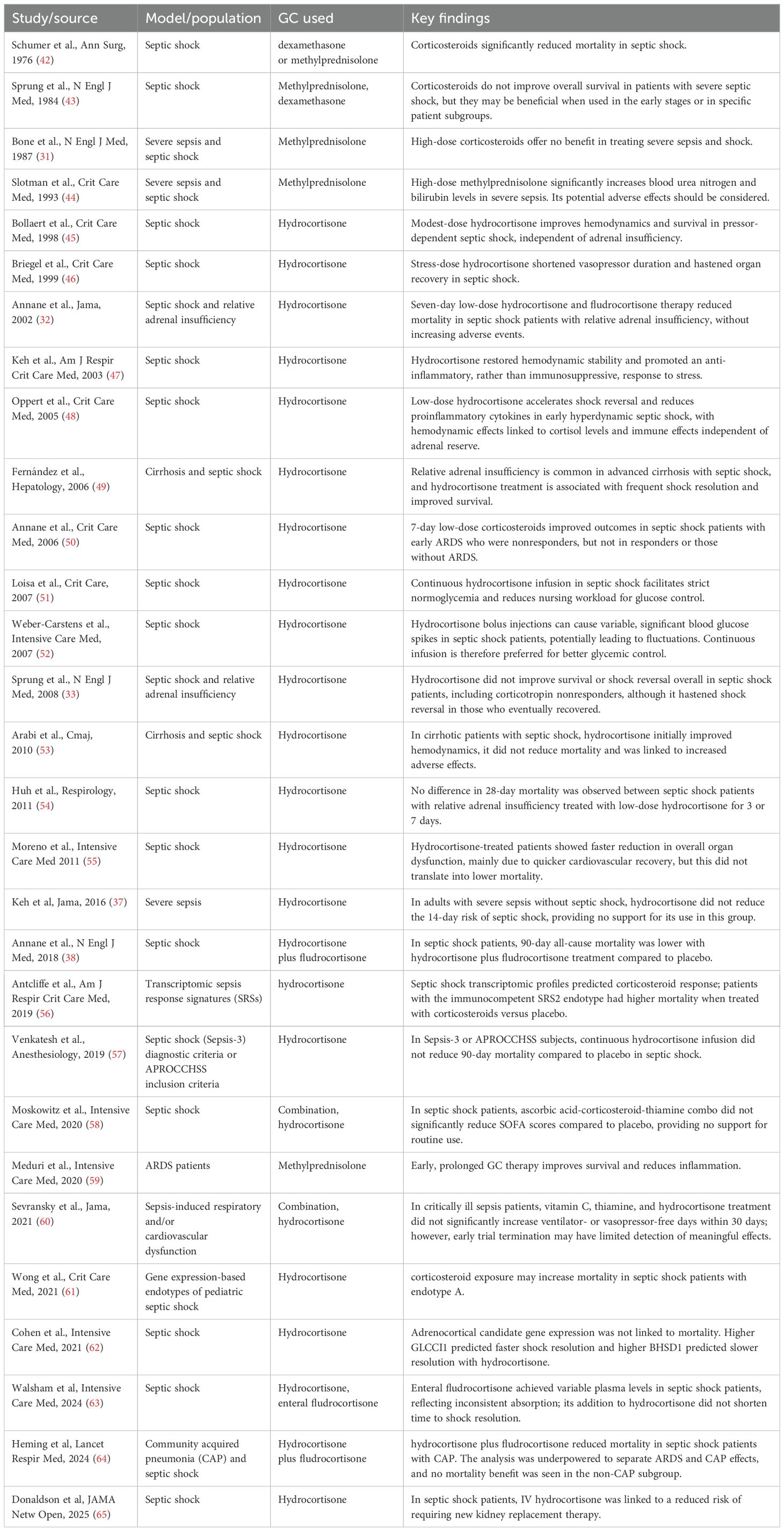
GC therapy has been extensively investigated in septic patients. Early studies using high-dose GC failed to demonstrate a survival benefit (31). Given the high prevalence of relative adrenal insufficiency (RAI) in sepsis, subsequent approaches have focused on administering low-dose GC in septic shock to meet the presumed increased physiological demand (13, 15, 23, 24). The French trial reported a significant reduction in mortality among septic shock patients with RAI who received GC therapy (32). However, the CORTICUS trial, which included a less severely ill cohort, did not replicate these findings (33). Meta-analyses have attempted to reconcile these conflicting results, but conclusions remain inconclusive (34–36). The HYPRESS trial evaluated hydrocortisone in patients with sepsis without shock and found no reduction in the progression to septic shock or improvement in survival within 14 days (37). In contrast, the APROCCHSS trial, which tested a combination of hydrocortisone and fludrocortisone in patients with severe vasopressor-dependent septic shock, demonstrated a significant reduction in both 90- and 180-day mortality (38). The large-scale ADRENAL trial, involving over 3,800 patients with septic shock, did not show a survival benefit from GC therapy (39). Notably, this trial did not stratify patients based on RAI or CIRCI status. Overall, the efficacy of GC therapy in sepsis remains controversial, particularly regarding whether treatment should be tailored based on adrenal function status (40, 41). For a comprehensive overview, refer to Table 1, which summarizes key clinical trials of GC therapy in sepsis.
The Problematic diagnosis of RAI/CIRCI and its implications for GC therapy in sepsis
RAI or CIRCI is defined as “insufficient glucocorticoid (GC) relative to increased physiological demand” or “inadequate cellular corticosteroid activity for the severity of critical illness.” The ACTH stimulation test is widely used to diagnose RAI/CIRCI, but its application in septic patients remains controversial. Several experts have questioned the validity of using the ACTH test in the context of sepsis (72, 73), and the most recent clinical guidelines have not reached a consensus on its utility for diagnosing CIRCI (28). The test is designed to assess the adrenal stress response by measuring inducible GC (iGC) production stimulated by ACTH. While appropriate for non-septic patients, its interpretation in septic patients is problematic. These patients are already under extreme physiological stress and typically exhibit elevated levels of endogenous iGC. In this context, the ACTH test evaluates the incremental adrenal response—referred to as “delta iGC”—on top of an already heightened iGC. This raises critical questions: What is the physiological significance of a low delta iGC (e.g., < 9 μg/dL)? Does it truly reflect “insufficient GC relative to demand”?
