- 1Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Immunology in Chronic Diseases, Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu, Anhui, China
- 2School of Laboratory Medicine, Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu, Anhui, China
Th9 cells, a distinct subset of T helper cells, are defined by their production of IL-9. Th9 cells play a role in the development of various diseases by participating in mucosal immune responses, defending tissue barriers, and regulating inflammatory responses. For instance, Th9 cells contribute to inflammatory bowel disease by secreting IL-9, which damages the intestinal epithelial barrier. The effects mediated by Th9-derived IL-9 exhibit environment-dependent characteristics. In allergic asthma, IL-9 drives inflammation, while in specific tumor microenvironments, IL-9 can exert anti-tumor effects. Th9 cell differentiation is governed by a complex, multi-layered regulatory network. This network centers on the synergistic action of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and interleukin-4 (IL-4). Additionally, it involves multiple other mechanisms. These include exogenous signals such as IL-2 and IL-35; intrinsic transcription factors like the ATF-like protein BATF and PU.1; epigenetic modifications, including histone acetylation and DNA methylation; and metabolic reprogramming, such as glycolysis and lipid metabolism, among others. This review systematically summarizes the regulatory mechanisms governing Th9 cell differentiation. It elucidates these mechanisms and reveals potential therapeutic targets, including transcription factors such as PU.1, IRF4, and BATF. This work paves the way for the development of Th9-related immunotherapies.
1 Introduction
As fundamental components of adaptive immunity, T cells play a key role in maintaining immune homeostasis and mediating cellular immunity. CD4+ T cell activation is initiated when their T cell receptors (TCRs) recognize antigen peptide-MHC class II complexes presented by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). This recognition, combined with the integration of co-stimulatory signals, triggers the activation cascade. After activation, CD4+T cells differentiate into distinct helper T (Th) cell subsets by expressing lineage-specific transcription factors, driven by a specific cytokine microenvironment. Among the various T cell subsets, Th9 cells have attracted considerable attention due to their unique biological properties (1, 2). Studies have shown that patients with allergic asthma have significantly higher numbers of Th9 cells than healthy individuals (3). Th9 cells secrete IL-9 to enhance the production of type 2 cytokines IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, induce airway mucus secretion, and promote eosinophil recruitment, amplifying the asthmatic inflammatory response. The number of Th9 cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is also significantly higher than that in normal individuals (4). These findings underscore the pivotal role of Th9 cells in disease pathogenesis. Therefore, it is essential to understand the intricate regulatory network governing Th9 cell differentiation to elucidate their contribution to disease and develop targeted therapeutic strategies.
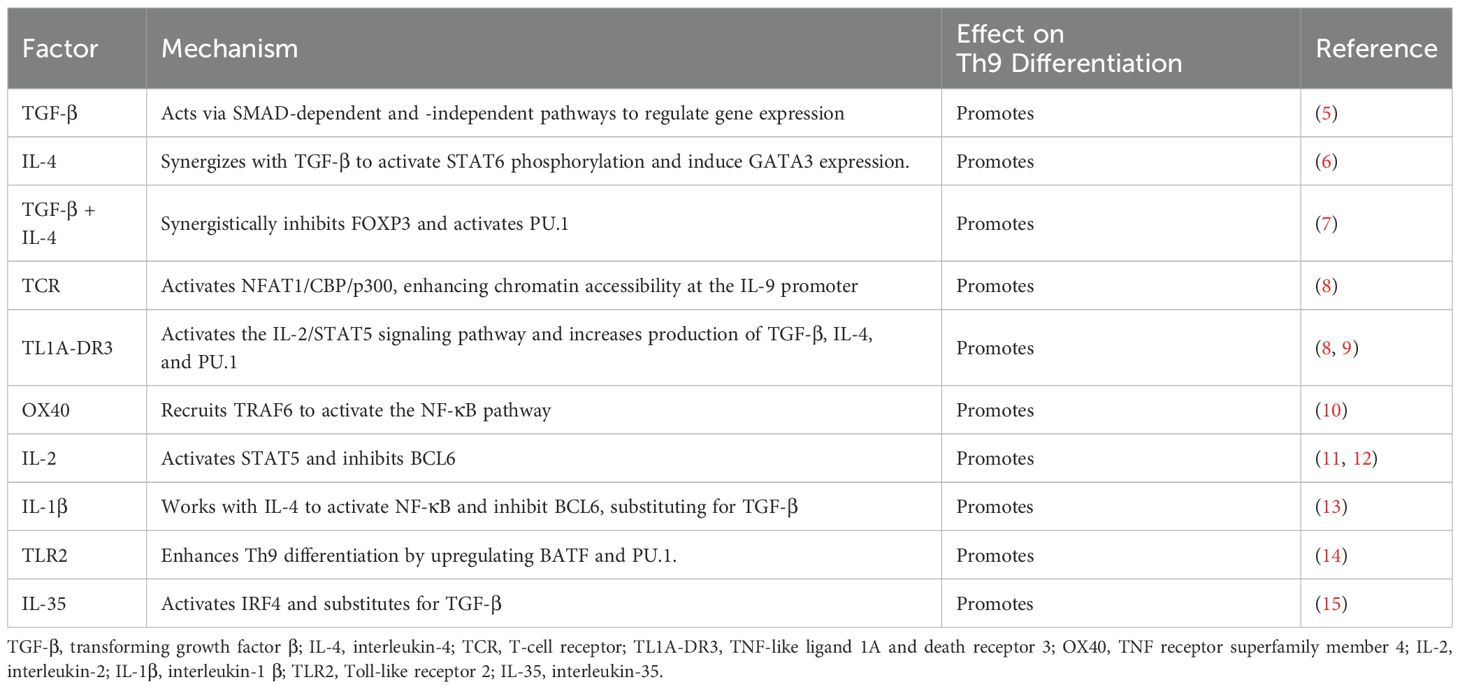
As shown in Figure 1 and Tables 1–3, Th9 cell differentiation is regulated by multiple factors. The process initiates with fundamental T cell receptor (TCR) recognition of antigen and co-stimulatory signals. These signals are mediated by molecules and pathways, such as NFAT1/CBP/P300 and NF-κB, which establish the foundation for subsequent lineage commitment. The synergistic action of the exogenous cytokines TGF-β and IL-4 then serves as the key signal that initiates the differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into the Th9 lineage (7, 38). TGF-β and IL-4 promote Th9 differentiation by suppressing FOXP3 expression and activating the STAT6/GATA3 axis in activated naïve CD4+ T cells. Endogenous transcription factor BATF is a key transcription factor in the early development of Th9 cells, which promotes Th9 cell differentiation by forming a complex with IRF4 (16). As a downstream transcription factor of TGF-β signaling, PU.1 is a core regulatory factor for both the differentiation and functional exertion of Th9 cells. PU.1 binds to the IL-9 promoter, regulates chromatin accessibility to enhance IL-9 transcription, thereby promoting the directional differentiation of Th9 cells (20). Epigenetic regulation, including histone acetylation and DNA methylation, finely regulates the expression of the key cytokine IL-9 and the core transcription factor PU.1 in Th9 cells by altering chromatin accessibility and gene expression levels. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is a key molecule linking metabolism and transcriptional regulation. HIF-1α supplies the necessary energy for Th9 cell differentiation by promoting metabolic pathways such as glycolysis (30). Moreover, it functions as a signaling molecule to regulate transcriptional programs. This reflects the close association between metabolism and Th9 cell differentiation. This review systematically summarizes the latest research progress in the field of Th9 cell subset differentiation, laying a theoretical foundation for elucidating the mechanisms of Th9 cell differentiation and developing novel immunotherapies for related diseases.
