- 1College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
- 2Department of Imaging, Jinan Second People’s Hospital, Jinan, China
- 3Second College of Clinical Medicine, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China
- 4Department of Imaging Center, Jinan Nanshan People’s Hospital, Jinan, China
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranks among the most lethal malignancies worldwide, characterized by its high metastatic potential and poor prognosis. Early and precise detection and diagnosis of HCC remain a major clinical challenge. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), as the most widely used noninvasive technique for diagnosing liver diseases, currently suffers from limitations in traditional contrast agents, including low specificity and limited sensitivity, particularly when detecting small lesions. The emergence of nanotechnology offers novel approaches to enhance the diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic efficacy for HCC. Under the framework of big data driven precision medicine, this study explores the application of nanomaterials in HCC MRI enhancement and multimodal therapy. This review comprehensively summarizes two types of responsive nanomaterials: (1) Chiral Ni(OH)2 nanoparticles, which suggeste enhanced contrast in T1 weighted MRI and selective imaging capabilities for primary HCC and lung metastases; (2) β Lapachone loaded mesoporous MnO2 nanoparticles (HLMn), which effectively enhance the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) within tumor cells, disrupt redox homeostasis, and significantly improve the efficacy of chemo dynamic therapy (CDT). These nanoplatforms also exhibit potential to activate the c-GAS STING innate immune pathway, thereby augmenting antitumor immune responses. Nanomaterials hold great promise not only as enhanced contrast agents but also as precise therapeutic carriers. By integrating radiomics based imaging features with biological markers, we summarize current personalized HCC diagnosis and treatment planning models based on multimodal data. Simultaneously, we provide a critical summary of the synergistic application of advanced imaging and therapeutic nanotechnologies. In the future, leveraging big data for precise HCC diagnosis and treatment is anticipated to significantly improve patient survival.
1 Introduction and literature search strategy
1.1 Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common and deadly malignant tumors globally, accounting for the majority of primary liver cancers (1). Due to its asymptomatic nature in early stages, rapid progression, and high metastatic potential, early and accurate diagnosis of HCC remains challenging (2). Consequently, patients often present at advanced stages, resulting in poor prognosis and limited treatment options (3, 4). Current diagnostic modalities, including ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), along with serum biomarkers such as alpha fetoprotein (AFP) and des γ carboxy prothrombin (DCP), face challenges such as limited sensitivity for small or early stage tumors, inability to fully capture tumor heterogeneity, and variability in detecting microvascular invasion. Similarly, conventional therapeutic approaches, including surgical resection, local ablation, transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), and systemic chemotherapy, often result in suboptimal treatment responses due to tumor heterogeneity and complex tumor microenvironment, contributing to the overall poor prognosis (5). While significant progress has been made in treatment modalities such as surgical resection, transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), and systemic chemotherapy, the five year survival rate remains suboptimal, with rates in many regions barely exceeding 30% (6). These factors underscore the urgent need to improve early detection and precision treatment to enhance patient outcomes and reduce mortality.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has become the gold standard for non-invasive liver cancer diagnosis due to its excellent spatial resolution, high soft tissue contrast, and multi parameter detection capabilities, enabling simultaneous detection of anatomical and functional abnormalities in liver tissue (7). However, traditional gadolinium based contrast agents have limitations such as low sensitivity, lack of tumor specificity, and potential nephrotoxicity. These limitations further highlight the need for advanced imaging strategies that can provide higher sensitivity, tumor specific contrast, and reliable quantitative biomarkers. Nanotechnology, as a highly promising research direction, suggests significant potential in biomedical applications due to its customizable size, shape, surface charge, and chemical composition (8). When applied to MRI, it can significantly enhance T1 or T2 contrast, improve tumor targeting, and serve as a delivery system for targeted therapeutic drugs (9, 10). Functionalized nanomaterials can detect overexpressed biomarkers on HCC cell membranes, such as glycoprotein 3 and CD44, achieving selective distribution to tumor sites while minimizing off target effects (11).
The emergence of radiomics (the efficient extraction of quantitative features from medical images) has opened up new dimensions for precision oncology. Research has shown that radiomics can analyze tumor heterogeneity, morphological changes, and the composition of the tumor microenvironment, while also revealing features that are not detectable by the naked eye. When combined with Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) approaches, radiomics enables integration of multi-dimensional imaging data with clinical, pathological, and molecular information, providing the theoretical and computational basis for AI driven predictive modeling of individualized treatment responses. This framework supports the rationale for leveraging nanomaterials to enhance imaging contrast and guide precise, personalized therapies. Additionally, the integration of image guided, data driven nanotechnology with MRI marks a paradigm shift in cancer treatment planning and optimization (12). This review aims to explore the application of nanomaterials in enhancing MRI contrast and promoting multimodal treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (13). In the future, by overcoming the limitations of current diagnostic and therapeutic methods and fully exploiting the capabilities of nanotechnology and radiomics, more accurate and personalized tools for HCC diagnosis and treatment can be established, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
1.2 Literature search strategy
To ensure a comprehensive and systematic review of nanomaterials in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) imaging and therapy, we conducted a thorough literature search across major scientific databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus, covering publications up to May 2025. The search strategy combined terms related to the disease, imaging modalities, nanomaterials, and therapeutic approaches, including: “hepatocellular carcinoma”, “HCC”, “magnetic resonance imaging”, “MRI”, “nanomaterials”, “nanoparticles”, “radiomics”, “multimodal therapy”, “photothermal therapy”, and “chemodynamic therapy”. Boolean operators (“AND”, “OR”) and truncation were applied to refine search results and ensure maximum coverage of relevant literature.
Inclusion criteria were: (1) Studies involving HCC patients or preclinical models relevant to human HCC. (2) Research focusing on nanomaterial-based MRI contrast enhancement, targeted drug delivery, or multimodal therapy. (3) Studies providing quantitative, mechanistic, or translational insights. (4) Peer-reviewed original research articles published in English.
Exclusion criteria included: (1) Articles not directly related to HCC or nanomaterials. (2) Conference abstracts, editorials, commentaries, or reviews without primary data. (3) Duplicate studies or studies with insufficient methodological details.
The initial search yielded over 1,200 publications. After screening titles and abstracts for relevance and removing duplicates, 320 articles were selected for full-text review. Each full-text article was evaluated for methodological rigor, experimental design, and clinical or preclinical relevance. Ultimately, 101 studies were included in this review, providing a comprehensive and balanced representation of current research on nanomaterial applications in HCC imaging and therapy.
To further enhance comprehensiveness, the reference lists of included studies were manually screened to capture additional relevant publications not indexed in the databases. Priority was given to recent studies (2020–2025) and highly cited works that provide mechanistic insights or novel applications.
For synthesis and analysis, the included studies were categorized based on key criteria: (1) type of nanomaterial (e.g., manganese-based, iron oxide, gold nanoparticles), (2) imaging modality and contrast enhancement mechanism, (3) therapeutic strategies (e.g., photothermal therapy, chemodynamic therapy, immunomodulation), and (4) preclinical versus clinical studies. Comparative tables and critical discussions were constructed to highlight the strengths, limitations, and translational potential of each approach. This structured methodology ensures that the review provides not only a comprehensive overview but also critical insights and guidance for future research directions in HCC nanomedicine.
2 Radiomics basis of MRI enhancement by nanomaterials in HCC imaging
MRI plays a significant role in assisting HCC diagnosis. Recent studies have integrated nanomaterials into hepatocellular carcinoma imaging technology, primarily to extract key features from medical imaging data and efficiently transmit this data to achieve a visual format suitable for further analysis. Additionally, the functionalized nanoparticles introduced during imaging provide critical features such as enhanced contrast, tumor specific distribution, and time and space specific interactions, which are essential for subsequent applications in radiomics (14). Advances in multimodal imaging technology have broken through the limitations of traditional imaging, meeting the current demands of precision medicine, and significantly promoting the detection of phenotypic patterns in the tumor microenvironment. In the future, the integration of nanomaterials with radiomics will further enhance diagnostic and prognostic capabilities, thereby solidifying MRI’s position as an indispensable clinical driver in HCC management (15, 16).
2.1 Synthesis of nanomaterials
The synthesis of nanomaterials plays a crucial role in biomedicine, particularly in the field of HCC imaging and treatment. This review explores three primary synthesis methods: vapor phase synthesis, solution phase synthesis, and solid phase synthesis. Vapor phase synthesis includes techniques such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD), which have been found to effectively prepare nanomaterials with high structural purity and morphological control (17). This method has been successfully applied to the preparation of magnetic nanomaterials for imaging applications. Liquid phase synthesis has become the most flexible method for biomedical applications due to its ease of operation, scalability, and high functionalization rate (18, 19). Studies have shown that precise control of particle morphology can be achieved by adjusting variables such as pH, temperature, and reaction time. Importantly, surface functionalization the grafting of targeted ligands or therapeutic molecules has been successfully achieved during synthesis, which is crucial for the tumor specific application of HCC (20). For example, MRI contrast agents and drug loaded nanocarriers. Solid phase synthesis, including techniques such as ball milling and spark plasma sintering, can produce crystalline nanoparticles with high structural integrity. Although this method is not suitable for surface modification, it offers significant advantages in preparing robust and scalable materials with high thermal and chemical stability (21).
