- 1Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, Ningxia, China
- 2Third Clinical Medical College, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, Ningxia, China
Liver transplantation remains the only curative treatment for end-stage liver disease (ESLD); however, immune rejection significantly hampers its long-term success. Dendritic cell-derived exosomes (DEXs) have emerged as a promising tool for inducing immune tolerance and enabling precise immunomodulation in liver transplantation, owing to their unique bidirectional immunoregulatory capabilities. This review systematically summarizes the biological characteristics and functional properties of DEXs, with a particular focus on their multidimensional regulatory mechanisms within the hepatic transplant immune microenvironment. These include: the mechanisms and pathways by which DEXs mediate immune tolerance; the synergistic immunoregulatory roles of DEXs and exosomes derived from other immune cells. Furthermore, we explore the potential of DEXs for integrated diagnostic and therapeutic applications, engineering upgrades to treatment strategies, and their prospects for clinical translation. Despite their promise, several challenges persist, including difficulties in exosome isolation and purification, prolonged preparation times, bioengineering limitations, and the lack of effective in vivo tracking methods. We propose that advancements in artificial intelligence, biomaterials science, and interdisciplinary technologies may help overcome these barriers, facilitating the precise isolation, functional optimization, and clinical translation of DEXs. This review emphasizes the molecular immunoregulatory networks governed by DEXs and discusses their translational pathways, aiming to promote individualized diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in liver transplantation.
1 Introduction
Liver disease causes more than 2 million deaths worldwide each year, accounting for approximately 4% (1 in 25) of all deaths globally (1). Both chronic injury (viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease) and acute injury (acetaminophen overdose) can lead to progressive deterioration of the liver’s structure and function, with the end stage known as ESLD (2). Currently, there are no approved drugs that can reverse or halt the progression of ESLD (3). Therefore, liver transplantation remains the only curative option (4). Recent advances in surgical techniques and perioperative management have dramatically improved the short-term success rate of liver transplantation.However, its long-term efficacy continues to be hindered by the imbalance between immune rejection and immune tolerance (5). The ideal immune state following liver transplantation is the establishment of immune tolerance, which allows the transplanted liver to function stably without continuous immunosuppressive therapy (6). In clinical practice,however, only about 20%–40% of liver transplant recipients achieve so-called “operational tolerance.” (7) Although the widespread use of immunosuppressive drugs has significantly reduced the incidence of acute rejection, their long-term administration is associated with serious side effects such as infections, tumorigenesis,and metabolic disorders, which severely affect patients’ quality of life (8). Therefore, the development of safer and more precise immunomodulatory strategies has become a core direction in liver transplantation research.
As an “immune-privileged organ”, the liver possesses a unique immune microenvironment that can promote graft-specific immune tolerance by modulating the function of local immune cells, such as dendritic cells (DCs) (9). DCs are recognized as the most potent antigen-presenting cells (APCs), capable of capturing, processing, and presenting antigens to naive T cells, thereby activating helper T cells or cytotoxic T cells to initiate antigen-specific immune responses (10). Serving as a critical bridge between innate and adaptive immunity, DCs not only enhance T cell-mediated rejection through antigen presentation (11) but also promote the differentiation of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and contribute to immune homeostasis (12). The immunological function of DCs—either promoting immune activation or inducing immune tolerance—largely depends on their maturation status. In vitro-generated exosomes from mature DCs typically activate T cells and enhance immune responses, whereas those from immature DCs tend to induce T-cell anergy or promote immune tolerance (13). In this review, the terms “immature” and “mature” DCs refer to bone marrow-derived or monocyte-derived DCs generated in vitro. In vivo, these correspond to steady-state or activated DCs, respectively. In vivo studies in humans have shown that donor-derived regulatory DCs(DCregs) may modulate host APCs, memory CD8+ T cells, and Tregs, potentially contributing to immune regulation at the time of transplantation (14). More recently, DCs have been found to secrete exosomes, which retain several biological properties of their parent cells (15) and carry surface molecules such as major histocompatibility complexes (MHCs), miRNAs, and various immunomodulatory proteins (16). These DEXs exhibit immunoregulatory functions comparable to those of DCs themselves. Depending on their cellular origin, DEXs may exert bidirectional immunomodulatory effects: exosomes derived from mature DCs promote antigen-specific T-cell activation and proliferation, thereby facilitating graft rejection (17, 18), whereas exosomes derived from immature DCs suppress anti-donor immune responses, prolong graft survival, and demonstrate a tolerogenic potential (19). This bidirectional regulatory capacity positions DEXs as key modulators in maintaining immune homeostasis in the context of transplantation.
As an emerging platform for integrated diagnostics and therapeutics, exosomes exhibit several unique biological advantages. Their phospholipid bilayer structure provides effective protection against enzymatic degradation; surface markers enable tissue-specific chemotaxis and targeted delivery; and their luminal contents—such as miRNAs and lncRNAs—serve as noninvasive biomarkers reflecting the immune status of both donors and recipients (20–22). Notably, exosomal miRNA profiles in the plasma of liver transplant recipients have been found to correlate closely with the severity of graft rejection (23). In addition to their diagnostic utility, exosomes can function as nanoscale delivery platforms for therapeutic agents, including small molecules and gene-editing tools. Their ability to traverse biological barriers and deliver cargo precisely to immune targets offers a promising strategy for achieving “invisible” immune modulation (24, 25). In conclusion, DEXs not only hold great promise in promoting immune tolerance following transplantation, but also represent a versatile theranostic platform—simultaneously serving as biomarkers and targeted delivery vehicles—to advance precision immunomodulation in liver transplantation.
2 Biological properties and functions of DEXs
In several Murine transplantation models, “cross-dressed” recipient APCs—bearing intact donor major histocompatibility complex(MHC) molecules transferred via small extracellular vesicles released from allogeneic grafts—have been described as a key mechanism in initiating and sustaining allogeneic immune responses (26). Experimental evidence suggests that this mechanism may underlie the spontaneous acceptance of liver allografts in the absence of immunosuppressive therapy (27).
