Abstract
As nucleic acid vaccine technology continues to advance, modern adjuvants are being engineered to quantitatively and qualitatively shape immune responses. Since their development in the early 1990’s, nucleic acid approaches have garnered significant attention, and numerous platform technologies have been developed both to improve delivery as well as immunogenicity. These advances were highlighted during the COVID-19 pandemic, with the approval of both mRNA-LNP and DNA vaccines for SARS-CoV-2. Early clinical trials with DNA antigens alone displayed suboptimal immunogenicity, supporting interest in adjuvant molecules. Molecular adjuvants, nucleic acid-encoded cytokines, chemokines, and enzymes, among others, are used to enhance and direct nucleic acid antigen-induced immunity in vivo. Additionally, mRNA-LNP vaccines, and more recently DNA-LNP vaccines, have demonstrated robust immunogenicity with intrinsic adjuvant activity based on the delivery mode. This review summarizes the molecular adjuvant landscape and highlights recent findings in the context of nucleic acid vaccines.
Introduction
Adjuvants are vaccine components that enhance and direct the immune response. The term comes from the Latin adjuvare, meaning to help or aide, and was first used by Gaston Ramon in 1925 after observing that horses with inflammation or abscesses at the site of injection developed higher antibody titers. A year later, the first adjuvant, alum, was discovered serendipitously by Alexander Glenny (1). While attempting to purify diphtheria toxin, he observed that aluminum salts precipitated the toxoid, leading to stronger antibody responses in guinea pigs. The resulting stable, insoluble complexes prolonged antigen exposure to immune cells. Alum was promptly incorporated into human vaccines and remained the only licensed adjuvant for most of the 20th century (1930s-1990s) (2).
Later decades saw growing interest in adjuvants, but alternatives such as Freund’s water-in-oil emulsions developed in the 1940s proved too toxic for human use (1). The next regulatory approvals would not come until the turn of the century, first with MF59, a squalene-based oil-in-water emulsion with surfactants approved in Italy in 1997 for seasonal influenza. AS04 followed in 2005, a combination of monophosphoryl lipid A (MPL) and aluminum salt (aluminum hydroxide) approved in the EU for use in Cervarix, a human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine. AS03 was approved in 2009 for the H1N1 pandemic, an oil-in-water emulsion containing squalene, DL-α-tocopherol (vitamin E), and polysorbate 80. AS01, a liposome-based adjuvant, was approved in 2017 for the shingles vaccine Shingrix. Finally, CpG 1018, a synthetic 22-mer phosphorothioate-linked oligodeoxynucleotide which acts as a Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) agonist, was approved in the US in 2017 for Heplisav B, a hepatitis B vaccine. This string of approvals marked a broader shift from empirical vaccinology to mechanistically-informed adjuvant selection (3) (reviewed by Goetz et al., 2024). These molecules have been used as chemical adjuvants in the context of inactivated virus and protein-based vaccine platforms for decades.
In the nucleic acid platform space, the ability to simultaneously deliver gene-encoded molecular adjuvants to modify vaccine-induced immunity has transformative potential. In 1990, Wolff et al. demonstrated the induced expression of reporter proteins in mouse muscle tissue from RNA and DNA vectors, opening the door for nucleic acid delivery (4). DNA vaccines emerged in the early 1990s, with pivotal work by Weiner and colleagues demonstrating “gene inoculation”, the successful delivery of plasmid DNA to elicit both humoral and cellular responses against HIV-1 env in mice (5). This breakthrough introduced endogenous antigen expression, in which transfected host cells produce the encoded immunogen. The new vaccine platform promised direct immune stimulation of cellular immunity along with traditional antibody responses and the ability to engineer tailored vaccines. Unlike other platforms, this approach reliably enabled antigen processing through the MHC Class I pathway, mimicking viral infection and robustly inducing cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses. However, early clinical trials in the late 1990s revealed low expression of the transgene in humans and poor antigen-presenting cell (APC) uptake from naked DNA (6), prompting advancements in delivery technologies and a new era of adjuvant research to enhance immunogenicity.
Electroporation, developed by Inovio and Ichor Medical in the 2000s, uses electrical pulses that transiently permeabilize cell membranes to enhance DNA plasmid uptake, improving immunogenicity in pre-clinical models and humans. Utilizing plasmid DNA as a vector enables co-delivery of gene-encoded adjuvant molecules alongside antigen. Molecular adjuvants can enhance (7–12) and direct (9, 13–17) vaccine-induced immunity in vivo, including in clinical trials (18, 19). Through the 2000s, early advancements in DNA vaccine technology included codon optimization (20–22) and exploration into molecular adjuvants, such as IL-12, GM-CSF, and CD40L. Promoter and intron optimizations were also leveraged to boost expression. The COVID-19 pandemic brought rapid development focus to the DNA platform. In 2020, Smith et al. developed a synthetic DNA vaccine, INO-4800, which elicited strong humoral and cellular immune responses in mice and guinea pigs, including neutralizing antibodies and T cells (23). Subsequent Phase 1 and 2 trials demonstrated a favorable safety profile and durable immune responses in humans (24, 25). In 2021, India’s drug regulator approved ZyCoV-D, the world’s first licensed DNA vaccine. Approved for emergency use during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, the vaccine delivered plasmid-encoded spike protein via jet injector and demonstrated 66% efficacy in Phase 3 (26). Since the pandemic, clinical development has continued to advance (27–29), with clinical trials for DNA vaccines against HIV-1, HPV, Zika, Ebola, TB (30), and immunotherapies (31, 32). Outside of physical delivery modalities, lipid-based formulations for plasmid DNA vaccines have historically shown limited immunogenicity in vivo. However, recent advances in lipid nanoparticle technology, microfluidics, and formulation have improved particle stability and immunogenicity, generating significant interest in LNP-mediated delivery as a viable strategy for the DNA vaccine platform (33–38).
The use of RNA to deliver antigens was initially hindered by instability, rapid degradation, and strong innate immune activation. A major breakthrough was achieved in 2005 when Karikó and Weissman demonstrated that nucleoside modifications including pseudouridine substitution reduced Toll-like receptor activation and enhanced translation efficiency (39). Subsequent innovations included optimized 5′ cap analogs, untranslated regions, and expanded nucleoside chemistries (38, 39). Delivery technologies also progressed, as ionizable lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) evolved from earlier liposome and cationic lipid systems (40). These LNPs were engineered to efficiently encapsulate mRNA, facilitate endosomal escape, and enable cytoplasmic delivery while minimizing toxicity (40) (Reviewed by Hou et al., 2021). By the late 2010s, these advances collectively enabled the first clinical successes in mRNA-based vaccines and therapeutics. In 2018, Alnylam’s Onpattro, became the first approved RNA therapeutic (siRNA-LNP) (41) and both Moderna and BioNTech, among other companies advanced clinical-stage mRNA vaccines for Zika, CMV, and certain cancers.
The COVID-19 pandemic potentiated unprecedented levels of development opportunity, accelerating the first widespread use and validation of mRNA vaccine technology. In 2020, mRNA vaccine candidates BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) (42) and mRNA-1273 (Moderna) (43) became the first nucleic acid vaccines approved for human use. Key studies have explored the potential of incorporating adjuvant molecules in the mRNA platform, as well as additional formulation, delivery, and sequence-level methods to reduce side effects and address waning immunity (44). Since 2022, the platform has expanded beyond COVID-19 with clinical trials for quadrivalent mRNA influenza vaccines (45), RSV (46, 47), EBV, and renewed efforts against Zika, CMV, and immunotherapies (48, 49). Emerging directions include self-amplifying RNA constructs, thermostable formulations, and tolerogenic vaccines for autoimmune diseases, while personalized cancer vaccines advance into phase 2 and 3 trials (49, 50).
The ability to co-deliver immune-modifying agents alongside the antigenic payload is a key feature of the nucleic acid platform, enabling precise stimulation and tailoring of vaccine-induced immunity in vivo (Figure 1). In this review, we summarize the history and current landscape of genetic, or molecular adjuvants, with a specific focus on vaccines targeting infectious diseases.
Figure 1
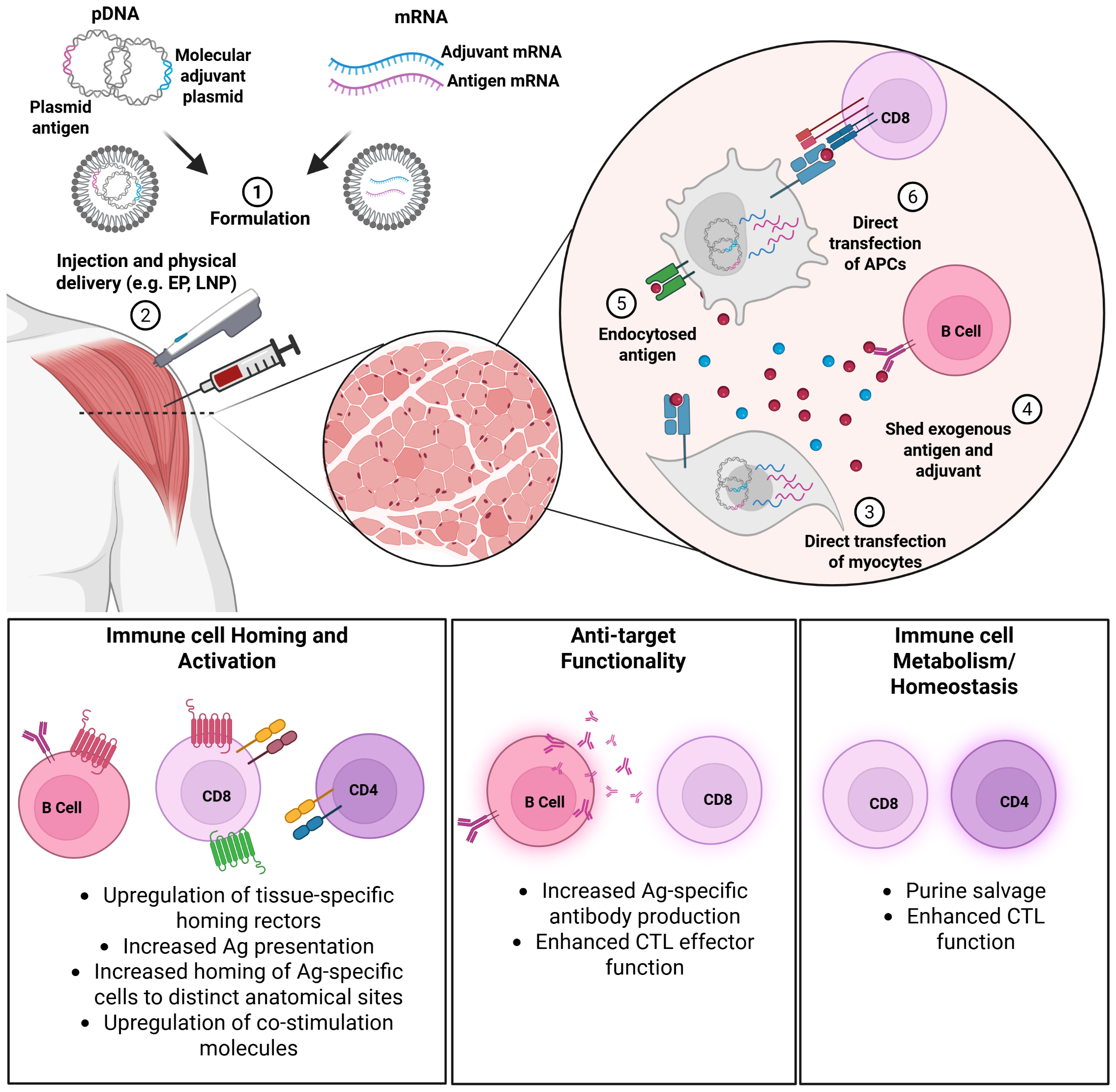
Mechanisms of molecular adjuvant action. Plasmid DNA (pDNA) or messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules encoding the antigen and adjuvant are formulated (1) and delivered (2) by direct injection or other physical delivery methods such as jet, electroporation (EP), or lipid nanoparticle (LNP) encapsulation.
Cytokine adjuvants
Cytokines are a broad class of molecules involved in intercellular communication and immune regulation, often promoting immune cell proliferation, differentiation, and effector function. Cytokine adjuvants are a subset of these molecules that have demonstrated potential to enhance vaccine-induced immune responses (Table 1).
Table 1
| Cytokines | Antigens | Significant Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-12 |
Mycobacterium
tuberculosis (Mtb), SARS-CoV-2, Listeria monocytogenes-OVA |
Sustained immunity to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-LNP, enhances CTL responses | Morelli et al. (51) Brook et al. (44) Aunins et al. (52) |
| IL-2 | rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus VP60, infectious bursal disease virus, Edwardsiella tarda, infectious laryngotracheitis virus, autoimmune diabetes | Enhances T cell proliferation and protection across many animal and disease models | Deng et al. (53) Huo et al. (54) Tang et al. (55) Hao et al. (56) Pagni et al. (57) |
| IL-4 | Influenza hemagglutinin, coccidiosis | Combination approaches preserve Th1-related responses |
Wei et al. (58) Tan et al. (59) |
| IL-15 | SIV-Gag/SIV-Nef, HPV16 E6/E7 |
Enhances CTL responses despite delivery constraints regarding trans-presentation | Leroy et al. (60) Zhou et al. (61) |
| IL-18 | genotype VII Newcastle Disease Virus | Enhances Th1-related responses in chickens and murine cancer models | Wang et al. (62) Yadav et al. (63) |
|
IL-28B
(IFN-λ3) |
H1N1 (inactivated virus vaccine), Newcastle Disease Virus, HPV16 E6/E7 |
Promotes robust CD8+ activation by Treg suppression | Sabbaghi et al. (64) Amoia et al. (65) Zhou et al. (61) |
| GM-CSF | SARS-CoV-2 WT, Omi, Influenza HA |
Enhances germinal center formation | Liu et al. (66) Wei et al. (58) |
| Chemokines | Antigens | Significant Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCR10 Ligands (CCL27, CCL28) | SARS-CoV-2 WT, BA.2, XBB.1.5, influenza, HIV-1 env |
Drive robust mucosal immunity in murine models of challenge | Gary et al. (13) Gary et al. (67) Liaw et al. (68) |
| CCR7 Ligands (CCL19, CCL21) |
Vibrio anguillarum antigen (VAA), VHSV, H7N9 HA |
Enhance systemic & mucosal immunity across animal models | Xu et al. (69) Kim et al. (70) Xiang et al. (71) |
| Co-stimulators | Antigens | Significant Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD40L | autoimmune glomerulonephritis (EAG), SARS-CoV-2, Tembusu virus, bovine herpesvirus 1 (BoHV-1) | Potent multi-faceted immune enhancement via dendritic cell activation across animal models | Li et al. (72) Tamming et al. (73) Huang et al. (74) Kornuta et al. (75) |
| CD80/86 | Vibrio anguillarum OmpK | increased IgM+ and CD4+ populations | Liu et al. (76) |
| Immunomodulators | Antigens | Significant Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adenosine deaminase | HIV-1, SARS-CoV-2 | Mitigates age-associated immunosenescence in mouse models | Gary et al. (13) Cusimano et al. (8) Gary et al. (7) |
| C3d | Porcine Circovirus Type 2 (PCV2) ORF2 , SARS-CoV-2 | Significantly increases antibody responses | Hou et al. (77) Li et al. (78) |
Molecular adjuvants by class.
