- 1College of Chinese Medicine for Cardiovascular-Cranial Disease, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
- 2Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine for Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
- 3The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 4Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou, China
Chronic inflammation linked to atherosclerosis is closely related to a trained immunoregulatory network. Traditional studies primarily focus on the pro-inflammatory memory of monocytes, they frequently neglect important aspects such as the cell’s plasticity, interactions between different organs, and the dynamic regulation of the metabolism-vascular axis. This review presents four novel frameworks, including the trained immunity plasticity spectrum model. It demonstrates how monocytes maintain a dynamic balance between pro-inflammatory, tolerogenic, and anti-inflammatory phenotypes, regulated by mTOR/AMPK signaling and competitive histone modifications. The trained immunity–metabolism–vascular axis shows that metabolic disorders can change the way immune memory is formed. They achieve this by modifying the vascular microenvironment through epigenetic changes, exosomes, and products of mitochondrial stress. The cross-organ trained immunity framework reveals how remote epigenetic communication between the bone marrow, gut, and liver influences the development of monocytes. Finally, dynamic immune reprogramming integrates CRISPR-based epigenetic editing, metabolism-focused interventions, and AI-driven multi-omics predictions. This approach signifies a major transition from simply alleviating symptoms to accurately reshaping immune memory. This review reinterprets the immunometabolic mechanisms of atherosclerosis. It also lays the foundation for personalized therapies enhanced by AI and explores new interdisciplinary research avenues.
1 Background
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory condition marked by lipid-related issues in blood vessels (1). It arises from inappropriate responses of the innate immune system (2). Monocytes and macrophages play key roles in the development and worsening of plaque in the arteries (3); they cause persistent inflammation by stimulating oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) (4), releasing cytokines (5), and forming foam cells (6). Even with lipid-lowering treatments, blood vessel inflammation continues (7), exposing a crucial gap in our understanding: the factors behind the prolonged activation of innate immune cells extend beyond traditional inflammatory processes (8).
The discovery of trained immunity (9, 10), has significantly changed our understanding of chronic inflammatory diseases. This term refers to the reprogramming of innate immune cells, allowing them to exhibit memory-like responses due to alterations in their epigenetic and metabolic profiles (11). Initially identified in the context of infections, trained immunity is now recognized as a factor in atherosclerosis (12), where triggers such as oxLDL and hyperglycemia lead to lasting proinflammatory changes in monocytes (13). These changes happen through mechanisms such as histone modifications, specifically H3K4me3 (14), and metabolic shifts like increased glycolysis (15). Most current research focuses on the pro-inflammatory aspects of trained immunity, often ignoring its flexibility and the wider regulatory networks involved (16). Bekkering (17) and colleagues showed that oxLDL can cause epigenetic changes in monocytes. However, the potential for trained immunity to also play tolerogenic or reparative roles has not been fully explored. Furthermore, the interactions between various organs, including the bone marrow’s role in blood cell production (18) and the effects of gut microbiota metabolites (19), have not been sufficiently explored in relation to trained immunity. Although evidence indicates that systemic metabolic issues may lead to vascular inflammation (20), this topic is still underexplored.
This review examines the limitations of our current knowledge by utilizing four interconnected frameworks. The trained immunity plasticity spectrum redefines trained immunity as a dynamic balance among pro-inflammatory, tolerogenic, and anti-inflammatory phenotypes, influenced by mTOR/AMPK signaling pathways (21) and opposing histone modifications (H3K4me3 versus H3K27me3) (22, 23). The trained immunity–metabolism–vascular axis shows how metabolic disturbances, like abnormal cholesterol synthesis and high blood sugar, can epigenetically influence monocytes (24). These disturbances also alter the vascular environment through exosomal miRNAs and signals from mitochondrial stress (25). The cross-organ trained immunity highlights the role of bone marrow-derived hematopoietic stem cells, metabolites from gut microbiota, like short-chain fatty acids (26), and apolipoproteins produced by the liver in regulating the fate of monocytes (27) (Figure 1). Dynamic immune reprogramming proposes several strategies. These include CRISPR-based epigenetic editing (28), therapies that target metabolism, and integrating computational multi-omics (29). Together, these approaches aim for precise modulation of trained immunity.
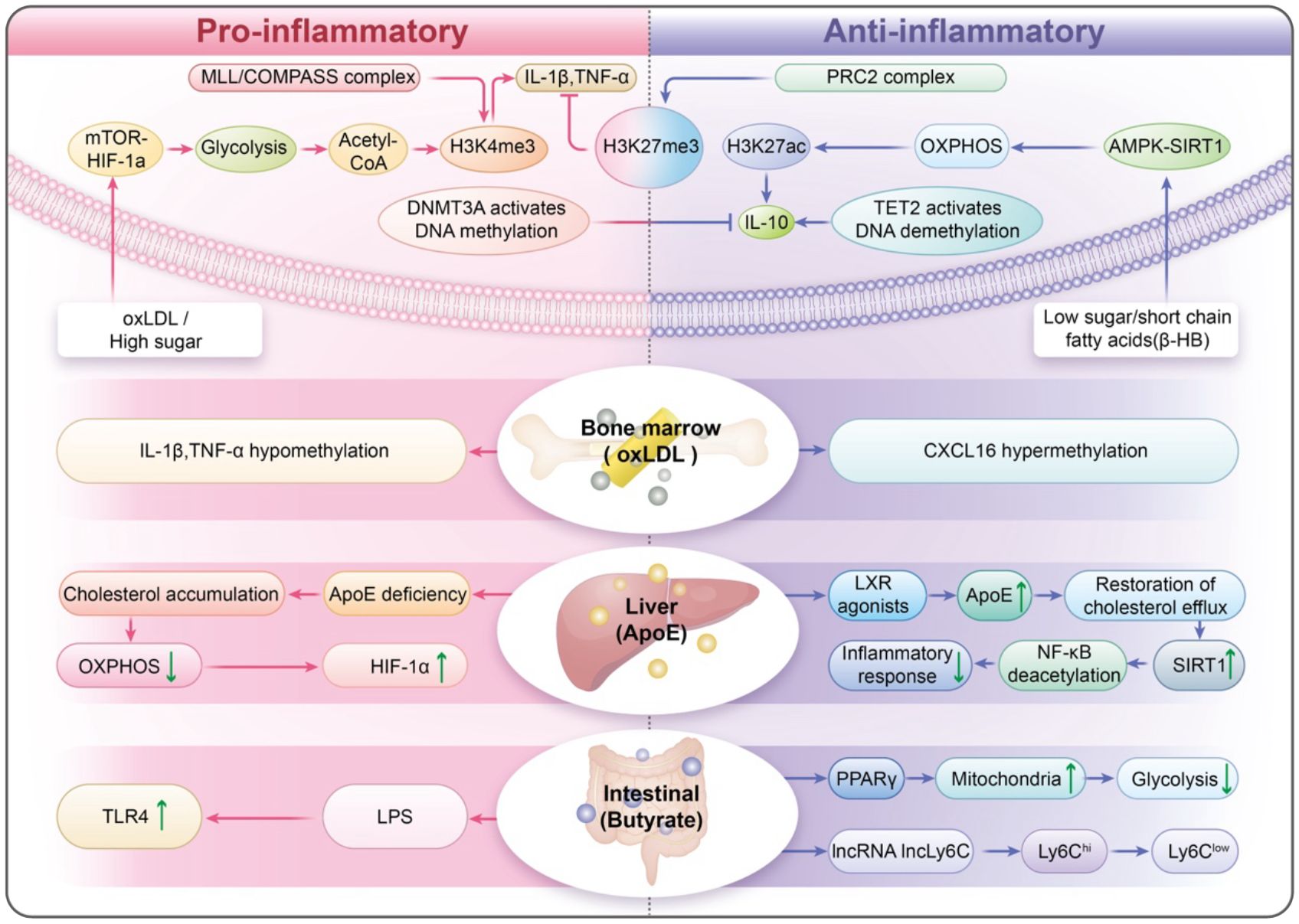
Figure 1. Trained Immunity Plasticity Spectrum (TIPS): A Dynamic Equilibrium of Immune Memory. The Cross-Organ Trained Immunity (COTI): highlights the role of bone marrow-derived hematopoietic stem cells, metabolites from gut microbiota, like short-chain fatty acids, and apolipoproteins produced by the liver in regulating the fate of monocytes.
By integrating mechanistic insights with translational innovation, this synthesis significantly redefines atherosclerosis as an “immune-metabolic memory disorder” and encourages the field to move beyond oversimplified models. Future initiatives should use interdisciplinary strategies that include spatial multi-omics, quantum-enabled epigenomic mapping, and global collaborations to fully explore the therapeutic potential of translational innovation.
2 The trained immunity plasticity spectrum: from proinflammatory dominance to dynamic equilibrium
2.1 The proinflammatory paradigm: foundations of classical trained immunity
The classical understanding of trained immunity focuses on its role in sustaining pro-inflammatory responses in innate immune cells (30). Early research indicates that, particularly in the context of infections or β-glucan exposure (31), monocytes and macrophages can undergo significant changes in metabolism and epigenetics when exposed to inflammatory stimuli such as oxidized LDL or lipopolysaccharides (LPS) (2). This reprogramming causes an increased production of cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, during subsequent challenges (32). The “proinflammatory-centric” model highlights mechanisms such as mTOR-HIF-1α signaling and trimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 4 (H3K4me3) at the promoters of proinflammatory genes, including IL-1β and TNF (33, 34). These mechanisms help stabilize glycolytic metabolism and enhance inflammatory memory. Although this framework established an important foundation, it fails to explain why inflammatory markers stay elevated even after the initial triggers have disappeared. It did not consider the variability in monocyte responses found in conditions such as atherosclerosis, where both proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory subsets exist in plaques (35).
