- 1Department of Chemistry, Technical University of Denmark, Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark
- 2Department of Biomedicine, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark
- 3Department of Molecular Medicine, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark
- 4Section of Rheumatology, Medical Diagnostic Center, Silkeborg, Denmark
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) involves a breakdown of immune tolerance to citrullinated proteins, leading to chronic inflammation and joint damage. Despite advances in treatment, achieving long-term remission remains a major challenge. Restoring immune tolerance to citrullinated proteins represents a promising strategy to halt disease progression and establish lasting remission. This review examines the potential of using citrullinated proteins or peptides to reestablish immune tolerance in RA. It explores the potential role of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) in disease pathology and how utilizing or targeting specific citrullinated antigens could modulate immune responses. The review also highlights the therapeutic relevance of altering T and B cell function to regulate immune state. We explore mechanisms through which tolerance can be induced, including the use of citrullinated peptides to promote regulatory T (Treg) cell expansion and alter pathogenic B cell subsets. Emerging strategies aimed at re-educating the immune system are discussed, focusing on their potential to provide effective and durable treatment outcomes. These tolerance-based approaches are evaluated for their capacity to shift the immune response away from autoimmunity and towards sustained remission.
1 Introduction
RA is a chronic, systemic, autoimmune disease characterized by synovial inflammation and joint destruction, which affects approximately 18 million patients worldwide (1). Patients often grapple with fatigue, depression, and the fear of progressive disability, contributing to a lower quality of life (2, 3).
RA is subcategorized into seropositive and seronegative forms based on the serological presence of the autoantibodies rheumatoid factor (RF) and ACPAs (4–10). Approximately 70% of RA patients test positive for these antibodies (4–10). ACPA positivity is especially relevant, as this is associated with a more severe disease course and involvement of other organs (11, 12). ACPAs appear up to 10 years before disease onset (6, 12, 13) and they have great value in clinic practice as diagnostic tools (14).
Loss of immune tolerance is a central event in RA pathogenesis, leading to persistent activation of autoreactive T and B cells and production of autoantibodies such as ACPAs. Unlike conventional therapies that broadly suppress the immune system, restoring immune tolerance offers a targeted strategy to reprogram autoreactive responses while preserving protective immunity. Antigen-specific immunotherapies aim to achieve this by inducing T cell exhaustion, expanding Treg cells, or modulating antigen-presenting cells toward a tolerogenic profile. In recent years, several approaches -ranging from tolerogenic vaccines and peptide-based antigen presentation to therapeutic ACPAs- have shown promise in preclinical and early clinical settings. This review summarizes emerging strategies that leverage citrullinated peptides and other autoantigen-based interventions to restore immune tolerance in RA, with a focus on their mechanisms, efficacy and translational potential.
2 Breach of immune tolerance in rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is widely recognized as a T cell mediated disease. In genetically predisposed individuals, modified self-antigens can be presented via major histocompatibility complex (MHC) to self-reactive T cells, initiating a series of immunological events that progressively involves other cell types and ultimately leads to stablished RA. Preclinical stages are marked by expansions of distinct T cell subsets, including CCR2+ CD4+ T, T peripheral (Tph), T helper 1 (Th1) and CXCR5+ CD8+ T cells (15, 16). CD4+ T cells differentiate into multiple effector lineages -Th1, Th2, Th17 and T follicular helper (Tfh) cells- to coordinate immune responses. Imbalances in these subsets cause a proinflammatory response (17–20). Consistent with this, both early and stablished RA display elevated frequences of CD4+T cells in synovium compared to blood (15, 21, 22), accompanied to skewed Th cell profiles (15, 23). Th1 cells are involved in the release of proinflammatory cytokines (such IFN-γ, IL-2 or TNF-α), leading to bone erosion; while Th17 cells also stimulate the production of proinflammatory cytokines in synovial fibroblasts, with IL-17A being the predominant one. Similar alterations are observed in cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, with RA patients exhibiting different populations of CD27−CD62L−, CXCR5+, GZMB+ and GZMK+ CD8+ T cell subsets, among others (15, 16, 24, 25).
While T cell dysregulation is central to RA pathogenesis, abnormal B cell subset composition and function are also closely linked to the breakdown of self-tolerance. Small subsets representing as little as 0.6% and 5% of blood B cells population as it is the case of B10 and B10pro cells, respectively, can have a major role in autoimmune regulation. Found within the CD24hiCD27+ B cell subpopulation, ex vivo B10 and B10pro cells were reported to negatively regulate monocyte related in vitro cytokine production through IL-10 dependent pathways (26). IL-10 knock out in B cells of collagen induced arthritis (CIA) murine models has also been shown to cause disease exacerbation characterized by an increase in inflammatory Th1 and Th17 cells, as well as a reduction in CD4+ T regulatory type 1 induced IL-10 production and increase in IL-17 levels (27). Other IL-10 knockout mice models such as the tamoxifen-induced model also proved the paper of IL-10 from Breg cells in CD4+ and CD8+ T cell mediated inflammatory cytokine expression (28). Subsequently, Aoun et al. reported natural autoreactive B cells specific for collagen type II C1 epitope (C1-B cells) present in the spleen, bone marrow and PBMCs of healthy mice, rats and humans, indicating its regulative role. However, RA patients showed an eight-fold decrease of C1-B cells while increasing the number of RA specific antibodies to C1 collagen epitope (29). Transfer of C1-B cells from anti-C1 mice into autoimmune prone mice model protected these against collagen type II arthritis induction (29). Antagonizing the previously described results on IL-10’s role in prevention of self-tolerance breach, IL-10 knockout C1-B cells from anti-C1 mice also suppressed collagen type II arthritis induction and increased activated T cells, pointing out that C1-B cells may tolerize T cells independently of IL-10 (29).
Autoimmune checkpoint molecule programmed cell death 1 (PD-1), expressed by T cells, B cells and other immune cells, plays a crucial role in maintaining immune tolerance and autoimmunity prevention by downregulating immune responses. Several publications pointed out the role of PD-1, its ligands or Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte Associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) overexpression, in T cell exhaustion (30–32), as well as synovium infiltration of PD-1hiTph cells in early RA (21). Nettersheim et al. identified higher expression of PD-1 and CD73 in self-specific CD4+ T cells from healthy mice, compared to exogenous-specific CD4+ T cells (33). After blockade of both PD-1 and CD73, vaccine-expansion of self-specific CD4+ T cells resulted into CD4+ T cells with transcriptomes of exogenous-specific CD4+ T cells, showing that PD-1 and CD73 co-operationally limit CD4+ T to self-antigens (33). PD-1 and its ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression has also been found upregulated in RA synovial tissue (34). Downregulation of PD-1 pathway was also observed during RA progression, attributed to increased levels of serum soluble (s)PD-1 in ACPA-positive (ACPA/+) RA patients (34, 35). sPD-1 was connected to severe CIA through Th1 and Th17 pathways (35), while PD-1 expression on CD4+ and CD8+ from PBMCs negatively correlated to disease activity (36). Further underlining the role of PD-1 in RA immune regulation, cases have been reported of RA occurring after PD-1 inhibiting cancer treatment (37). PD-1 can also drive T cells into apoptosis or a regulatory phenotype upon PD-L1, except in the case of RA patients (38). Generation of monocyte derived tolerogenic dendritic cells (tolDCs) with superior capacity to induce Th17 cells were obtained when precursor monocytes from peripheral blood of RA patients were treated with either P-selectin, IL-10 or PD-1 (39).
Upregulated levels of B cell activating factor (BAFF) in the peripheral blood was related to the survival of autoreactive B cells and further production of autoantibodies, exacerbating the disease (40, 41). Along with BAFF, toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands boost B cell activation, immunoglobulin isotype class switching, somatic hypermutation, and their transformation into plasma cells, which results in the production of harmful autoantibodies (42, 43). Likewise, in vivo studies on CIA mice indicate that silencing BAFF receptors expression lowers B cell counts and autoantibody levels significantly, which further reduces joint inflammation (44).
Furthermore, IL-6 produced by B cells and macrophages in the synovial fluid (SF) of RA patients, is needed for B cell differentiation and the formation of plasma cells (45). IL-21, secreted by subsets of helper T (Th) cells and found in higher levels on serum and SF of RA patients, is also essential for B cell activation, proliferation, differentiation and antibody production (46).
2.1 Environmental factors – smoking, neutrophil extracellular traps formation and role of mucosal immunity
The loss of immune tolerance in RA related to the impaired clearance and excessive presence neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) has been previously reviewed (47–49). When NET removal is compromised, they accumulate at inflammatory sites, thereby prolonging inflammation and producing new autoantigens (47). Elevated NET formation has been observed in the sputum of both individuals at risk for developing RA (being first degree relatives of RA patients) and in RA patients themselves (50, 51). This local NET buildup correlates with the generation of mucosal autoantibodies such as IgA and IgG ACPAs, suggesting that the airway may serve as an initiation site for systemic autoimmunity. In fact, high levels of both NETs and ACPAs have been detected in the sputum of at-risk patients, supporting a direct association between NET formation and autoantibody production (50–53). Environmental factors such as cigarette smoking exacerbate this process by inducing NET formation via protein arginine deaminase (PAD) 4-dependent pathways, which in turn increases the production of citrullinated antigens in the lung (Figure 1) (54). Smoking not only elevates the risk of ACPA development but also intensifies the inflammatory response by triggering spontaneous NETosis in neutrophils (54–56).

Figure 1. Representation of breach of tolerance during pre-articular stage in rheumatoid arthritis. Infective agents, environmental factors such cigarette smoking or some types of pollution and genetic factors mediate the loss of immune tolerance towards self-epitopes before disease onset. APCs, antigen presenting cells; NETs, Neutrophil Extracellular Traps; PAD, protein arginine deaminase. Created with BioRender.
In addition to environmental triggers, infectious agents have been noticed for their role in breaking immune tolerance (Figure 1) (57–59). Multiple pathogens -including Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB), Porphyromonas gingivalis (Pg) and others- have been implicated as potential instigators of RA (57–59). Antibodies towards these infections and dysbiosis of mucosae’s microbiota have been found in higher titters on RA and early RA patients, compared to healthy controls (60–64). These microorganisms may trigger autoimmunity through mechanisms such as molecular mimicry, where the structural similarities between microbial antigens and self-proteins provoke a cross-reactive immune response to self-antigens; epitope spreading, which broadens the autoimmune response to additional self-antigens; and bystander activation, where infection-induced inflammation and cytokine release non-specifically activate T cells (65). Together with NET formation, these mechanisms expand the pool of autoreactive T and B cells, lowering the threshold for autoimmunity (48, 58). As an example, high sequence homology between these microorganism’s antigens and key host molecules like interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5), involved in macrophage and dendritic cells (DCs) inflammatory response as well as B cell antibody production, has been found (66). This similarity results in cross-reactivity towards antigens from EBV, MAP and self-IRF5 (66, 67).
The mucosal endotype hypothesis further explains RA pathogenesis by emphasizing the role of different mucosal sites: lungs, gut and oral cavity (58). Each of these sites exhibits unique inflammatory responses that may contribute to the systemic generation of autoantibodies. As it has already been covered, early inflammatory changes and local antibody production in lungs have been linked to both smoking and chronic respiratory infections. Similarly, in the oral cavity, periodontal disease driven by pathogens such as Pg not only damages the local mucosal barrier but also promotes NETosis and subsequent citrullination of bacterial as well as host proteins (68–70). This process can initiate a B cell response that eventually leads to the production of autoantibodies, setting the stage for joint inflammation (69). Moreover, the gut microbiome in patients with RA often shows distinct patterns of dysbiosis that are associated with metabolic changes and immune activation (71–73). These gut bacteria alterations can further contribute to the systemic inflammatory setting that underlies RA. Autoreactive B cells, generated autoantibodies or new self-epitopes resulting from these mucosal inflammatory processes can migrate systemically towards the joint (52, 74–79). Collectively, these observations underscore a multifaceted interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental attacks - including smoking, microbial infections and possibly even exposure to inorganic particles like silica (80, 81) - that collectively disrupts immune tolerance, culminating in the onset and progression of RA. Given the multitude of factors and mechanisms capable of breaking tolerance, RA is inherently a heterogeneous and complex disease.
Breach of tolerance is characterized by the aberrant presentation of citrullinated proteins, which primes both innate and adaptive immune responses, ultimately leading to the chronic production of inflammatory cytokines, autoantibodies and perpetuation of tissue damage. Consequently, restoring immune tolerance, particularly to citrullinated proteins, represents a promising therapeutic avenue for achieving remission in RA.
3 Role of ACPAs in pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis
While ACPAs are well established as diagnostic biomarkers for RA (14), increasing experimental and clinical evidence indicates that ACPAs are not just markers of disease but active contributors of joint pathology. Beyond their value in diagnostics, ACPAs are associated with disease severity or treatment outcome (82). In addition, epitope spreading reflects ongoing activation of autoreactive B and T cells, pointing towards their active role in disease (83).
The following section examines evidence on processes leading to the generation of citrullinated antigens that drive ACPA generation, the B-cell subsets involved in ACPA production, their structural diversity and the cellular and molecular pathways by which ACPAs contribute to synovial inflammation and joint destruction.
3.1 Generation of citrullinated antigens
Citrullination of proteins is a posttranslational modification consisting of the deamination of arginine by PAD enzymes. Under physiological conditions, this modification serves as a regulatory mechanism for protein function and is well tolerated by the immune system (84). However, when citrullination overcomes physiological regulation, changes in conformation and charge distribution of peptides leads to disrupted protein interactions, converting citrullinated epitopes into self-antigens (85).
Excessive citrullination can promote protein autophagy and subsequent presentation by DCs, macrophages and thymic DCs, driving CD4+ T cell activation (86). It can also enhance peptide binding affinity to MHC-II (87), leading as well to CD4+ T cell activation and contributing to tolerance breakdown.
Normally, dominant factors of self-antigens interact with the MHC-II of antigen presenting cells (APCs), while “cryptic” epitopes remain unrecognized. As a result, dominant epitopes become available for recognition during thymic T-cell tolerance, while a population of CD4+ T cells remain capable of recognizing cryptic epitopes. As it has been mentioned, citrullination can unmask these epitopes by increasing their MHC-II binding affinity, enabling their presentation and recognition by autoreactive T cells (85).
Interestingly, overcitrullination does not only disrupt tolerance when it happens on a self-antigen; PAD2 enzyme has been reported to citrullinate transcription factors responsible for CD4+ T cell differentiation into Th1, Th2 and Th17, altering the differentiation itself and the populations of the resulting type helper T cells (85, 88). Citrullination of cytokines CXCL10 and CXCL11 reduce their interaction with T cells, hindering their chemotaxis to inflammation site (85, 89).
