- 1The First School of Clinical Medicine, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China
- 2Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, The First Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) drives immune dysregulation through its hallmark stressors—intermittent hypoxia (IH) and sleep fragmentation (SF). Beyond impaired sleep, OSA acts as a systemic inflammatory trigger that disrupts immune homeostasis and reshapes both innate and adaptive responses. Recent evidence shows that OSA activates hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), NF-κB signaling, and the NLRP3 inflammasome, promoting chronic inflammation and immune-cell dysfunction. These alterations mechanistically contribute to OSA-associated cardiovascular disease, metabolic disorders, cognitive impairment, and tumor progression. Reframing OSA as an immune-modulating disorder highlights the need for diagnostics and therapies guided by immunology rather than airway management alone.
1 Introduction
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a sleep disorder characterized by recurrent upper airway obstruction, leading to apnea or hypoventilation, which leads to IH, nocturnal awakenings, daytime sleepiness, and cognitive impairment. Approximately 936 million people worldwide between the ages of 30 and 69 are affected by OSA, including about 176 million in China, corresponding to a prevalence rate of approximately 8.8% (1). As metabolic syndrome rates rise, the number of individuals suffering from OSA is also rising, making it a significant public health issue. Risk factors for OSA include obesity, age, anatomical features (e.g., large tongue and short, thick neck), family history, and conditions like hypertension and diabetes may increase the risk of OSA by influencing upper airway obstruction or sleep quality. The apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) is currently the main indicator for assessing the severity of OSA. An AHI of 5–15 events per hour is considered mild, 15–30 events per hour is moderate, and ≥30 severe. OSA’s pathophysiology involves IH, sleep architecture disruption, and abnormal sympathetic nervous system activation. This disorder not only affects sleep quality but also leads to various systemic health issues, including cardiovascular and metabolic conditions, neurocognitive dysfunction, and even multi-organ and multi-system dysfunction (2–8). The complex pathophysiological mechanisms associated with OSA are commonly linked to oxidative stress induced by IH, ongoing inflammatory cascades, molecular-level alterations, and increased sympathetic nervous activity (9). Recent research has increasingly explored the intricate relationship between OSA and the immune system, which contributes to the elevated risk of chronic inflammation, cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndrome, neurocognitive disorders, and other related conditions. The involvement of immune responses in OSA has become more prominent. Furthermore, the bidirectional relationship between immune dysregulation and OSA also impacts disease progression and management.
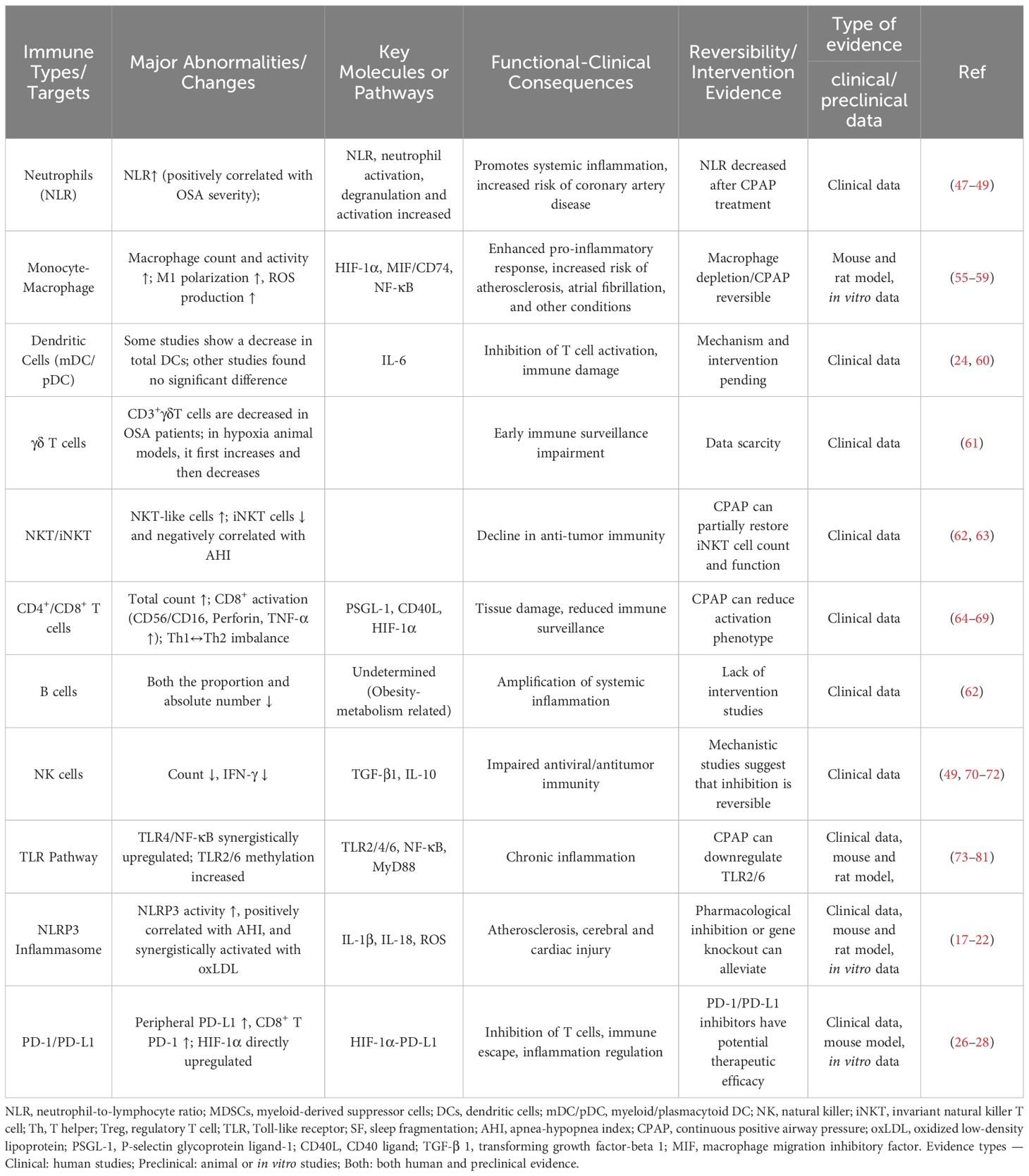
We systematically searched the PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science Core Collection databases for literature published between January 1, 1990, and January 30, 2025. The search terms combined Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) with free-text keywords, including “Obstructive Sleep Apnea” OR “OSA,” “Intermittent Hypoxia” OR “IH,” “Sleep Fragmentation” OR “SF,” “Immune” OR “Inflammation” OR “Immune Dysregulation” OR “Immune Response,” “Cardiovascular” OR “Metabolic” OR “Cognitive” OR “Cancer” OR “Comorbidity,” and “CPAP” OR “Immunotherapy.” We used Boolean operators (AND/OR) to combine the search terms, for example: “Obstructive Sleep Apnea” OR OSA AND (“Immune” OR “Inflammation” OR “Immune Dysregulation”) AND (“Cardiovascular” OR “Metabolic” OR “Cognitive” OR “Cancer” OR “Comorbidity”). Only peer-reviewed English-language articles, including original research, clinical studies, and relevant reviews, were included. Additionally, we manually searched the reference lists of the included articles to further identify potentially relevant studies. This review aims to examine the pathophysiological connections between OSA and immune dysfunction, highlighting the immune system’s critical role in OSA-related comorbidities. A better understanding of the relationship between OSA and immune responses will help clinicians manage patients more effectively, support the development of new treatments, provide more comprehensive treatment strategies for OSA patients. Figure 1 provides an overall overview of the review’s content, illustrating the key pathophysiological connections between OSA and immune dysfunction, as well as the role of the immune system in OSA-related comorbidities.
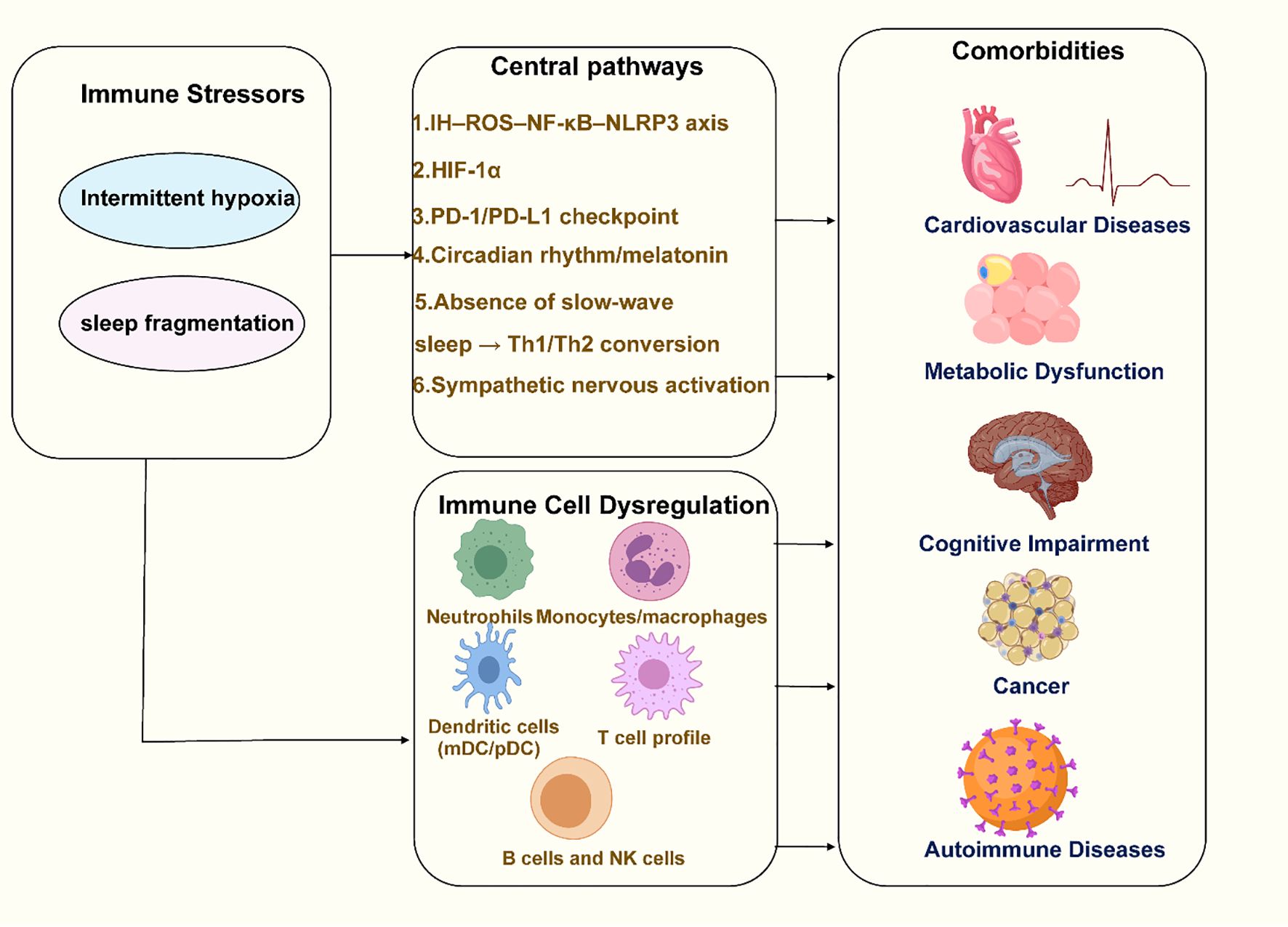
Figure 1. Overview of the pathophysiological connections between OSA and immune dysfunction. Created with MedPeer (medpeer.cn). Icons adapted and used under an institutional license for academic publication.
