- Department of Hematology, Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tianjin, China
Background: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)-M2b with t(8;21)(q22;q22)/RUNX1::RUNX1T1 (AML1-ETO) is associated with a high risk of relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD), particularly involving the central nervous system (CNS), confers a poor prognosis. Although CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy is established in B-cell malignancies, its application in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or CNS-PTLD has rarely been reported.
Case: A 24-year-old male with AML-M2b showed persistent RUNX1::RUNX1T1 (AML1-ETO) positivity after allo-HSCT. He developed an extramedullary relapse (presacral mass) at 7 months, followed by CNS-PTLD with limb palsy at 9 months post-HSCT. The disease subsequently progressed to bone marrow relapse (RUNX1::RUNX1T1 94.42%, MRD >5%).
Intervention: Given the co-expression of CD19 on both the AML and PTLD cells, the patient was treated with donor-derived CD19 CAR-T cells. He experienced manageable grade 1 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and grade 3 Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS).
Outcomes: The patient achieved a complete response (CR) with negative MRD, disappearance of the fusion gene, reduction of PTLD and extramedullary lesions, and recovery of limb strength.
Conclusion: This case demonstrates the efficacy and feasibility of CD19 CAR-T therapy for concomitant post-transplant AML-M2b relapse and CNS-PTLD, leveraging their shared CD19 expression. It provides clinical evidence that targeting a shared antigen with a single CAR-T product can effectively treat heterogeneous malignancies, offering a promising new strategy for such complex cases.
Introduction
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)-M2b, characterized by t(8;21)(q22;q22) translocation (1), is driven by the RUNX1::RUNX1T1 (AML1-ETO) fusion oncoprotein. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) is a curative option for AML-M2b, but post-transplant relapse remains a major challenge with poor prognosis. Notably, emerging research has revealed that a subset of AML patients, particularly those with t(8;21)-positive AML-M2b, may exhibit aberrant expression of CD19, and early case reports indicated that CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy could be effective (2–4).
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) is a severe complication following allo-HSCT, with 60%-80% associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) reactivation (5, 6). Central nervous system involvement (CNS-PTLD) occurs in 5%-20% of PTLD cases (7) and carries a dismal prognosis. This is largely attributed to the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and the immune-privileged status of the CNS. Conventional therapies, including immunosuppressant dose reduction, antiviral therapy, and chemotherapy, show limited efficacy, highlighting the need for novel approaches. CAR-T cells may cross the BBB, while clinical data for CNS-PTLD remain scarce.
This report describes the first case of AML-M2b with post-HSCT relapse and concurrent CNS-PTLD that achieved dual remission following CD19 CAR-T therapy. This successful outcome proposes a novel therapeutic paradigm for such complex cases and underscores the potential of CAR-T therapy in targeting heterogeneous malignancies.
Case presentation
A 24-year-old male patient was initially diagnosed with AML-M2b at an external hospital in April 2023. Cytogenetic analysis revealed a chromosomal karyotype of 45, X,−Y, t(8;21)(q22;q22), and transcripts of the RUNX1::RUNX1T1 (AML1-ETO) fusion gene were detected. Genetic testing identified several mutations, including WT1 (11.29%), EVI1 (0.2%), and potential germline mutations in CSF3R and CREBBP (P.Ser602Arg). The patient underwent induction chemotherapy with homoharringtonine (HHT), azacitidine (AZA), and a BCL-2 inhibitor (bcl2i). Then, he received consolidation therapy, including a CAG regimen, AZA plus arsenic trioxide (AAG), and regimens containing intermediate - dose cytarabine (Ara-c). Although minimal residual disease (MRD) remained low (0.01%), the RUNX1::RUNX1T1 (AML1-ETO) fusion transcript remained positive, indicating persistent disease activity.
