- 1Medical Research Center & Department of Pathology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Pathology, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, China
- 3Geneplus, Beijing, China
- 4Medical Research Center & Department of Pathology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Beijing, China
Background: Intimal sarcoma (IS) and angiosarcoma (AS), two rare yet highly aggressive vascular mesenchymal malignancies, present significant therapeutic challenges due to their scarcity, which underscoring the urgent need to investigate genetic alterations and tumor microenvironment (TME) features for novel therapeutic development.
Methods: We performed integrated analysis of whole-exome sequencing (WES)/1021-gene panel sequencing, RNA sequencing, and immunohistochemistry (IHC) data from 31 IS and 35 AS patients to identify potential precision therapy.
Results: Genomic profiling revealed 522 and 518 single nucleotide variants (SNVs) in the IS and AS cohorts, respectively. TP53 mutations predominated in AS versus IS (15/35 vs 2/31, p < 0.001). Conversely, IS exhibited significantly more copy number variants (CNVs), particularly involving the KDR/KIT/PDGFRA locus (chromosome 4) and the CDK4/MDM2 locus (chromosome 12) (p < 0.001). Strikingly, 25/31 (81%) IS patients harbored CDK4 copy number gains or CDKN2A/B losses, compared to only 2/35 (6%) AS patients (p < 0.001). TME analysis revealed no significant inter-group differences overall; however, pulmonary artery IS specimens demonstrated substantial immune infiltration. Notably, reduced CD3+ T-cell density correlated with shorter survival (p =0.029). PD-L1 expression analysis (≥1% cutoff) showed positivity in 6/8 evaluable patients, including 3 with >50% tumor cell staining. Two IS patients receiving postoperative Sintilimab (PD-1 inhibitor) experienced prolonged survival (overall survival: 14+ and 56+ months, respectively).
Conclusions: This study characterizes the distinct mutation landscape yet similar immune microenvironment of rare IS and AS. Given the frequent cell cycle dysregulation and the observed PD-L1 expression in a subset of patients, CDK4/6 inhibitors and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors warrant further clinical investigation for these patients.
Introduction
Angiosarcoma (AS) is a rare histological subtype of soft tissue sarcoma that arises from endothelial cells of the blood or lymphatic vasculature. It frequently arises in the skin of the head and neck region, the breast, and may develop in almost any anatomic location (1–3). Intimal sarcoma is an even rarer and highly malignant tumor that primarily arises in large arteries and blood vessels (4). It extends along the intimal surface with multifocal intramural growth, most commonly involving the pulmonary artery, major systemic arteries (especially the aorta), and the heart. Characterized by a polypoid growth pattern within the lumen, pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma often invades the vascular wall and metastasizes distantly (5, 6).
The scarcity of AS and IS likely accounts for the severely restricted spectrum of available therapeutic interventions (7). Currently, AS and IS are generally treated with surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Surgical resection is the most effective treatment for both tumor types. Although patients undergoing curative resection show longer overall survival than those with incomplete resection (8–13), local and distant recurrences remain common. Notably, clinical outcomes have not markedly improved in decades despite aggressive therapeutic approaches (14).
In patients with advanced disease, chemotherapy can be effective but generally fails to provide durable clinical benefit (15, 16). It was reported doxorubicin-based chemotherapy failed in most IS patients (17), other cytotoxic agents such as tubulin inhibitor were still under investigation (18). Immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) represents a promising therapeutic approach across various soft tissue sarcomas. Impressive responses to ICB have been reported in a subset of AS patients (2, 19–28), with potential predictive markers including CD8+ lymphocytes expressing programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and high tumor mutation burden (TMB) (29, 30). However, the efficacy of ICB in IS remains largely unknown. Recurrent alterations in the 12q12–15 region (encompassing MDM2 and CDK4) and the 4q12 region (containing PDGFRA) in IS suggest that MDM2 and PDGFRA inhibition may constitute a viable treatment strategy (31–35). MDM2 inhibitors such as BI907828 Alrizomadlin (APG-115) and Milademetan (DS-3032) have demonstrated promising pharmacological effects in advanced preclinical models and early-phase clinical trials (12, 31, 36–41). Nevertheless, resistance to targeted therapies has been documented in IS (39). Furthermore, MDM2/MDM4 amplifications have been associated with rapid disease progression, termed hyperprogressive disease (HPD), following ICB treatment in other contexts (42, 43). Consequently, whether ICB confers clinical benefit to IS patients requires further investigation.
In this study, we analyzed the clinical, genomic, and immune microenvironment characteristics of 31 patients with IS and 35 patients with AS to explore the potential for targeted therapy or immune checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in these rare but highly aggressive malignancies. We also present two cases of IS that benefited from ICB therapy, which may provide an additional treatment option for this devastating disease.
Materials and methods
Patient recruitment
This retrospective study analyzed 13 intimal sarcoma (IS) cases and 35 angiosarcoma (AS) cases identified from pathology archives between January 2017 and April 2025. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples from surgical resections or biopsies were collected for next-generation sequencing (NGS), immunohistochemistry (IHC), and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) when available. Clinical data were retrieved from hospital records, and patients were followed for survival outcomes. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Ethics Review Board of the China-Japan Friendship Hospital (2023-KY-045). Individual consent for this retrospective analysis was waived.
Given the rarity of IS, we supplemented our cohort with 18 IS patients from a publicly available dataset (Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, MSKCC) as an independent cohort. The genomic data (cancer panel) and clinical information for these 18 cases were obtained via cBioPortal (44).
IHC
Surgical and biopsy specimens underwent formalin fixation and paraffin embedding, followed by sectioning at 4.0 µm thickness. Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and immune-stained using the EnVision method, incorporating both negative and positive controls.
Primary antibodies were sourced as follows: CKpan (AE1/AE3), Vimentin (VMAB159), CD34 (EP88), Ki-67 (MIB-1), CD8 (SP16), and CD4 (EP204) from Beijing Zhong Shan - Golden Bridge Biological Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China); SMA (1H4), CD3 (MX036), CD68 (Kp-1), MDM2 (IF2), and CDK4 (EP180) from Fuzhou Maixin Biotechnology Development Co., Ltd. (Fuzhou, China); PD-L1 (22C3) from Dako North America, Inc.; CD3 (L26) along with all secondary antibodies and reagents from Roche Diagnostics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. Protein localization analyses were performed using established subcellular compartment criteria: nuclear staining for MDM2 and Ki-67; cytoplasmic staining for SMA, CKpan, CD3, CD8, CD4, CD68, and Vimentin; exclusive plasma membrane staining for PD-L1; combined cytoplasmic and plasma membrane staining for CD34; and cytoplasmic/nuclear dual localization for CDK4.
Immunostaining was scored as (+) when 1-10% of tumor cells were positive, (++) for 10% to 40% positive cells, and (+++) when positivity exceeded 40%. PD-L1 expression was assessed using the Tumor Proportion Score (TPS), defined as the percentage of viable tumor cells exhibiting partial or complete membrane staining at any intensity, with a positivity cutoff set at 1%.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
The MDM2 (12q15) gene probe was employed to assess corresponding gene amplification in tumor cells using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). The FISH probe kit was acquired from Guangzhou Amping Pharmaceutical Technology Co. Ltd. Procedures were performed in strict accordance with the manufacturer’s protocol. For interpretation, the average signals for MDM2 and CEP12 were enumerated across 50 tumor cells. MDM2 amplification was defined as an MDM2/CEP12 signal ratio ≥ 2.0.
DNA extraction, targeted capture, and NGS
Genetic analysis was performed as previously described (45). In brief, serial sections of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tumor tissues were subjected to genomic DNA extraction using the QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). Histologically confirmed adjacent noncancerous tissue served as the control. Sequencing libraries were prepared using Illumina TruSeq DNA Library Preparation Kits (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Libraries were hybridized with custom-designed biotinylated oligonucleotide probes targeting either 1021 genes or the whole-exome sequencing (WES) panel (Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc.; Supplementary Table 1). Final libraries were sequenced on the GenePlus-Seq-2000 platform (GenePlus-Suzhou Institute).