2 Immune stressors induced by OSA
Immune stressors induced by OSA refer to key stimuli triggered directly by the pathophysiological processes of OSA that activate the immune system. These stressors drive chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation through various molecular and cellular mechanisms, becoming central contributors to OSA-related comorbidities (Figure 2). The following are the major immune stressors and their mechanisms of action:
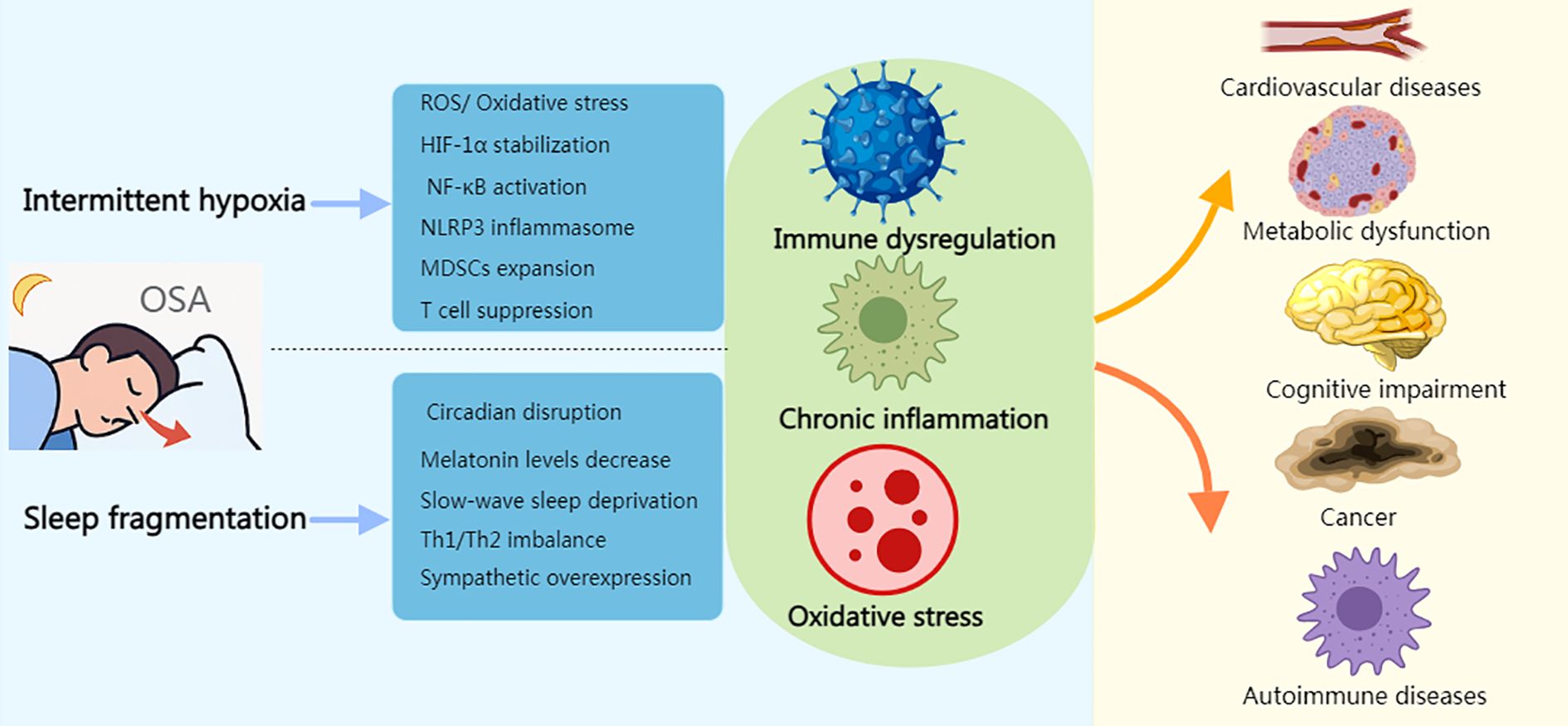
Figure 2. Immune stress response induced by OSA. Created with MedPeer (medpeer.cn). Icons adapted and used under an institutional license for academic publication.
2.1 Intermittent hypoxia
2.1.1 IH–ROS–NF-κB–NLRP3 axis
IH induced by OSA activates oxidative stress, metabolic, and immune pathways, leading to cumulative molecular and cellular damage, ultimately causing dysfunction and cell death (10). IH suppresses antioxidant defenses, raises ROS, and activates pro-inflammatory transcription factors such as NF-κB, creating a vicious cycle in which ROS both damages macromolecules and amplifies inflammation (11, 12). Phagocyte respiratory bursts and mitochondria-derived injury further increase ROS, reinforcing this feedback loop (13–15). In OSA patients, the alternating hypoxia and reoxygenation exacerbate ROS accumulation, leading to ATP depletion, calcium homeostasis disruption, and enhanced synthesis of pro-inflammatory factors and nitric oxide, impairing immune function (16). The NLRP3 inflammasome, activated by ROS, plays a central role in this cycle by promoting iNKT -1β maturation and triggering innate immunity (17). In severe OSA, NLRP3 activity is elevated, correlating with the AHI and hypoxia index. In vitro, OSA plasma enhances NLRP3 expression under both normoxic and hypoxic conditions, while oxLDL under IH further activates NLRP3 and IL-1β production (18, 19). Chronic IH upregulates NLRP3, and genetic or pharmacological inhibition reduces inflammation and oxidative stress in tissues (19–21). NLRP3-/- mice show reduced IL-1β secretion under IH, confirming the critical role of NLRP3 in IH-mediated inflammation (21, 22). This establishes the IH–ROS–NF-κB–NLRP3 axis, linking oxidative stress and inflammation in OSA-related pathogenesis (see Section 3.7 for related phenotypes and clinical associations).
2.1.2 HIF-1α-mediated metabolic reprogramming and immune suppression
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) is a transcription factor made up of α and β subunits, where HIF-1β is stably expressed in the nucleus and is not regulated by oxygen concentration, whereas HIF-1α is found in the cytoplasm, and its stability is highly dependent on oxygen levels. Under normoxic conditions, HIF-1α is rapidly degraded, but under hypoxic conditions, it accumulates and translocates to the nucleus, where it binds to HIF-1β to form a transcriptionally active HIF-1 complex, which then initiates the expression of downstream target genes (23). A study by Xie et al. observed differences in the immune cell response to hypoxia in the peripheral blood of OSA patients, with the response intensity being positively correlated to the level of hypoxia (24). Further mechanistic studies revealed that IH can mediate significant immunosuppressive effects through multiple HIF-1α-dependent signaling pathways, including inducing lactate accumulation and metabolic pathway remodeling in the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME), inhibiting T cell proliferation and cytokine production, weakening T cell infiltration into tumor tissues, while promoting the expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and suppressing the antitumor functions of CD8+ T cells and natural killer (NK) cells (25).
2.1.3 PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint
Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) and its ligand programmed death-ligand 1(PD-L1) constitute a key inhibitory axis that maintains T cell quiescence (26). HIF-1α can bind to the hypoxia response element in the PD-L1 promoter and directly regulate its transcriptional expression (27). Polasky et al. found that PD-L1 expression on peripheral monocytes and PD-1 expression on CD8+ T cells are significantly elevated in OSA patients (28) (see Section 3.8 for related phenotypes and clinical associations).
2.2 Sleep fragmentation
2.2.1 Circadian rhythm/melatonin pathway
Serum melatonin levels progressively decrease with the severity of OSA (29). Melatonin exerts its anticancer potential through various mechanisms, including inhibiting cell proliferation, scavenging ROS, promoting apoptosis, antagonizing estrogen effects, and suppressing angiogenesis (30). Additionally, it contributes to immune regulation and anti-inflammatory effects by suppressing the NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway and activating T cells, B cells, and macrophages, thereby further enhancing its antitumor effects (31).
2.2.2 Absence of slow-wave sleep → Th1/Th2 conversion
Sleep is a key regulator of endocrine, metabolic, and immune homeostasis; its disruption accelerates the development and progression of chronic disease (32). Regular sleep preserves immune integrity and defenses against pathogens and inflammation, whereas circadian misalignment or poor sleep quality disrupts immune balance and elevates infection and inflammation risk (33, 34). In OSA, prolonged sleep fragmentation (SF) weakens immune defense and amplifies systemic inflammation; together with intermittent hypoxia (IH), SF synergistically triggers and sustains inflammation—the core pathological feature of OSA (35, 36). Physiologically, early-night slow-wave sleep (SWS) features nadir cortisol and peaks in growth hormone, prolactin, and aldosterone, a milieu that supports Th1-type responses and antimicrobial defense (37). However, slow-wave activity (SWA) is significantly suppressed in moderate–severe OSA and reduced with abnormal dissipation even in mild OSA (38, 39). Loss of SWS also raises cerebrospinal fluid β-amyloid (Aβ), linking sleep disruption to cognitive impairment (40, 41). Experimentally, sleep deprivation shifts immunity from Th1 to Th2 dominance, and older adults with insufficient SWS show a similar Th2 bias—changes that compromise anti-infective and antitumor surveillance (42–44).
2.2.3 Sympathetic nervous activation
Activation of the sympathetic nervous system can inhibit the transcription of type I interferons (IFN-α/β) and their response genes, thereby weakening antiviral immunity (45). β-adrenergic receptor signaling can reduce T cell antitumor functions and has been shown in vitro to suppress Th1 responses while promoting Th2 responses (46). However, the causal relationship between SF-related immune phenotypes and sympathetic nervous system activation still requires further validation.
3 Immune cell dysregulation and regulation in OSA (phenotypes and evidence)
3.1 Neutrophils
The Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) is a key indicator of inflammation. Studies have shown that NLR levels in OSA patients are significantly higher than in healthy populations and are positively correlated with OSA severity. Additionally, NLR has been confirmed to have an independent association with coronary artery disease (47). Notably, in OSA patients treated with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), NLR values significantly decrease (48). This may be related to the activation and degranulation of neutrophils in the peripheral blood of OSA patients (49). In clinical practice, the reduction in NLR and its consistency depend on the quality of treatment: when compliance is adequate and residual events are well controlled, the decline is more significant and persistent. However, when compliance is poor, the follow-up period is short, or hypoxia persists, the changes in NLR are often not obvious. Residual heterogeneity may also stem from differences in research design, the composition of the subject population (especially the strong modifying effect of obesity/visceral fat on myeloid inflammation), concurrent infection or medication, and sampling/analysis variations, etc. Overall, the existing evidence supports that CPAP has an anti-inflammatory effect in reducing NLR. Meanwhile, it is suggested that when interpreting NLR, compliance indicators and hypoxia load endpoints (such as T90%, the lowest SaO2, ODI) should be combined, rather than relying solely on AHI.
3.2 Monocytes/macrophages (M1/M2 polarization)
Macrophages are widely distributed across tissues, and many originate from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) that migrate and differentiate into macrophages. Whether under physiological homeostasis or inflammatory stimuli, PBMCs can migrate to tissues and transform into macrophages (50). These blood-derived precursors of macrophages—monocytes—originate from hematopoietic stem cells during embryonic development and from the bone marrow in adults (51). Although most tissue-resident macrophages come from embryonic precursors, under specific conditions, circulating monocytes can also differentiate into tissue-resident macrophages with self-renewal capabilities (52). As key effector cells of the immune system, macrophages are responsible for clearing senescent cells, foreign particles, microorganisms, and tumor cells (53). Through their ability to phagocytose pathogens, recruit and regulate other immune cells, macrophages not only play a central role in host defense but also critically regulate the development of inflammation and degenerative diseases (54).
Studies have shown that following 4 weeks of continuous IH exposure, male mice exhibit a significant increase in pulmonary macrophages and ROS production (55). Macrophages are classified into two functionally distinct types: M1 (pro-inflammatory) and M2 (anti-inflammatory/repair) types (56). OSA promotes significant infiltration of M1 macrophages into subcutaneous adipose tissue and their accumulation within the aortic wall in chronic OSA mouse models, reflecting their critical role in systemic inflammation (57, 58). Mechanistically, OSA induces upregulation of HIF1α in atrial muscle cells through hypoxia/reoxygenation, which in turn enhances the expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). MIF binds to CD74 on macrophage surfaces, activating the NF-κB pathway and promoting M1 polarization. Polarized M1 macrophages release inflammatory cytokines, exacerbating atrial remodeling and increasing susceptibility to atrial fibrillation (AF). Macrophage depletion can reverse this process (59).