To investigate the reliability of the ACTH stimulation test in sepsis, we conducted the test in a murine model of sepsis (74). Strikingly, the ACTH test identified the majority of mice as having adrenal insufficiency during the early and intermediate stages of sepsis—even those with a demonstrably intact adrenal stress response. More concerning, ACTH administration significantly elevated inflammatory cytokine levels to lethal thresholds, resulting in a moderate but measurable increase in mortality. These findings highlight critical flaws in the use of the ACTH test for diagnosing RAI/CIRCI in sepsis. Not only does the test risk misclassifying patients and misguiding GC therapy, but it may also provoke a harmful inflammatory response under septic conditions. This raises the possibility that the inconclusive outcomes of clinical trials on GC therapy may stem not from the ineffectiveness of targeting adrenal insufficiency, but from the flawed diagnostic criteria used to identify it. This underscores the urgent need for a deeper understanding of GC biology in the context of sepsis—particularly the role of the adrenal stress response (iGC production). Mechanistic studies in animal models deficient in iGC production offer a promising avenue to elucidate the precise contribution of adrenal insufficiency to sepsis pathophysiology and to refine therapeutic strategies accordingly.
Scavenger receptor BI protects against sepsis
Scavenger receptor BI (SR-BI) is a membrane protein (75, 76). It is abundantly expressed in liver, endothelial cells and steroidogenic tissues. SR-BI functions as a high-density lipoprotein (HDL) receptor, mediating the uptake of cholesteryl ester from HDL, which is essential for reverse cholesterol transport in the liver. In SR-BI null mice, the deficiency in this receptor leads to elevated HDL levels, female infertility, autoimmune disorders when aging (77), and susceptible to atherosclerosis (78–81). Similarly, humans with loss-of-function mutations in SR-BI also exhibit impaired uptake of cholesteryl esters from HDL, elevated HDL levels, and an increased risk of coronary heart disease (82, 83). This indicates that SR-BI has similar functions in both humans and rodents [please refer to SR-BI review articles (76, 84)].
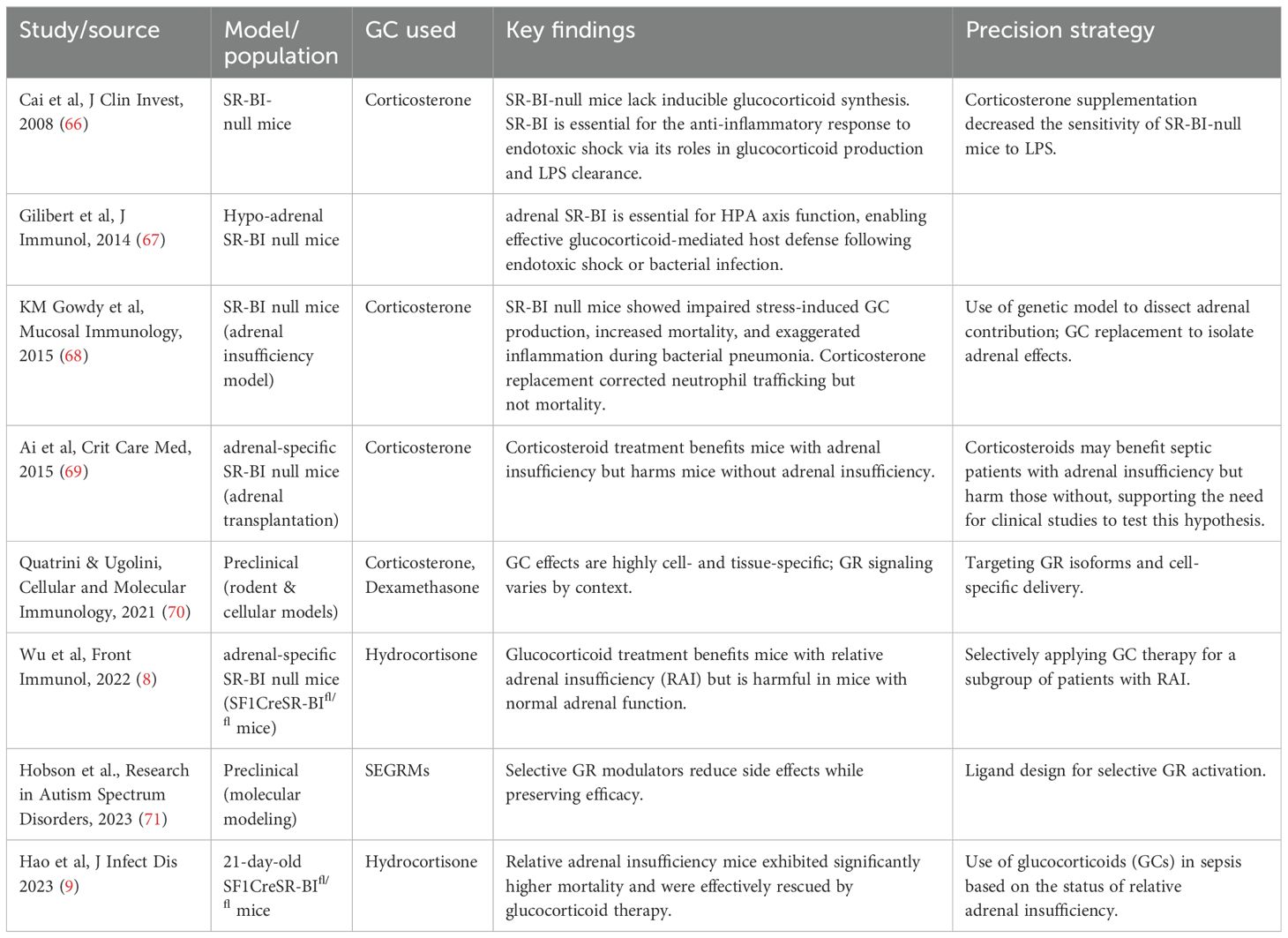
Dr. Li’s laboratory first reported SR-BI as a protective factor in sepsis (85, 86). They reported that LPS induces 90% fatality in SR-BI null mice versus 0% in wild type controls (85), and cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) induces 100% fatality in SR-BI null mice versus 20% in wild type controls (86). Using an LPS model, Dr van der Westhuyzen’s group confirmed the protective role of SR-BI in endotoxemia and showed that SR-BI null mice are susceptible to LPS-induced endotoxic death due to uncontrolled inflammation (66). They further found that SR-BI null mice lack GC production upon ACTH stimulation or LPS challenge and pretreatment of SR-BI null mice with dexamethasone 8 hours prior LPS challenge prevented the mice from LPS induced endotoxic death. Dr. Huby’s group generated adrenal specific SR-BI null (SF1CreHypoSR-BIfl/fl) mice and showed that the mice are more susceptible to CLP-induced septic death than control (HypoSR-BIfl/fl) mice (67). Using a bacterial pneumonia sepsis model (87), Gowdy et al. reported that SR-BI null mice suffer increased mortality associated with higher bacterial burden in the lung and blood, deficient in corticosterone production, higher serum cytokines, and organ injury. SR-BI null mice had significantly increased PMN recruitment and cytokine production in the infected airspace. Early efforts have revealed that SR-BI exerts its protection through multiple mechanisms including preventing nitric oxide-induced cytotoxicity (85), promoting neutrophil recruitment and LPS clearance (66, 86, 87), regulating cholesterol metabolism in liver (88) and suppressing TLR4 signaling in macrophages (86, 89, 90). These early studies establish SR-BI as a multiple protective molecule in sepsis [for detail, please refer to review article (91)].
