- 1Engineering Research Center of Tropical Medicine Innovation and Transformation of Ministry of Education, School of Pharmacy, Hainan Medical University, Haikou, China
- 2Hainan Provincial Key Laboratory of Research and Development on Tropical Herbs, Hainan Medical University, Haikou, China
Viral myocarditis (VMC) is a life-threatening inflammatory cardiomyopathy with a global incidence rate of 10–22 per 100,000 people. It is the most common clinical manifestation of myocardial inflammation. Myocardial cell injury and fibrosis are the pathological characteristics of VMC. Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3), parvovirus B19 (PVB19), Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and adenovirus (AdV) are the main causes that induce viral myocarditis. Among them, CVB3 has become the main pathogen, accounting for more than 50% of the confirmed cases of VMC. The clinical manifestations of this disease are extensive, ranging from asymptomatic carriers to sudden cardiac death caused by acute decompensated heart failure and arrhythmia. Current therapeutic strategies for VMC focus on four key approaches: (1) Anti-inflammatory interventions targeting inflammatory cells and mediators; (2) Antiviral therapies employing gene editing, viral protease inhibitors, and RNA polymerase inhibitors; (3) Myocardial protection through tissue repair promotion and nutritional support; (4) Oxidative stress mitigation using antioxidants. This article will systematically summarize the progress of VMC management in recent years and provide personal insights for VMC management.
1 Introduction
Myocarditis accounts for approximately 20% of adolescent mortality (1) and is classified as the third most prevalent etiology of cardiovascular death in young athletes (6% incidence), surpassed only by coronary artery anomalies (17%) and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (36%) (2, 3). The disease manifests with marked clinical heterogeneity (4), ranging from mild presentations (chest pain, palpitations, low-grade fever, exertional dyspnea) to fulminant cardiogenic shock (hypotension, peripheral hypoperfusion) or lethal arrhythmias (sustained ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation), with reported mortality rates of 10%-20% (5). A subset of patients reports prodromal upper respiratory or gastrointestinal infections 1–3 weeks preceding symptom onset (6), while those with localized inflammatory foci may remain clinically silent. Pathogenetically, myocarditis arises from diverse infectious (viral, bacterial, rickettsial) and non-infectious triggers (pharmacotoxic agents, giant cell myocarditis, sarcoidosis), with CVB3 infection representing the predominant etiology across all demographic groups. By diagnostic criteria, myocarditis constitutes a non-ischemic inflammatory cardiomyopathy characterized by lymphocytic infiltration and myocardial necrosis on histopathology (7).
Given this significant disease burden and etiological complexity, establishing a definitive viral myocarditis diagnosis becomes clinically imperative yet methodologically challenging. The pronounced clinical heterogeneity-spanning subclinical presentations to fulminant cardiogenic shock-necessitates correlating epidemiological patterns with precision diagnostic frameworks. Consequently, contemporary guidelines mandate systematic integration of histopathological evidence and multimodal assessment to address diagnostic ambiguities inherent in VMC’s variable manifestations, particularly given CVB3’s predominance across demographic strata.
VMC clinical diagnosis requires a comprehensive multimodal approach (Figure 1). This process begins with evaluating characteristic symptoms- such as chest pain, arrhythmias, or heart failure manifestations-alongside elevated serum biomarkers, including cardiac troponin I/T (cTnI/cTnT) and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). Subsequent non-invasive imaging assessments involve cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) with T1/T2 mapping and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) sequences to characterize myocardial inflammation, edema, and necrosis, while echocardiography quantifies functional impairment through left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) depression and wall motion abnormalities. Ischemic etiology must then be excluded via coronary angiography, supplemented by endomyocardial biopsy (EMB) demonstrating lymphocytic infiltrates with viral genome detection via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or in situ hybridization in refractory cases. Definitive diagnosis ultimately adheres to modified Lake Louise Criteria and WHF/ESC consensus guidelines, integrating histopathological, immunological, and functional evidence while rigorously excluding alternative cardiomyopathies.
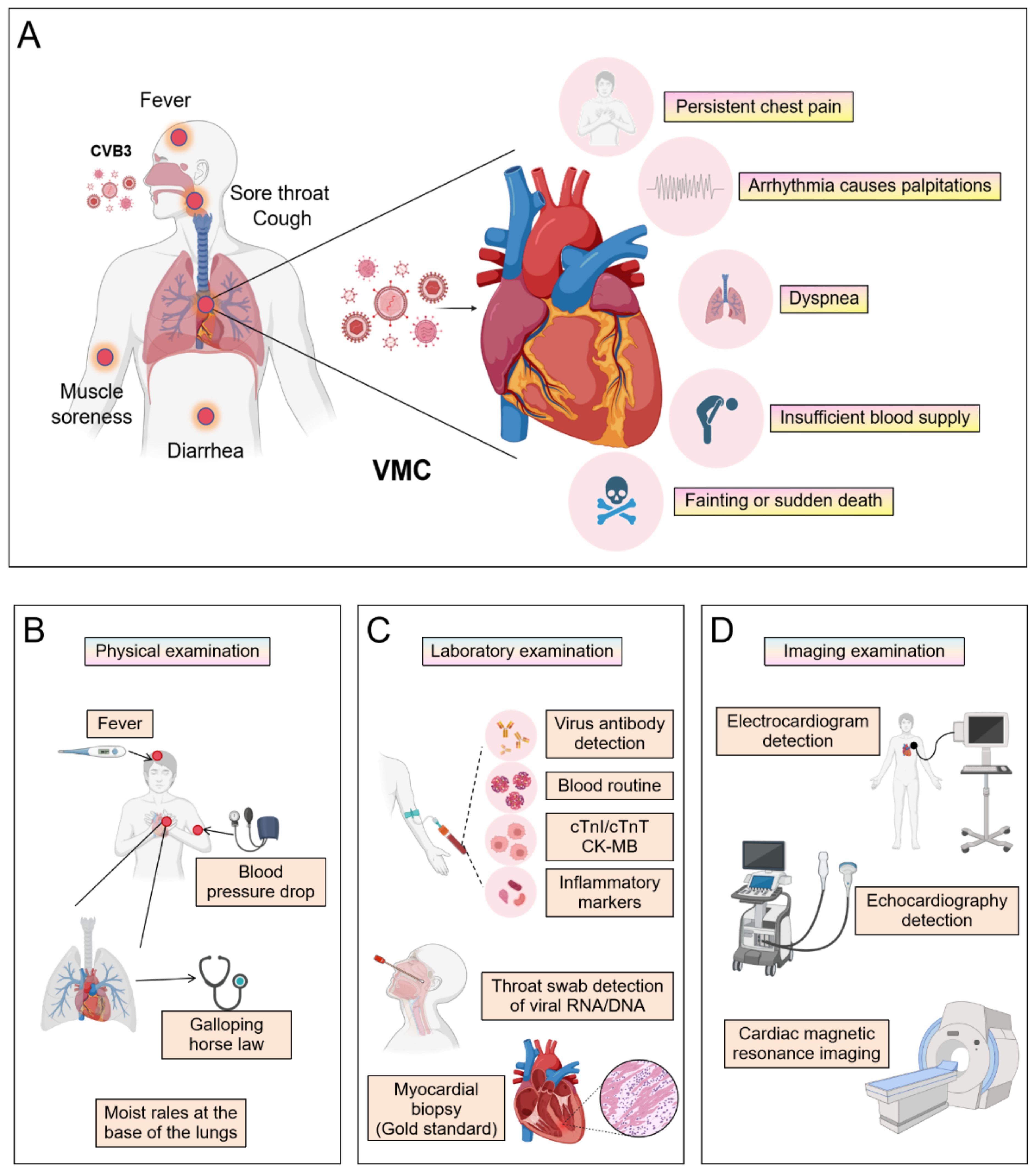
Figure 1. The clinical symptoms and diagnosis of VMC. (By Biorender). (A) The manifestations that occur when a virus invades the human body and the symptoms that may appear after invading the heart. The patient underwent (B) a physical examination, (C) laboratory examinations, and (D) imaging examinations.
VMC is pathologically defined by focal or diffuse myocardial inflammation (8), marked by significant infiltration of inflammatory cells-predominantly myeloid cells and T lymphocytes-into cardiac tissue (9). Sustained myocardial inflammation drives structural remodeling through fibrotic deposition and hypertrophic adaptations, progressively replacing functional myocardium with collagenous tissue. This pathological cascade ultimately impairs systolic or diastolic function and precipitates arrhythmogenesis. Furthermore, chronic systemic inflammation secondary to myocarditis accelerates atherosclerotic progression, elevating predisposition to lethal ischemic complications (10).
Current therapeutic paradigms prioritize four core strategies: (1) implementation of targeted antiviral interventions, (2) prescription of structured physical rest to reduce myocardial stress, (3) application of standardized heart failure management protocols, and (4) modulation of cytokine-mediated inflammatory responses within cardiac tissue. Notably, modulating the pathological inflammatory cascade remains a critical therapeutic priority requiring advanced intervention strategies.
Despite notable advances in VMC management, current therapeutic paradigms remain predominantly confined to anti-inflammatory interventions with suboptimal efficacy. Given myocardial inflammation’s centrality in VMC pathology, conventional strategies persistently target inflammatory cascades through two complementary approaches: (1) modulating specific immune cell populations to enhance anti-inflammatory precision, and (2) sustaining immunomodulation to remodel the inflammatory microenvironment. While this represents a strategic shift from direct antiviral action toward host immune regulation, such anti-inflammatory-centric frameworks exhibit inherent limitations. Consequently, achieving improved clinical outcomes necessitates innovative targeting beyond inflammation-particularly through emerging gene therapies, mesenchymal stem cell applications, and redox-modulating strategies. This review critically synthesizes recent advances in VMC classification and therapeutics, with focused analysis on CVB3-induced myocarditis pathogenesis and intervention gaps.
