- 1Department of Rheumatology, Weifang People’s Hospital, Weifang, Shandong, China
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Weifang People’s Hospital, Weifang, Shandong, China
- 3Department of Emergency Internal Medicine, Weifang People’s Hospital, Weifang, Shandong, China
- 4Department of Radiology, Weifang People’s Hospital, Weifang, Shandong, China
- 5School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
- 6Department of Dermatology, Tianjin Institute of Integrative Dermatology, Tianjin Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated Hospital, Tianjin, China
- 7Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University International Hospital, Beijing, China
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multisystem autoimmune disease that can affect the ocular system, with retinal vasculitis and optic neuritis being rare but serious manifestations. We present a case of a 26-year-old female with newly diagnosed SLE who developed both retinal vasculitis and optic neuritis, leading to progressive visual impairment. She was successfully treated with methylprednisolone and rituximab, achieving significant visual recovery. A review of existing literature highlights the diagnostic challenges, pathophysiology, and optimal treatment strategies for such cases. Our findings emphasize the importance of early recognition and aggressive immunosuppressive therapy in improving patient outcomes.
Introduction
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by multisystem involvement, including renal, neurological, cardiovascular, and ocular manifestations. Among its ocular complications, lupus retinopathy is the most common. Lupus retinopathy, referring specifically to retinal hemorrhages, cotton-wool spots, retinal edema, and vascular occlusions directly caused by SLE (excluding drug-induced forms such as chloroquine-induced retinopathy), occurs in approximately 10% to 29% of SLE patients (1). However, retinal vasculitis and optic neuritis remain rare but severe manifestations, often leading to significant visual impairment if left untreated (2). These complications typically arise in the context of high systemic disease activity and are associated with vascular inflammation, immune complex deposition, and autoantibody-mediated endothelial dysfunction (3, 4).
Retinal vasculitis in SLE is often characterized by perivascular inflammation, vascular leakage, and potential occlusion, leading to ischemic retinal damage and neovascularization (3, 5). Optic neuritis, on the other hand, results from inflammation of the optic nerve, leading to acute vision loss, dyschromatopsia, and relative afferent pupillary defects (6). These conditions pose significant diagnostic challenges, as their presentations can overlap with other autoimmune, infectious, and thrombotic disorders.
Early recognition and appropriate immunosuppressive treatment are crucial for preserving vision and preventing irreversible damage. Corticosteroids remain the mainstay of initial therapy, but refractory or severe cases may benefit from biologic therapies such as rituximab (7). In this report, we present a case of a young female with newly diagnosed SLE who developed concurrent retinal vasculitis and optic neuritis, successfully treated with corticosteroids and rituximab. A literature review is included to provide further insight into the epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment options for these rare but devastating ocular manifestations of SLE.
Case presentation
A 26-year-old woman presented with a one-month history of facial erythema and a 10-day history of progressive blurred vision. Initially, she noticed a symmetrical erythematous rash over her face but did not seek medical attention. Ten days prior to admission, she developed sudden bilateral vision loss without identifiable triggers. She reported no fever, chills, limb numbness, hair loss, dry eyes, dry mouth, Raynaud’s phenomenon, muscle pain or weakness, joint stiffness, or systemic symptoms such as abdominal pain or diarrhea.
She was evaluated at the local ophthalmic hospital and diagnosed with optic neuritis. She received three doses of intravenous methylprednisolone (500 mg/day) with minimal improvement in visual acuity. Two days later, she experienced intermittent headaches, palpitations, nausea, and vomiting, with systolic blood pressure peaking at 170 mmHg. These symptoms prompted her admission to our hospital for further evaluation.
