- 1Airport Emergency Center, The Affiliated Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 2The Fifth Affiliated Hospital, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming, Yunnan, China
- 3School of Medicine, Kunming University, Kunming, Yunnan, China
- 4Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of Neuropsychiatric Diseases, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming, Yunnan, China
Background: Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and COVID-19 continue to pose significant global public health challenges. Although vaccination is essential for preventing COVID-19 in people with HIV (PWH), evidence on the immunogenicity and safety of booster doses remains limited. This systematic review aimed to assess the immunogenicity and safety of COVID-19 booster vaccination in PWH.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive literature search in PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library. Eligible studies included PWH who had received three or more doses of a COVID-19 vaccine.
Results: Across 54 included studies, 4,685 of 5,229 PWH achieved seroconversion following a third or subsequent COVID-19 vaccine dose—an improvement over rates observed after the primary vaccine series. In 23 studies comparing 2,284 PWH with 1,813 healthy controls (HC), no significant differences in seroconversion rates were found (p ≥ 0.05). Among PWH, 22 studies reported significantly higher seroconversion rates in individuals with CD4+ T cell counts >200 cells/mm³ compared to those with counts <200 cells/mm³. Booster vaccination enhanced CD4+ T cell responses to levels comparable to HC, although CD8+ T cell responses remained markedly lower. Five studies reported adverse events following booster doses, none of which were classified as serious.
Conclusion: COVID-19 booster vaccination is effective in enhancing immune protection and reducing severe disease in PWH. Optimal vaccine dosing is especially important in individuals with low CD4+ T cell counts. Tailoring booster strategies may improve seroconversion and overall immune response in this population.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier CRD42024605151
1 Introduction
Although the World Health Organization has declared an end to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) public health emergency, the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 remains high (1). As of February 2, 2025, more than 770 million individuals worldwide have been infected, with over 7.08 million reported deaths (WHO COVID-19 Dashboard). The COVID-19 landscape is further complicated by acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition marked by profound immunodeficiency due to untreated human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. People with HIV (PWH) experience a higher burden of non-HIV comorbidities, which predispose to more severe COVID-19, particularly in the setting of untreated HIV infection or low CD4+ T cell counts (2–4). Recent data also indicate that PWH have had a relative increase in mortality with COVID-19 compared with the general population (5).
Vaccination remains a cornerstone of COVID-19 control, and several vaccine platforms—mRNA (BNT162b2, mRNA-1273), adenoviral vector (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, Ad26.COV2.S), and inactivated virus (BBIBP-CorV, CoronaVac)—were widely deployed during the pandemic. While numerous meta-analyses have examined primary vaccination outcomes in PWH, limited evidence exists regarding the immunogenicity and safety of COVID-19 booster doses in this population (6–9). Existing studies on primary vaccination show that PWH, across ethnic and geographic contexts, develop neutralizing antibodies and exhibit reduced COVID-19 risk post-vaccination (10). However, seroconversion rates remain lower in PWH compared to healthy controls (HC) (11). To maintain adequate protection, booster doses are recommended for immunocompromised individuals in many countries (12). Nonetheless, the magnitude and quality of humoral and T-cell responses to booster vaccination in PWH—particularly those with advanced immunosuppression—remain inadequately characterized.
Vaccine-induced protection depends not only on neutralizing antibodies but also on cellular immunity, particularly CD4+ T cell responses (13). CD4+ T cells, primary targets of HIV, are essential for orchestrating both humoral and cellular immunity. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) also contribute to immune modulation following vaccination (14). Diminished CD4+ T cell counts can impair neutralizing antibody production, lower seroconversion rates, and compromise overall vaccine efficacy.
This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated the immunogenicity and safety of administering three or more COVID-19 vaccine doses to PWH. It compared seroconversion rates between PWH and HC, and assessed the association between neutralizing antibody levels and CD4+ T cell counts, along with other immune correlates. The findings offer critical insights for optimizing booster vaccination strategies in PWH.
2 Methods
This systematic review adhered to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines (15) and was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42024605151).
2.1 Search strategy
We systematically searched PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library for studies evaluating SARS-CoV-2 vaccine immunogenicity in PWH. The final search was conducted on October 22, 2024. Search terms included combinations of (“COVID-19” OR “Coronavirus” OR “SARS-CoV-2”), (“HIV” OR “Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome Virus” OR “PLWH”), and (“Vaccines” OR “Vaccination”). The complete search strategy is provided in Supplementary Material. Two reviewers (CZZ and LXH) independently screened titles, abstracts, and full texts; discrepancies were resolved by two additional reviewers (MQY and JMQ).
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Studies were included if they met the following criteria: (1) observational studies (cohort, case-control, or cross-sectional), randomized controlled trials (RCTs), or non-randomized controlled trials; (2) involved PWH who had received ≥3 doses of a COVID-19 vaccine; and (3) reported extractable data on immunogenicity (humoral or cellular) or safety (local and systemic adverse reactions).
Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) non-original studies (e.g., reviews, commentaries, or meta-analyses); (2) preprints and unpublished data; (3) unavailable full texts; and (4) studies involving only one or two vaccine doses.
2.3 Data extraction
Two authors (CZZ and LXH) independently extracted data using a standardized Excel form. Collected variables included: (1) basic study characteristics (first author, publication year, country, and study design); (2) participant demographics for PWH and HC (sample size, age, sex, and antiretroviral therapy [ART] status, viral load); (3) COVID-19 vaccine details (booster type and dosage, time since vaccination, and interval between primary and booster doses); (4) immunogenicity outcomes (e.g., number of PWH with neutralizing antibody seroconversion, anti-receptor binding domain IgG or anti-spike IgG levels, mean CD4+ T cell count, CD4+/CD8+ ratio, ART status, assay type, and cellular immunity assessment); and (5) safety outcomes based on reported adverse events in PWH.
2.4 Risk of bias assessment
Cohort and case-control studies were assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale, while cross-sectional studies were evaluated using the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) criteria. Quality assessments were independently conducted by CZZ and LXH, with discrepancies resolved by WCP and CB.
2.5 Statistical analyses
Meta-analyses were performed using Review Manager Version 5.3 and STATA Version 15.1. For primary outcomes, relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using a random-effects model. RR values of <1 indicated lower seroconversion rates in vaccinated PWH compared to HC. Study heterogeneity was assessed using the I² statistic, with values ≥50% indicating substantial heterogeneity. Meta-regression and subgroup analyses were conducted to explore potential sources of heterogeneity. Sensitivity analyses were performed to evaluate the robustness of primary outcomes. Publication bias was assessed using funnel plots and Egger’s test.
3 Results
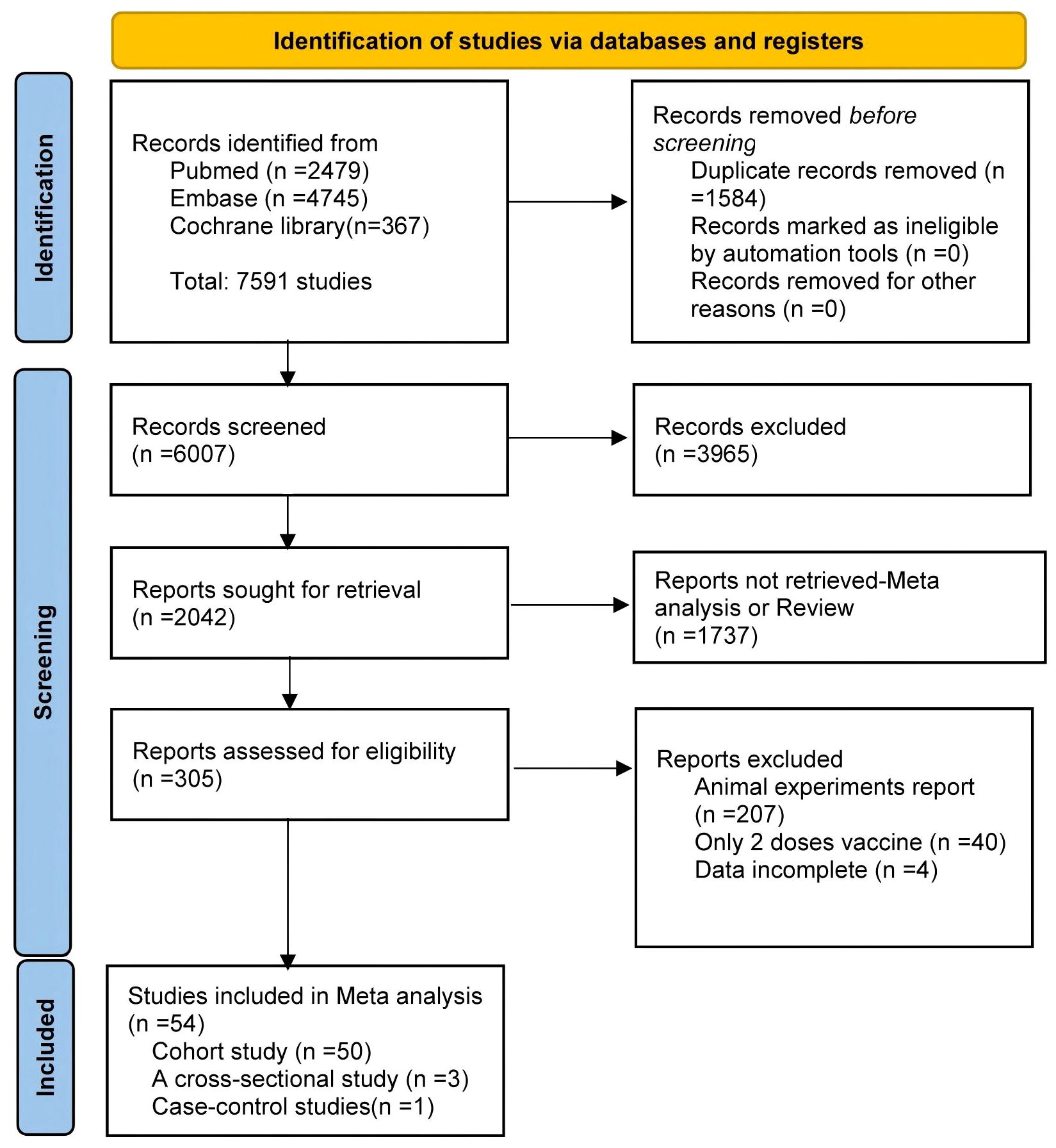
The study selection process is summarized in Figure 1. Of the 7,591 articles retrieved, 1,584 duplicates were removed. After screening titles and abstracts, 3,965 irrelevant studies and 1,737 reviews or meta-analyses were excluded. Full-text review excluded 207 animal studies, 40 studies involving only two vaccine doses, and four studies with unusable data. Ultimately, 54 articles were included in the meta-analysis (16–48) 23 of which conducted direct comparisons between PWH and HC.