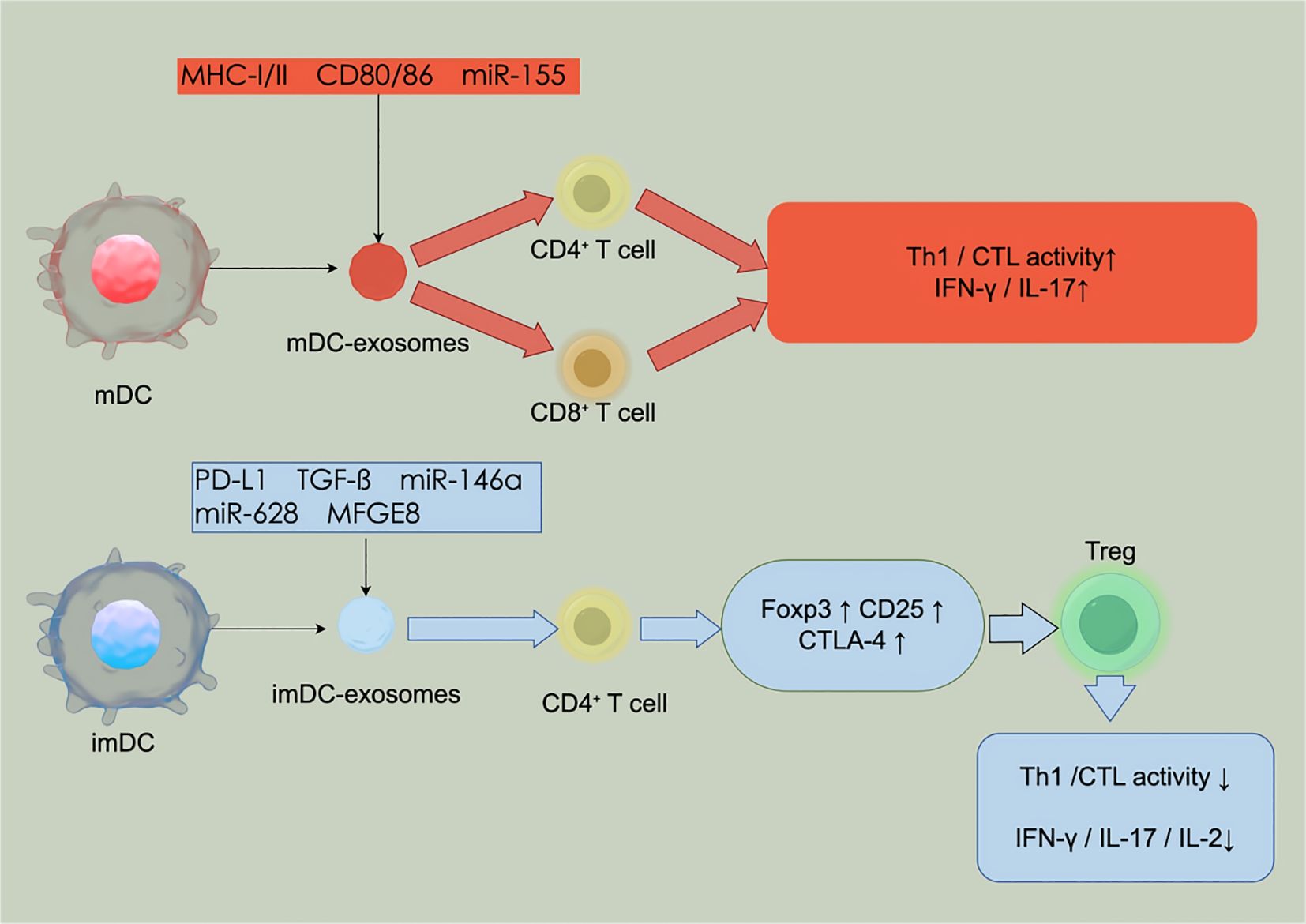
DEXs are enriched with immunoreactive components, including miRNAs, antigen-presenting molecules(MHC-I and MHC-II), and co-stimulatory molecules (CD80/CD86), which enable them to directly or indirectly modulate immune responses (28). The molecular composition and immunological functions of DEXs are highly dependent on the maturation state of their parental DCs. Exosomes derived from in vitro-generated immature DCs exhibit pronounced immunosuppressive properties. For instance, in a murine kidney transplantation model, Exosomes derived from in vitro-generated immature DCs enriched with miR-682—a microRNA that negatively regulates Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 2 (ROCK2)—promote the differentiation of Tregs and suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-2, IL-17, and IFN-γ, ultimately prolonging graft survival (29). Moreover, exosomes derived from in vitro-generated immature DCs contain various immunosuppressive proteins, including milk fat globule epidermal growth factor VIII (MFGE8), which mitigates systemic pro-inflammatory responses by enhancing phagocytosis and secondary immunosuppression (30). Conversely, exosomes derived from in vitro-generated mature DCs demonstrate a more potent immune-activating capacity. These exosomes carry pre-loaded major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) and class II (MHC-II) molecules, as well as co-stimulatory molecules (CD80/CD86), which can be transferred to recipient cells. While they do not actively process or present antigens, the transferred peptide–MHC complexes can modulate antigen presentation by recipient APCs (31). Via MHC-I and MHC-II molecules, exosomes derived from in vitro-generated mature DCs deliver antigenic signals to naive CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes(CTLs) and CD4+ helper T cells(Th), respectively, thereby inducing antigen-specific immune responses (32, 33). Additionally, exosomes derived fromin vitro-generated immature DCs carry immune-activating miRNAs such as miR-155, which further potentiate their immunostimulatory effects (34).
This molecular compositional plasticity arises from DC-specific cytosolic sorting mechanisms that selectively enrich distinct miRNAs and functional proteins, enabling precise immunomodulation tailored to specific microenvironmental cues (32). Functionally, DEXs not only display MHC molecules on their surface but also express programmed death ligand 1(PD-L1) (12). This allows them to present donor antigens and activate both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, inducing rejection responses (35, 36), while also inhibiting T cell activation through PD-L1–CD80 trans interactions, exerting a negative regulatory effect (37). Together, this DEX-centered immunoregulatory network plays a pivotal role in maintaining immune homeostasis and regulating graft tolerance. In summary, the highly tunable molecular features and functional diversity of DEXs provide a solid molecular foundation and theoretical framework for the development of individualized immunoregulatory strategies in liver transplantation through refined immune modulation mechanisms (Figure 1). In addition, DEXs possess the unique capacity to both activate immune responses and regulate immune tolerance. In one study, administration of interleukin-10(IL-10)-induced DEXs significantly suppressed the development of collagen-induced arthritis, mitigating inflammatory responses and tissue damage in a murine model (38). These findings suggest that exosomes derived from exosomes derived from immature DCs can effectively inhibit inflammatory and autoimmune responses.
Conversely, DEXs sensitized with Toxoplasma gondii antigens were shown to specifically localize to the spleen following adoptive transfer in mice, where they elicited a robust Th1-type antigen-specific immune response that markedly enhanced host resistance to infection (39). Furthermore, another study demonstrated that DEXs loaded with tumor-associated antigenic peptides successfully activated antigen-specific CTLs, which subsequently eradicated or suppressed tumor growth via a T cell-dependent mechanism (40).
Collectively, these results highlight the dual immunomodulatory capabilities of DEXs in the context of liver transplantation: not only can they facilitate the induction of immune tolerance to prevent graft rejection, but they can also potentiate protective immune responses against infections and malignancies when appropriately stimulated. This functional versatility positions DEXs as promising tools for both immune suppression and immune activation in transplant immunotherapy.
3 Mechanisms of DEXs involved in the immune microenvironment of liver transplantation
In a rat liver transplantation model exosomes from donor-derived steady-state DCs have been shown to induce immune tolerance, which is further enhanced when combined with Treg cells (41). DEXs act as critical regulators within the complex immune microenvironment of liver transplantation, dynamically modulating immune responses through multidimensional mechanisms to maintain the delicate balance between immune tolerance and rejection.
3.1 Mechanisms and pathways for the establishment of DEXs-mediated immune tolerance
Small extracellular vesicles released shortly after liver transplantation have been shown to exert immunosuppressive effects, whereas those released at later stages lack such activity, potentially influencing the immunogenicity of liver grafts (42). Donor-derived DEXs can enter the recipient’s circulation post-transplantation and migrate to secondary lymphoid organs, including the spleen and lymph nodes. The donor antigenic peptide-MHC complexes and immune co-stimulatory or inhibitory molecules (PD-L1) expressed on their surfaces directly interact with recipient T cells to modulate their activation or inhibition (43). For example, exosomes derived from immature or tolerant DCs generated in vitro may be enriched in immunosuppressive factors such as TGF-β1 and CTLA-4, which inhibit T cell activation and proliferation and modulate other immune cells(recipient DCs), synergistically promoting Treg differentiation and maintaining immune tolerance (44, 45), notably, immature dendritic cells can exhibit either tolerogenic or immunogenic properties, depending on the specific stimuli and the surrounding microenvironment. It was shown that donor-derived DEX increased the proportion of Tregs and the expression of Foxp3 mRNA in recipient spleens in a mouse kidney transplantation model (29). Furthermore, PD-L1 carried by exosomes can bind to PD-1 on T cells, suppressing their proliferation and cytotoxicity (46). This cell-free antigen delivery mechanism bypasses the need for direct cell contact, providing unique advantages over traditional pathways. Transforming growth factor β1(TGF-β1) contained within exosomes effectively induces naive T cell differentiation into CD25+CTLA-4+Foxp3+ Tregs, thereby exerting immunosuppressive effects (47). Mechanistically, TGF-β activates the Smad2/3 signaling pathway, upregulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α(PGC-1α), which promotes mitochondrial fusion and inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor 1α(HIF-1α). This leads to increased expression of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1(CPT1), a key enzyme in fatty acid oxidation(FAO), and decreased expression of glycolytic enzyme hexokinase 2(HK2), thus reprogramming T cell metabolism from glycolysis toward FAO (48). Such metabolic remodeling supports Treg differentiation and function, establishing a foundation for immune tolerance.
