- 1School of Basic Medical Sciences, Mudanjiang Medical University, Mudanjiang, China
- 2School of Clinical Medicine, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi, China
- 3Department of Biosciences, COMSATS University Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan
- 4Department of Immunology, Mudanjiang Medical University, Mudanjiang, China
- 5Department of Gastroenterology, Mudanjiang Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Mudanjiang, China
- 6School of Stomatology, Mudanjiang Medical University, Mudanjiang, China
1 Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, posing a major burden on global health system. Despite advancements in diagnosis and therapy, the underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms contributing to the development and progression of CVDs are not fully understood (1). Among them, the dysregulation of calcium signal transduction, as a crucial pathological physiological process, is receiving increasing attention, particularly in terms of calcium signal imbalance and its impact on the survival and function of cardiac cells. Therefore, Calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) can serve as an important target for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
CaSR is a cell surface receptor that functions by sensing the concentration of Ca2+ in the extracellular matrix (ECM), thus, serving as a primary regulator of calcium homeostasis. Calcium is an important ion in the cells, highly ubiquitous and an integral intracellular messenger that participates in various biological processes (2–4). The alterations in extracellular Ca2+ concentration can affect normal cellular activities and physiological functions of these systems.
Several cardiovascular conditions, including hypertension, atherosclerosis, cardiac hypertrophy, myocardial infarction (MI), and vascular calcification, have been associated with altered CaSR expression or signaling. These associations have spurred growing interest in the therapeutic modulation of CaSR using pharmacological agents such as calcimimetics and calcilytics. While these agents have shown potential in preclinical models, their use in cardiovascular therapy remains limited due to concerns regarding systemic side effects and inconsistent outcomes (5, 6).
Given the expanding body of literature on CaSR’s involvement in cardiovascular health and disease, a comprehensive review of its cellular biological behaviors is timely and necessary. This article aims to summarize current knowledge on CaSR expression and function in cardiovascular cell types, discuss its role in various cardiovascular pathologies, highlight contradictory findings and research gaps, and explore the therapeutic potential of CaSR-targeted interventions. Such insights may help pave the way toward more targeted and effective strategies for managing CVDs.
2 CASR structure and its functional significance
According to research (7), the CaSR was initially cloned from bovine parathyroid glands, where investigators identified a high degree of similarity to glutamate receptors.
CaSR is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family. The receptor possesses a substantial extracellular domain, which encompasses clusters of acidic amino acid residues potentially involved in calcium binding. Structurally, it consists of four parts: (i) a large N-terminal extracellular domain (ECD), (ii) a cysteine-rich domain, (iii) a seven-transmembrane helical domain (TMD), and (iv) a C-terminal tail (8–10). Adjacent to the C-terminus of the signal peptide at the N-terminal extremity of the protein lies a large bilobed structure known as the “Venus Flytrap domain” (VFT domain) (7). The ECD of CaSR is composed of two dimerized lobes, LB1 and LB2, which are separated by a central cavity. Calcium binds within the cleft between the two lobes of each VFT unit, leading to receptor activation. Receptor activation stimulates the intrinsic seven-transmembrane helical domain (7TM) in G protein-coupled homodimers (8, 11).
When CaSR is activated, its homodimer binds to various ligands and heterotrimeric modulators (12–15), mediating downstream signaling through G protein to generate biological effects such as Gi/o and Gq/11 (16–19). After binding to Gi/o protein, CaSR inhibits the production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) through adenylate cyclase, thereby, suppressing the activation of protein kinase A (PKA), which results in a reduction of Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (20). Gq/11 activates inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) pathways together with phospholipase (21, 22), as illustrated in the Figure 1 below. IP3 regulates the intracellular influx and efflux of Ca2+ by controlling calcium channels on the cell surface. Abnormal activation or inhibition of the cAMP signaling pathway plays an important role in the pathogenesis of CVDs. Although the published studies on CaSR have provided potential therapeutic strategies and directions for understanding CaSR signaling mechanisms, nonetheless, they still have limitations. At present, the downstream signaling pathways of CaSR have not been fully understood, and the specific mechanisms of action in different tissues and various pathological conditions have not been fully investigated either. These limitations indicate that in future research, a more in-depth clarification of the pathway mechanisms is still needed.
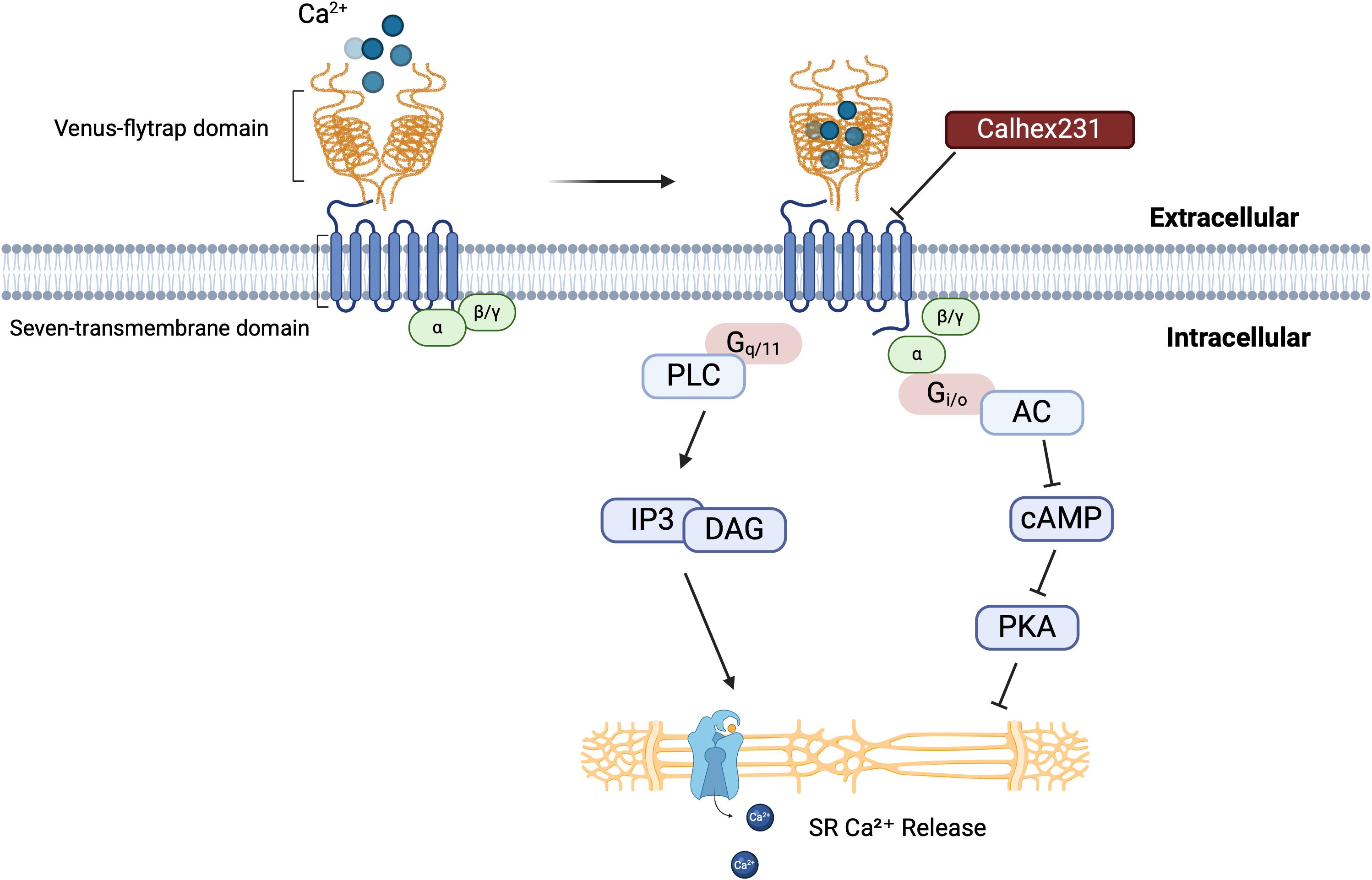
Figure 1. CaSR structure and activation mechanism. The interaction between the extracellular domain of the CaSR, known as the “Venus flytrap,” and calcium ions initiates receptor activation. This activation leads to conformational changes that trigger downstream signaling pathways. Calhex231, a well-characterized inhibitor of CaSR, can prevent this activation process. This figure provides a comprehensive overview of the CaSR activation mechanism and its role in regulating intracellular calcium levels through multiple signaling pathways. A thorough understanding of these mechanisms is essential for clarifying the physiological and pathophysiological roles of CaSR in various cellular processes.
CaSR plays a pivotal role in regulating extracellular Ca2+ homeostasis, influencing numerous physiological and pathophysiological processes across multiple organs, including the heart (23, 24), parathyroid glands (25, 26), kidneys (27–29), bones (30, 31), brain (32), and skin (33, 34). Decreased intracellular Ca2+ concentration eventually leads to reduced myocardial contractility and contraction rate. Ca2+ signals can potentially modulate cellular processes such as apoptosis, autophagy and pyroptosis, which are closely associated with cardiac diseases, including myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury, heart failure, myocardial fibrosis, and diabetic cardiomyopathy (35–37). The disruption of Ca2+ homeostasis can lead to various types of cell death, whereby, CaSR regulates processes such as apoptosis, autophagy, and pyroptosis by sensing changes in Ca2+ concentration and the pH. Additionally, it plays an integral role in various cellular aspects such as cell structure, protease activity, and ROS production, thus, influencing tissue remodeling, repair, and disease progression (4, 38–40). Therefore, CaSR emerges as a promising therapeutic target with substantial biological and clinical relevance for disease intervention. The current review aims to explore the emerging roles of CaSR in various cellular processes implicated in CVDs.
3 Role of CaSR in various cellular processes
CaSR regulates diverse cellular processes including proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammation. It modulates intracellular calcium signaling, thus, impacting cell differentiation, migration, and oxidative stress responses. Through these pathways, CaSR plays a crucial role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and contributing to disease pathogenesis including CVDs.
3.1 Apoptosis
Apoptosis is referred to as programmed cell death, a mechanism that does not trigger inflammatory responses and occurs autonomously, thus, eliminating unwanted cells within an organism and maintaining homeostasis. Cell apoptosis mainly has two pathways, (i) endogenous (intrinsic) cell apoptosis, and (ii) exogenous (extrinsic) cell apoptosis (41, 42), as illustrated in the Figure 2.
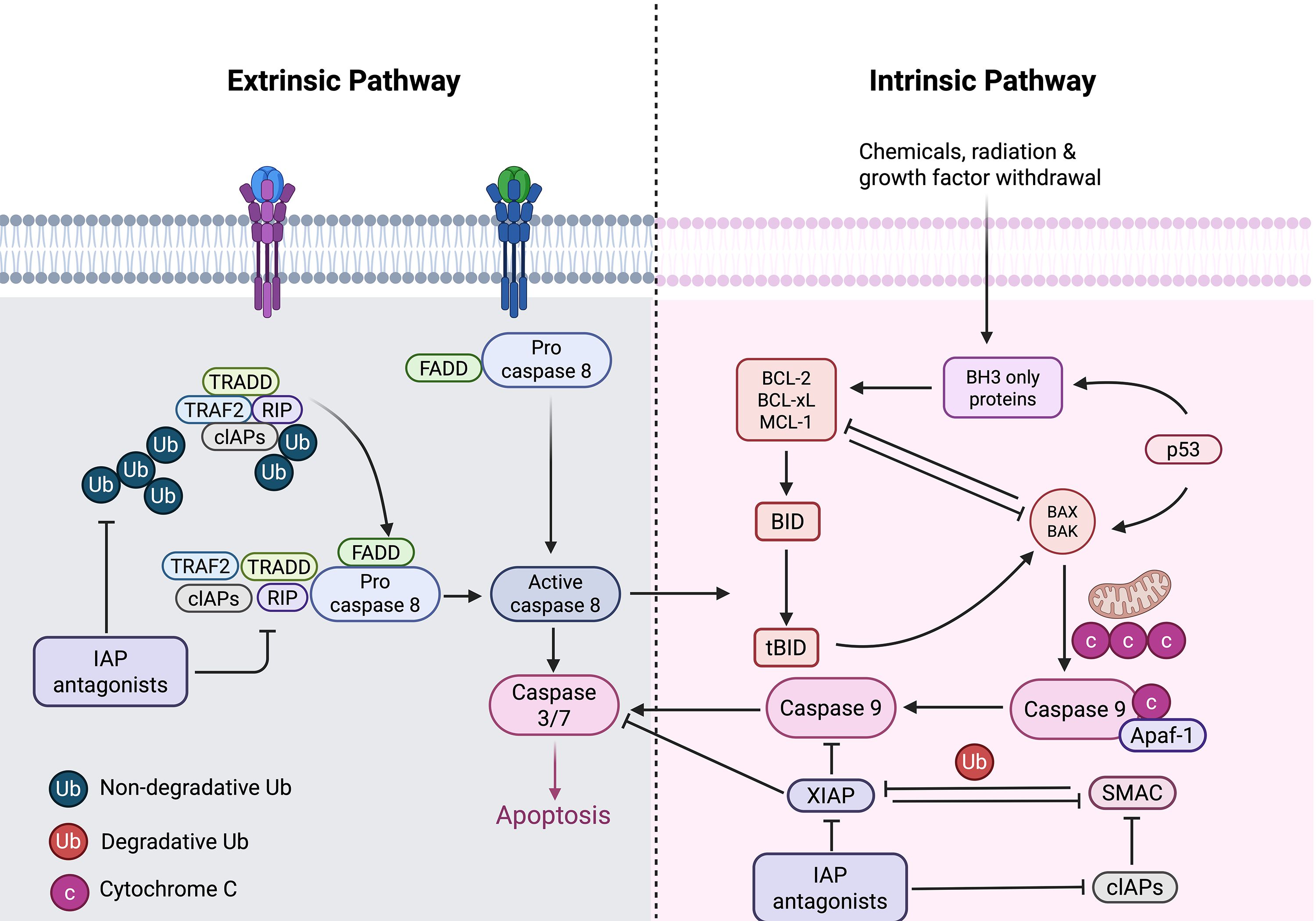
Figure 2. Intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis. The intrinsic pathway is initiated by various intracellular stress signals, including chemicals, radiation, and growth factors withdrawal. These signals cause permeation of the outer mitochondrial membrane, resulting in the release of Cyt C from apoptotic precursor proteins into the cell. Subsequently, it forms a complex with Apaf-1 and procaspase-9. Activation of caspase-9, which in turn activates executioner caspases, leading to apoptosis. The intrinsic pathway is regulated by the balance between pro-apoptotic (BAX, BAK) and anti-apoptotic (BCL-2, BCL-xL, MCL-1) Bcl-2 family proteins. In the extrinsic pathway, the ligand binds to the cell surface receptor, initiating the activation of pro-caspase-8, which then cleaves and activates the executioner proteases (protease-3/7), thereby leading to cell apoptosis. Caspase-8 activation can be modulated by the presence of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs), which can either be non-degradative (Ub) or degradative (Ub).
