- 1Zhangzhou Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Zhangzhou, Fujian, China
- 2Center for Developmental Biology, School of Life Sciences, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei, Anhui, China
- 3Anhui Provincial Key Laboratory of Tumor Evolution and Intelligent Diagnosis and Treatment, Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu, Anhui, China
Innate immunity is orchestrated by an array of conserved signaling pathways and transcriptional regulators. While Forkhead box O (Foxo) has emerged as a pivotal transcription factor in regulating immune homeostasis, its interaction with chromatin remodeling machinery remains poorly defined. Here, we identify the chromatin remodeler Mi-2 as a crucial component of the Drosophila antibacterial immune defense. Silencing of Mi-2 abrogates the induction of antimicrobial peptides in adult flies and leads to reduced host survival following systemic bacterial challenge. Co-immunoprecipitation assays demonstrate a physical interaction between endogenous Mi-2 and Foxo in the Drosophila fat body. Of interest, Foxo silencing phenocopies Mi-2 knockdown, suggesting a functional interdependence between the two factors. Mechanistically, the Mi-2/Foxo functional complex binds to the 5’ flanking region of Peptidoglycan recognition protein SC2 (PGRP-SC2), a negative regulator of the immune deficiency (IMD) signaling pathway, to prevent PGRP-SC2 expression. Genetic epistasis experiments support a hierarchical relationship, with PGRP-SC2 acting downstream of Mi-2/Foxo. Collectively, our findings uncover a previously uncharacterized chromatin-based regulatory mechanism whereby Mi-2 collaborates with Foxo to mediate the antibacterial immune response in Drosophila.
1 Introduction
Innate immunity serves as the first line of the host defense against invading pathogens across metazoan species (1–4). In recent decades, Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly) has been extensively utilized as a powerful animal model for dissecting the molecular mechanisms of innate immunity due to its clear genetic tractability, short life cycle, and the evolutionary conservation of key immune pathways (5, 6). Insights gained from Drosophila studies have significantly advanced our understanding of how innate immune responses are precisely regulated. In Drosophila, two major signaling pathways govern the host systemic immune response: the Toll and the immune deficiency (IMD) signaling pathways (5, 7–9). The activation of these pathways leads to the induction of a repertoire of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), which are primarily synthesized in the fat body, the fly analog of the mammalian liver. These AMPs serve as potent immune effectors that target microbial membranes, thereby directly limiting pathogen proliferation (5, 7, 10–12).
The regulation of AMP gene expression has been extensively investigated at the level of signaling cascade and transcription factor activity (9, 11). The Toll and IMD signaling pathways initiate distinct but partially overlapping immune responses (9, 13, 14). The Toll pathway is primarily activated upon recognition of lysine-type peptidoglycans (PGNs) and fungal β-glucans by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as Peptidoglycan recognition protein SA (PGRP-SA), Gram-negative bacteria binding protein 1 (GNBP1), and Peptidoglycan recognition protein SD (PGRP-SD) (15–17). This triggers a proteolytic cascade that cleaves and activates the cytokine-like molecule Spätzle (Spz), which in turn binds and activates the Toll receptor. Upon Toll activation, the adaptor proteins Myeloid differentiation factor 88 (Myd88), Tube (Tub), and the kinase Pelle (Pll) are recruited, leading to the degradation of the inhibitor Cactus (Cact) and the subsequent nuclear translocation of nucleic factor kappa B (NF-κB) transcription factors Dorsal (Dl) and Dorsal-related immunity factor (Dif). These transcription factors drive the expression of Toll-dependent AMP genes such as Drosomycin (Drs) and Metchnikowin (Mtk) (9, 18–21).
In contrast, the IMD signaling pathway is primarily activated upon detection of meso-diaminopimelic acid-type PGNs, which are characteristic of Gram-negative bacteria and some types of Gram-positive bacteria. This recognition is mediated by membrane-bound PRRs such as Peptidoglycan recognition protein LC (PGRP-LC) and intracellular receptors like Peptidoglycan recognition protein LE (PGRP-LE) (22–25). Activation of the IMD pathway results in recruitment of the adaptor protein Imd, the Fas-associated death domain (Fadd), and the caspase death related ced-3/Nedd2-like caspase (Dredd). This leads to a relatively complicated but fine-tuned signal transduction reaction by a series of modulators, and finally the cleavage and activation of the NF-κB transcription factor Relish (Rel), which enters the cell nucleus to promote transcription of IMD-dependent AMPs, including Attacin (Att), Cecropin (Cec), and Diptericin (Dpt) (9, 26–28).
Beyond canonical signaling, a growing body of evidence highlights the importance of chromatin dynamics and epigenetic mechanisms in controlling the accessibility and responsiveness of immune gene loci. These include histone modifications, nucleosome remodeling, and interactions with non-coding RNAs, all of which modulate the transcriptional landscape in response to infection (29–34). Chromatin remodeling proteins, such as members of the SWItch/sucrose nonfermentable (SWI/SNF) complex, the nucleosome remodeling and deacetylase (NuRD) complex, and the imitation switch (ISWI) complex, have emerged as pivotal regulators of transcriptional plasticity in development, differentiation, and immunity (35–40). Among these, Mi-2 is a central ATPase subunit of the NuRD complex, which coordinates ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling with histone deacetylation to mediate gene repression (41–44). In Drosophila, Mi-2 has been shown to regulate embryogenesis, neuronal development and stem cell proliferation (45–48), but its role in the host immune response remains poorly characterized.
Forkhead box O (Foxo) transcription factors act as central hubs in integrating environmental cues such as nutrient status, oxidative stress, and infection (49–52). In Drosophila, Foxo translocates into the cell nucleus under low insulin or stress conditions and regulates the expression of genes involved in autophagy, metabolism, longevity, and immunity (53–58). Notably, Foxo has been implicated in modulating basal immune tone, maintaining gut epithelial homeostasis, and limiting systemic inflammation (56, 59). However, transcriptional activation and repression by Foxo require cooperation with chromatin-modifying enzymes and remodeling complexes, which remain largely undefined in immune contexts.
In this study, we investigate the functional relationship between Mi-2 and Foxo in the context of antibacterial immune defense in Drosophila. Through a combination of genetic manipulation and transcriptional profiling, we demonstrate that Mi-2 is indispensable for AMP gene induction and host survival following bacterial infection. We further show that Mi-2 physically associates with Foxo and that together, they repress the expression of Peptidoglycan recognition protein SC2 (PGRP-SC2), a negative regulator of the IMD signaling pathway (59–63). Our findings reveal a novel chromatin-based mechanism through which Mi-2 and Foxo coordinate transcriptional responses to bacterial infection and provide new insights into the integration of chromatin remodeling and immune gene regulation.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Drosophila strains and husbandry
Flies were raised on the standard Drosophila medium (6.65% cornmeal, 7.15% dextrose, 5% yeast, 0.66% agar, 2.2% nipagin, and 3.4 mL/L propionic acid) at 25°C with 60% relative humidity under a 12 h/12 h light-dark cycle. To generate specific gene silencing at the adult stage using Gal4/Gal80ts system, crossings were first performed at 18°C. After eclosion, progenies were shifted to 29°C for 7 d. The following fly strains were purchased from public Drosophila stock centers: Mi-2 RNAi #1 (Vienna Drosophila RNAi Center, #107204), Mi-2 RNAi #2 (Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center, #51774), Foxo RNAi #1 (Vienna Drosophila RNAi Center, #106097), Foxo RNAi #2 (Vienna Drosophila RNAi Center, #107786), and PGRP-SC2 RNAi (Vienna Drosophila RNAi Center, #104578). The lpp-Gal4, tub-Gal80ts, GFP RNAi, and w1118 flies were described previously (64–67).
2.2 Antibodies
The following primary antibodies were used in this study: mouse anti-β-Tubulin (1:3000, Cowin, Cat#CW0098M), mouse anti-Flag (1:2000, Merck, Cat#F3165), rabbit anti-Flag (1:1000, Merck, Cat#F7425), rabbit anti-Myc (1:3000, Medical & Biological Laboratories, Cat#562), rabbit anti-PGRP-SC2 (1:1000, MyBioSource, Cat#MBS9013948), rabbit anti-Foxo (1:1000, Abcam, Cat#ab195977), and rat anti-Mi-2 (1:1000, Thermo Fisher, Cat#61463). The secondary antibodies used in this study include goat anti-mouse IgG H & L (1:5000, Abcam, Cat#ab150078), goat anti-rabbit IgG H & L (1:5000, Abcam, Cat#ab6789), and goat anti-rat IgG H & L (1:5000, Abcam, Cat#ab182018).
2.3 Bacterial infection, fly survival, and bacterial burden assays
Bacterial cultures were grown overnight at 30°C. Cultures were then pelleted and resuspended in sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution until the OD600 reached around 1. Male adult flies (3-d-old) were anesthetized with carbon dioxide on a flypad and injected with bacteria (4.6 nL) by using a tungsten nanoinjector. Subsequently, flies were carefully transferred into fresh vials (around 50 individuals per vial). Control flies were injected with the same volume of PBS solution. The detailed information of Pectobacterium carotovorum carotovorum 15 (Ecc15), Serratia marcescens (S. marcescens), and Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis) was described previously (68, 69).
