- 1Laboratory of Integrated Medicine Tumor Immunology, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Taiyuan, China
- 2Department of Pathobiology and Immunology, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang, China
- 3Department of Acute General Medicine, John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, United Kingdom
Background: Cisplatin (DDP) is a clinical first-line chemotherapy drug for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but treatment is often ineffective due to drug resistance. Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) is a critical regulator/factor in HCC tumor progression. Our previous research showed that DDP promoted the expression of YAP1 in mice bearing H22 cell in situ liver tumors, which might be related to the poor therapeutic effect of DDP.
Methods and results: DDP could inhibit tumor growth and decrease tumor volume in DEN/TCPOBOP-induced HCC mice, increase the number of CD8+ T cells in the tumor, reduce the proportion of PD-1+CD8+ T cells in the peripheral blood and spleen of mice, and reduce the immune exhaustion of the tumor microenvironment in HCC. Of note, that DDP treatment activated YAP1 expression in HCC cells. In addition, using a murine model of subcutaneous transplantation of HCC cells, it was found that the combined use of the YAP1 inhibitor, verteporfin, and DDP led to significant tumor regression. Inhibition of YAP1 reduced activation of the cGAS-STING pathway by DDP treatment. Furthermore, bioinformatics analysis revealed that YAP1 was positively correlated with cGAS and STING in HCC tissues. We further confirmed the correlation of YAP1 with cGAS-STING in HCC using two models: DEN/TCPOBOP induction of HCC in hepatocyte-specific Yap1 knockout mice; and giving verteporfin treatment to mice with subcutaneously transplanted HCC tumors. Inhibiting the expression of YAP1 in HCC tissues can reduce the expression of cGAS-STING and enhance the therapeutic effect of cisplatin.
Conclusions: The combination of YAP1 inhibitor, verteporfin and DDP enhances anti-tumor immunity by regulating the interaction between YAP1 and cGAS-STING in the tumor microenvironment, providing new insights into a combined chemotherapy strategy for HCC.
1 Introduction
As is well documented, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranks as the third most common cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide (1). Surgical resection and chemotherapy remain gold standards for HCC treatment. The chemotherapeutic drug cisplatin (DDP) has been extensively administered to treat neoplasms (2). However, its clinical efficacy is often limited by the tumor’s immunosuppressive microenvironment and the development of resistance mechanisms (3). Over the years, significant efforts have been made to explore strategies to improve the therapeutic response to DDP and to overcome its limitations, such as targeting the tumor microenvironment and modulating immune checkpoint pathways (4).
The PD-1/PD-L1 pathway has been recognized as a crucial component associated with cancer immunity (5). PD-L1, an immune checkpoint molecule, is abundantly expressed in tumor cells (6, 7). PD-L1, when overexpressed, binds to PD-1 on T cells and other immune cells, thereby facilitating immune evasion (8, 9). However, the impact of cisplatin on PD-1 and PD-L1 expression remains underexplored in HCC cells.
Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) acts as the Hippo signaling pathway downstream component (10). There exists a close correlation between aberrant hepatocyte proliferation and the abnormal activation of YAP (11). Furthermore, studies have linked YAP1 to key immune-related pathways, including cGAS-STING, a crucial pathway involved in the innate immune response (12, 13). However, the precise role of YAP1 in regulating immune responses during chemotherapy and its potential as a therapeutic target in HCC remains poorly understood.
The cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-stimulator of interferon genes (cGAS-STING) axis, an essential signaling pathway in innate immunity, is a DNA-sensing pathway that has been central to our understanding of intrinsic anti-tumour immunology in recent years. Cisplatin belongs to a class of chemotherapy drugs that can cause DNA breakage and damage in tumor cells. Therefore, cisplatin may induce tumor cells to activate endogenous cGAS-STING, which plays an anti-tumor role (14).
Overall, this study highlights the interaction of YAP1 with a key immune pathway, cGAS-STING. Our findings suggest that inhibiting YAP1, in combination with DDP, can modulate immune responses and enhance the therapeutic efficacy of chemotherapy in HCC. These results offer new insights into potential combination therapies for improving the clinical outcomes of HCC treatment.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Animal
All animals were maintained under SPF conditions at a constant temperature (22-24°C) and housed in plastic cages. Hepatocellular-specific Yap1 knockout mice were bred and confirmed by Guangzhou Cyagen Biosciences (Guangzhou, China). Hepatocellular-specific Yap1 knockout mice were denoted as Yap1LKO (with the genotype Yap1Flox/Flox; albumin-cre) and Yap1Flox mice (with genotype Yap1Flox/Flox).
The DEN/TCPOBOP modeling method was implemented following the methodology outlined in the study by Bergmann et al. (15). Mice were weighed, numbered, and randomly divided into four groups of 5 mice each. Following the successful establishment of the model, Mice in the DDP group were administered DDP dissolved in saline, whereas control mice were injected with saline alone.
The establishment method of subcutaneous tumor transplantation was referred to in the previous article (16). 5×10^6 Hepa1-6 cells were injected into the subcutaneous skin of the right hind limb of 4-6 weeks C57BL/6N mice. The dose of verteporfin was 100mg/kg, once every three days, and the dose of DDP was 2mg/kg, once every two days and the intervention time was 14 days. All experimental protocols involving animals were approved by the Ethics Committee for Animal Experimentation at Hebei University of Chinese Medicine (Permit number: DWLL202203064).
2.2 Flow cytometry
Mouse spleen tissue was placed in lymphocyte separation medium, then crushed with a grinding rod and filtered to obtain a spleen cell suspension. Mouse peripheral blood cells were processed by adding whole blood into an anticoagulant tube with red blood cell lysis buffer and incubating at room temperature in the dark for 20 minutes, to remove red blood cells. To 100μl of the processed lymphocyte samples, 1 μl of FITC Anti-Mouse CD3 antibody (553061, BD), 5 μl of PerCP-Cy5.5 Anti-Mouse CD8 antibody (551162, BD), and 5 μl of PE Anti-Mouse PD-1 antibody (551892, BD) were added sequentially. The samples were stained at 4°C for 20 minutes.
Using the blank tubes and single-stained tubes, the voltage was set and threshold and compensation were adjusted. According to the forward scatter (FSC) and side scatter (SSC) characteristics of the cells, a rough gating was first performed on the cells. FSC-A vs SSC-A was used to exclude debris and select intact lymphocytes. FSC-H vs FSC-A was used to exclude doublets and select single cells. For specific immune cell populations, we used the corresponding surface markers for precise gating. CD3 positivity allowed for selection of T cells. CD8 and PD-1 positivity allowed the PD-1+CD8+ cell subset to be analyzed.
2.3 Hematoxylin and eosin staining
Upon organ collection, 4% formaldehyde was applied for 48 hours to the liver and subcutaneous graft tumor tissues before being embedded in paraffin and sectioned at a thickness of 4 µm. The sliced sections were subsequently stained with H&E, and histopathological alterations were visualized under a microscope (Leica DM2255, Germany) at 100×/200× magnification.
2.4 Western blot
Extraction of mice liver protein, BCA method for the determination of protein concentration. Sample addition, electrophoresis. Thereafter, the isolated proteins were transferred to PVDF membrane, and then 5% skim milk was added for four hours at ambient temperature. Following this, the membrane was incubated with the primary antibodies: YAP1 antibody (1:1000, CST,14074s),.cGAS antibody (1:1000, Proteintech, 29958-1-AP), STING antibody (1:1000, CST, 13647s), GSDMD antibody (1:1000, Proteintech, 20770-1-AP) and GAPDH antibody (1:5000, Abways, AB0037).