2 Classification of VMC
VMC is mediated by diverse etiological agents, among which four viral pathogens have been identified as predominant contributors: CVB3, PVB19, SARS-CoV-2, and AdV. This review focuses on these four viral and delineates their distinct mechanisms of host invasion (Figure 2).
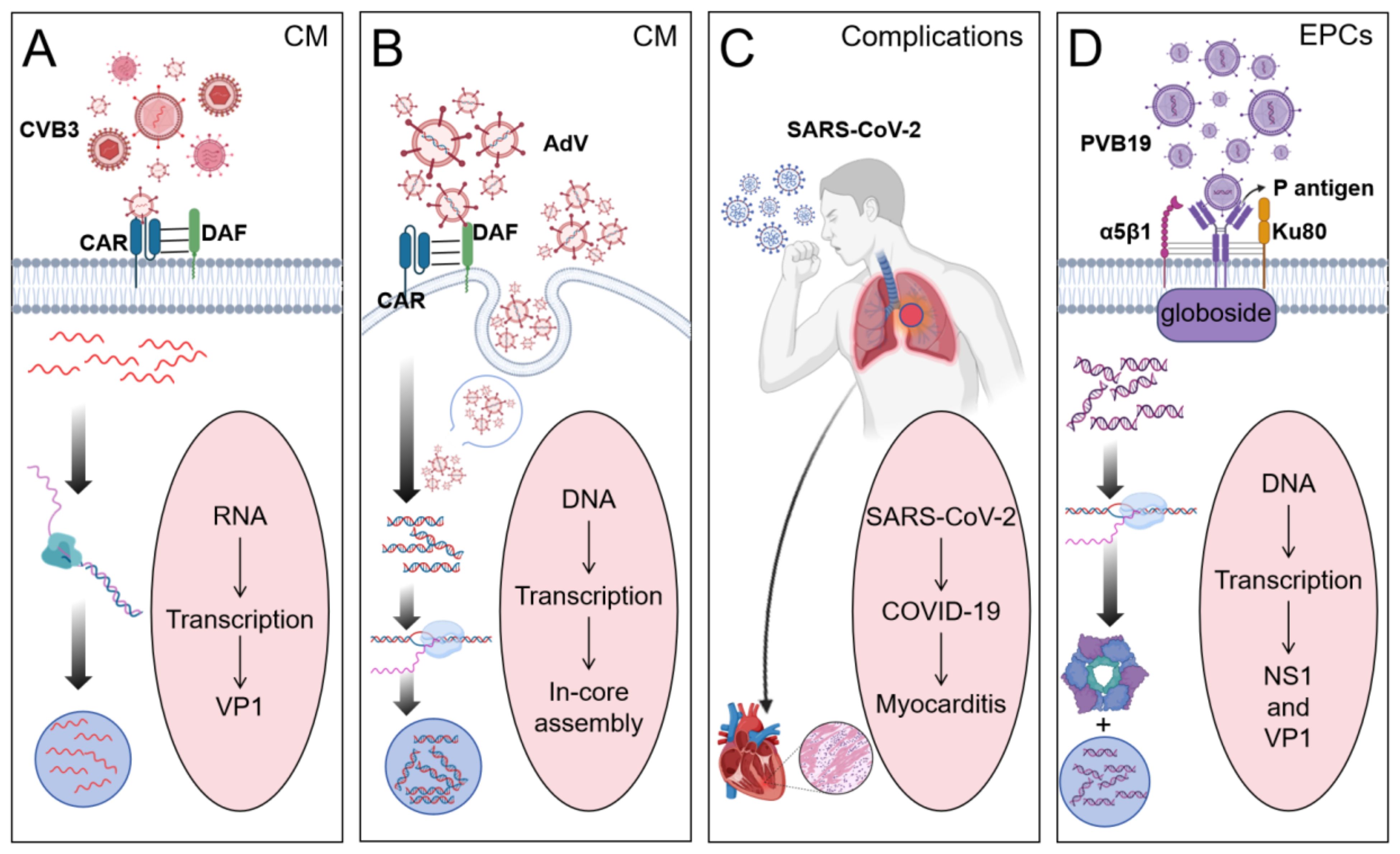
Figure 2. Four different viruses cause the occurrence of myocarditis. (By Biorender). (A) CVB3 binds to the Coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor (CAR) in cardiomyocytes (CM) to promote viral internalization and binds to the Decay acceleration factor (DAF) on the cell surface to initiate viral adhesion. Viruses replicate within host cells to form replication complexes. (B) Adenovirus promotes viral internalization by binding to CAR on the surface of CM through the head domain of its fiber protein, and can also enter CM through endocytosis. Viral DNA replicates within cells and assembles in the nucleus. (C) Human infection with SARS-CoV-2 induces COVID-19, leading to myocarditis as a complication. (D) PVB19 promotes viral adhesion to the cell membrane by recognizing and binding to the P antigen (globoside) on the surface of endothelial progenitor cells. The α5β1 integrin, while the Ku80 protein acts as a coreceptor, enhancing the binding efficiency of the virus to host cells. The non-structural protein NS1 has helicase activity and can promote the replication of viral DNA.
2.1 Coxsackievirus B3
The predominant etiological agent of VMC is recognized as CV (11), with enterovirus CVB3 identified as the most prevalent subtype during the 1980s-1990s. Viral entry into cardiomyocytes occurs through binding to the constitutively expressed transmembrane receptor coxsackie-adenovirus receptor (CAR) (12), facilitated by the decay-accelerating factor (DAF or CD55) co-receptor. This interaction initiates direct myocardial injury and cytoskeletal disruption (13), subsequently provoking persistent immune dysregulation post-viral clearance. Notably, the CVB3/28 strain demonstrates exclusive CAR-dependent infectivity (14), while the CVB3 Variant PD exhibits replication capability in DAF/CAR-deficient cells, with potential involvement of alternative adhesion molecules such as heparan sulfate proteoglycans (15). Current research delineates three principal mechanisms underlying CVB3-induced tissue pathology: direct viral cytotoxicity (16), infection-triggered inflammatory cascades, and their synergistic amplification of myocardial damage (17). The resolution mechanisms for CVB3-induced cardiac inflammatory cascades remain a critical unresolved question in pathogenesis research.
2.2 Parvovirus B19
PVB19 has been established as an additional causative agent of myocarditis alongside CVB3 (18). While typically manifesting as a mild, self-limiting condition, PVB19 infection demonstrates significant potential for triggering severe systemic sepsis and hematological complications. The virus can provoke acute cardiac infection during high-titer viremia (19) and establish persistent myocardial reservoirs with reactivation potential (20). Classified as a vasotropic pathogen, PVB19 primarily targets myocardial vascular endothelial cells and erythroid progenitor cells without directly infiltrating cardiomyocytes (21). Notably, endothelial cell infection may initiate secondary cardiomyocyte apoptosis through indirect mechanisms (22). Following acute symptom resolution, the virus transitions to a latent phase. The clinical implications of persistent PVB19 myocardial reservoirs remain controversial, requiring further investigation to clarify their prognostic significance (23).
2.3 Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
The Coronaviridae family members Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV), Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV), and SARS-CoV-2 all demonstrate cardiac involvement with documented myocarditis development (24). The pathogenic mechanism involves three key elements: viral tropism for angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors, cytokine-mediated myocardial injury, and autoimmune responses targeting cardiac antigens (25). SARS-CoV-2-induced myocarditis represents a severe cardiovascular complication of COVID-19, presenting with heterogeneous clinical manifestations ranging from chest discomfort and exertional dyspnea to cardiac arrhythmias and syncopal episodes (26). Notably, this complication exhibits pan-demographic susceptibility and may demonstrate prolonged latency, potentially extending therapeutic timelines. These characteristics underscore the critical need for optimized early detection protocols and targeted intervention strategies requiring urgent optimization through comprehensive clinical research.
2.4 Adenovirus
AdV represents a cardiotropic pathogen (27), classified as a non-enveloped dsDNA virus with approximately 50 characterized serotypes. These variants demonstrate clinical heterogeneity ranging from self-limiting respiratory infections to fatal systemic manifestations (28). Notably, human AdV serotypes 2 and 5 are predominantly associated with acute myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy development (29, 30). Viral entry into cardiomyocytes occurs through CAR binding (12), inducing myocardial injury and cytoskeletal disruption. This structural degradation initiates persistent immune activation persisting post-viral clearance (13). The sustained cardiac immune activation presents a significant therapeutic challenge, necessitating further investigation into targeted resolution mechanisms.
3 The treatment of VMC induced by CVB3
CVB3 has emerged as the primary etiological agent of VMC. Effective clinical management hinges on early intervention and targeted mitigation of inflammatory cascades. Recent advancements in preclinical model research and clinical evidence accumulation have facilitated significant therapeutic progress, enabling systematic development and evaluation of multiple innovative strategies. Current experimental therapies encompass several targeted approaches: inflammatory cell modulation therapy, inflammatory mediator regulation therapy, genetic intervention strategies, stem cell-based regenerative therapies, and redox homeostasis restoration protocols.
3.1 Inflammatory cell intervention
Inflammatory cell modulation therapy represents a therapeutic strategy that targets inflammation-associated pathologies through precise regulation of inflammatory cell dynamics, including population control, functional modification, and activity modulation. The therapeutic paradigm focuses on three critical cellular processes: targeted modulation of inflammatory cell infiltration patterns, activation states, and polarization phenotypes (including macrophages, T lymphocytes, and neutrophils). This approach achieves therapeutic effects through three primary mechanisms: suppression of pathological inflammation, alleviation of clinical manifestations, and facilitation of regenerative tissue remodeling.