DEXs also regulate T cell subset differentiation via delivery of specific noncoding RNAs. For example, miR-125a and miR-125b target and inhibit the transcription factor STAT3, thereby suppressing Th17 cell differentiation (49), while TGF-β enrichment promotes Treg expansion by inducing Foxp3 expression (50). Additionally, DEXs modulate inflammatory responses by targeting the TRAF6/IRAK-1/NLRP3 pathway, reducing secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β (51). In a murine colitis model, DEX miR-146a regulates Treg function through the IFN-γ/STAT1 signaling pathway, attenuating Th1 immune responses (52, 53). This non-cell-contact-dependent, targetable modulation mediated by exosomal noncoding RNAs holds great potential for gene-level immunointervention.
Moreover, DEXs facilitate the polarization of macrophages from a pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype to an immunosuppressive M2 phenotype, thereby enhancing the local immunosuppressive microenvironment (50). This indicates that DEXs exert immunoregulatory effects not only on T cells but also by remodeling the broader immune milieu, providing a molecular basis for tolerance maintenance. Collectively, DEXs play a central immunomodulatory role in establishing immune tolerance after liver transplantation through multiple mechanisms, including antigen presentation, inhibitory signaling, metabolic reprogramming, noncoding RNA regulation, and immune microenvironment remodeling.
However, it should be noted that most evidence supporting DEX-mediated tolerance induction arises from rodent models. Human liver transplant recipients often present with underlying conditions such as viral hepatitis or fatty liver disease, generating chronic inflammatory microenvironments potentially impairing exosomal immunomodulatory function. For example, HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients exhibit significantly higher Treg levels than HBeAg-negative patients (54), suggesting that species differences and disease heterogeneity may influence therapeutic efficacy.
3.2 Synergistic immunomodulation by DC-derived and multicellular exosomes in liver transplantation
Although DEXs have received considerable attention in the context of liver transplantation due to their potential to induce immune tolerance, exosomes from other cellular origins also play significant roles in modulating immune cell function and may act synergistically with DEXs to shape the perigraft immune microenvironment. Studies have demonstrated that hepatocyte-derived exosomes can alleviate hepatic inflammatory responses and promote regulatory Treg expansion in murine models (55). Furthermore,THP-1 monocytes pretreated with hepatocyte-derived exosomes exhibited a marked reduction in proinflammatory cytokine expression—such as IL-8 and IL-1β—upon lipopolysaccharide(LPS) stimulation (56). These endogenous exosomes may support the differentiation of anti-inflammatory immune subsets, thereby functionally cooperating with exosomes derived from immature DCs to promote Treg induction and suppress pro-rejection responses. Additionally, tumor-derived exosomes carrying immunosuppressive factors such as prostaglandin E2(PGE2) and transforming growth factor-β(TGF-β) can be internalized by bone marrow progenitor cells, promoting the differentiation of monocytes into DCs and the expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells, which inhibit T cell activity (57, 58). In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), TEXs have been shown to reprogram macrophages via activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, leading to increased secretion of proinflammatory cytokines and the formation of M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophages (59). Moreover, tumor-derived exosomes can reprogram neutrophils and macrophages, simultaneously suppressing IFN-γ and TNF-α production while upregulating PD-1 expression on T cells, thus contributing to an immunosuppressive phenotype (60). Although the immunological mechanisms of tumor-derived exosomes are primarily associated with tumor immune evasion, their ability to modulate the immune microenvironment suggests potential relevance in the context of transplantation tolerance. These findings imply that DEXs and exosomes from diverse cellular sources may collaboratively modulate immune responses in the liver transplant microenvironment through synergistic regulatory pathways.
4 A new paradigm for immunotherapy and diagnostics in liver transplantation
DEXs exhibit significant theranostic potential in the context of liver transplantation, owing to their unique capabilities in immune regulation, biomarker-based diagnosis, and targeted therapeutic delivery. These properties position them as a transformative platform in the development of next-generation strategies for transplantation immunotherapy.
4.1 Diagnostic potential and marker validation
DEXs have been extensively investigated as biovectors for non-invasive biomarker screening in liquid biopsies, owing to their high accessibility, structural stability, and resistance to enzymatic degradation. Exosomes are widely distributed in blood and other body fluids, and their phospholipid bilayer membranes protect encapsulated proteins and microRNAs (miRNAs) from degradation by extracellular nucleases and proteases, thus ensuring their integrity and diagnostic utility. In the field of organ transplantation, a critical clinical challenge is the lack of real-time and accurate methods to assess graft immune status. Donor-derived exosomes, particularly those originating from DCs, have been proposed as promising biomarkers for early immune responses following transplantation—including acute and chronic rejection. Their potential lies in enabling early detection and dynamic monitoring of immune rejection events, facilitating timely clinical intervention and potentially improving graft survival (61). In-depth analysis of DEXs derived from in vitro models (BMDCs/MoDCs) can reveal molecular signatures—such as miRNA and proteomic profiles—associated with distinct DC activation states(steady-state vs. activated). These signatures could serve as reference maps to interpret compositional changes in sEVs/DEXs directly isolated from patient biofluids (blood, bile), thereby enabling inference of the in vivo activation status of DCs and the prevailing immune microenvironment, and supporting the non-invasive diagnosis of graft rejection or tolerance. Recent studies have demonstrated that the miRNA profiles carried by DEXs closely reflect the post-transplant immune status. For example, bone marrow-derived dendritic cell exosomes are enriched in miR-34a and miR-21 (62), the latter of which is significantly upregulated during episodes of rejection and shows a strong positive correlation with immune activity (63). Moreover, downregulation or inhibition of miR-21 has been shown to exert anti-inflammatory effects by activating the STAT3 signaling pathway, promoting macrophage polarization toward the immunosuppressive M2 phenotype (64). Compared to exosomes from in vitro-generated immature DCs, those from in vitro-generated mature DCs are enriched in immunoregulatory miRNAs such as miR-146a, miR-125b-5p, and miR-148a-3p (65–67). Notably, miR-148a-3p has been suggested as a potential diagnostic biomarker for chronic graft-versus-host disease (68).In a murine transplant model, miR-146a was shown to Treg function through the IFN-γ/STAT1 pathway, with miR-146a deficiency associated with prolonged graft survival and reduced rejection severity (52). Additionally, miR-155 is significantly upregulated in exosomes from human monocyte-derived mature DCs compared to those from imDCs (69). Both miR-155 and miR-146a are strongly implicated in graft immune responses and have been identified as non-invasive biomarkers for chronic graft-versus-host disease, with high expression levels observed during active disease states (70). These findings indicate that DEX miRNA expression profiles can not only provide dynamic, time-resolved monitoring of immune status but also differentiate between distinct immunological conditions—such as acute rejection, chronic tolerance, and graft-versus-host disease—thereby offering precise molecular insights and potential diagnostic markers for immune surveillance in liver transplantation.
However, it is important to note that exosomal miRNA signatures can be influenced by fluctuations in hepatic function. For instance, patients with cirrhosis often exhibit elevated baseline levels of plasma exosomal miR-21 (71), which may obscure rejection-associated expression changes and increase the risk of false-negative interpretations. Therefore, the establishment of standardized baseline correction models will be essential for improving the accuracy and clinical applicability of exosome-based diagnostics in the future. At present, the exploration of DEXs/sEVs as diagnostic markers in liver transplantation remains at an early and largely speculative stage, requiring validation through extensive clinical studies.
4.2 Engineering upgrades to treatment strategies
DEXs not only exhibit passive cargo delivery capabilities but can also be genetically engineered to achieve enhanced functionality and targeted immunoregulation (38, 72–74). Accumulating evidence suggests that genetically modified DCs and their exosomal products can significantly suppress graft rejection and promote immune tolerance following transplantation. For instance, CD80+ DEXs have been shown to attenuate acute rejection after liver transplantation by downregulating the expression of the NLRP3 inflammasome and suppressing CD8+ T cell adhesion, infiltration, and proinflammatory cytokine production (75). In another study, a lentiviral vector system was employed to overexpress miR-193b-3p in DCs. The resulting exosomes were enriched with this miRNA and were capable of significantly increasing the proportion of Tregs, while simultaneously suppressing NLRP3 expression, decreasing the levels of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and IL-17A, and upregulating anti-inflammatory cytokines including IL-10 and TGF-β. These changes effectively mitigated immune rejection in a liver transplantation model (76).
