- Drug Dispending Department, The Third Hospital of Mianyang, Sichuan Mental Health Center, Mianyang, China
M2-type pyruvate kinase (PKM2) serves as the key rate-limiting enzyme in aerobic glycolysis within tumor cells, where its aberrantly high expression in numerous human malignancies facilitates tumor progression by enhancing glycolytic flux through diverse signaling pathways. Beyond its metabolic function, extensive studies have established PKM2 as a critical non-metabolic signaling regulator implicated in multiple oncogenic processes, including tumor proliferation, invasion, migration, immune evasion, and resistance to chemotherapy. The elucidation of PKM2-mediated oncogenic pathways has spurred the development of targeted therapeutic strategies, positioning PKM2 as a promising target in cancer therapy. However, comprehensive reviews addressing the relationship between PKM2 and tumorigenesis remain limited. This review systematically examines the biological functions of PKM2, the signaling mechanisms through which it exerts its effects in malignant tumors, and the latest advances in the development of PKM2-targeted therapeutics, offering insights into potential directions for future drug discovery.
1 Introduction
The Warburg effect represents a fundamental metabolic distinction between tumor cells and normal cells, wherein tumor cells preferentially rely on glycolysis for energy production, irrespective of oxygen availability. This metabolic adaptation is characterized by excessive glucose consumption, leading to the rapid generation of lactate and ATP (1). Consequently, cancer cells exhibit a heightened capacity for glucose uptake, sustaining their uncontrolled proliferation. Furthermore, numerous intermediate metabolites derived from aerobic glycolysis facilitate the activation of alternative metabolic pathways, such as the pentose phosphate pathway, thereby supporting biosynthetic processes essential for tumor growth (2). The accumulation and extracellular secretion of metabolic byproducts, particularly lactate, contribute to the acidification of the tumor microenvironment, which in turn enhances tumor invasiveness and metastatic potential.
During aerobic glycolysis, the final irreversible step is catalyzed by pyruvate kinase (PK), a key rate-limiting enzyme responsible for pyruvate generation. PK exists in four isoforms—PKM1, PKM2, PKL, and PKR—encoded by two genes: PKLR, which encodes the L and R isoforms, and PKM, responsible for the M1 and M2 isoforms (3, 4). At the protein expression level, multiple isoforms can coexist within the same tissue. PKM1 is predominantly expressed in highly differentiated tissues such as skeletal muscle, heart, and brain, whereas PKR is exclusive to erythrocytes, PKL is specific to the liver, and PKM2 serves as the predominant isoform in the kidney (5). PKM2 is also present in various adult tissues, including the lung, white and brown adipose tissue, intestine, ovary, testis, and pancreatic islets (5). Notably, during tumorigenesis, PKM2 is abundantly expressed, progressively replacing the tissue-specific PK isoform until it becomes the dominant form within malignant cells (6).
PKM2 exists primarily in two conformational states: tetrameric form and dimeric form (7). Emerging evidence suggests that PKM2 plays a critical role not only in tumor metabolism but also in non-metabolic processes across various diseases, including cardiovascular disorders (8). Beyond its established role in cancer metabolism, PKM2 contributes to tumor progression by regulating non-metabolic pathways implicated in key metastatic processes, such as cell migration, angiogenesis, and stemness maintenance (9). Notably, PKM2 has been shown to facilitate tumor-derived exosome secretion, thereby driving cancer progression (10). Additionally, nuclear translocation of PKM2 enhances the immunosuppressive properties of tumors, further promoting hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis (11). Moreover, the latest research also indicates that Nuclear PKM2 also functions as a non-classical RNA-binding protein (RBP), competitively blocking the binding of the inhibitory RBP (HNRNPF) to the folded G-quardruplex (rG4) structures within precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA). This promotes the expression of pre-mRNA containing rG4, with rG4 abundance exhibiting a negative correlation with cancer patient survival rates (12). Despite the growing body of research on PKM2’s oncogenic functions, comprehensive reviews integrating its metabolic and non-metabolic roles with recent advances in PKM2-targeted therapeutics remain scarce. This review provides a systematic analysis of PKM2’s biological functions, the signaling mechanisms through which it drives tumorigenesis, and recent advancements in the development of PKM2-targeted therapies.
2 PKM2 expression in tumors
PKM2 has been extensively documented as being aberrantly overexpressed across various malignancies. In comparative analyses of human brain tumor samples, PKM2 was found to be significantly upregulated in glioma tissues, particularly in glioblastoma (GBM) (13). Notably, one of the defining characteristics of GBM is its altered metabolic profile, marked by a substantial increase in glycolysis, with clinical data indicating a pronounced elevation in PKM2 expression among patients with GBM (14).
Mass spectrometry-based analyses of lung cancer cells and clinical specimens have also revealed high PKM2 expression and secretion, suggesting its potential as a serum biomarker for lung cancer diagnosis (15). Similarly, clinical tissue samples from lung adenocarcinoma exhibited elevated PKM2 expression, which was significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis and advanced TNM stage (16). In breast cancer, PKM2 was strongly expressed in a large cohort of clinical tissue samples, where its aberrant overexpression was linked to poor prognosis and resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (17). In the highly aggressive triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) subtype, PKM2 was found to be dysregulated and actively involved in accelerating tumor progression (18). Furthermore, PKM2 was markedly upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), where its expression was associated with unfavorable patient prognosis (19). In colorectal cancer (CRC), clinical tissue samples demonstrated elevated PKM2 levels, with a strong positive correlation between its expression and both lymph node metastasis and tumor stage (20). Similarly, significantly increased PKM2 expression was observed in renal cancer tissues (21). In patients with melanoma, PKM2 was highly expressed, and its activity was positively correlated with tumor malignancy and glycolytic capacity (22). Additionally, high PKM2 expression has been reported in malignant mesenchymal tumors and pancreatic cancer (PC), where its expression levels were closely linked to overall survival and progression-free survival outcomes in clinical cohorts (23). Collectively, these findings establish PKM2 as a consistently overexpressed factor across a broad spectrum of human malignancies, underscoring its pivotal role in tumor progression. The widespread dysregulation of PKM2 across diverse cancer types is further illustrated in Figure 1.
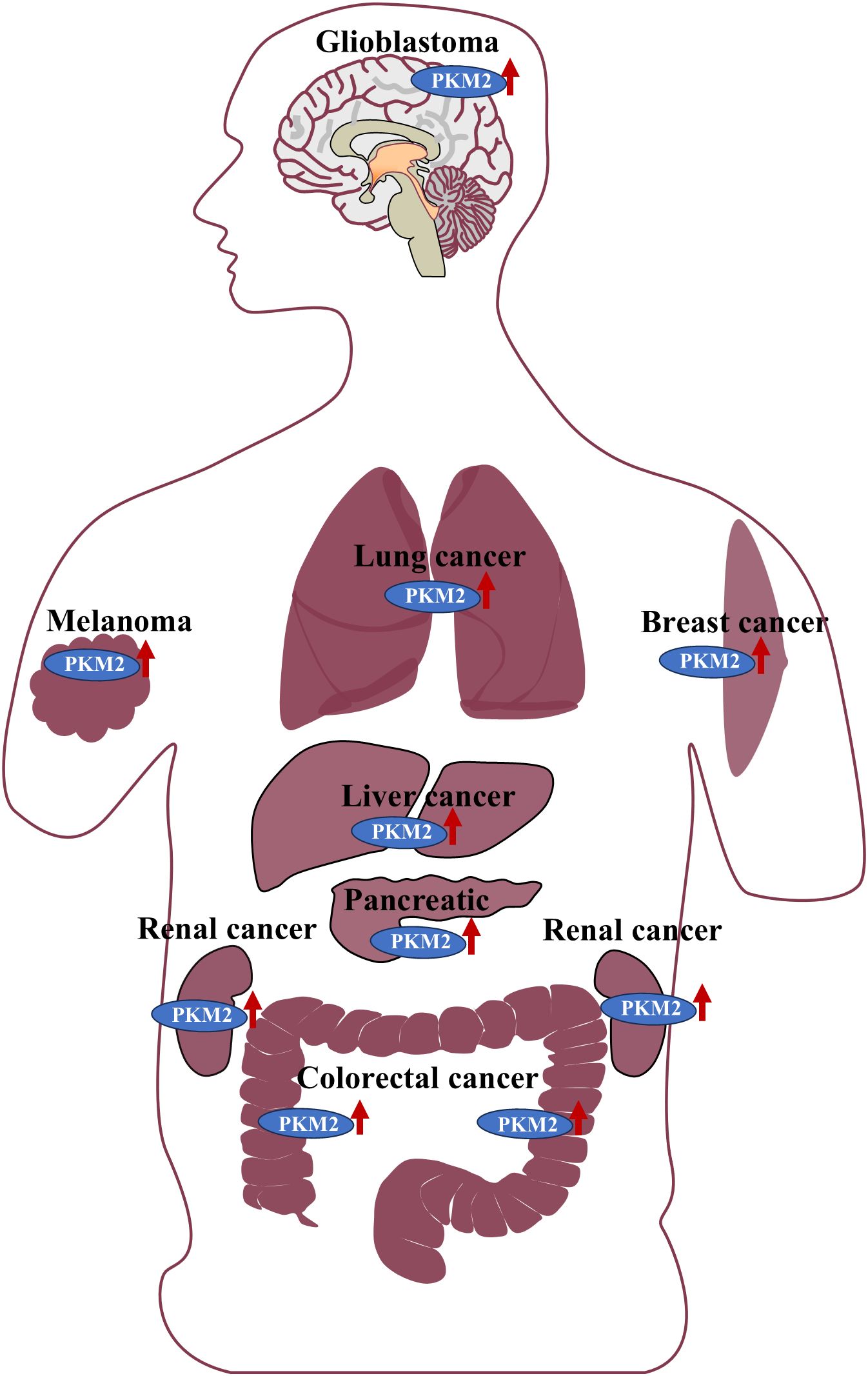
Figure 1. PKM2 is highly expressed in the tissues of various malignant tumors, including gliomas, lung cancer, breast cancer, melanoma, liver cancer, pancreatic cancer, kidney-related tumors, and colorectal cancer.