Endogenous apoptosis is activated by various stress conditions, and primarily mediated by the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Bak, while exogenous apoptosis is initiated by the activation of death receptors on the cell membrane, such as the Fas cell surface death receptor (FAS/CD95/APO-1) and TNF receptor superfamily member 1A (TNFRSF1A), which are activated upon binding to their cognate ligands. Both of these pathways mediate the release of cytochrome c (Cyt C) (43), making mitochondrial release of Cyt C an important feature of apoptosis (44, 45). Cyt C is first released from the damaged mitochondria, triggering the activation of cytosolic caspase-3 by forming a complex containing Cyt C, Apaf-1 and caspase-9, thus, leading to cell apoptosis (46). Bcl-2, on the other hand, is an effective inhibitor of apoptosis, which can prevent the destruction of mitochondria and the subsequent release of Cyt C (47–49).
In cardiomyocytes, persistent elevation of intracellular Ca2+ can lead to apoptosis, whereby, changes in free Ca2+ levels within cardiomyocytes are crucial for the reduction in contractility, thus triggering CaSR activation. Studies have shown that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) can induce increased damage to cardiomyocytes, leading to elevated levels of Cyt C and reduced levels of Bcl-2. Besides mitochondria, Bcl-2 is also localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane, where it confers protection against ER stress (50, 51). Consequently, CaSR activation contributes to myocardial cell injury and apoptosis by upregulating ER stress and autophagy pathways (37).
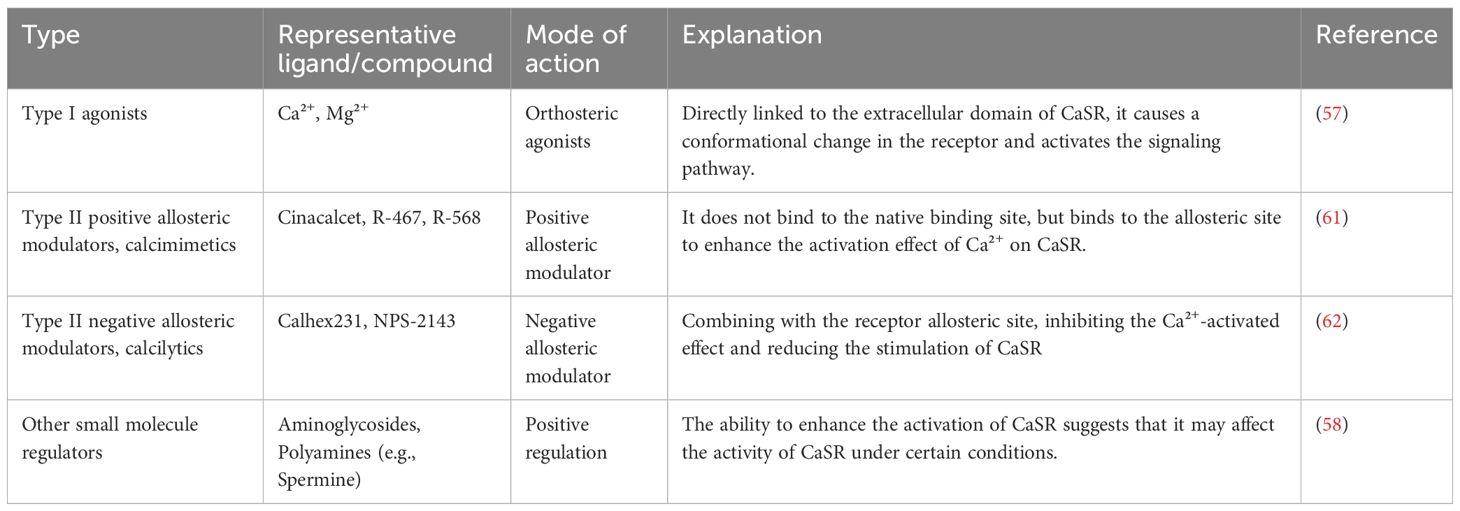
Studies have shown that mitochondria exhibit obvious Ca2+ overload under hypoxic injury conditions, causing mitochondrial damage that eventually leads to apoptosis and necrosis of cardiomyocytes (52–54). The inhibition of Ca2+ within mitochondria, thus, effectively reduces cardiomyocyte apoptosis in response to hypoxic injury (55). This suggests that CaSR not only participates in myocardial injury through the ER pathway, but also plays a significant role in cardiomyocytes apoptosis induced by hypertension by regulating mitochondrial dynamics. The research by Lu et al. indicates that after establishing the hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/Re) model, the increase in extracellular Ca2+ concentration induces its binding to the CaSR and activates the phospholipase C (PLC) signaling pathway, leading to IP3 accumulation and triggering the release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) into mitochondria and its concomitant uptake into the mitochondria (16, 56). Activation of CaSR results in mitochondrial dysregulation and aggregation, manifesting as swelling, disarray of cristae, and loss of normal striations. The CaSR is activated by Ca2+ and Mg2+ (type I activators) (57, 58), which are present in extracellular fluid. In addition to endogenous ions, there are also some exogenous small molecule regulators that can act as regulatory factors for CaSR. The calcimimetic agents such as Calhex231 can inhibit the effect of Ca2+ on CaSR (59–62). In the presence of type I CaSR activators, the specific inhibitor of CaSR, Calhex 231, can inhibit CaSR activation induced by Ca2+ by binding to the 7TM domain of CaSR that is distant from the Ca2+ orthosteric binding site (63). The action modes of different types of ligands on CaSR are illustrated in Table 1.
Calhex231 can increase the expression of OPA1 (Optic Atrophy 1) and MFN1 (Mitofusin 1), and reduce the expression of DRP1 (Dynamin-Related Protein 1) (64). Increased cytoplasmic Ca²+ stimulates the DRP1-mediated fragmentation of mitochondria, facilitating the translocation of DRP1 to mitochondria (65, 66). However, whether long-term inhibition of fission can exert a protective effect on the heart still requires further validation. Some studies have already attempted to explore this issue by modifying the DRP1 gene in animal models and using DRP1 inhibitors (such as Mdivi-1) (67–69), but the available evidence is still insufficient, suggesting that this is an important direction that requires further in-depth exploration in future research.
Additionally, CaSR activation has been communicated to stimulate calcium-dependent pathways, such as Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and the calcitonin pathways, thereby, inducing apoptosis in cardiomyocytes (70). CaSR can also promote the proliferation of cardiomyocytes by regulating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), thereby, alleviating cardiomyocyte apoptosis caused by ischemia and hypoxia (71, 72). Of these, VEGF121 and VEGF165 are the main drugs for treating ischemic cardiomyopathy (73). When there is excessive activation or abnormal elevation of calcium load, CaSR can induce cardiomyocyte death through mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptotic signaling pathways (74). However, under conditions of hypoxia without severe reperfusion injury or Ca²+ overload, CaSR may promote cell proliferation and survival by upregulating protective factors such as VEGF (74). Thus, it can be seen that the role of CaSR in myocardial injury is highly dependent on specific conditions.
3.2 Autophagy
Autophagy is a key degradation process that recycles damaged organelles and long-lived proteins in eukaryotic cells. It helps maintain cellular homeostasis by restoring macromolecules and clearing cytoplasmic debris (14, 37, 75). During autophagy, the substances in the cytoplasm are engulfed by spherical structures characterized by a double-membrane configuration called autophagosomes, and subsequently transported to lysosomes for degradation. Autophagosomes fuse with late endosomes or lysosomes, where their contents are degraded. The resulting products are recycled for macromolecular synthesis and energy metabolism (15, 76).
Autophagy is a highly conserved catabolic process that exhibits an intricate association with CVDs, whereby, Ca2+ serves as an important messenger molecule for regulating cell death, explicitly autophagic regulation (77), as shown in the Figure 3.
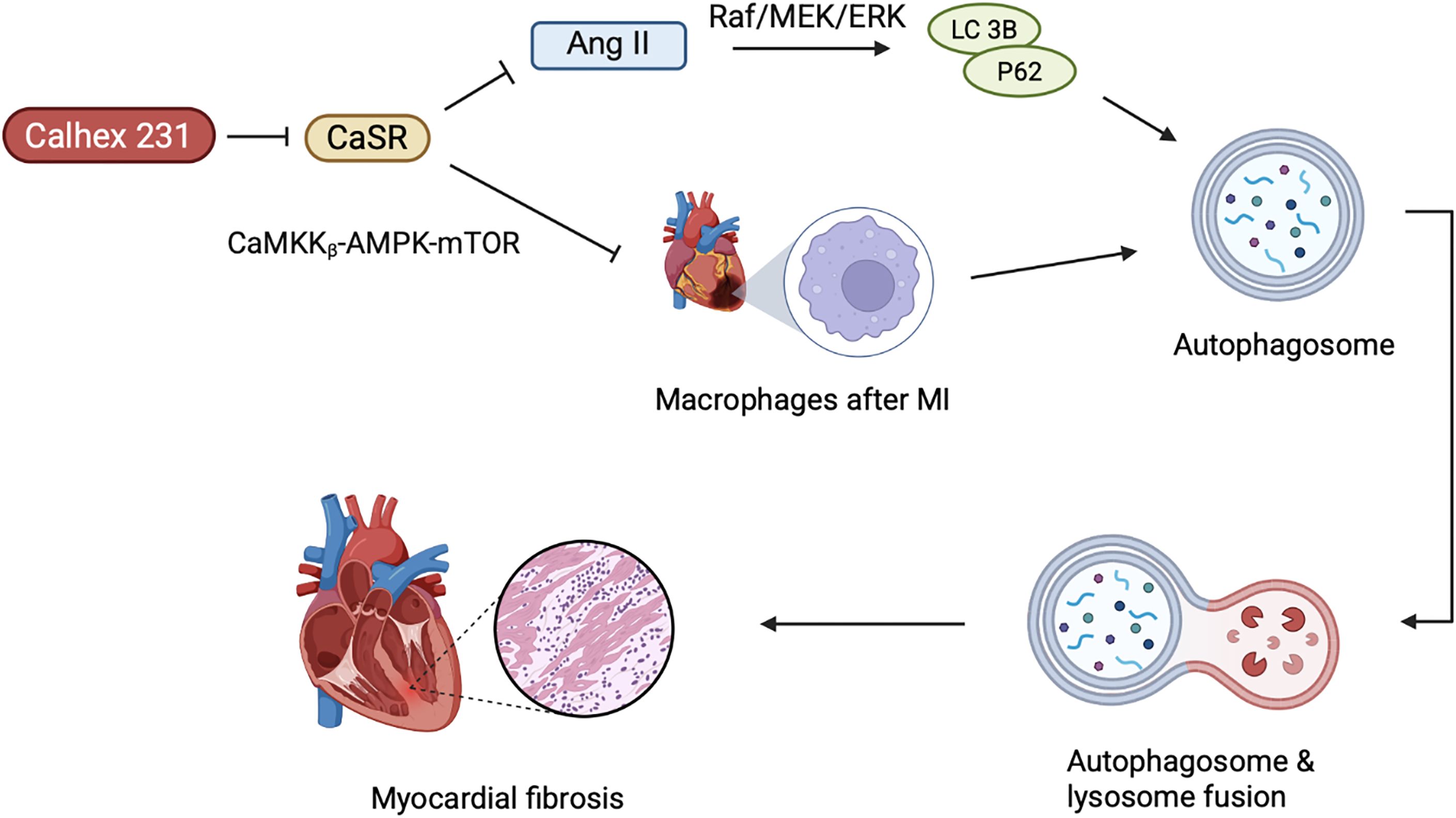
Figure 3. The role of CaSR-mediated autophagy in cardiac remodeling. The activation of CaSR promotes the autophagy process in cardiac fibroblasts, and autophagy further aggravates myocardial fibrosis. AngII can enhance the expression of CaSR and, by activating the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway, upregulates autophagy-related proteins (such as LC3B, P62). After MI, CaSR in macrophages further drives autophagy and activation of the inflammatory body through inhibiting the CaMKKβ-AMPK-mTOR pathway, thereby exacerbating ventricular remodeling. Calhex 231, as an antagonist of CaSR, can inhibit autophagy and alleviate inflammation, fibrosis, and hypertrophy.