Collectively, these findings demonstrate the potential of engineered DEXs as programmable, cell-free delivery vehicles for immunoregulatory molecules. Their ability to be customized at the molecular level highlights a promising platform for precise and durable immunomodulation in liver transplantation and beyond. DCs express CCR7, which guides their homing to lymph nodes via CCL19/CCL21 signaling, thereby enabling preferential interactions with T cells and other APCs in secondary lymphoid organs (77, 78). Enhancing CCR7 expression has been shown to markedly increase the accumulation of DEXs in secondary lymphoid organs and strengthen their interactions with T cells. For instance, in a myocardial infarction model, CCR7-high DEXs(MI-DEXs) exhibited greater splenic accumulation and an enhanced capacity to activate CD4+ T cells, inducing IL-4 and IL-10 expression as demonstrated by near-infrared imaging (79). Another study on dendritic cell vaccines demonstrated that nano-exosomes(Hy-M-Exo) fused with cell membranes expressing CCR7 exhibited significantly greater targeted accumulation in lymph nodes in vivo compared with conventional exosomes, and increased uptake by APCs(including DCs) in lymph nodes by approximately 1.7-fold (80). This evidence supports the mechanism by which the CCR7–CCL19/CCL21 axis mediates the targeting of DEXs to lymphoid organs and facilitates their interactions with T cells or APCs, providing a basis for the optimization of targeting strategies.
4.3 Translational prospects in clinical practice
In recent years, DEXs have emerged as a promising vector for developing novel immune tolerance-inducing strategies, owing to their low immunogenicity, high biological stability, and potential for engineered modifications. In various preclinical models related to liver transplantation, DEXs have demonstrated favorable bioactivity and safety profiles, underscoring their high translational potential.
For instance, in a murine model of liver ischemia–reperfusion (IR) injury, systemic administration of DEXs via tail vein successfully delivered heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) to naive T cells, activated the PI3K/mTOR signaling pathway, and regulated the Treg/Th17 cell balance. This intervention significantly attenuated IR-induced hepatic injury and preserved liver structure and function, providing a promising strategy to mitigate IR injury during transplantation (81).
Moreover, in a rat orthotopic liver transplantation model, the combined infusion of donor-derived exosomes derived from immature DCs and donor antigen–specific Tregs induced and sustained long-term transplantation tolerance without the use of conventional immunosuppressive agents (38). This approach not only circumvented the adverse effects and infection risks associated with long-term immunosuppressive therapy but also highlighted the unique capacity of DEXs to induce antigen-specific immune tolerance in vivo.
5 Current challenges and future directions
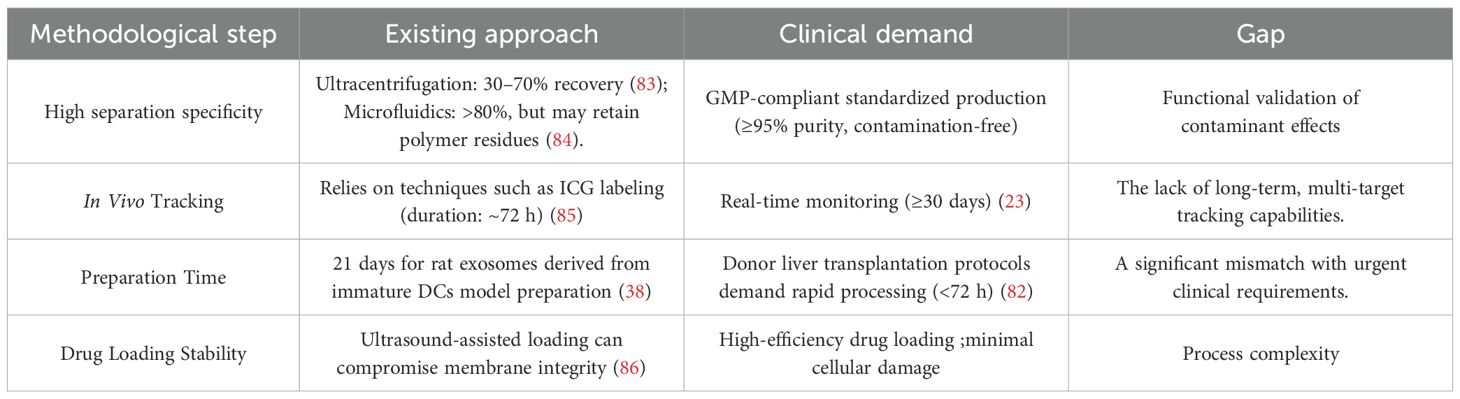
The successful clinical translation of current DEX therapies necessitates overcoming several critical bottlenecks. These include the standardization of exosome isolation protocols, reduction of production timelines, development of reliable long-term in vivo tracking technologies, and improvement of drug-loading stability.
For instance, the preparation cycle for DCreg-based therapy at the University of Pittsburgh requires approximately three weeks (14), which significantly exceeds the typical decision-making window for cadaveric donor liver transplantation—usually less than 72 hours (82). (Table 1) Summarizes the core discrepancies between the current technological capabilities and the clinical demands, underscoring the urgent need for innovative approaches to accelerate and optimize DEX manufacturing and application workflows.
5.1 technological bottleneck
Current isolation techniques for DEXs continue to face significant technical bottlenecks and methodological controversies. Due to their nanoscale size, low density, and fragile membrane structures, achieving efficient isolation and purification while maintaining biological activity remains a critical challenge in the field. At present, the predominant separation strategies include differential ultracentrifugation (DUCC), size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), and immunoaffinity capture (IAC), among these, DUCC has long been regarded as the “gold standard” due to its ability to preserve exosomal membrane integrity. However, its limitations—such as prolonged operation time, low throughput, and suboptimal purity—pose significant obstacles to meeting the demands of clinical standardization and large-scale production (87, 88). The SEC method, which separates particles based on size, offers advantages such as operational simplicity and minimal sample perturbation. Nevertheless, when target vesicles approach or exceed the upper limit of the chromatographic medium’s pore size, the resolution diminishes significantly, thereby compromising exosome purity (83). Immunoaffinity capture, while highly specific, suffers from issues related to the heterogeneous expression of surface antigens across exosomal subpopulations and the potential for incomplete removal of bound antibodies, which can interfere with downstream functional analyses (89). In recent years, viscoelastic microfluidics has emerged as a promising non-labeled, continuous-flow, and high-throughput alternative. This method employs biocompatible polymers added to the suspension medium to generate size-dependent elastic lift forces that enable the selective enrichment of exosomes, achieving >90% purity and recovery rates exceeding 80% (84). However, residual polymers may contaminate biological samples and negatively impact the structural and functional validation of isolated exosomes. It should be noted that the reported “enrichment” of specific molecules(miRNAs, proteins) in DEXs in many studies is typically based on comparisons with their parental DCs or with the total composition of the culture supernatant. However, the biological relevance and specificity of such “enrichment” should be interpreted with caution, as strictly matched, unpurified vesicle populations (total sEVs or conditioned medium) are often lacking as controls. Ideally, future studies should incorporate more comprehensive and appropriately matched comparison groups.
For in vivo tracking applications, the FDA-approved near-infrared fluorescent dye indocyanine green(ICG) has been successfully utilized for exosome labeling. For instance, HGI@Exo formulations enable real-time imaging of exosome biodistribution in liver transplant recipients (85). While this approach enhances visualization of homing and biodistribution, further refinement is required to minimize potential alterations in the exosomes intrinsic biological functions due to the labeling process.
To date, most exosome-tracking methods rely heavily on fluorescence-based techniques, which are limited by issues such as channel number constraints, spectral overlap, low signal flux, and poor multiplexing capabilities (90). Thus, the development of more sensitive, stable, and biologically compatible imaging technologies remains an urgent priority for advancing the clinical translation of exosome-based therapeutics.
