- 1Department of Nephrology, Institute of Kidney Diseases, West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 2Nephrology Research Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 3Department of Anesthesiology, Air Force Hospital of Western Theater Command, PLA, Chengdu, China
- 4Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Pain, an unpleasant but essential feeling for life, affects more than 20% of the global population and burdens health and the economy. Due to the lack of understanding of the exact fundamental mechanism, the existing therapeutic strategies for pain offer finite efficacy and troublesome side effects. The intricacy of the pathogenesis of pain enormously hinders the exploitation of therapeutic approaches. Ferroptosis is a novel mode of cell death characterized by mitochondrial damage, oxidative stress, massive intracellular iron accumulation, and lipid peroxidation. Multiple studies have demonstrated that ferroptosis is involved in the development of pain. We aim to focus on the underlying mechanisms by which ferroptosis participates in pain and recent findings on targeted therapies for ferroptosis in painful diseases. In this review, first, the pivotal mechanisms of ferroptosis are briefly summarized. Second, how ferroptosis participates in pain response is described. Finally, we summarized some substances that relieve pain by alleviating lipid peroxidation and iron accumulation and modulating ferroptosis. We propose that targeting ferroptosis holds tremendous promise in preventing and treating painful diseases.
1 Introduction
Pain is a protective response necessary for species survival and a global health problem affecting human life, health, and social development (1). The International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) recently defined pain as unpleasant sensory and emotional experiences related to actual or potential tissue damage or resembling such damage (2). Based on duration, pain can be divided into acute pain (which has survival value and is implicated in healing) and chronic pain (often considered a disease); chronic pain alone affects more than 30% of the global population, placing an enormous economic burden on individuals and society (3, 4). Pain varies widely in quality, intensity, duration, pathophysiologic mechanisms, and meanings; however, all are signaled by precise receptors and a system of fibers that extend from the periphery to the brain, alarming tissue injury (2, 5). Drugs and strategies for pain treatment are diverse, but some problems remain that need to be addressed in the field, such as the limited number of existing analgesics, poor analgesic efficacy, adverse reactions and social harms of therapeutics, and lack of original innovation in pain research mechanisms (6, 7). Optimizing the therapeutic effect of drugs and exploring the new mechanism of pain to find a new analgesic program has become an expectant problem in the clinical treatment of pain.
Ferroptosis, a unique form of oxidation and iron-driven programmed cell death, has been demonstrated to participate in various types of pain (8–10). Because it usually does not exhibit alterations in nuclear morphology or caspase-3 activity and is primarily uninhibited by caspase suppressors, ferroptosis is easily distinguished from other types of cell death, such as necrotic necroptosis, apoptosis, and autophagy (11, 12). Mitochondrial contraction, membrane concentration, and crista reduction or vanishment are generally considered to be ultrastructural signs of ferroptosis (13). Initially, Dixon et al. discovered that ferroptosis mainly involves three metabolic substances, including thiols, lipids, and iron, which produce iron-dependent lipid peroxides and ultimately cause cell death (12, 14). When ferroptosis occurs, transferrin increases iron intake through transferrin receptors; subsequently, excess iron generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) and activates iron-containing enzymes, causing lipid peroxidation, ultimately resulting in oxidative membrane damage (5). Some bioactive molecules regulate ferroptosis by directly or indirectly influencing iron metabolism and lipid peroxidation, such as glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), nuclear factor E2 associated factor 2 (NRF2), heat shock protein beta-1(HSPB1), NADPH oxidase (NOX), p53, etc. (8, 13, 15). Studies have highlighted that ferroptosis is involved in the occurrence and development of numerous diseases, including neurological diseases, systemic inflammatory autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and so on (16–18). In addition, recent studies have found ferroptosis is also associated with pain, as Guo et al. injected ferroptosis inhibitors into the rats’ peritoneum, attenuating their chronic sciatic nerve pain (19). In bone cancer pain (BCP) mice, the ferroptosis inhibitor (ferrostatin-1, Fer-1) hindered iron accumulation, reduced GPX4 activity, and alleviated BCP-induced lipid peroxidation (8).
Over the past few years, numerous studies on the correlation between pain and ferroptosis have exploded, making the mechanisms involved increasingly clear. This review will present the latest research progress between ferroptosis and pain in recent years, exploring pivotal findings and open questions to design more efficacious therapeutic approaches for pain.
2 Mechanisms of ferroptosis
2.1 Lipid peroxidation
Lipid peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in cell membranes is a crucial feature of ferroptosis (20). PUFAs are the major targets of peroxidation, especially arachidonic acid and epinephrine (20, 21). Lipid peroxidation involves a series of multifaceted events, including initiating reactive oxygen species, propagating chain and chain-branched reactions, and terminating free radical reactions (16). As essential substrates of lipid metabolism, PUFAs experience esterification into membrane phospholipids and oxidation, ultimately promoting the transmission of ferroptosis signals (Figure 1) (22–24). In addition, Acyl-CoA synthase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4) catalyzes PUFAs to bind CoA to form PUFA-CoA, which is further inserted into membrane phospholipids (PLs) under the action of lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3 (LPCAT3) to form PUFA-PL (25, 26). Large amounts of PUFAs oxidize and lipify to produce phospholipid hydroperoxides (PL-PUFA-OOH) and ROS, predisposing the cells to ferroptosis (16, 27). Continuous lipid peroxidation causes a breakdown of membrane integrity, eventually leading to the plasma membrane fracture (27).