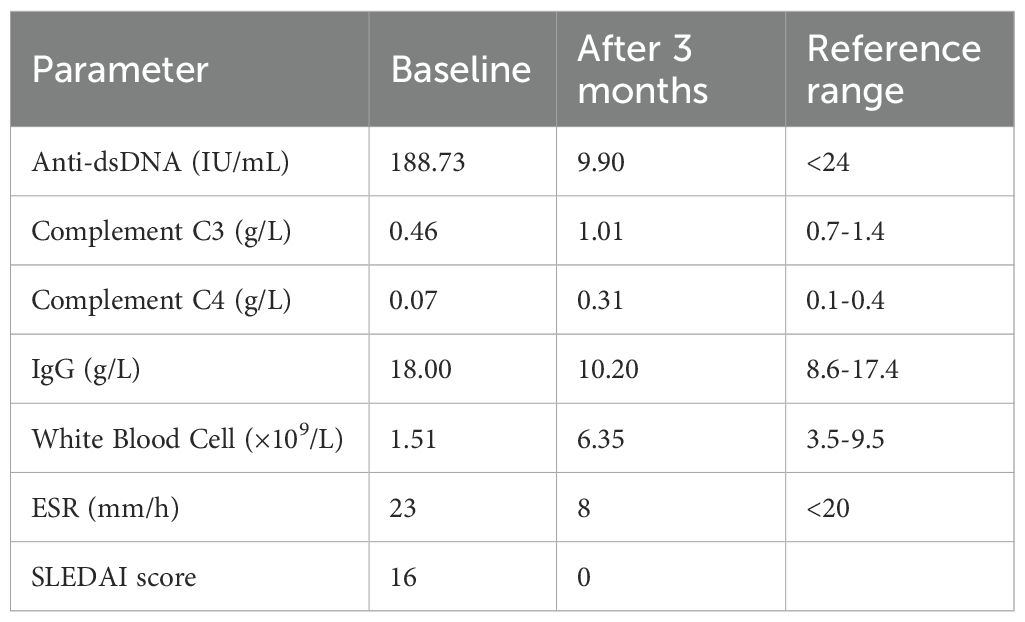
On admission, her best corrected visual acuity was 0.6 in the right eye and 0.8 in the left eye. Fundoscopic examination revealed bilateral optic disc edema with soft exudates, findings consistent with concurrent retinal vasculitis (Figure 1a). Enhanced vascular reflex is noted in the superior temporal retinal vessels, with scattered hemorrhagic spots. Scattered white exudates are observed in the posterior pole of the retina. Bilateral OCT scans of the optic nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness on admission reveal thinning of the nasal retinal nerve fiber layer and thickening of the temporal retinal nerve fiber layer (Figure 2). Her blood pressure was elevated, and physical examination showed a butterfly rash across her face. However, there was no alopecia, joint swelling, or other cutaneous abnormalities.
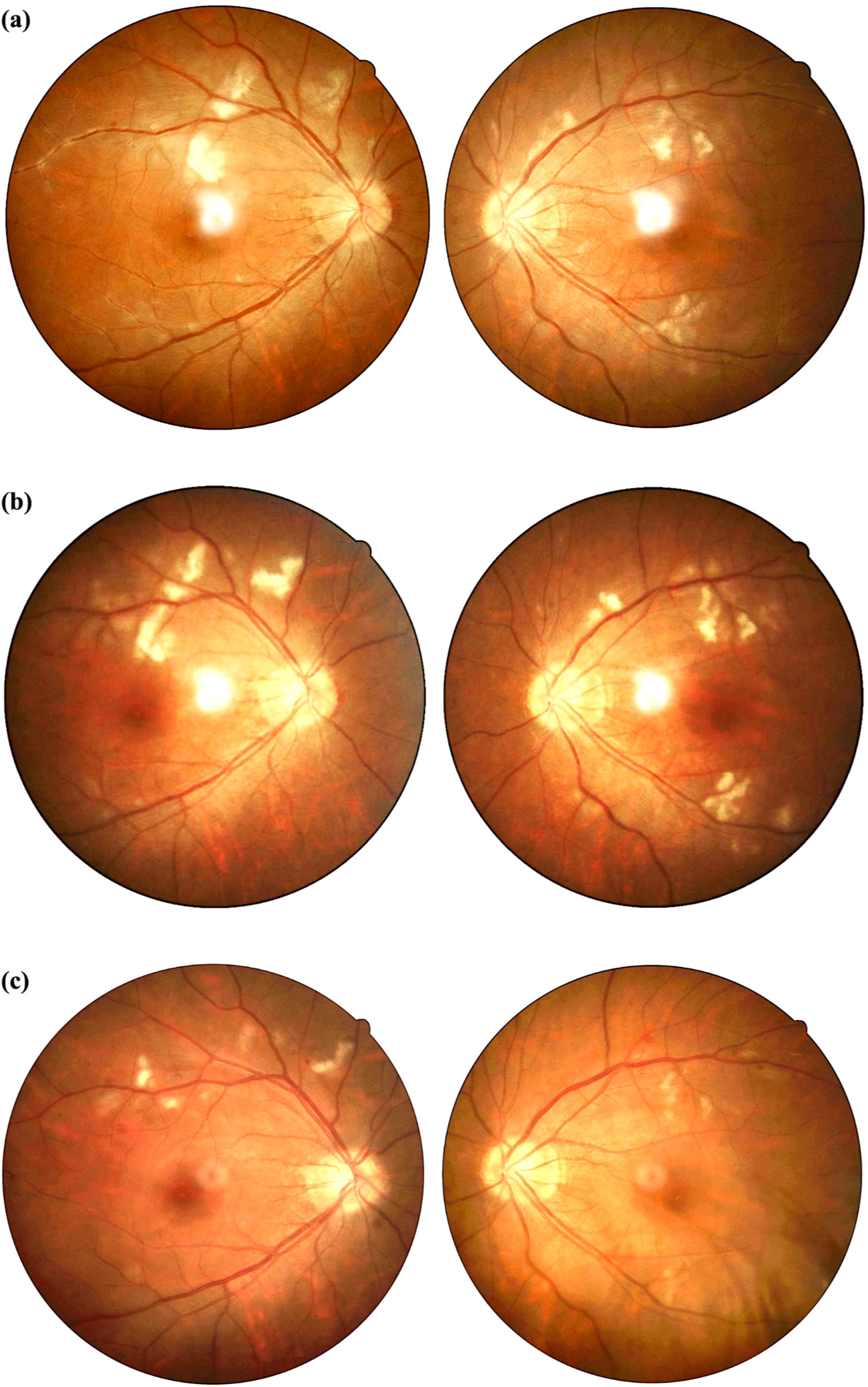
Figure 1. (a-c) Comparison of fundus photographs before and after treatment. (a) Fundus photographs obtained on admission. Bilateral optic disc edema with blurred margins. Posterior pole retinal white exudates. Right eye demonstrates enhanced superior temporal vascular reflex and hemorrhagic spots. (b) Fundus photographs obtained on 12 days after admission. Persistent bilateral disc edema and retinal exudates. (c) Fundus photographs at three-month post-treatment follow-up. Marked reduction of exudates in both eyes, with residual disc margin blurring. Compared with before treatment, the patient’s retinal vasculitis lesions showed significant improvement after treatment.