3 PKM2-mediated pathways in cancers
3.1 PKM2-mediated pathways in colorectal cancer
CRC ranks as the third most prevalent malignancy globally and is associated with substantial mortality. Metabolic reprogramming, particularly the predominance of aerobic glycolysis, represents a hallmark of CRC pathophysiology. Given the pivotal role of PKM2 in aerobic glycolysis, extensive investigations continue to elucidate its mechanistic involvement in CRC progression. In colon cancer cells, melanocyte proliferating gene 1 (MYG1) facilitates the recruitment of the HSP90/GSK3β complex, thereby enhancing PKM2 stability and activity, which further amplifies aerobic glycolysis to drive tumor progression (24). Additionally, CDK4 interacts with PKM2, augmenting glycolytic flux and promoting malignant progression (25). The tumor-suppressive miR-142-3p, which exhibits reduced expression in CRC, directly targets the 3′-UTR of PKM2, modulating its PK-like activity (26). Clinically, loss-of-function mutations in APC are observed in 90% of patients with CRC, and these mutations contribute to aberrant activation of the β-catenin-PKM2 regulatory axis, thereby sustaining tumor growth through enhanced glycolytic metabolism (27). Moreover, PKM2 promotes aerobic glycolysis via the heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein A1-b (HnRNPA1-b)/PKM2 axis, while HnRNPA1-b enhances the Warburg effect by promoting PKM2 expression and amplifying the PI3K/AKT pathway (28). Beyond its function as a glycolysis rate-limiting enzyme in CRC cell proliferation, PKM2 is implicated in tumor progression through mechanisms involving altered adhesion and migration. The calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein CPNE7 interacts with PKM2 in CRC tissues, triggering MAPK signaling to accelerate tumor cell proliferation and migration (29). Furthermore, dimeric PKM2, endowed with protein kinase activity, promotes adhesion and facilitates metastatic dissemination by modulating STAT3-associated signaling pathways (30). Extracellular stimuli have been implicated in CRC progression through PKM2-mediated mechanisms. Upon fructose ingestion, Ketohexokinase-A (KHK-A) phosphorylates PKM2, inhibiting tetramer formation while concurrently promoting its nuclear translocation (31). This nuclear accumulation of PKM2 activates epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and aerobic glycolysis, enhancing migratory capacity and facilitating the loss of nest-dependent anti-mutagenic properties, particularly in CRC liver metastases. Furthermore, Nuclear PKM2 activates the transcription of c-myc regulatory genes GLUT1 and LDHA, thereby promoting the expression of the KHK-A subtype. Elevated KHK-A subsequently enhances cytoplasmic PKM2 phosphorylation, facilitating its nuclear translocation and thus establishing a positive feedback loop that intensifies metabolic reprogramming (31). Environmental organic pollutants, such as p,p′-DDT, have also been shown to upregulate PKM2 and promote its nuclear translocation via ROS-mediated ERK/PKM2 signaling, further potentiating glycolytic activity in CRC cells (32). In surgical patients, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) derived from intraoperative infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria activates the NF-κB pathway, leading to increased PKM2 binding to the STAT3 promoter. This interaction induces STAT3 pathway activation, facilitates STAT3 nuclear translocation, and drives the expression of TNF-α and IL-1β, exacerbating inflammation and contributing to CRC recurrence and metastasis (33). Moreover, STAT3 activation perpetuates disease progression through the STAT3/PKM2/SNAP23 signaling axis, leading to PKM2 phosphorylation, metabolic reprogramming via enhanced glycolysis, and increased exosome secretion by tumor cells (34). Tumor-derived exosomes transport a diverse array of bioactive molecules, among which the long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) HOTAIR binds to PKM2 in regulatory B cells, preventing its ubiquitin-mediated degradation. This interaction facilitates STAT3 activation and upregulates PD-L1 expression, thereby enhancing the immunosuppressive properties of CRC (35). Additionally, small nucleolar RNA host gene 15 (SNHG15) promotes CRC glycolysis by upregulating PKM2 expression and 5-FU resistance (36). Similarly, an OTU deubiquitinase (OTUB2), which exhibits high expression in CRC, directly inhibits PKM2 ubiquitination by blocking the interaction between PKM2 and its ubiquitin E3 ligase Parkin, thereby stabilizing its activity and ultimately driving resistance to chemotherapeutic agents (37). Conversely, the ubiquitin E3 ligase TRIM29 selectively targets PKM1 for degradation, indirectly increasing the relative abundance of PKM2 and shifting CRC metabolism toward aerobic glycolysis, thereby reinforcing malignancy (38). Based on accumulated evidence, the molecular pathways and regulatory mechanisms of PKM2 in CRC progression have been systematically delineated to construct a comprehensive PKM2-mediated signaling network in CRC (Figure 2). These findings underscore the potential of targeting PKM2-associated pathways as a promising therapeutic strategy for CRC treatment.
3.2 PKM2-mediated pathways in liver cancer
Liver cancer ranks as the fourth leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with HCC being the most prevalent and highly aggressive subtype (39, 40). PKM2 has been identified as a critical regulator in HCC progression, with clinical analyses of extensive HCC tissue samples revealing a strong correlation between PKM2 expression levels, tumor aggressiveness, and immune cell infiltration (41). Notably, elevated PKM2 expression has been linked to poor responsiveness to transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) in over 40% of patients with intermediate-stage HCC, contributing to chemoresistance and reduced survival (42). Beyond its role as a metabolic enzyme, PKM2 functions as a key regulatory protein facilitating HCC progression by driving aerobic glycolysis. Tumor-derived endogenous miR-624 accelerates HCC cell proliferation through PKM2 proteome modulation (43). Additionally, Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4 (BMP4) directly binds to the PKM promoter via SMAD5, upregulating PKM2 expression and enhancing glycolytic flux, thereby promoting glucose metabolism reprogramming and tumor progression (44). The deubiquitinase FAM188B stabilizes PKM2 by facilitating hnRNPA1(a key protein involved in RNA metabolism) deubiquitination, activating the hnRNPA1/PKM2 axis to upregulate aerobic glycolysis to accelerate HCC proliferation (45). PKM2 also promotes HCC metastasis via the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway while concurrently suppressing autophagy by promoting autophagosome formations, further driving malignant progression (46). Epigenetic modifications of PKM2 contribute to HCC aggressiveness. Circular RNA HULC enhances PKM2 methylation, facilitating its involvement in autophagosome formation through CARM1 expression and driving malignant differentiation of HCC stem cells (47). Moreover, HCC cells elevate PKM2 expression by preventing its degradation, as ubiquitin-specific protease 35 (USP35) stabilizes PKM2 through deubiquitination, promoting aerobic glycolysis and tumor progression (48). Beyond its metabolic function, PKM2 acts as a transcriptional regulator in HCC. Histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) interacts with the PKM2 protein to perform deacetylation modification at position K62, reducing its cytoplasmic catalytic activity in glycolysis; however, this modification simultaneously facilitates PKM2 nuclear translocation, where it interacts with β-catenin to drive CCND1 transcription, disrupting cell cycle control and exacerbating tumor progression (49). Similarly, the intracellular lncRNA HClnc1 interacts with PKM2 to prevent its degradation, reinforcing aerobic glycolysis and activating PKM2-STAT3 signaling, which promotes angiogenesis, proliferation, chemoresistance, and anti-apoptotic mechanisms in HCC (50). Targeting PKM2 presents a potential therapeutic strategy, as Shikonin (SHK), which is isolated from Lithospermum erythrorhizon, has been shown to suppress PKM2 activity and glycolysis in HCC cells. However, in the refractory HCC cell line HCCLM3, SHK paradoxically induces PKM2 nuclear translocation, upregulating glycolysis-related gene transcription and metabolic activity (51). Additionally, high PKM2 expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells enhances resistance to gemcitabine by competitive inhibition of dNTP biosynthesis stimulates gemcitabine incorporation into DNA (52). In summary, PKM2 serves as a key oncogenic driver in HCC, particularly in HCC, exerting its influence through multiple mechanisms. Beyond its role in regulating aerobic glycolysis, PKM2 integrates into diverse interlinked signaling networks and functions as a protein kinase to modulate gene transcription.
3.3 PKM2-mediated pathways in breast cancer
Breast cancer (BC) remains a leading contributor to the female disease burden, exhibiting particularly high incidence rates in high-income countries (53). The malignancy of BC is significantly influenced by the expression profiles of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). While chemotherapy remains the primary treatment modality for non-triple-negative BC (non-TNBC), PKM2-mediated pathways have been increasingly implicated in the development of chemoresistance. USP46, which is highly expressed in BC cells, enhances the PKM2/PKM1 ratio via the USP46/PTBP1/PKM2 axis, promoting glycolysis and conferring resistance to tamoxifen (54). Additionally, in the TBX15/miR-152/KIF2C axis, domain-2 of KIF2C directly binds to PKM2, preventing its ubiquitin-mediated degradation and increasing PKM2 protein stability. This stabilization contributes to doxorubicin (DOX) resistance by modulating both autophagy and aerobic glycolysis (55). Beyond its metabolic function, PKM2 also exhibits protein kinase activity, participating in the PKM2-c-Myc-survivin cascade, which regulates BC cell proliferation, migration, and tamoxifen resistance (56). In refractory TNBC, PKM2 has been strongly associated with chemoresistance. The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF6 directly interacts with PKM2, promoting PKM2-mediated glycolysis and enhancing drug resistance, as demonstrated in both preclinical models and clinical tumor samples (57). Moreover, protein arginine methyltransferase-1 (PRMT1) reinforces TNBC chemoresistance by upregulating lipid biosynthesis during aerobic glycolysis (58). Within the nucleus, PKM2 interacts with the histone methyltransferase EZH2, repressing the expression of multiple target genes and consequently influencing TNBC cell lineage specification (59). Collectively, PKM2 functions as a central regulator of glycolysis and a protein kinase that drives BC chemoresistance through diverse molecular pathways, irrespective of tumor subtype or malignancy.
3.4 PKM2-mediated pathways in gastric cancer
Gastric cancer (GC) remains one of the most prevalent and lethal malignancies of the digestive system. PKM2 has been identified as a key regulator in GC progression, participating in multiple signaling pathways that drive aerobic glycolysis and tumor proliferation. In GC cells, Src homology 2 domain-containing phosphatase 2 (SHP2) directly interacts with specific sites on PKM2, activating its enzymatic function and exacerbating glycolytic metabolism and malignant transformation (60). Additionally, the significantly upregulated lncRNA VAL in GC competes for PKM2 binding, reducing the interaction between PKM2 and Parkin, thereby suppressing PKM2 ubiquitination and enhancing its enzymatic activity (61). Enolase 1 (ENO1), another key glycolytic enzyme in GC, directly interacts with PKM2, facilitating aerobic glycolysis, tumor cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis resistance (62). Beyond direct protein-protein interactions, endogenous signaling pathways also regulate PKM2-mediated GC progression. The highly expressed lncRNA CCAT1 promotes PKM2 expression through the PTBP1/PKM2/glycolysis axis, thereby enhancing glycolytic flux and driving tumor progression (63). Similarly, circular RNA circATP2B1, which is overexpressed in GC, functions as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA), directly binding to miR-326-3p and miR-330-5p, which serve as PKM2 inhibitors. This interaction leads to PKM2 upregulation, further promoting glycolysis and tumorigenesis (64). Moreover, histone methyltransferase SETD1A, which is highly expressed in GC tissues, interacts with and co-activates HIF1α, thereby upregulating multiple glycolytic enzymes, including PKM2, to reinforce glycolytic metabolism and tumor progression (65). Collectively, the abundant expression of PKM2 in GC cells, along with its involvement in various signaling cascades and protein interactions, plays a central role in driving aerobic glycolysis and malignant progression. These findings underscore the therapeutic potential of targeting intracellular PKM2 as a promising strategy for GC treatment.
3.5 PKM2-mediated pathways in pancreatic cancer
PC, a highly aggressive malignancy of obscure etiology, is often referred to as the “king of cancers” due to its exceptionally poor prognosis and resistance to conventional therapies. Research on PKM2 in PC remains in its early stages, yet emerging evidence suggests its significant involvement in key oncogenic processes.
The voltage-gated calcium channel α2δ1, expressed on the surface of PC cells, facilitates calcium influx, activating CaMKIIδ, which sequentially phosphorylates PKM2. This phosphorylation event promotes PKM2 nuclear translocation, ultimately enhancing the stem-like properties of PC cells and exacerbating tumor malignancy (66). Additionally, protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B), a putative oncogene in PC, modulates the PKM2/AMPK/mTORC1 signaling axis, increasing PKM2-associated protein kinase activity and enhancing mTORC1 activation, thereby accelerating PC cell proliferation (67). Tumor-associated macrophage-derived TGF-β1 further exploits PKM2 nuclear translocation to upregulate PD-L1 expression, facilitating immune evasion in PC (68). Moreover, upstream stimulatory factor 2 (USF2) negatively regulates lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis in PC cells by modulating PKM2-mediated transcriptional activity in the nucleus, further promoting tumor progression (69). Although comprehensive mechanistic insights into PKM2’s role in PC remain limited, existing studies highlight its potential significance in tumor stemness, immune escape, lipid peroxidation, and ferroptosis—hallmarks that drive PC malignancy. These findings provide a scientific foundation for further exploration of PKM2 as a therapeutic target in PC.