3.1 Characteristics of the included studies
Among the 54 studies included in this analysis, 33 (62.96%) evaluated mRNA vaccines (BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273), 15 (27.78%) assessed inactivated vaccines (BBIBP-CorV or CoronaVac), and one (1.85%) investigated an adenovirus vector vaccine (ChAdOx1). All of the PWH received ≥3 doses of a COVID-19 vaccine. Most studies were cohort designs (n = 50, 92.59%), followed by cross-sectional (n = 3, 5.56%) and case-control studies (n = 1, 1.85%). Geographically, 24 studies (44.44%) were conducted in Asia, 21 (38.89%) in Europe, and nine (16.67%) in North America. Supplementary Table S2 provides detailed study characteristics.
Risk of bias assessment showed that 45 studies (83.33%) had a moderate risk, while five (9.26%) and four (7.41%) had low and high risks of bias, respectively (Supplementary Tables S3-S5).
3.2 Immune response rates in PWH
Seroconversion outcomes were reported in 44 studies involving 5,229 PWH. After a third vaccine dose, 4,685 PWH seroconverted, yielding a pooled risk ratio (RR) of 0.977 (95% CI: 0.945–0.997) with substantial heterogeneity (I² = 96%; Figure 2).
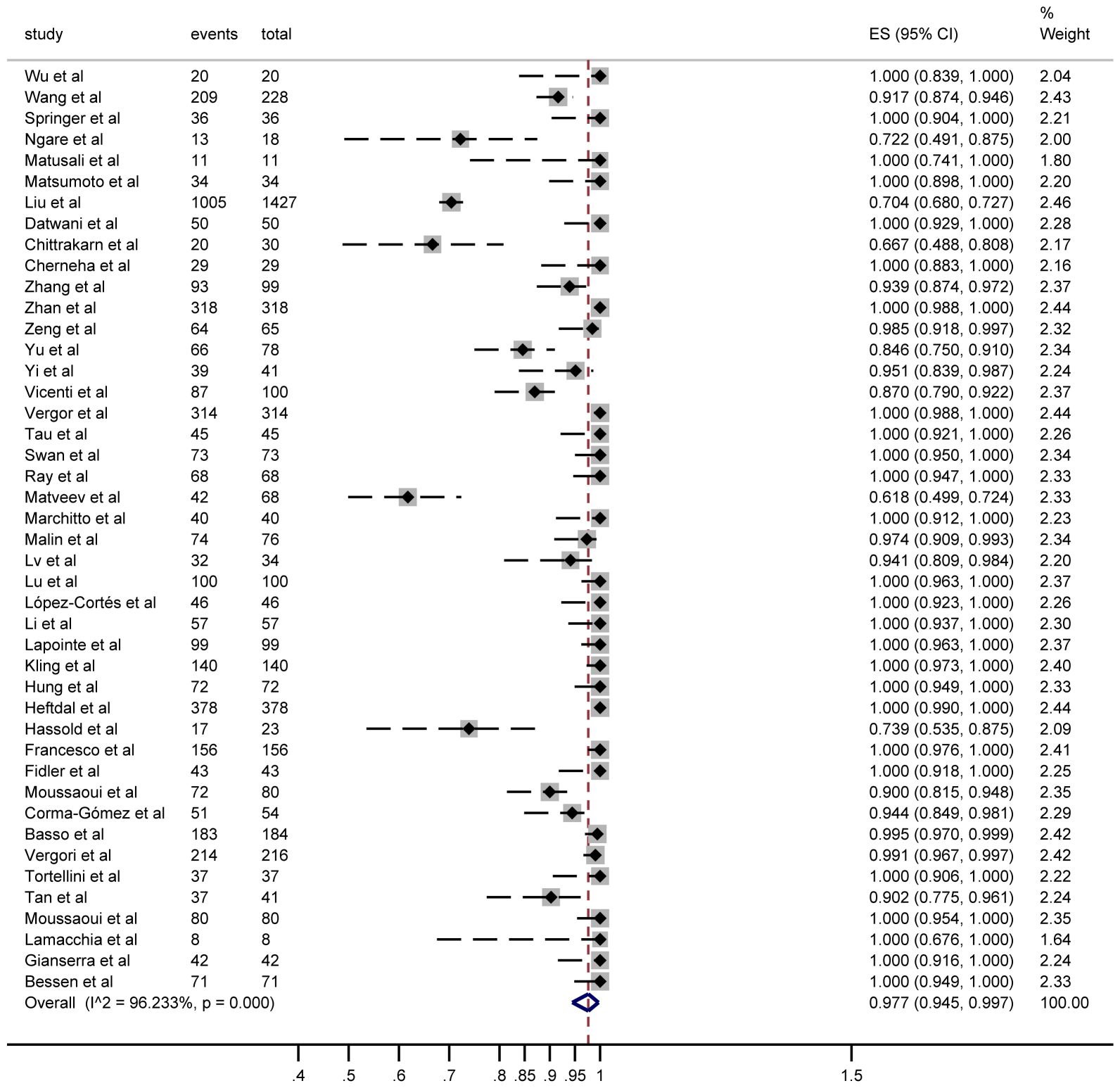
Figure 2. Forest plots of the included studies show the number of PWH seroconversions in each study (n, total number of PWHs; case, number of seroconversions in PWH).
3.3 Immune response comparison in PWH vs HC
In 23 studies comparing 2,284 PWH and 1,813 healthy controls (HC), seroconversion rates post–third dose were comparable between groups (RR = 0.99, 95% CI: 0.97–1.00), though heterogeneity remained considerable (I² = 85%; Figure 3, Supplementary Table S3).
