- 1Department of Oncology, Xinghua People’s Hospital Affiliated to Yangzhou University, Xinghua, Jiangsu, China
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Xinghua People’s Hospital Affiliated to Yangzhou University, Xinghua, Jiangsu, China
- 3Department of Oncology, Dongtai Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Dongtai, Jiangsu, China
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) presents challenges due to its high invasiveness and rapid progression, resulting in an inferior prognosis. Approximately 70% of patients have developed an extensive stage at the time of diagnosis. While most patients with extensive-stage SCLC (ES-SCLC) are sensitive to chemotherapy, they remain at high risk of local recurrence and distant metastasis in the short term. In the era of chemotherapy, studies have indicated the potential survival benefits of consolidative thoracic radiotherapy (cTRT) for patients responding to systemic treatment. The introduction of immunotherapy has significantly transformed the treatment landscape for SCLC. The combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) with chemotherapy has emerged as the new standard for first-line treatment of ES-SCLC. Nevertheless, controversy surrounds the role of cTRT after the first-line treatment of ES-SCLC in the context of immunotherapy, especially considering advancements in imaging staging methods and precise radiotherapy technology. This review focuses on the application value and latest research advancements in cTRT following first-line immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in ES-SCLC, providing valuable insights for clinical practice.
1 Introduction
SCLC represents the most prevalent primary neuroendocrine tumor of the lung and is recognized as one of the most lethal malignancies, characterized by a notably low 5-year survival rate (1). SCLC exhibits unique biological characteristics, characterized by high invasiveness, rapid growth, high sensitivity to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, and a tendency for early distant metastasis. Approximately 70% of patients are initially diagnosed with extensive stage (2). Over the past few decades, platinum-based chemotherapy has been the standard first-line treatment regimen for SCLC (3, 4). Despite the tumor’s initial sensitivity to chemotherapy, the disease is characterized by a high recurrence rate and a meager response to second-line treatment, resulting in a median overall survival (OS) of less than one year (4, 5). Radiotherapy is a pivotal component in the comprehensive management of SCLC. Previous studies (6–8) have demonstrated that cTRT administered to patients who respond well to systemic therapy yields a high degree of local disease control and extends overall survival within the context of the chemotherapy era.
Currently, the predominant immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in clinical practice include programmed death receptor 1/programmed death-ligand 1(PD-1/PD-L1) inhibitors and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4(CTLA-4) inhibitors. PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors restore the killing function of T cells against tumor cells by impeding the binding of PD-L1 on the surface of tumor cells to PD-1 on the surface of T cells, thereby enhancing anti-tumor immune responses. CTLA-4 inhibitors competitively bind to ligand B7 with CTLA-4, relieving the inhibitory factors that impede T cell activation, thereby exerting an anti-tumor effect (9). In recent years, multiple clinical studies (10–13) have demonstrated that first-line standard chemotherapy combined with immunotherapy can significantly prolong the survival of ES-SCLC patients, establishing its position as a first-line treatment for small cell lung cancer. The value of cTRT in the era of immunotherapy is still controversial. In this review, we summarized the advancements in research concerning immunotherapy and cTRT for ES-SCLC and explored the application value of cTRT after first-line immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in ES-SCLC.
2 Immunotherapy in ES-SCLC
2.1 Advancements in immunotherapy for ES-SCLC
Tumor cells can utilize immune checkpoints to evade recognition and clearance by the immune system. ICIs work by initiating a series of immune responses to restore anti-tumor immunity, achieving the goal of recognizing and killing tumor cells. Therefore, blocking PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 with ICIs to restore the body’s anti-tumor immune function is an effective measure for treating ES-SCLC.
Clinical trials of ICIs for SCLC started with CTLA-4 inhibitors. A phase II clinical trial (14) investigated the efficacy and safety of chemotherapy combined with ipilimumab in treating ES-SCLC. The results showed that compared with the chemotherapy group, the ipilimumab combined with chemotherapy group had no significant benefit in progression-free survival (PFS) and OS, but increased immune-related toxicity. Moreover, another large phase 3 confirmatory trial (15) demonstrated that ipilimumab in combination with chemotherapy failed to extend OS versus chemotherapy alone in ES-SCLC patients.
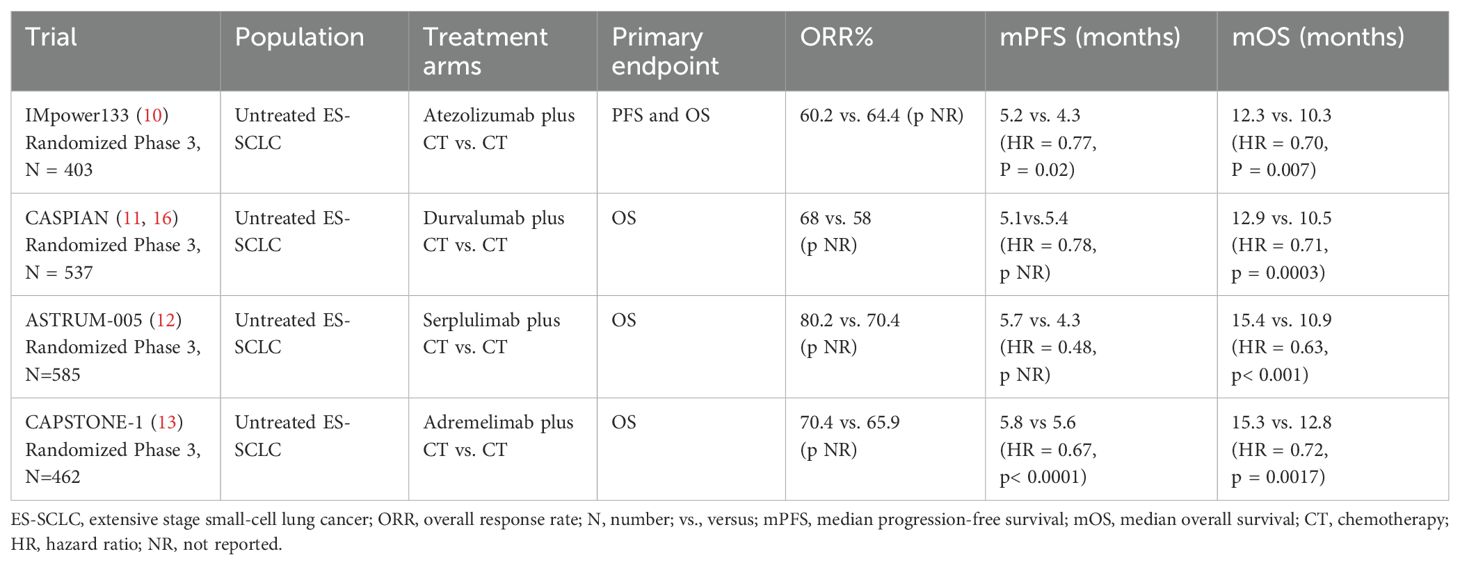
The IMpower 133 trial (10) evaluated the efficacy and safety of the combination of atezolizumab with chemotherapy as first-line treatment for ES-SCLC. The median PFS and OS in the atezolizumab group were significantly longer than those in the placebo group, and there was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of adverse events between the two groups. The CASPIAN study (11, 16) demonstrated that median OS was significantly improved in the durvalumab group (13.0 months [95% CI 11.5-14.8]) compared with the placebo group (10.3 months [95% CI 9.3-11.2]). Adebrelimab is a Chinese-made humanized anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody. In the CAPSTONE-1 study (13), the combination of adebrelimab with chemotherapy significantly prolonged median OS compared with chemotherapy alone in ES-SCLC patients. Based on the findings of the IMpower 133 and CASPIAN studies, atezolizumab/durvalumab combined with etoposide and carboplatin/cisplatin has been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in China as the preferred regimen for first-line treatment for ES-SCLC. In addition, the results of CAPSTONE-1 provide strong evidence for the combination of adebrelimab and chemotherapy as first-line treatment for ES-SCLC, and adebrelimab has also been approved by NMPA as a new option.