3.6 PKM2-mediated pathways in head and neck malignancies
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most prevalent malignancy of the central nervous system, characterized by rapid progression and resistance to conventional therapies. Analysis of PKM2 expression in 119 patients with GBM identified it as an independent prognostic factor, with elevated levels correlating with poor survival outcomes, particularly in patients undergoing radiotherapy. These findings suggest that PKM2 represents a promising therapeutic target for GBM (70). In GBM cells with high ALDH1A3 expression, enhanced PKM2 tetramerization following interaction with ALDH1A3 not only augments aerobic glycolysis but also facilitates the lactylation and nuclear translocation of XRCC1, thereby promoting DNA damage repair and conferring resistance to temozolomide (TMZ) and radiotherapy (71). Additionally, reduced expression of the RNA-binding protein ZCRB1 and circular RNA circHEATR5B leads to the accumulation of their binding partner JMJD5, which interacts with PKM2 to enhance the formation of its highly active tetrameric state, further reinforcing glycolytic metabolism in GBM cells (72). In the MBNL1/circNTRK2/PAX5 pathway, the transcription factor PAX5, which is highly expressed in GBM, directly binds to the PKM2 promoter, increasing its transcription and protein expression, thereby sustaining tumor glycolysis and progression (73). Moreover, GBM resistance to TMZ has been linked to PKM2, with hypoxic TMZ-resistant cells transmitting resistance to TMZ-sensitive cells through exosomal transfer of PKM2 (74). Beyond GBM, PKM2 has also been implicated in other head and neck malignancies. In head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), Enolase 2 (ENO2), a crucial glycolytic enzyme in cancer metabolic process, directly interacts with PKM2, preventing its degradation while enhancing its glycolytic activity. This interaction also mediates AKT phosphorylation and promotes PKM2 nuclear translocation, contributing to malignant progression through cell cycle dysregulation (75). Furthermore, the accumulation of lactate driven by high PKM2 expression suppresses NF-κB signaling and enhances immunosuppressive capacity by upregulating the expression of Galectin-9, a key immunosuppressive factor in HNSCC (76). In cytotrophoblastoma, the mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (C-MET) promotes PKM2 nuclear translocation via ERK1/2 phosphorylation, where it interacts with histone H3 to upregulate CCND1 and c-Myc, ultimately driving tumor proliferation and growth (77). Although research on PKM2 in head and neck cancers remains limited, existing studies highlight its critical role in therapy resistance, tumor metabolism, and immune evasion. Whether in GBM, where PKM2 contributes to chemoresistance and radiotherapy failure, or in other head and neck malignancies, where it facilitates aerobic glycolysis and immune suppression, these findings have redirected research focus toward the diverse oncogenic functions of PKM2, reinforcing its potential as a therapeutic target.
3.7 PKM2-mediated pathways in genitourinary cancers
Prostate cancer (PC) ranks among the most prevalent malignancies in men, with PKM2 playing a pivotal role in tumor progression and therapy resistance. Morphological and cytological analyses of PC cells have demonstrated that PKM2 is actively involved in the EMT, a process that facilitates lineage differentiation and contributes to resistance against antiandrogen therapies, ultimately driving tumor progression (78). In PC cells, PKM2 phosphorylation upon interaction with protein kinase C epsilon (PKCϵ) enhances its nuclear translocation, leading to the upregulation of oncogenes and the promotion of tumor proliferation (79). Bone metastases represent the primary cause of mortality in patients with metastatic PC. The lncRNA miR-541-3p has been identified as a key regulator of this process, facilitating PKM2 translational expression, which in turn promotes extracellular vesicle internalization and enhances metastatic potential in PC cells (80). Beyond PC, PKM2 has been implicated in other genitourinary malignancies. In bladder cancer, one of the most common urinary system malignancies, ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL1) directly binds to PKM2 and inhibits its ubiquitin-mediated degradation, leading to increased PKM2 protein levels and subsequently enhancing aerobic glycolysis, metastasis, and invasive activity (81). Similarly, in nephroblastoma, platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β (PDGFR-β) activates PKM2 via the PI3K/AKT pathway, promoting glycolytic metabolism while simultaneously upregulating VEGF transcription to drive tumor angiogenesis (82). PKM2 also plays a critical role in malignancies that predominantly affect women. Cervical cancer, a leading cause of cancer-related mortality in women, exhibits increased sorafenib resistance due to the Cdc25A/PKM2/ErbB2 pathway, in which Cdc25A suppresses ferroptosis by dephosphorylating PKM2 and upregulating ErbB2 expression (83). In ovarian cancer, platinum-based drug sensitivity is a key determinant of therapeutic efficacy. Anexelekto (Axl), a member of the TYRO3-AXL-MER receptor tyrosine kinase family, induces cisplatin resistance by phosphorylating PKM2 at Y105, thereby reinforcing glycolysis-driven tumor survival (84). Additionally, adrenomedullin has been found to promote aerobic glycolysis and cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer by significantly upregulating PKM2 protein levels (85). Collectively, these findings underscore PKM2’s central role in tumor metabolism, therapy resistance, and metastatic progression across multiple cancer types. A comprehensive visualization of PKM2-mediated mechanisms in cancers of the liver, breast, stomach, pancreas, head and neck, and genitourinary system is presented in Figure 3.
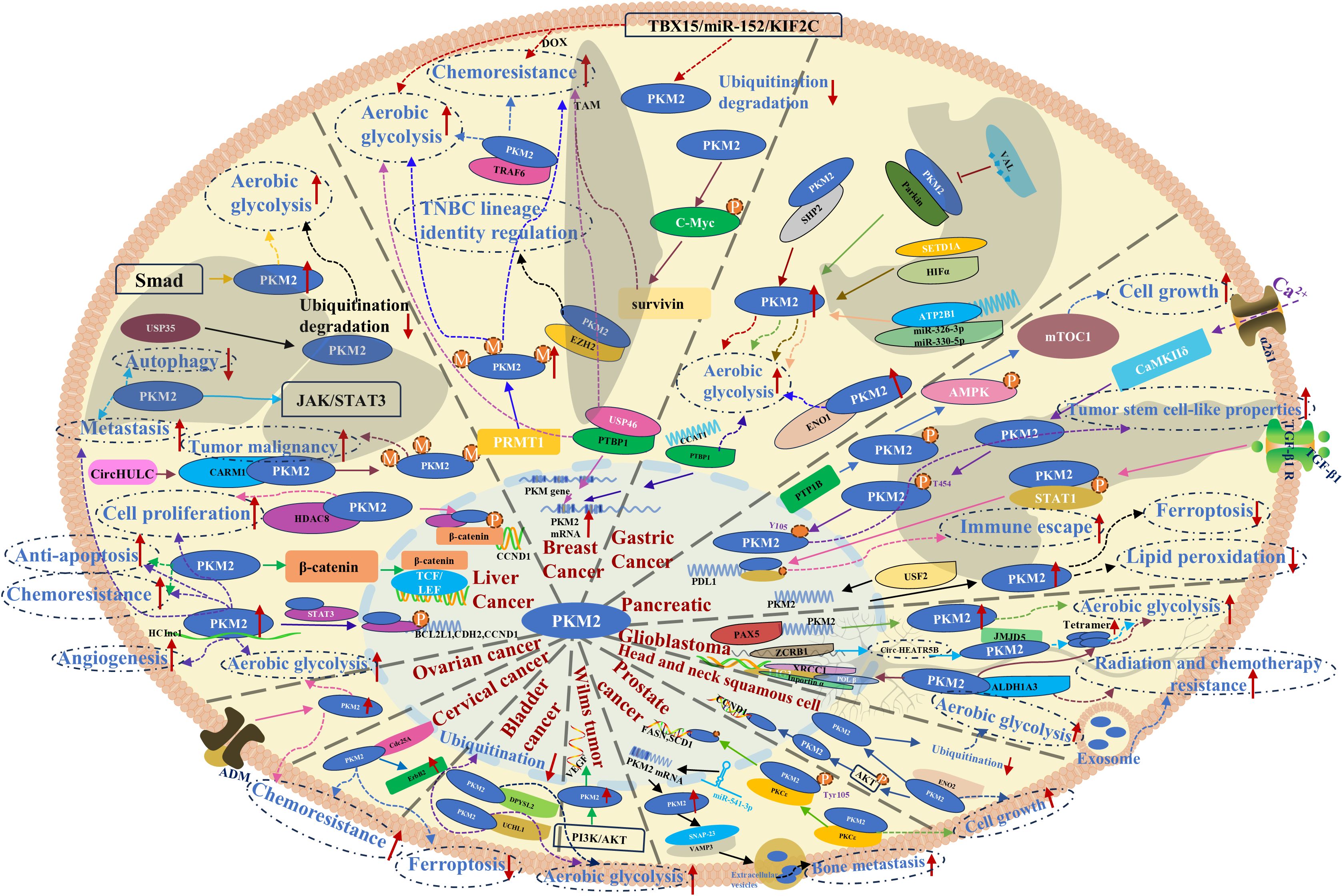
Figure 3. PKM2-mediated mechanisms and pathways in liver, breast, gastric, pancreatic, head and neck, and genitourinary system cancers.
4 Targeting PKM2 in tumors
4.1 Targeting PKM2 in colorectal cancer
The primary treatment modalities for CRC include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and targeted therapy. In recent years, increasing attention has been directed toward targeted therapies, particularly those aimed at PKM2, which has emerged as a critical regulator of CRC metabolic reprogramming. Strategies targeting PKM2 at the protein or gene level have become a major focus in anti-CRC research.
Direct inhibition of PKM2 disrupts its PK activity, thereby suppressing CRC proliferation. TEPP-46, a small-molecule inhibitor, prevents PKM2 nuclear accumulation and promotes its tetramerization, ultimately inhibiting EMT and aerobic glycolysis in CRC cells (31). Similarly, the boronic acid-based compound 6C mitigates aerobic glycolysis and CRC progression by stabilizing the dimeric interface of PKM2 while facilitating its transition into a tetrameric conformation with reduced aerobic glycolytic activity (86). To enhance the efficacy of PKM2-targeting agents, nanoparticle-based delivery systems have been explored. SHK-loaded colloidal mesoporous silica nanoparticles selectively deliver inhibitors to CRC cells, effectively suppressing PKM2 activity and aerobic glycolysis, thereby inhibiting tumor proliferation (87). Similarly, SHK-loaded and hyaluronic acid-modified mesoporous polydopamine (MPDA) nanoparticles reprogram CRC metabolism by targeting PKM2, reversing EMT, and suppressing colorectal liver metastasis (88). Betulinic acid-loaded nanoliposomes have also been shown to inhibit PKM2-mediated aerobic glycolysis, disrupting CRC metabolic pathways to enhance anti-tumor activity (89). Beyond direct PKM2 inhibition, targeting PKM2-associated signaling pathways offers an alternative therapeutic strategy. miR-206 regulates the miR-206/hnRNPA1/PKM2 axis, inducing a PKM2-to-PKM1 isoform switch, which suppresses PKM2 expression and attenuates CRC aerobic glycolysis and proliferation (90). Additionally, miR-490-3p directly binds to hnRNPA1-b and modulates the miR-490-3p/hnRNPA1-b/PKM2 axis, promoting CRC apoptosis by enhancing the Warburg effect via the PI3K/AKT pathway (28). The lncRNA LiNC01852 modulates the TRIM72/SRSF5/PKM2 signaling axis, indirectly downregulating PKM2 expression through a multi-stage regulatory mechanism, thereby suppressing CRC cell proliferation and chemoresistance (91). Additionally, small molecules have been identified as indirect modulators of PKM2 expression. The CD36-Glypican 4 interaction inhibits β-catenin/c-Myc signaling, downregulating PKM2 expression and impairing glycolysis in CRC cells (92). N-acetyl-L-cysteine prevents PKM2 nuclear translocation and aerobic glycolysis induced by the environmental pollutant p,p’-DDT by inhibiting ERK1/2 activation and PKM2 upregulation (32). The synthetic compound diethyldithiocarbamate-copper complex suppresses CRC progression by promoting PKM2 ubiquitination and degradation through inhibition of the miR-16-5p and miR-15b-5p/ALDH1A3/PKM2 axis (93). Furthermore, NPD10084, as confirmed by the cellular thermal shift assay in colon cancer cells, disrupts PKM2 interactions with β-catenin and STAT3, thereby inhibiting downstream oncogenic signaling and suppressing CRC proliferation (94). In duodenal cancer cells, the indole-3-carbinol derivative OSU-A9 reduces nuclear pTyr105-PKM2 levels and promotes apoptosis by inhibiting ROS generation (95). Given concerns regarding chemical toxicity, nutritional interventions targeting PKM2 in CRC have gained traction. The dietary flavonoid kaempferol enhances miR-326 expression, directly targeting the 3’-UTR of PKM2 to inhibit glycolysis, thereby reversing 5-FU resistance in CRC cells (96). Kaempferol also inhibits CRC growth by promoting miR-339-5p expression, modulating the miR-339-5p-hnRNPA1/PTBP1-PKM2 axis to suppress PKM2 expression while upregulating PKM1 (97). Another dietary factor, apigenin, binds to the K433 site of PKM2, thereby impairing aerobic glycolysis and suppressing CRC cell proliferation (98). Additionally, ferulic acid and p-coumaric acid, derived from cereal bran, inhibit the lncRNA 495810/PKM2 axis, thereby suppressing glycolysis in CRC cells (99). Synergistic targeting of PKM2 through combinatorial approaches has also been explored. The co-administration of PKM2-siRNA and oxaliplatin exhibits enhanced anti-CRC efficacy (100). Additionally, SHK enhances the therapeutic effect of PD-1 blockade by modulating the SHK-PKM2-ROS-Hsp70 axis, thereby improving immune responses in CRC (101).