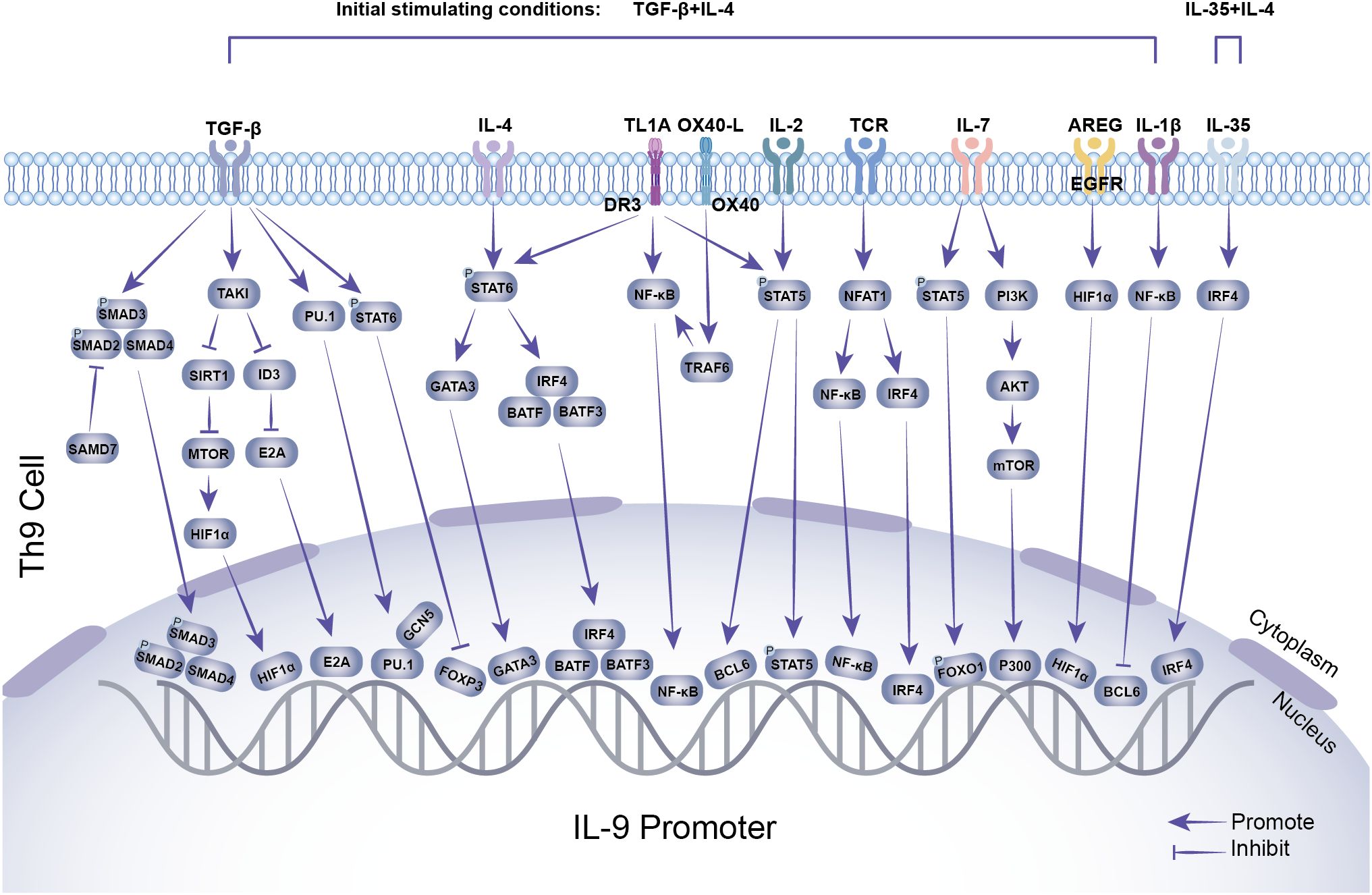
Figure 1. Transcriptional regulation of Th9 cell differentiation. TGF-β, IL-4, TL1A, OX40, IL-2, TCR, and other stimuli induce the expression of downstream transcription factors, including SMAD2/SMAD3/SMAD4, HIF-1α, E2A, PU.1, FOXP3, GATA3, BATF, BATF3, IRF4, NF-κB, BCL6, STAT5, and FOXO1. These transcription factors interact with the IL-9 promoter, while GCN5 and P300 enhance histone modifications, synergistically promoting IL-9 expression and secretion.
2 Discovery and establishment of Th9 cells
After activation, naïve CD4+ T cells differentiate into distinct Th cell subsets. This process is driven by TCR signals and cytokines, which activate lineage-defining transcription factors. These transcription factors then determine the cytokine secretion and immune functions of each subset. Th2 cell differentiation is primarily driven by the IL-4/STAT6 signaling pathway and regulated by the transcription factor GATA3 (39–41). IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 secreted by Th2 cells mediate IgE production and eosinophil recruitment, and are crucial in allergic reactions and anti-helminth immunity (42, 43).
Th17 cell differentiation depends on the TGF-β/IL-6 signaling pathway and is regulated by the transcription factor RORγt (44, 45). Th17 cells secrete IL-17 and IL-22, which play a role in defending against extracellular bacterial and fungal infections (46, 47). Regulatory T cells (Tregs) differentiate in response to TGF-β and IL-2 and are regulated by the transcription factor Foxp3 (48, 49). Treg cells maintain immune tolerance and regulate immune response intensity by secreting TGF-β and IL-10 (50–52).
Th9 cells are a subpopulation of CD4+ helper T cells that secrete IL-9. Although early studies initially categorized Th9 cells as a subset of Th2 cells due to their shared IL-9 production capacity, a 2008 study by Veldhoen et al. found that TGF-β induced the transformation of Th2 cells into IL-9-producing helper T cells, which did not express transcription factors characteristic of Th1 (T-bet), Th17 (RORγt), or regulatory T cells (FOXP3) (6). In the same year, Dardalhon et al. showed that TGF-β and IL-4 work together to decrease Foxp3 expression and differentiate naïve CD4+ T cells into a distinct subset of T cells that secreted IL-10 and IL-9 (7). Phenotypically, Th9 cells express CD183 (CXCR3), CD193 (CCR3), and CD196 (CCR6), but lack the Th2-characteristic markers CD194 (CCR4) or CD294 (CRTH2) (53, 54). As well as demonstrating that Th9 cells are a distinct subgroup (55–57), these studies also highlighted the crucial regulatory role that synergistic TGF-β and IL-4 signaling play in Th9 cell differentiation. Subsequent studies have further shown that this synergistic action collectively shapes the functional diversity of Th9 cells through multilayered mechanisms, including exogenous signaling, endogenous transcription factor networks, epigenetic modifications, and metabolic regulation.
3 Regulation of antigen recognition signaling
Th9 cell differentiation and IL-9 secretion are significantly regulated by activation of TCR and its co-stimulatory signals. Following TCR activation, nuclear factor of activated T cells 1(NFAT1) attracts the histone acetyltransferases CBP/P300, thereby enhancing chromatin accessibility and facilitating the recruitment of NF-κB to the IL-9 promoter to induce transcription (8). In addition, TCR promotes Th9 differentiation by upregulating the expression of interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) (18, 58). Similarly, the TNF family protein TL1A binds to Death Receptor 3 (DR3) to activate the IL-2/STAT5 signaling pathway and increase production of TGF-β, IL-4, and PU.1, which collectively induce Th9 differentiation (8, 9). Recent studies have revealed that activation of TNF receptor superfamily member 4 (OX40) promotes the differentiation of CD4+ T cells toward Th9 cells by inhibiting the differentiation of both induced regulatory T cells (iTregs) and Th17 cells (10, 59). Mechanistically, OX40 has been shown to induce Th9 cells through activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway via TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) (10).
4 Exogenous signal regulation
Th9 cell differentiation is precisely regulated by a range of exogenous signals, with TGF-β and IL-4 acting as the primary initiation signals. TGF-β and IL-4 work together with T cell receptors (TCRs), IL-2, and Toll-like receptors (TLRs) to drive Th9 differentiation. In addition, several regulatory pathways have been shown to operate independently of TGF-β and IL-4, highlighting the complexity and diversity of the Th9 differentiation network.
4.1 TGF-β and IL-4 signaling
As a crucial component of the transforming growth factor-β superfamily, the TGF-β controls Th9 cell development via dual mechanisms that are SMAD-dependent and SMAD-independent (6, 60, 61). In the SMAD-dependent pathway, TGF-β binds to its receptors to promote a SMAD2/3/4 heterotrimeric complex, which translocates to the nucleus, where it binds to transcription factors, thereby controlling the expression of target genes and subsequently promoting Th9 development (62). SMAD7 inhibits this process by preventing the SMAD complex from binding to DNA (63). In the non-SMAD pathway, TGF-β and IL-4 synergistically activate TAK1, downregulate ID3 expression, promote the binding of E2A/GATA binding protein 3 (GATA3) to the IL-9 promoter, and increase the transcriptional activity of IL-9 (5). Furthermore, suppression of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) deacetylase expression by TAK1 leads to increased IL-9 secretion and glycolytic activity, whereas overexpression of exogenous SIRT1 has the opposite effect (64).