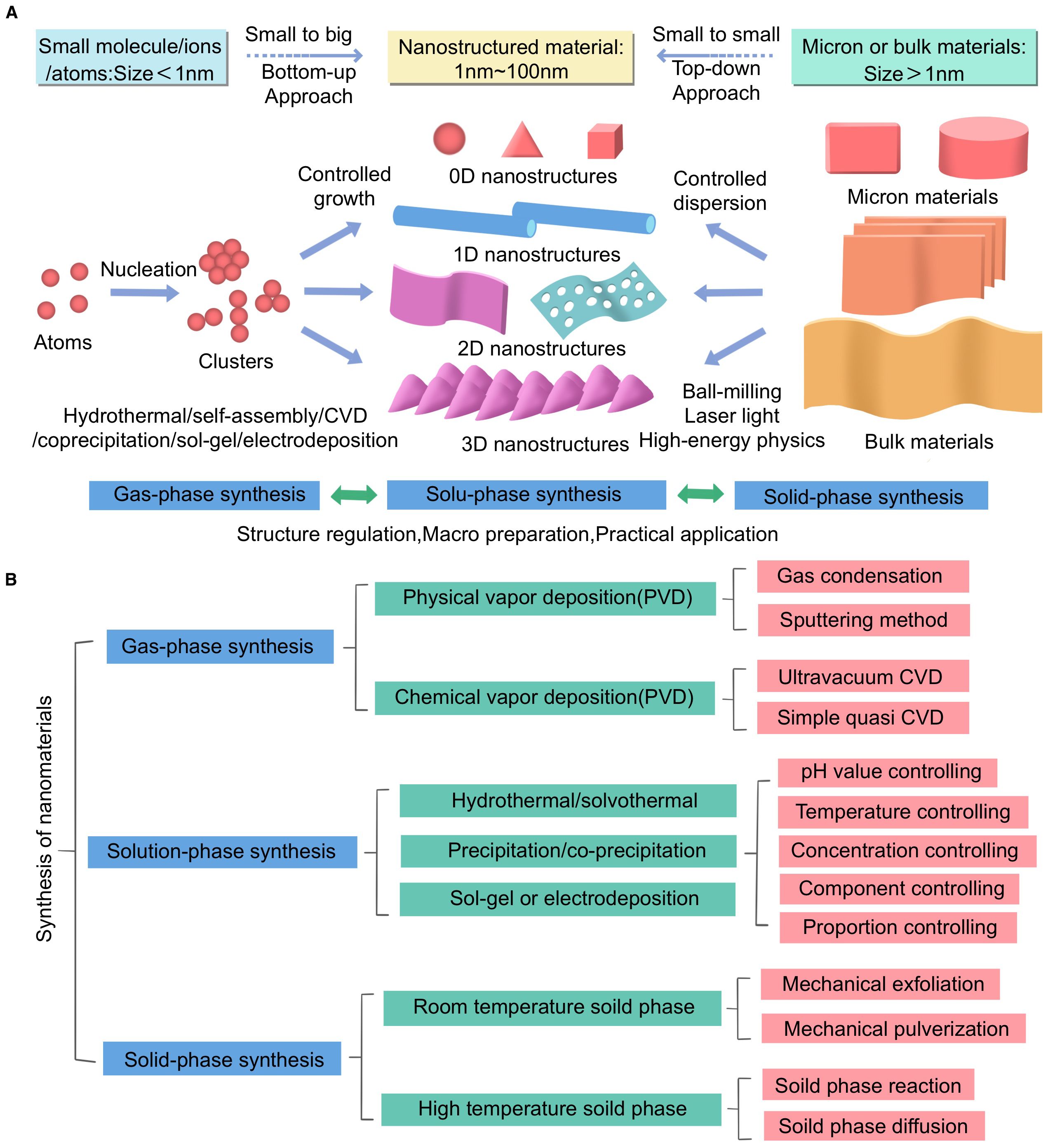
This figure illustrates the synthesis methods of nanomaterials and their applications in biomedical research, particularly in imaging and treatment of HCC. The figure is divided into two main sections: Section (A) shows different synthesis methods and their corresponding material size ranges, while Section (B) provides detailed descriptions of the specific techniques and control parameters involved in each synthesis method.
In Section A of Figure, two methods for synthesizing nanomaterials are presented: bottom up and top-down approaches. The bottom-up method starts with small molecules or atoms (size < 1 nm) and gradually constructs nanostructured materials (1 nm–100 nm) through controlled growth and nucleation processes. This method is closely related to techniques such as hydrothermal synthesis, sol gel synthesis, electroplating, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The top-down method, on the other hand, starts with micron sized or bulk materials (size > 1 μm) and reduces them to nanoscale materials through processes such as ball milling and laser processing.
In Section B of Figure, the three main synthesis methods are detailed. For gas phase synthesis, we list techniques such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD), as well as sub methods like sputtering and ultra-high vacuum CVD. Solution phase synthesis includes hydrothermal/solvothermal methods, precipitation/coprecipitation methods, and sol gel or electrodeposition methods. Here, particular emphasis is placed on parameters such as pH, temperature, and concentration control. Solid phase synthesis encompasses both ambient and high temperature processes, including key techniques such as mechanical exfoliation and solid state grinding.
Additionally, the figure highlights the importance of controlling various parameters during synthesis to achieve the desired properties of nanomaterials. In solution phase synthesis, factors such as pH, temperature, concentration, and component ratios are critical for regulating the structure and functionality of nanomaterials. This level of control is crucial for the application of nanomaterials in biomedical applications.
This figure aims to comprehensively summarize the complexity and diversity of nanomaterial synthesis methods, emphasizing the importance of selecting appropriate synthesis techniques based on the specific requirements of biomedical applications. It also highlights the potential of these nanomaterials in advancing HCC diagnostic and therapeutic strategies (Figure 1).
2.2 Mechanisms and advantages of nanomaterials in MRI imaging
Integrating magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) into nanomaterials by adjusting their magnetic and physicochemical properties can significantly improve the diagnostic accuracy of HCC. Although gadolinium-based contrast agents have seen some clinical use, their limited tumor specificity, low sensitivity, and potential nephrotoxicity continue to pose significant barriers to widespread adoption. In contrast, nanomaterials offer significant advantages in terms of magnetic responsiveness, biocompatibility, and surface functionalization, making them promising candidates for next generation MRI contrast agents (22).
Current research focuses on chiral nickel hydroxide nanoparticles [D/L Ni(OH)2], which exhibit a high longitudinal relaxation rate (r1), directly influencing T1 relaxation time. The enhancement in T1 weighted imaging stems from these nanoparticles increasing proton relaxation by modulating the local magnetic field, thereby amplifying the MRI signal (23). The chiral configuration also introduces stereoselective interactions with cellular components. DNi(OH)2 exhibits stronger affinity for specific tumor receptors, resulting in higher cellular uptake and more pronounced signal amplification in tumor regions compared to LNi(OH)2 or achiral analogues. This chiral selectivity enhances spatial resolution and tumor specificity, representing a significant advancement over traditional drugs.
Manganese dioxide nanoparticles (MnO2) are another class of effective T1 contrast agents (24). In the acidic and reducing tumor microenvironment (TME), MnO2 undergoes redox reactions, releasing Mn²+ ions. These Mn²+ ions exhibit paramagnetic properties, significantly shortening T1 relaxation times through interactions with water protons, thereby enhancing signal intensity in T1 weighted MRI sequences. Furthermore, MnO2 particles have an inherent ability to react with endogenous hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which is commonly overexpressed in tumor tissues. This catalyzed reaction generates oxygen (O2), alleviating tumor hypoxia and subsequently enhancing the efficacy of oxygen dependent treatments such as photodynamic therapy (PDT) (25). Manganese dioxide (MnO2) exhibits dual functionality in enhancing imaging contrast and modulating the tumor microenvironment (TME), which aligns closely with the principles of theranostics. Both D Ni(OH)2 and MnO2 nanoparticles can be further modified with tumor targeting ligands to enhance selectivity and systemic circulation time (26, 27). Ligands such as hyaluronic acid (HA) targeting the CD44 receptor or tumor specific peptides can be grafted onto the nanoparticle surface to achieve active targeting (28). This engineering strategy significantly enhances drug accumulation at the tumor site by enhancing the permeability retention effect and active targeting mechanism. Additionally, the structural parameters of these nanomaterials (including particle size, zeta potential, and hydrophilicity) can be finely tuned to further optimize biodistribution, cellular uptake, and MRI signal intensity. Furthermore, smaller nanoparticles (<50 nm) typically exhibit better tumor tissue penetration, while surface polyethylene glycolation (PEGylation) significantly improves systemic stability and reduces immune clearance (29, 30).
To visually illustrate these advantages, we have added representative MRI scans in Figure 2, comparing conventional gadolinium-based contrast MRI with nanomaterial enhanced MRI (D Ni(OH)2 and MnO2). Figure 2 shows preclinical T1 weighted imaging of HCC xenografts with MnO2 nanoparticles, highlighting enhanced tumor contrast and spatial resolution. These figures support the discussion of the unique imaging benefits provided by functionalized nanomaterials.
MRI contrast agents based on nanomaterials (such as D Ni(OH)2 and MnO2) provide a multifunctional platform with high relaxation rates, environmental responsiveness, and surface tunability. In the future, they could enable high resolution, high contrast, and tumor specific imaging of HCC, thereby further advancing precise diagnosis of HCC.
2.3 Feature extraction and diagnostic value of radiomics in HCC MRI
Radiomics, as an emerging discipline, is currently situated at the intersection of medical imaging and data science. In the context of HCC, radiomics offers a non-invasive method for analyzing tumor characteristics such as shape, texture, intensity distribution, and spatial heterogeneity. These features are primarily extracted from MRI sequences such as T1 weighted, T2 weighted, diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), and contrast enhanced imaging, and can help identify key biomarkers associated with tumor biology and clinical outcomes (31).
Radiomic analysis commonly involves the calculation of first order statistics (e.g., mean intensity, entropy), second order texture features (e.g., gray level cooccurrence matrix [GLCM] metrics), and higher order transformations (e.g., wavelet decomposition) from defined regions of interest (ROIs) (32). These data can reflect underlying tumor phenotypes such as vascularity, necrosis, or fibrotic changes, which are relevant in the clinical stratification and staging of HCC. To enhance clinical relevance, we have integrated a detailed workflow outlining the steps of image preprocessing, ROI segmentation, feature extraction, and feature selection, emphasizing how each step can impact downstream predictive modeling and reproducibility (33).