Then, a secondary antibody was incubated with the membrane, namely goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP (1:5000, Absin, abs20002). ECL luminescent solution was added to the strip (share-bio, SB-WB012).
2.5 Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining was conducted following the steps outlined in the Nanjing Zhongshan Jinqiao immunohistochemical kit. Ki67 antibody (1:150,CST, #34330). The remaining primary antibodies were the same as those used for Western blotting. Finally, two senior histopathologists analyzed the sections under a microscope at 200× and 400× magnification.
2.6 Bioinformatics analysis
We used the TIMER and GEPIA tools to analyze the association between YAP1, cGAS (C6ORF150/MB21D1), and STING(TMEM173) in HCC patients in the TCGA database.
2.7 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS23.0. Data were presented as Mean ± SD. Two groups were compared using a student’s t-test. When more than two groups were included, one-way ANOVA was used. P<0.05 was identified as statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 DDP reduced PD-1+CD8+ T cell numbers in the liver tumor niche and up-regulated hepatic YAP1 expression
Our previous research established that DDP promoted YAP1 expression in the liver of BALB/c mice loaded with H22 cells (17). To evaluate the effect of DDP, an in situ liver tumor mouse model was established following the method described above (Figure 1A). Interestingly, the saline group (NS) of mice liver visible large tumors. In contrast, no apparent tumors were observed in the liver of mice in the DDP group (Figure 1B). While DDP reduced the number of tumors, it also decrease the tumor volumes and weight of mice (Figure 1C). In conclusion, DDP inhibits liver tumor growth in C57BL/6 mice.
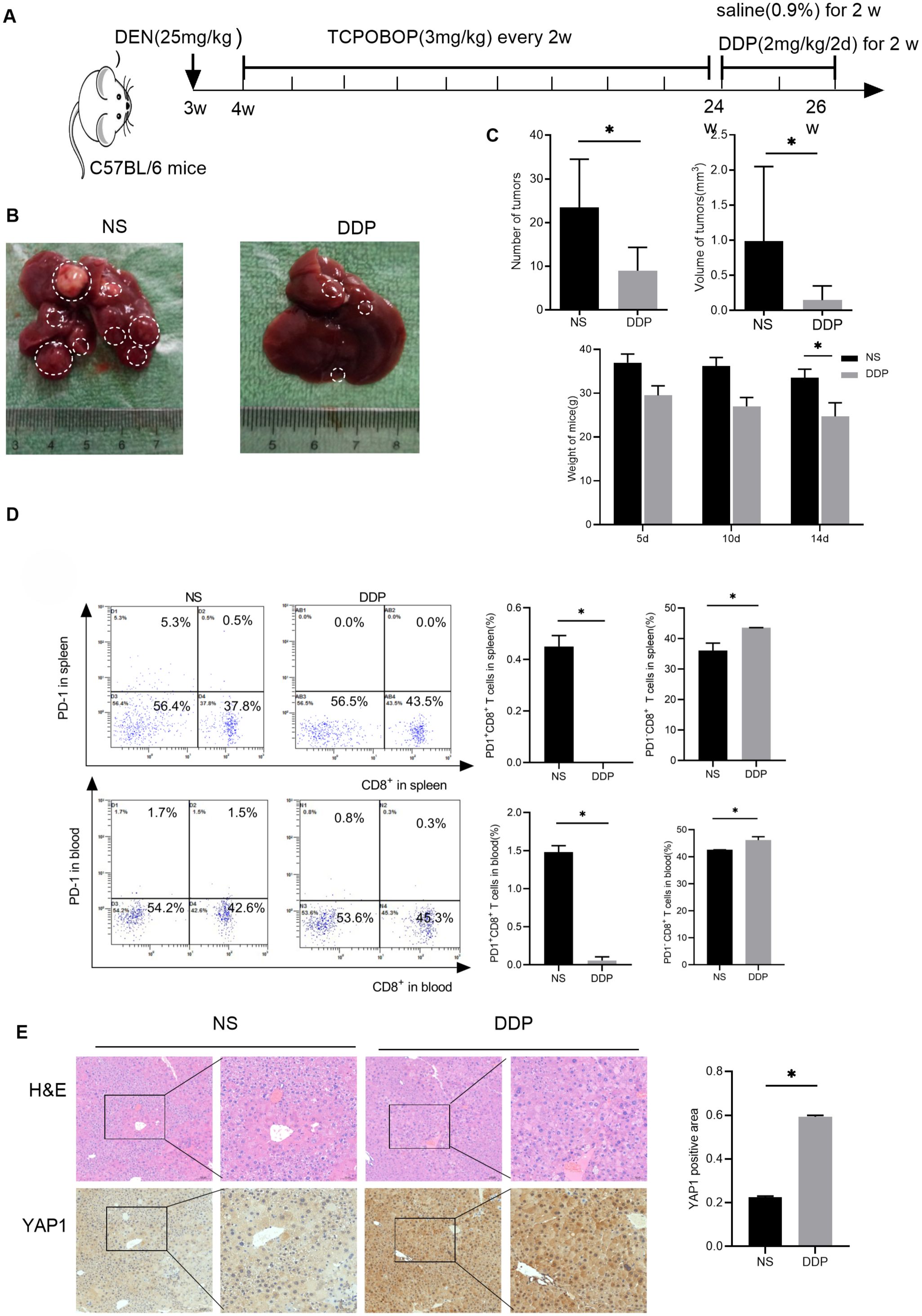
Figure 1. DDP reduced PD-1+CD8+ T cell numbers in the liver tumor niche and up-regulated hepatic YAP1 expression. (A) Flow chart of modeling DEN/TCPOBOP-induced HCC mice. DEN/TCPOBOP-induced HCC mice were given DDP and saline treatment. (B) Images of DEN/TCPOBOP-induced HCC mouse liver. Tumors are represented by white circles. (C) Tumor number and volume, as well as mouse weight, were measured. (D) Flow cytometry detected the number of CD8+ and PD-1+ cells in the spleen and blood of mice, the number of PD-1+CD8+T cells and PD-1-CD8+T cells were counted in the histogram. (E) Detection of YAP1 expression in the liver of DEN/TCPOBOP-induced HCC mice by IHC and the expression was statistically analyzed by bar chart. Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P<0.05.
In anti-cancer responses, CD8+ T cells play an instrumental role (18, 19). Our previous research indicates that that DDP fostered CD8+ T cell infiltration in the liver cancer microenvironment (20). Additionally, flow cytometry suggested that DDP reduced exhausted CD8+T lymphocytes (PD-1+CD8+ T cells) proportion and enhanced that of PD-1-CD8+ T cells in the spleen and blood (Figure 1D). These results conjointly suggested that DDP-promoted CD8+ T cell infiltration and decreased exhausted CD8+ T lymphocytes in the blood and spleen. Finally, immunohistochemistry analysis determined that DDP treatment up-regulated YAP1 expression in HCC mice (Figure 1E).
3.2 Verteporfin,YAP1 inhibitor, is more effective for HCC treatment
In order to analyze the mechanism of DDP treatment for liver cancer more comprehensively, we also established another liver cancer model-Hepa1-6 hepatocellular carcinoma bearing mouse model. Randomly divided into four group -control group, DDP group, YAP1 inhibitor -Verteporfin (VP) group, and DDP combined with Verteporfin group. We found that both DDP and Verteporfin, as well as the combination of DDP and Verteporfin effectively inhibited subcutaneous transplanted tumors of mouse hepatocellular carcinoma cells growth. After drug intervention, H&E staining showed that the nucleus of the tumor tissue became sparse and no longer so dense, and the Ki67 expression of immunohistochemistry showed that the proliferation ability of the tumor mass became weak after drug intervention, in which the combination of DDP and Verteporfin had the better therapeutic effect (Figures 2A–D). Western blot results showed that DDP could promote the YAP1 expression in subcutaneously transplanted tumors, but under the premise of using Verteporfin, DDP could not promote YAP1 expression in subcutaneously transplanted tumors. (Figure 2E). The IHC results indicated that both DDP and Verteporfin used alone could increase CD8+T cell numbers in the tumor mass tissue, and CD8+T cell numbers in the tumor mass tissue increased even more after combined use (Figure 2F).