Consequently, the patient underwent allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) in February 2024, using a modified BUCY conditioning regimen. He received unrelated cord blood stem cells (male donor, 6/10 HLA match, A+ blood type for AB+ recipient) and peripheral stem cells from his father (5/10 HLA match, A+ blood type for AB+ recipient). The total infused mononuclear cell (MNC) count was 9.37×108cells/kg, with CD34+ cell count of 0.84×106 cells/kg. Post-transplant remission was short-lived, with the RUNX1::RUNX1T1 (AML1-ETO) fusion gene becoming detectable again on day 42 and increasing to a level of 0.35%. Decitabine and donor lymphocyte infusion (DLI) briefly reduced the fusion gene levels but induced intestinal graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
Unfortunately, 7 months post-HSCT, a presacral soft tissue mass suggested extramedullary relapse. At 9 months, the patient presented with dysarthria, seizures, and complete loss of muscle strength (grade 0/5) in the left limb. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis revealed elevated protein levels, and next-generation sequencing (NGS) of the CSF detected 1335 copies of EBV sequence. Head contrast-enhanced MRI revealed multiple lesions. Surgical pathology confirmed CNS-PTLD (EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma), with tumor cells positive for CD19 (100%, Figures 1A, B). The brain tissue NGS test indicated an EBV copy number of 6699, which was at its peak. Subsequent treatment with rituximab and methotrexate resulted in the CSF EBV copy number falling below the detection limit. The patient has experienced slight improvement in left limb movement and sensation, but he still has occasional episodes of brief loss of consciousness.
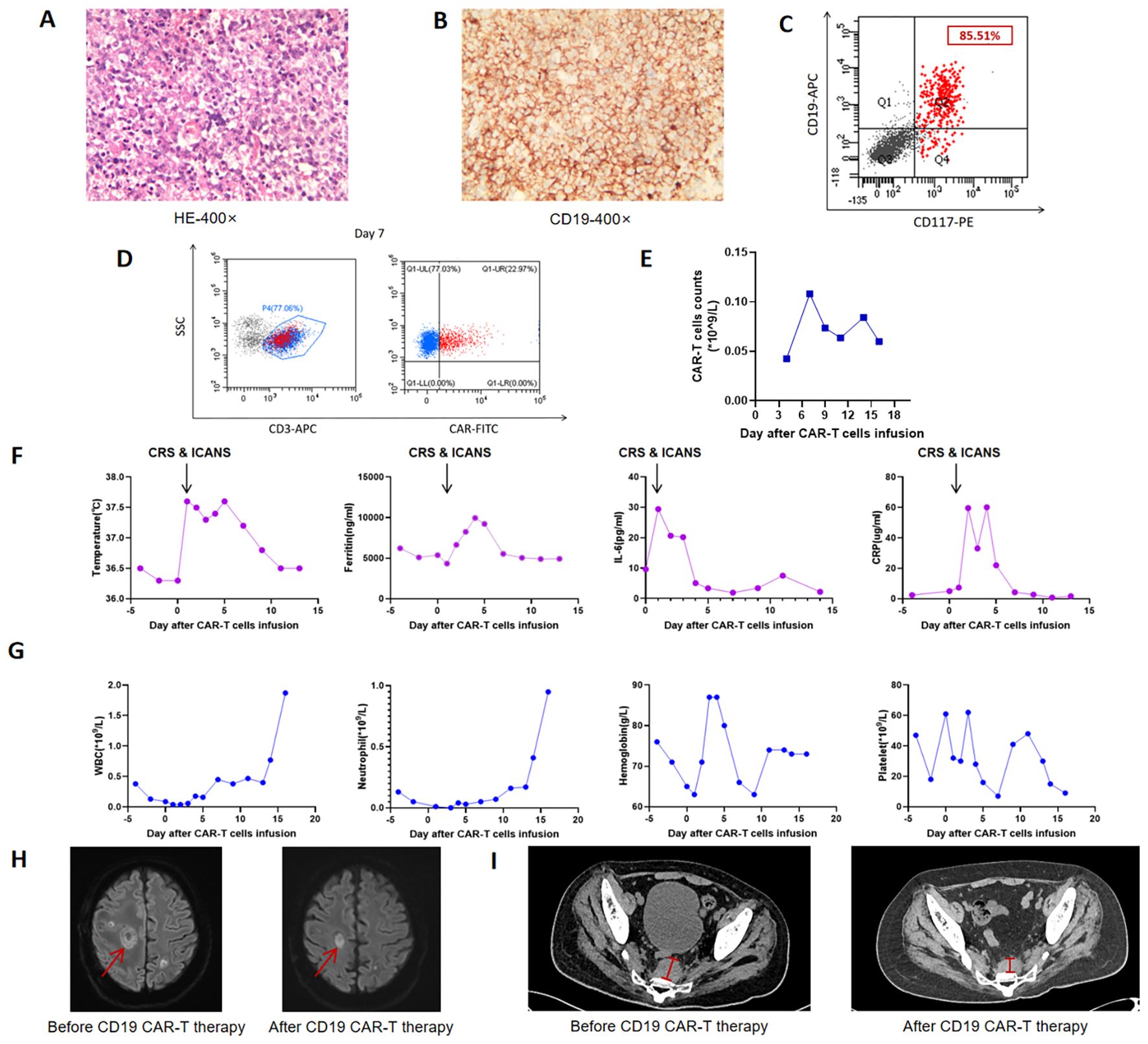
Figure 1. Clinical data during CAR-T cell therapy. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of intracranial tissues; (B) Immunohistochemistry of intracranial tissues showing high expression of CD19 (100%); (C) Flow cytometric analysis detecting CD19 expression on 85.51% of AML blasts; (D) Flow Cytometry analysis illustrating the expansion of CAR-T cells within the population of peripheral CD3-positive cells on Day +7; (E) Kinetics of CAR-T cell expansion in peripheral blood; (F) Changes in body temperature, ferritin, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels during therapy; (G) Changes