Sequencing data analysis and variant interpretation
The sequencing data were analyzed using default parameters (45). Adapter sequences and low-quality reads were removed. Clean reads were aligned to the human reference genome (hg19) using the Burrows-Wheeler Aligner (BWA; version 0.7.15-r1140). Single nucleotide variants (SNVs) were called using MuTect (version 1.1.4) and NChot. Small insertions and deletions (Indels) were identified with GATK. Somatic copy-number alterations (SCNAs) were detected using CONTRA (version 2.0.8). Significant SCNAs were defined as the log2 ratio of adjusted depth between tumor DNA and matched germline control DNA. All final candidate variants underwent manual verification in the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV). Targeted capture sequencing required a minimum mean effective depth of coverage of 300× for whole-exome sequencing (WES) and 500× for the 1021-gene panel. Variants were filtered to exclude synonymous alterations, known germline variants listed in dbSNP, and variants with a population frequency exceeding 1% in the Exome Sequencing Project.
RNA sequencing and tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte subpopulation analysis
We performed RNA-Seq as previously described (46). Briefly, total RNA was extracted from tumor FFPE specimens using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA integrity was assessed using the RNA Integrity Number (RIN) generated by the 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). RNA libraries were constructed with the NEBNext® Ultra™ RNA Library Prep Kit (New England Biolabs, Beverly, MA, USA). Libraries were sequenced on the Geneplus-2000 platform (Geneplus, Beijing, China).
The relative fractions of 22 infiltrating immune cell types within each tumor tissue were determined using CIBERSORT (http://cibersort.stanford.edu/). The algorithm was executed using the LM22 signature matrix with 1,000 permutations. The evaluated tumor-infiltrating immune cell populations included naïve B cells, memory B cells, plasma cells, naïve CD4+ T cells, resting memory CD4+ T cells, activated memory CD4+ T cells, follicular helper T cells (Tfh), regulatory T cells (Tregs), CD8+ T cells, gamma delta T cells (γδ T cells), M0 macrophages, M1 macrophages, M2 macrophages, resting natural killer (NK) cells, activated NK cells, resting dendritic cells (DC), activated DC, monocytes, resting mast cells, activated mast cells, neutrophils, and eosinophils. For each tumor sample, the sum of the fractions for all evaluated immune cell types equaled 1 (47, 48).
Results
Characteristics of the patient cohort
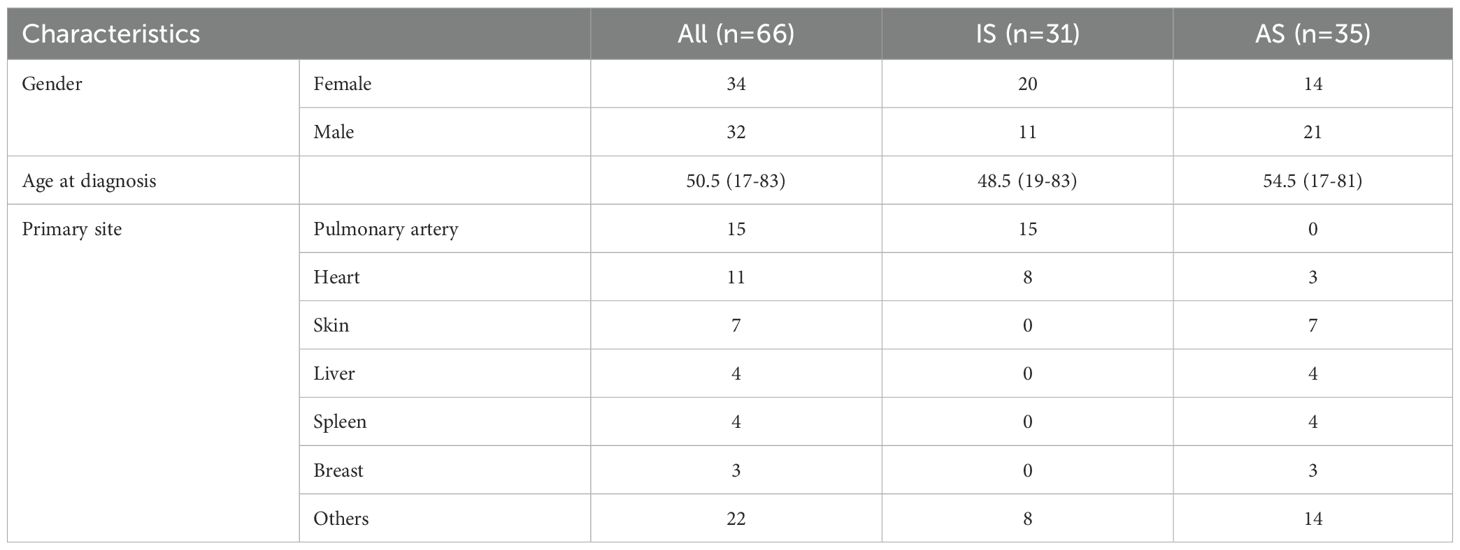
The cohort comprised 66 cases (34 females, 32 males) with a mean age of 50.5 years (range, 17–83 years). The IS subgroup exhibited a higher proportion of female patients (20/31) compared to the AS subgroup (15/35). Tumor primary sites differed significantly, with IS predominantly involving the pulmonary artery and heart, and AS primarily involving the skin (Table 1).
As pathological information for the 18 IS patients from the MSKCC cohort was unavailable (44), we focused on the 11 IS patients with detailed pathological analysis. Histologically, all tumors exhibited moderately to severely atypical spindle tumor cells. Epithelioid or giant tumor cells were present in 7 cases. Among the 8 cases with necrosis, these areas consistently featured severely atypical tumor cells, including epithelioid and bizarre giant tumor cells. Tumor cell density varied regionally. Some areas showed relatively sparse tumor cells with stromal myxoid degeneration, while others displayed densely packed spindle cells forming fascicles reminiscent of leiomyosarcoma. One case exhibited tumor invasion accompanied by destruction of the vascular wall. Osteosarcoma differentiation was identified in some cases (Figure 1A).