Scavenger receptor BI-HDL pathway is a key regulator of the adrenal stress response in sepsis
In adrenal gland, GC production is markedly induced in response to septic stress (92). In our previous study, we specifically defined iGC production as an adrenal stress response in sepsis (8). GC is derived from intracellular cholesterol. The intracellular cholesterol comes from three resources: 1) endocytosis from LDL through LDL receptor; 2) up taken from HDL through SR-BI; and 3) de novo synthesis. SR-BI-HDL pathway appears playing an essential role in iGC production. SR-BI null mice maintain normal basal GC levels at physiological conditions, but lack iGC under stress conditions induced by factors like LPS (66), ACTH stimulation (66), cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) (30, 67, 86), or long-term fasting (93, 94). The SR-BI null mice had normal expression in other key genes related to cholesterol de novo synthesis (66). Considering that rodents mainly have HDL with very low LDL in circulation, Dr. Li’s laboratory generated humanized SR-BI-/-ApoBtg mice (SR-BI null mice expressing ApoB) with high LDL in circulation. The mice did not produce iGC in response to ACTH stimulation or under sepsis conditions (95). Regarding the role of SR-BI in human, an early report showed that human carriers SR-BI P297S mutant, which has a 50% reduction in the uptake of cholesterol from HDL, displays a 50% reduction in iGC production to ACTH stimulation (83). In contrast, a 50% reduction in LDL receptor in familial hypercholesterolemia patients does not hinder cholesterol delivery to the adrenal cortex (96). These studies establish SR-BI-HDL pathway as a key regulator of iGC production in sepsis.
Scavenger receptor BI-mediated adrenal stress response is an essential host response against sepsis
As discussed above, SR-BI null mice have normal basal GC levels at physiological conditions, but lack iGC under stress conditions induced by ACTH stimulation (66) or CLP (30, 67, 86). Thus, SR-BI null mice are RAI/CIRCI. Dr. Li’s laboratory generated adrenal specific SR-BI null mice by adrenal transplantation and used the mice as the first RAI animal model to determine if GC therapy benefits mice with RAI (30). They demonstrated that mice deficient in adrenal SR-BI lack iGC production in response to CLP challenge and are more susceptible to CLP-induced septic death and kidney injury. Importantly, GC treatment 2- and 18-hours post CLP effectively rescued adrenal specific SR-BI null mice. Interestingly, GC treatment caused more death in wild type, which was associated with lower plasma IL-6 levels and higher bacterial load in the blood and in the peritoneal fluid, suggesting immunosuppression in GC-treated wildtype mice.
Considering that the adrenal transplantation may disrupt catecholamine production by adrenal gland, Dr. Li’s laboratory generated adrenal specific SR-BI null (SF1CreSR-BIfl/fl) mice using new floxed SR-BI mice (8, 97). The SF1CreSR-BIfl/fl mice were deficient in adrenal SR-BI expression but had normal SR-BI expression in other tissues. Using this new SF1CreSR-BIfl/fl mice, they showed that adrenal SR-BI-specific knockout mice have impaired iGC production in response to ACTH stimulation and to CLP-induced sepsis. They demonstrated that while both wild-type and RAI mice exhibit a hyperinflammatory phenotype in the early stage of sepsis, iGC keeps the inflammatory response under control in wild-type mice. However, RAI mice experience uncontrolled hyperinflammation due to a lack of iGC. Supplementing with GC restores control of the inflammatory response in RAI mice. SF1CreSR-BIfl/fl mice were susceptible to CLP-induced sepsis (6.7% survival in SF1CreSR-BIfl/fl mice versus 86.4% in SRBIfl/fl mice). Supplementation of a low stress dose of GC to SF1CreSR-BIfl/fl mice kept the inflammatory response under control and rescued the mice. However, SR-BIfl/fl mice receiving GC treatment exhibited significantly less survival compared to SR-BIfl/fl mice without GC treatment.
The importance of SR-BI-mediated iGC production in pediatric sepsis was assessed in 21-day-old mice (9). Mice deficient in adrenal SR-BI were susceptible to both CLP and cecal slurry induced septic death, with survival of 88.9% in SRBIfl/fl mice versus 15.4% in SF1CreSRBIfl/fl mice in CLP model; 33% SRBIfl/fl mice versus 0% in SF1CreSRBIfl/fl mice in cecal slurry model. SF1CreSRBIfl/fl mice featured persistent inflammatory responses, and were effectively rescued by administering GC 2 hours post CLP. GC treatment did not improve survival in CLP-challenged wild type mice. While GC has been shown to suppress many inflammatory signaling pathways in vitro, using an unbiased RNA-seq analysis, the study found that a lack of iGC production in SF1CreSRBIfl/fl mice causes persistent inflammatory responses mainly due to transcriptional dysregulation of AP-1 and NF-B (9). In addition, the study found that iGC functions to control cytokine-induced secondary inflammatory response (9).
In sum, SR-BI mediates iGC production in sepsis. Using SR-BI null mice as a model for adrenal insufficiency, early studies demonstrated that the adrenal stress response is an essential host response, which functions to keep the inflammatory response under control. GC therapy benefits mice with adrenal insufficiency but harms mice without it (Figure 1).