For fly survival analysis, infected flies were scored for daily mortality. Flies (< 5%) that died within 2 h post-injection were not considered. Survival data were collected from 3 biological replicates and shown as means plus standard errors.
For bacterial burden assays, flies (10 individuals for each sample) were homogenized in sterile PBS buffer, followed by serial dilutions, and finally, 100 μL of each diluent was spread on a Luria Bertani (LB) agar plate. All LB plates were further incubated at 30°C for 24 h. Flies that were collected immediately after bacterial injection were put in the 0-d group. The number of bacterial colonies was counted, and data were pooled from 21 independent biological replicates.
2.4 RT-qPCR
Reverse transcription plus quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) experiments were performed according to a previously described protocol (70). In brief, total RNA was extracted from dissected fat body tissues or whole flies using TRIzol reagent (Thermo Fisher, Cat#15596026). cDNA synthesis was performed using the TransScript All-in-one First-Strand cDNA Synthesis SuperMix kit (TransGen, Cat#AT341-01). Quantitative PCR was carried out using the SYBR Green One-Step kit (TransGen, Cat#AQ211-01) on a Light Cycler 480, in which RpL32 was used as an endogenous control. Relative fold changes were calculated using the ΔΔCt method. Data were collected from 5 independent biological replicates. The detailed information of gene-specific primers used in RT-qPCR is shown in Supplementary Table S1.
2.5 Western blotting
Whole flies or dissected fat body tissues were lysed in lysis buffer (150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH = 7.5, 10% glycerol, 0.5% Triton X-100, and 1 mM PMSF). Samples were centrifuged at 13,000 rpm at 4°C for 30 min. The supernatant was collected and resolved on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and probed with primary antibodies at 4°C overnight. After incubation with secondary antibodies for 1 h at room temperature, the membrane was subjected to Western blot assay by using the enhanced chemiluminescence substrate.
2.6 Co-IP
S2 cells were cultured in the insect medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and transfected with indicated expression plasmids. After 48 h, cells were lysed in lysis buffer (150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH = 7.5, 10% glycerol, 0.5% Triton X-100, and 1 mM PMSF). For in vivo samples, the fat body tissues were dissected from w1118 flies, and lysates were prepared as described above. After centrifugation (12,000 rpm) at 4°C for 10 min, 1/10 of the supernatant was collected as the “Input” sample. The remaining supernatant was incubated with indicated antibodies and agarose beads for immunoprecipitation at 4°C overnight. Samples were then washed with wash buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH = 7.5, 500 mM NaCl, 0.5% Triton X-100, and 10% glycerol) at 4°C for 3 times (1 h in total), followed by Western blot experiments. Twenty percent of the immunoprecipitant (IP) was used for the detection of immunoprecipitation efficiency, whereas eighty percent was used for co-IP examination.
2.7 Identification of Mi-2 interactome via IP-LC-MS/MS
The immunoprecipitation and liquid chromatography plus tandem mass spectrometry (IP-LC-MS/MS) was performed as described previously (71). Briefly, Drosophila S2 cells were transfected with Flag-Mi-2 expression plasmids, and immunoprecipitation was performed as described above. Flag-GFP was expressed in the control group. After immunoprecipitation, samples were washed with wash buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH = 7.5, 500 mM NaCl, 0.5% Triton X-100, and 10% glycerol) at 4°C for 3 times (1 h in total), followed by incubation with Flag peptide at 4°C for 30 min. After centrifugation (12,000 rpm) at 4°C for 2 min, the supernatant was transferred into a fresh Eppendorf tube, followed by digestion with Trypsin (Thermo Fisher, Cat#90057) at 37°C for 30 min. Samples were then desalted using the Pierce™ C-18 spin column (Thermo Fisher, Cat#89870) and subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis to identify the interactome of Mi-2. The LC-MS/MS data were processed using the Thermo Proteome Discovery (version 1.4.1.14) and searched against the UniProt-Drosophila database. The raw data is available online (https://data.mendeley.com/preview/3xshb9x6w4?a=53354993-4775-4d61-b454-bf123a85bf89).
2.8 ChIP-qPCR
The chromatin immunoprecipitation plus quantitative polymerase chain reaction (ChIP-qPCR) experiments were carried out according to protocols published previously (72). In detail, fat bodies were dissected from 100 adult male flies and incubated in 10 mL ice-cold swelling buffer (0.1 M Tris-HCl, pH = 7.5, 10 mM KOAc, 15 mM MgOAc, 1% NP-40, and 1 mM PMSF). Samples were homogenized for 2 min using a loose-fitting Dounce homogenizer, fixed with 1% formaldehyde for 10 min, and quenched with 125 mM glycine to stop fixation. After centrifugation at 1000 g for 5 min at 4°C, the pellet was resuspended in 10 mL fresh swelling buffer and filtered through 70 μm and 40 μm cell strainers, respectively. Samples were centrifuged at 1000 g for 5 min to obtain the nuclear pellet, followed by nuclear lysate preparation by using lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH = 7.5, 10 mM EDTA, 1% SDS, 1 mM DTT, and 1 mM PMSF). Samples were then sonicated for 30 min at 4°C. Immunoprecipitation was performed using anti-Mi-2 or anti-Foxo antibodies. Enrichment at different regions of PGRP-SC2 was assessed by qPCR using specific primers (Supplementary Table S1).
2.9 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using GraphPad Prism (version 10.1.2.324). The one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test was applied where appropriate. Survival curves were compared using the Log-Rank test. The P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, not significant.
3 Results
3.1 Drosophila Mi-2 is essential for the induction of antimicrobial peptides in response to bacterial infection
The loss-of-function mutant flies of Mi-2 are not viable due to severe defects in early embryonic development (47, 73). To assess the potential involvement of Mi-2 in the Drosophila innate immune response, we silenced Mi-2 specifically in the fat body using the Gal4/UAS system (lpp-Gal4 driver). In addition, we utilized the tub-Gal80ts strain to drive Mi-2 silencing (referred to as lppts>Mi-2 RNAi #1 and lppts>Mi-2 RNAi #2) at the adult stage (Figure 1A). Western blot experiments confirmed the knockdown efficiency of the two different Mi-2 RNAi lines in the Drosophila fat body (Figure 1B). We further challenged these flies and the age-paired controls (lppts>GFP RNAi) with Pectobacterium carotovorum carotovorum 15 (Ecc15). Ecc15 is one type of Gram-negative bacterial pathogens activating the immune deficiency (IMD) pathway in Drosophila (74). Quantitative reverse transcription plus polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analyses revealed that the induction of AMPs downstream of IMD signaling, including Attacin A (AttA), Cecropin A1 (CecA1), and Diptericin (Dpt), was impaired in Mi-2 knockdown flies compared to those in controls (Figures 1C–E). These data indicate that Mi-2 is required for robust AMP gene expression in response to bacterial infection. Consistently, we observed decreased transcript levels of AttA, CecA1, and Dpt in Mi-2 RNAi flies when we used Serratia marcescens (S. marcescens), another type of Gram-negative bacterial pathogens, for infection treatment (Figures 1F-H).