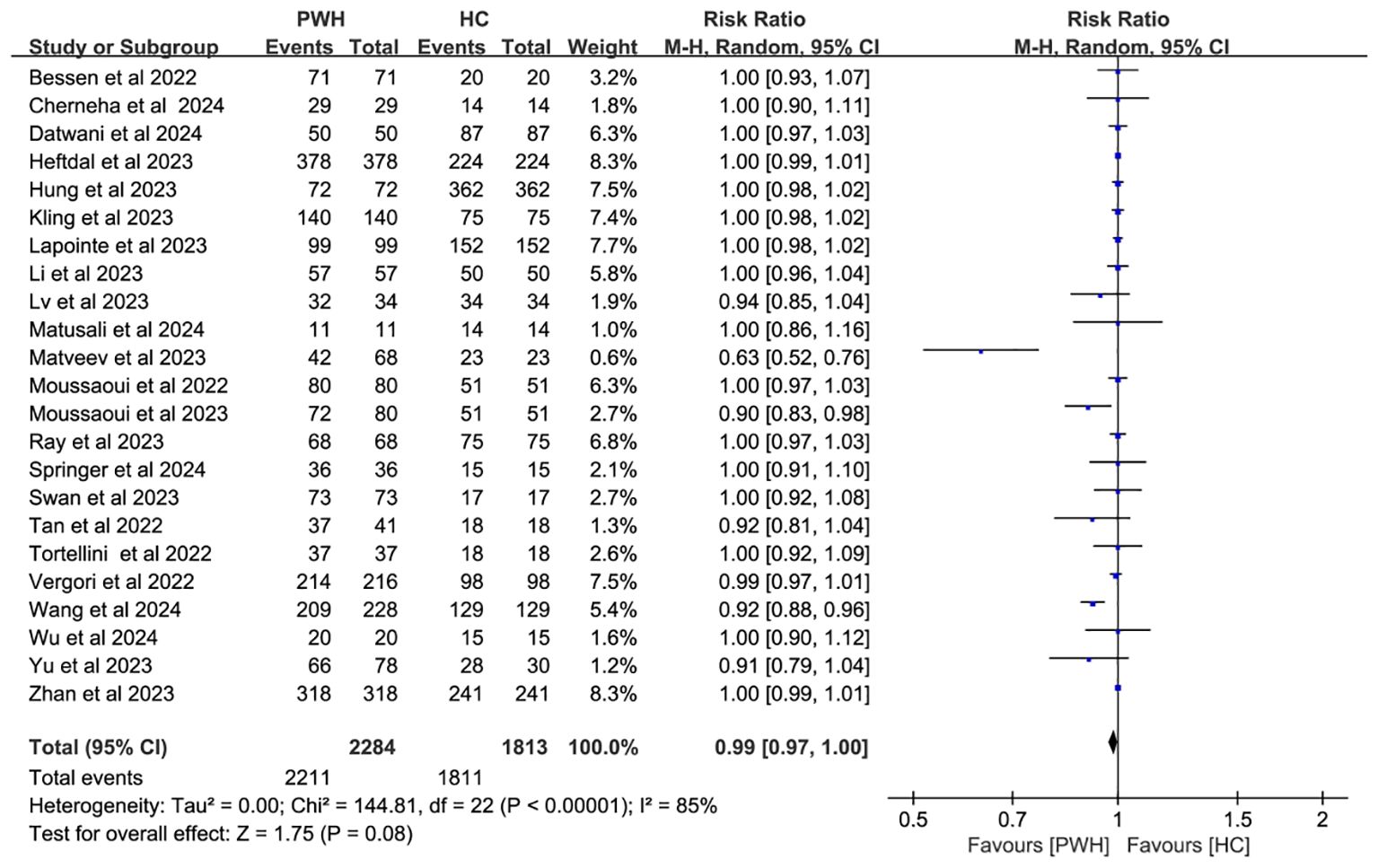
Figure 3. Risk ratios for seroconversion in PWH vs HC after the COVID-19 booster vaccine doses (CI, confidence interval; HC, healthy controls; M-H, Mantel–Haenszel; PWH, people with HIV).
Subgroup analyses by vaccine type and geographic region found no significant differences in seroconversion between PWH and HC (p ≥ 0.05). Notably, mRNA vaccines elicited immune responses in PWH that most closely resembled those in HC (RR = 1.00, 95% CI: 0.98–1.01; Figure 4). While regional variability may explain some heterogeneity (I² = 85%; Figure 5), evidence remains insufficient for definitive conclusions.
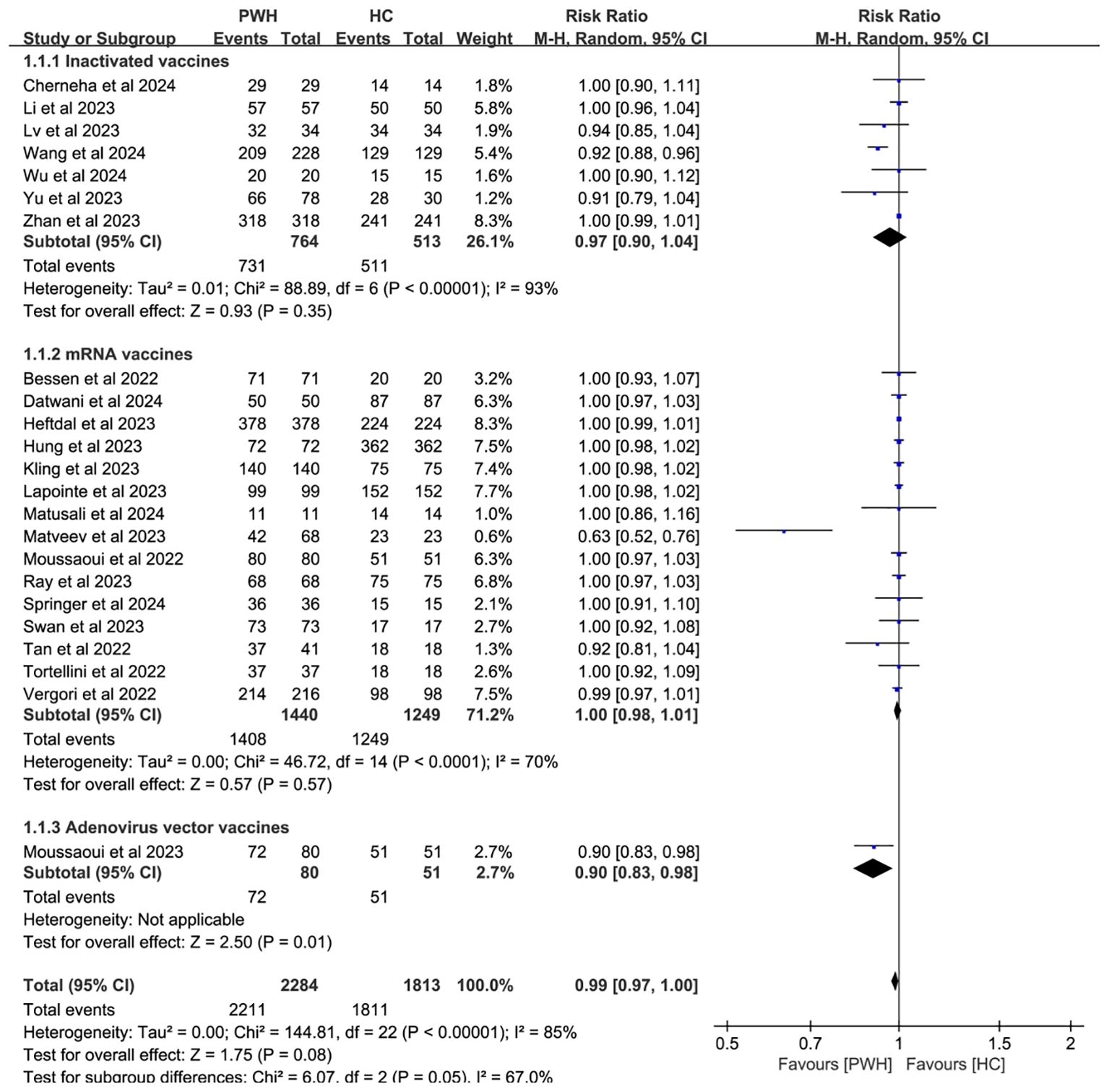
Figure 4. Subgroup analysis by vaccine type in PWH vs HC after booster COVID-19 vaccine doses (M-H, Mantel–Haenszel; PWH, people with HIV; HC, healthy controls; CI, confidence interval.).