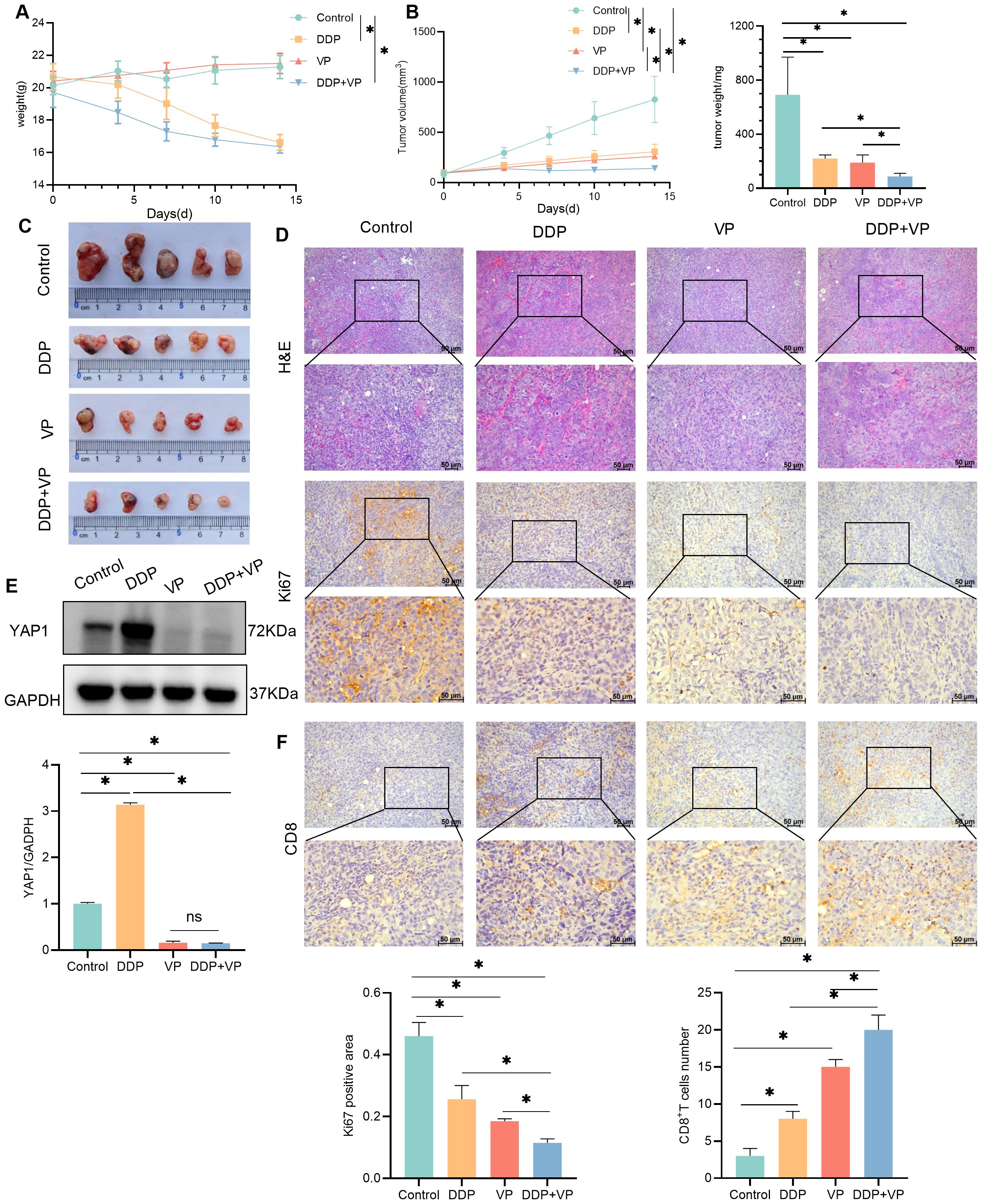
Figure 2. Verteporfin,YAP1 inhibitor, is more effective for HCC treatment. (A) Changes of body weight in control, DDP, VP, DDP +VP groups of mice. (B) Changes of tumor volume and final tumor weight in control, DDP, VP, DDP +VP groups of mice. (C) Photograph of tumors excised from subcutaneous transplanted tumor mice. (D) H&E and IHC detection of Ki67 expression in transplanted tumors. The expression was statistically analyzed in the histogram. (E) Western blot detection of YAP1 expression in transplanted tumors, as well as GAPDH as a loading control. The expression was statistically analyzed by bar chart. (F) IHC detection of CD8 expression in transplanted tumors, CD8+T cells were counted in the histogram. Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P<0.05.
3.3 Combining verteporfin with DDP reduced cGAS-STING expression
The relationship between cGAS-STING and liver cancer was introduced in a study by Li et al (14). Through bioinformatics analysis, we found that YAP1 was positively related to cGAS and STING in liver cancer (Figure 3A) (cor/R>0 and P<0.05). Western blot analysis showed that compared with the control group, DDP increased the abundance of cGAS and STING proteins. The abundance of cGAS and STING proteins was decreased by both verteporfin and the combination of DDP and verteporfin (Figure 3B).