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) and GATA3 are key regulators of Th9 cell differentiation (6, 7, 65). IL-4 induces GATA3 expression by activating STAT6 phosphorylation and driving Th2 cell differentiation (6). However, when IL-4 cooperates with TGF-β, it suppresses TGF-β-induced generation of Foxp3+, Tregs through the IL-4-STAT6-GATA3 axis while simultaneously downregulating the production of Th2-type cytokines (e.g., IL-4, IL-5, IL-13). This process consequently induces the generation of IL-9-secreting Foxp3- effector T cells, ultimately promoting Th9 cell differentiation (6). Paradoxically, IL-4 negatively regulates Th9 differentiation under specific conditions.IL-4-induced cytokine-inducible SH2-containing protein (CIS) suppresses activation of STAT3, STAT5, and STAT6, thereby inhibiting Th9 cell differentiation. Consequently, deficiency of CIS in T cells significantly enhances both Th2 and Th9 cell differentiation. This indicates that IL-4 inhibits Th9 differentiation by inducing CIS (66).
4.2 Cytokines
Cytokines play pivotal roles in Th9 cell differentiation through complex and diverse regulatory mechanisms, exhibiting both promoting and inhibitory effects. Among cytokines that enhance Th9 differentiation, IL-2 serves as a critical regulator. IL-2 controls Th9 differentiation and IL-9 secretion through two distinct mechanisms, which involve either the activation of STAT5 or the inhibition of B-cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6). IL-2-mediated phosphorylation of STAT5 results in the direct binding of STAT5 to the IL-9 promoter and subsequent IL-9 transcription, whereas a shortage or blockage of IL-2 inhibits IL-9 synthesis (11, 12). IL-2 can also promote Th9 differentiation by suppressing expression of the transcriptional repressor BCL6, which competes with STAT5 to bind to the IL-9 promoter (11). Jiang et al. elucidated that TNF-α comprehensively enhances Th9 cell differentiation, survival, and proliferation through the TNFR2-STAT5 and NF-κB signaling pathways (67). Furthermore, cytokines including IL-36γ from the IL-1 family (68), IL-1 (69), IL-2 (11, 70), IL-6 (71), IL-10 (7), IL-23 (72), IL-25 (73), IL-33 (74), IFNα/β (75), and TSLP (76, 77) contribute to Th9 cell induction. However, their precise molecular mechanisms require further elucidation. Conversely, certain cytokines suppress Th9 cell differentiation. Murugaiyan et al. have demonstrated that IFN-γ directly inhibits Th9 cell differentiation through STAT1-mediated signaling; moreover, it has induced dendritic cells to produce IL-27, which has partially suppressed Th9 cell development through STAT1 and T-bet (78).
4.3 TLRs
As receptors that recognize innate immunological patterns, Toll-like receptors (TLRs) control T cell growth and have a direct impact on Th9 differentiation (79). Studies have shown that in the presence of TGF-β and IL-4, the activation of TLR2 promotes Th9 cell differentiation by upregulating the transcription factors BATF and PU.1 (14). Moreover, a negative correlation between the activity of TLR2 and serum vitamin D levels has been observed, suggesting that vitamin D may negatively regulate Th9 differentiation by inhibiting the TLR2 pathway (34).
4.4 Regulatory mechanisms independent of TGF-β and IL-4
Although some interleukins, such as IL-35 and IL-1β, can functionally replace TGF-β under certain circumstances, they still need to work in concert with IL-4 to induce Th9 differentiation. For example, IL-35 has been shown to promote Th9 differentiation through activation of IRF4 via the IL-12Rβ2/GP130 receptor. However, the lack of synergistic effects between TGF-β1 and IL-35 at optimal doses indicates that they probably share partial downstream signaling pathways. In the presence of IL-4, IL-35 can replace TGF-β1 to induce the differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into Th9 cells, although the underlying mechanisms remain unclear and require further elucidation (15). Other studies have shown that when combined with IL-4, IL-1β can act through the IL-1R signaling pathway to replace TGF-β and promote Th9 differentiation (13). Initiating synergistic effects requires the presence of TGF-β or its alternative components, whereas IL-4 plays a crucial role in Th9 differentiation. Surprisingly, TGF-β and IL-4 are not required for IL-33 to promote Th9 differentiation. For example, dectin-1 signaling in dendritic cells has been shown to promote the production of IL-33, which then acts through its suppression of tumorigenicity 2 (ST2) receptor to induce differentiation of CD4+ T cells into Th9 cells, which produce IL-9 (80).
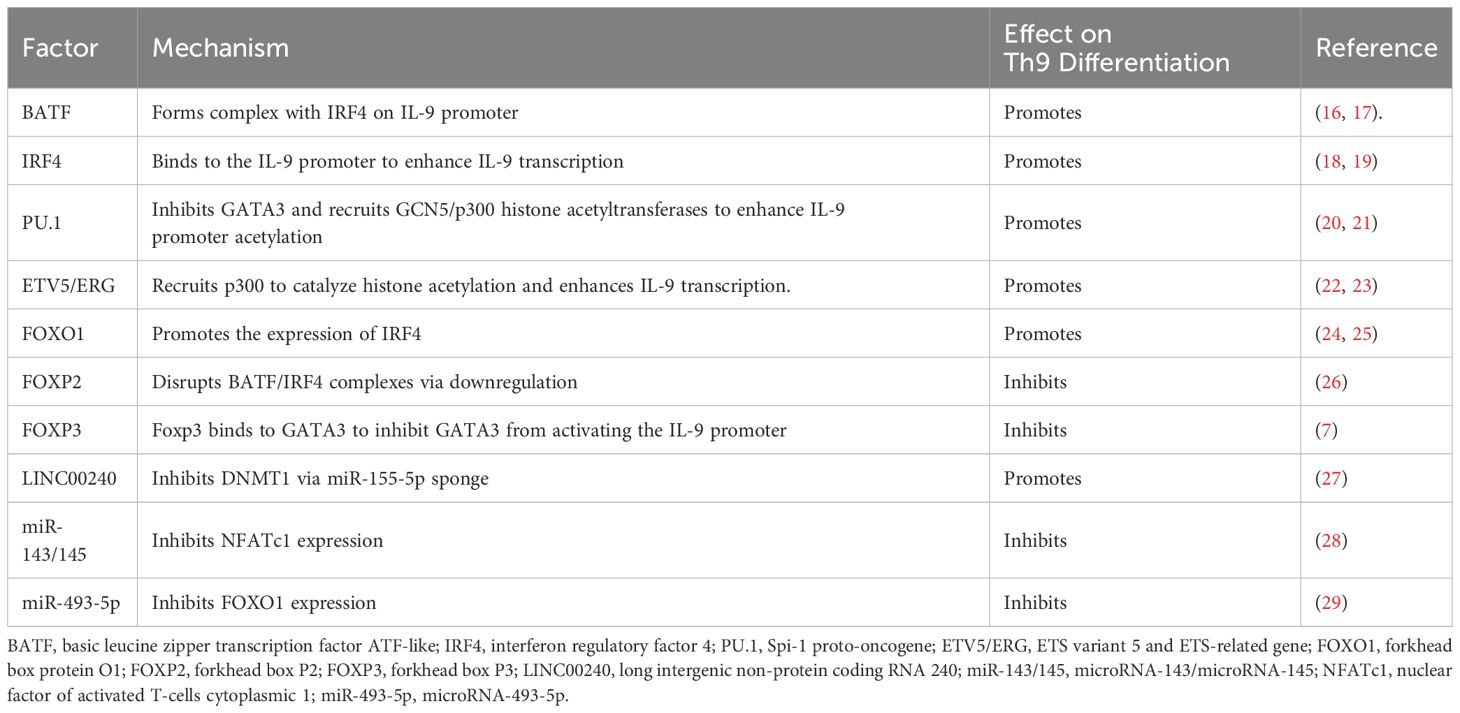
5 Endogenous regulation
The fate of Th9 cells depends not only on exogenous signals but also on endogenous regulatory networks. The endogenous regulatory network of Th9 cell development is provided by the synergistic signals of TGF-β and IL-4, which regulate key transcription factors like PU.1, IRF4, and BATF, leading to epigenetic changes like histone acetylation. Several levels of molecular regulation mediate this process to guarantee accurate Th9 cell differentiation.
5.1 Transcription factor BATF
BAFT, a key transcription factor for Th9 development, binds to the IL-9 promoter and controls its production by forming a complex with IRF4 downstream of the TGF-β/IL-4 signaling pathway. While co-expression of BAFT with IRF4 synergistically increases IL-9 production, BATF deficiency dramatically decreases IL-9 production (16). TL1A stimulation has been shown to upregulate Basic leucine zipper ATF-like transcription factor 3 (BATF3), a homolog of BATF, which combines with BATF and IRF4 to form a complex that enhances IL-9 promoter binding and dramatically increases IL-9 secretion (17).