Macrophage M1/M2 polarization equilibrium critically governs tissue homeostasis, with polarization dynamics being intrinsically linked to cellular metabolic profiles (Figure 3). M1 macrophages undergo profound metabolic reprogramming (31), while M2 counterparts predominantly utilize oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) pathways (32). Experimental evidence demonstrates that both microrNA-155 (miR-155) silencing and miR-30a-5p silencing exert convergent therapeutic effects through enhanced M2 polarization. Notably, miR-30a-5p operates via SOCS1-mediated mechanisms to attenuate viral myocarditis (33–35). miR-155−/− mice exhibit elevated anti-inflammatory cytokines with concomitant pro-inflammatory cytokine suppression post-CVB3 challenge. M2-derived exosomes (M2-EXO) demonstrate cardioprotective efficacy in CVB3-induced VMC through lncRNA AK083884/PKM2 axis-mediated metabolic reprogramming, modulating HIF-1α transcriptional activity via PKM2-HIF-1α complex formation (36, 37).These findings collectively establish macrophage polarization modulation as a pivotal therapeutic paradigm in myocarditis management, with targeted polarization strategies representing promising clinical interventions.
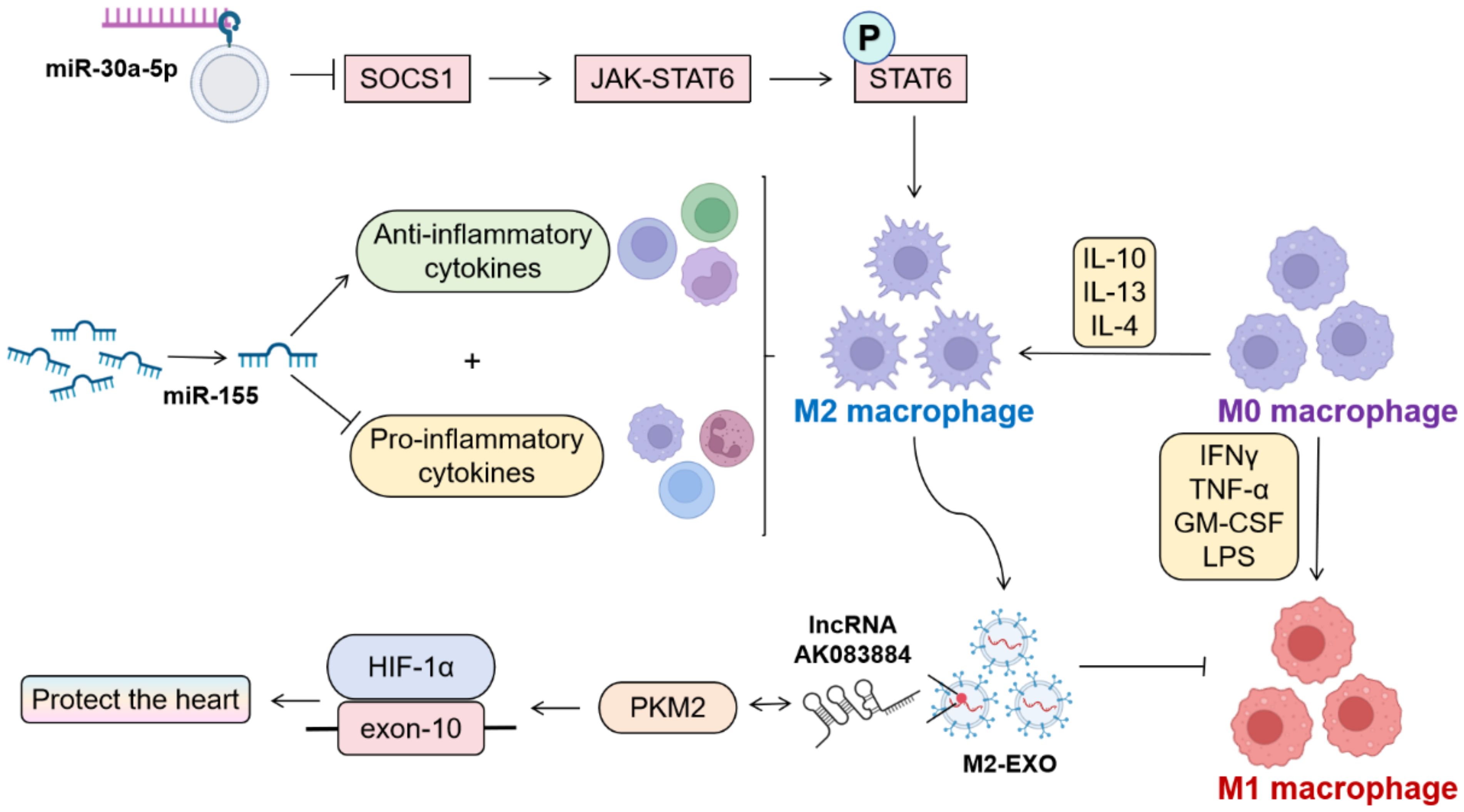
Figure 3. Influencing factors of M1/M2 polarization in macrophages. (By Biorender). Therapeutic suppression of miR-30a-5p and miR-155 has been shown to facilitate M2 macrophage polarization, thereby mitigating viral myocarditis-induced cardiac injury. Exosomes derived from M2-polarized macrophages (M2-Exo) demonstrate cardioprotective effects through dual mechanisms: modulation of the pyruvate kinase M2-hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (PKM2-HIF-1α) complex activity and concomitant downregulation of M1 phenotypic surface markers and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression.
Beyond macrophage polarization-mediated anti-inflammatory effects, T-cell-mediated immunity demonstrates a synergistic therapeutic potential. The activation of macrophages initiates the inflammatory cascade. Infiltrating pro-inflammatory macrophages demonstrate synergistic interaction with CD8+ effector T lymphocytes (38), with T-cells directly exacerbating myocardial injury via IFN-γ secretion, which induces cardiomyocyte apoptosis and disease progression through Spleen focus-forming virus (SFFV) proviral integration oncogene 1 (SPI1) transcription factor upregulation (39).
Study shows thrombospondin-2 (TSP-2) exerts critical cardioprotective effects in CVB3-induced myocarditis through immunomodulation of regulatory T lymphocytes (Tregs) (40). TSP-2 deficiency markedly elevates murine mortality, exacerbates myocardial inflammation, tissue necrosis, and collagen deposition, induces substantial infiltration of CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes within cardiac tissue. Meanwhile, TSP-2 overexpression activates Treg populations, attenuates lymphocyte infiltration, reduces necrotic lesions, and enhances cardiac functional recovery via interacting with CD47 (41). These findings elucidate the TSP-2/Treg axis as a central immunoregulatory mechanism, revealing therapeutic potential for both TSP-2 gene augmentation or Treg amplification strategies to mitigate myocardial injury and improve clinical outcomes through restoration of immunoregulatory homeostasis (42).
Neutrophil activation and extracellular trap (NET) formation exhibit marked elevation during VMC acute phase pathogenesis (43). Experimental evidence demonstrates that lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus G (anti-Ly6G) antibody-mediated neutrophil depletion attenuates myocardial necrosis and leukocyte infiltration while suppressing monocyte recruitment and pro-inflammatory macrophage differentiation. Furthermore, genetic ablation of peptidylarginine deiminase 4-dependent (PAD4-dependent) NET generation substantially mitigates cardiac injury and reduces myocardial myeloid cell infiltration, particularly monocyte and macrophage populations. These collective findings establish neutrophil activity suppression and NET response inhibition as viable therapeutic approaches to ameliorate disease pathology and myocardial inflammation (44).
Macrophages, T lymphocytes, and neutrophils collectively exert critical immunomodulatory functions in VMC pathogenesis. These immunocytes coordinate through synergistic interactions to maintain immune homeostasis, attenuate myocardial inflammation, and preserve cardiac functional integrity. Targeting immunocyte modulation therapies require comprehensive investigation to optimize their therapeutic potential and establish standardized protocols for clinical VMC management.
3.2 Inflammatory mediator modulation therapy
Modulating inflammatory mediators is a therapeutic strategy that targets key signaling molecules involved in the inflammatory response. This approach aims to optimize the inflammatory response, minimize tissue damage, and facilitate tissue repair and functional recovery by regulating components such as cytokines, metabolites, and the extracellular matrix (Figure 4). This therapeutic strategy demonstrates significant potential for application across various inflammatory diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and tumor-associated inflammation. The administration of drugs such as immunoglobulins and glucocorticoids can effectively suppress excessive immune responses, thereby reducing myocardial cell damage (45).