in peripheral blood cell counts, including white blood cells (WBC), neutrophils, hemoglobin, and platelets (PLT); (H) Comparative head magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans before and after CAR-T treatment; (I) Comparative imaging of recurrent presacral soft tissue lesions before and after CAR-T treatment. CRS, Cytokine release syndrome; ICANS, Immunoeffector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome.
Subsequently, the patient was admitted to our hospital in December 2024. Following radiotherapy of the brain, the muscle strength of the left limb partly improved. Reevaluation with dynamic contrast-enhanced head MRI showed partial reduction in the size of multiple abnormal signals and decreased local enhancement. But later, bone marrow MRD showed 5.34% blasts with 85.51% CD19 expression (Figure 1C), and RUNX1::RUNX1T1 (AML1-ETO) surged to 94.42%. Given the co-expression of CD19 on both PTLD and AML cells, donor-derived CD19 CAR-T therapy was administered at a dose of 1×106 and 1.9×106 cells/kg after conditioning with fludarabine (30 mg/m² per day) and cyclophosphamide (300 mg/m² per day). The peak of CAR-T expansion (22.97% in peripheral blood) occurred at day 7 (Figures 1D, E). Additionally, the trends of temperature, inflammatory factors, and blood routine parameters during CAR-T treatment are shown in Figures 1F, G. Grade 1 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and grade 3 Immunoeffector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) occurred on the first day after CAR-T infusion. Dexamethasone was administered for immune modulation, while valproic acid and intermittent phenobarbital controlled seizure activity. Additionally, mannitol was used to enhance brain dehydration. The patient had no further seizures 2 days after initiating this intervention, with gradual resolution of neurotoxic symptoms thereafter. No obvious acute or chronic GVHD signs were observed. Follow-up imaging showed significant reduction in brain and presacral lesions (Figures 1H, I). Currently, the muscle strength of the left upper limb has recovered to grade 4, greatly improving the quality of life. The patient is currently under follow-up to observe the durability of the CD19 CAR-T treatment (current duration 5 months). The entire treatment process and assessment of remission are comprehensively illustrated in Figure 2 and Supplementary Figure 1.