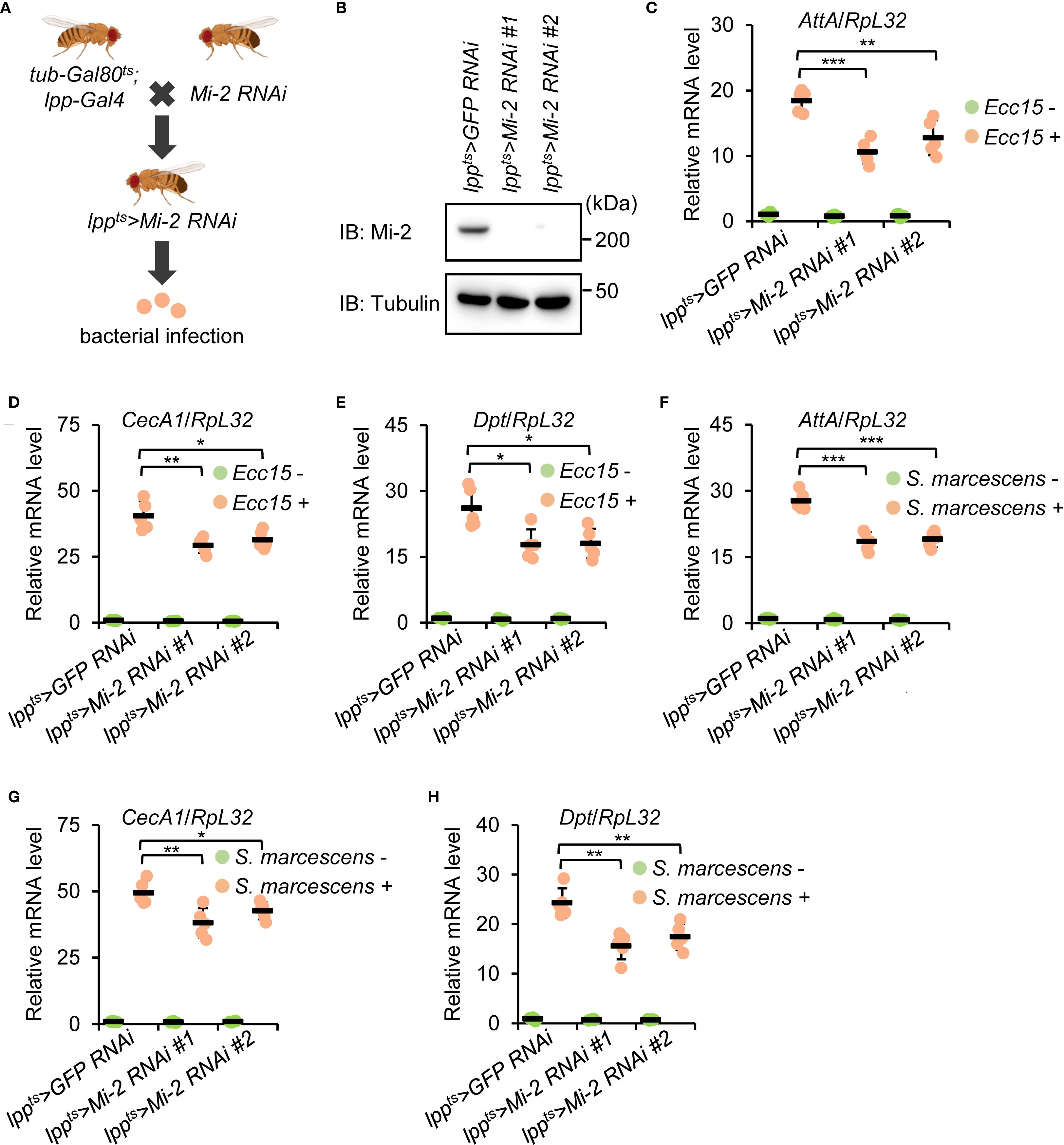
Figure 1. Drosophila Mi-2 is required for AMP induction following bacterial infection. (A) The diagram showing genetic manipulations to obtain flies with the fat body-specific silencing of Mi-2. (B) Western blot monitoring Mi-2 protein levels in the fat body dissected from control and Mi-2 RNAi flies. Tubulin was used as the loading control. (C-E) Adult flies, including lppts>GFP RNAi (control), lppts>Mi-2 RNAi #1, and lppts>Mi-2 RNAi #2, were infected with Ecc15, followed by RT-qPCR assays to examine the transcript levels of AttA (C), CecA1 (D), and Dpt (E). (F-H) Similar RT-qPCR experiments were performed as in C-E, except that S. marcescens were used for infection. In C-H, data were collected from 5 independent replicates and shown as means plus standard errors. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
3.2 Silencing of Mi-2 compromises the Drosophila survival and bacterial clearance activity
To determine the physiological relevance of Mi-2 in the Drosophila antibacterial immune defense, we performed survival assays following bacterial infections. Mi-2 knockdown flies exhibited a reduction in survival compared to controls after Ecc15 injection while they survived in a similar way after the injection of sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution (Figures 2A, B). The median survival time of Mi-2 RNAi flies after Ecc15 injection was decreased by more than 50% (Figure 2C). A similar trend was observed for S. marcescens injection, where Mi-2-silenced flies showed a median survival of 2.3 d, compared to 5.7 d in controls (Figures 2D, E).
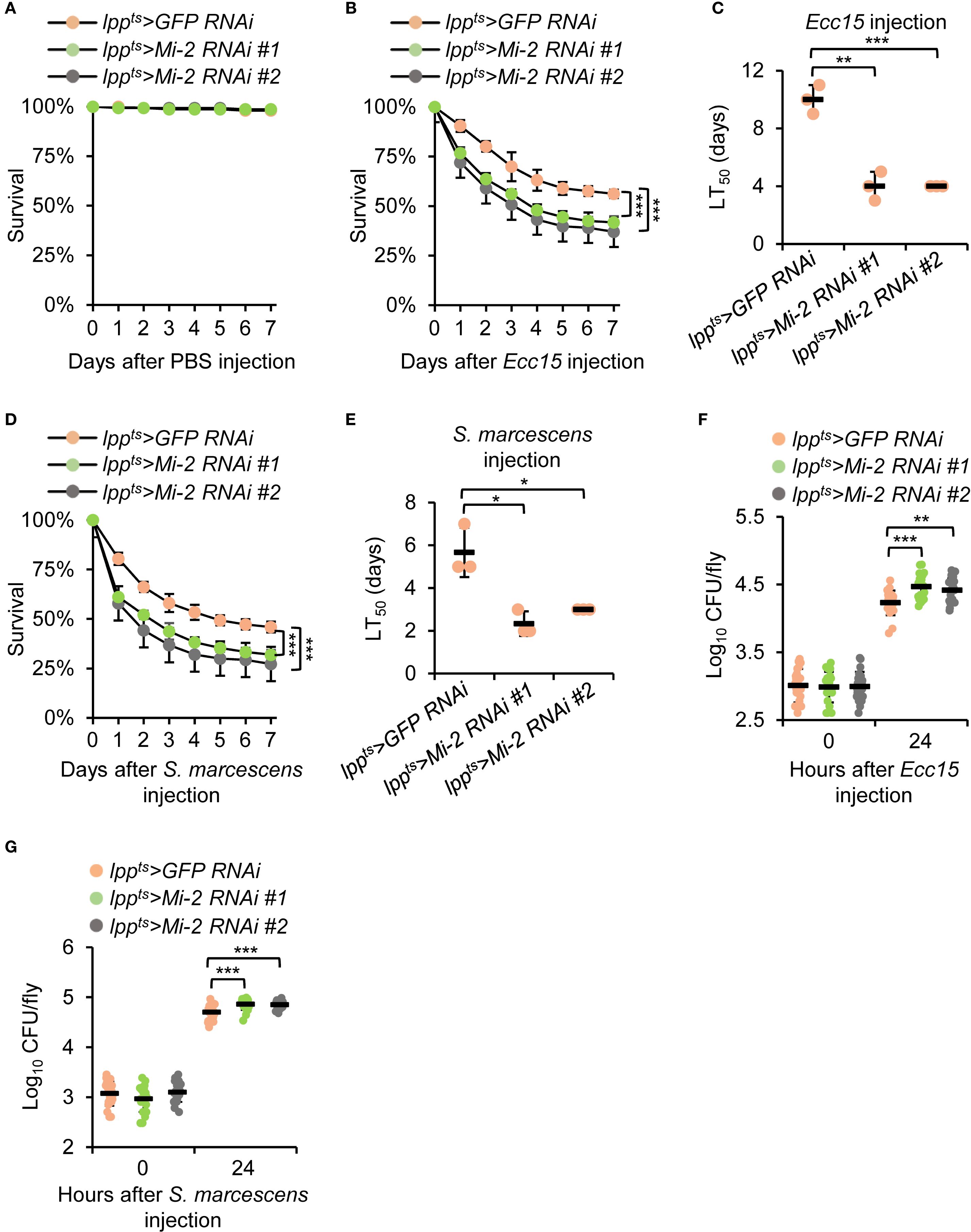
Figure 2. Mi-2 is essential for the Drosophila defense against bacterial challenge. (A-C) Survival curves of Mi-2 RNAi and control flies after the injection of PBS (A) or Ecc15 (B). The number of flies is as follows. In A, lppts>GFP RNAi: 50, 48, 50; lppts>Mi-2 RNAi #1: 49, 49, 50; lppts>Mi-2 RNAi #2: 50, 50, 49. In B, lppts>GFP RNAi: 50, 48, 48; lppts>Mi-2 RNAi #1: 49, 49, 48; lppts>Mi-2 RNAi #2: 49, 47, 50. The time points when half of the experimental flies (B) died (referred to as LT50) are shown in (C–E) Survival assays were performed as in A-C, except that S. marcescens were used for injection. In (D), the number of flies is as follows. lppts>GFP RNAi: 49, 50, 49; lppts>Mi-2 RNAi #1: 48, 49, 50; lppts>Mi-2 RNAi #2: 48, 48, 48. (F, G) Bacterial load (CFU per fly) at 24 h post-infection with Ecc15 (F) or S. marcescens (G). In (A-E), data were collected from 3 independent replicates and shown as means plus standard errors. In (F, G), data were pooled from 21 independent replicates. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
To assess the fly efficiency of bacterial clearance, we measured colony-forming units (CFUs) in whole-fly homogenates at 24 h post-infection of Ecc15 or S. marcescens. Mi-2 knockdown flies displayed higher bacterial loads than control flies (Figures 2F, G). These findings demonstrate that Mi-2 is essential for Drosophila survival and effective bacterial elimination upon infection.