Overall, there are subpopulations of both B and T cells reacting towards citrullinated epitopes in the synovial of RA patients, being the last ones commonly found mainly as Th1 and Th17 phenotypes (90–93). Several efforts have been carried out to identify pathogenic B cell subsets in ACPA/+ RA patients. By single cell RNA-sequencing of CD45+ hematopoietic cells, Wu et al. found differences between the synovial immune cell subsets of ACPA/+ and ACPA/- RA patients, pointing out different immunopathological mechanisms related to these autoantibodies (94). Aiming to find pathogenic B cell subsets, Thorarinsdottir et al. found that in ACPA/+ RA patients most of the B cells in SF belonged to a CD21-/low subset. Under IL-6 stimulation, these cells expressed CXCR3 and RANKL, leading to osteoclast differentiation and bone destruction (95). Among this subset, ACPA/+ patients displayed CD21-/lowCD27-IgG- class significantly increased in peripheral blood and comprising 40% of the CD21-/low cells in SF (95), matching posterior studies in which CD27-IgD- and memory CD27+ IgD- B cells were found in higher ratios in the SF compared to peripheral blood, suggesting these subgroups are key players in RA synovium inflammation (96). Consistent with previous results, Floudas et al. further proved the reduced presence of CD27+ IgD+ B cells along with the accumulation of PD-1+ B cells in SF and synovial tissue of RA patients, compared to healthy controls (97). Other subtypes found in higher percentages in ACPA/+ patients were CD19+ B cells (91); and for patients with early RA, human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR+-peripheral type helper T cells, PD-1hi CD8+ T cells, CXCR5− CD11c− CD38+ naive B cells (98) and CD19+ CD24hi CD38hi regulatory B cells (99).
3.2 Diversity and glycosylation of ACPAs
ACPAs isolated from serum, plasma and SF of RA patients have been found as targeting over 100 citrullinated proteins (100–104). Notably, the affinities of these antibodies vary significantly both among patients and as disease progresses (83, 105–107). While some ACPAs only bind a single target such as citrullinated vimentin, fibrinogen or collagen (108, 109), most are highly promiscuous towards multiple citrullinated epitopes (110–112) or even other posttranslational modifications as acetylation and carbamylation (10, 112–114). Structurally, ACPAs are heavily N-glycosylated in their fragment antigen-binding (Fab) domain. Over 90% of ACPAs (compared to 15-25% of IgGs in human serum) are N-glycosylated in their variable domain (115, 116), and over 80% of receptors on ACPA-producing B cells contains N-glycosylation sites (116, 117). It is suggested that N-glycosylation provides ACPA-producing B cells with a selective advantage, enabling them to escape negative selection of the B cell receptor, thereby promoting autoimmunity (116, 118). On the other hand, Zhao et al. unveiled the complexity N-glycosylation in ACPAs by proving that upregulating sialylation of the crystallizable fragment (Fc) of ACPAs in B cells from collagen induced arthritis CIA mice attenuates disease progression (119), correlating to previous literature reporting decreased sialylation in the Fc region of serum ACPAs from RA patients and how this desialylation is related to inflammatory processes (119–122).
3.3 Mechanisms of ACPA-mediated pathogenesis
The presence and pathogenesis of ACPA in murine arthritic models has been debated (108, 123). Their proposed pathogenic mechanisms include direct targeting and degradation of citrullinated proteins in joint cartilage, such as type II collagen; enhancing fibroblast-like synoviocyte migration and adhesion within the synovium, where they release proinflammatory cytokines, create an erosive interphase and are involved in the citrullination of new self-antigens (124, 125); direct targeting of osteoclast precursors promoting their differentiation (108, 126); or, as it will be further discussed, interaction with several immune system components resulting in a feedback loop that enhances the production of more ACPAs and proinflammatory agents such as cytokines, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and degradative enzymes, among others (Figure 2). Interestingly, ACPAs have different mechanisms when they interact on their own or via Fc gamma receptor (FcγR) after forming immune complex (IC) with RF (Figure 2). A protective role of ACPAs has also been suggested (127), highlighting the functional diversity of these autoantibodies.

Figure 2. Representation of ACPA-mediated pathogenesis in synovium and crosstalk of different immune and structural components in seropositive RA. Main ACPA-derived response on different cell types is stated. APCs, antigen presenting cells; CXCR3, chemokine receptor 3; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FcγR, Fc gamma receptor; FLS, fibroblast-like synoviocytes grp78, glucose regulated protein 78; JNK, Jun kinase; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; MCS, macrophage colony stimulator; NETs, neutrophil extracellular traps; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; PAD, protein arginine deaminase; PI, proinflammatory; RF, rheumatoid factor; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4; *reported via IC mediation; **reported both via IC and ACPA mediation. Created with BioRender.
Pointing out the effect of ACPA in different immune subsets, evidence shows that T follicular Th cells responses were reported higher in ACPA/+ than in ACPA/- (96). On the other hand, percentage of disease relevant Th17 was not dependent on seropositivity (91, 92).
ACPAs interaction with citrullinated glucose-regulated protein 78 (grp78) on macrophages’ surface reported activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK)1/2 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathways, as well as enhancing NF-κB activity and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) secretion (128–130). ACPAs can also activate macrophages via TLR4- and MyD88- dependent (131–133) or CD147-integrinb1-PI3K-Akt pathways, this last one activating NF-κB signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome cascade and pro-IL-1β release (134). Otherwise, when found as ICs with RF, monocytes were also stimulated by binding FcγRs which enhanced proinflammatory cytokine release in synovial membrane (135) as well as regulating differentiation into osteoclasts (136, 137). Breedveld et al. stimulated monocytes with SF isolated ICs, resulting in IL-6 and IL-8 release and subsequent activation of osteoclast activation (133, 138). Connection of PAD4 and macrophages in RA has been described. Enzymatically active PAD4 was found present on the monocyte surface, being a source of novel ACPA autoantigens by citrullinating both soluble and surface proteins (139). These findings correlate with the already reported role of SF and lymphoid tissue macrophages in citrullination of proteins and ACPA production (140). Interestingly, autocitrullination of PAD4, which is found in SF ACPA/- patients, exacerbated inflammatory arthritis in mice models through monocyte recruitment, suggesting an ACPA-independent role of PAD4 in RA pathogenesis (141).
Neutrophiles are another immune cell type targeted by ACPAs (142, 143). The already mentioned ICs have been reported to activate neutrophiles leading to cartilage and tissue destruction due to neutrophil degranulation, release of degradative enzymes, ROS, as well as activation of soluble receptors and cytokines causing general tissue inflammation (144, 145). NET formation has also been observed on SF and sera of RA patients (146–149), correlating to ACPA levels and their immune complexes, which enhances inflammatory response in synovial fibroblasts via activation of IL-6, IL-8 and adhesion molecules, among others (138, 147–149). Some forms of NETosis rely on PAD4 activity (150, 151) and results into citrullination of proteins (specially histones) in the synovial space, engaging a positive feedback loop for which either synovial autoreactive ACPA-producing B cells or direct presentation of citrullinated antigens to T cells by fibroblast-like synoviocytes leads to the production of more autoantibodies (148). Indirectly, neutrophils can also get activated through ACPA binding to osteoclasts, as this leads to secretion of CXCL8, promoting neutrophil attraction and NET release, which again increases ACPA activity through binding to citrullinated histones in the released NETs (152).
Even though the appearance of ACPAs has been linked to environmental factors as smoking and some viral infections (among others) (153, 154), ACPA/+ RA patients have shown a gene signature based on the already mentioned HLA complex, which is crucial for antigen presentation between immune cells. Both RA and ACPA development were found to be connected to HLA haplotypes expressing the shared epitope (SE), which codes for a QKRAA peptide motif on the MHC (153–157). Similarly, both humanized and non-humanized mice models expressing different RA-related haplotypes of HLA containing the SE generated ACPAs to a greater extent upon disease induction with PAD rather than those with haplotypes lacking SE (158, 159).
4 Current treatment landscape for rheumatoid arthritis
Current pharmacologic treatment options for RA can be divided into three major groups: steroids and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Steroids are only symptomatic and are not able to change the long-term course of the disease, therefore the European League Against Rheumatology (EULAR) recommendations for RA treatment utilizes conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs) methotrexate (MTX) as initial treatment, eventually in combination with short-term glucocorticoids during disease flares. In the case that csDMARDs are not effective, biological DMARDs (bDMARDs) (which are related mainly to cytokine regulation) or targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs) such as Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitors are employed. Here, multiple modes of action are available, underlining the immunopathological heterogeneity of RA (160). As it is illustrated in different cohorts, most of RA patients receive MTX while smaller fraction receive bDMARDs (161–163).
Treatments are aimed to reduce disease activity and prevent joint damage; managing RA follows treat-to-target strategies (164). If treatment target (which is based on remission in early disease and low disease activity in long-standing disease), is not achieved at 3 and 6 months, respectively, EULAR guidelines (2022) recommend a change in treatment regime.
The persistence of different groups of therapeutics in clinic has been reviewed over the last 6 years by several nation-wide organizations, with cohort ranging from 900 to 5100 RA patients. Depending on the cohort, TNF-α inhibitors (bDMARDs targeting TNF-α) have a retention rate of 29% to 58%, while in the case of JAK inhibitors, retention rates are 40% to 72% (165–167). Still, discontinuation rates due to adverse events are similar between TNF-α inhibitors and JAK inhibitors (168).
4.1 Challenges in achieving immunological remission
Existing treatments such as MTX and several costly biological therapies can slow disease progression but do not cure the disease. Depending on the cohort, range from 39% to 70% patients do not reach the preferred goal of sustained remission or low disease activity (161–163).
The effect of bDMARDs and JAK inhibitors can also be dependent on ACPA seropositivity. For example, drugs like the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (169), B cell depletor rituximab (170, 171) and T cell modulator abatacept (172) have better efficacy on seropositive groups, compared to seronegative groups. TNF inhibitors show similar efficacy in seropositive and seronegative disease (172).
In a cross-sectional analysis of RA patients treated with various csDMARDs and/or JAK inhibitors, Neppelenbroek et al. suggested that ACPA+ B cells retained their activated and proliferative phenotype, despite effective control of inflammation and clinical disease. The absence of immunological remission might explain why ACPA/+ patients rarely reach sustained drug-free remission. This continued activated state of ACPA-B cells indicates chronic exposure of these cells to stimulating triggers along disease course, which in this study was 11 years (average) (173). Tocilizumab, another FDA-approved bDMARD, managed to decrease synovial T cells and disease activity on patients after 8 weeks of treatment, but did not manage neither to decrease the count of CD68+ macrophages or CD20+ B cells in synovium, maintaining unchanged local levels of RANKL and significantly increasing systemic levels of IL-6 and RANKL (174), two cytokines that as previously mentioned, are expressed by synovial macrophages and B cells and are related to joint erosion (45, 133, 138).
Despite significant advances, current RA therapies do not achieve durable, immunological remission across all patient groups. Their effectiveness often depends on ACPA status, with seropositive individuals responding more favorably, yet still without showing immunological remission despite clinical improvement. To address this disparity, emerging antigen-specific therapeutic strategies are proposed as considerable therapeutics toward sustained immunological and disease-modifying remission.
5 Restoring immune tolerance: emerging mechanisms and therapeutic approaches
5.1 Fundamental mechanisms of tolerance restoration
Tolerogenesis or tolerance recovery is understood as the process by which the immune system re-establishes its ability to recognize and tolerate self-antigens, thereby preventing autoimmune responses and maintaining immune homeostasis. Mechanisms of immune tolerance can be broadly divided into central and peripheral tolerance. Central tolerance occurs primarily in the bone marrow and thymus, where autoreactive T cells undergo clonal deletion before entering the circulation (175, 176). Peripheral tolerance, by contrast, regulates mature T cells in the periphery through multiple mechanisms, including (i) T cell anergy, where T cells become non-proliferative upon antigen stimuli, commonly lack co-stimulatory molecules and are functionally inactive (177, 178); (ii) T cell ignorance, being ignorant T cells unresponsive to their autoantigens yet potentially able to be activated again (179); (iii) T cell exhaustion, associated with constant antigen exposure (180, 181); (iv) clonal deletion of mature T cells in the periphery, mediated through antigen presentation (182, 183).
Treg cells can suppress local immune responses elicited by Th cells upon receptor activation of disease-causing antigen (184, 185). Additionally, Treg expansion has been proved to reinduce tolerance (177, 186, 187). Highlighting the pivotal role of antigen-specific Treg expansion in tolerance recovery, imbalances in Th1/Treg and Th17/Treg (as well as Th1/Th2 ratios) are often associated with loss of tolerance in RA (17–20).
5.2 Established therapies with tolerogenic potential
The bDMARD abatacept targets CD80 and CD86 on the surface APCs including B cells. CD80 and CD86 are key co-stimulatory molecules for antigen presentation and T cell activation. In a study by Lorenzetti et al, in vitro abatacept treatment was shown to decrease CD80-CD86 expression on B cells in a dose-dependent manner. In contrast, clinical assessment revealed only a moderate reduction in ACPA levels but a significant decrease in the ACPA-specific B cell population, suggesting a restoration of tolerance (Figure 3) (188). The bDMARD rituximab targets CD20, leading to a depletion of B cell populations for 6-9 months (189), yet without elevating the likelihood of infections in patients relative to other forms of bDMARD treatment (190, 191). Tolerance recovery is suggested by the posterior regeneration of the B cell subpopulations, finding different subset composition than found before treatment (Figure 3) (192). Naïve B cell population increased, while CD27+ memory cells stayed significantly reduced (0.5-fold) for up to 2 years (192).

Figure 3. Principal mode of action of some of the tolerogenic drugs and drug candidates reviewed in this work. APCs, antigen presenting cells; CAR, Chimeric Antigen Receptor; CTLA-4, Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte Associated protein 4; PD-1, Programmed death cell protein; NETs, Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Created with BioRender.
6 Novel drug candidates and strategies for tolerance induction
Current RA treatments do not effectively target the underlaying immunologic causes of the disease, being reflected in the high relapse incidence and the large RA population that does not achieve complete remission. One study found that after 5 years of treatment, 55% of RA patients had switched treatment due to treatment failure or, to a lesser extent, due to adverse events (193). Given RA heterogeneity and that patients may require multiple successive therapies throughout life (160), there is a need for treatments employing different modes of action. This need is reflected in the several trials for RA treatment that have been reported during the last 10 years, where the main goal is to restore tolerance and “re-educate” the immune system rather than decrease inflammation by targeting its components (Figure 3, Table 1).