While some studies have suggested associations between radiomic features and prognostic indicators, such as microvascular invasion (MVI), tumor grade, or recurrence risk (34), the reproducibility of these findings remains an active area of investigation. ML methods, including LASSO regression, random forests, support vector machines, and DL approaches, are increasingly employed to identify robust feature subsets and construct predictive models for tumor diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy response prediction. Comparative analyses showing performance differences between conventional MRI features and nanomaterial enhanced MRI features are included to highlight the added diagnostic value of nanomaterial enhanced imaging (35).
Radiomics can also be integrated with conventional biomarkers, such as alpha fetoprotein (AFP), or molecular data (e.g., TP53 mutation status) to enhance diagnostic accuracy and biological interpretation (36). Multi parametric models combining radiomic features with clinical, genomic, and treatment data are now emphasized as a big data driven approach to improve individualized risk stratification and treatment planning (37). For instance, multi parametric models combining radiomic features with clinical data have shown improved performance in distinguishing HCC from benign hepatic lesions like focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) or hemangiomas (38). However, such approaches are still largely experimental and not yet adopted in routine clinical practice.
A major challenge limiting clinical translation lies in the lack of standardization in image acquisition, segmentation protocols, and feature computation (39). Inter scanner variability and institution dependent imaging parameters can significantly affect feature stability and model generalizability. Consequently, we stress the importance of harmonized radiomics pipelines, large annotated datasets, and integration with AI driven predictive modeling for robust, reproducible clinical applications (37).
In summary, radiomics holds considerable potential to complement MRI in the diagnosis and risk stratification of HCC. Although many of its current applications remain investigational, the integration of radiomics with big data analytics, ML, and nanomaterial enhanced imaging represents a promising strategy to improve non-invasive tumor assessment and guide individualized clinical decisions in precision medicine (40).
2.4 Integration strategies for multimodal imaging and clinical data
In the era of precision medicine, the integration of radiomics derived imaging features with clinical, pathological, molecular, and therapeutic response data is essential to build robust, data driven diagnostic and therapeutic decision-making frameworks (41). For hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which presents with heterogeneous biological behavior, combining MRI based radiomics with genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and biochemical markers provides a multidimensional perspective that enhances individualized disease assessment and patient stratification (42).
Tumor heterogeneity and microstructural changes can be quantitatively captured by extracting radiomic features from MRI sequences (e.g., T1 weighted, T2 weighted, and diffusion weighted imaging), which are then correlated with gene expression profiles, mutation status (e.g., TP53, CTNNB1), histological grading, and serum biomarkers such as alpha fetoprotein (AFP) and des γ carboxy prothrombin (DCP) (43, 44). This multidimensional integration facilitates more accurate prognostic stratification and individualized therapy planning.
By incorporating advanced computational techniques, including ML algorithms, deep neural networks, and multi modal data fusion frameworks, these heterogeneous datasets can be analyzed to identify predictive patterns and optimize treatment strategies. Different methods such as feature level fusion, decision level fusion, and model ensemble approaches can bring multiple data types together without redundant information while maintaining model interpretability (45).
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) are increasingly leveraging these fused data to provide oncologists with real time, evidence-based recommendations for diagnosis, risk assessment, and treatment selection (46). These systems enable dynamic, patient specific decision making based on tumor characteristics, molecular profiles, and risk factors, thereby supporting precision oncology in clinical practice.
Overall, the combination of imaging, molecular, and clinical data transforms traditional diagnostics into a systemic, data driven framework, enhancing HCC diagnosis, patient stratification, and personalized follow up strategies.
3 Mechanistic analysis and strategic design of nanomaterial mediated multimodal synergistic therapy
3.1 ROS amplification and mechanism of chemodynamic therapy
A study delved into the mechanistic analysis of nanomaterial mediated multimodal synergistic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), with a focus on ROS amplification and the integration of chemo dynamic therapy (CDT) with other therapeutic modalities (47). The β Lapachone (β Lap)/MnO2 nanoplatform was found to significantly enhance CDT through cascade ROS augmentation. When activated in the tumor microenvironment, it produces highly toxic hydroxyl radicals (•OH) via Fenton like reactions, inducing oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, and ultimately causing cancer cell apoptosis (48, 49). In addition, another research also developed a tandem nanoplatform integrating photothermal therapy (PTT), photodynamic therapy (PDT), and CDT. The NanoMn-Gox-PTX system, encapsulated in a DSPE-PEG lipid layer and containing Mn²+, glucose oxidase (GOx), and paclitaxel (PTX), suggested remarkable therapeutic and imaging capabilities (50). Upon reaching the tumor tissue, GOx catalyzes the oxidation of glucose to H2O2, which then reacts with Mn²+ to form •OH, triggering CDT (51). Meanwhile, the nanoplatform is activated by near infrared II (NIR II) laser irradiation, elevating local temperature to induce tumor cell apoptosis through PTT (52). The in situ production of oxygen improves PDT efficacy by reducing hypoxia induced resistance.
Furthermore, the release of Mn²+ enhances T1 weighted MRI contrast and facilitates real time imaging of nanoparticle distribution and therapeutic response through DiR molecules for NIR fluorescence imaging (53). Increased ROS levels upregulate tumor antigen release, activate the cGAS–STING immune axis, and promote dendritic cell maturation and cytotoxic T lymphocyte induction (54). The NanoMn-Gox-PTX nanoplatform, with its rational design and multifunctional capabilities, stands out as an ideal candidate for effective and precise image guided cancer treatment. The β Lap/MnO2 nano system offers a promising approach to achieving selective and efficient HCC treatment based on enhanced CDT and MRI detectability, aligning with the study’s objective of developing advanced nanomaterials to overcome traditional HCC treatment limitations (55).
3.2 Design and optimization of photothermal/photodynamic synergistic therapy system
Synergistic photothermal/photodynamic therapy (PTT/PDT) systems represent a novel strategic approach for HCC treatment that leverages the complementary advantages of multiple therapeutic modalities (56). The NanoMn-Gox-PTX platform integrates photothermal therapy (PTT), photodynamic therapy (PDT), and chemotherapy driven therapy (CDT) into a single nanostructure, thereby enabling precise drug delivery, real time imaging, and enhanced therapeutic efficacy.
Another nanoplatform employs a DSPE-PEG lipid bilayer to encapsulate components such as manganese ions (Mn²+), glucose oxidase (GOx), paclitaxel (PTX), and the fluorescent dye DiR (57). While ensuring near perfect biocompatibility and circulatory stability, it can achieve controlled, precise release under tumor specific stimulation. Following systemic administration, the nanoparticle platform passively accumulates in tumor tissues via the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect (58). Once localized in the tumor microenvironment (TME), the platform automatically responds to its unique biochemical conditions and external irradiation. Mechanistically, GOx catalyzes the oxidation of intratumoral-glucose to gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), leading to two critical outcomes (59): (1) depletion of glucose disrupts tumor cell metabolism and promotes starvation induced apoptosis; (2) the generated H2O2 reacts with Mn²+ via a Fenton like reaction to yield highly cytotoxic hydroxyl radicals (•OH), which induce oxidative stress and cellular damage—constituting the CDT component (60).
Simultaneously, under near infrared II (NIR II) laser irradiation, the nanostructure absorbs light and converts it into heat, elevating local temperatures to trigger apoptosis in cancer cells through PTT (61). This localized hyperthermia not only disrupts cellular integrity but also increases membrane permeability, facilitating drug penetration and potentiating chemotherapy. Furthermore, the elevated temperature accelerates ROS production, synergistically enhancing PDT. In the PDT mechanism, the DiR dyeactivated by NIR irradiation—transfers energy to surrounding oxygen molecules to produce singlet oxygen (^1O2), a potent ROS that damages intracellular organelles and DNA (62). However, the hypoxic nature of solid tumors often impairs PDT efficacy. To counter this, MnO2 reacts with H2O2 to generate oxygen in situ, thereby alleviating hypoxia and supporting continuous ROS generation (63). In terms of imaging, Mn²+ released from the platform improves T1 weighted MRI contrast due to its strong paramagnetic properties, enabling real time localization of the nanoplatform and monitoring of treatment progression (64). Concurrently, DiR fluorescence imaging supports near infrared visualization of nanoparticle biodistribution and tumor response.
