Abstract
Background:
Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) combined with targeted immunotherapy has emerged as a key therapeutic option for advanced (or unresectable) hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Nevertheless, treatment efficacy varies significantly among individuals. Sarcopenia, characterized by loss of muscle mass and strength, may adversely affect therapeutic outcomes and patient prognosis. This study investigates the clinical relevance of sarcopenia in patients undergoing HAIC combined with targeted immunotherapy.
Methods:
A total of 265 patients with unresectable HCC who received HAIC combined with targeted immunotherapy were retrospectively enrolled in this study and divided into two groups (sarcopenic and non-sarcopenic group). Sarcopenia was defined based on handgrip strength (HGS), with a cutoff value of less than 28kg(male) and 18kg(female). Overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were compared between groups using the log-rank test and multivariate Cox proportional hazards models. Additionally, propensity score matching (PSM) was applied to minimize baseline differences and enhance comparability. Then, differences in treatment response, survival outcomes, and adverse events between the sarcopenic and non-sarcopenic groups were evaluated using appropriate statistical analyses.
Results:
Patients in sarcopenia group exhibited significantly poorer OS and PFS compared to those with non-sarcopenic group. Sarcopenia was also associated with lower objective response rates. Multivariate analysis confirmed that sarcopenia was an independent prognostic factor for poor outcomes.
Conclusion:
Sarcopenia is a significant predictor of poor prognosis in patients with unresectable HCC treated with HAIC combined with targeted immunotherapy. Incorporating HGS assessment into clinical practice may help optimize individualized treatment strategies and enhance patient management.
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranks as the sixth most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide and is the third leading cause of cancer-related death (1). Due to its insidious onset, over 70% of HCC cases are diagnosed at an advanced stage, where curative surgical intervention is no longer feasible (2). In recent years, the combination of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) with targeted and immune therapies has demonstrated promising outcomes in treating unresectable HCC (3–5). However, owing to significant heterogeneity, there is a pressing need to identify simple and practical prognostic indicators (6). Sarcopenia is a syndrome marked by age-related loss of skeletal muscle mass, strength, or physical function (7), and it has been associated with poor outcomes across multiple cancer types (8–10). As a key indicator of sarcopenia (11), handgrip strength is easy to measure, highly repeatable, and especially suitable for HCC patients with impaired liver function (12). According to the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia (AWGS) 2019 guidelines, handgrip strength is considered a core diagnostic criterion for sarcopenia (13). This study aims to investigate the effect of sarcopenia, defined by reduced handgrip strength, on the treatment efficacy, survival outcomes, and safety in patients with unresectable HCC undergoing HAIC combined with targeted immunotherapy, providing valuable evidence to support clinical stratification and personalized therapeutic approaches.
Methods
Patients
This retrospective, single-center observational study included a total of 314 patients with unresectable HCC who received HAIC combined with targeted immunotherapy at Hepatic Surgery Center, Tongji Hospital, between August 2020 and December 2022. Inclusion criteria were: (1) pathologically confirmed HCC; (2) Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS) of 0-1; (3) Child-Pugh class A or B; and (4) assessed as surgically unresectable. Exclusion criteria included: non- HCC primary liver malignancies, loss to follow-up, incomplete clinical or imaging data, absence of measurable target lesions, and Child-Pugh class C. A final total of 265 patients met the eligibility criteria and were included in the analysis (Figure 1). All patients were followed up until January 24, 2024.
Figure 1

The flowchart of the study. SA, sarcopenia group; Non-SA, non-sarcopenia group; Psm-SA, propensity score-matched sarcopenia group; Psm-Non-SA, propensity score-matched non-sarcopenia group; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HAIC, hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy; PSM, propensity score matching.
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tongji Hospital, affiliated with Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Approval No. TJ-IRB202403001). Informed consent was waived. This study was conducted in full accordance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the institutional review board.
Treatment protocol
All patients were treated with HAIC using the mFOLFOX regimen (14), combined with programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) inhibitors and molecular targeted agents. The HAIC procedure was carried out in accordance with the “Expert Consensus on Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy for HCC in China” (15), with detailed steps outlined in Supplementary Appendix 1. HAIC was administered every 4–6 weeks and continued until disease progression, intolerable toxicity, or death. Immunotherapy andtargeted agents were given every 3 weeks, with at least three treatment cycles completed. Detailed drug information is provided in Supplementary Appendix 2.
Handgrip strength assessment
Handgrip strength was measured using a digital dynamometer (model EH101, Xiangshan Camry Electronic Co., Ltd., Guangdong, China). Each participant was seated with the shoulder adducted and in a neutral rotation, the elbow flexed at 90°, and the forearm and wrist in a neutral position. Using their dominant hand, participants performed three maximum-effort grip trials with a one-minute interval between attempts. The highest value was recorded. According to the AWGS 2019 criteria, sarcopenia was defined as handgrip strength <28kg(male) and 18kg(female) (13).