5.2 Transcription factor IRF4
IRF4, a transcription factor that is essential for Th9 differentiation, drives transcription by binding directly to the IL-9 promoter. IRF4-depleted CD4+ T cells are unable to differentiate into Th9 cells, highlighting the importance of IRF4 in this process (18). Meanwhile, TGF-β and IL-4 have been shown to promote the conversion of Th2 to Th9 cells through the SMAD3/SMAD4 signaling pathway and induction of IRF4 expression (19). Interferon Regulatory Factor 8 (IRF8) and IRF4 exhibit structural similarities, and have been shown to work together with BATF and PU.1 to form a transcriptional complex that binds to the IL-9 promoter to increase IL-9 expression (81).
5.3 ETS transcription factor family
PU.1 is a fundamental member of the ETS transcription factor family and the first transcription factor to be found to play an essential role in the specific production of IL-9 in Th9 cells. Studies indicate that PU.1-deficient mice exhibit reduced IL-9 expression. Conversely, PU.1 confers upon Th9 cells the capacity for robust IL-9 production (20). PU.1 suppresses Th2-specific gene expression downstream of TGF-β and IL-4 signaling through inhibition of GATA3 (20). Furthermore, PU.1 has been shown to form a complex with the histone acetyltransferase General Control Non-derepressible 5 (GCN5), which increases histone H3/H4 acetylation levels in the IL-9 promoter region, thereby markedly increasing transcriptional activity and chromatin accessibility (21, 82). Another member of the ETS family, ETS variant transcription factor 5 (ETV5), promotes histone H3K27 and H4K16 acetylation by recruiting the histone acetyltransferase P300, thereby enhancing IL-9 transcription (22). ERG has also been shown to combine with PU.1 and ETV5 to produce a complex that increases the transcriptional activity and binding effectiveness of the IL-9 promoter (23).
5.4 FOX family of transcription factors
Members of the FOX family are involved in regulating the differentiation of Th9 cells. One member, Forkhead box O1 (FOXO1), is a key positive regulatory factor that binds directly to the IL-9 promoter to boost its transcription. FOXO1 has also been shown to promote IRF4 expression, which greatly increases the efficiency of Th9 differentiation (24, 25). In contrast, Forkhead box P1 (FOXP1) has been identified as a negative regulator of Th9 differentiation since it inhibits IL-9 production and prevents Th9 differentiation. In a recent study, IL-7 signaling was found to induce FOXO1 to displace FOXP1 in the nucleus and promote IL-9 production (83). Forkhead box O4 (FOXO4), another member of the FOX family, has also been shown to promote Th9 differentiation (83). Conversely, Th9 differentiation is suppressed by Forkhead box P2 (FOXP2) and Forkhead box P3 (FOXP3). FOXP2 has been shown to adversely affect Th9 differentiation by downregulating the expression of BATF and IRF4 and subsequently destabilizing the core transcriptional complex necessary for Th9 development (26). Th9 differentiation is further negatively regulated by the binding of FOXP3 to GATA3, which inhibits the transcription of Th9-associated genes (7).
5.5 Epigenetic regulation
Covalent histone modifications and DNA methylation are two of the many ways that epigenetic regulation affects Th9 cell development. At the level of histone modifications, Chromobox protein homolog 4 (Cbx4) increases the transcriptional activity of the Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) protein, stabilizing it through SUMOylation, and thus promoting IL-9 expression (84). IL-7 induces the histone acetyltransferase p300 through the STAT5-PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway, thereby promoting histone acetylation at the IL-9 promoter region and activating transcription (83). By sponging miR-155-5p, the long non-coding RNA LINC00240 has been shown to control DNMT1-mediated PU.1 promoter methylation at the DNA methylation level. While high expression of LINC00240 inhibits this process, low expression alleviates PU.1 inhibition and promotes Th9 differentiation by lowering methylation levels (27).
5.6 Non-coding RNA
The lncRNA HOTAIRM1 has been shown to promote Th9 differentiation by competitively binding to miR-148a-3p and reducing its transcriptional repression on IRF4 (85). In contrast, miR-143/145 expression levels are significantly inversely correlated with Th9 differentiation, with miR-143/145 reducing the IL-9 transcriptional pathway by targeting and suppressing Nuclear factor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic 1 (NFATc1) expression (28). Finally, the tumor suppressor gene miR493-5p inhibits Th9 cell development by inhibiting the expression of FOXO1 (29).
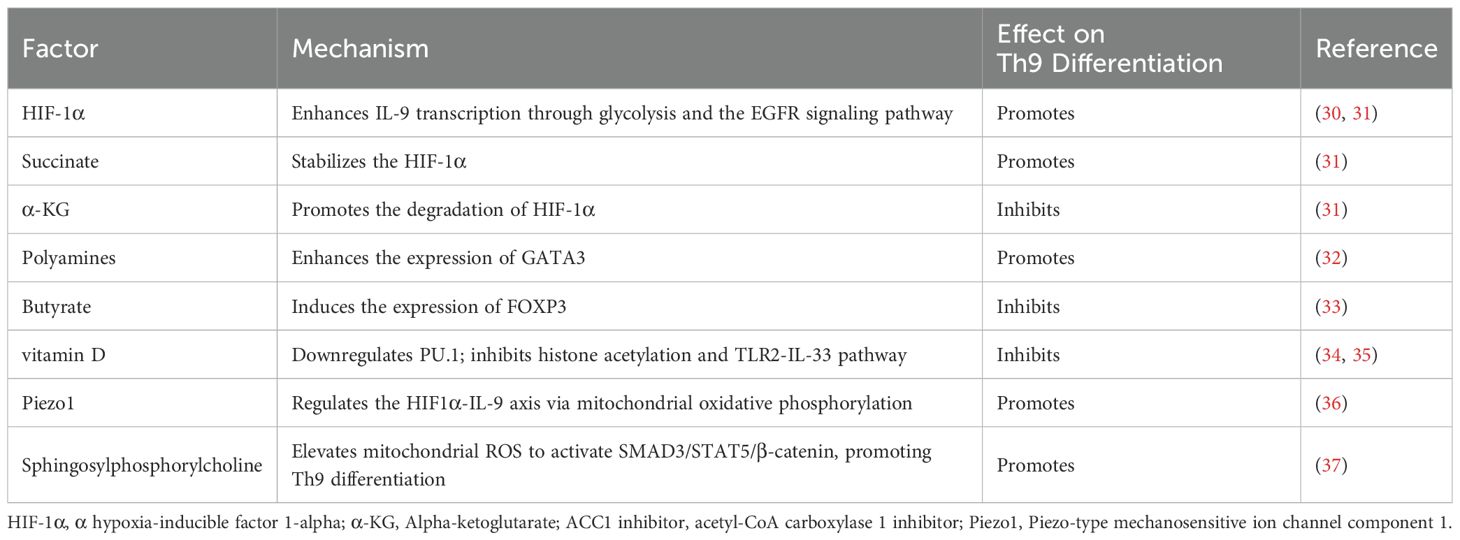
6 Metabolic regulatory network
Recent studies have elucidated the pivotal roles of metabolites in Th9 cell differentiation. Metabolic pathways not only supply energy and biosynthetic intermediates for cells but also influence the differentiation fate of Th9 cells by modulating key signaling pathways and transcription factors.
6.1 Metabolic reprogramming
Distinct metabolic characteristics are closely associated with Th9 differentiation. Extracellular ATP provides energy support for Th9 development by activating the purinergic receptor mTOR-HIF-1α signaling axis, which in turn induces the generation of NO (30). Furthermore, interactions between amphiregulin and the EGFR strengthen the differentiation process by increasing the ability of HIF-1α to bind to the IL-9 promoter (31). Notably, when compared to other Th subsets, Th9 cells show significantly more glycolytic dependence. In addition to reducing glycolytic capacity, HIF-1α deficiency also interferes with the tricarboxylic acid cycle, pentose phosphate pathway, and fatty acid metabolic network (30). Dysregulation of these metabolic pathways severely disrupts the energy homeostasis of Th9 cells, leading to significant inhibition of their differentiation.
6.2 Metabolites
The metabolic microenvironment further regulates Th9 differentiation through metabolitic homeostasis. While succinate stabilizes HIF-1α through succinylation modifications to promote Th9 differentiation, α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) suppresses Th9 differentiation by promoting degradation of HIF-1α (31). Butyrate from gut bacteria and polyamines from the host have opposing effects. Butyrate reduces IL-9 synthesis by activating FOXP3 (33), whereas polyamines positively regulate IL-9 production by increasing GATA3 expression (32). The regulatory network of metabolites provides novel treatment targets for metabolically-based immunomodulatory methods by highlighting the critical role of microenvironmental metabolic homeostasis on Th9 differentiation.