4.2 Targeting PKM2 in liver cancer
Characterized by its dual function as a classical aerobic glycolytic enzyme and a non-metabolic protein kinase-like entity in HCC cells, PKM2 has emerged as a critical therapeutic target, with numerous bioactive molecules demonstrating efficacy in suppressing HCC progression. Tumor-specific knockdown of PKM2 in a primary HCC model effectively reversed the Warburg effect and inhibited tumorigenesis in a genotype-dependent manner (102). The downregulation of PKM2 observed in sublethal heat treatment experiments, alongside tumor inhibition data, underscores its pivotal role in phase separation kinetics and pyroptotic pathways (103). ARHGAP24, an endogenous Rho-GTPase-activating protein in tumor cells, directly interacts with WWP1 and PKM2 to obstruct β-catenin signaling, thereby suppressing HCC cell proliferation and invasion (104). Additionally, the natural compound Chinese poplar propolis has been shown to attenuate aerobic glycolysis in HCC cells by reducing PKM2 protein levels in vitro (105). Beyond monotherapies targeting PKM2, combination regimens designed to enhance anti-HCC efficacy through synergistic PKM2 inhibition have gained increasing attention. SHK suppresses PKM2 expression to disrupt aerobic glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells, thereby enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of sorafenib. Furthermore, nuclear PKM2 inhibition also downregulates CCND1 to block the cell cycle and exert antiproliferative effects (106). However, SHK also facilitates PKM2 nuclear translocation, activating Nrf2-Bcl2-associated athanogene 3 (BAG3) signaling to confer anti-apoptotic effects, a process counteracted by the addition of a BAG3 inhibitor, which enhances SHK-induced apoptosis (107). Furthermore, Canagliflozin suppresses aerobic glycolysis in HCC cells by targeting PKM2 expression and promoting the formation of the PKM2-c-MYC complex. Furthermore, this complex formation promotes the ubiquitination and degradation of c-MYC while reducing expression of the key enzyme GLS1 in glutamine metabolism. This impairs glutamine utilization, inducing intracellular glutamine starvation and subsequent ferroptosis, thereby sensitizing HCC cells to cisplatin treatment (108). The natural coumarin analog osthole, in combination with radiotherapy, suppresses aerobic glycolysis and enhances HCC radiosensitivity by inhibiting the GSK-3β/AMPK/mTOR pathway and downregulating PKM2 protein expression (109). Additionally, indirect targeting of PKM2 or its associated signaling axis represents an alternative therapeutic strategy. Cannabinoid receptor-interacting protein 1 (CNRIP1) inhibits intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell proliferation, invasion, and migration by modulating the CNRIP1/Parkin/PKM2 pathway, thereby enhancing Parkin-PKM2 interactions and facilitating PKM2 ubiquitination and degradation (110). The multi-kinase inhibitor cabozantinib exerts potent anti-HCC effects by suppressing c-MET and ERK activity, leading to reduced PKM2 expression and impaired tumor angiogenesis (111). Inhibition of intracellular cleavage and polyadenylation-specific factor 6 (CPSF6) also suppresses PKM2 expression, thereby reversing the Warburg effect and impeding HCC progression (112). The ginsenoside metabolite compound K disrupts glycolysis and induces apoptosis in HCC cells by downregulating PKM2 through inhibition of the AKT/mTOR/c-MYC signaling pathway (113). Furthermore, antisense oligonucleotides (cEt/DNA ASO) promote PKM splicing transition, facilitating PKM2-to-PKM1 conversion, thereby restoring PK activity, normalizing glucose metabolism, and inhibiting HCC cell proliferation (114). Notably, fluorescent nanoparticles composed of carbon dots and dihydroartemisinin supramolecules suppress aerobic glycolysis via PKM2 inhibition while concurrently targeting the AKT/mTOR pathway to promote apoptosis. Beyond their therapeutic potential, these nanoparticles also offer real-time visualization, presenting a promising dual-functional approach for both HCC diagnosis and treatment (115).
4.3 Targeting PKM2 in breast cancer
Research on PKM2-targeted therapy in BC has advanced considerably, with numerous compounds demonstrating anti-BC effects by modulating PKM2 dimer-tetramer conversion and nuclear translocation. A novel glycopeptide-based PKM2 nano-activator has been developed to selectively accumulate in tumor-enriched regions, suppressing aerobic glycolysis in BC cells by sequestering PKM2 tetramers and preventing dimeric nuclear translocation. This metabolic shift effectively inhibits BC cell proliferation and metastasis while enhancing chemosensitivity (116). Additionally, β-elemene has been shown to counteract BC metastasis by regulating PKM2 dimerization and nuclear translocation, thereby modulating aerobic glycolysis in BC cells (117). Overexpression of the ubiquitin ligase Tripartite Motif-Containing 35 inhibits aerobic glycolysis by promoting PKM2 ubiquitination, thereby facilitating tetramer-to-dimer conversion (118). Furthermore, a novel sulfonamide-dithiocarbamate compound, 8k, suppresses BC cell proliferation by inhibiting PKM2 nuclear translocation and its downstream signaling cascade (119). Chinese poplar propolis has also demonstrated anti-proliferative effects in BC cells within an inflammatory microenvironment by targeting and downregulating PKM2, a key glycolytic enzyme (120). Innovative therapeutic strategies have emerged, including a nano-formulation integrating SiPKM2 with photothermal therapeutic materials, which precisely targets BC cells to disrupt PKM2-mediated aerobic glycolysis while synergistically potentiating photothermal ablation efficacy (121). Beyond direct PKM2 inhibition, several compounds exert antitumor effects by targeting upstream regulators of PKM2-associated signaling pathways. Pimozide, an antipsychotic agent, inhibits aerobic glycolysis and BC cell proliferation by suppressing the PI3K/AKT/MDM2 pathway, thereby upregulating p53 and downregulating PKM2 expression (122). Similarly, valproic acid impairs BC progression by inhibiting aerobic glycolysis through suppression of the HDAC1/ERK1/2/PKM2 axis (123). Additionally, cryptotanshinone, a bioactive component from traditional Chinese medicine, inhibits BC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via downregulation of PKM2 through the PKM2/β-catenin signaling pathway (124).
TNBC, the most aggressive BC subtype, is characterized by poor prognosis due to its low chemotherapy sensitivity and lack of predictive biomarkers or targeted therapies. However, significant progress has been made in PKM2-targeted approaches against TNBC. Inhibition of immunoglobulin-like transcript 4 (ILT4) significantly downregulates AKT-mTOR-mediated PKM2 overexpression, thereby suppressing aerobic glycolysis and impairing TNBC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion (125). Additionally, a manganese dioxide-coated metal-organic framework-based nanomedicine has been designed to enhance the stability and targeted delivery of the gene-silencing drug SiPKM2, effectively suppressing tumor glycolysis and exerting potent anti-TNBC effects in vivo (126). Combination strategies have also gained attention, with TEPP-46 demonstrated to synergize with CDK inhibitors by selectively binding PKM2pS37 and reducing its nuclear translocation, thereby amplifying anti-TNBC proliferation and invasion effects (127). Moreover, diindolylmethane (DIM), a dietary compound derived from cruciferous vegetables, not only reduces PKM2 expression to counteract aerobic glycolysis in TNBC cells but also enhances the efficacy of the anticancer agent Centchroman in TNBC treatment (128).
4.4 Targeting PKM2 in gastric cancer
Research on PKM2-targeted therapy in GC remains limited. DNA polymerase gamma has been identified as a binding partner of PKM2, modulating Tyr105 phosphorylation to suppress aerobic glycolysis and inhibit GC cell proliferation (129). Additionally, the traditional Chinese medicine formula Modified Jianpi Yangzheng Decoction (mJPYZ) has been shown to downregulate the PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis, promoting apoptosis while simultaneously reducing exosomal PKM2 secretion in GC (130). Further investigation revealed that mJPYZ also suppresses GC cell growth and EMT by inhibiting PKM2-dependent glycolysis through the PKM2/HIF-1α signaling pathway (131). Beyond direct PKM2 inhibition, indirect regulatory mechanisms also play a pivotal role. OSU-A9 increases intracellular ROS levels in GC cells, triggering apoptosis while concurrently reducing nuclear pTyr105-PKM2 expression (95). Despite the scarcity of research in this area, current findings underscore PKM2’s pivotal role in regulating key tumorigenic processes in GC, including exosomal PKM2 delivery, metabolic reprogramming, and apoptosis, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target.
4.5 Targeting PKM2 in glioblastoma
GBM, the most lethal intracranial malignancy, presents significant therapeutic challenges, particularly in overcoming radioresistance following surgical resection. Notably, TEPP-46 has been shown to directly activate intracellular PKM2 in GBM cells, enhancing radiosensitivity without inducing cytotoxicity in normal human astrocytes (132). In parallel, advancements have been made in chemotherapy strategies targeting PKM2 in GBM. A supra-indication study on the sedative drug chlorpromazine revealed that it selectively binds PKM2 tetramers in GBM cells, inhibiting aerobic glycolysis and suppressing malignant progression, while exerting minimal effects on non-cancerous neuroepithelial cells (133). Additionally, the combination of PKM2 inhibitors (SHK+compound 3K) markedly enhances late apoptosis in U87MG glioma cells, demonstrating a potent anti-GBM effect (13). Moreover, the natural cytokine isopentenyladenosine inhibits the β/NF-κB pathway and downregulates PKM2 expression, thereby suppressing aerobic glycolysis in GBM cells (134). Collectively, these findings emphasize the therapeutic and adjuvant potential of PKM2-targeted interventions in gliomas, offering promising avenues for future clinical applications.
4.6 Targeting PKM2 in genitourinary tumors
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC), a highly aggressive malignancy of the urinary tract, exhibits significant chemoresistance, directly impacting patient prognosis. A novel nanoparticle drug, the PKM2 allosteric converter, has been shown to induce PKM2 tetramerization in RCC cells, thereby suppressing aerobic glycolysis. Reduced PKM2 dimerization concomitantly diminishes nuclear translocation, restoring cancer cell sensitivity to first-line chemotherapeutic agents (135). Similarly, a glycopeptide-based PKM2 nano-activator has demonstrated efficacy in PC by promoting PKM2 tetramer formation and preventing dimeric nuclear translocation, ultimately impairing PC cell proliferation, chemoresistance, and metastatic potential (116). Additionally, in the context of castration-resistant PC, the tanshinone IIA analog TB3 has been identified as an effective therapeutic agent, inhibiting the degradation of androgen receptor (AR), concurrently reducing AR nuclear translocation and thereby affecting AR-mediated transcription pathways of key ARE-containing genes, ultimately downregulating PKM2 expression by targeting this AR/PKM2 axis to suppress aerobic glycolysis (136). Further studies indicate that, Xihuang Pills (XHP), a traditional Chinese medicine compound tablet formulation, suppress PKM2 protein expression, significantly reducing aerobic glycolysis in chemoresistant PC cells (137).
PKM2 has also emerged as a critical metabolic biomarker in female reproductive malignancies, though targeted therapeutic strategies remain limited. Cryptotanshinone directly binds to PKM2, inhibiting its expression in ovarian cancer cells, thereby suppressing both aerobic glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), leading to cell growth inhibition and apoptosis induction (138). Additionally, compound 3K has been shown to selectively suppress PKM2 expression in ovarian cancer cells, significantly impairing glycolytic capacity and inducing autophagy (139). Combination therapies targeting PKM2 have also demonstrated potential, with SHK significantly enhances the antitumor efficacy of olaparib, a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor that acts by blocking the homologous recombination pathway. The anti-tumor efficacy achieved by disrupting the homologous recombination pathway operates primarily through two mechanisms: firstly, SHK itself induces increased intracellular reactive oxygen species, leading to DNA double-strand breaks; secondly, SHK directly inhibits PKM2, thereby amplifying the effects of olaparib in inducing γH2AX upregulation, ATM phosphorylation activation, and BRCA1 downregulation (140). These findings underscore the therapeutic significance of targeting PKM2 in genitourinary and gynecologic malignancies, highlighting its potential role in overcoming aerobic glycolysis-mediated chemoresistance.
