- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
- 2Department of Medical Imaging Center, The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
- 3Department of Pathology, The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
- 4Department of Information, The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
Background: The clinical value of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in the treatment of unresectable locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (LA-ESCC) remains under investigation in large-scale randomized clinical trials. In this study, we aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of concurrent ICIs in combination with definitive chemoradiotherapy (dCRT) in a relatively large cohort of patients with unresectable LA-ESCC.
Methods: Between January 2019 and December 2023, this retrospective study included patients with LA-ESCC who received ICIs concurrently with dCRT at Jiangsu Cancer Hospital. The primary endpoints were overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS), while secondary endpoints included clinical response and safety.
Results: A total of 165 patients with LA-ESCC were included in this study, with a median age of 66 years (IQR 60–70 years), and 163 (98.8%) had stage III or IVA disease. After a median follow-up of 24 months (IQR 16–33 months), the 2-year OS was 64.3% (95%CI 57.2%-72.3%), and the 2-year PFS was 50.2% (95%CI 42.9%-58.8%). It is noteworthy that induction therapy before dCRT did not improve OS (HR = 1.09, 95% CI: 0.61–1.93, P = 0.770) or PFS (HR = 1.00, 95% CI: 0.59–1.72, P = 1.000). The objective response rate (ORR) was 70.9% and disease control rate (DCR) was 86.7%. The most common adverse event was grade 3 or worse lymphopenia, observed in 60.0% of the patients (90/165).
Conclusion: ICIs combined with concurrent dCRT demonstrated promising efficacy and manageable safety in patients with unresectable LA-ESCC.
Introduction
Esophageal cancer is the sixth leading cause of cancer-related mortality globally (1). Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the predominant histological subtype in Asia, accounting for approximately 90% of all cases (2). Definitive chemoradiotherapy (dCRT) is the standard treatment for patients with unresectable locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (LA-ESCC) (3). However, the three-year survival rate under this treatment regimen ranges between 26.9% and 55.4% (4–8), with approximately half of the patients experiencing recurrence within three years (4–6). Therefore, it is imperative to develop novel therapeutic strategies to improve patient outcomes and reduce recurrence rates.
Recently, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have demonstrated promising applications in the treatment of esophageal cancer. In patients with advanced or metastatic ESCC, the latest findings from the Keynote 590 (9) and ESCORT-1st (10) trials have demonstrated improved clinical outcomes, establishing ICIs as part of the standard treatment regimen. Moreover, in unresectable LA-ESCC, several studies (10, 11) have also reported encouraging efficacy of ICIs when combined with dCRT concurrently, although these findings are based on relatively small patient cohorts. These studies demonstrate potential clinical benefits with improved overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) outcomes compared to chemotherapy alone, with manageable treatment-related toxicity. Taken together, current evidence indicates that concurrent ICIs combined with dCRT may represent a promising therapeutic strategy for patients with unresectable LA-ESCC.
However, large-scale randomized phase III trials evaluating ICIs combined with dCRT concurrently for unresectable LA-ESCC remain under investigation. In this context, we conducted a retrospective analysis of LA-ESCC patients treated with this combination therapy at Jiangsu Cancer Hospital to evaluate its efficacy and safety profile.
Methods
Participants
This retrospective cohort study included patients aged 18–75 years diagnosed with ESCC. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) pathologically confirmed ESCC, (2) histological classification as II-IVA stage according to the 8th TNM staging system of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (12), and (3) unsuitable for surgery due to unresectable disease, surgical contraindications, or patient refusal. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) presence of secondary malignancies, (2) incomplete radiotherapy, (3) prior antitumor treatment for any malignancy, and (4) patients who underwent surgery after the completion of treatment. This study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Jiangsu Cancer Hospital (Approval No. KY-2024-067).
Procedures
Pretreatment evaluations included physical examinations, standard hematological and biochemical tests, pretreatment upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and biopsy, barium esophagograms, contrast-enhanced neck and upper abdominal computed tomography (CT), and high-resolution 3.0 -T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the chest and brain. Ultrasonography of the neck with fine-needle aspiration and positron emission tomography/CT (PET-CT) were performed optionally for clinical tumor–lymph node–metastasis staging.
Based on primary tumor size and clinical stage, a subset of patients received induction therapy prior to the initiation of concurrent ICIs and dCRT, which was defined as completion of at least one treatment cycle of immunotherapy, chemotherapy, or their combination before radiotherapy. All patients underwent concurrent immunotherapy combined with dCRT (during and within a half-month period before and after dCRT (13, 14)). The ICIs administered were PD-1 inhibitors, and the chemotherapy regimen consisted of a taxane combined with a platinum-based agent, administered every three weeks for two cycles. For patients who were intolerant to intravenous chemotherapy, oral S-1 was used as an alternative regimen.
All patients were treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) using 6-MV X-rays, receiving conventionally fractionated radiotherapy at 5 fractions per week. The gross tumor volume (GTV), which included the primary tumor (GTVp) and metastatic lymph nodes (GTVn), was determined using endoscopy, contrast-enhanced thoracic CT, and/or 18-fluorodeoxyglucose PET-CT. The primary clinical target volume (CTVp) included the GTVp with an additional radial margin of 0.5–1.0 cm and longitudinal margins of 2.5–3 cm. The clinical target volume for metastatic lymph nodes (CTVn) was delineated based on the involved field irradiation, excluding elective nodal irradiation. The planning target volume (PTV) was defined by adding a margin of 0.5–1.0 cm to the CTV. Cone-beam CT was used for daily verification during the first week of treatment, followed by weekly verification after that. The dose constraints for the organs at risk were as follows: a mean lung dose of < 17 Gy, a lung V20 (percentage of the total lung volume receiving ≥ 20 Gy) of < 30%, lung V5 (percentage of the total lung volume receiving ≥ 5 Gy) of < 65%, a mean heart dose of 26 Gy or lower, heart V30 (percentage of the total heart volume receiving ≥ 30 Gy) of < 35%, and maximum spinal cord dose of 45 Gy or lower.
Follow-up and assessments
The primary endpoints were OS (the time from the first treatment until death from any cause or censored at the last follow-up) and PFS (the time from the first treatment until tumor progression in any aspect or death from any cause or censored at the last follow-up). The secondary evaluation endpoints were clinical response and safety.
The clinical response of the tumor was independently evaluated by two experienced oncologists within three months after the completion of radiotherapy, using the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST, version 1.1) (15). Treatment failures were categorized as either locoregional or distant disease, based on CT scans confirmed by pathology or identified by the investigator and senior radiologist through integration with other imaging examinations. Deaths were confirmed through official statements. Adverse events were evaluated according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE, version 5.0) (16) during and up to 90 days post-completion of concurrent chemoradiotherapy. The highest score was recorded as the patient’s toxicity grade.
Statistical methods
Continuous variables are presented as median with range or mean with standard deviations, while categorical variables are presented as frequencies with percentages. Continuous variables were compared using the t-test. Survival was estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method. The log-rank test was employed to evaluate the significance of survival differences between groups based on baseline characteristics, and Cox proportional hazards regression models were used to estimate the hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). To account for multiple comparisons in univariate Cox regression analysis, the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure was applied to adjust P-values, controlling the false discovery rate (FDR). Variables with adjust P < 0.2 in the univariate analysis were included in the multivariate analysis. We assessed the proportional hazards (PH) assumption for the multivariable Cox regression models of OS and PFS using Schoenfeld residuals with the cox.zph function in R. A global test P-value > 0.05 was considered as no evidence of PH assumption violation. Immunotherapy cycles were analyzed separately by treatment phase. Induction and maintenance phases were grouped as none, short-term, or long-term. The concurrent phase was classified according to the actual number of cycles received.