Myocardial fibrosis represents one of the pathological hallmarks of diabetic cardiomyopathy. In T1D rats and primary neonatal rat cardiac fibroblasts (CFs), hyperglycemia has been observed to induce myocardial fibrosis (78). Interestingly, the effect of high glucose on CaSR expression varies depending on the cell type. In T1D rats and primary cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes, CaSR was noted to be inhibited by high glucose, while in CFs, it leads to excessive proliferation and collagen deposition (79–81). Upon activation in CFs, CaSR leads to Ca2+ release followed by activation of autophagy (35), whereby, autophagy further leads to cardiac fibrosis (82–84). Calhex231 can putatively ameliorate cardiac fibrosis by inhibiting autophagy in the cellular system of an organism (82). Furthermore, Angiotensin II (AngII) is implicated in cardiac fibrosis induced by CaSR, leading to cardiac remodeling and upregulation of autophagy in the heart (85), whereby, AngII not only enhances CaSR expression in the myocardial tissues, but also promotes the proliferation and transformation of fibroblasts. Chi et al. reported the onset of AngII mediated cardiac fibrosis, upon CaSR induced autophagy. Meanwhile, the Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway may play an important role in AngII-induced autophagy and proliferation of CFs (85). Recent studies have shown that Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway regulates autophagy by modulating the expression of key autophagy-related proteins LC3B and P62 (86, 87). Consequently, this leads to proliferation and phenotypic transformation of CFs induced by AngII, which is associated with the upregulation of CaSR-mediated autophagic pathways. However, the specific mechanism still requires further exploration.
Numerous studies have demonstrated increased concentration of Ca2+ in the infarcted area of the myocardium after MI, suggesting putative involvement of CaSR in the process of ventricular remodeling after MI. In rat cardiomyocytes, CaSR expression is positively correlated with sensitivity to MI (88). In macrophages, CaSR can increase ventricular remodeling by promoting the activation of NLRP 3 inflammasome (89). Liu et al. revealed Calhex 231 to alleviate myocardial inflammation and fibrosis by inhibiting autophagy of macrophages after MI, inhibiting the activation of NLRP 3 inflammasome and subsequently reducing the release of IL-1β (90). Additionally, the dynamic equilibrium of intracellular Ca2+ concentration is an initial factor in myocardial hypertrophy. During myocardial hypertrophy, CaSR mediated autophagy is increased, whereby, elevated Ca2+ triggers several Ca2+-dependent signaling pathways, culminating into cardiac hypertrophy (91–93). Calhex 231 inhibits autophagy by suppressing CaMKKβ-AMPK-mTOR pathway, thereby, ameliorating cardiac hypertrophy caused by CaSR activation (82). Simultaneously, activation of CaSR would induce the release of Ca2+ from SR of the cardiovascular system (94), and participate in the pathological process of cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury (95, 96).
3.3 Pyroptosis
Pyroptosis is a type of programmed cell death mode related to inflammation, which leads to cell death by activating the Caspase-1-mediated signaling pathway (97). Pyroptosis of cells is widely involved in the occurrence and development of various diseases such as infectious diseases (98), metabolic diseases (99), CVDs (100), neurological-related diseases (101), and atherosclerosis (100). Caspase-1, the most crucial member of the Caspase family, assembles the inflammatory sensing factors i.e, NLRP3 inflammasome, AIM2 inflammasome, NLRP1 inflammasome, PYRIN inflammasome, and NLRC4 inflammasome that respond to various stimuli during the process of pyroptosis (102). Studies have shown that caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis induced by NLRP3 inflammasome activation is involved in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury (103). CaSR regulates the generation of NLRP3 inflammasome through Ca2+ and cAMP (104), thus, upregulating the expression of ASC, GSDMD, pro-caspase-1, active caspase-1 (P10), IL-1β, and IL-18, thus, exacerbating pyroptosis of cardiomyocytes under hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) conditions (105), as illustrated in the Figure 4 below.
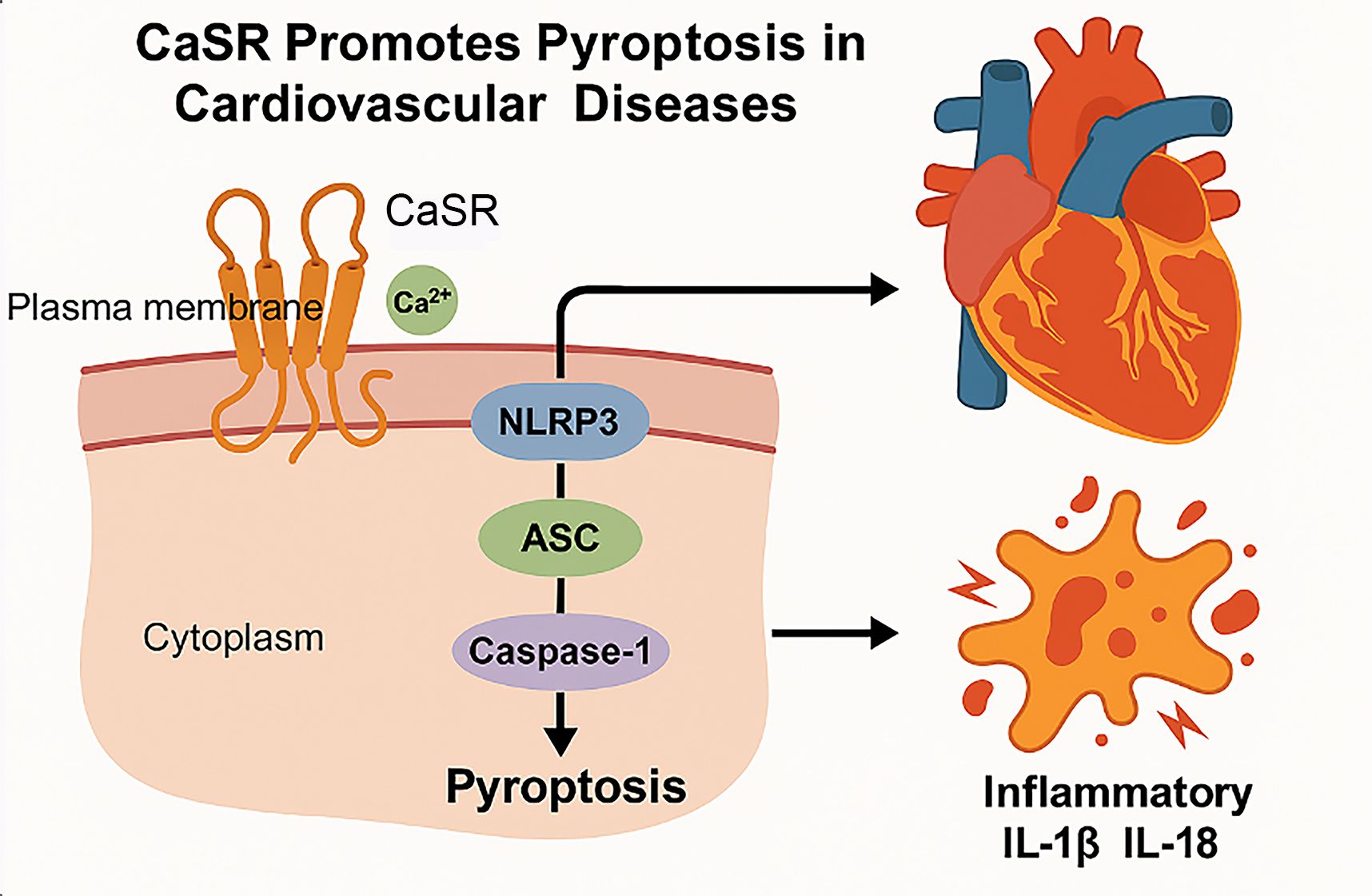
Figure 4. Mechanism of CaSR mediated pyroptosis in CVDs. Cell pyroptosis is a highly inflammatory form of programmed cell death. First, the CaSR located on the plasma membrane is activated by the extracellular Ca2+. Upon activation, CaSR triggers the assembly of the NLRP3 inflammasome. And then, the NLRP3 inflammasome recruits ASC (Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD) and pro-caspase-1, leading to the cleavage and activation of caspase-1. Finally, the activation of caspase-1 results in the execution of pyroptosis, characterized by cell lysis and the release of inflammatory cytokines. Pyroptosis leads to the release of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and IL-18, which can exacerbate inflammation and contribute to the pathogenesis of CVDs.
3.4 Cell proliferation
In CVDs, the occurrence of various pathological conditions may lead to the loss of control over cell proliferation. Therefore, the research on the regulatory mechanism of cell proliferation is particularly imperative.
In DCM, myocardial fibrosis represents a primary pathological hallmark (106). A study has shown that CaSR is expressed in the myocardial tissues of diabetic rats. After treatment with high-concentration glucose, it can be observed that the number of CFs significantly increases (107). CaSR upregulation in CFs may lead to an increase in intracellular Ca2+, and further activate the TGF-β1/SMADs pathway, promoting the proliferation and activation of fibroblasts, ultimately resulting in myocardial fibrosis (108).
Zhong et al. investigated CaSR activation in a diabetic model to increase intracellular Ca2+ concentration in VSMCs, enhancing the activity of cystathionine-γ-lyase (CSE) and elevating endogenous H2S levels by altering the phosphorylation of CaMK II, which subsequently inhibits VSMCs proliferation (109). This process is associated with the PLC-IP3 receptor, calmodulin (CaM) signaling pathway, and ERK 1/2-dependent signaling pathways (110). In addition, studies have shown that the inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase (ERK/MAPK) mediated by MFN2 leads to cell cycle arrest (111–113). Zhang et al. suggested that CaSR inhibition might partially attenuate the proliferation of VSMCs by suppressing mitochondrial fission (114).
Therefore, CaSR may regulate VSMCs proliferation through mitochondrial dynamics and ERK signaling pathways, providing a molecular basis for targeted intervention, but the mechanism still needs to be further studied and elucidated. CaSR can be used as a potential therapeutic target for DCM fibrosis and plausibly provide new ideas for the treatment of DCM.
3.5 Cell migration
Cell migration is one of the integral cellular process that plays an important role in physiological processes involved in disease pathogenesis such as CVDs. Based on the current landscape, CaSR is implicated in the process of cellular migration, and therefore, the current review also delineates the functional significance of CaSR in cellular migration within the context of CVDs.
I/R injury is a common aspect of CVDs which mediates the expression of high mobility group box-1 protein (HMGB1) and CaSR, thus, affecting cell migration and apoptosis through autophagy, leading to the upregulation of angiogenesis and apoptosis in the late stage (115). The migration of VSMCs also plays a pivotal role in the initiation and progression of intimal thickening associated with atherosclerotic lesions (116). Liu et al. demonstrated that reduced expression of NOTCH3 promotes the migration of VSMCs. Surprisingly, a high expression of CaSR was detected in NOTCH3 siRNA VSMCs, whereby, NOTCH3 knockout leads to a transition of VSMCs from a contractile to a synthetic phenotype, promoting migration. Therefore, CaSR may serve as a potential target for the treatment of atherosclerosis and vein grafting (117). High sugar treatment has also been indicated to enhance the migration and proliferation of CFs; however, this effect is inhibited upon treatment with Calhex 231, a specific inhibitor of CaSR. Calhex 231 alleviates the expression of TGF-β1/Smads pathway by decreasing intracellular Ca2+ and inhibiting Itch-ubiquitin proteasome in cardiomyocytes. It inhibits the migration and proliferation of CFs, and also reduces the deposition of collagen, thereby, alleviating glucose-induced myocardial fibrosis (78).
Although the triggers and cell types vary, they all involve changes in intracellular Ca2+ signals, which lead to the activation of CaSR. Eventually, they affect key signaling pathways (such as autophagy, TGF-β1/Smads.) to regulate cellular behaviors. Therefore, CaSR plays an important role in cell migration in different CVDs contexts, and is an important target for CVDs treatment.
3.6 Cell differentiation
Vascular calcification has been reported to increase the prevalence and mortality rate of CVDs (118). Pertinently, CaSR has also been implicated in vascular repair and maintenance of vascular integrity. Reduced expression of CaSR has been observed in calcified vessels (119). The normal expression of VSMCs receptors is crucial for preventing vascular calcification (120). The hydroxyapatite (HA) identified in these deposits is the same calcium polymorph present in bone, indicating that the calcification process may share mechanisms with bone formation. The transformation of VSMCs into osteoblast-like cells is a crucial mechanism in the progression of vascular calcification (121). Research has found that HA mineral deposits can stimulate the expression of BMP-2 through CaSR, whereby, BMP-2 pathway regulates the differentiation of VSMCs into osteoblast-like cells through SMAD-5 signaling (122).
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are multipotent cell lines that can potentially differentiate into distinct cell types (123). ESCs can differentiate into cardiomyocytes and may plausibly be employed in managing heart diseases through cell transplantation. Sun et al. found that CaSR protein exists in mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) and mESC-derived cardiomyocytes (mESC-CMs) (124). CaSR activation can increase intracellular Ca2+ concentration through the G-PLC-IP3 signal transduction pathway, participating in the differentiation of mESCs into cardiomyocytes through expressional modulation of NKx2.5 and GATA-4 (124). ESC-derived cardiomyocytes have the potential to replenish myocardial loss occurring in MI and other CVDs, thereby, providing new research directions for the treatment of CVDs.