5.2 Engineering dilemma
Exosomes have demonstrated remarkable potential as drug delivery vehicles; however, their engineering remains encumbered by several technical and translational challenges (91). Currently, widely adopted drug-loading strategies—such as ultrasound-assisted methods—are considered relatively mild and have been shown to enhance drug encapsulation efficiency by transiently remodeling the exosomal membrane without significantly disrupting protein or lipid components (92). Nonetheless, prolonged or excessive ultrasound exposure may compromise the structural and functional integrity of exosomal membranes, thereby reducing their biological stability (86). Endogenous cargo loading through genetic engineering has also emerged as a promising strategy. For instance, tumor-derived exosomes have been employed to deliver CRISPR/Cas9 systems targeting poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1), yielding potent therapeutic outcomes in solid tumor models (93). However, this approach is technically complex, costly, and difficult to scale, thereby limiting its feasibility for routine clinical application and industrial-scale production.
To address these limitations, there is a pressing need to develop more efficient, robust, and scalable exosome drug-loading technologies. Recent efforts have focused on integrating nanocomposite-modified microfluidic platforms with innovative approaches such as cellular nanoperforation, exosome-enveloped protein nanocage (EPN) capture systems, and tunable optimized particle-enhanced exosome vesicle technology. These emerging strategies aim to enable high-loading capacity, structural stability, and high-throughput engineered production of exosomes to meet clinical translational demands (94).
5.3 Future perspectives: toward precision and integration
With advancements in artificial intelligence(AI) and bioinformatics,exosome identification and function prediction models based on machine learning have been increasingly applied to cancer staging, disease diagnosis, and therapeutic target discovery (95). Recent studies have explored the integration of exosomal miRNA expression profiles with AI algorithms to enable early prediction of rejection in renal transplantation (96, 97). This concept holds significant potential for extension to liver transplantation, where the dynamic profiling of exosomal miRNAs, in combination with single-cell sequencing technologies and machine learning models, may facilitate the development of intelligent early warning systems for predicting postoperative immune rejection. In parallel, the rapid evolution of interdisciplinary technologies—such as cryo-electron microscopy (98), high-resolution microfluidics (99), and AI-assisted data analytics (100)—is paving the way for the construction of a comprehensive “precision isolation–functional validation–clinical translation” workflow. This approach would enable the systematic classification and targeted modulation of exosomal functional subpopulations. Moreover, combining exosomes with biomaterials—such as hydrogel-based sustained-release systems—may enhance their in vivo half-life and enable localized remodeling of the immune microenvironment within specific tissues (101). Additionally, optimization of freeze-drying and preservation techniques has been shown to improve the structural stability of exosomal proteins and RNAs (102), thereby supporting the feasibility of storage, transport, and formulation for large-scale, multi-center randomized controlled trials (RCTs). These advances will be essential for validating the safety and efficacy of DEXs in preventing acute rejection after liver transplantation.
6 Conclusion
DEXs have emerged as a promising immunotherapeutic modality in liver transplantation, owing to their unique immunomodulatory capabilities. By delivering key regulatory cargos—such as miRNAs, immunosuppressive proteins, and surface ligands—DEXs modulate both innate and adaptive immune responses, including the activity of T cells and myeloid cell subsets. This enables them to exert a dual role:inducing graft-specific immune tolerance while simultaneously enhancing host defense against infections and malignancies. In preclinical models, DEXs have demonstrated the ability to attenuate ischemia-reperfusion injury and prolong allograft survival without the need for conventional immunosuppressive agents. Furthermore, advances in bioengineering have enabled the customization of DEXs for targeted delivery and functional augmentation, underscoring their potential as both diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic vectors. However, several translational challenges persist, including low-yield isolation, exosome heterogeneity, and limited delivery efficiency. Notably, there is a paucity of clinical studies evaluating the safety, biodistribution, and immunological efficacy of human-derived DEXs in liver transplantation. Future investigator-initiated trials(IITs) are warranted to validate preclinical findings and assess clinical applicability. Looking ahead, the integration of microfluidic technologies, advanced imaging, artificial intelligence, and biocompatible scaffolds may enable large-scale production, high-resolution functional profiling, and personalized application of DEXs. With continued technological refinement and multicenter clinical validation, DEXs are poised to become a critical component of individualized immunotherapy and immune monitoring in liver transplantation.
Author contributions
XC: Writing – original draft. ZY: Writing – original draft. ML: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by project Ningxia Natural Science Foundation (2024AAC03450, 2025AAC020056);Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region People’s Hospital Science and Technology Innovation Talent Project ([2023] 72); Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region People’s Hospital National Natural Science Foundation Pre-Experimental Project (2024GZRYSY0015). Other than described, the authors have not received any funding or grants in support of the presented research or for the preparation of this work and have no additional declarations of potential conflicts of interest.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Correction note
A correction has been made to this article. Details can be found at: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1707327.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
AI, artificial intelligence; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; DC, dendritic cell; DEX, dendritic cell-derived exosome; DUC, differential ultracentrifugation; ESLD, end stage liver disease; IAC, immunoaffinity capture; IR, ischemia reperfusion; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; SEC, size-exclusion chromatography; Treg, regulatory T cell.
References
1. Devarbhavi H, Asrani SK, Arab JP, Nartey YA, Pose E, and Kamath PS. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J Hepatol. (2023) 79:516–37. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.017, PMID: 36990226
2. Zhang L, Deng Y, Bai X, Wei X, Ren Y, Chen S, et al. Cell therapy for end-stage liver disease: Current state and clinical challenge. Chin Med J (Engl). (2024) 137:2808–20. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003332, PMID: 39602326
3. Fallowfield JA, Jimenez-Ramos M, and Robertson A. Emerging synthetic drugs for the treatment of liver cirrhosis. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. (2021) 26:149–63. doi: 10.1080/14728214.2021.1918099, PMID: 33856246
4. Artru F, Trovato F, Morrison M, Bernal W, and McPhail M. Liver transplantation for acute-on-chronic liver failure. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 9:564–76. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00363-1, PMID: 38309288
5. Zhuang J and Hou J. The role of regulatory myeloid cell therapy in renal allograft rejection. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:625998. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.625998, PMID: 33717141
6. Ding M, He Y, Zhang S, and Guo W. Recent advances in costimulatory blockade to induce immune tolerance in liver transplantation. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:537079. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.537079, PMID: 33732228
7. Hann A, Osei-Bordom DC, Neil DAH, Ronca V, Warner S, and Perera MTPR. The human immune response to cadaveric and living donor liver allografts. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1227. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01227, PMID: 32655558
8. Nankivell BJ and Kuypers DR. Diagnosis and prevention of chronic kidney allograft loss. Lancet. (2011) 378:1428–37. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60699-5, PMID: 22000139
9. Pan J, Ye F, Li H, Yu C, Mao J, Xiao Y, et al. Dissecting the immune discrepancies in mouse liver allograft tolerance and heart/kidney allograft rejection. Cell Prolif. (2024) 57:e13555. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13555, PMID: 37748771
10. Wculek SK, Cueto FJ, Mujal AM, Melero I, Krummel MF, and Sancho D. Dendritic cells in cancer immunology and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. (2020) 20:7–24. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0210-z, PMID: 31467405
11. Ness S, Lin S, and Gordon JR. Regulatory dendritic cells, T cell tolerance, and dendritic cell therapy for immunologic disease. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:633436. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.633436, PMID: 33777019
