- 1Department of Neurology, Tokushima University Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Tokushima, Japan
- 2Division of Experimental Immunology, Institute of Advanced Medical Sciences, Tokushima University, Tokushima, Japan
- 3Laboratory of Developmental Immunology, Institute of Photonics and Human Health Frontier, Tokushima University, Tokushima, Japan
- 4Institute of Pathology, University of Gottingen, Gottingen, Germany
The thymus generates T cells from immature thymocytes and prevents autoimmune diseases through negative selection and the generation of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs). The thymic architecture is typically divided into two distinct microenvironments, the cortex and the medulla. These microenvironments are characterized by the presence of cortical thymic epithelial cells (cTECs) and medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs), respectively. Recent single-cell and spatial transcriptomic analyses have revealed the expanding diversity of TEC subpopulations in mice and humans. Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by fatigue resulting from muscle weakness, which is caused by antibodies toward structures within the neuromuscular junction. The most common target of pathogenic autoantibodies in MG is the acetylcholine receptor (AChR). MG patients are prone to thymic abnormalities, including thymic follicular hyperplasia and thymoma. Previous studies have suggested that mTECs expressing major histocompatibility complex (MHC)/AChR–peptide complexes are involved in the intrathymic pathogenesis of this MG type. However, the exact mechanisms are unknown. This review provides an update on the diversity of TEC subpopulations and other cellular alterations in the MG thymus. Additionally, we present hypotheses on the pathogenetic pathways leading to MG and suggest potential future directions in thymus research.
Introduction
The fortuitous association between the thymus and myasthenia gravis (MG) was first reported in 1939, when the excision of a cystic thymic tumor had a strikingly positive impact on myasthenic symptoms in a patient with MG (1). A study performed in 1949 indicated that thymic abnormalities, including hyperplasia and thymoma, were detectable in approximately 90% of patients with MG, and that thymectomy for non-thymoma was effective in 43 to 50% of patients (2). Since then, thymectomy has remained a crucial therapeutic intervention for MG patients with thymic abnormalities and an oncological necessity for patients with thymomas (3, 4), despite the emergence of new and highly effective therapeutic agents in recent years (5).
Notwithstanding the discovery of a link between thymus pathology and MG in 1949, as mentioned above, the belief persisted that the thymus was actually a superfluous organ, as its involution from childhood onwards seemed to have no consequences—until its crucial role in T cell production was recognized in 1961 (6). The function of the thymus largely depends on the function of thymic epithelial cells (TECs). Over the past two decades, our understanding of the mechanisms regulating TEC function and development has significantly advanced. Single-cell and spatial transcriptomic analyses have revealed a far greater diversity of TEC subpopulations than previously recognized (7, 8). However, most of these studies have been conducted using mouse thymuses. Therefore, comprehending the similarities and differences between mouse and human thymuses is crucial for clinicians seeking to understand human diseases associated with thymic abnormalities.
In this review, we summarize current advances in our understanding of TEC properties in mouse and human thymuses, as well as the pathomechanisms of MG thymus. We also discuss future directions in thymus research, including potential new therapeutic strategies and the development of appropriate biomarkers for MG.
Thymic epithelial cells in mouse and human thymuses
The thymus consists of two microenvironments, the cortex and the medulla, whose functions are characterized by the roles played by cortical TECs (cTECs) and medullary TECs (mTECs), respectively. cTECs express functional molecules, including IL7 and Dll4, that regulate early T cell development. Furthermore, cTECs express enzymes that produce self-peptide antigens, inducing the positive selection of T cells. These enzymes comprise the β5t-containing thymoproteasome, the thymus-specific serine protease, and cathepsin L (9, 10). On the other hand, mTECs regulate the establishment of T cell self-tolerance. For example, chemokine CCL21 produced by mTECs is involved in the migration of positively selected cortical thymocytes into the medulla, whereas the nuclear factor AIRE regulates the expression of tissue-specific antigens for the negative selection of self-reactive T cells and the generation of regulatory T cells (Tregs) (11–13). The importance of these cTEC- and mTEC-associated molecules in thymic function has been revealed through the analyses of animal models, particularly genetically modified mice. However, transcriptomic analysis of human TECs has demonstrated that cTEC- and mTEC-associated molecules are similarly present in human cTECs and mTECs, respectively (14, 15), indicating that similar molecular mechanisms govern the regulation of TEC functions in humans and animal models. These analyses have also revealed differences between human and mouse TECs, such as IL-25 expression, which characterizes mouse but not human tuft cells—a subset of mTECs present in both species.
Thymic epithelial progenitors in mouse and human thymuses
During embryonic thymus organogenesis, TEC emergence begins on embryonic day 11 in mice and the sixth week of gestation in humans, marked by the expression of Foxn1, a landmark transcription factor (16). Intrathymic transplantation of single TECs isolated from fetal mouse thymus, along with lineage tracing of transplanted TECs, has revealed that cTECs and mTECs are derived from a common TEC progenitor (17, 18). Bipotent TEC progenitors have also been identified in the adult mouse thymus (19, 20). In addition to bipotent TEC progenitors, mTEC-specific progenitors, including RANK+ TECs, Krt19+ TECs, and Sox9+ TECs, as well as Cldn3,4highSSEA1+ mTEC stem cells with self-renewing and clonogenic potential, have been unveiled in the fetal mouse thymus (21–25). Recently, we reported that mTECs expressing CCL21 in the fetal mouse thymus are capable of giving rise to AIRE+ mTECs (26), suggesting that the functional conversion of thymocyte-attracting mTECs into self-antigen-presenting mTECs contributes to the establishment of a functional medullary microenvironment.
In humans, TEC stem cells have been identified in the postnatal thymus (27, 28) through single-cell RNA sequencing of cTECs and mTECs, within a TEC cluster termed Polykeratin (PolyKRT). PolyKRT expresses multiple cytokeratins, including KRT5, KRT8, KRT13, KRT14, KRT15, KRT17, KRT18, and KRT19. The PolyKRT cluster is predominantly localized in the subcapsular and perivascular regions of the thymus. It exhibits long-term expansion potential in vitro, as well as the capacity to differentiate into multiple TEC lineages (28). However, it remains unclear whether the frequency and differentiation capacity of PolyKRT cells change with aging or in the context of thymic abnormalities. In addition, it is unknown whether lineage-restricted progenitor populations, such as Krt19+, RANK+, and CCL21+ embryonic TECs identified in the mouse thymus, are also present in the human thymus. Further studies are needed to elucidate the roles of human TEC stem and progenitor cells in thymic involution and the pathogenesis of thymus-associated diseases.
TEC subpopulations other than progenitors in mouse and human thymuses
As far as the mouse thymus is concerned, it is well known that mTECs are a heterogeneous population that is roughly divided into two subpopulations: mTEClow (CD80low MHC IIlow), which includes immature mTECs and those in the post-AIRE stage, and mTEChigh (CD80high MHC IIhigh), a mature mTEC subset that includes AIRE+ mTECs. The heterogeneity of cTECs has also been recognized on the basis of the expression of cTEC-associated molecules, such as CXCL12 and DLL4 (29, 30). However, single-cell transcriptomic analyses of TECs isolated from the mouse thymus have revealed a far greater diversity of mTEC subsets, including thymic mimetic cells, which exhibit transcriptional and epigenetic signatures resembling those of extrathymic cells and in the post-AIRE stage (7, 8, 31–33). These thymic mimetic cells are suggested to contribute to T cell tolerance by presenting self-antigens that are typically expressed in peripheral tissues (8). The functions of thymic mimetic cells beyond antigen presentation have also been reported, including the regulation of invariant NKT2 cell development and function by thymic tuft cells, the control of thymic cellularity by endocrine mTECs, and the generation of IgA+ plasma cells in the thymus by microfold mTECs (31, 33, 34).
Similar to mouse TECs, the diversity of human TEC subpopulations has been confirmed by single-cell transcriptomic analyses. These include various mTEC subpopulations, such as CCL21+ mTEClow/mTEC-I, AIRE+ mTEChigh/mTEC-II, and mimetic TECs, as well as a limited number of cTEC subpopulations (14, 15, 35). Immature TECs, which are committed to neither the cTEC nor the mTEC lineage, have also been detected in the human thymus (15, 35). These cells express KRT15, which is also found in PolyKRT human TEC stem cells (28). Spatial mapping of TECs has indicated that immature TECs are located in the subcapsular area of the fetal thymus and in both the subcapsular area and the cortico-medullary junction of the pediatric thymus (35). The shift in immature TEC localization from fetal to pediatric stage may suggest differences in differentiation preference toward cTECs or mTECs. Regarding thymic mimetic cells, Huisman and colleagues recently performed high-resolution profiling of human and zebrafish thymic mimetic cells, uncovering both species-specific and species-conserved mimetic cells in human, mouse, and zebrafish thymuses (36). Notably, multiple clusters of muscle and neuroendocrine mimetic cells were found in the human thymus, whereas only a single cluster of each was detected in the mouse thymus, and a single muscle mimetic cluster was noted in the zebrafish thymus (36). Given that autoantibodies in a substantial proportion of MG patients target acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) at neuromuscular junctions, Huisman and colleagues further focused on muscle mimetic cells and found that these mimetic clusters show a differentiation trajectory with a gene signature similar, but not identical, to that of peripheral muscle cells (36). The development of muscle mimetic cells may be regulated by mechanisms similar to those in the periphery, as mouse thymuses deficient in myogenin or Myf5, both of which are myogenic regulatory factors, exhibit an absence or a reduced number of thymic myoid cells (TMCs) (37). Histological analysis of human thymus tissues has shown that some muscle mimetic cells form neuromuscular junction-like structures. Thymic tuft cells expressing choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), an enzyme that synthesizes acetylcholine, are in close proximity to muscle mimetic cells, with their interfaces interspersed with α-bungarotoxin, which binds to AChR (36). However, the significance of the presence of multiple muscle and neuroendocrine mimetic clusters, as well as the formation of neuromuscular junction-like structures in the human thymus, in regulating the immune system, including the establishment of self-tolerance, remains unclear. Furthermore, differences in TEC clusters between human and animal models, such as the number of specific mimetic clusters, may highlight the limitations of translating findings from mouse to human.