3.3 Dendritic cells (mDC/pDC)
Dendritic cells (DCs) play a crucial role in the immune system. However, there is still controversy regarding whether there is a reduction in DCs in OSA patients and the immune damage associated with this reduction. A study by Calati et al. reported a significant decrease in all DC subsets in the peripheral blood of OSA patients, particularly myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs). Furthermore, the reduction in DCs was concomitant with elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines and negatively correlated with IL-6 expression, thereby impairing the body’s ability to activate T cells (60). However, recent studies show no significant differences between the OSA group and healthy controls in the numbers of mDCs, pDCs, and the mDC/pDC ratio. Additionally, no significant correlation was found between the numbers of mDCs and pDCs and the AHI or the lowest oxygen saturation levels in OSA patients (24). This contradiction may stem from multiple factors: (i) Differences in research design and sample size (cross-sectional vs longitudinal, small sample single-center, and lack of parallel controls) lead to insufficient statistical power. (ii) Population heterogeneity (age, gender, smoking, and coexisting cardiometabolic diseases), especially obesity/visceral fat, has a significant modifying effect on the DC phenotype and circulation level; (iii) The methods of quantifying disease burden are inconsistent (only using AHI, without including indicators closer to hypoxia burden such as T90%, the lowest SaO2 or ODI), which may underestimate the DC changes associated with hypoxia; (iv) Treatment status and sampling time points (whether CPAP has been used previously, compliance, morning/evening blood collection, and circadian rhythm) can all affect DC count and activation phenotype. (v) Biological distribution and redistribution: Inflammation or tissue hypoxia can promote the migration of DC from peripheral blood to tissues (upper airway mucosa or adipose tissue), resulting in a decrease in peripheral blood count rather than a reduction in total volume. The above-mentioned methodological and biological heterogeneity jointly drive the contradictory conclusions about DC changes in the literature.
3.4 Abnormal T cell profile
OSA significantly impacts the immune system, particularly T cell populations. γδT cells and natural killer T cells (NKT), which link innate and adaptive immunity, show specific alterations in OSA patients. Studies reveal a reduction in perforin-positive CD3+γδT cells in peripheral blood, with their inhibitory effect increasing as oxygen saturation decreases (61). Animal models demonstrate initial activation of CD3+γδT cells in hypoxic environments, followed by a decrease. iNKT cells are reduced in OSA patients, with the reduction correlating with disease severity, while NKT-like cells increase in peripheral blood (62, 63). Additionally, changes are observed in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, key cells of adaptive immunity. OSA patients show increased numbers of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, with CD8+ T cells exhibiting an activated phenotype, especially subsets expressing natural killer receptors CD56 and CD16, which exhibit stronger cytotoxicity (62–64). OSA promotes a type 2 cytokine dominance in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, enhancing their cytotoxicity and upregulating NK receptors, CD40L, perforin, and TNF-α (65, 66). In severe OSA, IH induces upregulation of PSGL-1 on T cells, impairing immune function and surveillance (67). CPAP treatment reduces the activation and cytotoxicity of these cells, with a decrease in total lymphocyte and CD4+ lymphocyte counts after 6 months, suggesting a reversal of immune activation in compliant patients (62, 65, 68). Studies on Th1/Th2 immune imbalance in OSA are inconsistent, with some showing Th1 cytokine activation and others indicating Th2 dominance linked to sleep disturbances and elevated catecholamines (65, 69).
3.5 B cells and NK cells
Studies show that both the proportion and number of B cells are significantly reduced in OSA patients, which is closely associated with metabolic disorders and obesity. B cell depletion appears to promote systemic inflammation (62). NK cells, essential for antiviral and antitumor responses, also play a critical role in maintaining the balance between innate and adaptive immunity (70, 71). In non-obese OSA patients, NK cell counts and IFN-γ levels are significantly lower compared to healthy controls, while infiltration of T cell subpopulations increases. Mechanistic studies show that IH upregulates TGF-β1 and IL-10 in human CD14+ monocytes, indicating a phenotypic shift that inhibits NK cell activity (72). OSA is strongly linked to immune system changes, with T cell activation and imbalance being key factors. CPAP treatment shows some reversing effects on these immune abnormalities.
3.6 Pattern recognition receptors phenotypes (TLR pathway)
Toll-like receptors (TLRs), as key components of the innate immune system, are crucial for recognizing pathogens and for initiating and sustaining systemic inflammatory cascade. Inhibiting TLR function can attenuate pro-inflammatory responses. OSA patients often exhibit concurrent upregulation of TLR4 and NF-κB, which together form the core axis of chronic IH-induced inflammatory responses (73–77). TLR4, as a typical pattern recognition receptor, can recognize pathogen signals or damage-associated molecular patterns, and through the adaptor protein MyD88, initiates a signaling cascade that rapidly activates NF-κB, leading to the expression of diverse inflammatory mediators (78, 79). In OSA patients, TLR2/6 expression is upregulated on immune cells, and this change correlates with the AHI. This may be explained by increased TLR2 promoter methylation and TLR6 gene body methylation accompanied by elevated protein expression. Chronic IH in vitro also induces upregulation of TLR2/6. These changes can be reversed by CPAP treatment (80, 81).
3.7 NLRP3 inflammasome
In severe OSA, NLRP3 activity in monocytes is elevated and positively correlates with the AHI and the hypoxia index. Under IH conditions, oxLDL or patient plasma can synergistically enhance NLRP3 activation and IL-1β production. Animal models show that genetic or pharmacological inhibition can alleviate brain, cardiovascular inflammation, and oxidative stress (18–22).
3.8 Immune checkpoint (PD-1/PD-L1)
In OSA patients, PD-L1 expression on peripheral monocytes and PD-1 expression on CD8+ T cells are elevated. The upregulation of PD-L1 transcription is mediated by HIF-1α, as detailed in section 2.1.3. This axis suggests a potential relevance to immunotherapy (27, 28).
The key points are summarized in Table 1.
4 Comorbidities associated with immune cluster changes in OSA
4.1 Cardiovascular diseases in OSA
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory condition caused by lipid metabolism disorders and abnormal adaptive immune responses (82). OSA triggers the following pathological cascade through IH:
IH first activates inflammatory pathways, directly damaging the vascular endothelium and contributing to OSA-associated hypertension and atherosclerosis (83). At the same time, sympathetic nervous system activation increases blood pressure and heart rate (84), promotes the extravasation of bone marrow progenitor cells, monocytosis, and upregulates inflammatory factors, further exacerbating endothelial dysfunction, amplifying systemic inflammation, and accelerating the formation and progression of atherosclerotic plaques (85).
In OSA-related immune dysregulation, multiple cellular pathways synergistically trigger vascular pathology: first, exosome-mediated intercellular communication enhances immune activation—B cells release exosomes carrying MHC-II-peptide complexes that directly stimulate CD4+ T cells (86); cardiovascular-associated cells, such as platelets, red blood cells, endothelial cells, monocytes/macrophages, and smooth muscle cells, release extracellular vesicles (EVs) that remodel macrophage phenotypes and inflammatory secretion, playing a continuous role in the development of atherosclerosis and hypertension (87–89).
Monocyte-macrophage system dysregulation constitutes the core pathological basis of vascular damage, where the signaling exchange between endothelial cells and monocytes/macrophages is not only a key link in maintaining cardiovascular homeostasis but also a core regulatory mechanism driving atherosclerosis (90). Specifically, IH mediates immune imbalance through dual pathways: 1) IH upregulates IL-6, driving macrophages to infiltrate adipose tissue and polarize to the pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype, inducing adipose inflammation and exacerbating insulin resistance and atherosclerosis (91); 2) IH simultaneously enhances CCR5 expression on monocytes, increasing their endothelial adhesion and chemotaxis to accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis (92). Meanwhile, T cell profile imbalance further aggravates the pathology—OSA patients show a significant increase in Th17 cell proportions, indicating that this subset plays a pathogenic role in inflammation-driven atherosclerosis (93). Ultimately, exosome-mediated immune activation, monocyte-macrophage dysregulation, and Th17 immune skewing collaboratively form the immunological network underlying OSA-IH-induced vascular damage.
Additionally, OSA exacerbates vascular damage by synergistically amplifying inflammatory signaling pathways: under sleep deprivation and IH, TLRs on macrophages are activated, inducing the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines like TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6, which cause endothelial dysfunction and initiate atherosclerosis (94). Clinical histological evidence shows that in moderate to severe OSA patients, TLR2, TLR4, TLR9, RAGE are elevated in carotid plaques, further emphasizing the critical role of the TLR-RAGE axis in OSA-related plaque formation (95). At the same time, the persistent activation of NF-κB upregulates miR-155 and miR-210, driving NLRP3 inflammasome formation and triggering inflammatory cascades, aggravating myocardial damage and vascular dysfunction (96).
Oxidative stress is closely associated with the loss of protective mechanisms, with melatonin playing a protective role by reducing oxidative stress and the generation of inflammatory factors in immune and vascular cells, as well as inhibiting the progression of atherosclerosis. Therefore, the decrease in melatonin levels caused by sleep deprivation weakens its antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-atherosclerotic effects, which may be a potential mechanism for inducing vascular damage (97). Further in vivo evidence shows that the diversity of macrophages in arterial plaques is highly correlated with their continued exposure to lipids and their oxidized derivatives (98) (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Immune-related mechanisms of atherosclerotic plaque formation induced by OSA. Created with MedPeer (medpeer.cn). Icons adapted and used under an institutional license for academic publication.
For clinicians, several practical insights emerge from current evidence. First, circulating exosome profiles (particularly B-cell–derived exosomes and EVs from vascular cells) and altered monocyte/macrophage phenotypes may serve as candidate biomarkers for early detection of OSA-associated atherosclerosis. Second, elevated Th17/Treg imbalance and upregulation of inflammatory mediators (e.g., IL-6, TNF-α, CCR5 expression) could provide threshold indicators for initiating early anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory interventions. Finally, reduced melatonin levels in OSA patients highlight the potential value of adjunctive antioxidant strategies in mitigating vascular injury.
4.2 Metabolic dysfunction in OSA
OSA patients are often at increased risk for metabolic issues like insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and dyslipidemia. Studies have shown that their adipose tissue exhibits inflammatory responses and functional impairments (99–102). It is important to emphasize that both IH and SF can independently contribute to metabolic disorders. Short-term exposure to IH has been found to decrease insulin sensitivity in healthy individuals (103, 104). In mouse models, although chronic hypoxia leads to weight gain, IH induces weight loss; however, both exacerbate visceral white adipose tissue (VWAT) inflammation and trigger metabolic disorders and insulin resistance. VWAT activates macrophages and spreads inflammatory signals through adipocyte-derived exosomes, which are key effectors in this pathological chain (105). Furthermore, substantial evidence from both human and rodent models consistently suggests that IH intervention disrupts systemic metabolic balance, but its specific mechanisms and key metabolic organs remain unclear (106–110). This also partly explains why OSA prevalence is higher in individuals with type 2 diabetes and hyperlipidemia (110). Notably, macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) play a crucial regulatory role in innate immunity and can mediate inflammatory responses in specific metabolic tissues like VWAT. Under normal physiological conditions, EVs secreted by phagocytes are the major component of circulating EVs and carry molecular markers with protective effects against insulin resistance (IR). However, when the secretory cells are exposed to the abnormal environment caused by OSA, these protective features change, triggering IR within VWAT. In obese individuals with impaired metabolic function, VWAT typically shows extensive infiltration of immune cells such as macrophages (110, 111). The proportion and absolute number of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages are significantly elevated, further exacerbating adipose tissue inflammation (112). Studies also indicate that exosomes released from adipocytes in obese individuals can activate tissue-resident macrophages in adipose tissue and induce them to secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby promoting insulin resistance (113). Existing evidence suggests that metabolic disorders and insulin resistance disrupt the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediators in macrophages, initiating a positive feedback loop that intensifies inflammatory macrophage activation and ultimately further impairs adipocyte function (110).