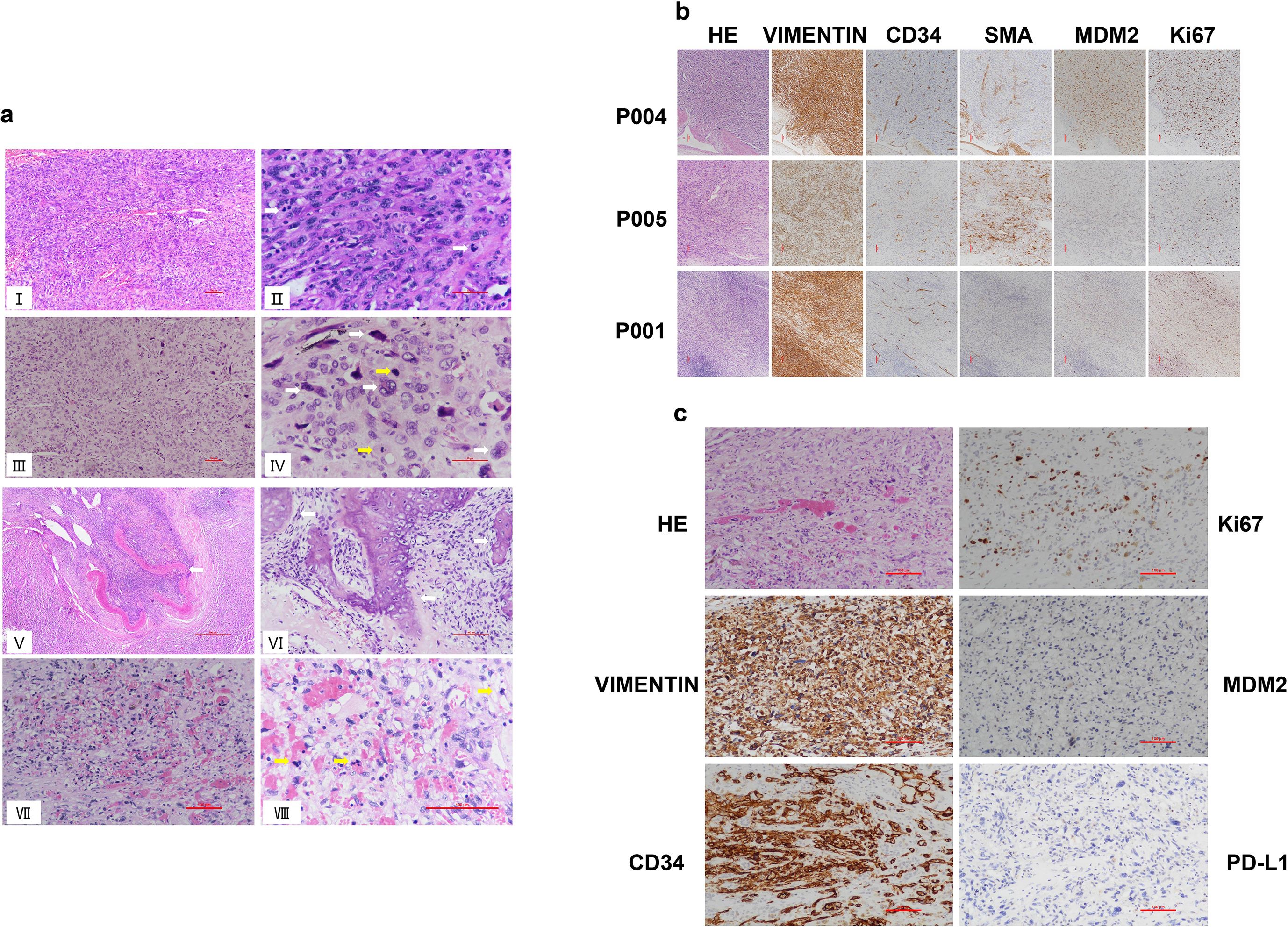
Figure 1. Histological analysis of intimal sarcoma and angiosarcoma. (A) Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of IS and AS cases. (I) Microscopically, the tumor tissue manifests as a poorly or undifferentiated malignant neoplasm of mesenchymal origin, predominantly composed of spindle cells within the tumor cell population. Scale bar: 100μm. (II) Spindle-shaped tumor cells are densely packed in fascicular formations akin to leiomyosarcoma, with mitotic figures readily discernible (white arrow). Scale bar: 50μm. (III) The tumor cells in some areas exhibit an epithelioid morphology, with relatively sparse cell density and prominent cellular pleomorphism. Scale bar: 100μm. (IV) High-power view showing highly atypical epithelioid and bizarre giant tumor cells (white arrows), with mitotic figures noted (yellow arrows). Scale bar: 50μm. (V) The tumor invades and destroys the vascular wall, with a small amount of residual vascular smooth muscle tissue visible (white arrow). Scale bar: 100μm. (VI) Region with osteosarcoma differentiation characterized by osteoid production (white arrow). Scale bar: 500μm. (VII) AS reveals variable tumor cell atypia, featuring anastomosing vascular channels lined by tumor cells and filled with numerous red blood cells. Scale bar: 100μm. (VIII) Tumor cells at high magnification exhibit abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, vesicular nuclei with distinct nucleoli, and noted mitotic figures (yellow arrows). Scale bar: 100μm. (B) Immunohistochemical staining of Vimentin, MDM2, SMA, CD34 and Ki67 in representative cases of pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma (P004, P005, P001, 100×). Scale bar: 100μm. (C) Immunohistochemical staining of Vimentin, MDM2, CD34, Ki67 and PD-L1 in representative cases of hepatic angiosarcoma (200×). Scale bar: 100μm.
The tumor cells of IS and AS were diffusely positive for Vimentin (11/11, 100%) but negative for CKpan. Some IS tumor cells expressed MDM2 (8/11, 72.7%), SMA (3/11, 27.3%), and CD34 (2/11,18.2%). The Ki-67 proliferation index ranged from 30% to 90%, indicating a relatively high proliferation rate (Figures 1B, C).
Archived FFPE samples were utilized for tumor genomic DNA and RNA extraction when available. For the 48 patients from our center, all provided sufficient DNA for subsequent NGS analysis, with 5 undergoing whole-exome sequencing (WES) and the remaining 43 analyzed using a 1021-gene panel. The 18 IS patients from the MSKCC cohort underwent sequencing with IMPACT341/410/468 panels. Additionally, qualified RNA was obtained from 17 patients (11 IS and 6 AS) for RNA sequencing.
Genomic profiling showed significant difference between IS and AS
Somatic mutations were identified in all 66 patients, with 522 single nucleotide variants (SNVs) detected in the 31 IS patients and 518 SNVs in the 35 AS patients. Copy number variants (CNVs) totaled 268 in IS patients and 65 in AS patients. Collectively, the most frequently mutated genes were MDM2 (36%, 24/66), CDK4 (27%, 18/66), TP53 (26%, 17/66), KIT (23%, 15/66) and PDGFRA (20%, 13/66) (Figure 2A).
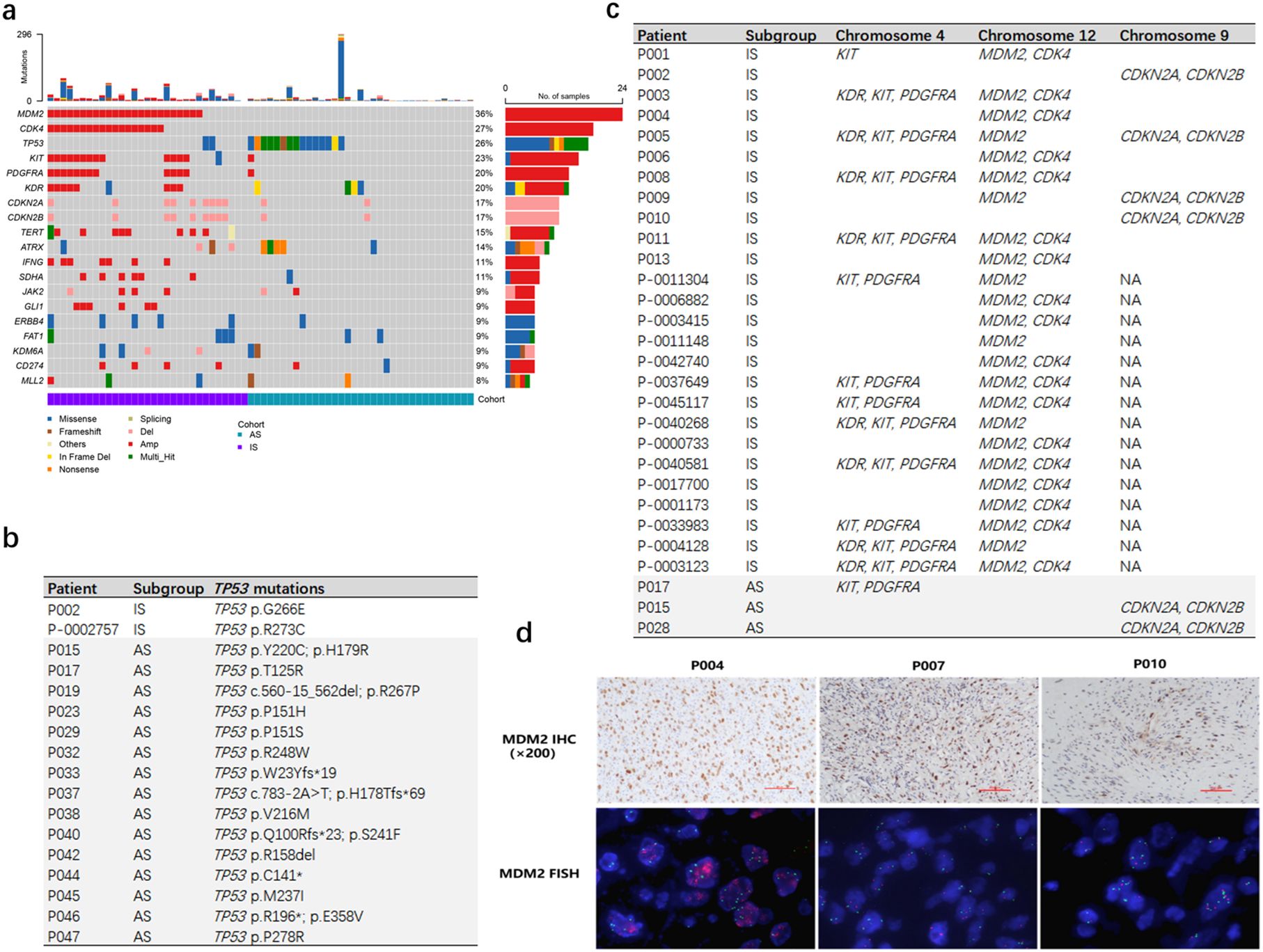
Figure 2. Genomic mutation analysis of IS and AS patients. (A) The genetic landscape and clinical characteristics of 66 patients. The mutation landscape shows the variation of the top 20 genes with the highest mutation frequency in tumors. Each square shows the mutation of each sample provided by the patient in one gene. Different colors denote 8 types of mutations. (B) IS patients had a lower proportion of TP53 mutations. (C) IS patients had a higher proportion of copy number amplification in MDM2, CDK4, KIT, PDGFRA, KDR genes. (D) FISH analysis of MDM2 CNV in patients (P004, P007, P010) confirmed true positive of MDM2 in P004, but negative in P007 and P010. (MDM2 IHC, 200×).