The transcriptomic analysis of MG-associated thymomas has led to the identification of a unique mTEC cluster, termed neuromuscular mTECs (nmTECs), which ectopically express neuromuscular molecules and exhibit a transcriptome profile consistent with active antigen presentation (38). Cell–cell interaction analysis has indicated that nmTECs act as a central hub for communication with various cells, including B cells and T cells, via the CXCL12–CXCR4 chemokine axis, as well as non-TEC stroma cells, through such growth factors as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) (38). These findings suggest a possible pathogenic role of nmTECs in thymoma-associated MG (TAMG). It is noteworthy that no developmental trajectory from mTECs to “mature myoid cells”—which express desmin and AChRs but not HLA-DR proteins (39)—has been demonstrated by transcriptomic analysis either in thymoma or in the human thymus, although immunohistochemical findings have suggested that such a link is likely in the thymus (8, 39).
Myasthenia gravis and thymus
MG is an autoimmune disease caused by autoantibodies against components of neuromuscular junctions. MG patients exhibit muscle weakness and fatigability due to impaired neuromuscular transmission (40, 41). Antibodies (Abs) against AChRs are found in 85% of patients (40, 42). In the remaining AChR Ab-negative patients, Abs against muscle-specific kinase (MuSK) are detected in 5% (42, 43), and Abs against lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4 (LRP4) have been reported in a minority of MG patients (44, 45). Another small fraction of patients do not have detectable circulating autoantibodies against known targets. Accordingly, these patients are diagnosed as having seronegative MG.
MG can be clinically divided into the following subtypes on the basis of age of onset, Ab specificity, and associated thymus pathology (Table 1): early-onset MG (EOMG); thymoma-associated MG (TAMG); and late-onset MG (LOMG). Seventy percent of EOMG patients exhibit morphological changes in their thymus, particularly thymic hyperplasia (46). Thymoma is observed over a wide age range (47). The thymus in LOMG patients is characterized by age-related involution without histologically recognizable pathology (47). In MuSK Ab-positive MG patients, thymic abnormalities are rare (48, 49). In LRP4 Ab-positive MG patients, thymus involvement remains unclear (50).
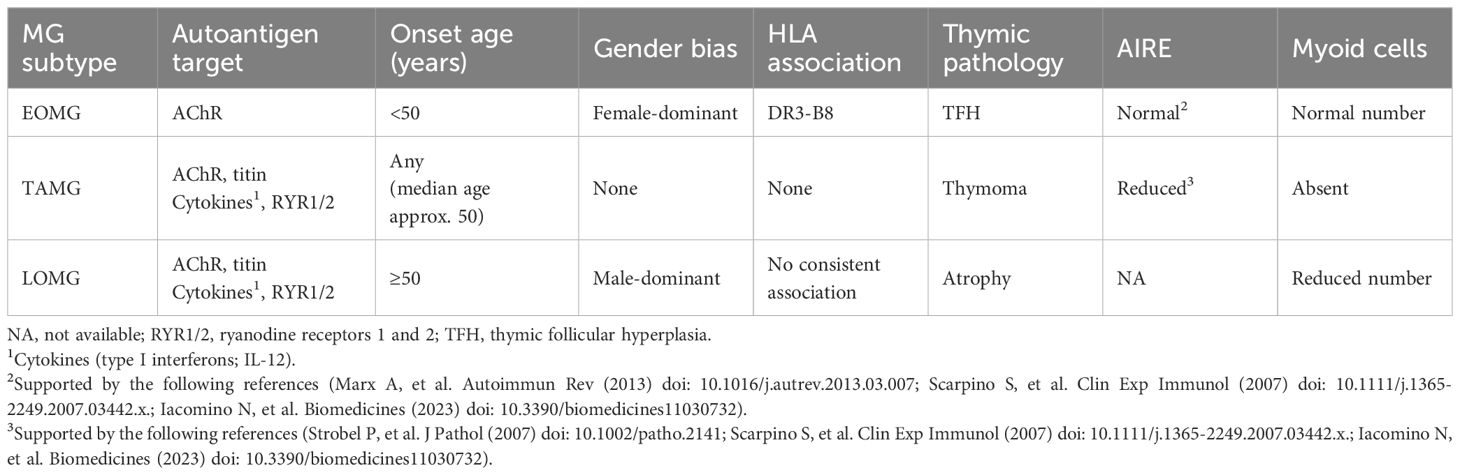
Table 1. Features and risk factors of myasthenia gravis (MG) subtypes with acetylcholine receptor (AChR) antibodies, comprising early-onset MG (EOMG), thymoma-associated MG (TAMG), and late-onset MG (LOMG).
EOMG thymus
EOMG may be triggered by genetic predisposition, including HLA genes, miRNA dysregulation, female gender, and immune dysregulation (46, 51–54). The hypothesis that viral infection is a contributor to MG has been posited for a long time, but there is little evidence to support it (42, 55–58). The representative pathogenic finding in EOMG thymus is thymic follicular hyperplasia (TFH), characterized by ectopic lymphoid follicles and germinal centers (GCs) in the perivascular space (PVS) margining with the thymic medulla (59, 60) (Figure 1). The exact mechanisms in the early stage of GCs are unknown. However, once formed, GCs drive the hypermutation of B cell receptor genes and the intrathymic production of high-affinity anti-AChR Abs (61). Females exhibit a higher number of GCs, particularly between ages 30 and 40, but the number of GCs decreases after the age of 50, regardless of gender (62). Corticosteroid treatment results in a reduction in the number and size of GCs (63).
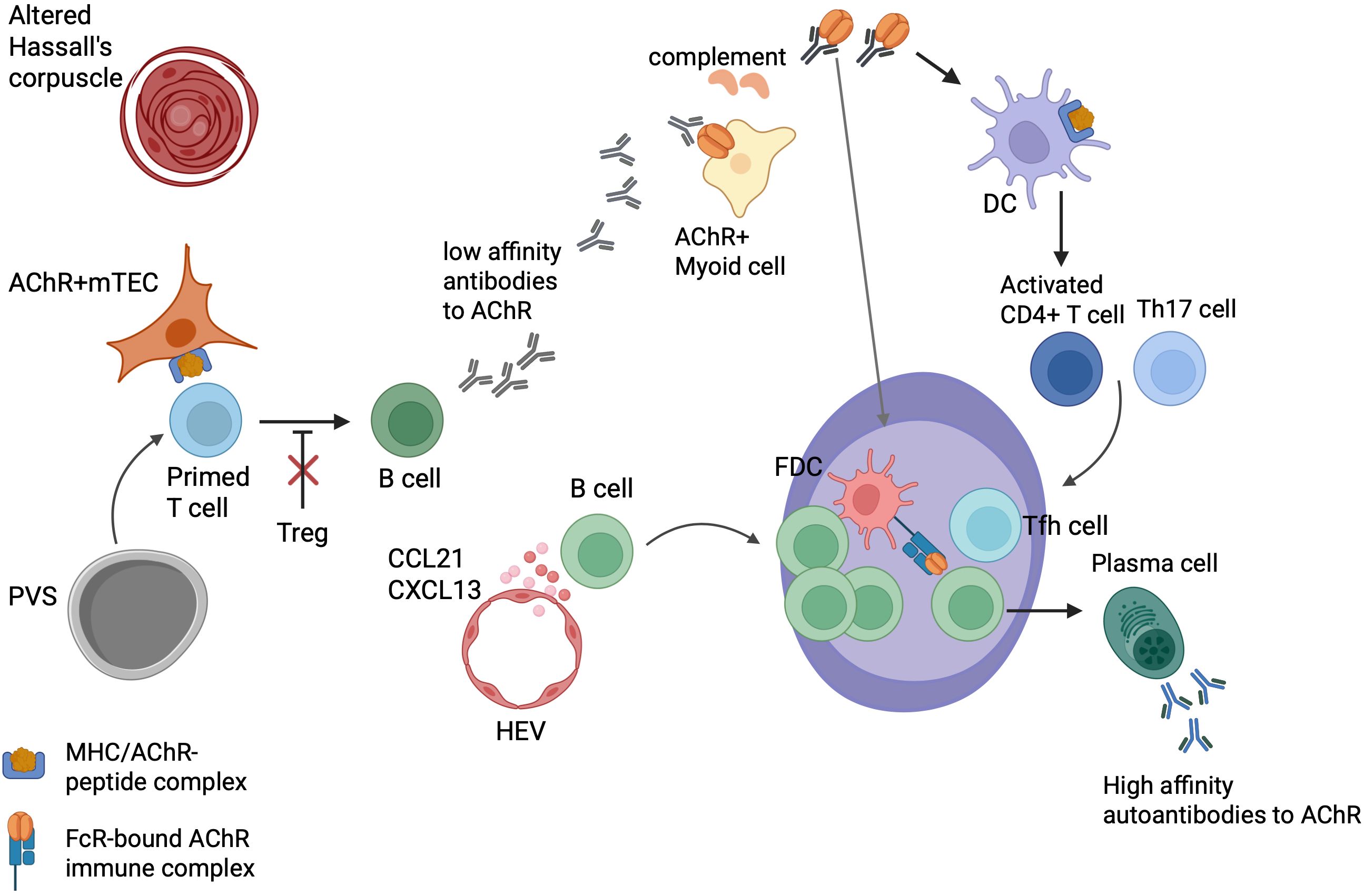
Figure 1. Intrathymic pathogenetic model of early-onset myasthenia gravis. Acetylcholine receptor (AChR)-reactive T cells in blood re-enter the thymus where they, activated by unknown triggers, are “primed” by medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs) expressing MHC/AChR–peptide complexes. The primed T cells activate thymic B cells to produce low-affinity anti-AChR Abs. These autoantibodies bind to TMCs expressing native AChRs, activate complement, and induce the release of AChR/Ab complexes from TMCs for processing by nearby dendritic cells (DCs) that bind to follicular dendritic cells (FDCs). CCL21 and CXCL13 facilitate the recruitment of B cells and the formation of ectopic germinal centers (GCs). T follicular helper (Tfh) cells promote GC development, and the GC reaction finally results in plasma cells producing high-affinity anti-AChR Abs. Functionally impaired regulatory T cells (Tregs) may contribute to the maintenance of EOMG. It is unknown whether lymphoid follicles arise primarily in the perivascular space (PVS) or the medulla, and why AChR-reactive T cells occur so commonly in the “physiological” T cell repertoire of healthy humans. This figure is a modification of Figure 3 from Thymus and Autoimmunity, Marx A, Yamada Y, Simon-Keller K, Willcox N, Ströbel P, Weis CA, Semin Immunopathol 43; 45-64 (2021), licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Cellular changes and autoimmunity in EOMG
The medullary area is thought to be a site of immune activation in the MG thymus, where relevant cells, including anti-AChR auto-reactive lymphocytes, TMCs, dendritic cells (DCs), and mTECs, are localized (60). The role of T cells in MG has been demonstrated in previous studies (64–67). B cells develop an anti-AChR autoimmune response upon encountering antigens, interacting with helper T cells (63). Myoid cells are rare non-innervated mesenchymal cells resembling myoblasts or myotubes (68). Myoid cells that are abundant in normal and EOMG thymic medullas express whole native adult and fetal AChRs, but not major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules (39, 69, 70). TMCs are attacked by active complement and autoantibodies in the EOMG thymus (71, 72). DCs are found in close proximity to myoid cells and likely “cross-present” processed AChR peptides to nearby auto-reactive T cells (73). Hyperplastic mTECs that express unfolded AChR subunits and MHC class II molecules are under attack by complement, and likely prime T cells for immunogenic AChR peptides (74–77). Intrathymic proinflammatory cytokines, CXCL12, CXCL13, CCL21, and B cell-activating factor (BAFF), are overexpressed by increased numbers of activated lymphatic vessels, high endothelial venules, and TECs, and likely contribute to the recruitment of B cells and DCs to the thymus (42, 63, 76, 78–83). The number of thymic Tregs is not decreased; nevertheless, thymic Treg dysfunction is associated with MG pathogenesis (42, 84–86). T follicular helper (Tfh) cells are crucial for the establishment of GC reactions (87). Preoperative immunosuppressive therapy reduces intrathymic Tfh profiles and is suspected to inhibit ectopic GC development (88).