From a clinical perspective, several practical points should be considered. First, circulating extracellular vesicles—particularly macrophage- or adipocyte-derived EVs—may serve as emerging biomarkers for early detection of insulin resistance and adipose inflammation in OSA patients. Second, monitoring the M1/M2 macrophage ratio in visceral adipose tissue could provide a threshold indicator of metabolic deterioration and help stratify patients at higher risk of diabetes. Finally, recognizing OSA-related declines in insulin sensitivity even in non-obese individuals highlights the importance of early screening and timely initiation of metabolic interventions in this population.
4.3 Cognitive impairment associated with OSA
Several studies have clearly identified cognitive impairment as one of the major complications of OSA (114), and the cognitive decline process in OSA patients shares certain similarities with the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (115). Notably, OSA is more common in patients with cognitive impairment (116). In OSA patients, peripheral inflammation can trigger central nervous system inflammation by disrupting the blood-brain barrier or transmitting via the vagus nerve (117). Subsequently, infiltrating neutrophils form extracellular traps (NETs), further damaging the blood-brain barrier and activating microglial cells, ultimately impairing neurocognitive function (118). Additionally, IH promotes the damage of mitochondria, the release of mtROS and mtDNA, facilitates NLRP3 inflammasome assembly, activates caspase-1 and IL-1β release, and accumulates pro-inflammatory cytokines, which produce more mtROS, thereby triggering neuronal apoptosis and impairing hippocampus-dependent learning and memory functions (20). Another study also found that neuroinflammation triggers autophagy-lysosomal dysfunction, activating the NLRP3-caspase-1 inflammasome in the hippocampus of mice and BV2 cells, closely related to neuronal damage (119). Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), the primary treatment for OSA, can rapidly improve blood oxygen saturation and cognitive function (120). After short-term CPAP treatment, functional MRI showed improvements in memory and attention in OSA patients, associated with changes in the cerebellar cortex and bilateral hippocampus (121, 122). Therefore, existing data suggest that by improving oxygen saturation and regulating hippocampal function, CPAP treatment can effectively alleviate cognitive impairment in OSA patients. Therefore, Peripheral inflammatory markers (e.g., NETs, NLRP3 activation products) may serve as candidate biomarkers for early cognitive decline in OSA. Monitoring hippocampal function via imaging could guide timely interventions. Early initiation of CPAP remains the most effective strategy to prevent or reverse neurocognitive impairment.
4.4 Cancer immune editing in OSA
Recent studies suggest that OSA may contribute to the development and progression of various solid tumors through mechanisms like IH, oxidative stress, immune dysregulation, and remodeling of the inflammatory microenvironment. Epidemiological data indicate a significantly higher risk of colorectal cancer in OSA patients: a prospective study in Korea found that the detection rate of high-grade colorectal tumors in OSA patients was 3.03 times that of the control group, even after adjusting for age, gender, BMI, and smoking (123). A cohort study in Taiwan also showed that the risk in this population was 1.8 times higher than in non-OSA individuals (124). Common risk factors for both OSA and cancer, such as obesity and chronic inflammation, further strengthen the potential link between the two (125). Meta-analyses have confirmed that OSA is significantly linked to the incidence of prostate, breast, lung, and colorectal cancer (126, 127). Focusing on lung cancer, several studies have shown that OSA patients experience a higher occurrence of lung cancer during follow-up, with severe OSA significantly increases the mortality risk in late-stage patients (128, 129). Kendzerska et al. confirmed that OSA-related hypoxia indicators (such as AHI and average SaO2) are independent risk factors for lung cancer (130), while Seijo and Justeau found that T90% is a stronger predictor than AHI (HR = 2.14, 95% CI 1.01-4.54) (131, 132). Notably, the prevalence of OSA is also higher in lung cancer patients (133, 134), although some studies have reported that OSA may be negatively correlated with lung cancer in certain populations (135, 136). This suggests that the effect may be influenced by confounding factors such as age, sex, tumor type, and follow-up duration.
In terms of mechanism, animal experiments have found that IH stimulates tumor growth in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) mouse models (137), but evidence on whether OSA affects lung cancer prognosis is insufficient (138). The synergistic impact of IH and SF may accelerate the occurrence and progression of lung cancer and promote treatment resistance through pathways like oxidative stress, chronic inflammation, immune dysfunction, and neuroendocrine disruption (139, 140). However, there is currently a lack of animal models that can accurately simulate both the IH and SF states in OSA patients, and the standards for IH exposure and SF quantification methods are not unified, limiting further research into the mechanisms. Research has demonstrated that chronic inflammation is strongly linked to the development of various cancers, with the immune system playing a crucial role in tumor angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis. Regulatory T cells (Tregs), MDSCs, and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) can promote tumor progression. The repeated IH and tissue hypoxia caused by OSA can create a pro-cancerous environment by stabilizing HIF, promoting tumor angiogenesis and proliferation, disrupting immune surveillance, and enhancing immune escape. Clinical studies have found that pro-tumor gene expression is upregulated in peripheral white blood cells of OSA patients, which can be partially reversed after CPAP treatment (141).
In cancers associated with OSA, the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway is critically involved in facilitating immune evasion by tumors. In both clinical OSA cases and animal models, there is an upregulation of PD-1/PD-L1 expression, along with CD8+ T cell dysfunction and a higher proportion of MDSCs (142). A mouse model of OSA combined with NSCLC created by Huang et al. confirmed that PD-L1 expression is closely related to the intensity of IH, and tumor burden increases in a PD-L1-dependent manner (143). Further studies show that IH can drive PD-L1 overexpression through the upregulation of HIF-1α (144, 145); IH increases HIF-1α and PD-L1 in tumor cells, weakening cytotoxic T cells and increasing TAMs, thus accelerating tumor progression (146). Additionally, exosomes released by lung cancer cells have been found to upregulate PD-L1 expression on TAMs (147). Clinical studies show that the levels of soluble PD-L1 (sPD-L1) in the serum of severe OSA patients are significantly elevated (148). Since elevated PD-L1 levels are closely linked to enhanced immune evasion by tumors, targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis may represent a promising treatment strategy for individuals with lung cancer who also suffer from OSA.
IH promotes the polarization of TAMs towards the M2 subtype, which is known to support tumor progression and facilitate cancer cell invasion. Animal experiments have confirmed that IH accelerates lung cancer progression, and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors can block M2 polarization of TAMs, delaying tumor deterioration (149–151). At the same time, IH induces tumor cells to secrete interleukin-10 (IL-10), which in turn facilitates the polarization of TAMs towards the M2 phenotype (152), and also promotes the enrichment of immunosuppressive cell populations, including MDSCs, granulocytes, and Tregs, together creating a pro-tumor immune-suppressive microenvironment (153).
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a core regulator of the tumor immune microenvironment, can regulate tumor proliferation, invasion, and microenvironment remodeling (154). Studies have shown that in untreated OSA patients, monocytes release TGF-β to suppress NK cell function (which can be restored with CPAP treatment) (72), and IH can activate the TGF-β pathway to promote lung cancer cell migration and activation of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) (155). In an OSA combined NSCLC model created by Akbarpour et al., IH and SF significantly weakened the tumor-killing effect of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), promoting cancer stem cell (CSC) immune evasion and maintaining self-renewal (156).
iNKT, important anti-tumor immune cells, are impaired in both number and function in severe OSA patients, and CPAP treatment can partially restore their function (63, 114), suggesting that iNKT dysfunction may also participate in the immune escape mechanism of OSA-related tumors. Zhang et al. found that IH can increase tumor volume and weight, while upregulating the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and endothelin-1, enhancing angiogenesis (157). Kang et al. provided further evidence that in a lung adenocarcinoma mouse model exposed to IH, VEGF levels were significantly elevated, and its regulation was mediated primarily by nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and β-catenin, rather than HIF-1α (158). Additionally, in the IH combined with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) model, the expression of ATAD2 (ATPase family protein) was significantly increased. Knockdown of ATAD2 inhibited lung cancer cell invasion and migration, reduced mtROS production, and decreased both the quantity and functional capacity of CSCs, suggesting that IH accelerates lung cancer progression by activating the HIF-1α/ATAD2 axis, regulating mtROS and CSC interactions (159).
Current research confirms that IH can trigger secondary inflammation, oxidative stress-induced cellular injury, immune system impairment, and alterations in tumor-related genes. Concurrently, IH elevates the expression of key signaling molecules, including PD-L1 and VEGF. It also promotes the expansion and specialization of TAMs, CSCs, and vascular endothelial cells. Furthermore, IH mediates intercellular communication via exosome signaling. Collectively, these mechanisms facilitate tumor cell proliferation, increase invasiveness, stimulate neovascularization, and accelerate malignant progression. However, there are still limitations in current research: first, there is currently no universally accepted animal model that can simultaneously simulate the core features of IH and SF, and studies on SF are relatively insufficient; second, the majority of in vivo and in vitro studies primarily concentrate on the roles of IH in enhancing tumor cell growth and invasiveness, without in-depth analysis of its effects on distant metastasis, and lack verification of the carcinogenic potential of IH; third, cancer development involves multiple mechanisms including redox imbalance, persistent inflammatory responses, immune evasion, and disturbances in neuroendocrine regulation, and there is still a lack of systematic research integrating these key mechanisms(Figure 4). We believe that serum soluble PD-L1 and VEGF may serve as candidate biomarkers for OSA-related tumor progression. Monitoring Treg/MDSC/TAM profiles could help identify patients at higher oncologic risk. Early CPAP intervention and potential PD-1/PD-L1–targeted therapies may mitigate cancer immune escape in OSA.