Patients were retrospectively classified according to whether they received induction therapy. To address baseline imbalances, propensity scores were estimated using logistic regression with clinically relevant covariates (age, sex, smoking, alcohol use, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, body mass index (BMI), tumor length, tumor location, and TNM stage) that may influence both treatment allocation and survival. Propensity score matching (PSM) was performed with a 1:1 nearest-neighbor algorithm (caliper = 0.1). As a sensitivity analysis, inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) was also applied using the same set of covariates. Balance was evaluated using standardized mean differences (SMDs), with values <0.1 considered indicative of good balance and values between 0.1 and 0.2 regarded as acceptable. Finally, weighted Cox proportional hazards models with robust standard errors were fitted to evaluate the impact of induction therapy on OS and PFS. All statistical analyses were performed using R (version 4.4.1), with a two-sided P < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient characteristics
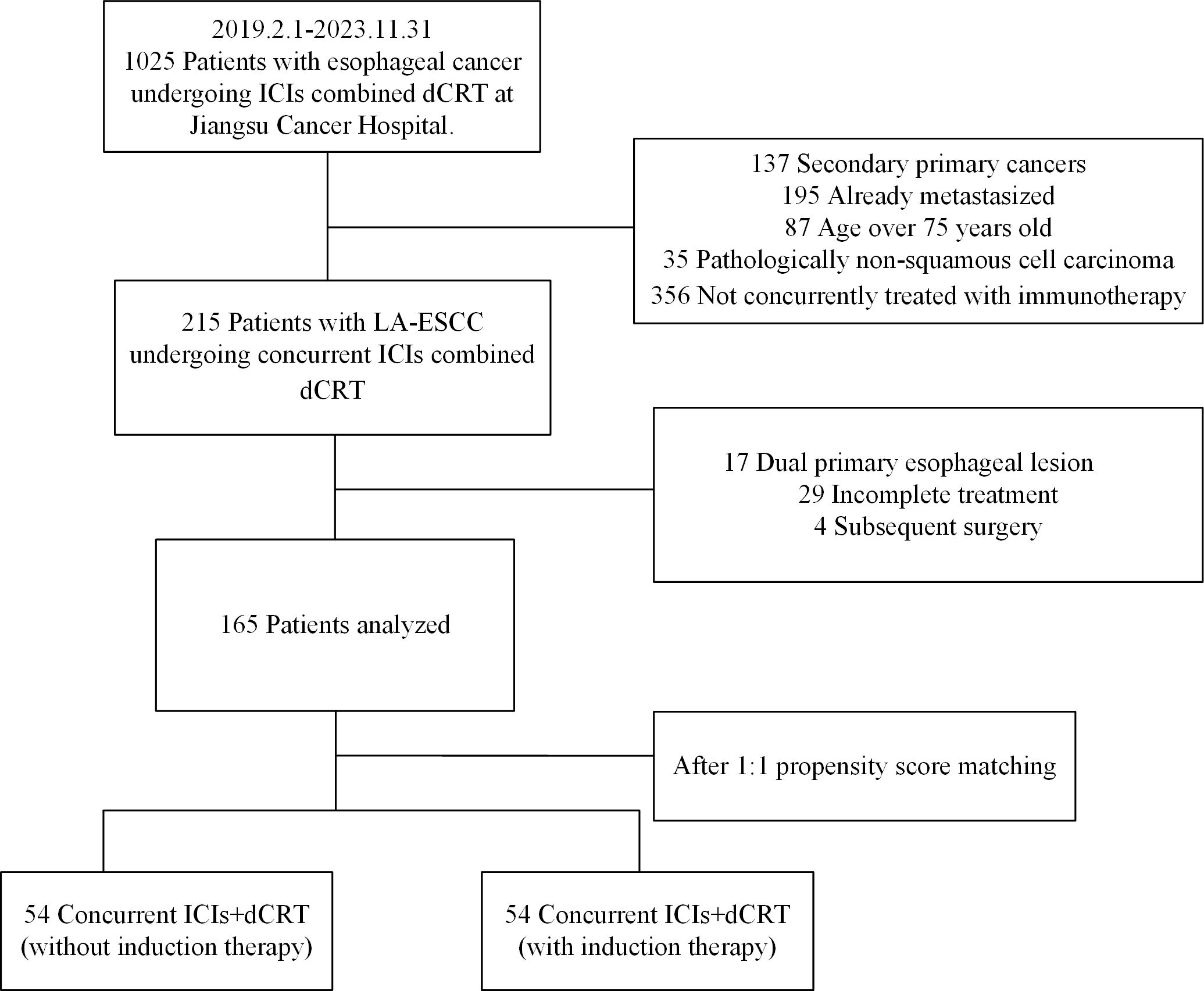
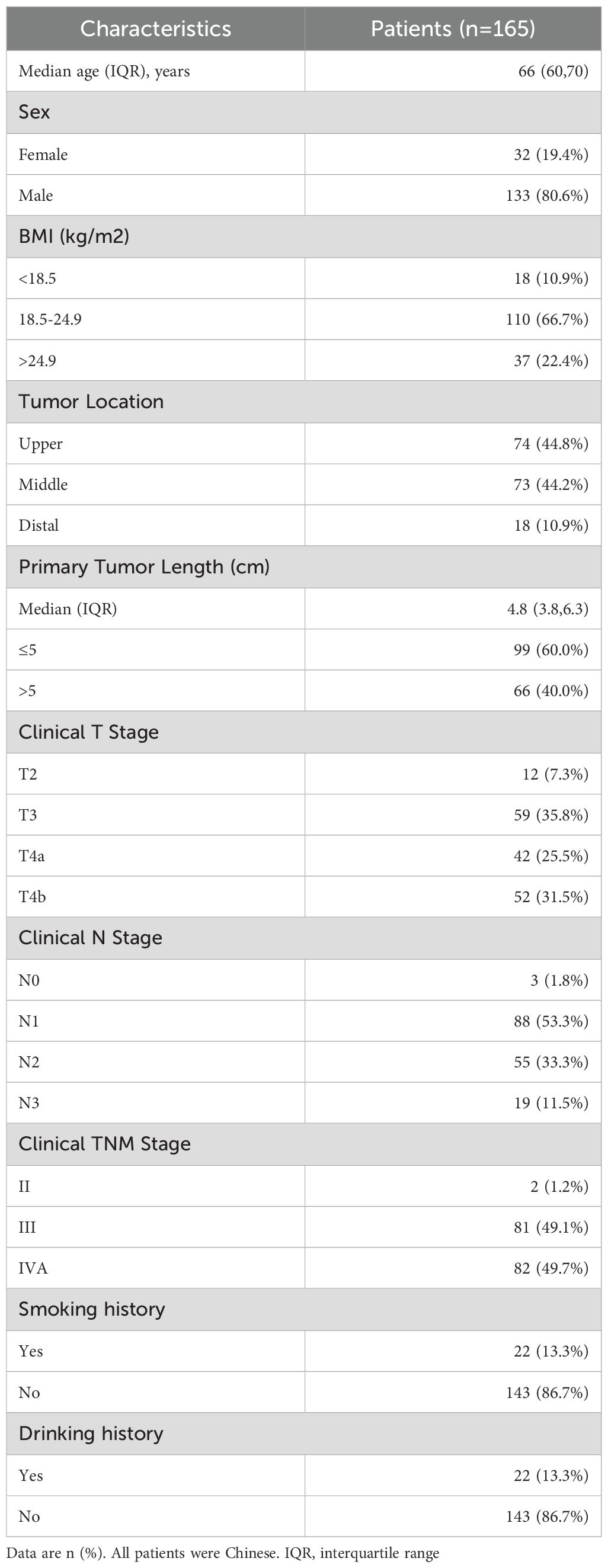
From January 1, 2019 to December 31, 2023, 165 patients treated with dCRT and concurrent ICIs were retrospectively included in this study (Figure 1). Patient characteristics are described in Table 1. The median age was 66 years (IQR 60–70 years). Among these patients, 81 (49.1%) had stage III disease, and 82 (49.7%) had stage IVA. Clinical T4 disease was observed in 94 patients (57.0%), while 74 (44.8%) had N2 or higher nodal involvement. A total of 66 individuals (40.0%) had a tumor length of > 5 cm, with a median tumor length of 4.8 cm (IQR 3.8–6.3 cm). Tumors located in the upper esophagus were identified in 74 cases (44.8%). Based on whether received induction therapy before dCRT, patients were stratified into induction and concurrent treatment groups. Following 1:1 PSM, 54 matched pairs were obtained, and most baseline covariates achieved good balance, with SMDs <0.1. BMI showed a slightly higher SMD of 0.130, which remained within the acceptable threshold of 0.2. In the IPTW analysis, age (SMD = 0.171) and tumor location (SMD = 0.117) showed modest residual imbalance, but all covariates were within acceptable limits. Detailed covariate balance before and after adjustment is presented in Supplementary Tables 1 and 2.