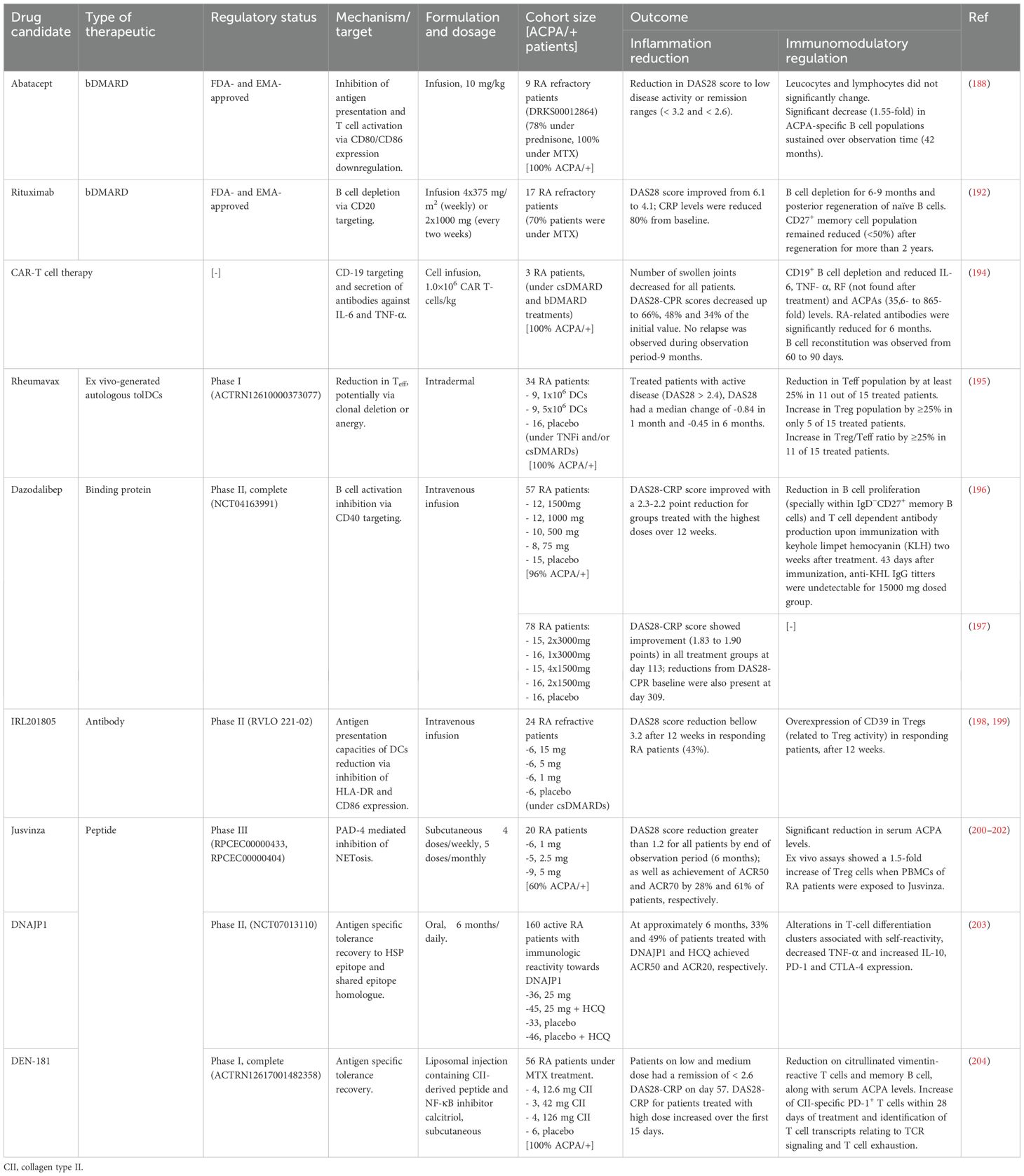
Table 1. Overview of therapeutic candidates discussed in this review with tolerogenic effects, either approved or under clinical investigation for RA.
6.1 Cell-based tolerance recovery therapies
In a small trial consisting of three patients with treatment resistant RA, CD19-directed Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell treatment caused B cell depletion and reduced the pathogenic interleukins IL-6 and TNF-α as well as RF and ACPA levels (194). Along with lowering joint inflammation and the absence of relapse, the progressive repopulation of B cells non-associated to an increase of pathogenic antibodies 9 months after treatment makes CAR-T therapy a promising tool to restore tolerance in difficult to treat cases (Table 1 for detailed information) (194). A reported case with this outcome described one RA patient treated with CD20/CD19-directed CAR-T cell therapy following a diagnosis of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (205). However, most available data for this type of treatment in RA come from very small cohorts, sometimes down to individual case reports (206, 207). In vitro data of similar CAR-T cell therapies backs up the previous results by eliminating autoreactive B cell populations from RA patients’ serum (208). However, longer and bigger trials need to be carried out to dismiss the serious toxic effects that this type of therapy is suspected to have in rheumatic autoimmune disease treatment (206, 209).
Ex vivo-generated autologous tolDCs introduced to a specific antigen have been explored due to their capacity to present antigens to T cells (210). TolDCs are not only able to cause T cell anergy or the expansion of Treg cells by providing constant exposition to the specific antigen in CIA murine model (211, 212), but they also express PD-1 and anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and IL-35 (213). Thus, it is understandable that peptide loaded tolDCs have been successfully utilized in multiple clinical trials aimed at restoring tolerance in autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis (214) and type I diabetes (215, 216). In the case of RA treatment, it is important to mention the few candidates that showed promising results in small cohort clinical trials phase I (9 to 18 patients), currently recruiting for further studies or ongoing clinical trials: Rheumavax (ACTRN12610000373077), AuToDeCRA (ISRCTN14999554) and CreaVax-RA (KCT0000894). AutoDeCRA tolDCs have been exposed to the antigens of the patients’ SF, while CreaVax-RA tolDCs have been exposed to PAD4, RA33 (heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 (hnRNP A2/B1)), citrullinated filaggrin and vimentin (217). AutoDeCRA trial failed to show efficacy on clinical inflammation parameters, changes in serum cytokine levels or in peripheral T cell phenotype (218). In the case of Rheumavax, consisting on tolDCs with the NF-κB pathway inhibited and exposed to citrullinated peptides derived from vimentin, collagen type II, aggrecan and fibrinogen, better results were observed. 1 month after Rheumavax treatment, T effector (Teff) cells were reduced compared to untreated controls, while the ratio of Treg/Teff increased, pointing to a shift in the immune balance (195). Cytokine IL-15, IL-29, CX3CL1 and CXCL11 levels as well as T cell mediated IL-6 response towards the citrullinated vimentin peptide found in Rheumavax were reduced (195). It is also worth mentioning the TOLERANT clinical study, which is in recruiting stage (phase I, NCT05251870). As well as the previously mentioned therapies, in this trial HSP70 peptide loaded DCs will be employed in order to induce and/or expand Treg populations (219).
6.2 Tolerogenic monoclonal antibodies and binding proteins
Peresolimab, an IgG monoclonal antibody that stimulates PD-1 pathway, showed a positive primary outcome by reducing DAS28 score compared to the placebo group 12 weeks after treatment in a phase II clinical trial. However, in secondary outcome measures, peresolimab was only significantly better than placebo with respect to ACR20 responses, but not with respect to ACR50 or ACR70 responses (220). Aiming for T cell activation suppression, peresolimab is intended to reset the immune response to restore immune tolerance (221). Differently, inhibiting B cell activation and plasma cell differentiation by means of CD40L binding protein targeting, dazodalibep was tested in a phase I trial (196). CD40 is expressed on many APCs (incl. DCs, macrophages and B cells) and non-hematopoietic cells. Effective humoral response to T cell-depending antigens rely heavily on CD40/CD40L interactions between B cells and T cells. Not only DAS28-CRP went down to -2.3 compared to baseline, but a significant reduction in B cell proliferation and T cell-dependent antibody production were reported (196). Further clinical trial (phase II, NCT04163991) confirmed the reduction of DAS28-CRP score over 309 days on a bigger cohort of 62 treated RA patients and 16 disease controls (197).
Part of HSP70 family, binding immunoglobulin protein (BiP) is involved in the peripheral blood monocytes differentiation into DCs and osteoclasts. Treatment of maturing monocytes with BiP results in reduced antigen presentation capacities of DCs due to lower expression of HLA-DR and CD86. Recombinant human BiP administration has been reported to prevent and ameliorate disease in murine CIA models (222, 223). BiP analogue IRL201805 was administrated to RA patients and its effects were monitored for 12 weeks in a phase I/IIa trial. DAS28 score was consistently reduced in the fraction of patients that responded to treatment (43%) (198) without any serious adverse drug reactions reported (199). When the 4 week-after treatment PBMCs of responder RA fraction was incubated with their own PBMCs before treatment, these ones produced significantly less IFN-γ than RA patients treated with placebo. As a part of the inflammatory response regulation, serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, TNF-α and IFN-γ were reduced while sCTLA-4 increased. Related to the pro- to anti-inflammatory shift observed in serum cytokine levels, Treg stability and potency related CD39 was found overexpressed in the Tregs of the patients responding to the treatment (198).
6.3 Peptide and antigen-based immunomodulatory therapies: emphasis on citrullination
Peptides emerge as highly specific and versatile drug candidates for tolerance recovery in RA and other autoimmune diseases (224–231). Their high specificity minimizes potential drug–drug interactions, making them suitable for combination with other RA therapeutics. Preliminary and exploratory trials in RA patients have employed them in combination with different csDMARDs reporting treatment efficacy and no concerning adverse effects (200, 203, 204). Compared to antibodies, their small size, enhanced stability, scalable production and customizable structure make peptides particularly attractive for achieving precise interactions with immune targets while maintaining relatively low immunogenicity and lower production cost characteristic of small molecules (232, 233).
The T cell-activating peptide based on the immunogenic HSP60 Jusvinza, approved in Cuba for cases of COVID-19 with hyperinflammation, is currently under clinical trials (phase III, RPCEC00000433) to treat RA patients. As it has been mentioned previously, NETosis is related to inflammation in RA as well as citrullination of new antigens and production of new ACPAs. Protein expression of neutrophiles from patients treated with Jusvinza was found to be differently modulated, including differences on the already mentioned NF-κB pathway (234). Overall, RA patients treated with Jusvinza displayed PAD4-mediated inhibition of NETosis, which was further confirmed with in vitro experiments (234). Phase I clinical trials in RA patients treated with Jusvinza showed a reduction on blood ACPA levels DAS28 score and achievement of ACR50 and ACR70 in 6 months (200, 201). Complementary, ex vivo assays showed a 1.5-fold increase of Treg cells when PBMCs of RA patients were exposed to Jusvinza (202), suggesting that tolerance recovery towards citrullinated antigens could be mediated by NETosis inhibition. Also derived from an HSP, T cell proinflammatory epitope DNAJP1 peptide was used to treat RA patients with PBMCs reactive towards the candidate (75% of the tested participants) in a clinical trial phase II (203). Upon treatment, TNF-α expressed by T cells decreased significantly while IL-10 expressed by T cell increased, along with PD-1 and CTLA-4 (203). These results match previous phase I outcomes for the same peptide, where DNAJP1-specific T cell number did not change over treatment (hence, there was no clonal deletion) but changes on clusters of differentiation on them pointed that immune reactivity towards the self-peptide did (235).
DEN-181, a subcutaneous formulation consisting of RA-joint HLA-DRB1*04:01- and *01:01-haplotypes specific collagen type II259-273 peptide and NF-κB pathway inhibitor calcitriol in liposome formulation, reduced the population of citrullinated vimentin-specific T cells in MTX-treated patients under a phase I clinical trial (204). The improvement in disease activity observed in RA patients was associated with the tolerogenic effects of the peptide-based therapy DEN-181, including an early expansion of PD1+ collagen type II– and citrullinated vimentin–specific T cells, followed by a reduction in ACPAs, an increase in CCR7+ naïve T cells and a decrease in memory B cells (204). CCR7+ expression in T cells is related to T cell migration from peripheral tissue to lymph node (236). Disruptions in this migratory process lead to peripheral tissue Teff cell accumulation in inflammation and autoimmunity, incl. RA (237). Used in DEN-181, calcitriol is a metabolite of vitamin D. Vitamin D has been reported to elevate the percentage of Tregs and lower the DAS-28 score just after 3 months of supplementation along MTX and hydroxychloroquine in RA patients, compared to a group that were just treated with the csDMARDs (238).
Citrullinated antigens have also demonstrated potential in promoting tolerance recovery. This process is typically achieved through the persistent exposure to the antigen via repeated administration of low doses, aiming to modulate T cell population by depleting or causing T cell exhaustion on pathologic Th1 and Th17 cells, reducing the expression of proinflammatory cytokines that mediate these, or increasing the population of Tregs (239). Gertel et al. utilized a multiepitope citrullinated peptide, containing motifs from key citrullinated proteins in RA such as filaggrin, fibrinogen, vimentin and collagen. Their approach successfully improved the clinical status of adjuvant-induced RA rats (Table 2). The increase of Treg and reduction in Th17 cells, previously associated with reactivity towards citrullinated epitopes (90–93), indicated tolerance induction (239).

Table 2. Summary of preclinical studies evaluating tolerogenic peptides and monoclonal ACPAs in murine RA models.
CEL-4000 consists of a proteoglycan (PG) non-citrullinated epitope derived from cartilage PG aggrecan (PG70) conjugated to a ligand specific for CD4+ T cells. This design allows the T cell presentation of the immunomodulatory peptide to an APC via MHC II while the CD4+ ligand modulates T- cell activity. CEL-4000 was tested in PG-induced arthritis (PGIA) and G1 domain-induced arthritis (GIA) mice models, switching cytokine production from Th1 and Th17 pro-inflammatory (TNF-α, IL-17 and IFN-γ) signature to an Th2 and Treg anti-inflammatory (IL-10, IL-4 and TGF-β) one, as well as an increase in Treg cells (240, 246). CEL-5000, which introduces a citrullinated PG epitope was also tested in PGIA and GIA mice models. CEL-4000 and CEL-5000 developed different immune responses, since mice did not produce high antibody titters for the citrullinated epitope conjugate while they did for CEL-4000’s. However, both treatments lowered arthritic score, reduced inflammation levels (assessed by immunohistochemistry) and achieved the same Th2-like anti-inflammatory cytokine response (240).
Fibrinogen-derived citrullinated peptides have been intensively investigated due to their high capacity to scavenge ACPA isolated from RA patients, showing that cyclized structures bind with higher affinities (247, 248). A fibrinogen-derived citrullinated cyclic peptide have also been reported to treat CIA rat, showing a significant decrease of joint swelling when compared to untreated or non-citrullinated peptide control groups, along with an increase of IL-10 (241). Data obtained from McElwee et al. suggests that citrullinated fibrinogen may have potent tolerogenic properties (242). When they immunized a transgenic HLA-DR mice model with citrullinated peptides derived from cartilage intermediate layer protein or fibrinogen, the arthritis-initiating response from CD4+ T cells upon presentation of citrullinated antigens was not observed. Instead, expansion of CD4+ T cell population binding to these HLA-DR:citrullinated peptides was observed, with lower levels of Th1 and higher levels of Treg cells. These results were not observed when same mice model was immunized with citrullinated vimentin or enolase 1 peptides (242). Restoration of Treg over Th or Teff cell populations and balance recovery was also seen in the already discussed Gertel et al. study, where the multiepitope used to treat adjuvant-induced RA rats contained citrullinated fibrinogen (239); or on the successful Rheumavax trial, which contained tolDCs introduced to citrullinated fibrinogen, among other citrullinated peptides (195).
6.4 Modulating ACPAs
Gomez et al. recently showed that the injection of several ACPAs isolated from RA patients ameliorated inflammation and disease severity in collagen antibody-induced arthritis (CAIA) model (127) adding up to a long list of examples where ACPAs had therapeutic or preventive effects in RA murine models (243, 244, 249). It is worth mentioning that in the experiments carried out by Gomez et al, patients derived ACPAs were grouped and dosed based on the predominant citrullinated antigen they targeted and all groups had similar effects specially when injecting in early steps of CAIA (127).