TP53 mutations were significantly more prevalent in AS patients compared to IS patients (15/35 vs 2/31, p < 0.001, Figure 2B). Conversely, amplifications of KDR, KIT and PDGFRA on chromosome 4, as well as CDK4 and MDM2 on chromosome 12, were enriched in IS patients (p < 0.001; Figure 2C).
Moreover, CDK4 copy number gains or CDKN2A/CDKN2B losses were observed in 25 of 31 IS patients but only in 2 of 35 AS patients (p < 0.001; Figure 2C). This cell cycle dysregulation may underlie the elevated Ki-67 index 30%- 90% in IS patients (Figure 1B).
Overexpression and amplification of MDM2 constitute an important characteristic in IS. Further analysis was performed on IS patients lacking MDM2 CNV within our cohort. Among the four patients with available MDM2 IHC staining results, two were MDM2 IHC ++ (P003, P007) and two were MDM2 IHC + (P002, P010). Subsequent MDM2 FISH analysis on samples P007 and P010 also showed no MDM2 copy number gain in either specimen. (Figure 2D, Supplementary Table S1). The observed discrepancies among IHC, NGS-CNV, and FISH results are likely attributable to the low tumor cell fraction in these samples.
Tumor microenvironment analysis showed similar features in IS and AS
Given the striking differences in genomic profiling between the IS and AS cohorts, we further investigated characteristics of the tumor microenvironment in these groups. Using the CIBERSORT algorithm to calculate the abundance of 22 immune cell types within each sample, we found no significant difference in immune infiltration between the IS and AS cohorts (Figure 3A).
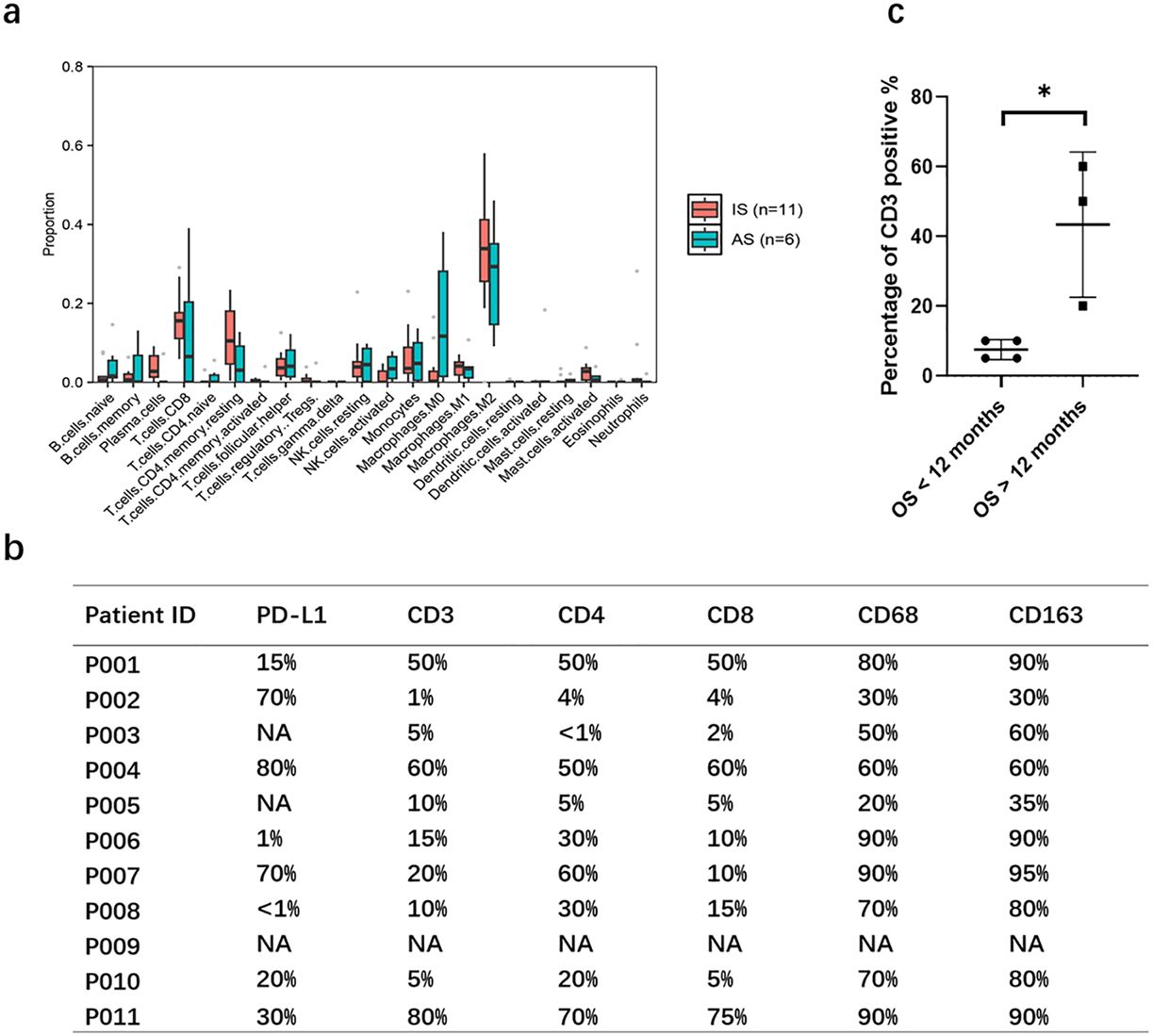
Figure 3. Characteristics of the immune microenvironment. (A) Analysis of 22 immune cell infiltration according to CIBERSORT algorithm showing the percentage of immune cells in each sample. (B) PD-L1 expression and immune cell infiltration of pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma. (C) Percentage of CD3 positive cells was lower in patients with overall survival (OS) less than 12 months. Statistical significance of differences between the groups was calculated with Mann Whiney U test. P-value< 0.05 is considered statistically significant. *p < 0.05.