12. Luo X, Du G, Long Y, Zheng M, Chen B, Li W, et al. Programmed death ligand-1-overexpressing donor exosomes mediate donor-specific immunosuppression by delivering co-inhibitory signals to donor-specific T cells. Adv Healthc Mater. (2023) 12:e2300670. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202300670, PMID: 37220874
13. Mellman I and Steinman RM. Dendritic cells: specialized and regulated antigen processing machines. Cell. (2001) 106:255–8. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00449-4, PMID: 11509172
14. Macedo C, Tran LM, Zahorchak AF, Dai H, Gu X, Ravichandran R, et al. Donor-derived regulatory dendritic cell infusion results in host cell cross-dressing and T cell subset changes in prospective living donor liver transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. (2021) 21:2372–86. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16393, PMID: 33171019
15. Elashiry M, Elsayed R, Elashiry MM, Rashid MH, Ara R, Arbab AS, et al. Proteomic characterization, biodistribution, and functional studies of immune-therapeutic exosomes: implications for inflammatory lung diseases. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:636222. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636222, PMID: 33841418
16. Xia J, Miao Y, Wang X, Huang X, and Dai J. Recent progress of dendritic cell-derived exosomes (Dex) as an anti-cancer nanovaccine. BioMed Pharmacother. (2022) 152:113250. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113250, PMID: 35700679
17. Admyre C, Johansson SM, Paulie S, and Gabrielsson S. Direct exosome stimulation of peripheral human T cells detected by ELISPOT. Eur J Immunol. (2006) 36:1772–81. doi: 10.1002/eji.200535615, PMID: 16761310
18. Segura E, Nicco C, Lombard B, Véron P, Raposo G, Batteux F, et al. ICAM-1 on exosomes from mature dendritic cells is critical for efficient naive T-cell priming. Blood. (2005) 106:216–23. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0220, PMID: 15790784
19. Pêche H, Renaudin K, Beriou G, Merieau E, Amigorena S, and Cuturi MC. Induction of tolerance by exosomes and short-term immunosuppression in a fully MHC-mismatched rat cardiac allograft model. Am J Transplant. (2006) 6:1541–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2006.01344.x, PMID: 16827854
20. Li W, Li C, Zhou T, Liu X, Liu X, Li X, et al. Role of exosomal proteins in cancer diagnosis. Mol Cancer. (2017) 16:145. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0706-8, PMID: 28851367
21. Zhou L, Shen M, Fan X, Liu Y, and Yang L. Pathogenic and potential therapeutic roles of exosomes derived from immune cells in liver diseases. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:810300. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.810300, PMID: 35185900
22. Wang C, Zhou H, Wu R, Guo Y, Gong L, Fu K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes and non-coding RNAs: Regulatory and therapeutic role in liver diseases. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 157:114040. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114040, PMID: 36423545
23. Millán O, Ruiz P, Julian J, Lizana A, Fundora Y, Crespo G, et al. A plasmatic score using a miRNA signature and CXCL-10 for accurate prediction and diagnosis of liver allograft rejection. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1196882. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1196882, PMID: 37325660
24. Wang J, Li G, Tu C, Chen X, Yang B, Huo Y, et al. High-throughput single-cell analysis of exosome mediated dual drug delivery, in vivo fate and synergistic tumor therapy. Nanoscale. (2020) 12:13742–56. doi: 10.1039/d0nr02344b, PMID: 32573602
25. Du J, Wan Z, Wang C, Lu F, Wei M, Wang D, et al. Designer exosomes for targeted and efficient ferroptosis induction in cancer via chemo-photodynamic therapy. Theranostics. (2021) 11:8185–96. doi: 10.7150/thno.59121, PMID: 34373736
26. Hughes AD, Zhao D, Dai H, Abou-Daya KI, Tieu R, Rammal R, et al. Cross-dressed dendritic cells sustain effector T cell responses in islet and kidney allografts. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:287–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI125773, PMID: 31763998
27. Ono Y, Perez-Gutierrez A, Nakao T, Dai H, Camirand G, Yoshida O, et al. Graft-infiltrating PD-L1hi cross-dressed dendritic cells regulate antidonor T cell responses in mouse liver transplant tolerance. Hepatology. (2018) 67:1499–515. doi: 10.1002/hep.29529, PMID: 28921638
28. Pitt JM, André F, Amigorena S, Soria JC, Eggermont A, Kroemer G, et al. Dendritic cell-derived exosomes for cancer therapy. J Clin Invest. (2016) 126:1224–32. doi: 10.1172/JCI81137, PMID: 27035813
29. Pang XL, Wang ZG, Liu L, Feng YH, Wang JX, Xie HC, et al. Immature dendritic cells derived exosomes promotes immune tolerance by regulating T cell differentiation in renal transplantation. Aging (Albany NY). (2019) 11:8911–24. doi: 10.18632/aging.102346, PMID: 31655796
30. Miksa M, Wu R, Dong W, Komura H, Amin D, Ji Y, et al. Immature dendritic cell-derived exosomes rescue septic animals via milk fat globule epidermal growth factor-factor VIII [corrected. J Immunol. (2009) 183:5983–90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802994, PMID: 19812188
31. Qazi KR, Gehrmann U, Domange Jordö E, Karlsson MC, and Gabrielsson S. Antigen-loaded exosomes alone induce Th1-type memory through a B-cell-dependent mechanism. Blood. (2009) 113:2673–83. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-04-153536, PMID: 19176319
32. Nikfarjam S, Rezaie J, Kashanchi F, and Jafari R. Dexosomes as a cell-free vaccine for cancer immunotherapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 39:258. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01781-x, PMID: 33228747
33. Utsugi-Kobukai S, Fujimaki H, Hotta C, Nakazawa M, and Minami M. MHC class I-mediated exogenous antigen presentation by exosomes secreted from immature and mature bone marrow derived dendritic cells. I. mmunol Lett. (2003) 89:125–31. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(03)00128-7, PMID: 14556969
34. Montecalvo A, Larregina AT, Shufesky WJ, Stolz DB, Sullivan ML, Karlsson JM, et al. Mechanism of transfer of functional microRNAs between mouse dendritic cells via exosomes. Blood. (2012) 119:756–66. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-02-338004, PMID: 22031862
35. Wei G, Jie Y, Haibo L, Chaoneng W, Dong H, Jianbing Z, et al. Dendritic cells derived exosomes migration to spleen and induction of inflammation are regulated by CCR7. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:42996. doi: 10.1038/srep42996, PMID: 28223684
36. Wang Y, Xiang Y, Xin VW, Wang XW, Peng XC, Liu XQ, et al. Dendritic cell biology and its role in tumor immunotherapy. J Hematol Oncol. (2020) 13:107. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00939-6, PMID: 32746880
37. Zhang Y, Song Q, Cassady K, Lee M, Tang H, Zheng M, et al. Blockade of trans PD-L1 interaction with CD80 augments antitumor immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2023) 120:e2205085120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2205085120, PMID: 37036990
38. Kim SH, Lechman ER, Bianco N, Menon R, Keravala A, Nash J, et al. Exosomes derived from IL-10-treated dendritic cells can suppress inflammation and collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. (2005) 174:6440–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.10.6440, PMID: 15879146
39. Aline F, Bout D, Amigorena S, Roingeard P, and Dimier-Poisson I. Toxoplasma gondii antigen-pulsed-dendritic cell-derived exosomes induce a protective immune response against T. gondii infection. Infect Immun. (2004) 72:4127–37. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.7.4127-4137.2004, PMID: 15213158
40. Zitvogel L, Regnault A, Lozier A, Wolfers J, Flament C, Tenza D, et al. Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat Med. (1998) 4:594–600. doi: 10.1038/nm0598-594, PMID: 9585234
41. Ma B, Yang JY, Song WJ, Ding R, Zhang ZC, Ji HC, et al. Combining exosomes derived from immature DCs with donor antigen-specific treg cells induces tolerance in a rat liver allograft model. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:32971. doi: 10.1038/srep32971, PMID: 27640806
42. Mastoridis S, Londoño MC, Kurt A, Kodela E, Crespo E, Mason J, et al. Impact of donor extracellular vesicle release on recipient cell “cross-dressing” following clinical liver and kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. (2021) 21:2387–98. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16123, PMID: 32515541
43. Liu Q, Rojas-Canales DM, Divito SJ, Shufesky WJ, Stolz DB, Erdos G, et al. Donor dendritic cell-derived exosomes promote allograft-targeting immune response. J Clin Invest. (2016) 126:2805–20. doi: 10.1172/JCI84577, PMID: 27348586
44. Elashiry M, Elsayed R, and Cutler CW. Exogenous and endogenous dendritic cell-derived exosomes: lessons learned for immunotherapy and disease pathogenesis. Cells. (2021) 11:115. doi: 10.3390/cells11010115, PMID: 35011677
45. Cai Z, Zhang W, Yang F, Yu L, Yu Z, Pan J, et al. Immunosuppressive exosomes from TGF-β1 gene-modified dendritic cells attenuate Th17-mediated inflammatory autoimmune disease by inducing regulatory T cells. Cell Res. (2012) 22:607–10. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.196, PMID: 22157651
46. Chen G, Huang AC, Zhang W, Zhang G, Wu M, Xu W, et al. Exosomal PD-L1 contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature. (2018) 560:382–6. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0392-8, PMID: 30089911
47. Yen EY, Miaw SC, Yu JS, and Lai IR. Exosomal TGF-β1 is correlated with lymphatic metastasis of gastric cancers. Am J Cancer Res. (2017) 7:2199–208. Available online at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5714749/.
