- 1Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Tongji Shanxi Hospital, Taiyuan, China
- 2Institute of Medical Technology Research, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China
With the rapid advancement of nanotechnology, the application of nanomedicine has become increasingly widespread, demonstrating remarkable potential for highly precise targeting and efficacious drug delivery. Compared to conventional drug delivery approaches, nanomedicine effectively addresses issues such as nonspecific drug distribution and severe adverse effects, significantly enhancing therapeutic efficacy through its targeted delivery mechanisms. As an innovative drug delivery vehicle, liposomes exhibit tremendous application potential owing to their outstanding biocompatibility, extensive applicability, remarkable ability to improve drug stability and bioavailability, precise targeting capabilities, membrane structures that facilitate drug permeation, and high degree of tunability. In the field of chronic disease management, liposomes serve as sophisticated vehicles for targeted and controlled drug delivery, offering innovative therapeutic approaches for various chronic conditions. Macrophages, which play a pivotal role in modulating inflammatory responses and promoting tissue repair, have emerged as crucial targets for alleviating inflammatory symptoms. Nevertheless, achieving precise and efficient targeting of macrophages remains a significant challenge in current research. This article systematically reviews recent advances in liposome-based therapies for chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases (e.g., chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary fibrosis, and asthma), and metabolic disorders (e.g., diabetes), with particular emphasis on the therapeutic potential of liposomes in modulating macrophage activity. Furthermore, it summarizes and analyzes the major challenges and obstacles currently faced in liposome research, providing novel insights for future research directions and facilitating the translation of research findings into clinical applications.
1 Introduction
Chronic diseases (non-communicable diseases, NCDs) have long courses and complex causes, involving the interaction of genetic, environmental and behavioral factors. These diseases mainly include cardiovascular diseases, malignant tumors, chronic respiratory diseases (e.g., pulmonary fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and asthma), and metabolic disorders (e.g., diabetes). Accounting for approximately 80% of all NCD-related deaths, they represent the leading cause of global disability and mortality (1, 2). The World Health Organization (WHO) predicts that by 2030, the mortality rate of NCDs will account for 70% of the total global deaths (3). Moreover, the cumulative economic losses from 2011 to 2030 are expected to reach 47 trillion US dollars (the above four categories account for 64%) (4). The pathogenesis of these diseases is closely related to macrophage dysfunction: abnormally activated macrophages in cardiovascular diseases drive atherosclerosis (5); tumor-associated macrophages in malignant tumors promote cancer progression and metastasis (6); macrophages mediate chronic inflammation and fibrosis in respiratory diseases (7); and they are directly involved in insulin resistance in metabolic disorders occur (8). Therefore, targeting the regulatory mechanism of macrophages will enable the development of innovative therapeutic interventions and significantly alleviate the global health burden and socio-economic pressure.
In the occurrence and development of chronic diseases, macrophages, serving as the core effector cells of the innate immune system and the “immune sentries” of the body’s homeostasis, play a crucial triple regulatory role in inflammatory responses, pathogen clearance, and tissue repair owing to their unique polarization plasticity (9–12). They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), thereby initiating a precise dual regulatory program: (1) pro-inflammatory M1-type macrophages secrete TNF-α, IL-6 and CCL2, and generate nitric oxide (NO) via inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) to enhance pathogen clearance ability; (2) reparative M2-type macrophages highly express arginase-1 (Arg-1), cluster of differentiation 36 (CD36), and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), secrete anti-inflammatory factors such as IL-10 and TGF-β, and promote tissue remodeling and fibrosis (13–17). This dynamic balance in M1/M2 polarization states constitutes the core mechanism through which macrophages coordinate inflammation control, pathogen clearance and tissue repair.
However, in chronic pathological environments (e.g., tumor microenvironment), this balance is frequently disrupted. Notably, DAMPs exhibit complex bidirectional effects: they can not only initiate protective immune responses but may also, due to excessive accumulation, exacerbate inflammation, reshape the microenvironment, and accelerate disease progression (18) (19). In tumors, infiltrated tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) mainly present a pro-tumor M2-like phenotype and drive tumor progression by promoting angiogenesis, metastasis, immunosuppression, and matrix remodeling (20) (21). The plasticity of macrophages (including TAMs) between inflammation and repair, as well as between promoting and resisting disease, and their core regulatory roles make them highly attractive targets for therapeutic interventions through reprogramming their polarization states.
Against this backdrop, the rapid development of nanotechnology has pushed nanomaterials to the forefront of biomedicine. Among them, liposomes, as the most mature and clinically verified nanocarriers, have demonstrated unique advantages in targeted therapy. Since Bangham et al. discovered the phospholipid vesicle structure in 1965 (22), liposomes have developed into biomimetic membrane delivery systems (as evidenced by multiple U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved formulations) (23, 24). The core features include: (1) an amphiphilic phospholipid bilayer structure (25) that enables hydrophobic drug incorporation into lipid membranes while encapsulating hydrophilic drugs within aqueous cores (26), achieving flexible adaptation to dual drug-loading modalities; (2) multiple functional advantages including targeted delivery capability (through surface engineering for lesion-specific targeting) (27), excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability, low toxicity and immunogenicity, as well as prolonged drug circulation time and enhanced stability (28, 29). These characteristics establish liposomes as an ideal platform for regulating the pathological microenvironment, with demonstrated applications in the following areas: cardiovascular diseases—precisely delivering therapeutics to plaque-resident macrophages to attenuate inflammatory progression (27); oncotherapy—targeting TAMs to reprogram M2 polarization and reverse immunosuppression (30); pulmonary diseases—enhancing pulmonary tissue bioavailability through alveolar macrophage-targeted sustained drug release (31); and diabetic ulcers—modulating macrophage polarization to promote wound healing (32).
Liposome-based nanotherapeutic strategies represent an innovative intervention approach for the treatment of chronic diseases by precisely regulating the balance of macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Engineered liposomes achieve efficient delivery to pathological sites through surface-modified targeting moieties (e.g., carbohydrates, peptides, antibodies, and proteins) and accurately drive macrophage phenotype switching via loaded immunomodulators. In cancer treatment, they promote M1 polarization to enhance anti-tumor immunity; in cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, they induce M2 polarization to accelerate tissue repair; and in diabetes, they modulate the M1/M2 balance to improve insulin sensitivity and facilitate wound healing. Given the crucial role of macrophages in chronic inflammatory diseases, this review systematically analyzes the application mechanisms of liposomes in four major areas: cardiovascular diseases, malignant tumors, chronic respiratory diseases, and metabolic disorders (Figure 1). It critically discusses how liposome platforms leverage macrophage biology to achieve targeted therapeutic effects, while also outlining current challenges and future directions in the field, providing new perspectives for advancing the clinical application of liposome-based therapies in the management of chronic diseases. Although this review aims to cover major chronic diseases, the more extensive body of research in oncology is emphasized, reflecting both the historical dominance and ongoing innovation of liposome technology in the field of cancer therapy.
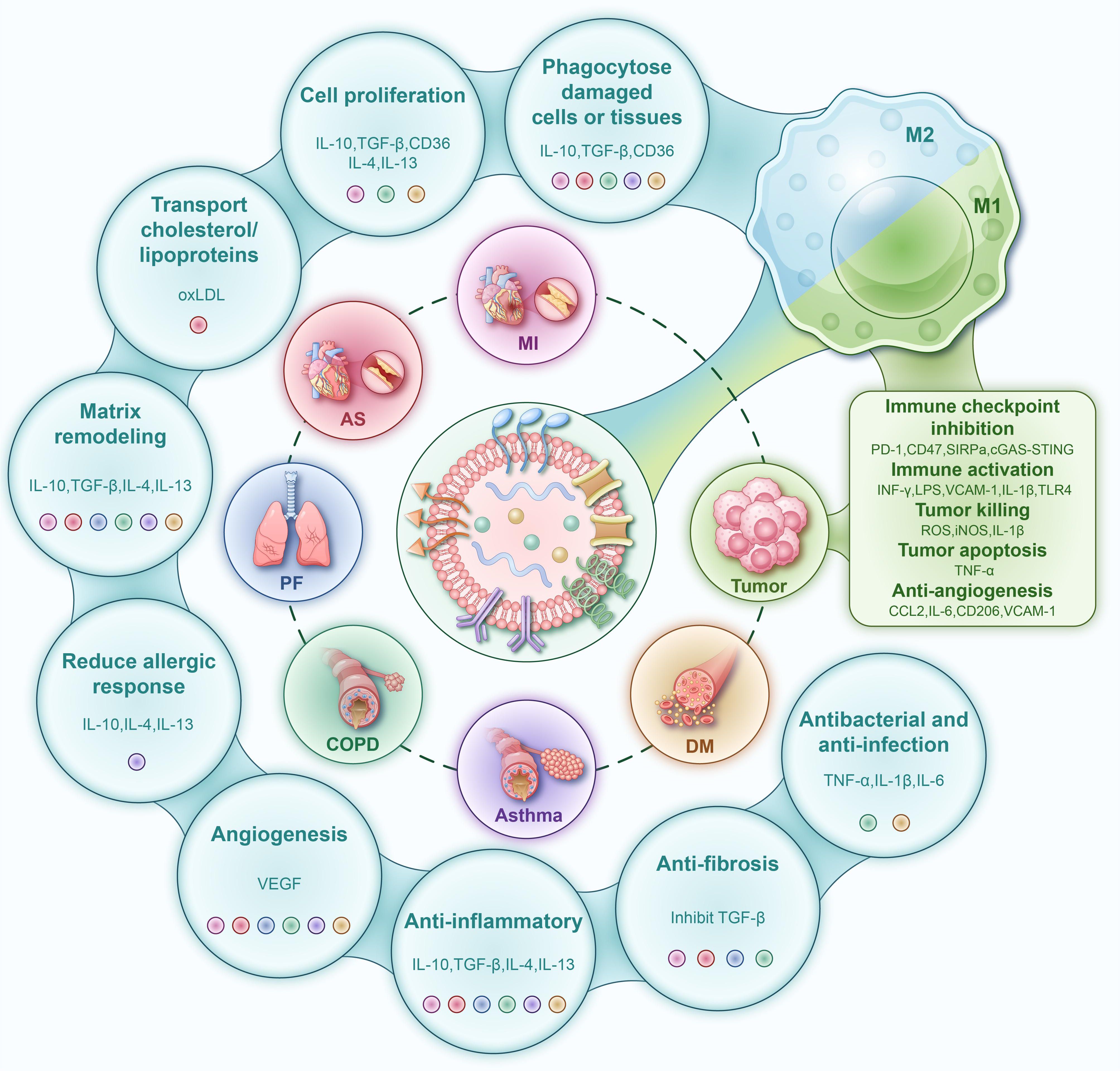
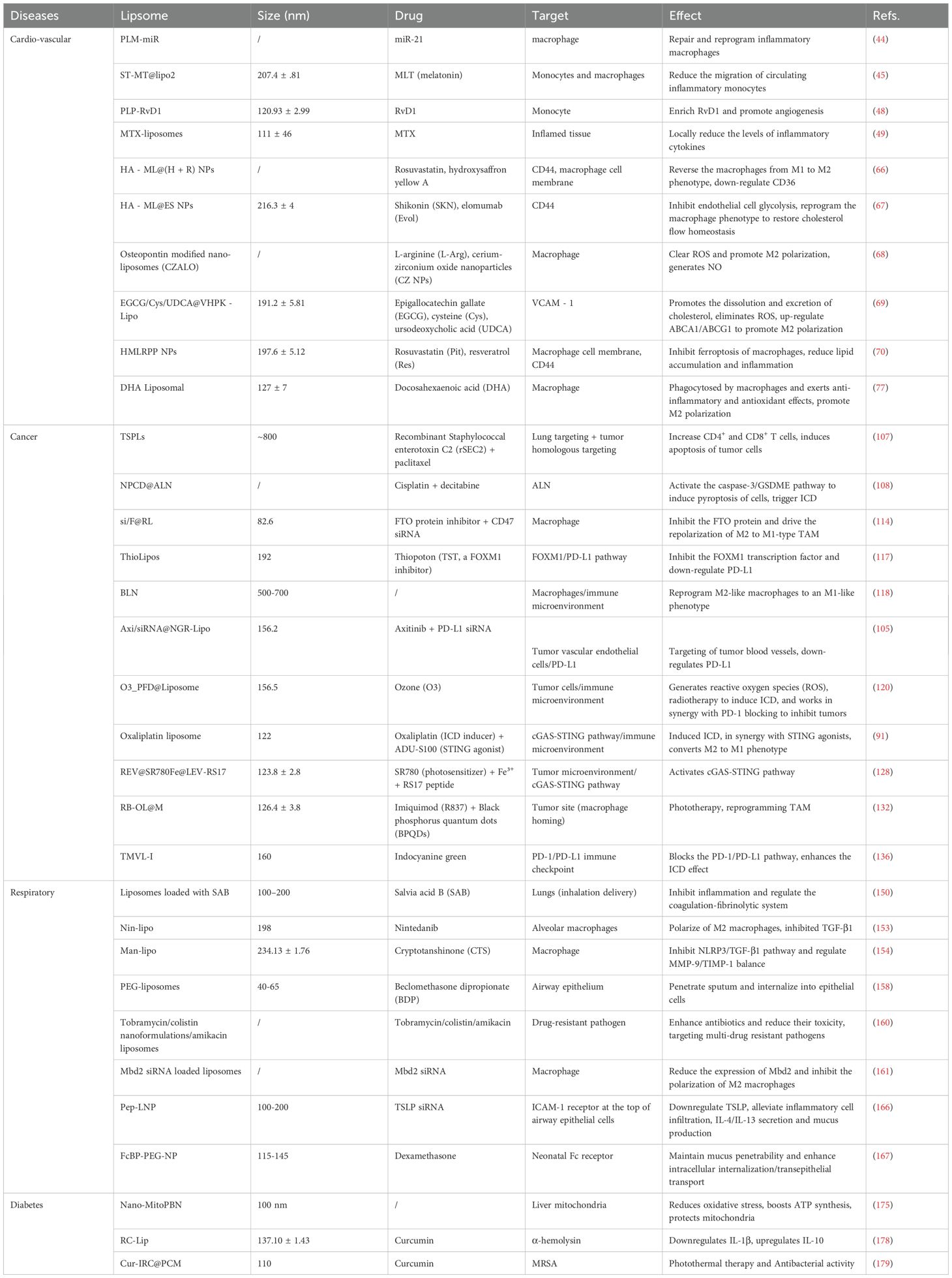
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the molecular mechanisms by which engineered liposomes modulate macrophage polarization for the treatment of chronic diseases. Promotion of M1 Polarization (Right Panel): Liposomes drive macrophages toward a pro-inflammatory, anti-tumor M1 phenotype. Activated M1 macrophages upregulate the expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, iNOS (producing NO), and ROS through pathways such as NF-κB, mediating tissue damage and tumor apoptosis. Concurrently, they secrete CCL2 and IL-6 and upregulate VCAM-1, thereby inhibiting angiogenesis and recruiting additional immune cells. Promotion of M2 Polarization (Left Panel): Liposomes drive macrophages toward an anti-inflammatory and pro-repair M2 phenotype. Activated M2 macrophages exert multiple functions including inflammation suppression (via IL-10, TGF-β, IL-4, IL-13), phagocytosis of damaged cells (mediated by CD36, IL-10, TGF-β), promotion of cell proliferation (via IL-10, TGF-β, CD36, IL-4, IL-13), matrix remodeling (through IL-10, TGF-β, IL-4, IL-13), reduction of allergic responses (by IL-10, IL-4, IL-13), anti-fibrotic effects (via TGF-β inhibition), and antibacterial/anti-infection activities (mediated by TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6). Additionally, the M2 phenotype facilitates physiological angiogenesis through VEGF-mediated mechanisms. PD-1, Programmed cell death protein 1; CD47, Cluster of Differentiation 47; SIRPα, Signal Regulatory Protein α; cGAS-STING, cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase-Stimulator of Interferon Genes; INF-γ, Interferon-gamma; LPS, Lipopolysaccharide; VCAM-1, Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1; IL-1β, Interleukin-1 beta; TLR4, Toll-Like Receptor 4; ROS, Reactive Oxygen Species; iNOS, inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase; TNF-α, Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha; CCL2, C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2; IL-6, Interleukin-6; CD206, Cluster of Differentiation 206; CD36, Cluster of Differentiation 36; IL-10, Interleukin-10; TGF-β, Transforming Growth Factor-beta; IL-4, Interleukin-4; IL-13, Interleukin-13; oxLDL, oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein; VEGF, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor.
2 Cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) have become a major global health burden (33–35). Although surgical operations are effective for some patients, they carry inherent surgical risks (36–38). To address these clinical challenges, liposome nanocarriers have been developed as a promising therapeutic alternative (22, 39, 40). The core therapeutic mechanism lies in precisely regulating the function of macrophages - which is precisely the key pathogenic link of cardiovascular diseases.
