- 1Department of Psychiatry, Chengdu Eighth People's Hospital (Geriatric Hospital of Chengdu Medical College), Chengdu, China
- 2Rehabilitation Medicine Center and Institute of Rehabilitation Medicine, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Rehabilitation Medicine in Sichuan Province, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- 5Rehabilitation Medicine and Engineering Key Laboratory of Luzhou, Luzhou, China
- 6Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu Medical College, Chengdu, China
- 7Centro Studi e Ricerche in Neuroscienze Cognitive, Dipartimento di Psicologia, Alma Mater Studiorum – Università di Bologna, Cesena, Italy
Background: Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder involving degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, abnormal aggregation of α-synuclein, and neuroinflammatory response. Although research on PD immunotherapy is advancing rapidly, bibliometric analysis in this field remains underdeveloped.
Methods: Literature related to “Parkinson’s disease” and “immunotherapy” from the Web of Science Core Collection and Scopus was used for data merging and bibliometric analysis via Bibliometrix. The characteristics of the relevant clinical trials in this field retrieved from the PubMed database were summarized, and the study protocols were traced back through the trials registry website.
Results: After merging the two databases, a total of 890 documents from 488 sources were covered. A total of 3,804 researchers from 1,483 institutions in 63 countries published research in this field. Authors, institutions, and countries/regions were classified into 5, 12, and 13 clusters, respectively. Keywords such as “Parkinson’s disease”, “immunotherapy”, and “alpha-synuclein” were frequently used. The maps of keyword co-occurrence and clusters revealed the generation of two clusters. A total of 8 clinical trials were searched and included. These trials focused on active immunotherapy and targeted antibodies, involving both healthy volunteers and patients with PD.
Conclusions: The field of PD immunotherapy has vigorous development potential. The current research focus in this field is concentrated on analyzing pathological mechanisms and innovating treatment strategies. Precise immunological intervention techniques are frontiers in this field. In the future, large-scale randomized controlled trials should be conducted to enhance the clinical translation efficiency of immunotherapy.
Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by movement disorders and non-motor symptoms. The main pathological changes include degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, abnormal aggregation of α-synuclein, and neuroinflammatory response (1). Globally, the number of patients with PD continues to increase as the aging population progresses. However, the underlying mechanism of PD has not been fully elucidated, and current treatment methods primarily focus on alleviating symptoms, rather than preventing disease progression (2, 3). In recent years, immunotherapy has become a research hotspot in the field of PD treatment due to its potential to regulate the immune microenvironment and target the clearance of pathological markers (4). Immunotherapy, by regulating both innate and adaptive immune responses, may slow down the aggregation of α-synuclein, inhibit neuroinflammation, and thereby delay the progression of the disease, providing a novel therapeutic strategy for PD.
Currently, the application forms of PD immunotherapy are diverse, primarily including passive immunity, such as monoclonal antibodies targeting α-synuclein, active immunization vaccines, and innate immune regulators (5, 6). For instance, monoclonal antibodies against α-synuclein have entered the clinical trial stage, aiming to reduce neuronal damage by neutralizing toxic protein aggregates (7, 8). However, immunotherapy still faces numerous challenges, including the efficiency of penetrating the blood-brain barrier, the off-target effects caused by the insufficient specificity of the targets, and the balance issue between the complexity of the immune system and the heterogeneity of the disease (9). These bottlenecks have restricted its clinical application and prompted the need for a systematic review of the research progress and shortcomings.
Notably, although clinical and basic research on PD immunotherapy is advancing rapidly, bibliometric analysis in this field remains lacking. Through the quantitative analysis of literature data, bibliometric analysis can reveal the research trends, hotspots, and knowledge structure of a field, providing a comprehensive perspective for the development of the discipline (10). The development of bibliometric visualization tools has also provided significant assistance to the hot topics in the field of visualization (11). However, many bibliometric studies mostly rely on a single database, neglecting the advantages of a combined database search, which may result in incomplete data coverage (12). Furthermore, most studies focus on quantitative indicators, such as the number of publications and author cooperation networks, while paying insufficient attention to the integrated analysis of key clinical elements, including clinical trial design, efficacy evaluation, and safety (13).The tendency to emphasize data statistics while neglecting clinical relevance weakens the support role of bibliometrics in actual clinical decision-making, highlighting the need for cross-database integration and clinically oriented analysis.
To summarize, this study aims to conduct a systematic assessment of the current research status and the evolution trajectory of the PD immunotherapy field by integrating resources from multiple databases and utilizing visualization tools. By constructing multidimensional indicators, such as cooperation networks, research hotspots, and clinical trial progress, and combining quantitative analysis with clinical evidence summaries, we further reveal the scientific issues and technical bottlenecks that remain unresolved in the field of PD immunotherapy.
Methods
Data search
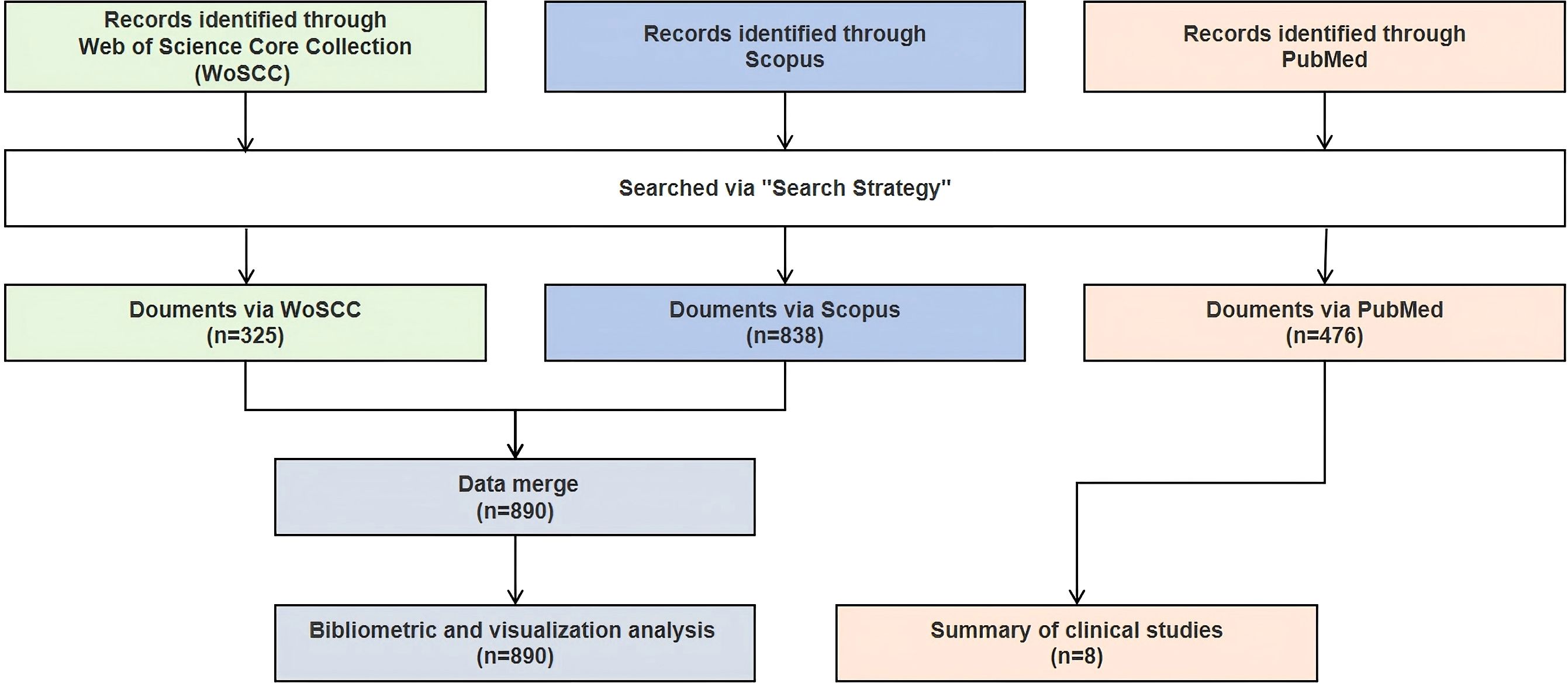
To explore the research landscape on PD and immunotherapy, we conducted a systematic literature search in three databases, including the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC), Scopus, and PubMed. The search aimed to identify relevant scientific publications for bibliometric analysis and clinical trials related to PD immunotherapy. We searched original articles and review papers from WoSCC and Scopus for bibliometric analysis, focusing on clinical trials from PubMed, including both interventional and observational studies.
The search strategies were specifically designed for each database and are presented in full detail in Supplementary Tables S1-S3, which include the verbatim search strings used. A combination of free words and subject terms was used to enhance the sensitivity and specificity of the search. All subject terms were derived from the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) database. No language restrictions were applied during the initial search to minimize potential bias from excluding non-English publications. To ensure data integrity and avoid double-counting, duplicate entries were identified and removed through a combination of automated deduplication and manual inspection. The last search date for all the databases was July 2nd, 2025. The search, de-duplication, and initial data organization were independently conducted by two researchers, with any discrepancies resolved through discussion and collaboration.