IL-12
Interleukin-12 (IL-12) is a proinflammatory cytokine that promotes cellular immunity by enhancing CD8+ T cell responses, driving Th1 polarization, and stimulating interferon-γ (IFN-γ) production. The first use of IL-12 as an adjuvant dates back to the mid-1990s, with several landmark studies shortly after it was first characterized in 1989 (79) Afonso and colleagues demonstrated recombinant IL-12 to be effective for the induction of cell-mediated immunity against leishmaniasis in 1994 (80). Three years later, the first study demonstrating plasmid-encoded IL-12 as a genetic adjuvant was published, with co-delivery generating enhanced cell-mediated immunity for a DNA vaccine encoding several HIV-1 antigens (81). Plasmid-encoded IL-12 has been well-tolerated and shown a significant dose-sparing effect in clinical trials for DNA-based HIV-1 and HCV vaccines (82–85) along with several immunotherapies (32, 86, 87).
Systemic administration of recombinant IL-12 was identified to cause toxicity in both humans and animal models (88), with early clinical trials reporting severe, sometimes fatal effects, including IFNy overproduction and cytokine storm–like responses (89). Subsequent studies confirmed comparable toxicity for IL-12 delivered systemically via naked DNA, however, IL-12 pre-dosing significantly attenuated toxicity, showing a schedule-dependent desensitization effect (88). Since then, strategies have centered on controlling expression through localized delivery, pre-dosing protocols, tunable plasmid-encoded expression vectors, and dosage control.
While IL-12 is a well-characterized cytokine adjuvant, recent studies have applied it in new vaccine contexts, including DNA-encoded delivery for tuberculosis and as a co-adjuvant to improve durability in SARS-CoV-2 mRNA models. A 2020 study demonstrated IL-12 robustly enhanced immune responses in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) vaccination (51). Prior to this work, IL-12 received limited investigation as an adjuvant for Mtb vaccines, hindered by delivery challenges and inconsistent protective outcomes. This study is among the first to demonstrate that IL-12 DNA co-delivery can robustly enhance Ag85A-specific lymphocytes and protection in challenge. In a DNA-A85A/MVA85A prime-boost regimen, IL-12 co-delivery significantly enhanced IFN-γ responses, expanded Ag85A-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and increased the cytotoxic CD107a-expressing CD8+ T cell population. Morelli et al. also observed increased anti-Ag85A antibody levels and reduced lung bacterial burden post-challenge, indicating improved protection. Importantly no severe adverse events (SAEs) were reported in these trials, further demonstrating the safety of local plasmid delivery of IL-12.
Although SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines induce robust acute immune responses in humans, numerous studies have shown that these responses have limited durability (90). A 2024 study found that IL-12p70-expressing mRNA-LNP could improve response durability (44). Co-delivery improved antibody and cell-mediated immune responses when combined with the Pfizer BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. In an aged mouse model, the IL-12 mRNA-LNP adjuvant increased humoral immune response durability and spike-specific IgG titers to levels comparable to young adult mice. The IL-12 mRNA-encoded adjuvant was designed with a multiorgan protection (MOP) sequence to restrict expression to the injection site, mitigating toxicity risks. By enhancing immunogenicity in both young and aged mice, this approach demonstrated promise for clinical use in at-risk groups.
Aunins and colleagues further demonstrated the potential of IL-12 as an adjuvant in the mRNA-LNP platform, in a study using models of both bacterial infection and cancer (52). IL-12 mRNA-LNP co-delivery enhanced antigen-specific CD8+ T cell expansion, effector function, and memory formation. This methodology led to improved protection in models of Listeria monocytogenes infection and B16 melanoma. The IL-12 construct consisted of codon-optimized mRNA encoding the p35 and p40 subunits joined by a flexible glycine-serine linker, enabling co-translation and efficient heterodimerization into functional IL-12p70.
IL-12 is one of the most extensively studied gene-encoded adjuvants, with consistent immunostimulatory effects in preclinical models and an acceptable safety profile in clinical settings. Plasmid-encoded delivery has been central to its development, enabling localized expression that significantly mitigates the systemic toxicity associated with recombinant protein approaches. In DNA-based platforms, p35 and p40 are often expressed from bicistronic plasmids using dual promoters, with staggered strength to favor proper heterodimer assembly, whereas in mRNA vaccines, a single transcript typically encodes both subunits joined by a flexible linker. Recent studies reinforce IL-12’s robust profile as a molecular adjuvant for nucleic acid vaccines, particularly in enhancing Th1-biased cellular immunity. Current efforts focus on refining delivery systems and dosing regimens to enhance efficacy and expand translational development.
IL-2
Interleukin-2 is a cytokine primarily produced by activated CD4+ T cells that plays a central role in the proliferation, survival, and functional differentiation of T cells and NK cells. IL-2 has long been explored for its ability to enhance vaccine-induced cellular immunity. It was first investigated as an adjuvant in a 1989 study that demonstrated systemic administration of recombinant IL-2 protein alongside an inactivated rabies virus vaccine improved cell-mediated protection in challenge (91). Later studies confirmed co-administration of IL-2 could enhance antigen-specific immune responses, particularly by promoting T cell proliferation and activity. IL-2 was first investigated as a plasmid-encoded adjuvant in 2005, when it was shown murine IL-2 fused to Ig (IL-2/Ig) co-administered with a DNA vaccine encoding HIV-1 env gp120 in mice, significantly enhanced both antibody and cell-mediated immune responses compared to the DNA vaccine alone (92). Recombinant IL-2 has been found to cause significant toxicity from systemic delivery, while plasmid-encoded IL-2 has been well-tolerated in trials for DNA-based cancer therapeutics (93, 94).
Recent findings in IL-2 as an adjuvant have primarily occurred in chicken models, with additional findings in rabbits, mice, and fish. In a 2019 study, researchers developed an oral DNA vaccine using attenuated Salmonella typhimurium to deliver a plasmid encoding both IL-2 and the VP60 capsid protein of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) (53). Co-expression of IL-2 significantly enhanced humoral and cellular immune responses, leading to 93.3% protection against viral challenge, surpassing the efficacy of vaccines lacking IL-2.
A DNA vaccine co-expressing chicken IL-2 (chIL-2) and IL-7 (chIL-7) with the VP2 antigen demonstrated enhanced immunogenicity and protective efficacy against infectious bursal disease (IBDV) in a 2019 study (54). The chIL-2/chIL-7/VP2 combination vaccine significantly increased IBDV VP2-specific antibody titers, T cell proliferation, and IFN-γ production. In 2020 Tang et al. demonstrated that plasmid encoded flounder IL-2 (poIL-2) enhanced protection against Edwardsiella tarda (55). Both recombinant (rIL-2) and plasmid-encoded (pcIL-2) forms of poIL-2 significantly improved survival rates, antigen-specific antibody production, and expression of immune-related genes when co-administered with a recombinant OmpV vaccine. However, recombinant IL-2 elicited stronger responses than the plasmid-encoded form.
Similarly, co-delivery of chicken IL-2 (chIL-2) with an infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) chicken embryo origin (CEO) vaccine significantly alleviated vaccine-induced clinical signs without compromising protective efficacy (56). Oral delivery of chIL-2 reduced viral loads in key respiratory tissues and shortened the duration of adverse reactions. IL-2 enhanced early activation and expansion of natural killer cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes, particularly in mucosal tissues.
Finally, a 2025 study reported a multi-component DNA-launched plasmid prevented autoimmune diabetes in nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice (57). The construct encoded the cytokines TGF-β1, IL-10, and IL-2 alongside preproinsulin2. IL-2 contributed to antigen-specific immune tolerance without systemic immunosuppression. These findings support the ability of IL-2 to boost cellular immunity across a variety of animal models.
IL-4
Another well-characterized adjuvant is Interleukin-4, a cytokine that induces differentiation of naive helper T cells (TH0 cells) to TH2 cells. IL-4 has been noted for its TH2 bias and its ability to promote humoral immunity and IgG1/IgE production. Early studies showed that plasmid-encoded IL-4 could enhance antibody responses when co-delivered with DNA vaccines (e.g., for HIV, influenza, or allergens). However, use of IL-4 has been limited due to concerns of skewing away from protective Th1 responses and dampening cell-mediated activity (58, 95).
The earliest study investigating IL-4 as an adjuvant was published in 1998, showing a DNA vaccine developed from an ovalbumin (OVA) and murine IL-4 fusion gene (95). Mice immunized with OVA/IL-4 DNA exhibited enhanced OVA-specific IL-4 production by CD4+ T cells and a higher ratio of anti-OVA IgG1 to IgG2a antibodies, indicating a TH2-biased response. The OVA/IL4 fusion gene induced TH2-biased cell-mediated responses while antigen alone or a mixture of antigen and IL-4 did not, supporting that direct linkage drives the immune response phenotype.
A recent study revisited IL-4 as an adjuvant in a dual-cytokine approach. Wei et al. (58) reported the use of mRNA-encoded GIFT4, a fusion cytokine (fusokine) combining GM-CSF and IL-4. It was originally characterized in 2014 for its ability to drive potent B cell proliferation and high levels of IL-1α, IL-6, IL-12, and IL-5 relative to the combined delivery of recombinant GM-CSF and IL-4 (96). When encoded by mRNA and co-delivered with antigen, GIFT4 enhanced both humoral and cellular responses to influenza in mice, including early germinal center formation and lung-resident T cell populations. The Th2-skewing effect of IL-4 was intentionally leveraged in this strategy, with the GM-CSF and IL-4 fusion selected for its cooperative enhancement of B cell activation and proliferation beyond that of either cytokine alone. This approach focused on improving antibody quality and breadth, rather than quantity alone. The preservation of robust cellular responses suggests that the inclusion of GM-CSF counterbalanced the typical suppressive effects of IL-4 on Th1-related immunity.
Plasmid-encoded IL-4 was implemented in another fusion-based strategy to enhance protection against coccidiosis in chickens (59). The construct pCI-IL-4-IL-2-EGFP, encoding chicken IL-4 and IL-2, significantly boosted both cellular and humoral responses when co-administered with a live coccidia vaccine. This combination increased the expression of IL-2, IL-4, TNF-α, and IFN-γ, and promoted the expansion of B cells, T cells, and APCs in the spleen and intestinal tissues - the primary site of infection. These findings highlight the value of combination approaches for refining the immunomodulatory role of IL-4 to further tailor vaccine-induced immune responses.
IL-15
Interleukin-15 (IL-15) drives the expansion and survival of memory CD8+ T cells and NK cells, which supports its role in promoting cell-mediated immunity. It was first studied as an adjuvant in the late 1990s when recombinant IL-15 was shown to enhance CD8+ T cell responses in a Toxoplasma gondii mouse model (97). The first use of IL-15 as a plasmid-encoded vaccine adjuvant came a decade later. Two key studies from 2005 reported plasmid-encoded IL-15 could enhance cellular immunity when delivered alongside DNA vaccines targeting HIV or herpes simplex virus in mice (98, 99). Plasmid-encoded IL-15 was shown to be well-tolerated in humans but offered no apparent augmentation in a 2012 clinical trial for a HIV gag DNA vaccine (18).
Research on IL-15 has been limited in recent years due to its biological dependence on trans-presentation via IL-15Rα for optimal T cell activation (100–103). Maintaining this complex in vivo has proven difficult, shifting focus to alternatives (100). In support of a more feasible nucleic acid based approach, a 2022 study showed that co-delivery of IL-15 as a DNA-encoded adjuvant with a non-integrating lentiDNA SHIV vaccine enhanced vaccine-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses in both mice and rhesus macaques (60). IL-15 co-expression also increased the durability of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) responses in plasma and mucosal compartments for up to 40 weeks. In 2025 researchers evaluated IL-15 and IL-28B as a gene-encoded adjuvants for an HPV16 DNA vaccine targeting E6/E7 antigens (61). Co-delivery of IL-15 plasmid enhanced CD8+ T cell responses, demonstrated by increased E7-specific IFN-γ secretion relative to antigen alone.
The broader use of IL-15 will likely depend on further improvements to stability and delivery mechanisms to overcome the challenges posed by trans-presentation and half-life constraints (100–104). The successful integration of IL-15 into recent DNA vaccine platforms suggests untapped potential. However, as seen in the HPV16 model, the choice of cytokine must align with the antigen and desired immune profile.
IL-18
Interleukin-18, initially referred to interferon-γ-inducing factor following its discovery (105) in 1995, is secreted primarily by activated monocytes. IL-18 is best known for promoting TH1-related differentiation in the presence of IL-12, though it can also support TH2 responses under certain conditions (106). Plasmid-encoded IL-18 has shown the most promise for enhancing cellular immunity in murine cancer models, with many studies in the 2000s (63, 107–110). Species-specific receptor interactions and pro-inflammatory toxicity have limited translation to humans. In contrast, livestock more readily tolerate elevated IFN-γ and permit less stringent formulation constraints. Recent progress in the context of infectious disease has been in veterinary models.