2.2 Redefining immune memory: the TIPS model and its dynamic equilibrium
The trained immunity plasticity spectrum model offers a fresh view of trained immunity, depicting it as a dynamic range that encompasses pro-inflammatory, tolerogenic, and anti-inflammatory phenotypes. Proinflammatory trained immunity is triggered by metabolic stressors like oxLDL or high glucose levels (36). In the Ldlr−/− model, a Western diet can induce persistent training-induced immunity (NLRP3-dependent), and inflammatory memory characteristics remain even after dietary correction (37). Short-term oxLDL pretreatment induces H3K4me3 enrichment and enhances re-stimulation responses in human monocytes, resulting in long-term pro-inflammatory/pro-foam cell memory (38). This state reduces glycolysis and boosts oxidative phosphorylation while also adding repressive histone modifications (H3K27me3) to proinflammatory enhancer regions (39). In ApoE−/− and AAV-PCSK9 mice fed a high-fat diet, 4-PBA-trained monocytes exhibited reduced adhesion and increased CD24 expression, among other pro-differentiation features, and achieved sustained reprogramming through inhibition of SYK–mTOR, restoration of peroxisomal homeostasis, and TOLLIP-PPARγ neddylation; Whether administered systemically or transplanted as trained monocytes, they significantly reduced plaque burden and increased collagen content, and transmitted anti-inflammatory memory via CD24 between recipient monocytes, providing direct evidence for anti-inflammatory trained immunity in an atherosclerotic context (40). In parallel, the ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate (β-HB) functions as an endogenous HDAC inhibitor, elevating histone H3 acetylation (e.g., H3K9/14ac) at immune-regulatory loci (41, 42). Consistent with this epigenetic shift, oral 3-hydroxybutyrate in ApoE−/− mice reduced plaque burden and redirected monocyte–macrophage responses toward a reparative program, while complementary human ex vivo and murine data show β-HB suppresses NLRP3-dependent IL-1β/IL-18 production (43, 44). These states are dynamic and maintain a balance, influenced by metabolic and epigenetic signals that can change the fate of monocytes (45).
2.3 Regulatory nodes of plasticity: metabolic, epigenetic, and microenvironmental control
Metabolic regulation is essential for cellular function, and the mTOR/AMPK axis acts as a key metabolic switch (21). Under low glucose conditions, AMPK activates and phosphorylates the autophagy-initiating kinase Unc-51-like kinase 1 (ULK1), promoting autophagosome formation and cellular energy recovery (46). In contrast, when nutrients are plentiful, mTORC1 inhibits autophagy by phosphorylating ULK1 (47). The dynamic interplay between AMPK and mTORC1 facilitates cellular adaptation to metabolic stress (48). In addition, metabolites such as α-Ketoglutaric acid (α-KG) and acetyl-CoA play important roles in regulating epigenetics (49). For example, α-KG activates the TET2 enzyme to promote DNA demethylation and activate anti-inflammatory genes, such as IL-10 (50). Acetyl-CoA drives histone acetylation and helps establish a pro-inflammatory memory within the cell (51). The interaction of epigenetic modifications causes antagonism. Competing histone modifications, particularly H3K4me3 and H3K27me3, function as a chromatin “toggle switch” (52). The MLL/COMPASS complex deposits H3K4me3 at inflammatory loci, while the PRC2 complex deposits H3K27me3, silencing these genes in conditions that promote tolerance (53). Moreover, antagonism of DNMT3A with TET2 ensures that gene promoter methylation levels are under dynamic regulation and adapt to environmental changes (54). The microenvironment also plays a significant role in shaping monocyte trained immunity, influenced by various signals such as cytokines (like IFN-γ and IL-10), metabolites (including lactate and succinate), and hypoxic conditions (55). Hypoxia within plaques stabilizes HIF-1α, which amplifies proinflammatory responses associated with trained immunity (56). Microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids—notably butyrate—act as endogenous histone deacetylase inhibitors and dampen trained-immunity induction in humans; in ApoE−/− mice, SCFAs mitigate atherosclerotic inflammation via GPR43/HDAC-linked pathways (57–60).Likewise, an ApoE-/- mouse model treated with orally sodium butyrate (NaB) demonstrated that butyrate derived from intestinal flora regulates Mψs polarization through the GPR43/HDAC-miRNAs axis. This regulation leads to a decrease in pro-inflammatory factors such as IL-6 and TNF-α in arterial plaques, while increasing the anti-inflammatory factor IL-10, which ultimately reduces plaque area (59).
3 Metabolic reprogramming and vascular axis: from epigenetic memory to therapeutic innovation
3.1 Metabolic derangements and epigenetic rewiring of immune memory
Metabolic disorders such as high cholesterol and high blood sugar significantly affect immune memory by changing the epigenetic characteristics of monocytes (61). In cases of hypercholesterolemia, oxLDL activates the mevalonate pathway, leading to the production of isoprenoid intermediates, such as farnesyl pyrophosphate (62, 63). By stabilizing HIF-1α and enhancing mTORC1 signaling, this process induces a metabolic shift that increases glycolytic flux (34). This transformation leads to the production of acetyl-CoA, which is utilized as a substrate by HATs (64, 65). Consequently, increased histone acetylation at inflammatory promoters sustains transcriptional memory in innate cells (66). Similarly, high blood sugar levels activate the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway (HBP), resulting in increased O-GlcNAcylation of nuclear factor κB and histones (67). This modification increases the transcription of inflammatory genes, even after glucose levels normalize. Epigenetic “scars” can remain even after metabolic disturbances have resolved. This persistence locks monocytes into a proinflammatory state, which promotes the onset and progression of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and AS (68, 69). For example, monocytes from APS display continuous H3K4 trimethylation at the ARID5B promoter, which plays a role in apoptosis and pyroptosis (70). This example illustrates epigenetic ‘scars’ in chronic inflammation outside atherosclerosis and is hypothesis-generating for vascular disease.
3.2 Metabolic-immune dialogue and vascular microenvironment remodeling
Altered monocytes interact with vascular cells, significantly influencing the development of atherosclerotic areas. This influence occurs through the release of extracellular vesicles and signals associated with mitochondrial dysfunction (71). Proinflammatory monocytes produce PC-EVs, which activate the NF-κB pathway in endothelial cell (71–73). This activation intersects with the circadian control of adhesion molecules (e.g., VCAM-1), thereby promoting leukocyte recruitment (74). Mitochondrial dysfunction in activated monocytes triggers the release of mitochondrial DNA fragments and reactive oxygen species (ROS). These releases, in turn, activate Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) and the NLRP3 inflammasome in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) (75). This activation causes vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) to adopt a synthetic phenotype, which is characterized by the secretion of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and collagen breakdown, further destabilizing atherosclerotic plaques (76). Anti-inflammatory metabolites, such as SCFAs, mitigate these harmful effects (60, 77). For instance, butyrate directly activates Nrf2 signaling in endothelial cells via p300-mediated transcriptional activation, enhancing antioxidant defenses and endothelial function (78). This activation increases antioxidant defenses and helps stabilize plaque (Figure 2).
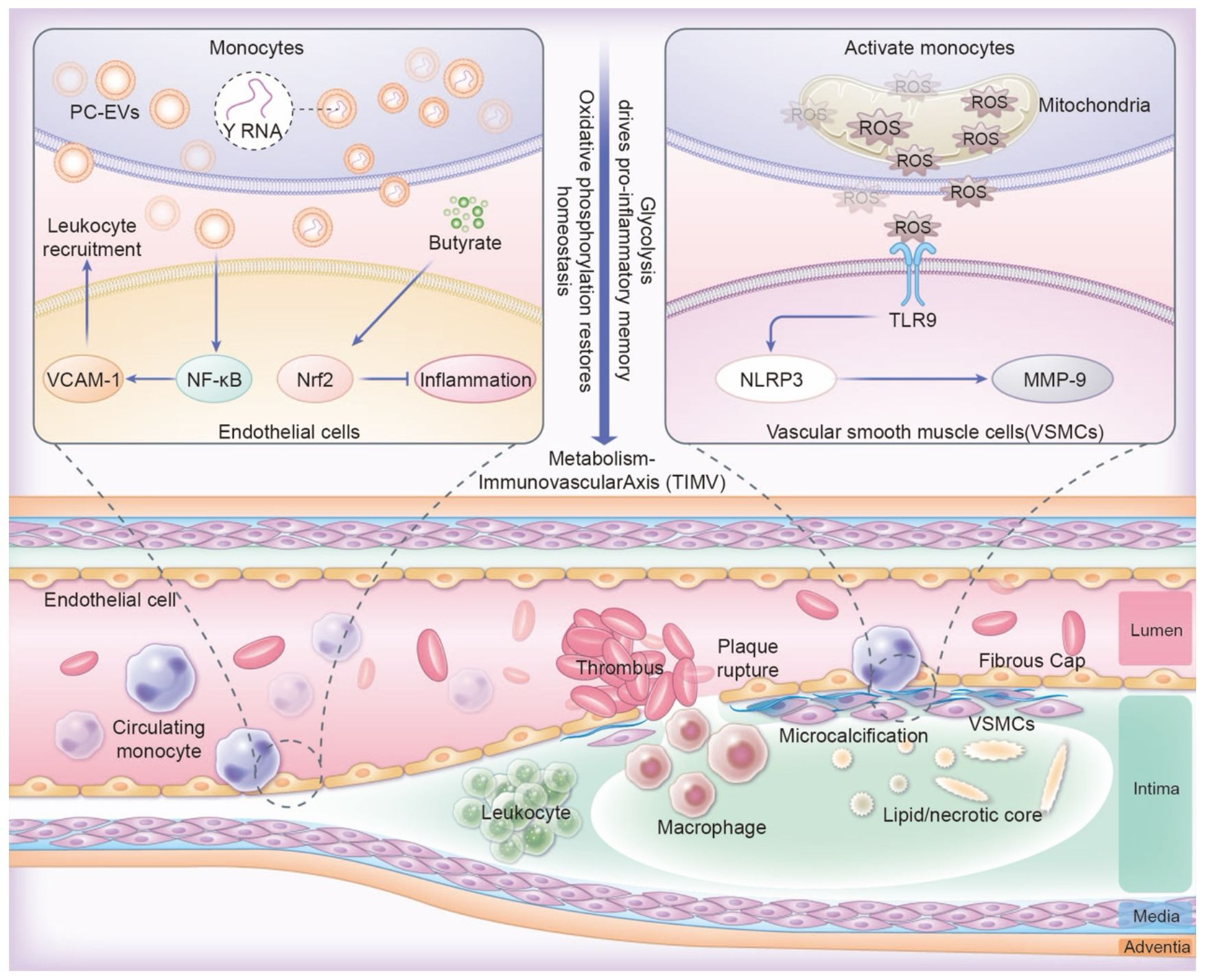
Figure 2. The TIMV axis links metabolism with trained immunity and vascular regulation. Pro-inflammatory PC-EVs activating NF-κB, disrupting VCAM-1 circadian control and amplifying leukocyte recruitment. Butyrate activating endothelial Nrf2 for plaque stabilization. Mitochondrial ROS in monocytes triggers TLR9/NLRP3 activation in VSMCs, driving MMP-9 secretion and collagen breakdown through macrophage infiltration, destabilization of atherosclerotic plaques.