3.3 Mi-2 is dispensable for mediating the Drosophila Toll antibacterial immune defense
To determine whether Drosophila Mi-2 is also involved in the Toll pathway-mediated immune response, we assessed the expression of Toll-dependent AMPs and host survival following Gram-positive bacterial infection. Adult flies with fat body-specific Mi-2 knockdown were challenged with Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis), a bacterial pathogen known to activate the Toll signaling pathway in Drosophila (74). RT-qPCR analyses revealed no significant differences in the E. faecalis-driven induction of Drosomycin (Drs) and Metchnikowin (Mtk) between Mi-2 RNAi and control flies (Supplementary Figures S1A, B). Consistently, survival assays showed that Mi-2 knockdown flies exhibited comparable resistance to E. faecalis infection as control flies (Supplementary Figure S1C). Bacterial burden analyses displayed similar E. faecalis proliferation levels between Mi-2 RNAi and control flies (Supplementary Figure S1D). These results collectively indicate that Mi-2 is not required for the Toll-mediated antimicrobial response, and its function in Drosophila innate immunity is specific to the IMD pathway.
3.4 Mi-2 physically interacts with Foxo
We explored the molecular mechanism by which Mi-2 modulates the Drosophila IMD antibacterial immune defense. For this, we transfected cultured Drosophila S2 cells with plasmids expressing Flag-tagged Mi-2. By performing immunoprecipitation and liquid chromatography plus tandem mass spectrometry (IP-LC-MS/MS) experiments (Figure 3A), we identified 28 proteins/peptides that potentially interact with Mi-2 (Figure 3B, Supplementary Table S2). Gene ontology (GO) analyses of these Mi-2-associated candidates revealed that they predominantly belonged to categories, including signaling homeostasis, cell communication, and sleep (Figure 3C). Intriguingly, we noted one candidate, Forkhead box O (Foxo), which was previously reported to physically associate with Mi-2 (75). Given that Drosophila Foxo has been implicated in regulating immune gene expression (59, 76, 77) and that chromatin remodeling complexes often interact with sequence-specific transcription factors, we hypothesized that Mi-2 may form a functional complex with Foxo for immune regulation in Drosophila. To test this idea, we co-transfected Drosophila S2 cells with Flag-tagged Mi-2 and Myc-tagged Foxo constructs and performed co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) assays. Foxo was specifically pulled down by anti-Flag beads only in the presence of Mi-2 (Figure 3D), confirming their physical interaction. To explore whether Mi-2 forms a functional complex with Foxo in vivo, we dissected the Drosophila fat body tissue for co-IP experiments using anti-Mi-2 antibodies. Our results indicated that the endogenous Mi-2 and Foxo associate with each other in the Drosophila fat body (Figure 3E).
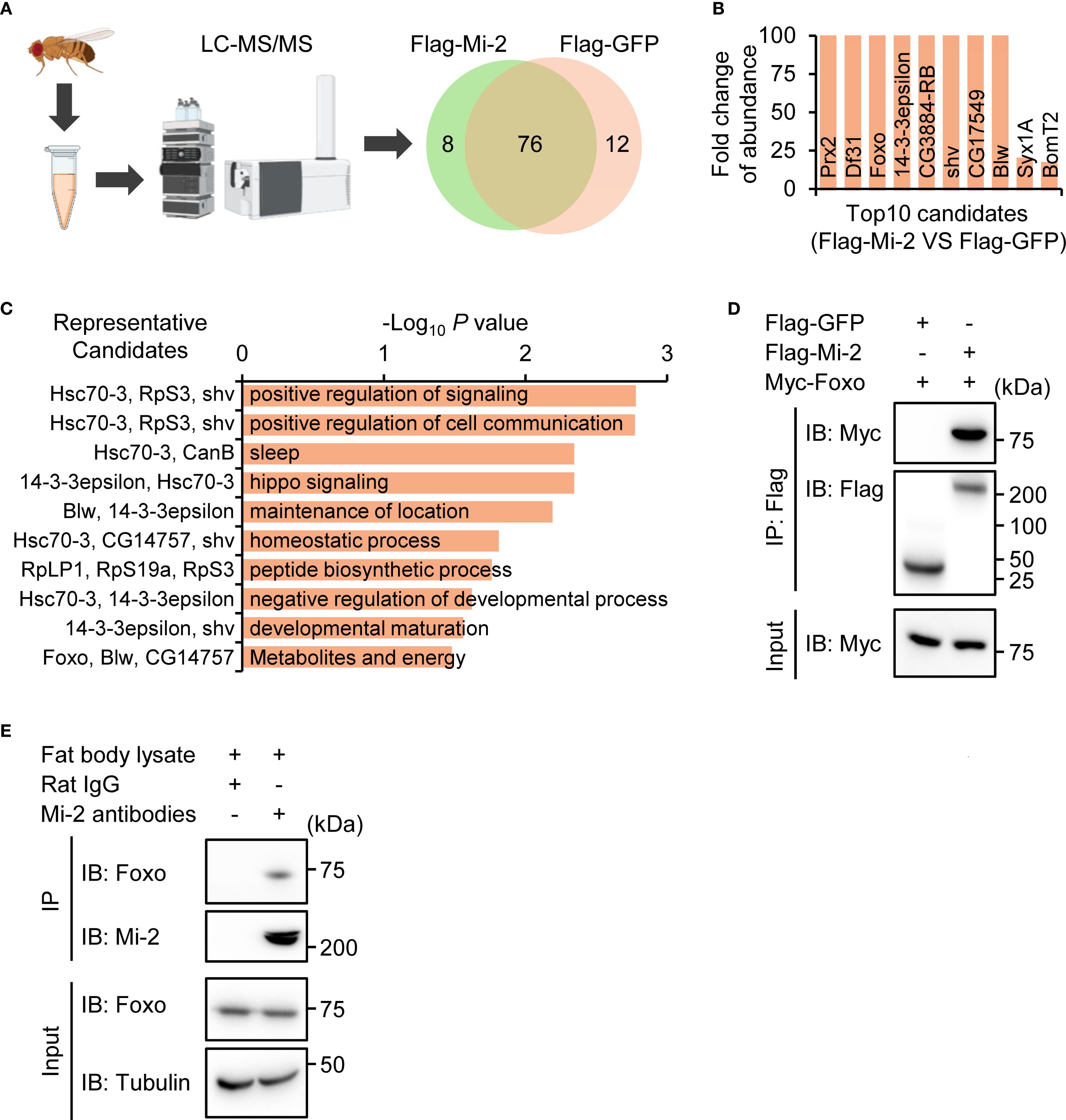
Figure 3. Mi-2 physically interacts with Foxo. (A) Schematic of IP-LC-MS/MS to identify potential Mi-2 interacting protein candidates. (B) The top 10 candidates of the Mi-2 interactome. (C) GO analysis of the Mi-2 interactome. (D) Co-IP from S2 cells expressing Flag-Mi-2 and Myc-Foxo. Input and IP blots are shown for Flag or Myc. (E) The fat body tissues were dissected from w1118 flies, followed by co-IP assays using anti-Mi-2 antibodies. Rat IgG was used in the control sample.
3.5 Foxo RNAi phenocopies Mi-2 RNAi in regulating Drosophila innate immunity
To determine whether Foxo functions in the same genetic pathway as Mi-2, we first performed Foxo knockdown using the Gal4/UAS system as described above (Figure 4A). We next analyzed the immune response of these flies upon bacterial infection. Similar to Mi-2 RNAi flies, Foxo-silenced flies showed reduced expressions of AttA, CecA1, and Dpt following Ecc15 injection (Figures 4B–D). Furthermore, Foxo knockdown flies exhibited heightened susceptibility to Ecc15 infection, with median survival reduced by around 6 d (Figures 4E–G). Of note, the Ecc15 burden in Foxo RNAi flies was increased by more than 50%, compared to that of control flies (Figure 4H). These results suggest that Mi-2 and Foxo function cooperatively to regulate the antibacterial immune response in Drosophila.