We next examined PD-L1 expression via IHC in IS patients. Among eight patients with sufficient FFPE samples, PD-L1 expression was detected in six, with three patients (P002, P004, P007) exhibiting strong positivity (70%, 80%, and 70%, respectively; Figure 3B, Supplementary Figure S1). Although the small sample size (n=8) limits broad conclusions, this preliminary finding suggests that PD-L1 expression is a clinically relevant feature in a considerable proportion of IS patients and may indicate a potential for response to ICB. Given the observed abundant immune cell infiltration- including lymphocytes, plasma cells, and histiocytes, with some lymphocytes forming stromal clusters- we characterized the immune microenvironment using the following markers: CD3+ for total T cells, CD4+ for helper T cells, CD8+ for cytotoxic T cells, CD68+ for macrophages, and CD163+ for monocytes/macrophages. Analysis revealed median immune cell infiltration levels of 13% CD3+ (range, 1–80%), 10% CD8+ (range, 2–75%), 30% CD4+ (range, <1–70%), 70% CD68+ (range, 20–90%), and 80% CD163+ (range, 30–90%) (Figure 3B, Supplementary Figure S2). Notably, patients who died within 12 months post-surgery (n=4, P003, P005, P008, P010) exhibited significantly lower CD3+ infiltration compared to those surviving beyond 12 months (n=3; P001, P004, P007; median 7.5% vs. 70%, P=0.029; Figure 3C).
Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitor in 3 IS patients
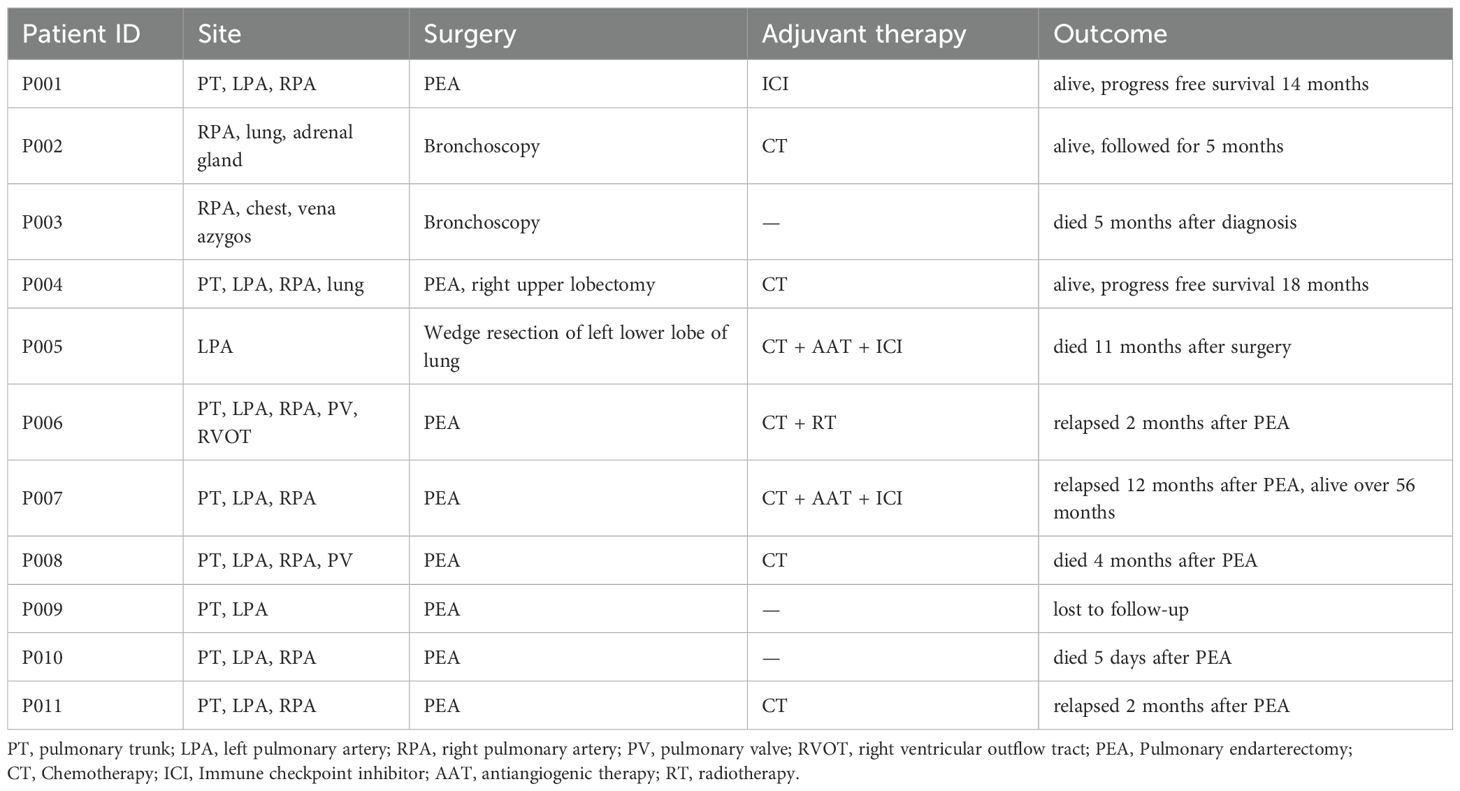
Among the 13 IS patients treated at our center, eight underwent pulmonary endarterectomy and one received wedge resection of the left lower lobe. Three patients died postoperatively on day 5, month 4, and month 11, respectively. Of the five surviving surgical patients, two maintained disease-free survival at 11–14 months. Two experienced relapse, while one patient relapsed at 12 months but remained alive for over 56 months with maintenance therapy comprising sintilimab (anti-PD-1 immunotherapy) and anlotinib (targeted therapy). Two patients did not undergo pulmonary artery tumor resection: one due to inoperability (adrenal metastasis) and another who refused surgery and succumbed to disease progression at 5 months (Table 2).
Three patients received immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy during their disease course. Patient P001, an adult patient with pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma involving the pulmonary trunk (PT), left pulmonary artery (LPA), and right pulmonary artery (RPA), received adjuvant sintilimab following pulmonary endarterectomy (PEA) and has remained progression-free for over 14 months to date. The tumor exhibited 15% PD-L1 expression and strong MDM2 positivity, with an MDM2 copy number gain (CNG) of 9.15. Patient P007, an adult patient also diagnosed with pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma involving the PT, LPA, and RPA, experienced tumor recurrence 12 months post-PEA. This patient subsequently underwent 4 cycles of combined therapy including chemotherapy, the antiangiogenic agent anlotinib, and sintilimab, followed by sintilimab maintenance therapy, achieving sustained tumor control for over 56 months since initial diagnosis (Figure 4). Patient P005, an adult patient with pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma confined to the LPA, underwent wedge resection of the left lower lobe. Despite negative PD-L1 expression, adjuvant therapy comprising combined chemotherapy, antiangiogenic therapy, and an ICI was administered; however, the patient died 11 months post-surgery. The tumor was MDM2-positive, with an MDM2 CNG of 5.37.