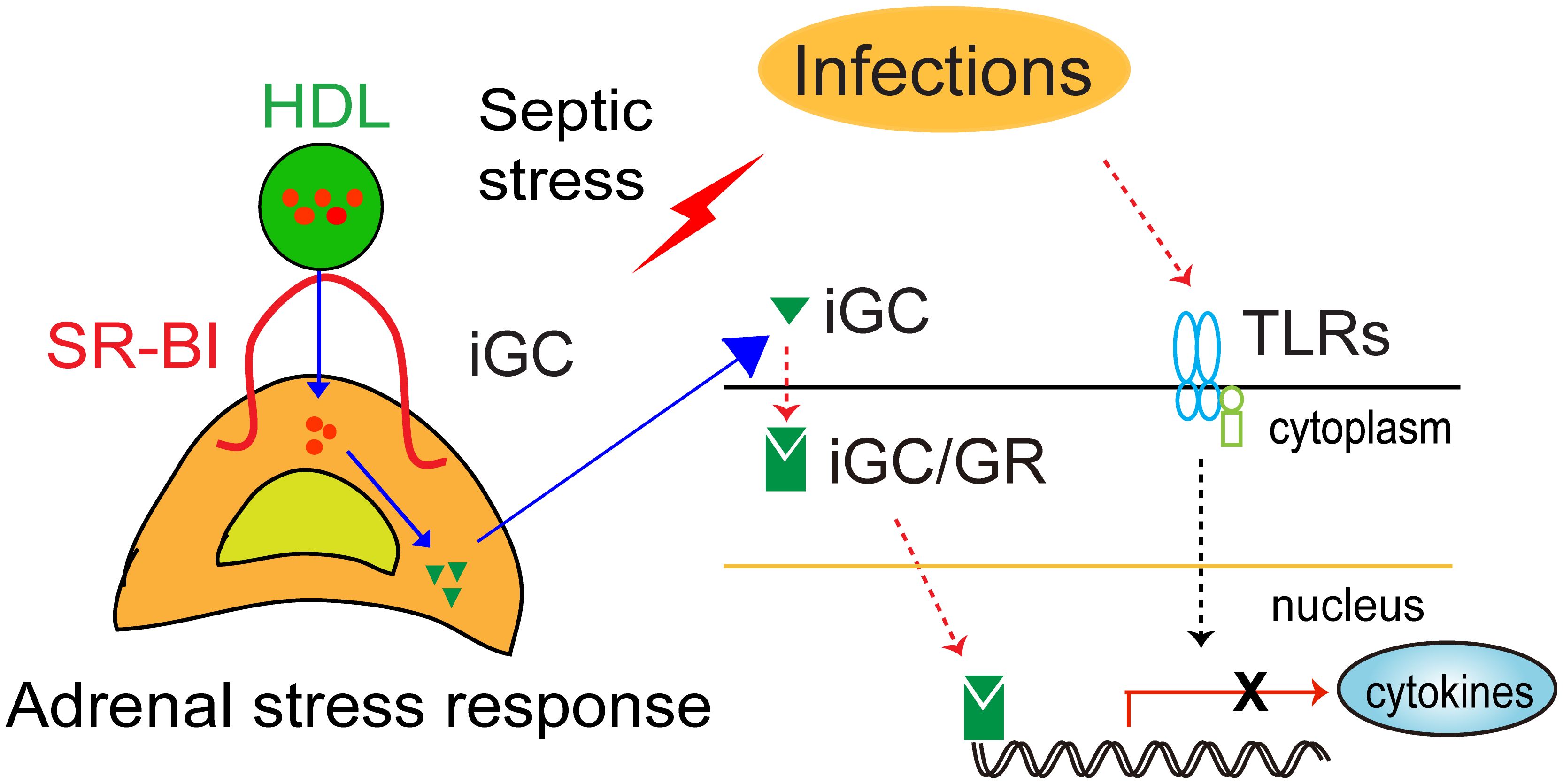
Figure 1. Schematic model of SR-BI-mediated adrenal stress response (iGC production) protection against sepsis. Upon infection, immune cells recognize the invading microorganism using pattern recognition receptors (TLRs). This triggers the innate immune system, releasing cytokines to fight infection. However, dysregulation of the host response causes organ injury, leading to organ dysfunction and death. In response to septic stress, adrenal SR-BI mediates the uptake of cholesterol from HDL into adrenal gland for induced glucocorticoid (iGC) production, which functions to keep the inflammatory response under control.
Translation of the mechanistic studies into a precision medicine approach to guide GC therapy for sepsis
The mechanistic findings using adrenal SR-BI null mice as a RAI model provide proof-of-concept that targeting RAI/CIRCI with GC can be an effective therapy for sepsis. However, clinical trials did not show a survival benefit of GC therapy in septic patients. There are a number of disconnections between GC therapy and the mechanisms of GC function, which may render GC therapy less effective. Let’s examine it through the lens of GC biology in sepsis.
1) Adrenal insufficiency versus diagnosis of RAI/CIRCI: RAI or CIRCI is commonly defined as “insufficient GC activity relative to increased physiological demand” or “inadequate cellular corticosteroid activity for the severity of critical illness.” However, these definitions are conceptually vague and lack mechanistic specificity, limiting their utility in guiding GC therapy. Mechanistically, sepsis triggers a robust host response, including activation of the adrenal stress axis and increased inducible glucocorticoid (iGC) production. As previously discussed, failure to mount this adrenal stress response is a recognized risk factor in sepsis, and targeting patients with impaired iGC production may improve outcomes. In clinical practice, the ACTH stimulation test is used to assess adrenal function. While appropriate for non-septic patients, its application in septic patients—who already exhibit elevated endogenous iGC due to extreme stress—raises concerns. In this context, the test measures the incremental adrenal response (delta iGC) on top of endogenous iGC. Our recent findings indicate that the ACTH test fails to elicit additional iGC production in mice with normal adrenal stress response during the early and intermediate phases of sepsis. Moreover, under septic conditions, ACTH administration can exacerbate cytokine production, potentially worsening patient outcomes (74). Consequently, the ACTH test may misclassify septic patients with an intact adrenal stress response as adrenal insufficient, leading to inappropriate GC therapy.
2) Functions of GC versus targets of GC therapy: Mechanistic studies have established that inducible glucocorticoids (iGC) play a critical role in modulating inflammation. Current clinical guidelines recommend GC therapy for septic patients experiencing shock (41), with hypotension serving as the primary criterion for intervention. Table 2 summarizes literature on phenotype-based GC therapy in animal models. While GCs are known to support blood pressure regulation, this recommendation is largely grounded in clinical observations rather than mechanistic understanding. Hypotension in sepsis is typically a downstream consequence of organ dysfunction, which is often driven by hyperinflammation. Given that iGCs function primarily to control inflammatory responses, a mechanistically informed approach would suggest that targeting patients with iGC insufficiency and a hyperinflammatory phenotype may be more effective than relying solely on the presence of hypotension as an indicator for GC therapy. This perspective raises an important question: could a precision medicine strategy that identifies and treats patients with impaired iGC production and hyperinflammation yield better outcomes than the current one-size-fits-all approach?
3) Timing of GC action versus timing of GC therapy: Following infection, immune effector cells rapidly initiate a robust inflammatory response characterized by the release of high levels of cytokines and chemokines. While essential for pathogen clearance, this response can become detrimental if not properly regulated, leading to tissue damage and organ dysfunction. Mechanistic studies have shown that inducible glucocorticoids (iGC) are produced early in the course of infection and play a critical role in modulating inflammation during the early and intermediate stages of sepsis. In contrast, current clinical guidelines recommend initiating GC therapy in septic patients who develop shock (41), —a condition that typically manifests in the later stages of sepsis. This temporal disconnect raises an important concern: is GC therapy being administered too late in the disease course to exert its full therapeutic benefit? If iGC’s anti-inflammatory effects are most critical during the early phases of sepsis, delayed intervention may limit the efficacy of exogenous GC therapy. This discrepancy underscores the need to re-evaluate the timing of GC administration and consider earlier, targeted intervention based on mechanistic insights.