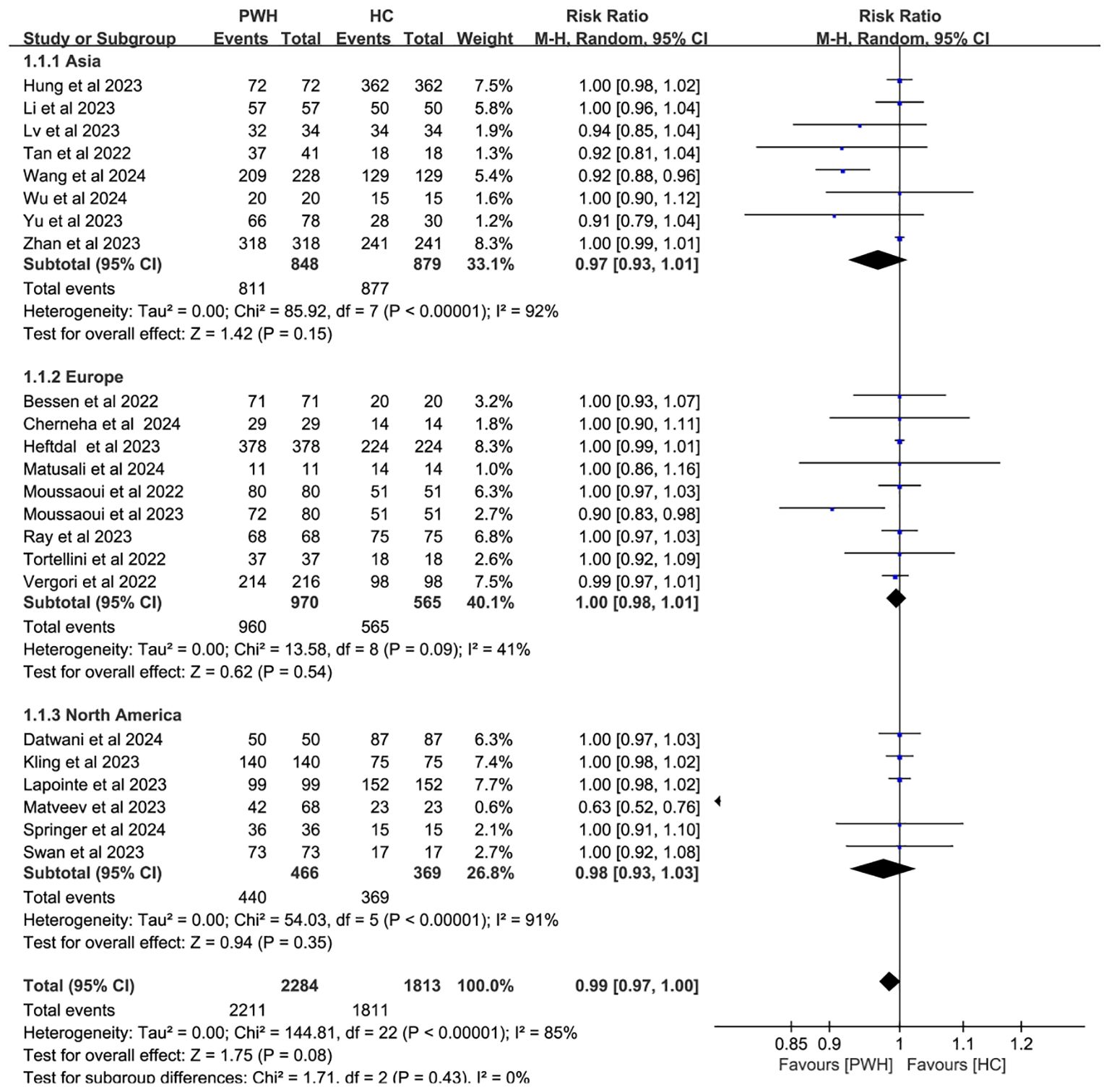
Figure 5. Subgroup analysis by continent in PWH vs HC after booster COVID-19 vaccine doses (CI, confidence interval; HC, healthy controls; M-H, Mantel–Haenszel; PWH, people with HIV).
3.4 CD4+ cell immune responses in PWH
Twenty-two studies analyzed CD4+ T cell–stratified seroconversion using a 200 cells/mm³ threshold. Among 2,487 PWH, 2,024 had CD4+ counts >200 cells/mm³ and 463 had <200 cells/mm³. Seroconversion was significantly lower in the <200 cells/mm³ group (p < 0.05; RR = 1.17, 95% CI: 1.02–1.35), with high heterogeneity (I² = 97%; Figure 6). Subgroup analyses confirmed that higher CD4+ counts favored better seroconversion outcomes (p < 0.05; Figures 7, 8).
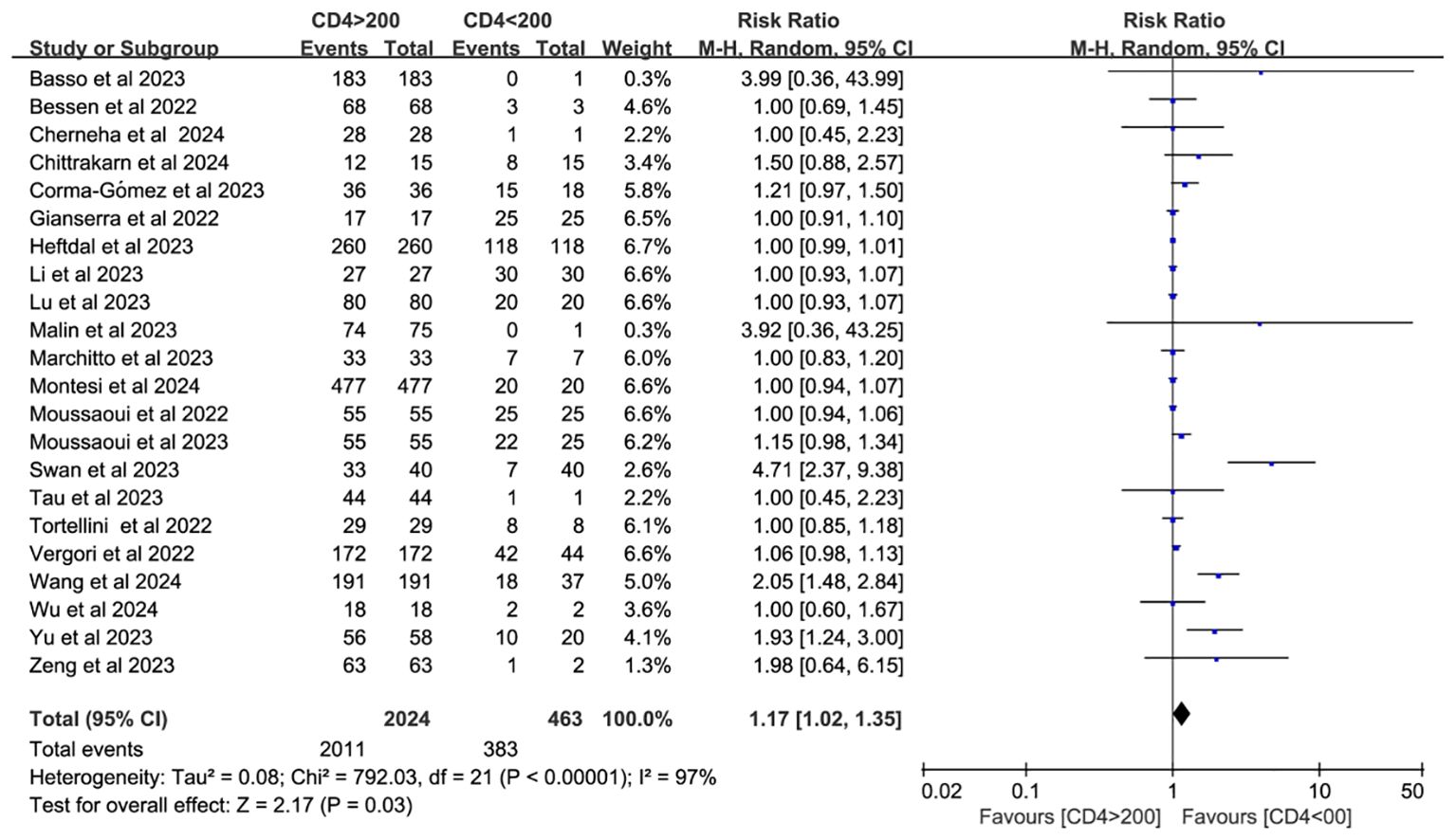
Figure 6. Risk ratio of PWH seroconversion after a booster dose of COVID-19 vaccine with 200 cells/mm³ CD4+ T cell count as the cutoff (CI, confidence interval; M-H, Mantel–Haenszel.).