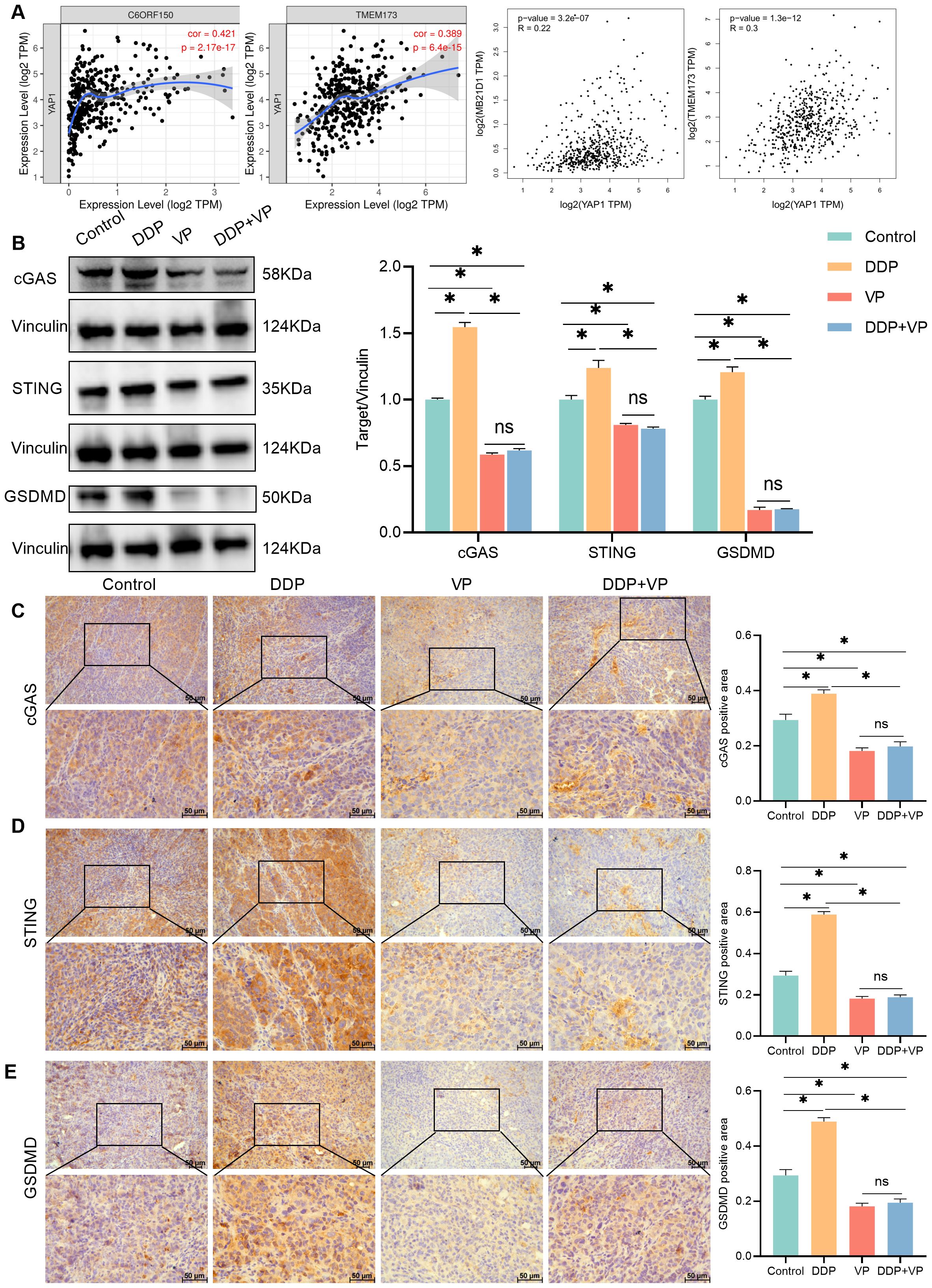
Figure 3. Combining verteporfin with DDP reduced cGAS-STING expression. (A) The correlation between YAP1 and cGAS(C6ORF150/MB21D1), STING(TMEM173) were analyzed by TIMER/GEPIA. (B) Western blot detection of cGAS,STING and GSDMD expression in transplanted tumors, as well as Vinculin as a loading control. (C–E) IHC staining for cGAS/STING/GSDMD expression in transplanted tumors. Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P<0.05.
Increased activation of the cGAS-STING pathway in cancer cells limits tumorigenesis, through the upregulation of inflammatory genes, which leads to the release of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines that slow down tumor growth and recruit anti-tumor immune cells (21). Gasdermin D (GSDMD) is a pyrogenic enforcer and GSDMD-induced pyrogenic cell death enhances the immune defense function (22). Compared to the control group, DDP increased GSDMD expression. Verteporfin inhibited GSDMD expression. The combination of Verteporfin and DDP had no impact on GSDMD expression (Figures 3B, E).
Our findings also confirmed that YAP1 was positively related to cGAS, STING, and GSDMD in liver cancer tissues. The results from IHC analysis were consistent with Western blot (Figures 3C–E). We therefore concluded that DDP stimulated cGAS/STING/GSDMD expression, whereas verteporfin inhibited the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway. The combined action of inhibiting the cGAS/STING pathway and YAP1 results in a better therapeutic effect on liver cancer. The decrease in expression of GSDMD following treatment with verteporfin and DDP together was not statistically different to that for verteporfin alone (Figures 3B, E).
3.4 YAP1 hepatocellular-specific knockout reduced the tumor size during DDP treatment
To investigate the mechanism by which DDP alters PD-L1 and PD-1 expression, and how YAP1 is associated with this, experiments were conducted in hepatocellular specific Yap1 knockout (Yap1LKO) and control (Yap1Flox) C57BL/6 mice. PCR detected Flox and Cre expression to identify the genotype of mice (Figure 4A). Yap1LKO and Yap1Flox mouse models were established following the method described above (Figure 4B). As anticipated, DDP treatment yielded a reduction in the number of tumors in both the Yap1Flox and Yap1LKO groups. Following treatment with DDP, treatment effect was greater in Yap1 knockout mice, compared to in the control group (Figures 4C–E).
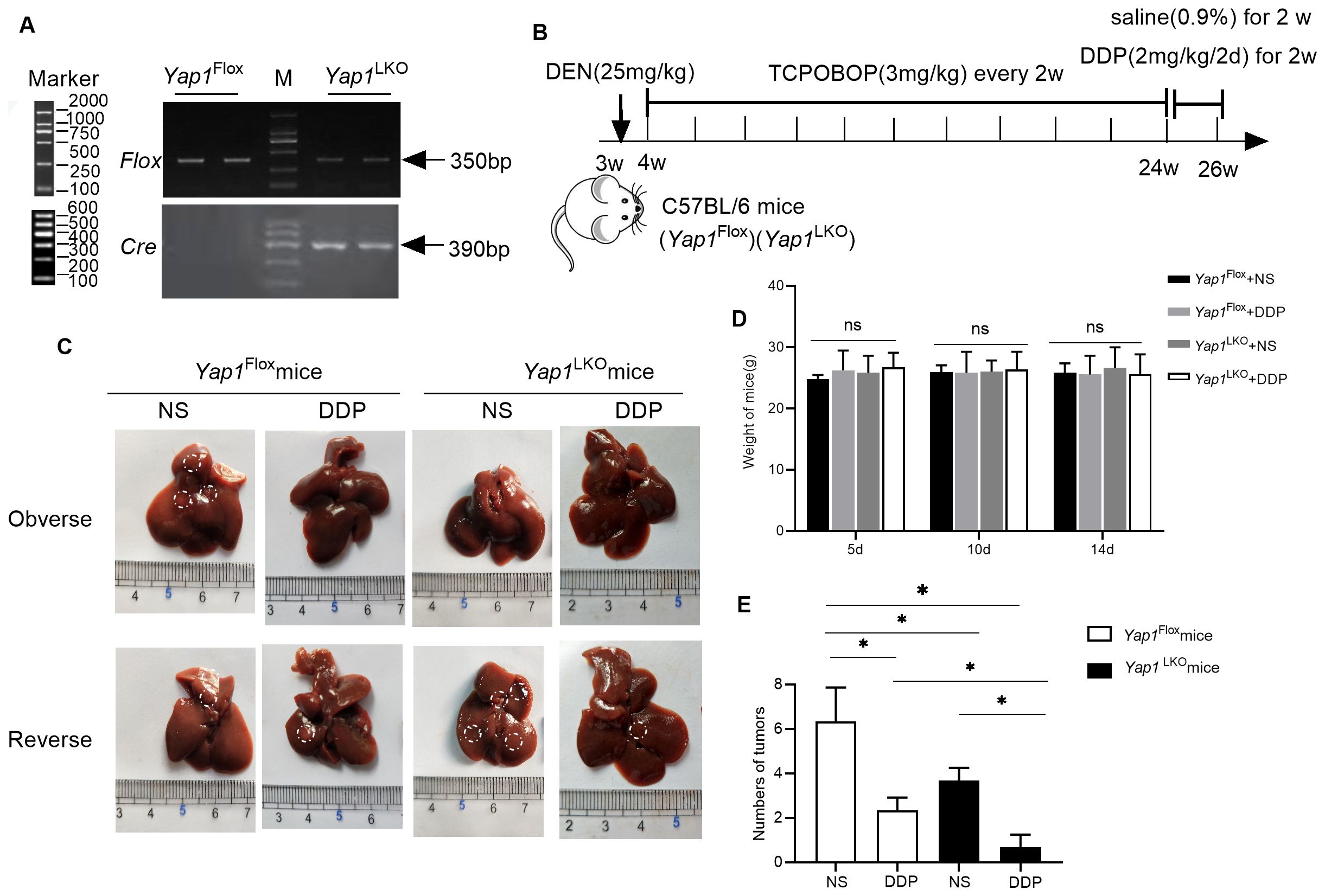
Figure 4. YAP1 hepatocellular specific knockout reduced the tumor size during DDP treatment (A) The expression of Flox and Cre was detected by PCR. (B) Schematic representation of the mouse model. (C) Macroscopic view of the liver specimens with visible tumors highlighted. (“Observe” and “Reserve“ represent the front and back sides of the gross liver image). (D) Fluctuations in body weight during the intervention. (E) The number of tumors on the liver after sampling. Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P<0.05.