This seems to point out that in a target independent manner, ACPAs have the ability to induce tolerance (in earlier stages) or prevent break of tolerance that will exacerbate the disease in a CAIA model (Figure 4A). He et al. also injected patient derived ACPAs in healthy mice to observe neither arthritogenicity nor pain signs. One of the antibodies protected the mice from antibody-induced arthritis (CAIA model) by forming ICs with citrullinated α-enolase and other few citrullinated proteins from SF which posteriorly bound to macrophages in the joints, resulting in increased secretion of anti-inflammatory IL-10 and reduced osteoclastogenesis (243). Authors attributed the reduction of osteoclastogenesis to the interaction of the interaction of these ICs with FcγRIIB in macrophages (Figure 4A) (136, 243). Another example of ACPA usage to prevent the development of inflammation not only in CAIA RA model but also in other NET-mediated pathologies as inflammatory bowel disease, pulmonary fibrosis and sepsis, was reported by Chirivi et al. (245) They developed an ACPA that specifically targets citrullinated histones citH2A and citH4, which are generated during NET release. Their lead therapeutic ACPA prevented the inflammatory response in several autoimmune models (incl. CAIA), reduced inflammation in CIA mice RA model, inhibited NET formation in both murine models and in vitro experiments where healthy individuals neutrophiles were stimulated with different disease-related stimuli (including SF containing ACPAs from RA patients) and potentially favoured macrophage mediated clearance of NETs (Figure 4B) (245).

Figure 4. Role of ACPAs in prevention of tolerance breach in murine RA models. (A) Injection of ACPAs isolated from RA patients prevented inflammation and disease progression in CAIA model (127, 243). ACPAs were shown to form ICs with citrullinated proteins and interact with FcγRs IIB from osteoclasts, promoting IL-10 release and reducing their osteoclastogenesis (136, 243). (B) Treatment with tACPA targeting citrullinated histones citH2A and citH4 prevented the development of inflammatory response in CAIA mice and inhibited NETosis in both murine model and human neutrophile stimulated with SF from RA patients and other disease stimuli. IC, Immune Complex; tACPA, therapeutic ACPA; cit., citrullinated (245). Created with BioRender.
7 Conclusions and future perspectives
Restoring immune tolerance in RA marks a meaningful transition in therapeutic strategies, focusing on re-educating the immune system rather than just suppressing its activity. Promising preclinical and early clinical evidence supports this approach, indicating that targeting the underlaying mechanisms of autoimmunity may provide durable disease control with reduced systemic immunosupresion.
Peptide-based immunotherapies, such as Jusvinza, DNAJP1, Rheumavax and DEN-181 have demonstrated the capacity to modulate key immune pathways, Treg populations, lowering Th1/Th17-driven inflammation, and, in some cases, reducing circulating ACPA levels. Parallelly, tolerogenic cell therapies and monoclonal antibodies targeting co-stimulatory pathways (e.g., abatacept, peresolimab, dazodalibep) further highlight the feasibility of antigen-specific or pathway-guided tolerance induction. Collectively, these advances mark a gradual yet meaningful transition toward tolerogenic disease-modifying strategies.
Among these emerging modalities, peptide-based therapies offer several advantages over extensively used monoclonal antibodies. Tolerogenic peptides engage with autoreactive T and B cells with high specificity while being synthetically accessible, structurally well defined, and easier to rationalize for epitope optimization. Compared to monoclonal antibodies or binding proteins, their lower production costs and stability further enhance their suitability for long-term or preventive use.
Dose requirements also illustrate peptides efficiencies for the described preliminary and exploratory trials. As summarized in Table 1, DEN-181 achieved immunomodulatory effects at only 126 µg of CII peptide in a single dose, and Jusvinza demonstrated clinical tolerogenic benefits with 5 doses of 5 mg, both markedly lower than conventional csDMARDs (e.g., ≥7.5 mg/week for methotrexate or 400 mg/day for hydroxychloroquine, both according to FDA label) and substantially below the 2 g required for B-cell depletion with rituximab.
Administration routes constitute another advantage of peptide-based tolerogenic approaches. Subcutaneous formulations, as shown for DEN-181, Jusvinza and CPEP02 (in preclinical development), successfully induced immune modulation, while oral administration of DNAJP1 achieved significant T-cell phenotypic and cytokine profile shifts. Although daily dosing over six months was required, the total 4.5 g peptide exposure remains feasible considering the production scales of peptides compared to those of monoclonal antibodies. The DNAJP1 trials thus represent a key milestone in advancing orally delivered tolerogenic immunotherapies, with future peptide design optimization likely to improve dosage efficiency and patient compliance.
Despite these advances, achieving long-term immune tolerance requires a deeper understanding of the immune regulation, ACPA biology and the precise mechanisms that drive autoimmunity in RA. The absence of a prevalent murine model used in preclinical research (Table 2), complicates preclinical translation. Therefore, quantitative joint swelling measurements (paw diameter) and harmonized disease scoring systems should be adopted as standardized endpoints to facilitate cross-study comparison. Splenic or synovial cell profiling, which is not carried out in most preclinical studies described, is essential to elucidate the tolerogenic effects of these treatments in immune cell differentiation and regulation.
Future research must address these gaps through systems-level analyses integrating multi-omics, single-cell immunophenotyping, and spatial transcriptomics to map the dynamics of tolerance restoration in vivo. Such efforts will be critical to distinguish true immune reprogramming from transient immunomodulation.
In summary, the combination of peptide-based therapies with conventional DMARDs or targeted biologics also represents a promising therapeutic framework to enhance efficacy and maintain remission while minimizing systemic immunosuppression, reducing the risk of relapsing and improving the quality of life for patients with RA.
Author contributions
AB: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MB: Writing – review & editing. TK: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. KA: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This review paper was funded by DTU Alliance PhD programme.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. World Health Organization. Rheumatoid arthritis (2023). Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/rheumatoid-arthritis (Accessed December 9, 2024).
2. Song Y, Chen Y, Wen L, He B, Ding Y, Liu M, et al. Health-related quality of life profiles in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a latent profile analysis. Front Public Heal. (2024) 12:1478376/BIBTEX. doi: 10.3389/FPUBH.2024.1478376/BIBTEX
3. Katchamart W, Narongroeknawin P, Chanapai W, and Thaweeratthakul P. Health-related quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Rheumatol. (2019) 3:1–8. doi: 10.1186/S41927-019-0080-9/TABLES/5
4. Alenius GM, Berglin E, and Rantapää Dahlqvist S. Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) in psoriatic patients with or without joint inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. (2006) 65:398–400. doi: 10.1136/ARD.2005.040998
5. Schellekens GA, De Jong BAW, Van Den Hoogen FHJ, Van De Putte LBA, and Van Venrooij WJ. Citrulline is an essential constituent of antigenic determinants recognized by rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies. J Clin Invest. (1998) 101:273. doi: 10.1172/JCI1316
6. Rantapää-Dahlqvist S, De Jong BAW, Berglin E, Hallmans G, Wadell G, Stenlund H, et al. Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide and IgA rheumatoid factor predict the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. (2003) 48:2741–9. doi: 10.1002/ART.11223
7. Bas S, Perneger TV, Seitz M, Tiercy JM, Roux-Lombard P, and Guerne PA. Diagnostic tests for rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies, anti-keratin antibodies and IgM rheumatoid factors. Rheumatology. (2002) 41:809–14. doi: 10.1093/RHEUMATOLOGY/41.7.809
8. Umemoto A, Kuwada T, Murata K, Shiokawa M, Ota S, Murotani Y, et al. Identification of anti-citrullinated osteopontin antibodies and increased inflammatory response by enhancement of osteopontin binding to fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2023) 25. doi: 10.1186/S13075-023-03007-9
9. Floris A, Angioni MM, Fadda M, Naitza MR, Congia M, Chessa E, et al. The role of Anti-PAD4, Anti-CarP, and Anti-RA33 antibodies combined with RF and ACPA in predicting abatacept response in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2025) 27:1–9. doi: 10.1186/S13075-024-03470-Y
10. Lara-Ramírez EE, Cuevas-Córdoba B, Olguín-Calderon D, Bastian Y, Ramos-Remus C, Castillo-Ortiz JD, et al. Evaluation of anti-citrullinated and anti-carbamylated antibodies in mexicans with rheumatoid arthritis and at-risk individuals. Rev Investig Clínica. (2024) 76:243–52. doi: 10.24875/RIC.24000181
11. Kronzer VL, Hayashi K, Yoshida K, Davis JM, McDermott GC, Huang W, et al. Autoantibodies against citrullinated and native proteins and prediction of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: A nested case-control study. Lancet Rheumatol. (2023) 5:e77–87. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(22)00380-0
12. Deane KD, O’Donnell CI, Hueber W, Majka DS, Lazar AA, Derber LA, et al. The number of elevated cytokines/chemokines in pre-clinical seropositive rheumatoid arthritis predicts time to diagnosis in an age-dependent manner. Arthritis Rheum. (2010) 62:3172. doi: 10.1002/ART.27638
13. Nielen MMJ, Van Schaardenburg D, Reesink HW, Van De Stadt RJ, Van Der Horst-Bruinsma IE, De Koning MHMT, et al. Specific autoantibodies precede the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis: a study of serial measurements in blood donors. Arthritis Rheum. (2004) 50:380–6. doi: 10.1002/ART.20018
14. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. (2010) 62:2569–81. doi: 10.1002/ART.27584
15. Chin A, Small A, Wong SW, and Wechalekar MD. T cell dysregulation in rheumatoid arthritis: from genetic susceptibility to established disease. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2025) 27:1–12. doi: 10.1007/S11926-025-01180-1/FIGURES/1
16. Inamo J, Keegan J, Griffith A, Ghosh T, Horisberger A, Howard K, et al. Deep immunophenotyping reveals circulating activated lymphocytes in individuals at risk for rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. (2025) 135:e185217. doi: 10.1172/JCI185217
17. Bettelli E, Oukka M, and Kuchroo VK. TH-17 cells in the circle of immunity and autoimmunity. Nat Immunol. (2007) 8:345–50. doi: 10.1038/ni0407-345
18. Hot A, Zrioual S, Toh ML, Lenief V, and Miossec P. IL-17A- versus IL-17F-induced intracellular signal transduction pathways and modulation by IL-17RA and IL-17RC RNA interference in rheumatoid synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis. (2011) 70:341–8. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.132233
19. Ding Q, Hu W, Wang R, Yang Q, Zhu M, Li M, et al. Signaling pathways in rheumatoid arthritis: implications for targeted therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:1–24. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01331-9
20. Schulze-Koops H and Kalden JR. The balance of Th1/Th2 cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. (2001) 15:677–91. doi: 10.1053/BERH.2001.0187
21. Murray-Brown W, Guo Y, Small A, Lowe K, Weedon H, Smith MD, et al. Differential expansion of T peripheral helper cells in early rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis synovium. RMD Open. (2022) 8:2563. doi: 10.1136/RMDOPEN-2022-002563
22. Dunlap G, Wagner A, Meednu N, Wang R, Zhang F, Ekabe JC, et al. Clonal associations between lymphocyte subsets and functional states in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:1–21. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49186-0
23. Zwerina J, Hayer S, Tohidast-Akrad M, Bergmeister H, Redlich K, Feige U, et al. Single and combined inhibition of tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, and RANKL pathways in tumor necrosis factor-induced arthritis: effects on synovial inflammation, bone erosion, and cartilage destruction. Arthritis Rheum. (2004) 50:277–90. doi: 10.1002/ART.11487;JOURNAL:JOURNAL:15290131;REQUESTEDJOURNAL:JOURNAL:15290131;WGROUP:STRING:PUBLICATION
24. Carvalheiro H, Duarte C, Silva-Cardoso S, Da Silva JAP, and Souto-Carneiro MM. CD8+ T cell profiles in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and their relationship to disease activity. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2015) 67:363–71. doi: 10.1002/ART.38941;PAGE:STRING:ARTICLE/CHAPTER
25. Moon JS, Younis S, Ramadoss NS, Iyer R, Sheth K, Sharpe O, et al. Cytotoxic CD8+ T cells target citrullinated antigens in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:1–15. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35264-8
26. Iwata Y, Matsushita T, Horikawa M, DiLillo DJ, Yanaba K, Venturi GM, et al. Characterization of a rare IL-10-competent B-cell subset in humans that parallels mouse regulatory B10 cells. Blood. (2011) 117:530–41. doi: 10.1182/BLOOD-2010-07-294249
27. Carter NA, Rosser EC, and Mauri C. Interleukin-10 produced by B cells is crucial for the suppression of Th17/Th1 responses, induction of T regulatory type 1 cells and reduction of collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2012) 14:R32. doi: 10.1186/AR3736
28. Mohib K, Cherukuri A, Zhou Y, Ding Q, Watkins SC, and Rothstein DM. Antigen-dependent interactions between regulatory B cells and T cells at the T:B border inhibit subsequent T cell interactions with DCs. Am J Transplant. (2020) 20:52–63. doi: 10.1111/AJT.15546/ATTACHMENT/DA3E9522-5899-4306-B2C1-08F8F3B2279F/MMC8-SUP8-LEGENDS.PDF
29. Aoun M, Coelho A, Krämer A, Saxena A, Sabatier P, Beusch CM, et al. Antigen-presenting autoreactive B cells activate regulatory T cells and suppress autoimmune arthritis in mice. J Exp Med. (2023) 220:e20230101. doi: 10.1084/jem.20230101
30. Honda T, Egen JG, Lämmermann T, Kastenmüller W, Torabi-Parizi P, and Germain RN. Tuning of antigen sensitivity by TCRT cell receptor-dependent negative feedback controls T cell effector function in inflamed tissues. Immunity. (2014) 40:235. doi: 10.1016/J.IMMUNI.2013.11.017
31. Oestreich KJ, Yoon H, Ahmed R, and Boss JM. NFATc1 regulates PD-1 expression upon T cell activation. J Immunol. (2008) 181:4832–9. doi: 10.4049/JIMMUNOL.181.7.4832
32. Nakamoto N, Cho H, Shaked A, Olthoff K, Valiga ME, Kaminski M, et al. Synergistic reversal of intrahepatic HCV-specific CD8 T cell exhaustion by combined PD-1/CTLA-4 blockade. PloS Pathog. (2009) 5:e1000313. doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PPAT.1000313