Nevertheless, the findings of PD-1 inhibitors exhibit considerable variability in SCLC patients. A pooled analysis (17) from KEYNOTE-028 and KEYNOTE-158 indicated durable antitumor activity of pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed or metastatic SCLC who had received two or more prior lines of therapy, irrespective of PD-L1 expression. Based on the results of the lung cancer cohorts from the KEYNOTE-028 and KEYNOTE-158 studies, the FDA granted accelerated approval for pembrolizumab monotherapy for relapsed ES-SCLC after two or more lines of therapy on June 17, 2019. KEYNOTE-604 study (18) investigated the efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy as a first-line treatment for ES-SCLC. The findings showed that compared with chemotherapy alone, pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy significantly improved PFS but not OS, and there was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of adverse events between the two groups. Pembrolizumab was withdrawn in 2021 due to the confirmatory phase 3 clinical KEYNOTE-604 study only achieving PFS among its primary endpoints, but not a statistically significant OS endpoint. A sustained anti-tumor response was observed in nivolumab as at least third-line therapy for recurrent SCLC (19). Based on this result, nivolumab was approved by the FDA for at least third-line therapy of recurrent SCLC in August 2018. Unfortunately, nivolumab was also withdrawn in December 2020 due to the disappointing results of the following studies. CheckMate 331 study (20) showed that nivolumab did not improve OS compared with chemotherapy in the second-line treatment of relapsed SCLC. CheckMate 451 trial (21) indicated that maintenance therapy with nivolumab in combination with ipilimumab failed to extend OS for ES-SCLC patients who responded to first-line treatment. The failure of pembrolizumab and nivolumab in treating SCLC does not imply that all PD-1 inhibitors are insensitive to this cancer. Serplulimab is a humanized anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody. The ASTRUM-005 study (12) showed that first-line treatment with serplulimab plus chemotherapy significantly improved PFS and OS compared with chemotherapy alone in ES-SCLC, while the incidence of adverse events did not differ significantly between the two groups. Serplulimab has become the world’s first PD-1 inhibitor for ES-SCLC based on these findings. Clinical trials changing the first-line treatment strategy for ES-SCLC are displayed in Table 1.
2.2 Biomarkers for immunotherapy in SCLC
Although immunotherapy has significantly prolonged the survival of patients with ES-SCLC, the proportion of those who benefit in the real world remains limited. Therefore, it is necessary to screen biomarkers predicting the efficacy of ICIs. Biomarkers that have predictive value for immunotherapy in NSCLC do not apply to SCLC. PD-L1 expression did not predict response to chemotherapy in combination with ICIs therapy in several previous studies (18, 21, 22). Furthermore, a meta-analysis (23) enrolling 2792 patients with SCLC indicates that PD-L1 expression was a favorable but not statistically significant prognostic factor. The reasons for the discrepancy in the predictive value of PD-L1 expression in NSCLC and SCLC immunotherapy may be as follows. On one hand, unlike NSCLC, PD-L1 expression is generally low in SCLC (24). On the other hand, due to tumor heterogeneity and limitations of PD-L1 detection methods, biopsy samples cannot fully reflect the expression of PD-L1 in SCLC tissues.
Besides PD-L1 expression, tumor mutation burden (TMB) is another important marker for predicting the response to immunotherapy. CheckMate 032 study (25) explored the predictive value of TMB and found that high TMB was associated with a superior response in the ipilimumab combined with nivolumab group but not the nivolumab monotherapy group. The role of TMB was also studied in the CASPIAN trial (26), evaluating durvalumab in combination with platinum-etoposide (EP) versus EP alone as first-line therapy in ES-SCLC. This research indicated that tissue TMB (tTMB) status was not associated with OS benefit. In exploratory biomarker analysis of the phase 3 KEYNOTE-604 study (27), an inferior OS was observed in the experimental compared with the control arm in the high TMB (>175 mut/exome) subgroup. Therefore, the predictive potential of TMB for immunotherapy efficacy in SCLC is still lacking evidence and needs to be further verified by subsequent studies.
In recent years, researchers have classified SCLC into four subtypes: SCLC-A, SCLC-N, SCLC-Y, and a distinct subtype of SCLC with lower expression of all three transcription factors, based on the differential expression of key transcriptional regulatory factors such as achaete-scute homologue 1 (ASCL1), neurogenic differentiation factor 1 (NeuroD1) and POU class 2 homeobox 3 (POU2F3) (28). Since the fourth subtype is characterized by expression of inflammatory genes, this subtype was named SCLC-Inflamed, or SCLC-I (28). The SCLC-I subtype benefits more from immunotherapy than the other three subtypes (28). An exploratory analysis from the IMpower133 trial indicated that a higher proportion of patients with long-term survival in both groups had SCLC-I subtype, which was more pronounced in the atezolizumab group (29). The SCLC-I subtype has potential predictive value for SCLC immunotherapy response and deserves further investigations to explore the related mechanisms. In addition, scholars have also explored the correlations between the activation of cellular signaling pathways (30) and the characteristics of the tumor immune microenvironment (31–34) with the efficacy of immunotherapy for SCLC, providing novel insights for subsequent research. In summary, accurately screening the populations that benefit most from immunotherapy is an urgent task and challenge.
3 cTRT for ES-SCLC in the era of chemotherapy
Over the past few decades, platinum-based chemotherapy has been recognized as the standard first-line treatment for ES-SCLC, yielding a median survival of approximately ten months (35). Nevertheless, approximately 70% to 90% of patients exhibit residual intrathoracic disease following chemotherapy, and progression to refractory disease typically transpires within the first year after initial treatments (36, 37). Therefore, the localized management of intrathoracic residual lesions is crucial for postponing disease progression and ensuring long-term survival. The feasibility of cTRT in ES-SCLC is partly due to the heightened radio-sensitivity of SCLC. Its clinical impact has been previously documented in both prospective and retrospective studies.