3.5 DDP increased PD-L1 expression and decreased PD-1 expression via YAP1
Furthermore, DDP treatment increased YAP1 and PD-L1 expression while decreasing that of PD-1 in Yap1Flox mice. On the other hand, when Yap1 was knocked out in liver cancer tissues, PD-L1 was decreased and PD-1 expression was increased. In hepatocellular-specific Yap1 knockout mice, DDP no longer increased PD-L1 expression or reduced PD-1 expression in liver cancer. These results demonstrated that DDP increased PD-L1 expression and decreased PD-1 expression via the action of YAP1 (Figures 5A–D).
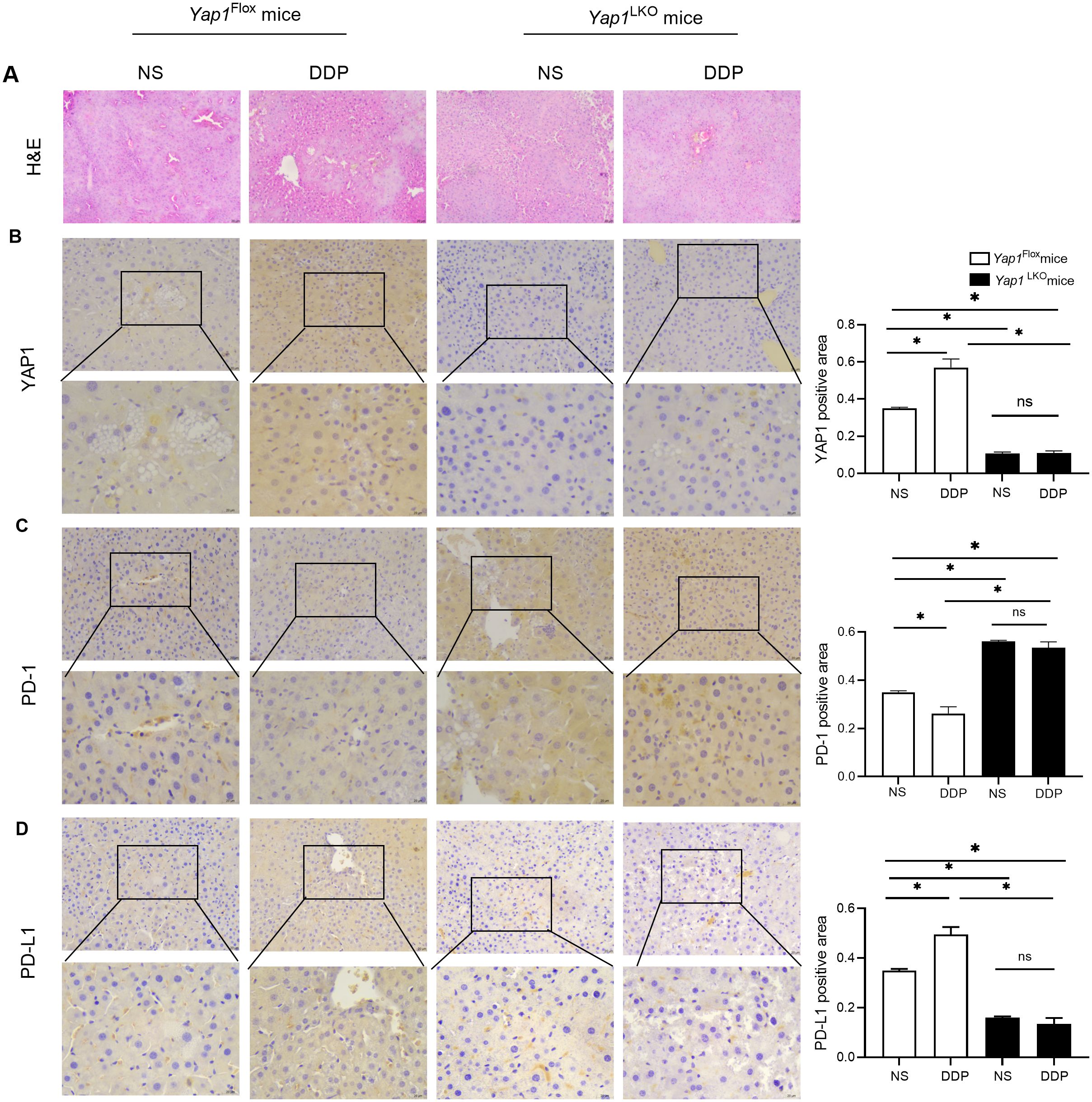
Figure 5. DDP increased PD-L1 expression and decreased PD-1 expression via YAP1. (A) H&E in liver of HCC mice. (B) YAP1 expression in liver of HCC mice was detected by IHC. (C) PD-1 expression in liver of HCC mice was detected by IHC. (D) PD-L1 expression in liver of HCC mice was detected by IHC. Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P<0.05.
3.6 DDP activated cGAS-STING by YAP1
To verify the correlation between YAP1 and cGAS-STING, we used hepatocellular-specific Yap1 gene knockout mice to establish liver in situ tumour-bearing mice using DEN/TCPOBOP induction. The expression of cGAS and STING was detected using immunohistochemistry. DDP increased the expression of cGAS and STING in liver cancer tissue. When Yap1 was knocked out in liver cancer tissues, the expressions of cGAS and STING decreased. With Yap1 expression knocked out, DDP no longer increased the expressions of cGAS and STING in liver cancer. These results demonstrated that DDP activated cGAS-STING expression by through the action of YAP1 (Figures 6A, B).