4.7 Targeting PKM2 in other tumors
Beyond the extensive body of research on PKM2-targeted therapies in common systemic malignancies, a smaller yet highly innovative subset of studies has explored cutting-edge therapeutic strategies targeting PKM2 in less frequently studied cancers. In the context of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), photodynamic therapy (PDT) has been shown to directly inhibit PKM2, thereby activating the PKM2/caspase-8/caspase-3/GSDME axis. This pathway suppresses aerobic glycolysis and promotes programmed cell death in ESCC cells, suggesting that PDT-mediated ESCC treatment is fundamentally linked to PKM2 inhibition (141, 142). Additionally, the small molecule compound 8 has been identified as a modulator of mitochondrial function, disrupting the PKM2-VDAC3 (a regulator of ferroptosis) interaction to inhibit tumor growth in vivo while concurrently inducing ferroptosis, highlighting a novel connection between PKM2 and iron-dependent cell death (143). PKM2 has also been implicated in melanoma, where it is highly expressed. Benserazide, a known inhibitor, directly binds to PKM2, suppressing aerobic glycolysis while upregulating OXPHOS, thereby inhibiting melanoma proliferation, including in BRAFi-resistant cells (22). Furthermore, HA344 has been found to covalently bind to PKM2, effectively counteracting melanoma drug resistance by inhibiting tumor cell glycolysis (144). A Metabolic Reprogramming Immunosurveillance Activation Nanomedicine (MRIAN) has been engineered to enhance immunosurveillance against leukemia cells. Upon degradation, MRIAN suppresses PKM2 activity and lowers ROS levels, thereby disrupting the immunosuppressive properties of leukemia cells and inducing their differentiation into normal hematopoietic lineages (145).
These findings underscore the significant therapeutic potential of PKM2-targeted interventions across various malignancies. Given the extensive body of evidence supporting the efficacy of PKM2 inhibition in tumor therapy, a systematic summary has been compiled, categorizing recent advancements into three primary strategies: direct targeting of PKM2 protein, modulation of PKM2-associated nuclear transcripts, and indirect inhibition via regulatory signaling pathways that modulate PKM2 activity. A schematic representation of these therapeutic approaches is provided in Figure 4.
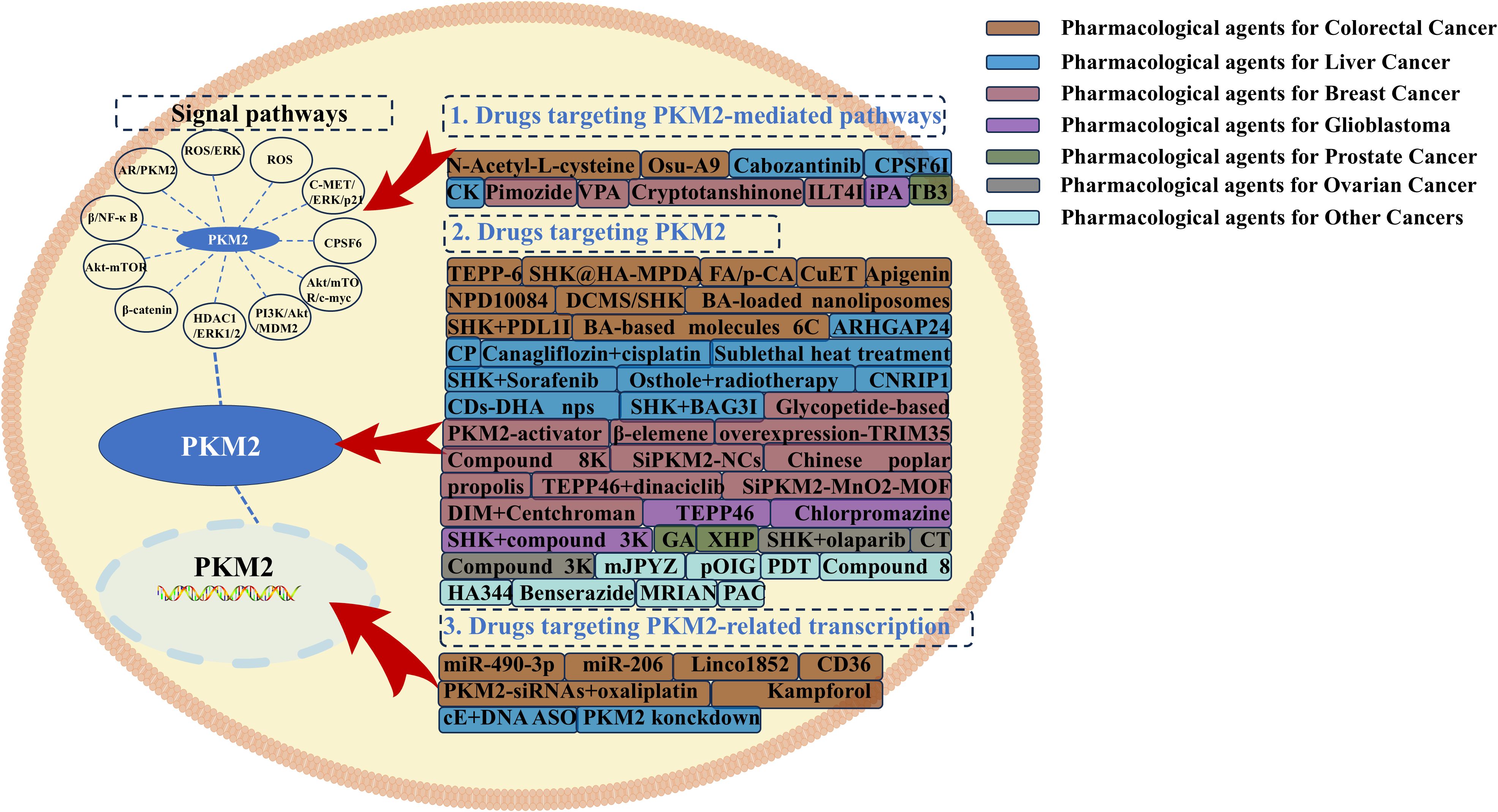
Figure 4. Therapeutic strategies targeting PKM2-mediated pathways, PKM2, and PKM2-mediated transcription in colorectal cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer, glioblastoma, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, and other tumors.
5 Conclusions and future perspectives
As the principal rate-limiting enzyme of aerobic glycolysis, PKM2 is aberrantly overexpressed in numerous malignancies, playing a critical role in tumor cell metabolism. However, accumulating evidence indicates that PKM2 exacerbates tumor progression beyond its metabolic function, contributing to oncogenesis through diverse non-metabolic mechanisms and signaling pathways. Moreover, PKM2 has been extensively studied as a tumor-associated protein kinase. The emergence of specific PKM2 inhibitors such as Shikonin (SHK) and Compound 3 has further reinforced the association between PKM2 and malignancy (51, 146, 147). In multiple human malignancies, including colorectal, hepatocellular, breast, gastric, and pancreatic cancers, PKM2 not only enhances aerobic glycolysis but also promotes tumor progression via alternative pathways. In CRC, aberrant PKM2 overexpression and nuclear translocation drive EMT, migration, immunosuppression, and inflammatory progression through non-metabolic mechanisms. Similarly, PKM2-mediated β-catenin signaling in HCC confers resistance to apoptosis and chemotherapy in a non-metabolic manner. In BC, particularly triple-negative subtypes, PKM2 regulates tumor phenotypes, modulates autophagy, and contributes to doxorubicin resistance. Furthermore, elevated PKM2 nuclear translocation in genitourinary tumors has been identified as a key factor in chemoresistance and metastatic dissemination. Building on these mechanistic insights, the emergence of PKM2-targeted therapies has significantly reshaped the current oncological treatment landscape. More intriguingly, the series of malignant effects induced by PKM2 translocation—such as cell cycle arrest, DNA damage repair, EMT progression, and the activation of associated transcription—may all be regulated by its function as an intranuclear RNA-binding protein. Given the expanding research on PKM2-mediated oncogenic pathways and targeted therapeutics, a systematic collation of recent findings is presented in Table 1. Despite advancements, investigations into PKM2-driven pathways remain insufficient, with numerous tumor-promoting effects arising from PKM2 interactions with other proteins yet to be elucidated. FurthHER2 exploration of these molecular mechanisms holds considerable promise. Therapeutic strategies targeting PKM2 have demonstrated notable efficacy, with existing approaches achieving anti-tumor effects through direct inhibition of PKM2 protein, modulation of PKM2-associated nuclear transcription, and indirect suppression of PKM2 activity via aerobic glycolysis, immunosuppression, and resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. These approaches have already yielded substantial breakthroughs. More innovatively, multimodal strategies, including combinatorial drug regimens, radio- and chemotherapy integration, thermal ablation, and PKM2-targeted nanotherapeutics, have demonstrated significant therapeutic potential.
However, based on current findings, numerous challenges and shortcomings remain. In-depth exploration of the specific mechanisms of PKM2 as a nuclear transcription factor and RNA-binding protein. Many studies concerning targeted anti-tumor drugs for PKM2 have remained confined to the description of purely phenomenological results, without delving into more profound investigations of the underlying mechanisms and pathways. Future PKM2-targeted treatment strategies can be refined and expanded based on these emerging paradigms. However, whether targeting PKM2 directly or its mediated pathways, the inherent toxicity of therapeutic agents, their low selectivity for PKM2, and the costs associated with formulation development all pose challenges that currently constrain the clinical translation of PKM2-targeting drugs as therapeutic options. In conclusion, PKM2 serves as a key therapeutic target for malignant tumors due to its abnormal expression. Furthermore, utilizing the stage-specific expression of PKM2 throughout the entire tumor treatment cycle as a potential therapeutic efficacy biomarker represents a promising strategy. Both approaches collectively open highly prospective innovative pathways for cancer treatment. The continued development of PKM2-targeted agents is expected to improve patient outcomes across a broad spectrum of malignancies, positioning PKM2 inhibition as a transformative strategy in precision oncology.
Author contributions
LL: Formal Analysis, Resources, Visualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Validation, Supervision, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Software, Methodology. JW: Visualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Conceptualization. LBL: Validation, Visualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. CC: Visualization, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. MX: Validation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Visualization. WT: Writing – original draft, Supervision, Methodology, Visualization, Validation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
Axl, Anexelekto; BC, Breast cancer; BMP4, Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4; CeRNA, competing endogenous RNA; cEt/DNA ASO, antisense oligonucleotides; CNRIP1, Cannabinoid receptor-interacting protein 1; CPSF6, cleavage and polyadenylation-specific factor 6; CRC, colorectal cancer; DIM, diindolylmethane; DOX, doxorubicin; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; ENO1, Enolase 1; ER, estrogen receptor; ESCC, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; GBM, glioblastoma; GC, Gastric cancer; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HDAC8, Histone deacetylase 8; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; ILT4, immunoglobulin-like transcript 4; KHK-A, Ketohexokinase-A; LncRNA, long noncoding RNA; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MET, mesenchymal-epithelial transition; mJPYZ, Modified Jianpi Yangzheng Decoction; MPDA, mesoporous polydopamine; MRIAN, Metabolic Reprogramming Immunosurveillance Activation Nanomedicine; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; PC, pancreatic cancer; PDGFR-β, platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β; PDT, photodynamic therapy; PK, pyruvate kinase; PKCϵ, protein kinase C epsilon; PKM2, M2-type pyruvate kinase; PRMT1, protein arginine methyltransferase-1; PTP1B, protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B; RCC, Renal cell carcinoma; SHK, Shikonin; SHP2, Src homology 2 domain-containing phosphatase 2; TACE, transarterial chemoembolization; TMZ, temozolomide; TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer; UCHL1, ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1; USF2, upstream stimulatory factor 2; USP35, ubiquitin-specific protease 35; XHP, Xihuang Pills.