6.3 Lipid metabolism and the physical microenvironment
Lipid metabolism plays a role in regulating Th9 differentiation through two independent pathways. First, Th9 differentiation and IL-9 production are markedly increased by the expression of Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1), a fatty acid synthase, and 3 - Hydroxy - 3 - methylglutaryl - CoA reductase (HMGCR), a rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis (86). Second, Th9 differentiation is negatively regulated by inhibiting ACC1-mediated fatty acid synthesis via the retinoic acid receptor-TGF-β-SMAD signaling axis. The crucial role of lipid metabolic homeostasis in Th9 differentiation is highlighted by the fact that exogenous oleic acid reverses the effects of ACC1 inhibitors or lipid uptake blockers, which markedly increase IL-9 release (87, 88). Furthermore, the mechanosensory receptor Piezo1 regulates HIF-1α signaling by modulating mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, while its functional deficiency suppresses Th9 differentiation (36). These studies reveal a novel mechanism through which the physical microenvironment governs Th9 differentiation.
6.4 Metabolic intervention molecules
Vitamin D, a crucial nutrient, inhibits Th9 differentiation by downregulating the expression of transcription factors including PU.1, IRF4, and BATF, and decreasing histone acetylation levels at the IL-9 promoter region (35). In contrast, sphingosylphosphorylcholine activates SMAD3, STAT5, and β-catenin signaling pathways by increasing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and positively regulating Th9 differentiation (37). These studies show that the metabolic network is closely associated with transcription factor activity and epigenetic modifications. However, since recent studies have focused on single metabolic pathways, future studies need to analyze the mutual effects between different metabolic axes to provide a theoretical basis for the development of precision therapies targeting metabolic pathways.
7 The application of omics technologies
The development of omics technologies has enabled further exploration of the differentiation mechanisms and functional heterogeneity of Th9 cells. Single-cell transcriptome analysis revealed functionally distinct Th9 subpopulations based on CD96 expression; the CD96low Th9 subpopulation exhibits higher IL-9 expression and greater inflammatory potential, indicating that CD96 negatively regulates Th9 cytokine production and inflammatory effects (89). An integrated analysis of epigenomics (ATAC-seq and ChIP-seq) and transcriptomics (RNA-seq) revealed that the chromatin state around the IL-9 gene locus undergoes dynamic changes during Th9 differentiation. Specifically, it opens during differentiation and closes upon return to the resting state. This process involves histone modification remodeling, and depends on the transcriptional regulation of STAT5 and STAT6. These changes contribute to the bystander activation and maintenance of lineage stability in Th9 cells (90). Retinoic acid (RA) suppresses Th9 differentiation and associated inflammation. It acts through its receptor RARα to downregulate IL-9 and related gene expression, interfere with chromatin accessibility, and disrupt transcription factor binding (91). Epigenomic DNA methylation analysis showed inconsistent changes in the methylation patterns of Th9 differentiation markers. This suggests DNA methylation may not be a primary regulator of Th9 differentiation (92). These omics studies reveal the complex regulatory network governing Th9 cell differentiation. They provide an important foundation for a deeper understanding of Th9 biology and the mechanisms of related diseases.
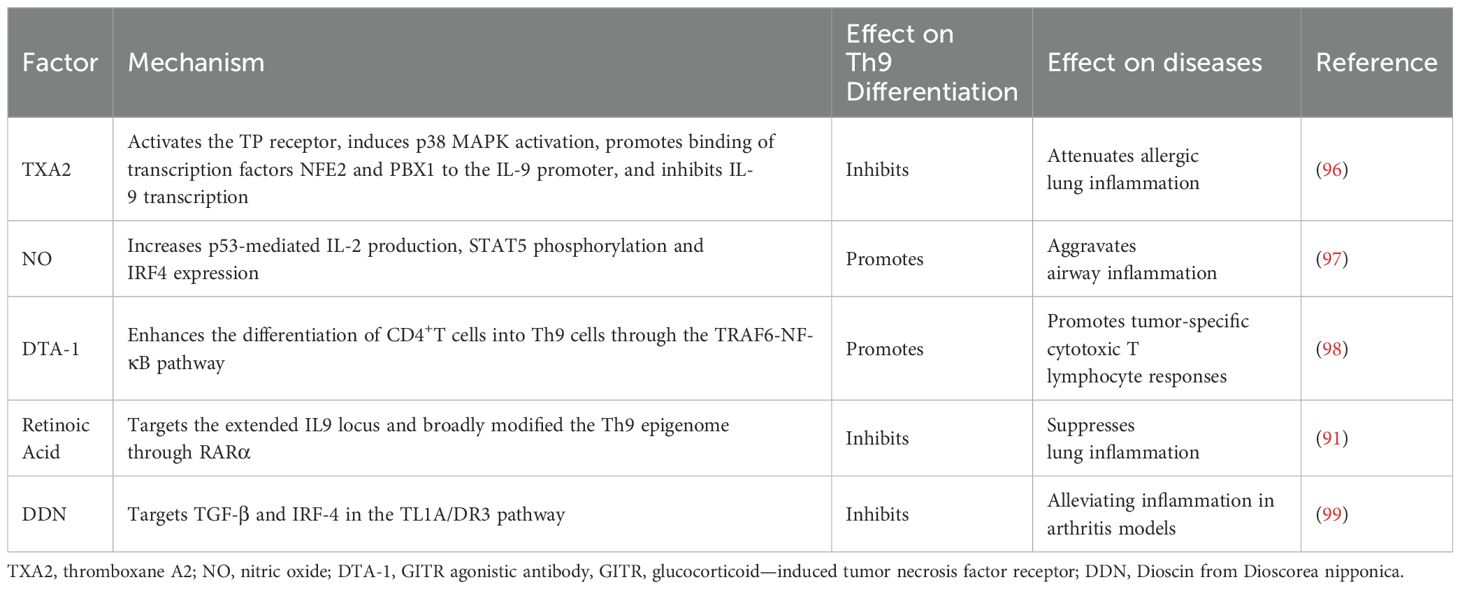
8 Therapeutic prospects of Th9 cells in diseases
Th9 cells influence the progression of various diseases. PU.1-mediated IL-9 secretion by Th9 cells disrupts the intestinal barrier, contributing to disease exacerbation in ulcerative colitis (82). Adoptive transfer of Th9 cells significantly inhibits melanoma progression. This anti-tumor effect relies on IL-9-mediated tumor cytotoxicity and activation of CD8+ T cells (93, 94).In children with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) pneumonia, miR-155 promotes Th9 cell differentiation by silencing the deacetylase Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), exacerbating pulmonary inflammation (95). Thus, Th9 cells have emerged as a potential therapeutic target for various diseases (Table 4). Studies have shown that Dioscin from Dioscorea nipponica Th9 cell differentiation by suppressing TGF-β and IRF4 in the tumor necrosis factor-like ligand 1A-death receptor 3 (TL1A-DR3) pathway, providing a new insight for the treatment of RA (99). These findings establish the therapeutic value of targeting Th9 cells and their associated signaling pathways, providing novel approaches for precision treatment of Th9-related diseases.
9 Discussion
This review synthesizes the multilayered regulatory architecture governing Th9 cell differentiation, encompassing exogenous signals, transcriptional networks, epigenetic dynamics, and metabolic reprogramming. These interconnected layers collectively determine Th9 differentiation fate through context-dependent mechanisms.
Current discoveries of molecules and pathways regulating Th9 differentiation offer foundational insights for clinical translation. For instance, vitamin D suppresses Th9 differentiation by downregulating the transcription factor PU.1. This mechanism identifies a potential therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases characterized by Th9 overactivation (35). Combining Th9 cells with anti-PD-1 therapy enhances antitumor activity through synergistic effects (100). The discovery of such therapeutic targets demonstrates the translational potential of Th9 differentiation regulatory mechanisms. Future studies should integrate single-cell sequencing and gene editing technologies to decipher the underlying mechanisms controlling Th9 differentiation, enabling effective intervention strategies for Th9-related diseases.