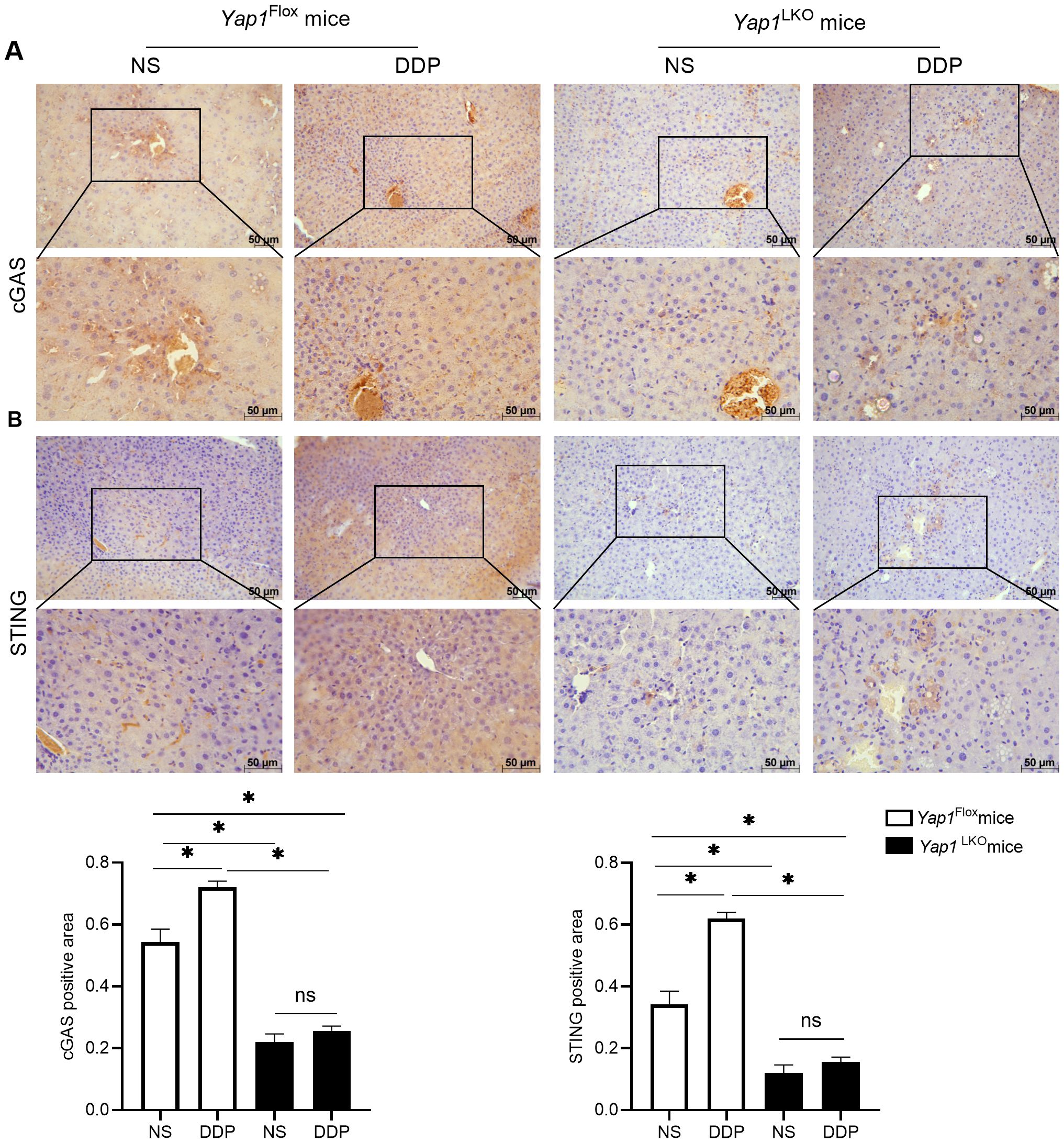
Figure 6. DDP activated cGAS-STING via YAP1. (A) cGAS expression was detected by IHC in liver of HCC mice. (B) STING expression was detected by IHC in liver of HCC mice. Data are presented as mean ± SD, *P<0.05.
4 Discussion
The pan-cancer analysis found that activation of YAP, a key downstream molecule of the Hippo pathway, was positively correlated with tumor-infiltrating cell abundance in several cancer types (23, 24). Previous research has indicated correlation between the expression levels of YAP1 and the infiltration of CD8+ T cells into liver cancer tissues (16). Furthermore, YAP1 may indirectly influence the migration, activation, and cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells by modulating the expression of other immune-related molecules, such as cytokines and chemokines (16, 25).
PD-1 is universally considered a key T-cell exhaustion marker. Consequently, an increase in PD-1 expression eventually leads to CD8+ T cell dysfunction (26). Previous studies have demonstrated that the expression of PD-L1 in HCC is significantly associated with immune evasion, impairing the immune response against HCC. We found that PD-1 expression was reduced and PD-L1 expression was increased when YAP1 was knocked out in vivo. According to a previous study, YAP1 specifically binds to the PD-L1 primer, promoting PD-L1 transcription (27).
Cisplatin has been widely used for the treatment of cancers. Indeed, it is globally administered as a chemotherapeutic agent to patients with advanced HCC (28, 29). One of the core findings of this study is that DDP treatment significantly activates the expression of YAP1 in DEN/TCPOBOP-induced HCC mice and leads to a reduction in the number of PD-1+CD8+ T cells in both the spleen and peripheral blood of mice. Moreover, CD8+T cells increased in HCC (Figure 7). This indicates that DDP may play a dual role in regulating tumor growth and the immune response in the tumor microenvironment. This finding was in line with a prior study that documented that DDP promoted CD8+ T cell infiltration in E.G7-OVA tumor tissues (30). It is worwhile emphasizing that higher abundance of PD-1+CD8+T cells are associated with adverse outcomes in multiple cancers including HCC (31–35).
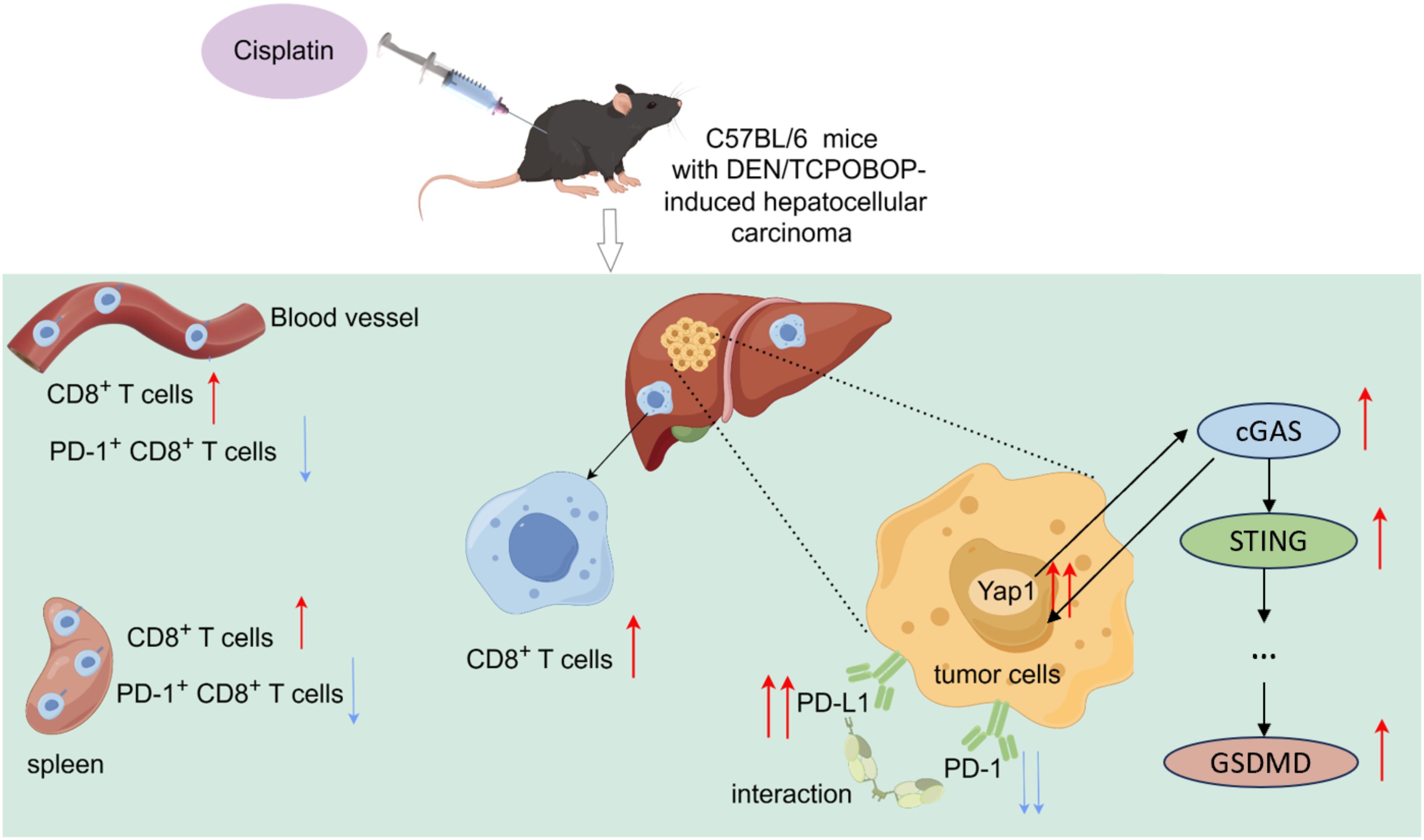
Figure 7. YAP1, cGAS and STING expression were increased in the liver of DEN/TCPOBOP-induced HCC mice after cisplatin administration. Furthermore, cisplatin treatment resulted in an increased number of CD8+T cells in both the spleen and peripheral blood of the mice while decreasing the number of PD-1+CD8+T cells. Moreover, there was an increase in the number of CD8+T cells in the liver. DDP increased the PD-L1 expression through YAP1 and downregulated that of PD-1.