4 Role of CaSR in cardiovascular cells
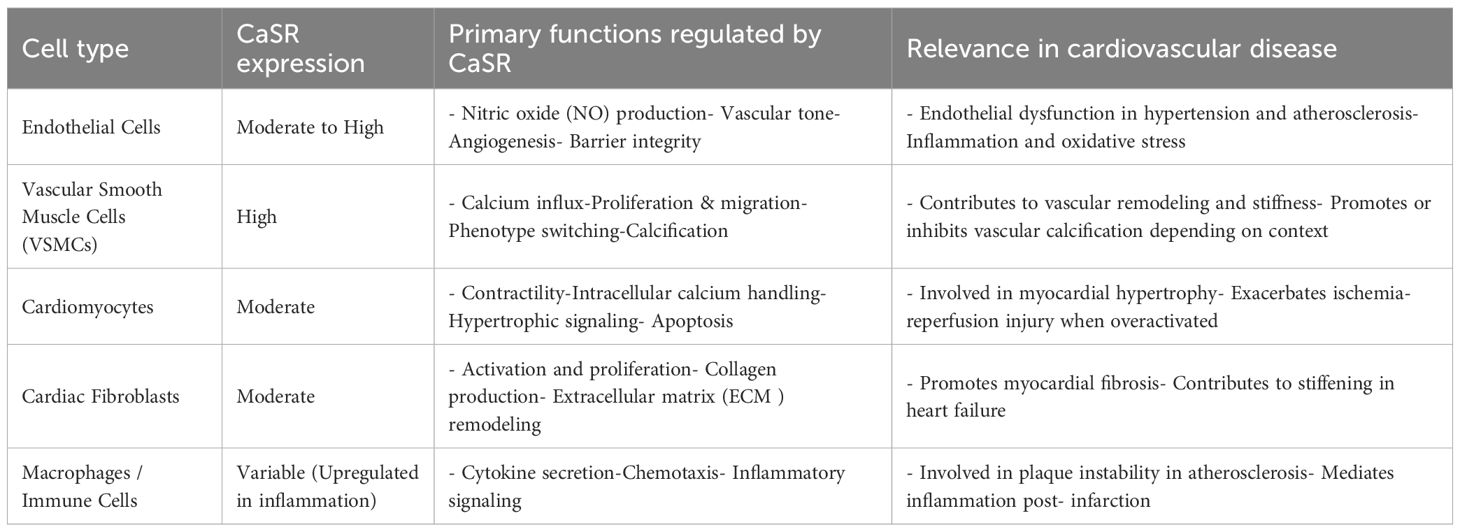
CaSR is expressed in various cardiovascular cell types, where it plays a significant role in modulating key cellular functions that contribute to both physiological regulation and disease progression. Its activity in endothelial cells, VSMCs, cardiomyocytes, and fibroblasts influences processes such as contractility, inflammation, remodeling, and calcification, as detailed below.
4.1 Endothelial cells
CaSR regulates vascular tone by influencing nitric oxide (NO) production and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity in the endothelial cells. Activation of CaSR has been associated with improved endothelial function under certain conditions, while in others, it promotes oxidative stress and inflammation, highlighting its context-dependent function. CaSR also modulates endothelial permeability and angiogenesis, critical for vascular repair and remodeling (125, 126).
4.2 Vascular smooth muscle cells
In VSMCs, CaSR contributes to vascular homeostasis by regulating intracellular calcium levels, proliferation, migration, and phenotype switching. In pathological conditions such as hypertension and atherosclerosis, CaSR activation has been linked to increased VSMCs proliferation and calcification, contributing to vascular stiffness and plaque development (127). CaSR can be activated when the extracellular Ca²+ concentration is increased, and the PLC is promoted to generate IP3 through Gq/11 coupling, while the MEK 1/ERK 1,2 pathway is activated. By continuously driving the proliferation of VSMCs, it leads to thickening of the middle layer of the blood vessel wall, narrowing of the lumen and increased stiffness, and exacerbates the progression of hypertension (114, 128).
However, in some models, CaSR appears to exert protective effects by preventing osteogenic differentiation of VSMCs. CaSR is a key binding partner of vasoconstriction-inhibiting factor (VIF) peptide and exerts a protective effect on vascular calcification through its activation (129). VIF inhibited the expression of osteogenic differentiation markers such as BMP2, MSX2, SOX9, and OCN through CaSR. In VSMCs, CaSR activation inhibits calcium influx, ROS production, inflammation, and apoptosis, thereby preventing calcification (129–131). CaSR has dual function and cell state-specific effects, especially in preventing osteogenic differentiation of VSMCs.
The activation of CaSR may result in different and even opposite outputs in the vascular system and the skeletal system, which is an important feature called ‘cell-state specificity’ and ensures the safety of the treatment. Therefore, CaSR therapy is expected to achieve the inhibition of ectopic vascular calcification without affecting physiological bone formation, but the molecular mechanism remains unclear and requires further exploration.
4.3 Cardiomyocytes
In cardiomyocytes, CaSR is expressed at both fetal and adult stages, where it modulates intracellular calcium handling, contractile function, and cell survival. CaSR activation has been implicated in myocardial hypertrophy, apoptosis, and I/R injury. The research by Hong et al. indicates that excessive stimulation of calcium-sensitive receptors may exacerbate myocardial cell damage under stress conditions, manifesting as mitochondrial dysfunction and increased cell apoptosis (64). The research conducted by Zhang et al. indicates that moderate activation of CaSR can exert protective effects, including maintaining myocardial contractility and alleviating myocardial fibrosis (132, 133). This indicates that the role of CaSR in the myocardium may be time-dependent and dose-dependent: short-term, moderate activation may maintain cellular function through protective pathways, while long-term or excessive activation may induce pathological signals, leading to cell damage.
4.4 Cardiac fibroblasts
CaSR influences ECM remodeling and fibrotic responses in CFs, whereby, it regulates fibroblast activation, proliferation, and collagen synthesis, crucial to the development of cardiac fibrosis following injury. Moreover, dysregulated CaSR signaling in these cells can lead to excessive ECM deposition, contributing to myocardial stiffness and impaired cardiac function (134, 135).
4.5 Adipocytes
Within the cardiovascular environment, immune cells have been reported to express CaSR, which may influence local inflammatory responses (136), although this niche still remains underexplored.
This pro-inflammatory effect of CaSR may also affect adipose tissue, which is a key factor in metabolic cardiovascular disease. According to new research, CaSR’s effects are not limited to classical immune cells, but are also found in adipocytes in perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) (137). CaSR activates and promotes adipocyte predifferentiation, adipogenesis, and adipocyte differentiation (137), while inhibiting lipolysis (138). Studies have shown that activation of CaSR in adipocytes promotes the release of pro-inflammatory adipokines such as leptin and resistin and inhibits adiponectin secretion, leading to metabolic dysfunction in the form of insulin resistance and dyslipidemia (139, 140). There is growing evidence that activation of calcium-sensitive receptors in adipocytes exacerbates inflammation and metabolic dysfunction, leading to atherosclerosis (141, 142). For example, in human and mouse adipocytes, stimulation of calcium-sensitive receptors promote a pro-inflammatory phenotype manifested by increased secretion of cytokines such as IL-6 and MCP-1, while reducing anti-inflammatory adiponectin levels (143). This transition creates a systemic inflammatory environment that accelerates vascular dysfunction. These findings link CaSR in adipocytes to novel mechanisms between metabolic disorders and cardiovascular inflammation, suggesting that modulating CaSR activity in adipose tissue may be a potential strategy to mitigate obesity-related atherosclerosis.
Overall, CaSR exhibits complex and cell-type-specific roles in cardiovascular biology. Its ability to influence diverse signaling pathways and cellular behaviors underscores its importance in cardiovascular health and disease, as indicated in Table 2.
5 Role of CaSR in specific CVDs
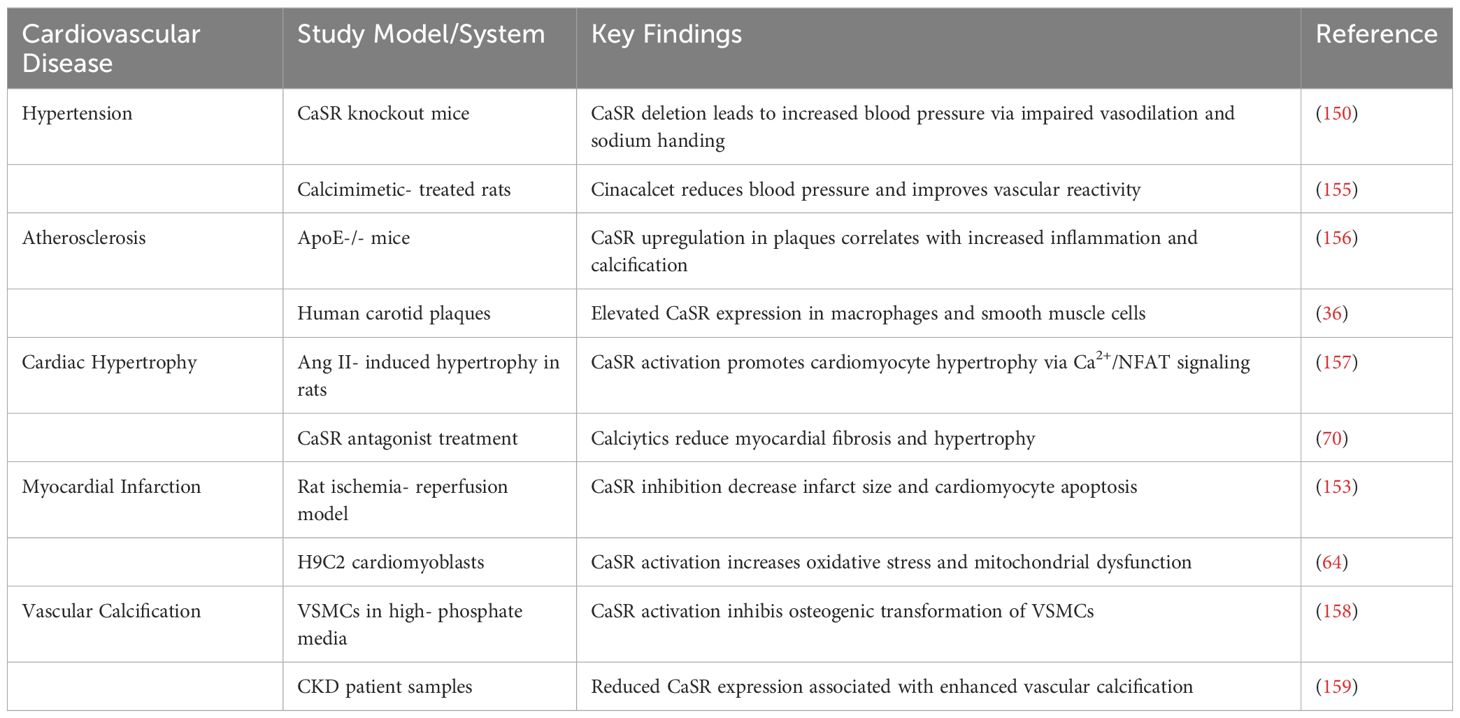
CaSR plays diverse cell-specific roles in the pathogenesis of several CVDs. Emerging evidence suggests that altered CaSR expression contributes to the development and progression of cardiovascular conditions such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, cardiac hypertrophy, MI and vascular calcification. However, its function appears to be highly context-dependent, with both protective and deleterious effects reported across various disease models (136).
5.1 Hypertension
A growing body of research has proven that RAAS is associated with the occurrence of hypertension caused by diabetes (144). CaSR is not only expressed in the heart, but also in the kidneys (145). Research indicates that reduced CaSR expression contributes to the development of primary hypertension by activating cAMP pathway and the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) (146). cAMP stimulates renin secretion (147), and a significant increase in renin secretion triggers an increase in Ang II and aldosterone, which leads to an increase in blood pressure. CaSR can increase intracellular Ca2+ concentration and reduce intracellular cAMP levels, thereby playing an important role in reducing blood pressure (148, 149).
Plasma renin values can directly reflect the degree of renin-mediated vasoconstriction. Studies have shown that CaSR in VSMCs plays a very important role in maintaining blood pressure levels within physiological limits, thus reducing hypertension (150). In VSMCs, CaSR modulates intracellular calcium levels, influencing vasoconstriction and vascular reactivity. Animal studies have shown that CaSR activation can lower blood pressure by promoting vasodilation and natriuresis. Conversely, impaired CaSR signaling may contribute to salt-sensitive hypertension (151). Clinical data on calcimimetics such as cinacalcet suggest potential antihypertensive effects, though their use remains limited in cardiovascular practice.
5.2 Atherosclerosis
CaSR is expressed in endothelial cells, macrophages, and VSMCs, which contribute to atherogenesis. In endothelial cells, CaSR may promote nitric oxide (NO) production and preserve barrier integrity under physiological conditions. However, in inflammatory environments, CaSR activation may exacerbate oxidative stress and cytokine release. In VSMCs and macrophages, CaSR appears to influence plaque stability by modulating cell migration, foam cell formation, and calcification. Notably, upregulation of CaSR in atherosclerotic plaques has been reported, suggesting its involvement in disease progression (125, 126, 132).
5.3 Cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure
Cardiomyocyte CaSR activity has been linked to pathological hypertrophy and apoptosis. Overactivation of CaSR can lead to increased intracellular Ca2+ levels, promoting pro-hypertrophic signaling through calcineurin/NFAT and MAPK pathways. Studies in rodent models indicate that CaSR inhibition may attenuate cardiac remodeling and fibrosis following pressure overload or neurohormonal stimulation. Additionally, CaSR may influence CFs, contributing to ECM deposition and myocardial stiffness (152).