Pathogenetic model of EOMG and unresolved issues
The early stages of EOMG pathogenesis are still largely unknown. A popular model suggests a two-step pathogenesis (89). In the first step, auto-reactive T cells are activated by mTECs expressing MHC/AChR–peptide complexes. Subsequently, thymic B cells produce low-affinity Abs toward AChRs. In the second step, early Abs attack nearby TMCs expressing folded AChRs on their surface and activate complement, resulting in the subsequent release of AChR/immune complexes. These AChR/immune complexes activate antigen-presenting cells (APCs), such as DCs, which in turn drive the further activation of auto-reactive CD4+ T cells. This leads to the initiation of ectopic follicle and GC formation with affinity maturation of their B cell receptors, and ultimately to the production of high-affinity late AChR Abs (89) (Figure 1).
The resulting thymic TFH responses may be self-perpetuating, likely due to dysfunctional Tregs in the EOMG thymus and blood (84, 90). Finally, the autoimmune process initiated in the thymus can spread to the periphery, where, hypothetically, skeletal muscle-derived AChR/Ab complexes in regional lymph nodes and functionally defective Tregs may contribute to the maintenance of EOMG (47, 91, 92).
It is believed that mimetic “muscle mTECs” in the human thymus are involved in acetylcholine-mediated interfaces, mimicking peripheral neuromuscular junctions (36). However, it remains unknown whether TMCs are identical to, if not a part of, muscle mTECs.
HCs represent the terminally differentiated stage of mTECs (93–96). The increased number and morphological changes of HCs in the TFH thymus are similar to those in infantile Down syndrome thymus, which exhibits altered AIRE expression (97–99). Down syndrome is associated with impaired Treg function and an increased risk of developing autoimmunity (100, 101). It is conceivable that the altered differentiation of mTECs, including the increase in the number of HCs, may be associated with impaired TEC/thymocyte crosstalk signals in EOMG. Several studies have reported that AIRE expression in the EOMG thymus is comparable to that in the control thymus (47, 102, 103). However, these studies were performed using thymus tissues rather than isolated mTECs. Moreover, other thymic cells, such as B cells or activated DCs, are also known to express AIRE (14, 104). Therefore, AIRE expression in non-mTEC thymic cells may contribute to the apparently undiminished AIRE expression in the EOMG thymus.
Recent single-cell studies have identified specific helper T cells or macrophages in the EOMG thymus (105–107). However, comprehensive single-cell analyses of human TECs and non-TECs from non-neoplastic MG thymus are needed to better understand the underlying immunopathogenesis of EOMG.
Thymoma-associated MG
TAMG is a subtype of AChR Ab-positive MG (60). Approximately 10 to 20% of generalized AChR Ab-positive MG patients have thymoma (46, 108). TAMG typically occurs after age 50; however, it has a wide age range, including children (109). Unlike EOMG, TAMG shows neither gender distribution nor strong HLA association (47, 50).
Thymomas are neoplasms of TECs, characterized by diverse cortical and medullary differentiation accompanied by thymopoiesis in more than 90% of patients (60). The current WHO classification categorizes thymomas into five main types: A, AB, B1, B2, and B3, on the basis of epithelial cell features and lymphocyte content (109). Thymomas containing spindled neoplastic epithelial cells at least focally are classified as type A if they have no or few immature thymic T cells, and as type AB if immature T cells among epithelial cells are at least focally abundant. By contrast, thymomas composed of polygonal tumor cells are classified as type B, and their further division into B1, B2, and B3 depends on the presence of a very high, intermediate, and low number of interepithelial immature T cells, respectively. Types AB, B1, and B2 thymomas are the most prevalent subtypes in MG patients (50) (Figure 2). Unlike in EOMG, more than 80% of patients with thymomas have autoantibodies against striational antigens, such as titin and ryanodine receptors (RYRs), as well as others that neutralize cytokines, including type I interferon (IFN) and IL-12 (110, 111). TAMG is the most common thymoma-associated autoimmune disease (30–40%). Others, such as thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, pure red cell aplasia, hypogammaglobulinemia, and other bone marrow failures, are less common (each 1–5%). Together with TAMG, they comprise over 50% of thymoma-associated autoimmune diseases (112, 113).
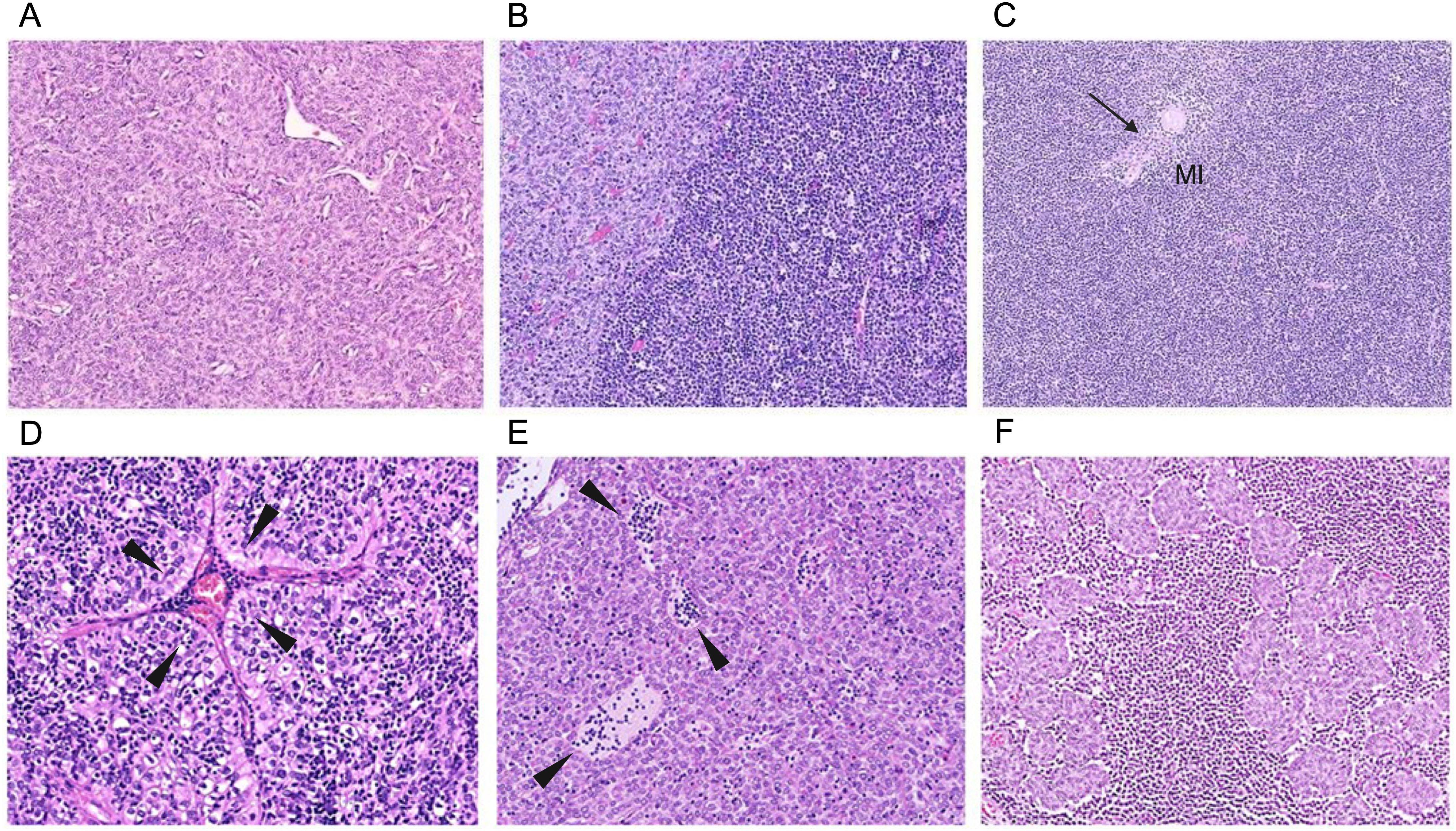
Figure 2. Representative images of typical thymomas (Types A, AB, B1–B3) commonly associated with MG. By definition, types AB, B1, and B2 thymomas consistently harbor interepithelial immature (TdT-positive) T cells, whereas immature T cells are rare and sometimes even absent in types A and B3 thymomas. Enigmatically, the scientifically largely neglected micronodular thymomas with lymphoid stroma are virtually never associated with MG, offering an “experiment of nature” to study the mechanisms driving or preventing the development of thymoma-associated MG. (A) Type A thymoma: predominant neoplastic spindle cells and rare (and sometimes no) immature T cells. (B) Type AB: biphasic architecture with lymphocyte-poor (left, light) and immature T cell-rich (right, dark) regions. Rarely, lymphocyte-poor regions can be missing altogether. (C) Type B1: predominant cortical areas with inconspicuous tumor cells, abundant lymphocytes, and a small medullary island (MI) with a single Hassall corpuscle (HC) (arrow). (D) Type B2: many lymphocytes and many conspicuous, large, polygonal epithelial cells arranged in lobules and around a prominent perivascular space (PVS) containing lymphocytes and a blood-filled vessel (arrowheads). (E) Type B3: confluent sheets of pink, polygonal tumor cells, few (and eventually no) interepithelial lymphocytes, PVS containing lymphocytes (arrowheads). (F) Micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma: small nodules of neoplastic epithelial cells resembling those of type A thymoma, surrounded by a lymphoid stroma composed of B cells (often forming follicles) as well as mature and immature T cells.