48. Fang Y, Zhang Q, Lv C, Guo Y, He Y, Guo P, et al. Mitochondrial fusion induced by transforming growth factor-β1 serves as a switch that governs the metabolic reprogramming during differentiation of regulatory T cells. Redox Biol. (2023) 62:102709. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102709, PMID: 37116255
49. Yang R, Huang H, Cui S, Zhou Y, Zhang T, and Zhou Y. IFN-γ promoted exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells to attenuate colitis via miR-125a and miR-125b. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:603. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02788-0, PMID: 32733020
50. Wang J, Zhao X, and Wan YY. Intricacies of TGF-β signaling in Treg and Th17 cell biology. Cell Mol Immunol. (2023) 20:1002–22. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-01036-7, PMID: 37217798
51. Bauer KM, Nelson MC, Tang WW, Chiaro TR, Brown DG, Ghazaryan A, et al. CD11c+ myeloid cell exosomes reduce intestinal inflammation during colitis. JCI Insight. (2022) 7:e159469. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.159469, PMID: 36214220
52. Lu J, Wang W, Li P, Wang X, Gao C, Zhang B, et al. MiR-146a regulates regulatory T cells to suppress heart transplant rejection in mice. Cell Death Discov. (2021) 7:165. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00534-9, PMID: 34226512
53. Wang H, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Zhao Y, Shu J, and Tang X. Exosomes derived from miR-146a-overexpressing fibroblast-like synoviocytes in cartilage degradation and macrophage M1 polarization: a novel protective agent for osteoarthritis? Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1361606. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1361606, PMID: 38846937
54. El-Badawy O, Sayed D, Badary MS, Abd-Alrahman ME, El-Feky MA, and Thabit AG. Relations of regulatory T cells with hepatitis markers in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hum Immunol. (2012) 73:335–41. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2012.01.014, PMID: 22342871
55. Khosrojerdi A, Soudi S, Hosseini AZ, Khaligh SG, and Hashemi SM. The combination of mesenchymal stem cell- and hepatocyte-derived exosomes, along with imipenem, ameliorates inflammatory responses and liver damage in a sepsis mouse model. Life Sci. (2023) 326:121813. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121813, PMID: 37257578
56. Holman NS, Church RJ, Nautiyal M, Rose KA, Thacker SE, Otieno MA, et al. Hepatocyte-derived exosomes promote liver immune tolerance: possible implications for idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Toxicol Sci. (2019) 170:499–508. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfz112, PMID: 31093666
57. Xiang X, Poliakov A, Liu C, Liu Y, Deng ZB, Wang J, et al. Induction of myeloid-derived suppressor cells by tumor exosomes. Int J Cancer. (2009) 124:2621–33. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24249, PMID: 19235923
58. Valenti R, Huber V, Filipazzi P, Pilla L, Sovena G, Villa A, et al. Human tumor-released microvesicles promote the differentiation of myeloid cells with transforming growth factor-beta-mediated suppressive activity on T lymphocytes. Cancer Res. (2006) 66:9290–8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1819, PMID: 16982774
59. Yin C, Han Q, Xu D, Zheng B, Zhao X, and Zhang J. SALL4-mediated upregulation of exosomal miR-146a-5p drives T-cell exhaustion by M2 tumor-associated macrophages in HCC. Oncoimmunology. (2019) 8:1601479. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2019.1601479, PMID: 31143524
60. Bi W, Li X, Jiang Y, Gao T, Zhao H, Han Q, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes induce neutrophil infiltration and reprogramming to promote T-cell exhaustion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics. (2025) 15:2852–69. doi: 10.7150/thno.104557, PMID: 40083930
61. Saravanan PB, Kalivarathan J, Khan F, Shah R, Levy MF, and Kanak MA. Exosomes in transplantation: Role in allograft rejection, diagnostic biomarker, and therapeutic potential. Life Sci. (2023) 324:121722. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121722, PMID: 37100379
62. Hashimi ST, Fulcher JA, Chang MH, Gov L, Wang S, and Lee B. MicroRNA profiling identifies miR-34a and miR-21 and their target genes JAG1 and WNT1 in the coordinate regulation of dendritic cell differentiation. Blood. (2009) 114:404–14. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-09-179150, PMID: 19398721
63. Usuelli V, Ben Nasr M, D’Addio F, Liu K, Vergani A, El Essawy B, et al. miR-21 antagonism reprograms macrophage metabolism and abrogates chronic allograft vasculopathy. Am J Transplant. (2021) 21:3280–95. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16581, PMID: 33764625
64. Wang X, Ren T, Zhang X, Pan T, Peng F, Feng J, et al. MiR-21 suppression in macrophages promotes M2-like polarization and attenuates kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. FASEB J. (2024) 38:e70251. doi: 10.1096/fj.202401834R, PMID: 39659245
65. Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ, and Baltimore D. NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2006) 103:12481–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605298103, PMID: 16885212
66. Tili E, Michaille JJ, Cimino A, Costinean S, Dumitru CD, Adair B, et al. Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J Immunol. (2007) 179:5082–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.8.5082, PMID: 17911593
67. Liu X, Zhan Z, Xu L, Ma F, Li D, Guo Z, et al. MicroRNA-148/152 impair innate response and antigen presentation of TLR-triggered dendritic cells by targeting CaMKIIα. J Immunol. (2010) 185:7244–51. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001573, PMID: 21068402
68. Reikvam H, Vo AK, Johansen S, Hemsing AL, Solheim MH, Mosevoll KA, et al. MicroRNA serum profiles and chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood Adv. (2022) 6:5295–306. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005930, PMID: 35443023
69. Ceppi M, Pereira PM, Dunand-Sauthier I, Barras E, Reith W, Santos MA, et al. MicroRNA-155 modulates the interleukin-1 signaling pathway in activated human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2009) 106:2735–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811073106, PMID: 19193853
70. Crossland RE, Norden J, Ghimire S, Juric MK, Pearce KF, Lendrem C, et al. Profiling Tissue and Biofluid miR-155-5p, miR-155*, and miR-146a-5p Expression in Graft vs. Host Disease. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:639171. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.639171, PMID: 33790910
71. Wu K, Ye C, Lin L, Chu Y, Ji M, Dai W, et al. Inhibiting miR-21 attenuates experimental hepatic fibrosis by suppressing both the ERK1 pathway in HSC and hepatocyte EMT. Clin Sci (Lond). (2016) 130:1469–80. doi: 10.1042/CS20160334, PMID: 27226339
72. Kim SH, Bianco NR, Shufesky WJ, Morelli AE, and Robbins PD. Effective treatment of inflammatory disease models with exosomes derived from dendritic cells genetically modified to express IL-4. J Immunol. (2007) 179:2242–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.4.2242, PMID: 17675485
73. Kim SH, Bianco N, Menon R, Lechman ER, Shufesky WJ, Morelli AE, et al. Exosomes derived from genetically modified DC expressing FasL are anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive. Mol Ther. (2006) 13:289–300. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2005.09.015, PMID: 16275099
74. Bianco NR, Kim SH, Ruffner MA, and Robbins PD. Therapeutic effect of exosomes from indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-positive dendritic cells in collagen-induced arthritis and delayed-type hypersensitivity disease models. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2009) 60:380–9. doi: 10.1002/art.24229, PMID: 19180475
75. Cui B, Sun J, Li SP, Zhou GP, Chen XJ, Sun LY, et al. CD80+ dendritic cell derived exosomes inhibit CD8+ T cells through down-regulating NLRP3 expression after liver transplantation. Int Immunopharmacol. (2022) 109:108787. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108787, PMID: 35490667