Myocardial infarction (MI) results from ischemic necrosis of the myocardium due to coronary artery occlusion (41). However, reperfusion therapy, as the cornerstone therapeutic strategy, presents a paradoxical dilemma. While restoring blood flow is essential, the reperfusion process itself precipitates a cascade of pathological events, including reactive oxygen species (ROS) burst, intracellular calcium overload, and maladaptive inflammatory responses. These mechanisms collectively contribute to the demise of otherwise salvageable cardiomyocytes (termed ischemia-reperfusion injury, IRI), with sustained inflammatory activation serving as the central pathogenic driver (42, 43). Consequently, effective modulation of inflammatory responses remains a major therapeutic challenge in myocardial infarction and reperfusion injury. Targeting the central pathological feature of macrophage polarization imbalance, research groups have investigated novel liposome-based delivery strategies. For instance, Tan et al. (44) constructed platelet-mimicking liposomes (PLP), which precisely delivered microRNA-21 (miR-21) to circulating monocytes via membrane fusion, driving M2 polarization and improving cardiac function. This strategy is minimally invasive and highly targeted, but it relies on the overlap of monocyte recruitment timing and the window period of the enhanced permeability and retention effect (EPR), which may limit its clinical applicability. Dong et al. (45) developed spleen-targeted liposomes (ST-MT@lipo2) to reduce inflammatory cell migration by regulating the heart-spleen axis monocyte chemoattractant protein-1/C-C chemokine receptor type 2 (MCP-1/CCR2) pathway. However, the size-dependent targeting efficiency of the nanoparticles cause inconsistent therapeutic effects, and the heterogeneity of the spleen microenvironment may pose off-target risks. Similarly, Cheng et al. (46) designed isogenic repair macrophages (PS-c@M) to restore immune homeostasis by synergistically inhibiting the STING pathway and repairing mitochondrial function. Their advantage lies in low immunogenicity and long-term retention characteristics, but the complexity of the preparation process and high production costs make it difficult to meet clinical demands. Additionally, Tan et al. (47) adopted a synergistic strategy of transgenic macrophages combined with CD47 antagonists, which can restore efferocytosis and block the “do not eat me” signal. However, the potential immunogenicity and long-term safety of gene editing have not been fully verified. Weng et al. (48) developed a ROS-responsive RvD1 delivery platform that achieves inflammation-targeted controlled release through a biomimetic platelet membrane. The challenge lies in the need to adapt the ROS response threshold to different pathological gradients, and the biological half-life limitation of RvD1 still needs to be overcome. Despite these strategies breaking through the limitations of insufficient targeting and single-pathway regulation of traditional therapies, they are still mired in three major translational quagmires. The mass production crisis of complex carriers, the safety black hole of gene/biomimetic materials, and the common predicament of dynamic pathological response mismatch.
Given the central role of macrophages in infarct repair and their dual value as therapeutic targets and drug delivery vehicles, Che et al. (49) revealed an innovative mechanism for the uptake of methotrexate liposomes (MTX-liposomes) by target cells, as a process dependent on a precisely regulated neutrophil-mediated cascade transport system. This study found that neutrophils carry MTX-liposomes and undergo physiological changes, safely releasing the nanocarriers into target macrophages through a strictly controlled cell lysis process, thereby achieving precise drug delivery and efficient utilization. This neutrophil-mediated delivery strategy exhibits remarkable adaptability and holds promise for application in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI) models. Another groundbreaking study (50) demonstrated that biomimetic neutrophil liposomes (Neu-Lipos) not only reduce the number of proliferating macrophages but also significantly lower the levels of key pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby improving the myocardial repair process. The strategy of inducing macrophage polarization toward a regenerative phenotype has emerged as a highly promising therapeutic approach for ameliorating post-myocardial infarction remodeling. Also, miR-21 plays a pivotal role in regulating macrophage polarization, Tan et al. (44) developed a novel platelet membrane-coated nano-delivery system. This system employs miR-21-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles as the core, enveloped by a fusion of platelet membranes and cationic liposomes. The innovative design enables specific targeting of macrophages in cardiac inflammatory sites, releasing miR-21 for anti-inflammatory regulation. It effectively protects cardiac function in mice with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and precisely modulates macrophage polarization states.
Atherosclerosis (AS), a prevalent cardiovascular disorder, is profoundly influenced by hemodynamic factors such as shear stress and vascular bifurcation geometry (27). The pathological process is characterized by a triad of key features, including endothelial dysfunction, chronic inflammation, and lipid-rich plaque formation (51–54). The progressive nature of AS ultimately leads to luminal stenosis or complete occlusion, resulting in compromised blood flow and subsequent ischemic tissue damage in downstream vascular beds. Although the early lesion microenvironment is more amenable to intervention (55, 56), its asymptomatic and insidious nature causes diagnostic difficulties and delays treatment (54, 57–59), urgently requiring early precise diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Traditional anti-inflammatory therapies are limited by non-specific distribution, poor water solubility, and dose toxicity (e.g., bleeding, kidney damage) (60–63). While nanocarrier delivery systems show the potential to address these limitations and achieve targeted lesion treatment (64, 65).
In the field of macrophage-targeted therapy for atherosclerosis, the lipid-mediated reprogramming strategy through multi-dimensional mechanisms demonstrates breakthrough potential. Dong et al. (66) developed HA-modified hybrid liposomes that reverse M1-to-M2 macrophage polarization and promote lipid metabolism via autophagy activation and CD36 downregulation, thereby enhancing plaque stability. Separately, Zhang et al. (67) designed a similar system for dual-targeting (plaque/macrophage) delivery, demonstrating efficacy in mitigating endothelial dysfunction and reprogramming macrophage phenotype to attenuate atherosclerosis. For microenvironment regulation, researchers have developed a targeted liposome delivery system (68) that innovatively exploits macrophage metabolic pathways to catalyze nitric oxide (NO) production. This system demonstrates dual therapeutic mechanisms by mitigating endothelial cell senescence and scavenging ROS, while simultaneously inhibiting the VEGF signaling pathway to suppress pathological angiogenesis. The integrated approach enables dynamic modulation of the plaque microenvironment. In response to the problem of cholesterol reverse transport, the targeted liposome developed by Shen et al. (69) significantly promotes cholesterol efflux and effectively clears ROS through drug synergy, simultaneously up-regulating the ATP-binding cassette transporter A1/G1 (ABCA1/G1) pathway and inducing macrophage polarization to M2 type, thereby achieving significant plaque clearance effects. While Yang et al. (70) pioneered the macrophage membrane hybrid liposomes, which take a different approach by regulating the BDH1/ORM1/RPS27L to form a metabolic-inflammation-stress response network, inhibiting the ferroptosis process, effectively blocking the positive feedback loop of lipid peroxidation and inflammation. While these technological advances uniformly exhibit key advantages including precise targeting capability, multifunctional therapeutic synergy, and excellent biocompatibility, their clinical translation remains hindered by challenges in complex carrier production processes.
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) demonstrates pleiotropic therapeutic effects against atherosclerosis, particularly through its potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiproliferative activities (71–76). Notably, this omega-3 fatty acid exhibits synergistic potential with liposomal delivery systems, which preferentially accumulate in plaque-resident macrophages. Chong et al. demonstrated that DHA-loaded liposomes are efficiently internalized by activated macrophages, triggering robust anti-inflammatory and antioxidant responses while effectively suppressing foam cell formation-a critical step in atherosclerotic plaque progression (Figure 2) (77). Mechanistically, intravenously administered DHA-liposomes exhibit selective homing to macrophage-rich atherosclerotic lesions, where they promote phenotypic reprogramming of these immune cells. Preclinical studies suggest that intravenous DHA-liposome delivery represents a pharmacologically superior approach compared to oral administration, offering enhanced bioavailability with minimal adverse effects (78). While these findings position liposomal DHA as a promising therapeutic strategy, further clinical translation is necessary to validate its efficacy and safety in human subjects. This targeted delivery paradigm not only improves drug bioavailability but also reduces systemic exposure, potentially overcoming the limitations of conventional small-molecule therapies. The ability to precisely modulate macrophage polarization through liposomal delivery opens new avenues for immunomodulatory approaches in cardiovascular disease management.
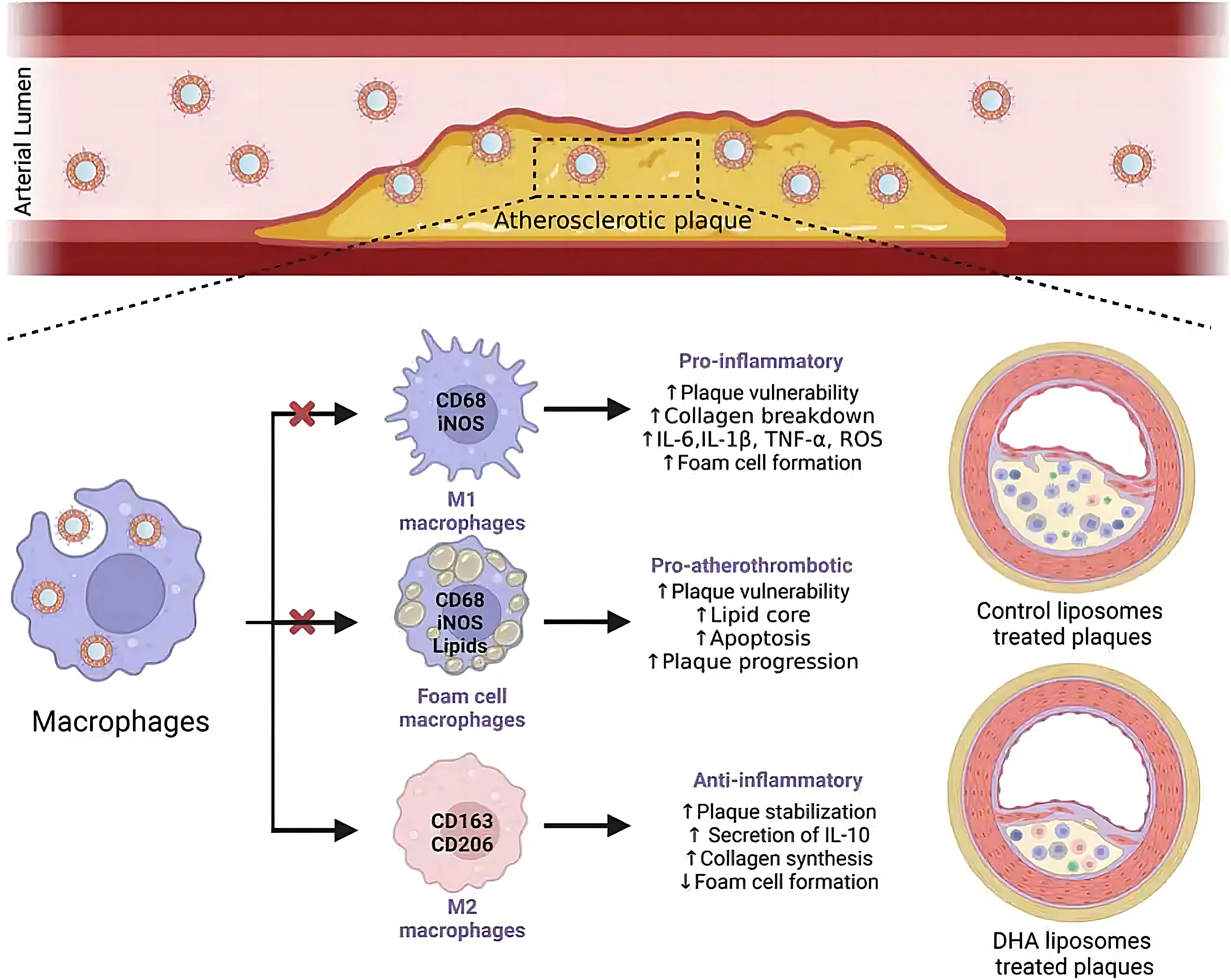
Figure 2. Liposome-encapsulated DHA targeting plaques after intravenous administration, uptake by macrophages, and improvement of atherosclerosis (77).
On the other hand, liposomes serve as versatile biomimetic platforms that can be strategically engineered to emulate biological membrane functions, thereby enabling innovative modulation of macrophage behavior (79, 80). Wu et al. developed an innovative apoptotic body-mimetic liposomal system that faithfully replicates the natural targeting properties of apoptotic vesicles. This system demonstrates remarkable precision in delivering anti-inflammatory payloads to atherosclerotic macrophages, achieving triple therapeutic benefits including inflammation modulation, plaque stabilization, and potential application for inflammatory comorbidities (81). Building on membrane-mimetic technology, P-Lipo was created by Song et al. through an extrusion-based fusion of conventional liposomes with platelet membranes (82). This biohybrid system retains native platelet targeting capabilities while gaining enhanced drug delivery functions. In vitro studies using RAW264.7-derived foam cells demonstrated that P-Lipo maintains multifunctional adhesion properties and exhibits selective accumulation in atherosclerotic lesions. The platform’s multivalent targeting capacity and biocompatibility enable effective intervention in macrophage-driven atherosclerosis without detectable toxicity, representing a significant advancement in both therapeutic efficacy and safety profiles. Further innovating this approach, Sha et al. developed macrophage membrane-cloaked nanoparticles by enveloping liposomal cores with native macrophage membranes (83). These biomimetic nanotherapeutics operate through a competitive binding mechanism in vivo, effectively scavenging pathogenic molecules (ox-LDL and LPS) that would normally be internalized by macrophages. This intervention achieves dual therapeutic effects including substantial reduction in foam cell formation (by up to 68% in murine models) and significant suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression. The most advanced iteration of this technology, MP-QT-NP, demonstrates unprecedented therapeutic potential through a multi-modal mechanism (84). These biomimetic platforms collectively represent a paradigm shift in atherosclerosis treatment, offering targeted therapeutic strategies that address multiple pathological pathways simultaneously. The successful translation of these technologies could revolutionize clinical management of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
3 Cancer
Cancer remains one of the most complex and challenging diseases in medical research, presenting ongoing therapeutic difficulties (85, 86). Liposomes have emerged as particularly promising drug delivery systems in cancer therapy due to their unique phospholipid bilayer structure, which provides exceptional drug encapsulation and delivery capabilities (87). These versatile nanocarriers can simultaneously transport multiple therapeutic agents including chemotherapeutic drugs (88–92), antigens (93–96), antibodies (97–99), and immunomodulators (100–106), enabling precise and synergistic therapeutic effects. Furthermore, liposomes demonstrate excellent compatibility with physical treatment modalities such as photothermal, photodynamic, and radiotherapy approaches, significantly enhancing their therapeutic potential. Through physical regulation mechanisms, liposomes allow precise control over their stability and permeability, enabling spatiotemporal regulation of drug release rate and locations. This controlled release ensures optimal drug concentrations in tumor tissues while minimizing leakage into normal tissues, thereby significantly improving drug bioavailability and therapeutic outcomes.
3.1 Liposomal co-delivery of immunomodulators for macrophage-based cancer immunotherapy
Liposomes serve as intelligent platforms that integrate chemotherapy and immunotherapy to modulate macrophages, thereby generating synergistic therapeutic benefits. For instance, the TSPLs system enhances lung targeting through the co-delivery of paclitaxel and rSEC2 while activating T-cell subsets to reverse immunosuppression (107). Similarly, a liposomal formulation combining oxaliplatin and STING agonists promotes immunogenic cell death (ICD), thereby enhancing antigen presentation and T-cell infiltration (91). Furthermore, the NPCD@ALN system significantly improves the therapeutic efficacy against osteosarcoma by synergistically inducing pyroptosis and ICD (108). The success of these strategies hinges on the sophisticated integration of the EPR effect with active targeting technologies to improve targeting accuracy. Additionally, spatiotemporally controlled release enables coordinated action between chemotherapeutic agents and immunomodulators, ultimately activating antitumor immunity. It is particularly noteworthy that such designs transcend the limitations of conventional chemotherapy, elevating liposomes from simple drug carriers to multifunctional regulators of the tumor immune microenvironment.
Liposome technology has made breakthrough progress in the field of antigen/antibody targeted delivery, demonstrating a powerful ability to precisely regulate the tumor immune microenvironment. In terms of targeting mechanisms, the bionic liposomes (TSPLs) of 4T1 cancer cell membrane hybridization have achieved precise co-delivery of chemotherapy drugs and immunomodulators through homologous targeting (107). Meanwhile, the CAR-T exosome fusion system (Lip-CExo@PTX) innovatively uses bispecific scFv to simultaneously target tumor antigens and immune checkpoints (109). These designs ingeniously leverage the natural targeting characteristics of biological systems, organically integrating the passive targeting EPR effect with the active targeting molecular recognition. In terms of immune regulation, the synergistic use of STING agonist liposomes and CD40 antibodies (110), as well as membrane fusion liposomes (MFL) targeting apoptotic bodies (111), significantly enhanced antigen presentation efficiency through spatiotemporal precise immune stimulation. Particularly worthy of attention are the designs of the nano-liposome-bacterial hybridization system (Figure 3) (112) and the protease-responsive eLipo (113). The former utilizes the biosynthetic ability of bacteria to achieve in situ expression of antibodies, while the latter overcomes the targeting barrier through microenvironmental response release. In the treatment of immunologically “cold” tumors like microsatellite-stable colorectal cancer (MSS-CRC), engineered cationic liposomes simultaneously enhance RNA m6A methylation through FTO protein inhibition and silence the CD47 immune checkpoint, effectively driving M2-to-M1 TAM repolarization while boosting macrophage phagocytic activity (114). Innovative “tail-flipped” nanoliposomes mimicking peroxidized phospholipids specifically target SR-B1 receptors on M2-TAMs to deliver STAT6 inhibitors, effectively disrupting pre-metastatic niche formation (115). Metabolic intervention strategies further expand the therapeutic scope, exemplified by PEGylated liposomes co-delivering mannose (glycolysis inhibitor) and levamisole (mitochondrial function blocker) to synchronously modulate cancer cell and TAM metabolism when combined with radiotherapy (116). These results not only address the key issues of traditional therapies such as poor targeting and high toxicity, but also achieve the integration of “delivery and activation” through engineering design, providing new ideas for tumor immunotherapy. However, to achieve clinical translation, challenges such as vector stability, large-scale production, and the precision of immune regulation still need to be addressed. The future development directions may focus on the optimization of intelligent response systems, the development of multi-target collaborative delivery strategies, and the establishment of individualized treatment plans, etc.