3.3 Future frontiers: competitive metabolite dynamics and spatial multi-omics
The intricate and unresolved complexities of metabolism-immune system interactions demand innovative strategies. Competition between metabolites is critical (79). Ketones (β-HB) and lactate influence the availability of acetyl-CoA and subsequently affect epigenetic outcomes by altering histone acetylation patterns (80). In areas of atherosclerotic plaques with low oxygen, the accumulation of lactate might reduce the anti-inflammatory effects of β-HB by shifting acetyl-CoA towards processes that promote inflammation (81). Advanced spatial multi-omics technologies, such as spatial transcriptomics and MALDI imaging mass spectrometry, are vital for understanding how tissue inflammation varies in atherosclerotic lesions (82). These technologies can identify unique metabolic and epigenetic signatures in various regions, enabling researchers to distinguish between pro-inflammatory monocytes in necrotic cores and reparative cells in fibrous caps (83, 84). We integrate dietary, genetic, and environmental data with a multi-omics human map to help uncover the complexities of multidimensional biological systems (85). This integration aims to develop predictive models that identify individual metabolic vulnerabilities. By addressing these challenges, we can formulate strategies to effectively modify tissue inflammation. This will change the management of atherosclerosis from simply managing risk factors to actively reshaping immune memory (22, 86).
4 Cross-organ regulation of immune memory: from bone marrow to therapeutic integration
4.1 Bone marrow as a hub of epigenetic inheritance
Tissue immunity is influenced by distant organs, which create a “training axis” that connects local and systemic immune responses (87). Bone marrow is a key center for systemic immune memory, and HSCs are essential for preserving epigenetic information (88). When exposed to chronic metabolic or inflammatory challenges, like high cholesterol levels or persistent cytokine exposure, HSCs undergo reprogramming that involves changes in DNA methylation and histone modifications (89). Under chronic metabolic/inflammatory stress relevant to atherosclerosis, bone-marrow progenitors and HSCs undergo durable reprogramming: Western diet in Ldlr−/− mice elicits NLRP3-dependent epigenomic/transcriptomic remodeling of myeloid progenitors with heightened innate responses; peripheral ischemia in Apoe−/− mice imposes epigenetic imprints in HSCs that propagate inflammation and accelerate atherosclerosis; conversely, enhancing cholesterol efflux (rHDL/LXR) or exercise restores HSPC quiescence and reduces inflammatory leukocyte output and plaque inflammation (37, 90–92). Epigenetic changes passed on to myeloid progenitors lead to monocytes that are ready for stronger inflammatory responses, even in the absence of ongoing triggers (93). This phenomenon is known as trained immunity (94). In studies using mouse models, HSCs from mice with high cholesterol produce monocytes that exhibit increased NLRP3 inflammasome activity (95), accelerating plaque progression in recipient animals. his systemic memory reveals the bone marrow’s critical role in sustaining vascular inflammation over time (96), thereby challenging the traditional view that atherosclerosis is strictly a localized condition.
4.2 Gut microbiota and SCFAs: orchestrating immune memory
The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in immune memory by producing metabolites, especially SCFAs such as butyrate, propionate, and acetate (97, 98). Butyrate is produced when bacteria ferment dietary fiber, and this compound plays a crucial role by inhibiting histone deacetylases (HDACs) in monocytes (99). Butyrate, a metabolite produced by microbiota, activates lncRNA lncLy6C, which in turn drives the differentiation of Ly6C(high) macrophages into Ly6C(int/neg) macrophages, mediated by the lncLy6C/C/EBPβ/Nr4A1 signaling axis (100). In the colonic lumen, it functions as a chemoprotective inhibitor of histone deacetylases and as an acetylation substrate for histone acetylases (101). Furthermore, SCFAs enhance mitochondrial biogenesis by activating PPARγ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α), which counteracts the glycolytic shift triggered by metabolic stressors such as oxLDL (102). On the other hand, dysbiosis, characterized by a decrease in SCFA-producing bacteria, can worsen trained immunity (103). This is particularly evident in models that mimic a Western diet, where increased gut permeability allows lipopolysaccharides (LPS) to enter the bloodstream, activating Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and priming monocytes in a pro-inflammatory manner (104). The gut-vascular axis may serve as a promising target for adjusting immune memory, indicating that dietary changes or probiotic treatments could be helpful.
4.3 Hepatic cholesterol metabolism: stabilizing immune memory
The liver is essential for regulating the flexibility of monocytes by managing cholesterol metabolism and producing apolipoproteins (105). A key player in this process is apolipoprotein E (ApoE), primarily produced by hepatocytes in the liver (106, 107). ApoE plays a key role in cholesterol removal from monocytes by interacting with ABCA1 transporters. This interaction is critical for maintaining mitochondrial health and ensuring the proper function of SIRT1, a protein involved in cellular metabolism regulation (108). In their studies of ApoE-deficient mice, researchers found that cholesterol accumulation disrupts mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (109). This disruption compels cells to increasingly depend on glycolytic pathways for energy, stabilizes HIF-1α (a protein that enhances inflammation), and intensifies proinflammatory signals, ultimately leading to the destabilization of atherosclerotic plaques (110). Conversely, the introduction of liver X receptor (LXR) agonists increases the expression of ApoE (111), which aids in restoring cholesterol efflux and promotes an anti-inflammatory response via SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of NF-κB, a crucial regulator of inflammation (112). Furthermore, the liver affects systemic immune responses by signaling through bile acids (113). For example, FXR agonists such as obeticholic acid upregulate SIRT3 in monocytes, thereby enhancing mitochondrial deacetylation and oxidative metabolism (114). These insights reveal that the liver’s metabolic functions are crucial for regulating immune memory stability, thereby linking dietary lipids to vascular inflammation.
4.4 Integrated therapeutic strategies: targeting cross-organ networks
The interdependence of bone marrow, gut, and liver in shaping immune memory highlights the need for therapies that can target multiple organs at once (115). Combination treatment strategies include the use of PCSK9 inhibitors to lower the activity of the mevalonate pathway and SCFA-producing probiotics. These strategies work together to suppress pro-inflammatory T cells and encourage a more balanced immune response (116). Additionally, engineered nanoparticles provide a means for precise delivery (117, 118). For instance, bone marrow-targeting particles can deliver DNMT3A inhibitors to reverse the hypermethylation of CXCL2 in hematopoietic stem cells, while nanoparticles targeting the gut can directly release butyrate to support the colonic microbiota (119). Techniques for gene editing, such as CRISPR-dCas9 systems that are delivered with lipid nanoparticles, can create specific epigenetic changes in various organs (120), and introduce the APOE4 variant in pluripotent stem cells (121). New tools, including AI platforms that utilize multi-omics data, can further refine these approaches by predicting how individual patients may respond to treatments that affect multiple organs (122). However, challenges remain, including reducing off-target effects and defining safe parameters for epigenetic editing. By combining insights from hematology, microbiology, and hepatology, this comprehensive strategy could transform atherosclerosis management. It shifts the focus from isolated risk factors to a holistic understanding of immune memory engineering.
5 Therapeutic innovation and clinical translation: targeting trained immunity
5.1 Rewriting immune memory: epigenetic editing and small molecule therapies
By providing precise control over chromatin states, epigenetic editing technologies are transforming our ability to modulate trained immunity (123). One of the key advancements is the use of CRISPR-dCas9 systems (124, 125), which utilize CRISPR/dCas9-based epigenetic modifiers to reactivate the endogenous TERT gene in unstimulated T cells found in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) by rewiring the epigenetic marks of the TERT promoter (126). Preclinical studies have demonstrated that BET inhibitors, like DDO-8926, and HDAC inhibitors, such as entinostat, offer complementary approaches for managing inflammation (127, 128). BET inhibitors block BRD4, a protein that activates enhancers at pro-inflammatory sites (129), In contrast, HDAC inhibitors increase histone acetylation, which promotes the expression of anti-inflammatory genes (130). Although there have been advancements, several challenges persist, such as off-target effects that unintentionally silence tumor suppressor genes and issues with delivery efficiency. To address these concerns, we must improve cell-specific targeting. This is illustrated by the development of monocyte-targeted nanoparticles and systems that utilize exosomes for delivery.