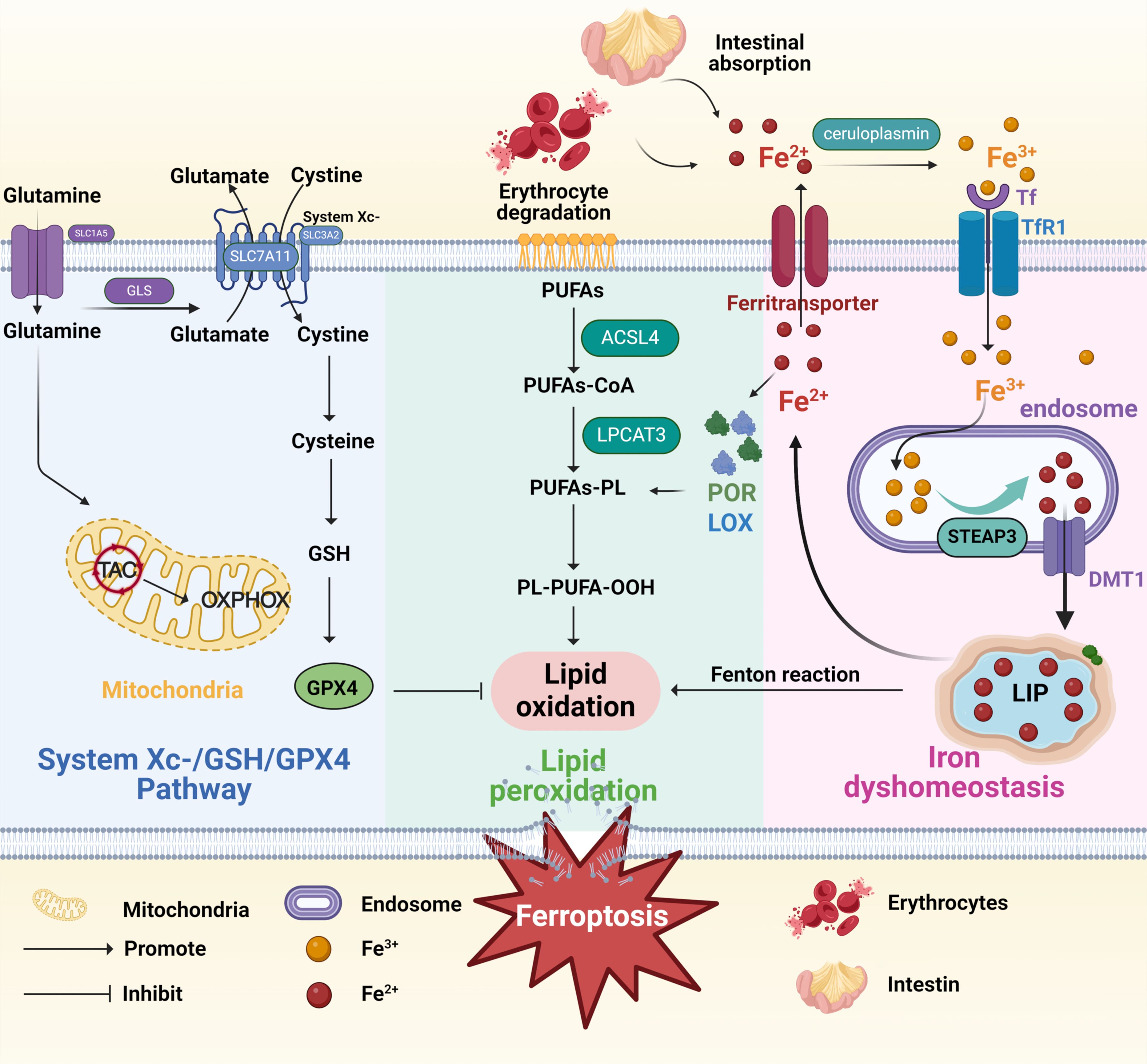
Figure 1. Mechanisms of ferroptosis. The figure shows mechanisms of ferroptosis induced by three pathways, including System Xc-/GSH/GPX4 Pathway (the blue box), lipid peroxidation (the green box), and iron dyshomeostasis (the pink box). The System Xc-/GSH/GPX4 Pathway: Cystine enters the cell through the system Xc- and is then converted into cysteine to promote GSH synthesis and ultimately inhibit ferroptosis. The lipid peroxidation: ACSL4 catalyzes PUFAs to bind CoA to form PUFA-CoA, which is further inserted into membrane PLs under the action of LPCAT3 to form PUFA-PL. Large amounts of PUFAs oxidize and lipify to produce PL-PUFA-OOH and ROS, predisposing the cells to ferroptosis. The iron dyshomeostasis: Ceruloplasmin oxidizes Fe2+ to Fe3+, which binds to Tf and endocytoses into cells through the action of TfR1. After the release from Tf, Fe3+ is reduced to Fe2+ through STEAP3 and transferred from the endosome/lysosome to the cytosol via apical DMT1. The iron present in the cytoplasm can be stored by ferritin as iron ions or in the transient LIP to eliminate cytotoxicity; on the other hand, it can be transported outside the cell by ferritransporters. TAC, tricarboxylic acid cycle; GLS, glutaminase; OXPHOX, oxidative phosphorylation; GSH, glutathione; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; ACSL4, Acyl-CoA synthase long-chain family member 4; PLs, phospholipids; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; PL-PUFA-OOH, phospholipid hydroperoxides; Tf, transferrin; TfR1, transferrin receptor 1; STEAP3, six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostatic 3; DMT1, divalent metal transporter 1; LIP, labile iron pool. Created in BioRender.
2.2 Iron dyshomeostasis
Iron is a significant material basis for metabolic processes, including mitochondrial respiration, DNA synthesis, and cell signaling, but ferroptosis may occur when it accumulates excessively (28). Iron is present in the body’s local microenvironment in two forms: ferrous (Fe2+) and ferric (Fe3+) ions (Figure 1) (29). Fe2+, primarily generated from erythrocyte degradation and intestinal absorption, can enhance ROS production through the Fenton reaction, thus facilitating lipid peroxidation (30). In vivo, free Fe2+ enhances the activity of lipoxygenase (LOX) and cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase (POR), enzymes that catalyze polyunsaturated fatty acid-containing phospholipids (PUFA-PLs) oxidation, thereby affecting lipid peroxidation (14). In addition, ceruloplasmin oxidizes Fe2+ to Fe3+, which binds to transferrin (Tf) and endocytosis into cells through the action of transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1) (31). After the release from Tf, Fe3+ is reduced to Fe2+ through six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostatic 3 (STEAP3) and transferred from endosome/lysosome to the cytosol via apical bivalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) (32). The iron present in the cytoplasm can be transported to the corresponding site to play its role. On the one hand, it can be stored by ferritin as iron ions or in the transient labile iron pool (LIP) to eliminate cytotoxicity; on the other hand, it can be transported outside the cell by ferritransporters (33). Overall, free intracellular iron exceeding a certain level triggers ferroptosis. Excess iron in cells increases the level of Fe2+, thus promoting lipid peroxidation through the Fenton reaction, and the heightened ROS eventually induces ferroptosis (34).
2.3 System Xc-/GSH/GPX4 pathway
Glutathione (GSH), which mainly includes cysteine, glutamic acid, and glycine, is a vital inhibitor and endogenous antioxidant in ferroptosis (35). In the body, an appropriate amount of GSH can effectively offset the increased ROS, thus acting as an elementary defense mechanism to protect cells from various forms of oxidative stress (OS) (36). Once the GSH-dependent lipid peroxide repair systems are damaged, ROS accumulate within the body, promoting ferroptosis (16, 27). Cystine-glutamate antiporter (System Xc−), a disulfide-linked heterodimer consisting of two subunits, SLC3A2 (the regulatory subunit 4F2hc) and SLC7A11 (the transporter subunit xCT) (Figure 1) (37, 38). xCT transits one cystine into the cell and one glutamate out of the cell, while 4F2hc stabilizes the xCT and assists in its subcellular localization (39, 40). Once cystine enters the cytoplasm, it is rapidly transformed into cysteine, an essential step for GSH production (16). Therefore, xCT regulates the production of GSH and, together with GSH, protects cells from oxidative damage. GPX4, the only member of the selenium-dependent glutathione peroxidase family, uses GSH as cofactors to convert toxic lipid peroxides on phospholipid membranes to nontoxic lipid alcohols (41, 42). GSH depletion can directly or indirectly result in the decrease of GPX4 activity and then induce ferroptosis (43). Unlike GSH, RSL3 (the first discovered ferroptotic compounds) and wathaferin A directly mediate GPX4’s inactivation or depletion (44).