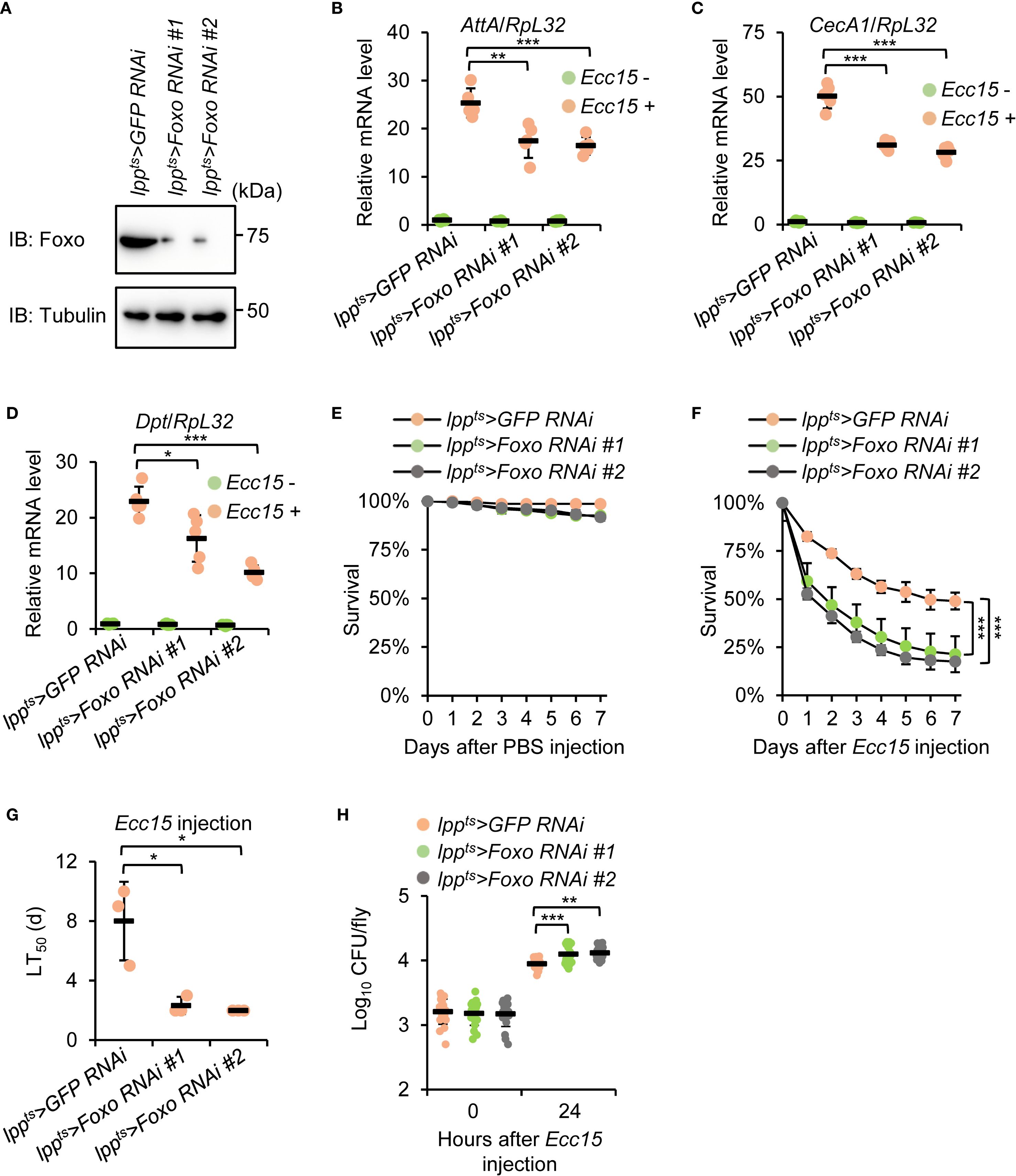
Figure 4. Foxo knockdown phenocopies Mi-2 depletion in the Drosophila antibacterial immune defense. (A) Western blots showing the knockdown efficiency of different Foxo RNAi strains. Tubulin was used as the loading control. (B-D) RT-qPCR of AMP genes in fat body-specific Foxo RNAi flies after Ecc15 infection. (E-G) Survival assays of Foxo RNAi and control flies after Ecc15 challenge. The number of flies is as follows. In E, lppts>GFP RNAi: 50, 48, 49; lppts>Foxo RNAi #1: 50, 49, 50; lppts>Foxo RNAi #2: 49, 49, 49. In F, lppts>GFP RNAi: 49, 50, 50; lppts>Foxo RNAi #1: 48, 48, 49; lppts>Foxo RNAi #2: 50, 48, 50. The time points when half of the experimental flies (F) died (LT50) were shown in (G, H) Bacterial load assays at 24 h after Ecc15 infection. In (B–D), data were collected from 5 independent replicates and shown as means plus standard errors. In (E–G), data were collected from 3 independent replicates. In (H), data were pooled from 21 independent replicates. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
3.6 Mi-2 and Foxo suppress PGRP-SC2 expression in the Drosophila fat body
Previous studies have demonstrated that Foxo prevents the expression of Peptidoglycan recognition protein SC2 (PGRP-SC2), which encodes a typical amidase that downregulates IMD signaling (59–63). We therefore proposed a working model in which Mi-2 forms a functional complex with Foxo to antagonize the expression of PGRP-SC2, thereby maintaining a robust transactivation of IMD signaling upon bacterial infection (Figure 5A). To test our proposal, we performed both RT-qPCR and Western blot experiments. As illustrated in Figures 5B, C, PGRP-SC2 expression was elevated in both Mi-2 RNAi and Foxo RNAi flies. We further carried out chromatin immunoprecipitation plus quantitative polymerase chain reaction (ChIP-qPCR) assays and found that both Mi-2 and Foxo were enriched at the 5’ flanking region of PGRP-SC2 (Figure 5D), suggesting a direct transcriptional repression of PGRP-SC2 by the Mi-2/Foxo complex.
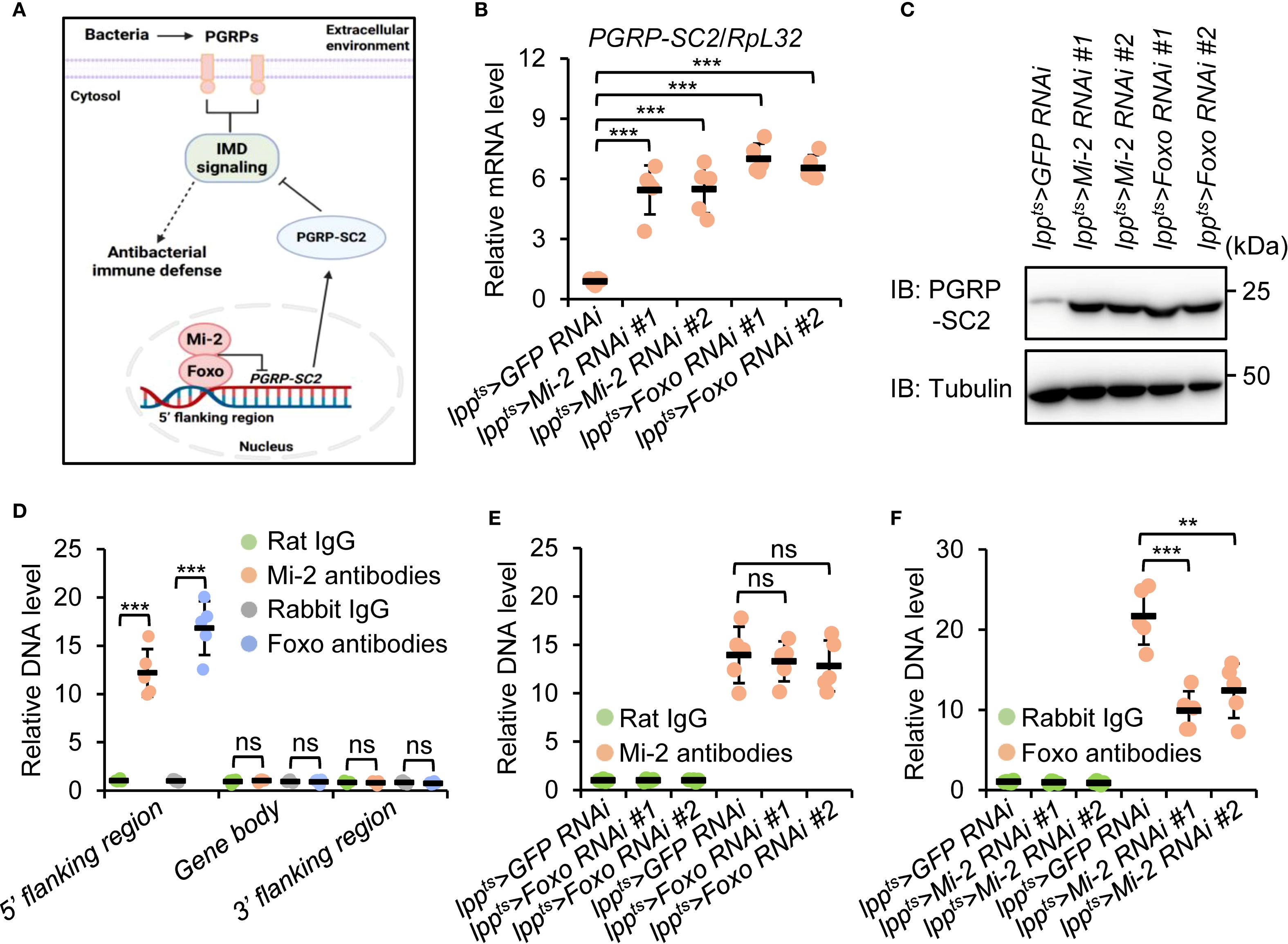
Figure 5. Mi-2 and Foxo antagonize PGRP-SC2 expression in the Drosophila fat body. (A) The diagram illustrating a working model in which Drosophila Mi-2 forms a functional complex with Foxo and prevents the expression of PGRP-SC2, thereby ensuring a robust immune response upon bacterial challenge. (B, C) RT-qPCR (B) and Western blot (C) assays validating the expression levels of PGRP-SC2 in the fat body dissected from indicated flies. (D-F) ChIP-qPCR experiments showing the enrichment of Mi-2 and Foxo at different regions of PGRP-SC2. In (B, D–F), data were collected from 5 independent replicates and shown as means plus standard errors. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant.