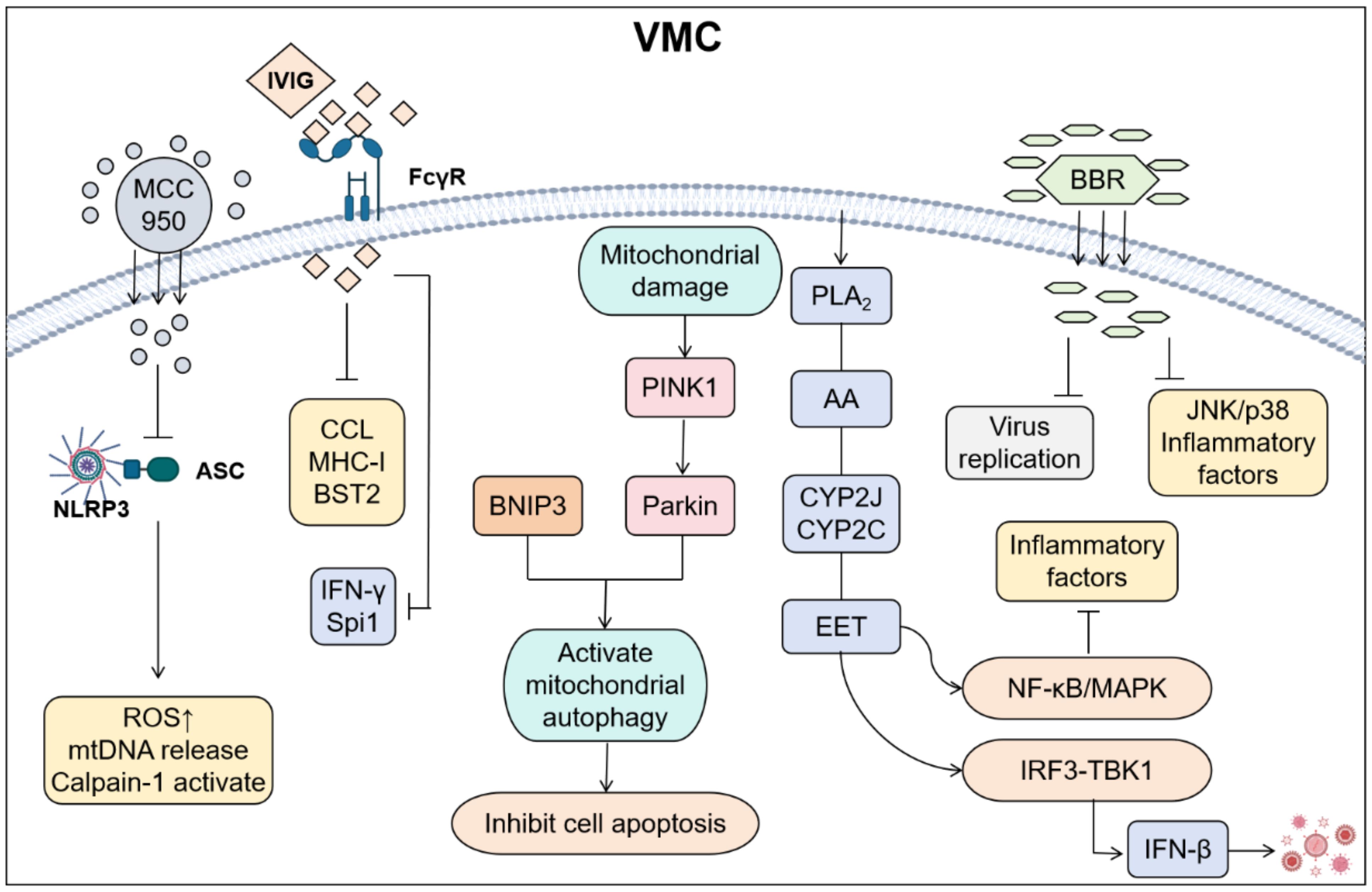
Figure 4. Cardiac injury was reduced by regulating inflammatory mediators in VMC. (By Biorender). MCC950 alleviates damage by inhibiting the binding of NLRP3 to Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC); The IgG of IVIG binds to FcγR on the surface of immune cells such as macrophages and neutrophils through the Fc segment, inhibiting excessive inflammatory responses and reducing the release of inflammatory mediators; Parkin/BNIP3 alleviates apoptosis by activating mitochondrial autophagy; EET inhibits the activation of NF-κB, reduces the expression of inflammatory cytokines, and promotes the interaction between GSK3β and TBK1. Coordinate type I interferon signal transduction to improve cardiac function and alleviate inflammatory responses; BBR can inhibit viral replication and suppress the JNK/p38 pathway and inflammatory factors.
Inflammasome inhibition diminishes inflammatory mediator production and release, thereby modulating inflammatory cascades. Current research confirms that the NLRP3 inflammasome exhibits marked upregulation in cardiomyocytes and infiltrating cardiac macrophages during VMC (46). This molecular complex acts as a cytoplasmic sensor that recognizes both exogenous pathogens and endogenous damage-associated molecular patterns. Subsequently, it initiates Caspase-1-dependent proteolytic cascades, which drive the maturation of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-18. These cascades further orchestrate pyroptotic cell death pathways (47). CVB3 structural proteins VP1 and VP2 serve as crucial NLRP3 activation triggers. Pharmacological inhibition using MCC950 significantly mitigates macrophage/T-cell infiltration (48), attenuates inflammation, and preserves cardiac function. Furthermore, either calpain enzymatic inhibition or upregulation of muscle-specific membrane repair protein MG53 effectively suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation (49, 50), ameliorating inflammatory responses and pyroptosis. Conversely, MG53 knockdown exacerbates both inflammation and pyroptotic cell death (51). Emerging evidence suggests that modulating mitochondrial quality control mechanisms and its crosstalk with inflammatory signaling pathways offers novel therapeutic avenues for myocarditis management.
Parkin, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, plays a pivotal role in mitophagy regulation. In CVB3-induced VMC murine models, Parkin/BNIP3-mediated mitophagy is initiated but autophagic flux remains impaired, with disrupted autophagosome-lysosome fusion (52–54). Parkin silencing increases mortality and worsens cardiac dysfunction in CVB3-infected mice. This impairment disrupts mitophagic clearance, leading to accumulated damaged mitochondria and enhanced apoptosis (55). Additionally, Parkin deficiency dysregulates both mitophagy and inflammatory responses in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Mechanistically, Parkin preserves cardiac function and modulates inflammation during acute VMC through coordinated regulation of mitophagy and NF-κB signaling. Notably, Parkin deficiency may compromise viral defense and autoimmune myocarditis protection via interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP) pathway. IL1RAP inhibition using mCAN10 monoclonal antibody substantially attenuates myocardial pathology severity, suppresses inflammatory infiltration, and downregulates IL-1 signaling/chemokine expression (56). Beyond IL1RAP targeting, exogenous anti-inflammatory agents such as epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) broaden therapeutic options by concurrently modulating NF-κB and type I interferon pathways in myocarditis management.
EETs, bioactive metabolites derived from arachidonic acid through cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases (57), demonstrate potent anti-inflammatory activity (58, 59). EETs undergo rapid conversion to relatively inactive dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids (DHETs) via soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH). sEH inhibitors exhibit therapeutic efficacy through endogenous EETs stabilization. EETs suppress inflammatory cytokine expression by inhibiting NF-κB nuclear translocation and preserve cardiac function in VMC through type I interferon pathway modulation (60–62). Specifically, EETs facilitate molecular interplay between glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β) and TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1), potentiating interferon-β biosynthesis to coordinate type I interferon signaling for enhanced cardiac functional recovery and inflammation resolution (63). Beyond synthetic EET analogs, natural pharmacological agents like berberine offer multi-target therapeutic approaches for myocarditis through concurrent modulation of viral replication mechanisms and inflammatory signaling cascades.
Berberine (BBR), a bioactive isoquinoline alkaloid isolated from Coptis chinensis, exhibits multifaceted anti-inflammatory properties. Experimental evidence demonstrates that BBR’s potent inhibition of CVB3 proliferation in HeLa cells while mitigating virus-induced cytopathic effects. Mechanistically, BBR suppresses c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) activation through reduced phosphorylation, consequently attenuating viral VP1 protein synthesis and double-stranded RNA production (64, 65). In murine CVB3 infection models, BBR administration significantly enhances survival rates, ameliorates myocardial pathology, preserves cardiac function, and reduces viral titers while suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokine release and macrophage infiltration. These findings establish BBR as a novel therapeutic framework for CVB3-induced myocarditis through dual mechanisms of viral replication inhibition and inflammatory response modulation. Unlike dual-targeting phytochemicals that modulate both viral and inflammatory pathways, biopharmaceutical agents (e.g., immunoglobulins) employ polypharmacology approaches. These interventions orchestrate immune cell polarization and facilitate crosstalk coordination between antiviral and inflammatory signaling networks. Consequently, they establish integrated therapeutic paradigms by modulating synergistic immune-inflammatory axis interactions.
Immunoglobulin treatment demonstrates enhanced survival rates in fulminant myocarditis mice (100% vs. 40%), improves cardiac functional parameters, attenuates myocardial inflammation, and balances cytokine profiles by suppressing pro-inflammatory mediators (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α) while promoting anti-inflammatory IL-10 expression (66). Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals immunoglobulin’s dual regulatory effects on cardiac immunity: restoring immune cell homeostasis through suppression of excessive innate immune activation, decreasing monocyte and neutrophil infiltration, and enhancing macrophage antigen presentation capacity to optimize antiviral responses. Mechanistically, immunoglobulins coordinate inflammatory regulation through three key pathways: modulating chemotaxis via CCL signaling, optimizing antigen presentation through MHC-I regulation, and fine-tuning antiviral responses via Bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2 (BST2) signaling (67). These findings substantiate immunoglobulin’s therapeutic potential for myocarditis via comprehensive immunomodulation. They demonstrate concurrent improvements in cardiac function and clinical outcomes, while also proposing novel mechanistic insights. These insights provide a foundation for clinical translation.
Beyond immunoglobulins, IVIG demonstrates therapeutic efficacy in VMC through triple mechanisms: viral neutralization, immunomodulation, and anti-inflammatory action. IVIG delivers broad-spectrum antiviral antibodies that directly neutralize viral particles to prevent cardiomyocyte injury. It concurrently suppresses pathological inflammation by downregulating pro-inflammatory mediator release and normalizing dysregulated immune pathways (68, 69). IVIG reduces mortality, suppresses viral load, and restores immune homeostasis via IFN-γ/Spi1. Unlike IVIG’s multi-targeted immune-antiviral synergy, adrenal corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone) primarily exert single-target anti-inflammatory effects through glucocorticoid receptor activation.
Adrenal corticosteroids, including prednisone and methylprednisolone, serve as cornerstone therapies for VMC owing to their potent anti-inflammatory effects. These agents effectively modulate hyperactive immune responses by suppressing inflammatory cell infiltration and limiting the production of pro-inflammatory mediators. However, clinical application requires cautious risk-benefit evaluation due to their dual-edged nature: immunosuppression may compromise host defense mechanisms while inadvertently exacerbating viral proliferation. Modern therapeutic approaches targeting inflammatory mediators have transitioned from isolated anti-inflammatory interventions to integrated strategies addressing virus-immune-metabolic crosstalk. Future advancements require precision-targeted interventions that transition therapeutic goals from symptom management to reversal of pathological remodeling. This shift demands innovations in spatiotemporal target identification and Artificial intelligence-driven drug development. Concurrently, immunophenotype-guided clinical stratification will enable achievable translation of these therapies.