3.1 The application value of cTRT in ES-SCLC
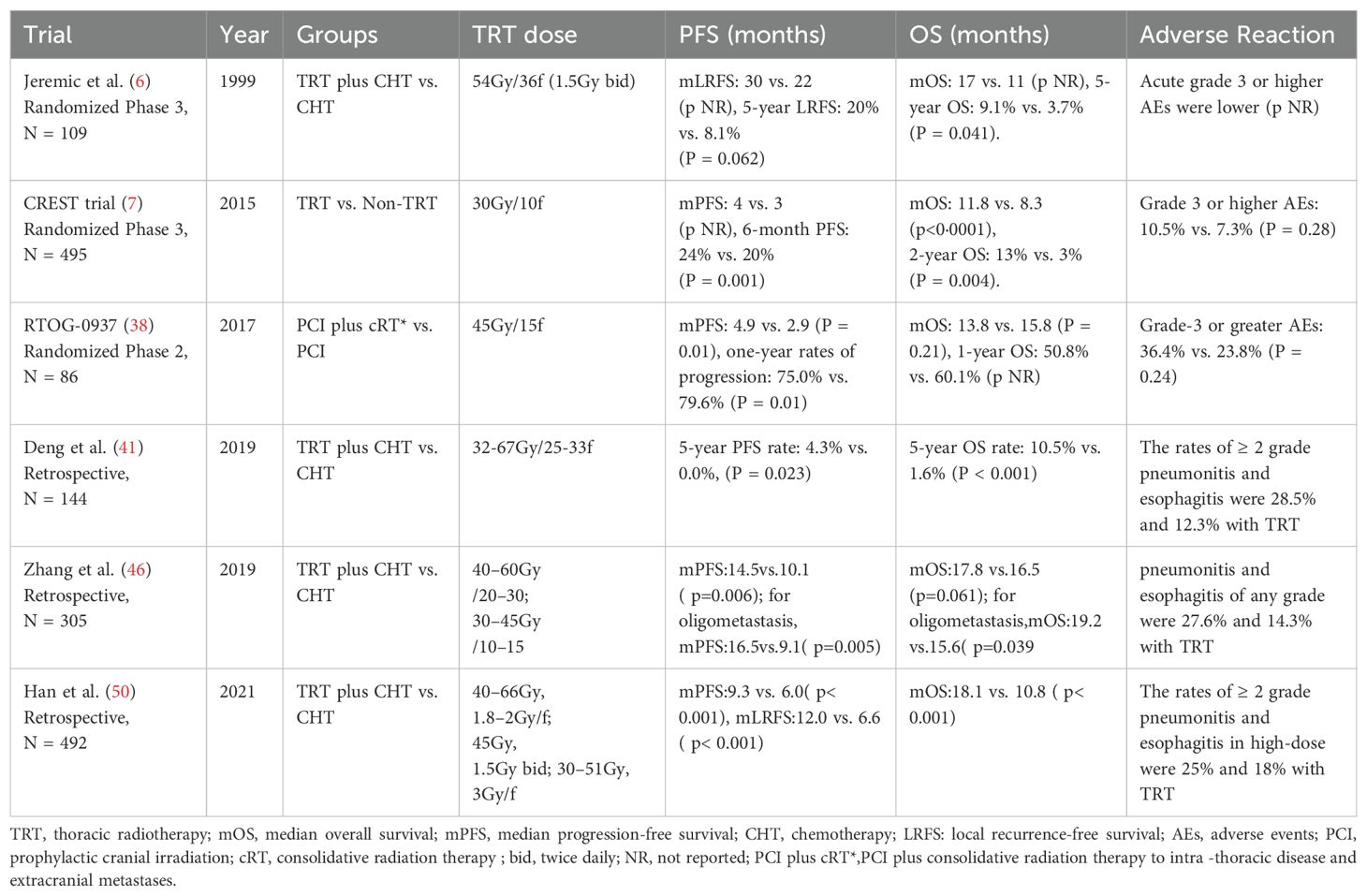
As early as 1999, Jeremic et al. first confirmed the value of thoracic radiotherapy in patients with ES-SCLC who achieved complete/partial remission (CR/PR) after initial chemotherapy (6). Their results showed that cTRT after chemotherapy could increase the 5-year OS rate by 5.4% (9.1% vs. 3.7%, P = 0.041). In 2007, the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) reported that approximately 75% of patients retained intrathoracic residual lesions post-chemotherapy, and nearly 90% of these patients experienced an intrathoracic recurrence within a year, indicating a potential benefit from thoracic radiotherapy (36). The CREST study (7) in 2015 encompassed 495 ES-SCLC patients who responded effectively to 4–6 cycles of platinum-based chemotherapy. These patients were then randomly assigned to receive cTRT (30Gy in 10fractions) or no cTRT. The primary endpoint was the difference in the one-year OS rate between the groups, which was not statistically significant (33% vs. 28%, HR = 0.84, P = 0.066). However, upon secondary analysis of the CREST study, it was observed that the cTRT group had a 10% increase in the 2-year OS rate (13% vs. 3%, P = 0.004) and improved median PFS (4 months vs. 3 months, P = 0.001). Additionally, thoracic radiotherapy significantly decreased the intrathoracic recurrence rate (79.8% vs. 43.7%, P < 0.0001). Although this study establishes the role of cTRT in ES-SCLC, it also raises several questions for future research. First, despite cTRT, the local recurrence rate remains alarmingly high at over 40%, suggesting that the radiotherapy dose may be inadequate for durable control. Second, a mere 13% of patients underwent brain CT/MRI evaluation post-chemotherapy, potentially overlooking those who had progressed. Third, in both the cTRT and non-cTRT groups, 66.4% and 43.9% of patients experienced extrathoracic progression. Could enhanced control of extrathoracic lesions enhance the benefits of cTRT? In addition, the phase II randomized controlled study, RTOG-0937, assessed the efficacy of prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) and the combination of PCI with consolidative radiation therapy (PCI+cRT) in treating intrathoracic disease and extracranial metastases for ES-SCLC (38). This study was discontinued in the interim analysis due to invalid OS in both groups. Despite no significant difference in one-year OS rates, the consolidation radiotherapy group demonstrated a lower locally regional recurrence rate (25.8% vs. 62.5%) and a significantly extended median PFS (4.9 months vs. 2.9 months, p=0.01). The insufficient OS benefit may be attributed to a higher number of patients with higher tumor burden, lower CR rates, and poorer performance status (PS) within the consolidation radiotherapy group, indicating significant selection bias. The use of PCI in patients with SCLC remains a topic of controversy. Risk factors for the development of brain metastases are largely unidentified, which hinders the development of personalized treatment strategies. A recent meta-analysis (39) indicated that younger age, higher T-stage, and extensive disease (ED) are risk factors for brain metastases, suggesting that PCI should be emphasized in these patients. What’s more, a retrospective study showed that neurotoxicity associated with PCI tends to occur more frequently in older patients (40). Therefore, it is reasonable to consider that PCI is not recommended for older patients and those with poor Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS).