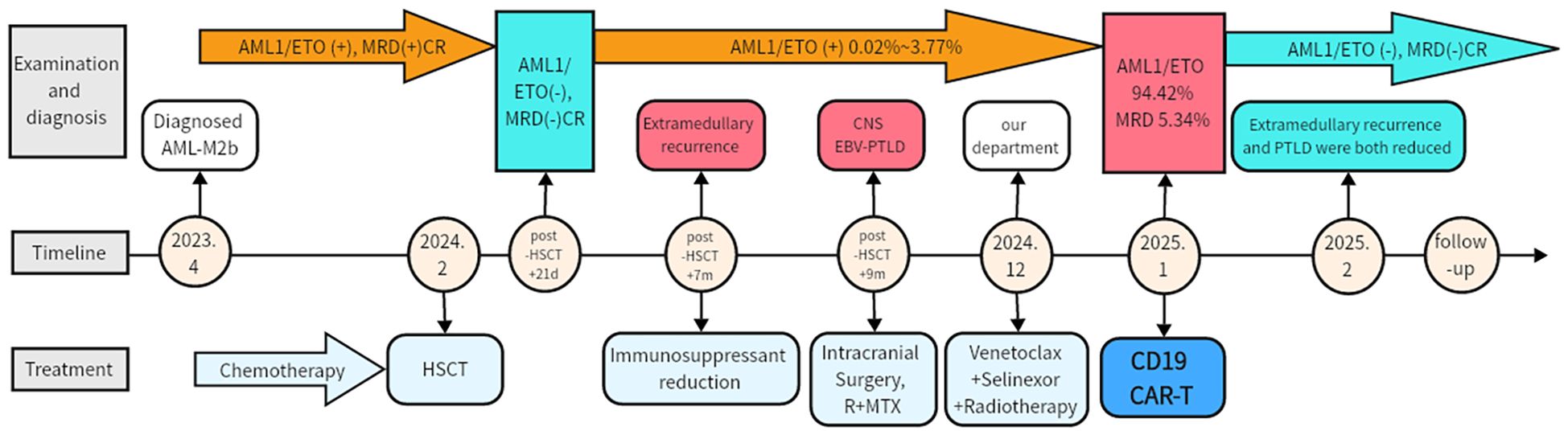
Figure 2. Clinical course and treatment timeline. MRD, Minimal residual disease; CR, complete response; HSCT, Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; EBV-PTLD, Epstein-Barr virus post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder; CNS, Central nervous system; R, Rituximab; MTX, Methotrexate.
Discussion
Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML)-M2b, characterized by the (8;21)(q22;q22) translocation leading to the RUNX1::RUNX1T1 (AML1-ETO) fusion gene, exhibits unique biological features that predispose to extramedullary relapse and treatment resistance. The RUNX1::RUNX1T1 (AML1-ETO) oncoprotein disrupts hematopoietic differentiation, promoting stem cell self-renewal and myeloid blast expansion (8). Notably, 78%-81% of AML1-ETO-positive cases aberrantly express CD19 (9–12), a B-cell lineage marker. The aberrant CD19 expression in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia is primarily driven by the AML1/ETO fusion protein, which induces expression of the B-cell transcription factor PAX5. PAX5 in turn binds to the CD19 promoter and enhancer to activate its transcription (13, 14). This expression is not merely a phenotypic aberration but has clinical relevance, as evidenced by higher complete remission rates with CD19 CAR-T therapy in CD19-positive AML-M2b patients. Our case underscores that CD19 positivity in AML-M2b (85.51% of blasts) can be leveraged for targeted therapy. Liu et al. reported a complete remission (CR) rate of 57.1% in 7 AML patients (2). Similarly, a Phase 2 trial demonstrated a 66.7% CR rate in relapsed/refractory (r/r) t(8;21) AML patients, with a median duration response of 8.5 months (3). Similarly, a prospective phase II clinical trial (NCT03896854) achieved 100% CR in 10 patients, though median leukemia-free survival was only 3.8 months (4), highlighting the need for consolidation therapy.
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) is a life-threatening complication of allo-HSCT. EBV-driven B-cell type PTLD accounts for over 90% of all cases. Central nervous system involvement of PTLD (CNS-PTLD) accounts for only 5%–20% of PTLD cases (7). It has a median survival of less than 6 months (5), largely due to the immune-privileged status of the CNS and the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Conventional therapies, such as immunosuppressant dose reduction, antiviral therapy, chemotherapy, rituximab administration, and local radiotherapy or surgical intervention, have limited efficacy. CD19 CAR-T therapy showed promise in solid organ transplantation (SOT)-associated PTLD, with an 82.4% overall objective response rate (ORR) and 58.5% CR rate in small series (15–18). Notably, there is limited literature on allo-HSCT-related PTLD, particularly CNS-PTLD. Recent investigations have demonstrated the feasibility and safety of CAR-T cell therapy, including CD19 CAR-T based approaches, in patients with CNS lymphoma (19–21). The ability of CAR-T cells to cross the BBB and be detected in the cerebrospinal fluid offers a potential therapeutic strategy for CNS-PTLD. In our case, donor-derived CD19 CAR-T cells successfully crossed the BBB, as evidenced by lesion regression and clinical recovery. Notably, CNS-PTLD tumor cells expressed CD19 uniformly, a rarity in solid tumors. This homogeneity may explain the robust response.