Data analysis
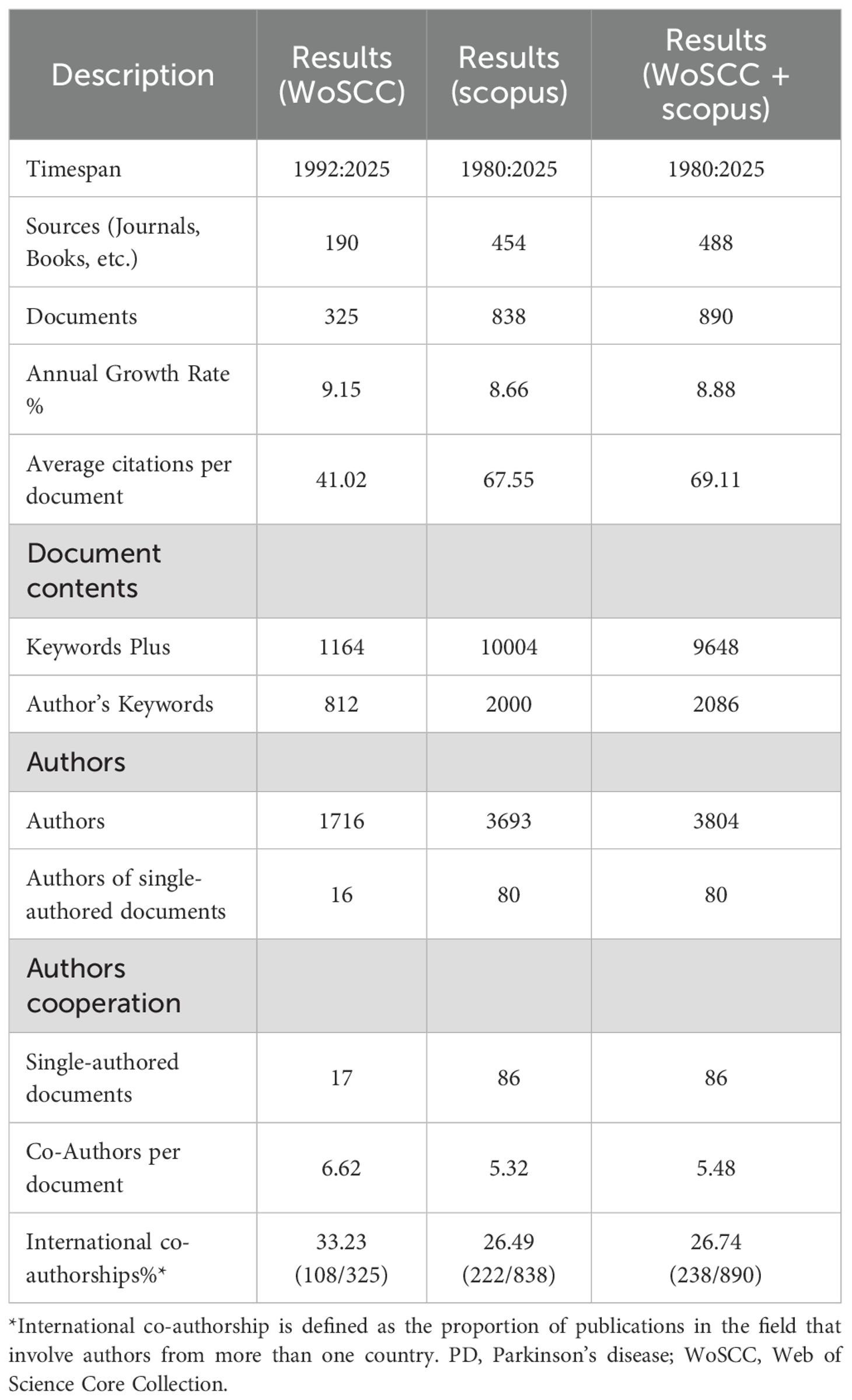
Bibliometrix, as a comprehensive analysis toolkit based on the R language, has become an essential support in the field of research due to its multi-dimensional analysis capabilities and visualization features (14). This tool supports cross-database data integration and can uniformly handle the metadata of multiple literature sources. In our study, we used Bibliometrix (Version 5.0) to merge data from the WoSCC and Scopus databases, and manually checked and recorded the key bibliometric indicators for each database.
The Overview module was used to compare the data differences between the databases. The Sources, Authors, and Cooperation Analysis modules were used to conduct a visual analysis of the merged data, and the Keywords module was used to analyze the research frontiers and characteristics of this field (15). Of note, international cooperation articles were determined based on whether a publication had authors from multiple countries/regions. The rate of international cooperation was calculated by dividing the number of these articles by the total number of papers in the field. The division of countries/regions is determined by using the institutional information in the database (WoSCC and Scopus) and is completed through processing with Bibliometrix.
In addition, based on the PubMed search results, we further summarized the characteristics of relevant clinical trials, including study design, interventions, and effects, to provide complementary insights into the translational and clinical aspects of PD immunotherapy research. Notably, only studies that explicitly employ immunotherapy in their intervention measures could be included. Furthermore, based on the clinical trial registration number (if applicable), we traced the original study protocol back through the trial registration website, such as ClinicalTrials.gov and the EU Clinical Trials Register (EU CTR), to strive for standardization and consistency in the research plan and results.
Author, institution, and keyword standardization
To ensure the comparability of the research data and the reliability of the analytical results, this study conducted systematic standardization of author information, institutions, and keywords in the original bibliographic dataset. In the raw data, author names exhibited various spelling variations, inconsistencies in capitalization, and formatting differences, such as “Wei Zhang,” “Zhang, W.”, and “W. Zhang”. After data integration, Bibliometrix was used to standardize author names into a unified format of ”surname + initial”, such as “Zhang W,” to facilitate statistical analysis and network construction. However, as unique author identifiers such as ORCID were not used, some author nodes may still have experienced minor duplication or incorrect merging. Therefore, the related results and conclusions are primarily based on macro-level cooperation patterns, rather than precise individual-level relationships.
For institutions, multiple variations in naming conventions, abbreviations, and aliases existed for the same organization. To improve the consistency of the institutional cooperation network, we applied the ”Affiliation Name Disambiguation” function in Bibliometrix to identify and merge variants under the same institutional entity. It should be noted that certain institutions, although administratively or organizationally part of the same university system, such as Harvard University and Harvard Medical School, may still appear as distinct entities in bibliometric data and network analysis—even when sharing the same institutional identifier such as ROR. Consistent with approaches used in other studies, these institutions were treated as independent nodes in our analysis to more accurately reflect their actual roles in scientific cooperation and knowledge production.
Due to the inconsistencies in capitalization, singular/plural forms, and formatting of the keywords, we manually standardized the synonymous/near-synonymous variants in the original data. This included merging “Parkinson’s disease” and “Parkinson disease” into “parkinson’s disease,” and combining “alpha-synuclein” and “alpha synuclein” into “alpha-synuclein.” Moreover, we deleted the general terms that were not directly related to the analysis of research hotspots, such as “review,” “article,”“ priority journal,” “unclassified drug,” “unindexed drug,” “animal,” “nonhuman,” and “human” to avoid diluting the relevance of the core topic.
Sensitivity analysis of citation indicators
Citations are commonly used as an indicator of the impact of scientific research. However, their values can be influenced by factors such as paper type, publication year, research field, and the presence of extremely highly cited papers, which may introduce bias in the calculation of average citation performance at the country or regional level. To ensure the reliability of the core findings related to the citation performance of countries/regions in this study, we conducted the following sensitivity analyses (1): Exclusion of review articles: We first excluded publications classified as “Review” (based on document type), and recalculated the average article citations for each country/region, to examine whether the core conclusions remained valid (2). Exclusion of extremely highly cited papers: A small number of papers may receive citation counts far above the average. To minimize the impact of such outliers on the statistical results, we excluded the top 5% of papers with the highest citation counts from the data and recalculated the average article citations (3). Citation analysis by publication year cohorts: Given the well-established time accumulation effect in citation performance, we divided the publication years into distinct time cohorts (1980–2005, 2006–2015, and 2016–2025), based on both year and publication volume. For each time cohort, we calculated the average number of article citations by country during the respective period.
Parameters setting
The parameter settings of Bibliometrix for different visualization networks are as follows (1): Cooperation analysis: Network Layout: Automatic layout; Clustering Algorithm: Walktrap; Normalization: association; Number of Nodes: 50; Repulsion Force: 0.1; Remove Isolated Nodes: Yes; Minimum Number of Edges: 1 (2). WordCloud: Word occurrence by: Frequency; Shape: Circle; Font type: Impact; Text colors: Random Dark; Font size: 1.3; Ellipticity: 0.65; Padding: 1; Rotate: 0 (3). Keyword co-occurrence analysis: Network Layout: Automatic layout; Clustering Algorithm: Walktrap; Normalization: association; Number of Nodes: 50; Repulsion Force: 0.1; Remove Isolated Nodes: Yes; Minimum Number of Edges: 2 (4). Thematic Evolution: Number of Words: 250; Min Cluster Frequency (per thousand docs): 5; Weight index: Inclusion Index weighted by Word-Occurrences; Min Weight Index: 0.1; Label size: 0.2; Number of Labels (for each cluster): 3; Clustering Algorithm: Walktrap. Time Slices: Number of Cutting Points: 4; Cutting Year 1: 2005; Cutting Year 2: 2010; Cutting Year 3: 2015; Cutting Year 4: 2020 (5). Trend topics: Word Minimum Frequency: 5; Number of Words per Year: 3.
Results
Overview
In the field of PD immunotherapy, WoSCC covered 325 documents from 190 sources, while Scopus covered 838 documents from 454 sources. After merging the two databases (WoSCC + Scopus), a total of 890 documents from 488 sources were covered (Figure 1). The annual growth rate of the combined database was 8.88%, and the average citation intensity reached 69.11 times per paper, which was higher than that of individual databases. Moreover, the combined database contained 9,648 keywords, and the international co-authorship ratio and the average number of authors per document were also within the range of WoSCC and Scopus (Table 1). Through the integration of complementary data resources, the breadth of literature coverage and the depth of knowledge association have been significantly enhanced.
From the perspective of the publication and citation trends, the publication volume of the combined database showed explosive growth in key years such as 2019 and 2022, covering the entire period from 1980 to 2025, with the average annual publication volume significantly higher than that of the single database (Figure 2A); in terms of citation intensity, the combined database reached its peak average citation frequency in 2007 (25.69 times per documents) and 2022 (73.03 times per documents), with the fluctuation range far exceeding that of the single database (Figure 2B).
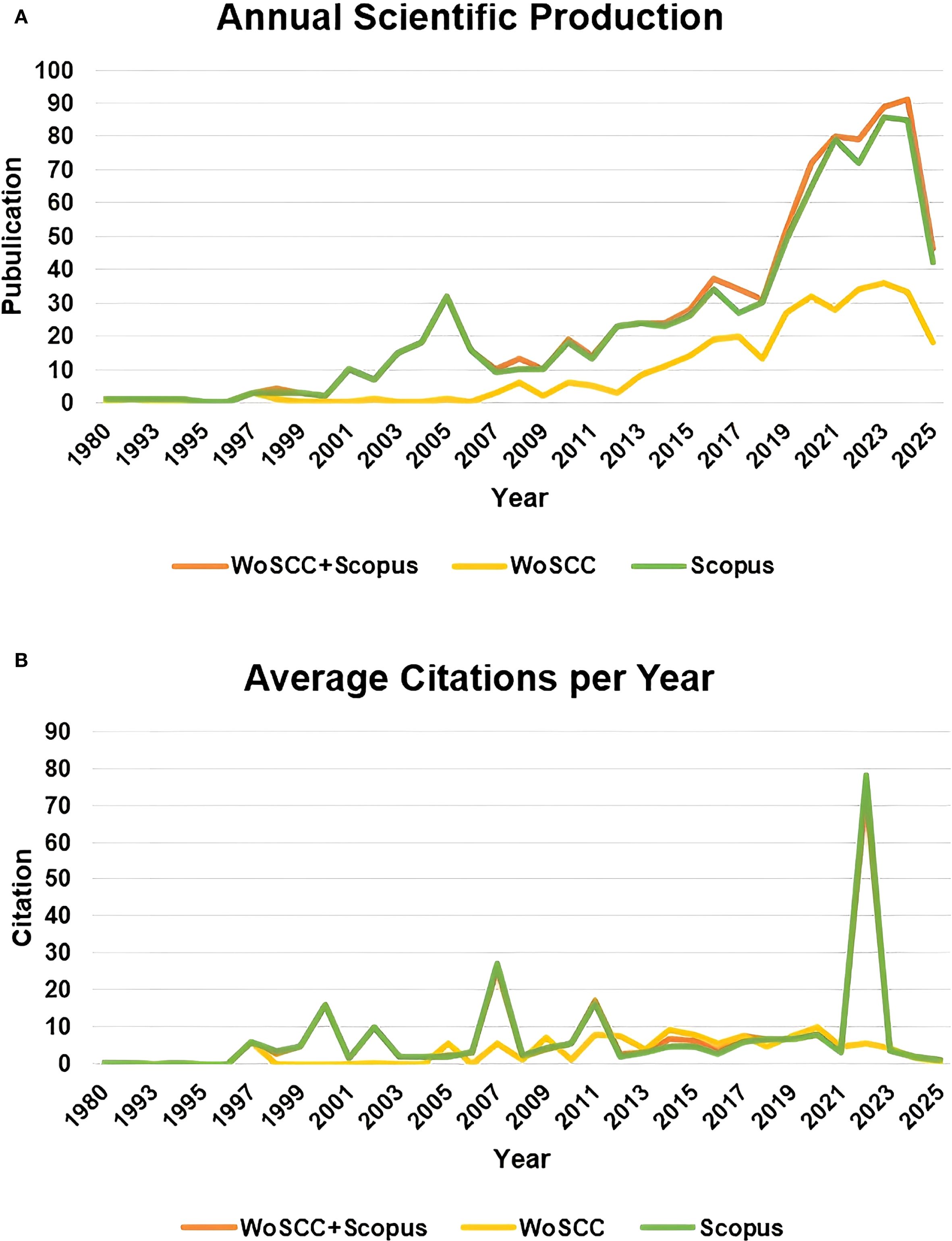
Figure 2. Publications and citations. (A) Annual scientific production. (B) Average citations per Year.