Recently, retrospective studies have further investigated the role of cTRT. In 2019, Deng et al. performed a retrospective analysis of the potential value of thoracic intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) in patients with ES-SCLC who responded to platinum-based chemotherapy (41). The findings revealed a significant reduction in the local recurrence rate in the group receiving cTRT compared with the chemotherapy alone (19.2% vs.75.6%, P = 0.001), and the 5-year OS rate increased by 8.7% (12.3% vs. 3.6%, P<0.001). A meta-analysis (42) also confirmed that cTRT can provide survival benefits to ES-SCLC patients who respond effectively to first-line treatments, while maintaining an overall acceptable adverse reaction profile. Prospective and retrospective trials of TRT for ES-SCLC in the chemotherapy era are displayed in Table 2.
3.2 Screening for beneficial populations in cTRT
ES-SCLC represents a group of highly heterogeneous diseases, necessitating the screening of populations that may benefit from cTRT. The CREST trial revealed that approximately 88% of patients possess intrathoracic remnants, with these individuals demonstrating a higher likelihood of benefiting from cTRT (43). In advanced NSCLC, the application of radical radiotherapy to both primary and metastatic lesions can confer survival advantages to patients with oligometastases (44). However, a contentious debate persists concerning both the definition of oligometastases and the potential benefits of localized treatment for patients with ES-SCLC. The secondary analysis of the CREST study (45) revealed that patients with fewer than or equal to two metastatic sites exhibited superior OS and PFS compared with those with more than three metastases, irrespective of cTRT treatment. Furthermore, patients with fewer than or equal to two metastatic sites who received cTRT demonstrated a significant improvement in PFS (p = 0.003). In a retrospective investigation (46), oligometastases were defined as single organ or non-regional lymph node metastasis, contiguous vertebral metastasis amenable to safe inclusion in the radiotherapy plan, or multiple brain metastases suitable for whole brain radiotherapy. The findings indicated that thoracic radiotherapy could enhance OS in patients with oligometastases, whereas patients with liver, brain or multiple metastases did not benefit from thoracic radiotherapy. Another retrospective study (47) also suggested that thoracic radiotherapy could improve the OS rate for patients with isolated metastasis. In summary, published evidence suggests that patients most likely to derive a significant survival benefit from cTRT are those with a good response to initial systemic therapy (CR/PR), limited extrathoracic disease burden (e.g. oligometastatic disease, defined as ≤ double metastatic sites or isolated metastasis), and the absence of high-risk metastatic sites such as the liver and brain. Conversely, patients with extensive metastatic involvement (e.g. > three sites, liver metastases) or rapid systemic progression are less likely to benefit from aggressive local consolidation. The evidence from retrospective analyses is inherently limited by their non-randomized design and potential for confounding factors.
3.3 Exploration of dose fractionation model
An early prospective investigation has demonstrated that a total dose of 54Gy in 36 fractions, administered twice daily, is both safe and effective for patients who achieve CR or PR following chemotherapy (6). In the CREST study (7), a palliative dose of 30Gy, administered in ten fractions, was utilized for thoracic radiotherapy, yet the local recurrence rate was as high as 43.7%, suggesting that the local dose may be insufficient. The RTOG 0937 study (38) recommended a consolidation radiotherapy dose of 45Gy in 15 fractions, resulting in a lower local regional recurrence rate (first site of recurrence) than that observed in the CREST study (25.8%). The multicenter, prospective, observational TRENDS study (48) evaluated the patterns of consolidative chest radiotherapy (including techniques, target volumes, and dosing) as well as its effectiveness in disease control and tolerability in patients with ES-SCLC. The study confirmed that consolidative chest radiotherapy is effective in reducing the risk of intrathoracic disease progression and is well-tolerated in extensive-stage SCLC patients who respond favorably to first-line chemotherapy. However, there is currently a lack of large-sample prospective studies to compare the benefits of different dose fractionation modes in ES-SCLC. Some retrospective studies suggest that increasing the dose of thoracic radiotherapy may confer survival benefits. One retrospective study (49) demonstrated that patients with a thoracic radiotherapy dose of ≥45Gy had a significantly better prognosis than those with a dose <45Gy (2-year OS rate was 25.2% vs.15.1%, P<0.001). Another retrospective study (50) found that increasing the dose of thoracic radiotherapy (time-adjusted biologically effective dose >50Gy) for patients who achieved CR/PR after chemotherapy did not improve prognosis, and the incidence of grade 2 or higher radiation esophagitis increased. Furthermore, compared with the conventional fractionation of 60Gy in 30 fractions, once daily, the over-fractionation mode of 45Gy in 30 fractions, twice daily, had a longer OS (P = 0.036).
In summary, cTRT remains a recommended treatment for patients with ES-SCLC who have been effectively treated with systemic therapy. Patients with residual intrathoracic lesions may benefit from thoracic radiotherapy. However, the optimal dose fractionation pattern continues to be a subject of debate.
4 cTRT for ES-SCLC in the era of immunotherapy.
4.1 Theoretical basis of cTRT
The prevailing consensus posits that radiotherapy can remodel the tumor immune microenvironment (51). In addition to the direct damage to tumor cells, radiotherapy can also promote the release of tumor-specific antigens, enhance the immunogenicity of tumor cells, regulate signal transduction, alter the inflammatory tumor immune microenvironment, activate adaptive immune responses, and induce immune-mediated anti-tumor effects within or outside the irradiated field, namely the “immune memory effect” and the “abscopal effect” (52). Furthermore, the effect can be significantly enhanced when radiotherapy is integrated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), transforming an ineffective immune response into a robust and enduring one (53). However, radiotherapy may also cause immunosuppressive effects by up-regulating the expression of PD-L1 and inhibiting T-cell activation (54). The immunomodulatory impact of radiotherapy is associated with its fractionation pattern. Research has indicated that low-dose radiotherapy, ranging from 0.5 to 2Gy per fraction, could stimulate innate and adaptive immunity. It also promotes the activation and infiltration of immune effector cells, such as CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and restructures the tumor microenvironment within the so-called “immune desert” (55). Compared with traditional fractionation, single high-dose radiotherapy can directly kill tumor cells and more effectively stimulate anti-tumor immune responses by promoting the release of tumor-associated antigens (56). However, this high dose can also lead to vascular damage, induce radioresistance due to tumor hypoxia, and activate DNA exonuclease Trex1, which has a negative immunomodulatory effect (56). The impact of radiotherapy on the immune microenvironment is bidirectional, with the outcome influenced by various factors such as radiation fractionation patterns, dose, mode of immunotherapy, and tumor type.
4.2 Investigation into the impact of cTRT on survival
Despite the significant improvement in survival for ES-SCLC patients treated with first-line chemotherapy and ICIs compared with chemotherapy alone, only 0.8% to 2.5% of patients achieved CR (10). Neither the IMPOWER133 nor the CASPIAN studies explored the potential value of cTRT after treatment with the combination of chemotherapy with ICIs. Consequently, there remains controversy over the safety and benefits of cTRT in the context of immunotherapy. Updated data from IMPOWER133 revealed that over 90% of patients had local residual lesions following first-line treatment, including progression of the primary lung lesion in 34% of cases, suggesting that local consolidation therapy may have potential benefits during immunotherapy (22).