The patient has maintained complete remission for 5 months post-CD19 CAR-T infusion. Key indicators include undetectable RUNX1::RUNX1T1 (AML1-ETO) fusion gene, negative bone marrow MRD, and reduced CNS/presacral lesions on follow-up imaging. The primary limitation of this report is the short duration of follow-up. Late relapse cannot be fully excluded. The main mechanisms of escape from CD19 CAR-T therapy in heterogeneous tumors include the outgrowth of pre-existing or newly evolved CD19-negative subclones and impaired CAR-T cell cytotoxicity due to T-cell exhaustion or suppression within the tumor microenvironment. Furthermore, targeting a single antigen inherently amplifies the risk of relapse, as it lacks redundant targeting mechanisms to counter tumor heterogeneity and selectively favors the expansion of antigen-loss variants. Longer-term surveillance will be critical to validate the durability of remission, and we plan to update this clinical outcome in future follow-up reports.
In this study, we have reported a rare case of targeting dual malignancies with CD19 CAR-T therapy via CD19 co-expression on CNS-PTLD and AML-M2b. The treatment resulted in significant efficacy, achieving dual remissions with manageable side effects. Overall, the strategy of targeting shared antigens across tumor types may revolutionize combinatorial immunotherapy for complex post-transplant syndromes.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article. Written informed consent was obtained from the participant/patient(s) for the publication of this case report.
Author contributions
YZ: Writing – original draft. HZ: Writing – original draft. XX: Writing – original draft. MZ: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82570277) and the major special project on public health science and technology in Tianjin (24ZXGZSY00120) and the Science and Technology Project of Tianjin Municipal Health Committee (TJWJ2024QN040, TJWJ2023XK010, TJWJ2023QN027, TJWJ2022XK018, TJWJ2022QN030, TJWJ2025MS011). And the incubation Fund of Tianjin First Central Hospital (No. 2025FYQN04). This work is also funded by Tianjin Key Clinical Specialty Construction Project and Tianjin Key Medical Discipline Construction Project (Grant No. TJYXZDXK-3-001A-004).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1672392/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | The timelines of the radiotherapy and CAR-T therapy.
References
1. Li Y, Wang H, Wang X, Jin W, Tan Y, Fang H, et al. Genome-wide studies identify a novel interplay between AML1 and AML1/ETO in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. (2016) 127:233–42. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-03-626671
2. Liu S, Yin Z, Yu X, Zhao Y, Pan J, and Song Y. CD19-specific CAR-T cell therapy for relapsed/refractory non-B-cell acute leukaemia with CD19 antigen expression. Eur J Cancer. (2021) 153:1–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.04.042
3. Danylesko I, Shem-Tov N, Yerushalmi R, Jacoby E, Toren A, Shouval R, et al. Point of care CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells for relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with aberrant CD19 antigen expression. Curr Res Transl Med. (2024) 72:103471. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2024.103471
4. Yin J, Cui QY, Dai HP, Qu CJ, Li Z, Kang LQ, et al. CD19 CAR-T in relapsed t(8;21) AML: a single-center prospective phase II clinical trial. J Hematol Oncol. (2025) 18:53. doi: 10.1186/s13045-025-01708-z
5. Clerico M, Dogliotti I, Aroldi A, Consoli C, Giaccone L, Bruno B, et al. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: biology and treatment options. J Clin Med. (2022) 11:7542. doi: 10.3390/jcm11247542
6. Al-Mansour Z, Nelson BP, and Evens AM. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD): risk factors, diagnosis, and current treatment strategies. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. (2013) 8:173–83. doi: 10.1007/s11899-013-0162-5
7. Dierickx D and Habermann TM. Post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders in adults. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:549–62. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1702693
8. Hatlen MA, Wang L, and Nimer SD. AML1-ETO driven acute leukemia: insights into pathogenesis and potential therapeutic approaches. Front Med. (2012) 6:248–62. doi: 10.1007/s11684-012-0206-6