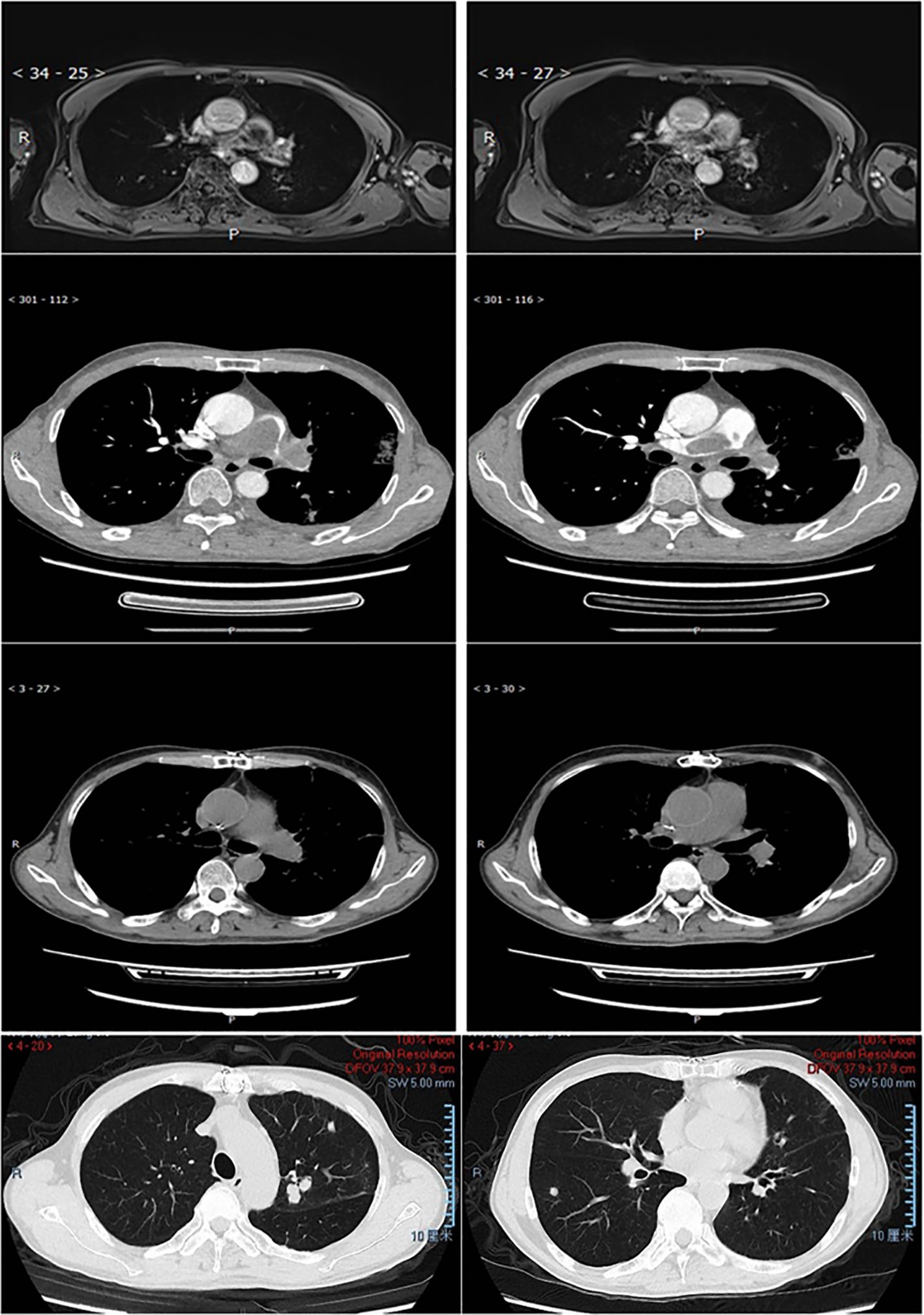
Figure 4. MRI/CT scan of the lung in patient P007. Row 1 (MRI) 2 (CTA), pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma involved PT, LPA, and RPA at diagnosis. Row 3-4, 12 months after PEA the patient relapsed with tumor involved left upper lobe, right lower lobe, and multiple little nodules in the peripheral lung.
Discussions
We performed comprehensive genetic profiling of intimal sarcoma (IS) and angiosarcoma (AS) by integrating WES/1021-panel, RNA-seq, and IHC data from our cohort with IS sequencing data from MSKCC cohorts. Our analysis demonstrated that IS and AS represent distinct sarcoma subtypes but with similar tumor microenvironment: copy number variations (CNVs) were highly enriched in IS, whereas TP53 mutations were predominant in AS. Thus, targeted therapies should be different for IS and AS, while immunotherapy might be of similar efficacy.
In terms of targeted therapy, consistent with prior reports in IS, the most frequent genetic alterations were copy number variations (CNVs) at 12q12-15 (encompassing MDM2 and CDK4) and 4q12 (encompassing KDR, KIT and PDGFRA) (6, 37, 38, 49–51). Thus, MDM2 and PDGFRA inhibition constitute a viable treatment strategy which warrant further clinical trials (12, 31–34, 36–41). In our study, we also observed an increased incidence ofCDKN2A/CDKN2B copy number loss at 9p21 in IS patients lacking CDK4 copy number gain. Collectively, these aberrations in cell cycle regulators may underlie the elevated Ki-67 indices (30%–90%) characteristic of IS tumors. Given that the phase II trial of the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in advanced sarcoma, which selected patients based onCDK4 mRNA expression relative to CDKN2A, achieved its primary endpoint (52), and the successful combination of ribociclib (CDK4/6 inhibitor) with everolimus (mTOR inhibitor) in advanced dedifferentiated liposarcoma and leiomyosarcoma (53), other CDK4/6 inhibitors warrant further investigation in IS.
Regarding immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), while several studies have reported impressive responses in a subset of AS patients (2, 19–28), clinical activity of ICB in intimal sarcomas was only reported in separated cases and its efficacy remains poorly characterized (54, 55). C Park et al. classified IS patients into CNV-high (CNV-H) or MSI-H-like subtypes based on copy number variation (CNV) enrichment (featuring frequent CDK4/MDM2 amplifications) or predominant MLH1 mutations, respectively. They described two MSI-H-like patients treated with pembrolizumab, one achieving complete remission lasting 2 years and the other exhibiting disease control for 6.5 months (56). In our cohort, we identified mutations (MLH1 p.P581L, MSH6 p.F1088Lfs*5, MLH3 p.T730Qfs*4), but all three occurred in a single patient (P006), who also had MDM2 copy number gain. This co-occurrence precluded definitive classification into the CNV-H or MSI-H-like subtypes within our IS cohort. Notably, however, we observed generally similar tumor microenvironments between AS and IS patients, suggesting potential ICB efficacy in a subset of IS patients as well. Our cohort included 13 IS patients of varying ages, with a predominance of females. Surgical resection remained the primary treatment for operable lesions, with chemotherapy (with or without antiangiogenic therapy) or radiation therapy serving as common adjuvant approaches. Reflecting the overall poor prognosis of pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma, three patients received immunotherapy to prevent recurrence or treat recurrent disease. In these three patients, survival duration appeared prolonged, and hyperprogression was not observed despite MDM2 copy number gain-a factor implicated in hyperprogression following ICB in other solid malignancies (42, 43). We speculate that the MDM2 copy number gain in these patients represents chromosome 12 polysomy rather than specific MDM2 amplification, as the IFNG gene (located at 12q15) exhibited similar copy number changes. Combined with the PD-L1 expression observed in a subset of our IS cohort and another study (57), these preliminary data suggest that the potential value of immunotherapy in this aggressive disease warrants further investigation in larger, prospective cohorts.
This study has several limitations: (1) Due to its retrospective nature, we were unable to collect complete therapeutic details, including imaging data, for all patients, and not all patients underwent PD-L1 testing or whole-exome sequencing (WES) due to insufficient tumor sample availability; (2) The rarity of this disease limited enrollment to a small cohort of immunosuppressed (IS) patients, necessitating the inclusion of MSKCC patients; (3) The immunohistochemical analysis in this study was primarily descriptive and semi-quantitative. Future studies with larger patient cohorts are needed to perform robust quantitative assessments of protein expression and immune cell infiltration to validate our findings.
In conclusion, we systematically analyzed the clinical characteristics, pathogenic mechanisms, molecular mutation landscape, and immune microenvironment of rare intimal sarcoma and angiosarcoma. Our data reveal frequent cell cycle dysregulation and identify PD-L1 expression in a subset of these tumors. These findings suggest that CDK4/6 inhibitors and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, may represent promising therapeutic strategies worthy of further investigation.
Data availability statement
The data presented in this study are deposited in the National Genomics Data Central (NGDC) repository, accession number HRA013989.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Institutional Ethics Review Board of the China-Japan Friendship Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because it was a retrospective analysis.
Author contributions
BW: Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation. RC: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis. HY: Formal Analysis, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Investigation. ZC: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. YL: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis. DZ: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Supervision. FL: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the following: (1) National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding, grant number 2023-NHLHCRF-YYPPLC-ZR-06; (2) CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS), grant number 2022-I2M-C&T-B-108; (3) National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 82400501.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1668537/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Immunohistochemical staining of PD-L1 (22C3) in representative patients (P005, P010, P011, P004), with PD-L1 ranging from 0% to 80% (200×).
Supplementary Figure 2 | Immunohistochemical staining of immune cells in representative patients (P004, P001, P010). Column 1, HE, 400×;column 2, CD3, 200×;column 3, CD4, 200×;column 4, CD8, 200×; column 5, CD68, 200×. Row 1, patient P004 showed high lymphocyte densities, row 2 patient P001 showed high lymphocyte densities with focal lymphocyte infiltration, row 3 P010 showed low infiltration of immune cells.