Conclusions - reevaluating GC therapy in sepsis through a precision medicine lens
Despite extensive clinical trials, glucocorticoid (GC) therapy has demonstrated limited impact on patient survival (5). The efficacy of GC treatment in sepsis and whether its use should be stratified based on adrenal insufficiency—remains a subject of ongoing debate (40, 41). This controversy is further complicated by the limitations of the ACTH stimulation test, which may not reliably diagnose adrenal insufficiency in septic patients.
Given the complexity and heterogeneity of sepsis, there is increasing support—including from our own studies (7–9, 21, 30)—for adopting a precision medicine approach to sepsis management (98, 99). A cornerstone of this strategy is the identification and targeted treatment of patient subgroups defined by specific endotypes (100, 101). Mechanistic studies using adrenal SR-BI knockout mice, a validated model of adrenal insufficiency, have identified adrenal insufficiency as both a risk factor and a distinct endotype in sepsis. Building on these insights, we advocate for two key shifts in clinical practice: 1) Redefining and developing improved diagnostic criteria for adrenal insufficiency in septic patients, moving beyond the limitations of current testing methods; 2) Implementing a precision medicine framework to guide GC therapy—administering treatment in a timely and selective manner to patients with confirmed adrenal insufficiency, while avoiding unnecessary use in those with an intact adrenal stress response.
Author contributions
LG: Formal Analysis, Validation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Project administration, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Resources. QW: Writing – review & editing. X-AL: Investigation, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Grants NIH R35GM141478, VA 1I01BX004639 and VA I01BX006408 (to X-A Li). Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health or VA.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
ACTH, Adrenocorticotropic Hormone; AP-1, Activator Protein 1; CIRCI, Critical Illness-Related Corticosteroid Insufficiency; CLP, Cecal Ligation and Puncture; GC, Glucocorticoid; HDL, High-Density Lipoprotein; iGC, Induced Glucocorticoid; LDL, Low-Density Lipoprotein; NF-κB, Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; RAI, Relative Adrenal Insufficiency; SR-BI, Scavenger Receptor BI; TLRs, Toll-Like Receptors.
References
1. Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. (2020) 395:200–11. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7
2. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. (2016) 315:801–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287
4. van der Poll T, Shankar-Hari M, and Wiersinga WJ. The immunology of sepsis. Immunity. (2021) 54:2450–64. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.10.012
6. Loftus TJ, Ungaro R, Dirain M, Efron PA, Mazer MB, Remy KE, et al. Overlapping but disparate inflammatory and immunosuppressive responses to SARS-coV-2 and bacterial sepsis: an immunological time course analysis. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:792448. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.792448
7. Li X, Guo L, and Ye X. GLUCOCORTICOID ONLY BENEFITS SEPTIC MICE WITH ADRENAL INSUFFICIENCY: A PRECISION MEDICINE APPROACH. Crit Care Med. (2016) 44:447. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000510159.48167.31
8. Wu CH, Guo L, Hao D, Wang Q, Ye X, Ito M, et al. Relative adrenal insufficiency is a risk factor and endotype of sepsis - A proof-of-concept study to support a precision medicine approach to guide glucocorticoid therapy for sepsis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1110516. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1110516
9. Hao D, Guo L, Wang Q, Ito M, Huang B, Mineo C, et al. Relative adrenal insufficiency is a risk factor for pediatric sepsis - a proof-of-concept study. J Infect Dis. (2023) 229:1166–77.
10. Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Aschenbrenner AC, Bauer M, Bock C, Calandra T, Gat-Viks I, et al. The pathophysiology of sepsis and precision-medicine-based immunotherapy. Nat Immunol. (2024) 25:19–28. doi: 10.1038/s41590-023-01660-5
11. Brakenridge SC, Wang Z, Cox M, Raymond S, Hawkins R, Darden D, et al. Distinct immunologic endotypes are associated with clinical trajectory after severe blunt trauma and hemorrhagic shock. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. (2021) 90:257–67. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000003029
12. Lovallo WR and Buchanan TW. Stress hormones in psychophysiological research: emotional, behavioral, and cognitive implications. Handbook of psychophysiology, 4th ed. Cambridge handbooks in psychology. New York, NY, US: Cambridge University Press; (2017). p. 465–94.
13. Busillo JM and Cidlowski JA. The five Rs of glucocorticoid action during inflammation: ready, reinforce, repress, resolve, and restore. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2013) 24:109–19. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.11.005
14. Dunlop D. Eighty-six cases of addison’s disease. Br Med J. (1963) 2:887–91. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5362.887
15. Vandevyver S, Dejager L, Tuckermann J, and Libert C. New insights into the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of glucocorticoids: an emerging role for glucocorticoid-receptor-mediated transactivation. Endocrinology. (2013) 154:993–1007. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-2045
16. Li CC, Munitic I, Mittelstadt PR, Castro E, and Ashwell JD. Suppression of dendritic cell-derived IL-12 by endogenous glucocorticoids is protective in LPS-induced sepsis. PloS Biol. (2015) 13:e1002269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002269
17. Bhattacharyya S, Brown DE, Brewer JA, Vogt SK, and Muglia LJ. Macrophage glucocorticoid receptors regulate Toll-like receptor 4–mediated inflammatory responses by selective inhibition of p38 MAP kinase. Blood. (2007) 109:4313–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-10-048215
18. Goodwin JE, Feng Y, Velazquez H, and Sessa WC. Endothelial glucocorticoid receptor is required for protection against sepsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2013) 110:306–11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1210200110
19. Guo L, Zheng Z, Ai J, Howatt DA, Mittelstadt PR, Thacker S, et al. Scavenger receptor BI and high-density lipoprotein regulate thymocyte apoptosis in sepsis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2014) 34:966–75. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302484
20. Russell G and Lightman S. The human stress response. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2019) 15:525–34. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0228-0