3.3 Gene therapy
GT introduces a novel therapeutic paradigm for VMC through modulating of immune response and inflammatory injury. Concurrently, targeted molecular interventions that disrupt viral replication cycles establish precise antiviral therapeutic avenues.
As a core enzymatic component of enteroviral replication, RNA helicase represents a strategic therapeutic target, with its pharmacological inhibition of which demonstrates potent blockade of CVB3 pathogenicity. Enterovirus-2C inhibitor (E2CI) targeting the enteroviral 2C protein through specific binding to effectively suppress ATPase activity and disrupt viral genomic RNA replication (70–72). Mechanistically, E2CI exhibits robust antiviral efficacy in vitro, achieving significant suppression of CVB3 proliferation in both HeLa cells (EC50 = 0.32 μM) and primary human cardiomyocytes while maintaining favorable host cell compatibility (CC50 > 50 μM) (73). Translational studies in CVB3-infected murine models confirm therapeutic superiority, with E2CI-treated cohorts demonstrating significantly enhanced survival rates (92% vs. 71%, p < 0.05) accompanied by multimodal cardioprotection: accelerated viral clearance, attenuated myocardial pathology, and preserved cardiac functional parameters. These findings underscore the therapeutic value of viral replication pathway interruption while highlighting complementary intervention opportunities through coordinated modulation of host inflammatory cascades in viral myocarditis management.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) constitute a distinct class of non-protein-coding transcripts exceeding 200 nucleotides in length. Experimental evidence demonstrates that long non-coding guanylate-binding protein 9 (lncGBP9) silencing suppresses NF-κB pathway activation, leading to reduced secretion of key pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β). In vitro validation reveals that lncGBP9 depletion in HL-1 cardiomyocytes significantly enhances cellular viability (p < 0.01) with concomitant decreases in apoptotic indices (p < 0.05), while effectively attenuating both cytokine storm and NF-κB nuclear translocation. These results mechanistically position lncGBP9 as a regulator of inflammatory-apoptotic crosstalk through NF-κB pathway inhibition, suggesting its therapeutic potential for VMC intervention (74). Building upon lncRNA-mediated inflammatory modulation mechanisms, subsequent investigations delineated miRNA’s dual regulatory capacity in balancing viral replication and host defense optimization, constructing a multi-dimensional molecular network of non-coding RNA synergistic intervention in VMC.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous small RNA molecules widely present in eukaryotic organisms that regulate post-transcriptional gene expression by binding to target mRNAs. In CVB3-induced myocarditis, specific miRNAs modulate both viral replication and host immune responses through targeted gene and pathway interactions. For instance, miR-203, miR-590-5p, and miR-126 enhance viral replication (74–76), whereas miR-221 and miR-222 demonstrate cardioprotective effects (77). miR-22-3p exhibits dual functionality during CVB3 infection: it suppresses viral RNA translation while paradoxically facilitating late-stage viral replication, with its downregulation of protocadherin-1 (PCDH1) further promoting viral propagation (78). The upregulated maternally expressed gene 3 (MEG3) acts as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) for miR-21, thereby enhancing viral replication. The MEG3/miR-223/TRAF6/NF-κB signaling pathway emerges as a promising therapeutic target for VMC (79). Additionally, miR-30d improves cardiac outcomes in ischemic cardiomyopathy by reducing cardiomyocyte apoptosis through targeting MAP4K4 in heart muscle cells and ITGA5 in cardiac fibroblasts (80).
Current GT target distinct pathological mechanisms, ranging from direct-acting antiviral approaches (e.g., RNA helicase inhibition) to host microenvironment modulation through non-coding RNA regulation. The synergistic application of these interventions enables comprehensive disease management targeting both symptomatic relief and pathogenic resolution. Future advancements require overcoming technical challenges such as precision drug delivery and real-time therapeutic modulation. This will facilitate the establishment of multidimensional gene therapy platforms and accelerate translation from preclinical research to clinical applications.
3.4 Mesenchymal stem cells therapy
MSCs exhibit multidimensional therapeutic potential in VMC management. In both CVB3-induced and autoimmune myocarditis models, MSCs administered via intramuscular or intravenous routes significantly mitigate disease progression. This therapeutic effect manifests as reduced myocardial tissue damage, improved cardiac systolic function, and decreased inflammatory cell infiltration (81). These therapeutic effects primarily stem from MSC-mediated paracrine immunoregulation, involving two synergistic mechanisms: nitric oxide (NO)-dependent viral replication suppression and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ)-associated preactivation inhibition. This dual action effectively blocks CVB3-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis, oxidative stress, and viral biosynthesis/release (82). MSCs administration downregulates proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6) while modulating cardiac monocyte activation patterns enhancing anti-apoptotic signaling pathways (83). MSCs simultaneously target virus-host interactions and fine-tune innate immune responses, thereby demonstrating myocardial protective capabilities. These dual actions establish a scientific foundation for developing precision stem cell-based therapies against viral myocarditis (VMC).
3.5 Antioxidant therapy
Oxidative stress (OS) represents a pathophysiological condition resulting from disrupted redox equilibrium between pro-oxidant and antioxidant systems, marked by reactive oxygen species (ROS) overproduction due to impaired peroxide metabolism (84). This redox imbalance initiates pathological cascades involving neutrophilic inflammation, dysregulated protease activity, and oxidative intermediate deposition, all of which exacerbate cellular damage. Study confirms OS serves not only as a fundamental mechanism of biological aging but also constitutes a critical pathological driver across multiple disease states (85). Antioxidants counteracting this process maintains redox homeostasis by scavenging free radicals and neutralizing their cytotoxic effects, thereby playing essential regulatory roles in oxidative balance (86, 87).
In the management of OS associated with VMC, antioxidant therapy plays a critical role, particularly in modulating inflammatory responses and preserving cellular function. Penfluridol (PF) demonstrates both anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated macrophages. Specifically, PF suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation, consequently decreasing secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α and IL-6 (88). Concurrently, through activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway, PF enhances superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity while reducing malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, effectively alleviating OS (89). These combined mechanisms substantially attenuate LPS-induced macrophage injury.
Beyond revealing PF’s dual-axis modulation of NLRP3/Nrf2 pathways in regulating inflammatory-oxidative equilibrium, the study demonstrated that sulfhydryl-containing antioxidants possessed distinct cardioprotective mechanisms with extended therapeutic promise in VMC. In CVB3-infected murine models, the thiol-based antioxidants captopril and N- (2-mercaptopropionyl)glycine (MPG) significantly improved survival rates, reduced myocardial injury markers (including cellular infiltration, necrosis, and calcification), and suppressed infection-induced upregulation of myocardial manganese superoxide dismutase (Mn-SOD) and copper-zinc superoxide dismutase (Cu/Zn-SOD) mRNA expression (90).
Antioxidants mitigate myocardial injury through scavenging ROS and modulating inflammatory/OS pathways. These findings establish a comprehensive experimental foundation for developing targeted therapeutic strategies against VMC with OS regulation as the core mechanism.
4 The treatment of VMC induced by other viruses
4.1 Coronavirus induced-myocarditis
The pathological mechanisms underlying COVID-19-associated VMC caused by SARS-CoV-2 remain incompletely understood. Evidence indicates that glucocorticoids combined with IVIG demonstrate clinical utility in such cases. While the use of glucocorticoids in VMC caused by CVB3 remains controversial, they may exert a myocardial-protective effect through combined immunosuppressive, anti-inflammatory, and anti-shock mechanisms (91). IVIG, with its dual antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties, has been shown to significantly improve outcomes in VMC when administered early and in adequate doses. The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines explicitly recommend evaluating a glucocorticoid-IVIG combination therapy strategy in high-risk patients (92).
A representative case study documented a male patient with SARS-CoV-2-induced VMC complicated by cardiogenic shock and pulmonary infection. Following treatment with methylprednisolone pulse therapy combined with IVIG, the patient demonstrated marked symptomatic improvement along with complete restoration of cardiac architecture and systolic function. Concurrently, myocardial injury biomarkers (troponin I and B-type natriuretic peptide) returned to normal levels (91). This clinical evidence provides compelling support for the critical importance of early combined immunomodulatory therapy in managing coronavirus-related myocarditis.
Given the absence of clinically approved SARS-CoV-2-specific vaccines and targeted antiviral therapies (93), the development of protease inhibitors targeting the viral main protease (Mpro) has emerged as a critical priority in antiviral research. FRET-based screening platforms have identified potent Mpro inhibitors including boceprevir and GC-376, which exhibit significant antiviral activity with IC50 values ranging from single-digit to submicromolar concentrations. These compounds demonstrated efficacy in cellular infection models, with EC50 values ranging from 0.49 to 3.37 μM. Structural characterization via X-ray crystallography (2.15 Å resolution) revealed GC-376’s unique R/S dual-conformation binding mode within the protease active site. This finding provides a structural framework for rational lead compound optimization (94). Therapeutically, these protease inhibitors may serve as monotherapies or combine with RNA polymerase inhibitors such as remdesivir, enhancing therapeutic outcomes through multitarget synergistic effects while mitigating resistance development risks.
Emerging research demonstrates that N5-methylcytidine (m5C) RNA modifications serve as key regulatory mechanisms in SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. This evolutionarily conserved epigenetic modification orchestrates multiple pathophysiological processes including embryonic development, tumor progression, and viral infection through modulating RNA stability, nucleocytoplasmic trafficking, and translational efficiency (95, 96). Within COVID-19-induced myocardial injury, m5C methylation drives disease progression via a tripartite pathogenic mechanism: (1) controlling viral genomic stability, (2) fine-tuning cytokine storm magnitude, and (3) mediating ACE2/angiotensin axis signaling. Crucially, experimental data confirm that hyperactivated m5C methyltransferases induce innate immune dysregulation and potentiate cardiomyocyte damage (97).