3 Correlation between ferroptosis and pain
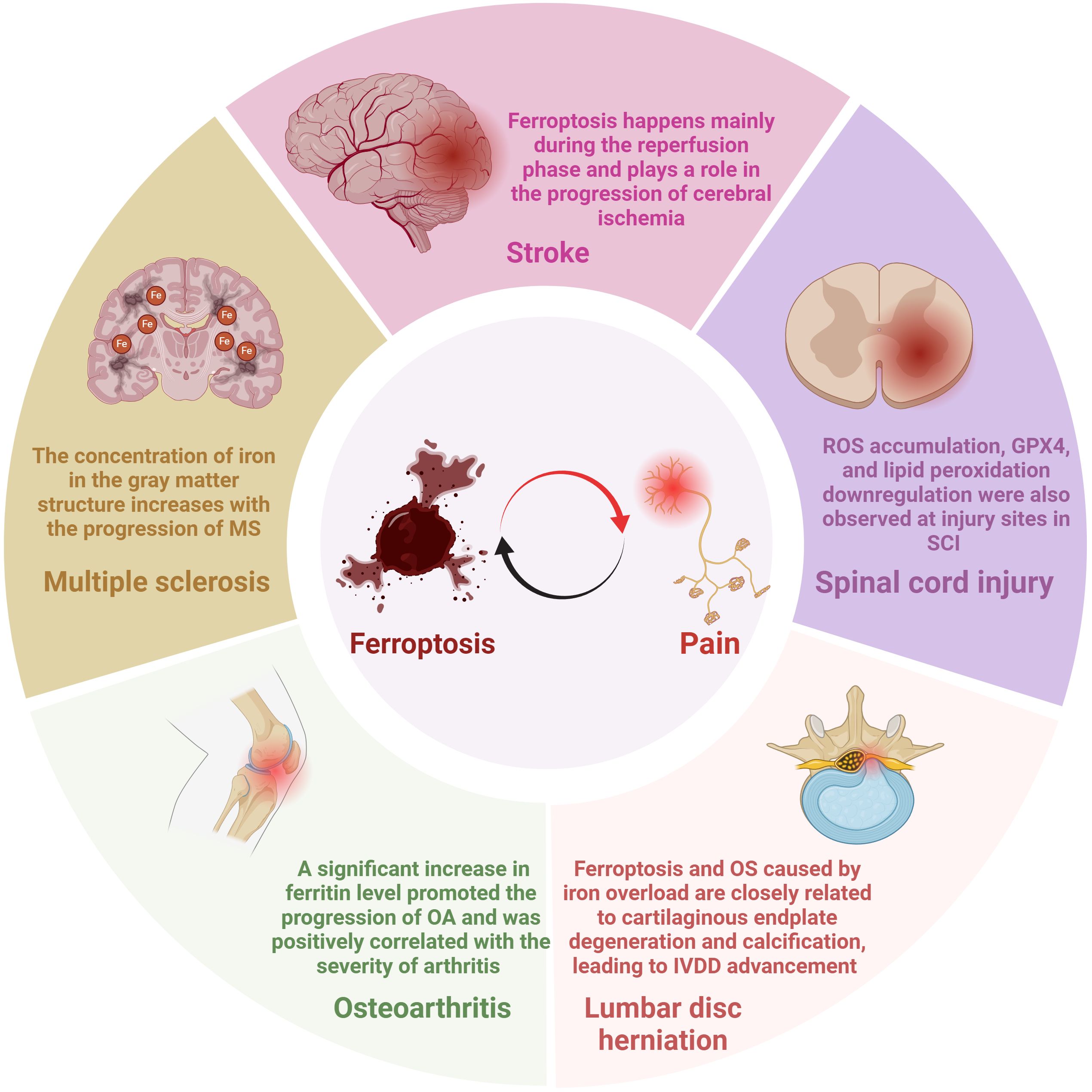
Previous studies have demonstrated the relationship between ferroptosis and neuropathic pain (NP) and bone pain (BP) (Figure 2) (8–10, 19). Unfortunately, the exact mechanism by which ferroptosis functions in these pains has not yet been fully established. NP, a type of chronic pain, is directly caused by trauma or disease involving the somatosensory system (45). A persuasive NP-causing factor is neuronal apoptosis or damage mediated by peripheral nerve or spinal cord injury (46). Some researchers believe that elevated iron ions in neurons of the damaged nervous system increase the risk of ferroptosis (46). Increased ROS levels during ferroptosis destroy the integrity of the cell membrane (47). Does the ROS produced by ferroptosis damage the cell membrane of nerve cells? It has been shown that elevated ROS-related oxidation activity is correlated with NP and plays a vital role in NP processes (48). Intracellular ROS activation may generate cell death, including in spinal dorsal horn neurons, presumably a crucial reason for ROS involvement in NP (45, 49). In the rat model of chronic contractile injury (CCI), ferroptosis was found to block neuron and astrocyte activation in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord to participate in the occurrence of NP (46). Similarly, Ding et al. found hallmarks of ferroptosis in the spinal dorsal horn of BCP mice, including mitochondrial morphological changes, iron accumulation, and lipid peroxidation (8). Therefore, ferroptosis is thought to participate in the development and maintenance of NP by blocking the activity of spinal dorsal horn neurons and astrocytes (46). These results all prove that ferroptosis is associated with the development of pain.