The above results reflected the integration advantage of multi-database analysis in integrating exceptionally high-impact papers, enabling a more comprehensive support for the construction and evolution path analysis of the knowledge map in a specific field. Therefore, our subsequent results were based on the thorough analysis of the merged data from the two databases.
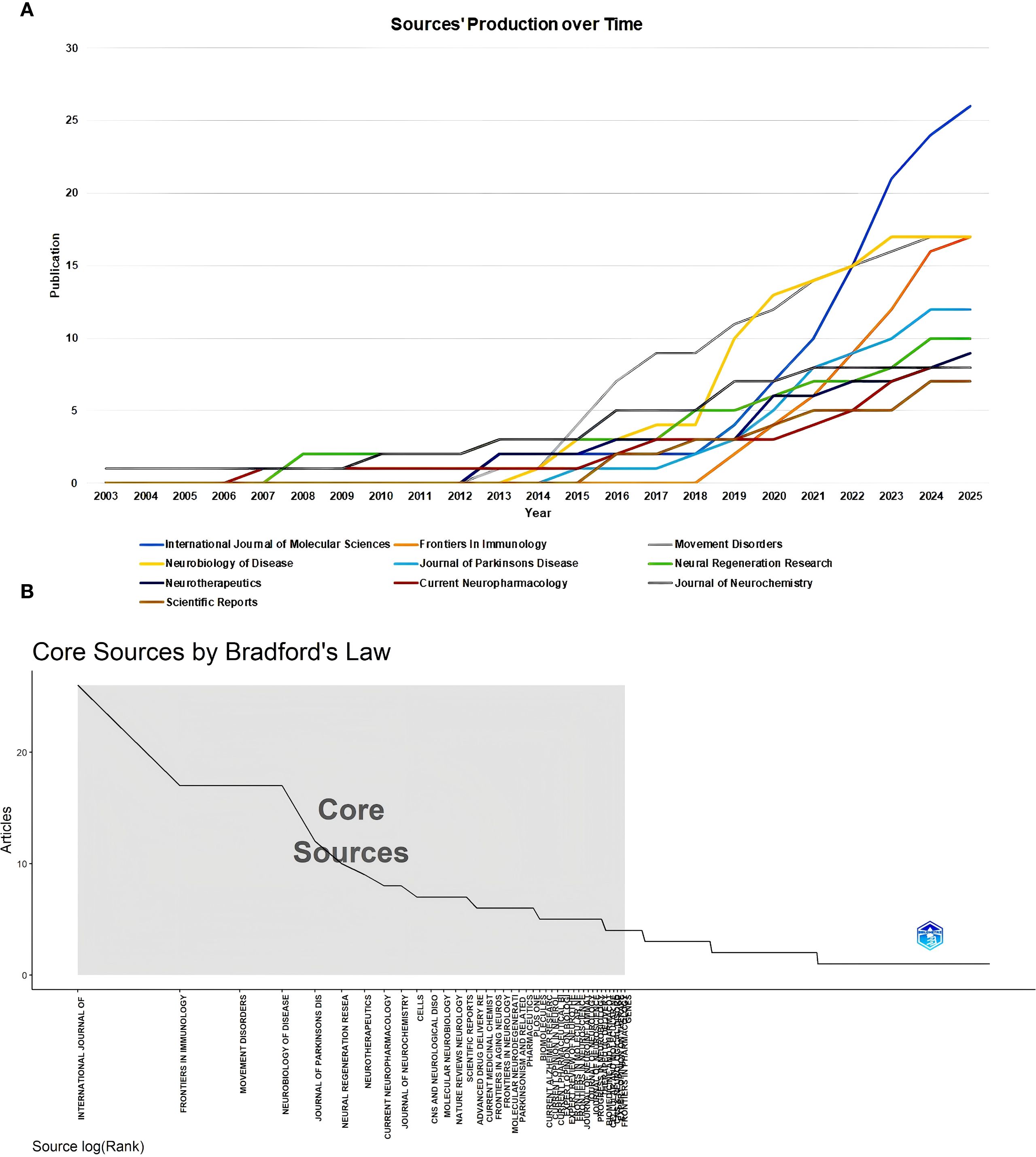
Sources
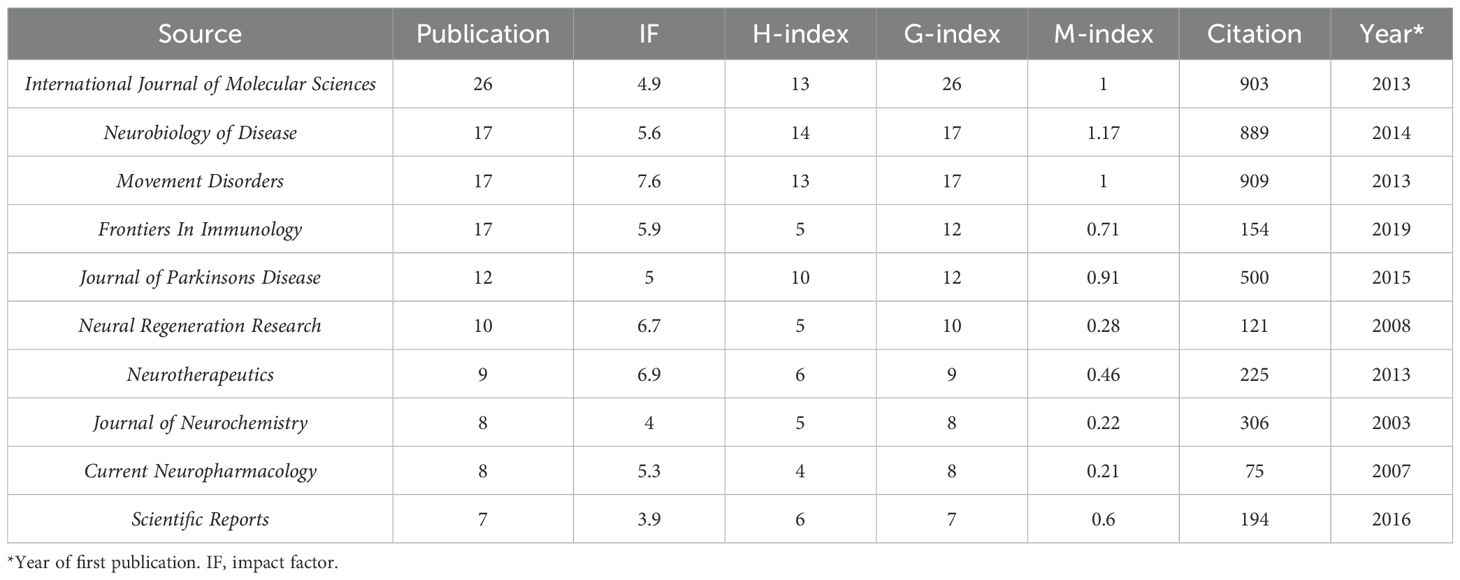
A total of 488 sources published all the documents in this field. The top 10 most popular sources have been seen in an increasing number of publications year by year (Figure 3A). As of now, the journal with the highest number of publications was the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, the journal with the highest impact factor (IF) was Movement Disorders, and the journal with the highest H-index was Neurobiology of Diseases (Table 2). We further determined the core sources in the field of immunotherapy for 41 sources using Bradford’s Law (Figure 3B).
Authors, institutions, and countries/regions
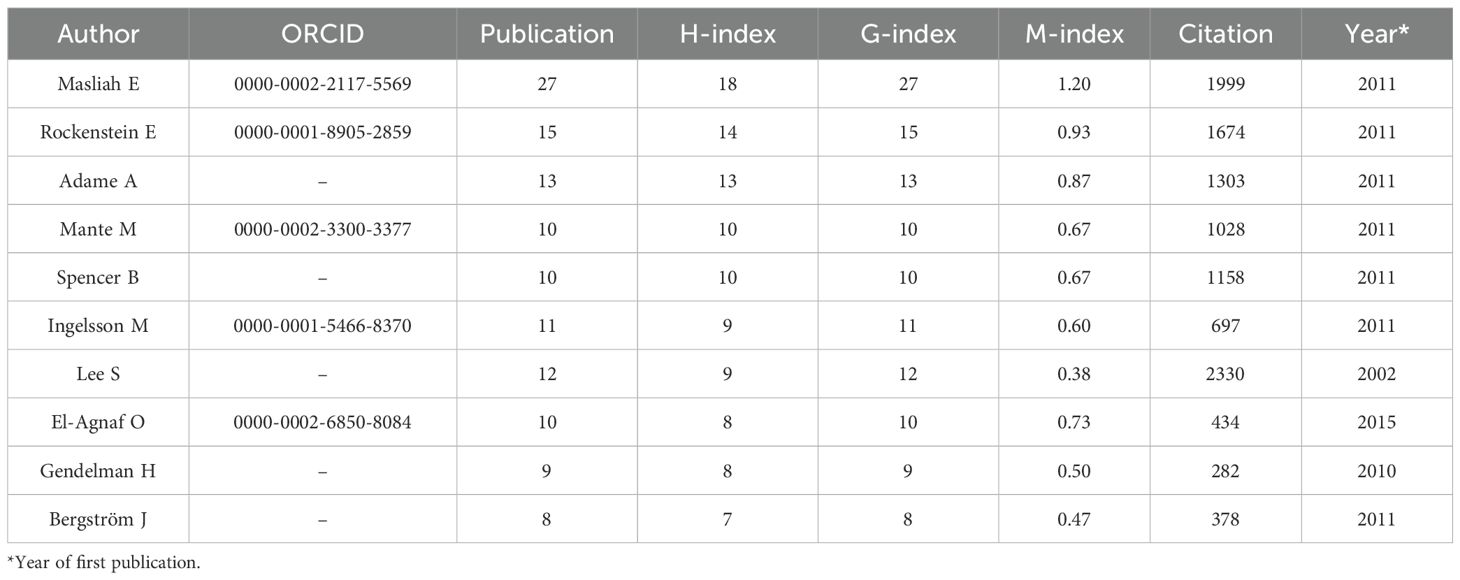
A total of 3,804 researchers from 1,483 institutions in 63 countries published research in this field. Masliah E ranked first with 27 publications and an H-index of 18, followed by Rockenstein E (15/14) and Adame A (13/13). Although the publication volume of some authors, such as Gendelman H and Bergstrom J, was not high, they had relatively small differences between their publication volume and H-index, which indirectly reflects the stability of their output scale and the influence of their achievements (Table 3, Figure 4A). Moreover, a large number of low-productivity authors dominate, with 85.96% publishing only one paper. The scale of high-productivity authors has significantly shrunk. In particular, only 19 people have published more than five publications, which deviates from the exponential decay pattern of Lotka’s law (Figure 4B).