Treatment
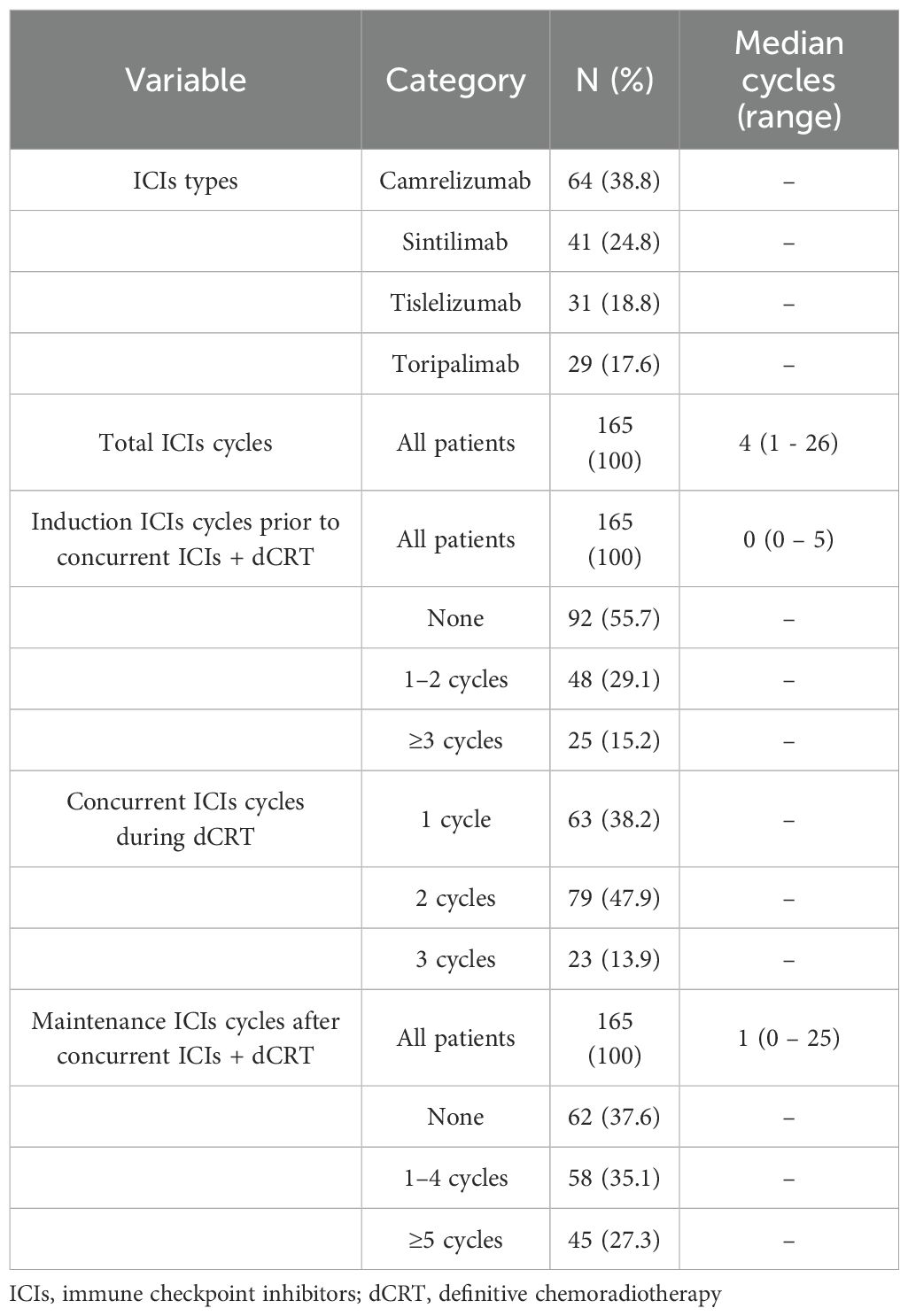
In this study, the median total number of immunotherapy cycles was 4 (range, 1–26), including a median of 0 cycles (range, 0–5) in the induction phase, 2 cycles (range, 1–3) in the concurrent phase, and 1 cycle (range, 0–25) in the maintenance phase. A total of 73 patients (44.3%) received induction ICIs prior to concurrent ICIs plus dCRT, all patients received concurrent programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) inhibitor therapy during dCRT, and 103 patients (62.4%) received maintenance ICIs after concurrent ICIs plus dCRT (Table 2). All patients received a median radiation dose of 60 Gy (IQR 50.4-60Gy) with single-fraction doses ranging from 1.8 to 2 Gy. The majority of patients (135/165, 81.8%) received taxane-platinum combination chemotherapy (Supplementary Table 3).
Survival
By the last follow-up on March 1, 2025, the entire cohort had a median follow-up of 24 months (IQR, 16–33 months), the one-year and two-year OS rates were 83.0% (95% CI, 77.5%–89.0%) and 64.3% (95% CI, 57.2%–72.3%), respectively. The corresponding PFS rates were 69.4% (95% CI, 62.6%–76.8%) at one year and 50.2% (95% CI, 42.9%–58.8%) at two years (Figures 2A, B).
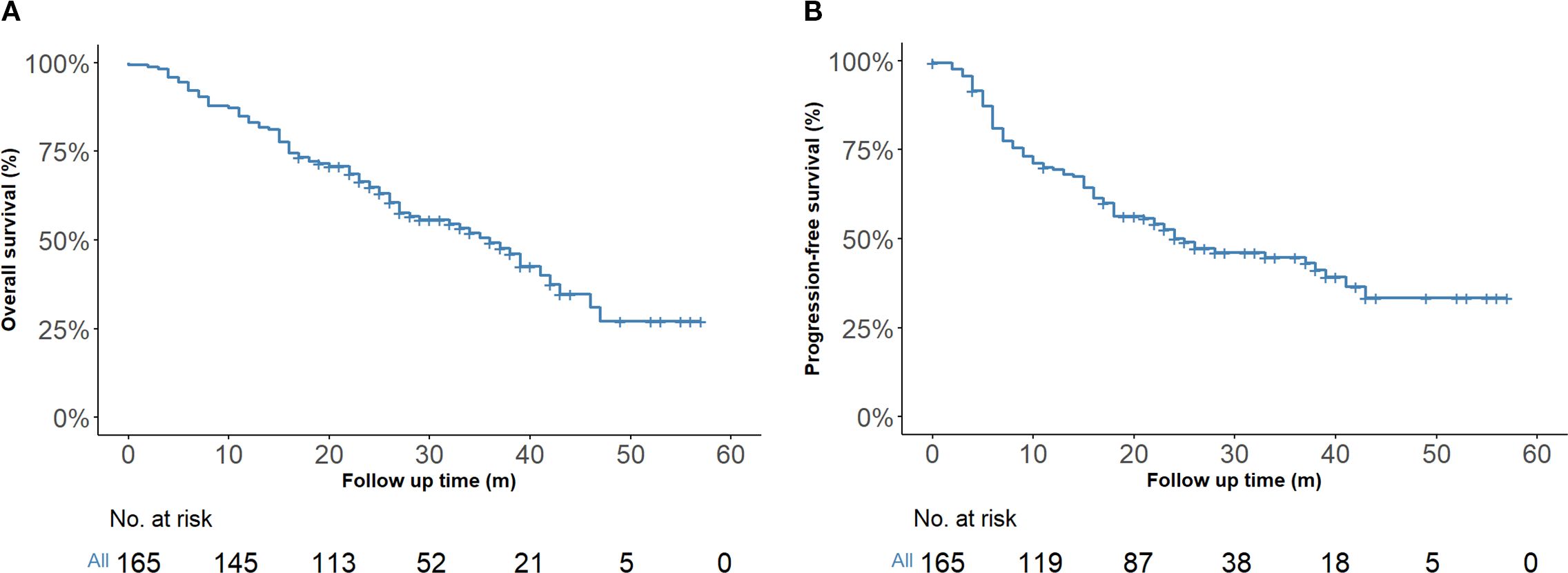
Figure 2. Kaplan–Meier survival estimates (n = 165). (A) Overall survival of the entire cohort. (B) Progression-free survival of the entire cohort.