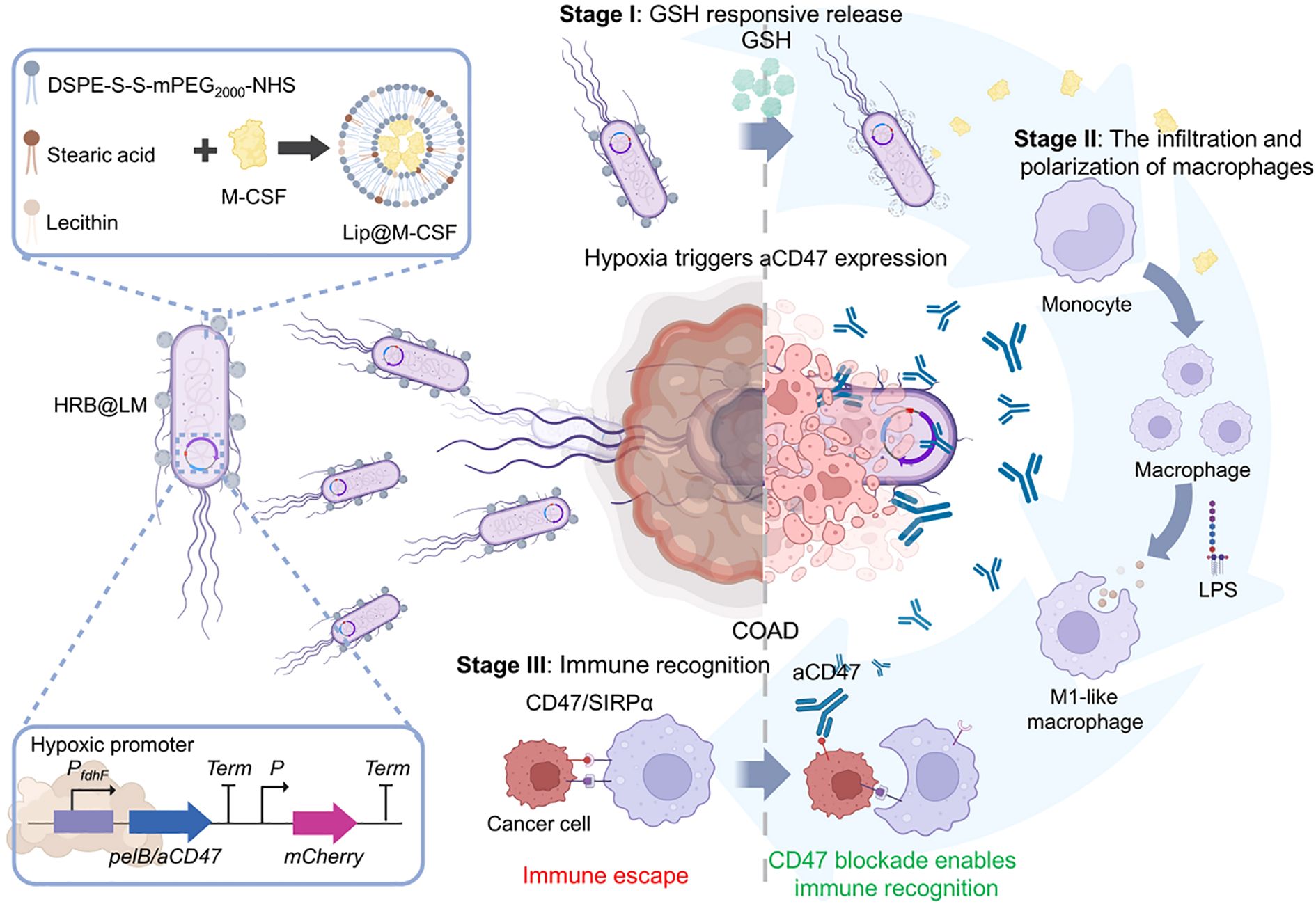
Figure 3. Hypoxia-responsive HRB@LM system targets CD47/SIRPα signaling to synergistically activate macrophage-T cell antitumor immune cascades (112).
Liposome technology has made contribution to PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy, primarily through the optimization of delivery strategies. ThioLipos developed by Shin et al. demonstrated significant monotherapy effects in colon cancer models by inhibiting FoxM1-mediated PD-L1 expression (117). This finding suggests that targeting the upstream regulatory factors of PD-L1 may be more advantageous than direct blocking. The BLN liposomes (118) demonstrated the significance of microenvironment regulation by inducing calmodulin exposure and macrophage polarization, and the NGR liposomes (105) achieved the dual effects of vascular normalization and PD-L1 down-regulation. The combined use of FAK inhibitors with liposomal doxorubicin (119) and the ozone-liposome enhanced radiotherapy technology (120) both demonstrate that tumor antigens produced by ICD can establish a self-reinforcing anti-tumor immune cycle. It is worth noting that metabolic reprogramming demonstrates unique value, which includes L-arginine metabolism (121), tryptophan metabolism (122), and iron metabolism (123). These studies suggest that future immunotherapy may need to adopt a “multi-pronged” strategy: blocking immune checkpoints, improving the tumor microenvironment (TME), activating innate immunity and reshaping the metabolic microenvironment at the same time. This comprehensive intervention approach might offer a new breakthrough in overcoming the current problem of drug resistance in immunotherapy.
Liposomes have emerged as a key platform for overcoming immunosuppression and enhancing anti-tumor immunity by efficiently regulating the TME through various innovative strategies as carriers of STING agonists. This system not only achieves the synergistic delivery and controlled release of drugs (91), but also directly reshapes the composition and function of the immune microenvironment through ingenious design: optimizing lipid composition to enhance lysosomal escape and type I interferon production (124). Intelligent responsive liposomes (ultrasound (125), pH (126) and enzyme responses (127) can achieve tumor site-specific STING activation, significantly enhancing treatment specificity. Furthermore, through targeted modification and multi-mechanism synergistic strategies, the liposome-STING agonist system has demonstrated a powerful potential for precise regulation of the TME. By integrating synergistic strategies such as photodynamic therapy, ferroptosis induction and STING activation (128) or exosome- liposome hybridization system (129), multiple immunosuppressive links in the TME can be targeted simultaneously, establishing a self-reinforcing anti-tumor immune cycle. Mitochondria-directed liposomes, BQR@MLipo, induce ferroptosis-specific HMGB1 release via DHODH inactivation, accompanied by mtDNA leakage that activates the cGAS-STING pathway, driving CD8+ T cell infiltration (130). These advancements highlight the significant value of STING-loaded agonist liposomes in coordinating innate and adaptive immune responses, addressing tumor heterogeneity, and reversing drug resistance. Future research should focus on enhancing the clinical translational ability of these complex systems and exploring their precise application in the regulation of individualized immune microenvironments.
3.2 Physically stimulated liposomes for macrophage-based cancer immunotherapy
Liposomes have significantly advanced the development of combined tumor immunotherapy strategies through the integration of photothermal therapy (PTT) and immune microenvironment regulation. A T-cell membrane-fused liposomes (TMVL-I) and M1 macrophage-bacterial outer membrane hybrid systems (RB@OL), overcome the spatiotemporal limitations of conventional therapies by leveraging biomimetic targeting and photothermal-immunological synergistic mechanisms, enabling precise immune activation against both primary and metastatic tumors (131, 132). On the other hand, liposomes serve as a delivery platform for photodynamic therapy (PDT), significantly expanding the therapeutic dimensions of PDT through precise modulation of ICD and tumor microenvironment remodeling. In melanoma treatment, a γδ-T exosome-modified Ce6-TEXO system enables targeted delivery mediated by CCR5/PD-1. Under 660–700 nm light irradiation, it generates ROS and synergizes with exosomal granzyme/perforin to induce ICD, releasing DAMPs such as CRT/ATP, thereby effectively activating CD8+ T cells (Figure 4) (133). This strategy lies in the integration of cell membrane-targeting technology with the immune-activating properties of PDT, achieving a spatiotemporal synergistic enhancement between exosomes and PDT. In the development of in situ vaccines, an endoplasmic reticulum-targeting liposome (Par-ICG-Lipo) fabricated using microfluidic technology to achieve high drug loading, induces ER-specific ICD under near-infrared light irradiation. Through the release of tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) and DAMPs, this process effectively transforms the tumor into an endogenous vaccine (134). This design overcomes the limitations of traditional vaccine preparation and demonstrates the unique advantages of PDT in initiating in situ immunity. To address the drug-resistant microenvironment, the Pt/Ce6-LP (135) depletes GSH through Pt(IV) prodrug conversion, alleviates hypoxia, and modulates ROS levels, thereby driving TAM repolarization towards the M1 phenotype and establishing long-term immune memory. This approach successfully triples the efficacy of PDT, proving that metabolic modulation and remodeling of the immune microenvironment can effectively reverse tumor drug resistance (136).
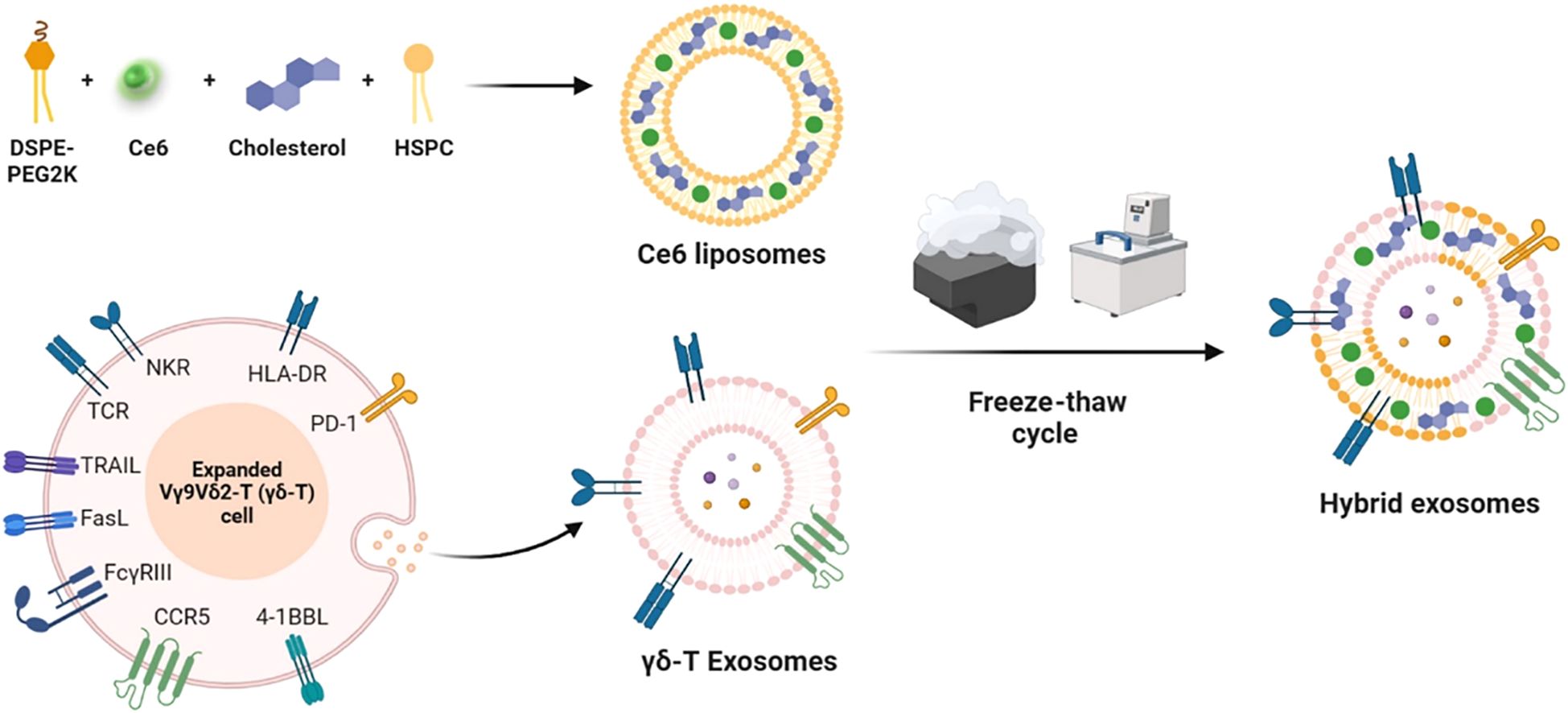
Figure 4. Schematic diagram of photobiological immunotherapy for melanoma based on the fusion of γδ-T exosomes and Ce6 liposomes (133).
Meanwhile, the synergistic therapy combining liposome and radiotherapy (RT) is evolving from a traditional physical radiosensitization strategy toward a new paradigm focused on remodeling the immune microenvironment. Central to this shift is leveraging the immunogenic effects of RT, achieved through precisely engineered liposomal delivery systems that enable multi-level modulation of the cancer-immunity cycle. During the immune initiation phase, RT not only directly induces ICD in tumor cells but also acts synergistically with intelligent lipid-based systems. For instance, the Lipo-Ele@CuO2 liposome developed by Jiang et al. utilizes RT to trigger cuproptosis, markedly enhancing the release of DAMPs, while simultaneously reprogramming immunosuppressive TAMs, thereby establishing a potent “in situ vaccine” effect (137). The Cold Exposure-SL liposome system leverages RT-induced burst generation of peroxynitrite to enhance oxidative stress and suppress myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), thereby creating a favorable microenvironment for immune activation (138). At the effector phase of immunity, tailored strategies designed for specific tumor microenvironments have demonstrated distinct advantages. In glioblastoma, an MMP-2-responsive liposome (D@MLL) (139) leverages RT-enhanced blood-brain barrier permeability to synergistically promote M1-type TAM polarization, effectively countering the immunosuppressive microenvironment. Meanwhile, the IR-LND@Lip nano-adjuvant developed by Zhou et al. achieves synergistic activation of the cGAS-STING pathway under radiotherapy, converting immunologically “cold” tumors into “hot” phenotypes, while simultaneously blocking immune checkpoint signals such as PD-L1 and TGF-β (140). Another innovative approach by Suo et al. involved TAFL biomimetic liposomes that exploit exosomal fusion properties to specifically target cancer stem cells (CSCs), releasing aspirin to induce CSC apoptosis and suppress stemness while utilizing photothermal therapy to alleviate hypoxia and indirectly reduce M2-TAM-derived immunosuppressive signals, thereby creating synergistic RT-immune modulation (141).
These advances signify a fundamental transformation in the role of liposome-based platforms in cancer therapy. Originally used merely as radiosensitizers in radiotherapy or as simple carriers for agents in photothermal/photodynamic therapy, they have now evolved into integrated multifunctional systems capable of simultaneously modulating tumor metabolism, the immune microenvironment, and cell death. By incorporating strategies such as spatiotemporal regulation of the STING pathway, these multimodal systems successfully achieve cascaded conversion of physical energy to chemical energy and then to biological effects. This not only enhances local therapeutic ablation but also drives the reprogramming of systemic anti-tumor immunity. This shift marks a strategic transition in cancer treatment paradigms from traditional “single-target inhibition” to a new era of “multimodal intervention”. The core breakthrough lies in the precise temporal control of DAMPs release and immune cell reprogramming, establishing an integrated framework of that progresses from in situ immune priming to microenvironment remodeling and finally to a systemic anti-tumor response. Current research is advancing the transition from laser-mediated local treatments to systemic immunomodulatory strategies, offering novel avenues to overcome the challenges in solid tumor therapy. Future efforts should focus on achieving precise matching between individualized drug delivery systems and radiotherapy regimens, as well as leveraging artificial intelligence and other technologies to optimize spatiotemporal treatment parameters, ultimately enabling comprehensive regulation from local irradiation to system-wide immune control.
4 Respiratory diseases
Chronic respiratory diseases, accompanied by structural abnormalities of the airways and lungs, pose a major global public health challenge, with continuously rising burdens of morbidity and mortality (142, 143). Among these, pulmonary fibrosis is characterized by persistent activation of myofibroblasts, excessive extracellular matrix deposition, and chronic inflammatory cell infiltration (144–146). COPD is primarily manifested as irreversible airflow limitation (147), and asthma is marked by recurrent episodes and acute exacerbations (148). Approximately 4 million annual deaths are attributed to these diseases, resulting in a substantial societal burden (149). In recent years, liposome-based strategies targeting the regulation of macrophages have achieved a series of advances in chronic respiratory disease treatment research.