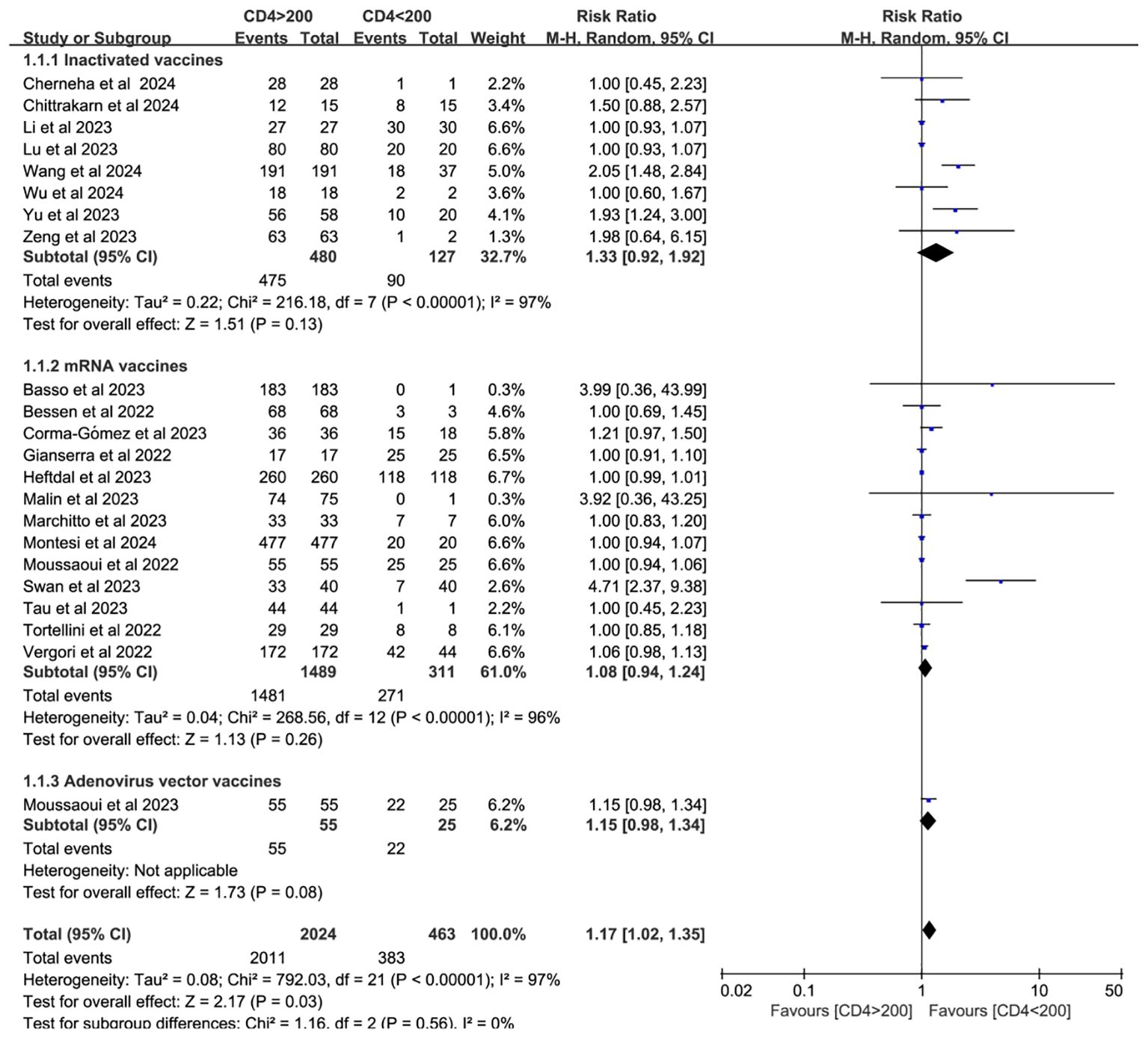
Figure 7. Subgroup analysis by vaccine type in PWH with CD4+ T cell counts of >200 cells/mm³ vs with <200 cells/mm³ after a booster COVID-19 vaccine dose (CI, confidence interval; M-H, Mantel–Haenszel).
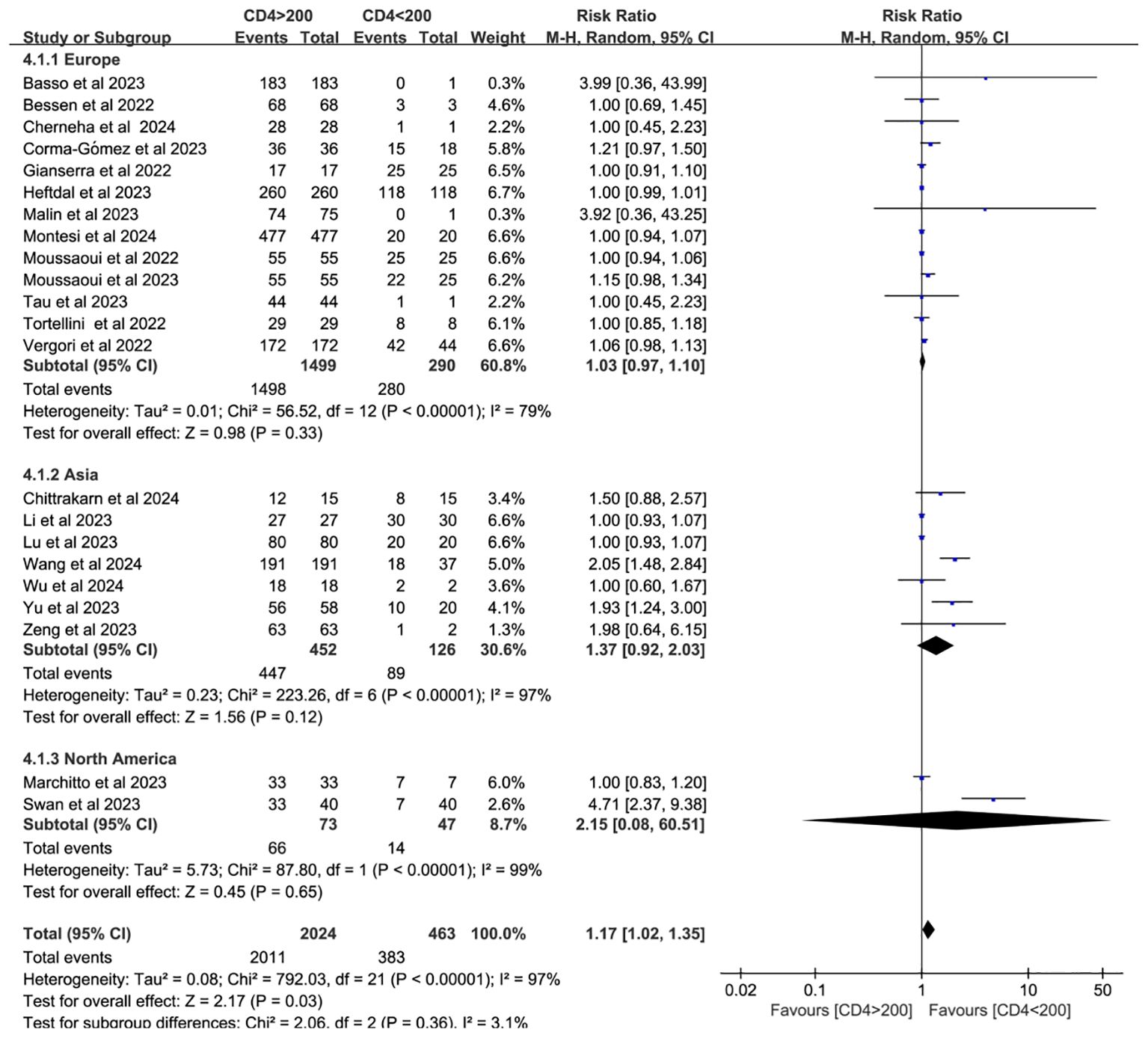
Figure 8. Subgroup analysis (based on continent) of PWH with CD4+ T-cell counts of >200 cells/mm³ vs <200 cells/mm³ after a booster COVID-19 vaccine dose (CI, confidence interval; M-H, Mantel–Haenszel).
3.5 T-cell immune responses in PWH
T-cell immune responses were evaluated in 12 studies (17, 26, 29, 41, 44, 47, 49–54). Markers used to characterize CD4+ T cells included CD4+CD25HighCD127Low Tregs, OX40+/CD137+, CCR4, CD137, CD154, and cytokines such as TNF, IFN-γ, and IL-2. Activation of Treg and T follicular helper (Tfh) cells was also assessed. While CD8+ T cell responses in PWH receiving three doses were less robust than in HC, they were more durable than responses observed in PWH who received only one or two doses.
3.6 COVID-19 booster vaccine safety in PWH
Booster vaccine safety in PWH was assessed in five studies (18, 29, 33, 44, 55). Most adverse events occurred within seven days and resolved spontaneously. Local reactions—pain, swelling, redness, and itching—were reported in 17.10% of cases (13/76), while systemic events—drowsiness, myalgia, arthralgia, and nausea—occurred in 11.84% (9/76). No severe adverse events were reported. Two studies compared adverse reaction incidence between PWH (18.84%, 65/345) and non-HIV individuals (14.11%, 23/163) (18, 44). Although further statistical analysis was not feasible, the evidence supports the safety of booster vaccination in PWH.
3.7 Study quality
Quality assessments (Supplementary Tables S3-S5) indicated that 45 studies were of moderate quality, five of low quality, and four of high quality. Low quality was primarily attributed to small sample sizes and insufficient data on predefined endpoints.
3.8 Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analysis identified significant heterogeneity in Matveev’s study (Supplementary Figure S1). Systematic exclusion confirmed this study as a major contributor to overall heterogeneity (Supplementary Figure S2).