5.4 Myocardial ischemia and infarction
During I/R injury, CaSR activation has been associated with calcium overload, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cell death. Inhibition of CaSR in cardiomyocytes during reperfusion has shown protective effects, as it reduced infarct size and improved cardiac function. These findings suggest a detrimental role for CaSR in acute ischemic injury, likely mediated through its influence on calcium signaling and oxidative stress (153).
5.5 Vascular calcification
CaSR plays a critical role in regulating mineral metabolism, and its dysregulation is closely linked with vascular calcification, particularly in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). In VSMCs, loss of CaSR function promotes osteogenic differentiation, matrix vesicle release, and calcium phosphate deposition. Restoration of CaSR activity via calcimimetics has been shown to inhibit vascular calcification in experimental models and clinical studies, highlighting its potential therapeutic relevance (154).
Comprehensively, CaSR contributes to the pathophysiology of multiple CVDs through diverse, cell-specific mechanisms (36, 64, 70, 150, 153, 155–159), as depicted in Table 3. Understanding these disease-specific roles is essential for developing CaSR-targeted therapies tailored to specific cardiovascular problems.
6 Clinical significance and therapeutic implications
The application of CaSR modulators has shown potential clinical value. CaSR presents a promising yet complex therapeutic target in CVDs. Pharmacological agents that modulate CaSR activity, namely calcimimetics (agonists) and calcilytics (antagonists), have been explored primarily in the context of bone and mineral disorders, such as hyperparathyroidism. However, emerging evidence suggests these agents may also influence cardiovascular outcomes by modulating CaSR activity in endothelial cells, VSMCs, and cardiomyocytes (152).
Cardiovascular complications are also one of the leading causes of death in CKD patients. Secondary hyperparathyroidism (SHPT) is a common complication of CKD and is closely related to cardiovascular pathologies (160, 161). Calcimimetics drugs (such as sinacarcet) have been approved for the treatment of SHPT, and several studies have shown that they may help treat CVDs by reducing parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels, inhibiting vascular calcification, and improving endothelial function (162, 163). In addition, studies have shown that transient hypocalcemia caused by cinalcium may be a risk of cardiovascular death in a time-dependent model (164). However, the current clinical evidence is limited. Most studies on the cardiovascular effects of CaSR modulators have focused on people with CKD, and results are not entirely consistent. Studies have shown that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of CASR alter the response to calcified cinnacalcium and help in the treatment of hypocalcemia in CKD hemodialysis patients (165).
Calcimimetics have been shown to reduce vascular calcification and lower blood pressure in some experimental models, while calcilytics may attenuate pathological cardiac remodeling and fibrosis. Despite these promising findings, the systemic activation or inhibition of CaSR can lead to adverse effects due to its widespread tissue distribution and diverse functions. This highlights the need for tissue-selective modulators or targeted drug delivery systems to minimize off-target effects. Currently, clinical data on the cardiovascular effects of CaSR modulators remain limited and inconclusive. While calcimimetics show promise in reducing vascular calcification, the current cardiovascular trial data remain limited, and concerns such as hypocalcemia still persist. Further preclinical and translational studies are essential to validate CaSR as a viable therapeutic target in CVDs and to guide the safe and effective use of its modulators in clinical settings (18, 166).
Additionally, understanding individual genetic variations in CaSR may inform personalized therapeutic strategies. Epidemiological studies have shown that calcium kidney stones are related to polymorphisms in the regulatory region of CaSR genes. rs6776158 located within promoter-1, rs1501899 located in intron 1, and rs7652589 in the 5’-untranslated region were found to reduce the transcriptional activity of promoter-1, and activation of rs1042636 polymorphisms was associated with calcium kidney stones and hypercalciuria (167–170). Gene polymorphisms that reduce CaSR expression may impair the protective effect of CaSR on calcium phosphate and oxalate precipitation, making it more likely to cause kidney stones, while activating the polymorphism rs1042636 may predispose to calcium stones by increasing calcium excretion.
Such variability may be attributed to disease heterogeneity, drug dose differences, and diversity in treatment response due to CaSR gene polymorphisms. Comprehensively, the clinical application of CaSR as a cross-disciplinary therapeutic target still faces challenges. By integrating genetic polymorphism screening with precision drug intervention, the potential of CaSR modulators in the prevention and treatment of CVDs may be maximized.
7 Current gaps and contradictory findings
Although numerous studies have highlighted the significance of CaSR in cardiovascular physiology and disease, findings remain inconsistent and sometimes contradictory. In endothelial and VSMCs, CaSR has been shown to both promote and inhibit inflammation and oxidative stress, suggesting a context-dependent role influenced by disease stage or cellular environment. Similarly, its effects on cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and survival vary between in vitro and in vivo models. A major limitation is the lack of cell-type-specific investigations, leading to conflicting interpretations of systemic versus localized CaSR activation. Moreover, discrepancies in experimental models, CaSR agonists/antagonists used, and dosage regimens contribute to variability in outcomes. The differential impact of CaSR in healthy versus diseased tissues remains poorly understood. These gaps hinder the translation of preclinical data into clinical therapies and underscore the need for more refined models to delineate specific functions of CaSR in cardiovascular pathologies.
8 Future directions
Despite significant progress in understanding the role of CaSR in CVDs, several concerns are yet to be addressed. Future research should prioritize the use of cell-type-specific and inducible CaSR knockout models to dissect its precise functions in different cardiovascular tissues. Advanced imaging and biosensing techniques could enable real-time monitoring of CaSR activity and downstream signaling under physiological and pathological conditions. Additionally, investigating the interplay of CaSR cross-talk with other key pathways, such as the renin-angiotensin system and β-adrenergic signaling, may uncover integrative roles in cardiovascular regulation. Likewise, exploring genetic variants of CaSR in patient populations could also provide insight into disease susceptibility and drug responsiveness. Moreover, the development of tissue-targeted CaSR modulators may overcome the limitations of current pharmacological agents and enhance therapeutic precision, at large.
It is worth noting that CaSR also plays a significant role in various physiological and pathological processes outside the cardiovascular system. For instance, adipose tissue not only serves as an energy storage organ, but its secreted adipokines (such as adiponectin and leptin) can affect cardiovascular homeostasis through the endocrine pathway. The high expression of CaSR in adipocytes can regulate adipocyte differentiation and lipid metabolism balance by sensing local calcium signals (such as calcium transient produced by fat breakdown), thereby causing metabolic disorders and further exacerbating atherosclerosis through the “metabolic inflammation” pathway. Additionally, the heart and kidneys form a “heart-kidney axis” through the neuro-humoral network, and their imbalance is the core mechanism of heart failure and the progression of CKD. A significant increase in renin secretion leads to excessive activation of the RAS, and CaSR can inhibit renin release to lower blood pressure and reduce the cardiac load. Therefore, CaSR can serve as a therapeutic target for combined heart-kidney diseases.
Screening patients through CaSR genotyping can achieve accurate selection of therapeutic drugs (such as calcium channel blockers, RAS inhibitors, calcium-sensitive receptor modulators), and predict the risk of adverse reactions (such as hypocalcemia and hyperkalemia), significantly improving the safety and efficacy of the treatment.
Overall, a deeper mechanistic understanding of the dual behavior of CaSR is crucial in order to translate basic findings into effective clinical interventions for CVDs.
9 Conclusion
CaSR is expressed on the surface of various cells/tissues, whereby, it functions by activating distinct signaling pathways by sensing Ca2+ concentration in the ECM. The findings of the current review paper revealed significant role of CASR in CVDs, whereby, it modulates various cellular processes such as apoptosis, autophagy, pyroptosis, proliferation, migration and differentiation as depicted in the Figure 5. Moreover, intracellular signaling pathways mediated by CaSR can lead to inflammation and fibrosis. Notably, CaSR has demonstrated its clinical relevance as a potential therapeutic target through a range of regulatory functions in CVDs. Therefore, it is imperative to explore specific mechanisms of CaSR function in CVDs and develop novel therapeutic strategies targeting CaSR in future.
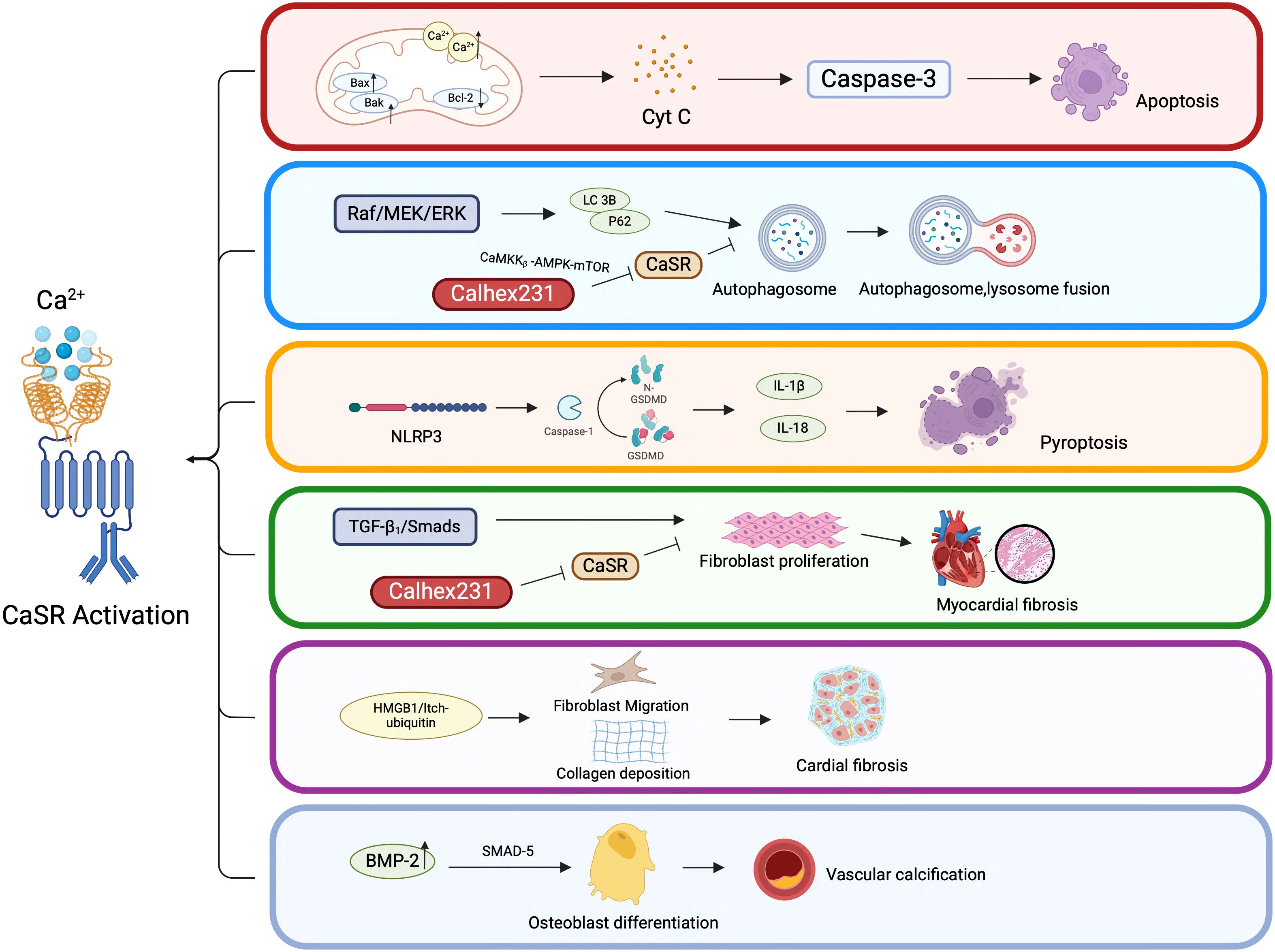
Figure 5. CaSR-mediated cellular behaviors in CVDs. CaSR-mediated cellular behaviors in CVDs. This figure highlights the complex interplay between CaSR activation and various cellular pathways that contribute to CVDs. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing targeted therapies to prevent or treat cardiovascular pathologies associated with CaSR dysregulation.