Efficacy and safety evaluation
All patients underwent contrast-enhanced CT or MRI every six weeks during treatment, along with hematological tests, to comprehensively evaluate therapeutic response and safety. Tumor response was evaluated by two independent radiologists based on the modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (mRECIST) (16), categorized as complete response (CR), partial response (PR), stable disease (SD), or progressive disease (PD). Objective response rate (ORR) was calculated as the percentage of patients achieving CR or PR, while disease control rate (DCR) included patients with CR, PR, or SD. Overall survival (OS) was defined as the time from initiation of triple therapy to death or last follow-up, and progression-free survival (PFS) as the time from treatment initiation to either radiologic progression or death. The primary endpoint was PFS, while secondary endpoints included OS, ORR, and DCR. All treatment-related adverse events (AEs) were recorded and graded according to the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 5.0 (NCI-CTCAE v5.0) (17).
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 26.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA), and graphs were generated with GraphPad Prism version 9.5 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Continuous variables were presented as mean ± standard deviation or median with interquartile range (IQR) and compared using the independent samples t-test or Mann-Whitney U test, as appropriate. Categorical variables were described as frequencies and percentages and compared using the chi- square test or Fisher’s exact test. Propensity score matching (PSM) was applied at a 1:1 ratio using a caliper width of 0.02 to balance baseline characteristics between groups. Kaplan-Meier curves were used to estimate OS and PFS, and differences were evaluated using the log-rank test. Univariate Cox proportional hazards models were performed to identify candidate predictors, and variables with P < 0.05 were further included in multivariate Cox regression to determine independent prognostic factors for OS and PFS. A two-sided P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Baseline characteristics of the patients
A total of 265 patients with unresectable HCC were included in this study. Baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Prior to PSM, significant differences were observed between the sarcopenia group (SA group, n=106) and the non-sarcopenia group (Non-SA group, n=159) in several variables, including Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS), Child-Pugh class, prothrombin time, serum albumin, total bilirubin, tumor number, maximum tumor diameter, portal vein tumor thrombus, and extrahepatic metastasis (all P < 0.05). After PSM, the clinical characteristics were well balanced between the two groups (Table 2).
Table 1
| Parameters | Total (n=265)(%) | SA (n=106)(%) | Non-SA (n=159)(%) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.810 | |||
| Male | 236 (89. 1) | 95 (89.6) | 141 (88.7) | |
| Female | 29 (10.9) | 11 (10.4) | 18 (11.3) | |
| Age, yr | 0.909 | |||
| ≥ 60 | 69 (26.0) | 28 (26.4) | 41 (25.8) | |
| < 60 | 196 (74.0) | 78 (73.6) | 118 (74.2) | |
| ECOG PS | 0.029 | |||
| 0 | 178 (67.2) | 63 (59.4) | 115 (72.3) | |
| ≥ 1 | 87 (32.8) | 43 (40.6) | 44 (27.7) | |
| BCLC stage | 0.198 | |||
| A | 25 (9.4) | 7 (6.6) | 18 (11.3) | |
| B-C | 240 (90.6) | 99 (93.4) | 141 (88.7) | |
| Child-Pugh class | 0.013 | |||
| A | 223 (84.2) | 82 (77.4) | 141 (88.7) | |
| B | 42 (15.8) | 24 (22.6) | 18 (11.3) | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 0.231 | |||
| < 24 | 184 (69.4) | 78 (73.6) | 106 (66.7) | |
| ≥ 24 | 81 (30.6) | 28 (26.4) | 53 (33.3) | |
| HBV-DNA, copies/ml | 0.960 | |||
| ≥ 1000 | 122 (46.0) | 49 (46.2) | 73 (45.9) | |
| < 1000 | 143 (54.0) | 57 (53.8) | 86 (54. 1) | |
| Cirrhosis | 0.330 | |||
| Yes | 231 (87.2) | 95 (41. 1) | 136 (58.9) | |
| No | 34 (12.8) | 11 (32.4) | 23 (67.6) | |
| Previous treatment | 0.497 | |||
| Yes | 71 (26.8) | 26 (24.5) | 45 (28.3) | |
| No | 194 (73.2) | 80 (75.5) | 114 (71.7) | |
| PLT, *109/L | 0.951 | |||
| ≤ 100 | 57 (21.5) | 23 (21.7) | 34 (21.4) | |
| > 100 | 208 (78.5) | 83 (78.3) | 125 (78.6) | |
| ALT, U/L | 0.601 | |||
| > 40 | 95 (35.8) | 40 (37.7) | 55 (34.6) | |
| ≤ 40 | 170 (64.2) | 66 (62.3) | 104 (65.4) | |
| AST, U/L | 0.394 | |||
| > 40 | 177 (66.8) | 74 (69.8) | 103 (64.8) | |
| ≤ 40 | 88 (33.2) | 32 (30.2) | 56 (35.2) | |
| ALB, g/L | 0.004 | |||
| < 35 | 79 (29.8) | 42 (39.6) | 37 (23.3) | |
| ≥ 35 | 186 (70.2) | 64 (60.4) | 122 (76.7) | |
| TBIL, µmol/L | 0.004 | |||
| > 20 | 70 (26.4) | 38 (35.8 | 32 (20. 1) | |
| ≤ 20 | 195 (73.6) | 68 (64.2) | 127 (79.9) | |
| AFP, ng/ml | 0.960 | |||
| ≥ 400 | 142 (53.6) | 57 (53.8) | 85 (53.5) | |
| < 400 | 123 (46.4) | 49 (46.2) | 74 (46.5) | |
| Tumor number | 0.028 | |||
| Multiple | 156 (58.9) | 71 (67.0) | 85 (53.5) | |
| Single | 109 (41. 1) | 35 (33.0) | 74 (46.5) | |
| Tumor diameter, cm | 0.001 | |||
| > 5 | 226 (85.3) | 100 (94.3) | 126 (79.2) | |
| ≤ 5 | 39 (14.7) | 6 (5.7) | 33 (20.8) | |
| PVTT | 0.019 | |||
| Present | 170(64.2) | 77 (72.6) | 93 (58.5) | |
| Absent | 95 (35.8) | 29 (27.4) | 66 (41.5) | |
| EM | 0.006 | |||
| Present | 53 (20.0) | 30 (28.3) | 23 (14.5) | |
| Absent | 212(80.0) | 76 (71.7) | 136 (85.5) |
Baseline characteristics of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (before PSM).