33. Nettersheim FS, Brunel S, Sinkovits RS, Armstrong SS, Roy P, Billitti M, et al. PD-1 and CD73 on naive CD4+ T cells synergistically limit responses to self. Nat Immunol. (2024) 26:105–15. doi: 10.1038/s41590-024-02021-6
34. Guo Y, Walsh AM, Canavan M, Wechalekar MD, Cole S, Yin X, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor PD-1 pathway is down-regulated in synovium at various stages of rheumatoid arthritis disease progression. PloS One. (2018) 13:e0192704. doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0192704
35. Liu C, Jiang J, Gao L, Wang X, Hu X, Wu M, et al. Soluble PD-1 aggravates progression of collagen-induced arthritis through Th1 and Th17 pathways. Arthritis Res Ther. (2015) 17:1–13. doi: 10.1186/S13075-015-0859-Z/FIGURES/6
36. Li S, Liao W, Chen M, Shan S, Song Y, Zhang S, et al. Expression of programmed death-1 PD-1. on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation. (2014) 37:116–21. doi: 10.1007/S10753-013-9718-8/FIGURES/3
37. Belkhir R, Le Burel S, Dunogeant L, Marabelle A, Hollebecque A, Besse B, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and polymyalgia rheumatica occurring after immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. (2017) 76:1747–50. doi: 10.1136/ANNRHEUMDIS-2017-211216
38. Fanelli G, Romano M, Nova-Lamperti E, Sunderland MW, Nerviani A, Scottà C, et al. PD-L1 signaling on human memory CD4+ T cells induces a regulatory phenotype. PloS Biol. (2021) 19:e3001199. doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PBIO.3001199
39. Estrada-Capetillo L, Hernández-Castro B, Monsiváis-Urenda A, Alvarez-Quiroga C, Layseca-Espinosa E, Abud-Mendoza C, et al. Induction of th17 lymphocytes and treg cells by monocyte-derived dendritic cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol Res. (2013) 2013:584303. doi: 10.1155/2013/584303
40. Moura RA, Cascão R, Perpétuo I, Canhão H, Vieira-sousa E, Mourão AF, et al. Cytokine pattern in very early rheumatoid arthritis favours B-cell activation and survival. Rheumatology. (2011) 50:278–82. doi: 10.1093/RHEUMATOLOGY/KEQ338
41. Zhang L, Xiao H, Zhang F, Wu YJ, Shu JL, Li Y, et al. BAFF, involved in B cell activation through the NF-κB pathway, is related to disease activity and bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2021) 42:1665–75. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-00582-4
42. Herlands RA, Christensen SR, Sweet RA, Hershberg U, and Shlomchik MJ. T cell-independent and toll-like receptor-dependent antigen-driven activation of autoreactive B cells. Immunity. (2008) 29:249–60. doi: 10.1016/J.IMMUNI.2008.06.009/ATTACHMENT/9130E48E-1041-4BF7-8090-92D63BB82F16/MMC1.PDF
43. Pone EJ, Zhang J, Mai T, White CA, Li G, Sakakura JK, et al. BCR-signalling synergizes with TLR-signalling for induction of AID and immunoglobulin class-switching through the non-canonical NF-κB pathway. Nat Commun. (2012) 3:767. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1769
44. Wu H, Su S, Wu Y, Wu Y, Zhang Z, and Chen Q. Nanoparticle-facilitated delivery of BAFF-R siRNA for B cell intervention and rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 88:106933. doi: 10.1016/J.INTIMP.2020.106933
45. Yeo L, Toellner KM, Salmon M, Filer A, Buckley CD, Raza K, et al. Cytokine mRNA profiling identifies B cells as a major source of RANKL in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2011) 70:2022–8. doi: 10.1136/ARD.2011.153312
46. Niu X, He D, Zhang X, Yue T, Li N, Zhang JZ, et al. IL-21 regulates Th17 cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Immunol. (2010) 71:334–41. doi: 10.1016/J.HUMIMM.2010.01.010
47. Fousert E, Toes R, and Desai J. Neutrophil extracellular traps NETs. Take the central stage in driving autoimmune responses. Cells. (2020) 9:915. doi: 10.3390/CELLS9040915
48. Skopelja-Gardner S, Jones JD, and Rigby WFC. NETtling” the host: Breaking of tolerance in chronic inflammation and chronic infection. J Autoimmun. (2018) 88:1–10. doi: 10.1016/J.JAUT.2017.10.008
49. O’Neil LJ and Kaplan MJ. Neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis: breaking immune tolerance and fueling disease. Trends Mol Med. (2019) 25:215–27. doi: 10.1016/J.MOLMED.2018.12.008
50. Demoruelle MK, Bowers E, Lahey LJ, Sokolove J, Purmalek M, Seto NL, et al. Antibody responses to citrullinated and noncitrullinated antigens in the sputum of subjects with rheumatoid arthritis and subjects at risk for development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2018) 70:516–27. doi: 10.1002/ART.40401
51. Demoruelle MK, Harrall KK, Ho L, Purmalek MM, Seto NL, Rothfuss HM, et al. Anti–citrullinated protein antibodies are associated with neutrophil extracellular traps in the sputum in relatives of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2017) 69:1165–75. doi: 10.1002/ART.40066
52. Ytterberg AJ, Joshua V, Reynisdottir G, Tarasova NK, Rutishauser D, Ossipova E, et al. Shared immunological targets in the lungs and joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Identification and validation. Ann Rheum Dis. (2015) 74:1772–7. doi: 10.1136/ANNRHEUMDIS-2013-204912/ATTACHMENT/4B04654F-910E-47A2-871A-8A084A62E899/MMC3.PDF
53. Willis VC, Demoruelle MK, Derber LA, Chartier-Logan CJ, Parish MC, Pedraza IF, et al. Sputum autoantibodies in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis and subjects at risk of future clinically apparent disease. Arthritis Rheum. (2013) 65:2545–54. doi: 10.1002/ART.38066
54. Makrygiannakis D, Hermansson M, Ulfgren AK, Nicholas AP, Zendman AJW, Eklund A, et al. Smoking increases peptidylarginine deiminase 2 enzyme expression in human lungs and increases citrullination in BAL cells. Ann Rheum Dis. (2008) 67:1488–92. doi: 10.1136/ARD.2007.075192
55. Chrysanthopoulou A, Mitroulis I, Apostolidou E, Arelaki S, Mikroulis D, Konstantinidis T, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote differentiation and function of fibroblasts. J Pathol. (2014) 233:294–307. doi: 10.1002/PATH.4359
56. Hosseinzadeh A, Thompson PR, Segal BH, and Urban CF. Nicotine induces neutrophil extracellular traps. J Leukoc Biol. (2016) 100:1105–12. doi: 10.1189/JLB.3AB0815-379RR
57. Gremese E, Tolusso B, Bruno D, Alivernini S, and Ferraccioli G. Infectious agents breaking the immunological tolerance: The holy grail in rheumatoid arthritis reconsidered. Autoimmun Rev. (2022) 21:103102. doi: 10.1016/J.AUTREV.2022.103102
58. Holers VM, Demoruelle KM, Buckner JH, James EA, Firestein GS, Robinson WH, et al. Distinct mucosal endotypes as initiators and drivers of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2024) 20:601–13. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01154-0
59. Arleevskaya MI, Kravtsova OA, Lemerle J, Renaudineau Y, and Tsibulkin AP. How rheumatoid arthritis can result from provocation of the immune system by microorganisms and viruses. Front Microbiol. (2016) 7:1296/PDF. doi: 10.3389/FMICB.2016.01296/PDF
60. Balandraud N, Roudier J, and Roudier C. Epstein–Barr virus and rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. (2004) 3:362–7. doi: 10.1016/J.AUTREV.2004.02.002
61. Scher JU, Joshua V, Artacho A, Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Öckinger J, Kullberg S, et al. The lung microbiota in early rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmunity. Microbiome. (2016) 4:60. doi: 10.1186/S40168-016-0206-X/FIGURES/4
62. Scher JU, Sczesnak A, Longman RS, Segata N, Ubeda C, Bielski C, et al. Expansion of intestinal Prevotella copri correlates with enhanced susceptibility to arthritis. Elife. (2013) 2013:e01202. doi: 10.7554/eLife.01202
63. Thompson KN, Bonham KS, Ilott NE, Britton GJ, Colmenero P, Bullers SJ, et al. Alterations in the gut microbiome implicate key taxa and metabolic pathways across inflammatory arthritis phenotypes. Sci Transl Med. (2023) 15. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abn4722
64. Zhang X, Zhang D, Jia H, Feng Q, Wang D, Liang D, et al. The oral and gut microbiomes are perturbed in rheumatoid arthritis and partly normalized after treatment. Nat Med. (2015) 21:895–905. doi: 10.1038/nm.3914
65. Yosri M, Dokhan M, Aboagye E, Al Moussawy M, and Abdelsamed HA. Mechanisms governing bystander activation of T cells. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1465889/XML. doi: 10.3389/FIMMU.2024.1465889/XML
66. Bo M, Niegowska M, Eames HL, Almuttaqi H, Arru G, Erre GL, et al. Antibody response to homologous epitopes of Epstein-Barr virus, Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis and IRF5 in patients with different connective tissue diseases and in mouse model of antigen-induced arthritis. J Transl Autoimmun. (2020) 3:100048. doi: 10.1016/J.JTAUTO.2020.100048
67. Duffau P, Menn-Josephy H, Cuda CM, Dominguez S, Aprahamian TR, Watkins AA, et al. Promotion of inflammatory arthritis by interferon regulatory factor 5 in a mouse model. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2015) 67:3146–57. doi: 10.1002/ART.39321
68. Kharlamova N, Jiang X, Sherina N, Potempa B, Israelsson L, Quirke AM, et al. Antibodies to porphyromonas gingivalis indicate interaction between oral infection, smoking, and risk genes in rheumatoid arthritis etiology. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2016) 68:604–13. doi: 10.1002/ART.39491
69. Lundberg K, Wegner N, Yucel-Lindberg T, and Venables PJ. Periodontitis in RA—the citrullinated enolase connection. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2010) 6:727–30. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2010.139
70. McGraw WT, Potempa J, Farley D, and Travis J. Purification, characterization, and sequence analysis of a potential virulence factor from porphyromonas gingivalis, peptidylarginine deiminase. Infect Immun. (1999) 67:3248. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.7.3248-3256.1999
71. Seifert JA, Bemis EA, Ramsden K, Lowell C, Polinski K, Feser M, et al. Association of antibodies to prevotella copri in anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide-positive individuals at risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis and in patients with early or established rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2023) 75:507–16. doi: 10.1002/ART.42370
72. Rooney CM, Mankia K, Mitra S, Moura IB, Emery P, and Wilcox MH. Perturbations of the gut microbiome in anti-CCP positive individuals at risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. (2021) 60:3380–7. doi: 10.1093/RHEUMATOLOGY/KEAA792
73. Luo Y, Tong Y, Wu L, Niu H, Li Y, Su LC, et al. Alteration of gut microbiota in individuals at high-risk for rheumatoid arthritis associated with disturbed metabolome and the initiation of arthritis through the triggering of mucosal immunity imbalance. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2023) 75:1736–48. doi: 10.1002/ART.42616
74. Pianta A, Arvikar S, Strle K, Drouin EE, Wang Q, Costello CE, et al. Evidence of the immune relevance of prevotella copri, a gut microbe, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2017) 69:964–75. doi: 10.1002/ART.40003/ABSTRACT
75. Lefferts AR, Norman E, Claypool DJ, Kantheti U, and Kuhn KA. Cytokine competent gut-joint migratory T Cells contribute to inflammation in the joint. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:932393/BIBTEX. doi: 10.3389/FIMMU.2022.932393/BIBTEX
76. Kinslow JD, Blum LK, Deane KD, Demoruelle MK, Okamoto Y, Parish MC, et al. Elevated igA plasmablast levels in subjects at risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2016) 68:2372–83. doi: 10.1002/ART.39771/ABSTRACT
77. Elliott SE, Kongpachith S, Lingampalli N, Adamska JZ, Cannon BJ, Mao R, et al. Affinity maturation drives epitope spreading and generation of proinflammatory anti–citrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2018) 70:1946–58. doi: 10.1002/ART.40587/ABSTRACT
78. Roos Ljungberg K, Martinsson K, Wetterö J, Svärd A, and Kastbom A. Circulating anti-citrullinated protein antibodies containing secretory component are prognostic for arthritis onset in at-risk patients. Clin Exp Immunol. (2021) 204:344–51. doi: 10.1111/CEI.13591
79. Chriswell ME, Lefferts AR, Clay MR, Hsu AR, Seifert J, Feser ML, et al. Clonal IgA and IgG autoantibodies from individuals at risk for rheumatoid arthritis identify an arthritogenic strain of Subdoligranulum. Sci Transl Med. (2022) 14. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abn5166
80. Fireman EM and Fireman Klein E. Association between silicosis and autoimmune disease. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. (2024) 24:45–50. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000966
81. Pollard KM. Silica, silicosis, and autoimmunity. Front Immunol. (2016) 7:97/BIBTEX. doi: 10.3389/FIMMU.2016.00097/BIBTEX
82. Choi ST and Lee KH. Clinical management of seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: A comparative study. PloS One. (2018) 13:e0195550. doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0195550
83. Kongpachith S, Lingampalli N, Ju CH, Blum LK, Lu DR, Elliott SE, et al. Affinity maturation of the anti–citrullinated protein antibody paratope drives epitope spreading and polyreactivity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2019) 71:507–17. doi: 10.1002/ART.40760/ABSTRACT
84. Alghamdi M, Alasmari D, Assiri A, Mattar E, Aljaddawi AA, Alattas SG, et al. An overview of the intrinsic role of citrullination in autoimmune disorders. J Immunol Res. (2019) 2019:7592851. doi: 10.1155/2019/7592851
85. Chen Y, Teng Y, Xu P, and Wang S. The role of citrullination modification in CD4+ T cells in the pathogenesis of immune-related diseases. Biomolecules. (2024) 14:400. doi: 10.3390/BIOM14040400
86. Ireland JM and Unanue ER. Autophagy in antigen-presenting cells results in presentation of citrullinated peptides to CD4 T cells. J Exp Med. (2011) 208:2625–32. doi: 10.1084/JEM.20110640
87. Hill JA, Southwood S, Sette A, Jevnikar AM, Bell DA, and Cairns E. Cutting edge: the conversion of arginine to citrulline allows for a high-affinity peptide interaction with the rheumatoid arthritis-associated HLA-DRB1*0401 MHC class II molecule. J Immunol. (2003) 171:538–41. doi: 10.4049/JIMMUNOL.171.2.538
88. Sun B, Chang HH, Salinger A, Tomita B, Bawadekar M, Holmes CL, et al. Reciprocal regulation of Th2 and Th17 cells by PAD2-mediated citrullination. JCI Insight. (2019) 4:e129687. doi: 10.1172/JCI.INSIGHT.129687
89. Loos T, Mortier A, Gouwy M, Ronsse I, Put W, Lenaerts JP, et al. Citrullination of CXCL10 and CXCL11 by peptidylarginine deiminase: a naturally occurring posttranslational modification of chemokines and new dimension of immunoregulation. Blood. (2008) 112:2648–56. doi: 10.1182/BLOOD-2008-04-149039
90. James EA, Rieck M, Pieper J, Gebe JA, Yue BB, Tatum M, et al. Citrulline-specific Th1 cells are increased in rheumatoid arthritis and their frequency is influenced by disease duration and therapy. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2014) 66:1712–22. doi: 10.1002/ART.38637
91. Wang T, Rui J, Shan W, Xue F, Feng D, Dong L, et al. Imbalance of Th17, Treg, and helper innate lymphoid cell in the peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. (2022) 41:3837–49. doi: 10.1007/S10067-022-06315-8