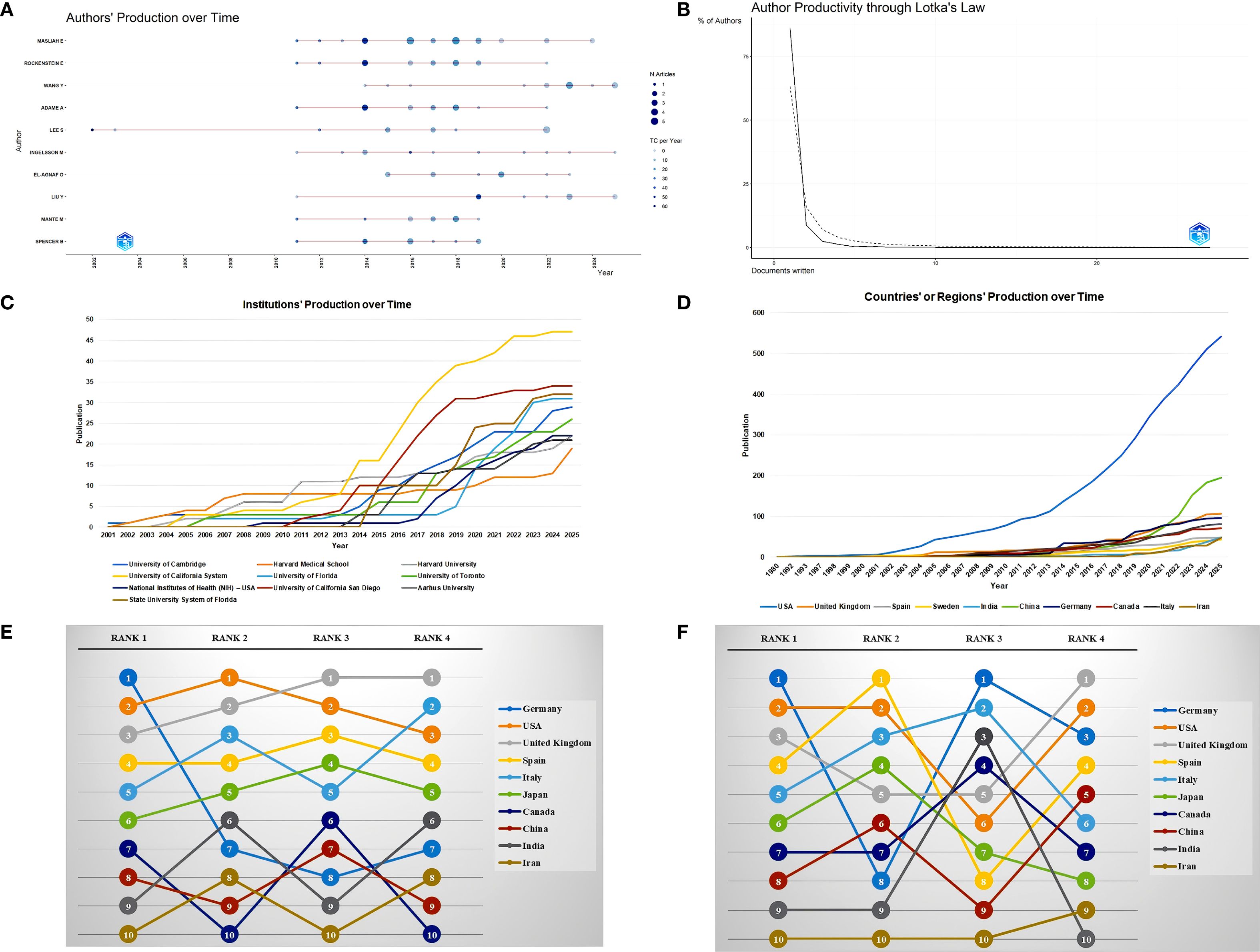
Figure 4. Author, institution, and country/region analysis. (A) Authors’ production over time. (B) Author Productivity through Lotka’s Law. (C) Institutions’ production over time. (D) Countries’ or regions’ production over time. (E) Sensitivity analysis of Countries/regions citation indicators. All rankings are based on the calculation of average article citation. RANK1: all articles; RANK2: no reviews; RANK3: no top 5% highly cited; RANK4: no reviews and top 5% highly cited. (F) Country/region citation analysis grouped by publication year. All rankings are based on the calculation of average article citation. RANK1: all articles; RANK2: articles published in 1980-2005; RANK3: articles published in 2006-2015; RANK4: articles published in 2016-2025.
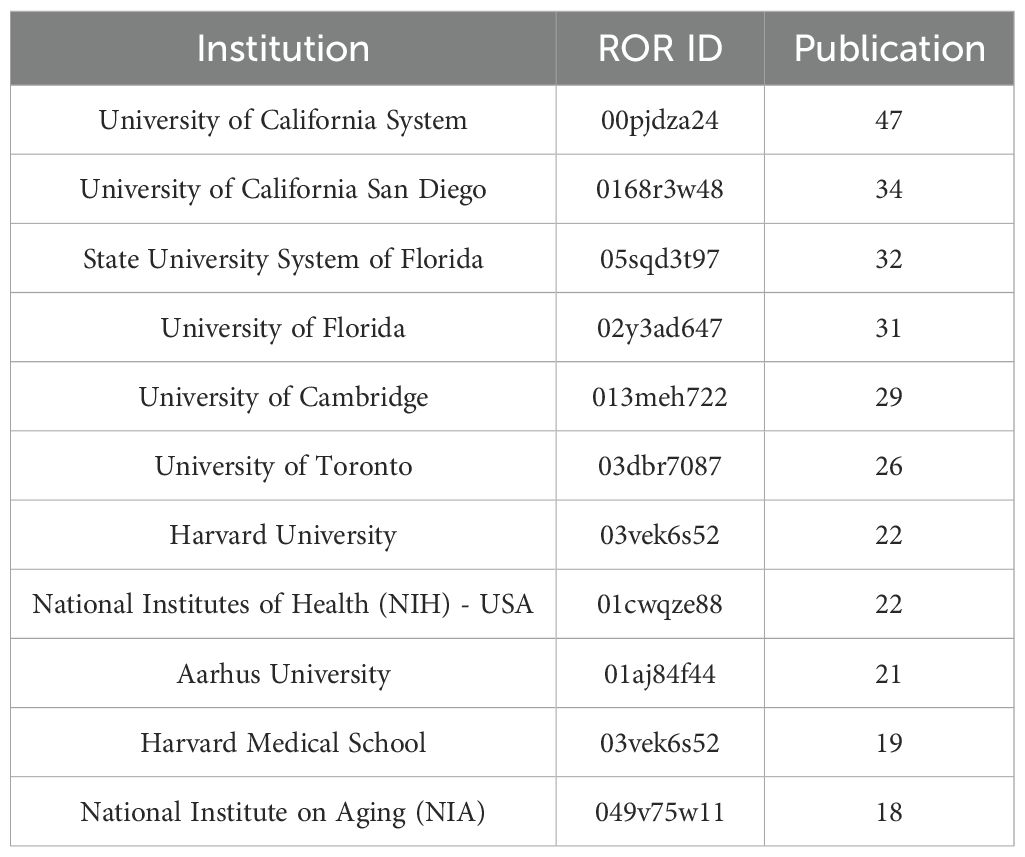
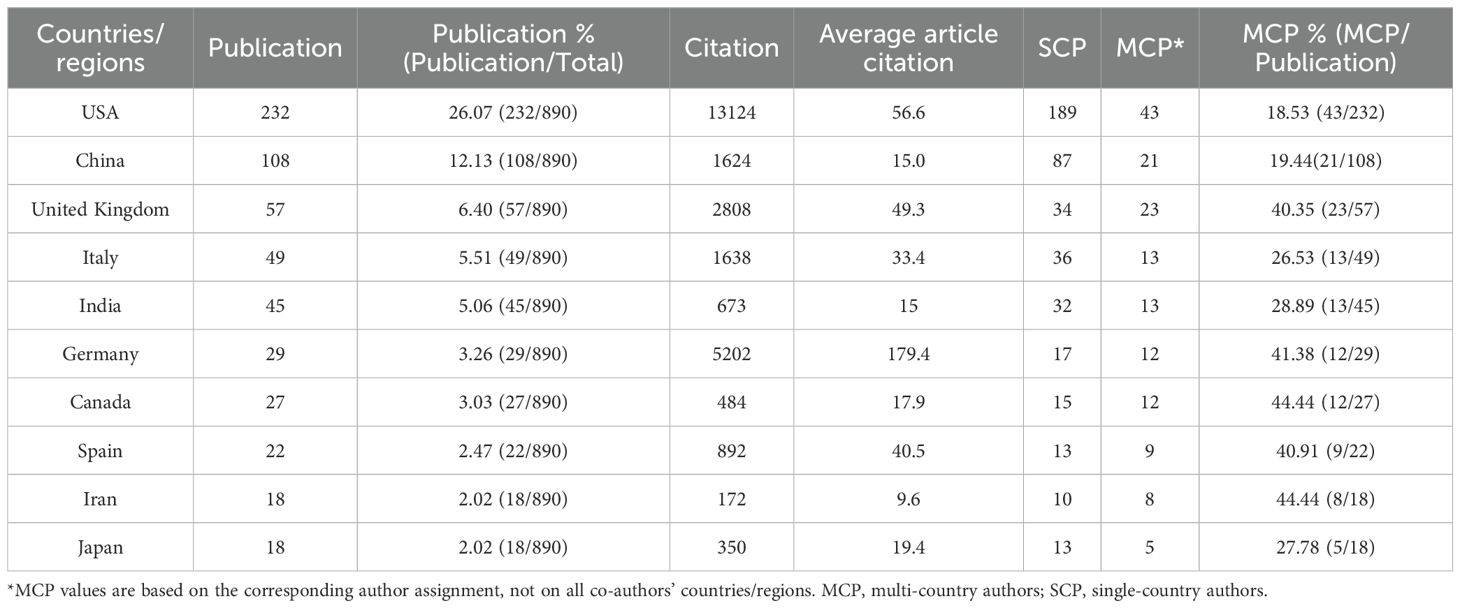
The University of California System ranked first with 47 publications, followed by the University of California San Diego (34) and the State University System of Florida (32). The top 10 most popular institutions consistently produced research outputs each year (Table 4, Figure 4C). We calculated the number of published papers for each country/region based on the country of the “corresponding author” (Table 5, Figure 4D). The results showed that the USA topped the list with 232 publications, followed by China with 108 publications. The United Kingdom (57), Italy (49), and India (45) ranked third to fifth, respectively.