A 2022 study demonstrated that co-delivery of chicken IL-18 significantly enhanced mucosal and systemic immunity against genotype VII Newcastle Disease Virus (62). The cytokine gene was delivered with a minicircle DNA vaccine (pYL58) via attenuated Salmonella in chickens. IL-18 co-expression boosted IFN-γ and IFN-α production, improved lymphocyte proliferation, and increased protection post-challenge (70% vs. 50%).
While these findings support the use of IL-18 in veterinary contexts, its efficacy in mammalian models of infectious disease remains underexplored. Future studies should focus on optimizing delivery and resolving its safety profile. Clinical translation of plasmid-encoded IL-18 delivery will require building on the progress in murine cancer models.
IL-28B
IL-28B, also known as interferon lambda 3 (IFN-λ3), is a member of the type III interferon family that signals through the heterodimeric receptor complex IFNLR1/IL10R2. It plays a critical role in mucosal antiviral defense by inducing interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) primarily in epithelial and barrier tissues (111). IL-28B is secreted primarily by dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages and enhances viral clearance by promoting robust CD8+ T cell responses while reducing regulatory T cell (Treg)-mediated suppression (112). Following the discovery of type III IFNs (IFN-λ or IL-28/29) in 2002, IL-28B’s antiviral and antitumor properties were characterized in multiple disease models (111). Recombinant IL-28 protein completely blocked mucosal replication and disease in an in vivo HSV-2 infection model and enhanced systemic IFN-γ responses (111). Plasmid-encoded IL-28B was first evaluated as a vaccine adjuvant in 2009, where co-delivery with an HIV Gag DNA vaccine reduced Treg populations, increased cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, and provided full protection in a lethal influenza challenge (112). These findings were extended to non-human primates, with plasmid-encoded IL-28B enhancing antigen-specific CTL responses and cytolytic activity in rhesus macaques vaccinated with plasmid DNA encoding HIV-1 gag and pol (113).
In recent years, IL-28b has been explored as an adjuvant across mice and poultry animal models. A 2021 study reported plasmid-encoded IL-28B co-administered intranasally with a gamma-irradiated H1N1 influenza vaccine, significantly enhanced both mucosal (IgA) and systemic (IgG) antibody responses, as well as T cell proliferation and Th1-related cytokine production (IFN-γ, IL-12) (64). Mice receiving the plasmid-encoded IL-28B adjuvant showed reduced lung viral titers and decreased inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-10) post-challenge, suggesting improved immune regulation.
The inclusion of IL-28b in a genotype-matched Newcastle disease virus DNA vaccine significantly improved immune responses and protective efficacy in chicks (65). The IL-28b-adjuvanted vaccine (pTwist-F-HN-VII-IL28b) induced stronger immunity and achieved 80% protection against a virulent NDV strain, outperforming both the non-adjuvanted plasmid and the conventional LaSota vaccine.
Zhou et al. reported that plasmid-encoded IL-28B significantly enhanced antigen-specific CD8+ T cell responses in a therapeutic HPV16 DNA vaccine targeting E6 and E7 oncoproteins in mice (61). IL-28B was delivered intramuscularly via a codon-optimized plasmid administered in trans alongside CpG-optimized antigen-encoding plasmids. When co-administered with CpG-enriched mE6/HSP70 and mE7/HSP70 plasmids, IL-28B significantly enhanced antigen-specific CD8+ T cell responses and improved both prophylactic and therapeutic control of E6/E7-expressing tumors in mice. In side-by-side comparison, both IL-28B and IL-15 significantly enhanced CTL responses. However, IL-28B induced superior CTL responses and significantly higher granzyme B mRNA levels, suggesting more robust activation of cytotoxic effector pathways (61). These studies demonstrate the potential of IL-28B as a robust cytokine adjuvant capable of enhancing cellular immunogenicity in various animal models, suggesting broad utility for improving vaccine potency.
GM-CSF
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), also known as colony-stimulating factor 2 (CSF2), is a monomeric glycoprotein secreted by macrophages, T cells, mast cells, natural killer cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts that functions as a pleiotropic cytokine that drives differentiation of myeloid precursors into APCs, enhances DC maturation, and supports the generation of TH1-biased immune responses. GM-CSF recruits and activates DCs and other myeloid cells at the site of antigen delivery. When co-delivered with vaccines, GM-CSF enhances antigen presentation and promotes robust humoral and cellular immune responses (114).
GM-CSF has been explored as an adjuvant since the early 1990s, with a 1994 review highlighting its potential to enhance immune responses by promoting DC maturation and increasing antibody titers in both animal and human studies (115). The cytokine was first used as a plasmid-encoded adjuvant in 1997, with co-delivery resulting in the enhancement of HIV-1 gag, pol, and env-specific antibody responses (81). GM-CSF has shown notable adjuvant capability in DNA vaccines targeting various infectious diseases (114). Plasmid-encoded GM-CSF has previously reported as well-tolerated in clinical trials evaluating DNA vaccines for advanced melanoma and prostate cancer (116–118).
Plasmid-encoded GM-CSF (pGM-CSF) enhanced the immunogenicity of an RBD-based DNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 by boosting both humoral and cellular responses, including robust neutralizing antibody production against ancestral and Omicron variants (66). pGM-CSF also promoted antigen expression, immune cell recruitment, germinal center B cell responses, and the formation of central and tissue-resident memory T cells, suggesting a multifaceted adjuvant role.
Likewise, mRNA-LNP delivery of a fusion gene of GM-CSF and IL-4 (GIFT4) broadly and robustly enhanced adaptive immune responses to influenza antigens in mice, including robust germinal center formation and lung-resident T cell induction (58). GM-CSF, as part of GIFT4, also promoted early germinal center formation and B cell activation in draining lymph nodes. Intradermal administration of this construct produced notable lung-resident T cell populations, indicating mucosal immune enhancement by GM-CSF-based adjuvanticity.
GM-CSF as a gene adjuvant enhances humoral responses and promotes DC activation, but its efficacy in boosting cellular immunity and protection varies widely by context, antigen, and delivery method. Encoded or locally secreted forms, especially via plasmid or mRNA, outperform recombinant cytokine delivery, with spatial-temporal control proving critical. Fusion constructs like GIFT4 further support the use of GM-CSF as a gene adjuvant, particularly for inducing germinal center and tissue-resident T cell responses. Overall, plasmid-encoded GM-CSF continues to be a promising adjuvant in nucleic acid vaccine development, with ongoing research focusing on optimizing its delivery and combination with other immunostimulatory agents to maximize vaccine efficacy.
Chemokine adjuvants
Chemokines are a specialized class of cytokines that control chemotaxis through chemical signaling, often directing the migration of immune cells to sites of infection or vaccination. They are typically thought of in terms of ligands for specific receptors. Chemokine adjuvants are often noted for their ability to tailor vaccine-induced immunity in mucosal and peripheral contexts (Table 1).
CCR10 ligands
Chemokine receptor 10 (CCR10) is expressed on IgA+ B cells and T cells at barrier surfaces, including the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and skin surfaces. CCR10 has two known ligands: chemokine ligands 27 (CCL27) and 28 (CCL28). We have previously reported that co-delivery of CCR10 ligands in the context of gag/pol/Env DNA immunogens supports increased protection from SHIV vaginal challenge in non-human primates (17).
CCL27, also known as cutaneous T cell-attracting chemokine (CTACK), is canonically known as a director of T lymphocyte chemotaxis in the epidermis. The chemokine was first used as a vaccine adjuvant by Kutzler and colleagues in 2010 (16), where plasmid-encoded CTACK (pCTACK) was shown to enhance systemic and mucosal immune responses to DNA vaccines, including increased antigen-specific IgG and IgA levels, as well as elevated IFN-γ production from CD8 T cells This approach also provided protection in a lethal influenza challenge.
Additional studies have characterized on the ability of plasmid-encoded CTACK to bolster mucosal immunity against respiratory pathogens like SARS-CoV-2 and influenza. We investigated the use of pCTACK co-delivered with a SARS-CoV-2 DNA vaccine in mice (67). Co-delivery of CTACK in the periphery led to increased spike-specific IgA at mucosal surfaces, but not in serum, suggesting a targeted mucosal response. pCTACK also led to higher frequencies of IFN-γ+ CD8+ T cells in the respiratory mucosa expressing a mucosal homing marker. pCTACK provided 100% protection against heterologous Delta variants in lethal challenge with complete survival, absence of weight loss, and reduced lung pathology compared to animals immunized with the spike DNA vaccine alone. When co-delivered with a DNA vaccine encoding a self-assembling influenza hemagglutinin (HA) head domain nanoparticle immunogen, pCTACK increased HA-specific antibody levels in the bronchoalveolar lavage and reduced lung pathology in a lethal challenge model relative to antigen alone (68).
Similarly, the second CCR10L, CCL28, also called mucosa-associated epithelial chemokine (MEC) has also been explored as a molecular adjuvant. We have previously reported that co-delivery of plasmid-encoded CCL28 (pMEC) with HIV-1 envelope DNA immunogens supported increased anti-HIV responses at mucosal sites including increased IgA in fecal extracts and frequencies of HIV-specific B cells in intestinal Peyer’s patches (13). These studies demonstrate that peripheral delivery of mucosal-homing chemokines can provide enhanced protection at key barrier sites of pathogen entry.
CCR6 ligands
Chemokine Ligand 20 (CCL20), also known as liver activation regulated chemokine (LARC) and macrophage inflammatory protein-3 (MIP-3a) is strongly chemotactic cytokine for lymphocytes and weakly attracts neutrophils. MIP-3α is the only known natural ligand for CCR6 and plays a specialized role in targeting immature dendritic cells (iDCs). It has been explored as a gene-encoded adjuvant since at least 2014, where it was shown to direct antigen presentation toward CCR6+ iDCs, enhancing antigen uptake and priming adaptive responses (119–121). For instance, a 2014 study reported fusion of the malaria antigen to MIP-3α in a DNA vaccine, combined with the lipid-based adjuvant Vaxfectin, significantly improved protective efficacy in a murine challenge model, with MIP-3α enhancing targeting of antigen to immature dendritic cells, leading to sterilizing immunity comparable to that induced by irradiated sporozoites (119).
Subsequent studies have extended these observations. A 2020 report found that plasmid-encoded MIP-3α boosted immune responses when co-delivered with an HIV-1 gp140 DNA vaccine, followed by mucosal protein boosting (122). The chemokine increased antigen-specific antibodies in both serum and mucosal sites, including the vaginal vault and intestinal lumen, and promoted immune cell recruitment to mucosal tissues. More recently, in a 2024 SARS-CoV-2 DNA vaccine study, inclusion of MIP-3α enhanced both the magnitude and durability of antibody responses, with neutralizing titers sustained for at least 12 months after intramuscular (IM) electroporation (123). In parallel, intranasal delivery of the same plasmid (without encapsulation or electroporation) elicited significantly stronger lung-localized T-cell responses compared to controls. MIP-3α has also improved immunogenicity in murine melanoma DNA vaccine models (124–126).
Together, these results support MIP-3α (CCL20) as a broadly functional gene-encoded adjuvant. Co-delivery with plasmid vaccines enhances systemic and mucosal immunity, promoting both sustained antibody production and lymphocyte recruitment to barrier tissues. Across multiple platforms, including HIV-1 and SARS-CoV-2, MIP-3α has improved humoral and T-cell responses even in the absence of advanced delivery technologies, reinforcing its translational potential for vaccines requiring mucosal or long-term protection.
CCR7 ligands
CCL19 and CCL21 are functional homologs and ligands for CCR7. They drive DC and T cell homing to lymph nodes, enhancing antigen presentation and T cell priming. CCL19 and CCL21 have been explored as vaccine adjuvants since the early 2000s, with many early studies in the cancer immunotherapy space. A 2004 study by Flanagan et al. used a recombinant vaccinia virus expressing CCL19 to induce a CD4+ T-cell dependent antitumor response in mice, marking one of its first vaccine applications (127).
Recent progress in plasmid-encoded CCL19 and CCL21 has been made in fish and mouse models. A 2020 study in flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) reported bicistronic DNA plasmids encoding both the Vibrio anguillarum bacterial antigen (VAA) and either CCL3, CCL4, CCL19, or CCL21 (69). Co-immunization with CCL19 or CCL21 plasmids significantly enhanced protection in challenge, leading to a relative percent survival (RPS) of 78.38% and 72.97% respectively, compared to 40.54% with antigen alone. Co-expression of CCL19 also led to increased sIgM+, CD4-1+, and CD4-2+ lymphocyte populations and VAA-specific antibody levels.
CCL19a.2 is a teleost-specific functional homolog of mammalian CCL19 that retains core chemotactic and immunostimulatory functions. A DNA vaccine encoding both viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) glycoprotein and CCL19a.2 significantly elevated early expression of interferon- and cytokine-related genes in lymphoid tissues of zebrafish (70). While co-expression with CCL19a.2 did not significantly improve survival following viral challenge, it induced pronounced innate immune activation within the first two weeks post-immunization. It is important to note that potential differences in expression kinetics or cellular targets may influence CCL19 adjuvant effect across species (128). In a 2024 study, CCL19 used in an intranasal H7N9 HA DNA vaccine significantly enhanced both cellular and humoral immune responses in mice (71). When combined with polyethylene imine and chitosan for mucosal delivery, the vaccine induced strong local mucosal and systemic immunity, providing 100% protection against lethal virus challenge. Mice immunized with the CCL19 composite vaccine also exhibited increased levels of IL-2 and IFN-γ and robust IgA production.
These findings demonstrate the diverse potential of CCL19 and CCL21 as plasmid-encoded adjuvants, with demonstrated benefits to both systemic and mucosal immunity across different species. The ability of these chemokines to enhance antigen-specific responses and provide protection against pathogenic challenges positions them as promising adjuvants for use in nucleic acid vaccine design.