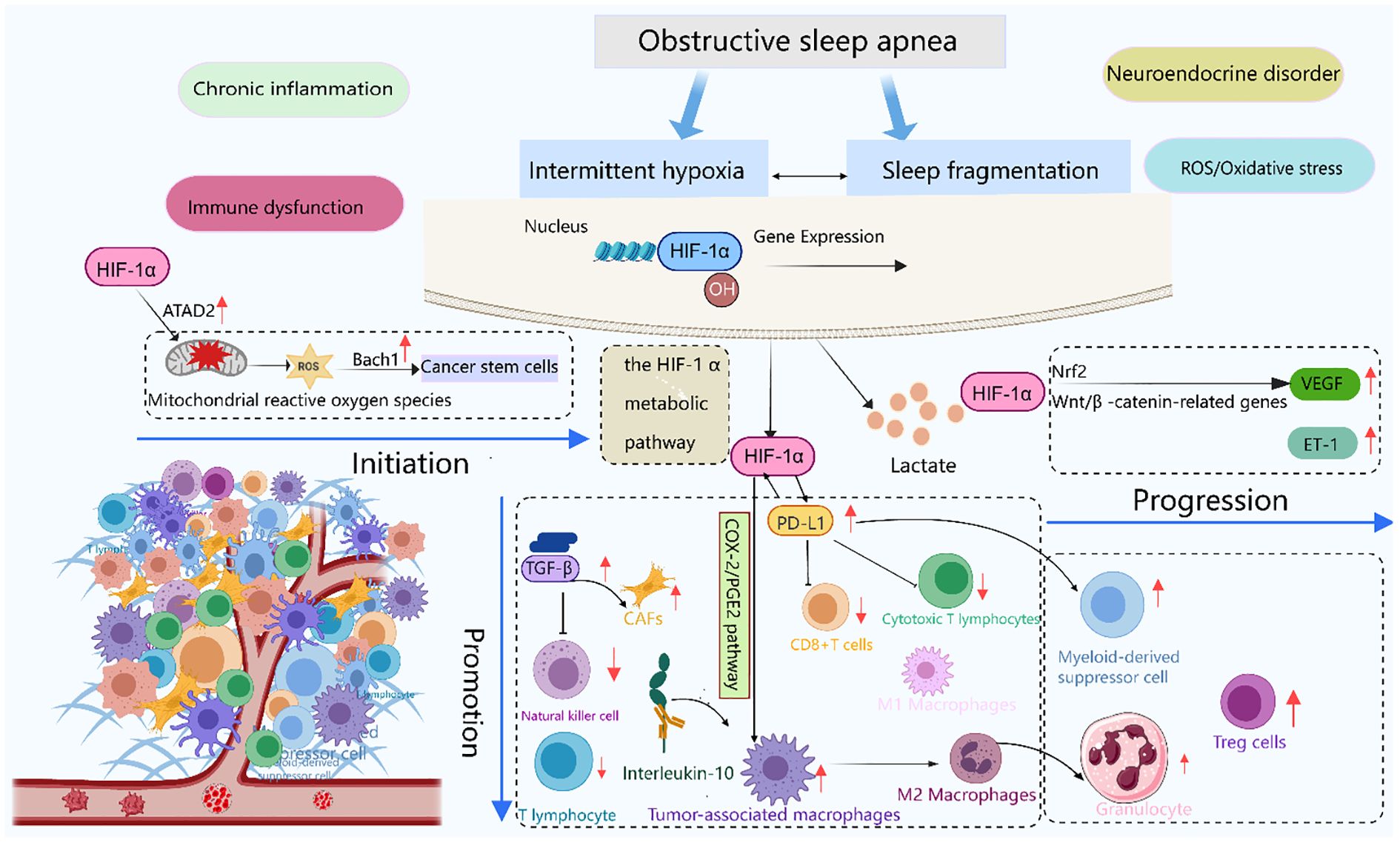
Figure 4. Immune stress response induced by OSA and its role in tumor evolution. This schematic illustrates the temporal sequence of tumor progression under OSA-induced immune stressors. Initiation: Intermittent hypoxia stabilizes HIF-1α, acting as the triggering molecular event. Promotion: HIF-1α signaling upregulates PD-L1 expression and drives TAMs toward M2 polarization, establishing an immunosuppressive microenvironment. Progression: VEGF-mediated angiogenesis, together with sustained immune evasion, facilitates tumor invasion and metastasis. Together, these steps outline the continuum from OSA-driven immune dysregulation to cancer progression. Created with MedPeer (medpeer.cn). Icons adapted and used under an institutional license for academic publication.
4.5 Autoimmune diseases in OSA
Th17 cells, as a critical effector population mediating cellular immunity, are essential in the development of autoimmune and allergic conditions, whereas Tregs function to preserve immune system tolerance, preventing organ-specific autoimmunity, allergies, and transplant rejection. The dynamic balance between these two cell types is a core mechanism regulating immune homeostasis and modulating inflammation. Research has revealed that in OSA patients, cytokines promoting Th17 differentiation, such as IL-6 and IL-17, are markedly increased, while TGF-β1 levels are decreased, creating an inflammatory cytokine-dominated immune microenvironment, thus disrupting the Th17/Treg balance (160, 161). Domestic studies have also found that the Th17/Treg ratio in individuals with OSA is significantly higher than in healthy individuals, and this ratio shows a positive association with both the severity of OSA and C-reactive protein levels (162), suggesting that it may be involved in the autoimmune pathological process related to OSA. Furthermore, some researchers have proposed that OSA may act as one of the triggers of autoimmune responses: repeated IH can cause cellular damage, leading to hyperuricemia and affecting the maturation and antigen-presenting function of dendritic cells. When sodium urate crystals accumulate to a certain extent, they can activate T cell responses, disrupting immune tolerance and promoting the initiation and advancement of autoimmune disorders (163). Based on existing evidence, the Th17/Treg ratio may represent a candidate biomarker for assessing OSA-related autoimmune risk. Elevated IL-6 and IL-17, together with reduced TGF-β1, could serve as potential thresholds for early immunomodulatory intervention. In addition, monitoring uric acid levels may help identify patients at risk of autoimmunity triggered by OSA.
5 Discussion and future perspectives
This review comprehensively highlights the significant influence of OSA on immune function and explains its pathological connections with multiple comorbidities across molecular, cellular, and organ systems. Overall, repeated IH and SF constitute the two core immune stressors of OSA. The former amplifies oxidative stress and inflammatory responses through the ROS-HIF-1-NF-κB-NLRP3 axis, while the latter further weakens immune homeostasis via multiple pathways, including circadian disruption, loss of slow-wave sleep, excessive sympathetic activation, and Th1/Th2 switching. Together, these factors synergistically drive the shared immune foundation for atherosclerosis, insulin resistance, neurodegenerative changes, and tumorigenesis.
At the cellular level, MDSC expansion, M1 macrophage polarization, variable dendritic cell function, and γδT/iNKT defects form the innate-adaptive immune network. Notably, T cell profile dysregulation deserves attention: (1) CD8+ cytotoxic T cells become excessively activated due to upregulation of NK receptors and perforin/TNF-α, exacerbating tissue damage; (2) CD4+ subsets exhibit plasticity in Th1↔Th2 oscillation, suggesting susceptibility to regulation by metabolic and neuroendocrine backgrounds; (3)The elevated Th17/Treg ratio is highly correlated with autoimmune and vascular wall inflammation. Meanwhile, HIF-1α enhances the expression of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway under OSA conditions, resulting in T cell dysfunction and facilitating tumor evasion from immune surveillance.
Clinical evidence indicates that CPAP can partially reverse early immune activation: it reduces NLR, restores γδT/iNKT function, inhibits CD8+ NK-like phenotypes, and downregulates PD-L1. However, efficacy is highly dependent on treatment adherence and duration, with limited improvement in established immune memory or organ damage. Notably, Beyond CPAP, several alternative and adjunctive interventions may mitigate OSA-related immune dysregulation through distinct biological mechanisms. Hypoglossal nerve stimulation (HNS) and other upper-airway neuromodulation techniques enhance airway patency and sleep architecture, thereby alleviating IH and SF. By reducing hypoxic burden, these approaches are expected to suppress HIF-1α stabilization, ROS generation, and downstream activation of the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway, resulting in lowered systemic inflammatory markers (e.g., NLR, IL-6) and partial restoration of T-cell and NK cell function. Targeted anti-inflammatory strategies—such as inhibitors of upstream mediators (e.g., NLRP3 or IL-1β), ROS scavengers, melatonin supplementation, and, in selected oncologic settings, modulation of the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint axis—represent mechanism-based approaches to interrupt IH-driven inflammation. However, clinical data in OSA populations remain limited, and the systemic safety profile, including infection risk, warrants careful evaluation. Lifestyle interventions and structured exercise programs (with or without weight loss) reduce visceral adiposity, downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines, enhance insulin sensitivity, and promote anti-inflammatory myeloid cell phenotypes, thereby addressing a key modifiable factor in OSA-related immune abnormalities. Finally, combination strategies—such as device-based therapies integrated with anti-inflammatory or metabolic treatments—may offer enhanced benefit for patients with persistent immune activation despite adequate airway management. Well-designed randomized controlled trials incorporating predefined immunologic endpoints and standardized adherence metrics are essential to elucidate the magnitude, durability, and clinical significance of immunomodulation achieved through these interventions.
In conclusion, OSA is not only a sleep-disordered breathing condition but also a “systemic immune disease.” Decoding its immune code, precisely blocking key pathways, and synergizing with traditional therapies may become a key breakthrough in reducing multi-organ damage and mortality burden in OSA patients.
Author contributions
ND: Writing – original draft, Software, Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. HY: Visualization, Formal analysis, Validation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by The First Hospital of Lanzhou University (No. ldyyyn2022-77 and No. ldyyyn2023-80) and Science and Technology Program of Gansu Province (No. 25JRRA574).
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Jinmin Ma for expert technical support. Pictures were created with medpeer (medpeer.cn).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
Aβ, amyloid-β; AHI, apnea–hypopnea index; CCR5, C-C chemokine receptor 5; CAFs, cancer-associated fibroblasts; CPAP, continuous positive airway pressure; CSC, cancer stem cell; DC, dendritic cell; GH, growth hormone; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; IH, intermittent hypoxia; IL, interleukin; iNKT, invariant natural killer T cell; mDC, myeloid dendritic cell; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; NK, natural killer cell; NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3; ODI, oxygen desaturation index; OSA, obstructive sleep apnea; pDC, plasmacytoid dendritic cell; PD-1, programmed cell death protein-1; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation end-products; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SaO2, arterial oxygen saturation; SF, sleep fragmentation; SWA, slow-wave activity; TAMs, tumor-associated macrophages; Th, T helper; TLR, toll-like receptor; T90%, percentage of total sleep time with SaO2 <90%; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VWAT, visceral white adipose tissue.