PSM, propensity score matching; SA, sarcopenia group; Non-SA, non-sarcopenia group; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; BCLC, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer; BMI, body mass index; HBV-DNA, hepatitis B virus deoxyribonucleic acid; PLT, platelet count; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALB, albumin; TBIL, total bilirubin; AFP, alpha-fetoprotein; PVTT, portal vein tumor thrombus; EM, extrahepatic metastasis.
Bold values means a P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Table 2
| Parameters | Total (n=154)(%) | SA (n=77)(%) | Psm-Non-SA (n=77)(%) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.632 | |||
| Male | 134 (87.0) | 68 (88.3) | 66 (85.7) | |
| Female | 20 (13.0) | 9 (11.7) | 11(14.3) | |
| Age, yr | 0.857 | |||
| ≥ 60 | 43 (27.9) | 22 (28.6) | 21 (27.3) | |
| < 60 | 111 (72. 1) | 55 (71.4) | 56 (72.7) | |
| ECOG PS | 0.866 | |||
| 0 | 99 (64.3) | 49 (63.6) | 50 (64.9) | |
| ≥ 1 | 55 (35.7) | 28 (36.4) | 27 (35. 1) | |
| BCLC stage | 0.597 | |||
| A | 16 (10.4) | 7 (9. 1) | 9 (11.7) | |
| B-C | 138 (89.6) | 70 (90.9) | 68 (88.3) | |
| Child-Pugh class | 1.000 | |||
| A | 126 (81.8) | 63 (81.8) | 63 (81.8) | |
| B | 28 (18.2) | 14 (18.2) | 14 (18.2) | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 0.713 | |||
| < 24 | 114 (74.0) | 56 (72.7) | 58 (75.3) | |
| ≥ 24 | 40 (26.0) | 21 (27.3) | 19 (24.7) | |
| HBV-DNA, copies/ml | 0.872 | |||
| ≥ 1000 | 77 (50.0) | 39 (50.6) | 38 (49.4) | |
| < 1000 | 77 (50.0) | 38 (49.4) | 39 (50.6) | |
| Cirrhosis | 0.415 | |||
| Yes | 139 (90.3) | 68 (88.3) | 71 (92.2) | |
| No | 15 (9.7) | 9 (11.7) | 6 (47.8) | |
| Previous treatment | 0.857 | |||
| Yes | 43 (27.9) | 21 (27.3) | 22 (28.6) | |
| No | 111 (72. 1) | 56 (72.7) | 55 (71.4) | |
| PLT, *109/L | 0.536 | |||
| ≤ 100 | 29 (18.8) | 13 (16.9) | 16 (20.8) | |
| > 100 | 125 (81.2) | 64 (83. 1) | 61 (79.2) | |
| ALT, U/L | 0.739 | |||
| > 40 | 58 (37.7) | 28 (36.4) | 30 (39.0) | |
| ≤ 40 | 96 (62.3) | 49 (63.6) | 47 (61.0) | |
| AST, U/L | 1.000 | |||
| > 40 | 108 (70. 1) | 54 (70. 1) | 54 (70. 1) | |
| ≤ 40 | 46 (29.9) | 23 (29.9) | 23 (29.9) | |
| ALB, g/L | 0.481 | |||
| < 35 | 46 (29.9) | 21 (27.3) | 25 (32.5) | |
| ≥ 35 | 108 (70. 1) | 56 (72.7) | 52 (67.5) | |
| TBIL, µmol/L | 0.853 | |||
| > 20 | 39 (25.3) | 20 (26.0) | 19 (24.7) | |
| ≤ 20 | 115 (74.7) | 57 (74.0) | 58 (75.3) | |
| AFP, ng/ml | 0.871 | |||
| ≥ 400 | 85 (55.2) | 42 (54.5) | 43 (55.8) | |
| < 400 | 69 (44.8) | 35 (45.5) | 34 (44.2) | |
| Tumor number | 0.739 | |||
| Multiple | 96 (62.3) | 49 (63.6) | 47 (61.0) | |
| Single | 58 (37.7) | 28 (36.4) | 30 (39.0) | |
| Tumor diameter, cm | 0.415 | |||
| > 5 | 139 (90.3) | 71 (92.2) | 68 (88.3) | |
| ≤ 5 | 15 (9.7) | 6 (7.8) | 9 (11.7) | |
| PVTT | 0.739 | |||
| Present | 96 (62.3) | 49 (63.6) | 47 (61.0) | |
| Absent | 58 (37.7) | 28 (36.4) | 30 (39.0) | |
| EM | 0.841 | |||
| Present | 31 (20. 1) | 15 (19.5) | 16 (20.8) | |
| Absent | 123 (79.9) | 62 (80.5) | 61 (79.2) |
Baseline characteristic of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (after PSM).