References
1. Vaupel P and Multhoff G. Revisiting the Warburg effect: historical dogma versus current understanding. J Physiol. (2021) 599:1745–57. doi: 10.1113/JP278810
2. Lao Y, Cui X, Xu Z, Yan H, Zhang Z, Zhang Z, et al. Glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase suppresses tumor progression and shapes an anti-tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. (2024) 81:847–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.05.034
3. Noguchi T, Inoue H, and Tanaka T. The M1- and M2-type isozymes of rat pyruvate kinase are produced from the same gene by alternative RNA splicing. J Biol Chem. (1986) 261:13807–12. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)67091-7
4. Tani K, Fujii H, Tsutsumi H, Sukegawa J, Toyoshima K, Yoshida MC, et al. Human liver type pyruvate kinase: cDNA cloning and chromosomal assignment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (1987) 143:431–8. doi: 10.1016/0006-291X(87)91372-6
5. Alquraishi M, Puckett DL, Alani DS, Humidat AS, Frankel VD, Donohoe DR, et al. Pyruvate kinase M2: A simple molecule with complex functions. Free Radic Biol Med. (2019) 143:176–92. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.08.007
6. Chaneton B and Gottlieb E. Rocking cell metabolism: revised functions of the key glycolytic regulator PKM2 in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. (2012) 37:309–16. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2012.04.003
7. Mazurek S, Boschek CB, Hugo F, and Eigenbrodt E. Pyruvate kinase type M2 and its role in tumor growth and spreading. Semin Cancer Biol. (2005) 15:300–8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2005.04.009
8. Rihan M and Sharma SS. Role of pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) in cardiovascular diseases. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. (2023) 16:382–402. doi: 10.1007/s12265-022-10321-1
9. İlhan M. Non-metabolic functions of pyruvate kinase M2: PKM2 in tumorigenesis and therapy resistance. Neoplasma. (2022) 69:747–54. doi: 10.4149/neo_2022_220119N77
10. Wei Y, Wang D, Jin F, Bian Z, Li L, Liang H, et al. Pyruvate kinase type M2 promotes tumour cell exosome release via phosphorylating synaptosome-associated protein 23. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:14041. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14041
11. Qian J, Huang C, Wang M, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Li M, et al. Nuclear translocation of metabolic enzyme PKM2 participates in high glucose-promoted HCC metastasis by strengthening immunosuppressive environment. Redox Biol. (2024) 71:103103. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103103
12. Anastasakis DG, Apostolidi M, Garman KA, Polash AH, Umar MI, Meng Q, et al. Nuclear PKM2 binds pre-mRNA at folded G-quadruplexes and reveals their gene regulatory role. Mol Cell. (2024) 84:3775–89. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.07.025
13. Park JH, Lee J-S, Oh Y, Lee JS, Park HE, Lee H, et al. PKM2 is overexpressed in glioma tissues, and its inhibition highly increases late apoptosis in U87MG cells with low-density specificity. In Vivo. (2022) 36:694–703. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12755
14. Stanke KM, Wilson C, and Kidambi S. High expression of glycolytic genes in clinical glioblastoma patients correlates with lower survival. Front Mol Biosci. (2021) 8:752404. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.752404
15. Wang C, Zhang S, Liu J, Tian Y, Ma B, Xu S, et al. Secreted pyruvate kinase M2 promotes lung cancer metastasis through activating the integrin beta1/FAK signaling pathway. Cell Rep. (2020) 30:1780–97. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.037
16. Long L, Chen M, Yuan Y, Ming AL, Guo W, Wu K, et al. High expression of PKM2 synergizes with PD-L1 in tumor cells and immune cells to predict worse survival in human lung adenocarcinoma. J Cancer. (2020) 11:4442–52. doi: 10.7150/jca.42610
17. Wang Y, Zhao H, Zhao P, and Wang X. Targeting PKM2 promotes chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer biomark. (2021) 32:221–30. doi: 10.3233/CBM-210111
18. Das R, Pulugu P, Singh AA, Chatterjee DR, Baviskar S, Vyas H, et al. Mechanistic investigation of thiazole-based pyruvate kinase M2 inhibitor causing tumor regression in triple-negative breast cancer. J Med Chem. (2024) 67:3339–57. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01512
19. Li T-E, Wang S, Shen X-T, Zhang Z, Chen M, Wang H, et al. PKM2 drives hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inducing immunosuppressive microenvironment. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:589997. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.589997
20. Wang J, Sun M, Ma R, Wang G, Li W, Yang B, et al. Down-regulation of NOTCH1 and PKM2 can inhibit the growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells. Am J Transl Res. (2022) 14:5455–65.
21. Xiao S, Xu G, Wang Z, and Chong T. Chaperon−mediated autophagy can promote proliferation and invasion of renal carcinoma cells and inhibit apoptosis through PKM2. Oncol Rep. (2021) 46:214. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8165
22. Zhou Y, Huang Z, Su J, Li J, Zhao S, Wu L, et al. Benserazide is a novel inhibitor targeting PKM2 for melanoma treatment. Int J Cancer. (2020) 147:139–51. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32756
23. Liang N, Mi L, Li J, Li T, Chen J, Dionigi G, et al. Pan-cancer analysis of the oncogenic and prognostic role of PKM2: A potential target for survival and immunotherapy. BioMed Res Int. (2023) 2023:3375109. doi: 10.1155/2023/3375109
24. Chen J, Duan S, Wang Y, Ling Y, Hou X, Zhang S, et al. MYG1 drives glycolysis and colorectal cancer development through nuclear-mitochondrial collaboration. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:4969. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49221-0
25. Lv J-L, Ren Y-S, Tan Y-J, Chu T, Cao X-Y, Liu H-Y, et al. Hernandezine acts as a CDK4 suppressor inhibiting tumor growth by the CDK4/PKM2/NRF2 axis in colon cancer. Phytomedicine. (2024) 131:155775. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155775
26. Ren J, Li W, Pan G, Huang F, Yang J, Zhang H, et al. miR-142-3p modulates cell invasion and migration via PKM2-mediated aerobic glycolysis in colorectal cancer. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). (2021) 2021:9927720. doi: 10.1155/2021/9927720
27. Cha P-H, Hwang J-H, Kwak D-K, Koh E, Kim K-S, and Choi K-Y. APC loss induces Warburg effect via increased PKM2 transcription in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. (2021) 124:634–44. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-01118-7
28. Wan X-H, Jin G-B, Yang Q, Hu J-L, Liu Z-L, Rao J, et al. Novel miR-490-3p/hnRNPA1-b/PKM2 axis mediates the Warburg effect and proliferation of colon cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway. World J Gastrointest Oncol. (2024) 16:2038–59. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.2038
29. Yu T, Huang C, Lai C, He Q, Yuan W, and Chen Z. Copine 7 promotes colorectal cancer proliferation through PKM2 interaction and MAPK signaling pathway. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1166444. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1166444
30. Yang P, Li Z, Fu R, Wu H, and Li Z. Pyruvate kinase M2 facilitates colon cancer cell migration via the modulation of STAT3 signalling. Cell Signal. (2014) 26:1853–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.03.020
31. Peng C, Yang P, Zhang D, Jin C, Peng W, Wang T, et al. KHK-A promotes fructose-dependent colorectal cancer liver metastasis by facilitating the phosphorylation and translocation of PKM2. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2024) 14:2959–76. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.04.024
32. Song L, Dong N, and Li Z. p,p’-Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane promotes aerobic glycolysis via reactive oxygen species-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase/M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase (PKM2) signaling in colorectal cancer cells. Environ Toxicol. (2020) 35:333–45. doi: 10.1002/tox.22869
33. Yang P, Li Z, Li H, Lu Y, Wu H, and Li Z. Pyruvate kinase M2 accelerates pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion and cell proliferation induced by lipopolysaccharide in colorectal cancer. Cell Signal. (2015) 27:1525–32. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.02.032
34. Fan M, Sun W, Gu X, Lu S, Shen Q, Liu X, et al. The critical role of STAT3 in biogenesis of tumor-derived exosomes with potency of inducing cancer cachexia in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. (2022) 41:1050–62. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-02151-3
35. Xie Z, Xia J, Jiao M, Zhao P, Wang Z, Lin S, et al. Exosomal lncRNA HOTAIR induces PDL1+ B cells to impede anti-tumor immunity in colorectal cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2023) 644:112–21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.01.005
36. Li M, Sun S, Bian Z, Yao S, Liu M, You X, et al. SNHG15 promotes chemoresistance and glycolysis in colorectal cancer. Pathol Res Pract. (2023) 246:154480. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154480
37. Yu S, Zang W, Qiu Y, Liao L, and Zheng X. Deubiquitinase OTUB2 exacerbates the progression of colorectal cancer by promoting PKM2 activity and glycolysis. Oncogene. (2022) 41:46–56. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-02071-2
38. Han J, Zhao Z, Zhang N, Yang Y, Ma L, Feng L, et al. Transcriptional dysregulation of TRIM29 promotes colorectal cancer carcinogenesis via pyruvate kinase-mediated glucose metabolism. Aging (Albany NY). (2021) 13:5034–54. doi: 10.18632/aging.202414
39. Wang C, Cao Y, Yang C, Bernards R, and Qin W. Exploring liver cancer biology through functional genetic screens. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 18:690–704. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00465-x
40. Marengo A, Rosso C, and Bugianesi E. Liver cancer: connections with obesity, fatty liver, and cirrhosis. Annu Rev Med. (2016) 67:103–17. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-090514-013832
41. Cheng Z, Huang H, Li M, Liang X, Tan Y, and Chen Y. Lactylation-related gene signature effectively predicts prognosis and treatment responsiveness in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pharm (Basel). (2023) 16:644. doi: 10.3390/ph16050644
42. Martin SP, Fako V, Dang H, Dominguez DA, Khatib S, Ma L, et al. PKM2 inhibition may reverse therapeutic resistance to transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 39:99. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01605-y
43. Jiang X, Lu Y, Xie S, Chen Y, Liu X, Li S, et al. miR-624 accelerates the growth of liver cancer cells by inhibiting EMC3. Noncoding RNA Res. (2023) 8:641–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.09.005
44. Zhong J, Kang Q, Cao Y, He B, Zhao P, Gou Y, et al. BMP4 augments the survival of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells under hypoxia and hypoglycemia conditions by promoting the glycolysis pathway. Am J Cancer Res. (2021) 11:793–811.