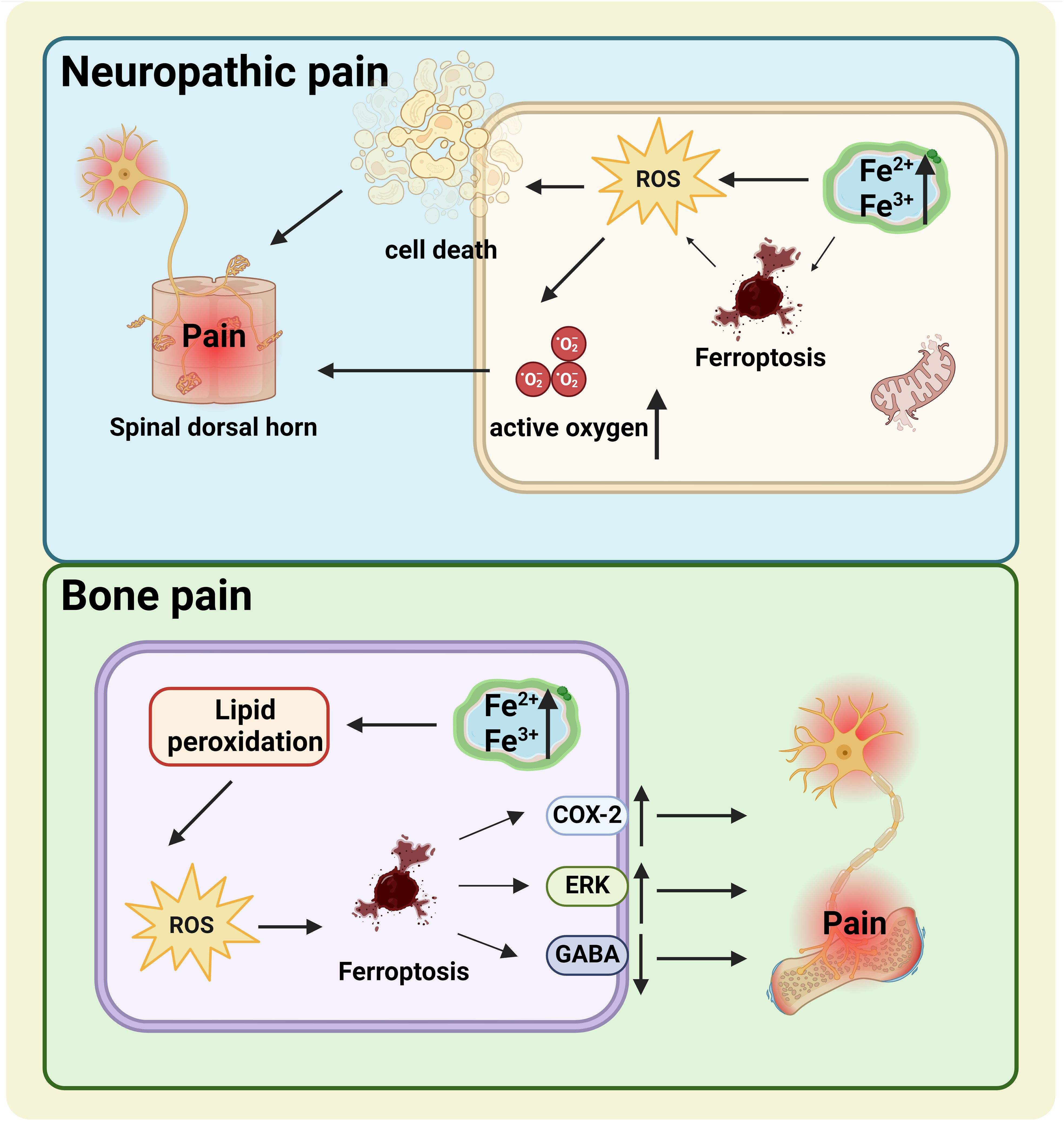
Figure 2. The relationship between ferroptosis and NP (the blue box) and BP (the green box). NP, Elevated iron ions in neurons of the damaged nervous system increase the risk of ferroptosis. Increased ROS levels during ferroptosis destroy the integrity of the cell membrane and cause NP. BP, The upregulation of COX-2 and ERK and the downregulation of GABA caused by cell ferroptosis may be important mechanisms of BP. NP, neuropathic pain; BP, bone pain; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
Analogously, increased iron levels were detected in the spinal cords of BCP mice (8). BCP, manifested as spontaneous persistent pain, may develop due to the destruction of dorsal horn neurons in the spinal cord (50, 51). One possible reason is decreased production of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (52). In other words, when GABAergic neurons are lost in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, pain behavior increases. GABAergic inhibitory interneurons have high energy demands and are especially vulnerable to OS, hypoxia, and glutamate accumulation (53, 54). Multiple studies have suggested that OS may be responsible for reducing GABaergic neurons in kinds of neurological diseases (8). Coincidentally, ferroptosis is driven by the excessive ROS caused by lipid peroxidation, which is closely related to OS (55). Lipid peroxidation and OS conduce to continuous chronic pain (8, 46, 56). The buildup of lipid ROS is primarily attributed to the disappearance of the GPX4 effect (57). GPX4 levels can be directly or indirectly affected by other compounds involving a variety of pathways, of which the extracellular regulated protein kinases (ERK) pathway is closely associated with neural cell ferroptosis (8, 58). Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), a biomarker for ferroptosis, is a crucial derivable polypeptide mediating pain and inflammation (59, 60). Research has confirmed that COX-2 and p-ERK1/2 levels were significantly increased in BCP mice (8). Thus, the idea that ferroptosis is associated with pain-related COX-2 activation and ERK pathways in BCP is scientific and rigorous. Ferroptosis is a feasible therapeutic target for patients with chronic pain. A deeper exploration of the fundamental mechanisms involved is crucial to developing effective pain treatments.
4 Ferroptosis and pain-related illness
4.1 Neuropathic pain-related diseases
4.1.1 Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS), a chronic inflammatory and demyelinating disease with the most common and severe symptoms of NP and spasticity, affects approximately 2.1 million people worldwide (61–63). As early as fifteen years ago, brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans displayed that the concentration of iron in the gray matter structure increases with the progression of MS (Figure 3) (64). In recent years, the idea of ferroptosis participants in the MS process has been repeatedly mentioned and increasingly accepted (65, 66). Hu et al. observed in an MS animal model that mRNA levels of all three GPX4 isoforms (cytoplasmic, mitochondrial, and nuclear) decreased in the MS gray matter (Figure 4) (65). To further support the hypothesis, the research found that other biomarkers involved in ferroptosis, such as system Xc and GSH, were also significantly reduced in this animal model (63, 65). In addition, a clinical trial study on MS has shown that iron chelators can delay the disease progression (67). At different stages of MS, ferroptosis affects its development through diverse mechanisms. In the early stages of MS, ferroptosis interacts with multiple cell types, including macrophages and microglia, resulting in cellular oxidative damage and cytotoxicity (68). Microglia, as the primary iron-handling cells in the central nervous system, demonstrate exceptional capacity for iron accumulation and storage. Iron overload can cause inflammatory phenotype of microglia, resulting in the production of proinflammatory cytokines and contributing to neurodegeneration (69). With the progression of MS, the dysregulation of the SystemXc-GSH-GPX4 pathway, which affects oligodendrocyte death and demyelination, has become a more critical factor impacting MS (70). In summary, ferroptosis functions in MS regulation and has excellent potential as a therapeutic target.