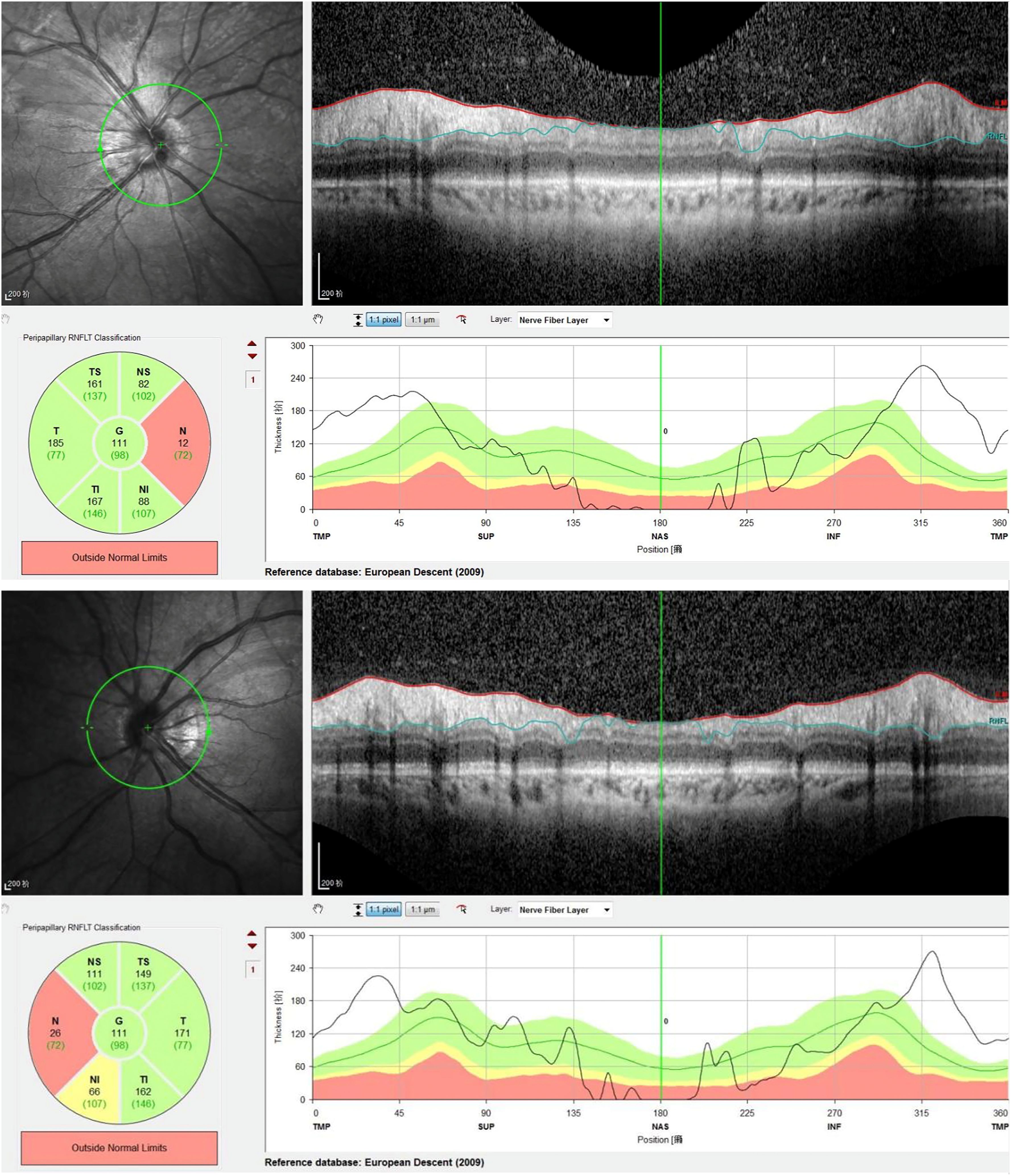
Figure 2. Bilateral retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) OCT scan reveals: thinning of nasal RNFL thickness and thickening of temporal RNFL thickness, indicating bilateral optic neuritis-induced RNFL damage. In this patient, the nasal RNFL is significantly thinned, being the first to be affected and suffering the most severe damage. The relative thickening of the temporal RNFL may be attributed to inflammation-induced axonal swelling and optic disc edema, leading to increased RNFL thickness.