Despite notable advancements in current studies, several pivotal scientific challenges remain to be addressed: First, the relationship between the therapeutic time window and dose-response dynamics of glucocorticoid administration. Second, optimizing the pharmacokinetic profiles of Mpro inhibitors for clinical translation. Third, elucidating the precise regulatory mechanisms underlying the m5C methylation network in myocardial tissue. The development of multi-omics analytical platforms and organoid-based models will serve as crucial breakthroughs for unraveling SARS-CoV-2-induced myocarditis mechanisms and advancing novel therapeutic approaches.
4.2 Adenovirus induced-myocarditis
Adenoviral myocarditis exhibits significant clinical heterogeneity. Early manifestations often mimic upper respiratory or gastrointestinal infections, yet rapid progression to fulminant heart failure remains a critical concern. Current clinical management relies primarily on supportive interventions: strict bed rest (≥3 months acutely), high-dose vitamin C for free radical scavenging, glucocorticoid/immunoglobulin therapy to counter hyperactive immunity (98), and mechanical circulatory support (e.g., ECMO) in severe cases. Antiviral agents such as ribavirin and interferon demonstrate limited efficacy due to narrow therapeutic windows and target non-specificity. Notably, these therapeutic constraints stem from insufficient mechanistic understanding of early viral cytopathic effects-particularly AdV serotype 5 (Ad5)-mediated disruption of cardiac electrophysiological homeostasis.
Preclinical breakthroughs reveal AdV serotype 5 (Ad5) pathogenesis mechanisms. Mechanistic studies establish that Ad5 suppresses GJA1 transcription via β-catenin-dependent pathways, consequently downregulating connexin 43 (Cx43) protein. The early viral protein E4orf1 induces β-catenin phosphorylation, effectively inhibiting Cx43 gene transcription. During initial Ad5 infection, Cx43 phosphorylation triggers electrophysiological abnormalities. Super-resolution imaging confirms dissociation of the Cx43/ZO-1 complex initiates gap junction remodeling in infected cardiomyocytes (99), ultimately provoking arrhythmias through impaired intercellular communication.
Existing therapies lack precision targeting. Future strategies should integrate multi-omic subtyping to develop combinatorial approaches, coupled with immunophenotype-guided individualized interventions. Key translational bottlenecks involve enhancing cardiac-targeted delivery efficiency and validating long-term safety in large-animal models.
4.3 PVB19-induced myocarditis
PVB19-induced myocarditis demonstrates marked clinical heterogeneity. This condition can progress rapidly to fulminant heart failure or cardiogenic shock, particularly in pediatric and adolescent populations where case fatality reaches 50-80%. Clinical management centers on supportive interventions: strict bed rest, mechanical circulatory support (e.g., ECMO/IABP), and respiratory assistance. Some clinical studies have shown complete clinical recovery after ECMO support combined with intravenous IVIG, but the efficacy of intravenous IVIG for patients with high viral load is still controversial (100).
Future strategies require multi-omic subtyping integration to develop individualized combination approaches. Concurrent optimization of IVIG timing and dosing regimens is essential. Critical translational barriers include enhancing cardiac-targeted delivery efficiency and validating long-term therapeutic outcomes in large-animal models.
5 Future and prospect
Although significant advances have been made in recent years in understanding the pathophysiology and treatment of myocarditis, further research remains critical. Treatment of myocarditis requires a thorough evaluation of the patient’s etiology, underlying pathophysiological mechanisms, and clinical manifestations.
Future research should prioritize the following strategic directions: (1) conduct comprehensive investigations into dynamic immune cell subset interactions (particularly CD8+ T lymphocytes and neutrophils) across disease progression phases; (2) design spatiotemporal-specific modulation strategies leveraging non-coding RNAs (microRNAs, lncRNAs); (3) enhance clinical translation of pathogen-specific vaccines and broad-spectrum antivirals including Mpro inhibitors; (4) innovate multimodal combination therapies (e.g., CRISPR-based editing coupled with stem cell engineering) to concurrently suppress viral proliferation and immune dysregulation; (5) implement multi-omics integration (single-cell transcriptomics, metabolic profiling) with organoid platforms to decode virus-host interface networks and enable precision subclassification with personalized regimens. Concurrently, longitudinal outcome optimization requires focused management of chronic inflammatory cascades and fibrotic transitions, aiming to transcend symptomatic palliation toward definitive disease modification.
Author contributions
JX: Writing – original draft. XC: Writing – original draft. XG: Writing – original draft. HZ: Writing – review & editing. YL: Writing – review & editing. MZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82460076), Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 825RC781) and Academic Ehancement Support Program of Hainan Medical University (Grant No. XSTS2025128). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, manuscript preparation, or decision to publish.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Generative AI was used to polish the article.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Feldman AM and McNamara D. Myocarditis. N Engl J Med. (2000) 343:1388–98. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200011093431908
2. Maron BJ, Doerer JJ, Haas TS, Tierney DM, and Mueller FO. Sudden deaths in young competitive athletes: analysis of 1866 deaths in the United States, 1980-2006. Circulation. (2009) 119:1085–92. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.804617
3. Trachtenberg BH and Hare JM. Inflammatory cardiomyopathic syndromes. Circ Res. (2017) 121:803–18. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.310221
4. Ammirati E, Veronese G, Bottiroli M, Wang DW, Cipriani M, Garascia A, et al. Update on acute myocarditis. Trends Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 31:370–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2020.05.008
5. Sagar S, Liu PP, and Cooper LT Jr. Myocarditis. Lancet. (2012) 379:738–47. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60648-X
6. Frustaci A, Alfarano M, Verardo R, Agrati C, Casetti R, Miraldi F, et al. Myocarditis-associated necrotizing coronary vasculitis: incidence, cause, and outcome. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42:1609–17. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa973
7. Blanco-Domínguez R, Sánchez-Díaz R, de la Fuente H, Jiménez-Borreguero LJ, Matesanz-Marín A, Relaño M, et al. A novel circulating microRNA for the detection of acute myocarditis. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:2014–27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2003608
8. Caforio AL, Pankuweit S, Arbustini E, Basso C, Gimeno-Blanes J, Felix SB, et al. Current state of knowledge on aetiology, diagnosis, management, and therapy of myocarditis: a position statement of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur Heart J. (2013) 34:2636–48. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht210
9. Chen W and Frangogiannis NG. The role of inflammatory and fibrogenic pathways in heart failure associated with aging. Heart Fail Rev. (2010) 15:415–22. doi: 10.1007/s10741-010-9161-y
10. Groenewegen A, Rutten FH, Mosterd A, and Hoes AW. Epidemiology of heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. (2020) 22:1342–56. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1858
11. Nie X, Li H, Wang J, Cai Y, Fan J, Dai B, et al. Expression profiles and potential functions of long non-coding RNAs in the heart of mice with coxsackie B3 virus-induced myocarditis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2021) 11:704919. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.704919
12. He Y, Chipman PR, Howitt J, Bator CM, Whitt MA, Baker TS, et al. Interaction of coxsackievirus B3 with the full length coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor. Nat Struct Biol. (2001) 8:874–8. doi: 10.1038/nsb1001-874
13. Badorff C, Lee GH, Lamphear BJ, Martone ME, Campbell KP, Rhoads RE, et al. Enteroviral protease 2A cleaves dystrophin: evidence of cytoskeletal disruption in an acquired cardiomyopathy. Nat Med. (1999) 5:320–6. doi: 10.1038/6543
14. Carson SD, Chapman NM, Hafenstein S, and Tracy S. Variations of coxsackievirus B3 capsid primary structure, ligands, and stability are selected for in a coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor-limited environment. J Virol. (2011) 85:3306–14. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01827-10
15. Zautner AE, Körner U, Henke A, Badorff C, and Schmidtke M. Heparan sulfates and coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor: each one mediates coxsackievirus B3 PD infection. J Virol. (2003) 77:10071–7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.77.18.10071-10077.2003
16. McManus BM, Chow LH, Wilson JE, Anderson DR, Gulizia JM, Gauntt CJ, et al. Direct myocardial injury by enterovirus: a central role in the evolution of murine myocarditis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. (1993) 68:159–69. doi: 10.1006/clin.1993.1113
17. Huber SA, Gauntt CJ, and Sakkinen P. Enteroviruses and myocarditis: viral pathogenesis through replication, cytokine induction, and immunopathogenicity. Adv Virus Res. (1998) 51:35–80. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60783-6
18. Schultz JC, Hilliard AA, Cooper LT Jr., and Rihal CS. Diagnosis and treatment of viral myocarditis. Mayo Clin Proc. (2009) 84:1001–9. doi: 10.1016/S0025-6196(11)60670-8
19. Manaresi E and Gallinella G. Advances in the development of antiviral strategies against parvovirus B19. Viruses. (2019) 11:659–18. doi: 10.3390/v11070659
20. Dominguez F, Kühl U, Pieske B, Garcia-Pavia P, and Tschöpe C. Update on myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy: reemergence of endomyocardial biopsy. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). (2016) 69:178–87. doi: 10.1016/j.recesp.2015.10.018
21. Badrinath A, Bhatta S, and Kloc A. Persistent viral infections and their role in heart disease. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:1030440. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1030440
22. Bültmann BD, Sotlar K, and Klingel K. Parvovirus B19. N Engl J Med. (2004) 350:2006–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200405063501920