45. Mu M, Lu Y, Tu K, Tu L, Guo C, Li Z, et al. FAM188B promotes the growth, metastasis, and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting the hnRNPA1/PKM2 axis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. (2024) 1871:119773. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2024.119773
46. Yu Z, Wang D, and Tang Y. PKM2 promotes cell metastasis and inhibits autophagy via the JAK/STAT3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. (2021) 476:2001–10. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-04041-w
47. Song S, Wang L, Jiang X, Liu X, Li S, Xie S, et al. CircHULC accelerates the growth of human liver cancer stem cells by enhancing chromatin reprogramming and chromosomal instability via autophagy. Cell Signal. (2023) 109:110772. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110772
48. Lv T, Zhang B, Jiang C, Zeng Q, Yang J, and Zhou Y. USP35 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by protecting PKM2 from ubiquitination−mediated degradation. Int J Oncol. (2023) 63:113. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5561
49. Zhang R, Shen M, Wu C, Chen Y, Lu J, Li J, et al. HDAC8-dependent deacetylation of PKM2 directs nuclear localization and glycolysis to promote proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:1036. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03212-3
50. Zhu Q, Lei Z, Xu C, Zhang Z, Yu Z, Cheng Z, et al. LncRNA HClnc1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating PKM2 signaling and indicates poor survival outcome after hepatectomy. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:14526–44. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6117
51. Yang W, Liu J, Hou L, Chen Q, and Liu Y. Shikonin differentially regulates glucose metabolism via PKM2 and HIF1α to overcome apoptosis in a refractory HCC cell line. Life Sci. (2021) 265:118796. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118796
52. Yu W, Zeng F, Xiao Y, Chen L, Qu H, Hong J, et al. Targeting PKM2 improves the gemcitabine sensitivity of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells via inhibiting β-catenin signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact. (2024) 387:110816. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110816
53. Britt KL, Cuzick J, and Phillips K-A. Key steps for effective breast cancer prevention. Nat Rev Cancer. (2020) 20:417–36. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0266-x
54. Gao S, Wang Y, Xu Y, Liu L, and Liu S. USP46 enhances tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells by stabilizing PTBP1 to facilitate glycolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2024) 1870:167011. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.167011
55. Jiang C-F, Xie Y-X, Qian Y-C, Wang M, Liu L-Z, Shu Y-Q, et al. TBX15/miR-152/KIF2C pathway regulates breast cancer doxorubicin resistance via promoting PKM2 ubiquitination. Cancer Cell Int. (2021) 21:542. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02235-w
56. Yu P, Li A-X, Chen X-S, Tian M, Wang H-Y, Wang X-L, et al. PKM2-c-myc-survivin cascade regulates the cell proliferation, migration, and tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:550469. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.550469
57. Xu H, Li L, Dong B, Lu J, Zhou K, Yin X, et al. TRAF6 promotes chemoresistance to paclitaxel of triple negative breast cancer via regulating PKM2-mediated glycolysis. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:19807–20. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6552
58. Yamamoto T, Hayashida T, Masugi Y, Oshikawa K, Hayakawa N, Itoh M, et al. PRMT1 sustains de novo fatty acid synthesis by methylating PHGDH to drive chemoresistance in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. (2024) 84:1065–83. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-2266
59. Bernard MJ and Goldstein AS. A metabolic-epigenetic mechanism directs cell fate and therapeutic sensitivity in breast cancer. Cancer Res. (2024) 84:1382–3. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-24-0460
60. Wang P, Han Y, Pan W, Du J, Zuo D, Ba Y, et al. Tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 aggravates tumor progression and glycolysis by dephosphorylating PKM2 in gastric cancer. MedComm (2020). (2024) 5:e527. doi: 10.1002/mco2.527
61. Dai T, Zhang X, Zhou X, Hu X, Huang X, Xing F, et al. Long non-coding RNA VAL facilitates PKM2 enzymatic activity to promote glycolysis and Malignancy of gastric cancer. Clin Transl Med. (2022) 12:e1088. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1088
62. Wang N, Qiao H, Hao J, Deng C, Zhou N, Yang L, et al. RNA-binding protein ENO1 promotes the tumor progression of gastric cancer by binding to and regulating gastric cancer-related genes. J Gastrointest Oncol. (2023) 14:585–98. doi: 10.21037/jgo-23-151
63. Zhang C, Wang H, Liu Q, et al. LncRNA CCAT1 facilitates the progression of gastric cancer via PTBP1-mediated glycolysis enhancement. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 42:246. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02827-6
64. Zhao X, Tian Z, and Liu L. circATP2B1 promotes aerobic glycolysis in gastric cancer cells through regulation of the miR-326 gene cluster. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:628624. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.628624
65. Wu J, Chai H, Xu X, Yu J, and Gu Y. Histone methyltransferase SETD1A interacts with HIF1α to enhance glycolysis and promote cancer progression in gastric cancer. Mol Oncol. (2020) 14:1397–409. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12689
66. Liu J, Tao M, Zhao W, Song Q, Yang X, Li M, et al. Calcium channel α2δ1 is essential for pancreatic tumor-initiating cells through sequential phosphorylation of PKM2. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 15:373–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2022.10.006
67. Xu Q, Wu N, Li X, Guo C, Li C, Jiang B, et al. Inhibition of PTP1B blocks pancreatic cancer progression by targeting the PKM2/AMPK/mTOC1 pathway. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10:874. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2073-4
68. Xia Q, Jia J, Hu C, Lu J, Li J, Xu H, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages promote PD-L1 expression in tumor cells by regulating PKM2 nuclear translocation in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. (2022) 41:865–77. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-02133-5
69. Chen M, Li X, Du B, Chen S, and Li Y. Upstream stimulatory factor 2 inhibits erastin-induced ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer through transcriptional regulation of pyruvate kinase M2. Biochem Pharmacol. (2022) 205:115255. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115255
70. Yavuz BB, Kilinc F, Kanyilmaz G, and Aktan M. Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM-2) expression and prognostic significance in glioblastoma patients. J Neurooncol. (2023) 165:527–33. doi: 10.1007/s11060-023-04521-1
71. Li G, Wang D, Zhai Y, Pan C, Zhang J, Wang C, et al. Glycometabolic reprogramming-induced XRCC1 lactylation confers therapeutic resistance in ALDH1A3-overexpressing glioblastoma. Cell Metab. (2024) 36:1696–710. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.07.011
72. Song J, Zheng J, Liu X, Dong W, Yang C, Wang D, et al. A novel protein encoded by ZCRB1-induced circHEATR5B suppresses aerobic glycolysis of GBM through phosphorylation of JMJD5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2022) 41:171. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02374-6
73. Zhao Y, Song J, Dong W, Liu X, Yang C, Wang D, et al. The MBNL1/circNTRK2/PAX5 pathway regulates aerobic glycolysis in glioblastoma cells by encoding a novel protein NTRK2-243aa. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:767. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05219-4
74. Li G, Xiong Z, Li Y, Yan C, Cheng Y, Wang Y, et al. Hypoxic microenvironment-induced exosomes confer temozolomide resistance in glioma through transfer of pyruvate kinase M2. Discov Oncol. (2024) 15:110. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-00963-9
75. Gao L, Yang F, Tang D, Xu Z, Tang Y, Yang D, et al. Mediation of PKM2-dependent glycolytic and non-glycolytic pathways by ENO2 in head and neck cancer development. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 42:1. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02574-0
76. Chang H, Xu Q, Li J, Li M, Zhang Z, Ma H, et al. Lactate secreted by PKM2 upregulation promotes Galectin-9-mediated immunosuppression via inhibiting NF-κB pathway in HNSCC. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:725. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03990-4
77. Dai H, Zeng W, and Luo H. C-MET-dependent signal transduction mediates retinoblastoma growth by regulating PKM2 nuclear translocation. Cell Biochem Funct. (2020) 38:204–12. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3464
78. Xu H, Liu Z, Gao D, Li P, Shen Y, Sun Y, et al. Reprogramming hormone-sensitive prostate cancer to a lethal neuroendocrine cancer lineage by mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC). Mol Metab. (2022) 59:101466. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101466
79. Lai X, Liang Y, Jin J, Zhang H, Wu Z, Li G, et al. Protein kinase C epsilon promotes de novo lipogenesis and tumor growth in prostate cancer cells by regulating the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of pyruvate kinase isoform M2. Exp Cell Res. (2023) 422:113427. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2022.113427
80. Hu C-Y, Chen J, Qin X-H, You P, Ma J, Zhang J, et al. Long non-coding RNA NORAD promotes the prostate cancer cell extracellular vesicle release via microRNA-541-3p-regulated PKM2 to induce bone metastasis of prostate cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 40:98. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01891-0
81. Zheng Y, Shi D, Chen L, Yang Y, and Yao M. UCHL1-PKM2 axis dysregulation is associated with promoted proliferation and invasiveness of urothelial bladder cancer cells. Aging (Albany NY). (2023) 15:10593–606. doi: 10.18632/aging.205097
82. Sang B-T, Wang C-D, Liu X, Guo J-Q, Lai J-Y, and Wu X-M. PDGF-BB/PDGFRβ induces tumour angiogenesis via enhancing PKM2 mediated by the PI3K/AKT pathway in Wilms’ tumour. Med Oncol. (2023) 40:240. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02115-5
83. Wang C, Zeng J, Li L-J, Xue M, and He S-L. Cdc25A inhibits autophagy-mediated ferroptosis by upregulating ErbB2 through PKM2 dephosphorylation in cervical cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:1055. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04342-y
84. Tian M, Chen X-S, Li L-Y, Wu H-Z, Zeng D, Wang X-L, et al. Inhibition of AXL enhances chemosensitivity of human ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin via decreasing glycolysis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2021) 42:1180–9. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-00546-8
85. Dou L, Lu E, Tian D, Li F, Deng L, and Zhang Y. Adrenomedullin induces cisplatin chemoresistance in ovarian cancer through reprogramming of glucose metabolism. J Transl Int Med. (2023) 11:169–77. doi: 10.2478/jtim-2023-0091
86. Patle R, Shinde S, Patel S, Maheshwari R, Jariyal H, Srivastava A, et al. Discovery of boronic acid-based potent activators of tumor pyruvate kinase M2 and development of gastroretentive nanoformulation for oral dosing. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. (2021) 42:128062. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128062
87. Wang X, Guo W, Han J, Li J, Zhao Q, Mao Y, et al. Oral spatial-to-point cascade targeting “sugar-coated bullets” for precise and safe chemotherapy by intervention Warburg effect. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. (2023) 222:113108. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.113108
88. Long L, Xiong W, Lin F, Hou J, Chen G, Peng T, et al. Regulating lactate-related immunometabolism and EMT reversal for colorectal cancer liver metastases using shikonin targeted delivery. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 42:117. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02688-z
89. Wang G, Yu Y, Wang Y-Z, Zhu Z-M, Yin P-H, and Xu K. Effects and mechanisms of fatty acid metabolism−mediated glycolysis regulated by betulinic acid−loaded nanoliposomes in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. (2020) 44:2595–609. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7787
90. Fu R, Yang P, Amin S, and Li Z. A novel miR-206/hnRNPA1/PKM2 axis reshapes the Warburg effect to suppress colon cancer growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2020) 531:465–71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.08.019
91. Bian Z, Yang F, Xu P, Gao G, Yang C, Cao Y, et al. LINC01852 inhibits the tumorigenesis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer by suppressing SRSF5-mediated alternative splicing of PKM. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:23. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01939-7
92. Fang Y, Shen Z-Y, Zhan Y-Z, Feng X-C, Chen K-L, Li Y-S, et al. CD36 inhibits β-catenin/c-myc-mediated glycolysis through ubiquitination of GPC4 to repress colorectal tumorigenesis. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:3981. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11662-3
93. Huang X, Hou Y, Weng X, Pang W, Hou L, Liang Y, et al. Diethyldithiocarbamate-copper complex (CuET) inhibits colorectal cancer progression via miR-16-5p and 15b-5p/ALDH1A3/PKM2 axis-mediated aerobic glycolysis pathway. Oncogenesis. (2021) 10:4. doi: 10.1038/s41389-020-00295-7
94. Nagasawa I, Muroi M, Kawatani M, Ohishi T, Ohba S-I, Kawada M, et al. Identification of a small compound targeting PKM2-regulated signaling using 2D gel electrophoresis-based proteome-wide CETSA. Cell Chem Biol. (2020) 27:186–96. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.11.010
95. Chiu C-F, Weng J-R, Lee S-L, Wu C-Y, Chu P-C, Shan Y-S, et al. OSU-A9 induced-reactive oxygen species cause cytotoxicity in duodenal and gastric cancer cells by decreasing phosphorylated nuclear pyruvate kinase M2 protein levels. Biochem Pharmacol. (2020) 174:113811. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113811
96. Wu H, Du Je, Li C, Li H, Guo H, and Li Z. Kaempferol can reverse the 5-fu resistance of colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting PKM2-mediated glycolysis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:3544. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073544
97. Wu H, Cui M, Li C, Li H, Dai Y, Cui K, et al. Kaempferol Reverses Aerobic Glycolysis via miR-339-5p-Mediated PKM Alternative Splicing in Colon Cancer Cells. J Agric Food Chem. (2021) 69:3060–8. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c07640
98. Shi J, Ji X, Shan S, Zhao M, Bi C, and Li Z. The interaction between apigenin and PKM2 restrains progression of colorectal cancer. J Nutr Biochem. (2023) 121:109430. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109430
99. Cui K, Wu H, Fan J, Zhang L, Li H, Guo H, et al. The Mixture of Ferulic Acid and P-Coumaric Acid Suppresses Colorectal Cancer through lncRNA 495810/PKM2 Mediated Aerobic Glycolysis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:12106. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012106
100. Yin C, Lu W, Ma M, Yang Q, He W, Hu Y, et al. Efficacy and mechanism of combination of oxaliplatin with PKM2 knockdown in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. (2020) 20:312. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12175
101. Chen J, Liu J, Liu X, Wang J, Wang X, Ye X, et al. Shikonin improves the effectiveness of PD-1 blockade in colorectal cancer by enhancing immunogenicity via Hsp70 upregulation. Mol Biol Rep. (2024) 51:86. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09056-2
102. Tang M, Zhao Y, Zhao J, Wei S, Liu M, Zheng N, et al. Liver cancer heterogeneity modeled by in situ genome editing of hepatocytes. Sci Adv. (2022) 8:eabn5683. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn5683
103. Fan Z, Yang G, Luo R, Qu X, Ye X, Wang J, et al. Sublethal heat treatment enhances lactic acid uptake in macrophages via MCT1, leading to reduced paraspeckle formation and a subsequent decrease in macrophage pyroptosis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1290185. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1290185
104. Yang W, Wang B, Yu Q, Liu T, Li T, Tian T, et al. ARHGAP24 represses β-catenin transactivation-induced invasiveness in hepatocellular carcinoma mainly by acting as a GTPase-independent scaffold. Theranostics. (2022) 12:6189–206. doi: 10.7150/thno.72134
105. Guo Y, Liu Z, Wu Q, Li Z, Yang J, and Xuan H. Integration with transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveals the in vitro cytotoxic mechanisms of chinese poplar propolis by triggering the glucose metabolism in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Nutrients. (2023) 15:4329. doi: 10.3390/nu15204329
106. Liu T, Li S, Wu L, Yu Q, Li J, Feng J, et al. Experimental study of hepatocellular carcinoma treatment by shikonin through regulating PKM2. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. (2020) 7:19–31. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S237614
107. Lu J, Liu S-Y, Zhang J, Yang G-M, Gao G-B, Yu N-N, et al. Inhibition of BAG3 enhances the anticancer effect of shikonin in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. (2021) 11:3575–93.