PSM, propensity score matching; SA, sarcopenia group; Non-SA, non-sarcopenia group; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; BCLC, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer; BMI, body mass index; HBV-DNA, hepatitis B virus deoxyribonucleic acid; PLT, platelet count; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALB, albumin; TBIL, total bilirubin; AFP, alpha-fetoprotein; PVTT, portal vein tumor thrombus; EM, extrahepatic metastasis.
Bold values means a P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Tumor response
Before PSM, based on the mRECIST, the PR rate in the Non-SA group was 49. 1%, higher than 33.0% in the SA group (P = 0.010). ORR was significantly higher in the Non-SA group (53.5%) compared to the SA group (34.9%) (P = 0.003). DCR was 93.7% in the Non-SA group and 91.5% in the SA group, (P = 0.487). After PSM, the PR rate remained higher in the Non-SA group (49.4%) than in the SA group (35. 1%) (P = 0.073). The ORR in the Non-SA group was 54.5%, significantly greater than 37.7% in the SA group (P = 0.036). DCR was 94.2% and 96. 1% in the Non-SA and SA groups, respectively, with no statistically significant difference (P = 0.495) (Table 3).
Table 3
| Before PSM | After PSM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Response | SA (n=106)(%) | Non-SA (n=159)(%) | P | SA (n=77)(%) | Non-SA (n=77)(%) | P |
| CR | 2 (1.9) | 7 (4.4) | 0.323 | 2 (2.6) | 4 (5.2) | 0.681 |
| PR | 35 (33.0) | 78 (49. 1) | 0.010 | 27 (35. 1) | 38 (49.4) | 0.073 |
| SD | 63 (59.4) | 67 (42. 1) | 0.006 | 45 (58.4) | 2 (2.6) | 0.010 |
| PD | 6 (5.7) | 7 (4.4) | 0.642 | 3 (3.9) | 6 (7.8) | 0.495 |
| ORR | 34.9% | 53.5% | 0.003 | 37.7% | 54.5% | 0.036 |
| DCR | 94.3% | 95.6% | 0.642 | 96. 1% | 94.2% | 0.495 |
Tumor response in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (Before and After PSM).
PSM, propensity score matching; SA, sarcopenia group; Non-SA, non-sarcopenia group; Psm-SA, propensity score-matched sarcopenia group; Psm-Non-SA, propensity score-matched non-sarcopenia group; CR, complete response; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease; PD, progressive disease; ORR, objective response rate; DCR, disease control rate.
Bold values means a P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Survival outcomes
Before PSM, mPFS was 17. 12 months in the Non-SA group, significantly longer than 5.22 months in the SA group (P < 0.001). mOS was 29.11 months in the Non-SA group versus 7.53 months in the SA group (P < 0.001)(Figure 2). After PSM, mPFS remained significantly longer in the Non-SA group (16.23 vs. 5.49 months, P < 0.001), as did mOS (25.13 vs. 8.31 months, P < 0.001), confirming that sarcopenia is associated with worse treatment outcomes (Figure 3). After PSM, the 6-, 12-, and 18- month PFS rates were 81.8%, 59.7%, and 37.7% in the Non-SA group, significantly higher than 46.8%, 27.3%, and 14.3% in the SA group (all P < 0.01). Similarly, the 6-, 12-, and 18-month OS rates were 96. 1%, 81.8%, and 55.8% in the Non-SA group, compared to 62.3%, 37.7%, and 23.4% in the SA group (all P < 0.001) (Supplementary Appendix 3).