23. Hjalmarsson C, Liljeqvist J, Lindh M, Karason K, Bollano E, Oldfors A, et al. Parvovirus B19 in endomyocardial biopsy of patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy: foe or bystander? J Card Fail. (2019) 25:60–3. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2018.07.466
24. Tschöpe C, Ammirati E, Bozkurt B, Caforio ALP, Cooper LT, Felix SB, et al. Myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy: current evidence and future directions. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2021) 18:169–93. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-00435-x
25. Song J, Lin LA, Tang C, Chen C, Yang Q, Zhang D, et al. DEMINERS enables clinical metagenomics and comparative transcriptomic analysis by increasing throughput and accuracy of nanopore direct RNA sequencing. Genome Biol. (2025) 26:76. doi: 10.1186/s13059-025-03536-3
26. Hu B, Guo H, Zhou P, and Shi ZL. Author correction: characteristics of SARS-coV-2 and COVID-19. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2022) 20:315. doi: 10.1038/s41579-022-00711-2
27. Heymans S, Van Linthout S, Kraus SM, Cooper LT, and Ntusi NAB. Clinical characteristics and mechanisms of acute myocarditis. Circ Res. (2024) 135:397–411. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.124.324674
28. Padget RL, Zeitz MJ, Blair GA, Wu X, North MD, Tanenbaum MT, et al. Acute adenoviral infection elicits an arrhythmogenic substrate prior to myocarditis. Circ Res. (2024) 134:892–912. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.322437
29. Bowles NE, Ni J, Kearney DL, Pauschinger M, Schultheiss HP, McCarthy R, et al. Detection of viruses in myocardial tissues by polymerase chain reaction. evidence of adenovirus as a common cause of myocarditis in children and adults. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2003) 42:466–72. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(03)00648-X
30. Pauschinger M, Bowles NE, Fuentes-Garcia FJ, Pham V, Kühl U, Schwimmbeck PL, et al. Detection of adenoviral genome in the myocardium of adult patients with idiopathic left ventricular dysfunction. Circulation. (1999) 99:1348–54. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.99.10.1348
31. Zou X, Xu H, and Qian W. Macrophage polarization in the osteoarthritis pathogenesis and treatment. Orthop Surg. (2025) 17:22–35. doi: 10.1111/os.14302
32. Yao M, Li M, Peng D, Wang Y, Li S, Zhang D, et al. Unraveling macrophage polarization: functions, mechanisms, and “Double-edged sword. Roles Host Antiviral Immune Responses Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:12078–22. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212078
33. Liu X, Dou B, Tang W, Yang H, Chen K, Wang Y, et al. Cardioprotective effects of circ_0002612 in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury correlate with disruption of miR-30a-5p-dependent Ppargc1a inhibition. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 117:110006. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110006
34. Lv XB, Niu QH, Zhang M, Feng L, and Feng J. Critical functions of microRNA-30a-5p-E2F3 in cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. (2021) 37:92–100. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12309
35. Zhang Y, Cai S, Ding X, Lu C, Wu R, Wu H, et al. MicroRNA-30a-5p silencing polarizes macrophages toward M2 phenotype to alleviate cardiac injury following viral myocarditis by targeting SOCS1. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2021) 320:H1348–h1360. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00431.2020
36. Zhang Y, Li X, Wang C, Zhang M, Yang H, and Lv K. lncRNA AK085865 promotes macrophage M2 polarization in CVB3-induced VM by regulating ILF2-ILF3 complex-mediated miRNA-192 biogenesis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2020) 21:441–51. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.06.017
37. Zhang Y, Zhu L, Li X, Ge C, Pei W, Zhang M, et al. M2 macrophage exosome-derived lncRNA AK083884 protects mice from CVB3-induced viral myocarditis through regulating PKM2/HIF-1α axis mediated metabolic reprogramming of macrophages. Redox Biol. (2024) 69:103016. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.103016
38. Santos-Zas I, Lemarié J, Zlatanova I, Cachanado M, Seghezzi JC, Benamer H, et al. Cytotoxic CD8(+) T cells promote granzyme B-dependent adverse post-ischemic cardiac remodeling. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:1483. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21737-9
39. Li H, Chen X, Wang JJ, Shen J, Abuduwufuer K, Zhang Z, et al. Spatiotemporal transcriptomics elucidates the pathogenesis of fulminant viral myocarditis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2025) 10:59. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02143-9
40. Yabkowitz R, Dixit VM, Guo N, Roberts DD, and Shimizu Y. Activated T-cell adhesion to thrombospondin is mediated by the alpha 4 beta 1 (VLA-4) and alpha 5 beta 1 (VLA-5) integrins. J Immunol. (1993) 151:149–58. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.151.1.149
41. Rebres RA, Kajihara K, and Brown EJ. Novel CD47-dependent intercellular adhesion modulates cell migration. J Cell Physiol. (2005) 205:182–93. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20379
42. Papageorgiou AP, Swinnen M, Vanhoutte D, VandenDriessche T, Chuah M, Lindner D, et al. Thrombospondin-2 prevents cardiac injury and dysfunction in viral myocarditis through the activation of regulatory T-cells. Cardiovasc Res. (2012) 94:115–24. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs077
43. Lv J, Zhang Y, Wu Q, Jiang P, and Lin Y. Inhibition of SIRT4 promotes bladder cancer progression and immune escape via attenuating CD8(+) T cells function. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 147:113906. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113906
44. Carai P, González LF, Van Bruggen S, Spalart V, De Giorgio D, Geuens N, et al. Neutrophil inhibition improves acute inflammation in a murine model of viral myocarditis. Cardiovasc Res. (2023) 118:3331–45. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvac052
45. Shinkai-Ouchi F, Shindo M, Doi N, Hata S, and Ono Y. Calpain-2 participates in the process of calpain-1 inactivation. Biosci Rep. (2020) 40:BSR20200552. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200552
46. Fu J and Wu H. Structural mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and activation. Annu Rev Immunol. (2023) 41:301–16. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-081022-021207
47. Bao J, Sun T, Yue Y, and Xiong S. Macrophage NLRP3 inflammasome activated by CVB3 capsid proteins contributes to the development of viral myocarditis. Mol Immunol. (2019) 114:41–8. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2019.07.012
48. Wei S, Guan G, Luan X, Yu C, Miao L, Yuan X, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome constrains liver regeneration through impairing MerTK-mediated macrophage efferocytosis. Sci Adv. (2025) 11:eadq5786. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adq5786
49. Liu X, Li M, Chen Z, Yu Y, Shi H, Yu Y, et al. Mitochondrial calpain-1 activates NLRP3 inflammasome by cleaving ATP5A1 and inducing mitochondrial ROS in CVB3-induced myocarditis. Basic Res Cardiol. (2022) 117:40. doi: 10.1007/s00395-022-00948-1
50. Yu Y, Shi H, Yu Y, Liu M, Li M, Liu X, et al. Inhibition of calpain alleviates coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis through suppressing the canonical NLRP3 inflammasome/caspase-1-mediated and noncanonical caspase-11-mediated pyroptosis pathways. Am J Transl Res. (2020) 12:1954–64.
51. Xue Y, Song T, Ke J, Lin S, Zhang J, Chen Y, et al. MG53 protects against Coxsackievirus B3-induced acute viral myocarditis in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis via the NF-κB signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. (2024) 223:116173. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116173
52. Fu J, Cheng L, Zhang J, Sun R, Yu M, Wu M, et al. Isoliquiritin targeting m5C RNA methylation improves mitophagy in doxorubicin-induced myocardial cardiotoxicity. Phytomedicine. (2025) 136:156293. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156293
53. Jiang H. AMPK: Balancing mitochondrial quality and quantity through opposite regulation of mitophagy pathways. Mol Cell. (2024) 84:4261–3. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.10.040
54. Wang W, Wang Q, Li W, Xu H, Liang X, Wang W, et al. Targeting APJ drives BNIP3-PINK1-PARKIN induced mitophagy and improves systemic inflammatory bone loss. J Adv Res. (2024) 24:611–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.12.033
55. Qiu Y, Xu J, Chen Y, Wu Y, Lin YN, Liu W, et al. Parkin plays a crucial role in acute viral myocarditis by regulating mitophagy activity. Theranostics. (2024) 14:5303–15. doi: 10.7150/thno.97675
56. Lema DA, Jakobsson G, Daoud A, Elias D, Talor MV, Rattik S, et al. IL1RAP blockade with a monoclonal antibody reduces cardiac inflammation and preserves heart function in viral and autoimmune myocarditis. Circ Heart Fail. (2024) 17:e011729. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.124.011729
57. Peng L, Song Z, Zhao C, Abuduwufuer K, Wang Y, Wen Z, et al. Increased soluble epoxide hydrolase activity positively correlates with mortality in heart failure patients with preserved ejection fraction: evidence from metabolomics. Phenomics. (2023) 3:34–49. doi: 10.1007/s43657-022-00069-8
58. McNab F, Mayer-Barber K, Sher A, Wack A, and O’Garra A. Type I interferons in infectious disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2015) 15:87–103. doi: 10.1038/nri3787
59. Mesev EV, LeDesma RA, and Ploss A. Decoding type I and III interferon signalling during viral infection. Nat Microbiol. (2019) 4:914–24. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0421-x
60. Ko R, Park JH, Ha H, Choi Y, and Lee SY. Glycogen synthase kinase 3β ubiquitination by TRAF6 regulates TLR3-mediated pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Nat Commun. (2015) 6:6765. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7765
61. Lei CQ, Zhong B, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Wang S, and Shu HB. Glycogen synthase kinase 3β regulates IRF3 transcription factor-mediated antiviral response via activation of the kinase TBK1. Immunity. (2010) 33:878–89. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.11.021
62. Qin Y, Liu Q, Tian S, Xie W, Cui J, and Wang RF. TRIM9 short isoform preferentially promotes DNA and RNA virus-induced production of type I interferon by recruiting GSK3β to TBK1. Cell Res. (2016) 26:613–28. doi: 10.1038/cr.2016.27