Survival analysis stratified by induction therapy status demonstrated that adding induction treatment to concurrent dCRT with ICIs had no significant impact on OS (HR = 1.09, 95% CI: 0.61–1.93, P = 0.770) or PFS (HR = 1.00, 95% CI: 0.59–1.72, P = 1.000) after PSM (Figures 3A, B). Consistently, IPTW-adjusted Cox models showed no significant survival difference between groups for either OS (HR = 1.10, 95% CI: 0.65–1.83, P = 0.728) or PFS (HR = 1.00, 95% CI: 0.61–1.63, P = 0.995), as shown in Supplementary Figures 1A, B. In addition, after adjustment for multiple comparisons, no significant survival differences were observed among different ICIs. Similarly, no significant associations were found between the number of immunotherapy cycles in any treatment phase and OS or PFS (Supplementary Tables 4A, B).
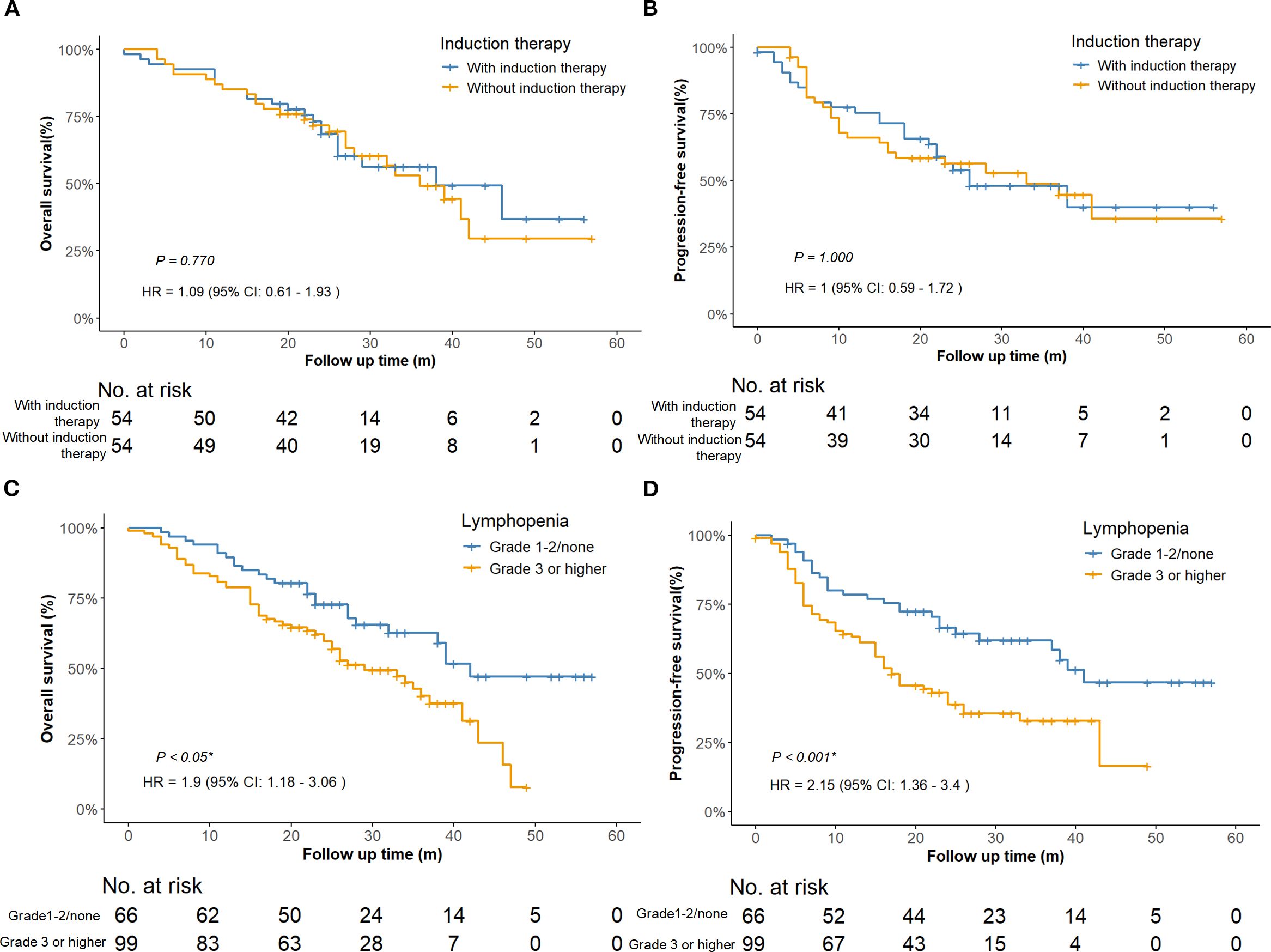
Figure 3. Survival curves comparing patients with or without induction therapy after PSM adjustment. (n = 108) (A) Overall survival. (B) Progression-free survival. Survival curves comparing patients with lymphopenia of Grade 1–2 or none to those with Grade 3 or higher (n = 165). (C) Overall survival of the entire cohort. (D) Progression-free survival of the entire cohort. PSM, propensity score matching; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
Clinical responses
165 patients were included in the clinical response evaluation. Among the 165 patients, 54 (32.7%) achieved a complete response (CR), 63 (38.2%) achieved a partial response (PR), 26 (15.8%) maintained stable disease (SD), and 22 (13.3%) experienced progressive disease (PD). The objective response rate (ORR) was 117/165 (70.9%), and the disease control rate (DCR) was 143/165 (86.7%).
Toxicity
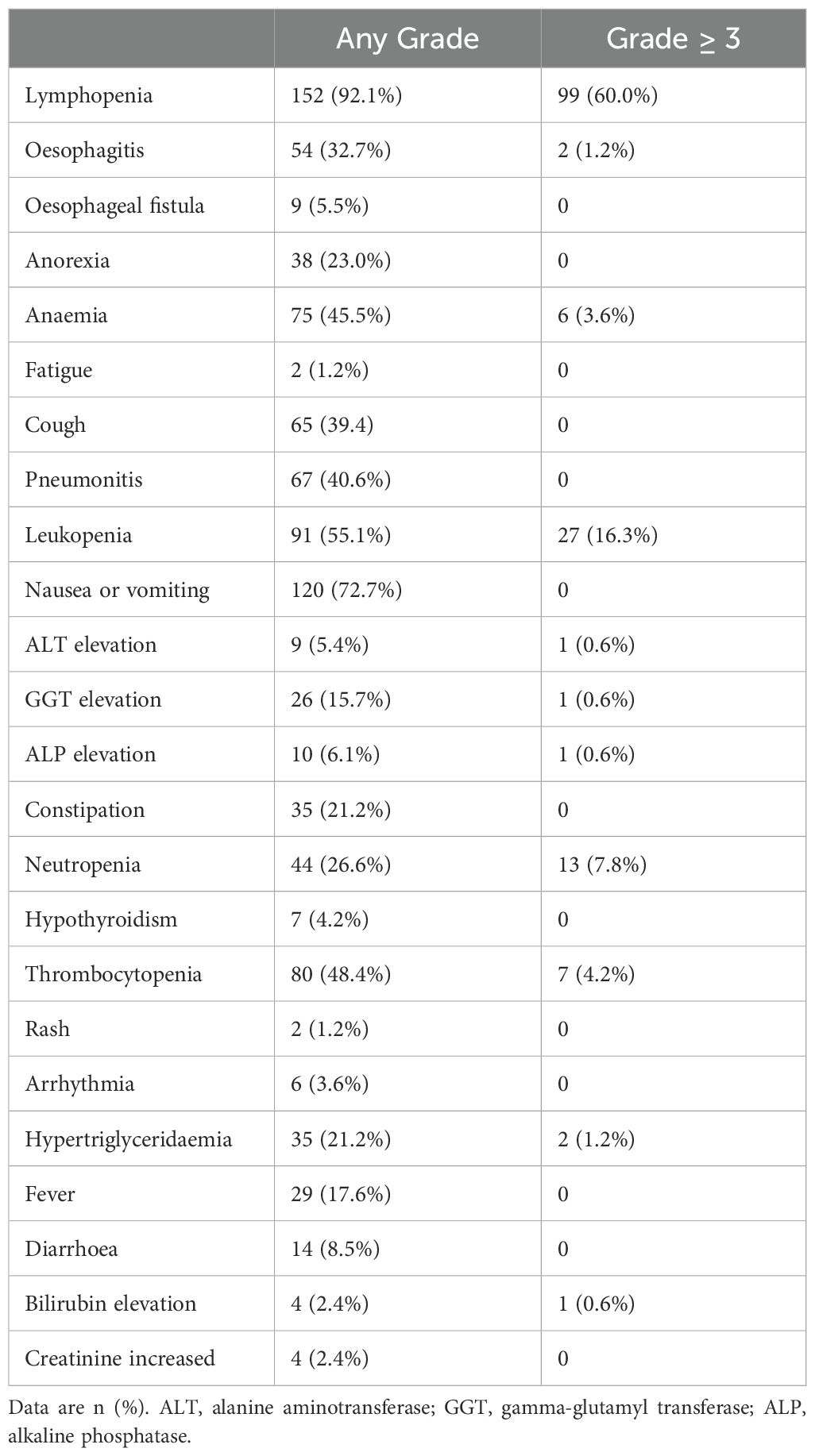
All patients experienced treatment-related adverse events of any grade (Table 3). The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were lymphopenia (99/165, 60.0%) and leukopenia (27/165, 16.3%). The incidence of esophagitis was 39.9%, with 2 (1.2%) cases graded as 3. Grade 1–2 pneumonitis occurred in 67 patients (40.6%), and grade 1–2 esophageal fistula in 9 (5.5%). No treatment-related deaths occurred.