The cGAS/STING signaling pathway connects innate and adaptive immunity, so its overreactive state has been characterized as a facilitating factor in various tumors (13). Multiple studies have shown that directly stimulating the cGAS-STING axis in the tumor microenvironment results in significant tumor regression and more effective immune responses across a variety of tumor models, suggesting that the cGAS-STING pathway holds promise as a healing target for liver cancer treatment (36). YAP1 plays an important role in modulating immune responses by influencing the cGAS-STING pathway and expression of immune checkpoint molecules in the liver tumor microenvironment (13). And other studies have shown that YAP1 and cGAS-STING are positively correlated in non-small cell lung cancer (13). YAP1-mediated regulation may contribute to the suppression of immune activation, which, in turn, impacts the anti-tumor response to chemotherapy (37, 38). Importantly, the combination of verteporfin and DDP not only enhanced the immune response but also reduced immune exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment, indicating YAP1 as a therapeutic target to overcome immune suppression during chemotherapy.
At present, there are no clinical reports of the combined use of YAP inhibition and cisplatin in the treatment of liver cancer or other tumors. Our research provides a preliminary investigation of the combined use of YAP inhibition and cisplatin in the treatment of liver cancer. Other studies have shown that in ovarian cancer and small cell lung cancer, activation of YAP1 can lead to cisplatin resistance. As a YAP1 inhibitor, verteporfin can inhibit cisplatin resistance by suppressing YAP1, thereby enhancing the efficacy of cisplatin (39, 40).
This study only focused on the improvement of liver cancer therapeutic efficacy by the combined use of cisplatin and verteporfin. It did not establish cisplatin-resistant liver cancer cell lines or cisplatin-resistant mice. Experimental research has been conducted on the correlation between YAP1 and cisplatin resistance in liver cancer treatment, as well as the issues of nephrotoxicity and weight loss in mice during cisplatin treatment. We aim to conduct further research on these limitations of cisplatin in the future.
In conclusion, our study provides compelling evidence that targeting YAP1 in combination with DDP can significantly enhance the immune response improve the efficacy of chemotherapy in HCC and enhance CD8+T cells in liver cancer tissues. By regulating the interaction between YAP1 and the cGAS-STING pathway, we demonstrate that inhibition of YAP1 can overcome immune suppression and enhance anti-tumor immunity, offering new therapeutic strategies for HCC treatment. Other studies have also confirmed the interaction between YAP and cGAS-STING pathways demonstrated previously in lung cancer tissues (13), Our findings also support that of current evidence in transplanted mouse tumor models for bladder cancer, showing that cGAS-STING signaling induced by cisplatin inhibits tumor proliferation and boosts CD8+ T cell infiltration (41). Additionally, activation of STING inhibits tumor-derived antigens from being incorporated into CD8+ T cells during in vivo immune responses (36, 42).
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Ethics Committee for Animal Experimentation at Hebei University of Chinese Medicine (Permit number: DWLL202203064). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YG: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Visualization. YX: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. YTG: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. XS: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YLG: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. DW: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. ZL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YY: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. JL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. IZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XS: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82274315),Traditional Chinese Medicine Innovation Team of Shanxi Province (zyytd2024021), the Project for Key Laboratory Construction of Shanxi Province (zyyyjs2024035), and the Foundation for High level talents of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine (2023RC03).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, and Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2018) 68:394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492
2. Ebara C, Yamazaki S, Moriguchi M, Mitsuka Y, Funada T, Higaki T, et al. Complete remission by transarterial infusion with cisplatin for recurrent bile duct tumor thrombus of hepatocellular carcinoma: report of a case. World J Surg Oncol. (2013) 11:1477–7819. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-11-78
3. Chen SH and Chang JY. New insights into mechanisms of cisplatin resistance: from tumor cell to microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20(17):4136. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174136
4. Gao ZX, Zhang ZS, Qin J, Zhang MZ, Cao JL, Li YY, et al. Aucubin enhances the antitumor activity of cisplatin through the inhibition of PD-L1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Phytomedicine. (2023) 112:154715. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154715
5. Lu P, Youngblood BA, Austin JW, Mohammed AU, Butler R, Ahmed R, et al. Blimp-1 represses CD8 T cell expression of PD-1 using a feed-forward transcriptional circuit during acute viral infection. J Exp Med. (2014) 211:515–27. doi: 10.1084/jem.20130208
6. Doroshow DB, Bhalla S, Beasley MB, Sholl LM, Kerr KM, Gnjatic S, et al. PD-L1 as a biomarker of response to immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2021) 18:345–62. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00473-5
7. de Miguel M and Calvo E. Clinical challenges of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Cell. (2020) 38:326–33. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.07.004
8. Alsaab HO, Sau S, Alzhrani R, Tatiparti K, Bhise K, Kashaw SK, et al. PD-1 and PD-L1 checkpoint signaling inhibition for cancer immunotherapy: mechanism, combinations, and clinical outcome. Front Pharmacol. (2017) 8:561. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00561
9. Yi M, Jiao D, Xu H, Liu Q, Zhao W, Han X, et al. Biomarkers for predicting efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Mol cancer. (2018) 17:129. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0864-3
10. Schlegelmilch K, Mohseni M, Kirak O, Pruszak J, Rodriguez JR, Zhou D, et al. Yap1 acts downstream of α-catenin to control epidermal proliferation. Cell. (2011) 144:782–95. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.031
11. Wang P, Pan J, Gong S, Zhang Z, and Li B. Yes-associated protein inhibition ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice by reducing VDR. Chem Biol Interact. (2024) 399:111139. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111139
12. Wang L, Zhang Y, Ren Y, Yang X, Ben H, Zhao F, et al. Pharmacological targeting of cGAS/STING-YAP axis suppresses pathological angiogenesis and ameliorates organ fibrosis. Eur J Pharmacol. (2022) 932:175241. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175241
13. Hao F. An overview of the crosstalk between YAP and cGAS-STING signaling in non-small cell lung cancer: it takes two to tango. Clin Transl Oncol. (2022) 24:1661–72. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-02826-7
14. Li K, Gong Y, Qiu D, Tang H, Zhang J, Yuan Z, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen facilitates teniposide-induced cGAS-STING activation to enhance the antitumor efficacy of PD-1 antibody in HCC. J immunotherapy Cancer. (2022) 10(8):e004006. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-004006
15. Bergmann J, Müller M, Baumann N, Reichert M, Heneweer C, Bolik J, et al. IL-6 trans-signaling is essential for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Hepatology. (2017) 65:89–103. doi: 10.1002/hep.28874