92. Paradowska-Gorycka A, Wajda A, Romanowska-Próchnicka K, Walczuk E, Kuca-Warnawin E, Kmiolek T, et al. Th17/treg-related transcriptional factor expression and cytokine profile in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:572858/BIBTEX. doi: 10.3389/FIMMU.2020.572858/BIBTEX
93. Dong L, Wang X, Tan J, Li H, Qian W, Chen J, et al. Decreased expression of microRNA-21 correlates with the imbalance of Th17 and Treg cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Cell Mol Med. (2014) 18:2213–24. doi: 10.1111/JCMM.12353
94. Wu X, Liu Y, Jin S, Wang M, Jiao Y, Yang B, et al. Single-cell sequencing of immune cells from anticitrullinated peptide antibody positive and negative rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:1–15. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25246-7
95. Thorarinsdottir K, Camponeschi A, Jonsson C, Granhagen Önnheim K, Nilsson J, Forslind K, et al. CD21-/low B cells associate with joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Scand J Immunol. (2019) 90:e12792. doi: 10.1111/SJI.12792
96. Floudas A, Canavan M, McGarry T, Mullan R, Nagpal S, Veale DJ, et al. ACPA status correlates with differential immune profile in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cells. (2021) 10:647. doi: 10.3390/CELLS10030647
97. Floudas A, Neto N, Marzaioli V, Murray K, Moran B, Monaghan MG, et al. Pathogenic, glycolytic PD-1+ B cells accumulate in the hypoxic RA joint. JCI Insight. (2020) 5:e12792. doi: 10.1172/JCI.INSIGHT.139032
98. Takada H, Demoruelle MK, Deane KD, Nakamura S, Katsumata Y, Ikari K, et al. Expansion of HLA-DR positive peripheral helper T and naive B cells in anticitrullinated protein antibody-positive individuals at risk for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2024) 76:1023–35. doi: 10.1002/ART.42839
99. Fortea-Gordo P, Villalba A, Nuño L, Santos-Bórnez MJ, Peiteado D, Monjo I, et al. Circulating CD19+CD24hiCD38hi regulatory B cells as biomarkers of response to methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. (2020) 59:3081–91. doi: 10.1093/RHEUMATOLOGY/KEAA186
100. Romero V, Fert-Bober J, Nigrovic PA, Darrah E, Haque UJ, Lee DM, et al. Immune-mediated pore-forming pathways induce cellular hypercitrullination and generate citrullinated autoantigens in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Transl Med. (2013) 5:209ra150. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006869
101. Tilvawala R, Nguyen SH, Maurais AJ, Nemmara VV, Nagar M, Salinger AJ, et al. The rheumatoid arthritis-associated citrullinome. Cell Chem Biol. (2018) 25:691–704.e6. doi: 10.1016/J.CHEMBIOL.2018.03.002
102. Wang F, Chen FF, Gao WB, Wang HY, Zhao NW, Xu M, et al. Identification of citrullinated peptides in the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis using LC-MALDI-TOF/TOF. Clin Rheumatol. (2016) 35:2185–94. doi: 10.1007/S10067-016-3247-4/FIGURES/2
103. Lee CY, Wang D, Wilhelm M, Zolg DP, Schmidt T, Schnatbaum K, et al. Mining the human tissue proteome for protein citrullination. Mol Cell Proteomics. (2018) 17:1378–91. doi: 10.1074/MCP.RA118.000696
104. Van Beers JJBC, Schwarte CM, Stammen-Vogelzangs J, Oosterink E, Božič B, and Pruijn GJM. The rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid citrullinome reveals novel citrullinated epitopes in apolipoprotein E, myeloid nuclear differentiation antigen, and β-actin. Arthritis Rheum. (2013) 65:69–80. doi: 10.1002/ART.37720
105. Van Der Woude D, Rantapää-Dahlqvist S, Ioan-Facsinay A, Onnekink C, Schwarte CM, Verpoort KN, et al. Epitope spreading of the anti-citrullinated protein antibody response occurs before disease onset and is associated with the disease course of early arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2010) 69:1554–61. doi: 10.1136/ARD.2009.124537
106. Johansson L, Pratesi F, Brink M, Ärlestig L, D’Amato C, Bartaloni D, et al. Antibodies directed against endogenous and exogenous citrullinated antigens pre-date the onset of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2016) 18:1–11. doi: 10.1186/S13075-016-1031-0/FIGURES/4
107. Van Beers JJBC, Willemze A, Jansen JJ, Engbers GHM, Salden M, Raats J, et al. ACPA fine-specificity profiles in early rheumatoid arthritis patients do not correlate with clinical features at baseline or with disease progression. Arthritis Res Ther. (2013) 15:1–10. doi: 10.1186/AR4322/TABLES/2
108. Harre U, Georgess D, Bang H, Bozec A, Axmann R, Ossipova E, et al. Induction of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss by human autoantibodies against citrullinated vimentin. J Clin Invest. (2012) 122:1791–802. doi: 10.1172/JCI60975
109. Li Q, Li Y, Liang B, Xu R, Xu B, Lönnblom E, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis sera antibodies to citrullinated collagen type II bind to joint cartilage. Arthritis Res Ther. (2022) 24:1–11. doi: 10.1186/S13075-022-02945-0/FIGURES/5
110. Ge C, Tong D, Liang B, Lönnblom E, Schneider N, Hagert C, et al. Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies cause arthritis by cross-reactivity to joint cartilage. JCI Insight. (2017) 2:e93688. doi: 10.1172/JCI.INSIGHT.93688
111. Ge C, Xu B, Liang B, Lönnblom E, Lundström SL, Zubarev RA, et al. Structural basis of cross-reactivity of anti–citrullinated protein antibodies. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2019) 71:210–21. doi: 10.1002/ART.40698/ABSTRACT
112. Steen J, Forsström B, Sahlström P, Odowd V, Israelsson L, Krishnamurthy A, et al. Recognition of amino acid motifs, rather than specific proteins, by human plasma cell–derived monoclonal antibodies to posttranslationally modified proteins in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2019) 71:196–209. doi: 10.1002/ART.40699/ABSTRACT
113. Kissel T, Reijm S, Slot LM, Cavallari M, Wortel CM, Vergroesen RD, et al. Antibodies and B cells recognising citrullinated proteins display a broad cross-reactivity towards other post-translational modifications. Ann Rheum Dis. (2020) 79:472–80. doi: 10.1136/ANNRHEUMDIS-2019-216499
114. Sahlström P, Hansson M, Steen J, Amara K, Titcombe PJ, Forsström B, et al. Different hierarchies of anti–modified protein autoantibody reactivities in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2020) 72:1643–57. doi: 10.1002/ART.41385/ABSTRACT
115. Hafkenscheid L, Bondt A, Scherer HU, Huizinga TWJ, Wuhrer M, Toes REM, et al. Structural analysis of variable domain glycosylation of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis reveals the presence of highly sialylated glycans. Mol Cell Proteomics. (2017) 16:278–87. doi: 10.1074/MCP.M116.062919
116. Lloyd KA, Steen J, Amara K, Titcombe PJ, Israelsson L, Lundström SL, et al. Variable domain N-linked glycosylation and negative surface charge are key features of monoclonal ACPA: Implications for B-cell selection. Eur J Immunol. (2018) 48:1030–45. doi: 10.1002/EJI.201747446
117. Vergroesen RD, Slot LM, Hafkenscheid L, Koning MT, Van Der Voort EIH, Grooff CA, et al. B-cell receptor sequencing of anti-citrullinated protein antibody ACPA. IgG-expressing B cells indicates a selective advantage for the introduction of N-glycosylation sites during somatic hypermutation. Ann Rheum Dis. (2018) 77:955–7. doi: 10.1136/ANNRHEUMDIS-2017-212052
118. Rombouts Y, Willemze A, Van Beers JJBC, Shi J, Kerkman PF, Van Toorn L, et al. Extensive glycosylation of ACPA-IgG variable domains modulates binding to citrullinated antigens in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:578–85. doi: 10.1136/ANNRHEUMDIS-2014-206598
119. Zhao H, Wang H, Qin Y, Ling S, Zhai H, Jin J, et al. CCCTC-binding factor: the specific transcription factor of β-galactoside α-2,6-sialyltransferase 1 that upregulates the sialylation of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. (2024) 63:826–36. doi: 10.1093/RHEUMATOLOGY/KEAD282
120. Ohmi Y, Ise W, Harazono A, Takakura D, Fukuyama H, Baba Y, et al. Sialylation converts arthritogenic IgG into inhibitors of collagen-induced arthritis. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:1–12. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11205
121. Ahmed AA, Giddens J, Pincetic A, Lomino JV, Ravetch JV, Wang LX, et al. Structural characterization of anti-inflammatory immunoglobulin G fc proteins. J Mol Biol. (2014) 426:3166–79. doi: 10.1016/J.JMB.2014.07.006
122. Sondermann P, Pincetic A, Maamary J, Lammens K, and Ravetch JV. General mechanism for modulating immunoglobulin effector function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2013) 110:9868–72. doi: 10.1073/PNAS.1307864110/-/DCSUPPLEMENTAL
123. Krishnamurthy A, Circiumaru A, Sun J, Kisten Y, Damberg P, Sakuraba K, et al. Combination of two monoclonal anti–citrullinated protein antibodies induced tenosynovitis, pain, and bone loss in mice in a peptidyl arginine deiminase-4-dependent manner. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2023) 75:164–70. doi: 10.1002/ART.42320
124. Sun M, Rethi B, Krishnamurthy A, Joshua V, Circiumaru A, Hensvold AH, et al. Anticitrullinated protein antibodies facilitate migration of synovial tissue-derived fibroblasts. Ann Rheum Dis. (2019) 78:1621–31. doi: 10.1136/ANNRHEUMDIS-2018-214967
125. Corsiero E, Jagemann L, Perretti M, Pitzalis C, and Bombardieri M. Characterization of a synovial B cell–derived recombinant monoclonal antibody targeting stromal calreticulin in the rheumatoid joints. J Immunol. (2018) 201:1373–81. doi: 10.4049/JIMMUNOL.1800346
126. Engdahl C, Bang H, Dietel K, Lang SC, Harre U, and Schett G. Periarticular bone loss in arthritis is induced by autoantibodies against citrullinated vimentin. J Bone Miner Res. (2017) 32:1681–91. doi: 10.1002/JBMR.3158
127. Gomez AM, Brewer RC, Moon JS, Acharya S, Kongpachith S, Wang Q, et al. Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies with multiple specificities ameliorate collagen antibody-induced arthritis in a time-dependent manner. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2024) 76:181–91. doi: 10.1002/ART.42679
128. Lu MC, Lai NS, Yin WY, Yu HC, Bin HH, Tung CH, et al. Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies activated ERK1/2 and JNK mitogen-activated protein kinases via binding to surface-expressed citrullinated GRP78 on mononuclear cells. J Clin Immunol. (2013) 33:558–66. doi: 10.1007/S10875-012-9841-6/FIGURES/6
129. Lu MC, Lai NS, Yu HC, Huang HB, Hsieh SC, and Yu CL. Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies bind surface-expressed citrullinated Grp78 on monocyte/macrophages and stimulate tumor necrosis factor α production. Arthritis Rheum. (2010) 62:1213–23. doi: 10.1002/ART.27386
130. Wang X, Sun L, He N, An Z, Yu R, Li C, et al. Increased expression of CXCL2 in ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis and its role in osteoclastogenesis. Clin Exp Immunol. (2021) 203:194–208. doi: 10.1111/CEI.13527
131. Sokolove J, Zhao X, Chandra PE, and Robinson WH. Immune complexes containing citrullinated fibrinogen costimulate macrophages via Toll-like receptor 4 and Fcγ receptor. Arthritis Rheum. (2011) 63:53–62. doi: 10.1002/ART.30081
132. Hatterer E, Shang L, Simonet P, Herren S, Daubeuf B, Teixeira S, et al. A specific anti-citrullinated protein antibody profile identifies a group of rheumatoid arthritis patients with a toll-like receptor 4-mediated disease. Arthritis Res Ther. (2016) 18:1–12. doi: 10.1186/S13075-016-1128-5/FIGURES/5
133. Anquetil F, Clavel C, Offer G, Serre G, and Sebbag M. IgM and igA rheumatoid factors purified from rheumatoid arthritis sera boost the fc receptor– and complement-dependent effector functions of the disease-specific anti–citrullinated protein autoantibodies. J Immunol. (2015) 194:3664–74. doi: 10.4049/JIMMUNOL.1402334
134. Dong X, Zheng Z, Lin P, Fu X, Li F, Jiang J, et al. ACPAs promote IL-1β production in rheumatoid arthritis by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Mol Immunol. (2020) 17:261–71. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0201-9
135. Clavel C, Nogueira L, Laurent L, Iobagiu C, Vincent C, Sebbag M, et al. Induction of macrophage secretion of tumor necrosis factor α through Fcγ receptor IIa engagement by rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies to citrullinated proteins complexed with fibrinogen. Arthritis Rheum. (2008) 58:678–88. doi: 10.1002/ART.23284
136. Negishi-Koga T, Gober HJ, Sumiya E, Komatsu N, Okamoto K, Sawa S, et al. Immune complexes regulate bone metabolism through FcRγ signalling. Nat Commun. (2015) 6:1–14. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7637
137. Seeling M, Hillenhoff U, David JP, Schett G, Tuckermann J, Lux A, et al. Inflammatory monocytes and Fcγ receptor IV on osteoclasts are critical for bone destruction during inflammatory arthritis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2013) 110:10729–34. doi: 10.1073/PNAS.1301001110/SUPPL_FILE/PNAS.201301001SI.PDF
138. Breedveld AC, Van Gool MMJ, Van Delft MAM, Van Der Laken CJ, De Vries TJ, Jansen IDC, et al. IgA immune complexes induce osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:651049/BIBTEX. doi: 10.3389/FIMMU.2021.651049/BIBTEX
139. Thomas MA, Naik P, Wang H, Giles JT, Girgis AA, Kim SY, et al. The monocyte cell surface is a unique site of autoantigen generation in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2024) 121:e2304199121. doi: 10.1073/PNAS.2304199121/SUPPL_FILE/PNAS.2304199121.SD06.XLSX
140. El Shikh MEM, El Sayed R, Nerviani A, Goldmann K, John CR, Hands R, et al. Extracellular traps and PAD4 released by macrophages induce citrullination and auto-antibody production in autoimmune arthritis. J Autoimmun. (2019) 105:102297. doi: 10.1016/J.JAUT.2019.06.008
141. Yoshida K, Ito H, Kurosaka D, Ikeda R, Noda K, Saito M, et al. Autocitrullination confers monocyte chemotactic properties to peptidylarginine deiminase 4. Sci Rep. (2023) 13. doi: 10.1038/S41598-023-34469-1
142. Cîrciumaru A, Gomes Afonso M, Wähämaa H, Krishnamurthy A, Hansson M, Mathsson-Alm L, et al. Anti-citrullinated protein antibody reactivity towards neutrophil-derived antigens: clonal diversity and inter-individual variation. Biomolecules. (2023) 13:630. doi: 10.3390/BIOM13040630/S1
143. Lloyd KA, Wigerblad G, Sahlström P, Garimella MG, Chemin K, Steen J, et al. Differential ACPA binding to nuclear antigens reveals a PAD-independent pathway and a distinct subset of acetylation cross-reactive autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2019) 9:3033/BIBTEX. doi: 10.3389/FIMMU.2018.03033/BIBTEX
144. Quayle JA, Watson F, Bucknall RC, and Edwards SW. Neutrophils from the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis express the high affinity immunoglobulin G receptor, FcγRI CD64.: role of immune complexes and cytokines in induction of receptor expression. Immunology. (1997) 91:266–73. doi: 10.1046/J.1365-2567.1997.00249.X
145. Robinson JJ, Watson F, Bucknall RC, and Edwards SW. Role of Fc gamma receptors in the activation of neutrophils by soluble and insoluble immunoglobulin aggregates isolated from the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (1994) 53:515–20. doi: 10.1136/ARD.53.8.515
146. Kempers AC, Reza Nejadnik M, Rombouts Y, Ioan-Facsinay A, Van Oosterhout M, Jiskoot W, et al. Fc gamma receptor binding profile of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies in immune complexes suggests a role for FcγRI in the pathogenesis of synovial inflammation. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2018) 36:284–93.