Costimulatory and immunomodulatory adjuvants
Costimulation is one of the essential signals required for full T cell activation during adaptive immune responses. Costimulatory molecules are typically cell surface proteins, though some soluble or enzymatic immunomodulators can also enhance T cell activation through costimulatory-like effects. By providing secondary signals to T cells, they enhance their proliferation, survival, and differentiation following antigen recognition. Certain costimulatory ligands have been shown to act as adjuvants when co-delivered alongside gene-encoded immunogens (Table 1). Other immunomodulatory adjuvants for nucleic acid vaccines include enzymes such as adenosine deaminase (ADA), the complement fragment C3d, and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery systems (Table 2).
CD40L/CD154
CD40 ligand (CD40L or CD154) is a costimulatory molecule that enhances vaccine-induced immunity by promoting DC activation, B cell help, and germinal center formation via engagement of CD40 on APCs. CD40L has been explored as a vaccine adjuvant since the late 1990s, with early studies demonstrating its potential to enhance both humoral and cellular immune responses (136, 137). The first study using CD40L as a DNA plasmid-encoded adjuvant was in 2006, with duck CD154 enhancing specific antibody responses to hepatitis B virus (138).
In recent years, studies have shown the ability of CD40L to enhance both humoral and cellular immune responses across various disease models. A 2019 study (72) reported a DC-targeted CD40 DNA vaccine (DEC-CD40) suppressed Th17 cell responses and reduced kidney damage in a rat model of autoimmune glomerulonephritis.
A 2022 study reported fusing CD40L to the SARS-CoV-2 spike in a DNA vaccine enhanced immunogenicity and reduced lung pathology in Syrian hamsters post-challenge (73). CD40L acted as both a targeting ligand and intrinsic adjuvant, amplifying neutralizing antibody responses and improving protection. Returning to poultry vaccines, Huang et al. used Duck CD40L (dusCD40L) in the context of a DNA vaccine against Tembusu virus. CD40L co-delivery significantly boosted both humoral and cellular immune responses against Tembusu virus (74) resulting in significantly improved neutralizing antibody titers, IFNγ production, and viral clearance in challenge.
Kornuta et al. evaluated the use of a plasmid encoding soluble CD40L combined with the adjuvant Montanide™ GEL01 to enhance a DNA vaccine (pCIgD) targeting bovine herpesvirus 1 (BoHV-1) (75). The combination improved DC activation in vitro and significantly boosted humoral and cellular immune responses in vaccinated cattle, including increased virus-specific IgG subclasses, neutralizing antibodies, and IFNγ/IL-4 secretion. Upon viral challenge, animals receiving the CD40L-enhanced vaccine showed reduced clinical symptoms, lower viral shedding, and stronger proliferation of lymphocytes, indicating improved protective efficacy.
These studies highlight the multi-faceted impact of CD40L as an adjuvant, capable of enhancing both humoral and cellular immune responses across animal models. CD40L was observed to mitigate immunopathology and facilitate antigen targeting to DCs, suggesting its potential as a molecular adjuvant for infectious disease and autoimmune vaccine strategies.
CD80/CD86
CD80 and CD86 (B7-1/B7-2) are functional homologs that serve as ligands for the co-stimulatory receptor CD28, which is constitutively expressed on naïve T cells. These molecules are expressed on APCs, with DCs typically expressing both, while monocytes and macrophages predominantly express CD86. Engagement of CD28 by CD80/86 delivers the secondary activation signal required for T cell activation, promoting proliferation, IL-2 production, resistance to anergy, and expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-xL (76, 139–141).
Following identification in the early 1990s (139, 140), CD80/86 were first used as DNA-encoded adjuvants in 1997, recognized for their ability to induce cellular responses. Co-immunization with CD86, and not CD80, was found to significantly enhance specific T-cell mediated responses, highlighting CD86’s more potent effect as a molecular adjuvant (141, 142).
In 2022, Liu et al. identified a homolog of CD80/86 expressed primarily on APCs in flounder and constructed a bicistronic DNA vaccine co-expressing CD80/86 with the Vibrio anguillarum antigen OmpK (76). Co-expression of CD80/86 enhanced humoral immune responses, evidenced by increased IgM+ and CD4+ cell proportions and elevated expression of activation markers and cytokines at the injection site. The vaccine combining CD80/86 with OmpK significantly improved survival after bacterial challenge compared to antigen alone, supporting the adjuvant potential of CD80/86 in teleost fish. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that bony fish CD80/86 is more closely related to mammalian CD86 than to CD80. CD80/86 has also been implemented as a DNA-encoded adjuvant in several cancer vaccines (143).
Despite early promise in the 2000s, interest in CD80/CD86 as molecular adjuvants has declined. Over time, research has shifted toward stronger or more multifunctional co-stimulatory ligands, like CD40L, which not only activate T cells but also directly license DCs and promote cytokine production.
Adenosine deaminase
Adenosine deaminase-1 (ADA) is a highly-conserved enzyme, known as a key regulator of the immune system and purine metabolism. ADA regulates intra- and extracellular levels of adenosine and has both enzymatic and extraenzymatic immune functions. Pegylated bovine ADA-1 (PEGademase) has been FDA-approved for use in humans since 1990 as an enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) for ADA-deficient severe combined immunodeficiency (ADA-SCID). The established regulatory and safety record of PEGademase offers potential benefit for clinical development of plasmid-encoded ADA. In 2017, Tardif et al. identified ADA1 expression as a key driver of T follicular helper (TFH) cell differentiation, both within germinal centers (GC TFH) and in circulating TFH (cTFH) and demonstrated that recombinant ADA enhanced antibody production in in vitro TFH and B cell coculture assays (144). This prompted the design of plasmid-encoded ADA-1 (pADA) for evaluation in the context of DNA immunization. In 2020, pADA was found to enhance the maturation of myeloid DCs and promote IL-6 secretion, fostering a microenvironment conducive to TFH polarization (9). Co-administration of pADA with an HIV-1 envelope DNA vaccine significantly increased TFH cell frequencies in draining lymph nodes and boosted serum HIV-specific IgG responses (9). In these studies, when delivered alongside both DNA and protein immunogens, pADA uniquely enabled the induction of homologous HIV-1 neutralizing antibodies, highlighting its capacity to qualitatively enhance germinal center and antibody responses in vivo.
Recent findings have further characterized these effects. In 2023, scRNAseq analysis revealed that aged mouse T cells had decreased ADA1 transcripts and we hypothesized that pADA could enhance vaccine-induced immunity in aged models of SARS-CoV-2 immunization and challenge. Indeed, we demonstrated that co-delivery of pADA significantly enhances both cellular and humoral responses in aged mouse models (7). Co-delivery of ADA enhanced both cellular and humoral responses to a SARS-CoV-2 DNA vaccine in aged mice, ameliorating age-associated declines in IFNγ secretion and antibody quality (7). pADA broadened the affinity and breadth of spike-specific antibodies and promoted a TH1-skewed transcriptional profile in lymph node lymphocytes while reducing FoxP3 expression. These effects correlated with reduced viral load and improved survival following SARS-CoV-2 challenge, demonstrating that pADA restores vaccine efficacy in immunosenescent hosts. Together, these studies highlight pADA as a broadly-active molecular adjuvant that enhances cellular and humoral immunity by shaping T and B cell interactions, promoting dendritic cell activation, and mitigating age-associated declines in immune responsiveness.
C3d
C3d, a fragment of the complement component C3, binds to complement receptor 2 (CR2) which is located on the surface of follicular dendritic cells (FDC), B cells, and T cells. C3d was first used as an adjuvant in 1996, with 2 or 3 copies of recombinant C3d delivered alongside the model antigen HEL, drastically increasing antibody responses by up to 10,000-fold (145). This finding highlighted the ability of C3d to amplify immune responses by targeting CR2/CD21 and lowering the activation threshold for B cell responses.
Recent studies have investigated the impact of C3d fusion across the pDNA and mRNA platforms. A 2019 study in pigs, reported a DNA vaccine encoding a fusion of porcine C3d and the Porcine Circovirus Type 2 (PCV2) ORF2 protein induced cross-protective immunity against different PCV2 genotypes (77). The C3d-fused construct (pVOC3) contained three copies of C3d and elicited stronger PCV2-specific antibody responses, increased IFNγ-secreting T cells, and reduced viremia compared to the non-adjuvanted construct (pVO).
A 2023 study investigated various improvements to mRNA vaccines including C3d fusion to the spike or RBD antigens (78). C3d fusion significantly enhanced immunogenicity, inducing up to tenfold higher antibody titers in mice compared to unmodified antigen mRNA. The C3d fusion promoted both humoral and cellular immune responses, with evidence of balanced Th1/Th2 polarization influenced by LNP composition and delivery route. This strategy also avoided systemic inflammation and showed efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 variants. These studies demonstrate the potential of C3d as a molecular adjuvant for nucleic acid vaccines, particularly for enhancing humoral immunity.
Adjuvanticity of lipid delivery
The first ionizable lipids were developed for DNA transfection starting in 1989, followed by iterations developed for siRNA delivery through the 2000s, and more recent formulations optimized for mRNA constructs (40). The development of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to deliver mRNA vaccine antigens was necessitated by the inherent instability of mRNA; LNPs protect the mRNA cargo and promote cellular uptake. Recently, multiple studies have noted and described an inherent adjuvanticity of LNPs (146–149) and systems vaccinology approaches have characterized innate and adaptive immune responses to mRNA-LNP (150–152). In 2021, Alameh et al. demonstrated that lipid nanoparticles possess intrinsic adjuvant activity independent of their mRNA cargo, eliciting strong T follicular helper cell responses and durable antibody production (147). This immunostimulatory effect was dependent on IL-6 induction but occurred independently of MyD88 or MAVS signaling. When co-administered with recombinant protein antigens, empty LNPs elicited superior humoral responses compared to a benchmark squalene adjuvant, underscoring their potential as stand-alone adjuvants in vaccine formulations.
Ndeupen et al. confirmed the highly inflammatory properties of LNP’s, noting empty LNP’s activate multiple inflammatory pathways, induce production of IL-1β and IL-6, and trigger l1b and Nlrp3 -associated inflammasome activation (146). Tahtinen et al., noted that RNA-LNP vaccines, regardless of administration route, activate the IL-1–IL-1ra axis and drive systemic inflammation in humans through IL-1β-dependent cytokine cascades, including IL-6 (152). In 2025, LNPs were identified to activate NF-κB and IRF signaling pathways in monocytes via Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in the absence of mRNA and further confirmed as the primary driver of innate immune activation using knockout cell lines (153). These findings characterize the immunostimulatory effects of LNP-mediated delivery, representing a tunable adjuvant component and potent construct design capability. While reducing reactogenicity has been an area of focus in the RNA space, the intrinsic adjuvant properties of LNP formulations offer a substantive and promising route to boost immunogenicity for DNA constructs.
Recently, ionizable LNP-encapsulated plasmid DNA (DNA-LNPs) have emerged as an immunogenic vaccine modality against infectious diseases (36–38, 129, 130, 132, 133, 154) and cancer (131, 134, 135). Numerous studies (Table 2) have characterized different ionizable lipids, namely SM-102, ALC-0315, MC3, and KC2. The relationship between the ionizable lipid amine groups and DNA backbone phosphates, or N/P ratio, has also been examined. Various studies report an N/P ratio of approximately 6 (or lower lipid to DNA weight ratios) (36, 37, 129, 134, 154). This variable was studied in depth with an H1N1 HA-expressing DNA-LNP, where Tursi et al. report that higher N/P ratios led to improved biophysical characteristics such as particle size and zeta potential, supporting improved immunogenicity (38). The LNP component, specifically the ionizable lipid, has intrinsic adjuvanticity as previously described. Unlike mRNA-LNPs, DNA-LNP formulations additionally drive cGAS-STING signaling due to the presence of plasmid DNA in the cytoplasm; this pathway contributes to the activation of innate immune subsets associated with immunization (38). Beyond the intrinsic adjuvanticity of ionizable lipids, molecular adjuvants have also been evaluated in combination with DNA-LNP vaccines, including studies utilizing CD40L and OX-40L (134).
Table 2
| Antigen | Ionizable Lipid, N/P or weight ratio (if specified) | Significant Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| SARS-CoV-2 spike (wild-type and Omicron BA.1) | SM-102 (N/P Ratio = 6) | Induced comparable or superior humoral immunity to a matched mRNA-LNP in multiple rodent models, improved protection from challenge | Liao et al. Molecular Therapy Methods & Clinical Development (36) |
| SARS-CoV-2 spike (Delta variant) fused to CD40L ectodomain | KC2 and SM-102 (N/P Ratio = 6) | Relative to naked DNA, LNP formulation led to superior neutralization titers and reduced viral loads in challenge, was dose-sparing in hamsters | Tamming et al. Molecular Therapy Methods & Clinical Development. (129) |
| Influenza H3N2 HA | MC3 (N/P ratio = 4.5) | Induced antibody titers and T cell responses in swine, with significantly reduced viral shedding and lung pathology in challenge | Nguyen et al. mSphere. (130) |
| Influenza H1N1 HA | MC3 (N/P ratio = 4.5 and 5.5) | Induced humoral and cellular responses as well as mediated protection in an influenza challenge model in mice and swine | Nguyen et al. mSphere. (130) |
| HPV16 and HPV18 E6/E7 | MC3, SM-102, and ALC-0315 | Enhanced T Cell responses relative to DNA delivered using electroporation. SM-102-based formulations drove superior immunogenicity relative to MC3 and ALC-0315. | Li et al. Vaccines. (131) |
| SARS-CoV-2 spike (Gamma variant) | Ionizable lipid not specified (Lipid to DNA weight ratio = 10:1) | Induced robust humoral and cellular immune responses, reduction in viral load, lung pathology in SARS-CoV-2 challenge models in mice and hamsters | Guimaraes et al. Nature Communications (37) |
| Influenza H1N1 HA and SARS-CoV-2 spike (wild-type) | SM-102 (N/P ratios 10.5, 5.3, and 2.6) | Robust innate immune responses, notably migratory DCs. Comparable humoral immune responses and superior T cell responses to mRNA-LNP and adjuvanted protein. Protection from challenge in SARS-CoV-2 model | Tursi et al. Cell Rep Med. (38) |
| SARS-CoV-2 spike (Omicron variant) | SM-102 (Total lipid to DNA weight ratio = 20:1) | Induced humoral immune responses and is protective in a wild-type SARS-CoV-2 challenge model in hamsters | Yang et al. Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids. (132) |
| B. burgdorferi OspC | KC2 | Elicited binding and functional antibody responses, mediates protection in B. burgdorferi challenge | Pfeifle et al. Frontiers in Immunology. (133) |
| OX-40L | KC2, MC3, C12-200 (Ionizable lipid to DNA weight ratio 5:1) | Intratumoral delivery of plasmid DNA in LNPs led to a reduction in tumor burden. OX-40L-expressing plasmid in combination with an siRNA led to improved challenge outcomes. | Qin et al. Journal of Controlled Release. (134) |
| SARS-CoV-2 spike, PD-L1, p53R172H | SM-102, ALC-0315, MC3 | Induced superior humoral and cellular immune responses relative to electroporation. Expression of PD-L1/p53 variant led to humoral immune responses and a reduction in tumor burden | Chai et al. Molecular Cancer. (135) |
Adjuvanticity of lipid delivery.