We further compared the performance of citation indicators among the top 10 countries/regions with the highest publication volumes. Germany ranked first with an average article citation of 179.4, followed by the USA (56.6) and the United Kingdom (49.3), which ranked second and third, respectively. China, despite having a relatively high publication volume, ranked relatively low in terms of citation data. After excluding review articles, Germany’s average article citations dropped sharply from first (179.4) to seventh (16.0), the United Kingdom (27.5) jumped to second, and the USA (47.4) remained first, showing that these two countries still had relatively high average article citations even when only original research was considered. After excluding the top 5% of papers with the highest citation counts, Germany’s average article citations further decreased to 12.5, dropping to eighth. In contrast, the United Kingdom (29.3) jumped to first, and the USA (28.6) ranked third. After excluding both review articles and the top 5% of papers with the highest citation counts simultaneously, Germany’s average article citations remained at 16.0, still ranking seventh, the United Kingdom (27.5) ranked first again, and the USA (20.9) ranked third (Supplementary Table S4; Figure 4E). In addition, we calculated and ranked the average article citations of papers from each country across different time periods, categorized by publication year cohort. Germany had a low ranking (Rank = 8) in the early stage, but its average article citations improved significantly in the mid-term (Rank = 1) and then declined somewhat in the recent period (Rank = 3). The USA maintained a leading position for a long time, but its ranking fluctuated in different stages. The United Kingdom rose steadily from fifth in the early stage and rose to first in the past decade (Supplementary Table S5; Figure 4F).
Cooperation analysis
Cooperation analysis can reveal the cooperative network structure of each individual (author, institution, or country/region) in this field, promote interdisciplinary and international cooperation, optimize research management, and drive innovation. In the field of PD immunotherapy, the authors were classified into 5 clusters (Figure 5A). Masliah E might lead the core cooperation with Lee S, El-Agnaf O, and Vaikath N. Lee S formed a close sub-network with Kim C, Rissman R (Supplementary Table S5). In terms of institutional cooperation, institutions were classified into 12 clusters (Figure 5B). Harvard Medical School was the core hub, connecting institutions such as Harvard University and Columbia University; the University of California System served as a cross-regional bridge, linking institutions such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) - USA and the University of Oxford (Supplementary Table S6). In terms of countries/regions cooperation, the countries/regions were classified into 13 clusters (Figure 5C). The USA served as the core hub, connecting countries and regions with high influence, such as Germany, Italy, and Canada. The United Kingdom led cross-regional cooperation, coordinating with countries and regions like France and Austria. Qatar acted as a bridge connecting China and Australia, but South Africa and Iraq, among others, had a betweenness of 0, indicating weak internal connections. China formed a regional cooperation core with Japan (Supplementary Table S7). We further analyzed the cooperation situation among the countries/regions where the “corresponding authors” of each publication were located. Among the countries with the highest number of publications, the USA (18.53%) and China (19.44%) had relatively low proportions of international cooperation (Figure 5D).
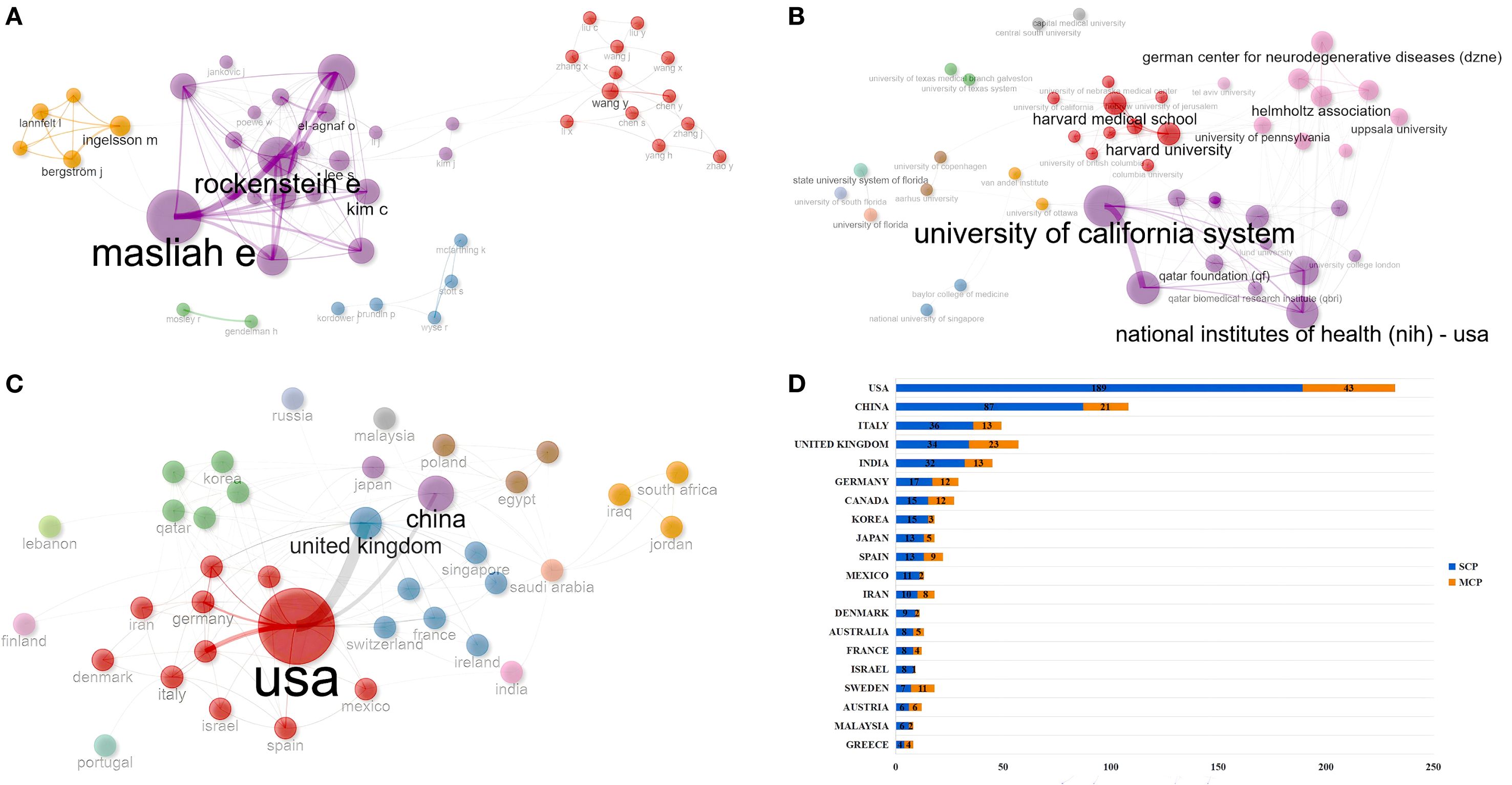
Figure 5. Cooperation analysis. (A) Map of author co-occurrence. (B) Map of institution co-occurrence. (C) Map of country/region co-occurrence. (D) The cooperation model between countries/regions. MCP, multi-country authors; SCP, single-country authors.
Keywords
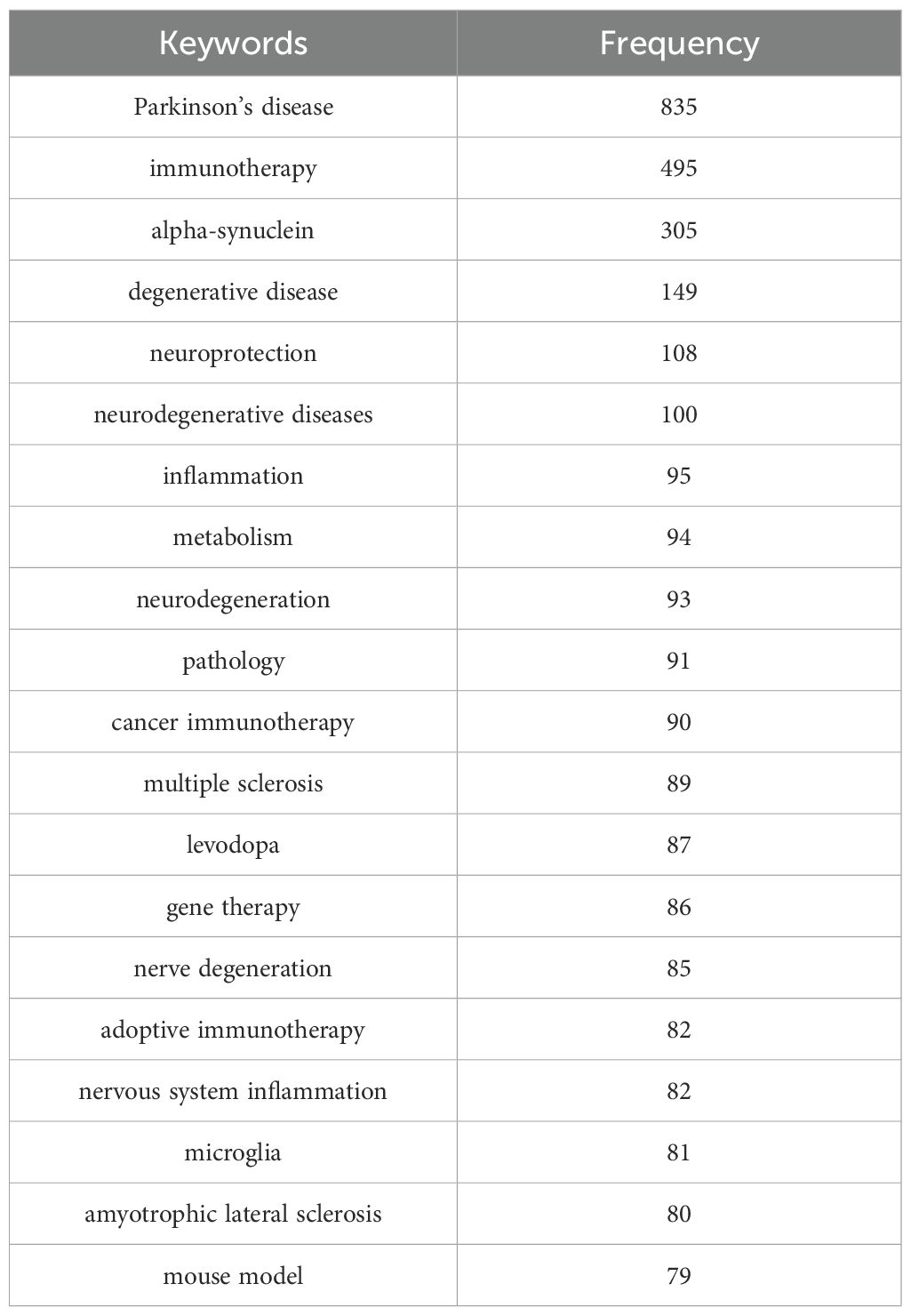
Keyword analysis plays a crucial role in identifying hotspots in the field and predicting the research frontiers. Keywords such as “Parkinson’s disease,” (835) “immunotherapy,” (495) and “alpha-synuclein” (305), were frequently used in this field (Figure 6A, Table 6). The maps of keyword co-occurrence and clusters revealed the generation of two main clusters (Figure 6B). Cluster 1, comprising largely methodological, experimental, and clinical keywords, functioned as a foundational domain centered on research design, diagnostic tools, and therapeutic interventions. This cluster was anchored by terms such as “clinical trial”, “controlled study”, and “dopamine”, all of which exhibited moderate centrality values. Other notable keywords included “levodopa”, “dopaminergic nerve cell” , “protein expression”, and “gene expression”. In contrast, Cluster 2 emerged as the dominant thematic hub, integrating concepts related to neurodegenerative pathology, therapeutic innovation, and disease mechanisms, with significantly higher betweenness centrality among its key nodes. The most influential and structurally central keyword in the entire network was “Parkinson’s disease”, which acted as the primary node bridging multiple sub-themes and anchoring the cluster’s conceptual identity. Other highly central terms within this cluster included “immunotherapy”, “neurodegeneration”, “neurodegenerative diseases”, “alpha-synuclein”, and “neuroprotection”. These keywords reflect the high emphasis on the mechanistic understanding of neurodegenerative processes, particularly those related to protein misfolding, inflammation, oxidative stress, and neuronal death, as well as covering emerging therapeutic strategies such as immunotherapy, gene therapy, and neuroprotective interventions (Supplementary Table S8). The heat map also indirectly indicated that Cluster 2 was currently the research hotspot in this field (Figure 6C).