To illustrate how Mi-2/Foxo bind to the 5’ flanking region of PGRP-SC2, we performed ChIP-qPCR assays in either Mi-2 RNAi or Foxo RNAi flies. Silencing of Foxo didn’t affect the binding of Mi-2 to the PGRP-SC2 5’ flanking region (Figure 5E). However, knockdown of Mi-2 prevented the existence of Foxo at the PGRP-SC2 5’ flanking region (Figure 5E). Taken together, our data indicate that Foxo binds to the 5’ flanking region of PGRP-SC2 and represses PGRP-SC2 expression in a Mi-2-dependent manner.
3.7 Genetic epistasis places PGRP-SC2 downstream of Mi-2/Foxo
To functionally validate the role of PGRP-SC2 as a downstream target of the Mi-2/Foxo complex, we performed genetic interaction experiments. Double knockdown of Mi-2 and PGRP-SC2 rescued AMP expression and fly survival compared to Mi-2 knockdown alone (Figures 6A–E, S2A). Bacterial load was also markedly reduced in double knockdown flies (Figure 6F). In addition, similar results were obtained by using Foxo and PGRP-SC2 double RNAi flies (Figures 6A–F and S2B). These results support a model wherein Mi-2 and Foxo cooperatively repress PGRP-SC2 to promote effective immune activation in the fly defense against bacterial infection.
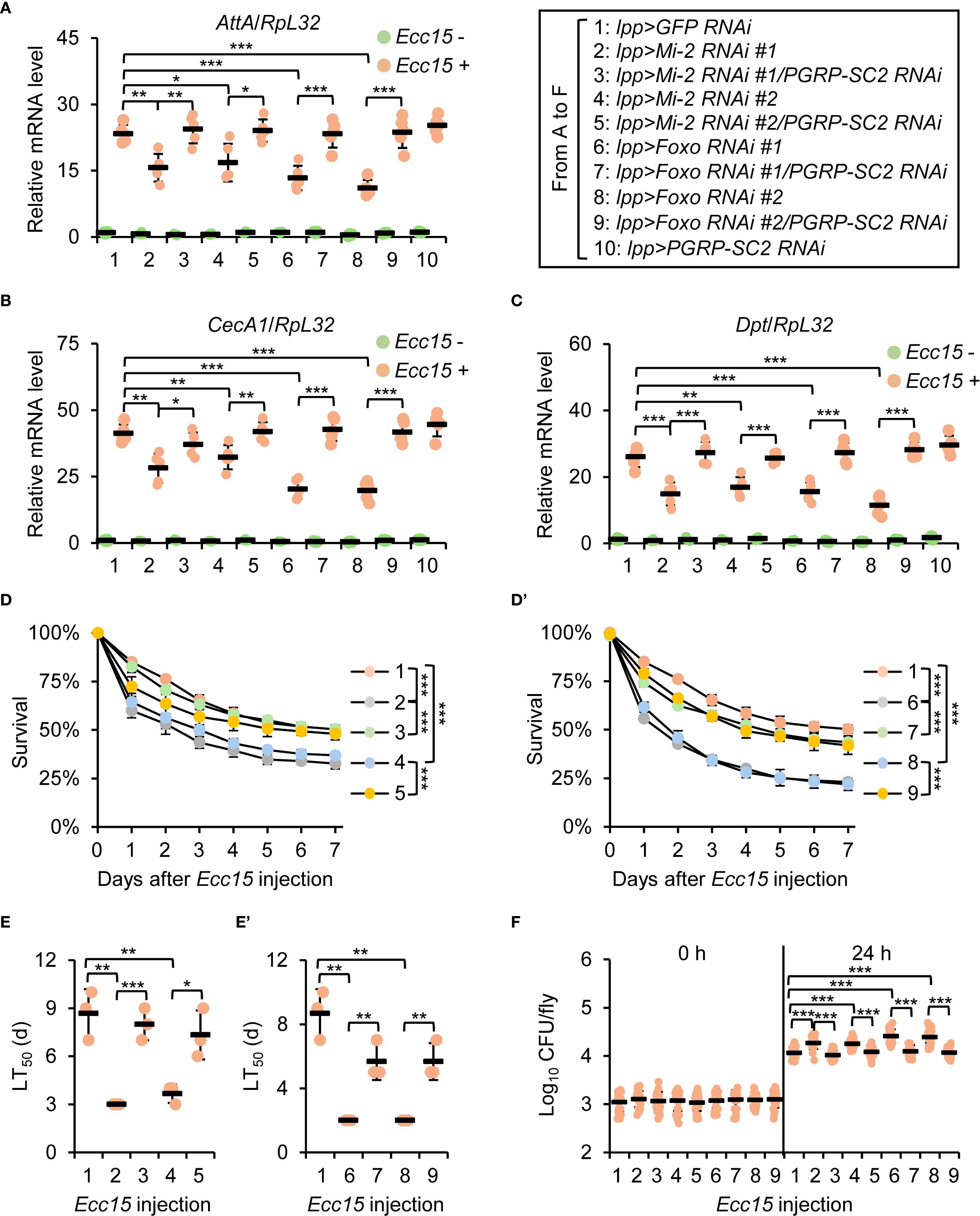
Figure 6. Genetic interaction between Mi-2/Foxo and PGRP-SC2. (A-C) RT-qPCR of AMPs in double knockdown of Mi-2;PGRP-SC2 or Foxo;PGRP-SC2, compared to single knockdown. (D-E’) Survival curves comparing Mi-2 RNAi, Foxo RNAi, and double RNAi flies. The number of flies is as follows. In (D), lpp>GFP RNAi: 49, 48, 50; lpp>Mi-2 RNAi #1: 48, 50, 49; lpp>Mi-2 RNAi #1;PGRP-SC2 RNAi: 49, 50, 50; lpp>Mi-2 RNAi #2: 48, 48, 50; lpp>Mi-2 RNAi #2;PGRP-SC2 RNAi: 49, 50, 49. In D’, lpp>GFP RNAi: 49, 48, 50; lpp>Foxo RNAi #1: 50, 49, 48; lpp>Foxo RNAi #1;PGRP-SC2 RNAi: 49, 48, 50; lpp>Foxo RNAi #2: 50, 48, 49; lpp>Foxo RNAi #2;PGRP-SC2 RNAi: 50, 49, 48. The time points when half of the experimental flies (D, D’) died (LT50) are shown in (E, E’), respectively. (F) Bacterial load assays in indicated flies. In (A–C), data were collected from 5 independent replicates (10 flies for each replicate) and shown as means plus standard errors. In (D–E’), data were collected from 3 independent replicates. In (F), data were pooled from 21 independent replicates (10 flies for each replicate). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
4 Discussion
This study identifies a previously unrecognized function of the chromatin remodeler Mi-2 in the innate immune defense of Drosophila melanogaster and establishes a mechanistic partnership with the transcription factor Foxo. Our results provide compelling evidence that Mi-2 is indispensable for the effective induction of AMPs and protection against bacterial infection in Drosophila. Moreover, the discovery of physical interaction between Mi-2 and Foxo advances our understanding of chromatin-level regulation of immune responses.
A central finding of this work is the convergence of chromatin remodeling and transcription factor signaling at the level of immune regulation. Foxo, a key effector of insulin signaling and stress responses, has been shown to regulate subsets of AMPs and immune-related genes (59, 76, 77). However, its broader regulatory potential in host defense is constrained by chromatin architecture. Mi-2, as part of the NuRD complex, remodels nucleosomes and contributes to both gene repression and activation depending on context (41–44). Our data show that Mi-2 is necessary for Foxo to suppress the expression of PGRP-SC2, which encodes a negative regulator of the IMD signaling pathway (59–63). This suggests that chromatin accessibility and histone deacetylation events mediated by Mi-2 are required for the repressive function of Foxo. Our follow-up projects would be focusing on exploring the mechanistic details of how Mi-2 influences Foxo recruitment to the 5’ flanking region of PGRP-SC2, for instance the potential changes in chromatin accessibility (via ATAC-seq), the status of histone modifications (via H3K9me3 and/or H3K27ac ChIP assays), and the post-translational modifications or localization dynamics of Foxo. These are indeed important and relevant avenues of investigations that could help elucidate the molecular basis of the Mi-2/Foxo regulatory axis.
The rescue of AMP expression and survival in Mi-2 or Foxo knockdown flies by co-silencing of PGRP-SC2 highlights the regulatory hierarchy in this axis. This genetic interaction provides not only functional validation of PGRP-SC2 as a downstream effector but also situates Mi-2/Foxo as key upstream regulators that fine-tune immune sensitivity. The functional importance of this repression in flies is particularly evident during infection, where an optimal level of immune activation is crucial. The repression of IMD signaling via PGRP-SC2 could dampen AMP production (59–63). Therefore, the repression of PGRP-SC2 expression through Mi-2/Foxo action promotes rapid immune mobilization.