Remaining challenges
Despite promising advances, gene-encoded adjuvants face several remaining limitations that constrain their translation and optimization. Beyond IL-12, few molecular adjuvants have been clinically evaluated in infectious disease contexts (82–85). Regulatory frameworks specific to gene-encoded adjuvants, particularly for mRNA platforms encoding cytokines or co-stimulatory ligands, are underdeveloped. Notably, most clinical evaluation of gene-encoded adjuvants has occurred in oncology, across both the DNA and mRNA platforms (31, 32, 48, 49).
A core technical challenge is achieving precise control over expression kinetics. Unlike conventional adjuvants with defined pharmacokinetics, gene-based adjuvants rely on in vivo transcription and translation, which introduces variability in expression timing, intensity, and tissue distribution. Because plasmids can persist in host cells for extended periods, sustained antigen or cytokine expression raises concerns about immune tolerance (155). Several studies report that prolonged or dysregulated expression can impair adaptive immunity, promote T-cell exhaustion, or diminish vaccine efficacy (28). Despite advances in vector design and delivery strategies, achieving real-time, tunable expression control in vivo remains difficult, particularly in balancing immunogenic potency with safety in dynamic immune environments.
While sustained expression may support effector T-cell persistence, it also carries risks. In prophylactic settings, prolonged antigen exposure can impair central memory formation or trigger tolerance and anergy. In chronic infection models such as hepatitis B virus (HBV), persistent antigen expression from DNA vaccination has led to circulating immune complexes and tissue pathology, raising context-dependent safety concerns (Hanke, 2006). These findings emphasize that unregulated or extended expression may compromise vaccine performance depending on disease setting and immunological mechanism (156).
Temporal control is also critical for optimizing immune outcomes. Irvine et al. (157) showed that the timing of cytokine expression from gene-encoded adjuvants affects cytokine expansion and shifts T helper polarization. For example, GM-CSF administered before versus after immunization produced divergent Th1/Th2 responses. While concerns persist regarding chronic inflammation from sustained proinflammatory cytokine expression (157), preclinical animal studies suggest that local adjuvant production is self-limiting, inducing effects in local draining lymph nodes and at the site of injection while being undetectable in circulation.
Another limitation is incomplete mechanistic understanding for many molecular adjuvants. While cytokines and co-stimulatory ligands have well-defined immunological functions, their specific roles when encoded as nucleic acid adjuvants remain incompletely characterized. Molecules such as ADA and C3d have demonstrated consistent immune enhancement across studies, yet their mechanisms of action are still not fully resolved.
Finally, safety remains a concern, particularly the risk of overactivation. Cytokines like IL-2 and IL-12 showed significant toxicity when delivered as recombinant proteins, although plasmid-encoded delivery and localized expression has significantly mitigated reactogenicity. For DNA-based platforms, a monitored safety risk is genomic integration. FDA guidance requires that integration frequencies remain below the spontaneous mutation rate. Existing studies overwhelmingly support the safety of DNA vaccines, with the approval of ZyCoV-D in 2021 representing a milestone in regulatory acceptance (26, 158).
Discussion and concluding remarks
Adjuvant development has historically been primarily empirical, with mechanistic insight often applied retrospectively. However, evolving methodologies, including growing insight into platform-specific immune signatures, supports a continued shift toward rational construct design. DNA and RNA vaccines differ in antigen expression kinetics and innate sensor engagement, shaping their downstream immune profiles (159, 160). mRNA–LNP vaccines activate endosomal and cytosolic RNA sensors such as TLR7/8 and RIG-I, often driving strong CD4 and antibody responses (161–163). Their rapid and transient cytosolic expression is frequently associated with high reactogenicity. In contrast, DNA vaccines often engage sensors including cGAS–STING and TLR9 and tend to induce more delayed, sustained antigen expression, eliciting characteristically strong CD8 T cell responses (27, 28, 38). These general trends point to opportunities for tuning adjuvant strategies to better complement each platform. Mechanistically informed adjuvants offer potential to tailor innate activation and moderate reactogenicity. Aligning adjuvants with the immune kinetics and qualitative response patterns of each platform may improve both efficacy and tolerability in next-generation vaccine development.
Route of administration and target tissue influence antigen presentation, innate activation, and immune priming, making them important variables in adjuvant design. Intramuscular (IM) injection remains the standard for nucleic acid vaccines due to practical advantages and regulatory precedent, but skeletal muscle contains few resident antigen-presenting cells (APCs), often requiring adjuvants that promote APC recruitment or strong immunostimulatory formulations like lipid nanoparticles. In contrast, intradermal and mucosal routes target tissues rich in specialized APCs and may support efficient priming at lower doses. However, these routes also introduce challenges, including local inflammation or tolerance induction, that necessitate route-specific tuning of adjuvant potency and formulation.
DNA vaccines have demonstrated greater versatility in non-intramuscular delivery routes (28, 29), including intradermal administration (164, 165), chitosan-based formulations, electroporation, and mucosal-targeting adjuvants. In contrast, mRNA–LNP vaccines are predominantly administered intramuscularly, where they have shown robust immunogenicity, with most innovation focused on particle stabilization, such as PEGylation, or optimizing lipid composition to enhance delivery and reduce reactogenicity (166). For both platforms, adaptation strategies include chemokines like CCL20 to recruit mucosal dendritic cells (167–170), mucoadhesive or pH-sensitive carriers for stability (168–170), and tissue-matched PRR agonists (171, 172). Some adjuvants show route-dependent efficacy. For example, CpG performs best parenterally (173, 174), while cholera toxin derivatives show greater efficacy at mucosal surfaces (175, 176). Ongoing work explores candidates like chitosan and cGAMP to improve mucosal delivery without excessive inflammation (28, 29). As rational adjuvant design advances, aligning formulations with the immunological features of each delivery route will be key to improving vaccine performance.
Nucleic acid vaccines have made remarkable progress since their inception over three decades ago. Molecular adjuvant technology has developed in parallel with nucleic acid vaccine platforms, with recent studies refining their characterization across diverse classes of antigens and building on the strong foundation of adjuvant delivery. Molecules such as IL-12, IL-2, and GM-CSF have shown continued promise in plasmid-encoded formats, where localized delivery has been essential for mitigating safety concerns. In contrast, candidates like IL-15, IL-18, and CD80/CD86 have faced developmental setbacks despite encouraging early data. Emerging adjuvants such as adenosine deaminase reflect the expanding platform-specific toolkit. Although challenges remain, including the need for precise expression control and a limited clinical footprint, momentum continues to build for DNA and mRNA vaccine technologies.
Molecular adjuvants are becoming increasingly mechanistically tailored and platform-adapted, solidifying their central role in nucleic acid vaccine technology. The distinct immunological profiles elicited by DNA and RNA vaccines demand adjuvants that are matched to their kinetics, antigen presentation pathways, and reactogenicity. Additionally, state-of-the-art computational tools (177) combined with structure-guided methods enable the development of a new generation of adjuvant molecules designed de novo (178–181). Advances in vector engineering, delivery technologies, combination approaches, optimization of immunogen–adjuvant pairings, and increased assessment in human patients will enable continued development for nucleic acid vaccines, supporting broader platform adoption to address major global health challenges.
Statements
Author contributions
CH: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Conceptualization. NT: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. CL: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Visualization. DW: Resources, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. EG: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Project administration, Visualization, Data curation, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. DW is supported by NIH P01AI165066, NIH U19AI166916, NIH/NIAID Collaborative Influenza Vaccine Innovation Centers (CIVIC) contract 75N93019C00051, and INOVIO Pharmaceuticals SRA 21-05. Additional funding to DW provided by the W.W. Smith Charitable Trust Distinguished Professorship in Cancer Research and The Jill and Mark Fishman Foundation, NJT is supported by NCBI T32 CA009171. The authors declare that this study received funding from INOVIO Pharmaceuticals. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication.
Conflict of interest
DW has received grant funding; participates in industry collaborations; has received speaking honoraria; and has received fees for consulting, including serving on scientific review committees. Remunerations received by DW include direct payments and equity/options. DW also discloses the following associations with commercial partners: Geneos (consultant/advisory board), AstraZeneca (advisory board, speaker), INOVIO (board of directors, consultant), Sanofi (advisory board), BBI (advisory board), Pfizer (advisory Board), and Advaccine (consultant).
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Di Pasquale A Preiss S Da Silva FT Garçon N . Vaccine adjuvants: From 1920 to 2015 and beyond. Vaccines (Basel). (2015) 3:320–43. doi: 10.3390/vaccines3020320
2
Kool M Fierens K Lambrecht BN . Alum adjuvant: Some of the tricks of the oldest adjuvant. J Med Microbiol. (2012) 61:927–34. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.038943-0
3
Goetz M Thotathil N Zhao Z Mitragotri S . Vaccine adjuvants for infectious disease in the clinic. Bioeng Transl Med. (2024) 9:3–5. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10663
4
Wolff JA Malone RW Williams P Chong W Acsadi G Jani A et al . Direct gene transfer into mouse muscle in vivo. Sci (1979). (1990) 247:1465–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1690918
5
Wang B Ugen KE Srikantan V Agadjanyan MG Dang K Refaeli Y et al . Gene inoculation generates immune responses against human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (1993) 90:4156–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4156
6
Kutzler MA Weiner DB . DNA vaccines: Ready for prime time? Nat Rev Genet. (2008) 9:776–88. doi: 10.1038/nrg2432
7
Gary EN Tursi NJ Warner BM Cuismano G Connors J Parzych EM et al . Adenosine deaminase augments SARS-CoV-2 specific cellular and humoral responses in aged mouse models of immunization and challenge. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1138609. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1138609
8
Cusimano GM Gary EN Bell MR Warner BM Connors J Tursi NJ et al . Improved durability to SARS-CoV-2 vaccine immunity following coimmunization with molecular adjuvant adenosine deaminase-1. J Immunol. (2022) 209:118–27. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200056
9
Gary E O’Connor M Chakhtoura M Tardif V Kumova OK Malherbe DC et al . Adenosine deaminase-1 enhances germinal center formation and functional antibody responses to HIV-1 Envelope DNA and protein vaccines. Vaccine. (2020) 38:3821–31. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.03.047
10
Boyer JD Robinson TM Kutzler MA Parkinson R Calarota SA Sidhu MK et al . SIV DNA vaccine co-administered with IL-12 expression plasmid enhances CD8 SIV cellular immune responses in cynomolgus macaques. J Med Primatol. (2005) 34:262–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0684.2005.00124.x
11
Kraynyak KA Kutzler MA Cisper NJ Laddy DJ Morrow MP Waldmann TA et al . Plasmid-encoded interleukin-15 receptor alpha enhances specific immune responses induced by a DNA vaccine in vivo. Hum Gene Ther. (2009) 20:1143–56. doi: 10.1089/hum.2009.025
12
Louis L Wise MC Choi H Villarreal DO Muthumani K Weiner DB . Designed DNA-encoded IL-36 gamma acts as a potent molecular adjuvant enhancing Zika synthetic DNA vaccine-induced immunity and protection in a lethal challenge model. Vaccines (Basel). (2019) 12(11):2258. doi: 10.3390/vaccines7020042
13
Gary EN Kathuria N Makurumidze G Curatola A Ramamurthi A Bernui ME et al . CCR10 expression is required for the adjuvant activity of the mucosal chemokine CCL28 when delivered in the context of an HIV-1 Env DNA vaccine. Vaccine. (2020) 38:2626–35. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.01.023
14
Kathuria N Kraynyak KA Carnathan D Betts M Weiner DB Kutzler MA . Generation of antigen-specific immunity following systemic immunization with DNA vaccine encoding CCL25 chemokine immunoadjuvant. Hum Vaccin Immunother. (2012) 8:1607–19. doi: 10.4161/hv.22574
15
Kraynyak KA Kutzler MA Cisper NJ Khan AS Draghia-Akli R Sardesal NY et al . Systemic immunization with CCL27/CTACK modulates immune responses at mucosal sites in mice and macaques. Vaccine. (2010) 28:1942–51. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.10.095
16
Kutzler MA Kraynyak KA Nagle SJ Parkinson RM Zharikova D Chattergoon M et al . Plasmids encoding the mucosal chemokines CCL27 and CCL28 are effective adjuvants in eliciting antigen-specific immunity in vivo. Gene Ther. (2010) 17:72–82. doi: 10.1038/gt.2009.112
17
Kutzler MA Wise MC Hutnick NA Moldoveanu Z Hunter M Reuter MA et al . Chemokine-adjuvanted electroporated DNA vaccine induces substantial protection from simian immunodeficiency virus vaginal challenge. Mucosal Immunol. (2016) 9:13–23. doi: 10.1038/mi.2015.31
18
Kalams SA Parker S Jin X Elizaga M Metch B Wang M et al . Safety and immunogenicity of an HIV-1 gag DNA vaccine with or without IL-12 and/or IL-15 plasmid cytokine adjuvant in healthy, HIV-1 uninfected adults. PloS One. (2012) 7. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029231
19