Author contributions
XL: Data curation, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TaX: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. JQ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. SL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. TiX: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. XG: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. HY: Data curation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research is supported by the Heilongjiang Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Project (No. ZHY2024-212); Basic Scientific Research Business Research Project of Heilongjiang (No. 2024-KYYWF-0502); Heilongjiang Provincial Department of Education Excellent Young Teachers Basic Research Support Program (No. YQJH2024254); Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (SS2023H003).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Rehman S, Rehman E, Ikram M, and Jianglin Z. Cardiovascular disease (CVD): assessment, prediction and policy implications. BMC Public Health. (2021) 21:1299. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-11334-2
2. Berridge MJ, Lipp P, and Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2000) 1:11–21. doi: 10.1038/35036035
4. Dhaouadi N, Vitto VAM, Pinton P, Galluzzi L, and Marchi S. Ca(2+) signaling and cell death. Cell Calcium. (2023) 113:102759. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2023.102759
5. Yuan M, Ma T, Fan Z, Li J, and Zhang S. The calcium-sensing receptor: a comprehensive review on its role in calcium homeostasis and therapeutic implications. Am J Transl Res. (2025) 17:2322–38. doi: 10.62347/QGTS5711
6. Dewenter M, von der Lieth A, Katus HA, and Backs J. Calcium Signaling and Transcriptional Regulation in Cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. (2017) 121:1000–20. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.310355
7. Brown EM, Gamba G, Riccardi D, Lombardi M, Butters R, Kifor O, et al. Cloning and characterization of an extracellular Ca(2+)-sensing receptor from bovine parathyroid. Nature. (1993) 366:575–80. doi: 10.1038/366575a0
8. Gao Y, Robertson MJ, Rahman SN, Seven AB, Zhang C, Meyerowitz JG, et al. Asymmetric activation of the calcium-sensing receptor homodimer. Nature. (2021) 595:455–9. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03691-0
9. Geng Y, Xiong D, Mosyak L, Malito DL, Kniazeff J, Chen Y, et al. Structure and functional interaction of the extracellular domain of human GABAB receptor GBR2. Nat Neurosci. (2012) 15:970–8. doi: 10.1038/nn.3133
10. Hu J and Spiegel AM. Structure and function of the human calcium-sensing receptor: insights from natural and engineered mutations and allosteric modulators. J Cell Mol Med. (2007) 11:908–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00096.x
11. Wen T, Wang Z, Chen X, Ren Y, Lu X, Xing Y, et al. Structural basis for activation and allosteric modulation of full-length calcium-sensing receptor. Sci Adv. (2021) 7(23):eabg1483. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abg1483
12. Huang Y, Zhou Y, Yang W, Butters R, Lee H-W, Li S, et al. Identification and Dissection of Ca2+-binding Sites in the Extracellular Domain of Ca2+-sensing Receptor. J Biol Chem. (2007) 282:19000–10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701096200
13. Huang Y, Zhou Y, Castiblanco A, Yang W, Brown EM, and Yang JJ. Multiple Ca2+-Binding Sites in the Extracellular Domain of the Ca2+-Sensing Receptor Corresponding to Cooperative Ca2+ Response. Biochemistry. (2008) 48:388–98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701096200
14. Liu H, Yi P, Zhao W, Wu Y, Acher F, Pin J-P, et al. Illuminating the allosteric modulation of the calcium-sensing receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2020) 117:21711–22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922231117
15. Chavez-Abiega S, Mos I, Centeno PP, Elajnaf T, Schlattl W, Ward DT, et al. Sensing Extracellular Calcium – An Insight into the Structure and Function of the Calcium-Sensing Receptor (CaSR). Adv Exp Med Biol. (2020) 1131:1031–63. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-12457-1_41
16. Hofer AM and Brown EM. Extracellular calcium sensing and signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2003) 4:530–8. doi: 10.1038/nrm1154
17. Leach K, Hannan FM, Josephs TM, Keller AN, Møller TC, Ward DT, et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CVIII. Calcium-Sensing Receptor Nomenclature, Pharmacology, and Function. Pharmacol Rev. (2020) 72:558–604. doi: 10.1124/pr.119.018531
18. Conigrave AD and Ward DT. Calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR): Pharmacological properties and signaling pathways. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2013) 27:315–31. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2013.05.010
19. Thomsen AR, Smajilovic S, and Bräuner-Osborne H. Novel strategies in drug discovery of the calcium-sensing receptor based on biased signaling. Curr Drug Targets. (2012) 13:1324–35. doi: 10.2174/138945012802429642
20. Liu Y, Chen J, Fontes SK, Bautista EN, and Cheng Z. Physiological and pathological roles of protein kinase A in the heart. Cardiovasc Res. (2022) 118:386–98. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab008
21. Kifor O, Diaz R, Butters R, and Brown EM. The Ca2+-sensing receptor (CaR) activates phospholipases C, A2, and D in bovine parathyroid and CaR-transfected, human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cells. J Bone Miner Res. (1997) 12:715–25. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1997.12.5.715
22. Hannan FM and Thakker RV. Calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) mutations and disorders of calcium, electrolyte and water metabolism. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2013) 27:359–71. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2013.04.007
23. März W, Seelhorst U, Wellnitz B, Tiran B, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Renner W, et al. Alanine to serine polymorphism at position 986 of the calcium-sensing receptor associated with coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, all-cause, and cardiovascular mortality. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2007) 92:2363–9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-0071
24. Zhang T, Tang N, Xi D, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Wang L, et al. Calcimimetic R568 improved cardiac remodeling by classic and novel renin-angiotensin system in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Exp Biol Med. (2019) 244:789–801. doi: 10.1177/1535370219854325
25. Rybczyńska A, Marchwińska A, Dyś A, Boblewski K, Lehmann A, and Lewko B. Activity of the calcium-sensing receptor influences blood glucose and insulin levels in rats. Pharmacol Rep. (2017) 69:709–13. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2017.01.034
26. Şenkal-Turhan S, Bulut-Okumuş E, Aydın M, Başak Türkmen N, Taşlıdere A, Şahin F, et al. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Parathyroid Organoids Resemble Parathyroid Morphology and Function. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2024) 11:e2407567. doi: 10.1002/advs.202407567
27. Jeon US. Kidney and calcium homeostasis. Electrolyte Blood Press. (2008) 6:68–76. doi: 10.5049/EBP.2008.6.2.68
28. Magagnoli L, Ciceri P, and Cozzolino M. Secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic kidney disease: pathophysiology, current treatments and investigational drugs. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. (2024) 33:775–89. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2024.2369307
29. Tinawi M. Disorders of Calcium Metabolism: Hypocalcemia and Hypercalcemia. Cureus. (2021) 13:e12420. doi: 10.7759/cureus.12420
30. Rybchyn MS, Brennan-Speranza TC, Mor D, Cheng Z, Chang W, Conigrave AD, et al. The mTORC2 Regulator Homer1 Modulates Protein Levels and Sub-Cellular Localization of the CaSR in Osteoblast-Lineage Cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(12):6509. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126509
31. Li X, Chen S, Hu Z, Chen D, Wang J, Li Z, et al. Aberrant upregulation of CaSR promotes pathological new bone formation in ankylosing spondylitis. EMBO Mol Med. (2020) 12:e12109. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202012109
32. Mao FX, Luo CH, Chen HJ, Zhang YX, and Zhang Q. CaSR is required for ischemia-induced proliferation and differentiation of white matter progenitor cells from neonatal rats. Brain Res Bull. (2020) 154:116–26. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.11.004
33. Wang R, Xu C, Zhao W, Zhang J, Cao K, Yang B, et al. Calcium and polyamine regulated calcium-sensing receptors in cardiac tissues. Eur J Biochem. (2003) 270:2680–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03645.x
34. Tfelt-Hansen J, Hansen JL, Smajilovic S, Terwilliger EF, Haunso S, and Sheikh SP. Calcium receptor is functionally expressed in rat neonatal ventricular cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiology-Heart Circulatory Physiol. (2006) 290:H1165–H71. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00821.2005
35. Zhang X, Zhang T, Wu J, Yu X, Zheng D, Yang F, et al. Calcium Sensing Receptor Promotes Cardiac Fibroblast Proliferation and Extracellular Matrix Secretion. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2014) 33:557–68. doi: 10.1159/000358634
36. Paccou J, Boudot C, Renard C, Liabeuf S, Kamel S, Fardellone P, et al. Total calcium-sensing receptor expression in circulating monocytes is increased in rheumatoid arthritis patients with severe coronary artery calcification. Arthritis Res Ther. (2014) 16:412. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0412-5
37. Han G, Wang HY, Han ZW, Xu CL, Chen GP, and Jiang CM. Relationship between CaSRs and LPS-injured cardiomyocytes. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2018) 11:1965–71.
38. Marchi S, Patergnani S, Missiroli S, Morciano G, Rimessi A, Wieckowski MR, et al. Mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum calcium homeostasis and cell death. Cell Calcium. (2018) 69:62–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2017.05.003
39. Ning B, Guo C, Kong A, Li K, Xie Y, Shi H, et al. Calcium Signaling Mediates Cell Death and Crosstalk with Autophagy in Kidney Disease. Cells. (2021) 10(11):3204. doi: 10.3390/cells10113204
40. Sridhar KC, Hersch N, Dreissen G, Merkel R, and Hoffmann B. Calcium mediated functional interplay between myocardial cells upon laser-induced single-cell injury: an in vitro study of cardiac cell death signaling mechanisms. Cell Communication Signaling. (2020) 18(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00689-5
41. Bertheloot D, Latz E, and Franklin BS. Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: an intricate game of cell death. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) 18:1106–21. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-00630-3
42. Newton K, Strasser A, Kayagaki N, and Dixit VM. Cell death. Cell. (2024) 187:235–56. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.11.044
43. Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams JM, Adam D, Agostinis P, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differentiation. (2018) 25:486–541. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4
44. Martínez-Fábregas J, Díaz-Moreno I, González-Arzola K, Janocha S, Navarro JA, Hervás M, et al. Structural and functional analysis of novel human cytochrome C targets in apoptosis. Mol Cell Proteomics. (2014) 13:1439–56. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.034322
45. Kalpage HA, Wan J, Morse PT, Zurek MP, Turner AA, Khobeir A, et al. Cytochrome c phosphorylation: Control of mitochondrial electron transport chain flux and apoptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2020) 121:105704. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2020.105704
46. Wang H, Zhu J, Jiang L, Shan B, Xiao P, Ai J, et al. Mechanism of Heshouwuyin inhibiting the Cyt c/Apaf-1/Caspase-9/Caspase-3 pathway in spermatogenic cell apoptosis. BMC Complement Med Ther. (2020) 20:180. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02904-9
47. Pinton P and Rizzuto R. Bcl-2 and Ca2+ homeostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Death Differentiation. (2006) 13:1409–18. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401960
48. Ferrari D, Pinton P, Szabadkai G, Chami M, Campanella M, Pozzan T, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum, Bcl-2 and Ca2+ handling in apoptosis. Cell Calcium. (2002) 32:413–20. doi: 10.1016/S0143416002002014
49. Marin MC, Fernandez A, Bick RJ, Brisbay S, Buja LM, Snuggs M, et al. Apoptosis suppression by bcl-2 is correlated with the regulation of nuclear and cytosolic Ca2+. Oncogene. (1996) 12:2259–66.
50. Liu C, Li H, Zheng H, Zhai M, Lu F, Dong S, et al. CaSR activates PKCδ to induce cardiomyocyte apoptosis via ER stress−associated apoptotic pathways during ischemia/reperfusion. Int J Mol Med. (2019) 44:1117–26. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4255
51. Pinton P, Giorgi C, Siviero R, Zecchini E, and Rizzuto R. Calcium and apoptosis: ER-mitochondria Ca2+ transfer in the control of apoptosis. Oncogene. (2008) 27:6407–18. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.308
52. Wang M, Tan J, Miao Y, Li M, and Zhang Q. Role of Ca²+ and ion channels in the regulation of apoptosis under hypoxia. Histol Histopathol. (2018) 33:237–46. doi: 10.14670/HH-11-918
53. Zhang N, Yu H, Liu T, Zhou Z, Feng B, Wang Y, et al. Bmal1 downregulation leads to diabetic cardiomyopathy by promoting Bcl2/IP3R-mediated mitochondrial Ca(2+) overload. Redox Biol. (2023) 64:102788. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102788
54. Wu S, Lu Q, Ding Y, Wu Y, Qiu Y, Wang P, et al. Hyperglycemia-Driven Inhibition of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase α2 Induces Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Promoting Mitochondria-Associated Endoplasmic Reticulum Membranes In Vivo. Circulation. (2019) 139:1913–36. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.033552
55. Nagoor Meeran MF, Laham F, Azimullah S, Tariq S, and Ojha S. α-Bisabolol abrogates isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction by inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction and intrinsic pathway of apoptosis in rats. Mol Cell Biochem. (2018) 453:89–102. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3434-5
56. Lu FH, Tian Z, Zhang WH, Zhao YJ, Li HL, Ren H, et al. Calcium-sensing receptors regulate cardiomyocyte Ca2+ signaling via the sarcoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrion interface during hypoxia/reoxygenation. J BioMed Sci. (2010) 17:50. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-17-50
57. Zhang C, Zhang T, Zou J, Miller CL, Gorkhali R, Yang JY, et al. Structural basis for regulation of human calcium-sensing receptor by magnesium ions and an unexpected tryptophan derivative co-agonist. Sci Adv. (2016) 2:e1600241. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1600241
58. Quinn SJ, Ye CP, Diaz R, Kifor O, Bai M, Vassilev P, et al. The Ca2+-sensing receptor: a target for polyamines. Am J Physiol. (1997) 273:C1315–23. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1997.273.4.C1315
59. Nemeth EF. The search for calcium receptor antagonists (calcilytics). J Mol Endocrinol. (2002) 29:15–21. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0290015
60. Liu LEI, Wang C, Lin YAN, Xi Y, Li H, Shi SA, et al. Suppression of calcium-sensing receptor ameliorates cardiac hypertrophy through inhibition of autophagy. Mol Med Rep. (2016) 14:111–20. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5279
61. Nemeth EF, Steffey ME, Hammerland LG, Hung BC, Van Wagenen BC, DelMar EG, et al. Calcimimetics with potent and selective activity on the parathyroid calcium receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1998) 95:4040–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.7.4040
62. Greenberg HZE, Jahan KS, Shi J, Vanessa Ho WS, and Albert AP. The calcilytics Calhex-231 and NPS 2143 and the calcimimetic Calindol reduce vascular reactivity via inhibition of voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels. Eur J Pharmacol. (2016) 791:659–68. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.10.008
63. Silve C, Petrel C, Leroy C, Bruel H, Mallet E, Rognan D, et al. Delineating a Ca2+ Binding Pocket within the Venus Flytrap Module of the Human Calcium-sensing Receptor. J Biol Chem. (2005) 280:37917–23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506263200
64. Hong S, Zhang X, Zhang X, Liu W, Fu Y, Liu Y, et al. Role of the calcium sensing receptor in cardiomyocyte apoptosis via mitochondrial dynamics in compensatory hypertrophied myocardium of spontaneously hypertensive rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 487:728–33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.04.126
65. Cereghetti GM, Stangherlin A, Martins de Brito O, Chang CR, Blackstone C, Bernardi P, et al. Dephosphorylation by calcineurin regulates translocation of Drp1 to mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2008) 105:15803–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808249105
66. Cereghetti GM, Costa V, and Scorrano L. Inhibition of Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fragmentation and apoptosis by a polypeptide antagonist of calcineurin. Cell Death Differ. (2010) 17:1785–94. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.61
67. Ong SB, Kwek XY, Katwadi K, Hernandez-Resendiz S, Crespo-Avilan GE, Ismail NI, et al. Targeting Mitochondrial Fission Using Mdivi-1 in A Clinically Relevant Large Animal Model of Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Pilot Study. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20(16):3972. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163972
68. Sharp WW, Fang YH, Han M, Zhang HJ, Hong Z, Banathy A, et al. Dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1)-mediated diastolic dysfunction in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: therapeutic benefits of Drp1 inhibition to reduce mitochondrial fission. FASEB J. (2014) 28:316–26. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-226225
69. Lees JG, Greening DW, Rudd DA, Cross J, Rosdah AA, Lai X, et al. Cardiac-targeted delivery of a novel Drp1 inhibitor for acute cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. (2024) 9:100085. doi: 10.1016/j.jmccpl.2024.100085
70. Lu M, Leng B, He X, Zhang Z, Wang H, and Tang F. Calcium Sensing Receptor-Related Pathway Contributes to Cardiac Injury and the Mechanism of Astragaloside IV on Cardioprotection. Front Pharmacol. (2018) 9:1163. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01163
71. Zhang Y, Yin W-h, Yang F, An Y-q, Zhou W, Yu H, et al. VEGF121 como Mediador de Efeitos Cardioprotetores Pós-Hipóxia via CaSR e via da Protease Dependente de Mitocôndria. Arquivos Brasileiros Cardiologia. (2021) 117:476–83. doi: 10.36660/abc.20190902
72. Sun YH, Liu MN, Li H, Shi S, Zhao YJ, Wang R, et al. Calcium-sensing receptor induces rat neonatal ventricular cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2006) 350:942–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.09.142
73. Masuda S, Doi K, Satoh S, Oka T, and Matsuda T. Vascular endothelial growth factor enhances vascularization in microporous small caliber polyurethane grafts. Asaio J. (1997) 43:M530–4.