5.2 Balancing metabolism and immunity: repurposing drugs for immune resilience
Metabolic modulators are gaining attention as therapies that fulfill two important roles: they address lipid and glucose dysregulation and reprogram immune memory (131, 132). PCSK9 inhibitors are well-known for lowering LDL cholesterol levels (133), but they also suppress the mevalonate pathway in monocytes (134). This suppression decreases the mTOR activation that requires geranylgeranylation, which helps maintain eTreg cells (135). When mTOR inhibitors and SIRT1 activators are combined, they balance glycolytic and oxidative metabolism, stabilizing T cell inflammation (136, 137). Researchers have demonstrated in studies with diabetic mouse models that this combination reduces plaque buildup by enhancing mitochondrial respiration (138). Similarly, FXR agonists improve cholesterol efflux and are involved in regulating lipid metabolism, which helps counter glycolytic inflammation (139, 140). These approaches underscore the promising potential of repurposing metabolic drugs for immunomodulation; however, further refinement is needed to determine the optimal dosing and timing for these therapies.
5.3 Personalized medicine: harnessing AI to predict and optimize treatments
The metabolic-vascular axis indicates that hyperglycemia may increase monocyte inflammatory responses through epigenetic modifications. However, the metabolic-vascular axis is complex and dynamic, making it challenging to fully understand its regulatory network using traditional experimental methods. Integrating multidimensional data to predict individual inflammatory phenotypes has become a significant challenge for clinical translation. AI-driven multi-omics integration technologies are revolutionizing tissue inflammation treatment by facilitating personalized predictions and designing targeted interventions (141). Multi-omics platforms, including single-cell ATAC-seq and metabolomics, generate extensive datasets that machine learning models can analyze to identify different immune states (142). For example, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) trained on chromatin accessibility profiles can predict enhancer-promoter interactions that play a role in proinflammatory trained immunity. This capability aids in selecting suitable CRISPR targets (143). Additionally, reinforcement learning frameworks help tailor treatment regimens by learning from patient responses to previous therapies (144). For example, in silico trials that simulate the use of PCSK9 inhibitors and SCFAs can help determine dosing schedules that improve plaque stability and lower toxicity (145). Convolutional neural networks (CNN) have been successfully applied to identify immune biomarkers in atherosclerosis. Han Zhang et al. constructed a deep learning model of convolutional neural network based on gene-immunity correlation, which achieved an AUC of 0.933, a sensitivity of 92.3%, and a specificity of 87.5% in an independent external test for diagnosing advanced plaque (146). Machine learning models are essential for integrating genetic, epigenetic, and clinical data to classify patients into distinct trained immunity subtypes, such as “hyperinflammatory” or “tolerogenic,” thus allowing for more targeted therapeutic approaches (147). However, challenges like ensuring that models are generalizable and addressing the diversity of data, especially for underrepresented populations, remain significant obstacles in this field.
6 Future directions: charting the next frontier in trained immunity research
Research on trained immunity in atherosclerosis has uncovered complex interactions between metabolic, epigenetic, and systemic regulatory networks. However, several critical questions remain that will influence future studies in this field. A significant area of research focuses on how immune memory is inherited across generations. High cholesterol levels or obesity may change germ cells in a way that increases the risk of inflammatory responses in offspring (148, 149). For example, studies involving mice have shown that maternal exposure to oxidized oxLDL causes DNA methylation at anti-inflammatory genes like IL-10 and TGF-β in oocytes, which leads to offspring monocytes that exhibit a lasting pro-inflammatory tendency (150, 151). In addition, factors from fathers, such as alterations in mitochondrial transfer RNAs in sperm due to Western diets, might also influence how immune memory is inherited by future generations (152). To fully understand these mechanisms, it is essential to conduct longitudinal studies involving human cohorts, combined with advanced multi-omics profiling. This approach will differentiate inherited epigenetic changes from environmental influences and guide interventions that break the cycle of cardiovascular risk across generations.
It is equally important to define the long-lasting duration of immune memory (153). Current therapies often neglect the timing of therapeutic interventions in the context of tissue inflammation. Early interventions in the early stages of plaque formation can change the epigenetic landscape. In contrast, plaques that have advanced to later stages often show persistent pro-inflammatory states (154). Researchers can identify the best times for intervention by using AI to analyze longitudinal multi-omics datasets, which combine data on chromatin accessibility, metabolite flow, and plaque imaging (155). For example, machine learning models trained on data from atherosclerotic mouse models and a single blood drop can diagnose and classify the severity of atherosclerosis. This indicates that biomarkers and vascular factors in the blood can be detected and are linked to the early stages of atherosclerosis development (156). Furthermore, targeted delivery systems like lipid nanoparticles, which are specifically designed to reach bone marrow and carry CRISPR/Cas9 protein, offer effective means to reverse maladaptive immune memory while minimizing systemic toxicity (157). However, to implement these strategies, it is essential to address the varying immune training conditions found within plaques. Hypoxic cores, rich in lactate and mitochondrial DNA fragments, may sustain pro-inflammatory trained immunity by stabilizing HIF-1 (158), While fibrous caps contain repairing monocytes that are influenced by AIM2 gradients (159, 160). Advanced spatial multi-omics technologies, including MIBI and spatial transcriptomics, will enable the mapping of distinct niches, which in turn will inform the development of localized therapies (161). For example, an injectable composite hydrogel (SFD/CS/ZIF-8@QCT) can target specific areas within plaques. This hydrogel contains quercetin-modified zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8@QCT) and demonstrates excellent functions, including antibacterial properties and immunomodulation, which enhance therapeutic outcomes (162).
AI and quantum computing have great potential to speed up medical discoveries (163, 164). Using quantum-enabled simulations, researchers can investigate the complex interactions between epigenetic and metabolic factors and predict the outcomes of specific perturbation events. In clinical practice, AI platforms and single-cell RNA can categorize patients into different T cell immunity subtypes, such as hyperinflammatory, tolerogenic, or metabolically resistant, thereby facilitating the development of more personalized treatment plans (165, 166). To realize this vision, it is crucial to confront and resolve significant moral and logistical challenges. The high costs of CRISPR therapies may increase existing health disparities, emphasizing the importance of global collaboration to guarantee fair access to these advanced treatments (167). Regulatory agencies must balance promoting innovation with the need for caution, particularly regarding inheritable epigenetic modifications. This balance requires the creation of international guidelines to ensure safety and informed consent.
Ultimately, advancing this field requires collaboration among immunologists, computational biologists, ethicists, and clinicians to turn research on trained immunity from a scientific curiosity into effective therapies. The future of trained immunity research will transform atherosclerosis management and shed light on immune memory’s role in chronic diseases worldwide by emphasizing teamwork across disciplines, promoting open-data initiatives, and designing patient-centered research.
7 Conclusion
The discovery of trained immunity has significantly changed our understanding of atherosclerosis, framing it as a disorder related to dysregulated immune responses and metabolic memory. The trained immunity plasticity spectrum model defines trained immunity as a dynamic balance among pro-inflammatory, tolerogenic, and anti-inflammatory states, shaped by mTOR/AMPK signaling and histone modifications. The trained immunity-metabolism-vascular axis explains how metabolic disturbances can affect monocytes at the epigenetic level and change vascular environments through exosomal microRNAs and signals from mitochondrial stress. The cross-organ trained immunity framework underscores the critical regulation among the bone marrow, gut, and liver, illustrating that atherosclerosis is significantly influenced by their inter-organ communication. Furthermore, dynamic immune reprogramming strategies hold great promise for resetting harmful immune memories. These strategies include CRISPR-based epigenetic editing, therapies aimed at metabolism, and AI-driven precision approaches. These advancements challenge traditional reductionist views and lead to new therapies aimed at engineering immune memory instead of merely managing symptoms. Future initiatives should aim to apply these findings in clinical practice, use spatial multi-omics, and promote global equity to ensure that these innovations benefit diverse populations and ultimately transform cardiovascular disease prevention and treatment.