Current research exhibits limitations regarding the dual regulatory functions of specific molecules in Th9 differentiation. Low-concentration IL-4 promotes differentiation via STAT6 signaling, serving as an early-stage driver (65). Conversely, high-concentration IL-4 indirectly suppresses Th9 differentiation through CIS induction (66). This bidirectional regulation may be modulated by multiple variables, including microenvironmental context, cytokine concentration, and temporal dynamics. Whereas existing studies remain largely limited to single-concentration paradigms and static observations. A systematic dissection of the dose-time-pathway axis is therefore imperative. Secondly, the specific transcription factors involved in Th9 cell differentiation have not yet been identified, which poses challenges for the precise regulation of Th9 cell differentiation. Furthermore, the fate plasticity of Th9 differentiation remains unclear. When the inflammatory microenvironment changes, will Th9 cells transdifferentiate into other helper T cell subsets? Most current studies have been conducted in animal models, and the role of Th9 cells in diseases still requires further verification in human samples. Moreover, the interaction mechanisms between Th9 and other helper T cell subsets remain elusive. It is poorly defined whether Th9 cells collaborate with or compete against other helper T cells during immune responses, and how such dynamic interplays influence disease progression. Answering these questions will improve our understanding of the biological characteristics of Th9 cells and help us develop more effective therapeutic strategies.
Author contributions
XL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YL: Writing – review & editing. WW: Writing – review & editing. HH: Writing – review & editing. YH: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. CS: Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Educational Committee (No. KJ2020ZD49, 2024AH051251), Anhui Provincial Key Laboratory (Bengbu Medical University) open project (No. YZ2024D04, MBDX202408), and 512 Talent Cultivation Program of Bengbu Medical College (No. by51201103).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Kaplan MH. Th9 cells: differentiation and disease. Immunol Rev. (2013) 252:104–15. doi: 10.1111/imr.12028
2. Khokhar M, Purohit P, Gadwal A, Tomo S, Bajpai NK, and Shukla R. The differentially expressed genes responsible for the development of T helper 9 cells from T helper 2 cells in various disease states: immuno-interactomics study. JMIR Bioinform Biotechnol. (2023) 4:e42421. doi: 10.2196/42421
3. Jones CP, Gregory LG, Causton B, Campbell GA, and Lloyd CM. Activin A and tgf-β Promote T(H)9 cell-mediated pulmonary allergic pathology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2012) 129:1000–10.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.12.965
4. Ciccia F, Guggino G, Rizzo A, Manzo A, Vitolo B, La Manna MP, et al. Potential involvement of il-9 and th9 cells in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2015) 54:2264–72. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev252
5. Chen W. Tgf-β Regulation of T cells. Annu Rev Immunol. (2023) 41:483–512. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-101921-045939
6. Veldhoen M, Uyttenhove C, van Snick J, Helmby H, Westendorf A, Buer J, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta ‘Reprograms’ the differentiation of T helper 2 cells and promotes an interleukin 9-producing subset. Nat Immunol. (2008) 9:1341–6. doi: 10.1038/ni.1659
7. Dardalhon V, Awasthi A, Kwon H, Galileos G, Gao W, Sobel RA, et al. Il-4 inhibits tgf-beta-induced foxp3+ T cells and, together with tgf-beta, generates il-9+ Il-10+ Foxp3(-) effector T cells. Nat Immunol. (2008) 9:1347–55. doi: 10.1038/ni.1677
8. Meylan F and Gomez-Rodriguez J. T cell receptor and co-stimulatory signals for th9 generation. Methods Mol Biol. (2017) 1585:59–71. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6877-0_5
9. Richard AC, Tan C, Hawley ET, Gomez-Rodriguez J, Goswami R, Yang XP, et al. Correction: the tnf-family ligand tl1a and its receptor dr3 promote T cell-mediated allergic immunopathology by enhancing differentiation and pathogenicity of il-9-producing T cells. J Immunol. (2015) 195:5839–40. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502026
10. Xiao X, Balasubramanian S, Liu W, Chu X, Wang H, Taparowsky EJ, et al. Ox40 signaling favors the induction of T(H)9 cells and airway inflammation. Nat Immunol. (2012) 13:981–90. doi: 10.1038/ni.2390
11. Liao W, Spolski R, Li P, Du N, West EE, Ren M, et al. Opposing actions of il-2 and il-21 on th9 differentiation correlate with their differential regulation of bcl6 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2014) 111:3508–13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301138111
12. Canaria DA, Yan B, Clare MG, Zhang Z, Taylor GA, Boone DL, et al. Stat5 represses a stat3-independent th17-like program during th9 cell differentiation. J Immunol. (2021) 207:1265–74. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100165
13. Xue G, Jin G, Fang J, and Lu Y. Il-4 together with il-1β Induces antitumor th9 cell differentiation in the absence of tgf-β Signaling. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:1376. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09401-9
14. Karim AF, Reba SM, Li Q, Boom WH, and Rojas RE. Toll like receptor 2 engagement on cd4(+) T cells promotes th9 differentiation and function. Eur J Immunol. (2017) 47:1513–24. doi: 10.1002/eji.201646846
15. Zhang J, Lian M, Li B, Gao L, Tanaka T, You Z, et al. Interleukin-35 promotes th9 cell differentiation in igg4-related disorders: experimental data and review of the literature. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2021) 60:132–45. doi: 10.1007/s12016-020-08803-8
16. Jabeen R, Goswami R, Awe O, Kulkarni A, Nguyen ET, Attenasio A, et al. Th9 cell development requires a batf-regulated transcriptional network. J Clin Invest. (2013) 123:4641–53. doi: 10.1172/jci69489
17. Tsuda M, Hamade H, Thomas LS, Salumbides BC, Potdar AA, Wong MH, et al. A role for batf3 in T(H)9 differentiation and T-cell-driven mucosal pathologies. Mucosal Immunol. (2019) 12:644–55. doi: 10.1038/s41385-018-0122-4
18. Staudt V, Bothur E, Klein M, Lingnau K, Reuter S, Grebe N, et al. Interferon-regulatory factor 4 is essential for the developmental program of T helper 9 cells. Immunity. (2010) 33:192–202. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.07.014
19. Abdelaziz MH, Wang H, Cheng J, and Xu H. Th2 cells as an intermediate for the differentiation of naïve T cells into th9 cells, associated with the smad3/smad4 and irf4 pathway. Exp Ther Med. (2020) 19:1947–54. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8420
20. Chang HC, Sehra S, Goswami R, Yao W, Yu Q, Stritesky GL, et al. The transcription factor pu.1 is required for the development of il-9-producing T cells and allergic inflammation. Nat Immunol. (2010) 11:527–34. doi: 10.1038/ni.1867
21. Goswami R and Kaplan MH. Gcn5 is required for pu.1-dependent il-9 induction in th9 cells. J Immunol. (2012) 189:3026–33. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201496
22. Koh B, Hufford MM, Pham D, Olson MR, Wu T, Jabeen R, et al. The ets family transcription factors etv5 and pu.1 function in parallel to promote th9 cell development. J Immunol. (2016) 197:2465–72. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502383
23. Kharwadkar R, Ulrich BJ, Chu M, Koh B, Hufford MM, Fu Y, et al. Erg functionally overlaps with other ets proteins in promoting th9 cell expression of il9 during allergic lung inflammation. J Immunol. (2023) 210:537–46. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200113
24. Buttrick TS, Wang W, Yung C, Trieu KG, Patel K, Khoury SJ, et al. Foxo1 promotes th9 cell differentiation and airway allergy. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:818. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19315-z
25. Malik S, Sadhu S, Elesela S, Pandey RP, Chawla AS, Sharma D, et al. Transcription factor foxo1 is essential for il-9 induction in T helper cells. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:815. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00674-6
26. Zhang X, Ma Y, He Y, Gu W, Yan Y, Ji W, et al. Foxp2 inhibits th9 cell differentiation and attenuates allergic airway inflammation in a mouse model of ovalbumin-induced asthma. Int Immunopharmacol. (2022) 111:109060. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109060
27. Liu J, Jiang X, Liu K, Deng J, Qiu Y, Wei W, et al. Role of linc00240 on T-helper 9 differentiation in allergic rhinitis through influencing dnmt1-dependent methylation of pu.1. Immunol Res. (2024) 72:197–211. doi: 10.1007/s12026-023-09435-8
28. Qiu X, Shi Q, Huang Y, Jiang H, and Qin S. Mir-143/145 inhibits th9 cell differentiation by targeting nfatc1. Mol Immunol. (2021) 132:184–91. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.01.001