Cellular changes and autoimmunity in TAMG
In TAMG, the most common MG-associated thymoma types (AB, B1 to B3) typically show prominent cortex-like regions, with medulla-like regions usually attenuated (114) (Figure 2). These thymomas mostly contain abundant immature thymocytes and export high numbers of mature T cells into the peripheral blood, where the export of mature emigrant CD4+ T cells is strongly associated with the development of MG (115–117).
Abnormalities in TECs, including the reduced expression of antigen-processing proteases in cTECs and MHC class II antigens in mTECs, as well as defective FOXP3+ Treg generation, may contribute to TAMG development (77, 114, 118–120). The loss or reduction of AIRE+ mTECs has also been observed in the TAMG thymus (103, 121) (Table 1). Molecular components essential for thymic tolerance are deficient in MG thymoma. This may account for the frequent presence of autoantibodies against non-AChR skeletal muscle antigens, including titin and RyR, and against type I IFN (122, 123). The lack of TMCs in thymoma and/or the expression of AChR, titin, and RyR epitopes in neoplastic TECs may also account for the generation of muscle Abs (112, 124, 125). These findings suggest that thymic T cell selection may be altered, or that auto-reactive T cells may be inappropriately activated in the thymic environment.
Pathogenetic model of TAMG and unresolved issues
The above findings suggest the following pathogenetic model: First, the reduced levels of some HLA variants and neoplastic linear AChR/titin peptide-overexpressing TECs may contribute to altered positive selection (77, 121, 124). Next, auto-reactive thymocytes survive, partly because of the absence of AIRE+ mTECs and Tregs, and also because of the combined defects of medullary functions, including a lack of myoid cell-derived AChRs and titin for tolerogenic cross-presentation by APCs (89). Finally, thymoma-derived auto-reactive mature thymocytes escape negative selection in the thymoma, exit into the blood, gradually diluting and eventually replacing the existing tolerant peripheral T cell repertoire (115, 117, 126). In the periphery, including the remnant thymus, these escaping auto-reactive thymocytes stimulate B cells to generate autoantibodies against naïve AChRs after appropriate stimulation. Once initiated, skeletal muscle-derived AChR/autoantibody complexes present in regional lymph nodes perpetuate TAMG even after thymoma removal (108, 124, 127, 128).
Those abnormalities in TECs, which are related to positive and negative selections, are not specific to MG but are commonly detected in thymoma. Despite the loss of AIRE+ mTECs, MG is not a common manifestation of human autoimmune polyendocrinopathy–candidiasis–ectodermal dystrophy, which results from various mutations in AIRE (129, 130). Thus, the loss of AIRE+ mTECs may be partially, but not entirely, linked to MG pathogenesis. A single-cell sequencing study suggested that a subset of mTECs, named nmTECs, exhibits a significant function through the ectopic expression of neuromuscular molecules in MG thymoma (38). However, nmTEC marker-positive cells are also present in some non-MG thymomas (38). Therefore, the accumulation of neuromuscular-related antigens in nmTECs is not a sufficient condition for MG pathogenesis, and an increased number of nmTECs alone is insufficient to initiate TAMG. Spatial transcriptomic analysis has revealed specific immune niches in the medulla and nmTEC enrichment in the corticomedullary junction (131). Furthermore, a specific chemokine pattern, i.e., CXCL12–CXCR4, and immune cells, including CXCL13+ Tfh cells and migratory DCs, have been detected in the MG–thymoma niche (38, 131). Those immune microenvironments, such as CXCL13 interactions, are often observed in TFH (63, 78). Because occasional GCs are enriched by high endothelial venules in TAMG (50, 132), further investigation is needed to elucidate the pathogenesis of TAMG.
LOMG
There is no consensus on the age threshold for distinguishing between LOMG and EOMG. The most common age threshold of 50 years shows a gender bias distinct from EOMG, i.e., a predominance of males, and a higher frequency of AChR seropositivity (42, 50, 133, 134). LOMG patients, by definition, do not have thymoma. The aging thymus is gradually replaced by fat, but residual parenchyma may continue to export some T cells at least into middle age (135). In LOMG, these remnants may rarely show signs of expansion and even infiltration. However, morphometric analysis did not reveal significant differences between LOMG and normal thymuses (136). TMCs and AIRE-positive cells decline with age. However, there is no apparent difference between LOMG thymuses and age-matched controls (68, 72, 73). Although the genetic background is likely different from that of EOMG and is of pathogenetic relevance, the aged thymus in LOMG is assumed to export and possibly activate non-tolerant T cells (89, 108). Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have demonstrated that several genes are associated with T cell tolerance (42, 137–139). The following factors are believed to contribute to the pathogenesis of LOMG: 1) immune system aging, which is associated with increased rates of autoimmunity; 2) AChR-reactive T cells, generated in the near absence of myoid cells within a largely AIRE-negative atrophic thymus, may become activated after export to the periphery and subsequently trigger LOMG; and 3) a pathogenic T cell population, derived from an atrophic thymus lacking myoid cells and AIRE expression, is accumulated in the periphery over a long period before the outbreak of LOMG, similar to rare thymoma patients who develop TAMG years after thymoma removal (42, 115). Once initiated, LOMG may become self-perpetuating as described above for TAMG, owing to stimulatory AChR/autoantibody complexes in muscle-draining lymph nodes.
Other MG subtypes
Patients with MuSK Abs demonstrate a propensity for bulbar muscle involvement (42). Thymoma has been reported as a rare exception in MuSK Ab-positive MG patients (49). Most autoantibodies in MuSK Ab-positive MG are of the IgG4 subclass, in contrast to AChR Abs. Immunopathology of MuSK Abs is less currently known, but the proposed mechanism underlying autoantibody production in MuSK MG is as follows. Peripheral naïve B cells likely encounter self-antigens and receive T cell help in lymphoid tissue. These naïve B cells differentiate into memory B cells and short-lived plasmablasts that produce MuSK Abs (140). LRP4 Abs are primarily of IgG1 and IgG2 subtypes and are associated with clinical presentations resembling the mild form of EOMG (141). Patients without these other autoantibodies, namely triple seronegative MG represent a highly heterogeneous group, and there is limited information regarding their disease mechanisms (42).
Thymectomy
Thymectomy is a standard treatment option in AChR Ab-positive MG. It should be performed as early as possible, ideally within two years of MG onset (142, 143). Thymectomy can effectively remove AChR-like proteins, antigen-specific T cells, and Ab-producing B cells (144–146). Whereas clinical improvement is observed in half of patients following thymectomy, complete remission is rare (147, 148). Potent autoantibody-producing B cells can differentiate into long-lived plasma cells in the thymus, leading to the production of some of the circulating AChR-specific autoantibodies (140, 149, 150). Thymus-derived B cell clones persist in the circulation after thymectomy, and these B cells are thought to be associated with poor outcome (151). Thymectomy has not resulted in clinical improvement in MuSK Ab-positive patients, unlike in AChR Ab-positive patients (152, 153). MuSK Ab-positive thymus shows few GCs, and these thymic changes are thought to be associated with responses to thymectomy (48). Several studies have demonstrated that rituximab, which depletes B cells, achieves a higher improvement rate in MuSK Ab-positive MG than in AChR Ab-positive MG. However, rituximab has been reported to reduce the risk of relapse in AChR Ab-positive MG, although its benefit appears greater in MuSK Ab-positive MG (154). It is speculated that autoantibody-producing B cell clones residing in AChR Ab-positive MG thymus can also populate lymphoid tissues outside the thymus. In those cases, there may be pathogeneses in which thymectomy or rituximab is ineffective.
Conclusions and perspectives
Thymic abnormalities are observed in a substantial proportion of patients with MG, prompting extensive investigation into the involvement of the thymus in the immunopathogenesis of the disease. Recent studies have shown the expanding diversity of TEC subpopulations in relation to neuromuscular junctions. ChAT-expressing thymic tuft cells are in close proximity to muscle mimetic cells in the normal human thymus. However, the role of these TEC subpopulations in the MG thymus remains to be investigated. Further studies are required to determine whether muscle mTECs are identical to, or represent a subset of, TMCs, and whether a specific TEC subpopulation, such as muscle mTECs, expresses immunogenic AChRs in the thymus of MG patients.
The understanding of TEC biology in humans lags behind that in mouse models. In this regard, the development of methods for purifying TEC subpopulations from both non-thymomatous and neoplastic thymic tissues is highly anticipated, as this will facilitate the identification of triggers leading to MG. Experimental autoimmune MG (EAMG) animal models have been established to investigate pathogenic mechanisms (155). However, these EAMG animal models lack thymic abnormalities, limiting their utility in elucidating the pathogenic mechanisms associated with the abnormal thymus in MG. A comprehensive understanding of TEC biology in the MG thymus will positively impact the engineering of EAMG animal models with thymic abnormalities, thereby further advancing research on MG thymus.