de Rosa SC Edupuganti S Huang Y Han X Elizaga M Swann E et al . Robust antibody and cellular responses induced by DNA-only vaccination for HIV. JCI Insight. (2020) 5. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.137079
20
Gao F Li Y Decker JM Peyerl FW Bibollet-Ruche F Rodenburg CM et al . Codon usage optimization of HIV type 1 subtype C gag, pol, env, and nef genes: In vitro expression and immune responses in DNA-vaccinated mice. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. (2003) 19:817–23. doi: 10.1089/088922203769232610
21
Ramakrishna L Anand KK Mohankumar KM Ranga U . Codon optimization of the tat antigen of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 generates strong immune responses in mice following genetic immunization. J Virol. (2004) 78:9174–89. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.17.9174-9189.2004
22
Frelin L Ahlén G Alheim M Weiland O Barnfield C Liljeström P et al . Codon optimization and mRNA amplification effectively enhances the immunogenecity of the hepatitis C virus nonstructural 3/4A gene. Gene Ther. (2004) 11:522–33. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3302184
23
Smith TRF Patel A Ramos S Elwood D Zhu X Yan J et al . Immunogenicity of a DNA vaccine candidate for COVID-19. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:2448405. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16505-0
24
Kraynyak KA Blackwood E Agnes J Tebas P Giffear M Amante D et al . SARS-CoV-2 DNA vaccine INO-4800 induces durable immune responses capable of being boosted in a phase 1 open-label trial. J Infect Dis. (2022) 225:1923–32. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac016
25
Jia S Shao C Cheng X Pan H Wang Z Xia Y et al . Immunogenicity and safety of a COVID-19 DNA vaccine in healthy adults and elderly: A randomized, observer-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Hum Vaccin Immunother. (2025) 21:2448405. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2448405
26
Khobragade A Bhate S Ramaiah V Deshpande S Giri K Phophle H et al . Efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of the DNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (ZyCoV-D): the interim efficacy results of a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in India. Lancet. (2022) 399:1313–21. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00151-9
27
Gary EN Weiner DB . DNA vaccines: prime time is now. Curr Opin Immunol. (2020) 65:21–7. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2020.01.006
28
Berger S Zeyn Y Wagner E Bros M . New insights for the development of efficient DNA vaccines. Microb Biotechnol. (2024) 17:e70053. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.70053
29
Lu B Lim JM Yu B Song S Neeli P Sobhani N et al . The next-generation DNA vaccine platforms and delivery systems: advances, challenges and prospects. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1332939. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1332939
30
Kazakova A Zhelnov P Sidorov R Rogova A Vasileva O Ivanov R et al . DNA and RNA vaccines against tuberculosis: a scoping review of human and animal studies. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1457327. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1457327
31
Lopes A Vandermeulen G Préat V . Cancer DNA vaccines: current preclinical and clinical developments and future perspectives. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 38:146. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1154-7
32
Bhojnagarwala PS Jose J Zhao S Weiner DB . DNA-based immunotherapy for cancer: In vivo approaches for recalcitrant targets. Mol Ther. (2025) 33(6):2719–39. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2025.04.008
33
Cui L Renzi S Quagliarini E Digiacomo L Amenitsch H Masuelli L et al . Efficient delivery of DNA using lipid nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics. (2022) 14(8):1698. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081698
34
Zhu Y Shen R Vuong I Reynolds RA Shears MJ Yao ZC et al . Multi-step screening of DNA/lipid nanoparticles and co-delivery with siRNA to enhance and prolong gene expression. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:4282. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31993-y
35
Algarni A Pilkington EH Suys EJA Al-Wassiti H Pouton CW Truong NP . In vivo delivery of plasmid DNA by lipid nanoparticles: the influence of ionizable cationic lipids on organ-selective gene expression. Biomater Sci. (2022) 11. doi: 10.1039/d2bm00168c
36
Liao H-C Shen K-Y Yang C-H Chiu F-F Chiang C-Y Chai KM et al . Lipid nanoparticle-encapsulated DNA vaccine robustly induce superior immune responses to the mRNA vaccine in Syrian hamsters. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. (2024) 32:101169. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2023.101169
37
Guimaraes LC Costa PAC Scalzo Júnior SRA Ferreira HAS Braga ACS de Oliveira LC et al . Nanoparticle-based DNA vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 variants in female preclinical models. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:590. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44830-1
38
Tursi NJ Tiwari S Bedanova N Kannan T Parzych E Okba N et al . Modulation of lipid nanoparticle-formulated plasmid DNA drives innate immune activation promoting adaptive immunity. Cell Rep Med. (2025) 6:102035. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102035
39
Karikó K Buckstein M Ni H Weissman D . Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: The impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity. (2005) 23:165–75. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.06.008
40
Hou X Zaks T Langer R Dong Y . Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat Rev Mater. (2021) 6:1078–94. doi: 10.1038/s41578-021-00358-0
41
Akinc A Maier MA Manoharan M Fitzgerald K Jayaraman M Barros S et al . The Onpattro story and the clinical translation of nanomedicines containing nucleic acid-based drugs. Nat Nanotechnol. (2019) 14:1084–7. doi: 10.1038/s41565-019-0591-y
42
Polack FP Thomas SJ Kitchin N Absalon J Gurtman A Lockhart S et al . Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. New Engl J Med. (2020) 383:2603–15. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa2034577
43
Baden LR El Sahly HM Essink B Kotloff K Frey S Novak R et al . Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. New Engl J Med. (2021) 384:403–16. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa2035389
44
Brook B Duval V Barman S Speciner L Sweitzer C Khanmohammed A et al . Adjuvantation of a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine with controlled tissue-specific expression of an mRNA encoding IL-12p70. Sci Transl Med. (2024) 16(757). doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adm8451
45
McMahon M O’Dell G Tan J Sárközy A Vadovics M Carreño JM et al . Assessment of a quadrivalent nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccine that protects against group 2 influenza viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2022) 119(45):e2206333119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2206333119
46
Wilson E Goswami J Baqui AH Doreski PA Perez-Marc G Zaman K et al . Efficacy and safety of an mRNA-based RSV preF vaccine in older adults. New Engl J Med. (2023) 389:2233–44. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa2307079
47
Goswami J Cardona JF Hsu DC Simorellis AK Wilson L Dhar R et al . Safety and immunogenicity of mRNA-1345 RSV vaccine coadministered with an influenza or COVID-19 vaccine in adults aged 50 years or older: an observer-blinded, placebo-controlled, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Infect Dis. (2024) 25(4):411–23. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00589-9
48
Lorentzen CL Haanen JB Met Ö Svane IM . Clinical advances and ongoing trials on mRNA vaccines for cancer treatment. Lancet Oncol. (2022) 23:e450–8. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00372-2
49
Berraondo P Cuesta R Sanmamed MF Melero I . Immunogenicity and efficacy of personalized adjuvant mRNA cancer vaccines. Cancer Discov. (2024) 14:2021–4. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-1196
50
Pardi N Krammer F . mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases — advances, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2024) 23:838–61. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-01042-y
51
Morelli MP Del Medico Zajac MP Pellegrini JM Amiano NO Tateosian NL Calamante G et al . IL-12 DNA displays efficient adjuvant effects improving immunogenicity of Ag85A in DNA prime/MVA boost immunizations. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2020) 10:581812. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.581812
52
Aunins EA Phan AT Alameh M-G Dwivedi G Cruz-Morales E Christian DA et al . An Il12 mRNA-LNP adjuvant enhances mRNA vaccine–induced CD8 T cell responses. Sci Immunol. (2025) 10(108). doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.ads1328
53
Deng Z Geng Y Wang K Yu Z Yang PO Yang Z et al . Adjuvant effects of interleukin-2 co-expression with VP60 in an oral vaccine delivered by attenuated Salmonella typhimurium against rabbit hemorrhagic disease. Vet Microbiol. (2019) 230:49–55. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.01.008
54
Huo S Zhang J Fan J Wang X Wu F Zuo Y et al . Co-expression of chicken il-2 and il-7 enhances the immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a vp2-expressing dna vaccine against ibdv in chickens. Viruses. (2019) 11(5):476. doi: 10.3390/v11050476
55
Tang X Guo M Sheng X Xing J Zhan W . Interleukin-2 (IL-2) of flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) as immune adjuvant enhance the immune effects of E. tarda subunit vaccine OmpV against Edwardsiellosis. Dev Comp Immunol. (2020) 106:103615. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2020.103615
56
Hao X Li J Wang J Zhou Z Yuan X Pan S et al . Co-administration of chicken IL-2 alleviates clinical signs and replication of the ILTV chicken embryo origin vaccine by pre-activating natural killer cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Virol. (2023) 97:11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01322-23
57
Pagni PP Chaplin J Wijaranakula M Wesley JD Granger J Cracraft J et al . Multicomponent plasmid protects mice from spontaneous autoimmune diabetes. Diabetes. (2022) 71:157–69. doi: 10.2337/db21-0327
58
Wei L Zhu W Dong C Kim JK Ma Y Denning TL et al . Lipid nanoparticles encapsulating both adjuvant and antigen mRNA improve influenza immune cross-protection in mice. Biomaterials. (2025) 317:123039. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.123039
59
Tan F Zhang L Yin L Wang L Zhang H Zheng L et al . Immune synergistic mechanism of recombinant plasmid adjuvant containing chicken IL-4 and IL-2 fusion genes on chicken coccidia live vaccine. Poult Sci. (2024) 103. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.103204
60
Leroy LA Donald AM Kandlur A Bose D Xiao P Gagnon J et al . Cytokine adjuvants IL-7 and IL-15 improve humoral responses of a SHIV lentiDNA vaccine in animal models. Vaccines (Basel). (2022) 10(3):461. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10030461
61
Zhou Y Zhang T Wang Z Xu X . Augmented immunogenicity of the HPV16 DNA vaccine via dual adjuvant approach: integration of CpG ODN into plasmid backbone and co-administration with IL-28B gene adjuvant. Virol J. (2025) 22:3. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02604-7
62
Wang Z Wang Y Sun C Zhao X Sun M Gao X et al . Protection against genotype VII Newcastle disease virus challenge by a minicircle DNA vaccine coexpressing F protein and chicken IL-18 adjuvant. Vet Microbiol. (2022) 270:109474. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2022.109474
63
Yadav PK Gupta SK Kumar S Ghosh M Yadav BS Kumar D et al . IL-18 immunoadjuvanted xenogeneic canine MMP-7 DNA vaccine overcomes immune tolerance and supresses the growth of murine mammary tumor. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 82:106370. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106370
64
Sabbaghi A Zargar M Zolfaghari MR Motamedi-Sedeh F Ghaemi A . Protective cellular and mucosal immune responses following nasal administration of a whole gamma-irradiated influenza A (subtype H1N1) vaccine adjuvanted with interleukin-28B in a mouse model. Arch Virol. (2021) 166:545–57. doi: 10.1007/s00705-020-04900-3
65
Amoia CF Chengula AA Hakizimana JN Wambura PN Munir M Misinzo G et al . Development of a genotype-matched Newcastle disease DNA vaccine candidate adjuvanted with IL-28b for the control of targeted velogenic strains of Newcastle disease virus in Africa. Vet Res Commun. (2025) 49:33. doi: 10.1007/s11259-024-10590-y
66
Liu C Xue RY Li GC Zhang Y Wu WY Liu JY et al . pGM-CSF as an adjuvant in DNA vaccination against SARS-CoV-2. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 264:130660. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130660
67
Gary EN Tursi NJ Warner B Parzych EM Ali AR Frase D et al . Mucosal chemokine adjuvant enhances synDNA vaccine-mediated responses to SARS-CoV-2 and provides heterologous protection in vivo. Cell Rep Med. (2022) 3(7):100693. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100693
68
Liaw K Konrath KM Trachtman AR Tursi NJ Gary EN Livingston C et al . DNA co-delivery of seasonal H1 influenza hemagglutinin nanoparticle vaccines with chemokine adjuvant CTACK induces potent immunogenicity for heterologous protection in vivo. Vaccine. (2025) 59:127231. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2025.127231
69
Xu H Xing J Tang X Sheng X Zhan W . The effects of CCL3, CCL4, CCL19 and CCL21 as molecular adjuvants on the immune response to VAA DNA vaccine in flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Dev Comp Immunol. (2020) 103:103492. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2019.103492
70
Kim JY Kim HJ Park JS Kwon SR . DNA vaccine dual-expressing viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus glycoprotein and C-C motif chemokine ligand 19 induces the expression of immune-related genes in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Microbiol. (2022) 60:1032–8. doi: 10.1007/s12275-022-2231-8
71
Xiang Y Zhang H An Y Chen Z . Intranasal immunization with DNA vaccine HA-CCL19/polyethylenimine/chitosan composite provides immune protection against H7N9 infection. Vaccines (Basel). (2025) 13(1):10. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13010010
72
Li Q Cao Q Wang C Nguyen H Wang XM Zheng G et al . Dendritic cell-targeted CD40 DNA vaccine suppresses Th17 and ameliorates progression of experimental autoimmune glomerulonephritis. J Leukoc Biol. (2019) 105:809–19. doi: 10.1002/JLB.5A0818-333R
73
Tamming LA Duque D Tran A Zhang W Pfeifle A Laryea E et al . DNA based vaccine expressing SARS-CoV-2 spike-CD40L fusion protein confers protection against challenge in a Syrian hamster model. Front Immunol. (2022) 12:785349. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.785349