Prognostic factors
Univariate analysis revealed that T stage, tumor length, lymphopenia, and clinical response were associated with both OS and PFS. In addition, tumor location was associated with OS, while BMI and N stage were related to PFS. After Benjamini–Hochberg adjustment, T stage, lymphopenia, and clinical response remained significantly associated with both OS and PFS, whereas tumor length and BMI also reached statistical significance for PFS (Supplementary Tables 5A, B). Notably, grade ≥3 lymphopenia, the most frequent toxicity observed in our study, was significantly associated with worse OS (HR = 1.90; 95% CI 1.18–3.06; P < 0.05; Figure 3C) and PFS (HR = 2.15; 95% CI 1.36–3.40; P < 0.001; Figure 3D). However, the association between lymphopenia and survival outcomes was not statistically significant in multivariate analysis. Multivariate analysis further confirmed that T4 stage (HR = 2.34, 95%CI: 1.31–4.16, P = 0.004), middle esophageal tumor location (HR = 2.18, 95%CI: 1.05–4.52, P = 0.036), and SD/PD response (HR = 2.25, 95%CI: 1.39–3.65, P < 0.001) were independent predictors of worse OS (Figure 4A). For PFS, BMI ≥25 was identified as a protective factor (HR = 0.49, 95%CI: 0.27–0.89, P = 0.020), whereas SD/PD response remained an independent risk factor for disease progression (HR = 2.51, 95%CI: 1.59–3.95, P < 0.001) (Figure 4B). Notably, induction therapy prior to dCRT did not confer a survival benefit in terms of PFS or OS (P > 0.05). The proportional hazards assumption was tested for both the OS and PFS multivariable Cox models. For the OS model, χ² = 5.412 (df = 9, P = 0.800), and for the PFS model, the global test yielded χ² = 13.742 (df = 10, P = 0.190), indicating no violation of the PH assumption. All individual covariates also showed non-significant P-values (> 0.05), confirming that the Cox regression models were appropriate for our data. Detailed results for individual covariates are provided in Supplementary Table 6.
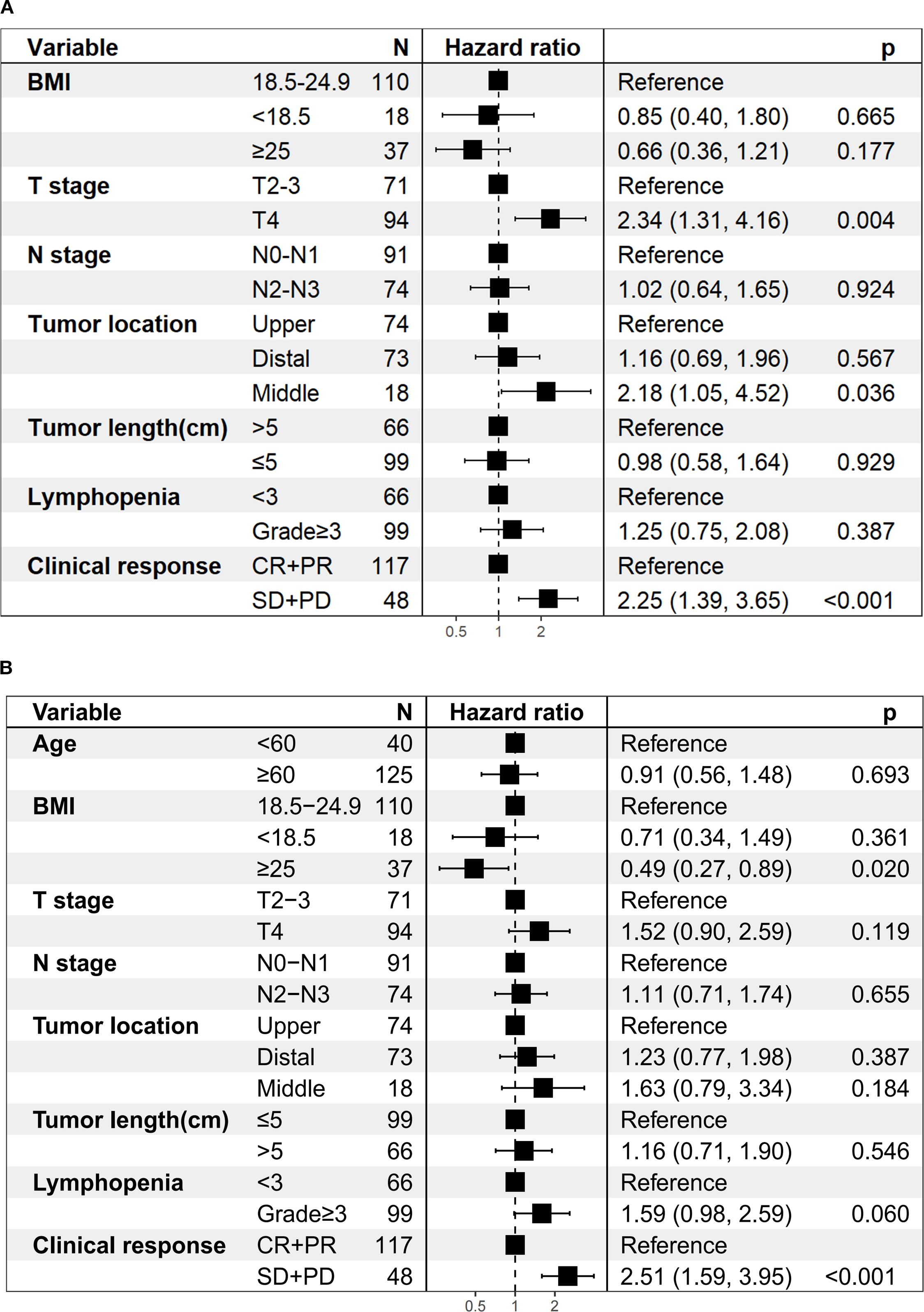
Figure 4. Multivariate regression analysis of prognostic factors. (A) Overall survival. (B) Progression-free survival.
Discussion
This retrospective study evaluated the strategy of dCRT combined with concurrent ICIs in a relatively large cohort of patients with unresectable LA-ESCC. The one-year and two-year OS rates were 83.0% (95% CI, 77.5%–89.0%) and 64.3% (95% CI, 57.2%–72.3%), respectively. The corresponding PFS rates were 69.4% (95% CI, 62.6%–76.8%) at one year and 50.2% (95% CI, 42.9%–58.8%) at two years. This study also showed manageable treatment-related toxicity with no treatment-related deaths. Additionally, the induction therapy prior to dCRT demonstrated no survival benefit. While its application in real-world settings requires further investigation and should be guided by clinical judgment. In conclusion, the combination of dCRT with concurrent ICIs demonstrates potential as a therapeutic strategy for unresectable LA-ESCC, though its efficacy needs to be validated through large-scale randomized controlled trials.