In the field of pulmonary fibrosis, Peng et al. (150) and Cheng et al. (151) collectively confirm the critical influence of liposomal physicochemical properties on delivery efficiency from the perspective of liposome design. Liposomes constructed with saturated neutral and anionic phospholipids exhibit high stability and pulmonary permeability, When loaded with salvianolic acid B, they achieve therapeutic effects by inhibiting inflammation and imbalances in the coagulation-fibrinolysis system. In contrast, a Gal3 siRNA-loaded liposome that intervenes in the pathological crosstalk among endothelial cells, macrophages, and fibroblasts by blocking the Gal3-TGFBR1/TLR4 signaling axis. This targeting strategy provides a new paradigm for precise regulation of intercellular communication based on optimized liposome physicochemical properties. Notably, macrophage polarization regulation has emerged as a core strategy in multiple research efforts. The NAMPT drives M2 polarization through a non-enzymatic activation of STAT6 signaling, while clodronate liposome-mediated macrophage depletion and reconstitution experiments revealed the central role of monocyte/macrophage populations in fibrosis (152). Nin-lipo is a biomimetic liposome that mechanically interferes with M2 polarization by mimicking pulmonary surfactant and simultaneously reduces TGF-β1 secretion (Figure 5) (153). This dual physico-chemical and biological regulatory mechanism highlights the multi-faceted efficacy of liposome therapy. Furthermore, surface modifications of liposomes (e.g., mannose ligands (154)) can specifically enhance macrophage uptake and modulate their polarization direction. When combined with the localized high-concentration advantage of inhalation administration (e.g., a 2 mg/kg nebulized dose outperforming a 60 mg/kg oral dose (153)), future developments may involve intelligent liposome platforms that integrate targeted delivery, polarization regulation, and combination therapy (e.g., siRNA-small molecule co-delivery strategies (155)). Such approaches could break through the current limitations of anti-fibrotic therapy from the perspective of multi-cellular interaction networks.
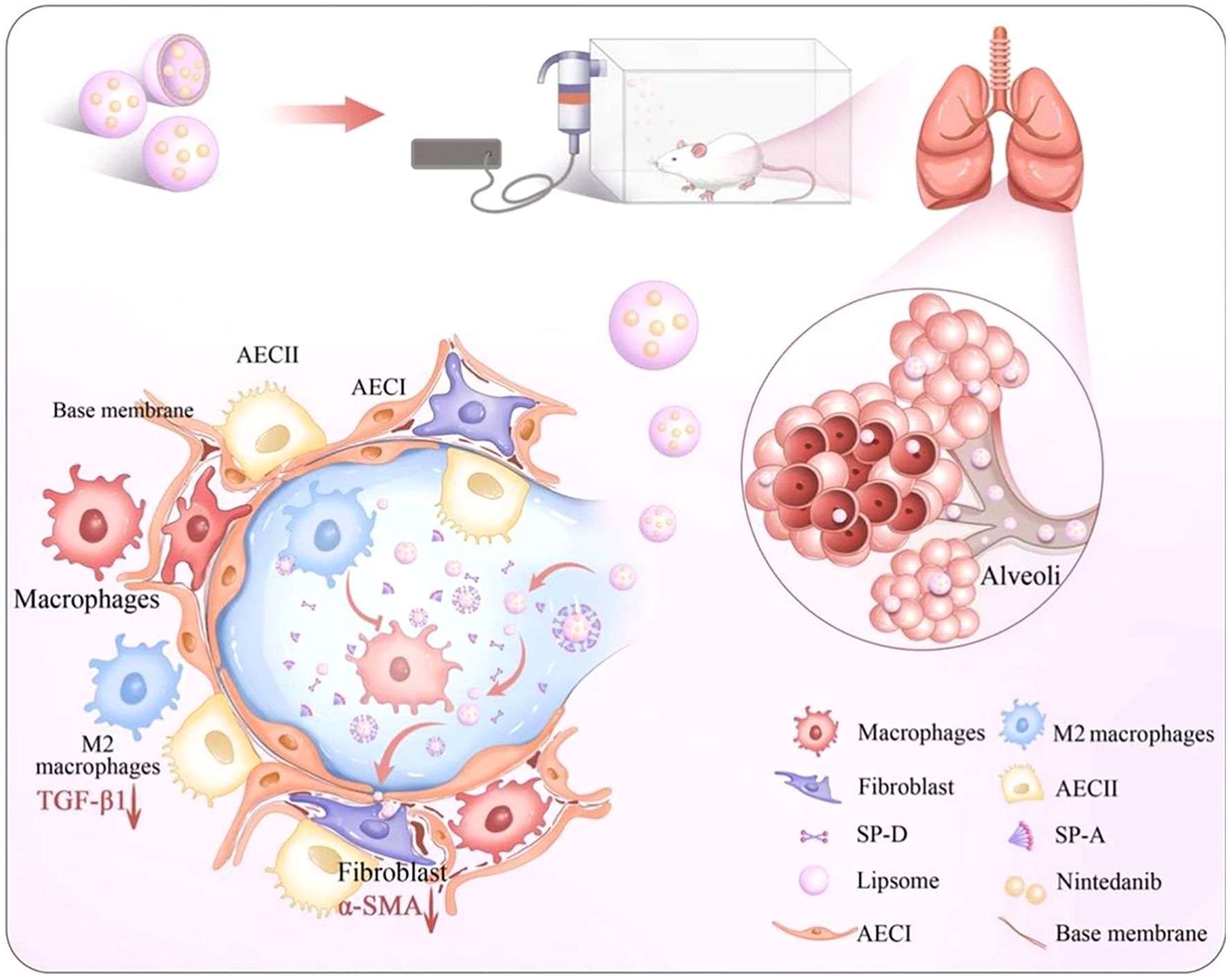
Figure 5. Macrophage involvement in PF therapy. Impact of Nin-lipo on M2 macrophage polarization and lung fibrosis (153).
COPD not only severely impairs patients’ quality of life but also significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular events, recurrent respiratory failure, and susceptibility to lung cancer, thereby contributing to elevated overall morbidity and mortality (156). The pathological core of COPD involves macrophage polarization imbalance and chronic airway inflammation, yet conventional drug delivery systems struggle to precisely intervene in the immune microenvironment of affected areas. In response to this challenge, nanomedicine has emerged as a pioneering therapeutic strategy through precision drug delivery systems that molecularly target diseased tissues (157). It offers new avenues to enhance treatment efficacy while reducing reliance on conventional drugs and their associated adverse effects. Studies have shown that surface-modified (e.g., PEGylated) liposomes exhibit superior penetration capability and epithelial uptake efficiency in the pathological mucus of COPD, laying the foundation for targeting airway-resident macrophages (158). PEG modification not only reduces mucoadhesion through steric hindrance but may also influence macrophage phagocytic behavior by modulating liposomal surface properties. Specifically, PEGylated liposomes with a neutral charge and a nano-scale size (40–65 nm) are more readily internalized by macrophages, thereby enabling targeted delivery of anti-inflammatory drugs such as beclomethasone dipropionate or genetic regulators like miRNA/siRNA. This characteristic aligns well with the requirements for oligonucleotide delivery proposed by Li et al. (159): liposome-encapsulated silencing of M1 polarization-related genes (e.g., NF-κB or TNF-α) may reverse the hyperactivation of pro-inflammatory macrophages in COPD. Furthermore, antibiotic-loaded liposomes (e.g., tobramycin/colistin) developed by Zhang et al. (Figure 6) (160) not only target and eliminate pulmonary pathogens but may also break the “infection-inflammation” vicious cycle by modulating macrophage phagocytic function. Future directions may explore multifunctional designs, such as surface conjugation of CD206 antibodies to enhance M2 macrophage-specific targeting, combined with co-delivery of IL-10 mRNA and antibacterial agents to achieve dual “pro-repair/anti-infection” regulation. However, caution is warranted regarding the potential long-term impact on macrophage functional homeostasis. This could be mitigated by using biodegradable lipid materials to construct stimulus-responsive release systems that activate drug delivery exclusively within inflammatory microenvironments, thereby balancing efficacy and safety.
Figure 6. Inhalable antibiotic nanoformulations for the treatment of chronic respiratory diseases (160).
As central effector cells in asthma-related inflammatory regulation, macrophages contribute directly to airway hyperresponsiveness and amplification of inflammation through M2 polarization (161) or maturation defects (162). Over the past 15 years, significant advances in medical interventions have led to a substantial decline in asthma incidence and mortality, with most patients achieving adequate symptom control through conventional treatment regimens (163). However, current therapies remain insufficient for severe or refractory cases, where symptom management continues to pose major challenges. This unmet clinical need is driving the exploration of more precise and effective treatment strategies. Through multifunctional liposomal design, precise modulation of macrophage phenotypes has become achievable: MBD2 siRNA-loaded liposomes suppress the M2 polarization program in macrophages, thereby blocking the allergic inflammatory cascade at an upstream stage (161), while MPLA/Dex hybrid nanoparticles actively target macrophages via TLR4 ligands, simultaneously inhibiting pro-inflammatory phenotypes and promoting IL-10-mediated immune tolerance (164). Notably, intelligent modulation of liposome surface properties (165) can optimize pulmonary retention and transmembrane efficiency. For instance, highly hydrophilic liposomes prolong budesonide retention in alveolar macrophages, and cyclic peptide modifications targeting ICAM-1 (166) provide molecular guidance to enhance macrophage-specific uptake. Zhang et al. successfully prepared cyclopeptide-modified lipid nanoparticles (Pep-LNPs) that can precisely deliver siRNA to human and mouse epithelial cells, significantly reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TSLP), modulating asthma-related signaling pathways, decreasing MUC5AC mucin secretion, alleviating airway inflammation, lowering airway hyperreactivity, and improving asthma symptoms (166). Additionally, Yu et al. prepared PEG-coated PLGA-liposomes (PEG-NP) modified with FcBP to enhance targeting recognition capabilities (Figure 7) (167). Experiments showed that FcBP-NP@Dex efficiently delivered Dex to macrophages, exhibited significant anti-inflammatory effects, and demonstrated promising therapeutic outcomes in asthmatic mice. These synergistic innovations suggest that future systems may integrate “targeted delivery–phenotypic reprogramming–long-term regulation” into a unified liposomal platform. For example, co-delivery of MBD2 siRNA (161) and GM-CSF (162) could simultaneously rectify maturation defects and suppress aberrant polarization. Nonetheless, caution is warranted regarding potential long-term impacts on innate immune function, which may be mitigated through spatiotemporally controlled release technologies to balance therapeutic efficacy and immune homeostasis. In summary, although PF, COPD, and asthma exhibit distinct pathological features, they share a central link in chronic inflammation and dysregulation of the immune microenvironment, where macrophages play a critical role. In light of this, adopting multi-pronged strategies holds promise for fundamentally reversing the immune imbalance underlying the progression of these diseases. Although current research has only just unveiled the beginning of this field, it has already revealed the immense potential and fascinating prospects of nanomedicine-based approaches in tackling complex chronic respiratory diseases.
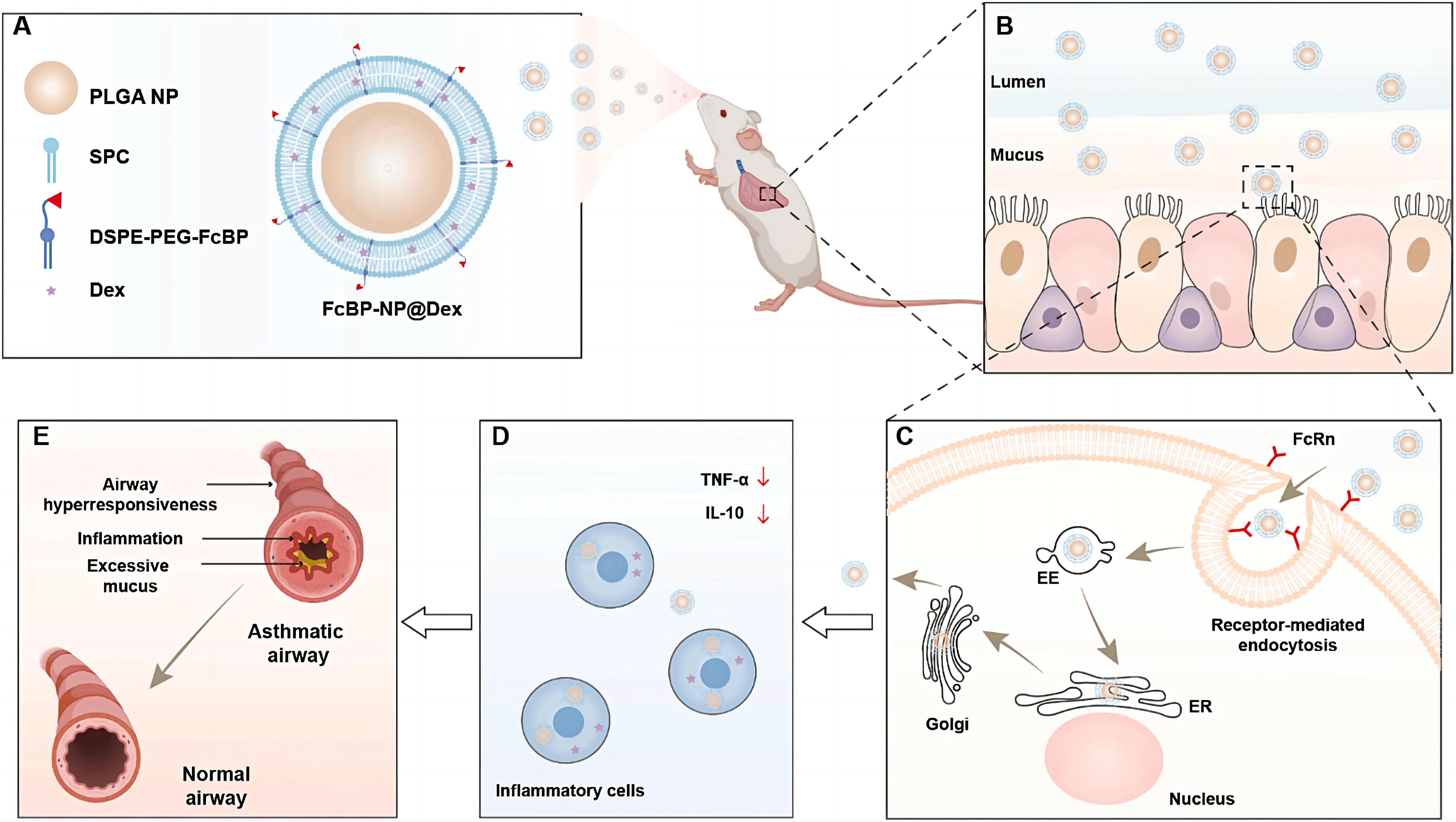
Figure 7. FcBP-functionalized PEG nanoparticles overcoming airway barriers and enhancing asthma therapy (167).
5 Diabetes mellitus
Metabolic disorders (MDs) represent a complex group of interconnected pathological conditions characterized by dysregulation in the metabolism of fundamental macronutrients including carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins (168). This disease spectrum encompasses a range of clinically significant conditions such as obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), hypertension, osteoporosis, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disorders, all of which share common metabolic dysfunctions (169). The global impact of these conditions is profound, with diabetes mellitus alone affecting more than 415 million individuals worldwide, creating significant challenges for healthcare systems and socioeconomic structures (170). These disorders not only compromise patients’ quality of life through multiple organ system involvement but also contribute to substantial morbidity and mortality rates. The alarming prevalence of MDs highlights the urgent need for enhanced research efforts to develop more effective diagnostic, preventive, and therapeutic approaches. Given the extensive clinical implications and research significance, this section will particularly focus on diabetes mellitus (DM) as a representative metabolic disorder.
DM comprises a group of complex metabolic disorders characterized by chronic hyperglycemia resulting from either deficient insulin secretion, impaired insulin action, or both pathological mechanisms (171, 172). The growing global prevalence of diabetes presents a significant public health challenge, with millions affected by persistent elevated blood glucose levels (173, 174). These challenges have driven the urgent need for developing more effective therapeutic agents and improved drug delivery systems with enhanced precision and reduced adverse effects. In this context, liposome-based delivery systems have emerged as a promising approach, offering several potential advantages including versatile applicability, targeted delivery capabilities, and modifiable properties for optimized therapeutic outcomes. Liposomes have demonstrated significant potential in improving mitochondrial function and regulating blood glucose metabolism in diabetic mice. Wu et al. developed Nano-MitoPBN, a novel liposomal nanoparticle designed to enhance mitochondrial performance and promote hepatic oxidative metabolism (175). This formulation improves the efficiency of both glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid cycle, thereby accelerating glucose metabolism and cellular uptake. In diabetic animal models, Nano-MitoPBN effectively reduces peripheral blood glucose levels and improves glucose tolerance, representing a promising therapeutic strategy for diabetes management.