Figure 2
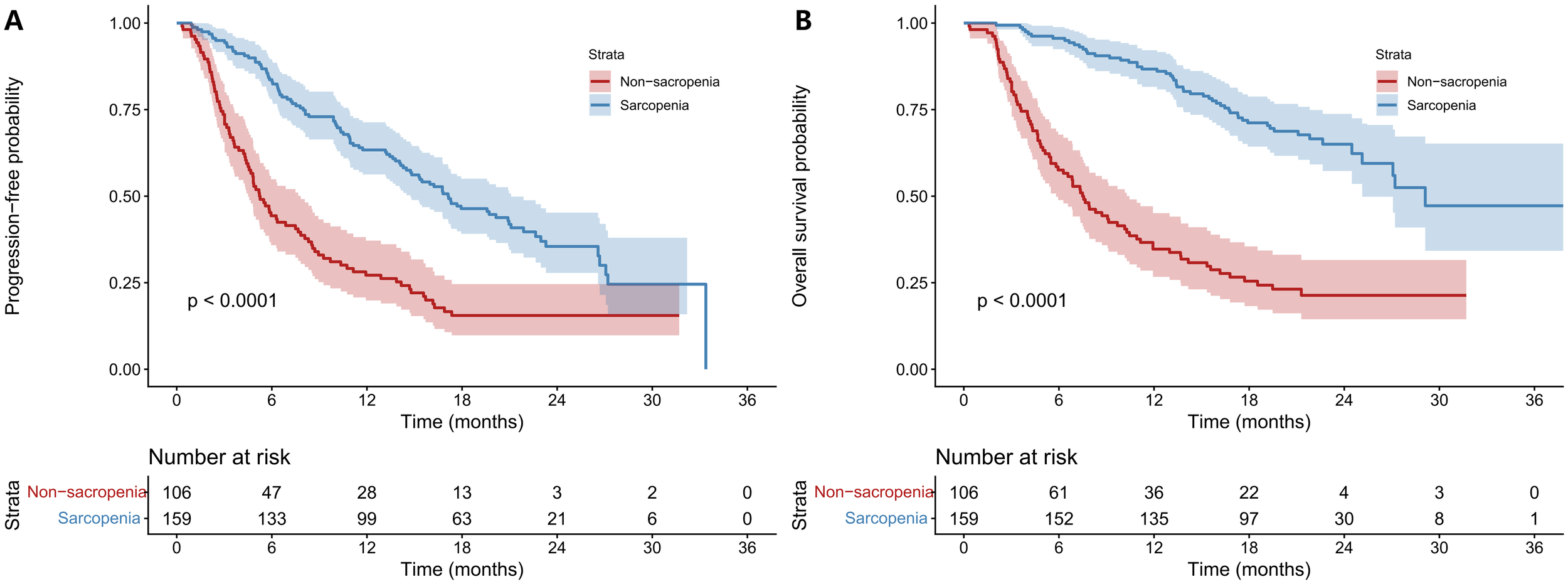
Comparisons of survival outcomes between sarcopenia and non-sarcopenia groups before PSM. Kaplan–Meier curves were plotted PFS (A) and OS (B) in patients with unresectable HCC receiving HAIC combined with immunotherapy and targeted therapy. The non-sarcopenia group exhibited superior survival outcomes. HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; PFS: progression-free survival; OS: overall survival; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; PSM: propensity score matching; HAIC: hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy.
Figure 3

Comparisons of survival outcomes between sarcopenia and non-sarcopenia groups after PSM. Kaplan–Meier curves were plotted PFS (A) and OS (B) in patients with unresectable HCC receiving HAIC combined with immunotherapy and targeted therapy. The non-sarcopenia group consistently exhibited superior survival outcomes. HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; PFS: progression-free survival; OS: overall survival; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; PSM: propensity score matching; HAIC: hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy.
Risk factors analysis
Table 4 shows that multivariate Cox regression analysis identified sarcopenia (HR: 2.30; 95% CI: 1.58–3.36; P < 0.001), high Hepatitis B virus DNA (HBV-DNA) levels (HR: 2.30; 95% CI: 1.53–3.46; P < 0.001), prior treatment (HR: 2. 15; 95% CI: 1.41–3.28; P < 0.001), and multiple tumors (HR: 2.27; 95% CI: 1.46–3.51; P < 0.001) as independent prognostic factors for PFS. For OS, significant factors included sarcopenia (HR: 3.76; 95% CI: 2.39–5.91; P < 0.001), ECOG PS ≥1 (HR: 1.73; P = 0.011), HBV-DNA ≥1000 copies/ml (HR: 1.62; P = 0.025), and multiple tumors (HR: 2.25; P = 0.001) (Table 5).
Table 4
| Parameter | Univariate analysis | P | Multivariate analysis | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | HR(95% CI) | |||
| ALB (< 35 vs. ≥ 35 g/L) | 1.425(0.965~2. 104) | 0.075 | ||
| TBIL (> 20 vs. ≤ 20 μmol/L) | 1.039(0.678~ 1.592) | 0.861 | ||
| AFP (≥ 400 vs. < 400 ng/ml) | 0.977(0.675~ 1.412) | 0.900 | ||
| Tumor number (Multiple vs. Single) | 2.556(1.674~3.903) | < 0.001 | 2.265(1.464~3.507) | < 0.001 |
| Tumor diameter (> 5 vs. ≤ 5 cm) | 1.014(0.543~ 1.892) | 0.966 | ||
| PVTT (Present vs. Absent) | 1. 141(0.779~ 1.670) | 0.498 | ||
| EM (Present vs. Absent) | 1.494(0.963~2.317) | 0.073 |
Univariate and multivariate analyses of PFS.
PFS, progression-free survival; HR, hazard ratio ; CI, confidence interval ; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status;BC, C, Barcelona Clinic, iver Cancer;BMI, body mass index ;HBV-DNA, hepatitis B virus deoxyribonucleic acid ;P, T, platelet ;A, T, alanine aminotransferase;AST, aspartate aminotransferase;A, B, albumin;TBI, , total bilirubin;AFP, alpha-fetoprotein;PVTT, portal vein tumor thrombus;EM, extrahepatic metastasis.