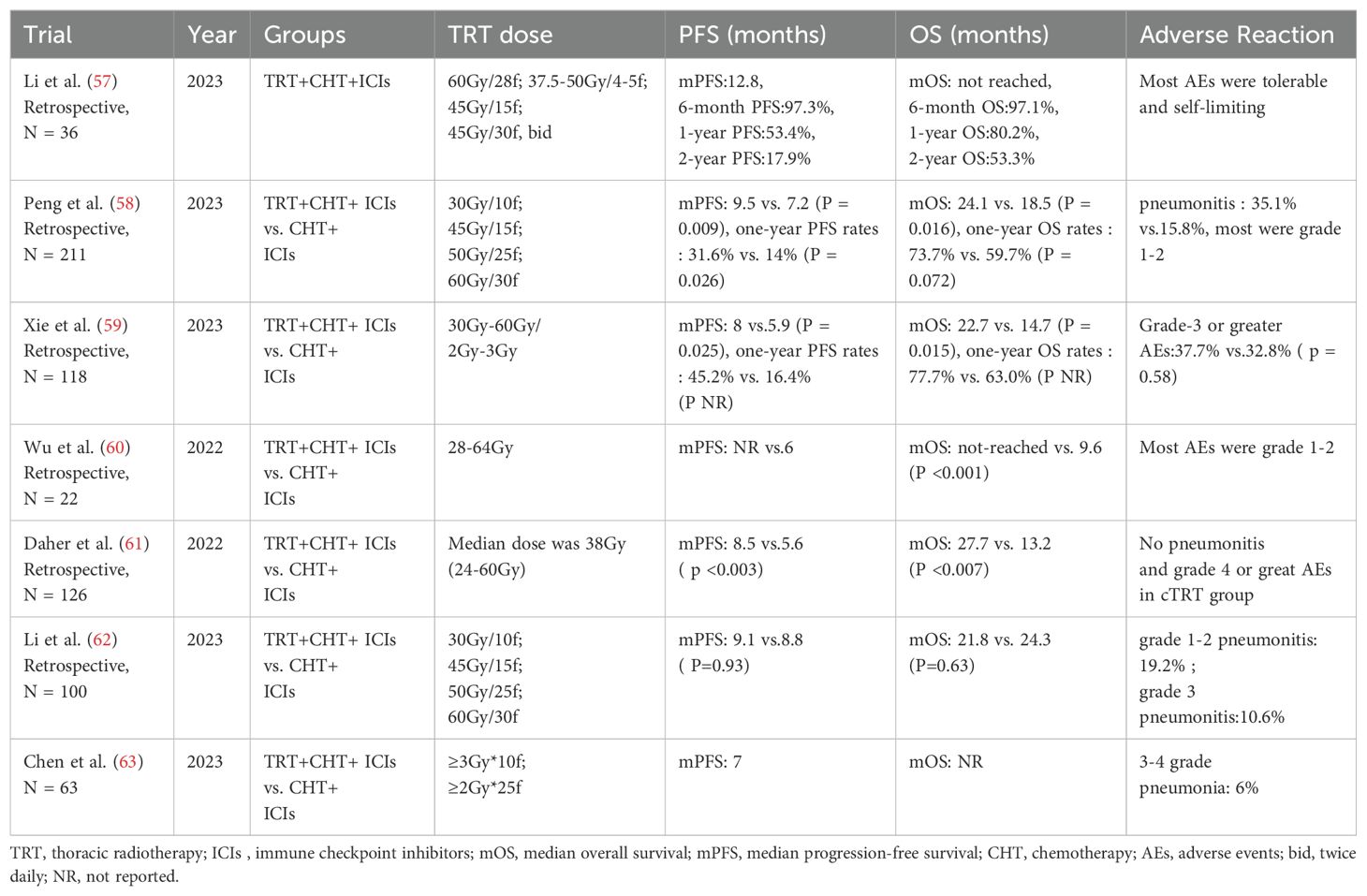
Recent studies have explored the potential values of cTRT in the context of first-line chemotherapy and immunotherapy. A retrospective study (57) involving ES-SCLC patients found that those who received cTRT following first-line chemotherapy in combination with PD-L1 monoclonal antibody therapy had a one-year OS rate of 80.2%. Furthermore, only 8% of these patients developed grade 1 or 2 radiation pneumonia. The biologically effective dose of thoracic radiotherapy ranged from 52 to 113Gy, providing preliminary evidence for the feasibility of this therapy for patients who respond effectively to first-line chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Another retrospective study (58), which included 211 patients who underwent first-line chemotherapy and PD-L1 antibody therapy, demonstrated that the group receiving cTRT had a significantly longer OS (median OS: 24.1 months vs.18.5 months, P = 0.016). It is important to note that in both studies, over 80% of the patients who received thoracic radiotherapy had ≤2 metastatic sites. This suggests that patients with a limited extrathoracic tumor burden are more likely to benefit from cTRT. Xie et al. observed that after first-line chemotherapy in conjunction with ICIs for ES-SCLC patients, the cTRT group exhibited a significant improvement in both PFS (8.0 months vs.5.9 months, HR = 0.64, p = 0.025) and OS (22.7 months vs.14.7 months, HR = 0.52, p = 0.015) (59). These findings align with those of two other studies (60, 61). However, a small-sample retrospective study (62) indicated that cTRT following first-line chemotherapy and immunotherapy did not yield a survival benefit (median PFS: 9.1 vs.8.8 months, P = 0.93, median OS: 21.8 vs.24.3 months, P = 0.63), which may be attributed to the higher rate of extrathoracic progression in the cTRT group (91.4% vs. 67.6%, P = 0.02). Since the studies above are all small-sample retrospective studies, they lack sufficient evidence-based support.
At the 2023 annual meetings of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), a report was presented on the efficacy and safety of first-line adebrelimab combined with chemotherapy, followed by thoracic radiotherapy for patients with ES-SCLC (63). The findings indicated that the objective response rate (ORR) for patients who underwent thoracic radiotherapy reached 80%, with a median PFS of 7 months. Additionally, grade 3-4 pneumonia occurred in 6% of patients. The conflicting results from these retrospective studies underscore the significant heterogeneity in patient selection, radiotherapy dosing, and patterns of failure. This highlights a critical selection bias. Overall, the current evidence base for combining cTRT with chemo-immunotherapy consists solely of retrospective data with small sample sizes, significant methodological heterogeneity, and potential for confounding. This precludes definitive conclusions regarding efficacy and necessitates validation from prospective randomized trials. Currently, several prospective studies such as NCT05544149, NCT05552846, RAPTOR/NRG, and LU007/NCT04402788, are exploring the potential value and safety of cTRT after first-line chemotherapy in combination with immunotherapy for ES-SCLC. Studies of TRT for ES-SCLC in the immunotherapy era are displayed in Table 3.