Author contributions
BZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JW: Writing – review & editing. HZ: Writing – review & editing. JY: Writing – review & editing. HW: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by The National key R & D projects of China Mongolian medicine based on the concept of simultaneous treatment of brain and heart in the treatment of coronary heart.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the College of Chinese Medicine for Cardiovascular-Cranial Disease, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University for their support of this project.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1669796/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Weber C and Noels H. Atherosclerosis: current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat Med. (2011) 17:1410–22. doi: 10.1038/nm.2538
2. Ochando J, Mulder WJM, Madsen JC, Netea MG, and Duivenvoorden R. Trained immunity - basic concepts and contributions to immunopathology. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2023) 19:23–37. doi: 10.1038/s41581-022-00633-5
3. Jaipersad AS, Lip GY, Silverman S, and Shantsila E. The role of monocytes in angiogenesis and atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2014) 63:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.09.019
4. Dong Z, Hou L, Luo W, Pan LH, Li X, Tan HP, et al. Myocardial infarction drives trained immunity of monocytes, accelerating atherosclerosis. Eur Heart J. (2024) 45:669–84. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad787
5. Shi C and Pamer EG. Monocyte recruitment during infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2011) 11:762–74. doi: 10.1038/nri3070
6. Ma C, Xia R, Yang S, Liu L, Zhang J, Feng K, et al. Formononetin attenuates atherosclerosis via regulating interaction between KLF4 and SRA in apoE(-/-) mice. Theranostics. (2020) 10:1090–106. doi: 10.7150/thno.38115
7. Xu S, Ilyas I, Little PJ, Li H, Kamato D, Zheng X, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases and beyond: from mechanism to pharmacotherapies. Pharmacol Rev. (2021) 73:924–67. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000096
8. Moorlag S, Folkman L, Ter Horst R, Krausgruber T, Barreca D, Schuster LC, et al. Multi-omics analysis of innate and adaptive responses to BCG vaccination reveals epigenetic cell states that predict trained immunity. Immunity. (2024) 57:171–187.e114. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.12.005
9. Netea MG, Joosten LA, Latz E, Mills KH, Natoli G, Stunnenberg HG, et al. Trained immunity: A program of innate immune memory in health and disease. Sci (New York NY). (2016) 352:aaf1098. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf1098
10. Domínguez-Andrés J, Dos Santos JC, Bekkering S, Mulder WJM, van der Meer JWM, Riksen NP, et al. Trained immunity: adaptation within innate immune mechanisms. Physiol Rev. (2023) 103:313–46. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00031.2021
11. Bekkering S, Domínguez-Andrés J, Joosten LAB, Riksen NP, and Netea MG. Trained immunity: reprogramming innate immunity in health and disease. Annu Rev Immunol. (2021) 39:667–93. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-102119-073855
12. Lim GB. Hyperglycaemia-induced trained immunity promotes atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2021) 18:687. doi: 10.1038/s41569-021-00606-4
13. Giacco F and Brownlee M. Oxidative stress and diabetic complications. Circ Res. (2010) 107:1058–70. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.223545
14. Zhang Y, Jiang H, Dong M, Min J, He X, Tan Y, et al. Macrophage MCT4 inhibition activates reparative genes and protects from atherosclerosis by histone H3 lysine 18 lactylation. Cell Rep. (2024) 43:114180. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114180
15. Koelwyn GJ, Corr EM, Erbay E, and Moore KJ. Regulation of macrophage immunometabolism in atherosclerosis. Nat Immunol. (2018) 19:526–37. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0113-3
16. Keating ST, Groh L, van der Heijden C, Rodriguez H, Dos Santos JC, Fanucchi S, et al. The set7 lysine methyltransferase regulates plasticity in oxidative phosphorylation necessary for trained immunity induced by β-glucan. Cell Rep. (2020) 31:107548. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107548
17. Bekkering S, Blok BA, Joosten LA, Riksen NP, van Crevel R, and Netea MG. In vitro experimental model of trained innate immunity in human primary monocytes. Clin Vaccine immunology: CVI. (2016) 23:926–33. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00349-16
18. Florian MC. Powerful microscopy reveals blood-cell production in bone marrow. Nature. (2024) 627:741–2. doi: 10.1038/d41586-024-00504-y
19. Jeyanathan M, Vaseghi-Shanjani M, Afkhami S, Grondin JA, Kang A, D’Agostino MR, et al. Parenteral BCG vaccine induces lung-resident memory macrophages and trained immunity via the gut-lung axis. Nat Immunol. (2022) 23:1687–702. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01354-4
20. Neeland IJ, Lim S, Tchernof A, Gastaldelli A, Rangaswami J, Ndumele CE, et al. Metabolic syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2024) 10:77. doi: 10.1038/s41572-024-00563-5
21. Ji Z, Liu GH, and Qu J. Mitochondrial sirtuins, metabolism, and aging. J Genet Genomics = Yi Chuan xue bao. (2022) 49:287–98. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2021.11.005
22. Riksen NP, Bekkering S, Mulder WJM, and Netea MG. Trained immunity in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2023) 20:799–811. doi: 10.1038/s41569-023-00894-y
23. Liu R, Wu J, Guo H, Yao W, Li S, Lu Y, et al. Post-translational modifications of histones: Mechanisms, biological functions, and therapeutic targets. MedComm. (2023) 4:e292. doi: 10.1002/mco2.292
24. Chavakis T, Alexaki VI, and Ferrante AW Jr. Macrophage function in adipose tissue homeostasis and metabolic inflammation. Nat Immunol. (2023) 24:757–66. doi: 10.1038/s41590-023-01479-0
25. Gao P, Yi J, Chen W, Gu J, Miao S, Wang X, et al. Pericyte-derived exosomal miR-210 improves mitochondrial function and inhibits lipid peroxidation in vascular endothelial cells after traumatic spinal cord injury by activating JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway. J nanobiotechnology. (2023) 21:452. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02110-y
26. Zeng X, Li X, Li X, Wei C, Shi C, Hu K, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation from young mice rejuvenates aged hematopoietic stem cells by suppressing inflammation. Blood. (2023) 141:1691–707. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022017514
27. Sharma RS, Harrison DJ, Kisielewski D, Cassidy DM, McNeilly AD, Gallagher JR, et al. Experimental nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis are ameliorated by pharmacologic activation of nrf2 (NF-E2 p45-related factor 2). Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2018) 5:367–98. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2017.11.016
28. Wu Y, Huang Z, Liu Y, He P, Wang Y, Yan L, et al. Ultrasound control of genomic regulatory toolboxes for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:10444. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54477-7
29. Xu JC, Chen ZY, Huang XJ, Wu J, Huang H, Niu LF, et al. Multi-omics analysis reveals that linoleic acid metabolism is associated with variations of trained immunity induced by distinct BCG strains. Sci Adv. (2024) 10:eadk8093. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adk8093
30. Mulder WJM, Ochando J, Joosten LAB, Fayad ZA, and Netea MG. Therapeutic targeting of trained immunity. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2019) 18:553–66. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0025-4
31. Woeste MR, Shrestha R, Geller AE, Li S, Montoya-Durango D, Ding C, et al. Irreversible electroporation augments β-glucan induced trained innate immunity for the treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J immunotherapy Cancer. (2023) 11:e006221. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-006221
32. Auger JP, Zimmermann M, Faas M, Stifel U, Chambers D, Krishnacoumar B, et al. Metabolic rewiring promotes anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids. Nature. (2024) 629:184–92. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07282-7
33. Pan T, Sun S, Chen Y, Tian R, Chen E, Tan R, et al. Immune effects of PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α-regulated glycolysis in polymorphonuclear neutrophils during sepsis. Crit Care (London England). (2022) 26:29. doi: 10.1186/s13054-022-03893-6
34. Cheng SC, Quintin J, Cramer RA, Shepardson KM, Saeed S, Kumar V, et al. mTOR- and HIF-1α-mediated aerobic glycolysis as metabolic basis for trained immunity. Science. (2014) 345:1250684. doi: 10.1126/science.1250684
35. Henein MY, Vancheri S, Longo G, and Vancheri F. The role of inflammation in cardiovascular disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:12906. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112906
36. Bahrar H, Bekkering S, Stienstra R, Netea MG, and Riksen NP. Innate immune memory in cardiometabolic disease. Cardiovasc Res. (2024) 119:2774–86. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvad030
37. Christ A, Günther P, Lauterbach MAR, Duewell P, Biswas D, Pelka K, et al. Western diet triggers NLRP3-dependent innate immune reprogramming. Cell. (2018) 172:162–175.e114. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.013
38. Bekkering S, Quintin J, Joosten LA, van der Meer JW, Netea MG, and Riksen NP. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein induces long-term proinflammatory cytokine production and foam cell formation via epigenetic reprogramming of monocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2014) 34:1731–8. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303887
39. Serio S, Pagiatakis C, Musolino E, Felicetta A, Carullo P, Laura Frances J, et al. Cardiac aging is promoted by pseudohypoxia increasing p300-induced glycolysis. Circ Res. (2023) 133:687–703. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.322676
40. Geng S, Lu R, Zhang Y, Wu Y, Xie L, Caldwell BA, et al. Monocytes reprogrammed by 4-PBA potently contribute to the resolution of inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2024) 135:856–72. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.124.325023
41. Shimazu T, Hirschey MD, Newman J, He W, Shirakawa K, Le Moan N, et al. Suppression of oxidative stress by β-hydroxybutyrate, an endogenous histone deacetylase inhibitor. Science. (2013) 339:211–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1227166
42. Newman JC and Verdin E. β-hydroxybutyrate: A signaling metabolite. Annu Rev Nutr. (2017) 37:51–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-071816-064916