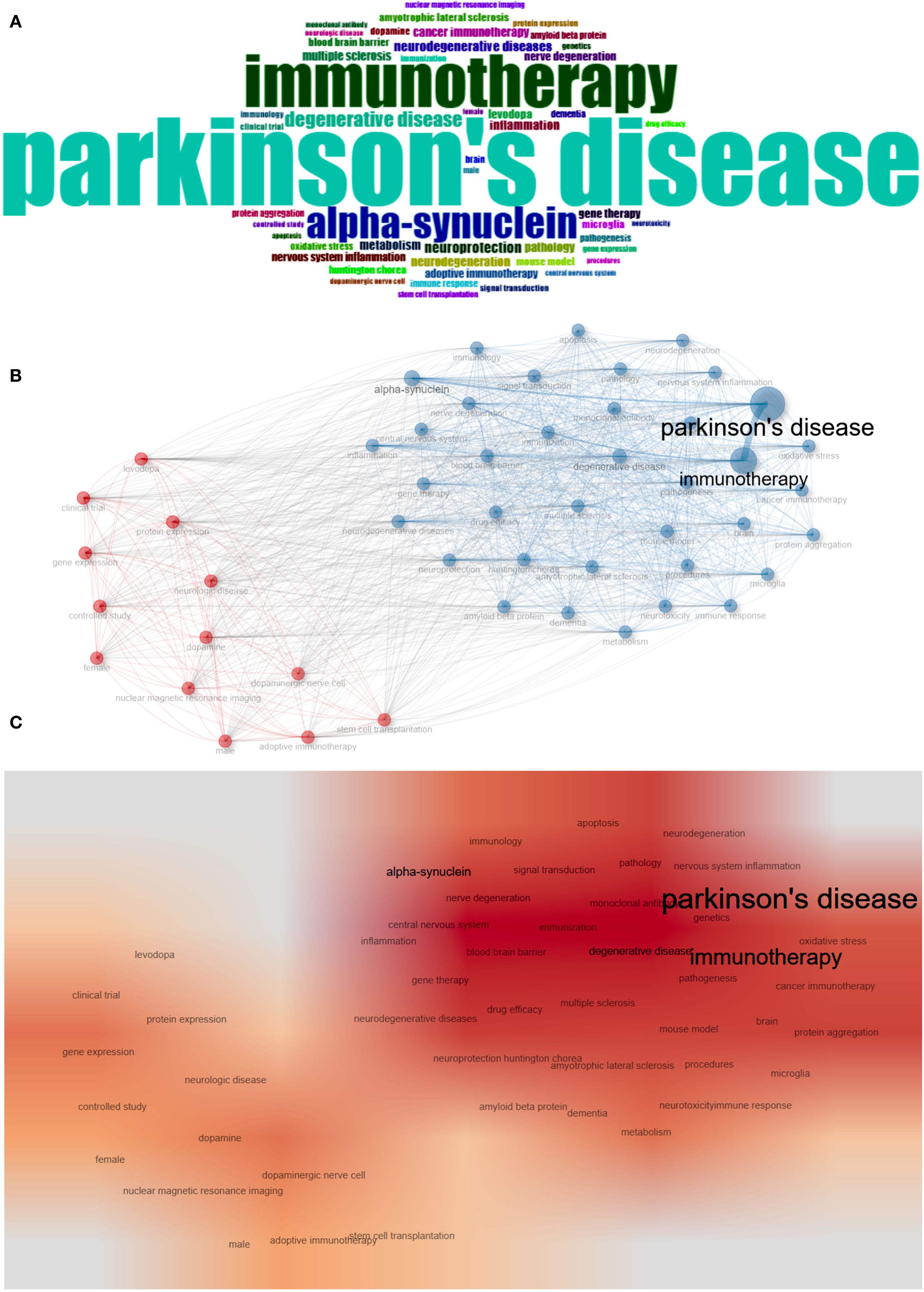
Figure 6. Keyword analysis. (A) WordCloud. (B) Map of keyword co-occurrence. (C) Heat map of keyword co-occurrence.
The Thematic Evolution function demonstrated the evolution process of key terms within the field. As time advanced, new themes emerged and interconnected, showing a shift toward more targeted and mechanistic studies. The rise of “alpha-synuclein” as a central research focus, alongside advancements in “adoptive immunotherapy,” “immunization,” and investigations into “microglia” and “mouse model” systems. In more recent years (2021–2025), the research scope expanded to include gender-specific considerations (“male” and “female”), cross-disease insights (“cancer immunotherapy”), and continued deep dives into the role of “alpha-synuclein” in Parkinson’s pathology (Figures 7A, B). The Topic Trends analysis also yielded similar results. Keywords related to precise immunotherapy intervention and efficacy assessment have become increasingly frequent since 2018. From the perspective of keyword duration, research on the immune mechanisms of PD and treatment technologies has exhibited a synergistic growth trend, reflecting the advancement of this field from pathogenesis analysis to clinical application and translation (Figure 7C).
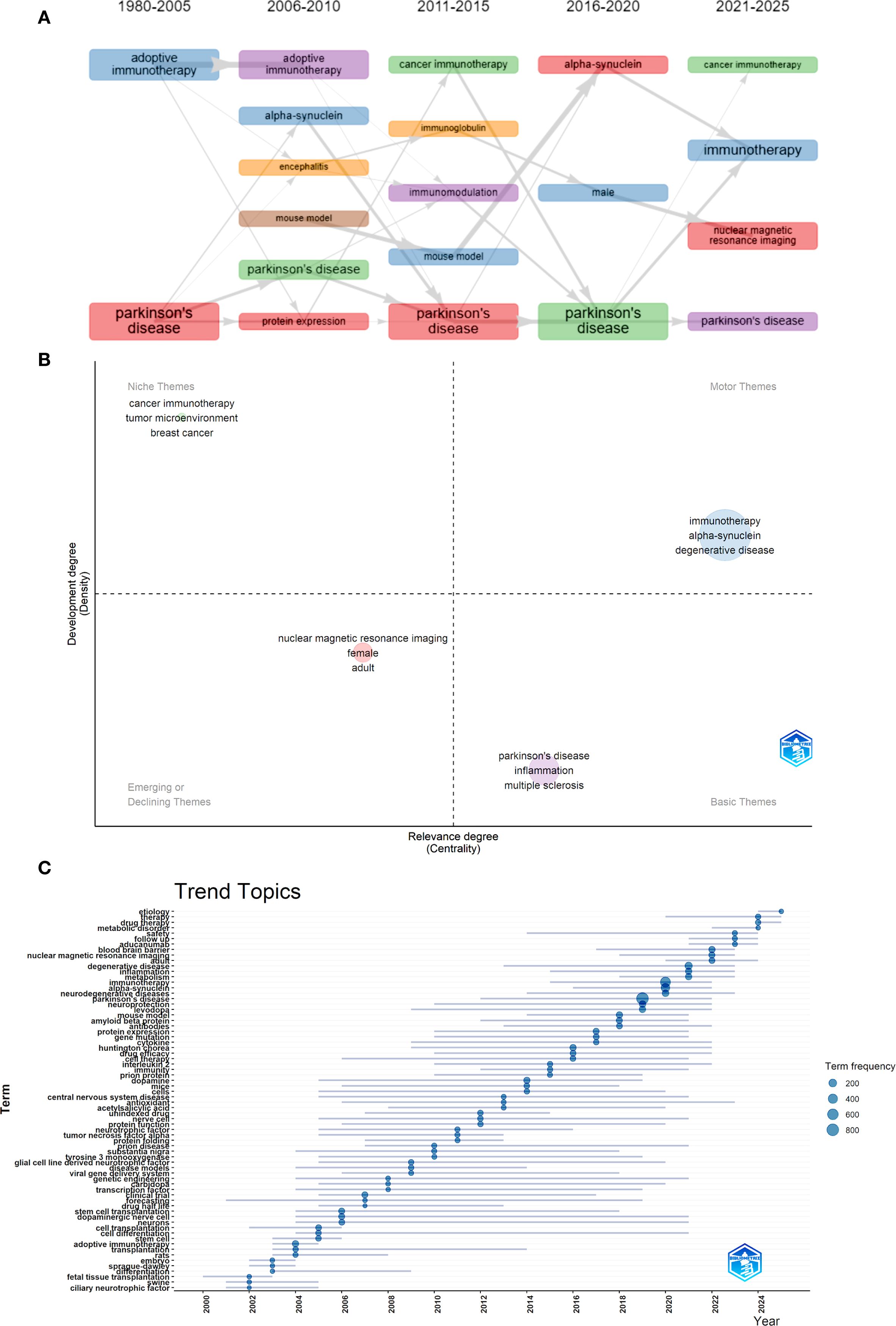
Figure 7. Hotspot and frontier analysis. (A) Thematic evolution. (B) Thematic Evolution in 2021-2025. (C) Trends Topics.
Clinical trials
Given that the keyword analysis indicates that clinical translation is currently the focus of research, we further utilized the PubMed database to search for relevant clinical trials in this field, providing additional references for researchers. Since the clinical study was not reviewed in accordance with the systematic review method, the summary of clinical trials is mainly presented in the supplementary materials. In total, eight clinical trials were searched and included (Supplementary Table S10; Figure 1). Tracing the registration number of the eight included clinical trials revealed that for six studies (7, 8, 16–19), the registered trial information was largely consistent with the designs reported in the original publications, indicating that these studies were conducted in strict accordance with their protocols and ensuring the reliability and consistency of the results. In contrast, two studies were registered in the EU CTR. Still, due to access limitations or a delay in updating by the investigator, the detailed trial protocols could not be fully retrieved (19, 20).