Liposomes show promise in enhancing wound healing in diabetic patients. Diabetic wounds are particularly vulnerable to bacterial infection due to persistent hyperglycemia and elevated ROS levels, which significantly impair the healing process (176). These factors interact synergistically, worsening wound progression. Conventional therapeutic approaches can provide partial symptomatic relief through oral hypoglycemic agents for blood glucose control, intravenous antibiotics for infection management, and topical antiseptics for pathogen elimination. However, these interventions often prove insufficient to fully resolve the complexity of diabetic wounds (177). While these approaches provide temporary symptom management, they typically do not address the underlying mechanisms hindering wound repair. Excessive inflammation is a key obstacle in diabetic wound healing. To address this, Tang et al. designed red blood cell-mimicking liposomes (RC-Lips) loaded with curcumin, which neutralize bacterial toxin α-hemolysin, modulate M2 macrophage polarization, and fine-tune the inflammatory response, thereby accelerating diabetic wound healing (Figure 8) (178). Similarly, Liu et al. co-encapsulated a near-infrared-II (NIR-II) photothermal agent (IRC) and curcumin into thermosensitive liposomes, creating the Cur-IRC@PCM nanoplatform for precise and effective treatment of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)-infected diabetic wounds (179). Furthermore, Wei et al. engineered Janus liposomes capable of reprogramming macrophage polarization and stimulating tissue regeneration. Using single-cell RNA sequencing and T-cell-deficient mouse models, they demonstrated the critical role of γδ T cells in M1/M2 macrophage switching (180). In summary, these liposome-based strategies represent a paradigm shift in diabetic wound management, moving from conventional symptomatic treatment to multi-mechanism-based synergistic intervention. Such platforms simultaneously address hyperglycemia, bacterial infection, oxidative stress, and immune dysregulation, demonstrating notable therapeutic superiority over traditional approaches. In the future, the efforts should focus on developing biomarker-responsive smart liposomes, optimizing combination therapies targeting multiple pathological pathways, and establishing standardized protocols for clinical evaluation of nanotherapeutics in diabetic wound healing.
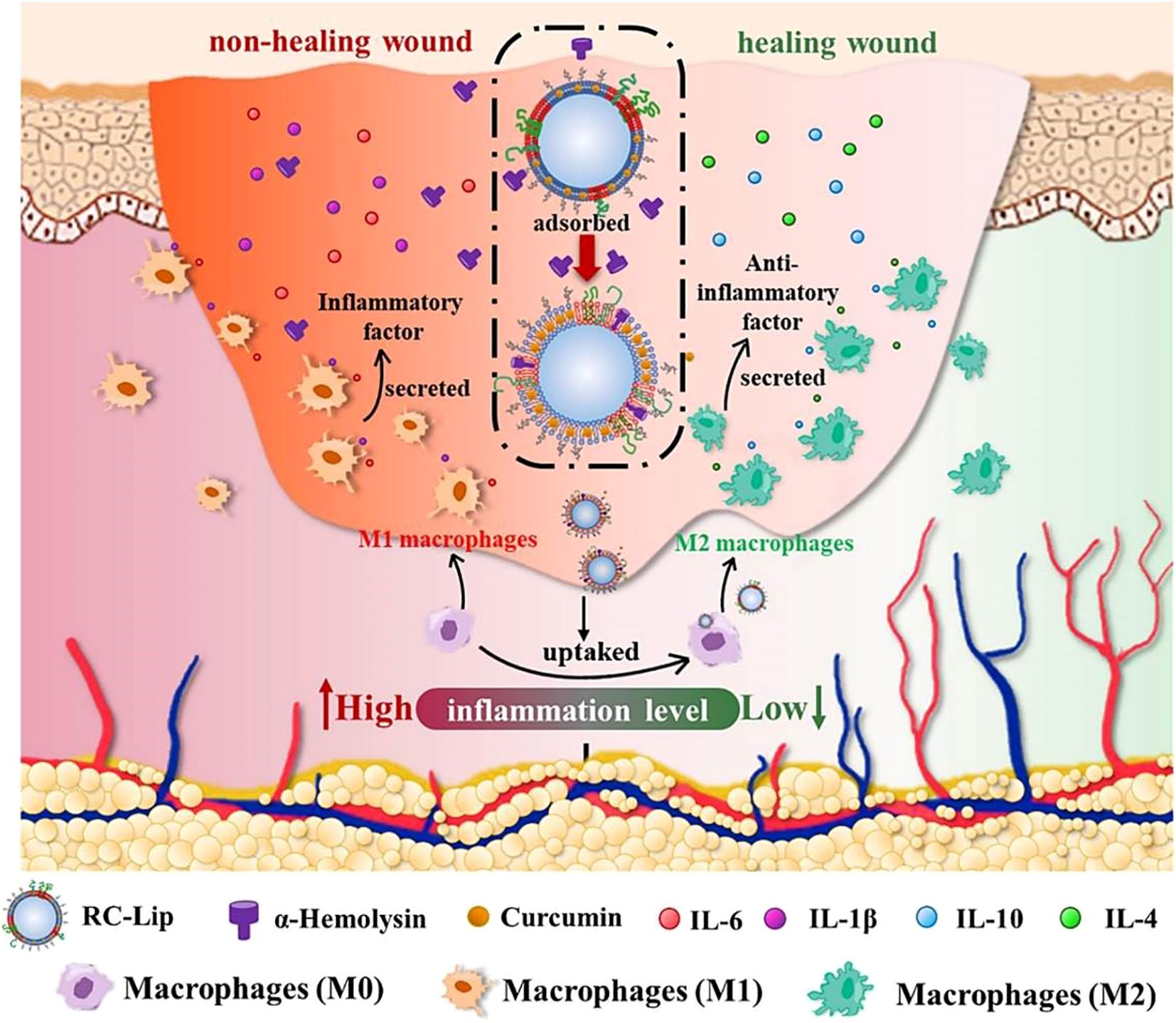
Figure 8. Mechanism of multimodal therapeutic hybrid liposomes in promoting wound healing in diabetes and infection (178).
6 Challenges and outlook
As key regulators of the innate immune system, macrophages play a dual role in the pathogenesis of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer, respiratory diseases, and diabetes. Macrophages can not only promote inflammation and tissue damage, but also participate in repair and homeostasis restoration through phenotypic polarization (e.g., transition from pro-inflammatory M1 to anti-inflammatory M2 phenotypes) (181, 182). Owing to the good biocompatibility (183), drug-loading capacity (184), and potential for targeted modification (185), liposomes have emerged as important tools for modulating macrophage functions (Table 1). However, the clinical translation of this strategy still faces multiple challenges, and future breakthroughs will require technological innovation and interdisciplinary collaboration.
The primary technical bottleneck lies in the limitations of liposomal targeted delivery and stability. First, insufficient targeting precision is a key constraint. Although surface modifications can enhance directional delivery capabilities (186), liposomes still struggle to efficiently recognize and specifically accumulate in target macrophages within highly heterogeneous in vivo environments (187), compromising treatment accuracy. Second, liposomes are susceptible to adsorption by plasma proteins, enzymatic degradation, and interference from blood components during systemic circulation, leading to structural integrity loss and premature drug leakage (188). This not only reduces reprogramming efficiency but may also increase off-target toxicity risks due to non-specific release.
Although surface modifications (e.g., antibodies, peptides) can achieve macrophage-targeted delivery, the circulation time of liposome systems is significantly compromised by rapid clearance via the reticuloendothelial system (RES), resulting in predominant accumulation in the liver/spleen and insufficient deposition at disease sites (189). Therefore, there is an urgent need to improve targeting precision. By the way, high shear stress in atherosclerotic plaques hinders the stable retention of liposomes, while in myocardial infarction models, rapid endothelial barrier repair before the peak of macrophage infiltration leads to low systemic delivery efficiency (44). Furthermore, as carriers for RNA therapies (e.g., miRNA), liposomes require substantial improvements in loading and release efficiency, facing challenges such as degradation by serum RNases and insufficient endosomal escape, which hinder cytoplasmic delivery (190). Stimuli-responsive liposomes (e.g., pH- or enzyme-sensitive types) exhibit poor spatiotemporal control in complex pathological microenvironments, often resulting in burst release or abnormal drug retention (191).
In terms of immunogenicity, although liposomes generally exhibit good biocompatibility (192), certain surface modifications or encapsulated drugs may enhance their immunogenicity. This not only facilitates rapid clearance by the immune system, reducing therapeutic efficacy, but may also trigger adverse reactions such as allergies, posing risks to patient safety. For instance, cationic liposomes, while enhancing cellular uptake, may activate the complement system and induce complement activation-related pseudoallergy (CARPA), characterized by histamine release and acute inflammation (193), presenting immunogenicity and toxicity concerns. Systemic immune activation may lead to severe immune-related adverse events, such as cytokine release syndrome (CRS), neurotoxicity, or autoimmune tissue damage (194, 195). Furthermore, a more comprehensive evaluation of the long-term safety and immunogenicity of liposome components and their metabolites is required. Additionally, excessive uptake of liposomes by macrophages may inhibit phagocytic function, impair host antimicrobial defense, and result in immunosuppression risks. Regarding long-term efficacy, data on the application of this strategy for chronic disease treatment remain limited (196). It is unclear whether the reprogrammed state can be sustained long-term or what the enduring impact on disease progression might be. Prolonged use may also lead to macrophage dysfunction and potential side effects, significantly limiting its clinical translation prospects. Moreover, there is a lack of long-term toxicity data on liposome components and their metabolites, particularly a deficiency in lifetime longitudinal safety studies.
There are also limitations in therapeutic mechanisms and disease models, since macrophage polarization regulation exhibits duality. For example, DHA- or miR-21-loaded liposomes induce M2 polarization to alleviate inflammation, but excessive suppression of the M1 phenotype in advanced plaques may impair pathogen clearance capacity and increase the risk of plaque rupture (197). Different lipid components yield significantly divergent therapeutic effects: anionic liposomes promote cholesterol efflux from foam cells (189) whereas cationic liposomes instead enhance inflammatory cytokine secretion (198). There are complexities in therapeutic strategies and clinical applications. Due to inter-patient heterogeneity in tumors (199), significant differences exist in the phenotype and distribution of TAMs among different patients (200), across various tumor types, and even within the same tumor. Universal targeting strategies may therefore fail to effectively cover all relevant immunosuppressive macrophage subsets. Furthermore, current regulatory strategies remain relatively simplistic, leading to limited efficacy or phenotypic reversal. Even if TAMs are successfully “reversed” from the M2 to the M1 phenotype via liposomes, the highly immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment may cause them to revert to a pro-tumor phenotype, resulting in transient and unsustainable therapeutic effects (201, 202). Additionally, single-target therapeutic strategies face limitations in efficacy. Most approaches focus on a single signaling pathway, but tumor immunosuppression results from complex interactions within multiple signaling networks. Blocking one pathway can easily be bypassed by compensatory mechanisms, leading to limited efficacy or drug resistance. Moreover, the complexity of combining these strategies with existing clinical treatments further complicates translation. While combination with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or immune checkpoint inhibitors is most likely, this makes clinical trial design extremely complex (203) particularly in determining the optimal dosing timing and sequence, while also increasing the risk of unpredictable synergistic toxicities. A critical translational gap exists between disease models and human pathophysiology: the immune microenvironment in mouse atherosclerosis models (e.g., ApoE-/-) differs significantly from that of human plaques (204), particularly in terms of macrophage subtype complexity. This explains why anti-inflammatory strategies successful in animal models frequently fail in clinical trials. In myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury models, due to differences in cardiovascular anatomy, the targeting efficiency of liposomes in large animals is markedly lower than in rodents, limiting the predictive value of preclinical data.
The core challenges in the clinical translation of liposomes lie in the barriers associated with production, preparation, and quality control. The manufacturing process for complex liposomes (e.g., those modified with antibodies, peptides, or exosomes) is highly intricate, making it difficult to precisely control particle size, encapsulation efficiency, and batch-to-batch consistency, which severely restricts their industrial-scale production and clinical applicability. Additionally, technologies such as directional membrane protein integration pose challenges for GMP compliance, and large-scale production entails high costs, limiting scalability. Regulatory frameworks lag behind technological advancements, and existing drug classification systems struggle to clearly define multi-component or surface-engineered liposome products, creating bottlenecks in the approval of combination therapies. Traditional RECIST criteria may fail to accurately capture delayed immune responses or changes in the immune status of the TME (205), leading to misinterpretation of early clinical trial results. Furthermore, the biological behavior of liposomal drugs is complex. The timing, location, and mechanisms of drug release remain poorly understood, and current analytical methods are inadequate for distinguishing between released drugs and those still encapsulated within the carrier, hindering precise efficacy evaluation. The production costs of targeted liposome therapies are significantly higher than those of conventional drugs, and when combined with the long-term treatment requirements for cardiovascular diseases, this imposes a substantial economic burden on healthcare payment systems.
Despite numerous challenges, liposome-mediated macrophage reprogramming holds broad clinical translation potential through multidimensional strategy optimization and interdisciplinary collaboration. First, it is essential to strengthen collaboration between pharmaceutical researchers and clinicians to identify ideal candidate drugs suitable for liposomal formulation development that address clinical needs. Second, basic research should focus on elucidating the physicochemical and biological principles underlying liposome preparation and therapeutic mechanisms. A deeper understanding of drug-lipid interactions, molecular dynamics during liposome self-assembly, and liposome-biofluid-cell interactions will facilitate the design of more efficient and safer liposomal delivery systems. Clarifying the pharmacokinetic behavior of liposomal drugs will provide critical guidance for optimizing therapeutic strategies.
In terms of design, smart targeted liposomes can be developed by utilizing targeting ligands such as aptamers (206), antibodies (207) or peptides (208) to specifically recognize macrophage surface markers, thereby enhancing targeting efficiency. Additionally, designing liposomes that respond to the disease microenvironment enables precise drug release (209). In terms of preparation processes, microfluidic technology (210, 211) shows increasingly broad prospects in liposome production. The introduction of techniques such as microfluidics (212) facilitates precise control over particle size and morphology, enabling stable and continuous large-scale manufacturing while ensuring batch consistency through real-time quality monitoring. These advanced manufacturing methods can significantly improve production efficiency and reduce costs, but rigorous quality control protocols must be established to ensure efficacy and safety standards.
In terms of therapeutic mechanism research and personalized treatment, The integration of multi-omics technologies such as transcriptomics (213), proteomics, and metabolomics (214), enables systematic elucidation of key signaling pathways and targets during the reprogramming process,. Single-cell analysis techniques (215) should be applied to uncover macrophage subset heterogeneity and differences in liposome intervention effects, providing a basis for personalized treatment. Regarding safety and efficacy, immune modulation strategies need to be developed, such as optimizing liposome surface modifications (216) to reduce immunogenicity or combining with immunomodulators to enhance therapeutic outcomes. Concurrently, long-term clinical follow-up studies should be conducted to systematically evaluate efficacy and safety, while leveraging clinical big data and artificial intelligence to optimize treatment regimens.
Finally, interdisciplinary collaboration should be strengthened by integrating expertise from biomedical science, materials science, chemical engineering, and other fields to drive technological innovation. Through deep integration of industry, academia, and research, the clinical translation and application of liposome technology in macrophage reprogramming therapy can be accelerated. Enhanced collaboration among pharmacology, clinical medicine, materials science, and regulatory science will facilitate the selection of ideal candidate drugs, optimization of treatment strategies, and advancement of regulatory frameworks. Establishing long-term follow-up study systems, combined with clinical big data and artificial intelligence, will enable systematic evaluation of efficacy and safety, ultimately achieving widespread application of liposome-mediated macrophage regulation therapy in the treatment of chronic diseases.
Looking ahead, overcoming these challenges requires a multifaceted approach. Strengthening collaboration between pharmaceutical researchers and clinical physicians is crucial. While pharmaceutical researchers focus on developing novel liposome formulations, clinicians possess deeper insights into patients’ actual needs and treatment responses. By working together, they can identify the optimal candidate drugs that meet clinical demands, ensuring liposome therapies are better aligned with real-world treatment scenarios.
Author contributions
HZ: Writing – original draft. NH: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. ZW: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. SZ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32201165), Research and Innovation Team Project for Scientific Breakthroughs at Shanxi Bethune Hospital (2024ZHANCHI09), Scientific Research Foundation of Shanxi Bethune Hospital (2021RC012).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
Non-communicable diseases, NCDs; Pulmonary fibrosis, PF; Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD; World Health Organization, WHO; Pathogen-associated molecular patterns, PAMPs; Damage-associated molecular patterns, DAMPs; Programmed cell death protein 1, PD-1; Cluster of Differentiation 47, CD47; Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1/C-C chemokine receptor type 2, MCP-1/CCR2; Resolvin D1, RvD1; Signal Regulatory Protein α, SIRPα; cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase-Stimulator of Interferon Genes, cGAS-STING; Cancer stem cell, CSC; Interferon-gamma, INF-γ; Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1, VCAM-1; Interleukin-1 beta, IL-1β; Toll-Like Receptor 4, TLR4; Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha, TNF-α; C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2, CCL2; Interleukin-6, IL-6; Cluster of Differentiation 206, CD206; Arginase-1, Arg-1; Cluster of Differentiation 36, CD36; Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, Nrf2; Interleukin-10, IL-10; Transforming Growth Factor-beta, TGF-β; Interleukin-4, IL-4; Interleukin-13, IL-13; Complement activation-related pseudoallergy, CARPA; Pattern recognition receptors, PRRs; Food and Drug Administration, FDA; Tumor-associated macrophages, TAMs; Cardiovascular diseases, CVDs; myocardial infarction, MI; myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, MIRI; Ischemia-reperfusion injury, IRI; MicroRNA-21, miR-21; Atherosclerosis, AS; ATP - binding cassette transporter A1/G1, ABCA1/G1; 3 - hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase 1, BDH1; Orosomucoid 1(ORM1; Ribosomal protein S27 – like, RPS27L; Hyaluronic acid, HA; Nitric oxide, NO; Reactive oxygen species, ROS; Vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF; Docosahexaenoic acid, DHA; Oxidized low-density lipoprotein, oxLDL; Lipopolysaccharide, LPS; Immunogenic cell death, ICD; Tumor microenvironment, TME; Tumor - associated antigens, TAAs; Photothermal Therapy, PTT; Photodynamic therapy, PDT; Radiotherapy, RT; Doxorubicin, DOX; Cancer stem cells, CSCs; Inducible nitric oxide synthase, iNOS; Metabolic diseases, MDs; Type 2 diabetes, T2D; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, NAFLD; Diabetes mellitus, DM.