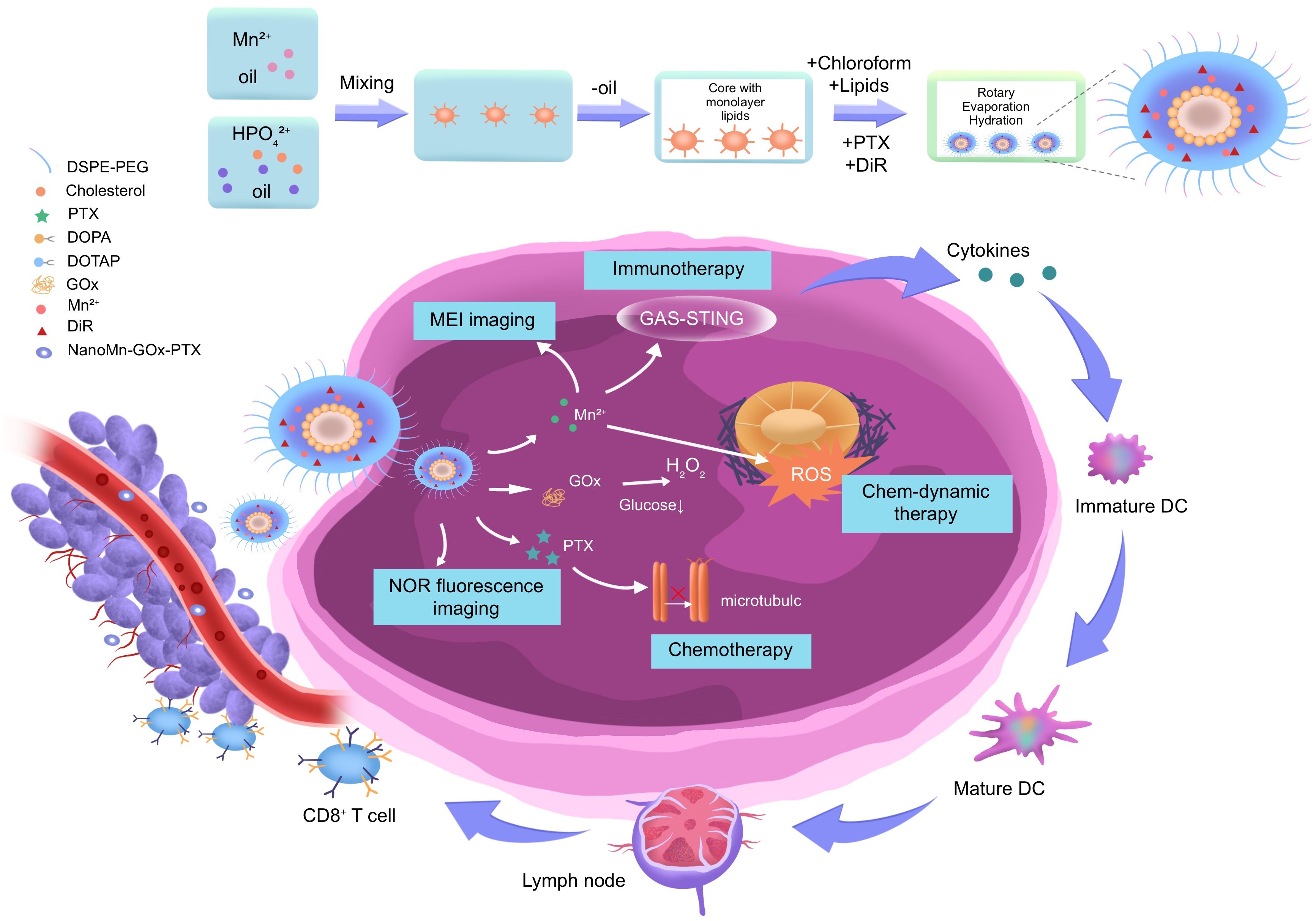
The schematic diagram illustrates the modular design and mechanistic interactions of the NanoMn-Gox-PTX nanoplatform for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) therapy. The figure outlines each stage of the nanoparticle’s fabrication process, beginning with the integration of therapeutic and diagnostic components—including manganese ions (Mn²+), DSPE PEG for enhanced stability and biocompatibility, hydrogenated poly(glycerol) (HPG), paclitaxel (PTX), cholesterol PEG, cationic lipid DOTAP, magnetically active material MAG, and the near infrared fluorescent dye DiR. These components are co assembled via molecular lipid core formation, followed by chloroform evaporation and aqueous phase hydration to yield a stable, uniform nanostructure. This formulation strategy ensures precise control over particle size, zeta potential, and encapsulation efficiency, all critical parameters influencing tumor penetration and systemic circulation time.
Following intravenous administration, the nanomaterials passively accumulate in tumor tissues via the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect. Once successfully localized, the platform is functionally activated through endogenous tumor microenvironment stimulation and external near infrared II (NIR II) laser irradiation. At this point, in the tumor site, glucose oxidase (GOx) catalyzes glucose oxidation, producing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and inducing glucose starvation (65). This metabolic effect makes tumor cells more sensitive to further treatment. The generated H2O2 acts as a substrate for a Fenton like reaction with Mn²+, producing highly reactive hydroxyl radicals (•OH), which trigger chemotherapy driven therapy (CDT) through DNA damage and oxidative stress (66). Simultaneously, the release of Mn²+ enhances T1 weighted MRI signal intensity, enabling real time anatomical localization and monitoring of therapeutic progression. DiR encapsulated in the lipid bilayer supports NIR fluorescence imaging, offering dynamic tracking of nanoparticle distribution and therapeutic response.
Laser triggered photothermal conversion elevates the local temperature of the tumor microenvironment, inducing direct thermal ablation of malignant cells and improving tumor perfusion. This not only amplifies the effectiveness of photothermal therapy (PTT) but also facilitates greater intratumoral drug delivery and immune infiltration. The temperature increase also enhances reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, thereby synergizing with photodynamic therapy (PDT) mechanisms mediated by the DiR molecule. A particularly significant outcome of the ROS cascade is its immunological impact. The increased oxidative stress promotes immunogenic cell death (ICD), leading to the release of damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) such as calreticulin and HMGB1. These DAMPs activate the cyclic GMP AMP synthase (cGAS)–stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway in antigen presenting cells. As a result, dendritic cells (DCs) mature and prime cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), mounting a systemic anti-tumor immune response that may suppress both primary tumors and distant metastases.
In summary, the diagram not only visualizes the structural complexity and synthetic methodology of the NanoMn GOx PTX system but also encapsulates its multi-dimensional therapeutic strategy. Through the integration of CDT, PTT, PDT, chemotherapy, imaging, and immune activation within a single platform, this nanoplatform embodies the future of precision oncology offering highly localized, image guided, and immunologically engaged treatment for advanced HCC.
3.3 Application of manganese based nanomaterials in medical imaging
Manganese-based nanomaterials have gained significant attention in HCC imaging due to their intrinsic paramagnetic properties, particularly the presence of Mn²+ ions, which enhance T1-weighted MRI contrast. This makes them highly effective for T1 weighted MRI contrast enhancement (67). Unlike gadolinium-based agents, Mn based materials offer better biocompatibility and lower risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Importantly, many manganese containing compounds, such as MnO2 or manganese carbonate (MnCO3), are designed to be “activatable” undergoing redox reactions or pH triggered dissolution within the tumor microenvironment to release Mn²+ ions precisely where imaging contrast is needed (68). This site-specific release improves imaging sensitivity while minimizing systemic exposure.
Comparative analyses of different manganese-based formulations indicate that MnO2 nanoparticles are particularly effective in the acidic and reductive tumor microenvironment, where they release Mn²+ ions in situ, shortening T1 relaxation times and enhancing MRI sensitivity. From a mechanistic standpoint, MnO2 nanoparticles play a dual role in both imaging and therapy. In the reductive and acidic conditions of the tumor microenvironment—characterized by elevated glutathione (GSH) and H2O2 levels MnO2 is reduced to free Mn²+, which shortens the T1 relaxation time and enhances imaging contrast (69). Concurrently, MnO2 acts as a catalyst for the decomposition of H2O2 into oxygen, alleviating hypoxia—a major barrier to photodynamic therapy (PDT) efficacy. This oxygen generating capability restores ROS production during PDT and boosts treatment response (70). Moreover, the acidic tumor environment triggers degradation of the nanoparticle structure, improving payload release (e.g., drugs or immunostimulants), thus linking the imaging signal with therapeutic action—a concept known as “image guided therapy.
In addition to common diagnostic functions, manganese-based nanomaterials are increasingly being used as an important component of multimodal treatment systems. When combined with photothermal therapy (PTT), chemotherapy, and immunomodulators, the insiturelease of Mn²+ ions can not only promote MRI tracking but also directly activate the cGAS STING innate immune pathway, enhancing type I interferon production and dendritic cell maturation. Recent studies have suggested that manganese nanoparticles, such as TPA Mn and ROS sensitive NPMn, trigger cGAS STING signaling, increase secretion of pro inflammatory cytokines (TNF α, IL 6, IL 2), promote cytotoxic T lymphocyte infiltration, and reduce immunosuppressive regulatory T cells. Furthermore, when combined with DNA damaging agents or anti PD 1 therapy, these manganese-based systems synergistically remodel the tumor immune microenvironment and improve immunotherapy efficacy (71) (72). Moreover, manganese nanoparticles functionalized with tumor targeting ligands (e.g., folate, RGD peptides) or surface modifiers (e.g., PEG, lipids) exhibit improved tumor selectivity, circulation halflife, and biosafety. Overall, manganese-based nanomaterials offer a highly integrated solution for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. They can serve not only as contrast agents but also as active drugs to trigger or guide therapeutic responses.
4 Construction of big data driven precision medical pathways and clinical prospects
4.1 Synergistic role of big data and radiomics in optimizing individualized treatment pathways
The integration of multimodal data analysis and radiomics provides key insights for precision treatment of HCC. Radiomics can systematically extract high dimensional quantitative features from MRI and other medical imaging data, capturing tumor heterogeneity, microstructural patterns, and spatial complexity that are not apparent to clinicians. When combined with clinical biomarkers, genomics, transcriptomics, and patient history, these features provide a robust, data driven framework for individualized clinical decision making (41).
ML and DL algorithms play a central role in this framework by processing multi parametric MRI data, including T1, T2, diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps, and converting them into predictive models for treatment response, recurrence risk, and survival outcomes (73, 74). Feature selection, model training, and validation strategies are highlighted to ensure reproducibility and generalizability across heterogeneous datasets. Although promising, many models remain in the research stage, constrained by limited prospective validation and inter institutional variability (37) (Table 1).