43. Zhang SJ, Li ZH, Zhang YD, Chen J, Li Y, Wu FQ, et al. Ketone body 3-hydroxybutyrate ameliorates atherosclerosis via receptor gpr109a-mediated calcium influx. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2021) 8:2003410. doi: 10.1002/advs.202003410
44. Youm YH, Nguyen KY, Grant RW, Goldberg EL, Bodogai M, Kim D, et al. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. (2015) 21:263–9. doi: 10.1038/nm.3804
45. Su H, Liang Z, Weng S, Sun C, Huang J, Zhang T, et al. miR-9-5p regulates immunometabolic and epigenetic pathways in β-glucan-trained immunity via IDH3α. JCI Insight. (2021) 6:e144260. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.144260
46. Egan DF, Shackelford DB, Mihaylova MM, Gelino S, Kohnz RA, Mair W, et al. Phosphorylation of ULK1 (hATG1) by AMP-activated protein kinase connects energy sensing to mitophagy. Sci (New York NY). (2011) 331:456–61. doi: 10.1126/science.1196371
47. Hajdú B, Holczer M, Horváth G, Szederkényi G, and Kapuy O. Fine-Tuning of mTORC1-ULK1-PP2A Regulatory Triangle Is Crucial for Robust Autophagic Response upon Cellular Stress. Biomolecules. (2022) 12:1587. doi: 10.3390/biom12111587
48. Holczer M, Hajdú B, Lőrincz T, Szarka A, Bánhegyi G, and Kapuy O. A Double Negative Feedback Loop between mTORC1 and AMPK Kinases Guarantees Precise Autophagy Induction upon Cellular Stress. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:5543. doi: 10.3390/ijms20225543
49. Liu Y, Chen C, Wang X, Sun Y, Zhang J, Chen J, et al. An epigenetic role of mitochondria in cancer. Cells. (2022) 11:2518. doi: 10.3390/cells11162518
50. Joshi K, Liu S, Breslin SJP, and Zhang J. Mechanisms that regulate the activities of TET proteins. Cell Mol Life sciences: CMLS. (2022) 79:363. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04396-x
51. Luda KM, Longo J, Kitchen-Goosen SM, Duimstra LR, Ma EH, Watson MJ, et al. Ketolysis drives CD8(+) T cell effector function through effects on histone acetylation. Immunity. (2023) 56:2021–2035.e2028. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.07.002
52. Zhang D, Deng Y, Kukanja P, Agirre E, Bartosovic M, Dong M, et al. Spatial epigenome-transcriptome co-profiling of mammalian tissues. Nature. (2023) 616:113–22. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05795-1
53. Putiri EL, Tiedemann RL, Liu C, Choi JH, and Robertson KD. Impact of human MLL/COMPASS and polycomb complexes on the DNA methylome. Oncotarget. (2014) 5:6338–52. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2215
54. He F, Wu H, Zhou L, Lin Q, Cheng Y, and Sun YE. Tet2-mediated epigenetic drive for astrocyte differentiation from embryonic neural stem cells. Cell Death Discov. (2020) 6:30. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-0264-5
55. Murphy DM, Mills KHG, and Basdeo SA. The effects of trained innate immunity on T cell responses; clinical implications and knowledge gaps for future research. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:706583. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.706583
56. Chen S, Zhang W, Tang C, Rong X, Liu Y, Luo Y, et al. Macrophage membrane-functionalized manganese dioxide nanomedicine for synergistic treatment of atherosclerosis by mitigating inflammatory storms and promoting cholesterol efflux. J nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22:664. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02939-x
57. Cleophas MCP, Ratter JM, Bekkering S, Quintin J, Schraa K, Stroes ES, et al. Effects of oral butyrate supplementation on inflammatory potential of circulating peripheral blood mononuclear cells in healthy and obese males. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:775. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37246-7
58. Schulthess J, Pandey S, Capitani M, Rue-Albrecht KC, Arnold I, Franchini F, et al. The short chain fatty acid butyrate imprints an antimicrobial program in macrophages. Immunity. (2019) 50:432–445.e437. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.12.018
59. Ma H, Yang L, Liu Y, Yan R, Wang R, Zhang P, et al. Butyrate suppresses atherosclerotic inflammation by regulating macrophages and polarization via GPR43/HDAC-miRNAs axis in ApoE-/- mice. PloS One. (2023) 18:e0282685. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282685
60. Haghikia A, Zimmermann F, Schumann P, Jasina A, Roessler J, Schmidt D, et al. Propionate attenuates atherosclerosis by immune-dependent regulation of intestinal cholesterol metabolism. Eur Heart J. (2022) 43:518–33. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab644
61. Minderjahn J, Fischer A, Maier K, Mendes K, Nuetzel M, Raithel J, et al. Postmitotic differentiation of human monocytes requires cohesin-structured chromatin. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:4301. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31892-2
62. Weinberger C. A model for farnesoid feedback control in the mevalonate pathway. Trends Endocrinol metabolism: TEM. (1996) 7:1–6. doi: 10.1016/1043-2760(95)00180-8
63. Bekkering S, Arts RJW, Novakovic B, Kourtzelis I, van der Heijden C, Li Y, et al. Metabolic induction of trained immunity through the mevalonate pathway. Cell. (2018) 172:135–146.e139. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.025
64. Shvedunova M and Akhtar A. Modulation of cellular processes by histone and non-histone protein acetylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2022) 23:329–49. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00441-y
65. Wellen KE, Hatzivassiliou G, Sachdeva UM, Bui TV, Cross JR, and Thompson CB. ATP-citrate lyase links cellular metabolism to histone acetylation. Science. (2009) 324:1076–80. doi: 10.1126/science.1164097
66. Lavertu-Jolin M, Chattopadhyaya B, Chehrazi P, Carrier D, Wünnemann F, Leclerc S, et al. Acan downregulation in parvalbumin GABAergic cells reduces spontaneous recovery of fear memories. Mol Psychiatry. (2023) 28:2946–63. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02085-0
67. Lam C, Low JY, Tran PT, and Wang H. The hexosamine biosynthetic pathway and cancer: Current knowledge and future therapeutic strategies. Cancer Lett. (2021) 503:11–8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.01.010
68. Xourgia E and Tektonidou MG. An update on antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2022) 23:84. doi: 10.1007/s11926-021-01051-5
69. Salet DM, Bekkering S, Middeldorp S, and van den Hoogen LL. Targeting thromboinflammation in antiphospholipid syndrome. J Thromb haemostasis: JTH. (2023) 21:744–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2022.12.002
70. Tan Y, Qiao J, Yang S, Wang Q, Liu H, Liu Q, et al. ARID5B-mediated LINC01128 epigenetically activated pyroptosis and apoptosis by promoting the formation of the BTF3/STAT3 complex in β2GPI/anti-β2GPI-treated monocytes. Clin Trans Med. (2024) 14:e1539. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1539
71. Olejarz W, Sadowski K, and Radoszkiewicz K. Extracellular vesicles in atherosclerosis: state of the art. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 25:388. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010388
72. Wang JG, Williams JC, Davis BK, Jacobson K, Doerschuk CM, Ting JP, et al. Monocytic microparticles activate endothelial cells in an IL-1β-dependent manner. Blood. (2011) 118:2366–74. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-330878
73. Zisser L and Binder CJ. Extracellular vesicles as mediators in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. J Lipid Atheroscler. (2024) 13:232–61. doi: 10.12997/jla.2024.13.3.232
74. He W, Holtkamp S, Hergenhan SM, Kraus K, de Juan A, Weber J, et al. Circadian expression of migratory factors establishes lineage-specific signatures that guide the homing of leukocyte subsets to tissues. Immunity. (2018) 49:1175–1190.e1177. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.10.007
75. Tanase DM, Valasciuc E, Gosav EM, Ouatu A, Buliga-Finis ON, Floria M, et al. Portrayal of NLRP3 inflammasome in atherosclerosis: current knowledge and therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:8162. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098162
76. Li T, Li X, Feng Y, Dong G, Wang Y, and Yang J. The role of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in atherosclerotic plaque instability. Mediators Inflammation. (2020) 2020:3872367. doi: 10.1155/2020/3872367
77. Aguilar EC, Leonel AJ, Teixeira LG, Silva AR, Silva JF, Pelaez JM, et al. Butyrate impairs atherogenesis by reducing plaque inflammation and vulnerability and decreasing NFκB activation. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2014) 24:606–13. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2014.01.002
78. Wu J, Jiang Z, Zhang H, Liang W, Huang W, Zhang H, et al. Sodium butyrate attenuates diabetes-induced aortic endothelial dysfunction via P300-mediated transcriptional activation of Nrf2. Free Radic Biol Med. (2018) 124:454–65. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.06.034
79. Zhai K, Liang D, Li H, Jiao F, Yan B, Liu J, et al. NLRs guard metabolism to coordinate pattern- and effector-triggered immunity. Nature. (2022) 601:245–51. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04219-2
80. Mao Y, Zhang J, Zhou Q, He X, Zheng Z, Wei Y, et al. Hypoxia induces mitochondrial protein lactylation to limit oxidative phosphorylation. Cell Res. (2024) 34:13–30. doi: 10.1038/s41422-023-00864-6
81. Deng Y, Xie M, Li Q, Xu X, Ou W, Zhang Y, et al. Targeting mitochondria-inflammation circuit by β-hydroxybutyrate mitigates HFpEF. Circ Res. (2021) 128:232–45. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317933
82. Nurmohamed NS, Kraaijenhof JM, Mayr M, Nicholls SJ, Koenig W, Catapano AL, et al. Proteomics and lipidomics in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk prediction. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44:1594–607. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad161
83. Vandereyken K, Sifrim A, Thienpont B, and Voet T. Methods and applications for single-cell and spatial multi-omics. Nat Rev Genet. (2023) 24:494–515. doi: 10.1038/s41576-023-00580-2
84. Baysoy A, Bai Z, Satija R, and Fan R. The technological landscape and applications of single-cell multi-omics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2023) 24:695–713. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00615-w
85. Pan L, Parini P, Tremmel R, Loscalzo J, Lauschke VM, Maron BA, et al. Single Cell Atlas: a single-cell multi-omics human cell encyclopedia. Genome Biol. (2024) 25:104. doi: 10.1186/s13059-024-03246-2
86. Xiong T, Lv XS, Wu GJ, Guo YX, Liu C, Hou FX, et al. Single-cell sequencing analysis and multiple machine learning methods identified G0S2 and HPSE as novel biomarkers for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:907309. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.907309
87. Mo YY, Han YX, Xu SN, Jiang HL, Wu HX, Cai JM, et al. Adipose tissue plasticity: A comprehensive definition and multidimensional insight. Biomolecules. (2024) 14:1223. doi: 10.3390/biom14101223