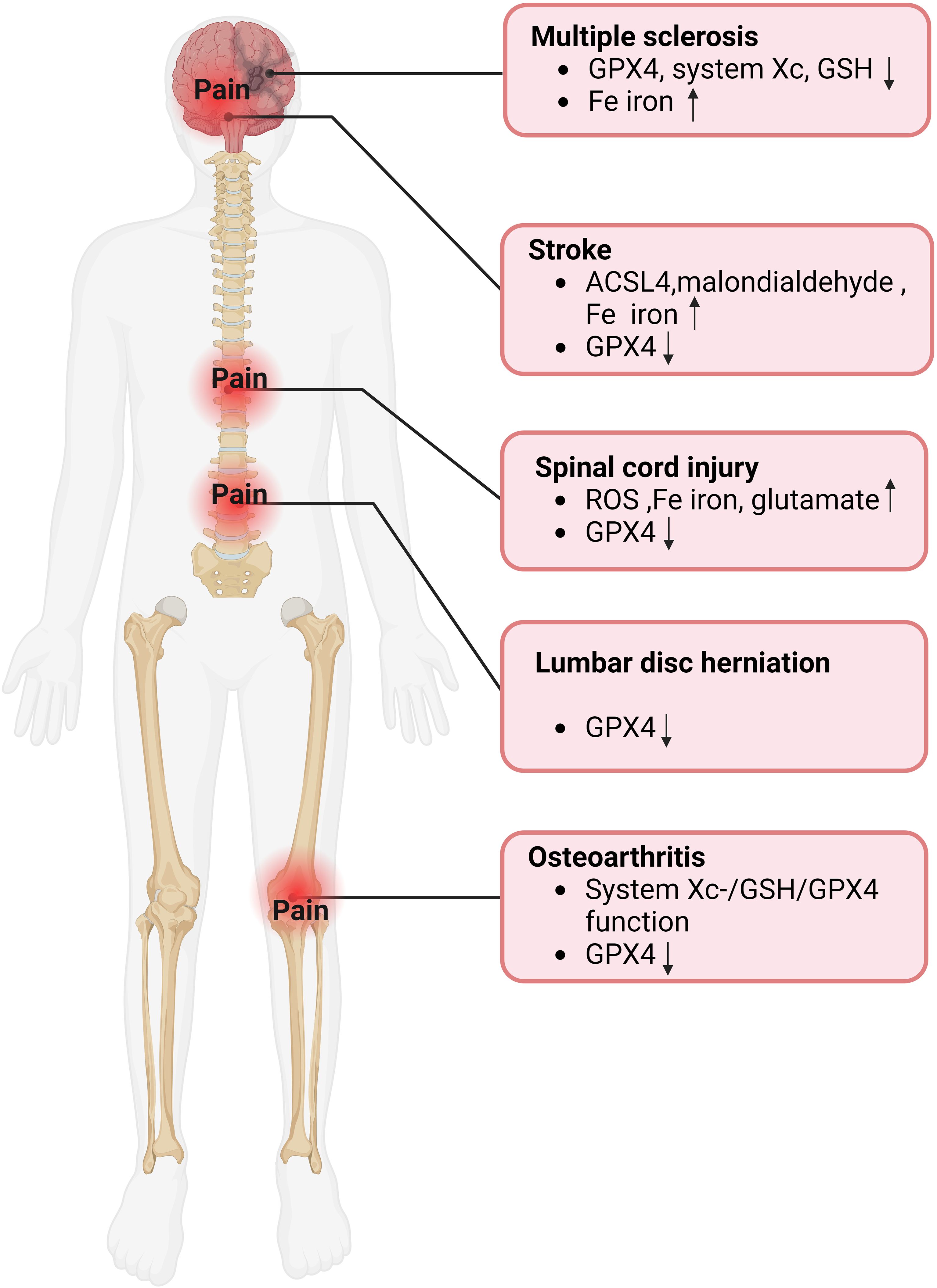
Figure 4. Evidence of ferroptosis in pain-related diseases. GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GSH, Glutathione; ACSL4, Acyl-CoA synthase long-chain family member 4; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
4.1.2 Stroke
The number of new strokes each year is enormous, with about 12 million in 2019, and about 11% of stroke patients develop central post-stroke pain (CPSP) (71, 72). CPSP, a disabling and intractable NP syndrome, is the most frequent form of central NP all over the world (73–75). Ischemic stroke (IS), which accounts for more than 80% of all stroke events, is modulated by ferroptosis (76, 77). Cerebral blood flow obstruction is the primary pathological mechanism of IS, while brain damage persists and continues to progress during reperfusion (78, 79). Interestingly, studies have indicated that ferroptosis happens mainly during the reperfusion phase and plays a role in the progression of cerebral ischemia (Figure 3) (80). Specifically, with the extension of reperfusion time, ACSL4 level, iron content, and malondialdehyde level gradually increased, while GPX4 level decreased, but all the above indexes did not change significantly during ischemia (Figure 4) (81). Ischemia reduces the supply of oxygen and nutrients to brain tissue, triggering OS and inflammation, directly or indirectly influencing metal ion metabolism, including iron ions (82, 83). Due to the destruction of the blood-brain barrier and increased vascular permeability, iron content in the brain tissue of stroke patients is significantly increased, especially around the infarction (83, 84). In addition, serum iron levels are associated with an increased risk of IS and a lousy outcome (79, 85). Although ferroptosis is involved in secondary brain injury associated with IS, the current understanding of its role in IS is still limited, and its underlying pathological mechanisms remain to be elucidated.
4.1.3 Spinal cord injury
Spinal cord injuries (SCI) often contribute to widespread sensorimotor and autonomic nerve damage, affecting about 2.5 million people worldwide (86, 87). Chronic pain is an ordinary complication after SCI, accounting for about 61% of all patients, while NP is considered the most severe pain post-SCI, with an estimated prevalence of 53% reported (88, 89). The molecular mechanism of SCI remains not entirely explicit, so there is no effective therapy for SCI in the clinic (87). It has been verified that ferroptosis is involved in the pathophysiological process of SCI, mainly manifested as ROS increased, iron overload, glutamate, and lipid peroxidation accumulation related to ferroptosis in SCI (Figure 4) (90). The concentration of iron in the spinal cord tissue of SCI rats was significantly increased for more than a week, and mitochondrial morphological characteristics of ferroptosis were observed (91). In addition, ROS accumulation, GPX4, and lipid peroxidation downregulation were also observed at injury sites in SCI mouse models (Figure 3) (92). Evidence of the involvement of ferroptosis in SCI appeared not only in the spinal cord of animal models but also in the significant increase in iron deposition and iron-induced lipid ROS accumulation detected in the intracranial motor cortex of SCI rats (93). Neurons and oligodendrocytes are the main types of nerve cells involved in ferroptosis (94, 95). Ferroptosis of neurons leads to structural atrophy of neurons in the motor cortex accompanied by the death of corresponding axons (93, 94). This ultimately shortens the number of neurons in the motor cortex, a crucial reason for the problematic restoration of function in patients with SCI (93, 94). Notably, pain’s activity-dependent sensitization occurs in peripheral receptors, neurons, and glial cells (96). The overlap of action sites further proves a strong link between pain and ferroptosis. Similar to the previous two diseases, extensive literature has proved that ferroptosis is closely related to SCI. However, there is no sufficient specific explanation of its involvement in the pathological process of SCI and the possible problems in the clinical conversion of ferroptosis inhibitors.
4.2 Bone pain-related diseases
4.2.1 Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA), an intricate and heterogeneous disease affecting multiple joints, causes chronic pain and permanent damage to the body’s joints (97, 98). The prevalence of OA continues to rise, affecting an estimated 303 million adults worldwide (99). Despite the high prevalence of OA, the mechanisms of OA-related pain are still not fully understood, so prescription drugs suggested by international guidelines for OA management can only relieve the pain for symptoms (99–101). A significant increase in ferritin level promoted the progression of OA and was positively correlated with the severity of arthritis (Figure 3) (102, 103). The joint synovium and subchondral bone are the main sites of origin for OA-related pain (99). When these areas are subjected to harmful mechanical, chemical, and other stimuli, these harmful inputs are converted into electrical signals that travel along the spinal cord’s dorsal root ganglion and dorsal horn to the brain, causing pain (99). Zhang et al. demonstrated the critical role of chondrocyte ferroptosis in the development of OA for the first time (104). Ferroptosis in chondrocytes increased the expression of matrix-degrading enzymes but decreased collagen II expression (99). Collagen II constitutes the extracellular matrix (ECM), which, together with chondrocytes, is the main component of articular cartilage (105). The System Xc-/GSH/GPX4 pathway is critical in the pathogenesis of chondrocyte ferroptosis. Researchers discovered ferroptosis-related morphological alterations, including mitochondrial contraction and mitochondrial membrane thickening in cartilage samples from OA patients (106). In addition, GPX4 protein expression was markedly decreased in the cartilage tissue of the OA mouse model (Figure 4) (106). In the progression of OA, GPX4, on the one hand, regulates ferroptosis or OS in chondrocytes and, on the other hand, promotes ECM degradation via the MAPK/NF-KB signaling pathway (107).