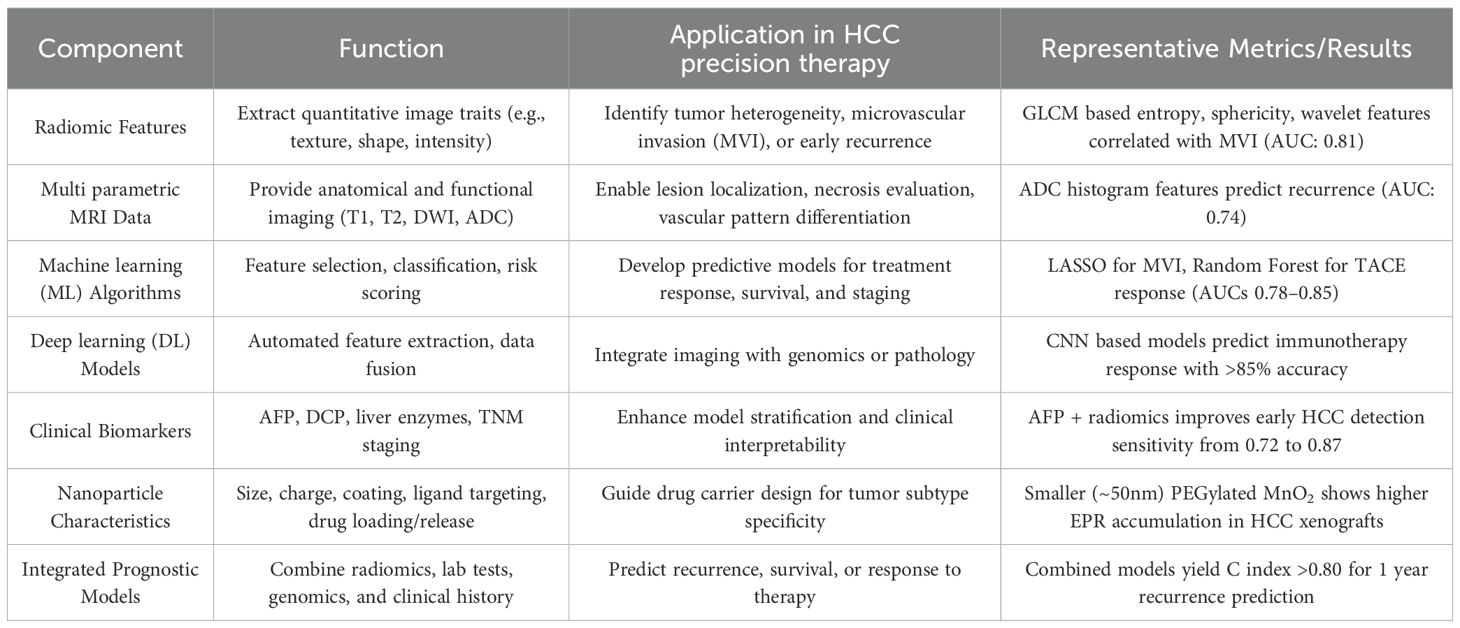
Table 1. Radiomics and big data integration in precision therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
This integrated framework underscores the pivotal role of radiomics and big data in enhancing the granularity and precision of HCC management across diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic dimensions. By leveraging quantitative imaging features—many of which are imperceptible to human observers—radiomics offers a non-invasive, reproducible, and high throughput methodology to characterize tumor phenotypes. When aligned with ML algorithms, these features can be transformed into robust predictive tools for assessing microvascular invasion, tumor differentiation, or therapeutic response potential, all of which are critical in informing individualized treatment strategies. Importantly, recent studies have suggested that combining radiomics with conventional clinical biomarkers such as AFP or DCP significantly improves the accuracy of early HCC detection and recurrence prediction. For example, multi parametric models integrating arterial phase texture features with AFP levels have shown superior predictive performance (AUC > 0.85) compared to either modality alone (75). Similarly, radiomics signatures extracted from contrast enhanced MRI and DWI sequences have been correlated with immunotherapy outcomes and TACE responsiveness, suggesting their utility in patient stratification and treatment personalization (76).
Beyond predictive modeling, big data driven approaches facilitate the integration of diverse data layers, including genomics, proteomics, histopathology, and therapeutic history, into unified analytical pipelines. This multidimensional perspective enables the construction of comprehensive patient profiles that account for tumor biology, host response, and environmental variables (77). The insights gained can inform not only the selection of optimal therapeutic regimens (e.g., systemic therapy vs. local ablation) but also the design of drug delivery systems, such as nanoparticle size and surface modification, tailored to specific tumor characteristics. Despite this progress, the clinical translation of radiomics and AI based models remains limited by several challenges. These issues include inconsistent imaging protocols between different hospital institutions, a lack of standardized feature definitions, and insufficient relevant datasets (78). Additionally, many ML models have limited interpretability, which are key barriers to clinical adoption of AI models. To overcome these limitations, future research should prioritize multi center collaboration, standardization of radiomics workflows, and the construction of large annotated datasets incorporating longitudinal follow up results (79). Initiatives such as the Imaging Biomarker Standardization Initiative (IBSI) and the establishment of FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reproducible) data principles in the field of radiomics are critical steps toward enhancing model reproducibility and clinical trustworthiness (80).
The synergistic integration of radiomics, big data analysis, and clinical information has brought significant progress to personalized HCC treatment. As this field continues to evolve, it is expected to transition from retrospective risk assessment to real time clinical decision support. Additionally, it will find comprehensive applications from treatment selection to nanomedicine design and long-term monitoring. Under appropriate validation and regulatory frameworks, precision oncology based on radiomics has the potential to become a key solution for the next generation of clinical diagnosis and treatment in HCC therapy.
4.2 Tumor microenvironment modulation and response prediction modeling
The tumor microenvironment (TME) promotes cell invasion, metastasis, immune evasion, and treatment resistance. The TME is a dynamic, highly heterogeneous system characterized by hypoxia, acidic pH, abnormal vascular structures, and abundant immune suppressive cells, which collectively influence therapeutic outcomes. These unique features significantly impair the efficacy of systemic therapies, particularly immunotherapy and photodynamic therapy (81). Therefore, precise characterization and dynamic monitoring of the TME are critical for precision oncology strategies.
Multi parametric MRI techniques, including diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) imaging, and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) mapping, provide non-invasive, quantitative measures of TME related parameters (82). Studies have shown that decreased ADC values may indicate increased cell density due to active tumor proliferation, while higher K^trans values in DCE MRI correlate with vascular permeability and leakage (83).
Radiomics adds an additional analytical dimension by extracting spatial, textural, and heterogeneity features from imaging data that reflect underlying biological processes. When integrated with circulating biomarkers such as VEGF, HIF 1α, and IL 6, radiomics enables stratification of tumors into immunologically “hot” or “cold” categories, guiding immunotherapy selection, including immune checkpoint inhibitors (84) (85).
ML and DL algorithms, including support vector machines (SVM), random forests, and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), have been applied to develop predictive models of treatment response (86). CNN based radiomics models have achieved >85% accuracy in predicting recurrence following TACE (87), while radiogenomics linking MRI texture to TP53 or CTNNB1 mutation status can predict recurrence with precision up to 0.83. These approaches allow dynamic modeling of tumor evolution and real time adjustment of treatment strategies based on TME heterogeneity (88).
Engineered nanomaterials serve as active modulators of the TME. MnO2-based nanoparticles not only function as T1 MRI contrast agents but also react with elevated H2O2 in the TME to generate oxygen, alleviating tumor hypoxia and enhancing photodynamic therapy efficacy (89). Similarly, glucose oxidase (GOx)-loaded nanoparticles induce tumor starvation via glucose oxidation while generating H2O2, which synergizes with Mn²+ ions to trigger chemodynamic therapy (90). These therapeutic effects can be dynamically monitored via MRI or near-infrared fluorescence imaging, creating a theranostic feedback loop between diagnosis and treatment.
Importantly, modulation of TME conditions—such as oxygenation, ROS levels, and acidity—can sensitize tumors to immune activation. For example, these changes can trigger the cGAS–STING pathway, promoting dendritic cell maturation and enhancing cytotoxic T cell infiltration (91). This provides a rational basis for combination therapies involving nanoparticles, immune checkpoint blockade, and targeted therapies. Together, the convergence of radiomics, AI-driven predictive modeling, and TME-responsive nanotechnology paves the way for adaptive, image-guided, and immuno-integrated strategies for HCC treatment, offering a framework for personalized, precision oncology.
4.3 Translational prospects and challenges of nano-imaging therapy integration
The integration of nanotechnology with imaging and therapeutic platforms holds immense translational potential in clinical oncology, particularly in the treatment of HCC. Theranostics, which combines diagnostic imaging with therapy, enables simultaneous, image guided diagnosis and treatment through a single nanotechnology platform, providing a promising avenue for personalized and precision HCC therapy (40).
For example, manganes based nanoparticles not only function as T1 MRI contrast agents but also act as reactive oxygen species (ROS) amplifiers in chemodynamic therapy (CDT). Their ability to respond to the tumor microenvironment (e.g., elevated H2O2 or acidic pH) enables selective drug release, minimizes off target toxicity, and provides a theoretical basis for MRI guided, data driven treatment planning (84).
However, before nanomaterials can be widely applied in clinical settings, several challenges must be addressed:
1. Toxicity control: Accumulation of inorganic nanomaterials in organs such as the liver or spleen can cause long term adverse effects. Optimizing biodegradability, enhancing renal clearance, and employing bioresponsive or biodegradable nanocarriers are crucial for clinical safety.
2. Targeting accuracy: Although ligand modification (e.g., hyaluronic acid or antibodies) improves tumor selectivity, heterogeneity of receptor expression often leads to low delivery efficiency (41). Emerging strategies include adaptive, dual targeting, or stimuli responsive nanoparticles that leverage imaging and radiomics data to enhance site specific delivery.
3. Standardization of imaging and analysis: Significant differences exist among institutions in MRI acquisition protocols, radiomics feature extraction, and image quality (92). This variability limits reproducibility and the reliability of imaging guided therapeutic decisions. Establishing standardized imaging protocols, open source radiomics pipelines, and data sharing frameworks is essential for clinical validation and broader adoption of nanomedicine platforms.
Currently, integrated nano imaging and therapeutic systems suggeste substantial potential for advancing HCC management. By combining radiomics, AI driven predictive modeling, and TME responsive nanomaterials, clinicians can implement adaptive, image guided treatment regimens that account for tumor heterogeneity, predict therapeutic response, and optimize combination strategies.
Translating these approaches from research to clinical practice requires addressing toxicology, targeting efficiency, and standardization challenges. Successful integration of big data analytics, standardized imaging, and nanomedicine will enable safe, precise, and personalized HCC therapy, ultimately expanding treatment options and improving patient outcomes.