Bold values means a P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Table 5
| Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | HR (95% CI) | P | HR (95% CI) | P |
| Gender (Male vs. Female) | 0.918(0.527~ 1.599) | 0.763 | ||
| Age (≥ 60 vs. < 60 yr) | 0.778(0.485~ 1.248) | 0.298 | ||
| Sarcopenia (Yes vs. No) | 2.681(1.760~4.085) | < 0.001 | 3.757(2.388~5.912) | < 0.001 |
| ECOG PS (≥ 1 vs. 0) | 1.594(1.055~2.409) | 0.027 | 1.729(1.134~2.635) | 0.011 |
| BCLC stage (B-C vs. A) | 1.045 (0.551~ 1.983) | 0.893 | ||
| Child-Pugh Class (B vs. A) | 2. 104(1.308~3.385) | 0.002 | 1.450(0.811~2.594) | 0.210 |
| BMI (< 24 vs. ≥ 24 kg/m2) | 1.336(0.820~2. 177) | 0.244 | ||
| HBV-DNA (≥ 1000 vs. < 1000 copies/ml) | 1.802(1.190~2.727) | 0.005 | 1.622(1.064~2.474) | 0.025 |
| Cirrhosis (Yes vs. No) | 2. 120(0.925~4.857) | 0.076 | ||
| Previous treatment (Yes vs. No) | 1.383(0.897~2. 130) | 0. 142 | ||
| PLT (≤ 100 vs. > 100 *109/L) | 1.328(0.807~2. 185) | 0.264 | ||
| ALT (> 40 vs. ≤ 40 U/L) | 1.464 (0.971~2.207) | 0.069 | ||
| AST (> 40 vs. ≤ 40 U/L) | 1.572(0.987~2.505) | 0.057 | ||
| ALB (< 35 vs. ≥ 35 g/L) | 1.648(1.079~2.517) | 0.021 | 1.630(0.974~2.727) | 0.063 |
| TBIL (> 20 vs. ≤ 20 μmol/L) | 1.450(0.926~2.270) | 0.104 | ||
| AFP (≥ 400 vs. < 400 ng/ml) | 0.876(0.583~ 1.315) | 0.523 | ||
| Tumor number (Multiple vs. Single) | 2.235(1.406~3.552) | 0.001 | 2.248(1.380~3.662) | 0.001 |
| Tumor diameter (> 5 vs. ≤ 5 cm) | 0.982(0.509~ 1.893) | 0.956 | ||
| PVTT (Present vs. Absent) | 1.052(0.691~ 1.602) | 0.813 | ||
| EM (Present vs. Absent) | 1.745(1.101~2.767) | 0.018 | 1.562(0.954~2.559) | 0.076 |
Univariate and multivariate analyses of OS.
PFS, progression-free survival; HR, hazard ratio ; CI, confidence interval ; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status;BCLC, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer;BMI, body mass index ;HBV-DNA, hepatitis B virus deoxyribonucleic acid ;PLT, platelet ;ALT, alanine aminotransferase;AST, aspartate aminotransferase;ALB, albumin;TBIL, total bilirubin;AFP, alpha-fetoprotein;PVTT, portal vein tumor thrombus;EM, extrahepatic metastasis.
Bold values means a P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Safety
AEs related to HAIC combined with targeted immunotherapy are summarized in Supplementary Appendix 3. Common grade 1–2 events included elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels (38.9%), thrombocytopenia (27.5%), anemia (27.2%), diarrhea (23.4%), and neutropenia (23.0%). Grade 3–4 toxicities were less frequent and primarily involved elevated AST (9.8%), thrombocytopenia (9.4%), neutropenia (7.5%), hyperbilirubinemia (5.7%), anemia (2.3%), and nausea/vomiting (1.5%).
Discussion
This study of 265 patients with unresectable HCC receiving HAIC combined with targeted immunotherapy demonstrated significantly worse response rates and survival outcomes among those with sarcopenia, defined by low handgrip strength. ORR was lower in sarcopenic patients (37.7% vs. 54.5%), and mPFS and mOS were also significantly shorter (5.49 vs. 16.23 months; 8.31 vs. 25.13 months). Multivariate analysis confirmed sarcopenia as an independent predictor of both PFS and OS. These results highlight handgrip strength as a simple yet effective prognostic marker in the context of triple combination therapy.
While previous studies have linked sarcopenia to poor prognosis in HCC, they have largely relied on imaging-based measures like the skeletal muscle index (SMI) (18–20). Our findings demonstrate that handgrip strength, a more accessible clinical tool, offers similar prognostic value, especially for patients lacking imaging resources. Few studies have evaluated it in HAIC combined with targeted immunotherapy. Our study addresses this gap (21).
Sarcopenia may affect the efficacy of HAIC combined with immunotherapy through multiple mechanisms. First, as the primary reservoir of protein, muscle loss reflects poor nutritional status, which may compromise patients ‘ tolerance to chemotherapy and immunotherapy (22–24). Second, skeletal muscle is known to secrete various myokines that play essential roles in maintaining immune homeostasis and promoting T-cell activation (25, 26). A reduction in muscle mass may therefore impair antitumor immune responses and diminish the effectiveness of immune checkpoint inhibitors (23). Additionally, sarcopenic patients often exhibit chronic inflammatory states, such as elevated IL-6 and TNF-α levels, which may promote tumor progression and suppress immune response (27, 28). Collectively, these mechanisms suggest that decreased muscle strength not only reflects diminished nutritional and functional reserves but may also directly influence the tumor microenvironment and therapeutic responsiveness.