References
1. Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. (2012) 380:2095–128. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0
2. Hunter DJ and Reddy KS. Noncommunicable diseases. New Engl J Med. (2013) 369:1336–43. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1109345
3. Mathers CD and Loncar D. Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PloS Med. (2006) 3:e442. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030442
4. Bloom DE, Cafiero E, Jané-Llopis E, Abrahams-Gessel S, Bloom LR, Fathima S, et al. The global economic burden of noncommunicable diseases. In: Program on the global demography of aging Geneva (2012).
5. Frodermann V and Nahrendorf M. Macrophages and cardiovascular health. Physiol Rev. (2018) 98:2523–69. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00068.2017
6. Cassetta L and Pollard JW. Targeting macrophages: Therapeutic approaches in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2018) 17(12):887–904. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2018.169
7. Byrne AJ, Mathie SA, Gregory LG, and Lloyd CM. Pulmonary macrophages: key players in the innate defence of the airways. Thorax. (2015) 70(12):1189–96. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2015-207020
8. Liu Y, Su W, Liu Z, Hu Z, Shen J, Zheng Z, et al. Macrophage CREBZF orchestrates inflammatory response to potentiate insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Advanced Sci. (2024) 11:2306685. doi: 10.1002/advs.202306685
9. Merad M and Martin JC. Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: a key role for monocytes and macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. (2020) 20:355–62. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0331-4
10. Fujiwara N and Kobayashi K. Macrophages in inflammation. Current drug targets. Inflammation Allergy. (2005) 4 3:281–6. doi: 10.2174/1568010054022024
11. Qian BZ and Pollard JW. Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell. (2010) 141:39–51. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.014
12. Wynn TA, Chawla A, and Pollard JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. (2013) 496:445–55. doi: 10.1038/nature12034
13. Murray PJ. Macrophage polarization. Annu Rev Physiol. (2017) 79:541–66. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034339
14. Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena P, Vecchi A, Locati M, et al. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. (2004) 25:677–86. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2004.09.015
15. Buckley CD. Why does chronic inflammation persist: An unexpected role for fibroblasts. Immunol Lett. (2011) 138:12–4. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2011.02.010
16. Ueha S, Shand FHW, and Matsushima K. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of chronic inflammation-associated organ fibrosis. Front Immunol. (2012) 3:71. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00071
17. Khan MSH and Hegde V. Obesity and diabetes mediated chronic inflammation: A potential biomarker in alzheimer’s disease. J Personalized Med. (2020) 10(2):42. doi: 10.3390/jpm10020042
18. Mishra A, Gill J, Mishra Y, and Medhashri S. Relationship between tumor microenviroment and development and progression of cancer: A Review. Ann Oncol. (2017) 28:vii32. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx510.004
19. Hernandez C, Huebener P, and Schwabe RF. Damage-associated molecular patterns in cancer: a double-edged sword. Oncogene. (2016) 35:5931–41. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.104
20. Quatromoni JG and Eruslanov E. Tumor-associated macrophages: function, phenotype, and link to prognosis in human lung cancer. Am J Trans Res. (2012) 4:376.
21. Tang X, Mo C, Wang Y, Wei D, and Xiao H. Anti-tumour strategies aiming to target tumour-associated macrophages. Immunology. (2013) 138:93–104. doi: 10.1111/imm.12023
22. Bardania H, Tarvirdipour S, and Dorkoosh F. Liposome-targeted delivery for highly potent drugs. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. (2017) 45:1478–89. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2017.1290647
23. Akbarzadeh A, Rezaei-Sadabady R, Davaran S, Joo SW, Zarghami N, Hanifehpour Y, et al. Liposome: classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res Lett. (2013) 8:102. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-8-102
24. Bulbake U, Doppalapudi S, Kommineni N, and Khan W. Liposomal formulations in clinical use: an updated review. Pharmaceutics. (2017) 9(2):12. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics9020012
25. Sabir F, Barani M, Rahdar A, Bilal M, and Nadeem M. How to face skin cancer with nanomaterials: A review. Biointerface Res Appl Chem. (2021) 11:11931–55. doi: 10.33263/BRIAC114.1193111955
26. Marqués-Gallego P and de Kroon AI. Ligation strategies for targeting liposomal nanocarriers. BioMed Res Int. (2014) 2014:129458. doi: 10.1155/2014/129458
27. Smith BR and Edelman ER. Nanomedicines for cardiovascular disease. Nat Cardiovasc Res. (2023) 2:351–67. doi: 10.1038/s44161-023-00232-y
28. Bauer UE, Briss PA, Goodman RA, and Bowman BA. Prevention of chronic disease in the 21st century: elimination of the leading preventable causes of premature death and disability in the USA. Lancet. (2014) 384:45–52. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60648-6
29. Nsairat H, Khater D, Sayed U, Odeh F, Al Bawab A, Alshaer W, et al. Liposomes: Structure, composition, types, and clinical applications. Heliyon. (2022) 8(5):e09394. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09394
30. Liu L, Tu B, Sun Y, Liao L, Lu X, Liu E, et al. Nanobody-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. J Controlled Release. (2025) 381:113562. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.02.058
31. Liu D, Long M, Gao L, Chen Y, Li F, Shi Y, et al. Nanomedicines targeting respiratory injuries for pulmonary disease management. Advanced Funct Materials. (2022) 32:2112258. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202112258
32. Yang Y, Chen N, Fan J, Fan L, Cai Y, Xue L, et al. Spatiotemporal immunomodulation of macrophages via NLRP3/IL-1β Pathway by core-shell microneedles to promote healing of biofilm-infected diabetic ulcers. Small. (2025) p:e2505179. doi: 10.1002/smll.202505179
33. Sanz J and Fayad ZA. Imaging of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nature. (2008) 451:953–7. doi: 10.1038/nature06803
34. Riehle C and Abel ED. Insulin signaling and heart failure. Circ Res. (2016) 118:1151–69. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.306206
35. Poller WC, Nahrendorf M, and Swirski FK. Hematopoiesis and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. (2020) 126:1061–85. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.315895
36. Terashima M, Uchida M, Kosuge H, Tsao PS, Young MJ, Conolly SM, et al. Human ferritin cages for imaging vascular macrophages. Biomaterials. (2011) 32:1430–7. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.09.029
37. Beldman TJ, Malinova TS, Desclos E, Grootemaat AE, Misiak AL, Van Der Velden S, et al. Nanoparticle-aided characterization of arterial endothelial architecture during atherosclerosis progression and metabolic therapy. ACS nano. (2019) 13:13759–74. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b08875
38. MacRitchie N, Di Francesco V, Ferreira MFM, Guzik TJ, Decuzzi P, Maffia P, et al. Nanoparticle theranostics in cardiovascular inflammation. Semin Immunol. (2021) 56:101536. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2021.101536
39. Valizadeh H, Ghanbarzadeh S, and Zakeri-Milani P. Fusogenic liposomal formulation of sirolimus: improvement of drug anti-proliferative effect on human T-cells. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. (2015) 41:1558–65. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2014.971032
40. Alavi M, Karimi N, and Safaei M. Application of various types of liposomes in drug delivery systems. Advanced Pharm Bull. (2017) 7:3. doi: 10.15171/apb.2017.002
41. Alvarez Bello M, Fraile Sanz A, Martin Munoz M, Perela Alvarez C, Nieto Ibanez D, Olsen Rodriguez R, et al. Clinical profile and prognosis of Myocardial Infarction with Non-Obstructive Coronary Arteries (MINOCA) in patients with previous Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS). Eur Heart J. (2024) 45(Supplement_1):ehae666. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae666.1710
42. Li D, Wang X, Huang Q, Li S, Zhou Y, Li Z, et al. Cardioprotection of CAPE-oNO(2) against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion induced ROS generation via regulating the SIRT1/eNOS/NF-κB pathway in vivo and in vitro. Redox Biol. (2018) 15:62–73. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.023
43. Yellon DM and Hausenloy DJ. Myocardial reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med. (2007) 357:1121–35. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra071667
44. Tan H, Song Y, Chen J, Zhang N, Wang Q, Li Q, et al. Platelet-like fusogenic liposome-mediated targeting delivery of miR-21 improves myocardial remodeling by reprogramming macrophages post myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2021) 8:e2100787. doi: 10.1002/advs.202100787
45. Dong J, Li Z, Fu C, Yang D, Yang H, Lin L, et al. Cardiosplenic axis-targeted immunomodulatory liposome for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury treatment. J Controlled Release. (2025) 383:113799. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.113799
46. Cheng J, Gao R, Lyu Y, Xiong Z, Yang K, Zhao X, et al. Homotransplantation of engineered macrophages with surface-modified nanomedicines for mitigating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. ACS nano. (2025) 19:25069–87. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5c05068
47. Tan H, Li W, Pang Z, Weng X, Gao J, Chen J, et al. Genetically engineered macrophages co-loaded with CD47 inhibitors synergistically reconstruct efferocytosis and improve cardiac remodeling post myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Advanced Healthcare Materials. (2024) 13:2303267. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202303267
48. Weng X, Tan H, Huang Z, Chen J, Zhang N, Wang Q, et al. Targeted delivery and ROS-responsive release of Resolvin D1 by platelet chimeric liposome ameliorates myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury. J Nanobiotechnology. (2022) 20:454. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01652-x
49. Che J, Najer A, Blakney AK, McKay PF, Bellahcene M, Winter CW, et al. Neutrophils enable local and non-invasive liposome delivery to inflamed skeletal muscle and ischemic heart. Advanced Materials. (2020) 32:2003598. doi: 10.1002/adma.202003598
50. Chen J, Huang ZY, and Ge JB. Mimetic nanoparticles regulate the inflammation of ischemic myocardium. Eur Heart J. (2020) 41:ehaa946. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/ehaa946.3621
51. Wang JC and Bennett M. Aging and atherosclerosis: mechanisms, functional consequences, and potential therapeutics for cellular senescence. Circ Res. (2012) 111:245–59. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.261388
52. Hansson GK and Hermansson A. The immune system in atherosclerosis. Nat Immunol. (2011) 12:204–12. doi: 10.1038/ni.2001
53. Tabas I and Bornfeldt KE. Macrophage phenotype and function in different stages of atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2016) 118:653–67. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306256
54. Wolf D and Ley K. Immunity and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2019) 124:315–27. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313591
55. Lobatto ME, Fuster V, Fayad ZA, and Mulder WJ. Perspectives and opportunities for nanomedicine in the management of atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2011) 10:835–52. doi: 10.1038/nrd3578
56. Wang Y, Zhang K, Qin X, Li T, Qiu J, Yin T, et al. Biomimetic nanotherapies: red blood cell based core–shell structured nanocomplexes for atherosclerosis management. Advanced Sci. (2019) 6:1900172. doi: 10.1002/advs.201900172
57. Boudoulas KD, Triposkiadis F, Geleris P, and Boudoulas H. Coronary atherosclerosis: pathophysiologic basis for diagnosis and management. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. (2016) 58:676–92. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2016.04.003
58. Park J, Gao H, Wang Y, Hu H, Simon DI, Steinmetz NF, et al. S100A9-targeted tobacco mosaic virus nanoparticles exhibit high specificity toward atherosclerotic lesions in ApoE–/– mice. J Materials Chem B. (2019) 7:1842–6. doi: 10.1039/C8TB02276C
59. Marchio P, Guerra-Ojeda S, Vila JM, Aldasoro M, Victor VM, Mauricio MD, et al. Targeting early atherosclerosis: a focus on oxidative stress and inflammation. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2019) 2019:8563845. doi: 10.1155/2019/8563845
60. Moubayed SP, Heinonen TM, and Tardif J-C. Anti-inflammatory drugs and atherosclerosis. Curr Opin lipidology. (2007) 18:638–44. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e3282f0ee11
61. Chistiakov DA, Melnichenko AA, Grechko AV, Myasoedova VA, and Orekhov AN. Potential of anti-inflammatory agents for treatment of atherosclerosis. Exp Mol Pathol. (2018) 104:114–24. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2018.01.008
62. Simonetto M, Infante M, Sacco RL, Rundek T, and Della-Morte D. A novel anti-inflammatory role of omega-3 PUFAs in prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis and vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Nutrients. (2019) 11:2279. doi: 10.3390/nu11102279
63. Chen J, Zhang X, Millican R, Sherwood J, Martin S, Jo H, et al. Recent advances in nanomaterials for therapy and diagnosis for atherosclerosis. Advanced Drug delivery Rev. (2021) 170:142–99. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.01.005
64. Cheraghi M, Negahdari B, Daraee H, and Eatemadi A. Heart targeted nanoliposomal/nanoparticles drug delivery: An updated review. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy. (2017) 86:316–23. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.009
65. Dai T, He W, Yao C, Ma X, Ren W, Mai Y, et al. Applications of inorganic nanoparticles in the diagnosis and therapy of atherosclerosis. Biomaterials Sci. (2020) 8:3784–99. doi: 10.1039/D0BM00196A
66. Dong X, Suo Y, Yu J, Yu F, Li F, Zheng J, et al. Biomimetic nanoparticles simultaneously targeting modulation of lipid metabolism and phenotype of macrophages for programmed atherosclerosis management. ACS Nano. (2025) 19:25628–44. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5c00216
67. Zhang Q, Ma S, Kang X, Liu Y, Ma F, Yu F, et al. A dual-targeting bio-liposomes nanodrug repair endothelial cell dysfunction and restore macrophage cholesterol flow homeostasis to treat early atherosclerosis. J Nanobiotechnology. (2025) 23:365. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03436-5
68. Peng Y, Feng W, Huang H, Chen Y, and Yang S. Macrophage-targeting Antisenescence nanomedicine enables in-Situ NO induction for Gaseous and antioxidative atherosclerosis intervention. Bioactive Materials. (2025) 48:294–312. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.02.025
69. Shen L, Jiang C, Song J, Bi Y, Chen W, Lu C, et al. Microenvironment responsive nanoplatform for targeted removal of cholesterol and reshaping inflammatory microenvironment in atherosclerotic plaques. J Control Release. (2025) 385:114000. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.114000
70. Yang A, Zhang H, Zhang H, Li N, Chen C, Yang X, et al. Pitavastatin and resveratrol bio-nanocomplexes against hyperhomocysteinemia-induced atherosclerosis via blocking ferroptosis-related lipid deposition. J Controlled Release. (2025) 381:113598. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.113598
71. Calder PC, Bond JA, Harvey DJ, Gordon S, and Newsholme EA. Uptake and incorporation of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids into macrophage lipids and their effect upon macrophage adhesion and phagocytosis. Biochem J. (1990) 269:807–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2690807
72. Shin S, Jing K, Jeong S, Kim N, Song KS, Heo JY, et al. The omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid DHA induces simultaneous apoptosis and autophagy via mitochondrial ROS-mediated Akt-mTOR signaling in prostate cancer cells expressing mutant p53. BioMed Res Int. (2013) 2013:568671. doi: 10.1155/2013/568671
73. Ali M, Heyob K, and Rogers LK. DHA suppresses primary macrophage inflammatory responses via Notch 1/Jagged 1 signaling. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:22276. doi: 10.1038/srep22276
74. Kishikawa A, Kitaura H, Kimura K, Ogawa S, Qi J, Shen WR, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits inflammation-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vivo through GPR120 by inhibiting TNF-α production in macrophages and directly inhibiting osteoclast formation. Front Endocrinol. (2019) 10:157. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00157
75. Clementi ME, Lazzarino G, Sampaolese B, Brancato A, and Tringali G. DHA protects PC12 cells against oxidative stress and apoptotic signals through the activation of the NFE2L2/HO-1 axis. Int J Mol Med. (2019) 43:2523–31. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4170
76. Dierge E, Debock E, Guilbaud C, Corbet C, Mignolet E, Mignard L, et al. Peroxidation of n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the acidic tumor environment leads to ferroptosis-mediated anticancer effects. Cell Metab. (2021) 33:1701–15. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.05.016
77. Chong SY, Wang X, van Bloois L, Huang C, Syeda NS, Zhang S, et al. Injectable liposomal docosahexaenoic acid alleviates atherosclerosis progression and enhances plaque stability. J Controlled Release. (2023) 360:344–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.06.035
78. Chong SY, Wang X, Van Bloois L, Huang C, Yu X, Sayed N, et al. Liposomal docosahexaenoic acid halts atherosclerosis progression. Eur Heart J. (2022) 43:ehac544. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac544.1229
79. Oberholzer T, Albrizio M, and Luisi PL. Polymerase chain reaction in liposomes. Chem Biol. (1995) 2:677–82. doi: 10.1016/1074-5521(95)90031-4
80. Oberholzer T, Nierhaus KH, and Luisi PL. Protein expression in liposomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (1999) 261:238–41. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.0404