147. Khandpur R, Carmona-Rivera C, Vivekanandan-Giri A, Gizinski A, Yalavarthi S, Knight JS, et al. NETs are a source of citrullinated autoantigens and stimulate inflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Transl Med. (2013) 5:178ra40. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005580
148. Carmona-Rivera C, Carlucci PM, Moore E, Lingampalli N, Uchtenhagen H, James E, et al. Synovial fibroblast-neutrophil interactions promote pathogenic adaptive immunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Immunol. (2017) 2:eaag3358. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aag3358
149. Ribon M, Seninet S, Mussard J, Sebbag M, Clavel C, Serre G, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps exert both pro- and anti-inflammatory actions in rheumatoid arthritis that are modulated by C1q and LL-37. J Autoimmun. (2019) 98:122–31. doi: 10.1016/J.JAUT.2019.01.003
150. Bawadekar M, Shim D, Johnson CJ, Warner TF, Rebernick R, Damgaard D, et al. Peptidylarginine deiminase 2 is required for tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced citrullination and arthritis, but not neutrophil extracellular trap formation. J Autoimmun. (2017) 80:39–47. doi: 10.1016/J.JAUT.2017.01.006
151. Li P, Li M, Lindberg MR, Kennett MJ, Xiong N, and Wang Y. PAD4 is essential for antibacterial innate immunity mediated by neutrophil extracellular traps. J Exp Med. (2010) 207:1853–62. doi: 10.1084/JEM.20100239
152. Malmström V, Catrina AI, and Klareskog L. The immunopathogenesis of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: from triggering to targeting. Nat Rev Immunol. (2016) 17:60–75. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.124
153. Hensvold AH, Magnusson PKE, Joshua V, Hansson M, Israelsson L, Ferreira R, et al. Environmental and genetic factors in the development of anticitrullinated protein antibodies ACPAs. and ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis: an epidemiological investigation in twins. Ann Rheum Dis. (2015) 74:375–80. doi: 10.1136/ANNRHEUMDIS-2013-203947
154. Hedström AK, Rönnelid J, Klareskog L, and Alfredsson L. Complex relationships of smoking, HLA–DRB1 genes, and serologic profiles in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: update from a swedish population-based case–control study. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2019) 71:1504–11. doi: 10.1002/ART.40852/ABSTRACT
155. Balandraud N, Picard C, Reviron D, Landais C, Toussirot E, Lambert N, et al. HLA-DRB1 genotypes and the risk of developing anti citrullinated protein antibody ACPA. Positive rheumatoid arthritis. PloS One. (2013) 8:e64108. doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0064108
156. Ali AA, Khalid KE, Mohammed SE, Akhtar MS, and Saeed OK. Association of Human Leukocyte Antigen HLA. class II DRB1 and DQB1. alleles and haplotypes with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Sudanese patients. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1178546/BIBTEX. doi: 10.3389/FIMMU.2023.1178546/BIBTEX
157. Snir O, Widhe M, Von Spee C, Lindberg J, Padyukov L, Lundberg K, et al. Multiple antibody reactivities to citrullinated antigens in sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis: association with HLA-DRB1 alleles. Ann Rheum Dis. (2009) 68:736–43. doi: 10.1136/ARD.2008.091355
158. Hemon MF, Lambert NC, Roudier J, and Auger I. PAD2 immunization induces ACPA in wild-type and HLA-DR4 humanized mice. Eur J Immunol. (2022) 52:1464–73. doi: 10.1002/EJI.202249889
159. Arnoux F, Mariot C, Peen E, Lambert NC, Balandraud N, Roudier J, et al. Peptidyl arginine deiminase immunization induces anticitrullinated protein antibodies in mice with particular MHC types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2017) 114:E10169–77. doi: 10.1073/PNAS.1713112114/SUPPL_FILE/PNAS.201713112SI.PDF
160. Smolen JS, Landewé RBM, Bergstra SA, Kerschbaumer A, Sepriano A, Aletaha D, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82:3–18. doi: 10.1136/ARD-2022-223356
161. Deng Y, Qiao L, Li H, Yu C, Jin S, Wang J, et al. Chinese registry of rheumatoid arthritis CREDIT. VI: temporal trends in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis and moderate-to-severe disease activity - A multicenter cohort study of treatment strategies and outcomes. Int J Rheum Dis. (2025) 28:e70066. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.70066
162. Suzuki M, Asai S, Hara R, Hirano Y, Nagamine S, Kaneko T, et al. Choice of and response to treatment in patients with early-diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis: Real-world data from an inception cohort in Japan NICER-J. J Orthop Sci. (2024) 29:921–6. doi: 10.1016/J.JOS.2023.03.020
163. Fornaro M, Benaglio F, Montecucco C, Raffeiner B, Di Franco M, Iannuccelli C, et al. Adherence of Italian rheumatologists to the EULAR recommendations and outcomes in early rheumatoid arthritis patients after starting conventional DMARDs: Methotrexate in Italian patients wiTh Rheumatoid Arthritis the MITRA study. A cohort study of the Italian Society for Rheumatology. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2022) 40:1693–700. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/77i56a
164. Aletaha D, Alasti F, and Smolen JS. Optimisation of a treat-to-target approach in rheumatoid arthritis: strategies for the 3-month time point. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:1479–85. doi: 10.1136/ANNRHEUMDIS-2015-208324
165. Scheepers L, Yang Y, Chen YL, and Jones G. Persistence of Janus-kinase JAK. inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis: Australia wide study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. (2024) 64:152314. doi: 10.1016/J.SEMARTHRIT.2023.152314
166. Lee MY, Shin JY, Park SY, Kim D, Cha HS, and Lee EK. Persistence of biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: An analysis of the South Korean National Health Insurance Database. Semin Arthritis Rheum. (2018) 47:485–91. doi: 10.1016/J.SEMARTHRIT.2017.08.007
167. Fiehn C, Zinke S, Haas JS, Meise D, Theil J, Gurrath M, et al. Real-world treatment persistence in patients with rheumatoid arthritis initiating DMARDs in Germany—a health insurance claims data analysis. Z Rheumatol. (2023) 82:739–53. doi: 10.1007/S00393-023-01323-8/FIGURES/5
168. Aymon R, Mongin D, Bergstra SA, Choquette D, Codreanu C, De Cock D, et al. Evaluation of discontinuation for adverse events of JAK inhibitors and bDMARDs in an international collaboration of rheumatoid arthritis registers the ‘JAK-pot’ study. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 83:421–8. doi: 10.1136/ARD-2023-224670/ATTACHMENT/E1FA2A52-EA05-4377-AAA6-E34AE045233A/MMC1.PDF
169. Bird P, Hall S, Nash P, Connell CA, Kwok K, Witcombe D, et al. Treatment outcomes in patients with seropositive versus seronegative rheumatoid arthritis in Phase III randomised clinical trials of tofacitinib. RMD Open. (2019) 5:e000742. doi: 10.1136/RMDOPEN-2018-000742
170. Chatzidionysiou K, Lie E, Nasonov E, Lukina G, Hetland ML, Tarp U, et al. Highest clinical effectiveness of rituximab in autoantibody-positive patients with rheumatoid arthritis and in those for whom no more than one previous TNF antagonist has failed: pooled data from 10 European registries. Ann Rheum Dis. (2011) 70:1575–80. doi: 10.1136/ARD.2010.148759
171. Sellam J, Hendel-Chavez H, Rouanet S, Abbed K, Combe B, Le Loët X, et al. B cell activation biomarkers as predictive factors for the response to rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis: a six-month, national, multicenter, open-label study. Arthritis Rheum. (2011) 63:933–8. doi: 10.1002/ART.30233
172. Sokolove J, Schiff M, Fleischmann R, Weinblatt ME, Connolly SE, Johnsen A, et al. Impact of baseline anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide-2 antibody concentration on efficacy outcomes following treatment with subcutaneous abatacept or adalimumab: 2-year results from the AMPLE trial. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:709–14. doi: 10.1136/ANNRHEUMDIS-2015-207942
173. Neppelenbroek S, Blomberg NJ, Kampstra ASB, Van Der Hem JGK, Huizinga TWJ, Toes REM, et al. Autoreactive B cells remain active despite clinical disease control in rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. (2024) 149:103320. doi: 10.1016/J.JAUT.2024.103320
174. Chatzidionysiou K, Circiumaru A, Rethi B, Joshua V, Engstrom M, Hensvold A, et al. Tocilizumab decreases T cells but not macrophages in the synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis while it increases the levels of serum interleukin-6 and RANKL. RMD Open. (2021) 7:e001662. doi: 10.1136/RMDOPEN-2021-001662
175. Breed ER, Watanabe M, and Hogquist KA. Measuring thymic clonal deletion at the population level. J Immunol. (2019) 202:3226–33. doi: 10.4049/JIMMUNOL.1900191
176. Cebula A, Kuczma M, Szurek E, Pietrzak M, Savage N, Elhefnawy WR, et al. Dormant pathogenic CD4+ T cells are prevalent in the peripheral repertoire of healthy mice. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:1–15. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12820-3
177. Kalekar LA, Schmiel SE, Nandiwada SL, Lam WY, Barsness LO, Zhang N, et al. CD4+ T cell anergy prevents autoimmunity and generates regulatory T cell precursors. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:304–14. doi: 10.1038/ni.3331
178. Tuncel J, Benoist C, and Mathis D. T cell anergy in perinatal mice is promoted by T reg cells and prevented by IL-33. J Exp Med. (2019) 216:1328–44. doi: 10.1084/JEM.20182002
179. Parish IA and Heath WR. Too dangerous to ignore: self-tolerance and the control of ignorant autoreactive T cells. Immunol Cell Biol. (2008) 86:146–52. doi: 10.1038/SJ.ICB.7100161
180. Selck C, Jhala G, De George DJ, Kwong CTJ, Christensen MK, Pappas EG, et al. Extraislet expression of islet antigen boosts T cell exhaustion to partially prevent autoimmune diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2024) 121:e2315419121. doi: 10.1073/PNAS.2315419121/SUPPL_FILE/PNAS.2315419121.SAPP.PDF
181. De George DJ, Jhala G, Selck C, Trivedi P, Brodnicki TC, Mackin L, et al. Altering β Cell antigen exposure to exhausted CD8+ T cells prevents autoimmune diabetes in mice. J Immunol. (2024) 212:1658–69. doi: 10.4049/JIMMUNOL.2300785/1655607/JI2300785.PDF
182. Redmond WL, Marincek BC, and Sherman LA. Distinct Requirements for Deletion versus Anergy during CD8 T Cell Peripheral Tolerance In Vivo. J Immunol. (2005) 174:2046–53. doi: 10.4049/JIMMUNOL.174.4.2046
183. Mukherjee G, Geliebter A, Babad J, Santamaria P, Serreze DV, Freeman GJ, et al. DEC-205-mediated antigen targeting to steady-state dendritic cells induces deletion of diabetogenic CD8+ T cells independently of PD-1 and PD-L1. Int Immunol. (2013) 25:651–60. doi: 10.1093/INTIMM/DXT031
184. Sakaguchi S, Mikami N, Wing JB, Tanaka A, Ichiyama K, and Ohkura N. Regulatory T cells and human disease. Annu Rev Immunol. (2020) 38:541–66. doi: 10.1146/ANNUREV-IMMUNOL-042718-041717/CITE/REFWORKS
185. Ferreira LMR, Muller YD, Bluestone JA, and Tang Q. Next-generation regulatory T cell therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2019) 18:749–69. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0041-4
186. Jamison BL, Dilisio JE, Scott Beard K, Neef T, Bradley B, Goodman J, et al. Tolerogenic delivery of a hybrid insulin peptide markedly prolongs islet graft survival in the NOD mouse. Diabetes. (2022) 71:483–96. doi: 10.2337/DB20-1170
187. Yamazaki S, Dudziak D, Heidkamp GF, Fiorese C, Bonito AJ, Inaba K, et al. CD8+CD205+ Splenic dendritic cells are specialized to induce foxp3+ Regulatory T cells. J Immunol. (2008) 181:6923–33. doi: 10.4049/JIMMUNOL.181.10.6923
188. Lorenzetti R, Janowska I, Smulski CR, Frede N, Henneberger N, Walter L, et al. Abatacept modulates CD80 and CD86 expression and memory formation in human B-cells. J Autoimmun. (2019) 101:145–52. doi: 10.1016/J.JAUT.2019.04.016
189. Kneitz C, Wilhelm M, and Tony HP. Effective B cell depletion with rituximab in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Immunobiology. (2002) 206:519–27. doi: 10.1078/0171-2985-00200
190. Van Der Kolk LE, Baars JW, Prins MH, and Van Oers MHJ. Rituximab treatment results in impaired secondary humoral immune responsiveness. Blood. (2002) 100:2257–9. doi: 10.1182/BLOOD.V100.6.2257
191. Shi Y, Wu Y, Ren Y, Jiang Y, and Chen Y. Infection risks of rituximab versus non-rituximab treatment for rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Rheum Dis. (2019) 22:1361–70. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13596
192. Roll P, Palanichamy A, Kneitz C, Dorner T, and Tony H-P. Regeneration of B cell subsets after transient B cell depletion using anti-CD20 antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. (2006) 54:2377–86. doi: 10.1002/ART.22019
193. Bhushan V, Lester S, Briggs L, Hijjawi R, Shanahan EM, Pontifex E, et al. Real-life retention rates and reasons for switching of biological DMARDs in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. Front Med. (2021) 8:708168/BIBTEX. doi: 10.3389/FMED.2021.708168/BIBTEX
194. Li Y, Li S, Zhao X, Sheng J, Xue L, Schett G, et al. Fourth-generation chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy is tolerable and efficacious in treatment-resistant rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Res. (2025) 35:1–4. doi: 10.1038/s41422-024-01068-2
195. Benham H, Nel HJ, Law SC, Mehdi AM, Street S, Ramnoruth N, et al. Citrullinated peptide dendritic cell immunotherapy in HLA risk genotype-positive rheumatoid arthritis patients. Sci Transl Med. (2015) 7:290ra87. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa9301
196. Karnell JL, Albulescu M, Drabic S, Wang L, Moate R, Baca M, et al. A CD40L-targeting protein reduces autoantibodies and improves disease activity in patients with autoimmunity. Sci Transl Med. (2019) 11. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aar6584
197. Kivitz A, Wang L, Alevizos I, Gunsior M, Falloon J, Illei G, et al. The MIDORA trial: a phase II, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, mechanistic insight and dosage optimisation study of the efficacy and safety of dazodalibep in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open. (2023) 9:e003317. doi: 10.1136/RMDOPEN-2023-003317
198. Hall C, Pleasance J, Hickman O, Kirkham B, Panayi GS, Eggleton P, et al. The biologic IRL201805 alters immune tolerance leading to prolonged pharmacodynamics and efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:4394. doi: 10.3390/IJMS25084394/S1
199. Kirkham B, Chaabo K, Hall C, Garrood T, Mant T, Allen E, et al. Safety and patient response as indicated by biomarker changes to binding immunoglobulin protein in the phase I/IIA RAGULA clinical trial in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. (2016) 55:1993–2000. doi: 10.1093/RHEUMATOLOGY/KEW287
200. Oramas L, Domínguez Horta MDC, Padrón G, González LJ, Besada V, Carlos C, et al. Phase I clinical trial with a novel altered peptide ligand derived from human heat-shock protein 60 for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: safety, pharmacokinetics and preliminary therapeutic effects. J Clin Trials. (2018) 8:1000339. doi: 10.4172/2167-0870.1000339