Thymectomy is one of the long-acting immunotherapies. However, it is currently not possible to predict the postoperative MG course owing to the lack of preoperative biomarkers and predictive morphological features of the resected thymic tissue. The problem with performing scRNA-seq/spatial transcriptomic analysis of MG thymus lies in the preoperative use of corticosteroids, which can lead to pathological changes in the thymus. However, the integration of recent advancements, such as in situ single-nucleus barcoding, may provide a solution to this problem. Biomarkers should aim at identifying highly active and refractory MG patients. Given the expanding treatment landscape in MG, highly disease-active and refractory cases should be considered for new targeted therapies, such as complement inhibitors or B cell depletion. We hope that thymus research will contribute to a better understanding of MG pathogenesis and enable the establishment of biomarkers for MG-specific therapy that interrupt AChR/MuSK-directed autoimmunity without compromising other aspects of immune function.
Author contributions
NM: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. IO: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AM: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research C (Grant Number 25K10660); the Health and Labour Sciences Research Grant on Intractable Diseases (Neuroimmunological Diseases) from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan (20FC1030); Joint Usage and Joint Research, the Institute of Advanced Medical Sciences, Tokushima University (to N. Matsui); the Japan Science and Technology Agency PRESTO Grant (22712940); Takeda Science Foundation (2024085060); the Program for Forming Japan’s Peak Research Universities, and the Inter-University Research Network for High Depth Omics (to I. Ohigashi).
Acknowledgments
The image was created using Biorender.com.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Blalock A, Mason MF, Morgan HJ, and Riven SS. Myasthenia gravis and tumors of the thymic region: report of a case in which the tumor was removed. Ann Surg. (1939) 110:544–61. doi: 10.1097/00000658-193910000-00005
2. Castleman B and Norris EH. The pathology of the thymus in myasthenia gravis; a study of 35 cases. Med (Baltimore). (1949) 28:27–58. doi: 10.1097/00005792-194902000-00002
3. Wolfe GI, Kaminski HJ, Aban IB, Minisman G, Kuo HC, Marx A, et al. Randomized trial of thymectomy in myasthenia gravis. N Engl J Med. (2016) 375:511–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1602489
4. Wolfe GI, Kaminski HJ, Aban IB, Minisman G, Kuo HC, Marx A, et al. Long-term effect of thymectomy plus prednisone versus prednisone alone in patients with non-thymomatous myasthenia gravis: 2-year extension of the MGTX randomised trial. Lancet Neurol. (2019) 18:259–68. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30392-2
5. Binks SNM, Morse IM, Ashraghi M, Vincent A, Waters P, and Leite MI. Myasthenia gravis in 2025: five new things and four hopes for the future. J Neurol. (2025) 272:226. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-12922-7
6. Miller JF. Immunological function of the thymus. Lancet. (1961) 2:748–9. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)90693-6
7. Baran-Gale J, Morgan MD, Maio S, Dhalla F, Calvo-Asensio I, Deadman ME, et al. Ageing compromises mouse thymus function and remodels epithelial cell differentiation. Elife. (2020) 9:e56221. doi: 10.7554/eLife.56221
8. Michelson DA, Hase K, Kaisho T, Benoist C, and Mathis D. Thymic epithelial cells co-opt lineage-defining transcription factors to eliminate autoreactive T cells. Cell. (2022) 185:2542–58 e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.05.018
9. Anderson G and Takahama Y. Thymic epithelial cells: working class heroes for T cell development and repertoire selection. Trends Immunol. (2012) 33:256–63. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2012.03.005
10. Ohigashi I, Kozai M, and Takahama Y. Development and developmental potential of cortical thymic epithelial cells. Immunol Rev. (2016) 271:10–22. doi: 10.1111/imr.12404
11. Mathis D and Benoist C. Aire. Annu Rev Immunol. (2009) 27:287–312. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141532
12. Ueno T, Saito F, Gray DH, Kuse S, Hieshima K, Nakano H, et al. CCR7 signals are essential for cortex-medulla migration of developing thymocytes. J Exp Med. (2004) 200:493–505. doi: 10.1084/jem.20040643
13. Kozai M, Kubo Y, Katakai T, Kondo H, Kiyonari H, Schaeuble K, et al. Essential role of CCL21 in establishment of central self-tolerance in T cells. J Exp Med. (2017) 214:1925–35. doi: 10.1084/jem.20161864
14. Park JE, Botting RA, Dominguez Conde C, Popescu DM, Lavaert M, Kunz DJ, et al. A cell atlas of human thymic development defines T cell repertoire formation. Science. (2020) 367(6480):eaay3224. doi: 10.1126/science.aay3224
15. Bautista JL, Cramer NT, Miller CN, Chavez J, Berrios DI, Byrnes LE, et al. Single-cell transcriptional profiling of human thymic stroma uncovers novel cellular heterogeneity in the thymic medulla. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:1096. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21346-6
16. Gordon J, Bennett AR, Blackburn CC, and Manley NR. Gcm2 and Foxn1 mark early parathyroid- and thymus-specific domains in the developing third pharyngeal pouch. Mech Dev. (2001) 103:141–3. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(01)00333-1
17. Rossi SW, Jenkinson WE, Anderson G, and Jenkinson EJ. Clonal analysis reveals a common progenitor for thymic cortical and medullary epithelium. Nature. (2006) 441:988–91. doi: 10.1038/nature04813
18. Bleul CC, Corbeaux T, Reuter A, Fisch P, Monting JS, and Boehm T. Formation of a functional thymus initiated by a postnatal epithelial progenitor cell. Nature. (2006) 441:992–6. doi: 10.1038/nature04850
19. Wong K, Lister NL, Barsanti M, Lim JM, Hammett MV, Khong DM, et al. Multilineage potential and self-renewal define an epithelial progenitor cell population in the adult thymus. Cell Rep. (2014) 8:1198–209. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.07.029
20. Ulyanchenko S, O’Neill KE, Medley T, Farley AM, Vaidya HJ, Cook AM, et al. Identification of a bipotent epithelial progenitor population in the adult thymus. Cell Rep. (2016) 14:2819–32. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.02.080
21. Hamazaki Y, Fujita H, Kobayashi T, Choi Y, Scott HS, Matsumoto M, et al. Medullary thymic epithelial cells expressing Aire represent a unique lineage derived from cells expressing claudin. Nat Immunol. (2007) 8:304–11. doi: 10.1038/ni1438
22. Sekai M, Hamazaki Y, and Minato N. Medullary thymic epithelial stem cells maintain a functional thymus to ensure lifelong central T cell tolerance. Immunity. (2014) 41:753–61. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.10.011
23. Akiyama N, Takizawa N, Miyauchi M, Yanai H, Tateishi R, Shinzawa M, et al. Identification of embryonic precursor cells that differentiate into thymic epithelial cells expressing autoimmune regulator. J Exp Med. (2016) 213:1441–58. doi: 10.1084/jem.20151780
24. Lucas B, White AJ, Klein F, Veiga-Villauriz C, Handel A, Bacon A, et al. Embryonic keratin19(+) progenitors generate multiple functionally distinct progeny to maintain epithelial diversity in the adult thymus medulla. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:2066. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37589-4
25. Farley AM, Chengrui A, Palmer S, Liu D, Kousa AI, Rouse P, et al. Thymic epithelial cell fate and potency in early organogenesis assessed by single cell transcriptional and functional analysis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1202163. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1202163
26. Ohigashi I, White AJ, Yang MT, Fujimori S, Tanaka Y, Jacques A, et al. Developmental conversion of thymocyte-attracting cells into self-antigen-displaying cells in embryonic thymus medulla epithelium. Elife. (2024) 12:RP92552. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92552
27. Campinoti S, Gjinovci A, Ragazzini R, Zanieri L, Ariza-McNaughton L, Catucci M, et al. Reconstitution of a functional human thymus by postnatal stromal progenitor cells and natural whole-organ scaffolds. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:6372. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20082-7
28. Ragazzini R, Boeing S, Zanieri L, Green M, D’Agostino G, Bartolovic K, et al. Defining the identity and the niches of epithelial stem cells with highly pleiotropic multilineage potency in the human thymus. Dev Cell. (2023) 58:2428–46. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2023.08.017
29. Fiorini E, Ferrero I, Merck E, Favre S, Pierres M, Luther SA, et al. Cutting edge: thymic crosstalk regulates delta-like 4 expression on cortical epithelial cells. J Immunol. (2008) 181:8199–203. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.12.8199
30. White AJ, Parnell SM, Handel A, Maio S, Bacon A, Cosway EJ, et al. Diversity in cortical thymic epithelial cells occurs through loss of a foxn1-dependent gene signature driven by stage-specific thymocyte cross-talk. J Immunol. (2022) 210:40–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200609
31. Miller CN, Proekt I, von Moltke J, Wells KL, Rajpurkar AR, Wang H, et al. Thymic tuft cells promote an IL-4-enriched medulla and shape thymocyte development. Nature. (2018) 559:627–31. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0345-2
32. Bornstein C, Nevo S, Giladi A, Kadouri N, Pouzolles M, Gerbe F, et al. Single-cell mapping of the thymic stroma identifies IL-25-producing tuft epithelial cells. Nature. (2018) 559:622–6. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0346-1
33. Givony T, Leshkowitz D, Del Castillo D, Nevo S, Kadouri N, Dassa B, et al. Thymic mimetic cells function beyond self-tolerance. Nature. (2023) 622:164–72. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06512-8
34. Lucas B, White AJ, Cosway EJ, Parnell SM, James KD, Jones ND, et al. Diversity in medullary thymic epithelial cells controls the activity and availability of iNKT cells. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:2198. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16041-x
35. Yayon N, Kedlian VR, Boehme L, Suo C, Wachter BT, Beuschel RT, et al. A spatial human thymus cell atlas mapped to a continuous tissue axis. Nature. (2024) 635:708–18. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07944-6