4.2.2 Lumbar disc herniation
A common reason for chronic low back pain is lumbar disc herniation, which influences 70-85% of the global population (108). One of the leading causes of lumbar disc herniation is intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD), which can be triggered by the OS of nucleus pulposus cells and degeneration of cartilage endplates (109, 110). Interestingly, recent research proposes that ferroptosis may also be innegligible in this process (111). The specific manifestations were down-regulated GPX4 expression in disc tissue of patients with disc degeneration (Figure 4) (112). In addition, morphological features of ferroptosis, such as dense and shrunken mitochondria, were observed in in vitro cell models of IVDD, and ferroptosis inhibitors could reverse these effects (112). Like articular cartilage, chondrocytes are also the principal cells of the cartilage endplate, which transport nutrients to the intervertebral disc (113). Studies have indicated that ferroptosis and OS caused by iron overload are closely related to cartilaginous endplate degeneration and calcification, leading to IVDD advancement (Figure 3) (114, 115). It is worth noting that although most studies have not observed the presence of iron deposition in the nucleus pulposus, since iron deposition in the human body is a long process, focusing on iron’s role in the nucleus pulposus may benefit patients (113). The studies mentioned above have validated the link between disc degeneration and ferroptosis, and more research should focus on the specific mechanisms involved.
In addition, emerging evidence implicates ferroptosis functions in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteosarcoma pathogenesis, both of which can manifest clinically as significant bone pain (116, 117). Ferroptosis contributes to articular cartilage destruction in RA, and Yang et al. developed a hydrogel-based therapeutic strategy that protects chondrocytes from ferroptosis (117). What is particularly noteworthy is that ferroptosis compromises the survival ability of osteosarcoma cells, and inducing ferroptosis significantly increases their sensitivity to cisplatin (116, 118).
Much of the specific mechanism that ferroptosis participates in pain-related diseases has not been fully elucidated. Exploring the mechanisms involved could be a promising way to develop new methods for ferroptosis in painful diseases.
5 New methods for pain-related illness treatment based on ferroptosis
As the link between ferroptosis and pain is widely revealed, researchers are pyramidally concentrating on seeking novel means of pain treatment based on ferroptosis, aiming to explore more potential targets for pain easement (Table 1).
5.1 Neuropathic pain-related diseases
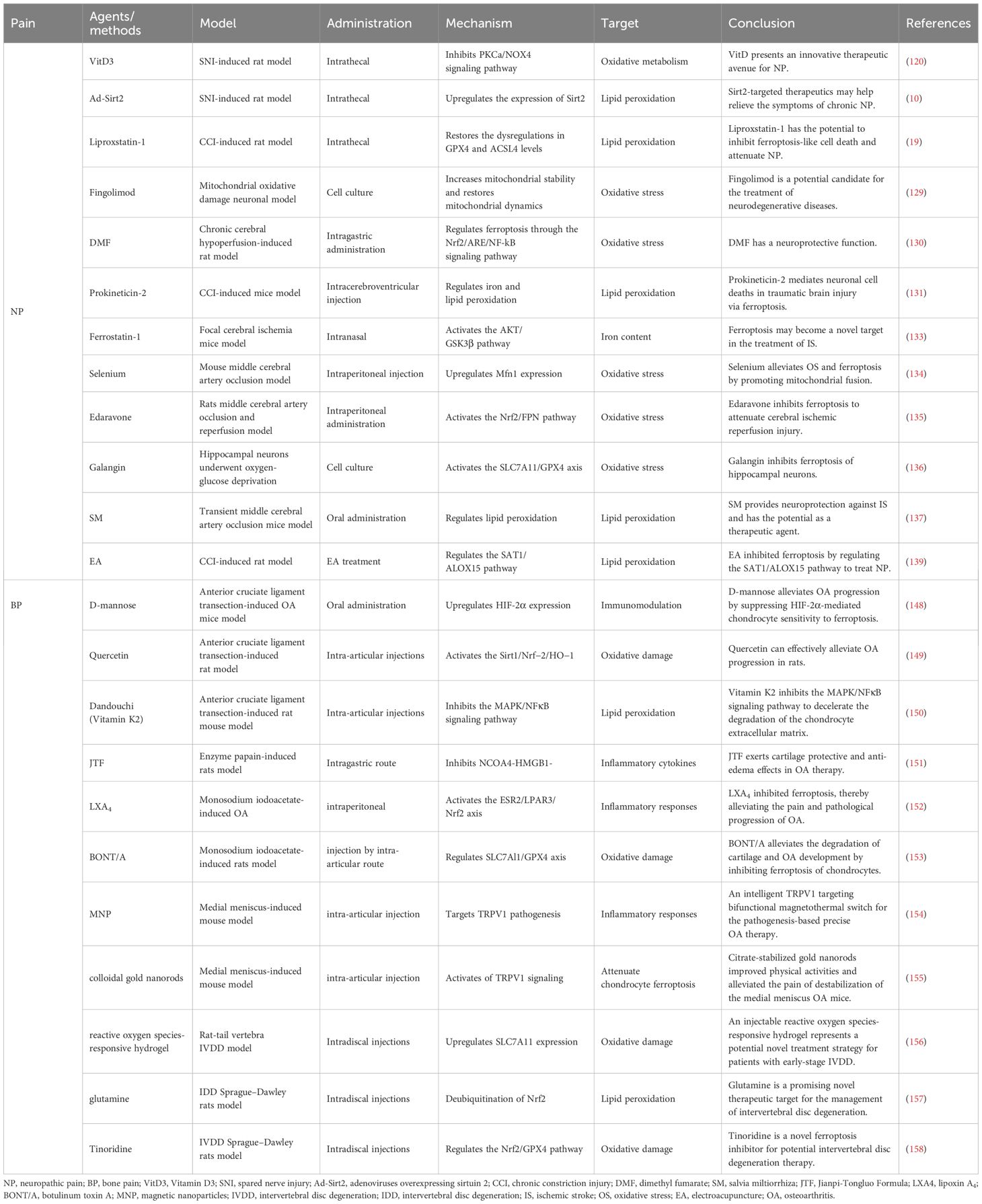
In the laboratory, Vitamin D has been found to serve as an alternative treatment for NP, involving mechanisms that may be associated with ferroptosis (119, 120). VitD3 relieves NP by inhibiting mitochondria-associated ferroptosis mediated by PKCα/NOX4 signaling, preserving spinal GABaergic interneurons (Figure 5) (120). Used alone or in combination with existing analgesics, VitD offers an innovative treatment avenue for NP. In addition, Zhang et al. injected adenoviruses overexpressing Sirtuin 2 (Ad-Sirt2, which can regulate OS and inhibit ferroptosis) into rats to reduce iron accumulation, suppress lipid peroxidation, affect the expression of ACSL4 and GPX4, and thus alleviate chronic NP of rats (10, 121, 122). In a recent study, intraperitoneal injection of liproxstatin-1 (Lip-1, a ferroptosis inhibitor) in rats reduced iron content and lipid peroxidation in spinal cord tissue, alleviating CCI-induced mechanical and thermal nociceptive abnormalities (Table 1) (19). It was further found that intrathecal injection of Lip-1 efficiently reversed the rats’ mechanical nociceptive abnormalities and significantly relieved pain in a dose-dependent manner (45).