63. Zhou Z, Zhang M, Zhao C, Gao X, Wen Z, Wu J, et al. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids prevent cardiac dysfunction in viral myocarditis via interferon type I signaling. Circ Res. (2023) 133:772–88. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.322619
64. Dai Q, He X, Yu H, Bai Y, Jiang L, Sheng H, et al. Berberine impairs coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis through the inhibition of virus replication and host pro-inflammatory response. J Med Virol. (2021) 93:3581–9. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26747
65. Dai Q, Zhang D, Yu H, Xie W, Xin R, Wang L, et al. Berberine Restricts Coxsackievirus B Type 3 Replication via Inhibition of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) and p38 MAPK Activation In Vitro. Med Sci Monit. (2017) 23:1448–55. doi: 10.12659/MSM.899804
66. Wen J, Li H, Zhou Y, Du H, Hu G, Wen Z, et al. Immunoglobin attenuates fulminant myocarditis by inhibiting overactivated innate immune response. Br J Pharmacol. (2024) 10:1111. doi: 10.1111/bph.17372
67. Hematianlarki M and Nimmerjahn F. Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties of immunoglobulin G antibodies. Immunol Rev. (2024) 328:372–86. doi: 10.1111/imr.13404
68. Coustal C, Vanoverschelde J, Quantin X, Lesage C, Michot JM, Lappara A, et al. Prognosis of immune checkpoint inhibitors-induced myocarditis: a case series. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11:e004792. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004792
69. Daetwyler E, Wallrabenstein T, König D, Cappelli LC, Naidoo J, Zippelius A, et al. Corticosteroid-resistant immune-related adverse events: a systematic review. J Immunother Cancer. (2024) 12:e007409. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007409
70. Moore MJ. From birth to death: the complex lives of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science. (2005) 309:1514–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1111443
71. Ranji A and Boris-Lawrie K. RNA helicases: emerging roles in viral replication and the host innate response. RNA Biol. (2010) 7:775–87. doi: 10.4161/rna.7.6.14249
72. Yedavalli VS, Zhang N, Cai H, Zhang P, Starost MF, Hosmane RS, et al. Ring expanded nucleoside analogues inhibit RNA helicase and intracellular human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication. J Med Chem. (2008) 51:5043–51. doi: 10.1021/jm800332m
73. Yun SH, Shin HH, Ju ES, Lee YJ, Lim BK, and Jeon ES. Inhibition of RNA helicase activity prevents coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis in human iPS cardiomyocytes. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:3041–10. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093041
74. Xue Y, Zhang J, Ke J, Zeng L, Cheng K, Han X, et al. LncGBP9 knockdown alleviates myocardial inflammation and apoptosis in mice with acute viral myocarditis via suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway. Inflammation Res. (2022) 71:1559–76. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01644-5
75. Germano JF, Sawaged S, Saadaeijahromi H, Andres AM, Feuer R, Gottlieb RA, et al. Coxsackievirus B infection induces the extracellular release of miR-590-5p, a proviral microRNA. Virology. (2019) 529:169–76. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2019.01.025
76. Ye X, Hemida MG, Qiu Y, Hanson PJ, Zhang HM, and Yang D. MiR-126 promotes coxsackievirus replication by mediating cross-talk of ERK1/2 and Wnt/β-catenin signal pathways. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2013) 70:4631–44. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1411-4
77. Corsten MF, Heggermont W, Papageorgiou AP, Deckx S, Tijsma A, Verhesen W, et al. The microRNA-221/-222 cluster balances the antiviral and inflammatory response in viral myocarditis. Eur Heart J. (2015) 36:2909–19. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv321
78. Rani P, George B, V S, Biswas S, V M, Pal A, et al. MicroRNA-22-3p displaces critical host factors from the 5’ UTR and inhibits the translation of Coxsackievirus B3 RNA. J Virol. (2024) 98:e0150423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01504-23
79. He F, Liu Z, Feng M, Xiao Z, Yi X, Wu J, et al. The lncRNA MEG3/miRNA-21/P38MAPK axis inhibits coxsackievirus 3 replication in acute viral myocarditis. Virus Res. (2024) 339:199250. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199250
80. Li J, Salvador AM, Li G, Valkov N, Ziegler O, Yeri A, et al. Mir-30d regulates cardiac remodeling by intracellular and paracrine signaling. Circ Res. (2021) 128:e1–e23. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317244
81. Du J, Zheng L, Gao P, Yang H, Yang WJ, Guo F, et al. A small-molecule cocktail promotes mammalian cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart regeneration. Cell Stem Cell. (2022) 29:545–558.e513. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2022.03.009
82. Ren G, Zhang L, Zhao X, Xu G, Zhang Y, Roberts AI, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression occurs via concerted action of chemokines and nitric oxide. Cell Stem Cell. (2008) 2:141–50. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2007.11.014
83. Van Linthout S, Savvatis K, Miteva K, Peng J, Ringe J, Warstat K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells improve murine acute coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis. Eur Heart J. (2011) 32:2168–78. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq467
84. Sies H. Oxidative stress: a concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. (2015) 4:180–3. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.01.002
85. van der Pol A, van Gilst WH, Voors AA, and van der Meer P. Treating oxidative stress in heart failure: past, present and future. Eur J Heart Fail. (2019) 21:425–35. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1320
86. Lu X, He Z, Xiao X, Wei X, Song X, and Zhang S. Natural antioxidant-based nanodrug for atherosclerosis treatment. Small. (2023) 19:e2303459. doi: 10.1002/smll.202303459
87. Qian Z, Sun C, Li Q, Xie Y, Zhan L, Liu X, et al. Unravelling the antioxidant behaviour of self-assembly β-Sheet in silk fibroin. Redox Biol. (2024) 76:103307. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103307
88. Coll RC, Robertson AA, Chae JJ, Higgins SC, Muñoz-Planillo R, Inserra MC, et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Nat Med. (2015) 21:248–55. doi: 10.1038/nm.3806
89. Li Q, Wu L, Cheng B, Tao S, Wang W, Luo Z, et al. Penfluroidol attenuates the imbalance of the inflammatory response by repressing the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and reduces oxidative stress via the nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in LPS-induced macrophages. Mediators Inflammation. (2023) 2023:9940858. doi: 10.1155/2023/9940858
90. Suzuki H, Matsumori A, Matoba Y, Kyu BS, Tanaka A, Fujita J, et al. Enhanced expression of superoxide dismutase messenger RNA in viral myocarditis. An SH-dependent reduction of its expression and myocardial injury. J Clin Invest. (1993) 91:2727–33. doi: 10.1172/JCI116513
91. Hu H, Ma F, Wei X, and Fang Y. Coronavirus fulminant myocarditis treated with glucocorticoid and human immunoglobulin. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42:206. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa190
92. Kishimoto C, Shioji K, Hashimoto T, Nonogi H, Lee JD, Kato S, et al. Therapy with immunoglobulin in patients with acute myocarditis and cardiomyopathy: analysis of leukocyte balance. Heart Vessels. (2014) 29:336–42. doi: 10.1007/s00380-013-0368-4
93. Wang RS and Loscalzo J. Repurposing drugs for the treatment of COVID-19 and its cardiovascular manifestations. Circ Res. (2023) 132:1374–86. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321879
94. Ma C, Sacco MD, Hurst B, Townsend JA, Hu Y, Szeto T, et al. Boceprevir, GC-376, and calpain inhibitors II, XII inhibit SARS-CoV-2 viral replication by targeting the viral main protease. Cell Res. (2020) 30:678–92. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0356-z
95. Liu J, Huang T, Chen W, Ding C, Zhao T, Zhao X, et al. Developmental mRNA m(5)C landscape and regulatory innovations of massive m(5)C modification of maternal mRNAs in animals. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:2484. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30210-0
96. Zhang Y, Zhang LS, Dai Q, Chen P, Lu M, Kairis EL, et al. 5-methylcytosine (m(5)C) RNA modification controls the innate immune response to virus infection by regulating type I interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2022) 119:e2123338119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2123338119
97. Xiong Y, Li Y, Qian W, and Zhang Q. RNA m5C methylation modification: a potential therapeutic target for SARS-CoV-2-associated myocarditis. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1380697. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1380697
98. Robinson J, Hartling L, Vandermeer B, Sebastianski M, and Klassen TP. Intravenous immunoglobulin for presumed viral myocarditis in children and adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2020) 8:Cd004370. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004370.pub4
99. Calhoun PJ, Phan AV, Taylor JD, James CC, Padget RL, Zeitz MJ, et al. Adenovirus targets transcriptional and posttranslational mechanisms to limit gap junction function. FASEB J. (2020) 34:9694–712. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000667R
100. Drwiła R, Rubiś P, Kapelak B, Rudnicka-Sosin L, Pankuweit S, and Gackowski A. Complete recovery of a patient with cardiogenic shock due to parvovirus B19 fulminant myocarditis after treatment with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and intravenous immunoglobulin. Pol Arch Med Wewn. (2015) 125:199–201. doi: 10.20452/pamw.2717
Keywords: viral myocarditis, inflammation intervention, gene therapy, antioxidant, myocardial repair
Citation: Xu J, Chen X, Guan X, Zhang H, Liu Y and Zhang M (2025) Therapeutic frontiers in viral myocarditis: targeting inflammation, viruses, oxidative stress, and myocardial repair. Front. Immunol. 16:1643502. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1643502
Received: 10 June 2025; Accepted: 29 July 2025;
Published: 14 August 2025.
Edited by:
Kunal Bhattacharya, Patanjali Research Institute, IndiaReviewed by:
Shreyas Bhave, Boston Scientific, United StatesCecilia Salzillo, University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Chen, Guan, Zhang, Liu and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Min Zhang, bWluemhhbmdAbXVobi5lZHUuY24=; Yan Liu, aHkwMjA3MTE3QG11aG4uZWR1LmNu
 Jingyao Xu1,2
Jingyao Xu1,2 Min Zhang
Min Zhang