74
Huang J Luo G Wang W Lu Y Wang M Liu M et al . Duck CD40L as an adjuvant enhances systemic immune responses of avian flavivirus DNA vaccine. NPJ Vaccines. (2024) 9. doi: 10.1038/s41541-024-00926-9
75
Kornuta CA Langellotti CA Bidart JE Soria I Quattrocchi V Gammella M et al . A plasmid encoding the extracellular domain of CD40 ligand and Montanide™ GEL01 as adjuvants enhance the immunogenicity and the protection induced by a DNA vaccine against BoHV-1. Vaccine. (2021) 39:1007–17. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.11.071
76
Liu W Xing J Tang X Sheng X Chi H Zhan W . Characterization of Co-Stimulatory Ligand CD80/86 and Its Effect as a Molecular Adjuvant on DNA Vaccine Against Vibrio Anguillarum in Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Front Immunol. (2022) 13:881753. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.881753
77
Hou Z Wang H Feng Y Li Q Li J . A candidate DNA vaccine encoding a fusion protein of porcine complement C3d-P28 and ORF2 of porcine circovirus type 2 induces cross-protective immunity against PCV2b and PCV2d in pigs. Virol J. (2019) 16:57. doi: 10.1186/s12985-019-1156-2
78
Li B Jiang AY Raji I Atyeo C Raimondo TM Gordon AGR et al . Enhancing the immunogenicity of lipid-nanoparticle mRNA vaccines by adjuvanting the ionizable lipid and the mRNA. Nat BioMed Eng. (2023) 9:167–84. doi: 10.1038/s41551-023-01082-6
79
Kobayashi M Fitz L Ryan M Hewick RM Clark SC Chan S et al . Identification and purification of natural killer cell stimulatory factor (NKSF), a cytokine with multiple biologic effects on human lymphocytes. J Exp Med. (1989) 170:827–45. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.827
80
Afonso LCC Scharton TM Vieira LQ Wysocka M Trinchieri G Scott P . The adjuvant effect of interleukin-12 in a vaccine against Leishmania major. Sci (1979). (1994) 263:235–7. doi: 10.1126/science.7904381
81
Kim JJ Ayyavoo V Bagarazzi ML Chattergoon MA Dang K Wang B et al . In vivo engineering of a cellular immune response by coadministration of IL-12 expression vector with a DNA immunogen. J Immunol. (1997) 158:816–26. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.158.2.816
82
Kalams SA Parker SD Elizaga M Metch B Edupuganti S Hural J et al . Safety and comparative immunogenicity of an HIV-1 DNA vaccine in combination with plasmid interleukin 12 and impact of intramuscular electroporation for delivery. J Infect Dis. (2013) 208:818–29. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit236
83
Jacobson JM Zheng L Wilson CC Tebas P Matining RM Egan MA et al . The safety and immunogenicity of an interleukin-12-enhanced multiantigen DNA vaccine delivered by electroporation for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr (1988). (2016) 71:163–71. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000000830
84
Edupuganti S De Rosa SC Elizaga M Lu Y Han X Huang Y et al . Intramuscular and intradermal electroporation of hiv-1 pennvax-gp® DNA vaccine and IL-12 is safe, tolerable, acceptable in healthy adults. Vaccines (Basel). (2020) 8:1–15. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8040741
85
Jacobson JM Zahrieh D Strand CA Cruz-Correa M Pungpapong S Roberts LR et al . Phase I trial of a therapeutic DNA vaccine for preventing hepatocellular carcinoma from chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). (2023) 16:163–73. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-22-0217
86
Reardon DA Brem S Desai AS Bagley SJ Kurz SC de la Fuente MI et al . Intramuscular (IM) INO-5401 + INO-9012 with electroporation (EP) in combination with cemiplimab (REGN2810) in newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:2004–4. doi: 10.1200/jco.2022.40.16_suppl.2004
87
Viborg N Kleine-Kohlbrecher D Rønø B . Personalized neoantigen DNA cancer vaccines: current status and future perspectives. J Cell Immunol. (2024) 6:15–24. doi: 10.33696/immunology.6.188
88
Lui VWY Falo LD Huang L . Systemic production of IL-12 by naked DNA mediated gene transfer: Toxicity and attenuation of transgene expression in vivo. J Gene Med. (2001) 3:384–93. doi: 10.1002/jgm.201
89
Leonard JP Sherman ML Fisher GL Buchanan LJ Larsen G Atkins MB et al . Effects of single-dose interleukin-12 exposure on interleukin-12 associated toxicity and interferon-γ production. Blood. (1997) 90:2541–8. doi: 10.1182/blood.V90.7.2541
90
Nguyen DC Hentenaar IT Morrison-Porter A Solano D Haddad NS Castrillon C et al . SARS-CoV-2-specific plasma cells are not durably established in the bone marrow long-lived compartment after mRNA vaccination. Nat Med. (2024) 31:235–44. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03278-y
91
Nunberg JH Doyle MV York SM York CJ . Interleukin 2 acts as an adjuvant to increase the potency of inactivated rabies virus vaccine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (1989) 86:4240–3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4240
92
Aggarwal P Kumar S Vajpayee M Seth P . Adjuvant action of murine IL-2/Ig plasmid after intramuscular immunization with Indian HIV-1 subtype C recombinant env.gp 120 construct. Viral Immunol. (2005) 18:649–56. doi: 10.1089/vim.2005.18.649
93
O’Malley BW Li D McQuone SJ Ralston R . Combination nonviral interleukin-2 gene immunotherapy for head and neck cancer: From bench top to bedside. Laryngoscope. (2005) 115:391–404. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200503000-00002
94
Richards JM Gonzalez R Schwarzenberger P Whitman E Stardal K Westhoff C et al . Phase I trial of IL-2 plasmid DNA with electroporation in metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol. (2007) 25:8578–8. doi: 10.1200/jco.2007.25.18_suppl.8578
95
Lim YS Kang BY Kim EJ Kim SH Hwang SY Kim KM et al . Vaccination with an ovalbumin/interleukin-4 fusion DNA efficiently induces Th2 cell-mediated immune responses in an ovalbumin-specific manner. Arch Pharm Res. (1998) 21:537–42. doi: 10.1007/BF02975371
96
Deng J Yuan S Pennati A Murphy J Wu JH Lawson D et al . Engineered fusokine GIFT4 licenses the ability of B cells to trigger a tumoricidal T-cell response. Cancer Res. (2014) 74:4133–44. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0708
97
Khan IA Kasper LH . IL-15 augments CD8+ T cell-mediated immunity against Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice. J Immunol. (1996) 157:2103–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.157.5.2103
98
Kutzler MA Robinson TM Chattergoon MA Choo DK Choo AY Choe PY et al . Coimmunization with an optimized IL-15 plasmid results in enhanced function and longevity of CD8 T cells that are partially independent of CD4 T cell help. J Immunol. (2005) 175:112–23. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.1.112
99
Toka FN Rouse BT . Mucosal application of plasmid-encoded IL-15 sustains a highly protective anti-Herpes simplex virus immunity. J Leukoc Biol. (2005) 78:178–86. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1004621
100
Patidar M Yadav N Dalai SK . Development of stable chimeric IL-15 for trans-presentation by the antigen presenting cells. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:646159. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.646159
101
Yajima T Yoshihara K Nakazato K Kumabe S Koyasu S Sad S et al . IL-15 regulates CD8+ T cell contraction during primary infection. J Immunol. (2006) 176:507–15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.1.507
102
Xue D Hsu E Fu YX Peng H . Next-generation cytokines for cancer immunotherapy. Antib Ther. (2021) 4:123–33. doi: 10.1093/abt/tbab014
103
Kermer V Baum V Hornig N Kontermann RE Müller D . An antibody fusion protein for cancer immunotherapy mimicking IL-15 trans-presentation at the tumor site. Mol Cancer Ther. (2012) 11:1279–88. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0019
104
Kim D Park JH Kim TY Kim DG Byun JH Kim HS . Enhanced half-life and antitumor activity of interleukin-15 through genetic fusion of a serum albumin-specific protein binder. Int J Pharm. (2022) 625:122059. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.122059
105
Okamura H Tsutsul H Komatsu T Yutsudo M Tanimoto T Torigoe K et al . Cloning of a new cytokine that induces IFN-γ production by T cells. Nature. (1995) 378:88–91. doi: 10.1038/378088a0
106
Uchida T Kinoshita M Fukasawa M Habu Y Shinomiya N Seki S . IL-18 time-dependently modulates Th1/Th2 cytokine production by ligand-activated NKT cells. Eur J Immunol. (2007) 37:966–77. doi: 10.1002/eji.200636465
107
Hanlon L Argyle D Bain D Nicolson L Dunham S Golder MC et al . Feline leukemia virus DNA vaccine efficacy is enhanced by coadministration with interleukin-12 (IL-12) and IL-18 expression vectors. J Virol. (2001) 75:8424–33. doi: 10.1128/jvi.75.18.8424-8433.2001
108
Shi F Gunn GR Snyder L Goletz TJ . Intradermal vaccination of MUC1 transgenic mice with MUC1/IL-18 plasmid DNA inhibits experimental pulmonary metastases (2004). Available online at: https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article/64/7_Supplement/292/512644/Intradermal-vaccination-of-MUC1-transgenic-mice?utm_source=chatgpt.com (Accessed May 3, 2025).
109
Marshall D Mateo LS Rudnick K McCarthy S Snyder L . IL-18 enhances the immune response to a PSA DNA vaccine in Balb/c mice (2004). Available online at: https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article/64/7_Supplement/153/517350/IL-18-enhances-the-immune-response-to-a-PSA-DNA?utm_source=chatgpt.com (Accessed May 3, 2025).
110
Snyder LA Goletz TJ Gunn GR Shi FF Harris MC Cochlin K et al . A MUC1/IL-18 DNA vaccine induces anti-tumor immunity and increased survival in MUC1 transgenic mice. Vaccine. (2006) 24:3340–52. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.01.014
111
Ank N West H Bartholdy C Eriksson K Thomsen AR Paludan SR . Lambda interferon (IFN-λ), a type III IFN, is induced by viruses and IFNs and displays potent antiviral activity against select virus infections in vivo. J Virol. (2006) 80:4501–9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.80.9.4501-4509.2006
112
Morrow MP Pankhong P Laddy DJ Schoenly KA Yan J Cisper N et al . Comparative ability of IL-12 and IL-28B to regulate Treg populations and enhance adaptive cellular immunity. Blood. (2009) 113:5868–77. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-11-190520
113
Morrow MP Yan J Pankhong P Shedlock DJ Lewis MG Talbott K et al . IL-28B/IFNλ-3 drives granzyme B loading and significantly increases CTL killing activity in macaques. Mol Ther. (2010) 18:1714–23. doi: 10.1038/mt.2010.118
114
Vernet R Charrier E Cosset E Fièvre S Tomasello U Grogg J et al . Local Sustained GM-CSF Delivery by Genetically Engineered Encapsulated Cells Enhanced Both Cellular and Humoral SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Specific Immune Response in an Experimental Murine Spike DNA Vaccination Model. Vaccines (Basel). (2021) 9(5):484. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9050484
115
Jones T Stern A Lin R . Potential role of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor as vaccine adjuvant. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. (1994) 13:S47–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01973602
116
Perales MA Yuan J Powel S Gallardo HF Rasalan TS Gonzalez C et al . Phase I/II study of GM-CSF DNA as an adjuvant for a multipeptide cancer vaccine in patients with advanced melanoma. Mol Ther. (2008) 16:2022–9. doi: 10.1038/mt.2008.196
117
Pavlenko M Roos AK Lundqvist A Palmborg A Miller AM Ozenci V et al . A phase I trial of DNA vaccination with a plasmid expressing prostate-specific antigen in patients with hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. (2004) 91:688–94. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602019
118
Kyriakopoulos CE Eickhoff JC Ferrari AC Schweizer MT Wargowski E Olson BM et al . Multicenter phase I trial of a DNA vaccine encoding the androgen receptor ligand-binding domain (pTVG-AR, MVI-118) in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:5162–71. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-0945
119
Luo K Zhang H Zavala F Biragyn A Espinosa DA Markham RB . Fusion of antigen to a dendritic cell targeting chemokine combined with adjuvant yields a malaria DNA vaccine with enhanced protective capabilities. PloS One. (2014) 9:e90413. doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0090413
120
Hartoonian C Sepehrizadeh Z Mahdavi M Arashkia A Jang YS Ebtekar M et al . Modulation of hepatitis C virus core DNA vaccine immune responses by co-immunization with CC-chemokine ligand 20 (CCL20) gene as immunoadjuvant. Mol Biol Rep. (2014) 41:5943–52. doi: 10.1007/S11033-014-3470-5/FIGURES/5
121
Jayeshbhai C Hajam IA Verma AK Bhanuprakash V Kondabattula G Kishore S . Chemokine CCL20 plasmid improves protective efficacy of the Montanide ISA™ 206 adjuvanted foot-and-mouth disease vaccine in mice model. Vaccine. (2018) 36:5318–24. doi: 10.1016/J.VACCINE.2018.07.003
122
Aldon Y Kratochvil S Shattock RJ McKay PF . Chemokine-adjuvanted plasmid DNA induces homing of antigen-specific and non–antigen-specific B and T cells to the intestinal and genital mucosae. J Immunol. (2020) 204:903–13. doi: 10.4049/JIMMUNOL.1901184
123
Gordy JT Hui Y Schill C Wang T Chen F Fessler K et al . A SARS-CoV-2 RBD vaccine fused to the chemokine MIP-3α elicits sustained murine antibody responses over 12 months and enhanced lung T-cell responses. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1292059/BIBTEX. doi: 10.3389/FIMMU.2024.1292059/BIBTEX
124
Fessler K Zhang J Sandhu AK Hui Y Kapoor AR Ayeh SK et al . Brief communication: combination of an MIP3α-antigen fusion therapeutic DNA vaccine with treatments of IFNα and 5-aza-2′Deoxycytidine enhances activated effector CD8+ T cells expressing CD11c in the B16F10 melanoma model. J Immunotherapy. (2025) 48:1–5. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000542
125
Gordy JT Luo K Zhang H Biragyn A Markham RB . Fusion of the dendritic cell-targeting chemokine mip3α to melanoma antigen gp100 in a therapeutic dna vaccine significantly enhances immunogenicity and survival in a mouse melanoma model. J Immunother Cancer. (2016) 4:1–11. doi: 10.1186/S40425-016-0189-Y/FIGURES/6
126
Gordy JT Luo K Francica B Drake C Markham RB . Anti-IL-10-mediated enhancement of antitumor efficacy of a dendritic cell-targeting MIP3α-gp100 vaccine in the B16F10 mouse melanoma model is dependent on type I interferons. J Immunotherapy. (2018) 41:181–9. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000212
127
Flanagan K Hörig H Kaufman H . The lymphoid chemokine CCL19 (ELC) promotes T cell proliferation in vitro and mediates T cell migration when expressed in a recombinant vaccinia virus: A strategy for local tumor vaccine delivery (2004). Available online at: https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article/64/7_Supplement/152/517297/The-lymphoid-chemokine-CCL19-ELC-promotes-T-cell (Accessed May 3, 2025).