The implications of this work extend beyond innate immunity. Foxo is a central node in the regulation of longevity, stress resistance, and metabolism (49–52). By uncovering Mi-2 as a critical cofactor, we open new avenues for understanding how chromatin remodeling integrates environmental cues and transcriptional responses. Furthermore, since excessive immune activation or chronic inflammation underlies many age-related pathologies, elucidating Mi-2/Foxo-mediated repression mechanisms may inform strategies to modulate immune tone for therapeutic benefit. Future studies should explore the dynamic recruitment of Mi-2/Foxo to target loci upon infection, the potential involvement of additional NuRD subunits, and whether similar regulatory paradigms govern other immune genes or signaling pathways. Integration with metabolomics and epigenomics could also reveal how nutrient availability or stress conditions influence Mi-2/Foxo function and chromatin landscape in the fat body and other tissues.
In summary, we demonstrate that Mi-2 and Foxo cooperate to modulate antibacterial defense in Drosophila, in part through the repression of PGRP-SC2. This chromatin-transcription interface represents a novel regulatory layer in immune homeostasis and highlights the importance of integrating chromatin remodeling with signal-dependent gene expression programs. While this study provides compelling evidence for the functional interaction between Mi-2 and Foxo in regulating Drosophila antibacterial immunity, it primarily focuses on one downstream target, PGRP-SC2, and does not explore other potential transcriptional targets of the Mi-2/Foxo complex. Additionally, the dynamic recruitment of Mi-2 and Foxo to immune loci under varying physiological or stress conditions remains uncharacterized.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the study involving animals in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because Ethical approval is not required for Drosophila study.
Author contributions
XZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. UA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YJ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. ED: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. MU: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. QC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. SJ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the Zhangzhou Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University (PDA202402) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32100702).
Acknowledgments
We thank the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center and the Vienna Drosophila RNAi Center for the fly resources. We thank the staff members at the Omics-Laboratory of Biotechnology Centre of Anhui Agricultural University for providing technical supports in mass data collection.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1664564/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Akira S, Uematsu S, and Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. (2006) 124:783–801. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.015
2. Beutler B. Innate immunity: an overview. Mol Immunol. (2004) 40:845–59. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2003.10.005
3. Hoffmann JA, Kafatos FC, Janeway CA, and Ezekowitz RA. Phylogenetic perspectives in innate immunity. Science. (1999) 284:1313–8. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5418.1313
4. Kimbrell DA and Beutler B. The evolution and genetics of innate immunity. Nat Rev Genet. (2001) 2:256–67. doi: 10.1038/35066006
5. Lemaitre B and Hoffmann J. The host defense of Drosophila melanogaster. Annu Rev Immunol. (2007) 25:697–743. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141615
6. Sackton TB, Lazzaro BP, Schlenke TA, Evans JD, Hultmark D, and Clark AG. Dynamic evolution of the innate immune system in Drosophila. Nat Genet. (2007) 39:1461–8. doi: 10.1038/ng.2007.60
7. Hoffmann JA. The immune response of Drosophila. Nature. (2003) 426:33–8. doi: 10.1038/nature02021
8. Hultmark D. Drosophila immunity: paths and patterns. Curr Opin Immunol. (2003) 15:12–9. doi: 10.1016/S0952-7915(02)00005-5
9. Yu S, Luo F, Xu Y, Zhang Y, and Jin LH. Drosophila innate immunity involves multiple signaling pathways and coordinated communication between different tissues. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:905370. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.905370
10. Buchon N, Silverman N, and Cherry S. Immunity in Drosophila melanogaster–from microbial recognition to whole-organism physiology. Nat Rev Immunol. (2014) 14:796–810. doi: 10.1038/nri3763
11. Ferrandon D, Imler JL, Hetru C, and Hoffmann JA. The Drosophila systemic immune response: sensing and signalling during bacterial and fungal infections. Nat Rev Immunol. (2007) 7:862–74. doi: 10.1038/nri2194
12. Hanson MA and Lemaitre B. New insights on Drosophila antimicrobial peptide function in host defense and beyond. Curr Opin Immunol. (2020) 62:22–30. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2019.11.008
13. Tanji T, Hu X, Weber AN, and Ip YT. Toll and IMD pathways synergistically activate an innate immune response in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. (2007) 27:4578–88. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01814-06
14. Tanji T, Yun EY, and Ip YT. Heterodimers of NF-kappaB transcription factors DIF and Relish regulate antimicrobial peptide genes in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2010) 107:14715–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009473107
15. Bischoff V, Vignal C, Boneca IG, Michel T, Hoffmann JA, and Royet J. Function of the Drosophila pattern-recognition receptor PGRP-SD in the detection of Gram-positive bacteria. Nat Immunol. (2004) 5:1175–80. doi: 10.1038/ni1123
16. Gobert V, Gottar M, Matskevich AA, Rutschmann S, Royet J, Belvin M, et al. Dual activation of the Drosophila toll pathway by two pattern recognition receptors. Science. (2003) 302:2126–30. doi: 10.1126/science.1085432
17. Michel T, Reichhart JM, Hoffmann JA, and Royet J. Drosophila Toll is activated by Gram-positive bacteria through a circulating peptidoglycan recognition protein. Nature. (2001) 414:756–9. doi: 10.1038/414756a
18. Hetru C and Hoffmann JA. NF-kappaB in the immune response of Drosophila. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2009) 1:a000232. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000232
19. Kurata S. Peptidoglycan recognition proteins in Drosophila immunity. Dev Comp Immunol. (2014) 42:36–41. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2013.06.006
20. Valanne S, Vesala L, Maasdorp MK, Salminen TS, and Ramet M. The Drosophila Toll pathway in innate immunity: from the core pathway toward effector functions. J Immunol. (2022) 209:1817–25. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200476
21. Valanne S, Wang JH, and Ramet M. The Drosophila Toll signaling pathway. J Immunol. (2011) 186:649–56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002302
22. Choe KM, Werner T, Stoven S, Hultmark D, and Anderson KV. Requirement for a peptidoglycan recognition protein (PGRP) in Relish activation and antibacterial immune responses in Drosophila. Science. (2002) 296:359–62. doi: 10.1126/science.1070216
23. Gottar M, Gobert V, Michel T, Belvin M, Duyk G, Hoffmann JA, et al. The Drosophila immune response against Gram-negative bacteria is mediated by a peptidoglycan recognition protein. Nature. (2002) 416:640–4. doi: 10.1038/nature734
24. Ramet M, Manfruelli P, Pearson A, Mathey-Prevot B, and Ezekowitz RA. Functional genomic analysis of phagocytosis and identification of a Drosophila receptor for E. coli. Nature. (2002) 416:644–8. doi: 10.1038/nature735
25. Takehana A, Katsuyama T, Yano T, Oshima Y, Takada H, Aigaki T, et al. Overexpression of a pattern-recognition receptor, peptidoglycan-recognition protein-LE, activates imd/relish-mediated antibacterial defense and the prophenoloxidase cascade in Drosophila larvae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2002) 99:13705–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.212301199
26. Kleino A and Silverman N. The Drosophila IMD pathway in the activation of the humoral immune response. Dev Comp Immunol. (2014) 42:25–35. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2013.05.014
27. Myllymaki H, Valanne S, and Ramet M. The Drosophila imd signaling pathway. J Immunol. (2014) 192:3455–62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1303309
28. Zhai Z, Huang X, and Yin Y. Beyond immunity: The Imd pathway as a coordinator of host defense, organismal physiology and behavior. Dev Comp Immunol. (2017) 83:51–9. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2017.11.008
29. Fuse N, Okamori C, Okaji R, Tang C, Hirai K, and Kurata S. Transcriptome features of innate immune memory in Drosophila. PloS Genet. (2022) 18:e1010005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010005
30. Mukherjee K and Dobrindt U. Epigenetic remodeling in insect immune memory. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1397521. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1397521
31. Netea MG, Joosten LA, Latz E, Mills KH, Natoli G, Stunnenberg HG, et al. Trained immunity: A program of innate immune memory in health and disease. Science. (2016) 352:aaf1098. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf1098
32. Novakovic B, Habibi E, Wang SY, Arts RJW, Davar R, Megchelenbrink W, et al. beta-Glucan reverses the epigenetic state of LPS-induced immunological tolerance. Cell. (2016) 167:1354–68. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.09.034
33. Zhang Q and Cao X. Epigenetic regulation of the innate immune response to infection. Nat Rev Immunol. (2019) 19:417–32. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0151-6
34. Zhang Q and Cao X. Epigenetic remodeling in innate immunity and inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol. (2021) 39:279–311. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-093019-123619