5 Conclusion and the future directions
5.1 Conclusion
The comprehensive application of nanomaterials, radiomics, and big data technology in the precise diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has emerged as a prominent research frontier in recent years. By critically evaluating the latest advancements in manganese-based nanoparticles for MRI enhancement and multimodal synergistic therapy—including chemotherapy, chemodynamic therapy (CDT), photothermal therapy (PTT), and photodynamic therapy (PDT)—this review highlights the dual diagnostic and therapeutic roles of nanomedicine. The application of these multifunctional nanoplatforms enables real-time tumor localization, dynamic treatment response monitoring, and image-guided intervention, collectively driving enhanced precision in therapeutic decision-making.
Furthermore, the integration of radiomics provides critical quantitative insights into tumor heterogeneity, microenvironmental changes, and functional dynamics that are otherwise undetectable by conventional imaging. When combined with machine learning algorithms, these radiomic features can be harnessed for predictive modeling of treatment response and individualized therapy planning. The fusion of imaging biomarkers with clinical and molecular data facilitates the development of adaptive, closed-loop treatment workflows, supporting personalized and evidence-based clinical decision-making.
The tumor microenvironment (TME) remains a critical determinant of treatment efficacy, influencing both imaging outcomes and therapeutic responses. Predictive modeling incorporating molecular markers, imaging data, and nanomaterial-induced microenvironmental modulation can enhance treatment adaptability and precision. However, significant challenges remain for clinical translation, including systemic toxicity, off-target effects, limited targeting accuracy, and the lack of standardized protocols for imaging and radiomic analysis. These limitations underscore the need for interdisciplinary research, rigorous preclinical validation, and carefully designed clinical trials.
In summary, this review provides a comprehensive synthesis of the immense potential of nanomaterial-enabled radiomics and big data-driven models in HCC diagnosis and therapy. Looking forward, the convergence of advanced imaging technologies, intelligent data modeling, and multifunctional nanotherapeutics promises to establish a new era of personalized, image-guided, and data-driven medicine for HCC, ultimately improving patient outcomes and enabling precision oncology at scale.
5.2 Future directions
Despite significant advances in the application of nanomaterials for HCC imaging and therapy, several research gaps and challenges remain that warrant further investigation. First, although manganese-based and other functionalized nanoparticles have suggested promising preclinical imaging performance and therapeutic potential, their clinical translation is limited by issues such as systemic toxicity, long-term metabolism, and heterogeneous tumor uptake. Future studies should focus on optimizing nanoparticle design, including size, surface chemistry, and targeting ligands, to maximize tumor specificity and biosafety.
Second, integration of nanomaterials with radiomics and big data-driven predictive modeling remains in its early stages. While preliminary studies suggest that combining quantitative imaging features with machine learning can enhance individualized treatment planning, standardized protocols for data acquisition, feature extraction, and validation across multiple centers are urgently needed to ensure reproducibility and clinical applicability.
Third, the tumor microenvironment and immune response play critical roles in both imaging performance and therapeutic efficacy. Future research should explore multimodal nanomaterials capable of modulating hypoxia, ROS levels, or immune pathways (e.g., cGAS-STING activation) to enhance both diagnostic accuracy and treatment response. Mechanistic studies linking nanoparticle behavior with microenvironmental factors will be crucial for rational design of next-generation theranostic platforms.
Finally, translational studies bridging preclinical models and human patients are essential. Large-scale, well-controlled clinical trials, along with regulatory standardization and long-term safety assessments, will be necessary to realize the full potential of nanotechnology-enabled precision medicine in HCC.
In summary, future directions should emphasize rational nanoparticle design, integration with radiomics and AI, tumor microenvironment modulation, and rigorous translational evaluation, thereby paving the way for more precise, safe, and effective HCC diagnosis and therapy.
Author contributions
HS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DR: Writing – original draft. JZ: Writing – original draft. AT: Writing – original draft. QZ: Writing – original draft. KZ: Writing – original draft. HW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This project is funded by the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine's Key Discipline Construction Project for High-Level Traditional Chinese Medicine (zyyzdxk-2023118) and the Key Laboratory Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine Classics Theory, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ministry of Education.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the support from the High-Level Key Disciplines of Traditional Chinese Medicine Basic Theory of Traditional Chinese Medicine, National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, PR China; and the Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Classical Theory, Ministry of Education, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, PR China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Generative AI was used in the preparation of this manuscript to assist in drafting and refining sections of the text.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Crawford CK, Arshad H, and LC C. Fishman EK: Hepatic angiosarcoma: A challenging diagnosis. Radiol Case Rep. (2025) 20:2342 2345. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2025.01.084
2. Wang Y and Deng B. Hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular mechanism, targeted therapy, and biomarkers. Cancer metastasis Rev. (2023) 42:629 652. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10084-4
3. Tsuzaki J, Ueno A, Masugi Y, Tamura M, Yamazaki S, Matsuda K, et al. Abe Y et al: Chronological changes in etiology, pathological and imaging findings in primary liver cancer from 2001 to 2020. Japanese J Clin Oncol. (2025) 55:362 371. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyae187
4. Koshy A. Evolving global etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): insights and trends for 2024. J Clin Exp Hepatol. (2025) 15:102406. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2024.102406
5. Wu DA, Vassallo J, Worsley C, Bellamy C, Gordon Smith J, and Adair A. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: differences in pre transplant radiology versus explant pathology and impact on survival. HPB: Off J Int Hepato Pancreato Biliary Assoc. (2025) 27:853 860. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2025.02.009
6. Ronot M. Advancing care: managing small late recurrence hepatocellular carcinoma with image guided therapy. Radiology. (2025) 314:e243768. doi: 10.1148/radiol.243768
7. Song W, Xu Y, Zhou J, Yu J, He X, Jiang C, et al. Predicting postresection outcomes in solitary small hepatocellular carcinoma via pretreatment MR imaging features: subgroup analysis according to alpha fetoprotein expression. Eur Radiol. (2025) 35(10):6527–40. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11558-5
8. Zhou S, Song C, Liu P, Ju S, and Wang YC. A nationwide investigation on imaging follow up after Locoregional therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in China: Current practices and challenges. Eur J Radiol. (2025) 186:112057. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2025.112057
9. Ghenciu LA, Grigoras ML, Rosu LM, Bolintineanu SL, Sima L, and Cretu O. Differentiating liver metastases from primary liver cancer: A retrospective study of imaging and pathological features in patients with histopathological confirmation. Biomedicines. (2025) 13(1):164. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010164
10. Li ZW, Ren AH, Yang DW, Xu H, Wei J, Yuan CW, et al. Preoperatively predicting early response of HCC to TACE using clinical indicators and MRI features. BMC Med Imaging. (2022) 22:176. doi: 10.1186/s12880-022-00900-8
11. Ebel S, Busse H, Beeskow A, Meyer HJ, Seehofer D, Berg T, et al. Denecke T et al: Hepatobiliary phase MRI guided radiofrequency ablation of small hepatocellular carcinomas invisible on precontrast MRI. Eur J Radiol. (2025) 186:112026. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2025.112026
12. Schindler P, von Beauvais P, Hoffmann E, Morgül H, Börner N, Masthoff M, et al. Trebicka J et al: Combining radiomics and imaging biomarkers with clinical variables for the prediction of HCC recurrence after liver transplantation. Liver transplantation: Off Publ Am Assoc Study Liver Dis Int Liver Transplant Soc. (2025) 18. doi: 10.1097/LVT.0000000000000603
13. Lin Z, Wang W, Yan Y, Ma Z, Xiao Z, and Mao K. A deep learning based clinical radiomics model predicting the treatment response of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) based conversion therapy in potentially convertible hepatocelluar carcinoma patients: a tumor marker prognostic study. Int J Surg (London England). (2025) 111:3342 3355. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002322
14. Mansouri Z, Salimi Y, Hajianfar G, Knappe L, Wolf NB, Xhepa G, et al. : Potential of Radiomics, Dosiomics, and Dose Volume Histograms for Tumor Response Prediction in Hepatocellular Carcinoma following (90)Y SIRT. Mol Imaging Biol. (2025) 27:201 214. doi: 10.1007/s11307-025-01992-8
15. Mian A, Kamnitsas K, and Gordon Weeks A. Radiomics for treatment planning in liver cancers. JAMA Surg. (2025) 26. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2024.4346
16. Colak C, Yagin FH, Algarni A, Algarni A, Al Hashem F, and Ardigò LP. Untargeted lipidomic biomarkers for liver cancer diagnosis: A tree based machine learning model enhanced by explainable artificial intelligence. Med (Kaunas Lithuania). (2025) 61(3):405. doi: 10.3390/medicina61030405
17. Zhao X, Wen J, Zhu A, Cheng M, Zhu Q, Zhang X, et al. Manipulation and applications of hotspots in nanostructured surfaces and thin films. Nanomaterials (Basel Switzerland). (2020) 10(9):166. doi: 10.3390/nano10091667
18. Zhang H, Ji X, Li P, Liu C, Lou J, Wang Z, et al. Liquid liquid phase separation in biology: mechanisms, physiological functions and human diseases. Sci China Life Sci. (2020) 63:953 985. doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1702-x