201. Corrales O, Hernández L, Prada D, Gómez J, Reyes Y, López AM, et al. CIGB-814, an altered peptide ligand derived from human heat-shock protein 60, decreases anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides antibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. (2019) 38:955–60. doi: 10.1007/S10067-018-4360-3/FIGURES/3
202. Dominguez MDC, Lorenzo N, Barbera A, Darrasse-Jeze G, Hernández MV, Torres A, et al. An altered peptide ligand corresponding to a novel epitope from heat-shock protein 60 induces regulatory T cells and suppresses pathogenic response in an animal model of adjuvant-induced arthritis. Autoimmunity. (2011) 44:471–82. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2010.550590
203. Koffeman EC, Genovese M, Amox D, Keogh E, Santana E, Matteson EL, et al. Epitope-specific immunotherapy of rheumatoid arthritis: Clinical responsiveness occurs with immune deviation and relies on the expression of a cluster of molecules associated with T cell tolerance in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, pilot phase II trial. Arthritis Rheum. (2009) 60:3207–16. doi: 10.1002/ART.24916
204. Sonigra A, Nel HJ, Wehr P, Ramnoruth N, Patel S, Van Schie KA, et al. Randomized phase I trial of antigen-specific tolerizing immunotherapy with peptide/calcitriol liposomes in ACPA+ rheumatoid arthritis. JCI Insight. (2022) 7:e160964. doi: 10.1172/JCI.INSIGHT.160964
205. Szabo D, Balogh A, Gopcsa L, Giba-Kiss L, Lakatos G, Paksi M, et al. Sustained drug-free remission in rheumatoid arthritis associated with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma following tandem CD20-CD19-directed non-cryopreserved CAR-T cell therapy using zamtocabtagene autoleucel. RMD Open. (2024) 10:e004727. doi: 10.1136/RMDOPEN-2024-004727
206. Lidar M, Rimar D, David P, Jacoby E, Shapira-Frommer R, Itzhaki O, et al. CD-19 CAR-T cells for polyrefractory rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2024) 84:370–2. doi: 10.1136/ARD-2024-226437
207. Haghikia A, Hegelmaier T, Wolleschak D, Böttcher M, Pappa V, Motte J, et al. Clinical efficacy and autoantibody seroconversion with CD19-CAR T cell therapy in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and coexisting myasthenia gravis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2024) 83:1597–8. doi: 10.1136/ARD-2024-226017
208. Zhang B, Wang Y, Yuan Y, Sun J, Liu L, Huang D, et al. In vitro elimination of autoreactive B cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients by universal chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Ann Rheum Dis. (2021) 80:176–84. doi: 10.1136/ANNRHEUMDIS-2020-217844
209. Sheng L, Zhang Y, Song Q, Jiang X, Cao W, Li L, et al. Concurrent remission of lymphoma and Sjögren’s disease following anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor-T cell therapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a case report. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1298815/BIBTEX. doi: 10.3389/FIMMU.2023.1298815/BIBTEX
210. Hilligan KL and Ronchese F. Antigen presentation by dendritic cells and their instruction of CD4+ T helper cell responses. Cell Mol Immunol. (2020) 17:587–99. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0465-0
211. Ning B, Wei J, Zhang A, Gong W, Fu J, Jia T, et al. Antigen-specific tolerogenic dendritic cells ameliorate the severity of murine collagen-induced arthritis. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0131152. doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0131152
212. Yuan R, Wan X, Bao L, Long T, Li H, Zhou Y, et al. Tolerogenic dendritic cells alleviate collagen-induced arthritis by regulating T-cell differentiation and inhibiting NLRP3-mediated apoptosis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 130:111764. doi: 10.1016/J.INTIMP.2024.111764
213. Dixon KO, Van Der Kooij SW, Vignali DAA, and Van Kooten C. Human tolerogenic dendritic cells produce IL-35 in the absence of other IL-12 family members. Eur J Immunol. (2015) 45:1736–47. doi: 10.1002/EJI.201445217
214. Zubizarreta I, Flórez-Grau G, Vila G, Cabezón R, España C, Andorra M, et al. Immune tolerance in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica with peptide-loaded tolerogenic dendritic cells in a phase 1b trial. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2019) 116:8463–70. doi: 10.1073/PNAS.1820039116/SUPPL_FILE/PNAS.1820039116.SAPP.PDF
215. Nikolic T, Zwaginga JJ, Uitbeijerse BS, Woittiez NJ, De Koning EJ, Aanstoot HJ, et al. Safety and feasibility of intradermal injection with tolerogenic dendritic cells pulsed with proinsulin peptide—for type 1 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2020) 8:470–2. doi: 10.1016/S2213-858720.30104-2
216. Nikolic T, Suwandi JS, Wesselius J, Laban S, Joosten AM, Sonneveld P, et al. Tolerogenic dendritic cells pulsed with islet antigen induce long-term reduction in T-cell autoreactivity in type 1 diabetes patients. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1054968/BIBTEX. doi: 10.3389/FIMMU.2022.1054968/BIBTEX
217. Bin Joo Y, Park J-E, Choi C-B, Choi J, Jang J, Heo M, et al. Phase 1 study of immunotherapy using autoantigen-loaded dendritic cells in patients with anti-citrullinated peptide antigen positive rheumatoid arthritis - ACR meeting abstracts. ACR/AHRP Annu Meet. (2014) 946.
218. Bell GM, Anderson AE, Diboll J, Reece R, Eltherington O, Harry RA, et al. Autologous tolerogenic dendritic cells for rheumatoid and inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2017) 76:227–34. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208456
219. Stoppelenburg AJ, Schreibelt G, Koeneman B, Welsing P, Breman EJ, Lammers L, et al. Design of TOLERANT: phase I/II safety assessment of intranodal administration of HSP70/mB29a self-peptide antigen-loaded autologous tolerogenic dendritic cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. BMJ Open. (2024) 14:e078231. doi: 10.1136/BMJOPEN-2023-078231
220. Tuttle J, Drescher E, Simón-Campos JA, Emery P, Greenwald M, Kivitz A, et al. A phase 2 trial of peresolimab for adults with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. (2023) 388:1853–62. doi: 10.1056/NEJMOA2209856/SUPPL_FILE/NEJMOA2209856_DATA-SHARING.PDF
221. Gravallese EM and Thomas R. Reinforcing the checkpoint in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. (2023) 388:1905–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJME2300734/SUPPL_FILE/NEJME2300734_DISCLOSURES.PDF
222. Brownlie RJ, Myers LK, Wooley PH, Corrigall VM, Bodman-Smith MD, Panayi GS, et al. Treatment of murine collagen-induced arthritis by the stress protein BiP via interleukin-4–producing regulatory T cells: A novel function for an ancient protein. Arthritis Rheum. (2006) 54:854–63. doi: 10.1002/ART.21654
223. Corrigall VM, Bodman-Smith MD, Fife MS, Canas B, Myers LK, Wooley PH, et al. The human endoplasmic reticulum molecular chaperone biP is an autoantigen for rheumatoid arthritis and prevents the induction of experimental arthritis. J Immunol. (2001) 166:1492–8. doi: 10.4049/JIMMUNOL.166.3.1492
224. Ali MA, Liu YF, Arif S, Tatovic D, Shariff H, Gibson VB, et al. Metabolic and immune effects of immunotherapy with proinsulin peptide in human new-onset type 1 diabetes. Sci Transl Med. (2017) 9. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf7779
225. Thrower SL, James L, Hall W, Green KM, Arif S, Allen JS, et al. Proinsulin peptide immunotherapy in type 1 diabetes: report of a first-in-man Phase I safety study. Clin Exp Immunol. (2009) 155:156–65. doi: 10.1111/J.1365-2249.2008.03814.X
226. Lalive PH, Neuhaus O, Benkhoucha M, Burger D, Hohlfeld R, Zamvil SS, et al. Glatiramer acetate in the treatment of multiple sclerosis: Emerging concepts regarding its mechanism of action. CNS Drugs. (2011) 25:401–14. doi: 10.2165/11588120-000000000-00000/FIGURES/1
227. Messina S and Patti F. The pharmacokinetics of glatiramer acetate for multiple sclerosis treatment. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. (2013) 9:1349–59. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2013.811489
228. Muller S, Monneaux F, Schal N, Rashkov RK, Oparanov BA, Wiesel P, et al. Spliceosomal peptide P140 for immunotherapy of systemic lupus erythematosus: Results of an early phase II clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum. (2008) 58:3873–83. doi: 10.1002/ART.24027
229. Zimmer R, Scherbarth HR, Rillo OL, Gomez-Reino JJ, and Muller S. Lupuzor/P140 peptide in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIb clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis. (2013) 72:1830–5. doi: 10.1136/ANNRHEUMDIS-2012-202460
230. Monneaux F, Hoebeke J, Sordet C, Nonn C, Briand J-P, Maillère B, et al. Selective modulation of CD4+ T cells from lupus patients by a promiscuous, protective peptide analog. J Immunol. (2005) 175:5839–47. doi: 10.4049/JIMMUNOL.175.9.5839
231. Schall N and Muller S. Resetting the autoreactive immune system with a therapeutic peptide in lupus. Lupus. (2015) 24:412–8. doi: 10.1177/0961203314556138/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/10.1177_0961203314556138-FIG3.JPEG
232. Passioura T. The road ahead for the development of macrocyclic peptide ligands. Biochemistry. (2020) 59:139–45. doi: 10.1021/ACS.BIOCHEM.9B00802/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/BI9B00802_0003.JPEG
233. Dougherty PG, Qian Z, and Pei D. Macrocycles as protein–protein interaction inhibitors. Biochem J. (2017) 474:1109–25. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160619
234. Hernández-Cedeño M, Rodríguez-Ulloa A, Ramos Y, González LJ, Serrano-Díaz A, Zettl K, et al. Proteomic profile regulated by the immunomodulatory jusvinza drug in neutrophils isolated from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Biomedicines. (2024) 12:2740. doi: 10.3390/BIOMEDICINES12122740/S1
235. Prakken BJ, Samodal R, Le TD, Giannoni F, Yung GP, Scavulli J, et al. Epitope-specific immunotherapy induces immune deviation of proinflammatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2004) 101:4228–33. doi: 10.1073/PNAS.0400061101/ASSET/2E282928-4438-476F-A26D-27D6EE6EB463/ASSETS/GRAPHIC/ZPQ0100441620004.JPEG
236. Bromley SK, Thomas SY, and Luster AD. Chemokine receptor CCR7 guides T cell exit from peripheral tissues and entry into afferent lymphatics. Nat Immunol. (2005) 6:895–901. doi: 10.1038/ni1240
237. Burman A, Haworth O, Hardie DL, Amft EN, Siewert C, Jackson DG, et al. A chemokine-dependent stromal induction mechanism for aberrant lymphocyte accumulation and compromised lymphatic return in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. (2005) 174:1693–700. doi: 10.4049/JIMMUNOL.174.3.1693
238. Samy El-Banna H, Gado E, and Gado SE. Vitamin D: does it help Tregs in active rheumatoid arthritis patients. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. (2020) 16:847–53. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2020.1805317
239. Gertel S, Serre G, Shoenfeld Y, and Amital H. Immune tolerance induction with multiepitope peptide derived from citrullinated autoantigens attenuates arthritis manifestations in adjuvant arthritis rats. J Immunol. (2015) 194:5674–80. doi: 10.4049/JIMMUNOL.1402457
240. Zimmerman DH, Mikecz K, Markovics A, Carambula RE, Ciemielewski JC, Toth DM, et al. Vaccination by two DerG LEAPS conjugates incorporating distinct proteoglycan PG, aggrecan. epitopes provides therapy by different immune mechanisms in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis. Vaccines. (2021) 9:448. doi: 10.3390/VACCINES9050448/S1
241. Khatri S, Hansen J, Pedersen NB, Brandt-Clausen IP, Gram-Nielsen S, Mendes AC, et al. Cyclic citrullinated peptide aptamer treatment attenuates collagen-induced arthritis. Biomacromolecules. (2022) 23:2126–37. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.2c00144
242. McElwee MK, Dileepan T, Mahmud SA, and Jenkins MK. The CD4+ T cell repertoire specific for citrullinated peptides shows evidence of immune tolerance. J Exp Med. (2023) 220:e20230209. doi: 10.1084/jem.20230209
243. He Y, Ge C, Moreno-Giró À, Xu B, Beusch CM, Sandor K, et al. A subset of antibodies targeting citrullinated proteins confers protection from rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:1–19. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36257-x
244. Raposo B, Afonso M, Israelsson L, Wähämaa H, Stålesen R, Wermeling F, et al. Divergent and dominant anti-inflammatory effects of patient-derived anticitrullinated protein antibodies ACPA. in arthritis development. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82:724–6. doi: 10.1136/ARD-2022-223417
245. Chirivi RGS, Van Rosmalen JWG, Van Der Linden M, Euler M, Schmets G, Bogatkevich G, et al. Therapeutic ACPA inhibits NET formation: a potential therapy for neutrophil-mediated inflammatory diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) 18:1528–44. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0381-3
246. Mikecz K, Glant TT, Markovics A, Rosenthal KS, Kurko J, Carambula RE, et al. An epitope-specific DerG-PG70 LEAPS vaccine modulates T cell responses and suppresses arthritis progression in two related murine models of rheumatoid arthritis. Vaccine. (2017) 35:4048–56. doi: 10.1016/J.VACCINE.2017.05.009
247. Fernandes-Cerqueira C, Ossipova E, Gunasekera S, Hansson M, Mathsson L, Catrina AI, et al. Targeting of anti-citrullinated protein/peptide antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis using peptides mimicking endogenously citrullinated fibrinogen antigens. Arthritis Res Ther. (2015) 17. doi: 10.1186/S13075-015-0666-6
248. Gunasekera S, Fernandes-Cerqueira C, Wennmalm S, Wähämaa H, Sommarin Y, Catrina AI, et al. Stabilized cyclic peptides as scavengers of autoantibodies: neutralization of anticitrullinated protein/peptide antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. ACS Chem Biol. (2018) 13:1525–35. doi: 10.1021/ACSCHEMBIO.8B00118
Keywords: rheumatoid arthritis, citrullinated peptides, tolerance recovery, anti-citrullinated protein antibodies, antigen-specific therapy
Citation: Bustos AH, Brüner M, Kragstrup TW and Astakhova K (2025) Citrullinated peptides as drug candidates for rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Immunol. 16:1648913. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1648913
Received: 17 June 2025; Accepted: 05 November 2025; Revised: 31 October 2025;
Published: 25 November 2025.
Edited by:
Emanuele Bizzi, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, ItalyReviewed by:
Angela Mauro, ASST Fatebenefratelli-Sacco, ItalyYue Zhai, Air Force Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Bustos, Brüner, Kragstrup and Astakhova. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kira Astakhova, a2lyYWFzQGtlbWkuZHR1LmRr
 Adrian H. Bustos
Adrian H. Bustos Mads Brüner
Mads Brüner Tue Wenzel Kragstrup
Tue Wenzel Kragstrup Kira Astakhova
Kira Astakhova