74. Hong S, Zhang X, Zhang X, Liu W, Fu Y, Liu Y, et al. Role of the calcium sensing receptor in cardiomyocyte apoptosis via mitochondrial dynamics in compensatory hypertrophied myocardium of spontaneously hypertensive rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 487(3):728–33.
75. Levine B and Kroemer G. Biological Functions of Autophagy Genes: A Disease Perspective. Cell. (2019) 176:11–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.048
76. Yu L, Chen Y, and Tooze SA. Autophagy pathway: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Autophagy. (2018) 14:207–15. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1378838
77. La Rovere RM, Roest G, Bultynck G, and Parys JB. Intracellular Ca(2+) signaling and Ca(2+) microdomains in the control of cell survival, apoptosis and autophagy. Cell Calcium. (2016) 60:74–87. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2016.04.005
78. Yuan H, Xu J, Xu X, Gao T, Wang Y, Fan Y, et al. Calhex(231) Alleviates High Glucose-Induced Myocardial Fibrosis via Inhibiting Itch-Ubiquitin Proteasome Pathway in Vitro. Biol Pharm Bull. (2019) 42:1337–44. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b19-00090
79. Bai SZ, Sun J, Wu H, Zhang N, Li HX, Li GW, et al. Decrease in calcium-sensing receptor in the progress of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2012) 95:378–85. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2011.11.007
80. Yuan H, Xu J, Zhu Y, Li L, Wang Q, Yu Y, et al. Activation of calcium−sensing receptor−mediated autophagy in high glucose−induced cardiac fibrosis in vitro. Mol Med Rep. (2020) 22:2021–31. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11277
81. Wang Y, Chen J, Li S, Zhang X, Guo Z, Hu J, et al. Exogenous spermine attenuates rat diabetic cardiomyopathy via suppressing ROS-p53 mediated downregulation of calcium-sensitive receptor. Redox Biol. (2020) 32:101514. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101514
82. Liu L, Wang C, Sun D, Jiang S, Li H, Zhang W, et al. Calhex231 Ameliorates Cardiac Hypertrophy by Inhibiting Cellular Autophagy in Vivo and in Vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2015) 36:1597–612. doi: 10.1159/000430322
83. Teng G, Svystonyuk D, Mewhort HEM, Turnbull JD, Belke DD, Duff HJ, et al. Tetrandrine reverses human cardiac myofibroblast activation and myocardial fibrosis. Am J Physiology-Heart Circulatory Physiol. (2015) 308:H1564–H74. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00126.2015
84. Zhao J, Feng Y, Yan H, Chen Y, Wang J, Chua B, et al. β-arrestin2/miR-155/GSK3β regulates transition of 5′-azacytizine-induced Sca-1-positive cells to cardiomyocytes. J Cell Mol Med. (2014) 18:1562–70. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12339
85. Chi J, Wang L, Zhang X, Fu Y, Liu Y, Chen W, et al. Activation of calcium-sensing receptor-mediated autophagy in angiotensinII-induced cardiac fibrosis in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2018) 497:571–6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.098
86. Kim J-H, Hong S-K, Wu P-K, Richards AL, Jackson WT, and Park J-I. Raf/MEK/ERK can regulate cellular levels of LC3B and SQSTM1/p62 at expression levels. Exp Cell Res. (2014) 327:340–52. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.08.001
87. Wu PK, Hong SK, Veeranki S, Karkhanis M, Starenki D, Plaza JA, et al. A mortalin/HSPA9-mediated switch in tumor-suppressive signaling of Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Mol Cell Biol. (2013) 33:4051–67. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00021-13
88. Guo J, Li HZ, Zhang WH, Wang LC, Wang LN, Zhang L, et al. Increased expression of calcium-sensing receptors induced by ox-LDL amplifies apoptosis of cardiomyocytes during simulated ischaemia–reperfusion. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2010) 37(3):e128–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2010.05345.x
89. Liu W, Zhang X, Zhao M, Zhang X, Chi J, Liu Y, et al. Activation in M1 but not M2 Macrophages Contributes to Cardiac Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction in Rats: a Critical Role of the Calcium Sensing Receptor/NRLP3 Inflammasome. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2015) 35:2483–500. doi: 10.1159/000374048
90. Liu W, Sun J, Guo Y, Liu N, Ding X, Zhang X, et al. Calhex231 ameliorates myocardial fibrosis post myocardial infarction in rats through the autophagy-NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in macrophages. J Cell Mol Med. (2020) 24:13440–53. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15969
91. Nakamura M and Sadoshima J. Mechanisms of physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2018) 15:387–407. doi: 10.1038/s41569-018-0007-y
92. Hunter JJ and Chien KR. Signaling pathways for cardiac hypertrophy and failure. N Engl J Med. (1999) 341:1276–83. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199910213411706
93. Molkentin JD and Dorn GW 2nd. Cytoplasmic signaling pathways that regulate cardiac hypertrophy. Annu Rev Physiol. (2001) 63:391–426. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.63.1.391
94. Lu F-H, Fu S-B, Leng X, Zhang X, Dong S, Zhao Y-J, et al. Role of the Calcium-Sensing Receptor in Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis via the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondrial Death Pathway in Cardiac Hypertrophy and Heart Failure. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2013) 31:728–43. doi: 10.1159/000350091
95. Zhang WH, Fu SB, Lu FH, Wu B, Gong DM, Pan ZW, et al. Involvement of calcium-sensing receptor in ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis in rat cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2006) 347:872–81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.06.176
96. Zhang W-h, Lu F-h, Zhao Y-j, Wang L-n, Tian Y, Pan Z-w, et al. Post-conditioning protects rat cardiomyocytes via PKCϵ-mediated calcium-sensing receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2007) 361:659–64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.07.077
97. Jia C, Chen H, Zhang J, Zhou K, Zhuge Y, Niu C, et al. Role of pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases. Int Immunopharmacology. (2019) 67:311–8. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.12.028
98. Xiao C, Cao S, Li Y, Luo Y, Liu J, Chen Y, et al. Pyroptosis in microbial infectious diseases. Mol Biol Rep. (2023) 51:42. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09078-w
99. Sharma BR and Kanneganti TD. NLRP3 inflammasome in cancer and metabolic diseases. Nat Immunol. (2021) 22:550–9. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00886-5
100. Liu X, Luo P, Zhang W, Zhang S, Yang S, and Hong F. Roles of pyroptosis in atherosclerosis pathogenesis. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 166:115369. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115369
101. Sharma BR and Kanneganti TD. NLRP3 inflammasome in cancer and metabolic diseases. Nat Immunol. (2021) 22(5):550–9.
102. Gao W, Wang X, Zhou Y, Wang X, and Yu Y. Autophagy, ferroptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis in tumor immunotherapy. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2022) 7(1):196. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01046-3
103. Qiu Z, Lei S, Zhao B, Wu Y, Su W, Liu M, et al. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation-Mediated Pyroptosis Aggravates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Diabetic Rats. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2017) 2017:9743280. doi: 10.1155/2017/9743280
104. Lee G-S, Subramanian N, Kim AI, Aksentijevich I, Goldbach-Mansky R, Sacks DB, et al. The calcium-sensing receptor regulates the NLRP3 inflammasome through Ca2+ and cAMP. Nature. (2012) 492:123–7. doi: 10.1038/nature11588
105. Zhu Y, Chi J, Cai S, Liu S, Yuan J, Xu H, et al. High-dose remifentanil exacerbates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through activation of calcium-sensing receptor-mediated pyroptosis. Int J Med Sci. (2023) 20:1570–83. doi: 10.7150/ijms.83207
106. Westermeier F, Riquelme JA, Pavez M, Garrido V, Díaz A, Verdejo HE, et al. New Molecular Insights of Insulin in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Front Physiol. (2016) 7:125. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00125
107. Wang Y, Gao P, Wei C, Li H, Zhang L, Zhao Y, et al. Correction: Calcium sensing receptor protects high glucose-induced energy metabolism disorder via blocking gp78-ubiquitin proteasome pathway. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:784. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02957-1
108. Yuan H, Fan Y, Wang Y, Gao T, Shao Y, Zhao B, et al. Calcium−sensing receptor promotes high glucose−induced myocardial fibrosis via upregulation of the TGF−β1/Smads pathway in cardiac fibroblasts. Mol Med Rep. (2019) 20(2):1093–102. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10330
109. Zhong X, Wang Y, Wu J, Sun A, Yang F, Zheng D, et al. Calcium Sensing Receptor Regulating Smooth Muscle Cells Proliferation Through Initiating Cystathionine-Gamma-Lyase/Hydrogen Sulfide Pathway in Diabetic Rat. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2015) 35:1582–98. doi: 10.1159/000373973
110. Wang Y, Wang X, Liang X, Wu J, Dong S, Li H, et al. Inhibition of hydrogen sulfide on the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells involved in the modulation of calcium sensing receptor in high homocysteine. Exp Cell Res. (2016) 347:184–91. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.08.004
111. Chen KH, Guo X, Ma D, Guo Y, Li Q, Yang D, et al. Dysregulation of HSG triggers vascular proliferative disorders. Nat Cell Biol. (2004) 6:872–83. doi: 10.1038/ncb1161
112. Wen X, Xi Y, Zhang Y, Jiao L, Shi S, Bai S, et al. DR1 activation promotes vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis via up-regulation of CSE/H(2) S pathway in diabetic mice. FASEB J. (2022) 36:e22070. doi: 10.1096/fj.202101455R
113. Lin Q, Cui C, Zhao Y, Geng Y, Gao H, Shao X, et al. Cystathionine γ-Lyase Attenuates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Senescence via Foxm1-Gas1 Pathway to Mediate Arterial Stiffness. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2025) 42:655–71. doi: 10.1089/ars.2024.0602
114. Zhang X, Chen W, Li J, Qi S, Hong S, Wang Y, et al. Involvement of mitochondrial fission in calcium sensing receptor-mediated vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation during hypertension. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2018) 495:454–60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.048
115. Xie X, Zhu T, Chen L, Ding S, Chu H, Wang J, et al. MCPIP1-induced autophagy mediates ischemia/reperfusion injury in endothelial cells via HMGB1 and CaSR. Sci Rep. (2018) 8(1):1735. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20195-6
116. Chen L, Yang G, Zhang X, Wu J, Gu Q, Wei M, et al. Induction of MIF expression by oxidized LDL via activation of NF-kappaB in vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis. (2009) 207:428–33. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.05.021
117. Liu N, Li Y, Chen H, Wei W, An Y, and Zhu G. RNA interference-mediated NOTCH3 knockdown induces phenotype switching of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Int J Clin Exp Med. (2015) 8:12674–84.