81. Wu Y, Zhang Y, Dai L, Wang Q, Xue L, Su Z, et al. An apoptotic body-biomimic liposome in situ upregulates anti-inflammatory macrophages for stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques. J Controlled Release. (2019) 316:236–49. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.10.043
82. Song Y, Zhang N, Li Q, Chen J, Wang Q, Yang H, et al. Biomimetic liposomes hybrid with platelet membranes for targeted therapy of atherosclerosis. Chem Eng J. (2021) 408:127296. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127296
83. Sha X, Dai Y, Chong L, Wei M, Xing M, Zhang C, et al. Pro-efferocytic macrophage membrane biomimetic nanoparticles for the synergistic treatment of atherosclerosis via competition effect. J Nanobiotechnology. (2022) 20:506. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01720-2
84. Gao C, Liu C, Chen Q, Wang Y, Kwong CHT, Wang Q, et al. Cyclodextrin-mediated conjugation of macrophage and liposomes for treatment of atherosclerosis. J Controlled Release. (2022) 349:2–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.06.053
85. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
86. Niculescu A-G and Grumezescu AM. Novel tumor-targeting nanoparticles for cancer treatment—A review. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:5253. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095253
87. Mastrobattista E, Koning GA, and Storm G. Immunoliposomes for the targeted delivery of antitumor drugs. Advanced Drug Delivery Rev. (1999) 40:103–27. doi: 10.1016/S0169-409X(99)00043-5
88. Feng L, Gao M, Tao D, Chen Q, Wang H, Dong Z, et al. Cisplatin-prodrug-constructed liposomes as a versatile theranostic nanoplatform for bimodal imaging guided combination cancer therapy. Advanced Funct Materials. (2016) 26:2207–17. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201504899
89. Naumenko VA, Vodopyanov SS, Vlasova KY, Potashnikova DM, Melnikov PA, Vishnevskiy DA, et al. Intravital imaging of liposome behavior upon repeated administration: A step towards the development of liposomal companion diagnostic for cancer nanotherapy. J Controlled Release. (2021) 330:244–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.12.014
90. Yang L, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Li Y, Xie Z, et al. Live macrophage-delivered doxorubicin-loaded liposomes effectively treat triple-negative breast cancer. ACS Nano. (2022) 16:9799–809. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c03573
91. Gu Z, Hao Y, Schomann T, Ossendorp F, Ten Dijke P, Cruz LJ, et al. Enhancing anti-tumor immunity through liposomal oxaliplatin and localized immunotherapy via STING activation. J Control Release. (2023) 357:531–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.04.011
92. Menachem R, Nudelman I, Vorontsova A, Livneh I, Sela M, Benguigui M, et al. Bone marrow-targeted liposomes loaded with bortezomib overcome multiple myeloma resistance. ACS Nano. (2025) 19:11684–701. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c10597
93. Sheng J, Liu Y, Ding H, Wu L, Liu L, Si G, et al. Magnetic delivery of antigen-loaded magnetic liposomes for active lymph node targeting and enhanced anti-tumor immunity. Advanced Healthcare Materials. (2023) 12:2301232. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202301232
94. Yuba E, Kado Y, Kasho N, and Harada A. Cationic lipid potentiated the adjuvanticity of polysaccharide derivative-modified liposome vaccines. J Controlled Release. (2023) 362:767–76. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.10.016
95. Li W, Zhang QL, Ma XY, Zeng X, and Zhang XZ. A multi-adjuvant nanovaccine platform based on targeted delivery of specific antigens for cancer immunotherapy. Nano Today. (2024) 59:102481. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2024.102481
96. Zhou S, Song Y, Nilam A, Luo Y, Huang WC, Long MD, et al. The predominant Quillaja Saponaria fraction, QS-18, is safe and effective when formulated in a liposomal murine cancer peptide vaccine. J Controlled Release. (2024) 369:687–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.04.002
97. Liu J, Xavy S, Mihardja S, Chen S, Sompalli K, Feng D, et al. Targeting macrophage checkpoint inhibitor SIRPα for anticancer therapy. JCI Insight. (2020) 5(12):e134728. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.134728
98. Yuan D, Zhang Y, Lim KH, Leung SKP, Yang X, Liang Y, et al. Site-selective lysine acetylation of human immunoglobulin G for immunoliposomes and bispecific antibody complexes. J Am Chem Soc. (2022) 144:18494–503. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c07594
99. Arai T, Kokubo T, Tang R, Abo H, Terui A, Hirakawa J, et al. Tumor-associated neutrophils and macrophages exacerbate antidrug IgG-mediated anaphylactic reaction against an immune checkpoint inhibitor. J ImmunoTherapy Cancer. (2022) 10:e005657. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005657
100. Chou L, Callmann CE, Dominguez D, Zhang B, and Mirkin CA. Disrupting the interplay between programmed cell death protein 1 and programmed death ligand 1 with spherical nucleic acids in treating cancer. ACS Cent Sci. (2022) 8:1299–305. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.2c00717
101. Nel AE, Mei KC, Liao YP, and Liu X. Multifunctional lipid bilayer nanocarriers for cancer immunotherapy in heterogeneous tumor microenvironments, combining immunogenic cell death stimuli with immune modulatory drugs. ACS Nano. (2022) 16:5184–232. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c01252
102. Fu S, Chang L, Liu S, Gao T, Sang X, Zhang Z, et al. Temperature sensitive liposome based cancer nanomedicine enables tumour lymph node immune microenvironment remodelling. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:2248. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38014-6
103. Liu X, Liang S, Sang X, Chang L, Fu S, Yang H, et al. On-demand integrated nano-engager converting cold tumors to hot via increased DNA damage and dual immune checkpoint inhibition. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2023) 13:1740–54. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.09.004
104. Gao Z, Wang N, Ma Y, Sun H, Li M, Dai Y, et al. Targeting neutrophils potentiates hitchhiking delivery of drugs and agonists for postsurgical chemo-immunotherapy. Nano Today. (2024) 54:102096. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2023.102096
105. Liu Y, Gong L, Feng J, Xiao C, Liu C, Chen B, et al. Co-delivery of axitinib and PD-L1 siRNA for the synergism of vascular normalization and immune checkpoint inhibition to boost anticancer immunity. J Nanobiotechnology. (2025) 23:194. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03170-y
106. Chao PH, Chan V, Wu J, Andrew LJ, and Li SD. Resiquimod-loaded cationic liposomes cure mice with peritoneal carcinomatosis and induce specific anti-tumor immunity. J Controlled Release. (2024) 372:362–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.06.041
107. Yuan B, Zhang F, Yan Q, Wang W, Li Z, Du L, et al. Submicron-sized superantigen biomimetic liposomes with highly efficient pulmonary accumulation to remodel local immune microenvironment for cancer chemoimmunotherapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2025) 15:2900–14. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2025.03.019
108. Bi J, Han Y, Han X, Wu Y, Liao S, Zhang Y, et al. Activation of pyroptosis and immunogenic cell death by targeted liposomal cisplatin for enhanced chemo-immunotherapy for osteosarcoma. Nano Today. (2025) 62:102717. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2025.102717
109. Zhu T, Chen Z, Jiang G, and Huang X. Sequential targeting hybrid nanovesicles composed of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell-derived exosomes and liposomes for enhanced cancer immunochemotherapy. ACS Nano. (2023) 17:16770–86. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c03456
110. Ostroumov D, Benne N, Lozano Vigario F, Escalona-Rayo O, Dodz K, Sauer S, et al. Sequential STING and CD40 agonism drives massive expansion of tumor-specific T cells in liposomal peptide vaccines. Cell Mol Immunol. (2025) 22:150–60. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01249-4
111. Wang B, Guo R, Qiu F, Zhang Z, Lu X, Zhang H, et al. In situ vaccine “seeds” for enhancing cancer immunotherapy by exploiting apoptosis-associated morphological changes. J Controlled Release. (2025) 379:757–67. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.01.055
112. Xie XT, Guan M, Cheng K, Li Y, Zhang B, Zhou YT, et al. Programmable engineered bacteria as sustained-releasing antibody factory in situ for enhancing tumor immune checkpoint therapy. Sci Adv. (2025) 11:eadt7298. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adt7298
113. Liu Y, Xie Y, Chen Y, Duan J, Bao C, Wang J, et al. A protease-cleavable liposome for co-delivery of anti-PD-L1 and doxorubicin for colon cancer therapy in mice. Nat Commun. (2025) 16:2854. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57965-6
114. Li C, Chen G, Li T, Xie P, Ma D, Yang L, et al. Multifunctional Nanodrug-Mediated Immunotherapy in Microsatellite Stable Colorectal Cancer via Promoting m6A Modification and M1-Like Tumor-Associated Macrophages Polarization. Small Structures. (2024) 5:2400100. doi: 10.1002/sstr.202400100
115. Kuninty PR, Binnemars-Postma K, Jarray A, Pednekar KP, Heinrich MA, Pijffers HJ, et al. Cancer immune therapy using engineered ‘tail-flipping’ nanoliposomes targeting alternatively activated macrophages. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:4548. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32091-9
116. Shen W, Liu T, Pei P, Li J, Yang S, Zhang Y, et al. Metabolic homeostasis-regulated nanoparticles for antibody-independent cancer radio-immunotherapy. Adv Mater. (2022) 34:e2207343. doi: 10.1002/adma.202207343
117. Shin M, Choi YE, Yan L, Goh SH, and Choi Y. FOXM1 inhibitor-loaded nanoliposomes for enhanced immunotherapy against cancer. Chem Eng J. (2023) 454:140400. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.140400
118. Deng S, Wang J, Hu Y, Sun Y, Yang X, Zhang B, et al. Induction of therapeutic immunity and cancer eradication through biofunctionalized liposome-like nanovesicles derived from irradiated-cancer cells. J Nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22:156. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02413-8
119. Zhang B, Li N, Gao J, Zhao Y, Jiang J, Xie S, et al. Targeting of focal adhesion kinase enhances the immunogenic cell death of PEGylated liposome doxorubicin to optimize therapeutic responses of immune checkpoint blockade. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2024) 43:51. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-02974-4
120. Zheng D, Li Y, Song L, Xu T, Jiang X, Yin X, et al. Improvement of radiotherapy with an ozone-carried liposome nano-system for synergizing cancer immune checkpoint blockade. Nano Today. (2022) 47:101675. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2022.101675
121. Zhang J, Wang S, Guo X, Lu Y, Liu X, Jiang M, et al. Arginine supplementation targeting tumor-killing immune cells reconstructs the tumor microenvironment and enhances the antitumor immune response. ACS Nano. (2022) 16:12964–78. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c05408
122. Kim M, Lee JS, Kim W, Lee JH, Jun BH, Kim KS, et al. Aptamer-conjugated nano-liposome for immunogenic chemotherapy with reversal of immunosuppression. J Controlled Release. (2022) 348:893–910. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.06.039
123. Zhu X, Zheng W, Wang X, Li Z, Shen X, Chen Q, et al. Enhanced photodynamic therapy synergizing with inhibition of tumor neutrophil ferroptosis boosts anti-PD-1 therapy of gastric cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2024) 11:e2307870. doi: 10.1002/advs.202307870
124. Liu X, Zhao Z, Xu X, Yi W, Yan D, Wang D, et al. Mobilizing STING pathway via a cationic liposome to enhance doxorubicin-induced antitumor immunity. Advanced Funct Materials. (2025) 35:2416406. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202416406
125. Wang C, Zhang R, He J, Yu L, Li X, Zhang J, et al. Ultrasound-responsive low-dose doxorubicin liposomes trigger mitochondrial DNA release and activate cGAS-STING-mediated antitumour immunity. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:3877. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39607-x
126. Zhu S, He T, Wang Y, Ma Y, Li W, Gong S, et al. A hierarchically acidity-unlocking nanoSTING stimulant enables cascaded STING activation for potent innate and adaptive antitumor immunity. Theranostics. (2024) 14:5984. doi: 10.7150/thno.98272
127. Yu J, Li X, Li J, Sun N, Cheng P, Huang J, et al. Single-dose physically cross-linked hyaluronic acid and lipid hybrid nanoparticles containing cyclic guanosine monophosphate–adenosine monophosphate eliminate established tumors. ACS Nano. (2024) 18:29942–55. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c10673
128. Guo Y, Lv T, Li Z, Wei X, Yang C, Li W, et al. Acidity-activatable dynamic hybrid nanoplatforms derived from extracellular vesicles of M1 macrophages enhance cancer immunotherapy through synergistic triple immunotherapy. J Nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22:430. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02719-7
129. Ning S, Shangguan P, Zhu X, Ou X, Wang K, Suo M, et al. Pyridinium rotor strategy toward a robust photothermal agent for STING activation and multimodal image-guided immunotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer. J Am Chem Soc. (2025) 147:7433–44. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c15534
130. Ding Q, Tang W, Li X, Ding Y, Chen X, Cao W, et al. Mitochondrial-targeted brequinar liposome boosted mitochondrial-related ferroptosis for promoting checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in bladder cancer. J Controlled Release. (2023) 363:221–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.09.024
131. Cao Y, Wen E, Chen Q, Li X, and Wang Z. Multifunctional ICG-SB@Lip-ZA nanosystem focuses on remodeling the inflammatory-immunosuppressive microenvironment after photothermal therapy to potentiate cancer photothermal immunotherapy. Adv Healthc Mater. (2025) 14:e2402211. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202402211
132. Fu C, Tang L, Cao Y, Yin Y, Liu H, Feng J, et al. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles-clothed nanoparticles delivered by live macrophages for potentiating antitumor photoimmunotherapy. Chem Eng J. (2024) 499:156420. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2024.156420
133. Gao Y, Liu J, Wu M, Zhang Y, Wang M, Lyu Q, et al. Photosensitive hybrid γδ-T exosomes for targeted cancer photoimmunotherapy. ACS Nano. (2025) 19:4251–68. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c11024
134. Liu X, Liu Y, Li X, Huang J, Guo X, Zhang J, et al. ER-targeting PDT converts tumors into in situ therapeutic tumor vaccines. ACS Nano. (2022) 16:9240–53. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c01669
135. Yang Y, Liu X, Ma W, Xu Q, Chen G, Wang Y, et al. Light-activatable liposomes for repetitive on-demand drug release and immunopotentiation in hypoxic tumor therapy. Biomaterials. (2021) 265:120456. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120456
136. Liu J, You Q, Ye S, Wang J, Du R, Liang F, et al. T lymphocyte-derived immunogenic hybrid nanovesicles for immunosuppression reversion and boosted photothermal immunotherapy. Nano Today. (2024) 55:102148. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2024.102148
137. Jiang T, Jia T, Yin Y, Li T, Song X, Feng W, et al. Cuproptosis-inducing functional nanocomposites for enhanced and synergistic cancer radiotherapy. ACS Nano. (2025) 19:5429–46. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c13753
138. Qiao K, Pan Y, Zhang S, Shi G, Yang J, Zhang Z, et al. Cold exposure therapy sensitizes nanodrug-mediated radioimmunotherapy of breast cancer. ACS Nano. (2024) 18:29689–703. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c09021
139. Kuang J, Rao Z-Y, Zheng D-W, Kuang D, Huang Q-X, Pan T, et al. Nanoparticles hitchhike on monocytes for glioblastoma treatment after low-dose radiotherapy. ACS Nano. (2023) 17:13333–47. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c01428
140. Zhou Z, Li C, Li C, Zhou L, Tan S, Hou W, et al. Mitochondria-targeted nanoadjuvants induced multi-functional immune-microenvironment remodeling to sensitize tumor radio-immunotherapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2024) 11:e2400297. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400297
141. Suo M, Shen H, Lyu M, Jiang Y, Liao X, Tang W, et al. Biomimetic nano-cancer stem cell scavenger for inhibition of breast cancer recurrence and metastasis after FLASH-radiotherapy. Small. (2024) 20:e2400666. doi: 10.1002/smll.202400666
142. Yin P, Wu J, Wang L, Luo C, Ouyang L, Tang X, et al. The burden of COPD in China and its provinces: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:859499. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.859499
143. Lancet T. GBD 2017: a fragile world. Lancet. (2018) 392:1683. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32858-7
144. Weiskirchen R, Weiskirchen S, and Tacke F. Organ and tissue fibrosis: Molecular signals, cellular mechanisms and translational implications. Mol Aspects Med. (2019) 65:2–15. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2018.06.003
145. Moss BJ, Ryter SW, and Rosas IO. Pathogenic mechanisms underlying idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. (2022) 17:515–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-042320-030240
146. King TE Jr., Pardo A, and Selman M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. (2011) 378:1949–61. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60052-4
147. Gale CP, Berg DD, and Bhutani M. The Global Working Group on Cardiopulmonary Risk in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Heart J. (2024) 45(44):4676–8. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae628
148. Martin J, Townshend J, and Brodlie M. Diagnosis and management of asthma in children. BMJ Paediatrics Open. (2022) 6:e001277. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2021-001277