88. Cheong JG, Ravishankar A, Sharma S, Parkhurst CN, Grassmann SA, Wingert CK, et al. Epigenetic memory of coronavirus infection in innate immune cells and their progenitors. Cell. (2023) 186:3882–3902.e3824. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.07.019
89. Adelman ER, Huang HT, Roisman A, Olsson A, Colaprico A, Qin T, et al. Aging human hematopoietic stem cells manifest profound epigenetic reprogramming of enhancers that may predispose to leukemia. Cancer Discov. (2019) 9:1080–101. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1474
90. Coppin E, Zhang X, Ohayon L, Johny E, Dasari A, Zheng KH, et al. Peripheral ischemia imprints epigenetic changes in hematopoietic stem cells to propagate inflammation and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2023) 43:889–906. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.123.318956
91. Yvan-Charvet L, Pagler T, Gautier EL, Avagyan S, Siry RL, Han S, et al. ATP-binding cassette transporters and HDL suppress hematopoietic stem cell proliferation. Science. (2010) 328:1689–93. doi: 10.1126/science.1189731
92. Frodermann V, Rohde D, Courties G, Severe N, Schloss MJ, Amatullah H, et al. Exercise reduces inflammatory cell production and cardiovascular inflammation via instruction of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Nat Med. (2019) 25:1761–71. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0633-x
93. Mitroulis I, Ruppova K, Wang B, Chen LS, Grzybek M, Grinenko T, et al. Modulation of myelopoiesis progenitors is an integral component of trained immunity. Cell. (2018) 172:147–161.e112. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.034
94. Mitroulis I, Hajishengallis G, and Chavakis T. Trained immunity and cardiometabolic disease: the role of bone marrow. Arteriosclerosis thrombosis Vasc Biol. (2021) 41:48–54. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314215
95. Jimenez Calvente C, Del Pilar H, Tameda M, Johnson CD, and Feldstein AE. MicroRNA 223 3p negatively regulates the NLRP3 inflammasome in acute and chronic liver injury. Mol therapy: J Am Soc Gene Ther. (2020) 28:653–63. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.09.013
96. Vandoorne K, Rohde D, Kim HY, Courties G, Wojtkiewicz G, Honold L, et al. Imaging the vascular bone marrow niche during inflammatory stress. Circ Res. (2018) 123:415–27. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313302
97. Zhou Y, Xie L, Schröder J, Schuster IS, Nakai M, Sun G, et al. Dietary fiber and microbiota metabolite receptors enhance cognition and alleviate disease in the 5xFAD mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. J neuroscience: Off J Soc Neurosci. (2023) 43:6460–75. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0724-23.2023
98. Bartolomaeus H, Balogh A, Yakoub M, Homann S, Markó L, Höges S, et al. Short-chain fatty acid propionate protects from hypertensive cardiovascular damage. Circulation. (2019) 139:1407–21. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.036652
99. Lin MY, de Zoete MR, van Putten JP, and Strijbis K. Redirection of epithelial immune responses by short-chain fatty acids through inhibition of histone deacetylases. Front Immunol. (2015) 6:554. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00554
100. Gao Y, Zhou J, Qi H, Wei J, Yang Y, Yue J, et al. LncRNA lncLy6C induced by microbiota metabolite butyrate promotes differentiation of Ly6C(high) to Ly6C(int/neg) macrophages through lncLy6C/C/EBPβ/Nr4A1 axis. Cell Discov. (2020) 6:87. doi: 10.1038/s41421-020-00211-8
101. Triff K, McLean MW, Callaway E, Goldsby J, Ivanov I, and Chapkin RS. Dietary fat and fiber interact to uniquely modify global histone post-translational epigenetic programming in a rat colon cancer progression model. Int J Cancer. (2018) 143:1402–15. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31525
102. Yamaguchi A, Teratani T, Chu PS, Suzuki T, Taniki N, Mikami Y, et al. Hepatic adenosine triphosphate reduction through the short-chain fatty acids-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ-uncoupling protein 2 axis alleviates immune-mediated acute hepatitis in inulin-supplemented mice. Hepatol Commun. (2021) 5:1555–70. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1742
103. Pan LL, Ren ZN, Yang J, Li BB, Huang YW, Song DX, et al. Gut microbiota controls the development of chronic pancreatitis: A critical role of short-chain fatty acids-producing Gram-positive bacteria. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2023) 13:4202–16. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.08.002
104. Inaba T, Yamashiro K, Kurita N, Ueno Y, Miyamoto N, Hira K, et al. Microbial lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation contributes to cognitive impairment and white matter lesion progression in diet-induced obese mice with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2023) 29 Suppl 1:200–12. doi: 10.1111/cns.14301
105. Fima R, Dussaud S, Benbida C, Blanchet M, Lanthiez F, Poupel L, et al. Loss of embryonically-derived Kupffer cells during hypercholesterolemia accelerates atherosclerosis development. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:8341. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52735-2
106. Liu CC, Zhao J, Fu Y, Inoue Y, Ren Y, Chen Y, et al. Peripheral apoE4 enhances Alzheimer’s pathology and impairs cognition by compromising cerebrovascular function. Nat Neurosci. (2022) 25:1020–33. doi: 10.1038/s41593-022-01127-0
107. Xu Y, Li Y, Jadhav K, Pan X, Zhu Y, Hu S, et al. Hepatocyte ATF3 protects against atherosclerosis by regulating HDL and bile acid metabolism. Nat Metab. (2021) 3:59–74. doi: 10.1038/s42255-020-00331-1
108. Feng T, Liu P, Wang X, Luo J, Zuo X, Jiang X, et al. SIRT1 activator E1231 protects from experimental atherosclerosis and lowers plasma cholesterol and triglycerides by enhancing ABCA1 expression. Atherosclerosis. (2018) 274:172–81. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.04.039
109. Solsona-Vilarrasa E, Fucho R, Torres S, Nuñez S, Nuño-Lámbarri N, Enrich C, et al. Cholesterol enrichment in liver mitochondria impairs oxidative phosphorylation and disrupts the assembly of respiratory supercomplexes. Redox Biol. (2019) 24:101214. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101214
110. Kierans SJ and Taylor CT. Regulation of glycolysis by the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF): implications for cellular physiology. J Physiol. (2021) 599:23–37. doi: 10.1113/JP280572
111. Zhou E, Ge X, Nakashima H, Li R, van der Zande HJP, Liu C, et al. Inhibition of DHCR24 activates LXRα to ameliorate hepatic steatosis and inflammation. EMBO Mol Med. (2023) 15:e16845. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202216845
112. Teng Y, Huang Y, Yu H, Wu C, Yan Q, Wang Y, et al. Nimbolide targeting SIRT1 mitigates intervertebral disc degeneration by reprogramming cholesterol metabolism and inhibiting inflammatory signaling. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2023) 13:2269–80. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.02.018
113. Xiang D, Yang J, Liu L, Yu H, Gong X, and Liu D. The regulation of tissue-specific farnesoid X receptor on genes and diseases involved in bile acid homeostasis. Biomedicine pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine pharmacotherapie. (2023) 168:115606. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115606
114. Wang XX, Wang D, Luo Y, Myakala K, Dobrinskikh E, Rosenberg AZ, et al. FXR/TGR5 dual agonist prevents progression of nephropathy in diabetes and obesity. J Am Soc Nephrology: JASN. (2018) 29:118–37. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2017020222
115. Chan KL, Poller WC, Swirski FK, and Russo SJ. Central regulation of stress-evoked peripheral immune responses. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2023) 24:591–604. doi: 10.1038/s41583-023-00729-2
116. Seidah NG and Prat A. The multifaceted biology of PCSK9. Endocrine Rev. (2022) 43:558–82. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnab035
117. Mitchell MJ, Billingsley MM, Haley RM, Wechsler ME, Peppas NA, and Langer R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2021) 20:101–24. doi: 10.1038/s41573-020-0090-8
118. Fang RH, Gao W, and Zhang L. Targeting drugs to tumours using cell membrane-coated nanoparticles. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2023) 20:33–48. doi: 10.1038/s41571-022-00699-x
119. Ray S, Moonshi SS, and Ta HT. Therapies through gut:” Targeted drug delivery for non-gastrointestinal diseases by oral administration. Adv Healthc Mater. (2025) 14(17):e2403162. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202403162
120. Woodward EA, Wang E, Wallis C, Sharma R, Tie AWJ, Murthy N, et al. Protocol for delivery of CRISPR/dCas9 systems for epigenetic editing into solid tumors using lipid nanoparticles encapsulating RNA. Methods Mol Biol. (2024) 2842:267–87. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4051-7_14
121. Rottner AK, Lundin A, Li S, Firth M, Maresca M, and Sienski G. Optimized prime editing of the Alzheimer’s disease-associated APOE4 mutation. Stem Cell Rep. (2025) 20:102372. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2024.11.002
122. Cui H, Wang C, Maan H, Pang K, Luo F, Duan N, et al. scGPT: toward building a foundation model for single-cell multi-omics using generative AI. Nat Methods. (2024) 21:1470–80. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02201-0
123. Papathanasiou S, Mynhier NA, Liu S, Brunette G, Stokasimov E, Jacob E, et al. Heritable transcriptional defects from aberrations of nuclear architecture. Nature. (2023) 619:184–92. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06157-7
124. Cai R, Lv R, Shi X, Yang G, and Jin J. CRISPR/dCas9 tools: epigenetic mechanism and application in gene transcriptional regulation. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:14865. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914865
125. Karlson CKS, Mohd-Noor SN, Nolte N, and Tan BC. CRISPR/dCas9-based systems: mechanisms and applications in plant sciences. Plants (Basel Switzerland). (2021) 10:2055. doi: 10.3390/plants10102055
126. Huang S, Lau CH, Tin C, and Lam RHW. Extended replicative lifespan of primary resting T cells by CRISPR/dCas9-based epigenetic modifiers and transcriptional activators. Cell Mol Life sciences: CMLS. (2024) 81:407. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05415-9
127. Du X, Yu W, Chen F, Jin X, Xue L, Zhang Y, et al. HDAC inhibitors and IBD: Charting new approaches in disease management. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 148:114193. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114193
128. Chen X, Cao D, Liu C, Meng F, Zhang Z, Xu R, et al. Discovery of 1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine derivatives as potent and selective BET inhibitors for the management of neuropathic pain. J medicinal Chem. (2023) 66:8725–44. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00372