118. Wayhs R, Zelinger A, and Raggi P. High coronary artery calcium scores pose an extremely elevated risk for hard events. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2002) 39:225–30. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(01)01737-5
119. Molostvov G, Bland R, and Zehnder D. Expression and role of the calcium-sensing receptor in the blood vessel wall. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. (2009) 10:282–8. doi: 10.2174/138920109787847466
120. Alam MU, Kirton JP, Wilkinson FL, Towers E, Sinha S, Rouhi M, et al. Calcification is associated with loss of functional calcium-sensing receptor in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res. (2009) 81:260–8. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn279
121. Watson KE, Boström K, Ravindranath R, Lam T, Norton B, and Demer LL. TGF-beta 1 and 25-hydroxycholesterol stimulate osteoblast-like vascular cells to calcify. J Clin Invest. (1994) 93:2106–13. doi: 10.1172/JCI117205
122. Nahar-Gohad P, Gohad N, Tsai CC, Bordia R, and Vyavahare N. Rat aortic smooth muscle cells cultured on hydroxyapatite differentiate into osteoblast-like cells via BMP-2-SMAD-5 pathway. Calcif Tissue Int. (2015) 96:359–69. doi: 10.1007/s00223-015-9962-z
123. Guasch G and Fuchs E. Mice in the world of stem cell biology. Nat Genet. (2005) 37:1201–6. doi: 10.1038/ng1667
124. Sun J, He W, Bai S-z, Peng X, Zhang N, Li H-x, et al. The expression of calcium-sensing receptor in mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) and its influence on differentiation of mESC into cardiomyocytes. Differentiation. (2013) 85:32–40. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2012.11.002
125. Leong IL, Tsai TY, Shiao LR, Zhang YM, Wong KL, Chan P, et al. Characterization of Ca(2+)-Sensing Receptor-Mediated Ca(2+) Influx in Microvascular bEND.3 Endothelial Cells. Chin J Physiol. (2021) 64:80–7. doi: 10.4103/cjp.cjp_93_20
126. Bonomini M, Giardinelli A, Morabito C, Di Silvestre S, Di Cesare M, Di Pietro N, et al. Calcimimetic R-568 and its enantiomer S-568 increase nitric oxide release in human endothelial cells. PloS One. (2012) 7:e30682. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030682
127. Smajilovic S, Hansen JL, Christoffersen TE, Lewin E, Sheikh SP, Terwilliger EF, et al. Extracellular calcium sensing in rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2006) 348:1215–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.07.192
128. Molostvov G, Fletcher S, Bland R, and Zehnder D. Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor mediated signalling is involved in human vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2008) 22:413–22. doi: 10.1159/000185484
129. de la Puente-Secades S, Mikolajetz D, Gayrard N, Hermann J, Jankowski V, Bhargava S, et al. Vasoconstriction-inhibiting factor: an endogenous inhibitor of vascular calcification as a calcimimetic of calcium-sensing receptor. Cardiovasc Res. (2025) 121:507–21. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaf016
130. Dai C and Khalil RA. Calcium Signaling Dynamics in Vascular Cells and Their Dysregulation in Vascular Disease. Biomolecules. (2025) 15(6):892. doi: 10.3390/biom15060892
131. Hénaut L, Boudot C, Massy ZA, Lopez-Fernandez I, Dupont S, Mary A, et al. Calcimimetics increase CaSR expression and reduce mineralization in vascular smooth muscle cells: mechanisms of action. Cardiovasc Res. (2014) 101:256–65. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt249
132. Schreckenberg R and Schlüter KD. Calcium sensing receptor expression and signalling in cardiovascular physiology and disease. Vascul Pharmacol. (2018) 4:S1537-1891(17)30323-3. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2018.02.007
133. Zhang L, Cao S, Deng S, Yao G, and Yu T. Ischemic postconditioning and pinacidil suppress calcium overload in anoxia-reoxygenation cardiomyocytes via down-regulation of the calcium-sensing receptor. PeerJ. (2016) 4:e2612. doi: 10.7717/peerj.2612
134. Perreault LR, Daley MC, Watson MC, Rastogi S, Jaiganesh A, Porter EC, et al. Characterization of cardiac fibroblast-extracellular matrix crosstalk across developmental ages provides insight into age-related changes in cardiac repair. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2024) 12:1279932. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1279932
135. Lu ML, Wang J, Sun Y, Li C, Sun TR, Hou XW, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates mechanical stress-induced cardiac injury via calcium sensing receptor-related pathway. J Ginseng Res. (2021) 45:683–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2021.03.006
136. Sundararaman SS and van der Vorst EPC. Calcium-Sensing Receptor (CaSR), Its Impact on Inflammation and the Consequences on Cardiovascular Health. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(5):2478. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052478
137. He YH, He Y, Liao XL, Niu YC, Wang G, Zhao C, et al. The calcium-sensing receptor promotes adipocyte differentiation and adipogenesis through PPARγ pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. (2012) 361:321–8. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-1118-5
138. He Y, Zhang H, Teng J, Huang L, Li Y, and Sun C. Involvement of calcium-sensing receptor in inhibition of lipolysis through intracellular cAMP and calcium pathways in human adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2011) 404:393–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.11.129
139. Zemel MB. Calcium modulation of hypertension and obesity: mechanisms and implications. J Am Coll Nutr. (2001) 20:428S–35S; discussion 40S-42S. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2001.10719180
140. Zemel MB, Shi H, Greer B, Dirienzo D, and Zemel PC. Regulation of adiposity by dietary calcium. FASEB J. (2000) 14:1132–8. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.14.9.1132
141. Sundararaman SS, Peters LJF, Jansen Y, Gencer S, Yan Y, Nazir S, et al. Adipocyte calcium sensing receptor is not involved in visceral adipose tissue inflammation or atherosclerosis development in hyperlipidemic Apoe(-/-) mice. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:10409. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89893-y
142. Adam S, Maas SL, Huchzermeier R, Rakateli L, Abschlag K, Hohl M, et al. The calcium-sensing-receptor (CaSR) in adipocytes contributes to sex-differences in the susceptibility to high fat diet induced obesity and atherosclerosis. EBioMedicine. (2024) 107:105293. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105293
143. Cifuentes M, Fuentes C, Tobar N, Acevedo I, Villalobos E, Hugo E, et al. Calcium sensing receptor activation elevates proinflammatory factor expression in human adipose cells and adipose tissue. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2012) 361:24–30. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.03.006
144. Lastra G, Syed S, Kurukulasuriya LR, Manrique C, and Sowers JR. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension: an update. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. (2014) 43:103–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2013.09.005
145. Riccardi D, Park J, Lee WS, Gamba G, Brown EM, and Hebert SC. Cloning and functional expression of a rat kidney extracellular calcium/polyvalent cation-sensing receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1995) 92:131–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.1.131
146. Quintas LEM, Qu Y-y, Hui J, Wang L-m, Tang N, Zhong H, et al. Reduced Expression of the Extracellular Calcium-Sensing Receptor (CaSR) Is Associated with Activation of the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) to Promote Vascular Remodeling in the Pathogenesis of Essential Hypertension. PloS One. (2016) 11(7):e0157456. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157456
147. Churchill PC. Second messengers in renin secretion. Am J Physiol. (1985) 249:F175–84. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.2.F175
148. Di Mise A, Tamma G, Ranieri M, Centrone M, van den Heuvel L, Mekahli D, et al. Activation of Calcium-Sensing Receptor increases intracellular calcium and decreases cAMP and mTOR in PKD1 deficient cells. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:5704. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23732-5
149. Liu N, Li M, Liu S, Kang J, Chen L, Huang J, et al. Exogenous H(2)S Attenuates Hypertension by Regulating Renin Exocytosis under Hyperglycaemic and Hyperlipidaemic Conditions. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(2):1690. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021690
150. Schepelmann M, Yarova PL, Lopez-Fernandez I, Davies TS, Brennan SC, Edwards PJ, et al. The vascular Ca2+-sensing receptor regulates blood vessel tone and blood pressure. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2016) 310:C193–204. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00248.2015
151. Brozovich FV, Nicholson CJ, Degen CV, Gao YZ, Aggarwal M, and Morgan KG. Mechanisms of Vascular Smooth Muscle Contraction and the Basis for Pharmacologic Treatment of Smooth Muscle Disorders. Pharmacol Rev. (2016) 68:476–532. doi: 10.1124/pr.115.010652
152. Chu H, Qin Z, Ma J, Xie Y, Shi H, Gu J, et al. Calcium-Sensing Receptor (CaSR)-Mediated Intracellular Communication in Cardiovascular Diseases. Cells. (2022) 11(19):3075. doi: 10.3390/cells11193075
153. Yin B, Hou XW, and Lu ML. Astragaloside IV attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via inhibition of calcium-sensing receptor-mediated apoptotic signaling pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2019) 40:599–607. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0082-y
154. Liu CJ, Cheng CW, Tsai YS, and Huang HS. Crosstalk between Renal and Vascular Calcium Signaling: The Link between Nephrolithiasis and Vascular Calcification. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(7):3590. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073590
155. Sun R, Zhang W, Zhong H, Wang L, Tang N, Liu Y, et al. Calcimimetic R568 reduced the blood pressure and improved aortic remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rats by inhibiting local renin-angiotensin system activity. Exp Ther Med. (2018) 16:4089–99. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6734
156. Jiang Y, Xing W, Li Z, Zhao D, Xiu B, Xi Y, et al. The calcium-sensing receptor alleviates endothelial inflammation in atherosclerosis through regulation of integrin β1-NLRP3 inflammasome. FEBS J. (2025) 292:191–205. doi: 10.1111/febs.17308
157. Li N, Si B, Ju JF, Zhu M, You F, Wang D, et al. Nicotine Induces Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy Through TRPC3-Mediated Ca(2+)/NFAT Signalling Pathway. Can J Cardiol. (2016) 32:1260.e1–.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2015.12.015
158. Alesutan I, Tuffaha R, Auer T, Feger M, Pieske B, Lang F, et al. Inhibition of osteo/chondrogenic transformation of vascular smooth muscle cells by MgCl2 via calcium-sensing receptor. J Hypertens. (2017) 35:523–32. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001202
159. Mary A, Objois T, Brazier M, Bennis Y, Boudot C, Lenglet G, et al. Decreased monocyte calcium sensing receptor expression in patients with chronic kidney disease is associated with impaired monocyte ability to reduce vascular calcification. Kidney Int. (2021) 99:1382–91. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.01.026
160. Lu M, Leng B, He X, Zhang Z, Wang H, Tang F, et al. Calcium Sensing Receptor-Related Pathway Contributes to Cardiac Injury and the Mechanism of Astragaloside IV on Cardioprotection. Front Pharmacol. (2018) 9:1163.
161. Romero Y, Balderas-Martínez YI, Vargas-Morales MA, Castillejos-López M, Vázquez-Pérez JA, Calyeca J, et al. Effect of Hypoxia in the Transcriptomic Profile of Lung Fibroblasts from Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cells. (2022) 11(19):3014. doi: 10.3390/cells11193014
162. Block GA, Bushinsky DA, Cheng S, Cunningham J, Dehmel B, Drueke TB, et al. Effect of Etelcalcetide vs Cinacalcet on Serum Parathyroid Hormone in Patients Receiving Hemodialysis With Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama. (2017) 317:156–64. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.19468
163. Wang AY, Lo WK, Cheung SC, Tang TK, Yau YY, and Lang BH. Parathyroidectomy versus oral cinacalcet on cardiovascular parameters in peritoneal dialysis patients with advanced secondary hyperparathyroidism (PROCEED): a randomized trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2023) 38:1823–35. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfad043
164. Goto S, Hamano T, Fujii H, Taniguchi M, Abe M, Nitta K, et al. Hypocalcemia and cardiovascular mortality in cinacalcet users. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2024) 39:637–47. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfad213
165. Moe SM, Wetherill L, Decker BS, Lai D, Abdalla S, Long J, et al. Calcium-Sensing Receptor Genotype and Response to Cinacalcet in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2017) 12:1128–38. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11141016
166. Brown EM. Clinical utility of calcimimetics targeting the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Biochem Pharmacol. (2010) 80:297–307. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.04.002
167. Kapur K, Johnson T, Beckmann ND, Sehmi J, Tanaka T, Kutalik Z, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis for serum calcium identifies significantly associated SNPs near the calcium-sensing receptor (CASR) gene. PloS Genet. (2010) 6:e1001035. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001035
168. Vezzoli G, Terranegra A, Arcidiacono T, Gambaro G, Milanesi L, Mosca E, et al. Calcium kidney stones are associated with a haplotype of the calcium-sensing receptor gene regulatory region. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2010) 25:2245–52. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp760
169. Vezzoli G, Scillitani A, Corbetta S, Terranegra A, Dogliotti E, Guarnieri V, et al. Polymorphisms at the regulatory regions of the CASR gene influence stone risk in primary hyperparathyroidism. Eur J Endocrinol. (2011) 164:421–7. doi: 10.1530/EJE-10-0915
Keywords: CaSR, calcium homeostasis, cardiovascular diseases, apoptosis, autophagy, pyroptosis
Citation: Liu X, Xie T, Qadir J, Li S, Xu T, Lu Y, Ge X and Yuan H (2025) Research progress on cellular behavior of CaSR in cardiovascular diseases. Front. Immunol. 16:1672536. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1672536
Received: 24 July 2025; Accepted: 10 October 2025;
Published: 23 October 2025.
Edited by:
Lucia Natarelli, LMU Munich University Hospital, GermanyReviewed by:
Mengjia Sun, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Command, ChinaZahra Abedi, University Hospital of Munich, Germany
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Xie, Qadir, Li, Xu, Lu, Ge and Yuan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hui Yuan, aHVpeXVhbjE5ODJAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Xinyu Liu
Xinyu Liu Tao Xie
Tao Xie Javeria Qadir
Javeria Qadir Shuang Li1
Shuang Li1 Tianshuang Xu
Tianshuang Xu Hui Yuan
Hui Yuan