References
1. Fayette J, Martin E, Piperno-Neumann S, Le Cesne A, Robert C, Bonvalot S, et al. Angiosarcomas, a heterogeneous group of sarcomas with specific behavior depending on primary site: a retrospective study of 161 cases. Ann Oncol. (2007) 18:2030–6. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdm381
2. Painter CA, Jain E, Tomson BN, Dunphy M, Stoddard RE, Thomas BS, et al. The Angiosarcoma Project: enabling genomic and clinical discoveries in a rare cancer through patient-partnered research. Nat Med. (2020) 26:181–7. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0749-z
3. Lim RMH, Lee JY, Kannan B, Ko TK, and Chan JY. Molecular and immune pathobiology of human angiosarcoma. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2024) 1879:189159. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189159
4. Wang HQ, Sun AQ, Liu P, Chen W, Cao C, Song X, et al. Clinicopathological features of pulmonary artery and vein intimal sarcomas: case series of rare pulmonary vessel intimal sarcoma. Transl Cancer Res. (2021) 10:3033–43. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-3468
5. Van Dievel J, Sciot R, Delcroix M, Vandeweyer RO, Debiec-Rychter M, Dewaele B, et al. Single-center experience with intimal sarcoma, an ultra-orphan, commonly fatal mesenchymal Malignancy. Oncol Res Treat. (2017) 40:353–9. doi: 10.1159/000476036
6. Jimbo N, Komatsu M, Itoh T, and Hirose T. MDM2 dual-color in situ hybridization (DISH) aids the diagnosis of intimal sarcomas. Cardiovasc Pathol. (2019) 43:107142. doi: 10.1016/j.carpath.2019.07.001
7. Levy E, Korach A, Amir G, and Milgalter E. Undifferentiated sarcoma of the pulmonary artery mimicking pulmonary thromboembolic disease. Heart Lung Circ. (2006) 15:62–3. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2005.06.009
8. Fernandez-Golfin C, Escribano P, Cortina J, Tello R, Hernandez F, Lopez-Rios F, et al. Management of primary pulmonary artery sarcoma: experience of a single center. Angiology. (2008) 59:636–9. doi: 10.1177/0003319707305981
9. Bandyopadhyay D, Panchabhai TS, Bajaj NS, Patil PD, and Bunte MC. Primary pulmonary artery sarcoma: a close associate of pulmonary embolism-20-year observational analysis. J Thorac Dis. (2016) 8:2592–601. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.08.89
10. Shehatha J, Saxena P, Clarke B, Dunning J, and Konstantinov IE. Surgical management of extensive pulmonary artery sarcoma. Ann Thorac Surg. (2009) 87:1269–71. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2008.08.030
11. Secondino S, Grazioli V, Valentino F, Pin M, Pagani A, Sciortino A, et al. Multimodal approach of pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma: A single-institution experience. Sarcoma. (2017) 2017:7941432. doi: 10.1155/2017/7941432
12. Wong HH, Gounaris I, McCormack A, Berman M, Davidson D, Horan G, et al. Presentation and management of pulmonary artery sarcoma. Clin Sarcoma Res. (2015) 5:3. doi: 10.1186/s13569-014-0019-2
13. Ito S, Tahara N, and Fukumoto Y. Refractory pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44:3484. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad500
14. Florou V and Wilky BA. Current and future directions for angiosarcoma therapy. Curr Treat Options Oncol. (2018) 19:14. doi: 10.1007/s11864-018-0531-3
15. Young RJ, Natukunda A, Litiere S, Woll PJ, Wardelmann E, and van der Graaf WT. First-line anthracycline-based chemotherapy for angiosarcoma and other soft tissue sarcoma subtypes: pooled analysis of eleven European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group trials. Eur J Cancer. (2014) 50:3178–86. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.10.004
16. Penel N, Bui BN, Bay JO, Cupissol D, Ray-Coquard I, Piperno-Neumann S, et al. Phase II trial of weekly paclitaxel for unresectable angiosarcoma: the ANGIOTAX Study. J Clin Oncol. (2008) 26:5269–74. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.3146
17. Penel N, Taieb S, Ceugnart L, Dansin E, Hoguet D, Vanseymortier L, et al. Report of eight recent cases of locally advanced primary pulmonary artery sarcomas: failure of Doxorubicin-based chemotherapy. J Thorac Oncol. (2008) 3:907–11. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318180720d
18. Wang Y, Wozniak A, Cornillie J, Aviles P, Debiec-Rychter M, Sciot R, et al. Plocabulin, a novel tubulin inhibitor, has potent antitumour activity in patient-derived xenograft models of soft tissue sarcoma. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:7454. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137454
19. Florou V, Rosenberg AE, Wieder E, Komanduri KV, Kolonias D, Uduman M, et al. Angiosarcoma patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a case series of seven patients from a single institution. J Immunother Cancer. (2019) 7:213. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0689-7
20. Wagner MJ, Othus M, Patel SP, Ryan C, Sangal A, Powers B, et al. Multicenter phase II trial (SWOG S1609, cohort 51) of ipilimumab and nivolumab in metastatic or unresectable angiosarcoma: a substudy of dual anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 blockade in rare tumors (DART). J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e002990. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002990
21. Rosenbaum E, Antonescu CR, Smith S, Bradic M, Kashani D, Richards AL, et al. Clinical, genomic, and transcriptomic correlates of response to immune checkpoint blockade-based therapy in a cohort of patients with angiosarcoma treated at a single center. J Immunother Cancer. (2022) 10:e004149. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-004149
22. Tawbi HA, Burgess M, Bolejack V, Van Tine BA, Schuetze SM, Hu J, et al. Pembrolizumab in advanced soft-tissue sarcoma and bone sarcoma (SARC028): a multicentre, two-cohort, single-arm, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2017) 18:1493–501. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30624-1
23. D’Angelo SP, Mahoney MR, Van Tine BA, Atkins J, Milhem MM, Jahagirdar BN, et al. Nivolumab with or without ipilimumab treatment for metastatic sarcoma (Alliance A091401): two open-label, non-comparative, randomised, phase 2 trials. Lancet Oncol. (2018) 19:416–26. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30006-8
24. Chen AP, Sharon E, O’Sullivan-Coyne G, Moore N, Foster JC, Hu JS, et al. Atezolizumab for advanced alveolar soft part sarcoma. N Engl J Med. (2023) 389:911–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2303383
25. D’Angelo SP, Richards AL, Conley AP, Woo HJ, Dickson MA, Gounder M, et al. Pilot study of bempegaldesleukin in combination with nivolumab in patients with metastatic sarcoma. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:3477. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30874-8
26. Movva S, Seier K, Avutu V, Banks LB, Chan J, Chi P, et al. Histology-specific clinical trial of lenvatinib and pembrolizumab in patients with sarcoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2024) 30:5612–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-2519
27. Liu Z, Weitao Y, Cui K, Gao S, Wang X, Zhang P, et al. The outcomes and treatment strategies in metastatic soft tissue sarcoma treated with immunotherapy-based therapy: a three-center study. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1504117. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1504117
28. Wilky BA, Schwartz GK, Gordon MS, El-Khoueiry AB, Bullock AJ, Henick B, et al. Botensilimab (Fc-enhanced anti-cytotoxic lymphocyte-association protein-4 antibody) Plus Balstilimab (anti-PD-1 antibody) in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Metastatic Sarcomas. J Clin Oncol. (2025) 43:1358–68. doi: 10.1200/JCO-24-02524
29. Fujii H, Arakawa A, Utsumi D, Sumiyoshi S, Yamamoto Y, Kitoh A, et al. CD8(+) tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes at primary sites as a possible prognostic factor of cutaneous angiosarcoma. Int J Cancer. (2014) 134:2393–402. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28581
30. Honda Y, Otsuka A, Ono S, Yamamoto Y, Seidel JA, Morita S, et al. Infiltration of PD-1-positive cells in combination with tumor site PD-L1 expression is a positive prognostic factor in cutaneous angiosarcoma. Oncoimmunology. (2017) 6:e1253657. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1253657