36. Huisman BD, Michelson DA, Rubin SA, Kohlsaat K, Gomarga W, Fang Y, et al. Cross-species analyses of thymic mimetic cells reveal evolutionarily ancient origins and both conserved and species-specific elements. Immunity. (2025) 58:108–23 e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.11.025
37. Hu B, Simon-Keller K, Kuffer S, Strobel P, Braun T, Marx A, et al. Myf5 and Myogenin in the development of thymic myoid cells - Implications for a murine in vivo model of myasthenia gravis. Exp Neurol. (2016) 277:76–85. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.12.010
38. Yasumizu Y, Ohkura N, Murata H, Kinoshita M, Funaki S, Nojima S, et al. Myasthenia gravis-specific aberrant neuromuscular gene expression by medullary thymic epithelial cells in thymoma. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:4230. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31951-8
39. Schluep M, Willcox N, Vincent A, Dhoot GK, and Newsom-Davis J. Acetylcholine receptors in human thymic myoid cells in situ: an immunohistological study. Ann Neurol. (1987) 22:212–22. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220205
40. Vincent A. Unravelling the pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis. Nat Rev Immunol. (2002) 2:797–804. doi: 10.1038/nri916
41. Gilhus NE, Skeie GO, Romi F, Lazaridis K, Zisimopoulou P, and Tzartos S. Myasthenia gravis - autoantibody characteristics and their implications for therapy. Nat Rev Neurol. (2016) 12:259–68. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2016.44
42. Kaminski HJ, Sikorski P, Coronel SI, and Kusner LL. Myasthenia gravis: the future is here. J Clin Invest. (2024) 134:e179742. doi: 10.1172/JCI179742
43. Hoch W, McConville J, Helms S, Newsom-Davis J, Melms A, and Vincent A. Auto-antibodies to the receptor tyrosine kinase MuSK in patients with myasthenia gravis without acetylcholine receptor antibodies. Nat Med. (2001) 7:365–8. doi: 10.1038/85520
44. Higuchi O, Hamuro J, Motomura M, and Yamanashi Y. Autoantibodies to low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4 in myasthenia gravis. Ann Neurol. (2011) 69:418–22. doi: 10.1002/ana.22312
45. Zhang B, Tzartos JS, Belimezi M, Ragheb S, Bealmear B, Lewis RA, et al. Autoantibodies to lipoprotein-related protein 4 in patients with double-seronegative myasthenia gravis. Arch Neurol. (2012) 69:445–51. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2011.2393
46. Berrih-Aknin S and Le Panse R. Myasthenia gravis: a comprehensive review of immune dysregulation and etiological mechanisms. J Autoimmun. (2014) 52:90–100. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.12.011
47. Marx A, Pfister F, Schalke B, Saruhan-Direskeneli G, Melms A, and Strobel P. The different roles of the thymus in the pathogenesis of the various myasthenia gravis subtypes. Autoimmun Rev. (2013) 12:875–84. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2013.03.007
48. Leite MI, Strobel P, Jones M, Micklem K, Moritz R, Gold R, et al. Fewer thymic changes in MuSK antibody-positive than in MuSK antibody-negative MG. Ann Neurol. (2005) 57:444–8. doi: 10.1002/ana.20386
49. Saka E, Topcuoglu MA, Akkaya B, Galati A, Onal MZ, and Vincent A. Thymus changes in anti-MuSK-positive and -negative myasthenia gravis. Neurology. (2005) 65:782–3; author reply -3. doi: 10.1212/wnl.65.5.782
50. Huijbers MG, Marx A, Plomp JJ, Le Panse R, and Phillips WD. Advances in the understanding of disease mechanisms of autoimmune neuromuscular junction disorders. Lancet Neurol. (2022) 21:163–75. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00357-4
51. Gregersen PK, Kosoy R, Lee AT, Lamb J, Sussman J, McKee D, et al. Risk for myasthenia gravis maps to a (151) Pro–>Ala change in TNIP1 and to human leukocyte antigen-B*08. Ann Neurol. (2012) 72:927–35. doi: 10.1002/ana.23691
52. Maniaol AH, Elsais A, Lorentzen AR, Owe JF, Viken MK, Saether H, et al. Late onset myasthenia gravis is associated with HLA DRB1*15:01 in the Norwegian population. PloS One. (2012) 7:e36603. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036603
53. Cron MA, Maillard S, Delisle F, Samson N, Truffault F, Foti M, et al. Analysis of microRNA expression in the thymus of Myasthenia Gravis patients opens new research avenues. Autoimmun Rev. (2018) 17:588–600. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2018.01.008
54. Altintas A, Dargvainiene J, Schneider-Gold C, Asgari N, Ayzenberg I, Ciplea AI, et al. Gender issues of antibody-mediated diseases in neurology: (NMOSD/autoimmune encephalitis/MG). Ther Adv Neurol Disord. (2020) 13:1756286420949808. doi: 10.1177/1756286420949808
55. Kakalacheva K, Maurer MA, Tackenberg B, Munz C, Willcox N, and Lunemann JD. Intrathymic Epstein-Barr virus infection is not a prominent feature of myasthenia gravis. Ann Neurol. (2011) 70:508–14. doi: 10.1002/ana.22488
56. Cavalcante P, Maggi L, Colleoni L, Caldara R, Motta T, Giardina C, et al. Inflammation and epstein-barr virus infection are common features of myasthenia gravis thymus: possible roles in pathogenesis. Autoimmune Dis. (2011) 2011:213092. doi: 10.4061/2011/213092
57. Leopardi V, Chang YM, Pham A, Luo J, and Garden OA. A systematic review of the potential implication of infectious agents in myasthenia gravis. Front Neurol. (2021) 12:618021. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.618021
58. Nowlan K, Hannolainen L, Assimakopoulou IM, Durnsteiner P, Sarkkinen J, Suokas S, et al. Parvovirus B19 and human herpes virus 6B and 7 are frequently found DNA viruses in the human thymus but show no definitive link with myasthenia gravis. J Infect Dis. (2025) 231:e601–e6. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae600
59. Weis CA, Schalke B, Strobel P, and Marx A. Challenging the current model of early-onset myasthenia gravis pathogenesis in the light of the MGTX trial and histological heterogeneity of thymectomy specimens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2018) 1413:82–91. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13563
60. Marx A, Yamada Y, Simon-Keller K, Schalke B, Willcox N, Strobel P, et al. Thymus and autoimmunity. Semin Immunopathol. (2021) 43:45–64. doi: 10.1007/s00281-021-00842-3
61. Sims GP, Shiono H, Willcox N, and Stott DI. Somatic hypermutation and selection of B cells in thymic germinal centers responding to acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis. J Immunol. (2001) 167:1935–44. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.4.1935
62. Truffault F, de Montpreville V, Eymard B, Sharshar T, Le Panse R, and Berrih-Aknin S. Thymic germinal centers and corticosteroids in myasthenia gravis: an immunopathological study in 1035 cases and a critical review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2017) 52:108–24. doi: 10.1007/s12016-016-8558-3
63. Berrih-Aknin S, Ragheb S, Le Panse R, and Lisak RP. Ectopic germinal centers, BAFF and anti-B-cell therapy in myasthenia gravis. Autoimmun Rev. (2013) 12:885–93. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2013.03.011
64. Hohlfeld R, Kalies I, Ernst M, Ketelsen UP, and Wekerle H. T-lymphocytes in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. Isolation of T-helper cell lines. J Neurol Sci. (1982) 57:265–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90033-8
65. Hohlfeld R, Toyka KV, Heininger K, Grosse-Wilde H, and Kalies I. Autoimmune human T lymphocytes specific for acetylcholine receptor. Nature. (1984) 310:244–6. doi: 10.1038/310244a0
66. Berrih-Aknin S, Cohen-Kaminsky S, Lepage V, Neumann D, Bach JF, and Fuchs S. T-cell antigenic sites involved in myasthenia gravis: correlations with antibody titre and disease severity. J Autoimmun. (1991) 4:137–53. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(91)90013-3
67. Wang ZY, Karachunski PI, Howard JF Jr., and Conti-Fine BM. Myasthenia in SCID mice grafted with myasthenic patient lymphocytes: role of CD4+ and CD8+ cells. Neurology. (1999) 52:484–97. doi: 10.1212/wnl.52.3.484
68. Van de Velde RL and Friedman NB. Thymic myoid cells and myasthenia gravis. Am J Pathol. (1970) 59:347–68.
69. Wekerle TH, Paterson B, Ketelsen U, and Feldman M. Striated muscle fibres differentiate in monolayer cultures of adult thymus reticulum. Nature. (1975) 256:493–4. doi: 10.1038/256493a0
70. Kao I and Drachman DB. Thymic muscle cells bear acetylcholine receptors: possible relation to myasthenia gravis. Science. (1977) 195:74–5. doi: 10.1126/science.831257
71. Leite MI, Jones M, Strobel P, Marx A, Gold R, Niks E, et al. Myasthenia gravis thymus: complement vulnerability of epithelial and myoid cells, complement attack on them, and correlations with autoantibody status. Am J Pathol. (2007) 171:893–905. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070240
72. Roxanis I, Micklem K, McConville J, Newsom-Davis J, and Willcox N. Thymic myoid cells and germinal center formation in myasthenia gravis; possible roles in pathogenesis. J Neuroimmunol. (2002) 125:185–97. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(02)00038-3
73. Kirchner T, Schalke B, Melms A, von Kugelgen T, and Muller-Hermelink HK. Immunohistological patterns of non-neoplastic changes in the thymus in Myasthenia gravis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. (1986) 52:237–57. doi: 10.1007/BF02889966
74. Roxanis I, Micklem K, and Willcox N. True epithelial hyperplasia in the thymus of early-onset myasthenia gravis patients: implications for immunopathogenesis. J Neuroimmunol. (2001) 112:163–73. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(00)00415-x
75. Wakkach A, Guyon T, Bruand C, Tzartos S, Cohen-Kaminsky S, and Berrih-Aknin S. Expression of acetylcholine receptor genes in human thymic epithelial cells: implications for myasthenia gravis. J Immunol. (1996) 157:3752–60. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.157.8.3752
76. Poea-Guyon S, Christadoss P, Le Panse R, Guyon T, De Baets M, Wakkach A, et al. Effects of cytokines on acetylcholine receptor expression: implications for myasthenia gravis. J Immunol. (2005) 174:5941–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.10.5941
77. Willcox N, Schluep M, Ritter MA, Schuurman HJ, Newsom-Davis J, and Christensson B. Myasthenic and nonmyasthenic thymoma. An expansion of a minor cortical epithelial cell subset? Am J Pathol. (1987) 127:447–60.