128
Peatman E Liu Z . Evolution of CC chemokines in teleost fish: A case study in gene duplication and implications for immune diversity. Immunogenetics. (2007) 59:613–23. doi: 10.1007/s00251-007-0228-4
129
Tamming L Duque D Tran A Lansdell C Frahm G Wu J et al . Lipid nanoparticle encapsulation of a Delta spike-CD40L DNA vaccine improves effectiveness against Omicron challenge in Syrian hamsters. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. (2024) 32:101325. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101325
130
Nguyen TN Lai DC Sillman S Petro-Turnquist E Weaver EA Vu HLX . Lipid nanoparticle-encapsulated DNA vaccine confers protection against swine and human-origin H1N1 influenza viruses. mSphere. (2024) 9:8. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00283-24
131
Li M Liu L Li X Li J Zhao C Zhao Y et al . Lipid nanoparticles outperform electroporation in delivering therapeutic HPV DNA vaccines. Vaccines (Basel). (2024) 12(6):666. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12060666
132
Yang CH Shen KY Ho HM Huang CY Cheng YJ Pu CC et al . Boosting DNA vaccine power by lipid nanoparticles surface engineered with amphiphilic bioresorbable copolymer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2024) 35. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102261
133
Pfeifle A Thulasi Raman SN Lansdell C Zhang W Tamming L Cecillon J et al . DNA lipid nanoparticle vaccine targeting outer surface protein C affords protection against homologous Borrelia burgdorferi needle challenge in mice. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1020134. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1020134
134
Qin Y Rouatbi N Wang JTW Baker R Spicer J Walters AA et al . Plasmid DNA ionisable lipid nanoparticles as non-inert carriers and potent immune activators for cancer immunotherapy. J Controlled Release. (2024) 369:251–65. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.03.018
135
Chai D Wang J Lim JM Xie X Yu X Zhao D et al . Lipid nanoparticles deliver DNA-encoded biologics and induce potent protective immunity. Mol Cancer. (2025) 24:12. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02211-8
136
Mendoza RB Cantwell MJ Kipps TJ . Immunostimulatory effects of a plasmid expressing CD40 ligand (CD154) on gene immunization. J Immunol. (1997) 159:5777–81. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.159.12.5777
137
Hashem AM Algaissi A Agrawal AS Al-Amri SS Alhabbab RY Sohrab SS et al . A highly immunogenic, protective, and safe adenovirus-based vaccine expressing Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus S1-CD40L fusion protein in a transgenic human dipeptidyl peptidase 4 mouse model. J Infect Dis. (2019) 220:1558–67. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz137
138
Gares SL Fischer KP Congly SE Lacoste S Addison WR Tyrrell DL et al . Immunotargeting with CD154 (CD40 ligand) enhances DNA vaccine responses in ducks. Clin Vaccine Immunol. (2006) 13:958–65. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00080-06
139
Freeman GJ Gribben JG Boussiotis VA Ng JW Restivo VA Lombard LA et al . Cloning of B7-2: A CTLA-4 counter-receptor that costimulates human T cell proliferation. Sci (1979). (1993) 262:909–11. doi: 10.1126/science.7694363
140
Subauste CS de Waal Malefyt R Fuh F . Role of CD80 (B7.1) and CD86 (B7.2) in the immune response to an intracellular pathogen. J Immunol. (1998) 160:1831–40. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.160.4.1831
141
Kirn JJ Bagarazzi ML Trivedi N Hu Y Kazahaya K Wilson DM et al . Engineering of in vivo immune responses to DNA immunization via codelivery of costimulatory molecule genes. Nat Biotechnol. (1997) 15:641–6. doi: 10.1038/nbt0797-641
142
Iwasaki A Stiernholm BJ Chan AK Berinstein NL Barber BH . Enhanced CTL responses mediated by plasmid DNA immunogens encoding costimulatory molecules and cytokines. J Immunol. (1997) 158:4591–601. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.158.10.4591
143
Thorne AH Malo KN Wong AJ Nguyen TT Cooch N Reed C et al . Adjuvant screen identifies synthetic DNA-encoding Flt3L and CD80 immunotherapeutics as candidates for enhancing anti-tumor T cell responses. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:327. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00327
144
Tardif V Gary E Muir R Chakhtoura M Cubas R Metcalf T et al . Adenosine DeAminase (ADA) as an adjuvant molecule for human HIV-1 vaccine. J Immunol. (2017) 198:225.15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.198.supp.225.15
145
Dempsey PW Allison MED Akkaraju S Goodnow CC Fearon DT . C3d of complement as a molecular adjuvant: Bridging innate and acquired immunity. Sci (1979). (1996) 271:348–50. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5247.348
146
Ndeupen S Qin Z Jacobsen S Bouteau A Estanbouli H Igyártó BZ . The mRNA-LNP platform’s lipid nanoparticle component used in preclinical vaccine studies is highly inflammatory. iScience. (2021) 24(12):103479. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103479
147
Alameh MG Tombácz I Bettini E Lederer K Sittplangkoon C Wilmore JR et al . Lipid nanoparticles enhance the efficacy of mRNA and protein subunit vaccines by inducing robust T follicular helper cell and humoral responses. Immunity. (2021) 54:2877–2892.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.11.001
148
Moghimi SM Simberg D . Pro-inflammatory concerns with lipid nanoparticles. Mol Ther. (2022) 30:2109–10. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.04.011
149
Pardi N Hogan MJ Naradikian MS Parkhouse K Cain DW Jones L et al . Nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines induce potent T follicular helper and germinal center B cell responses. J Exp Med. (2018) 215:1571–88. doi: 10.1084/jem.20171450
150
Arunachalam PS Scott MKD Hagan T Li C Feng Y Wimmers F et al . Systems vaccinology of the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in humans. Nature. (2021) 596:410–6. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03791-x
151
Li C Lee A Grigoryan L Arunachalam PS Scott MKD Trisal M et al . Mechanisms of innate and adaptive immunity to the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine. Nat Immunol. (2022) 23:543–55. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01163-9
152
Tahtinen S Tong AJ Himmels P Oh J Paler-Martinez A Kim L et al . IL-1 and IL-1ra are key regulators of the inflammatory response to RNA vaccines. Nat Immunol. (2022) 23:532–42. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01160-y
153
Zelkoski AE Lu Z Sukumar G Dalgard C Said H Alameh MG et al . Ionizable lipid nanoparticles of mRNA vaccines elicit NF-κB and IRF responses through toll-like receptor 4. NPJ Vaccines. (2025) 10:73. doi: 10.1038/s41541-025-01124-x
154
Nguyen TN Kumari S Sillman S Chaudhari J Lai DC Vu HLX . A single-dose intramuscular immunization of pigs with lipid nanoparticle DNA vaccines based on the hemagglutinin antigen confers complete protection against challenge infection with the homologous influenza virus strain. Vaccines (Basel). (2023) 11(10):1596. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11101596
155
Pagliari S Dema B Sanchez-Martinez A Montalvo Zurbia-Flores G Rollier CS . DNA vaccines: history, molecular mechanisms and future perspectives. J Mol Biol. (2023) 435(23):168297. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168297
156
Hanke T . On DNA vaccines and prolonged expression of immunogens. Eur J Immunol. (2006) 36:806–9. doi: 10.1002/eji.200635986
157
Irvine DJ Aung A Silva M . Controlling timing and location in vaccines. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. (2020) 158:91–115. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.06.019
158
Kozak M Hu J . DNA vaccines: their formulations, engineering and delivery. Vaccines (Basel). (2024) 12(1):71. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12010071
159
Liu MA . A comparison of plasmid DNA and mRNA as vaccine technologies. Vaccines. (2019) 7:37. doi: 10.3390/VACCINES7020037
160
Andrade VM Maricic I Kalia R Jachimowicz L Bedoya O Kulp DW et al . Delineation of DNA and mRNA COVID-19 vaccine-induced immune responses in preclinical animal models. Hum Vaccin Immunother. (2023) 19(3):2281733. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2281733
161
Pardi N Hogan MJ Porter FW Weissman D . mRNA vaccines-a new era in vaccinology. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2018) 17:261–79. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2017.243
162
Rehwinkel J Gack MU . RIG-I-like receptors: their regulation and roles in RNA sensing. Nat Rev Immunol. (2020) 20:537–51. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0288-3
163
Heidegger S Kreppel D Bscheider M Stritzke F Nedelko T Wintges A et al . RIG-I activating immunostimulatory RNA boosts the efficacy of anticancer vaccines and synergizes with immune checkpoint blockade. EBioMedicine. (2019) 41:146–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.02.056
164
Hegazy-Hassan W Zepeda-Escobar JA Ochoa-García L Contreras-Ortíz JME Tenorio-Borroto E Barbabosa-Pliego A et al . TcVac1 vaccine delivery by intradermal electroporation enhances vaccine induced immune protection against Trypanosoma cruzi infection in mice. Vaccine. (2019) 37:248–57. doi: 10.1016/J.VACCINE.2018.11.041
165
Platteel ACM Henri S Zaiss DM Sijts AJAM . Dissecting antigen processing and presentation routes in dermal vaccination strategies. Vaccine. (2017) 35:7057–63. doi: 10.1016/J.VACCINE.2017.10.044
166
Lu RM Hsu HE Perez SJLP Kumari M Chen GH Hong MH et al . Current landscape of mRNA technologies and delivery systems for new modality therapeutics. J Biomed Sci. (2024) 31:1–36. doi: 10.1186/S12929-024-01080-Z
167
Kodama S Abe N Hirano T Suzuki M . A single nasal dose of CCL20 chemokine induces dendritic cell recruitment and enhances nontypable Haemophilus influenzae-specific immune responses in the nasal mucosa. Acta Otolaryngol. (2011) 131:989–96. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2011.576429
168
Gaglio SC Perduca M Zipeto D Bardi G . Efficiency of chitosan nanocarriers in vaccinology for mucosal immunization. Vaccines. (2023) 11:1333. doi: 10.3390/VACCINES11081333
169
Song Y Mehl F Zeichner SL . Vaccine strategies to elicit mucosal immunity. Vaccines. (2024) 12:191. doi: 10.3390/VACCINES12020191
170
Neutra MR Kozlowski PA . Mucosal vaccines: The promise and the challenge. Nat Rev Immunol. (2006) 6:148–58. doi: 10.1038/NRI1777;KWRD=BIOMEDICINE
171
Guzelj S Weiss M Slütter B Frkanec R Jakopin Ž . Covalently conjugated NOD2/TLR7 agonists are potent and versatile immune potentiators. J Med Chem. (2022) 65:15085–101. doi: 10.1021/ACS.JMEDCHEM.2C00808/SUPPL_FILE/JM2C00808_SI_002.CSV
172
Correa VA Portilho AI De Gaspari E . Vaccines, adjuvants and key factors for mucosal immune response. Immunology. (2022) 167:124–38. doi: 10.1111/IMM.13526
173
McCluskie MJ Weeratna RD Payette PJ Davis HL . Parenteral and mucosal prime-boost immunization strategies in mice with hepatitis B surface antigen and CpG DNA. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. (2002) 32:179–85. doi: 10.1111/J.1574-695X.2002.TB00551.X
174
Gursel M Klinman DM . Use of CpG oligonucleotides as mucosal adjuvants. Mucosal Immunology: Fourth Edition. (2015) 1–2:1201–9. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-415847-4.00062-8
175
Holmgren J Lycke N Czerkinsky C . Cholera toxin and cholera B subunit as oral—mucosal adjuvant and antigen vector systems. Vaccine. (1993) 11:1179–84. doi: 10.1016/0264-410X(93)90039-Z
176
Fukuyama Y Okada K Yamaguchi M Kiyono H Mori K Yuki Y . Nasal administration of cholera toxin as a mucosal adjuvant damages the olfactory system in mice. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0139368. doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0139368
177
Albanese KI Barbe S Tagami S Woolfson DN Schiex T . Computational protein design. Nat Rev Methods Primers. (2025) 5:13. doi: 10.1038/s43586-025-00383-1
178
Soleymani S Janati-fard F Housaindokht MR . Designing a bioadjuvant candidate vaccine targeting infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) using viral VP2 fusion and chicken IL-2 antigenic epitope: A bioinformatics approach. Comput Biol Med. (2023) 163:107087. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107087
179
Silva DA Yu S Ulge UY Spangler JB Jude KM Labão-Almeida C et al . De novo design of potent and selective mimics of IL-2 and IL-15. Nature. (2019) 565:186–91. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0830-7
180
Ma J Wang S Zhao C Yan X Ren Q Dong Z et al . Computer-aided discovery of potent broad-spectrum vaccine adjuvants. Angewandte Chemie. (2023) 135(18):e202301059. doi: 10.1002/ange.202301059
181
Soleymani S Tavassoli A Housaindokht MR . An overview of progress from empirical to rational design in modern vaccine development, with an emphasis on computational tools and immunoinformatics approaches. Comput Biol Med. (2022) 140:105057. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.105057
Summary
Keywords
nucleic acid vaccines, adjuvant, gene-encoded adjuvants, molecular adjuvants, plasmid-encoded, DNA Vaccines, mRNA vaccines
Citation
Hojecki CE, Tursi NJ, Livingston C, Weiner DB and Gary EN (2025) Advances in molecular adjuvants for nucleic acid vaccines. Front. Immunol. 16:1646800. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1646800
Received
13 June 2025
Accepted
04 August 2025
Published
29 September 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Srinivasa Reddy Bonam, Indian Institute of Chemical Technology (CSIR), India
Reviewed by
Paulo J. G. Bettencourt, Universidade Católica Portuguesa, Portugal
Francesco Peri, University of Milano-Bicocca, Italy
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Hojecki, Tursi, Livingston, Weiner and Gary.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Casey E. Hojecki, chojecki@wistar.org; David B. Weiner, dweiner@wistar.org; Ebony N. Gary, egary@wistar.org
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.