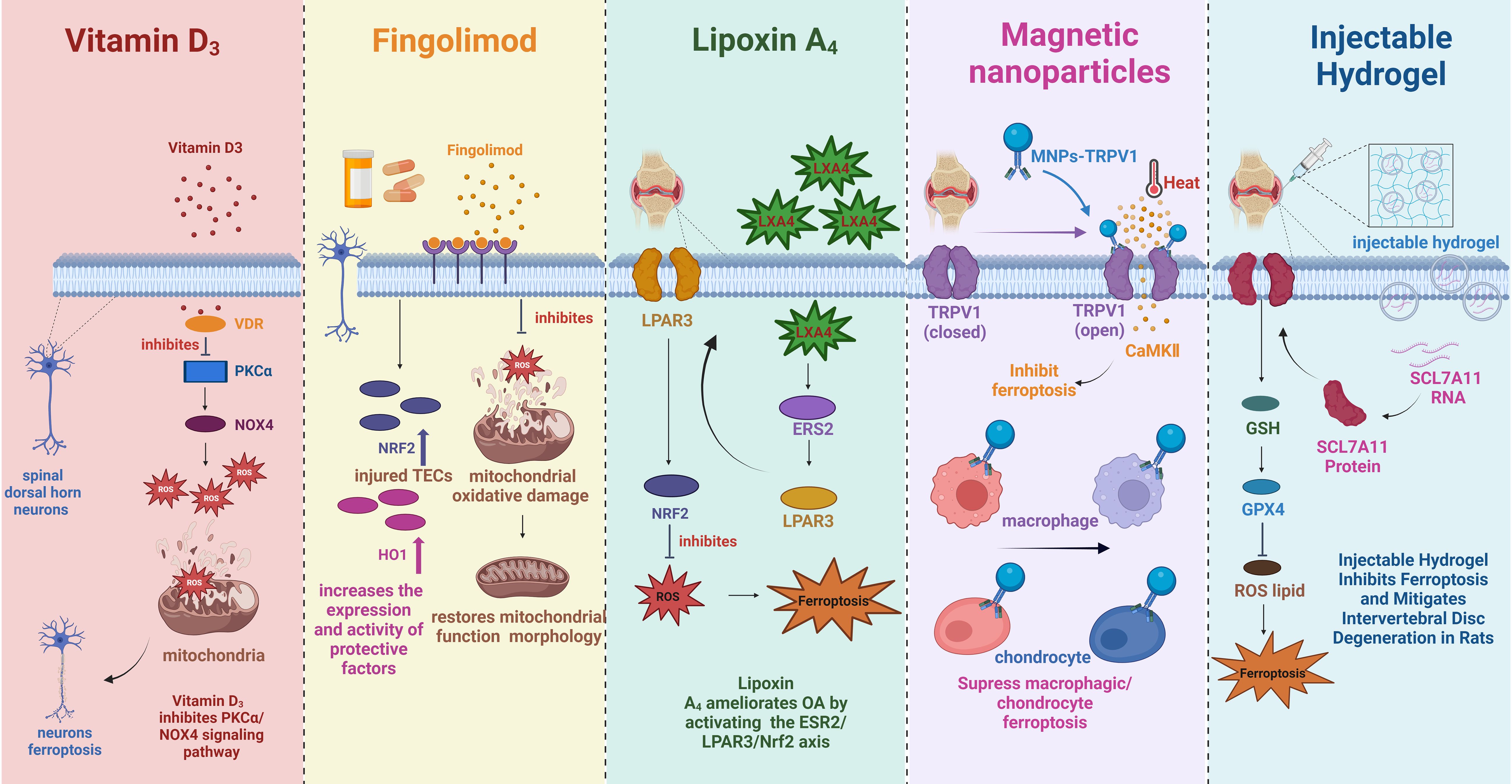
Figure 5. The mechanism of multiple substances to treat pain-related diseases by inhibiting ferroptosis. VDR, vitamin D receptor; PKCα, protein kinase C alpha; ROS, reactive oxygen species; NOX4, NADPH oxidase 4, Nrf2, nuclear factor E2 associated factor 2; HO1, heme oxygenase-1; LXA4, lipoxA4; LPAR3, lysophosphatidic acid receptor-3; ERS2, estrogen receptor beta; TRPV1, transient acceptor potential vanillic acid 1; MNPs, Magnetic nanoparticles; CaMKII, calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; GSH, glutathione; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4.
In clinical treatment, the most ordinary drug used to treat MS is glucocorticoids (GC) (123). Although rare articles directly clarify the link between GC and ferroptosis, studies have confirmed that prolonged or excessive use of GC induces mitochondrial dysfunction, resulting in increased ROS levels and decreased GSH production (124–126). In addition, other drugs used to treat MS, such as fingolimod, teriflunomide, and dimethyl fumarate, may affect the ferroptosis process to varying degrees (127). All three drugs affect OS and thus regulate the ferroptosis process. Fingolimod and teriflunomide play an antioxidant role by regulating mitochondrial OS (Figure 5); meanwhile, fingolimod also reduces iron deposition (128, 129). Unlike the above two drugs, dimethyl fumarate is protective in regulating ferroptosis through the Nrf2/ARE/nuclear faction-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway (130). Similarly, inhibiting ferroptosis is also expected to improve the prognosis of SCI, focusing on targeting obstruction of lipid peroxidation and iron overload (94). Lip-1, prokineticin-2, lipoxin A4 (Figure 5) and NRF2 alleviate SCI by affecting lipid peroxidation processes through different mechanisms (94). For example, Lipro-1 inhibits mitochondrial lipid peroxidation, while prokineticin-2 restrains lipid peroxidation substrate synthesis, ultimately impeding lipid peroxidation (131, 132). On the other hand, iron overload is mainly treated by up-regulating ferroportin 1 and using deferoxamine (an iron chelating agent) or dynasore (a dynamin protein inhibitor) (94). Other substances that target ferroptosis for IS include natural materials (salvia miltiorrhiza, galangin, etc), drugs (edaravone, dimethyl fumarate, etc), trace elements (selenium), and synthetic substances (Fer-1) (Table 1) (130, 133–137). Most of them affect ferroptosis by acting on NRF2, GPX4, and ACSL4, thereby treating IS. In addition to medications, electroacupuncture (EA), a pain management method, inhibits ferroptosis by regulating OS and iron-related proteins, thereby relieving NP as well as symptoms associated with ferroptosis in the dorsal root ganglion (138, 139).