The optimal timing for cTRT intervention remains a crucial and unresolved issue. Some scholars contend that early cTRT, administered within three cycles of chemotherapy, does not confer significant survival benefits compared with cTRT administered later, after three cycles (64). However, another study indicates that initiating TRT within six cycles of chemotherapy can lead to improved local control rates (50). For patients with ES-SCLC, we believe that systemic therapy is of utmost importance. Local cTRT may be more effectively administered after the disease has been adequately controlled and stabilized, rather than too early in the treatment process. Additionally, the optimal sequence for cTRT and maintenance immunotherapy remains uncertain. According to current guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology, cTRT should be administered within six to eight weeks following chemotherapy and before starting maintenance immunotherapy. It is posited that delivering cTRT during the maintenance immunotherapy phase is a promising treatment strategy. Available evidence indicates that this approach is well-tolerated and is associated with improved local control in ES-SCLC patients with residual thoracic lesions following induction chemo-immunotherapy.
4.3 Safety of cTRT
The increased adverse events associated with cTRT following first-line immunotherapy are a significant concern. Currently, the safety data about the combination of immunotherapy with TRT in ES-SCLC patients predominantly originates from small samples or retrospective clinical studies. A phase I clinical study (65) conducted on ES-SCLC assessed the safety of pembrolizumab combined with TRT after induction chemotherapy. The findings indicated that patients treated with this combination had good tolerance, with only 6% experiencing grade 4 adverse events. A real-world study demonstrated that cTRT following first-line chemotherapy in conjunction with ICIs did not increase the incidence of adverse events (59). Another study (66) that combined results from three single-institution phase I/II trials demonstrated that cTRT combined with immunotherapy has acceptable safety and feasibility in the short term. Only three out of 53 patients who received cTRT (45Gy in 15 fractions) in combination with immunotherapy developed grade 3 or higher adverse events. In a retrospective study (57) of 36 patients with ES-SCLC, the majority underwent TRT (60Gy in 28 fractions) after first-line chemotherapy in conjunction with ICIs. Only 8% of these patients developed radiation-related pneumonitis, all of which were grade 1-2. Four patients discontinued immunotherapy due to immune-related pneumonitis but completed the planned cTRT treatment. However, in a real-world study (58) involving 211 ES-SCLC patients, 70 participants received TRT after first-line chemotherapy in conjunction with ICIs. The incidence of treatment-related pneumonitis in the TRT group significantly increased (P = 0.018), but most cases were grade 1 or 2. Overall, for ES-SCLC patients, cTRT would increase the incidence of treatment-related pneumonitis, but the grade is low and within a controllable stage. It is important to note that most current studies exploring the safety of cTRT combined with immunotherapy in ES-SCLC are single-center retrospective studies. The included patients have significant heterogeneity and selection bias, so the data should be interpreted with caution. Therefore, the reported acceptable toxicity profile may not be generalizable to all ES-SCLC patients. Larger, prospective studies are urgently needed to definitively establish the safety of this combination.
5 Conclusions
In the chemotherapy era, multiple retrospective and prospective studies have demonstrated that cTRT can improve survival in ES-SCLC patients who respond effectively to systemic treatment, particularly those with intrathoracic residuals and a lower extrathoracic tumor burden. However, as the first-line treatment for ES-SCLC transitions into the immunotherapy era, the value of cTRT has been widely debated. In the distinct immunosuppressive microenvironment of SCLC, the combination of radiotherapy and immunotherapy may enhance efficacy, but the potential for increased toxicity must be carefully considered. Multiple clinical studies have confirmed that cTRT is safe and feasible. The pattern of failure in the IMPOWER133 trial suggests that local treatment may offer potential benefits after first-line chemotherapy combined with immunotherapy for ES-SCLC. Multiple retrospective studies and several phase I and II prospective studies have preliminarily demonstrated the safety and effectiveness of cTRT for ES-SCLC. In the context of immunotherapy, future research should explore the selection of appropriate populations for thoracic radiotherapy, determine the optimal radiation dose and fractionation mode, and establish the timing for adding radiotherapy.
Author contributions
JAL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JHL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. DC: Writing – original draft. YZ: Writing – original draft. XW: Writing – original draft. YC: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, and Jemal A. Cancer statistics 2023. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2023) 73:17–48. doi: 10.3322/caac.21763
2. Dingemans AC, Früh M, Ardizzoni A, Besse B, Faivre-Finn C, Hendriks LE, et al. Small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up(☆). Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. (2021) 32:839–53. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.03.207
3. Chen P, Zhao L, Wang H, Zhang L, Zhang W, Zhu J, et al. Human leukocyte antigen class II-based immune risk model for recurrence evaluation in stage I-III small cell lung cancer. J immunotherapy Cancer. (2021) 9(8):e002554. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002554
4. Rossi A, Di Maio M, Chiodini P, Rudd RM, Okamoto H, Skarlos DV, et al. Carboplatin- or cisplatin-based chemotherapy in first-line treatment of small-cell lung cancer: the COCIS meta-analysis of individual patient data. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. (2012) 30:1692–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.40.4905
5. Lally BE, Urbanic JJ, Blackstock AW, Miller AA, and Perry MC. Small cell lung cancer: have we made any progress over the last 25 years? oncologist. (2007) 12:1096–104. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.12-9-1096
6. Jeremic B, Shibamoto Y, Nikolic N, Milicic B, Milisavljevic S, Dagovic A, et al. Role of radiation therapy in the combined-modality treatment of patients with extensive disease small-cell lung cancer: A randomized study. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. (1999) 17:2092–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1999.17.7.2092
7. Slotman BJ, van Tinteren H, Praag JO, Knegjens JL, El Sharouni SY, Hatton M, et al. Use of thoracic radiotherapy for extensive stage small-cell lung cancer: a phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet (London England). (2015) 385:36–42. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61085-0
8. Singer L and Yom SS. Consolidative radiation therapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. Trans Lung Cancer Res. (2015) 4:211–4. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2015.04.02
9. Wei SC, Levine JH, Cogdill AP, Zhao Y, Anang NAS, Andrews MC, et al. Distinct cellular mechanisms underlie anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 checkpoint blockade. Cell. (2017) 170:1120–1133 e1117. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.024
10. Horn L, Mansfield AS, Szczęsna A, Havel L, Krzakowski M, Hochmair MJ, et al. First-line atezolizumab plus chemotherapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med. (2018) 379:2220–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1809064
11. Paz-Ares L, Dvorkin M, Chen Y, Reinmuth N, Hotta K, Trukhin D, et al. Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet (London England). (2019) 394:1929–39. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32222-6
12. Cheng Y, Han L, Wu L, Chen J, Sun H, Wen G, et al. Effect of first-line serplulimab vs placebo added to chemotherapy on survival in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: the ASTRUM-005 randomized clinical trial. Jama. (2022) 328:1223–32. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.16464