In our study, Previous treatment emerged as an independent predictor of worse PFS in patients receiving HAIC combined with targeted immunotherapy. This finding is clinically plausible for several reasons. First, patients who have received prior locoregional or systemic therapies often represent a subgroup with more advanced disease burden or biologically aggressive tumors, which intrinsically predisposes to poorer outcomes after subsequent lines of therapy (29, 30). Second, repeated locoregional interventions such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) can cause structural and functional changes to the hepatic arterial tree (including spasm, inflammation, and even occlusion) and may impair liver functional reserve, such changes can reduce the delivery efficiency and tolerability of subsequent HAIC (31, 32). Third, prior exposure to targeted agents or immune checkpoint inhibitors may select for resistant tumor subclones or promote immune-escape mechanisms (33, 34), thereby diminishing responsiveness to later targeted–immunotherapy combinations. Finally, a history of multiple previous treatments often correlates with cumulative liver injury and altered systemic and intratumoral immune landscapes, both of which may further compromise treatment efficacy (35). Taken together, these clinical and biological considerations provide a plausible explanation for the inferior PFS observed among previously treated patients and highlight the need to consider prior treatment history when stratifying patients and designing subsequent therapeutic strategies.
Nonetheless, this study has limitations. Its retrospective, single-center design introduces selection bias, and dynamic muscle strength data were unavailable. Sarcopenia was defined solely by grip strength without imaging-based confirmation, possibly underestimating occult cases. Inflammatory and immunologic markers were not analyzed. Future prospective multicenter studies should develop comprehensive risk models integrating functional, morphological, and metabolic indicators, and evaluate the role of muscle-strengthening interventions during immunotherapy.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that sarcopenia, defined by reduced handgrip strength, is independently associated with poorer treatment response, reduced survival, and higher recurrence in patients with unresectable HCC treated with HAIC combined with targeted immunotherapy.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Author contributions
X-ZW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft. PW: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology. XL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft. Z-LZ: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Methodology, Software. E-LZ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. G-BJ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declared that financial support was received for this work and/or its publication. The study was supported by grants from the Scientific Research Projects from Wuhan Municipal Health Commission (No. WX23Q27).The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study was supported by grants from the Scientific Research Projects from Wuhan Municipal Health Commission (No. WX23Q27).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The reviewer YB declared a shared affiliation with the author(s) XL, and E-LZ to the handling editor at the time of review.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declared that Generative AI was not used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1672519/full#supplementary-material
References
1
Sung H Ferlay J Siegel RL Laversanne M Soerjomataram I Jemal A et al . Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2
Forner A Reig M Bruix J . Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. (2018) 391:1301–14. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30010-2
3
Zuo M Zheng G Cao Y Lu H Li D An C et al . Hepatic arterial chemotherapy infusion combined with tyrosine kinase inhibitors and PD-1 inhibitors for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with high risk: a propensity score matching study. Int J Surg. (2025) 111:104–12. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001940
4
Zheng K Zhu X Fu S Cao G Li WQ Xu L et al . Sorafenib plus hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy versus sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma with major portal vein tumor thrombosis: A randomized trial. Radiology. (2022) 303:455–64. doi: 10.1148/radiol.211545
5
Guan R Zhang N Deng M Lin Y Huang G Fu Y et al . Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma extrahepatic metastases can benefit from hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy combined with lenvatinib plus programmed death-1 inhibitors. Int J Surg. (2024) 110:4062–73. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001378
6
Chan YT Zhang C Wu J Lu P Xu L Yuan H et al . Biomarkers for diagnosis and therapeutic options in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:189. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02101-z
7
Cruz-Jentoft AJ Bahat G Bauer J Boirie Y Bruyère O Cederholm T et al . Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. (2019) 48:16–31. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afy169
8
Prado CM Baracos VE McCargar LJ Reiman T Mourtzakis M Tonkin K et al . Sarcopenia as a determinant of chemotherapy toxicity and time to tumor progression in metastatic breast cancer patients receiving capecitabine treatment. Clin Cancer Res. (2009) 15:2920–6. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2242
9
Wu CH Ho MC Chen CH Liang JD Huang KW Cheng MF et al . Computed tomography-defined sarcopenia in outcomes of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing radioembolization: assessment with total abdominal, psoas, and paraspinal muscles. Liver Cancer. (2023) 12:550–64. doi: 10.1159/000529676
10
Hamaguchi Y Kaido T Okumura S Kobayashi A Shirai H Yao S et al . Preoperative visceral adiposity and muscularity predict poor outcomes after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer. (2019) 8:92–109. doi: 10.1159/000488779
11
Zanker J Sim M Anderson K Balogun S Brennan-Olsen SL Dent E et al . Consensus guidelines for sarcopenia prevention, diagnosis and management in Australia and New Zealand. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2023) 14:142–56. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13115
12
Yang J Chen K Zheng C Chen K Lin J Meng Q et al . Impact of sarcopenia on outcomes of patients undergoing liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2022) 13:2383–92. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13040
13
Chen LK Woo J Assantachai P Auyeung TW Chou MY Iijima K et al . Asian working group for sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2020) 21:300–307.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.12.012
14
Li QJ He MK Chen HW Fang WQ Zhou YM Xu L et al . Hepatic arterial infusion of oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin versus transarterial chemoembolization for large hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:150–60. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.00608
15
Zhao M Guo Z Zou YH Li X Yan ZP Chen MS et al . Arterial chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in China: consensus recommendations. Hepatol Int. (2024) 18:4–31. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10599-6
16
Lencioni R Llovet JM . Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. (2010) 30:52–60. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1247132
17
U.S. Department of health and human services . Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0 (2017). Available online at: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm (Accessed July 22, 2025).