Laboratory investigations revealed leukopenia with a white blood cell count of 1.51 × 109/L, while routine liver and kidney function tests were normal. Inflammatory markers showed a serum amyloid A level of 12.45 mg/L and an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 23 mm/h. Autoantibody testing revealed a nuclear homogeneous pattern on ANA with a titer of 1:3200 and strongly positive anti-dsDNA antibodies at 188.73 IU/mL. Additional positive findings included antibodies against ds-DNA, nucleosome, histone, U1-snRNP, SS-A/Ro52, SS-A/Ro60, SS-B/La, and AMA-M2. Complement levels were significantly reduced, with C3 at 0.46 g/L and C4 at 0.07 g/L. Immunoglobulin G was elevated at 18.00 g/L. Other tests, including antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA), lupus anticoagulant, antiphospholipid antibodies, anticardiolipin antibodies, C-reactive protein, ferritin, and 24-hour urine protein quantification, were within normal limits. The patient tested negative for infectious diseases such as tuberculosis and hepatitis B. Imaging studies further supported the diagnosis. Cranial magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) demonstrated vascular abnormalities consistent with secondary cerebral vasculitis (Figure 3). Ultrasonography of the heart, abdomen, and other systemic evaluations revealed no abnormalities. Transient hypertension observed was likely due to acute inflammatory response and corticosteroid administration. Renal function tests and proteinuria assessments were normal, ruling out active lupus nephritis. Cranial imaging (MRI/MRA) excluded posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES). Due to the patient’s urgent admission and personal preference, fluorescein angiography and visual evoked potentials (VEP) were not performed initially. However, optic nerve OCT and cranial MRI/MRA clearly documented optic nerve inflammation and cerebral vasculitis.
Figure 3. Cranial MRA demonstrated vascular abnormalities consistent with secondary cerebral vasculitis. Cranial MRA demonstrated patent bilateral anterior cerebral arteries, middle cerebral arteries, and posterior cerebral arteries with diminished distal branching, diffuse luminal caliber irregularities, and multiple foci of severe stenosis.
Based on her clinical presentation, ophthalmic findings, strongly positive anti-dsDNA and other autoantibodies, reduced complement levels, and systemic symptoms, a diagnosis of SLE was made. The ocular findings of optic neuritis and retinal vasculitis were identified as severe complications of SLE. Differential diagnoses such as infectious etiologies (tuberculosis, syphilis), autoimmune disorders (granulomatosis with polyangiitis, neuromyelitis optica), and hypertensive retinopathy were considered and systematically excluded through laboratory tests and imaging. The patient was treated with intravenous methylprednisolone (80 mg/d), followed by two doses of intravenous Rituximab (500 mg on the 2nd day post-admission and two weeks after admission) to control systemic inflammation and immunologic activity. Significant improvement was noted: her visual acuity returned to 1.0 bilaterally, and the facial erythema resolved before discharge. Fundus photographs obtained on 12 days after admission. Persistent bilateral disc edema and retinal exudates (Figure 1b). Hydroxychloroquine initiation was temporarily deferred due to severe ocular involvement. Ophthalmology consultation advised postponing it to avoid confounding retinal assessments. Initiation is planned after confirming retinal stability at 6 months. A lower initial dose of mycophenolate mofetil (750 mg/day) was chosen due to the patient’s low body weight and gastrointestinal sensitivity, with gradual escalation to 1500 mg/day after three months.
The patient was discharged on the 15th day after admission. She was prescribed oral prednisolone (40 mg/d) and mycophenolate mofetil (750 mg/d) for maintenance therapy. Antihypertensive medications were briefly administered during hospitalization but discontinued prior to discharge. At three months post-discharge, the patient maintained clinical stability with successful corticosteroid tapering and absence of systemic disease activity. Blood pressure remained stable within normal range throughout the follow-up period. Follow-up fundoscopic examination demonstrated significant improvement in retinal findings. Scattered white exudates are observed in the posterior pole of the retina, with a significant reduction in exudates compared to previous examinations. (Figure 1c). Laboratory test indicators and disease activity show significant improvement compared with before treatment (Table 1).