78. Meraouna A, Cizeron-Clairac G, Panse RL, Bismuth J, Truffault F, Tallaksen C, et al. The chemokine CXCL13 is a key molecule in autoimmune myasthenia gravis. Blood. (2006) 108:432–40. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-06-2383
79. Berrih-Aknin S, Ruhlmann N, Bismuth J, Cizeron-Clairac G, Zelman E, Shachar I, et al. CCL21 overexpressed on lymphatic vessels drives thymic hyperplasia in myasthenia. Ann Neurol. (2009) 66:521–31. doi: 10.1002/ana.21628
80. Weiss JM, Cufi P, Bismuth J, Eymard B, Fadel E, Berrih-Aknin S, et al. SDF-1/CXCL12 recruits B cells and antigen-presenting cells to the thymus of autoimmune myasthenia gravis patients. Immunobiology. (2013) 218:373–81. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2012.05.006
81. Thangarajh M, Masterman T, Helgeland L, Rot U, Jonsson MV, Eide GE, et al. The thymus is a source of B-cell-survival factors-APRIL and BAFF-in myasthenia gravis. J Neuroimmunol. (2006) 178:161–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.05.023
82. Bernasconi P, Barberis M, Baggi F, Passerini L, Cannone M, Arnoldi E, et al. Increased toll-like receptor 4 expression in thymus of myasthenic patients with thymitis and thymic involution. Am J Pathol. (2005) 167:129–39. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62960-4
83. Cufi P, Dragin N, Ruhlmann N, Weiss JM, Fadel E, Serraf A, et al. Central role of interferon-beta in thymic events leading to myasthenia gravis. J Autoimmun. (2014) 52:44–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.12.016
84. Balandina A, Lecart S, Dartevelle P, Saoudi A, and Berrih-Aknin S. Functional defect of regulatory CD4(+)CD25+ T cells in the thymus of patients with autoimmune myasthenia gravis. Blood. (2005) 105:735–41. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-11-3900
85. Matsui N, Nakane S, Saito F, Ohigashi I, Nakagawa Y, Kurobe H, et al. Undiminished regulatory T cells in the thymus of patients with myasthenia gravis. Neurology. (2010) 74:816–20. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181d31e47
86. Gradolatto A, Nazzal D, Truffault F, Bismuth J, Fadel E, Foti M, et al. Both Treg cells and Tconv cells are defective in the Myasthenia gravis thymus: roles of IL-17 and TNF-alpha. J Autoimmun. (2014) 52:53–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.12.015
87. Crotty S. T follicular helper cell differentiation, function, and roles in disease. Immunity. (2014) 41:529–42. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.10.004
88. Yamamoto Y, Matsui N, Uzawa A, Ozawa Y, Kanai T, Oda F, et al. Intrathymic plasmablasts are affected in patients with myasthenia gravis with active disease. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. (2021) 8:e1087. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000001087
89. Willcox N, Leite MI, Kadota Y, Jones M, Meager A, Subrahmanyam P, et al. Autoimmunizing mechanisms in thymoma and thymus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2008) 1132:163–73. doi: 10.1196/annals.1405.021
90. Thiruppathi M, Rowin J, Ganesh B, Sheng JR, Prabhakar BS, and Meriggioli MN. Impaired regulatory function in circulating CD4(+)CD25(high)CD127(low/-) T cells in patients with myasthenia gravis. Clin Immunol. (2012) 145:209–23. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2012.09.012
91. Marx A, Wilisch A, Schultz A, Gattenlohner S, Nenninger R, and Muller-Hermelink HK. Pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis. Virchows Arch. (1997) 430:355–64. doi: 10.1007/s004280050044
92. Cavalcante P, Bernasconi P, and Mantegazza R. Autoimmune mechanisms in myasthenia gravis. Curr Opin Neurol. (2012) 25:621–9. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0b013e328357a829
93. Michel C, Miller CN, Kuchler R, Brors B, Anderson MS, Kyewski B, et al. Revisiting the road map of medullary thymic epithelial cell differentiation. J Immunol. (2017) 199:3488–503. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700203
94. Kadouri N, Nevo S, Goldfarb Y, and Abramson J. Thymic epithelial cell heterogeneity: TEC by TEC. Nat Rev Immunol. (2020) 20:239–53. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0238-0
95. Watanabe N, Wang YH, Lee HK, Ito T, Wang YH, Cao W, et al. Hassall’s corpuscles instruct dendritic cells to induce CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in human thymus. Nature. (2005) 436:1181–5. doi: 10.1038/nature03886
96. Hanabuchi S, Ito T, Park WR, Watanabe N, Shaw JL, Roman E, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin-activated plasmacytoid dendritic cells induce the generation of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in human thymus. J Immunol. (2010) 184:2999–3007. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0804106
97. Matsui N, Ohigashi I, Tanaka K, Sakata M, Furukawa T, Nakagawa Y, et al. Increased number of Hassall’s corpuscles in myasthenia gravis patients with thymic hyperplasia. J Neuroimmunol. (2014) 269:56–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2014.01.011
98. Gimenez-Barcons M, Casteras A, Armengol Mdel P, Porta E, Correa PA, Marin A, et al. Autoimmune predisposition in Down syndrome may result from a partial central tolerance failure due to insufficient intrathymic expression of AIRE and peripheral antigens. J Immunol. (2014) 193:3872–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400223
99. Skogberg G, Lundberg V, Lindgren S, Gudmundsdottir J, Sandstrom K, Kampe O, et al. Altered expression of autoimmune regulator in infant down syndrome thymus, a possible contributor to an autoimmune phenotype. J Immunol. (2014) 193:2187–95. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400742
101. Marcovecchio GE, Bortolomai I, Ferrua F, Fontana E, Imberti L, Conforti E, et al. Thymic epithelium abnormalities in diGeorge and down syndrome patients contribute to dysregulation in T cell development. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:447. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00447
102. Scarpino S, Di Napoli A, Stoppacciaro A, Antonelli M, Pilozzi E, Chiarle R, et al. Expression of autoimmune regulator gene (AIRE) and T regulatory cells in human thymomas. Clin Exp Immunol. (2007) 149:504–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03442.x
103. Iacomino N, Scandiffio L, Conforti F, Salvi E, Tarasco MC, Bortone F, et al. Muscle and muscle-like autoantigen expression in myasthenia gravis thymus: possible molecular hint for autosensitization. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:732. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030732
104. Cepeda S, Cantu C, Orozco S, Xiao Y, Brown Z, Semwal MK, et al. Age-associated decline in thymic B cell expression of aire and aire-dependent self-antigens. Cell Rep. (2018) 22:1276–87. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.01.015
105. Ingelfinger F, Krishnarajah S, Kramer M, Utz SG, Galli E, Lutz M, et al. Single-cell profiling of myasthenia gravis identifies a pathogenic T cell signature. Acta Neuropathol. (2021) 141:901–15. doi: 10.1007/s00401-021-02299-y
106. Verdier J, Fayet OM, Hemery E, Truffault F, Pinzon N, Demeret S, et al. Single-cell mass cytometry on peripheral cells in Myasthenia Gravis identifies dysregulation of innate immune cells. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1083218. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1083218
107. Terroba-Navajas P, Lu IN, Quast I, Heming M, Keller CW, Ostendorf L, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics identifies a prominent role for the MIF-CD74 axis in myasthenia gravis thymus. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. (2025) 12:e200384. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200384
108. Marx A, Willcox N, Leite MI, Chuang WY, Schalke B, Nix W, et al. Thymoma and paraneoplastic myasthenia gravis. Autoimmunity. (2010) 43:413–27. doi: 10.3109/08916930903555935
109. Marx A, Chan JKC, Chalabreysse L, Dacic S, Detterbeck F, French CA, et al. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the thymus and mediastinum: what is new in thymic epithelial, germ cell, and mesenchymal tumors? J Thorac Oncol. (2022) 17:200–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.10.010
110. Wolff AS, Karner J, Owe JF, Oftedal BE, Gilhus NE, Erichsen MM, et al. Clinical and serologic parallels to APS-I in patients with thymomas and autoantigen transcripts in their tumors. J Immunol. (2014) 193:3880–90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401068
111. Meager A, Wadhwa M, Dilger P, Bird C, Thorpe R, Newsom-Davis J, et al. Anti-cytokine autoantibodies in autoimmunity: preponderance of neutralizing autoantibodies against interferon-alpha, interferon-omega and interleukin-12 in patients with thymoma and/or myasthenia gravis. Clin Exp Immunol. (2003) 132:128–36. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02113.x
112. Marx A, Porubsky S, Belharazem D, Saruhan-Direskeneli G, Schalke B, Strobel P, et al. Thymoma related myasthenia gravis in humans and potential animal models. Exp Neurol. (2015) 270:55–65. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.02.010
113. Bernard C, Frih H, Pasquet F, Kerever S, Jamilloux Y, Tronc F, et al. Thymoma associated with autoimmune diseases: 85 cases and literature review. Autoimmun Rev. (2016) 15:82–92. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.09.005
114. Strobel P, Hartmann E, Rosenwald A, Kalla J, Ott G, Friedel G, et al. Corticomedullary differentiation and maturational arrest in thymomas. Histopathology. (2014) 64:557–66. doi: 10.1111/his.12279
115. Strobel P, Helmreich M, Menioudakis G, Lewin SR, Rudiger T, Bauer A, et al. Paraneoplastic myasthenia gravis correlates with generation of mature naive CD4(+) T cells in thymomas. Blood. (2002) 100:159–66. doi: 10.1182/blood.v100.1.159
116. Buckley C, Douek D, Newsom-Davis J, Vincent A, and Willcox N. Mature, long-lived CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are generated by the thymoma in myasthenia gravis. Ann Neurol. (2001) 50:64–72. doi: 10.1002/ana.1017
117. Hoffacker V, Schultz A, Tiesinga JJ, Gold R, Schalke B, Nix W, et al. Thymomas alter the T-cell subset composition in the blood: a potential mechanism for thymoma-associated autoimmune disease. Blood. (2000) 96:3872–9. doi: 10.1182/blood.V96.12.3872
118. Zettl A, Strobel P, Wagner K, Katzenberger T, Ott G, Rosenwald A, et al. Recurrent genetic aberrations in thymoma and thymic carcinoma. Am J Pathol. (2000) 157:257–66. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64536-1