Our findings suggest that combining dCRT with concurrent ICIs may improve survival outcomes, representing a promising therapeutic strategy for LA-ESCC patients. In our study, the addition of ICIs to concurrent dCRT resulted in a two-year OS rate of 64.3% (95% CI, 57.2%–72.3%) and a two-year PFS rate of 50.2% (95% CI, 42.9%–58.8%). Consistent with two-year OS rates ranging from 50% to 66.7% and PFS rates between 46.4% and 54.4% for standard dCRT regimens (4, 5, 17). The EC-CRT-001 phase II trial (11) evaluating concurrent ICIs with dCRT for LA-ESCC reported a promising 1-year OS rate of 78.4%, though the 1-year PFS rate (54.5%) did not exceed standard dCRT regimen. The investigators attributed this unexpected PFS outcome to their higher enrollment of stage IVA patients (38%) compared to previous studies. Notably, our cohort included a substantially greater proportion of stage IVA disease (49.7%) than reported in prior studies (8.5%-38.7%) (4, 5, 11, 17), yet still demonstrated encouraging survival outcomes, suggesting potential therapeutic benefit across advanced disease stages. Consistent with our findings, Zhang et al. (18) conducted a phase 1b study of camrelizumab combined with concurrent dCRT and reported 2-year OS and PFS rates of 69.6% and 65.0% respectively. Additional supportive evidence includes a durvalumab plus tremelimumab regimen, which achieved 2-year OS and PFS rates of 75% and 57.5% (19). A recent multicenter real-world study involving 102 ESCC patients treated with concurrent ICIs and dCRT reported 1- and 2-year OS rates of 86.7% and 66.9%, and PFS rates of 66.7% and 47.3%, respectively (20), which are generally consistent with our findings. Several ongoing phase III trials, such as KEYNOTE-975 (pembrolizumab), RATIONALE-311 (tislelizumab), KUNLUN (durvalumab), and ESCORT-CRT (camrelizumab), are expected to provide high-level evidence to further define the role of concurrent ICIs combined with dCRT in this setting. It is also important to note that the present study was conducted in a real-world clinical setting, where treatment adherence and patient management may vary from the strictly regulated conditions of prospective clinical trials. Despite these potential sources of variability, the survival outcomes observed in our study underscore the clinical value of integrating ICIs into dCRT regimens for unresectable LA-ESCC patients, even for patients with advanced-stage disease. These results provide further support for the application of immunotherapy in this population and contribute to the growing body of real-world evidence on its effectiveness.
In the era of ICIs, induction immunochemotherapy before dCRT has not been incorporated into standard guidelines for LA-ESCC, due to insufficient high-level evidence and potential toxicity concern. Large primary tumor volume has been identified as a poor prognostic factor in ESCC treated with definitive CCRT (21). Tumor volume reduction before CCRT may improve local control and survival outcomes. Phase II studies (22, 23) of this novel induction immunochemotherapy regimen have demonstrated promising improvements in local control rates and survival. These clinical benefits are biologically supported by preclinical validation of related mechanisms, including tumor vascular normalization and hypoxia alleviation (24). However, these regimens carry toxicity burdens, a high proportion of patients (80%–90%) experienced grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse events, and cases of grade 5 pneumonitis have been reported (23). In our study, while no treatment-related deaths occurred, induction therapy combined with dCRT did not confer a survival benefit in patients with ESCC, as measured by either OS (P = 0.770, Figure 3A) or PFS (P = 1.000, Figure 3B). This difference may be attributed to the relatively small sample size in our study, as only 72 patients (43.6%) received induction immunochemotherapy, potentially limiting the statistical power to detect the therapeutic benefits of induction therapy. In conclusion, while our findings suggest induction therapy may offer limited clinical benefit in esophageal cancer management, further investigations are warranted to definitively establish its therapeutic role and fully characterize potential toxicities.
Several studies have shown that patients achieving CR after dCRT have significantly better survival than those with residual disease (7, 25). Consistent with these findings, our results demonstrated that the CR + PR group exhibited a longer OS (HR = 2.25; 95% CI 1.39–3.65; P < 0.001; Figure 4A) and PFS (HR = 2.51; 95% CI 1.59–3.95; P < 0.001; Figure 4B) compared to the SD + PD group. These findings underscore that early tumor shrinkage following dCRT combined with ICIs represents not only a marker of treatment sensitivity but also an independent prognostic indicator. Clinically, this highlights the value of early response evaluation, as patients who fail to achieve CR or PR face substantially higher risks of disease progression and mortality, and may require closer surveillance or consideration of additional systemic therapy. From a mechanistic perspective, radiotherapy can trigger the release of tumor antigens and activate antigen-presenting cells, and when combined with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade, it enhances cancer cell immunogenicity and improves long-term antitumor responses (26, 27). When considering overall response, the ORR rate in our study was 70.9%, comparable with that reported in previous studies using dCRT alone (70.9% versus 65%–74.6%) (6, 7), despite the higher disease burden in our cohort. In earlier reports, the proportion of T3–T4 patients was 72.7% (7), whereas our study included 92.7%. Similarly, stage IV patients accounted for only 10% in previous studies (6), compared with 49.7% in our cohort. To conclude, despite enrolling a high proportion of patients with advanced disease, our study achieved promising ORR and survival outcomes. This suggests that combining concurrent ICIs with dCRT not only improves tumor response but also turns these responses into real survival benefits, supporting the therapeutic value of this combined approach.
In our study, a BMI ≥25 was identified as an independent protective factor for PFS (HR = 0.49, 95% CI: 0.27–0.89, P = 0.020; Figure 4B), suggesting that patients with higher BMI may derive greater benefit from dCRT combined with immunotherapy. Although obesity is generally recognized as a risk factor for the development of several cancers (28), increasing evidence indicates that overweight (BMI 25–29) and obese (BMI ≥ 30) patients may experience improved outcomes with ICIs (29–31), a phenomenon known as the obesity paradox (32). This has been partially explained by previous preclinical studies showing that obesity-associated metabolic signalling and inflammatory cues cause tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs)to induce PD-1 expression, which then drives a TAM-specific feedback mechanism that impairs tumour immune surveillance. This may contribute to increased cancer risk yet improved response to PD-1 immunotherapy in obesity (33). Nevertheless, only 37 patients (22.4%) in our cohort had a BMI ≥25, and no cases of severe obesity (BMI >35) were included. Thus, while our findings highlight a potentially important prognostic role for BMI in this treatment setting, they should be interpreted with caution and warrant confirmation in larger prospective studies.
T4 stage was also identified as an independent adverse prognostic factor for OS (HR = 2.34, 95% CI: 1.31–4.16, P = 0.04; Figure 4A), underscoring the prognostic importance of local invasion into adjacent structures. Chen et al. found that tracheal/bronchial invasion and ulcerative tumors were independent risk factors for esophagotracheal fistula after dCRT (34). Historically, T4b disease has been associated with poor outcomes, with a 3-year OS of only 22.2% and locoregional failure in 60% of cases (35). In the immunotherapy era, the EPOC1802 trial, which included nearly 95% of patients with cT4 LA-ESCC, reported that maintenance ICIs after dCRT improved response rates and intermediate-term survival, even among patients with a high T4 tumor burden (36). Notably, in our study, despite a high proportion of T4 cases (94/165, 57%), the combination of dCRT and concurrent ICIs yielded encouraging survival outcomes without an increased incidence of post-dCRT esophagotracheal fistula, suggesting that immunotherapy integration may confer benefit with acceptable safety in this high-risk population. Prospective validation is warranted.
The prognostic impact of tumor location in the setting of dCRT remains understudied, and existing evidence is inconsistent. Gao et al (37). reported that tumor location was independently associated with OS and PFS in multivariate analysis, with upper thoracic tumors achieving the highest 5-year OS (46.0%). This suggests that middle and lower thoracic tumors may have worse outcomes, possibly due to their proximity to critical structures such as the heart, lungs, and great vessels, which can limit radiation dose delivery and increase the risk of severe cardiopulmonary complications. Other dCRT studies found no statistically significant association between location and survival but noted a trend toward poorer outcomes for upper/middle thoracic disease compared with lower thoracic disease (P = 0.055) (38). In our cohort, middle esophageal tumor location was independently associated with worse OS (HR = 2.18, 95% CI: 1.05–4.52, P = 0.036; Figure 4A), supporting the clinical value of incorporating tumor location into individualized target delineation and dose optimization. However, the number of patients with middle esophageal tumors was small (18/165, 10.9%), which may limit the statistical power and highlights the need for validation in larger, multicenter cohorts.