9. Ball ED, Davis RB, Griffin JD, Mayer RJ, Davey FR, Arthur DC, et al. Prognostic value of lymphocyte surface markers in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. (1991) 77:2242–50. doi: 10.1182/blood.V77.10.2242.2242
10. Shang L, Chen X, Liu Y, Cai X, Shi Y, Shi L, et al. The immunophenotypic characteristics and flow cytometric scoring system of acute myeloid leukemia with t(8;21) (q22;q22); RUNX1-RUNX1T1. Int J Lab Hematol. (2019) 41:23–31. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.12916
11. Kita K, Nakase K, Miwa H, Masuya M, Nishii K, Morita N, et al. Phenotypical characteristics of acute myelocytic leukemia associated with the t(8;21)(q22;q22) chromosomal abnormality: frequent expression of immature B-cell antigen CD19 together with stem cell antigen CD34. Blood. (1992) 80:470–7. doi: 10.1182/blood.V80.2.470.470
12. Hurwitz CA, Raimondi SC, Head D, Krance R, Mirro J Jr, Kalwinsky DK, et al. Distinctive immunophenotypic features of t(8;21)(q22;q22) acute myeloblastic leukemia in children. Blood. (1992) 80:3182–8. doi: 10.1182/blood.V80.12.3182.3182
13. Ray D, Kwon SY, Tagoh H, Heidenreich O, Ptasinska A, and Bonifer C. Lineage-inappropriate PAX5 expression in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia requires signaling-mediated abrogation of polycomb repression. Blood. (2013) 122:759–69. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-02-482497
14. Walter K, Cockerill PN, Barlow R, Clarke D, Hoogenkamp M, Follows GA, et al. Aberrant expression of CD19 in AML with t(8;21) involves a poised chromatin structure and PAX5. Oncogene. (2010) 29:2927–37. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.56
15. McKenna M, Epperla N, Ghobadi A, Liu J, Lazaryan A, Ibrahim U, et al. Real-world evidence of the safety and survival with CD19 CAR-T cell therapy for relapsed/refractory solid organ transplant-related PTLD. Br J Haematol. (2023) 202:248–55. doi: 10.1111/bjh.18828
16. Kline K, Chen W, Kallen ME, Koka R, Omili D, Fan X, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells for the treatment of a kidney transplant patient with post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD). Hum Vaccin Immunother. (2023) 19:2216116. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2216116
17. Portuguese AJ, Gauthier J, Tykodi SS, Hall ET, Hirayama AV, Yeung CCS, et al. CD19 CAR-T therapy in solid organ transplant recipients: case report and systematic review. Bone Marrow Transplant. (2023) 58:353–9. doi: 10.1038/s41409-022-01907-z
18. Krishnamoorthy S, Ghobadi A, Santos RD, Schilling JD, Malone AF, Murad H, et al. CAR-T therapy in solid organ transplant recipients with treatment refractory posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Am J Transplant. (2021) 21:809–14. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16367
19. Siddiqi T, Wang X, Blanchard MS, Wagner JR, Popplewell LL, Budde LE, et al. CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy for treatment of primary CNS lymphoma. Blood Adv. (2021) 5:4059–63. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020004106
20. Karschnia P, Rejeski K, Winkelmann M, Schöberl F, Bücklein VL, Blumenberg V, et al. Toxicities and response rates of secondary CNS lymphoma after adoptive immunotherapy with CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Neurology. (2022) 98:884–9. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000200608
Keywords: CD19 CAR-T, AML-M2b, extramedullary relapse, post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder, case report
Citation: Zhang Y, Zhu H, Xiao X and Zhao M (2025) Case Report: CD19 CAR-T therapy induces dual remission in AML-M2b patient with CNS-PTLD and relapse. Front. Immunol. 16:1672392. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1672392
Received: 24 July 2025; Accepted: 27 October 2025;
Published: 05 November 2025.
Edited by:
Jean Koff, Emory University, United StatesReviewed by:
Guangsheng He, Nanjing Medical University, ChinaSongmi Wang, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Zhu, Xiao and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xia Xiao, eHhpaWFhb0AxMjYuY29t; Mingfeng Zhao, bWluZ2Zlbmd6aGFvQHNpbmEuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yu Zhang
Yu Zhang Haibo Zhu†
Haibo Zhu† Xia Xiao
Xia Xiao Mingfeng Zhao
Mingfeng Zhao