References
1. Benjafield AV, Ayas NT, Eastwood PR, Heinzer R, Ip MSM, Morrell MJ, et al. Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of obstructive sleep apnoea: a literature-based analysis. Lancet Respir Med. (2019) 7:687–98. doi: 10.1016/s2213-2600(19)30198-5
2. Bock JM, Vungarala S, Karim S, and Somers VK. Obstructive sleep apnea as a cardiovascular risk factor-beyond CPAP. Can J Cardiol. (2021) 37:756–65. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2021.01.027
3. Rimke AN, Ahmed SB, Turin TC, Pendharkar SR, Raneri JK, Lynch EJ, et al. Effect of CPAP therapy on kidney function in patients with chronic kidney disease: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Chest. (2021) 159:2008–19. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.11.052
4. Jordan AS, McSharry DG, and Malhotra A. Adult obstructive sleep apnoea. Lancet (London England). (2014) 383:736–47. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(13)60734-5
5. Cai XH, Li XC, Jin SW, Liang DS, Wen ZW, Cao HC, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress plays critical role in brain damage after chronic intermittent hypoxia in growing rats. Exp Neurol. (2014) 257:148–56. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.04.029
6. Rothermel BA and Hill JA. Autophagy in load-induced heart disease. Circ Res. (2008) 103:1363–9. doi: 10.1161/circresaha.108.186551
7. Lavie L. Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome–an oxidative stress disorder. Sleep Med Rev. (2003) 7:35–51. doi: 10.1053/smrv.2002.0261
8. Dewan NA, Nieto FJ, and Somers VK. Intermittent hypoxemia and OSA: implications for comorbidities. Chest. (2015) 147:266–74. doi: 10.1378/chest.14-0500
9. Lv R, Liu X, Zhang Y, Dong N, Wang X, He Y, et al. Pathophysiological mechanisms and therapeutic approaches in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:218. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01496-3
10. Douglas RM and Haddad GG. Can O2 dysregulation induce premature aging? Physiol (Bethesda Md). (2008) 23:333–49. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00023.2008
11. Yuan G, Nanduri J, Khan S, Semenza GL, and Prabhakar NR. Induction of HIF-1alpha expression by intermittent hypoxia: involvement of NADPH oxidase, Ca2+ signaling, prolyl hydroxylases, and mTOR. J Cell Physiol. (2008) 217:674–85. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21537
12. Lavie L. Oxidative stress in obstructive sleep apnea and intermittent hypoxia–revisited–the bad ugly and good: implications to the heart and brain. Sleep Med Rev. (2015) 20:27–45. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2014.07.003
13. van Horssen J, van Schaik P, and Witte M. Inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction: A vicious circle in neurodegenerative disorders? Neurosci Lett. (2019) 710:132931. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.06.050
14. Nesci S, Trombetti F, Pagliarani A, Ventrella V, Algieri C, Tioli G, et al. Molecular and supramolecular structure of the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system: implications for pathology. Life (Basel Switzerland). (2021) 11:242. doi: 10.3390/life11030242
15. Marchi S, Guilbaud E, Tait SWG, Yamazaki T, and Galluzzi L. Mitochondrial control of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2023) 23:159–73. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00760-x
16. Córdoba-Izquierdo A, Drouot X, Thille AW, Galia F, Roche-Campo F, Schortgen F, et al. Sleep in hypercapnic critical care patients under noninvasive ventilation: conventional versus dedicated ventilators. Crit Care Med. (2013) 41:60–8. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31826764e3
17. Blevins HM, Xu Y, Biby S, and Zhang S. The NLRP3 inflammasome pathway: A review of mechanisms and inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Front Aging Neurosci. (2022) 14:879021. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.879021
18. Díaz-García E, García-Tovar S, Alfaro E, Jaureguizar A, Casitas R, Sánchez-Sánchez B, et al. Inflammasome activation: A keystone of proinflammatory response in obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2022) 205:1337–48. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202106-1445OC
19. Díaz-García E, Sanz-Rubio D, García-Tovar S, Alfaro E, Cubero P, Gil AV, et al. Inflammasome activation mediated by oxidised low-density lipoprotein in patients with sleep apnoea and early subclinical atherosclerosis. Eur Respir J. (2023) 61:2201401. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01401-2022
20. Wu X, Gong L, Xie L, Gu W, Wang X, Liu Z, et al. NLRP3 deficiency protects against intermittent hypoxia-induced neuroinflammation and mitochondrial ROS by promoting the PINK1-parkin pathway of mitophagy in a murine model of sleep apnea. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:628168. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.628168
21. Du P, Wang J, Han Y, and Feng J. Blocking the lncRNA MALAT1/miR-224-5p/NLRP3 axis inhibits the hippocampal inflammatory response in T2DM with OSA. Front Cell Neurosci. (2020) 14:97. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00097
22. Sun ZM, Guan P, Luo LF, Qin LY, Wang N, Zhao YS, et al. Resveratrol protects against CIH-induced myocardial injury by targeting Nrf2 and blocking NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Life Sci. (2020) 245:117362. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117362
23. Påhlman S and Mohlin S. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in neuroblastoma. Cell Tissue Res. (2018) 372:269–75. doi: 10.1007/s00441-017-2701-1
24. Xie H, Yin J, Bai Y, Peng H, Zhou X, and Bai J. Differential expression of immune markers in the patients with obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol: Off J Eur Fed Oto-Rhino-Laryngol Societies (EUFOS): Affiliated German Soc Oto-Rhino-Laryngol Head Neck Surg. (2019) 276:735–44. doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-5219-6
25. Romero-Garcia S, Moreno-Altamirano MM, Prado-Garcia H, and Sánchez-García FJ. Lactate contribution to the tumor microenvironment: mechanisms, effects on immune cells and therapeutic relevance. Front Immunol. (2016) 7:52. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00052
26. Dammeijer F, van Gulijk M, Mulder EE, Lukkes M, Klaase L, van den Bosch T, et al. The PD-1/PD-L1-checkpoint restrains T cell immunity in tumor-draining lymph nodes. Cancer Cell. (2020) 38:685–700.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.09.001
27. Noman MZ, Desantis G, Janji B, Hasmim M, Karray S, Dessen P, et al. PD-L1 is a novel direct target of HIF-1α, and its blockade under hypoxia enhanced MDSC-mediated T cell activation. J Exp Med. (2014) 211:781–90. doi: 10.1084/jem.20131916
28. Polasky C, Steffen A, Loyal K, Lange C, Bruchhage KL, and Pries R. Redistribution of monocyte subsets in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome patients leads to an imbalanced PD-1/PD-L1 cross-talk with CD4/CD8 T cells. J Immunol (Baltimore Md: 1950). (2021) 206:51–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2001047
29. Wei Z, Shen H, Wang F, Huang W, Li X, Xu H, et al. Melatonin mediates intestinal barrier dysfunction and systemic inflammation in moderate-severe OSA patients. Ann Med. (2024) 56:2361825. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2361825
30. Wehr TA. The durations of human melatonin secretion and sleep respond to changes in daylength (photoperiod). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (1991) 73:1276–80. doi: 10.1210/jcem-73-6-1276
31. Luo J, Zhang Z, Sun H, Song J, Chen X, Huang J, et al. Effect of melatonin on T/B cell activation and immune regulation in pinealectomy mice. Life Sci. (2020) 242:117191. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117191
32. Irwin MR. Sleep and inflammation: partners in sickness and in health. Nat Rev Immunol. (2019) 19:702–15. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0190-z
33. Irwin MR and Opp MR. Sleep health: reciprocal regulation of sleep and innate immunity. Neuropsychopharmacol: Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol. (2017) 42:129–55. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.148
34. de Lima FF, Mazzotti DR, Tufik S, and Bittencourt L. The role inflammatory response genes in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: a review. Sleep Breathing = Schlaf Atmung. (2016) 20:331–8. doi: 10.1007/s11325-015-1226-7
35. Garbarino S, Lanteri P, Bragazzi NL, Magnavita N, and Scoditti E. Role of sleep deprivation in immune-related disease risk and outcomes. Commun Biol. (2021) 4:1304. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02825-4
36. Unnikrishnan D, Jun J, and Polotsky V. Inflammation in sleep apnea: an update. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. (2015) 16:25–34. doi: 10.1007/s11154-014-9304-x
37. Besedovsky L, Lange T, and Haack M. The sleep-immune crosstalk in health and disease. Physiol Rev. (2019) 99:1325–80. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00010.2018
38. Ju YE, Finn MB, Sutphen CL, Herries EM, Jerome GM, Ladenson JH, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea decreases central nervous system-derived proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid. Ann Neurol. (2016) 80:154–9. doi: 10.1002/ana.24672
39. Ondze B, Espa F, Dauvilliers Y, Billiard M, and Besset A. Sleep architecture, slow wave activity and sleep spindles in mild sleep disordered breathing. Clin Neurophysiol: Off J Int Fed Clin Neurophysiol. (2003) 114:867–74. doi: 10.1016/s1388-2457(02)00389-9
40. Ju YS, Ooms SJ, Sutphen C, Macauley SL, Zangrilli MA, Jerome G, et al. Slow wave sleep disruption increases cerebrospinal fluid amyloid-β levels. Brain: J Neurol. (2017) 140:2104–11. doi: 10.1093/brain/awx148
41. Ju YS, Zangrilli MA, Finn MB, Fagan AM, and Holtzman DM. Obstructive sleep apnea treatment, slow wave activity, and amyloid-β. Ann Neurol. (2019) 85:291–5. doi: 10.1002/ana.25408
42. Axelsson J, Rehman JU, Akerstedt T, Ekman R, Miller GE, Höglund CO, et al. Effects of sustained sleep restriction on mitogen-stimulated cytokines, chemokines and T helper 1/T helper 2 balance in humans. PloS One. (2013) 8:e82291. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082291
43. Dimitrov S, Lange T, Tieken S, Fehm HL, and Born J. Sleep associated regulation of T helper 1/T helper 2 cytokine balance in humans. Brain Behav Immunity. (2004) 18:341–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2003.08.004
44. Moser EK, Field NS, and Oliver PM. Aberrant Th2 inflammation drives dysfunction of alveolar macrophages and susceptibility to bacterial pneumonia. Cell Mol Immunol. (2018) 15:480–92. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2016.69
45. Collado-Hidalgo A, Sung C, and Cole S. Adrenergic inhibition of innate anti-viral response: PKA blockade of Type I interferon gene transcription mediates catecholamine support for HIV-1 replication. Brain Behav Immunity. (2006) 20:552–63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2006.01.005
46. Kalinichenko VV, Mokyr MB, Graf LH Jr., Cohen RL, and Chambers DA. Norepinephrine-mediated inhibition of antitumor cytotoxic T lymphocyte generation involves a beta-adrenergic receptor mechanism and decreased TNF-alpha gene expression. J Immunol (Baltimore Md: 1950). (1999) 163:2492–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.163.5.2492
47. Kıvanc T, Kulaksızoglu S, Lakadamyalı H, and Eyuboglu F. Importance of laboratory parameters in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and their relationship with cardiovascular diseases. J Clin Lab Anal. (2018) 32:e22199. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22199
48. Al-Halawani M, Kyung C, Liang F, Kaplan I, Moon J, Clerger G, et al. Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea with CPAP improves chronic inflammation measured by neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio. J Clin Sleep Med: JCSM: Off Publ Am Acad Sleep Med. (2020) 16:251–7. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.8176
49. Liu Q, Ou Y, Liu T, He Y, Quan X, Ouyang R, et al. Preliminary evidence of immune infiltration and neutrophil degranulation in peripheral blood of non-obese OSA patients related to cognitive decline. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:3481. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88034-z
50. Gordon S and Taylor PR. Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. (2005) 5:953–64. doi: 10.1038/nri1733
51. Mosser DM and Edwards JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2008) 8:958–69. doi: 10.1038/nri2448
52. Guilliams M and Scott CL. Does niche competition determine the origin of tissue-resident macrophages? Nat Rev Immunol. (2017) 17:451–60. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.42
53. Parisi L, Gini E, Baci D, Tremolati M, Fanuli M, Bassani B, et al. Macrophage polarization in chronic inflammatory diseases: killers or builders? J Immunol Res. (2018) 2018:8917804. doi: 10.1155/2018/8917804
54. Van den Bossche J and Saraber DL. Metabolic regulation of macrophages in tissues. Cell Immunol. (2018) 330:54–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.01.009
55. Tuleta I, Stöckigt F, Juergens UR, Pizarro C, Schrickel JW, Kristiansen G, et al. Intermittent hypoxia contributes to the lung damage by increased oxidative stress, inflammation, and disbalance in protease/antiprotease system. Lung. (2016) 194:1015–20. doi: 10.1007/s00408-016-9946-4
56. Mantovani A, Biswas SK, Galdiero MR, Sica A, and Locati M. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling. J Pathol. (2013) 229:176–85. doi: 10.1002/path.4133
57. Wang Y, Lee MYK, Mak JCW, and Ip MSM. Low-frequency intermittent hypoxia suppresses subcutaneous adipogenesis and induces macrophage polarization in lean mice. Diabetes Metab J. (2019) 43:659–74. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0196