In our study, 60% of patients developed grade ≥ 3 lymphopenia, including 20 cases (12.1%) of grade 4, with no grade 5 events observed. Lymphocytes are highly radiosensitive, with significant depletion occurring even at relatively low radiation doses (39). This suggests that the observed lymphopenia is more likely attributable to radiotherapy rather than ICIs. Thoracic radiation, especially when involving large planning target volumes or vertebral bone marrow, has been shown to induce profound lymphocyte loss (40). Mechanistic studies have further demonstrated that radiation not only reduces circulating lymphocytes and suppresses lymphopoiesis, but also upregulates immune inhibitory molecules such as PD-L1 and CTLA-4, contributing to systemic immunosuppression (41, 42). Similar patterns of lymphopenia have been reported in previous studies of dCRT without the use of ICIs. Davuluri et al. observed a 27% incidence of grade 4 lymphopenia in esophageal cancer patients treated with dCRT alone (43), and Deng et al. reported grade 3–4 lymphopenia in up to 50% of patients receiving thoracic IMRT (44). These findings support the safety and feasibility of concurrently integrating ICIs into dCRT without significantly increasing severe lymphopenia. Moreover, severe lymphopenia has been associated with inferior survival outcomes across multiple studies (43–45). In our univariate analysis, patients with grade ≥3 lymphopenia had significantly shorter overall survival (HR = 1.90; 95% CI: 1.18–3.06; P < 0.05; Figure 3C) and progression-free survival (HR = 2.15; 95% CI: 1.36–3.40; P < 0.001; Figure 3D). Although these associations were not statistically significant in the multivariate analysis, the findings raise the possibility that lymphopenia may negatively impact clinical outcomes. Importantly, the combination of ICIs with dCRT did not appear to worsen treatment-related lymphopenia, further supporting its potential as a safe therapeutic strategy.
Our study has certain limitations. As this was a single-center, retrospective study, the generalizability of our findings is inevitably limited. The sample size was relatively small, and the median follow-up duration was only 24 months, which may hinder a thorough evaluation of long-term survival outcomes and delayed toxicities, including the potential long-term impact of immune-related adverse events. Future larger prospective studies with extended follow-up are needed to provide a more robust evaluation of long-term efficacy and safety. Although PSM was performed to minimize confounding, the retrospective and single-center nature of this study may still introduce selection bias. Therefore, our findings should be interpreted with caution, and validation through prospective, multi-center randomized trials will be essential to confirm the reliability and generalizability of our findings. In addition, the inability to standardize the type of PD-1 inhibitors could have introduced variability in treatment response. The assessment of clinical response was primarily based on CT imaging, which may compromise the accuracy of short-term efficacy evaluation. Further use of EUS and PET/CT in future studies could be integral in identifying regional nodes and assessing the risk of metastasis. Since this study was conducted in a single hospital within a real-world clinical setting, treatment decisions were made by clinicians based on routine practice, potentially influencing the observed outcomes and mirroring the practical complexities inherent in everyday patient management. In addition to the primary endpoints of OS and PFS, further research should include a comprehensive analysis of PD-L1 expression and the role of the tumor microenvironment in predicting treatment efficacy.
Conclusion
Our study provides preliminary evidence that the combination of dCRT with concurrent ICIs offers promising survival benefits for patients with unresectable LA-ESCC, while maintaining a manageable safety profile. However, phase III randomized controlled trials are warranted to validate these findings and further establish the role of this treatment strategy.
Data availability statement
The data analyzed in this study is subject to the following licenses/restrictions: The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation. Requests to access these datasets should be directed to Jiang Ning, bmppYW5nMTE3QG5qbXUuZWR1LmNu.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Jiangsu Cancer Hospital (Approval No. KY-2024-067). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because This study is a retrospective clinical investigation. All patient treatment records and imaging data were obtained from our hospital’s medical database. The study poses no physiological risks to participants, involves no patient-related conflicts of interest, and all researchers are committed to protecting the confidentiality of patient information to prevent any privacy breaches.
Author contributions
YH: Investigation, Software, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Methodology, Formal analysis. QT: Formal analysis, Data curation, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YL: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation. BY: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. YW: Project administration, Supervision, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Visualization, Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Visualization, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Software. YC: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Data curation. ZZ: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Visualization, Software. XZ: Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Conceptualization, Project administration, Investigation. LG: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Data curation, Visualization. NJ: Resources, Investigation, Conceptualization, Project administration, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by the Talents Program of Jiangsu Cancer Hospital, Wu Jieping Medical Foundation (320.6750.2020-13-5), a Research Project of Jiangsu Cancer Hospital (No. ZL202305), a Jiangsu Province “333” Talents Project (No. LGY2018070), Beijing Life Oasis Public Service Center (No. BH004506), and the Jiangsu Province Capability improvement Project through Science, Technology and Education, Jiangsu Provincial Medical Innovation Center (No. CXZX202224).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Declaration of generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the writing process During the preparation of this work the authors used Chatgpt in order to improve language and readability. After using this tool/service, the authors reviewed and edited the content as needed and take full responsibility for the content of the publication.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1646568/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Morgan E, Soerjomataram I, Rumgay H, Coleman HG, Thrift AP, Vignat J, et al. The global landscape of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence and mortality in 2020 and projections to 2040: new estimates from GLOBOCAN 2020. Gastroenterology. (2022) 163:649–658.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.05.054
3. Ajani JA, D’Amico TA, Bentrem DJ, Cooke D, Corvera C, Das P, et al. Esophageal and Esophagogastric Junction Cancers, Version 2.2023, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2023) 21(4):393–422. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2023.0019
4. Xu Y, Dong B, Zhu W, Li J, Huang R, Sun Z, et al. A phase III multicenter randomized clinical trial of 60 gy versus 50 gy radiation dose in concurrent chemoradiotherapy for inoperable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2022) 28:1792–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3843
5. Ai D, Ye J, Wei S, Li Y, Luo H, Cao J, et al. Comparison of 3 paclitaxel-based chemoradiotherapy regimens for patients with locally advanced esophageal squamous cell cancer: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. (2022) 5:e220120. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.0120
6. Conroy T, Galais M-P, Raoul J-L, Bouché O, Gourgou-Bourgade S, Douillard J-Y, et al. Definitive chemoradiotherapy with FOLFOX versus fluorouracil and cisplatin in patients with oesophageal cancer (PRODIGE5/ACCORD17): final results of a randomised, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2014) 15:305–14. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70028-2
7. Liu S, Luo L, Zhao L, Zhu Y, Liu H, Li Q, et al. Induction chemotherapy followed by definitive chemoradiotherapy versus chemoradiotherapy alone in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a randomized phase II trial. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:4014. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24288-1
8. Xi M, Xu C, Liao Z, Hofstetter WL, Blum Murphy M, Maru DM, et al. The impact of histology on recurrence patterns in esophageal cancer treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. (2017) 124:318–24. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.06.019
9. Sun J-M, Shen L, Shah MA, Enzinger P, Adenis A, Doi T, et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for first-line treatment of advanced oesophageal cancer (KEYNOTE-590): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet. (2021) 398:759–71. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01234-4
10. Luo H, Lu J, Bai Y, Mao T, Wang J, Fan Q, et al. Effect of camrelizumab vs placebo added to chemotherapy on survival and progression-free survival in patients with advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: the ESCORT-1st randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2021) 326:916. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.12836
11. Zhu Y, Wen J, Li Q, Chen B, Zhao L, Liu S, et al. Toripalimab combined with definitive chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (EC-CRT-001): a single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2023) 24:371–82. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00060-8
12. Rice TW, Ishwaran H, Ferguson MK, Blackstone EH, and Goldstraw P. Cancer of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction: an eighth edition staging primer. J Thorac Oncol. (2017) 12:36–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.10.016
13. Tian S, Switchenko JM, Buchwald ZS, Patel PR, Shelton JW, Kahn SE, et al. Lung stereotactic body radiation therapy and concurrent immunotherapy: A multicenter safety and toxicity analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol. (2020) 108:304–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.12.030
14. Porte J, Martin CS, Moreau TF, Massiani MA, Jadaud E, Otz J, et al. Loco-regional control and survival outcomes after combined stereotactic radiation therapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors for brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol. (2021) 111:e577. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.07.1553
15. Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1. 1) Eur J Cancer. (2009) 45:228–47. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
16. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Version 5.0. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute; 2017.