13. Wang J, Zhou C, Yao W, Wang Q, Min X, Chen G, et al. Adebrelimab or placebo plus carboplatin and etoposide as first-line treatment for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CAPSTONE-1): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2022) 23:739–47. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00224-8
14. Reck M, Bondarenko I, Luft A, Serwatowski P, Barlesi F, Chacko R, et al. Ipilimumab in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin as first-line therapy in extensive-disease-small-cell lung cancer: results from a randomized, double-blind, multicenter phase 2 trial. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. (2013) 24:75–83. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mds213
15. Reck M, Luft A, Szczesna A, Havel L, Kim SW, Akerley W, et al. Phase III randomized trial of ipilimumab plus etoposide and platinum versus placebo plus etoposide and platinum in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. (2016) 34:3740–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.67.6601
16. Paz-Ares L, Chen Y, Reinmuth N, Hotta K, Trukhin D, Statsenko G, et al. Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, plus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: 3-year overall survival update from CASPIAN. ESMO Open. (2022) 7:100408. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100408
17. Chung HC, Piha-Paul SA, Lopez-Martin J, Schellens JHM, Kao S, Miller WH Jr., et al. Pembrolizumab after two or more lines of previous therapy in patients with recurrent or metastatic SCLC: results from the KEYNOTE-028 and KEYNOTE-158 studies. J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer. (2020) 15:618–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.12.109
18. Rudin CM, Awad MM, Navarro A, Gottfried M, Peters S, Csőszi T, et al. Pembrolizumab or placebo plus etoposide and platinum as first-line therapy for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: randomized, double-blind, phase III KEYNOTE-604 study. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. (2020) 38:2369–79. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.00793
19. Ready N, Farago AF, de Braud F, Atmaca A, Hellmann MD, Schneider JG, et al. Third-line nivolumab monotherapy in recurrent SCLC: checkMate 032. J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer. (2019) 14:237–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.10.003
20. Spigel DR, Vicente D, Ciuleanu TE, Gettinger S, Peters S, Horn L, et al. Second-line nivolumab in relapsed small-cell lung cancer: CheckMate 331 (☆). Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. (2021) 32:631–41. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.01.071
21. Owonikoko TK, Park K, Govindan R, Ready N, Reck M, Peters S, et al. Nivolumab and ipilimumab as maintenance therapy in extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer: checkMate 451. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:1349–59. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.02212
22. Liu SV, Reck M, Mansfield AS, Mok T, Scherpereel A, Reinmuth N, et al. Updated overall survival and PD-L1 subgroup analysis of patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer treated with atezolizumab, carboplatin, and etoposide (IMpower133). J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:619–30. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01055
23. Acheampong E, Abed A, Morici M, Bowyer S, Amanuel B, Lin W, et al. Tumour PD-L1 expression in small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cells. (2020) 9(11):2393. doi: 10.3390/cells9112393
24. George J, Lim JS, Jang SJ, Cun Y, Ozretić L, Kong G, et al. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature. (2015) 524:47–53. doi: 10.1038/nature14664
25. Hellmann MD, Callahan MK, Awad MM, Calvo E, Ascierto PA, Atmaca A, et al. Tumor mutational burden and efficacy of nivolumab monotherapy and in combination with ipilimumab in small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell. (2018) 33:853–861 e854. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.04.001
26. Paz-Ares L, Garassino MC, Chen Y, Reinmuth N, Hotta K, Poltoratskiy A, et al. Durvalumab ± Tremelimumab + Platinum-etoposide in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer , (CASPIAN) : outcomes by PD-L1 expression and tissue tumor mutational burden. Clin Cancer research: an Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. (2024) 30:824–35. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-1689
27. Rudin CM, Kim HR, Navarro A, Gottfried M, Peters S, Csoszi T, et al. Exploratory biomarker analysis of the phase 3 KEYNOTE-604 study of pembrolizumab plus etoposide for extensive-stage SCLC. J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:8503–3. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2023.41.16_suppl.8503
28. Gay CM, Stewart CA, Park EM, Diao L, Groves SM, Heeke S, et al. Patterns of transcription factor programs and immune pathway activation define four major subtypes of SCLC with distinct therapeutic vulnerabilities. Cancer Cell. (2021) 39:346–360 e347. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.12.014
29. Liu SV, Mok TSK, Nabet BY, Mansfield AS, De Boer R, Losonczy G, et al. Clinical and molecular characterization of long-term survivors with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer treated with first-line atezolizumab plus carboplatin and etoposide. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam Netherlands). (2023) 186:107418. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2023.107418
30. Li W, Ye L, Huang Y, Zhou F, Wu C, Wu F, et al. Characteristics of Notch signaling pathway and its correlation with immune microenvironment in SCLC. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam Netherlands). (2022) 167:25–33. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2022.03.019
31. Tian Y, Li Q, Yang Z, Zhang S, Xu J, Wang Z, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic profiling reveals the tumor heterogeneity of small-cell lung cancer. Signal transduction targeted Ther. (2022) 7:346. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01150-4
32. Muppa P, Parrilha Terra SBS, Sharma A, Mansfield AS, Aubry MC, Bhinge K, et al. Immune cell infiltration may be a key determinant of long-term survival in small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer. (2019) 14:1286–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.03.028
33. Chan JM, Quintanal-Villalonga Á, Gao VR, Xie Y, Allaj V, Chaudhary O, et al. Signatures of plasticity, metastasis, and immunosuppression in an atlas of human small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell. (2021) 39:1479–1496 e1418. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.09.008
34. Hardy-Werbin M, Rocha P, Arpi O, Taus Á, Nonell L, Durán X, et al. Serum cytokine levels as predictive biomarkers of benefit from ipilimumab in small cell lung cancer. Oncoimmunology. (2019) 8:e1593810. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2019.1593810
35. Foster NR, Renfro LA, Schild SE, Redman MW, Wang XF, Dahlberg SE, et al. Multitrial evaluation of progression-free survival as a surrogate end point for overall survival in first-line extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer. (2015) 10:1099–106. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000548
36. Slotman B, Faivre-Finn C, Kramer G, Rankin E, Snee M, Hatton M, et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation in extensive small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med. (2007) 357:664–72. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa071780
37. Takahashi T, Yamanaka T, Seto T, Harada H, Nokihara H, Saka H, et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation versus observation in patients with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2017) 18:663–71. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30230-9
38. Gore EM, Hu C, Sun AY, Grimm DF, Ramalingam SS, Dunlap NE, et al. Randomized phase II study comparing prophylactic cranial irradiation alone to prophylactic cranial irradiation and consolidative extracranial irradiation for extensive-disease small cell lung cancer (ED SCLC): NRG oncology RTOG 0937. J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer. (2017) 12:1561–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.06.015
39. Zeng H, Zheng D, Witlox WJA, Levy A, Traverso A, Kong FS, et al. Risk factors for brain metastases in patients with small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:889161. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.889161