108. Zeng Y, Jiang H, Zhang X, Xu J, Wu X, Xu Q, et al. Canagliflozin reduces chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma through PKM2-c-Myc complex-mediated glutamine starvation. Free Radic Biol Med. (2023) 208:571–86. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.09.006
109. Huang H, Xue J, Xie T, and Xie M-L. Osthole increases the radiosensitivity of hepatoma cells by inhibiting GSK-3β/AMPK/mTOR pathway-controlled glycolysis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. (2023) 396:683–92. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02347-8
110. Chen D, Wu H, Feng X, Chen Y, Lv Z, Kota VG, et al. DNA methylation of cannabinoid receptor interacting protein 1 promotes pathogenesis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma through suppressing parkin-dependent pyruvate kinase M2 ubiquitination. Hepatology. (2021) 73:1816–35. doi: 10.1002/hep.31561
111. Shang R, Song X, Wang P, Zhou Y, Lu X, Wang J, et al. Cabozantinib-based combination therapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. (2021) 70:1746–57. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-320716
112. Sim DY, Lee H-J, Ahn C-H, Park J, Park S-Y, Kil B-J, et al. Negative regulation of CPSF6 suppresses the warburg effect and angiogenesis leading to tumor progression via c-myc signaling network: potential therapeutic target for liver cancer therapy. Int J Biol Sci. (2024) 20:3442–60. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.93462
113. Shin N, Lee H-J, Sim DY, Im E, Park JE, Park WY, et al. Apoptotic effect of compound K in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via inhibition of glycolysis and Akt/mTOR/c-Myc signaling. Phytother Res. (2021) 35:3812–20. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7087
114. Ma WK, Voss DM, Scharner J, Costa ASH, Lin K-T, Jeon HY, et al. ASO-based PKM splice-switching therapy inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth. Cancer Res. (2022) 82:900–15. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-0948
115. Li Y, Shi N, Zhang W, Zhang H, Song Y, Zhu W, et al. Supramolecular hybrids of carbon dots and dihydroartemisinin for enhanced anticancer activity and mechanism analysis. J Mater Chem B. (2020) 8:9777–84. doi: 10.1039/d0tb01826k
116. Hou D-Y, Xiao W-Y, Wang J-Q, Yaseen M, Wang Z-J, Fei Y, et al. OGA activated glycopeptide-based nano-activator to activate PKM2 tetramerization for switching catabolic pathways and sensitizing chemotherapy resistance. Biomaterials. (2022) 284:121523. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121523
117. Pan Y, Wang W, Huang S, Ni W, Wei Z, Cao Y, et al. Beta-elemene inhibits breast cancer metastasis through blocking pyruvate kinase M2 dimerization and nuclear translocation. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23:6846–58. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14568
118. Wu H, Guo X, Jiao Y, Wu Z, and Lv Q. TRIM35 ubiquitination regulates the expression of PKM2 tetramer and dimer and affects the Malignant behaviour of breast cancer by regulating the Warburg effect. Int J Oncol. (2022) 61:144. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5434
119. Li R, Ning X, He J, Lin Z, Su Y, Li R, et al. Synthesis of novel sulfonamide derivatives containing pyridin-3-ylmethyl 4-(benzoyl)piperazine-1-carbodithioate moiety as potent PKM2 activators. Bioorg Chem. (2021) 108:104653. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104653
120. Li J, Liu H, Liu X, Hao S, Zhang Z, and Xuan H. Chinese poplar propolis inhibits MDA-MB-231 cell proliferation in an inflammatory microenvironment by targeting enzymes of the glycolytic pathway. J Immunol Res. (2021) 2021:6641341. doi: 10.1155/2021/6641341
121. Dang J, Ye H, Li Y, Liang Q, Li X, and Yin L. Multivalency-assisted membrane-penetrating siRNA delivery sensitizes photothermal ablation via inhibition of tumor glycolysis metabolism. Biomaterials. (2019) 223:119463. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119463
122. Li J, Qu P, Zhou X-Z, Ji Y-X, Yuan S, Liu S-P, et al. Pimozide inhibits the growth of breast cancer cells by alleviating the Warburg effect through the P53 signaling pathway. BioMed Pharmacother. (2022) 150:113063. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113063
123. Li Z, Yang L, Zhang S, Song J, Sun H, Shan C, et al. Valproic acid suppresses breast cancer cell growth through triggering pyruvate kinase M2 isoform mediated warburg effect. Cell Transplant. (2021) 30:9636897211027524. doi: 10.1177/09636897211027524
124. Zhou J, Su C-M, Chen H-A, Du S, Li C-W, Wu H, et al. Cryptanshinone inhibits the glycolysis and inhibits cell migration through PKM2/β-catenin axis in breast cancer. Onco Targets Ther. (2020) 13:8629–39. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S239134
125. Zhang H, Gao A, Liu Q, Zhang F, Wang S, Chen X, et al. ILT4 reprograms glucose metabolism to promote tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer. J Cell Sci. (2023) 136:jcs260964. doi: 10.1242/jcs.260964
126. Huang S, Zhu W, Zhang F, Chen G, Kou X, Yang X, et al. Silencing of pyruvate kinase M2 via a metal-organic framework based theranostic gene nanomedicine for triple-negative breast cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. (2021) 13:56972–87. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c18053
127. Apostolidi M, Vathiotis IA, Muthusamy V, Gaule P, Gassaway BM, Rimm DL, et al. Targeting pyruvate kinase M2 phosphorylation reverses aggressive cancer phenotypes. Cancer Res. (2021) 81:4346–59. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-4190
128. Penta D, Tripathi P, Rajarajan D, Natesh J, Mondal P, and Meeran SM. Diindolylmethane promotes metabolic crisis and enhances the efficacy of centchroman in breast cancer: A 1H NMR-based approach. ACS Omega. (2022) 7:43147–60. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c05832
129. Lv M, Zhang S, Dong Y, Cao L, and Guo S. PolG inhibits gastric cancer glycolysis and viability by suppressing PKM2 phosphorylation. Cancer Manag Res. (2021) 13:1559–70. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S292306
130. Wu J, Yuan M, Shen J, Chen Y, Zhang R, Chen X, et al. Effect of modified Jianpi Yangzheng on regulating content of PKM2 in gastric cancer cells-derived exosomes. Phytomedicine. (2022) 103:154229. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154229
131. Sun Q, Yuan M, Wang H, Zhang X, Zhang R, Wang H, et al. PKM2 is the target of a multi-herb-combined decoction during the inhibition of gastric cancer progression. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:767116. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.767116
132. Bailleul J, Ruan Y, Abdulrahman L, Scott AJ, Yazal T, Sung D, et al. M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase rewires glucose metabolism during radiation therapy to promote an antioxidant response and glioblastoma radioresistance. Neuro Oncol. (2023) 25:1989–2000. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noad103
133. Abbruzzese C, Matteoni S, Matarrese P, Signore M, Ascione B, Iessi E, et al. Chlorpromazine affects glioblastoma bioenergetics by interfering with pyruvate kinase M2. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:821. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06353-3
134. Pagano C, Coppola L, Navarra G, Avilia G, Savarese B, Torelli G, et al. N6-isopentenyladenosine inhibits aerobic glycolysis in glioblastoma cells by targeting PKM2 expression and activity. FEBS Open Bio. (2024) 14:843–54. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13766
135. Wang L, Fu B, Hou D-Y, Lv Y-L, Yang G, Li C, et al. PKM2 allosteric converter: A self-assembly peptide for suppressing renal cell carcinoma and sensitizing chemotherapy. Biomaterials. (2023) 296:122060. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122060
136. Yu J, Li S, Cheng S, Ahmad M, Chen C, Wan X, et al. Tanshinone analog inhibits castration-resistant prostate cancer cell growth by inhibiting glycolysis in an AR-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. (2024) 300:107139. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107139
137. Lin F, Long Y, Li M, Cai C, Wu Y, You X, et al. Xihuang pills targeting the Warburg effect through inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in prostate cancer. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e32914. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32914
138. Wang T, Zhang M, Khan M, Li J, Wu X, Ma T, et al. Cryptotanshinone suppresses ovarian cancer via simultaneous inhibition of glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. BioMed Pharmacother. (2024) 170:115956. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115956
139. Park JH, Kundu A, Lee SH, Jiang C, Lee SH, Kim YS, et al. Specific pyruvate kinase M2 inhibitor, compound 3K, induces autophagic cell death through disruption of the glycolysis pathway in ovarian cancer cells. Int J Biol Sci. (2021) 17:1895–908. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.59855
140. Zhou S, Li D, Xiao D, Wu T, Hu X, Zhang Y, et al. Inhibition of PKM2 enhances sensitivity of olaparib to ovarian cancer cells and induces DNA damage. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:1555–68. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.62947
141. Li L, Song D, Qi L, Jiang M, Wu Y, Gan J, et al. Photodynamic therapy induces human esophageal carcinoma cell pyroptosis by targeting the PKM2/caspase-8/caspase-3/GSDME axis. Cancer Lett. (2021) 520:143–59. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.07.014
142. Gan J, Li S, Meng Y, Liao Y, Jiang M, Qi L, et al. The influence of photodynamic therapy on the Warburg effect in esophageal cancer cells. Lasers Med Sci. (2020) 35:1741–50. doi: 10.1007/s10103-020-02966-8
143. Ning X, Qi H, Yuan Y, Li R, Wang Y, Lin Z, et al. Identification of a new small molecule that initiates ferroptosis in cancer cells by inhibiting the system Xc- to deplete GSH. Eur J Pharmacol. (2022) 934:175304. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175304
144. Zerhouni M, Martin AR, Furstoss N, Gutierrez VS, Jaune E, Tekaya N, et al. Dual covalent inhibition of PKM and IMPDH targets metabolism in cutaneous metastatic melanoma. Cancer Res. (2021) 81:3806–21. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2114
145. Li C, You X, Xu X, Wu B, Liu Y, Tong T, et al. A metabolic reprogramming amino acid polymer as an immunosurveillance activator and leukemia targeting drug carrier for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2022) 9:e2104134. doi: 10.1002/advs.202104134
146. Vander Heiden MG, Christofk HR, Schuman E, Subtelny AO, Sharfi H, Harlow EE, et al. Identification of small molecule inhibitors of pyruvate kinase M2. Biochem Pharmacol. (2010) 79:1118–24. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.12.003
Keywords: M2-type pyruvate kinase, aerobic glycolysis, PKM2-targeted therapeutics, signaling networks, anti-cancer
Citation: Liu L, Wang J, Liang L, Chen C, Xie M and Tang W (2025) Targeting PKM2 in cancer therapeutics: mechanistic advances and translational opportunities. Front. Immunol. 16:1649488. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1649488
Received: 18 June 2025; Accepted: 26 September 2025;
Published: 15 October 2025.
Edited by:
Shameer Khader, Sanofi, FranceReviewed by:
Mohd Amir, Aligarh Muslim University, IndiaMary L. Taub, University at Buffalo, United States
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Wang, Liang, Chen, Xie and Tang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wencheng Tang, NDY0OTE3ODBAcXEuY29t
 Lin Liu
Lin Liu Junyi Wang
Junyi Wang Libo Liang
Libo Liang Meng Xie
Meng Xie