119. Inoue M, Marx A, Zettl A, Strobel P, Muller-Hermelink HK, and Starostik P. Chromosome 6 suffers frequent and multiple aberrations in thymoma. Am J Pathol. (2002) 161:1507–13. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64426-4
120. Strobel P, Rosenwald A, Beyersdorf N, Kerkau T, Elert O, Murumagi A, et al. Selective loss of regulatory T cells in thymomas. Ann Neurol. (2004) 56:901–4. doi: 10.1002/ana.20340
121. Strobel P, Chuang WY, Chuvpilo S, Zettl A, Katzenberger T, Kalbacher H, et al. Common cellular and diverse genetic basis of thymoma-associated myasthenia gravis: role of MHC class II and AIRE genes and genetic polymorphisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2008) 1132:143–56. doi: 10.1196/annals.1405.018
122. Wolff AS, Sarkadi AK, Marodi L, Karner J, Orlova E, Oftedal BE, et al. Anti-cytokine autoantibodies preceding onset of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I features in early childhood. J Clin Immunol. (2013) 33:1341–8. doi: 10.1007/s10875-013-9938-6
123. Kisand K, Boe Wolff AS, Podkrajsek KT, Tserel L, Link M, Kisand KV, et al. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis in APECED or thymoma patients correlates with autoimmunity to Th17-associated cytokines. J Exp Med. (2010) 207:299–308. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091669
124. Radovich M, Pickering CR, Felau I, Ha G, Zhang H, Jo H, et al. The integrated genomic landscape of thymic epithelial tumors. Cancer Cell. (2018) 33:244–58 e10. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.01.003
125. Romi F, Bo L, Skeie GO, Myking A, Aarli JA, and Gilhus NE. Titin and ryanodine receptor epitopes are expressed in cortical thymoma along with costimulatory molecules. J Neuroimmunol. (2002) 128:82–9. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(02)00145-5
126. Strobel P, Preisshofen T, Helmreich M, Muller-Hermelink HK, and Marx A. Pathomechanisms of paraneoplastic myasthenia gravis. Clin Dev Immunol. (2003) 10:7–12. doi: 10.1080/10446670310001598528
127. Fujii Y, Monden Y, Hashimoto J, Nakahara K, and Kawashima Y. Acetylcholine receptor antibody-producing cells in thymus and lymph nodes in myasthenia gravis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. (1985) 34:141–6. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90018-2
128. Shiono H, Wong YL, Matthews I, Liu JL, Zhang W, Sims G, et al. Spontaneous production of anti-IFN-alpha and anti-IL-12 autoantibodies by thymoma cells from myasthenia gravis patients suggests autoimmunization in the tumor. Int Immunol. (2003) 15:903–13. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxg088
129. Finnish-German AC. An autoimmune disease, APECED, caused by mutations in a novel gene featuring two PHD-type zinc-finger domains. Nat Genet. (1997) 17:399–403. doi: 10.1038/ng1297-399
130. Strobel P, Murumagi A, Klein R, Luster M, Lahti M, Krohn K, et al. Deficiency of the autoimmune regulator AIRE in thymomas is insufficient to elicit autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome type 1 (APS-1). J Pathol. (2007) 211:563–71. doi: 10.1002/path.2141
131. Yasumizu Y, Kinoshita M, Zhang MJ, Motooka D, Suzuki K, Nojima S, et al. Spatial transcriptomics elucidates medulla niche supporting germinal center response in myasthenia gravis-associated thymoma. Cell Rep. (2024) 43:114677. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114677
132. Lefeuvre CM, Payet CA, Fayet OM, Maillard S, Truffault F, Bondet V, et al. Risk factors associated with myasthenia gravis in thymoma patients: The potential role of thymic germinal centers. J Autoimmun. (2020) 106:102337. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.102337
133. Zivkovic SA, Clemens PR, and Lacomis D. Characteristics of late-onset myasthenia gravis. J Neurol. (2012) 259:2167–71. doi: 10.1007/s00415-012-6478-6
134. Aarli JA. Myasthenia gravis in the elderly: Is it different? Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2008) 1132:238–43. doi: 10.1196/annals.1405.040
135. Douek DC, McFarland RD, Keiser PH, Gage EA, Massey JM, Haynes BF, et al. Changes in thymic function with age and during the treatment of HIV infection. Nature. (1998) 396:690–5. doi: 10.1038/25374
136. Strobel P, Moritz R, Leite MI, Willcox N, Chuang WY, Gold R, et al. The ageing and myasthenic thymus: a morphometric study validating a standard procedure in the histological workup of thymic specimens. J Neuroimmunol. (2008) 201-202:64–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.06.017
137. Seldin MF, Alkhairy OK, Lee AT, Lamb JA, Sussman J, Pirskanen-Matell R, et al. Genome-wide association study of late-onset myasthenia gravis: confirmation of TNFRSF11A and identification of ZBTB10 and three distinct HLA associations. Mol Med. (2016) 21:769–81. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2015.00232
138. Handunnetthi L, Knezevic B, Kasela S, Burnham KL, Milani L, Irani SR, et al. Genomic insights into myasthenia gravis identify distinct immunological mechanisms in early and late onset disease. Ann Neurol. (2021) 90:455–63. doi: 10.1002/ana.26169
139. Chia R, Saez-Atienzar S, Murphy N, Chio A, and Blauwendraat C. International Myasthenia Gravis Genomics C, et al. Identification of genetic risk loci and prioritization of genes and pathways for myasthenia gravis: a genome-wide association study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2022) 119:e2108672119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2108672119
140. Fichtner ML, Jiang R, Bourke A, Nowak RJ, and O’Connor KC. Autoimmune pathology in myasthenia gravis disease subtypes is governed by divergent mechanisms of immunopathology. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:776. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00776
141. Zisimopoulou P, Evangelakou P, Tzartos J, Lazaridis K, Zouvelou V, Mantegazza R, et al. A comprehensive analysis of the epidemiology and clinical characteristics of anti-LRP4 in myasthenia gravis. J Autoimmun. (2014) 52:139–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.12.004
142. Narayanaswami P, Sanders DB, Wolfe G, Benatar M, Cea G, Evoli A, et al. International consensus guidance for management of myasthenia gravis: 2020 update. Neurology. (2021) 96:114–22. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000011124
143. Wiendl H, Abicht A, Chan A, Della Marina A, Hagenacker T, Hekmat K, et al. Guideline for the management of myasthenic syndromes. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. (2023) 16:17562864231213240. doi: 10.1177/17562864231213240
144. Newsom-Davis J, Willcox N, and Calder L. Thymus cells in myasthenia gravis selectively enhance production of anti-acetylcholine-receptor antibody by autologous blood lymphocytes. N Engl J Med. (1981) 305:1313–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198111263052203
145. Scadding GK, Vincent A, Newsom-Davis J, and Henry K. Acetylcholine receptor antibody synthesis by thymic lymphocytes: correlation with thymic histology. Neurology. (1981) 31:935–43. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.8.935
146. Nagane Y, Utsugisawa K, Akutsu H, Sato Y, and Terayama Y. Perivascular infiltrate of memory lymphocytes and mature dendritic cells in MG thymomas. Neurology. (2005) 65:770–2. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000174560.35190.84
147. Kaufman AJ, Palatt J, Sivak M, Raimondi P, Lee DS, Wolf A, et al. Thymectomy for myasthenia gravis: complete stable remission and associated prognostic factors in over 1000 cases. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2016) 28:561–8. doi: 10.1053/j.semtcvs.2016.04.002
148. Yu S, Li F, Chen B, Lin J, Yang M, Fu X, et al. Eight-year follow-up of patients with myasthenia gravis after thymectomy. Acta Neurol Scand. (2015) 131:94–101. doi: 10.1111/ane.12289
149. Vincent A, Scadding GK, Thomas HC, and Newsom-Davis J. In-vitro synthesis of anti-acetylcholine-receptor antibody by thymic lymphocytes in myasthenia gravis. Lancet. (1978) 1:305–7. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90073-9
150. Hill ME, Shiono H, Newsom-Davis J, and Willcox N. The myasthenia gravis thymus: a rare source of human autoantibody-secreting plasma cells for testing potential therapeutics. J Neuroimmunol. (2008) 201-202:50–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.06.027
151. Jiang R, Hoehn KB, Lee CS, Pham MC, Homer RJ, Detterbeck FC, et al. Thymus-derived B cell clones persist in the circulation after thymectomy in myasthenia gravis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2020) 117:30649–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2007206117
152. Pompeo E, Tacconi F, Massa R, Mineo D, Nahmias S, and Mineo TC. Long-term outcome of thoracoscopic extended thymectomy for nonthymomatous myasthenia gravis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. (2009) 36:164–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2009.02.021
153. Clifford KM, Hobson-Webb LD, Benatar M, Burns TM, Barnett C, Silvestri NJ, et al. Thymectomy may not be associated with clinical improvement in MuSK myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve. (2019) 59:404–10. doi: 10.1002/mus.26404
154. Randall AJ and Post DJ. A comprehensive review of the treatment options in myasthenia gravis. Dis Mon. (2025) 71:101970. doi: 10.1016/j.disamonth.2025.101970
Keywords: myasthenia gravis, thymectomy, thymic epithelial cell, thymic follicular hyperplasia, thymoma
Citation: Matsui N, Ohigashi I and Marx A (2025) Thymus research in relation to myasthenia gravis: a new perspective on cell subpopulations and future directions. Front. Immunol. 16:1649171. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1649171
Received: 18 June 2025; Accepted: 29 September 2025;
Published: 14 October 2025.
Edited by:
Miho Shinzawa, National Institutes of Health (NIH), United StatesReviewed by:
Yingkai Li, Duke University, United StatesNadine Dragin, INSERM U974 Institut de Myologie, France
Copyright © 2025 Matsui, Ohigashi and Marx. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Naoko Matsui, bmFva29AdG9rdXNoaW1hLXUuYWMuanA=; Izumi Ohigashi, b2hpZ2FzaGlAZ2Vub21lLnRva3VzaGltYS11LmFjLmpw
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Naoko Matsui
Naoko Matsui Izumi Ohigashi
Izumi Ohigashi Alexander Marx4†
Alexander Marx4†