Discussion
Through integrating the complementary resources of the WoSCC and Scopus databases, not only has the literature coverage been significantly expanded, but also the vigorous development potential and dynamic evolution characteristics of the PD immunotherapy field have been revealed. After merging the databases, the breadth of literature coverage and the depth of knowledge association have both improved significantly, suggesting that this field is currently in a critical stage of simultaneous expansion in academic output and influence. The complete timeline encompasses a higher average annual number of publications than a single database, further verifying the accumulated knowledge base and stable growth in research investment in this field.
The results of the journal analysis provide descriptive evidence of research activity and trends in the field of PD immunotherapy. The extensive coverage of 488 sources and the continuous increase in the number of publications in the top 10 journals directly reflect the expansion of research investment and the concentration of academic output in this field. The screening of core journals via Bradford’s Law reveals a concentration of publications in a subset of high-output journals, with journals that integrate neuroscience-focused and molecular biology-related content noted as prominent within the field. This distribution pattern aligns with the interdisciplinary characteristics of PD immunotherapy research.
At the author level, high-productivity scholars, such as Masliah E and Rockenstein E form a core influential group through their high publication volume and high H-index. Moreover, 85.96% of the authors have only published one paper, indicating that a large number of low-productivity authors limit the depth and sustainability of research. Notably, although researchers with high publication volumes and high H-indexes often form core, influential groups in a particular field, academic practices have also shown that there are cases where researchers have had multiple papers withdrawn due to suspected academic misconduct. This reminds us that the evaluation of research influence should take into account both academic output and research integrity, and avoid relying excessively on a single indicator.
Moreover, the University of California system and Harvard Medical School have a cooperation through institutions to enhance research output. The USA has the highest number of publications. Germany had the highest average article citations, but its average article citation and ranking dropped significantly after sequentially excluding review articles, extremely highly cited papers, or both, indicating that its high average citation mainly relied on special paper types such as reviews or extremely highly cited papers. The citation performance of countries/regions such as the USA, the United Kingdom, and China was relatively stable, especially the United Kingdom, which maintained the leading position in multiple analysis, followed by the USA, while China ranked in the middle to lower range but with minor fluctuations, suggesting that its citation indicators were not sensitive to reviews and extreme values. We further conducted a grouped analysis of the average article citations of various countries/regions by publication year period. Although the USA had fluctuations in rankings in individual stages, it generally ranked high. Overall, the citation performance of countries/regions changed over time, indicating that citation indicators have dynamic characteristics and need to be examined by time period to more comprehensively and scientifically evaluate the scientific research influence of each country. Notably, these metrics do not directly indicate differences in research quality or clinical translation potential. In addition, the USA and China have a lower proportion of international co-authorship compared to many other countries/regions. Despite the relatively low proportion of international cooperation among major countries like the USA and China, their large research volume and central roles in the network suggest potential for enhanced cooperation. However, the actual impact on clinical translation remains to be empirically validated.
Research in the field of PD immunotherapy has formed a highly interconnected core hotspot area within the current knowledge network. PD, as the central hub node of this network, is not only the focus of clinical research but also the convergence point of various pathological mechanisms and treatment strategies, reflecting its significant position in neurodegenerative diseases. Among them, nodes such as alpha-synuclein, neurodegeneration, and neuroinflammation reveal the key pathological processes of abnormal protein aggregation causing neuroinflammation and neuronal damage in PD, and these processes are precisely the important targets of current immunotherapy (21–26). At the same time, nodes related to the immune system, such as immune response, immune regulation, and immune system diseases, further highlight the therapeutic idea of regulating the immune microenvironment to slow disease progression. Moreover, nodes related to treatment methods, such as gene therapy, drug efficacy, and stem cell transplantation, have also been integrated into the research network, indicating that immunotherapy is not isolated but rather coexists with various emerging therapies to form part of a comprehensive intervention strategy for PD (27–29). Overall, this result reflects that current PD research is shifting from traditional symptomatic treatment to targeted immune regulation and multi-pathway combined treatment models. Immunotherapy, as a crucial bridge connecting neuroprotection, inflammation control, and disease modification, has become a key research direction and a potential breakthrough point in this field.
From a mechanistic perspective, α-synuclein, as the core research target, continues to make significant progress. The research on its association with microglia and neurodegenerative pathological processes is also deepening (30, 31). A recent study also indicates that in mice injected with α-synuclein collagen, reducing the activity of microglia can slow down the spread of pathological α-synuclein lesions (32). In terms of treatment strategies, precise immunological intervention has become the trend. Technologies such as adoptive immunotherapy and immunization are constantly emerging, driving the translation from basic research to clinical application. For example, the targeted delivery system mediated by nanocarriers fosters the development of precise treatment (33). Meanwhile, cross-dimensional research has expanded the frontier boundaries, and gender-specific research incorporates perspectives of differences between men and women, providing possibilities for personalized treatment (34).
Currently, clinical research on immunotherapy for PD remains in the early validation stage, with most studies focusing on active immunotherapy, such as PD01A and UB-312, which aim to regulate α-synuclein aggregation or restore the dopaminergic system (7, 20). Volc et al. reported that PD01A induced a significant humoral immune response, binding to the intended target; however, the study was limited by its non-randomized design and small sample size (20). Similarly, Poewe et al. demonstrated that PD03A elicited antibody responses with acceptable safety, supporting further development of active immunotherapy, but also highlighted the need for long-term follow-up (35). UB-312 was initially tested in healthy participants, showing good safety and the induction of anti-α-synuclein (8). A subsequent phase revealed that reduced α-synuclein core structures in cerebrospinal fluid, although without significant clinical improvement. Other approaches have included Lu AF82422, which was shown to be safe and pharmacokinetically suitable for further development (8). Moreover, Olson et al. demonstrated that sargramostim was safe and could restore immune balance, but in a small sample. In addition, trials with the monoclonal antibody BIIB054 in both healthy participants and PD patients consistently confirmed favorable safety and target engagement, although these findings were again limited by small cohorts (16, 17, 19). Overall, these trials suggest that active immunotherapy and targeted antibodies generally demonstrate favorable safety and immunogenicity in PD.
However, most trials were exploratory, involved small sample sizes, and often relied on non-randomized designs. Furthermore, they also lacked long-term follow-up data. For example, some studies have focused only on immune responses rather than clinical symptoms, and have shown limited population diversity, with many studies restricted to healthy participants or Western cohorts (7, 8, 19). These limitations reduce the reliability of conclusions regarding efficacy and safety. Looking ahead, large-scale randomized controlled trials involving diverse populations, long-term follow-up, and dynamic biomarker monitoring are needed to verify the stability of therapeutic effects. New biomarkers based on cerebrospinal fluid have been discovered, and they may gradually influence the overall design of clinical intervention trials. Identifying biomarkers for PD may enable earlier and more accurate diagnosis and treatment (36–38).
Comparison of the registered protocols with the actual studies revealed that most trials were conducted mainly in accordance with their initial registrations, with only minor modifications observed. For example, in the study by Brys, the registered duration was 20 weeks, whereas the actual trial lasted 16 weeks (20). Additional cohorts (135-mg/kg HV and early PD groups) were introduced after trial initiation, based on safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetic, and adverse event considerations, reflecting a participant-centered approach with timely adjustments to ensure safety and feasibility. Interestingly, one of the studies represented a secondary analysis of samples from previous clinical trials (19). It aimed to develop a zero-length crosslinking method, combined with Meso Scale Discovery technology, to enable the quantitative analysis of cinpanemab-α-synuclein complexes in clinical cerebrospinal fluid samples by preventing signal loss due to rapid dissociation. This work not only highlights the challenges and resource demands of clinical trials but also emphasizes the significance of methodological innovation. Applying fundamental research techniques, such as chemical crosslinking, directly to clinical samples addresses practical issues in drug development and disease diagnosis. Such secondary analyses, or “post-hoc dissections” of completed trials, provide critical insights for subsequent development and create a translational feedback loop from clinic to laboratory and back, representing an innovative and resource-efficient research strategy.
Limitations
Our study has some limitations. Firstly, the bibliometric indicators are difficult to capture the heterogeneity of research quality. For instance, the achievements of prolific authors may include low-impact conference papers, while breakthrough studies by less productive authors may not have been adequately measured. Importantly, when assessing the influence of scientific research, it is essential to consider not only academic output indicators but also the credibility and academic ethics of the research. Future research can further explore how to incorporate indicators such as academic integrity records and research reproducibility into the comprehensive evaluation system. Secondly, although keyword co-occurrence analysis can map research hotspots, it cannot reveal the implicit interdisciplinary connections, and it relies on the standardized use of terms by researchers. Furthermore, we are unable to obtain the unique identifiers for all authors. Some author nodes may have duplication, incorrect merging or splitting issues (39).Visualization analysis only reflects the co-occurrence intensity and cannot verify the causal relationship of mechanisms, nor can it provide biological evidence (40, 41). Finally, due to the lack of pre-established strict criteria for including intervention types and relying on the descriptions of intervention measures in the literature, there is a potential misclassification risk in the current summary of clinical trials.
Conclusions
The present bibliometric analysis shows that PD immunotherapy is a rapidly expanding field. The extensive coverage of 488 sources and the continuous increase in the number of publications in the top 10 journals directly reflect the expansion of research investment and the concentration of academic output in this field. A large number of low-productivity authors limit the depth and sustainability of research. The USA has the highest number of publications. The citation indicators among different countries/regions change over time and exhibit dynamic characteristics. Additionally, the USA and China have a lower proportion of international co-authorship compared to many other countries or regions.