40. Nakahara Y, Takagi Y, Okuma Y, Hosomi Y, Okamura T, Shibuya M, et al. Neurotoxicity due to prophylactic cranial irradiation for small-cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis. Mol Clin Oncol. (2015) 3:1048–52. doi: 10.3892/mco.2015.581
41. Deng L, Zhou Z, Xiao Z, Chen D, Feng Q, Liang J, et al. Impact of thoracic radiation therapy after chemotherapy on survival in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: A propensity score-matched analysis. Thorac Cancer. (2019) 10:799–806. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13001
42. Li AM, Zhou H, Xu YY, Ji XQ, Wu TC, Yuan X, et al. Role of thoracic radiotherapy in extensive stage small cell lung cancer: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Ann Trans Med. (2021) 9:299. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-5765
43. Slotman BJ, van Tinteren H, Praag JO, Knegjens JL, El Sharouni SY, Hatton M, et al. Radiotherapy for extensive stage small-cell lung cancer - Authors' reply. Lancet (London England). (2015) 385:1292–3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60679-1
44. Ashworth A, Rodrigues G, Boldt G, and Palma D. Is there an oligometastatic state in non-small cell lung cancer? A systematic review of the literature. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam Netherlands). (2013) 82:197–203. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.07.026
45. Slotman BJ, Faivre-Finn C, van Tinteren H, Keijser A, Praag J, Knegjens J, et al. Which patients with ES-SCLC are most likely to benefit from more aggressive radiotherapy: A secondary analysis of the Phase III CREST trial. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam Netherlands). (2017) 108:150–3. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.03.007
46. Zhang H, Deng L, Wang X, Wang D, Teng F, and Yu J. Metastatic location of extensive stage small-cell lung cancer: implications for thoracic radiation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2019) 145:2605–12. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-03000-3
47. Shang X, Lin J, Li Z, and Wang H. Radiotherapy may improve survival of ES-SCLC with distant metastasis only for patients with one metastatic site: A population-based study. Oncol Lett. (2020) 19:139–46. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.11092
48. Cozzi S, Bruni A, Ruggieri MP, Borghetti P, Scotti V, Franceschini D, et al. Thoracic radiotherapy in extensive disease small cell lung cancer: multicenter prospective observational TRENDS study. Cancers. (2023) 15(2):434. doi: 10.3390/cancers15020434
49. Hasan S, Renz P, Turrisi A, Colonias A, Finley G, and Wegner RE. Dose escalation and associated predictors of survival with consolidative thoracic radiotherapy in extensive stage small cell lung cancer (SCLC): A National Cancer Database (NCDB) propensity-matched analysis. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam Netherlands). (2018) 124:283–90. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.08.016
50. Han J, Fu C, and Li B. Clinical outcomes of extensive-stage small cell lung cancer patients treated with thoracic radiotherapy at different times and fractionations. Radiat Oncol (London England). (2021) 16:47. doi: 10.1186/s13014-021-01773-x
51. Charpentier M, Spada S, Van Nest SJ, and Demaria S. Radiation therapy-induced remodeling of the tumor immune microenvironment. Semin Cancer Biol. (2022) 86:737–47. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.04.003
52. Deng L, Liang H, Burnette B, Beckett M, Darga T, Weichselbaum RR, et al. Irradiation and anti-PD-L1 treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice. J Clin Invest. (2014) 124:687–95. doi: 10.1172/JCI67313
53. Herrera FG, Bourhis J, and Coukos G. Radiotherapy combination opportunities leveraging immunity for the next oncology practice. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2017) 67:65–85. doi: 10.3322/caac.21358
54. Barker HE, Paget JT, Khan AA, and Harrington KJ. The tumour microenvironment after radiotherapy: mechanisms of resistance and recurrence. Nat Rev Cancer. (2015) 15:409–25. doi: 10.1038/nrc3958
55. Herrera FG, Ronet C, Ochoa de Olza M, Barras D, Crespo I, Andreatta M, et al. Low-dose radiotherapy reverses tumor immune desertification and resistance to immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. (2022) 12:108–33. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0003
56. Vanpouille-Box C, Alard A, Aryankalayil MJ, Sarfraz Y, Diamond JM, Schneider RJ, et al. DNA exonuclease Trex1 regulates radiotherapy-induced tumour immunogenicity. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:15618. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15618
57. Li L, Yang D, Min Y, Liao A, Zhao J, Jiang L, et al. First-line atezolizumab/durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide combined with radiotherapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. (2023) 23:318. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10784-8
58. Peng J, Zhang L, Wang L, Feng H, Yao D, Meng R, et al. Real-world outcomes of PD-L1 inhibitors combined with thoracic radiotherapy in the first-line treatment of extensive stage small cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol (London England). (2023) 18:111. doi: 10.1186/s13014-023-02308-2
59. Xie Z, Liu J, Wu M, Wang X, Lu Y, Han C, et al. Real-world efficacy and safety of thoracic radiotherapy after first-line chemo-immunotherapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Med. (2023) 12(11):3828. doi: 10.3390/jcm12113828
60. Wu JJ, Huang JW, Hsu KH, Huang YH, Chen KC, Tseng JS, et al. Thoracic radiotherapy may improve the outcome of extensive stage small cell lung carcinoma patients treated with first-line immunotherapy plus chemotherapy. Anti-cancer Drugs. (2022) 33:e842–9. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001374
61. Daher SN, Allen A, Rottenberg Y, Nasrallah H, Yosef L, Blumenfeld P, et al. 144P Real -world data of consolidative radiotherapy for extensive stage, (ES) -SCLC treated by chemo – immunotherapy (chemo - IO). Ann Oncol. (2022) 33:S99–S100. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.02.175
62. Li Y, Jing W, Jing X, Sun Y, Tang X, Guo J, et al. Role of consolidative thoracic radiation in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer with first-line chemoimmunotherapy: a retrospective study from a single cancer center. Discover Oncol. (2023) 14:55. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00666-7
63. Chen DW, Gao AQ, Huang W, Shao Q, Meng XJ, Tang XY, et al. Updated safety and efficacy results of SHR - 1316 combined with chemotherapy and sequential chest radiotherapy as first-line therapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer , (ES-SCLC) from a phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:8580. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2023.41.16_suppl.8580
64. Luo J, Xu L, Zhao L, Cao Y, Pang Q, Wang J, et al. Timing of thoracic radiotherapy in the treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: important or not? Radiat Oncol (London England). (2017) 12:42. doi: 10.1186/s13014-017-0779-y
65. Welsh JW, Heymach JV, Chen D, Verma V, Cushman TR, Hess KR, et al. Phase I trial of pembrolizumab and radiation therapy after induction chemotherapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer. (2020) 15:266–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.10.001
Keywords: small cell lung cancer, ES-SCLC, immune checkpoint inhibitors, immunotherapy, chemotherapy, thoracic radiotherapy
Citation: Liu J, Liu J, Chen D, Zhu Y, Wu X and Cai Y (2025) Advancements in consolidative thoracic radiotherapy following first-line immunotherapy in conjunction with chemotherapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. Front. Immunol. 16:1665072. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1665072
Received: 13 July 2025; Accepted: 17 October 2025;
Published: 03 November 2025.
Edited by:
Lilia Bardoscia, Healthcare Company Tuscany Nord Ovest, ItalyReviewed by:
György – Losonczy, Semmelweis University, HungaryValeria Dionisi, Integrated University Hospital Verona, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Liu, Chen, Zhu, Wu and Cai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiang Liu, bGl1amlhbmc4OTAxQDE2My5jb20=; Yin Cai, MTg4NjEwNjc3ODlAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jiang Liu
Jiang Liu Jianhua Liu2†
Jianhua Liu2†