3.9 Publication bias
Funnel plot analysis and Egger’s test indicated no evidence of publication bias in immune response outcomes comparing PWH and HC following booster vaccination (t = –0.24, df = 23, p = 0.287). These findings suggest that PWH mount immune responses comparable to those of HC (Supplementary Figure S3).
4 Discussion
Given the proven efficacy of vaccination in reducing infection risk and disease severity among PWH, enhancing vaccine coverage in this population is imperative (9). This meta-analysis included 54 studies, with 44 studies assessing seroconversion in 5,229 PWH. Additionally, 23 studies comparing PWH to HC after a third vaccine dose found no significant difference in seroconversion rates between the two groups. Subgroup analyses by vaccine type and geographic region revealed that exclusion of the highly biased Matveev study substantially reduced heterogeneity. Consistent with previous findings, mRNA vaccines produced the highest seroconversion rates for booster doses (11, 56). These results suggest that a third vaccine dose elicits a humoral immune response in PWH comparable to that in HC, enhancing antibody production, which has been demonstrated by others to correlate with reduced disease severity (57) and hospitalization (58).
A significant correlation exists between neutralizing antibody levels and both the quantity and proportion of CD4+ T cells (59, 60). CD4+ T cells (helper T lymphocytes) are central to anti-HIV immunity but are also the primary targets of HIV infection. Therefore, monitoring CD4+ T cells can help assess the extent of immune damage and determine the effectiveness of antiretroviral therapy (ART) (61). As such, CD4+ T cell quantification is essential for staging HIV infection and AIDS, as well as monitoring treatment response (62). In SARS-CoV-2 infection, CD4+ T cell responses are more prominent than those of CD8+ T cells. Notably, SARS-CoV-2–specific CD4+ T cells demonstrate the strongest association with reduced COVID-19 severity compared to antibody or CD8+ T cell responses (14). A meta-analysis of individuals receiving one to two doses of hepatitis B virus (HBV) vaccine found that PWH with CD4+ T cell counts below 500 cells/mm3 exhibited diminished seroconversion responses to hepatitis B virus, although response rates were generally consistent across studies (63). To assess seroconversion after a third vaccine dose, this study stratified PWH by CD4+ T cell count using the 200 cells/mm³ threshold. The antibody conversion rate was significantly higher in those with counts above 200 cells/mm³ compared to those below this threshold. Although subgroup analyses by vaccine type and geographic region did not explain the heterogeneity, further analysis identified individuals with CD4+ T cell counts <200 cells/mm³ as the main source of heterogeneity. This heterogeneity may also be influenced by HIV disease progression and ART status.
T helper 1 (Th1) and follicular helper T (Tfh) cells—differentiated subsets of CD4+ T cells—are critical for establishing long-term antiviral immunity (64). Upon differentiation, these cells activate phagocytes and cytotoxic CD8+ T cells (65), and support B cell maturation in germinal centers to produce high-affinity, long-lived antibodies (66). Accordingly, CD4+ and Tfh cells are considered key markers of durable, protective antibody responses (67). CD4+ T cells produce a broad array of cytokines, including TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-10, IL-17, and IL-22. Th1 cells predominantly secrete TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-2, while Th2 cells produce IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, and IL-13. Th17 and regulatory T cells (Tregs) are sources of IL-17 and IL-10, respectively. Notably, IL-22 is highly expressed by mucosal CD4+ T cells specific to SARS-CoV-2 (14, 17, 29, 37, 41, 44, 51). Findings from included studies showed that in PWH, a third vaccine dose activated Th1, Treg, and Tfh cells and increased cytokine expression—including IFN-γ, IL-17, and IL-22 (17, 41). Both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells contributed to enhanced antibody responses, with CD4+ T cells showing a more pronounced role in SARS-CoV-2 immunity (29, 44, 49, 66, 68, 69).
This study also found no differences in the safety profile of COVID-19 booster vaccines between PWH and HC. Previous research suggests that PWH experience fewer adverse events after the second dose compared to the first (70–72). However, limited data exist on the safety of booster doses, and individuals who tolerate initial doses well may be more likely to receive boosters (73, 74). Our findings support the safety of booster vaccination in PWH and may help reduce vaccine hesitancy in this population.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the most comprehensive analysis of COVID-19 booster vaccine immunogenicity and safety in PWH. The study included all relevant literature published from January 1, 2020, to October 22, 2024, involving PWH who received ≥3 doses of a COVID-19 vaccine. These findings provide valuable evidence to address booster vaccine hesitancy among PWH.
Nonetheless, this study has limitations. Firstly, we did not evaluate the real-world effectiveness of booster doses in PWH due to a lack of original studies. Taking into account various factors, such as ART, previous COVID-19 infection, the timing of vaccination, and other viral infections, further research should be designed to explicitly evaluate the effectiveness of booster vaccination in this population. Secondly, although seroconversion indicates potential protection against SARS-CoV-2, it is not a definitive clinical endpoint, which would be better assessed by infection rates. However, few studies address this outcome. Lastly, substantial heterogeneity across studies—likely due to differences in study location, timing, and sample size—underscores the need for future research to validate these findings.
5 Conclusion
The findings of our research suggest that the humoral immune response elicited in PWH following administration of the COVID-19 booster vaccine is comparable to that observed in HC. The enhanced antibody response following the administration of a booster shot may similarly contribute to this protective effect. However, PWH with CD4+ T cell counts below 200 cells/mm³ continue to exhibit suboptimal antibody seroconversion despite receiving booster doses. These results underscore the importance of booster vaccination in PWH, particularly those with advanced immunosuppression, and suggest that optimizing booster regimens may improve immune outcomes in this population.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
ZC: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BC: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. QM: Writing – review & editing. MJ: Writing – review & editing. KD: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. XL: Supervision, Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. DQ: Writing – original draft, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Applied Basic Research Programs of Science and Technology Commission Foundation of Yunnan Province (202401AS070007), Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of Neuropsychiatric Diseases, Yunnan Provincial Department of Education; Scientific Research Projects for High-level Talents of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine (2019YZG01), Young Top-Notch Talent in 10,000 Talent Program of Yunnan Province (YNWR-QNBJ-2019-235 and YNWR-QNBJ-2018-223).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1668576/full#supplementary-material
References
1. WHO. Statement on the fifteenth meeting of the International Health Regulations, (2005) emergency committee regarding the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, (2023) World Health Organization(2023). Available online at: https://www.who.int/zh/news/item/05-05-2023-statement-on-the-fifteenth-meeting-of-the-international-health-regulations-(2005)-emergency-committee-regarding-the-coronavirus-disease-(covid-19)-pandemic (Accessed May 6 2023).