Discussion
This case underscores the importance of early recognition and prompt immunosuppressive therapy in SLE-related ocular vasculitis and optic neuritis, particularly in severe cases requiring biologic intervention. The concurrence of retinal vasculitis and optic neuritis in SLE presents a diagnostic challenge due to overlapping clinical features with other autoimmune and infectious etiologies. The patient initially presented with ocular manifestations as the first clinical sign of SLE, significantly complicating both diagnosis and therapeutic management. To contextualize the findings, we compared the present case with 30 previously published cases of SLE-related severe ocular manifestations (Tables 2, 3). The dataset categorized these cases into three groups: SLE with both retinal vasculitis and optic neuritis (7 cases) (8–14), SLE with retinal vasculitis alone (10 cases) (7, 15–23), and SLE with optic neuritis alone (13 cases) (6, 24–33). Our case falls into the first category, which represents the most severe ocular involvement.
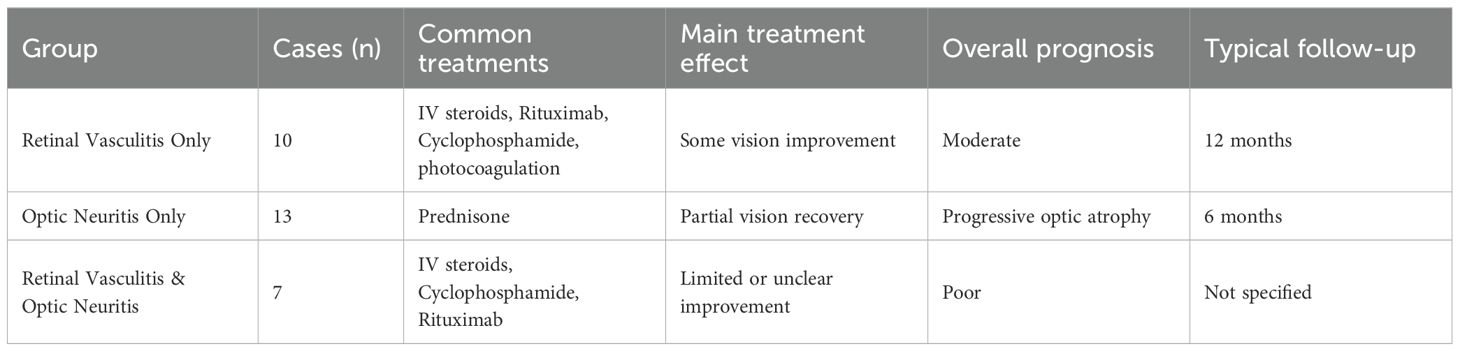
Table 2. The common treatments, overall prognosis and typical follow-up for retinal vasculitis and optic neuritis in SLE.
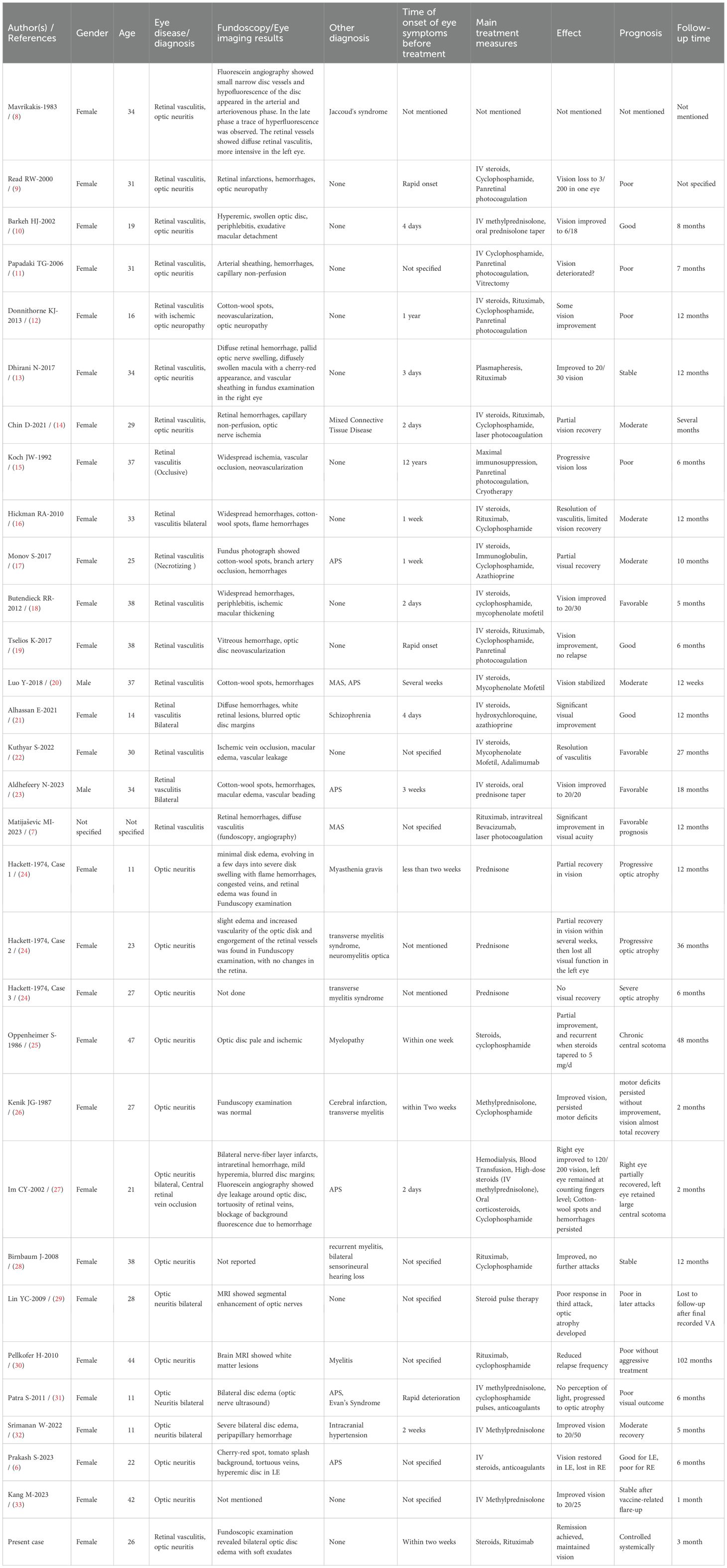
Table 3. Clinical characteristics of SLE patients with retinal vasculitis and optic neuritis: A comparative overview.