21. Guo L, Wang W, Wang Q, Hao D, Ito M, Huang B, et al. The adrenal stress response is an essential host response against therapy-induced lethal immune activation. Sci Signal. (2023) 16:eadd4900. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.add4900
22. Annane D, Maxime V, Ibrahim F, Alvarez JC, Abe E, and Boudou P. Diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency in severe sepsis and septic shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2006) 174:1319–26. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200509-1369OC
23. Prigent H, Maxime V, and Annane D. Science review: mechanisms of impaired adrenal function in sepsis and molecular actions of glucocorticoids. Crit Care. (2004) 8:243–52. doi: 10.1186/cc2878
24. Coutinho AE and Chapman KE. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2011) 335:2–13. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.04.005
25. Siraux V, De Backer D, Yalavatti G, Melot C, Gervy C, Mockel J, et al. Relative adrenal insufficiency in patients with septic shock: comparison of low-dose and conventional corticotropin tests. Crit Care Med. (2005) 33:2479–86. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000185641.87051.7C
26. Burry L, Little A, Hallett D, and Mehta S. Detection of critical illness-related corticosteroid insufficiency using 1 mug adrenocorticotropic hormone test. Shock. (2013) 39:144–8. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31827daf0b
27. Marik PE, Pastores SM, Annane D, Meduri GU, Sprung CL, Arlt W, et al. Recommendations for the diagnosis and management of corticosteroid insufficiency in critically ill adult patients: consensus statements from an international task force by the American College of Critical Care Medicine. Crit Care Med. (2008) 36:1937–49. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31817603ba
28. Annane D, Pastores SM, Rochwerg B, Arlt W, Balk RA, Beishuizen A, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of critical illness-related corticosteroid insufficiency (CIRCI) in critically ill patients (Part I): society of critical care medicine (SCCM) and European society of intensive care medicine (ESICM) 2017. Crit Care Med. (2017) 45:2078–88. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002737
29. Vandewalle J, Timmermans S, Paakinaho V, Vancraeynest L, Dewyse L, Vanderhaeghen T, et al. Combined glucocorticoid resistance and hyperlactatemia contributes to lethal shock in sepsis. Cell Metab. (2021) 33:1763–1776.e1765. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.07.002
30. Ai J, Guo L, Zheng Z, Wang S-X, Huang B, and Li X-A. Corticosteroid therapy benefits septic mice with adrenal insufficiency but harms septic mice without adrenal insufficiency*. Crit Care Med. (2015) 43:e490–8. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001264
31. Bone RC, Fisher CJ Jr., Clemmer TP, Slotman GJ, Metz CA, and Balk RA. A controlled clinical trial of high-dose methylprednisolone in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. (1987) 317:653–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709103171101
32. Annane D, Sebille V, Charpentier C, Bollaert PE, Francois B, Korach JM, et al. Effect of treatment with low doses of hydrocortisone and fludrocortisone on mortality in patients with septic shock. Jama. (2002) 288:862–71. doi: 10.1001/jama.288.7.862
33. Sprung CL, Annane D, Keh D, Moreno R, Singer M, Freivogel K, et al. Hydrocortisone therapy for patients with septic shock. N Engl J Med. (2008) 358:111–24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa071366
34. Annane D, Bellissant E, Bollaert PE, Briegel J, Confalonieri M, De Gaudio R, et al. Corticosteroids in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock in adults: a systematic review. Jama. (2009) 301:2362–75. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.815
35. Minneci PC, Deans KJ, Eichacker PQ, and Natanson C. The effects of steroids during sepsis depend on dose and severity of illness: an updated meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect. (2009) 15:308–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02752.x
36. Sligl WI, Milner DA Jr., Sundar S, Mphatswe W, and Majumdar SR. Safety and efficacy of corticosteroids for the treatment of septic shock: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. (2009) 49:93–101. doi: 10.1086/599343
37. Keh D, Trips E, Marx G, Wirtz SP, Abduljawwad E, Bercker S, et al. Effect of hydrocortisone on development of shock among patients with severe sepsis: the HYPRESS randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2016) 316:1775–85. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.14799
38. Annane D, Renault A, Brun-Buisson C, Megarbane B, Quenot JP, Siami S, et al. Hydrocortisone plus fludrocortisone for adults with septic shock. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:809–18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1705716
39. Venkatesh B, Finfer S, Myburgh J, Cohen J, and Billot L. Long-term outcomes of the ADRENAL trial. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:1744–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1803563
40. Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Crit Care Med. (2017). 45:486–552.
41. Chaudhuri D, Nei AM, Rochwerg B, Balk RA, Asehnoune K, Cadena R, et al. 2024 focused update: guidelines on use of corticosteroids in sepsis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and community-acquired pneumonia. Crit Care Med. (2024) 52:e219–33. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000006172
42. Schumer W. Steroids in the treatment of clinical septic shock. Ann Surg. (1976) 184:333–41. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197609000-00011
43. Sprung CL, Caralis PV, Marcial EH, Pierce M, Gelbard MA, Long WM, et al. The effects of high-dose corticosteroids in patients with septic shock. A prospective, controlled study. N Engl J Med. (1984) 311:1137–43. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411013111801
44. Slotman GJ, Fisher CJ Jr., Bone RC, Clemmer TP, and Metz CA. Detrimental effects of high-dose methylprednisolone sodium succinate on serum concentrations of hepatic and renal function indicators in severe sepsis and septic shock. The Methylprednisolone Severe Sepsis Study Group. Crit Care Med. (1993) 21:191–5. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199302000-00008
45. Bollaert PE, Charpentier C, Levy B, Debouverie M, Audibert G, and Larcan A. Reversal of late septic shock with supraphysiologic doses of hydrocortisone. Crit Care Med. (1998) 26:645–50. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199804000-00010
46. Briegel J, Forst H, Haller M, Schelling G, Kilger E, Kuprat G, et al. Stress doses of hydrocortisone reverse hyperdynamic septic shock: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, single-center study. Crit Care Med. (1999) 27:723–32. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199904000-00025