16. Gao Y, Gong Y, Lu J, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Xiong Y, et al. Dihydroartemisinin breaks the positive feedback loop of YAP1 and GLUT1-mediated aerobic glycolysis to boost the CD8(+) effector T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Pharmacol. (2024) 225:116294. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116294
17. Li S, Ji J, Zhang Z, Peng Q, Hao L, Guo Y, et al. Cisplatin promotes the expression level of PD-L1 in the microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma through YAP1. Mol Cell Biochem. (2020) 475:79–91. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03861-0
18. Tsukumo SI and Yasutomo K. Regulation of CD8(+) T cells and antitumor immunity by notch signaling. Front Immunol. (2018) 9. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00101
19. Dong MB, Wang G, Chow RD, Ye L, Zhu L, Dai X, et al. Systematic immunotherapy target discovery using genome-scale in vivo CRISPR screens in CD8 T cells. Cell. (2019) 178:1189–204. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.07.044
20. Yang Y, Gao Y, Gong Y, Lu J, Li S, Xiong Y, et al. Dihydroartemisinin breaks the immunosuppressive tumor niche during cisplatin treatment in Hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Histochem. (2024) 126:152171. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2024.152171
21. Kwon J and Bakhoum SF. The cytosolic DNA-sensing cGAS-STING pathway in cancer. Cancer discovery. (2020) 10:26–39. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0761
22. Lv T, Xiong X, Yan W, Liu M, Xu H, and He Q. Targeting of GSDMD sensitizes HCC to anti-PD-1 by activating cGAS pathway and downregulating PD-L1 expression. J immunotherapy Cancer. (2022) 10(6):e004763. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004763
23. Kim CL, Choi SH, and Mo JS. Role of the hippo pathway in fibrosis and cancer. Cells. (2019) 8(5):468. doi: 10.3390/cells8050468
24. Wang Y, Xu X, Maglic D, Dill MT, Mojumdar K, Ng PK, et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of the hippo signaling pathway in cancer. Cell Rep. (2018) 25:1304–17. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.001
25. Peng Q, Li S, Shi X, Guo Y, Hao L, Zhang Z, et al. Dihydroartemisinin broke the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment by inhibiting YAP1 expression to enhance anti-PD-1 efficacy. Phytother Res. (2023) 37:1740–53. doi: 10.1002/ptr.v37.5
26. Ma J, Zheng B, Goswami S, Meng L, Zhang D, Cao C, et al. PD1(Hi) CD8(+) T cells correlate with exhausted signature and poor clinical outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. J immunotherapy cancer. (2019) 7:331. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0814-7
27. Lee BS, Park DI, Lee DH, Lee JE, Yeo MK, Park YH, et al. Hippo effector YAP directly regulates the expression of PD-L1 transcripts in EGFR-TKI-resistant lung adenocarcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 491:493–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.07.007
28. Tang Z, He J, Zou J, Yu S, Sun X, and Qin L. Cisplatin-resistant HepG2 cell-derived exosomes transfer cisplatin resistance to cisplatin-sensitive cells in HCC. PeerJ. (2021) 9:e11200. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11200
29. Wu PY, Hasanah U, Yang SH, Chen SY, Luo YH, Chen CC, et al. Enhancing cisplatin efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma with selenocystine: The suppression of DNA repair and inhibition of proliferation in hepatoma cells. Chem Biol Interact. (2024) 405:111291. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111291
30. Wakita D, Iwai T, Harada S, Suzuki M, Yamamoto K, and Sugimoto M. Cisplatin augments antitumor T-cell responses leading to a potent therapeutic effect in combination with PD-L1 blockade. Anticancer Res. (2019) 39:1749–60. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13281
31. Jin S, Xu B, Yu L, Fu Y, Wu H, Fan X, et al. The PD-1, PD-L1 expression and CD3+ T cell infiltration in relation to outcome in advanced gastric signet-ring cell carcinoma, representing a potential biomarker for immunotherapy. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:38850–62. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16407
32. Golden-Mason L, Palmer B, Klarquist J, Mengshol JA, Castelblanco N, and Rosen HR. Upregulation of PD-1 expression on circulating and intrahepatic hepatitis C virus-specific CD8+ T cells associated with reversible immune dysfunction. J Virol. (2007) 81:9249–58. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00409-07
33. Kansy BA, Concha-Benavente F, Srivastava RM, Jie HB, Shayan G, Lei Y, et al. PD-1 status in CD8(+) T cells associates with survival and anti-PD-1 therapeutic outcomes in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:6353–64. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-3167
34. Shen T, Zhou L, Shen H, Shi C, Jia S, Ding GP, et al. Prognostic value of programmed cell death protein 1 expression on CD8+ T lymphocytes in pancreatic cancer. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:017–08479. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08479-9
35. Yeong J, Lim JCT, Lee B, Li H, Ong CCH, Thike AA, et al. Prognostic value of CD8 + PD-1+ immune infiltrates and PDCD1 gene expression in triple negative breast cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2019) 7:019–0499. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0499-y
36. Corrales L, Glickman LH, McWhirter SM, Kanne DB, Sivick KE, Katibah GE, et al. Direct activation of STING in the tumor microenvironment leads to potent and systemic tumor regression and immunity. Cell Rep. (2015) 11:1018–30. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.04.031
37. Sa P, Singh P, Panda S, Swain RK, Dash R, and Sahoo SK. Reversal of cisplatin resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma by piperlongumine loaded smart nanoparticles through inhibition of Hippo-YAP signaling pathway. Transl Res. (2024) 268:63–78. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2024.03.004
38. Pan Q, Zou C, Lin Z, Tang H, Long Z, and Wang L. TFAP2C drives cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer by upregulating YAP and activating β-catenin signaling. J Biol Chem. (2025) 301(8):110387. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110387
39. Shen XJ, Wei HL, Mo XC, Mo XX, Li L, He JC, et al. Adaptor protein CEMIP reduces the chemosensitivity of small cell lung cancer via activation of an SRC-YAP oncogenic module. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2024) 45:2657–71. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01342-4
40. Xiao L, Shi XY, Li ZL, Li M, Zhang MM, Yan SJ, et al. Downregulation of LINC01508 contributes to cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer via the regulation of the Hippo-YAP pathway. J Gynecol Oncol. (2021) 32:e77. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2021.32.e77
41. Fu G, Wu Y, Zhao G, Chen X, Xu Z, Sun J, et al. Activation of cGAS-STING signal to inhibit the proliferation of bladder cancer: the immune effect of cisplatin. Cells. (2022) 11(19):3011. doi: 10.3390/cells11193011
Keywords: cisplatin, Yap1, hepatocellular carcinoma, PD-1, CGAS, STING, CD8 + T cells
Citation: Gong Y, Xiong Y, Gao Y, Song X, Gong Y, Wang D, Liu Z, Yang Y, Lu J, Zou IX and Shi X (2025) Verteporfin inhibits the cGAS-STING pathway and improves the tumor microenvironment during cisplatin treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 16:1658042. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1658042
Received: 02 July 2025; Accepted: 04 August 2025;
Published: 22 August 2025.
Edited by:
Chunjing Wang, University College London, United KingdomReviewed by:
Fangfang Tao, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, ChinaHonggang Zheng, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, China
Guiying Peng, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2025 Gong, Xiong, Gao, Song, Gong, Wang, Liu, Yang, Lu, Zou and Shi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xinli Shi, c3hsc3Vuc2hpbmVAc2luYS5jb20=
 Yi Gong1,2
Yi Gong1,2 Yajun Xiong
Yajun Xiong Yuting Gao
Yuting Gao Yanguang Yang
Yanguang Yang Xinli Shi
Xinli Shi