17. Hulshof MCCM, Geijsen ED, Rozema T, Oppedijk V, Buijsen J, Neelis KJ, et al. Randomized study on dose escalation in definitive chemoradiation for patients with locally advanced esophageal cancer (ARTDECO study). J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:2816–24. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.03697
18. Zhang W, Yan C, Zhang T, Chen X, Dong J, Zhao J, et al. Addition of camrelizumab to docetaxel, cisplatin, and radiation therapy in patients with locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a phase 1b study. OncoImmunology. (2021) 10:1971418. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1971418
19. Park S, Oh D, Choi Y, Chi SA, Kim K, Ahn M, et al. Durvalumab and tremelimumab with definitive chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. (2022) 128:2148–58. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34176
20. Yang X, Wang X, Xiao Q, Ge X, Yu N, Li J, et al. Definitive chemoradiotherapy combined with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy for inoperable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a multicenter real-world study. Cancer Biol Ther. (2025) 26:2504726. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2025.2504726
21. Chen J, Lin Y, Cai W, Su T, Wang B, Li J, et al. A new clinical staging system for esophageal cancer to predict survival after definitive chemoradiation or radiotherapy. Dis Esophagus. (2018) 31. doi: 10.1093/dote/doy043
22. Ai D, Hao S, Shen W, Wu Q, Zhang S, Chen Y, et al. Induction sintilimab and chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced esophageal cancer: a proof-of-concept, single-arm, multicenter, phase 2 trial. eClinicalMedicine. (2024) 69:102471. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102471
23. Liu F, Wang D, Rong Y, Wei S, SiTu Y, Wang M, et al. Safety and efficacy of neoadjuvant toripalimab plus chemotherapy followed by chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in China (GASTO 1071): a non-randomised, two-cohort, phase 2 trial. EClinicalMedicine. (2025) 82:103184. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2025.103184
24. Wang Y, Liu Z-G, Yuan H, Deng W, Li J, Huang Y, et al. The reciprocity between radiotherapy and cancer immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 25:1709–17. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2581
25. Suntharalingam M, Winter K, Ilson D, Dicker AP, Kachnic L, Konski A, et al. Effect of the addition of cetuximab to paclitaxel, cisplatin, and radiation therapy for patients with esophageal cancer: the NRG oncology RTOG 0436 phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. (2017) 3:1520. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.1598
26. Kordbacheh T, Honeychurch J, Blackhall F, Faivre-Finn C, and Illidge T. Radiotherapy and anti-PD-1/PD-L1 combinations in lung cancer: building better translational research platforms. Ann Oncol. (2018) 29:301–10. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx790
27. Jiang J, Li H, Ma Q, Liu J, Ren F, Song Y, et al. Synergies between radiotherapy and immunotherapy: a systematic review from mechanism to clinical application. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1554499. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1554499
28. Hopkins BD, Goncalves MD, and Cantley LC. Obesity and cancer mechanisms: cancer metabolism. J Clin Oncol. (2016) 34:4277–83. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.67.9712
29. Murphy WJ and Longo DL. The surprisingly positive association between obesity and cancer immunotherapy efficacy. JAMA. (2019) 321:1247. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.0463
30. McQuade JL, Daniel CR, Hess KR, Mak C, Wang DY, Rai RR, et al. Association of body-mass index and outcomes in patients with metastatic melanoma treated with targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or chemotherapy: a retrospective, multicohort analysis. Lancet Oncol. (2018) 19:310–22. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30078-0
31. Ahmed M, Von Itzstein MS, Sheffield T, Khan S, Fattah F, Park JY, et al. Association between body mass index, dosing strategy, and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e002349. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002349
32. Lennon H, Sperrin M, Badrick E, and Renehan AG. The obesity paradox in cancer: a review. Curr Oncol Rep. (2016) 18:56. doi: 10.1007/s11912-016-0539-4
33. Bader JE, Wolf MM, Lupica-Tondo GL, Madden MZ, Reinfeld BI, Arner EN, et al. Obesity induces PD-1 on macrophages to suppress anti-tumour immunity. Nature. (2024) 630:968–75. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07529-3
34. Chen B, Deng M, Yang C, Dragomir MP, Zhao L, Bai K, et al. High incidence of esophageal fistula on patients with clinical T4b esophageal squamous cell carcinoma who received chemoradiotherapy: A retrospective analysis. Radiother Oncol. (2021) 158:191–9. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2021.02.031
35. Huang T-T, Li S-H, Chen Y-H, Lu H-I, Lo C-M, Fang F-M, et al. Definitive chemoradiotherapy for clinical T4b esophageal cancer – Treatment outcomes, failure patterns, and prognostic factors. Radiother Oncol. (2021) 157:56–62. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2021.01.007
36. Bando H, Kumagai S, Kotani D, Mishima S, Irie T, Itahashi K, et al. Atezolizumab following definitive chemoradiotherapy in patients with unresectable locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma – a multicenter phase 2 trial (EPOC1802). Nat Cancer. (2025) 6:445–59. doi: 10.1038/s43018-025-00918-1
37. Gao Q, Liu Z-Y, Cheng Y, Di X-K, Zhang Y-M, Sun X-C, et al. Prognostic factors for 495 nonoperative esophageal squamous cancer patients receiving IMRT plus chemotherapy: A retrospective analysis. Cancer/Radiothérapie. (2022) 26:1002–7. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2022.01.008
38. Zhang P, Xi M, Zhao L, Li QQ, He LR, Liu SL, et al. Efficacy and prognostic analysis of chemoradiotherapy in patients with thoracic esophageal squamous carcinoma with cervical lymph nodal metastasis alone. Radiat Oncol. (2014) 9:256. doi: 10.1186/s13014-014-0256-9
39. Pham T-N, Coupey J, Candeias SM, Ivanova V, Valable S, and Thariat J. Beyond lymphopenia, unraveling radiation-induced leucocyte subpopulation kinetics and mechanisms through modeling approaches. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 42:50. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02621-4
40. Newman NB, Anderson JL, Sherry AD, and Osmundson EC. Dosimetric analysis of lymphopenia during chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer. J Thorac Dis. (2020) 12(5):2395–405. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2020.03.93
41. Demaria S, Golden EB, and Formenti SC. Role of local radiation therapy in cancer immunotherapy. JAMA Oncol. (2015) 1:1325. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.2756
42. Cho Y, Park S, Byun HK, Lee CG, Cho J, Hong MH, et al. Impact of treatment-related lymphopenia on immunotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol. (2019) 105:1065–73. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.08.047
43. Davuluri R, Jiang W, Fang P, Xu C, Komaki R, Gomez DR, et al. Lymphocyte nadir and esophageal cancer survival outcomes after chemoradiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol. (2017) 99:128–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.05.037
44. Deng W, Xu C, Liu A, Van Rossum PSN, Deng W, Liao Z, et al. The relationship of lymphocyte recovery and prognosis of esophageal cancer patients with severe radiation-induced lymphopenia after chemoradiation therapy. Radiother Oncol. (2019) 133:9–15. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2018.12.002
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, immunotherapy, chemoradiotherapy (CRT), survival analysis, toxicity
Citation: Hong Y, Tan Q, Li Y, Yang B, Wu Y, Zhao L, Zhao Y, Chen Y, Zhu Z, Zhu X, Gu L and Jiang N (2025) Immunotherapy combined with definitive chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced unresectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 16:1646568. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1646568
Received: 13 June 2025; Accepted: 15 September 2025;
Published: 30 September 2025.
Edited by:
Xuefeng Leng, Sichuan Cancer Hospital, ChinaReviewed by:
Renxian Xie, Shantou University, ChinaXiaohan Zhao, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Hong, Tan, Li, Yang, Wu, Zhao, Zhao, Chen, Zhu, Zhu, Gu and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiangzhi Zhu, MTMxODI5NDgwNjhAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Lingling Gu, MTM4NTE3MDYxNTdAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Ning Jiang, bmppYW5nMTE3QG5qbXUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Yidan Hong1†
Yidan Hong1† Yang Zhao
Yang Zhao Xiangzhi Zhu
Xiangzhi Zhu Lingling Gu
Lingling Gu Ning Jiang
Ning Jiang