19. Tong X, Tang R, Xu J, Wang W, Zhao Y, Yu X, et al. Liquid liquid phase separation in tumor biology. Signal transduction targeted Ther. (2022) 7:221. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01076-x
20. Zhan L, Yin X, Zhang Y, Ju J, Wu Y, Ding L, et al. Polydopamine guarded metal organic frameworks as co delivery systems for starvation assisted chemo photothermal therapy. Biomaterials Adv. (2023) 146:213306. doi: 10.1016/j.bioadv.2023.213306
21. Frandsen M, El Chami K, Palmfeldt J, Melgaard Smidt J, Langballe MET, Sandahl A, et al. Automated solid phase oligo(disulfide) synthesis. Angewandte Chemie (International ed English). (2023) 62:e202303170. doi: 10.1002/anie.202303170
22. Saul P, Schröder L, Schmidt AB, and Hövener JB. Nanomaterials for hyperpolarized nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomedicine nanobiotechnology. (2023) 15:e1879. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1879
23. Wang G, Li X, Wang J, Yan H, Zhang D, Tian C, et al. Vanadium Modulated Molybdenum/Nickel Based Multi Heterostructures finely tailoring d Band centers for electrocatalytic water splitting. J colloid Interface Sci. (2025) 693:137543. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2025.137543
24. Yang L, Zhu X, Xu T, Han F, Liu G, Bu Y, et al. Defect engineered transition metal hydroxide nanosheets realizing tumor microenvironment responsive multimodal imaging guided NIR II photothermal therapy. J materials Chem B. (2020) 8:8323 8336. doi: 10.1039/D0TB01608J
25. Liu G, Liu M, Li X, Ye X, Cao K, Liu Y, et al. Peroxide simulating and GSH depleting nanozyme for enhanced chemodynamic/photodynamic therapy via induction of multisource ROS. ACS Appl materials interfaces. (2023) 15:47955 47968. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c09873
26. Tarek YA, Shakil R, Reaz AH, Roy CK, Barai HR, and Firoz SH. Wrinkled Flower Like rGO intercalated with Ni(OH)(2) and MnO(2) as High Performing Supercapacitor Electrode. ACS omega. (2022) 7:20145 20154. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01986
27. Wang L, Fu R, Qi X, Xu J, Li C, Chen C, et al. Deashing strategy on biomass carbon for achieving high performance full supercapacitor electrodes. ACS Appl materials interfaces. (2024) 16:52663 52673. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c11778
28. Salathia S, Gigliobianco MR, Casadidio C, Di Martino P, and Censi R. Hyaluronic acid based nanosystems for CD44 mediated anti inflammatory and antinociceptive activity. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(8):7286. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087286
29. Ibrahim M, Ramadan E, Elsadek NE, Emam SE, Shimizu T, Ando H, et al. Hussein AK et al: Polyethylene glycol (PEG): The nature, immunogenicity, and role in the hypersensitivity of PEGylated products. J Controlled release: Off J Controlled Release Soc. (2022) 351:215 230. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.09.031
30. Tenchov R, Sasso JM, and Zhou QA. PEGylated lipid nanoparticle formulations: immunological safety and efficiency perspective. Bioconjugate Chem. (2023) 34:941 960. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.3c00174
31. Xia T, Zhao B, Li B, Lei Y, Song Y, Wang Y, et al. MRI based radiomics and deep learning in biological characteristics and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: opportunities and challenges. J magnetic resonance imaging: JMRI. (2024) 59:767 783. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28982
32. Yang WL, Zhu F, and Chen WX. Texture analysis of contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging predicts microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Radiol. (2022) 156:110528. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2022.110528
33. Wang K-D, Guan M-J, Bao Z-Y, Shi Z-J, Tong H-H, Xiao Z-Q, et al. Radiomics analysis based on dynamic contrast enhanced MRI for predicting early recurrence after hepatectomy in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:22240. doi: 10.1038/s41598025022916
34. Li K, Zhang R, Wen F, Zhao Y, Meng F, Li Q, et al. Cui Y et al: Single cell dissection of the multicellular ecosystem and molecular features underlying microvascular invasion in HCC. Hepatol (Baltimore Md). (2024) 79:1293 1309. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000673
35. Chen X, Tang Y, Wu D, Li R, Lin Z, Zhou X, et al. From imaging to clinical outcome: dual region CT radiomics predicting FOXM1 expression and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1278467. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1278467
36. Yan X, Li Y, Qin W, Liao J, Fan J, Xie Y, et al. Radiomics model based on contrast enhanced computed tomography imaging for early recurrence monitoring after radical resection of AFP negative hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. (2024) 24:700. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12436-x
37. Jin J, Jiang Y, Zhao Y-L, and Huang P-T. Radiomics based machine learning to predict the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta analysis. Acad Radiol. (2023) 30:1157 1166. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2023.02.004
38. Dong M, Li C, Zhang L, Zhou J, Xiao Y, Zhang T, et al. Han Y et al: Intertumoral Heterogeneity Based on MRI Radiomic Features Estimates Recurrence in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J magnetic resonance imaging: JMRI. (2025) 61:168 181. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29428
39. Zhang W, Guo Q, Zhu Y, Wang M, Zhang T, Cheng G, et al. Cross institutional evaluation of deep learning and radiomics models in predicting microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: validity, robustness, and ultrasound modality efficacy comparison. Cancer imaging: Off Publ Int Cancer Imaging Soc. (2024) 24:142. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00790-9
40. Escutia Gutiérrez R, Sandoval Rodríguez A, Zamudio Ojeda A, Guevara Martínez SJ, and Armendáriz Borunda J. Advances of nanotechnology in the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:6867. doi: 10.3390/jcm12216867
41. Wang Y, Ma S, Liu X, Wei Y, Xu H, Liang Z, et al. Hyaluronic acid mediated Fe(3)O(4) nanocubes reversing the EMT through targeted cancer stem cell. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. (2023) 222:113071. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.113071
42. Long S, Li M, Chen J, Zhong L, Abudulimu A, Zhou L, et al. Fu K et al: Spatial patterns and MRI based radiomic prediction of high peritumoral tertiary lymphoid structure density in hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter study. J immunotherapy Cancer. (2024) 12(12):e009879. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009879
43. Carbonell G, Kennedy P, Bane O, Kirmani A, El Homsi M, Stocker D, et al. Lewis S et al: Precision of MRI radiomics features in the liver and hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Radiol. (2022) 32:2030 2040. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08282-1
44. Zhou Z, Cao S, Chen C, Chen J, Xu X, Liu Y, et al. A novel nomogram for the preoperative prediction of edmondson steiner grade III IV in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J hepatocellular carcinoma. (2023) 10:1399 1409. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S417878
45. Maung ST, Tanpowpong N, Satja M, Treeprasertsuk S, and Chaiteerakij R. MRI for hepatocellular carcinoma and the role of abbreviated MRI for surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 39:1969 1981. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16643
46. Zhao Y, Wang S, Wang Y, Li J, Liu J, Liu Y, et al. Song Q et al: Deep learning radiomics based on contrast enhanced MRI for preoperatively predicting early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1446386. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1446386
47. Niu B, Liao K, Zhou Y, Wen T, Quan G, Pan X, et al. Application of glutathione depletion in cancer therapy: Enhanced ROS based therapy, ferroptosis, and chemotherapy. Biomaterials. (2021) 277:121110. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121110
48. Cheng J, Chen S, Geng M, Wei X, Meng S, Gong L, et al. Li X et al: Carrier Free Self Assembled Nanoparticles for Triple Amplified Tumor Chemodynamic Therapy and Cuproptosis Induction. Advanced healthcare materials. (2025) 2025:e2501507. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202501507
49. He Y, Guo S, Zhang Y, Liu Y, and Ju H. NIR II reinforced intracellular cyclic reaction to enhance chemodynamic therapy with abundant H(2)O(2) supply. Biomaterials. (2021) 275:120962. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120962
50. Zhu C, Ma Q, Gong L, Di S, Gong J, Wang Y, et al. Fu JJ et al: Manganese based multifunctional nanoplatform for dual modal imaging and synergistic therapy of breast cancer. Acta biomaterialia. (2022) 141:429 439. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.01.019
51. Jia C, Guo Y, and Wu FG. Chemodynamic therapy via fenton and fenton like nanomaterials: strategies and recent advances. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse Germany). (2022) 18:e2103868. doi: 10.1002/smll.202103868
52. Chen LL, Zhao L, Wang ZG, Liu SL, and Pang DW. Near infrared II quantum dots for in vivo imaging and cancer therapy. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse Germany). (2022) 18:e2104567. doi: 10.1002/smll.202104567
53. Kang H, Kang MW, Kashiwagi S, and Choi HS. NIR fluorescence imaging and treatment for cancer immunotherapy. J immunotherapy Cancer. (2022) 10(7):e004936. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004936
54. Oduro PK, Zheng X, Wei J, Yang Y, Wang Y, Zhang H, et al. The cGAS STING signaling in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: Future novel target option for pharmacotherapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2022) 12:50 75. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.05.011
55. Hong SB, Lee NK, Kim S, Seo HI, Kim HS, Kim DU, et al. Modified CAIPIRINHA VIBE without view sharing on gadoxetic acid enhanced multi arterial phase MR imaging for diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with the CAIPIRINHA Dixon TWIST VIBE. Eur Radiol. (2019) 29:3574 3583. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06095-x
56. Qi S, Liu G, Chen J, Cao P, Lei X, Ding C, et al. Targeted multifunctional nanoplatform for imaging guided precision diagnosis and photothermal/photodynamic therapy of orthotopic hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J nanomedicine. (2022) 17:3777 3792. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S377080