129. Reggiani F, Talarico G, Gobbi G, Sauta E, Torricelli F, Manicardi V, et al. BET inhibitors drive Natural Killer activation in non-small cell lung cancer via BRD4 and SMAD3. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:2567. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46778-8
130. Zhang LY, Zhang SY, Wen R, Zhang TN, and Yang N. Role of histone deacetylases and their inhibitors in neurological diseases. Pharmacol Res. (2024) 208:107410. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107410
131. Cai J, Rimal B, Jiang C, Chiang JYL, and Patterson AD. Bile acid metabolism and signaling, the microbiota, and metabolic disease. Pharmacol Ther. (2022) 237:108238. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108238
132. Kalafati L, Kourtzelis I, Schulte-Schrepping J, Li X, Hatzioannou A, Grinenko T, et al. Innate immune training of granulopoiesis promotes anti-tumor activity. Cell. (2020) 183:771–785.e712. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.058
133. Hummelgaard S, Vilstrup JP, Gustafsen C, Glerup S, and Weyer K. Targeting PCSK9 to tackle cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol Ther. (2023) 249:108480. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108480
134. Zapatero-Belinchón FJ, Ötjengerdes R, Sheldon J, Schulte B, Carriquí-Madroñal B, Brogden G, et al. Interdependent impact of lipoprotein receptors and lipid-lowering drugs on HCV infectivity. Cells. (2021) 10:1626. doi: 10.3390/cells10071626
135. Su W, Chapman NM, Wei J, Zeng H, Dhungana Y, Shi H, et al. Protein prenylation drives discrete signaling programs for the differentiation and maintenance of effector T(reg) cells. Cell Metab. (2020) 32:996–1011.e1017. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.10.022
136. Wang Y, Bi Y, Chen X, Li C, Li Y, Zhang Z, et al. Histone deacetylase SIRT1 negatively regulates the differentiation of interleukin-9-producing CD4(+) T cells. Immunity. (2016) 44:1337–49. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.05.009
137. Yu Q, Dong L, Li Y, and Liu G. SIRT1 and HIF1α signaling in metabolism and immune responses. Cancer Lett. (2018) 418:20–6. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.12.035
138. Friederich-Persson M, Persson P, Hansell P, and Palm F. Deletion of Uncoupling Protein-2 reduces renal mitochondrial leak respiration, intrarenal hypoxia and proteinuria in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Acta Physiol (Oxf). (2018) 223:e13058. doi: 10.1111/apha.13058
139. Liang X, Zhang Z, Lv Y, Lu H, Liu T, Yi H, et al. Krill Oil Combined with Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis F1–7 Alleviates the Atherosclerosis of ApoE(-/-) Mice. Foods (Basel Switzerland). (2021) 10:2374. doi: 10.3390/foods10102374
140. Sayin SI, Wahlström A, Felin J, Jäntti S, Marschall HU, Bamberg K, et al. Gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism by reducing the levels of tauro-beta-muricholic acid, a naturally occurring FXR antagonist. Cell Metab. (2013) 17:225–35. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.01.003
141. Belge Bilgin G, Bilgin C, Burkett BJ, Orme JJ, Childs DS, Thorpe MP, et al. Theranostics and artificial intelligence: new frontiers in personalized medicine. Theranostics. (2024) 14:2367–78. doi: 10.7150/thno.94788
142. Song Q, Hou Y, Zhang Y, Liu J, Wang Y, Fu J, et al. Integrated multi-omics approach revealed cellular senescence landscape. Nucleic Acids Res. (2022) 50:10947–63. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac885
143. Lindsay GW. Convolutional neural networks as a model of the visual system: past, present, and future. J Cogn Neurosci. (2021) 33:2017–31. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01544
144. Wise T, Emery K, and Radulescu A. Naturalistic reinforcement learning. Trends Cogn Sci. (2024) 28:144–58. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2023.08.016
145. Caparrós-Martín JA, Maher P, Ward NC, Saladié M, Agudelo-Romero P, Stick SM, et al. An analysis of the gut microbiota and related metabolites following PCSK9 inhibition in statin-treated patients with elevated levels of lipoprotein(a). Microorganisms. (2024) 12:170. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12010170
146. Zhang H, Wang Y, Liu M, Qi Y, Shen S, Gang Q, et al. Deep learning and single-cell sequencing analyses unveiling key molecular features in the progression of carotid atherosclerotic plaque. J Cell Mol Med. (2024) 28:e70220. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70220
147. Peiffer-Smadja N, Rawson TM, Ahmad R, Buchard A, Georgiou P, Lescure FX, et al. Machine learning for clinical decision support in infectious diseases: a narrative review of current applications. Clin Microbiol infection: Off Publ Eur Soc Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. (2020) 26:584–95. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.09.009
148. Rotllan N, Chamorro-Jorganes A, Araldi E, Wanschel AC, Aryal B, Aranda JF, et al. Hematopoietic Akt2 deficiency attenuates the progression of atherosclerosis. FASEB J. (2015) 29:597–610. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-262097
149. Hernandez R, Li X, Shi J, Dave TR, Zhou T, Chen Q, et al. Paternal hypercholesterolemia elicits sex-specific exacerbation of atherosclerosis in offspring. JCI Insight. (2024) 9:e179291. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.179291
150. Katzmarski N, Domínguez-Andrés J, Cirovic B, Renieris G, Ciarlo E, Le Roy D, et al. Transmission of trained immunity and heterologous resistance to infections across generations. Nat Immunol. (2021) 22:1382–90. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-01052-7
151. Keating ST and El-Osta A. Metaboloepigenetics in cancer, immunity, and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Res. (2023) 119:357–70. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvac058
152. Tomar A, Gomez-Velazquez M, Gerlini R, Comas-Armangué G, Makharadze L, Kolbe T, et al. Epigenetic inheritance of diet-induced and sperm-borne mitochondrial RNAs. Nature. (2024) 630:720–7. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07472-3
153. Chen Z and Natarajan R. Epigenetic modifications in metabolic memory: What are the memories, and can we erase them? Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2022) 323:C570–c582. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00201.2022
154. Zhang X, Sun J, Canfrán-Duque A, Aryal B, Tellides G, Chang YJ, et al. Deficiency of histone lysine methyltransferase SETDB2 in hematopoietic cells promotes vascular inflammation and accelerates atherosclerosis. JCI Insight. (2021) 6:e147984. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.147984
155. Prelaj A, Miskovic V, Zanitti M, Trovo F, Genova C, Viscardi G, et al. Artificial intelligence for predictive biomarker discovery in immuno-oncology: a systematic review. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. (2024) 35:29–65. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.10.125
156. Lee S, Jue M, Cho M, Lee K, Paulson B, Jo H, et al. Label-free atherosclerosis diagnosis through a blood drop of apolipoprotein E knockout mouse model using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy validated by machine learning algorithm. Bioengineering Trans Med. (2023) 8:e10529. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10529
157. Li T, Yang Y, Qi H, Cui W, Zhang L, Fu X, et al. CRISPR/Cas9 therapeutics: progress and prospects. Signal transduction targeted Ther. (2023) 8:36. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01309-7
158. Huang Y, Liu X, Zhu J, Chen Z, Yu L, Huang X, et al. Enzyme core spherical nucleic acid that enables enhanced cuproptosis and antitumor immune response through alleviating tumor hypoxia. J Am Chem Soc. (2024) 146:13805–16. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c14247
159. Kasikara C, Schilperoort M, Gerlach B, Xue C, Wang X, Zheng Z, et al. Deficiency of macrophage PHACTR1 impairs efferocytosis and promotes atherosclerotic plaque necrosis. J Clin Invest. (2021) 131:e145275. doi: 10.1172/JCI145275
160. Fidler TP, Xue C, Yalcinkaya M, Hardaway B, Abramowicz S, Xiao T, et al. The AIM2 inflammasome exacerbates atherosclerosis in clonal haematopoiesis. Nature. (2021) 592:296–301. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03341-5
161. Ji AL, Rubin AJ, Thrane K, Jiang S, Reynolds DL, Meyers RM, et al. Multimodal analysis of composition and spatial architecture in human squamous cell carcinoma. Cell. (2020) 182:497–514.e422. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.039
162. Yang S, Zhu Y, Ji C, Zhu H, Lao A, Zhao R, et al. A five-in-one novel MOF-modified injectable hydrogel with thermo-sensitive and adhesive properties for promoting alveolar bone repair in periodontitis: Antibacterial, hemostasis, immune reprogramming, pro-osteo-/angiogenesis and recruitment. Bioactive materials. (2024) 41:239–56. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.07.016
163. Zinner M, Dahlhausen F, Boehme P, Ehlers J, Bieske L, and Fehring L. Quantum computing’s potential for drug discovery: Early stage industry dynamics. Drug Discov Today. (2021) 26:1680–8. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2021.06.003
164. Wang J and Xia T. Accountability in AI medicine: A critical appraisal of ChatGPT in patient self-management and screening. Clin Mol Hepatol. (2025) 31:e1–2. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0769
165. Hu CB, Wang J, Hong Y, Li H, Fan DD, Lin AF, et al. Single-cell transcriptome profiling reveals diverse immune cell populations and their responses to viral infection in the spleen of zebrafish. FASEB journal: Off Publ Fed Am Societies Exp Biol. (2023) 37:e22951. doi: 10.1096/fj.202201505RRRR
166. Liu F, Liu X, Powell CA, Chen C, Zeng Y, Fang H, et al. Initiative of clinical single-cell biomedicine in clinical and translational medicine. Clin Trans Med. (2023) 13:e1173. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1173
Keywords: trained immunity, atherosclerosis, metabolic-vascular axis, immune plasticity, AI-driven precision medicine
Citation: Zhao B, Wan J, Zhou H, Yang J and Wan H (2025) Trained immunity in atherosclerosis: plasticity, metabolic-vascular axis, and AI-driven precision remodeling. Front. Immunol. 16:1669796. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1669796
Received: 20 July 2025; Accepted: 25 September 2025;
Published: 10 October 2025.
Edited by:
Scott N. Mueller, The University of Melbourne, AustraliaReviewed by:
Cyrille Mionnet, INSERM U1104 Centre d’immunologie de Marseille-Luminy (CIML), FranceYuhuai Xie, Fudan University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Wan, Zhou, Yang and Wan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Haitong Wan, d2h0b25nQDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Bing Zhao
Bing Zhao Jiayang Wan3
Jiayang Wan3 Haitong Wan
Haitong Wan