2. Ambrosioni J, Blanco JL, Reyes-Urueña JM, Davies MA, Sued O, Marcos MA, et al. Overview of SARS-CoV-2 infection in adults living with HIV. Lancet HIV. (2021) 8:e294–305. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(21)00070-9
3. Pourcher V, Gourmelen J, Bureau I, and Bouee S. Comorbidities in people living with HIV: An epidemiologic and economic analysis using a claims database in France. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0243529. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243529
4. Funke B, Spinner CD, Wolf E, Heiken H, Christensen S, Stellbrink HJ, et al. High prevalence of comorbidities and use of concomitant medication in treated people living with HIV in Germany - results of the BESIDE study. Int J STD AIDS. (2021) 32:152–61. doi: 10.1177/0956462420942020
5. Inzaule S, Silva R, Ford N, Thwin SS, Waasila J, Zumla A, et al. Comparative analyses of COVID-19 in-hospital mortality in people living with HIV during SARS-CoV-2 pre-delta, delta, and omicron waves: data from the who global clinical platform. Aids. (2025). doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000004323
6. Hadj Hassine I. Covid-19 vaccines and variants of concern: A review. Rev Med Virol. (2022) 32:e2313. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2313
7. Chun HM, Milligan K, Agyemang E, Ford N, Rangaraj A, Desai S, et al. A systematic review of COVID-19 vaccine antibody responses in people with HIV. Open Forum Infect Dis. (2022) 9:ofac579. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofac579
8. Griffin DWJ, Pai Mangalore R, Hoy JF, and Mcmahon JH. Immunogenicity, effectiveness, and safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in people with HIV. Aids. (2023) 37:1345–60. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000003579
9. Cheng MQ, Li R, Weng ZY, and Song G. Immunogenicity and effectiveness of COVID-19 booster vaccination among people living with HIV: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). (2023) 10:1275843. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1275843
10. Søndergaard MH, Thavarajah JJ, Churchill Henson H, and Wejse CM. SARS-CoV-2 vaccine immunogenicity for people living with HIV: A systematic review and meta-analysis. HIV Med. (2024) 25:16–37. doi: 10.1111/hiv.13537
11. Zhao T, Yang Z, Wu Y, and Yang J. Immunogenicity and safety of COVID-19 vaccines among people living with HIV: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiol Infect. (2023) 151:e176. doi: 10.1017/S095026882300153X
12. Fiolet T, Kherabi Y, Macdonald CJ, Ghosn J, and Peiffer-Smadja N. Comparing COVID-19 vaccines for their characteristics, efficacy and effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern: a narrative review. Clin Microbiol Infect. (2022) 28:202–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2021.10.005
13. Premkumar L, Segovia-Chumbez B, Jadi R, Martinez DR, Raut R, Markmann A, et al. The receptor binding domain of the viral spike protein is an immunodominant and highly specific target of antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 patients. Sci Immunol. (2020) 5(48):eabc8413. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abc8413
14. Sette A and Crotty S. Adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Cell. (2021) 184:861–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.007
15. Page MJ, Mckenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
16. Wu Y, Wang X, Huang Y, Chen R, Xu Y, Wei W, et al. Immunogenicity of an inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in people living with HIV in Guangxi, China: A prospective cohort study. Viruses. (2024) 16(9):1481. doi: 10.3390/v16091481
17. Wang X, Li Y, Jin J, Chai X, Ma Z, Duan J, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2-specific T-cell responses are induced in people living with human immunodeficiency virus after booster vaccination. Chin Med J (Engl). (2024) 137:2734–44. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003176
18. Wang Y, Lan X, Qiao Y, Huo Y, Wang L, Liang S, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of homologous prime-boost CoronaVac vaccine in people living with HIV in China: A multicenter prospective cohort study. J Med Virol. (2024) 96:e29395. doi: 10.1002/jmv.29395
19. Tan Y, Wu S, Ming F, Liu J, Marley G, Yu A, et al. People living with HIV with the Omicron variant infection have milder COVID-19 symptoms: results from a cross-sectional study. AIDS Res Ther. (2024) 21:53. doi: 10.1186/s12981-024-00633-4
20. Springer DN, Daller S, Knappik M, Prüger K, Hartl S, Breyer-Kohansal R, et al. A Multivariant Surrogate Virus Neutralization Test Demonstrates Distinct SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibody Responses in People Living with HIV after a Fourth Monovalent mRNA Vaccination or an Omicron Breakthrough Infection. Diagnostics (Basel). (2024) 14(8):822. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14080822
21. Ngare I, Tan TS, Toyoda M, Kuwata T, Takahama S, Nakashima E, et al. Factors associated with neutralizing antibody responses following 2-dose and 3rd booster monovalent COVID-19 vaccination in Japanese people living with HIV. Viruses. (2024) 16(4):555. doi: 10.3390/v16040555
22. Montesi G, Augello M, Polvere J, Marchetti G, Medaglini D, and Ciabattini A. Predicting humoral responses to primary and booster SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in people living with HIV: a machine learning approach. J Transl Med. (2024) 22:432. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05147-1
23. Matusali G, Mazzotta V, Meschi S, Colavita F, Gagliardini R, Bettini A, et al. JN.1 neutralizing antibody titers after XBB.1.5 monovalent vaccine boost in healthcare workers and people with HIV. J Med Virol. (2024) 96:e29631. doi: 10.1002/jmv.29631
24. Matsumoto Y, Murata M, Ohta A, Yamasaki S, Ikezaki H, Toyoda K, et al. The humoral and cellular immune responses following booster vaccination with SARS-CoV-2 mRNA in people living with human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Chemother. (2024) 30:417–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2023.11.014
25. Liu WD, Lin MS, Sun HY, Shih MC, Chuang YC, Huang YS, et al. Effectiveness and evolution of anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike protein titers after three doses of COVID-19 vaccination in people with HIV. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. (2024) 57:554–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2024.02.004
26. Datwani S, Kalikawe R, Waterworth R, Mwimanzi FM, Liang R, Sang Y, et al. T-cell responses to COVID-19 vaccines and breakthrough infection in people living with HIV receiving antiretroviral therapy. Viruses. (2024) 16(5):661. doi: 10.3390/v16050661
27. Chittrakarn S, Siripaitoon P, Chusri S, Kanchanasuwan S, Charoenmak B, Hortiwakul T, et al. Comparative immunogenicity and neutralizing antibody responses post heterologous vaccination with CoronaVac (Sinovac) and Vaxzevria (AstraZeneca) in HIV-infected patients with varying CD4+ T lymphocyte counts. Hum Vaccin Immunother. (2024) 20:2309734. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2309734
28. Cherneha M, Zydek I, Braß P, Korth J, Jansen S, Esser S, et al. Immunogenicity of the monovalent omicron XBB.1.5-adapted BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in people living with HIV (PLWH). Vaccines (Basel). (2024) 12(7):785. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12070785
29. Zhang W, Liu S, Miao L, Fu A, Bao J, Zheng L, et al. Dynamics of CD4(+) T-cells and neutralizing antibody responses to three consecutive doses of inactivated COVID-19 vaccines in PLWH. Infect Drug Resist. (2023) 16:2695–707. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S409147
30. Zhan H, Gao H, Liu Y, Zhang X, Li H, Li X, et al. Booster shot of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine induces potent immune responses in people living with HIV. J Med Virol. (2023) 95:e28428. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28428
31. Zeng G, He F, Zhang X, Li G, Wang X, Gan Y, et al. Antibody response to the third dose of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in people living with HIV (PLWH): A longitudinal cohort. J Med Virol. (2023) 95:e28797. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28797
32. Yu H, Guo P, Yang Y, Dai J, Tang X, and Li L. A three-dose inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine is sufficient to elicit humoral immune responses in people living with HIV-1. Chin Med J (Engl). (2023) 136:2243–5. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002810
33. Yi Y, Han X, Cui X, Wang P, Wang X, Liu H, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the inactivated COVID-19 vaccine booster in people living with HIV in China. Vaccines (Basel). (2023) 11(6):1019. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11061019
34. Yang X, Wang X, Zhang X, Ding H, Wang H, Huang T, et al. Durable natural killer cell response after three doses of SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine in HIV-infected individuals. Chin Med J (Engl). (2023) 136:2948–59. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002947
35. Vicenti I, Basso M, Pirola N, Bragato B, Rossi MC, Giobbia M, et al. SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies to B.1 and to BA.5 variant after booster dose of BNT162b2 vaccine in HIV patients COVID-naïve and on successful antiretroviral therapy. Vaccines (Basel). (2023) 11(4):871. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11040871
36. Vergori A, Cozzi-Lepri A, Matusali G, Cicalini S, Bordoni V, Meschi S, et al. Long Term Assessment of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Immunogenicity after mRNA Vaccine in Persons Living with HIV. Vaccines (Basel). (2023) 11(12):1739. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11121739
37. Tau L, Hagin D, Freund T, Halperin T, Adler A, Marom R, et al. Humoral and cellular immune responses of people living with human immunodeficiency virus after 3 doses of messenger RNA BNT162b2 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 vaccine: A prospective cohort study. Open Forum Infect Dis. (2023) 10:ofad347. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofad347
38. Swan CL, Dushimiyimana V, Ndishimye P, Buchanan R, Yourkowski A, Semafara S, et al. Third COVID-19 vaccine dose boosts antibody function in Rwandans with high HIV viral load. iScience. (2023) 26:107959. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107959
39. Ray S, Narayanan A, Vesterbacka J, Blennow O, Chen P, Gao Y, et al. Impact of the gut microbiome on immunological responses to COVID-19 vaccination in healthy controls and people living with HIV. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. (2023) 9:104. doi: 10.1038/s41522-023-00461-w
40. Qu MM, Song B, Yang BP, Wang Z, Yu M, Zhang Y, et al. Effect of SARS-coV-2 breakthrough infection on HIV reservoirs and T-cell immune recovery in 3-dose vaccinated people living with HIV. Viruses. (2023) 15(12):2427. doi: 10.3390/v15122427