149. Momtazmanesh S, Moghaddam SS, Ghamari S-H, Rad EM, Rezaei N, Shobeiri P, et al. Global burden of chronic respiratory diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: an update from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. EClinicalMedicine. (2023) 59:101936. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101936
150. Peng J, Wang Q, Sun R, Zhang K, Chen Y, Gong Z, et al. Phospholipids of inhaled liposomes determine the in vivo fate and therapeutic effects of salvianolic acid B on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Controlled Release. (2024) 371:1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.05.026
151. Cheng D, Lian W, Jia X, Wang T, Sun W, Jia Z, et al. Senescent endothelial cell-derived Galectin 3 promotes silicosis through endothelial-fibroblast and endothelial-macrophage crosstalk. J Hazardous Materials. (2025) 489:137605. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.137605
152. Chen Y, Wang T, Liang F, Han J, Lou Z, Yu Y, et al. Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase prompts bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by driving macrophage M2 polarization in mice. Theranostics. (2024) 14:2794–815. doi: 10.7150/thno.94482
153. Rao L, Zhu P, Guo M, Hu M, Guo X, Du Y, et al. Nebulized inhalation of nintedanib-loaded biomimetic nano-liposomes attenuated bleomycin-induced interstitial lung fibrosis in mice. Nano Today. (2024) 56:102298. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2024.102298
154. Wang X, Wan W, Zhang J, Lu J, and Liu P. Efficient pulmonary fibrosis therapy via regulating macrophage polarization using respirable cryptotanshinone-loaded liposomal microparticles. J Controlled Release. (2024) 366:1–17. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.12.042
155. Yu C, Xu Q, Cao X, Cheng S, Zhang Z, Huang J, et al. siTGF-β1 and pirfenidone contained Ionizable-Liposomal nanodrug for enhanced treatment of Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chem Eng J. (2024) 497:154850. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2024.154850
156. Rodríguez-Roisin R and Soriano JB. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with lung cancer and/or cardiovascular disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc. (2008) 5:842–7. doi: 10.1513/pats.200807-075TH
157. Al Faraj A, Shaik AS, Afzal S, Al Sayed B, and Halwani R. MR imaging and targeting of a specific alveolar macrophage subpopulation in LPS-induced COPD animal model using antibody-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. (2014) 9:1491–503. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S59394
158. De Leo V, Ruscigno S, Trapani A, Di Gioia S, Milano F, Mandracchia D, et al. Preparation of drug-loaded small unilamellar liposomes and evaluation of their potential for the treatment of chronic respiratory diseases. Int J Pharmaceutics. (2018) 545:378–88. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.04.030
159. Mehta M, Deeksha Tewari D, Gupta G, Awasthi R, Singh H, Pandey P, et al. Oligonucleotide therapy: An emerging focus area for drug delivery in chronic inflammatory respiratory diseases. Chemico-Biological Interact. (2019) 308:206–15. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.05.028
160. Alyami MH, Ahmad MZ, Ahmad J, Abdel-Wahab BA, and Pathak K. Advances in lipid-based nanoformulations for inhaled antibiotic therapy in respiratory infections. Drug Discov Today. (2025) 30:104380. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2025.104380
161. Wu GR, Zhou M, Wang Y, Zhou Q, Zhang L, He L, et al. Blockade of Mbd2 by siRNA-loaded liposomes protects mice against OVA-induced allergic airway inflammation via repressing M2 macrophage production. Front Immunol. (2022) 13. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.930103
162. Naessens T, Schepens B, Smet M, Pollard C, Van Hoecke L, De Beuckelaer A, et al. GM-CSF treatment prevents respiratory syncytial virus–induced pulmonary exacerbation responses in postallergic mice by stimulating alveolar macrophage maturation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2016) 137:700–709.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.09.031
163. Porsbjerg C, Melén E, Lehtimäki L, and Shaw D. Asthma. Lancet. (2023) 401:858–73. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02125-0
164. An EK, Zhang W, Park HB, Kim SJ, Ryu D, Kim DY, et al. Tolerogenic dendritic cell- and M2 macrophage polarization-inducible hybrid nanoparticles alleviate asthma in mice. ACS Nano. (2025) 19:23606–19. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5c01226
165. Liu X, Zhang L, Li S, Xing L, Ni M, Huang M, et al. Harnessing surface hydrophilicity of inhalable nanoparticles for precision delivery of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists or anti-asthmatic therapeutics. ACS Nano. (2025) 19:22357–75. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5c05745
166. Zhang M, Jiang H, Wu L, Lu H, Bera H, Zhao X, et al. Airway epithelial cell-specific delivery of lipid nanoparticles loading siRNA for asthma treatment. J Controlled Release. (2022) 352:422–37. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.10.020
167. Yu Y, Ni M, Zheng Y, and Huang Y. Airway epithelial-targeted nanoparticle reverses asthma in inhalation therapy. J Controlled Release. (2024) 367:223–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.01.044
168. Shi S, Kong N, Feng C, Shajii A, Bejgrowicz C, Tao W, et al. Drug delivery strategies for the treatment of metabolic diseases. Adv Healthc Mater. (2019) 8:e1801655. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201801655
169. Hotamisligil GS and Erbay E. Nutrient sensing and inflammation in metabolic diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. (2008) 8:923–34. doi: 10.1038/nri2449
170. Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2017) 128:40–50. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.03.024
171. Rochette L, Zeller M, Cottin Y, and Vergely C. Diabetes, oxidative stress and therapeutic strategies. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2014) 1840:2709–29. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.05.017
172. Crawford K. Review of 2017 diabetes standards of care. Nurs Clin North Am. (2017) 52:621–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cnur.2017.07.010
173. Katsarou A, Gudbjörnsdottir S, Rawshani A, Dabelea D, Bonifacio E, Anderson BJ, et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2017) 3:1–17. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.16
174. Lemp JM, Bommer C, Xie M, Michalik F, Jani A, Davies JI, et al. Quasi-experimental evaluation of a nationwide diabetes prevention programme. Nature. (2023) 624:138–44. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06756-4
175. Wu M, Liao L, Jiang L, Zhang C, Gao H, Qiao L, et al. Liver-targeted Nano-MitoPBN normalizes glucose metabolism by improving mitochondrial redox balance. Biomaterials. (2019) 222:119457. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119457
176. Zhao H, Huang J, Li Y, Lv X, Zhou H, Wang H, et al. ROS-scavenging hydrogel to promote healing of bacteria infected diabetic wounds. Biomaterials. (2020) 258:120286. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120286
177. Wang S, Zheng H, Zhou L, Cheng F, Liu Z, Zhang H, et al. Nanoenzyme-reinforced injectable hydrogel for healing diabetic wounds infected with multidrug resistant bacteria. Nano Lett. (2020) 20:5149–58. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c01371
178. Tang Q, Dong M, Xu Z, Xue N, Jiang R, Wei X, et al. Red blood cell-mimicking liposomes loading curcumin promote diabetic wound healing. J Ophthalmol Clinics Res. (2023) 361:871–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.07.049
179. Liu J, Wang Y, Gao W, Cao M, Bian H, Wang S, et al. Development of D–A–D-type NIR-II photothermal agents for synergistic eradication of multidrug-resistant bacteria and promoting diabetic wound healing. Advanced Funct Materials. (2025) 35:2411986. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202411986
180. Wei T, Pan T, Peng X, Zhang M, Guo R, Guo Y, et al. Janus liposozyme for the modulation of redox and immune homeostasis in infected diabetic wounds. Nat Nanotechnology. (2024) 19:1178–89. doi: 10.1038/s41565-024-01660-y
181. Hamidzadeh K, Christensen SM, Dalby E, Chandrasekaran P, and Mosser DM. Macrophages and the recovery from acute and chronic inflammation. Annu Rev Physiol. (2017) 79:567–92. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034348
182. He W, Kapate N, Shields CW, and Mitragotri S. Drug delivery to macrophages: A review of targeting drugs and drug carriers to macrophages for inflammatory diseases. Advanced Drug Delivery Rev. (2020) 165-166:15–40. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2019.12.001
183. Gao C, Kwong CHT, Wang Q, Kam H, Xie B, Lee SMY, et al. Conjugation of macrophage-mimetic microalgae and liposome for antitumor sonodynamic immunotherapy via hypoxia alleviation and autophagy inhibition. ACS Nano. (2023) 17:4034–49. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c00041
184. Han R, Ren Z, Wang Q, Zha H, Wang E, Wu M, et al. Synthetic biomimetic liposomes harness efferocytosis machinery for highly efficient macrophages-targeted drug delivery to alleviate inflammation. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2024) 11:e2308325. doi: 10.1002/advs.202308325
185. Tie Y, Zheng H, He Z, Yang J, Shao B, Liu L, et al. Targeting folate receptor β positive tumor-associated macrophages in lung cancer with a folate-modified liposomal complex. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2020) 5:6. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0115-0
186. Liu H, Wang H, Li Q, Wang Y, He Y, Li X, et al. LPS adsorption and inflammation alleviation by polymyxin B-modified liposomes for atherosclerosis treatment. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2023) 13:3817–33. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.06.005
187. Tang Y, Tang Z, Li P, Tang K, Ma Z, Wang Y, et al. Precise delivery of nanomedicines to M2 macrophages by combining “Eat me/don’t eat me” Signals and its anticancer application. ACS Nano. (2021) 15:18100–12. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c06707
188. Guimarães D, Cavaco-Paulo A, and Nogueira E. Design of liposomes as drug delivery system for therapeutic applications. Int J Pharmaceutics. (2021) 601:120571. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120571
189. Liu H, Wang H, Li Q, Wang Y, He Y, Li X, et al. Liposome interaction with macrophages and foam cells for atherosclerosis treatment: effects of size, surface charge and lipid composition. Nanotechnology. (2021) 32:505105. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ac2810
190. Song R and Zhang L. MicroRNA-210 controls mitochondrial metabolism and protects heart function in myocardial infarction. Circulation. (2022) 145:1140–53. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.056929
191. Song Y, Jing H, Vong LB, Wang J, and Li N. Recent advances in targeted stimuli-responsive nano-based drug delivery systems combating atherosclerosis. Chin Chem Lett. (2022) 33:1705–17. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2021.10.055
192. Dymek M and Sikora E. Liposomes as biocompatible and smart delivery systems – the current state. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. (2022) 309:102757. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2022.102757
193. Mészáros T, Szénási G, Rosivall L, Szebeni J, and Dézsi L. Paradoxical rise of hemolytic complement in the blood of mice during zymosan-and liposome-induced CARPA: a pilot study. Eur J Nanomedicine. (2015) 7:257–62. doi: 10.1515/ejnm-2015-0022
194. Hamida O, Karlsson F, Lundqvist A, Gerling M, and Liu LL. Cytokine release syndrome after treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors: an observational cohort study of 2672 patients from Karolinska University Hospital in Sweden. Oncoimmunology. (2024) 13:2372875. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2024.2372875
195. Shimabukuro-Vornhagen A, Gödel P, Subklewe M, Stemmler HJ, Schlößer HA, Schlaak M, et al. Cytokine release syndrome. J Immunother Cancer. (2018) 6:56. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0343-9
196. Singh AP, Biswas A, Shukla A, and Maiti P. Targeted therapy in chronic diseases using nanomaterial-based drug delivery vehicles. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2019) 4:33. doi: 10.1038/s41392-019-0068-3
197. Zhang Y, Yan C, Dong Y, Zhao J, Yang X, Deng Y, et al. ANGPTL3 accelerates atherosclerotic progression via direct regulation of M1 macrophage activation in plaque. J Adv Res. (2024) 70:125–38. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.05.011
198. Hwang TL, Hsu CY, Aljuffali IA, Chen CH, Chang YT, Fang JY, et al. Cationic liposomes evoke proinflammatory mediator release and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) toward human neutrophils. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. (2015) 128:119–26. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.02.022
199. Pombo Antunes AR, Scheyltjens I, Duerinck J, Neyns B, Movahedi K, Van Ginderachter JA, et al. Understanding the glioblastoma immune microenvironment as basis for the development of new immunotherapeutic strategies. Elife. (2020) 9:e52176. doi: 10.7554/eLife.52176
200. Wang C, Lan X, Zhu L, Wang Y, Gao X, Li J, et al. Construction strategy of functionalized liposomes and multidimensional application. Small. (2024) 20(25):e2309031. doi: 10.1002/smll.202309031
201. Wen ZF, Liu H, Gao R, Zhou M, Ma J, Zhang Y, et al. Tumor cell-released autophagosomes (TRAPs) promote immunosuppression through induction of M2-like macrophages with increased expression of PD-L1. J Immunother Cancer. (2018) 6:151. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0452-5
202. Park JE, Dutta B, Tse SW, Gupta N, Tan CF, Low JK, et al. Hypoxia-induced tumor exosomes promote M2-like macrophage polarization of infiltrating myeloid cells and microRNA-mediated metabolic shift. Oncogene. (2019) 38:5158–73. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-0782-x
203. Huang X, Wang J, Lin W, Zhang N, Du J, Long Z, et al. Kanglaite injection plus platinum-based chemotherapy for stage III/IV non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis of 27 RCTs. Phytomedicine. (2020) 67:153154. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153154
204. Parathath S, Mick SL, Feig JE, Joaquin V, Grauer L, Habiel DM, et al. Hypoxia is present in murine atherosclerotic plaques and has multiple adverse effects on macrophage lipid metabolism. Circ Res. (2011) 109:1141–52. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.246363
205. Matos I, Martin-Liberal J, García-Ruiz A, Hierro C, Ochoa de Olza M, Viaplana C, et al. Capturing hyperprogressive disease with immune-checkpoint inhibitors using RECIST 1.1 criteria. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:1846–55. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2226
206. Wayne EC, Long C, Haney MJ, Batrakova EV, Leisner TM, Parise LV, et al. Targeted delivery of siRNA lipoplexes to cancer cells using macrophage transient horizontal gene transfer. Advanced Sci. (2019) 6:1900582. doi: 10.1002/advs.201900582
207. Li H, Somiya M, and Kuroda SI. Enhancing antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis by Re-education of tumor-associated macrophages with resiquimod-encapsulated liposomes. Biomaterials. (2021) 268:120601. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120601
208. Bai Z, Yang Y, Cui Z, Liang W, Zhang X, Zhang Z, et al. Double-targeted liposomes coated with matrix metallopeptidase-2-responsive polypeptide nanogel for chemotherapy and enhanced immunotherapy against cervical cancer. Materials Today Bio. (2025) 30:101412. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101412
209. Chen M, Miao Y, Qian K, Zhou X, Guo L, Qiu Y, et al. Detachable liposomes combined immunochemotherapy for enhanced triple-negative breast cancer treatment through reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages. Nano Lett. (2021) 21:6031–41. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c01210
210. William B, Noémie P, Brigitte E, and Géraldine P. Supercritical fluid methods: An alternative to conventional methods to prepare liposomes. Chem Eng J. (2020) 383:123106. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123106
211. Li C and Deng Y. A novel method for the preparation of liposomes: freeze drying of monophase solutions. J Pharm Sci. (2004) 93:1403–14. doi: 10.1002/jps.20055
212. Liu Y, Yang G, Hui Y, Ranaweera S, and Zhao CX. Microfluidic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Small. (2022) 18:2106580. doi: 10.1002/smll.202106580
213. Shen Y, Zheng Z, Hu X, Zhou Z, Xu Y, Wang S, et al. Nanodelivery of Y-27632 by RGD-modified liposome enhances radioimmunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma via tumor microenvironment matrix stiffness reprogramming. Theranostics. (2025) 15:8569–86. doi: 10.7150/thno.114892
214. Barnholtz-Sloan JS. BIOM-20. PROTEOMICS PROVIDES POTENTIAL THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES TO GLIOBLASTOMA TREATMENT: RESULTS FROM THE CLINICAL PROTEOMICS TUMOR ANALYSIS CONSORTIUM (CPTAC). Neuro-Oncology. (2020) 22:ii6. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noaa215.020
215. Li X, Liu W, Yan Z, Jiang X, Gao Y, Jin H, et al. Modulating autophagy in the tumor microenvironment with a salinomycin-loaded liposome hybrid nanovesicle system for tumor immunotherapy. Nano Today. (2025) 61:102644. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2025.102644
Keywords: liposome, macrophage, chronic diseases, nanomedicines, inflammation
Citation: Zhang H, Hu N, Wang Z and Zhai S (2025) Liposome-mediated macrophage reprogramming: emerging strategies for chronic disease therapy. Front. Immunol. 16:1653642. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1653642
Received: 25 June 2025; Accepted: 29 September 2025;
Published: 17 October 2025.
Edited by:
Qihui Zhou, University of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences, ChinaReviewed by:
Pramod Kumar Gupta, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC), IndiaDivya Suares, SVKM’s Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies, India
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Hu, Wang and Zhai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shaodong Zhai, emhhaXNoYW9kb25nQHN4YnFlaC5jb20uY24=
 Hongnv Zhang
Hongnv Zhang Nan Hu1
Nan Hu1 Zhenghao Wang
Zhenghao Wang Shaodong Zhai
Shaodong Zhai