The present case exhibited highly active systemic lupus, with markedly elevated ds-DNA titers, low complement levels, and concurrent neurovascular involvement, as suggested by MRA findings. This aligns with trends observed in patients with both retinal vasculitis and optic neuritis, who frequently exhibited multisystem disease, including lupus nephritis and CNS lupus (20, 34) In contrast, patients with retinal vasculitis alone also had active SLE but tended to have fewer concurrent neuropsychiatric symptoms (19, 22). Retinal vasculitis in these cases was often the first sign of systemic lupus exacerbation. Patients with isolated optic neuritis had a more variable degree of systemic lupus activity. Some had isolated optic neuritis with minimal systemic manifestations, while others developed CNS lupus over time (35).
In terms of treatment, our patient received intravenous methylprednisolone followed by rituximab and mycophenolate mofetil, achieving significant visual recovery. This aligns with treatment approaches observed in previous reports of concurrent retinal vasculitis and optic neuritis in SLE, where corticosteroid monotherapy was typically inadequate, necessitating additional immunosuppressive agents such as cyclophosphamide or rituximab to effectively control disease activity and preserve vision (12–14).
Notably, therapeutic responses and prognoses differ substantially between lupus-associated retinal vasculitis and optic neuritis. Patients with isolated retinal vasculitis generally show good initial responses to corticosteroids alone; however, maintaining remission frequently requires additional long-term immunosuppression (e.g., azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil) (15, 19, 22). Early and aggressive intervention usually results in favorable outcomes, although visual prognosis can vary significantly depending on the extent and rapidity of vascular occlusion. Those with limited vaso-occlusion often achieve better visual prognoses, whereas cases involving severe ischemic retinopathy may lead to permanent vision loss despite therapy (15, 16).
In contrast, patients presenting with lupus-associated optic neuritis tend to respond initially to high-dose corticosteroids, often with noticeable improvement in acute visual symptoms. However, unlike typical demyelinating optic neuritis (as seen in multiple sclerosis), visual recovery in lupus-related optic neuritis is frequently incomplete. Long-term outcomes tend to be less favorable, marked by partial visual recovery, progressive optic nerve atrophy, or recurrent episodes despite continued immunosuppressive therapy (6, 29–31, 33). Approximately one-third of these patients experience relapses, underscoring the difficulty of achieving sustained remission (30, 31).
Patients like ours, presenting concurrently with both retinal vasculitis and optic neuritis, generally experience the most severe ocular involvement and thus have the worst prognoses overall. Many previously reported cases resulted in irreversible visual impairment due to profound retinal ischemia or persistent optic nerve damage (9, 11, 12). However, our patient achieved remarkable visual recovery, making her one of the best responders within this severe subgroup. Nonetheless, the high risk of disease recurrence mandates ongoing, carefully tailored immunosuppressive management. Therefore, recognizing these distinct therapeutic responses and prognostic outcomes is critical for rheumatologists, ophthalmologists, and neurologists involved in managing ocular manifestations of SLE. Early, aggressive, and individualized immunosuppressive therapy—along with diligent monitoring—is essential to optimize long-term visual outcomes in these challenging cases.
Conclusion
This case highlights the need for rapid diagnosis and aggressive immunosuppression in severe SLE-related ocular disease. Given that retinal vasculitis often signals active systemic lupus, early recognition is crucial. The association with antiphospholipid antibodies suggests that anticoagulation may be beneficial in select cases to prevent further vaso-occlusive events (6, 27, 31). Additionally, biologic therapies such as rituximab is emerging as promising treatments for refractory disease (7, 22).