47. Keh D, Boehnke T, Weber-Cartens S, Schulz C, Ahlers O, Bercker S, et al. Immunologic and hemodynamic effects of “low-dose” hydrocortisone in septic shock: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2003) 167:512–20. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200205-446OC
48. Oppert M, Schindler R, Husung C, Offermann K, Gräf KJ, Boenisch O, et al. Low-dose hydrocortisone improves shock reversal and reduces cytokine levels in early hyperdynamic septic shock. Crit Care Med. (2005) 33:2457–64. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000186370.78639.23
49. Fernández J, Escorsell A, Zabalza M, Felipe V, Navasa M, Mas A, et al. Adrenal insufficiency in patients with cirrhosis and septic shock: Effect of treatment with hydrocortisone on survival. Hepatology. (2006) 44:1288–95. doi: 10.1002/hep.21352
50. Annane D, Sébille V, and Bellissant E. Effect of low doses of corticosteroids in septic shock patients with or without early acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. (2006) 34:22–30. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000194723.78632.62
51. Loisa P, Parviainen I, Tenhunen J, Hovilehto S, and Ruokonen E. Effect of mode of hydrocortisone administration on glycemic control in patients with septic shock: a prospective randomized trial. Crit Care. (2007) 11:R21. doi: 10.1186/cc5696
52. Weber-Carstens S, Deja M, Bercker S, Dimroth A, Ahlers O, Kaisers U, et al. Impact of bolus application of low-dose hydrocortisone on glycemic control in septic shock patients. Intensive Care Med. (2007) 33:730–3. doi: 10.1007/s00134-007-0540-3
53. Arabi YM, Aljumah A, Dabbagh O, Tamim HM, Rishu AH, Al-Abdulkareem A, et al. Low-dose hydrocortisone in patients with cirrhosis and septic shock: a randomized controlled trial. Cmaj. (2010) 182:1971–7. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.090707
54. Huh JW, Choi HS, Lim CM, Koh Y, Oh YM, Shim TS, et al. Low-dose hydrocortisone treatment for patients with septic shock: a pilot study comparing 3days with 7days. Respirology. (2011) 16:1088–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2011.02018.x
55. Moreno R, Sprung CL, Annane D, Chevret S, Briegel J, Keh D, et al. Time course of organ failure in patients with septic shock treated with hydrocortisone: results of the Corticus study. Intensive Care Med. (2011) 37:1765–72. doi: 10.1007/s00134-011-2334-x
56. Antcliffe DB, Burnham KL, Al-Beidh F, Santhakumaran S, Brett SJ, Hinds CJ, et al. Transcriptomic signatures in sepsis and a differential response to steroids. From the VANISH randomized trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2019) 199:980–6. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201807-1419OC
57. Venkatesh B, Finfer S, Cohen J, Rajbhandari D, Arabi Y, Bellomo R, et al. Hydrocortisone compared with placebo in patients with septic shock satisfying the sepsis-3 diagnostic criteria and APROCCHSS study inclusion criteria: A post hoc analysis of the ADRENAL trial. Anesthesiology. (2019) 131:1292–300. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000002955
58. Moskowitz A, Huang DT, Hou PC, Gong J, Doshi PB, Grossestreuer AV, et al. Effect of ascorbic acid, corticosteroids, and thiamine on organ injury in septic shock: the ACTS randomized clinical trial. Jama. (2020) 324:642–50. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.11946
59. Meduri GU, Annane D, Confalonieri M, Chrousos GP, Rochwerg B, Busby A, et al. Pharmacological principles guiding prolonged glucocorticoid treatment in ARDS. Intensive Care Med. (2020) 46:2284–96. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06289-8
60. Sevransky JE, Rothman RE, Hager DN, Bernard GR, Brown SM, Buchman TG, et al. Effect of vitamin C, thiamine, and hydrocortisone on ventilator- and vasopressor-free days in patients with sepsis: the VICTAS randomized clinical trial. Jama. (2021) 325:742–50. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.24505
61. Wong HR, Hart KW, Lindsell CJ, and Sweeney TE. External corroboration that corticosteroids may be harmful to septic shock endotype A patients. Crit Care Med. (2021) 49:e98–e101. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004709
62. Cohen J, Blumenthal A, Cuellar-Partida G, Evans DM, Finfer S, Li Q, et al. The relationship between adrenocortical candidate gene expression and clinical response to hydrocortisone in patients with septic shock. Intensive Care Med. (2021) 47:974–83. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06464-5
63. Walsham J, Hammond N, Blumenthal A, Cohen J, Myburgh J, Finfer S, et al. Fludrocortisone dose-response relationship in septic shock: a randomised phase II trial. Intensive Care Med. (2024) 50:2050–60. doi: 10.1007/s00134-024-07616-z
64. Heming N, Renault A, Kuperminc E, Brun-Buisson C, Megarbane B, Quenot JP, et al. Hydrocortisone plus fludrocortisone for community acquired pneumonia-related septic shock: a subgroup analysis of the APROCCHSS phase 3 randomised trial. Lancet Respir Med. (2024) 12:366–74. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00430-7
65. Donaldson LH, Devaux A, White KC, Rajbhandari D, Cohen J, Bellomo R, et al. Hydrocortisone and risk factors for kidney replacement therapy in septic shock. JAMA Netw Open. (2025) 8:e2512279. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.12279
66. Cai L, Ji A, de Beer FC, Tannock LR, and van der Westhuyzen DR. SR-BI protects against endotoxemia in mice through its roles in glucocorticoid production and hepatic clearance. J Clin Invest. (2008) 118:364–75. doi: 10.1172/JCI31539
67. Gilibert S, Galle-Treger L, Moreau M, Saint-Charles F, Costa S, Ballaire R, et al. Adrenocortical scavenger receptor class B type I deficiency exacerbates endotoxic shock and precipitates sepsis-induced mortality in mice. J Immunol. (2014) 193:817–26. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1303164
68. Gowdy KM, Madenspacher JH, Azzam KM, Gabor KA, Janardhan KS, Aloor JJ, et al. Key role for scavenger receptor B-I in the integrative physiology of host defense during bacterial pneumonia. Mucosal Immunol. (2015) 8:559–71. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.88
69. Ai J, Guo L, Zheng Z, Wang SX, Huang B, and Li XA. Corticosteroid therapy benefits septic mice with adrenal insufficiency but harms septic mice without adrenal insufficiency. Crit Care Med. (2015) 43:e490–498. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001264
70. Quatrini L and Ugolini S. New insights into the cell- and tissue-specificity of glucocorticoid actions. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) 18:269–78. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-00526-2
71. Hobson H, Linden A, Crane L, and Kalandadze T. Towards reproducible and respectful autism research: Combining open and participatory autism research practices. Res Autism Spectr Disord. (2023) 106:102196. doi: 10.1016/j.rasd.2023.102196
72. Dickstein G. On the term “relative adrenal insufficiency”–or what do we really measure with adrenal stimulation tests? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2005) 90:4973–4.