18
Harimoto N Shirabe K Yamashita YI Ikegami T Yoshizumi T Soejima Y et al . Sarcopenia as a predictor of prognosis in patients following hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Surg. (2013) 100:1523–30. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9258
19
Yabusaki N Fujii T Yamada S Suzuki K Sugimoto H Kanda M et al . Adverse impact of low skeletal muscle index on the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatic resection. Int J Surg. (2016) 30:136–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.04.049
20
Li Z Zhao Y Xie Y Zhang L Sun Y Yang K et al . Impact of CT-relevant skeletal muscle parameters on post-liver transplantation survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int. (2024) 18:1516–27. doi: 10.1007/s12072-024-10708-z
21
Liu D Wang S Liu S Wang Q Che X Wu G et al . Frontiers in sarcopenia: Advancements in diagnostics, molecular echanisms, and therapeutic strategies. Mol Aspects Med. (2024) 97:101270. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2024.101270
22
Prado CM Baracos VE McCargar LJ Mourtzakis M Mulder KE Reiman T et al . Body composition as an independent determinant of 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy toxicity. Clin Cancer Res. (2007) 13:3264–8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-3067
23
Ganju RG Morse R Hoover A TenNapel M Lominska CE . The impact of sarcopenia on tolerance of radiation and outcome in patients with head and neck cancer receiving chemoradiation. Radiother Oncol. (2019) 137:117–24. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.04.023
24
Liu M Jin Q Wang H Li Y . Progressive sarcopenia and myosteatosis predict prognosis of advanced HCC patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1396927. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1396927
25
Pedersen BK Febbraio MA . Muscles, exercise and obesity: skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2012) 8:457–65. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2012.49
26
Karneris A Dedeilia A Boland GM . Association of sarcopenia with a poor prognosis and decreased tumor-infiltrating CD8-positive T cells in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A retrospective analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. (2024) 31:16–8. doi: 10.1245/s10434-023-14395-2
27
Li CW Yu K Ng SC Li GX Jiang LJ Yu SL et al . Circulating factors associated with sarcopenia during ageing and after intensive lifestyle intervention. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2019) 10:586–600. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12417
28
Gagnon B Murphy J Simonyan D Penafuerte CA Sirois J Chasen M et al . Cancer anorexia-cachexia syndrome is characterized by more than one inflammatory pathway. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2024) 15:1041–53. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13430
29
Yen C Sharma R Rimassa L Arizumi T Bettinger D Choo HY et al . Treatment stage migration maximizes survival outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib: an observational study. Liver Cancer. (2017) 6:313–24. doi: 10.1159/000480441
30
Talbot T D'Alessio A Pinter M Balcar L Scheiner B Marron TU et al . Progression patterns and therapeutic sequencing following immune checkpoint inhibition for hepatocellular carcinoma: An international observational study. Liver Int. (2023) 43:695–707. doi: 10.1111/liv.15502
31
Sneiders D Boteon APCS Lerut J Iesari S Gilbo N Blasi F et al . Transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma before liver transplantation and risk of post-transplant vascular complications: a multicentre observational cohort and propensity score-matched analysis. Br J Surg. (2021) 108:1323–31. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znab268
32
Sueyoshi E Hayashida T Sakamoto I Uetani M . Vascular complications of hepatic artery after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2010) 195:245–51. doi: 10.2214/AJR.08.2301
33
Ohata Y Shimada S Akiyama Y Mogushi K Nakao K Matsumura S et al . Acquired resistance with epigenetic alterations under long-term antiangiogenic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. (2017) 16:1155–65. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0728
34
Kou L Xie X Chen X Li B Li J Li Y et al . The progress of research on immune checkpoint inhibitor resistance and reversal strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2023) 72:3953–69. doi: 10.1007/s00262-023-03568-3
35
Li R Liu J Ye F He S Huang J Zhou M et al . Microbial metabolism dysfunction induced by transarterial chemoembolization aggravates postprocedural liver injury in HCC. J Hepatol. (2025), S0168–8278(25)02557–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2025.10.008
Summary
Keywords
handgrip strength, sarcopenia, hepatocellular carcinoma, HAIC, targeted immunotherapy, prognosis
Citation
Wang X-Z, Wang P, Lv X, Zhang Z-L, Zhang E-L and Ji G-B (2025) Prognostic significance of reduced handgrip strength in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma receiving HAIC combined with targeted immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 16:1672519. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1672519
Received
24 July 2025
Revised
24 November 2025
Accepted
24 November 2025
Published
11 December 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Jun Li, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China
Reviewed by
Yaowei Bai, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China
Kratika Singh, Centre of Bio-Medical Research (CBMR), India
Liangjing Xia, Panzhihua Central Hospital, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Wang, Wang, Lv, Zhang, Zhang and Ji.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Er-Lei Zhang, baiyu19861104@163.com; Gui-Bao Ji, kloseji11@126.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.