29. Rao X, Dong H, Zhang W, Sun H, Gu W, Zhang X, et al. Mir-493-5p inhibits th9 cell differentiation in allergic asthma by targeting foxo1. Respir Res. (2022) 23:286. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02207-2
30. Roy S and Awasthi A. Atp triggers human th9 cell differentiation via nitric oxide-mediated mtor-hif1α Pathway. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1120. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01120
31. Roy S, Rizvi ZA, Clarke AJ, Macdonald F, Pandey A, Zaiss DMW, et al. Egfr-hif1α Signaling positively regulates the differentiation of il-9 producing T helper cells. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:3182. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23042-x
32. Nakamura A, Takahashi D, Nakamura Y, Yamada T, Matsumoto M, and Hase K. Polyamines polarized th2/th9 cell-fate decision by regulating gata3 expression. Arch Biochem Biophys. (2020) 693:108587. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108587
33. Vieira RS, Castoldi A, Basso PJ, Hiyane MI, Câmara NOS, and Almeida RR. Butyrate attenuates lung inflammation by negatively modulating th9 cells. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:67. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00067
34. Vyas SP, Srivastava RN, and Goswami R. Calcitriol attenuates tlr2/il-33 signaling pathway to repress th9 cell differentiation and potentially limits the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Cell Biochem. (2021) 476:369–84. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03914-4
35. Vyas SP, Hansda AK, Kaplan MH, and Goswami R. Calcitriol regulates the differentiation of il-9-secreting th9 cells by modulating the transcription factor pu.1. J Immunol. (2020) 204:1201–13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901205
36. Yang Q, Cao Y, Wang L, Dong Y, Zhao L, Geng Z, et al. Mechanical force receptor piezo1 regulates T(H)9 cell differentiation. Cell Rep. (2025) 44:115136. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.115136
37. Kim JC, Hu W, Lee M, Bae GH, Park JY, Lee SY, et al. Sphingosylphosphorylcholine promotes th9 cell differentiation through regulation of smad3, stat5, and β-catenin pathways. Immune Netw. (2024) 24:e45. doi: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e45
38. Schmitt E, Germann T, Goedert S, Hoehn P, Huels C, Koelsch S, et al. Il-9 production of naive cd4+ T cells depends on il-2, is synergistically enhanced by a combination of tgf-beta and il-4, and is inhibited by ifn-gamma. J Immunol. (1994) 153:3989–96. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.153.9.3989
39. Takeda K, Tanaka T, Shi W, Matsumoto M, Minami M, Kashiwamura S, et al. Essential role of stat6 in il-4 signalling. Nature. (1996) 380:627–30. doi: 10.1038/380627a0
40. Shimoda K, van Deursen J, Sangster MY, Sarawar SR, Carson RT, Tripp RA, et al. Lack of il-4-induced th2 response and ige class switching in mice with disrupted stat6 gene. Nature. (1996) 380:630–3. doi: 10.1038/380630a0
41. Kaplan MH, Schindler U, Smiley ST, and Grusby MJ. Stat6 is required for mediating responses to il-4 and for development of th2 cells. Immunity. (1996) 4:313–9. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80439-2
42. Coffman RL, Seymour BW, Hudak S, Jackson J, and Rennick D. Antibody to interleukin-5 inhibits helminth-induced eosinophilia in mice. Science. (1989) 245:308–10. doi: 10.1126/science.2787531
43. Kopf M, Le Gros G, Bachmann M, Lamers MC, Bluethmann H, and Köhler G. Disruption of the murine il-4 gene blocks th2 cytokine responses. Nature. (1993) 362:245–8. doi: 10.1038/362245a0
44. Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ, Locksley RM, and Stockinger B. Tgfbeta in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of il-17-producing T cells. Immunity. (2006) 24:179–89. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.01.001
45. Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T, Strom TB, Oukka M, et al. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector th17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. (2006) 441:235–8. doi: 10.1038/nature04753
46. Ouyang W, Kolls JK, and Zheng Y. The biological functions of T helper 17 cell effector cytokines in inflammation. Immunity. (2008) 28:454–67. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.03.004
47. Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, and Kuchroo VK. Il-17 and th17 cells. Annu Rev Immunol. (2009) 27:485–517. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132710
48. Fontenot JD, Rasmussen JP, Gavin MA, and Rudensky AY. A function for interleukin 2 in foxp3-expressing regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. (2005) 6:1142–51. doi: 10.1038/ni1263
49. Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, and Rudensky AY. Foxp3 programs the development and function of cd4+Cd25+ Regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. (2003) 4:330–6. doi: 10.1038/ni904
50. Zhu J, Yamane H, and Paul WE. Differentiation of effector cd4 T cell populations (*). Annu Rev Immunol. (2010) 28:445–89. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-030409-101212
51. Crotty S. Follicular helper cd4 T cells (Tfh). Annu Rev Immunol. (2011) 29:621–63. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-031210-101400
52. Bilate AM and Lafaille JJ. Induced cd4+Foxp3+ Regulatory T cells in immune tolerance. Annu Rev Immunol. (2012) 30:733–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075043
53. Gloghini A and Bongarzone I. Cell-secreted signals shape lymphoma identity. Semin Cancer Biol. (2015) 34:81–91. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.02.001
54. Keating P, Munim A, and Hartmann JX. Effect of vitamin D on T-helper type 9 polarized human memory cells in chronic persistent asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. (2014) 112:154–62. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2013.11.015
55. Raphael I, Nalawade S, Eagar TN, and Forsthuber TG. T cell subsets and their signature cytokines in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine. (2015) 74:5–17. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2014.09.011
56. Genain CP, Abel K, Belmar N, Villinger F, Rosenberg DP, Linington C, et al. Late complications of immune deviation therapy in a nonhuman primate. Science. (1996) 274:2054–7. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5295.2054
57. Zielinski CE, Corti D, Mele F, Pinto D, Lanzavecchia A, and Sallusto F. Dissecting the human immunologic memory for pathogens. Immunol Rev. (2011) 240:40–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2010.01000.x
58. Jash A, Sahoo A, Kim GC, Chae CS, Hwang JS, Kim JE, et al. Nuclear factor of activated T cells 1 (Nfat1)-induced permissive chromatin modification facilitates nuclear factor-κb (Nf-κb)-mediated interleukin-9 (Il-9) transactivation. J Biol Chem. (2012) 287:15445–57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.340356
59. Kaplan MH, Hufford MM, and Olson MR. The development and in vivo function of T helper 9 cells. Nat Rev Immunol. (2015) 15:295–307. doi: 10.1038/nri3824
60. Liu G, Qian L, Xu T, Yu J, Li M, and Cui Y. Changes in the th9 cell population and related cytokines in the peripheral blood of infants with recurrent wheezing. Cent Eur J Immunol. (2020) 45:60–8. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2020.94683
61. Do-Thi VA, Lee JO, Lee H, and Kim YS. Crosstalk between the producers and immune targets of il-9. Immune Netw. (2020) 20:e45. doi: 10.4110/in.2020.20.e45
62. Batlle E and Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-β Signaling in immunity and cancer. Immunity. (2019) 50:924–40. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.024
63. Laudisi F, Stolfi C, Monteleone I, and Monteleone G. Tgf-β1 signaling and smad7 control T-cell responses in health and immune-mediated disorders. Eur J Immunol. (2023) 53:e2350460. doi: 10.1002/eji.202350460
64. Wang Y, Bi Y, Chen X, Li C, Li Y, Zhang Z, et al. Histone deacetylase sirt1 negatively regulates the differentiation of interleukin-9-producing cd4(+) T cells. Immunity. (2016) 44:1337–49. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.05.009
65. Goswami R, Jabeen R, Yagi R, Pham D, Zhu J, Goenka S, et al. Stat6-dependent regulation of th9 development. J Immunol. (2012) 188:968–75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102840
66. Yang XO, Zhang H, Kim BS, Niu X, Peng J, Chen Y, et al. The signaling suppressor cis controls proallergic T cell development and allergic airway inflammation. Nat Immunol. (2013) 14:732–40. doi: 10.1038/ni.2633
67. Anuradha R, Munisankar S, Bhootra Y, Jagannathan J, Dolla C, Kumaran P, et al. Il-10- and tgfβ-mediated th9 responses in a human helminth infection. PloS Negl Trop Dis. (2016) 10:e0004317. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004317
68. Vyas SP and Goswami R. A decade of th9 cells: role of th9 cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1139. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01139