Moving forward, continued research is needed to establish standardized treatment protocols for these rare but vision-threatening complications. Our findings reinforce the value of a multidisciplinary approach, integrating rheumatologists, ophthalmologists, and neurologists to achieve optimal patient outcomes. This case contributes to the growing body of literature on SLE-related ocular disease, providing valuable comparative insights between a real-world case and previously documented cases. Future studies with larger cohorts and long-term follow-up are necessary to refine therapeutic strategies and improve patient prognosis.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
DJ: Writing – original draft. XL: Writing – original draft. YW: Writing – original draft. LF: Writing – original draft. WN: Writing – original draft. CL: Writing – review & editing. ML: Writing – review & editing. S-GL: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by grants from the Weifang Health Commission’s scientific research program (grant No. WFWSJK-2023–222 and WFWSJK-2023-240); the Weifang Youth Medical Talent lift project and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82374272).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all the researchers who contributed to this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. de Andrade FA, Guimarães Moreira Balbi G, Bortoloti de Azevedo LG, Provenzano Sá G, Vieira de Moraes Junior H, Mendes Klumb E, et al. Neuro-ophthalmologic manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. (2017) 26(5):522–8. doi: 10.1177/0961203316683265
2. Preble JM, Silpa-archa S, and Foster CS. Ocular involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. (2015) 26:540–5. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000209
3. Lo JE and Ma KS. Risk of ocular manifestations and complications in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Rheum Dis. (2024) 27:e15334. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.15334
4. Meng L, Wang Y, Yang Z, Lin S, Wang Y, Chen H, et al. Ocular fundus changes and association with systemic conditions in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1395609. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395609
5. Chiou YR, Chang YS, Su CF, Li TH, Lai CC, Hwang DK, et al. Risks of posterior segment ocular ischaemic events in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Br J Ophthalmol. (2023) Nov; 107:1687–92. doi: 10.1136/bjo-2022-321653
6. Prakash S, Gunderia AM, and Khadar SMA. A rare simultaneous presentation of combined occlusion and optic neuritis in a lupus erythematosus patient with anti-phospholipid antibody syndrome. Lupus. (2023) 32:804–9. doi: 10.1177/09612033231171342
7. Ikić Matijašević M, Kilić P, Ikić L, Galić I, Brzović Šarić V, and Galić E. Rituximab, Intravitreal Bevacizumab and Laser Photocoagulation for Treatment of Macrophage Activation Syndrome and Retinal Vasculitis in Lupus: A Case Report. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(3):2594. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032594
8. Mavrikakis M, Anastasiou-Nana M, Kalaitzidou C, and Papageorgiou C. Optic neuritis and Jaccoud’s syndrome in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Rheumatol. (1983) 12:367–8. doi: 10.3109/03009748309099742
9. Read RW, Chong LP, and Rao NA. Occlusive retinal vasculitis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Ophthalmol. (2000) 118:588–9. doi: 10.1001/archopht.118.4.588
10. Barkeh HJ and Muhaya M. Optic neuritis and retinal vasculitis as primary manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Med J Malaysia. (2002) 57:490–2.
11. Papadaki TG, Zacharopoulos IP, Papaliodis G, Iaccheri B, Fiore T, and Foster CS. Plasmapheresis for lupus retinal vasculitis. Arch Ophthalmol. (2006) 124:1654–6. doi: 10.1001/archopht.124.11.1654
12. Donnithorne KJ, Read RW, Lowe R, Weiser P, Cron RQ, and Beukelman T. Retinal vasculitis in two pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. (2013) 11:25. doi: 10.1186/1546-0096-11-25
13. Ali Dhirani N, Ahluwalia V, and Somani S. Case of combination therapy to treat lupus retinal vasculitis refractory to steroids. Can J Ophthalmol. (2017) 52:e13–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjo.2016.07.027
14. Chin D, Gan NY, Holder GE, Tien M, Agrawal R, and Manghani M. Severe retinal vasculitis in systemic lupus erythematosus leading to vision threatening paracentral acute middle maculopathy. Mod Rheumatol Case Rep. (2021) 5:265–71. doi: 10.1080/24725625.2021.1893961
15. Koch JW, al Nawaiseh I, and Koch FH. Severe occlusive bilateral retinal vasculitis within the scope of seronegative systemic lupus erythematosus. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. (1992) 201:330–6. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1045912
16. Hickman RA, Denniston AK, Yee CS, Toescu V, Murray PI, and Gordon C. Bilateral retinal vasculitis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus and its remission with rituximab therapy. Lupus. (2010) 19:327–9. doi: 10.1177/0961203309347332
17. Monov S, Hristova R, Dacheva R, Toncheva R, Shumnalieva R, Shoumnalieva-Ivanova V, et al. Acute necrotizing retinal vasculitis as onset of systemic lupus erythematosus: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). (2017) 96(2):e5754. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005754