The key pathological processes, such as neuroinflammation and neuronal damage caused by the abnormal aggregation of α-synuclein, as well as therapeutic ideas for regulating the immune microenvironment to delay disease progression, are current research hotspots. Precise immunological intervention techniques, such as adoptive immunotherapy and targeted delivery via nanocarriers, are continually emerging, promoting the translation of basic research into clinical applications, and are frontiers in this field. While clinical trials remain exploratory and limited in scale, bibliometric evidence suggests an increasing interest in bridging the gap between basic and clinical research. Future progress will require large-scale, collaborative studies with robust designs and dynamic biomarker monitoring, as well as exploration of combination strategies, to strengthen clinical translation and advance personalized immunotherapy for PD.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
XF: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JS: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CC: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YH: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Southwest Medical University Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project Fund (Grant Numbers: 202310632045 and 202310632059).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1659848/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Pradhan SP, Tejaswani P, Behera A, and Sahu PK. Phytomolecules from conventional to nano form: Next-generation approach for Parkinson’s disease. Ageing Res Rev. (2024) 93:102136. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2023.102136
2. Ravenhill SM, Evans AH, and Crewther SG. Escalating bi-directional feedback loops between proinflammatory microglia and mitochondria in ageing and post-diagnosis of parkinson’s disease. Antioxidants (Basel Switzerland). (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/antiox12051117
3. Tecilla M, Großbach M, Gentile G, Holland P, Sporn S, Antonini A, et al. Modulation of motor vigor by expectation of reward probability trial-by-trial is preserved in healthy ageing and parkinson’s disease patients. J neuroscience: Off J Soc Neurosci. (2023) 43:1757–77. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.1583-22.2022
4. Manoutcharian K and Gevorkian G. Recombinant antibody fragments for immunotherapy of parkinson’s disease. BioDrugs: Clin immunotherapeutics biopharmaceuticals Gene Ther. (2024) 38:249–57. doi: 10.1007/s40259-024-00646-5
5. Levite M. Neuro faces of beneficial T cells: essential in brain, impaired in aging and neurological diseases, and activated functionally by neurotransmitters and neuropeptides. Neural regeneration Res. (2023) 18:1165–78. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.357903
6. Palermo G and Ceravolo R. Clues to reshaping anti-α-synuclein immunotherapy in early parkinson’s disease patients. Movement disorders: Off J Movement Disord Society. (2023) 38:196–7. doi: 10.1002/mds.29294
7. Yu HJ, Thijssen E, van Brummelen E, van der Plas JL, Radanovic I, Moerland M, et al. A randomized first-in-human study with UB-312, a UBITh® α-synuclein peptide vaccine. Movement disorders: Off J Movement Disord Society. (2022) 37:1416–24. doi: 10.1002/mds.29016
8. Eijsvogel P, Misra P, Concha-Marambio L, Boyd JD, Ding S, Fedor L, et al. Target engagement and immunogenicity of an active immunotherapeutic targeting pathological α-synuclein: a phase 1 placebo-controlled trial. Nat Med. (2024) 30:2631–40. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03101-8
9. Pardo-Moreno T, García-Morales V, Suleiman-Martos S, Rivas-Domínguez A, Mohamed-Mohamed H, Ramos-Rodríguez JJ, et al. Current treatments and new, tentative therapies for parkinson’s disease. Pharmaceutics. (2023) 2515. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030770
10. Fei X and Hu Y. A call for the establishment of bibliometric reporting guidelines. J Clin nursing. (2024) 34:3425–6. doi: 10.1111/jocn.17574
11. Hu Y, Zheng Y, Yang Y, Fang W, Huang M, Li D, et al. A bibliometric analysis of cerebral palsy from 2003 to 2022. Front neurology. (2024) 15:1292587. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1292587
12. Fei XX, Wang SQ, Li JY, Xu ZY, Wang JX, Gao YQ, et al. Near-infrared spectroscopy in schizophrenia: A bibliometric perspective. World J Psychiatry. (2024) 14:1755–65. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i11.1755
13. Zhang Y, Zhang L, Huang X, Cao H, Ma N, Wang P, et al. Emotional labour in nursing research: A bibliometric analysis. J advanced nursing. (2025) 81:316–28. doi: 10.1111/jan.16233
14. Aria M and Cuccurullo C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informetrics. (2017) 11:959–75. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
15. Wang S, Wang L, Cheng H, Li H, Zhang Q, He C, et al. Targeting autophagy in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: A comprehensive review of scientific landscapes and therapeutic innovations. Ageing Res Rev. (2025) 110:102818. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2025.102818
16. Olson KE, Namminga KL, Lu Y, Schwab AD, Thurston MJ, Abdelmoaty MM, et al. Safety, tolerability, and immune-biomarker profiling for year-long sargramostim treatment of Parkinson’s disease. EBioMedicine. (2021) 67:103380. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103380
17. Brys M, Fanning L, Hung S, Ellenbogen A, Penner N, Yang M, et al. Randomized phase I clinical trial of anti-α-synuclein antibody BIIB054. Movement disorders: Off J Movement Disord Society. (2019) 34:1154–63. doi: 10.1002/mds.27738
18. Buur L, Wiedemann J, Larsen F, Ben Alaya-Fourati F, Kallunki P, Ditlevsen DK, et al. Randomized phase I trial of the α-synuclein antibody lu AF82422. Movement disorders: Off J Movement Disord Society. (2024) 39:936–44. doi: 10.1002/mds.29784
19. Liu Y, Yang M, Fraser K, Graham D, Weinreb PH, Weihofen A, et al. Quantification of cinpanemab (BIIB054) binding to α-synuclein in cerebrospinal fluid of phase 1 single ascending dose samples. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2025) 392:100003. doi: 10.1124/jpet.124.002199
20. Volc D, Poewe W, Kutzelnigg A, Lührs P, Thun-Hohenstein C, Schneeberger A, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the α-synuclein active immunotherapeutic PD01A in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a randomised, single-blinded, phase 1 trial. Lancet Neurology. (2020) 19:591–600. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(20)30136-8
21. Aminabad ED, Hasanzadeh M, Ahmadalipour A, Mahmoudi T, Feizi MAH, Safaralizadeh R, et al. Sensitive electrochemical recognition of α-synuclein protein in human plasma samples using bioconjugated gold nanoparticles: An innovative immuno-platform to assist in the early stage identification of Parkinson’s disease by biosensor technology. J Mol recognition: JMR. (2023) 36:e2952. doi: 10.1002/jmr.2952
22. Anis E, Xie A, Brundin L, and Brundin P. Digesting recent findings: gut alpha-synuclein, microbiome changes in Parkinson’s disease: (Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism 33, 147-157; 2022). Trends Endocrinol metabolism: TEM. (2023) 34:426. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2022.01.003
23. Simuni T, Chahine LM, Poston K, Brumm M, Buracchio T, Campbell M, et al. A biological definition of neuronal α-synuclein disease: towards an integrated staging system for research. Lancet Neurology. (2024) 23:178–90. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(23)00405-2
24. Belur NR, Bustos BI, Lubbe SJ, and Mazzulli JR. Nuclear aggregates of NONO/SFPQ and A-to-I-edited RNA in Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neuron. (2024) 112:2558–2580.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2024.05.003
25. Borghammer P, Okkels N, and Weintraub D. Parkinson’s disease and dementia with lewy bodies: one and the same. J Parkinson’s disease. (2024) 14:383–97. doi: 10.3233/jpd-240002
26. Geng L, Gao W, Saiyin H, Li Y, Zeng Y, Zhang Z, et al. and motor deficits in the α-synuclein transgenic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Mol neurodegeneration. (2023) 18:94. doi: 10.1186/s13024-023-00686-5
27. Mostafa-Tehrani S, Saffari M, Balali E, Khadivi R, and Jebali A. The dopaminergic and anti-neuroinflammatory properties of functionalized nanoliposomes containing levodopa and ibuprofen and conjugated with anti-alpha-synuclein aptamer. J neuroimmune pharmacology: Off J Soc NeuroImmune Pharmacol. (2025) 20:66. doi: 10.1007/s11481-025-10227-0
28. Mansour HM and El-Khatib AS. Exploring Parkinson-associated kinases for CRISPR/Cas9-based gene editing: beyond alpha-synuclein. Ageing Res Rev. (2023) 92:102114. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2023.102114
29. Kong W, Li X, Guo X, Sun Y, Chai W, Chang Y, et al. Ultrasound-assisted CRISPRi-exosome for epigenetic modification of α-synuclein gene in a mouse model of parkinson’s disease. ACS nano. (2024) 18:7837–51. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c05864
30. Bellini G, D’Antongiovanni V, Palermo G, Antonioli L, Fornai M, Ceravolo R, et al. α-synuclein in parkinson’s disease: from bench to bedside. Medicinal Res Rev. (2025) 45:909–46. doi: 10.1002/med.22091
31. Na J, Ryu HG, Park H, Park H, Lee E, Nam Y, et al. FoxO1 alleviates the mitochondrial ROS levels induced by α-synuclein preformed fibrils in BV-2 microglial cells. Inflammation. (2025) 48:1300–12. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02119-x
32. Xiong M, Xia D, Yu H, Meng L, Zhang X, Chen J, et al. Microglia process α-synuclein fibrils and enhance their pathogenicity in a TREM2-dependent manner. Advanced Sci (Weinheim Baden-Wurttemberg Germany). (2025) 12:e2413451. doi: 10.1002/advs.202413451
33. Guo W, Ji M, Li Y, Qian M, Qin Y, Li W, et al. Iron ions-sequestrable and antioxidative carbon dot-based nano-formulation with nitric oxide release for Parkinson’s disease treatment. Biomaterials. (2024), 309:122622. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122622
34. Pellecchia MT, Picillo M, Russillo MC, Andreozzi V, Oliveros C, and Cattaneo C. The effects of safinamide according to gender in Chinese parkinsonian patients. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:20632. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48067-8
35. Poewe W, Volc D, Seppi K, Medori R, Lührs P, Kutzelnigg A, et al. Safety and tolerability of active immunotherapy targeting α-synuclein with PD03A in patients with early parkinson’s disease: A randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 1 study. J Parkinson’s disease. (2021) 11:1079–89. doi: 10.3233/jpd-212594
36. Parnetti L, Gaetani L, Eusebi P, Paciotti S, Hansson O, El-Agnaf O, et al. CSF and blood biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurology. (2019) 18:573–86. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(19)30024-9
37. Karayel O, Virreira Winter S, Padmanabhan S, Kuras YI, Vu DT, Tuncali I, et al. Proteome profiling of cerebrospinal fluid reveals biomarker candidates for Parkinson’s disease. Cell Rep Med. (2022) 3:100661. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100661
38. Andersen AD, Binzer M, Stenager E, and Gramsbergen JB. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease - a systematic review. Acta neurologica Scandinavica. (2017) 135:34–56. doi: 10.1111/ane.12590
39. Fei X, Wang S, Li J, Zeng Q, Gao Y, and Hu Y. Bibliometric analysis of research on Alzheimer’s disease and non-coding RNAs: Opportunities and challenges. Front Aging Neurosci. (2022) 14:1037068. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1037068
40. Zeng Q, Liu X, Li L, Zhang Q, Luo C, Yang S, et al. Bibliometric analysis of research on traditional chinese exercise and osteoarthritis. J Pain Res. (2024) 17:559–69. doi: 10.2147/jpr.S436457
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease, immunotherapy, bibliometrics, hotspots, frontiers
Citation: Fei X, Wang S, Song J, Cao C, Gao Y and Hu Y (2025) Research on Parkinson’s disease immunotherapy: a bibliometric analysis via multiple databases. Front. Immunol. 16:1659848. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1659848
Received: 04 July 2025; Accepted: 23 September 2025;
Published: 08 October 2025.
Edited by:
Jessica Mandrioli, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, ItalyReviewed by:
Tino Prell, University Hospital Jena, GermanyVittorio Rispoli, University Hospital of Modena, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Fei, Wang, Song, Cao, Gao and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yaqian Gao, NjczNTA5MzY2QHFxLmNvbQ==; Yue Hu, aHV5dWVAc3dtdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xinxing Fei
Xinxing Fei Shiqi Wang
Shiqi Wang Jiayi Song4,5
Jiayi Song4,5 Yaqian Gao
Yaqian Gao Yue Hu
Yue Hu