69. Anuradha R, George PJ, Hanna LE, Chandrasekaran V, Kumaran P, Nutman TB, et al. Il-4-, tgf-β-, and il-1-dependent expansion of parasite antigen-specific th9 cells is associated with clinical pathology in human lymphatic filariasis. J Immunol. (2013) 191:2466–73. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300911
70. Gomez-Rodriguez J, Meylan F, Handon R, Hayes ET, Anderson SM, Kirby MR, et al. Itk is required for th9 differentiation via tcr-mediated induction of il-2 and irf4. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:10857. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10857
71. Schütze N, Trojandt S, Kuhn S, Tomm JM, von Bergen M, Simon JC, et al. Allergen-induced il-6 regulates il-9/il-17a balance in cd4+ T cells in allergic airway inflammation. J Immunol. (2016) 197:2653–64. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501599
72. Beriou G, Bradshaw EM, Lozano E, Costantino CM, Hastings WD, Orban T, et al. Tgf-beta induces il-9 production from human th17 cells. J Immunol. (2010) 185:46–54. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000356
73. Angkasekwinai P, Sodthawon W, Jeerawattanawart S, Hansakon A, Pattanapanyasat K, and Wang YH. Ilc2s activated by il-25 promote antigen-specific th2 and th9 functions that contribute to the control of trichinella spiralis infection. PloS One. (2017) 12:e0184684. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184684
74. Verma M, Liu S, Michalec L, Sripada A, Gorska MM, and Alam R. Experimental asthma persists in il-33 receptor knockout mice because of the emergence of thymic stromal lymphopoietin-driven il-9(+) and il-13(+) type 2 innate lymphoid cell subpopulations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2018) 142:793–803.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.10.020
75. Pritchard AL, Carroll ML, Burel JG, White OJ, Phipps S, and Upham JW. Innate ifns and plasmacytoid dendritic cells constrain th2 cytokine responses to rhinovirus: A regulatory mechanism with relevance to asthma. J Immunol. (2012) 188:5898–905. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103507
76. Siracusa MC, Saenz SA, Hill DA, Kim BS, Headley MB, Doering TA, et al. Tslp promotes interleukin-3-independent basophil haematopoiesis and type 2 inflammation. Nature. (2011) 477:229–33. doi: 10.1038/nature10329
77. Yao W, Zhang Y, Jabeen R, Nguyen ET, Wilkes DS, Tepper RS, et al. Interleukin-9 is required for allergic airway inflammation mediated by the cytokine tslp. Immunity. (2013) 38:360–72. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.01.007
78. Murugaiyan G, Beynon V, Pires Da Cunha A, Joller N, and Weiner HL. Ifn-Γ Limits th9-mediated autoimmune inflammation through dendritic cell modulation of il-27. J Immunol. (2012) 189:5277–83. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200808
79. Janeway CA Jr. and Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. (2002) 20:197–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.20.083001.084359
80. Oh S, Li K, Prince A, Wheeler ML, Hamade H, Nguyen C, et al. Pathogen size alters C-type lectin receptor signaling in dendritic cells to influence cd4 th9 cell differentiation. Cell Rep. (2022) 38:110567. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110567
81. Humblin E, Thibaudin M, Chalmin F, Derangère V, Limagne E, Richard C, et al. Irf8-dependent molecular complexes control the th9 transcriptional program. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:2085. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01070-w
82. Gerlach K, Hwang Y, Nikolaev A, Atreya R, Dornhoff H, Steiner S, et al. Th9 cells that express the transcription factor pu.1 drive T cell-mediated colitis via il-9 receptor signaling in intestinal epithelial cells. Nat Immunol. (2014) 15:676–86. doi: 10.1038/ni.2920
83. Bi E, Ma X, Lu Y, Yang M, Wang Q, Xue G, et al. Foxo1 and foxp1 play opposing roles in regulating the differentiation and antitumor activity of T(H)9 cells programmed by il-7. Sci Signal. (2017) 10:6–8. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aak9741
84. Huang W, Yu C, Wu H, Liang S, Kang J, Zhou Z, et al. Cbx4 governs hif-1α to involve in th9 cell differentiation promoting asthma by its sumo E3 ligase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. (2023) 1870:119524. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2023.119524
85. Li L, Deng J, Huang T, Liu K, Jiang X, Chen X, et al. Irf4 transcriptionally activate hotairm1, which in turn regulates irf4 expression, thereby affecting th9 cell differentiation and involved in allergic rhinitis. Gene. (2022) 813:146118. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2021.146118
86. Reilly NA, Sonnet F, Dekkers KF, Kwekkeboom JC, Sinke L, Hilt S, et al. Oleic acid triggers metabolic rewiring of T cells poising them for T helper 9 differentiation. iScience. (2024) 27:109496. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109496
87. Peesari S and McAleer JP. Regulation of human th9 cell differentiation by lipid modulators targeting ppar-Γ and acetyl-coa-carboxylase 1. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1509408. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1509408
88. Nakajima T, Kanno T, Ueda Y, Miyako K, Endo T, Yoshida S, et al. Fatty acid metabolism constrains th9 cell differentiation and antitumor immunity via the modulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling. Cell Mol Immunol. (2024) 21:1266–81. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01209-y
89. Stanko K, Iwert C, Appelt C, Vogt K, Schumann J, Strunk FJ, et al. Cd96 expression determines the inflammatory potential of il-9-producing th9 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2018) 115:E2940–e9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1708329115
90. Son A, Meylan F, Gomez-Rodriguez J, Kaul Z, Sylvester M, Falduto GH, et al. Dynamic chromatin accessibility licenses stat5- and stat6-dependent innate-like function of T(H)9 cells to promote allergic inflammation. Nat Immunol. (2023) 24:1036–48. doi: 10.1038/s41590-023-01501-5
91. Schwartz DM, Farley TK, Richoz N, Yao C, Shih HY, Petermann F, et al. Retinoic acid receptor alpha represses a th9 transcriptional and epigenomic program to reduce allergic pathology. Immunity. (2019) 50:106–20.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.12.014
92. Shao MM, Chen QY, Zhang X, Dong SF, Wei RQ, Shi HZ, et al. Dynamic alterations in DNA methylation of cd4(+) T cells and macrophages in a murine model of tuberculous pleural infection induced by bcg vaccination. MedComm (2020). (2025) 6:e70166. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70166
93. Purwar R, Schlapbach C, Xiao S, Kang HS, Elyaman W, Jiang X, et al. Robust tumor immunity to melanoma mediated by interleukin-9-producing T cells. Nat Med. (2012) 18:1248–53. doi: 10.1038/nm.2856
94. Lu Y, Hong S, Li H, Park J, Hong B, Wang L, et al. Th9 cells promote antitumor immune responses in vivo. J Clin Invest. (2012) 122:4160–71. doi: 10.1172/jci65459
95. Tian K and Xu W. Mir-155 regulates th9 differentiation in children with methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus pneumonia by targeting sirt1. Hum Immunol. (2021) 82:775–81. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2021.07.002
96. Li H, Bradbury JA, Edin ML, Gruzdev A, Li H, Graves JP, et al. Txa2 attenuates allergic lung inflammation through regulation of th2, th9, and treg differentiation. J Clin Invest. (2024) 134:5–6, 10–12. doi: 10.1172/jci165689
97. Niedbala W, Besnard AG, Nascimento DC, Donate PB, Sonego F, Yip E, et al. Nitric oxide enhances th9 cell differentiation and airway inflammation. Nat Commun. (2014) 5:4575. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5575
98. Kim IK, Kim BS, Koh CH, Seok JW, Park JS, Shin KS, et al. Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein co-stimulation facilitates tumor regression by inducing il-9-producing helper T cells. Nat Med. (2015) 21:1010–7. doi: 10.1038/nm.3922
99. Gao Y, Xia D, You Y, Cheng Y, Bai B, Feng G, et al. Effects of dioscin from dioscorea nipponica on tl1a/dr3 and th9 cells in a collagen-induced arthritis mouse model. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 147:114028. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114028
Keywords: Th9 cells, IL-9, differentiation regulation, TGF-β, IL-4, epigenetic regulation, metabolic reprogramming
Citation: Liu X, Li Y, Wu W, Huang H, Hao Y and Song C (2025) Regulatory mechanisms of Th9 cell differentiation. Front. Immunol. 16:1650972. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1650972
Received: 20 June 2025; Accepted: 22 August 2025;
Published: 05 September 2025.
Edited by:
Mehdi Benamar, Boston Children’s Hospital, United StatesReviewed by:
Fatma Betul Oktelik, Istanbul University, TürkiyeNidhi Jadon, University of Massachusetts Amherst, United States
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Li, Wu, Huang, Hao and Song. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanmei Hao, MTAzNjgzNTMyMkBxcS5jb20=; Chuanwang Song, YmJtdTEyN0BvdXRsb29rLmNvbQ==
 Xingyue Liu
Xingyue Liu Ya Li
Ya Li Wenwen Wu
Wenwen Wu Han Huang1
Han Huang1