41. Matveev VA, Mihelic EZ, Benko E, Budylowski P, Grocott S, Lee T, et al. Immunogenicity of COVID-19 vaccines and their effect on HIV reservoir in older people with HIV. iScience. (2023) 26:107915. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107915
42. Marchitto L, Chatterjee D, Ding S, Gendron-Lepage G, Tauzin A, Boutin M, et al. Humoral responses elicited by SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in people living with HIV. Viruses. (2023) 15(10):2004. doi: 10.3390/v15102004
43. Malin JJ, Suárez I, Biehl LM, Schommers P, Knops E, Di Cristanziano V, et al. Immune response to mRNA-based COVID-19 booster vaccination in people living with HIV. HIV Med. (2023) 24:785–93. doi: 10.1111/hiv.13481
44. Lv Z, Lv S, Li Q, Xia Y, Feng Z, Zhang H, et al. A third (booster) dose of the inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine elicits immunogenicity and T follicular helper cell responses in people living with HIV. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1264160. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1264160
45. Lu T, Chen Z, Cao Y, Ao L, Li Z, Gu X, et al. Dynamic immunogenicity after primary and booster inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in people living with HIV: A longitudinal observational study. J Med Virol. (2023) 95:e28730. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28730
46. Loubet P, Wittkop L, Ninove L, Chalouni M, Barrou B, Blay JY, et al. One-month humoral response following two or three doses of messenger RNA coronavirus disease 2019 vaccines as primary vaccination in specific populations in France: first results from the Agence Nationale Recherche contre le Sida (ANRS)0001S COV-POPART cohort. Clin Microbiol Infect. (2023) 29:388.e1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2022.10.009
47. López-Cortés LF, Saborido-Alconchel A, Trujillo-Rodríguez M, Serna-Gallego A, Llaves-Flores S, Muñoz-Muela E, et al. Humoral and cellular immunity to SARS-COV-2 after vaccination with mRNA vaccines in PLWH with discordant immune response. Influence of the vaccine administered. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1129753. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1129753
48. Li J, Nie L, Guo C, Deng Y, Guo Q, Pang C, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in people living with HIV: A longitudinal cohort study. J Med Virol. (2023) 95:e29334. doi: 10.1002/jmv.29334
49. Jin J, Wang X, Li Y, Yang X, Wang H, Han X, et al. Weak SARS-CoV-2-specific responses of TIGIT-expressing CD8 + T cells in people living with HIV after a third dose of a SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine. Chin Med J (Engl). (2023) 136:2938–47. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002926
50. Hung CY, Hsiao SH, Huang CG, Chang CS, Chen GY, Huang YL, et al. Relatively preserved functional immune capacity with standard COVID-19 vaccine regimen in people living with HIV. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1204314. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1204314
51. Alexandrova Y, Yero A, Mboumba Bouassa RS, Comeau E, Samarani S, Brumme ZL, et al. SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-induced T-cell response after three doses in people living with HIV on antiretroviral therapy compared to seronegative controls (CTN 328 COVAXHIV study). Viruses. (2023) 15(2):575. doi: 10.3390/v15020575
52. Tortellini E, Zingaropoli MA, Mancarella G, Marocco R, Carraro A, Jamhour M, et al. Quality of T-cell response to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in ART-treated PLWH. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(23):14988. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314988
53. Moussaoui ME, Desmecht S, Tashkeev A, Lambert N, Maes N, Braghini J, et al. Reduced T-cell response following a third dose of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in infection-naïve people living with HIV. J Infect. (2022) 85:702–69. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2022.09.006
54. Bessen C, Plaza-Sirvent C, Simsek A, Bhat J, Marheinecke C, Urlaub D, et al. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination on systemic immune responses in people living with HIV. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1049070. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1049070
55. Gianserra L, Donà MG, Giuliani E, Stingone C, Pontone M, Buonomini AR, et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of BNT162b2 Homologous Booster Vaccination in People Living with HIV under Effective cART. Vaccines (Basel). (2022) 10(8):1243. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10081243
56. Wu JD, Li JX, Liu J, Wang HM, Zhou GH, Li J, et al. Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the mRNA vaccine CS-2034 as a heterologous booster versus homologous booster with BBIBP-CorV in adults aged ≥18 years: a randomised, double-blind, phase 2b trial. Lancet Infect Dis. (2023) 23:1020–30. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00199-8
57. Johnson AG, Amin AB, Ali AR, Hoots B, Cadwell BL, Arora S, et al. COVID-19 incidence and death rates among unvaccinated and fully vaccinated adults with and without booster doses during periods of delta and omicron variant emergence - 25 U.S. Jurisdictions, April 4-December 25, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. (2022) 71:132–8. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7104e2
58. Thompson MG, Natarajan K, Irving SA, Rowley EA, Griggs EP, Gaglani M, et al. Effectiveness of a third dose of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19-associated emergency department and urgent care encounters and hospitalizations among adults during periods of delta and omicron variant predominance - VISION network, 10 States, August 2021-January 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. (2022) 71:139–45. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7104e3
59. Khoury DS, Cromer D, Reynaldi A, Schlub TE, Wheatley AK, Juno JA, et al. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Med. (2021) 27:1205–11. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01377-8
60. Khoury DS, Schlub TE, Cromer D, Steain M, Fong Y, Gilbert PB, et al. Correlates of protection, thresholds of protection, and immunobridging among persons with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Emerg Infect Dis. (2023) 29:381–8. doi: 10.3201/eid2902.221422
61. Inderbitzin A, Loosli T, Opitz L, Rusert P, and Metzner KJ. Transcriptome profiles of latently- and reactivated HIV-1 infected primary CD4(+) T cells: A pooled data-analysis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:915805. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.915805
62. Kok YL, Vongrad V, Chaudron SE, Shilaih M, Leemann C, Neumann K, et al. HIV-1 integration sites in CD4+ T cells during primary, chronic, and late presentation of HIV-1 infection. JCI Insight. (2021) 6(9):e143940. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.143940
63. Tian Y, Hua W, Wu Y, Zhang T, Wang W, Wu H, et al. Immune response to hepatitis B virus vaccine among people living with HIV: A meta-analysis. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:745541. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.745541
64. Koutsakos M, Lee WS, Wheatley AK, Kent SJ, and Juno JA. T follicular helper cells in the humoral immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. J Leukoc Biol. (2022) 111:355–65. doi: 10.1002/JLB.5MR0821-464R
65. Sekine T, Perez-Potti A, Rivera-Ballesteros O, Strålin K, Gorin JB, Olsson A, et al. Robust T cell immunity in convalescent individuals with asymptomatic or mild COVID-19. Cell. (2020) 183:158–68.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.017
66. Nelson RW, Chen Y, Venezia OL, Majerus RM, Shin DS, Carrington MN, et al. SARS-CoV-2 epitope-specific CD4(+) memory T cell responses across COVID-19 disease severity and antibody durability. Sci Immunol. (2022) 7:eabl9464. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abl9464
67. Crotty S. T follicular helper cell biology: A decade of discovery and diseases. Immunity. (2019) 50:1132–48. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.04.011
68. Painter MM, Mathew D, Goel RR, Apostolidis SA, Pattekar A, Kuthuru O, et al. Rapid induction of antigen-specific CD4(+) T cells is associated with coordinated humoral and cellular immunity to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. Immunity. (2021) 54:2133–42.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.08.001
69. Van Der Ploeg K, Kirosingh AS, Mori DAM, Chakraborty S, Hu Z, Sievers BL, et al. TNF-α(+) CD4(+) T cells dominate the SARS-CoV-2 specific T cell response in COVID-19 outpatients and are associated with durable antibodies. Cell Rep Med. (2022) 3:100640. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100640
70. Kang L, Shang W, Gao P, Wang Y, Liu J, and Liu M. Immunogenicity and safety of COVID-19 vaccines among people living with HIV: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vaccines (Basel). (2022) 10(9):1569. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10091569
71. Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, Absalon J, Gurtman A, Lockhart S, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383:2603–15. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2034577
72. Netto LC, Ibrahim KY, Picone CM, Alves A, Aniceto EV, Santiago MR, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of CoronaVac in people living with HIV: a prospective cohort study. Lancet HIV. (2022) 9:e323–31. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(22)00033-9
73. Geers AL, Clemens KS, Colagiuri B, Jason E, Colloca L, Webster R, et al. Do side effects to the primary COVID-19 vaccine reduce intentions for a COVID-19 vaccine booster? Ann Behav Med. (2022) 56:761–8. doi: 10.1093/abm/kaac027
Keywords: COVID-19, booster vaccines, HIV, immunogenicity, CD4+ T cell, seroconversion
Citation: Chen Z, Wan C, Chen B, Mo Q, Ju M, Deng K, Li X and Qin D (2025) Immunogenicity and safety of the booster COVID-19 vaccine among people with HIV: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 16:1668576. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1668576
Received: 18 July 2025; Accepted: 29 August 2025;
Published: 17 September 2025.
Edited by:
Cristian Apetrei, University of Pittsburgh, United StatesReviewed by:
Catalina Lunca, Grigore T. Popa University of Medicine and Pharmacy, RomaniaDavid Griffin, Monash University, Australia
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Wan, Chen, Mo, Ju, Deng, Li and Qin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dongdong Qin, cWluZG9uZzEwOEAxNjMuY29t; Xiaohong Li, bGl4aWFvaG9uZzg3OUAxNjMuY29t; Kunlong Deng, ZGt1bmxAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zhenzhen Chen1†
Zhenzhen Chen1† Chunping Wan
Chunping Wan Xiaohong Li
Xiaohong Li Dongdong Qin
Dongdong Qin