73. Loriaux DL and Fleseriu M. Relative adrenal insufficiency. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. (2009) 16:392–400. doi: 10.1097/MED.0b013e3283307d53
74. Hao D, Wang Q, Ito M, Xue J, Guo L, Huang B, et al. The ACTH test fails to diagnose adrenal insufficiency and augments cytokine production in sepsis. JCI Insight. (2025). doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.187487
75. Acton SL, Scherer PE, Lodish HF, and Krieger M. Expression cloning of SR-BI, a CD36-related class B scavenger receptor. J Biol Chem. (1994) 269:21003–9. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)31921-X
76. Krieger M. CHARTING THE FATE OF THE “GOOD CHOLESTEROL”: identification and characterization of the high-density lipoprotein receptor SR-BI. Annu Rev Biochem. (1999) 68:523–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.68.1.523
77. Feng H, Guo L, Wang D, Gao H, Hou G, Zheng Z, et al. Deficiency of scavenger receptor BI leads to impaired lymphocyte homeostasis and autoimmune disorders in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2011) 31:2543–51. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.234716
78. Braun A, Trigatti BL, Post MJ, Sato K, Simons M, Edelberg JM, et al. Loss of SR-BI expression leads to the early onset of occlusive atherosclerotic coronary artery disease, spontaneous myocardial infarctions, severe cardiac dysfunction, and premature death in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circ Res. (2002) 90:270–6. doi: 10.1161/hh0302.104462
79. Kozarsky KF, Donahee MH, Glick JM, Krieger M, and Rader DJ. Gene transfer and hepatic overexpression of the HDL receptor SR-BI reduces atherosclerosis in the cholesterol-fed LDL receptor-deficient mouse. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2000) 20:721–7. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.20.3.721
80. Yu H, Zhang W, Yancey PG, Koury MJ, Zhang Y, Fazio S, et al. Macrophage apolipoprotein E reduces atherosclerosis and prevents premature death in apolipoprotein E and scavenger receptor-class BI double-knockout mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2006) 26:150–6. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000194096.89476.73
81. Van Eck M, Twisk J, Hoekstra M, Van Rij BT, Van Der Lans CA, Bos IS, et al. Differential effects of scavenger receptor BI deficiency on lipid metabolism in cells of the arterial wall and the liver. J Biol Chem. (2003) 278:23699–705. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211233200
82. Zanoni P, Khetarpal SA, Larach DB, Hancock-Cerutti WF, Millar JS, Cuchel M, et al. Rare variant in scavenger receptor BI raises HDL cholesterol and increases risk of coronary heart disease. Science. (2016) 351:1166–71. doi: 10.1126/science.aad3517
83. Vergeer M, Korporaal SJ, Franssen R, Meurs I, Out R, Hovingh GK, et al. Genetic variant of the scavenger receptor BI in humans. N Engl J Med. (2011) 364:136–45. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0907687
84. Zheng Z, Ai J, and Li XA. Scavenger receptor class B type I and immune dysfunctions. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. (2014) 21:121–8. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000046
85. Li XA, Guo L, Asmis R, Nikolova-Karakashian M, and Smart EJ. Scavenger receptor BI prevents nitric oxide-induced cytotoxicity and endotoxin-induced death. Circ Res. (2006) 98:e60–65. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000219310.00308.10
86. Guo L, Song Z, Li M, Wu Q, Wang D, Feng H, et al. Scavenger Receptor BI Protects against Septic Death through Its Role in Modulating Inflammatory Response. J Biol Chem. (2009) 284:19826–34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.020933
87. Gowdy KM, Madenspacher JH, Azzam KM, Gabor KA, Janardhan KS, Aloor JJ, et al. Key role for scavenger receptor B-I in the integrative physiology of host defense during bacterial pneumonia. Mucosal Immunol. (2014). doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.88
88. Wang Q, Guo L, Hao D, Ito M, Mineo C, Shaul PW, et al. Elevated free cholesterol levels due to impaired reverse cholesterol transport are a risk factor for polymicrobial sepsis in mice. J Biol Chem. (2024) 300:107974. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107974
89. Cai L, Wang Z, Ji A, Meyer JM, and van der Westhuyzen DR. Macrophage SR-BI regulates pro-inflammatory signaling in mice and isolated macrophages. J Lipid Res. (2012) 53:1472–81. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M023234
90. Feng H, Guo L, Song Z, Wang D, Fu W, Han J, et al. Caveolin-1 protects against sepsis through modulating inflammatory response, alleviating bacterial burden and suppressing thymocyte apoptosis. J Biol Chem. (2010) 285:25154–60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.116897
91. Hao D, Xue J-Y, Wang Q, Guo L, and Li X-A. The role of scavenger receptor BI in sepsis. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:13441. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413441
92. Petta I, Dejager L, Ballegeer M, Lievens S, Tavernier J, De Bosscher K, et al. The interactome of the glucocorticoid receptor and its influence on the actions of glucocorticoids in combatting inflammatory and infectious diseases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. (2016) 80:495–522. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00064-15
93. Hoekstra M, Meurs I, Koenders M, Out R, Hildebrand RB, Kruijt JK, et al. Absence of HDL cholesteryl ester uptake in mice via SR-BI impairs an adequate adrenal glucocorticoid-mediated stress response to fasting. J Lipid Res. (2008) 49:738–45. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M700475-JLR200
94. Hoekstra M, van der Sluis RJ, Van Eck M, and Van Berkel TJ. Adrenal-specific scavenger receptor BI deficiency induces glucocorticoid insufficiency and lowers plasma very-low-density and low-density lipoprotein levels in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2013) 33:e39–46. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300784
95. Ito M, Ye X, Wang Q, Guo L, Hao D, Howatt D, et al. SR-BI (Scavenger receptor BI), not LDL (Low-density lipoprotein) receptor, mediates adrenal stress response-brief report. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2020) 40:1830–7. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314506
96. Allen J, Thompson G, and Myant N. Normal adrenocortical response to adrenocorticotrophic hormone in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia. J Clin Sci (Lond). (1983) 65:99–101. doi: 10.1042/cs0650099
97. Huang L, Chambliss KL, Gao X, Yuhanna IS, Behling-Kelly E, Bergaya S, et al. SR-B1 drives endothelial cell LDL transcytosis via DOCK4 to promote atherosclerosis. Nature. (2019) 569:565–9. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1140-4
98. Coopersmith CM, De Backer D, Deutschman CS, Ferrer R, Lat I, Machado FR, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: research priorities for sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med. (2018) 46:1334–56. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003225
99. Buchman TG, Billiar TR, Elster E, Kirk AD, Rimawi RH, Vodovotz Y, et al. Precision medicine for critical illness and injury. Crit Care Med. (2016) 44:1635–8. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002028
100. Mirnezami R, Nicholson J, and Darzi A. Preparing for precision medicine. N Engl J Med. (2012) 366:489–91. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1114866
Keywords: precision medicine, sepsis, scavenger receptor BI, adrenal stress response, glucocorticoid
Citation: Guo L, Wang Q and Li X-A (2025) The Role of SR-BI in sepsis: leveraging mechanistic insights to advance precision steroid therapy. Front. Immunol. 16:1643395. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1643395
Received: 08 June 2025; Accepted: 07 July 2025;
Published: 28 July 2025.
Edited by:
Daolin Tang, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, United StatesReviewed by:
Guo-Chang Fan, University of Cincinnati, United StatesMonowar Aziz, Feinstein Institute for Medical Research, United States
Copyright © 2025 Guo, Wang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiang-An Li, eGxpMkBlbWFpbC51a3kuZWR1
 Ling Guo
Ling Guo Qian Wang1
Qian Wang1 Xiang-An Li
Xiang-An Li