18. Butendieck RR, Parikh K, Stewart M, Davidge-Pitts C, and Abril A. Systemic lupus erythematosus-associated retinal vasculitis. J Rheumatol. (2012) 39:1095–6. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.111462
19. Tselios K, Lam WC, Urowitz MB, and Gladman DD. Rituximab for sight-threatening lupus-related retinal vasculitis. J Clin Rheumatol. (2018) 24:93–4. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000000600
20. Luo Y, Wen Y, Arevalo Molina AB, Dahal P, Leuprecht L, and Bsrat M. Macrophage activation syndrome, glomerulonephritis, pericarditis, and retinal vasculitis as initial presentation of systemic lupus erythematosus. Case Rep Med. (2018) 2018:5979386. doi: 10.1155/2018/5979386
21. Alhassan E, Gendelman HK, Sabha MM, Hawkins-Holt M, and Siaton BC. Bilateral retinal vasculitis as the first presentation of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Case Rep. (2021) 22:e930650. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.930650
22. Kuthyar S, Barnes AC, Bhawal J, Christiansen J, Shantha JG, and Yeh S. Systemic lupus erythematosus-associated retinal vasculitis treated with adalimumab. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. (2022) 30:981–5. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2020.1828937
23. Aldhefeery N, Alhadhood N, and Alkadi A. Bilateral retinal vasculitis as initial presentation of systemic lupus erythematosus with secondary antiphospholipid syndrome. Am J Case Rep. (2023) 24:e942085. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.942085
24. Hackett ER, Martinez RD, Larson PF, and Paddison RM. Optic neuritis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Neurol. (1974) 31:9–11. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490370035002
25. Oppenheimer S and Hoffbrand BI. Optic neuritis and myelopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Can J Neurol Sci. (1986) 13:129–32. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100036064
26. Kenik JG, Krohn K, Kelly RB, Bierman M, Hammeke MD, and Hurley JA. Transverse myelitis and optic neuritis in systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report with magnetic resonance imaging findings. Arthritis Rheumatol. (1987) 30:947–50. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300818
27. Im CY, Kim SS, and Kim HK. Bilateral optic neuritis as first manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus. Korean J Ophthalmol. (2002) 16:52–8. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2002.16.1.52
28. Birnbaum J and Kerr D. Optic neuritis and recurrent myelitis in a woman with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. (2008) 4:381–6. doi: 10.1038/ncprheum0818
29. Lin YC, Wang AG, and Yen MY. Systemic lupus erythematosus-associated optic neuritis: clinical experience and literature review. Acta Ophthalmol. (2009) 87:204–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.2008.01193.x
30. Pellkofer HL, Hohlfeld R, and Kuempfel T. Thirty-one episodes of myelitis and optic neuritis in a woman with neuromyelitis optica and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Neurol. (2010) 67:779–80. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2010.109
31. Patra S, Krishnamurthy S, Seth A, Beri S, and Aneja S. Bilateral optic neuritis in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Indian J Pediatr. (2011) 78:234–6. doi: 10.1007/s12098-010-0228-5
32. Srimanan W and Panyakorn S. Concurrent intracranial hypertension and bilateral optic neuritis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: A case report. Clin Med Insights Case Rep. (2022) 15:11795476221122649. doi: 10.1177/11795476221122649
33. Kang M, Kim S, Park JS, and Seok HY. Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated optic neuritis following third dose of BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Neurol Sci. (2023) 44:2247–9. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-06715-x
34. Wang X, Xie H, Yi Y, Zhou J, Yang H, and Li J. Clinical Research of Lupus Retinopathy: Quantitative Analysis of Retinal Vessels by Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Diagnostics (Basel). (2023) 13(20):3222. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13203222
Keywords: systemic lupus erythematosus, retinal vasculitis, optic neuritis, autoimmune ocular disease, immunosuppressive therapy
Citation: Jin D, Liu X, Wang Y, Fang L, Nie W, Li C, Li S-G and Li M (2025) Case Report: Concurrent retinal vasculitis and optic neuritis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 16:1646850. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1646850
Received: 14 June 2025; Accepted: 28 July 2025;
Published: 18 August 2025.
Edited by:
Andreas Goules, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, GreeceReviewed by:
George Bertsias, University of Crete, GreeceMarina Ikic Matijasevic, University Hospital Sveti Duh, Croatia
Copyright © 2025 Jin, Liu, Wang, Fang, Nie, Li, Li and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sheng-Guang Li, bGlzaGVuZ2d1YW5nQHZpcC4xNjMuY29t; Ming Li, bGFsd2xtQGFsaXl1bi5jb20=; Chen Li, Y2FzaW8xOTgxQDE2My5jb20=
†ORCID: Chen Li, orcid.org/0000-0002-8527-1680
 Di Jin1
Di Jin1 Chen Li
Chen Li Sheng-Guang Li
Sheng-Guang Li Ming Li
Ming Li