31. Shangary S and Wang S. Small-molecule inhibitors of the MDM2-p53 protein-protein interaction to reactivate p53 function: a novel approach for cancer therapy. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. (2009) 49:223–41. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.48.113006.094723
32. Dewaele B, Floris G, Finalet-Ferreiro J, Fletcher CD, Coindre JM, Guillou L, et al. Coactivated platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor are potential therapeutic targets in intimal sarcoma. Cancer Res. (2010) 70:7304–14. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1543
33. Qin J, Ng CS, He P, Lin X, Lin X, and Hou P. Pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma - A primeval or rediscovered tumor? A report of 14 new cases with literature review. Pathol Res Pract. (2021) 224:153548. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153548
34. Assi T, Kattan J, Rassy E, Moussa T, Nassereddine H, Honore C, et al. A comprehensive review on the diagnosis and management of intimal sarcoma of the pulmonary artery. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2020) 147:102889. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2020.102889
35. Nistor C, Carsote M, Cucu AP, Stanciu M, Popa FL, Ciuche A, et al. Primary cardiac intimal sarcoma: multi-layered strategy and core role of MDM2 amplification/co-amplification and MDM2 immunostaining. Diagnostics (Basel). (2024) 14:919. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14090919
36. Carmagnani Pestana R, Groisberg R, Roszik J, and Subbiah V. Precision oncology in sarcomas: divide and conquer. JCO Precis Oncol. (2019) 3:PO.18.00247. doi: 10.1200/PO.18.00247
37. Frezza AM, Assi T, Lo Vullo S, Ben-Ami E, Dufresne A, Yonemori K, et al. Systemic treatments in MDM2 positive intimal sarcoma: A multicentre experience with anthracycline, gemcitabine, and pazopanib within the World Sarcoma Network. Cancer. (2020) 126:98–104. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32508
38. Roszik J, Khan A, Conley AP, Livingston JA, Groisberg R, Ravi V, et al. Unique aberrations in intimal sarcoma identified by next-generation sequencing as potential therapy targets. Cancers (Basel). (2019) 11:1283. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091283
39. Koyama T, Shimizu T, Kojima Y, Sudo K, Okuma HS, Shimoi T, et al. Clinical activity and exploratory resistance mechanism of milademetan, an MDM2 inhibitor, in intimal sarcoma with MDM2 amplification: an open-label phase Ib/II study. Cancer Discov. (2023) 13:1814–25. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-23-0419
40. Cornillie J, Wozniak A, Li H, Gebreyohannes YK, Wellens J, Hompes D, et al. Anti-tumor activity of the MDM2-TP53 inhibitor BI-907828 in dedifferentiated liposarcoma patient-derived xenograft models harboring MDM2 amplification. Clin Transl Oncol. (2020) 22:546–54. doi: 10.1007/s12094-019-02158-z
41. Zhang X, Wen X, Peng R, Pan Q, Weng D, Ma Y, et al. A first-in-human phase I study of a novel MDM2/p53 inhibitor alrizomadlin in advanced solid tumors. ESMO Open. (2024) 9:103636. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.103636
42. Kato S, Goodman A, Walavalkar V, Barkauskas DA, Sharabi A, and Kurzrock R. Hyperprogressors after immunotherapy: analysis of genomic alterations associated with accelerated growth rate. Clin Cancer Res. (2017) 23:4242–50. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-3133
43. Forschner A, Hilke FJ, Bonzheim I, Gschwind A, Demidov G, Amaral T, et al. MDM2, MDM4 and EGFR amplifications and hyperprogression in metastatic acral and mucosal melanoma. Cancers (Basel). (2020) 12:540. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030540
44. Nacev BA, Sanchez-Vega F, Smith SA, Antonescu CR, Rosenbaum E, Shi H, et al. Clinical sequencing of soft tissue and bone sarcomas delineates diverse genomic landscapes and potential therapeutic targets. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:3405. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30453-x
45. Ai X, Cui J, Zhang J, Chen R, Lin W, Xie C, et al. Clonal architecture of EGFR mutation predicts the efficacy of EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced NSCLC: A prospective multicenter study (NCT03059641). Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:704–12. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3063
46. Wang B, Chen R, Wang C, Guo J, Yuan M, Chen H, et al. Identification of novel ALK fusions using DNA/RNA sequencing in immunohistochemistry/RT-PCR discordant NSCLC patients. Hum Pathol. (2021) 114:90–8. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2021.05.005
47. Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ, Feng W, Xu Y, et al. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods. (2015) 12:453–7. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3337
48. Charoentong P, Finotello F, Angelova M, Mayer C, Efremova M, Rieder D, et al. Pan-cancer immunogenomic analyses reveal genotype-immunophenotype relationships and predictors of response to checkpoint blockade. Cell Rep. (2017) 18:248–62. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.019
49. Sai S, Imamura Y, Kiyota N, Jimbo N, Toyoda M, Funakoshi Y, et al. Relationship between PDGFR expression and the response to pazopanib in intimal sarcoma of the pulmonary artery: A case report. Mol Clin Oncol. (2021) 14:6. doi: 10.3892/mco.2020.2168
50. Harbhajanka A, Dahoud W, Michael CW, and Elliot R. Cytohistological correlation, immunohistochemistry and Murine Double Minute Clone 2 amplification of pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma: A case report with review of literature. Diagn Cytopathol. (2019) 47:494–7. doi: 10.1002/dc.24131
51. Chang DY, Lin KC, Pan JY, Liu HW, Kuo SH, and Lee L. Pulmonary artery intimal sarcoma: a case report and literature review. Respirol Case Rep. (2020) 8:e00530. doi: 10.1002/rcr2.530
52. Martin-Broto J, Martinez-Garcia J, Moura DS, Redondo A, Gutierrez A, Lopez-Pousa A, et al. Phase II trial of CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in advanced sarcoma based on mRNA expression of CDK4/CDKN2A. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:405. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01661-8
53. Movva S, Matloob S, Handorf EA, Choy E, Merriam P, Flieder DB, et al. SAR-096: phase II clinical trial of ribociclib in combination with everolimus in advanced dedifferentiated liposarcoma (DDL) and leiomyosarcoma (LMS). Clin Cancer Res. (2024) 30:315–22. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-2469
54. Ribeiro MF, Demicco EG, and Razak ARA. Clinical activity of pembrolizumab in refractory MDM2-amplified advanced intimal sarcomas. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2024) 16:17588359241250158. doi: 10.1177/17588359241250158
55. Liao H, Fang Y, Li D, Pan Y, Niu Z, Fu T, et al. Tislelizumab combined with GT chemotherapy for intimal sarcoma of inferior vena cava: A case report. Med (Baltimore). (2024) 103:e38056. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038056
56. Park C, Kim R, Bae JM, Lee T, Song S, Kwak Y, et al. Genomic profiling of intimal sarcoma reveals molecular subtypes with distinct tumor microenvironments and therapeutic implications. ESMO Open. (2025) 10:104097. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.104097
Keywords: intimal sarcoma, angiosarcoma, cell cycle dysregulation, immunotherapy, tumor micro environment (TME)
Citation: Wang B, Chen R, Yin H, Chang Z, Liu Y, Zhong D and Li F (2025) Multi-omics analysis revealed potential use of immunotherapy and CDK4/6 inhibitors in intimal sarcoma. Front. Immunol. 16:1668537. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1668537
Received: 18 July 2025; Accepted: 13 October 2025;
Published: 30 October 2025.
Edited by:
Ti Wen, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Takafumi Koyama, National Cancer Center Hospital, JapanJin-Fen Xiao, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, United States
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Chen, Yin, Chang, Liu, Zhong and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dingrong Zhong, NzQ4ODAzMDY5QHFxLmNvbQ==; Feng Li, bGlmZW5nNzg1NUAxMjYuY29t
 Bei Wang1,2
Bei Wang1,2 Rongrong Chen
Rongrong Chen Huan Yin
Huan Yin Dingrong Zhong
Dingrong Zhong Feng Li
Feng Li