58. Cortese R, Gileles-Hillel A, Khalyfa A, Almendros I, Akbarpour M, Khalyfa AA, et al. Aorta macrophage inflammatory and epigenetic changes in a murine model of obstructive sleep apnea: Potential role of CD36. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:43648. doi: 10.1038/srep43648
59. He H, Zhou Z, Zhang L, Lu Z, Li B, and Li X. HIF1α/MIF/CD74 signaling mediated OSA-induced atrial fibrillation by promoting M1 macrophages polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 149:114248. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114248
60. Galati D, Zanotta S, Canora A, Polistina GE, Nicoletta C, Ghinassi G, et al. Severe depletion of peripheral blood dendritic cell subsets in obstructive sleep apnea patients: A new link with cancer? Cytokine. (2020) 125:154831. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154831
61. Staats R, Rodrigues R, Barros A, Bacelar-Nicolau L, Aguiar M, Fernandes D, et al. Decrease of perforin positive CD3(+)γδ-T cells in patients with obstructive sleep disordered breathing. Sleep Breathing = Schlaf Atmung. (2018) 22:211–21. doi: 10.1007/s11325-017-1602-6
62. Domagała-Kulawik J, Osińska I, Piechuta A, Bielicki P, and Skirecki TT. B, and NKT cells in systemic inflammation in obstructive sleep apnoea. Mediators Inflamm. (2015) 2015:161579. doi: 10.1155/2015/161579
63. Gaoatswe G, Kent BD, Corrigan MA, Nolan G, Hogan AE, McNicholas WT, et al. Invariant natural killer T cell deficiency and functional impairment in sleep apnea: links to cancer comorbidity. Sleep. (2015) 38:1629–34. doi: 10.5665/sleep.5062
64. Tan HL, Gozal D, Wang Y, Bandla HP, Bhattacharjee R, Kulkarni R, et al. Alterations in circulating T-cell lymphocyte populations in children with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep. (2013) 36:913–22. doi: 10.5665/sleep.2724
65. Dyugovskaya L, Lavie P, Hirsh M, and Lavie L. Activated CD8+ T-lymphocytes in obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J. (2005) 25:820–8. doi: 10.1183/09031936.05.00103204
66. Dyugovskaya L, Lavie P, and Lavie L. Lymphocyte activation as a possible measure of atherosclerotic risk in patients with sleep apnea. Ann New York Acad Sci. (2005) 1051:340–50. doi: 10.1196/annals.1361.076
67. Díaz-García E, García-Sánchez A, Alfaro E, López-Fernández C, Mañas E, Cano-Pumarega I, et al. PSGL-1: a novel immune checkpoint driving T-cell dysfunction in obstructive sleep apnea. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1277551. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1277551
68. Steiropoulos P, Kotsianidis I, Nena E, Tsara V, Gounari E, Hatzizisi O, et al. Long-term effect of continuous positive airway pressure therapy on inflammation markers of patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep. (2009) 32:537–43. doi: 10.1093/sleep/32.4.537
69. Nadeem R, Molnar J, Madbouly EM, Nida M, Aggarwal S, Sajid H, et al. Serum inflammatory markers in obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. J Clin Sleep Med: JCSM: Off Publ Am Acad Sleep Med. (2013) 9:1003–12. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.3070
70. Moretta A, Marcenaro E, Parolini S, Ferlazzo G, and Moretta L. NK cells at the interface between innate and adaptive immunity. Cell Death Differ. (2008) 15:226–33. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402170
71. Vivier E, Raulet DH, Moretta A, Caligiuri MA, Zitvogel L, Lanier LL, et al. Innate or adaptive immunity? The example of natural killer cells. Sci (New York NY). (2011) 331:44–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1198687
72. Hernández-Jiménez E, Cubillos-Zapata C, Toledano V, Pérez de Diego R, Fernández-Navarro I, Casitas R, et al. Monocytes inhibit NK activity via TGF-β in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J. (2017) 49:1602456. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02456-2016
73. Yuan X, Deng Y, Guo X, Shang J, Zhu D, and Liu H. Atorvastatin attenuates myocardial remodeling induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia in rats: partly involvement of TLR-4/MYD88 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2014) 446:292–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.02.091
74. Lin ZP, Lin HL, Yu XP, Zheng YJ, and Cheng SY. TLR4 mediates inflammation and hepatic fibrosis induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia in rats. Mol Med Rep. (2020) 22:651–60. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11134
75. Deng Y, Yuan X, Guo XL, Zhu D, Pan YY, and Liu HG. Efficacy of atorvastatin on hippocampal neuronal damage caused by chronic intermittent hypoxia: Involving TLR4 and its downstream signaling pathway. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. (2015) 218:57–63. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2015.07.006
76. Song D, Fang G, Mao SZ, Ye X, Liu G, Miller EJ, et al. Selective inhibition of endothelial NF-κB signaling attenuates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced atherosclerosis in mice. Atherosclerosis. (2018) 270:68–75. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.01.027
77. Akinnusi M, Jaoude P, Kufel T, and El-Solh AA. Toll-like receptor activity in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breathing = Schlaf Atmung. (2013) 17:1009–16. doi: 10.1007/s11325-012-0791-2
78. Kuzmich NN, Sivak KV, Chubarev VN, Porozov YB, Savateeva-Lyubimova TN, and Peri F. TLR4 signaling pathway modulators as potential therapeutics in inflammation and sepsis. Vaccines. (2017) 5. doi: 10.3390/vaccines5040034
79. Sun SC. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2017) 17:545–58. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.52
80. Chen YC, Su MC, Liou CW, Liu SF, Chen CJ, Lin HC, et al. Co-upregulation of Toll-like receptors 2 and 6 on peripheral blood cells in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breathing = Schlaf Atmung. (2015) 19:873–82. doi: 10.1007/s11325-014-1116-4
81. Huang KT, Chen YC, Tseng CC, Chang HC, Su MC, Wang TY, et al. Aberrant DNA methylation of the toll-like receptors 2 and 6 genes in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. PloS One. (2020) 15:e0228958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228958
82. Weber C and Noels H. Atherosclerosis: current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat Med. (2011) 17:1410–22. doi: 10.1038/nm.2538
83. Yan YR, Zhang L, Lin YN, Sun XW, Ding YJ, Li N, et al. Chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction mediates endothelial injury via the TXNIP/NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway. Free Radical Biol Med. (2021) 165:401–10. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.01.053
84. Anothaisintawee T, Reutrakul S, Van Cauter E, and Thakkinstian A. Sleep disturbances compared to traditional risk factors for diabetes development: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev. (2016) 30:11–24. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2015.10.002
85. Kadoya M and Koyama H. Sleep, autonomic nervous function and atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040794
86. Chaput N and Théry C. Exosomes: immune properties and potential clinical implementations. Semin Immunopathol. (2011) 33:419–40. doi: 10.1007/s00281-010-0233-9
87. Helal O, Defoort C, Robert S, Marin C, Lesavre N, Lopez-Miranda J, et al. Increased levels of microparticles originating from endothelial cells, platelets and erythrocytes in subjects with metabolic syndrome: relationship with oxidative stress. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis: NMCD. (2011) 21:665–71. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2010.01.004
88. He S, Wu C, Xiao J, Li D, Sun Z, and Li M. Endothelial extracellular vesicles modulate the macrophage phenotype: Potential implications in atherosclerosis. Scand J Immunol. (2018) 87:e12648. doi: 10.1111/sji.12648
89. Osada-Oka M, Shiota M, Izumi Y, Nishiyama M, Tanaka M, Yamaguchi T, et al. Macrophage-derived exosomes induce inflammatory factors in endothelial cells under hypertensive conditions. Hypertens Res: Off J Japanese Soc Hypertens. (2017) 40:353–60. doi: 10.1038/hr.2016.163
90. Haney MJ, Klyachko NL, Zhao Y, Gupta R, Plotnikova EG, He Z, et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J Controlled Release: Off J Controlled Release Society. (2015) 207:18–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.03.033
91. Schaefer E, Wu W, Mark C, Yang A, DiGiacomo E, Carlton-Smith C, et al. Intermittent hypoxia is a proinflammatory stimulus resulting in IL-6 expression and M1 macrophage polarization. Hepatol Commun. (2017) 1:326–37. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1045
92. Chuang LP, Chen NH, Lin SW, Hu HC, Kao KC, Li LF, et al. Monocytic C-C chemokine receptor 5 expression increases in in vitro intermittent hypoxia condition and in severe obstructive sleep apnea patients. Sleep Breathing = Schlaf Atmung. (2019) 23:1177–86. doi: 10.1007/s11325-019-01797-4
93. Taleb S, Tedgui A, and Mallat Z. IL-17 and Th17 cells in atherosclerosis: subtle and contextual roles. Arteriosc Thromb Vasc Biol. (2015) 35:258–64. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.114.303567
94. Di Giulio C. Is intermittent hypoxia a cause of aging? Copd. (2013) 10:542–4. doi: 10.3109/15412555.2012.761961
95. Olejarz W, Głuszko A, Cyran A, Bednarek-Rajewska K, Proczka R, Smith DF, et al. TLRs and RAGE are elevated in carotid plaques from patients with moderate-to-severe obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Breathing = Schlaf Atmung. (2020) 24:1573–80. doi: 10.1007/s11325-020-02029-w
96. Park M, Choi S, Kim S, Kim J, Lee DK, Park W, et al. NF-κB-responsive miR-155 induces functional impairment of vascular smooth muscle cells by downregulating soluble guanylyl cyclase. Exp Mol Med. (2019) 51:1–12. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0212-8
97. Li HY, Leu YL, Wu YC, and Wang SH. Melatonin inhibits in vitro smooth muscle cell inflammation and proliferation and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J Agric Food Chem. (2019) 67:1889–901. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b06217
98. Chinetti-Gbaguidi G, Colin S, and Staels B. Macrophage subsets in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2015) 12:10–7. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2014.173
99. Gileles-Hillel A, Kheirandish-Gozal L, and Gozal D. Biological plausibility linking sleep apnoea and metabolic dysfunction. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2016) 12:290–8. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.22
100. Peppard PE, Young T, Barnet JH, Palta M, Hagen EW, and Hla KM. Increased prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in adults. Am J Epidemiol. (2013) 177:1006–14. doi: 10.1093/aje/kws342
101. Poroyko VA, Carreras A, Khalyfa A, Khalyfa AA, Leone V, Peris E, et al. Chronic sleep disruption alters gut microbiota, induces systemic and adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance in mice. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:35405. doi: 10.1038/srep35405
102. Wang Y, Carreras A, Lee S, Hakim F, Zhang SX, Nair D, et al. Chronic sleep fragmentation promotes obesity in young adult mice. Obes (Silver Spring Md). (2014) 22:758–62. doi: 10.1002/oby.20616
103. Kent BD, Grote L, Ryan S, Pépin JL, Bonsignore MR, Tkacova R, et al. Diabetes mellitus prevalence and control in sleep-disordered breathing: the European Sleep Apnea Cohort (ESADA) study. Chest. (2014) 146:982–90. doi: 10.1378/chest.13-2403
104. Perrini S, Cignarelli A, Quaranta VN, Falcone VA, Kounaki S, Porro S, et al. Correction of intermittent hypoxia reduces inflammation in obese subjects with obstructive sleep apnea. JCI Insight. (2017) 2. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.94379
105. Khalyfa A, Kheirandish-Gozal L, and Gozal D. Exosome and macrophage crosstalk in sleep-disordered breathing-induced metabolic dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113383
106. Louis M and Punjabi NM. Effects of acute intermittent hypoxia on glucose metabolism in awake healthy volunteers. J Appl Physiol (Bethesda Md: 1985). (2009) 106:1538–44. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.91523.2008
107. Jun JC, Shin MK, Devera R, Yao Q, Mesarwi O, Bevans-Fonti S, et al. Intermittent hypoxia-induced glucose intolerance is abolished by α-adrenergic blockade or adrenal medullectomy. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2014) 307:E1073–83. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00373.2014
108. Tripathi A, Melnik AV, Xue J, Poulsen O, Meehan MJ, Humphrey G, et al. Intermittent hypoxia and hypercapnia, a hallmark of obstructive sleep apnea, alters the gut microbiome and metabolome. mSystems. (2018) 3. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00020-18
109. Thomas A, Belaidi E, Moulin S, Horman S, van der Zon GC, Viollet B, et al. Chronic intermittent hypoxia impairs insulin sensitivity but improves whole-body glucose tolerance by activating skeletal muscle AMPK. Diabetes. (2017) 66:2942–51. doi: 10.2337/db17-0186
110. Thomas D and Apovian C. Macrophage functions in lean and obese adipose tissue. Metab: Clin Exp. (2017) 72:120–43. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2017.04.005
111. Ivanov S, Merlin J, Lee MKS, Murphy AJ, and Guinamard RR. Biology and function of adipose tissue macrophages, dendritic cells and B cells. Atherosclerosis. (2018) 271:102–10. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.01.018
112. Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL, and Saltiel AR. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J Clin Invest. (2007) 117:175–84. doi: 10.1172/jci29881