57. Paolino D, Accolla ML, Cilurzo F, Cristiano MC, Cosco D, Castelli F, et al. Interaction between PEG lipid and DSPE/DSPC phospholipids: An insight of PEGylation degree and kinetics of de PEGylation. Colloids surfaces B Biointerfaces. (2017) 155:266 275. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.04.018
58. Shinde VR, Revi N, Murugappan S, Singh SP, and Rengan AK. Enhanced permeability and retention effect: A key facilitator for solid tumor targeting by nanoparticles. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2022) 39:102915. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2022.102915
59. Xu Y, Liu SY, Zeng L, Ma H, Zhang Y, Yang H, et al. Xu Y et al: An Enzyme Engineered Nonporous Copper(I) Coordination Polymer Nanoplatform for Cuproptosis Based Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Advanced materials (Deerfield Beach Fla). (2022) 34:e2204733. doi: 10.1002/adma.202300773
60. Fan W, Lu N, Huang P, Liu Y, Yang Z, Wang S, et al. He Q et al: Glucose Responsive Sequential Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide and Nitric Oxide for Synergistic Cancer Starving Like/Gas Therapy. Angewandte Chemie (International ed English). (2017) 56:1229 1233. doi: 10.1002/anie.201610682
61. Wang W, Zhang G, Wang Y, Ran J, Chen L, Wei Z, et al. An inject able and thermosensitive hydrogel with nano aided NIR II phototherapeutic and chemical effects for periodontal antibacteria and bone regeneration. J nanobiotechnology. (2023) 21:367. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02124-6
62. Wang Q, Yuan J, Zhang Q, Hu D, Li S, Zhu X, et al. Near infrared II photoactivated iron(III) complexes for highly efficient RNS and ROS synergistic therapy. ACS Appl Bio materials. (2024) 7:6800 6807. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.4c00947
63. Xue S, Zhou X, Sang W, Wang C, Lu H, Xu Y, et al. Cartilage targeting peptide modified dual drug delivery nanoplatform with NIR laser response for osteoarthritis therapy. Bioactive materials. (2021) 6:2372 2389. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.01.017
64. Kumasaka S, Panek R, Neves R, Suri M, Jagani S, Kumasaka Y, et al. Quantification of liver fat fraction using T1 weighted mDixon MRI in young patients with ataxia telangiectasia undergoing whole body MRI: an exploratory study. Orphanet J rare Dis. (2025) 20:316. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03786-1
65. Zeng H, Shi G, Mai S, Liu H, and Wu Z. Imaging and clinical features of colorectal liver metastases with macroscopic intrabiliary growth. Eur J Radiol. (2021) 137:109616. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.109616
66. Xiong G, Huang D, Lu L, Luo X, Wang Y, Liu S, et al. You C et al: Near Infrared II Light Induced Mild Hyperthermia Activate Cisplatin Artemisinin Nanoparticle for Enhanced Chemo/Chemodynamic Therapy and Immunotherapy. Small Methods. (2022) 6:e2200379. doi: 10.1002/smtd.202200379
67. Zhao M, Song X, Lu J, Liu S, Sha X, Wang Q, et al. DNA aptamer based dual responsive nanoplatform for targeted MRI and combination therapy for cancer. RSC Adv. (2022) 12:3871 3882. doi: 10.1039/D1RA08373B
68. Cai X, Zhu Q, Zeng Y, Zeng Q, Chen X, and Zhan Y. Manganese oxide nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents in tumor multimodal imaging and therapy. Int J nanomedicine. (2019) 14:8321 8344. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S218085
69. Zheng Z, Jia Z, Qu C, Dai R, Qin Y, Rong S, et al. Biodegradable silica based nanotheranostics for precise MRI/NIR II fluorescence imaging and self reinforcing antitumor therapy. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse Germany). (2021) 17:e2006508. doi: 10.1002/smll.202006508
70. Lv Y, Kan J, Luo M, Yang C, Luo X, Lin X, et al. Yang C et al: Multifunctional Nanosnowflakes for T1 T2 Double Contrast Enhanced MRI and PAI Guided Oxygen Self Supplementing Effective Anti Tumor Therapy. Int J nanomedicine. (2022) 17:4619 4638. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S379526
71. Liang X, Wang D, Zhao Y, Wang X, Yao S, Huang W, et al. Tumor microenvironment responsive manganese based nano modulator activate the cGAS STING pathway to enhance innate immune system response. J Nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22:535. doi: 10.1186/s12951024028096
72. Zhang X, Tang D, Xiao H, Li B, Shang K, Zhao D, et al. Activating the cGAS STING pathway by manganese based nanoparticles for ovarian cancer immunotherapy. ACS Nano. (2024) 18:12345–57. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c12237
73. Tian Q, Bilgic B, Fan Q, Liao C, Ngamsombat C, Hu Y, et al. DeepDTI: High fidelity six direction diffusion tensor imaging using deep learning. NeuroImage. (2020) 219:117017. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117017
74. Kawahara D, Yoshimura H, Matsuura T, Saito A, and Nagata Y. MRI image synthesis for fluid attenuated inversion recovery and diffusion weighted images with deep learning. Phys Eng Sci Med. (2023) 46:313 323. doi: 10.1007/s13246-023-01220-z
75. Said D, Carbonell G, Stocker D, Hectors S, Vietti Violi N, Bane O, et al. Lewis S et al: Semiautomated segmentation of hepatocellular carcinoma tumors with MRI using convolutional neural networks. Eur Radiol. (2023) 33:6020 6032. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09613-0
76. Wang G, Jian W, Cen X, Zhang L, Guo H, Liu Z, et al. Prediction of microvascular invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma based on preoperative diffusion weighted MR using deep learning. Acad Radiol. (2021) 28 Suppl 1:S118 s127. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2020.11.014
77. Chen B, Garmire L, Calvisi DF, Chua MS, Kelley RK, and Chen X. Harnessing big ‘omics’ data and AI for drug discovery in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 17:238 251. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0240-9
78. Duan T, Zhang Z, Chen Y, Bashir MR, Lerner E, Qu Y, et al. Deep learning based compressed SENSE improved diffusion weighted image quality and liver cancer detection: A prospective study. Magnetic resonance Imaging. (2024) 111:74 83. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2024.04.010
79. Zeng Q, Liu B, Xu Y, and Zhou W. An attention based deep learning model for predicting microvascular invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma using an intra voxel incoherent motion model of diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Phys Med Biol. (2021) 66(18). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ac22db
80. Borges KA, Dai J, Parikh ND, Schwartz M, Nguyen MH, Roberts LR, et al. Feng Z et al: Rationale and design of the Hepatocellular carcinoma Early Detection Strategy study: A multi center longitudinal initiative of the National Cancer Institute’s Early Detection Research Network. Contemp Clin trials. (2019) 76:49 54. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2018.11.008
81. Kim DW, Choi SH, Kim SY, Byun JH, Lee SS, Park SH, et al. Diagnostic performance of MRI for HCC according to contrast agent type: a systematic review and meta analysis. Hepatol Int. (2020) 14:10091022. doi: 10.1007/s12072-020-10100-7
82. Qiu C, Xie S, Sun Y, Yu Y, Zhang K, Wang X, et al. Multi parametric magnetic resonance imaging of liver regeneration in a standardized partial hepatectomy rat model. BMC Gastroenterol. (2022) 22:430. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02517-1
83. Zheng J, Du PZ, Yang C, Tao YY, Li L, Li ZM, et al. DCE MRI based radiomics in predicting angiopoietin 2 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Abdominal Radiol (New York). (2023) 48:3343 3352. doi: 10.1007/s00261-023-04007-8
84. Liu Y, Bhattarai P, Dai Z, and Chen X. Photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging via nanotheranostics in fighting cancer. Chem Soc Rev. (2019) 48:2053 2108. doi: 10.1039/c8cs00794a
85. Kim D-H, Yoon J-H, Choi M-H, Lee C-H, Kang T-W, Kim H-A, et al. Comparison of non contrast abbreviated MRI and ultrasound as surveillance modalities for HCC. J Hepatol. (2024) 81:461 470. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.04.022
86. Zhao S, Liu M, and Zhou H. Identification of novel M2 macrophage related molecule ATP6V1E1 and its biological role in hepatocellular carcinoma based on machine learning algorithms. J Cell Mol Med. (2024) 28:e70072. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70072
87. Cho EEL, Law M, Yu Z, Yong JN, Tan CS, Tan EY, et al. Soon GST et al: Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Predicting Transarterial Chemoembolization Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Digestive Dis Sci. (2025) 70:533 542. doi: 10.1007/s10620-024-08747-5
88. Wu Q, Zhang T, Xu F, Cao L, Gu W, Zhu W, et al. MRI based deep learning radiomics to differentiate dual phenotype hepatocellular carcinoma from HCC and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multicenter study. Insights into Imaging. (2025) 16:27. doi: 10.1186/s13244-025-01904-y
89. Wang Y, Shang W, Zhong H, Luo T, Niu M, Xu K, et al. Tumor vessel targeted self assemble nanoparticles for amplification and prediction of the embolization effect in hepatocellular carcinoma. ACS nano. (2020) 14:14907 14918. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c04341
90. Chen Y, Bei J, Chen M, Cai W, Zhou Z, Cai M, et al. Liu M et al: Intratumoral Lactate Depletion Based on Injecta ble Nanoparticles Hydrogel Composite System Synergizes with Immunotherapy against Postablative Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence. Advanced healthcare materials. (2024) 13:e2303031. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202303031
91. Chang CC, Dinh TK, Lee YA, Wang FN, Sung YC, Yu PL, et al. Huang YD et al: Nanoparticle Delivery of MnO(2) and Antiangiogenic Therapy to Overcome Hypoxia Driven Tumor Escape and Suppress Hepatocellular Carcinoma. ACS Appl materials interfaces. (2020) 12:44407 44419. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c08473
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, nanomaterials, MRI enhancement, multimodal therapy, AI driven radiomics
Citation: Shen H, Ran D, Zhu J, Tao A, Zheng K, Zhu Q and Wang H (2025) Harnessing big data for precision medicine: radiomics based application of nanomaterials in MRI enhancement and multimodal therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 16:1659180. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1659180
Received: 04 July 2025; Accepted: 11 September 2025;
Published: 20 October 2025.
Edited by:
Sipho Mdanda, Nuclear Medicine Research Infrastructure, South AfricaReviewed by:
Runsang Pan, Guizhou Provincial People’s Hospital, ChinaMahsa Sedighi, Birjand University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Shen, Ran, Zhu, Tao, Zheng, Zhu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Haijun Wang, d2hqbmVpamluZ0AxNjMuY29t; Qing Zhu, MTU5NjQ1Mzk3ODlAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Hongbin Shen
Hongbin Shen Deshui Ran
Deshui Ran Jida Zhu2
Jida Zhu2 Haijun Wang
Haijun Wang