76. Cui B, Chen XJ, Sun J, Li SP, Zhou GP, Sun LY, et al. Dendritic cells originating exosomal miR-193b-3p induces regulatory T cells to alleviate liver transplant rejection. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 114:109541. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109541, PMID: 36700764
77. Liu J, Zhang X, Cheng Y, and Cao X. Dendritic cell migration in inflammation and immunity. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) 18:2461–71. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00726-4, PMID: 34302064
78. Hong W, Yang B, He Q, Wang J, and Weng Q. New insights of CCR7 signaling in dendritic cell migration and inflammatory diseases. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:841687. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.841687, PMID: 35281921
79. Zhang Y, Gao W, Yuan J, Zhong X, Yao K, Luo R, et al. CCR7 mediates dendritic-cell-derived exosome migration and improves cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Pharmaceutics. (2023) 15:461. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020461, PMID: 36839783
80. Xu J, Liu H, Wang T, Wen Z, Chen H, Yang Z, et al. CCR7 mediated mimetic dendritic cell vaccine homing in lymph node for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma therapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) 10:e2207017. doi: 10.1002/advs.202207017, PMID: 37092579
81. Zheng L, Li Z, Ling W, Zhu D, Feng Z, and Kong L. Exosomes derived from dendritic cells attenuate liver injury by modulating the balance of treg and th17 cells after ischemia reperfusion. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2018) 46:740–56. doi: 10.1159/000488733, PMID: 29621784
82. Bonney GK, Chew CA, Lodge P, Hubbard J, Halazun KJ, Trunecka P, et al. Liver transplantation for non-resecta ble colorectal liver metastases: the International Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association consensus guidelines. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 6:933–46. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00219-3, PMID: 34506756
83. Guan S, Yu H, Yan G, Gao M, Sun W, and Zhang X. Characterization of urinary exosomes purified with size exclusion chromatography and ultracentrifugation. J Proteome Res. (2020) 19:2217–25. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00693, PMID: 32248692
84. Liu C, Guo J, Tian F, Yang N, Yan F, Ding Y, et al. Field-free isolation of exosomes from extracellular vesicles by microfluidic viscoelastic flows. ACS Nano. (2017) 11:6968–76. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b02277, PMID: 28679045
85. Sun M, Li M, Hu M, Fan Y, Liu Y, Sun J, et al. Fully bioactive nanodrugs: stem cell-derived Exosomes Engineered with Biomacromolecules to Treat CCl4- and Extreme Hepatectomy-Induced Acute Liver failure. ACS Nano. (2024) 18:33907–21. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c07408, PMID: 39626080
86. Wen X and Hao Y. The combined application of exosomes/exosome-based drug preparations and ultrasound. J Mater Chem B. (2025) 13(23):6626–37. doi: 10.1039/d4tb01530d, PMID: 40390561
87. Ding L, Yang X, Gao Z, Effah CY, Zhang X, Wu Y, et al. A holistic review of the state-of-the-art microfluidics for exosome separation: an overview of the current status, existing obstacles, and future outlook. Small. (2021) 17:e2007174. doi: 10.1002/smll.202007174, PMID: 34047052
88. Gupta S, Rawat S, Arora V, Kottarath SK, Dinda AK, Vaishnav PK, et al. An improvised one-step sucrose cushion ultracentrifugation method for exosome isolation from culture supernatants of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2018) 9:180. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0923-0, PMID: 29973270
89. Zheng X, Ai H, Qian K, Li G, Zhang S, Zou Y, et al. Small extracellular vesicles purification and scale-up. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1344681. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1344681, PMID: 38469310
90. Wang J, Tu C, Zhang H, Zhang J, Feng Y, Deng Y, et al. Loading of metal isotope-containing intercalators for mass cytometry-based high-throughput quantitation of exosome uptake at the single-cell level. Biomaterials. (2020) 255:120152. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120152, PMID: 32505035
91. Wang Z, Rich J, Hao N, Gu Y, Chen C, Yang S, et al. Acoustofluidics for simultaneous nanoparticle-based drug loading and exosome encapsulation. Microsyst Nanoeng. (2022) 8:45. doi: 10.1038/s41378-022-00374-2, PMID: 35498337
92. Kim MS, Haney MJ, Zhao Y, Yuan D, Deygen I, Klyachko NL, et al. Engineering macrophage-derived exosomes for targeted paclitaxel delivery to pulmonary metastases: in vitro and in vivo evaluations. Nanomedicine. (2018) 14:195–204. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2017.09.011, PMID: 28982587
93. Kim SM, Yang Y, Oh SJ, Hong Y, Seo M, and Jang M. Cancer-derived exosomes as a delivery platform of CRISPR/Cas9 confer cancer cell tropism-dependent targeting. J Control Release. (2017) 266:8–16. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.09.013, PMID: 28916446
94. Zou Z, Li H, Xu G, Hu Y, Zhang W, and Tian K. Current knowledge and future perspectives of exosomes as nanocarriers in diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Int J Nanomedicine. (2023) 18:4751–78. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S417422, PMID: 37635911
95. Lin X, Zhu J, Shen J, Zhang Y, and Zhu J. Advances in exosome plasmonic sensing: Device integration strategies and AI-aided diagnosis. Biosens Bioelectron. (2024) 266:116718. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2024.116718, PMID: 39216205
96. El Fekih R, Franzen K, Hurley J, Haynes BC, Merhej T, Alghamdi A, et al. An exosomal mRNA urine test for detection and risk stratification of human kidney transplant rejection. Kidney Int Rep. (2025) 10:1131–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2025.01.036, PMID: 40303229
97. El Fekih R, Hurley J, Tadigotla V, Alghamdi A, Srivastava A, Coticchia C, et al. Discovery and validation of a urinary exosome mRNA signature for the diagnosis of human kidney transplant rejection. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2021) 32:994–1004. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020060850, PMID: 33658284
98. Powell BM, Brant TS, Davis JH, and Mosalaganti S. Rapid structural analysis of bacterial ribosomes in situ. Commun Biol. (2025) 8:131. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07586-y, PMID: 39875527
99. Lai JJ, Chau ZL, Chen SY, Hill JJ, Korpany KV, Liang NW, et al. Exosome processing and characterization approaches for research and technology development. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2022) 9:e2103222. doi: 10.1002/advs.202103222, PMID: 35332686
100. Picchio V, Pontecorvi V, Dhori X, Bordin A, Floris E, Cozzolino C, et al. The emerging role of artificial intelligence applied to exosome analysis: from cancer biology to other biomedical fields. Life Sci. (2025) 375:123752. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2025.123752, PMID: 40409585
101. Yang Z, Li X, Gan X, Wei M, Wang C, Yang G, et al. Hydrogel armed with Bmp2 mRNA-enriched exosomes enhances bone regeneration. J Nanobiotechnology. (2023) 21:119. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01871-w, PMID: 37020301
Keywords: dendritic cells, exosomes, liver transplantation, immune tolerance, clinical translation
Citation: Chen X, Yang Z and Li M (2025) Molecular regulatory mechanisms and diagnostic potential of dendritic cell-derived exosomes in liver transplantation: from immune tolerance induction to translational challenges. Front. Immunol. 16:1657956. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1657956
Received: 02 July 2025; Accepted: 11 August 2025;
Published: 28 August 2025; Corrected: 03 October 2025.
Edited by:
Laura Santambrogio, Cornell University, United StatesReviewed by:
Javeed Ahmad, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIH), United StatesChristian H. K. Lehmann, University Hospital Erlangen, Germany
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Yang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Minghao Li, bGltaW5naGFvMzE3QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xiaopeng Chen
Xiaopeng Chen Zhiqi Yang1†
Zhiqi Yang1†