113. Deng ZB, Poliakov A, Hardy RW, Clements R, Liu C, Liu Y, et al. Adipose tissue exosome-like vesicles mediate activation of macrophage-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes. (2009) 58:2498–505. doi: 10.2337/db09-0216
114. Gildeh N, Drakatos P, Higgins S, Rosenzweig I, and Kent BD. Emerging co-morbidities of obstructive sleep apnea: cognition, kidney disease, and cancer. J Thorac Dis. (2016) 8:E901–e17. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.09.23
115. Polsek D, Gildeh N, Cash D, Winsky-Sommerer R, Williams SCR, Turkheimer F, et al. Obstructive sleep apnoea and Alzheimer’s disease: In search of shared pathomechanisms. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2018) 86:142–9. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.12.004
116. Wallace A and Bucks RS. Memory and obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Sleep. (2013) 36:203–20. doi: 10.5665/sleep.2374
117. Liu X, Ma Y, Ouyang R, Zeng Z, Zhan Z, Lu H, et al. The relationship between inflammation and neurocognitive dysfunction in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Neuroinflam. (2020) 17:229. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01905-2
118. Shafqat A, Noor Eddin A, Adi G, Al-Rimawi M, Abdul Rab S, Abu-Shaar M, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps in central nervous system pathologies: A mini review. Front Med. (2023) 10:1083242. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1083242
119. Wang D, Zhang J, Jiang W, Cao Z, Zhao F, Cai T, et al. The role of NLRP3-CASP1 in inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation and autophagy dysfunction in manganese-induced, hippocampal-dependent impairment of learning and memory ability. Autophagy. (2017) 13:914–27. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1293766
120. Gong LJ, Chang SC, Wu QH, Liu ZL, Wu X, and Li SQ. Diagnostic accuracy of the Berlin questionnaire and therapeutic effect of nasal continuous positive airway pressure in OSAHS patients with glucose metabolic dysfunction. Sleep Breathing = Schlaf Atmung. (2021) 25:867–76. doi: 10.1007/s11325-020-02198-8
121. Canessa N, Castronovo V, Cappa SF, Aloia MS, Marelli S, Falini A, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea: brain structural changes and neurocognitive function before and after treatment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2011) 183:1419–26. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201005-0693OC
122. Rosenzweig I, Glasser M, Crum WR, Kempton MJ, Milosevic M, McMillan A, et al. Changes in neurocognitive architecture in patients with obstructive sleep apnea treated with continuous positive airway pressure. EBioMedicine. (2016) 7:221–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.03.020
123. Lee S, Kim BG, Kim JW, Lee KL, Koo DL, Nam H, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea is associated with an increased risk of colorectal neoplasia. Gastrointest Endosc. (2017) 85:568–73.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2016.07.061
124. Chen CY, Hu JM, Shen CJ, Chou YC, Tian YF, Chen YC, et al. Increased incidence of colorectal cancer with obstructive sleep apnea: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Sleep Med. (2020) 66:15–20. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2019.02.016
125. Chang JL, Goldberg AN, Alt JA, Mohammed A, Ashbrook L, Auckley D, et al. International consensus statement on obstructive sleep apnea. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. (2023) 13:1061–482. doi: 10.1002/alr.23079
126. Nieto FJ, Peppard PE, Young T, Finn L, Hla KM, and Farré R. Sleep-disordered breathing and cancer mortality: results from the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2012) 186:190–4. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201201-0130OC
127. Cheng L, Guo H, Zhang Z, Yao Y, and Yao Q. Obstructive sleep apnea and incidence of Malignant tumors: a meta-analysis. Sleep Med. (2021) 84:195–204. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2021.05.029
128. Cheong AJY, Tan BKJ, Teo YH, Tan NKW, Yap DWT, Sia CH, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Am Thorac Society. (2022) 19:469–75. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202108-960OC
129. Huang HY, Lin SW, Chuang LP, Wang CL, Sun MH, Li HY, et al. Severe OSA associated with higher risk of mortality in stage III and IV lung cancer. J Clin Sleep Med: JCSM: Off Publ Am Acad Sleep Med. (2020) 16:1091–8. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.8432
130. Kendzerska T, Povitz M, Leung RS, Boulos MI, McIsaac DI, Murray BJ, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and incident cancer: A large retrospective multicenter clinical cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prevent: Publ Am Assoc Cancer Res Cosponsored by Am Soc Prev Oncol. (2021) 30:295–304. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.Epi-20-0975
131. Seijo LM, Pérez-Warnisher MT, Giraldo-Cadavid LF, Oliveros H, Cabezas E, Troncoso MF, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and nocturnal hypoxemia are associated with an increased risk of lung cancer. Sleep Med. (2019) 63:41–5. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2019.05.011
132. Justeau G, Gervès-Pinquié C, Le Vaillant M, Trzepizur W, Meslier N, Goupil F, et al. Association between nocturnal hypoxemia and cancer incidence in patients investigated for OSA: data from a large multicenter French cohort. Chest. (2020) 158:2610–20. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.055
133. Bhaisare S, Gupta R, Saini J, Chakraborti A, and Khot S. Sleep-disordered breathing in newly diagnosed patients of lung cancer. Cureus. (2022) 14:e25230. doi: 10.7759/cureus.25230
134. Liu W, Zhou L, Zhao D, Wu X, Yue F, Yang H, et al. Development and validation of a prognostic nomogram in lung cancer with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Front Med. (2022) 9:810907. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.810907
135. Park MJ, Han KD, Cho JH, and Choi JH. Incidence disparities of obstructive sleep apnea-associated lung cancer by gender; Korean National Health Insurance data analysis. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1214279. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1214279
136. Sillah A, Watson NF, Schwartz SM, Gozal D, and Phipps AI. Sleep apnea and subsequent cancer incidence. Cancer Causes Control: CCC. (2018) 29:987–94. doi: 10.1007/s10552-018-1073-5
137. Guo X, Liu Y, Kim JL, Kim EY, Kim EQ, Jansen A, et al. Effect of cyclical intermittent hypoxia on Ad5CMVCre induced solitary lung cancer progression and spontaneous metastases in the KrasG12D+; p53fl/fl; myristolated p110fl/fl ROSA-gfp mouse. PloS One. (2019) 14:e0212930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212930
138. Liu W, Luo M, Fang YY, Wei S, Zhou L, and Liu K. Relationship between occurrence and progression of lung cancer and nocturnal intermittent hypoxia, apnea and daytime sleepiness. Curr Med Sci. (2019) 39:568–75. doi: 10.1007/s11596-019-2075-6
139. Javaheri S and Javaheri S. Update on persistent excessive daytime sleepiness in OSA. Chest. (2020) 158:776–86. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.02.036
140. Eckert DJ. Phenotypic approaches to obstructive sleep apnoea - New pathways for targeted therapy. Sleep Med Rev. (2018) 37:45–59. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2016.12.003
141. Gozal D, Farré R, and Nieto FJ. Obstructive sleep apnea and cancer: Epidemiologic links and theoretical biological constructs. Sleep Med Rev. (2016) 27:43–55. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2015.05.006
142. Cubillos-Zapata C, Avendaño-Ortiz J, Hernandez-Jimenez E, Toledano V, Casas-Martin J, Varela-Serrano A, et al. Hypoxia-induced PD-L1/PD-1 crosstalk impairs T-cell function in sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J. (2017) 50. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00833-2017
143. Huang MH, Zhang XB, Wang HL, Li LX, Zeng YM, Wang M, et al. Intermittent hypoxia enhances the tumor programmed death ligand 1 expression in a mouse model of sleep apnea. Ann Trans Med. (2019) 7:97. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.01.44
144. Boussiotis VA. Molecular and biochemical aspects of the PD-1 checkpoint pathway. New Engl J Med. (2016) 375:1767–78. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1514296
145. Bardhan K, Anagnostou T, and Boussiotis VA. The PD1:PD-L1/2 pathway from discovery to clinical implementation. Front Immunol. (2016) 7:550. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00550
146. Cui Z, Ruan Z, Li M, Ren R, Ma Y, Zeng J, et al. Intermittent hypoxia inhibits anti-tumor immune response via regulating PD-L1 expression in lung cancer cells and tumor-associated macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 122:110652. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110652
147. Liu Y, Lu M, Chen J, Li S, Deng Y, Yang S, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from lung cancer cells exposed to intermittent hypoxia upregulate programmed death ligand 1 expression in macrophages. Sleep Breathing = Schlaf Atmung. (2022) 26:893–906. doi: 10.1007/s11325-021-02369-1
148. Cubillos-Zapata C, Martínez-García M, Campos-Rodríguez F, Sánchez de la Torre M, Nagore E, Martorell-Calatayud A, et al. Soluble PD-L1 is a potential biomarker of cutaneous melanoma aggressiveness and metastasis in obstructive sleep apnoea patients. Eur Respir J. (2019) 53. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01298-2018
149. Barber GN. STING: infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. (2015) 15:760–70. doi: 10.1038/nri3921
150. Almendros I, Wang Y, Becker L, Lennon FE, Zheng J, Coats BR, et al. Intermittent hypoxia-induced changes in tumor-associated macrophages and tumor Malignancy in a mouse model of sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2014) 189:593–601. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201310-1830OC
151. Campillo N, Torres M, Vilaseca A, Nonaka PN, Gozal D, Roca-Ferrer J, et al. Role of cyclooxygenase-2 on intermittent hypoxia-induced lung tumor Malignancy in a mouse model of sleep apnea. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:44693. doi: 10.1038/srep44693
152. Vitale I, Manic G, Coussens LM, Kroemer G, and Galluzzi L. Macrophages and metabolism in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Metab. (2019) 30:36–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.06.001
153. Hakim F, Wang Y, Zhang SX, Zheng J, Yolcu ES, Carreras A, et al. Fragmented sleep accelerates tumor growth and progression through recruitment of tumor-associated macrophages and TLR4 signaling. Cancer Res. (2014) 74:1329–37. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-13-3014
154. Tauriello DVF, Sancho E, and Batlle E. Overcoming TGFβ-mediated immune evasion in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. (2022) 22:25–44. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00413-6
155. Cui Z, Ruan Z, Li M, Ren R, Ma Y, Zeng J, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea promotes the progression of lung cancer by modulating cancer cell invasion and cancer-associated fibroblast activation via TGFβ signaling. Redox Report: Commun Free Radical Res. (2023) 28:2279813. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2023.2279813
156. Akbarpour M, Khalyfa A, Qiao Z, Gileles-Hillel A, Almendros I, Farré R, et al. Altered CD8+ T-cell lymphocyte function and TC1 cell stemness contribute to enhanced Malignant tumor properties in murine models of sleep apnea. Sleep. (2017) 40. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsw040
157. Zhang XB, Yang YY, Zeng Y, Zeng HQ, Fu BB, Ko CY, et al. Anti-tumor effect of endostatin in a sleep-apnea mouse model with tumor. Clin Trans Oncol Off Publ Fed Spanish Oncol Societies Natl Cancer Institute Mexico. (2019) 21:572–81. doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-1955-8
158. Kang HS, Kwon HY, Kim IK, Ban WH, Kim SW, Kang HH, et al. Intermittent hypoxia exacerbates tumor progression in a mouse model of lung cancer. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:1854. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58906-7
159. Hao S, Li F, Jiang P, and Gao J. Effect of chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced HIF-1α/ATAD2 expression on lung cancer stemness. Cell Mol Biol Lett. (2022) 27:44. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00345-5
160. Noack M and Miossec P. Th17 and regulatory T cell balance in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun Rev. (2014) 13:668–77. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2013.12.004
161. Reale M, Velluto L, Di Nicola M, D’Angelo C, Costantini E, Marchioni M, et al. Cholinergic markers and cytokines in OSA patients. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093264
162. Ye J, Liu H, Zhang G, Li P, Wang Z, Huang S, et al. The treg/th17 imbalance in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Mediators Inflamm. (2012) 2012:815308. doi: 10.1155/2012/815308
Keywords: obstructive sleep apnea, intermittent hypoxia, inflammation, immune dysregulation, CPAP, immunotherapy
Citation: Dong N and Yue H (2025) Advances in immunology of obstructive sleep apnea: mechanistic insights, clinical impact, and therapeutic perspectives. Front. Immunol. 16:1654450. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1654450
Received: 26 June 2025; Accepted: 07 October 2025;
Published: 21 October 2025.
Edited by:
Verena Tretter, Medical University of Vienna, AustriaReviewed by:
Christian Barbato, National Research Council (CNR), ItalyEnrique Hernández Jiménez, Loop Diagnostics S.L., Spain
Copyright © 2025 Dong and Yue. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongmei Yue, eXVlaG1AbHp1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Na Dong
Na Dong Hongmei Yue1,2*
Hongmei Yue1,2*