35. Barisic D, Stadler MB, Iurlaro M, and Schubeler D. Mammalian ISWI and SWI/SNF selectively mediate binding of distinct transcription factors. Nature. (2019) 569:136–40. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1115-5
36. Bieluszewski T, Prakash S, Roule T, and Wagner D. The role and activity of SWI/SNF chromatin remodelers. Annu Rev Plant Biol. (2023) 74:139–63. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-102820-093218
37. Hoffmann A and Spengler D. Chromatin remodeling complex NuRD in neurodevelopment and neurodevelopmental disorders. Front Genet. (2019) 10:682. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00682
38. Mittal P and Roberts CWM. The SWI/SNF complex in cancer - biology, biomarkers and therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2020) 17:435–48. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-0357-3
39. Reid XJ, Low JKK, and Mackay JP. A NuRD for all seasons. Trends Biochem Sci. (2023) 48:11–25. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.06.002
40. Reyes AA, Marcum RD, and He Y. Structure and function of chromatin remodelers. J Mol Biol. (2021) 433:166929. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166929
41. Gnanapragasam MN, Scarsdale JN, Amaya ML, Webb HD, Desai MA, Walavalkar NM, et al. p66Alpha-MBD2 coiled-coil interaction and recruitment of Mi-2 are critical for globin gene silencing by the MBD2-NuRD complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2011) 108:7487–92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015341108
42. Li DQ and Kumar R. Mi-2/NuRD complex making inroads into DNA-damage response pathway. Cell Cycle. (2010) 9:2071–9. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.11.11735
43. Ramirez J and Hagman J. The Mi-2/NuRD complex: a critical epigenetic regulator of hematopoietic development, differentiation and cancer. Epigenetics. (2009) 4:532–6. doi: 10.4161/epi.4.8.10108
44. Torchy MP, Hamiche A, and Klaholz BP. Structure and function insights into the NuRD chromatin remodeling complex. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2015) 72:2491–507. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1880-8
45. Angulo B, Srinivasan S, Bolival BJ, Olivares GH, Spence AC, and Fuller MT. DREF genetically counteracts Mi-2 and Caf1 to regulate adult stem cell maintenance. PloS Genet. (2019) 15:e1008187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008187
46. Aughey GN, Forsberg E, Grimes K, Zhang S, and Southall TD. NuRD-independent Mi-2 activity represses ectopic gene expression during neuronal maturation. EMBO Rep. (2023) 24:e55362. doi: 10.15252/embr.202255362
47. Kehle J, Beuchle D, Treuheit S, Christen B, Kennison JA, Bienz M, et al. dMi-2, a hunchback-interacting protein that functions in polycomb repression. Science. (1998) 282:1897–900. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5395.1897
48. Zacharioudaki E, Falo Sanjuan J, and Bray S. Mi-2/NuRD complex protects stem cell progeny from mitogenic Notch signaling. Elife. (2019) 8:e41637. doi: 10.7554/eLife.41637.028
49. Arden KC. FoxO: linking new signaling pathways. Mol Cell. (2004) 14:416–8. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(04)00213-8
50. Hedrick SM, Hess Michelini R, Doedens AL, Goldrath AW, and Stone EL. FOXO transcription factors throughout T cell biology. Nat Rev Immunol. (2012) 12:649–61. doi: 10.1038/nri3278
51. Martins R, Lithgow GJ, and Link W. Long live FOXO: unraveling the role of FOXO proteins in aging and longevity. Aging Cell. (2016) 15:196–207. doi: 10.1111/acel.12427
52. Rodriguez-Colman MJ, Dansen TB, and Burgering BMT. FOXO transcription factors as mediators of stress adaptation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2024) 25:46–64. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00649-0
53. Arden KC. FOXO animal models reveal a variety of diverse roles for FOXO transcription factors. Oncogene. (2008) 27:2345–50. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.27
54. Barthel A, Schmoll D, and Unterman TG. FoxO proteins in insulin action and metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2005) 16:183–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2005.03.010
55. Giannakou ME and Partridge L. The interaction between FOXO and SIRT1: tipping the balance towards survival. Trends Cell Biol. (2004) 14:408–12. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.07.006
56. Khan SA, Kojour MAM, and Han YS. Recent trends in insect gut immunity. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1272143. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1272143
57. Puig O and Mattila J. Understanding Forkhead box class O function: lessons from Drosophila melanogaster. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2011) 14:635–47. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3407
58. Santos BF, Grenho I, Martel PJ, Ferreira BI, and Link W. FOXO family isoforms. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:702. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06177-1
59. Guo L, Karpac J, Tran SL, and Jasper H. PGRP-SC2 promotes gut immune homeostasis to limit commensal dysbiosis and extend lifespan. Cell. (2014) 156:109–22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.018
60. Bischoff V, Vignal C, Duvic B, Boneca IG, Hoffmann JA, and Royet J. Downregulation of the Drosophila immune response by peptidoglycan-recognition proteins SC1 and SC2. PloS Pathog. (2006) 2:e14. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020014
61. Costechareyre D, Capo F, Fabre A, Chaduli D, Kellenberger C, Roussel A, et al. Tissue-specific regulation of Drosophila NF-κB pathway activation by peptidoglycan recognition protein SC. J Innate Immun. (2016) 8:67–80. doi: 10.1159/000437368
62. Mellroth P, Karlsson J, and Steiner H. A scavenger function for a Drosophila peptidoglycan recognition protein. J Biol Chem. (2003) 278:7059–64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208900200
63. Paredes JC, Welchman DP, Poidevin M, and Lemaitre B. Negative regulation by amidase PGRPs shapes the Drosophila antibacterial response and protects the fly from innocuous infection. Immunity. (2011) 35:770–9. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.09.018
64. Cai Q, Wang Z, Xiao Y, Zhang C, Yang Y, Kong F, et al. MESR4 targets bam to mediate intestinal homeostasis and aging in adult flies. Insect Sci. (2025). doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.13506
65. Ji S and Hoffmann JA. Toll-9 prevents the proliferation of injected oncogenic cells in adult flies. J Genet Genomics. (2024) 51:1331–3. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2024.07.002
66. Ji S, Zhou X, and Hoffmann JA. Toll-mediated airway homeostasis is essential for fly survival upon injection of RasV12-GFP oncogenic cells. Cell Rep. (2024) 43:113677. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.113677
67. Zheng X, Jin Y, Zhang C, Zhu Y, Guo H, Duan R, et al. RNA-binding protein Roq modulates the Drosophila STING antiviral immune response. Cell Invest. (2025) 1:100002. doi: 10.1016/j.clnves.2024.100002
68. Hu Y, Kong F, Guo H, Hua Y, Zhu Y, Zhang C, et al. Drosophila eIF3f1 mediates host immune defense by targeting dTak1. EMBO Rep. (2024) 25:1415–35. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00067-z
69. Zhu Y, Liu L, Zhang C, Zhang C, Han T, Duan R, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation contributes to Toll innate immune defense in Drosophila melanogaster. Front Immunol. (2023) 13:1099637. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1099637
70. Duan R, Hu B, Ding E, Zhang S, Wu M, Jin Y, et al. Cul2 is essential for the Drosophila IMD signaling-mediated antimicrobial immune defense. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26:2627. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062627
71. Kong F, Wang Z, Zhang C, Xiao Y, Saeed MAR, Li W, et al. Drosophila Cul3 contributes to Diap2-mediated innate immune signaling for antimicrobial defense. hLife. (2025) 3:38–51. doi: 10.1016/j.hlife.2024.10.001
72. Cai Q, Guo H, Fang R, Hua Y, Zhu Y, Zheng X, et al. A Toll-dependent Bre1/Rad6-cact feedback loop in controlling host innate immune response. Cell Rep. (2022) 41:111795. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111795
73. Khattak S, Lee BR, Cho SH, Ahnn J, and Spoerel NA. Genetic characterization of drosophila mi-2 ATPase. Gene. (2002) 293:107–14. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(02)00698-4
74. Neyen C, Bretscher AJ, Binggeli O, and Lemaitre B. Methods to study Drosophila immunity. Methods. (2014) 68:116–28. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.02.023
75. Vinayagam A, Kulkarni MM, Sopko R, Sun X, Hu Y, Nand A, et al. An integrative analysis of the InR/PI3K/Akt network identifies the dynamic response to insulin signaling. Cell Rep. (2016) 16:3062–74. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.08.029
76. Becker T, Loch G, Beyer M, Zinke I, Aschenbrenner AC, Carrera P, et al. FOXO-dependent regulation of innate immune homeostasis. Nature. (2010) 463:369–73. doi: 10.1038/nature08698
Keywords: Mi-2, Foxo, PGRP-SC2, IMD signaling pathway, antibacterial immune defense, Drosophila melanogaster
Citation: Zheng X, Ali U, Jin Y, Ding E, Zhu Y, Usama M, Cai Q and Ji S (2025) The functional Mi-2/Foxo complex targets PGRP-SC2 for the Drosophila immune defense against bacterial infection. Front. Immunol. 16:1664564. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1664564
Received: 12 July 2025; Accepted: 09 September 2025;
Published: 29 September 2025.
Edited by:
Orestes Foresto-Neto, University of São Paulo, BrazilReviewed by:
Yinan Jiang, University of Pittsburgh, United StatesYongzhi Hua, Fuyang Normal University, Fuyang, China
Copyright © 2025 Zheng, Ali, Jin, Ding, Zhu, Usama, Cai and Ji. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xianrui Zheng, eHJ6aGVuZzAxOEAxMjYuY29t; Shanming Ji, amlzbUBhaGF1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xianrui Zheng1,2*†
Xianrui Zheng1,2*† Yiheng Jin
Yiheng Jin Yangyang Zhu
Yangyang Zhu Shanming Ji
Shanming Ji