5.2 Bone pain-related diseases
Targeted ferroptosis for OA treatment principally focuses on reducing iron levels, and iron chelators, including deferoxamine (DFO), deferasirox (DFX), and deferiprone (DFP) have been used clinically (111, 140). The three iron chelators are used in different ways, except for DFO, administered intravenously or subcutaneously; DFX and DFP are oral formulations, and they all have been shown to chelate iron effectively and have a good safety profile (141–144). In fact, iron chelation therapy is more commonly used to treat patients with osteopenia or osteoporosis because iron chelation restrains osteoclast production and bone resorption (145, 146). Given that osteoclastogenesis of subchondral bone has been identified as a critical disruptive factor in the development and progression of OA, iron chelators hold great therapeutic promise in ferroptosis-induced OA (147). In addition, D-mannose, a ferroptosis inhibitor, can reduce the sensitivity of chondrocytes to ferroptosis and play a chondroprotective role, thereby delaying the progression of OA (Table 1) (148). Since lipid peroxidation-induced ferroptosis plays an important role in the cartilage degradation of OA, antioxidants, including enzymatic antioxidants (superoxide dismutases, catalase, glutathione peroxidase) and nonenzymatic antioxidants (glutathione, vitamin, coenzyme Q10), provide new ideas for OA treatment by inhibiting lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis in chondrocytes (104). In recent months, extensive experiments have emerged using natural Chinese herbs or their extracts, such as Quercetin (149), Dandouchi (150), Jianpi-Tongluo formula (151); anti-inflammatory lipid mediator, such as lipoxA4 (LXA4) (152); botulinum toxin A (BONT/A) produced by the anaerobic bacterium Clostridium botulinum (153); magnetic nanoparticles (MNP) (Figure 5) (154) or colloidal gold nanorods (AuNR) (155) by coupling with transient acceptor potential vanillic acid 1 (TRPV1), modulating ferroptosis to treat OA, and all have achieved excellent therapeutic effects. Similarly, the use of iron chelators (DFO) to deduce iron content, antioxidants to inhibit OS, and ferroptosis inhibitors (Fer-1) to impede ferroptosis are also feasible ways to rescue IVDD associated with iron overload (113). The specific mechanism involves DFO reversing the downregulation of GPX4 and SLC7A11, thereby blocking chondrocyte ferroptosis, while Fer-1 alleviates iron overload-induced endplate chondrocyte degeneration (113). Recently published materials for the treatment of IVDD based on ferroptosis mainly include composite biomaterials (injectable reactive oxygen species-responsive hydrogels) (Figure 5) (156), endogenous multifunctional and conditionally essential amino acids (glutamine) (157), novel ferroptosis inhibitors (Tinoridine) (Table 1) (158).
Although the number of drugs approved for treating diseases related to ferroptosis is increasing, there is still some uncertainty about these drugs’ clinical translation, mode of administration, dosage, time window of administration, and pharmacokinetics in the human body. Numerous impediments remain to be solved, and the research in this area shows a flourishing trend. At the same time, we also expect more studies to explore the relevant signaling pathways and specific mechanisms of ferroptosis’s involvement in pain to enhance the understanding of the pathogenesis of these diseases and develop new, safer, and more effective inhibitors for the treatment of ferroptosis-related pain, along with achieving clinical conversion and application, is prospective.
6 Conclusions and future perspectives
In recent years, the number of articles linking ferroptosis to pain-related illnesses has increased rapidly. Many crucial mechanisms have been elucidated, but a comprehensive particular opinion is far from being achieved. Exploring the mechanism of ferroptosis involved in pain and attenuating pain by targeting ferroptosis has become a prominent topic. As previously mentioned, pharmacological induction of ferroptosis is a prospective approach for treating pain-related disorders. The research and development of more medicines that target ferroptosis may significantly improve the prognosis of painful diseases. However, the method of administration, dose, time window of administration, pharmacokinetic study, and potential side effects of the drug are all urgent problems that need to be solved.
In addition, clinical treatments targeting ferroptosis continue to face multiple obstacles. On the one hand, whether ferroptosis is involved in all pain-related diseases has not been confirmed. In other words, whether a drug that targets ferroptosis would work for most pain-related diseases? On the other hand, the intricacy of the known regulatory pathways of ferroptosis makes it ineluctably function in various diseases, including cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and cancer. The development of specific therapies to inhibit ferroptosis in painful diseases and avoid systemic adverse severe consequences are the obstacles that must be overcome to achieve clinical application. Finally, treating pain-related diseases by targeting ferroptosis is primarily performed in animal experiments, and the use of drugs targeting ferroptosis has yet to be promoted in clinical application. We expect more data from large sample populations to determine whether targeting ferroptosis can improve outcomes for painful diseases.
To our knowledge, this review is the first to summarize the molecular mechanism of ferroptosis and pain systematically, the association between ferroptosis and pain-related diseases, and the methods of targeting ferroptosis for pain-related diseases. However, our review also needs some improvement. First, we only concentrated on the association of ferroptosis with neuropathic and bone pain diseases and did not discuss other types of painful diseases connected with ferroptosis, such as cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and endometriosis. Second, the list of diseases that illustrate the association between ferroptosis and neuropathic or bone pain diseases may need to be completed. For example, the association between rheumatoid arthritis (RA), osteosarcoma, and ferroptosis is well documented, which we did not include in this review. Finally, there are few studies on ferroptosis and pain and many gaps in the specific mechanisms. The literature we can refer to is restricted. In conclusion, the vital link between pain and ferroptosis requires further investigation of the underlying mechanisms, which will hopefully boost the exploitation of novel, more refined therapeutic strategies for the handling of pain.
Author contributions
QY: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. FW: Writing – original draft. ML: Writing – review & editing. JM: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. ZZ: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. BW: Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Kohrt BA, Griffith JL, and Patel V. Chronic pain and mental health: integrated solutions for global problems. Pain. (2018) 159:S85–90. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001296
2. Raja SN, Carr DB, Cohen M, Finnerup NB, Flor H, Gibson S, et al. The revised International Association for the Study of Pain definition of pain: concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain. (2020) 161:1976–82. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001939
3. Cohen SP, Vase L, and Hooten WM. Chronic pain: an update on burden, best practices, and new advances. Lancet. (2021) 397:2082–97. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00393-7
4. Dean BJF. Chronic pain: a flawed and harmful dichotomisation. BMJ. (2023) 382:1890. doi: 10.1136/bmj.p1890
5. Li L, Li T, Qu X, Sun G, Fu Q, and Han G. Stress/cell death pathways, neuroinflammation, and neuropathic pain. Immunol Rev. (2024) 321:33–51. doi: 10.1111/imr.13275
6. Yekkirala AS, Roberson DP, Bean BP, and Woolf CJ. Breaking barriers to novel analgesic drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2017) 16:545–64. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2017.87
7. Vardeh D, Mannion RJ, and Woolf CJ. Towards a mechanism-based approach to pain diagnosis. J Pain. (2016) 17:T50–69. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2016.03.001
8. Ding Z, Liang X, Wang J, Song Z, Guo Q, Schäfer MKE, et al. Inhibition of spinal ferroptosis-like cell death alleviates hyperalgesia and spontaneous pain in a mouse model of bone cancer pain. Redox Biol. (2023) 62:102700. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102700
9. Deng Y-F, Xiang P, Du J-Y, Liang J-F, and Li X. Intrathecal liproxstatin-1 delivery inhibits ferroptosis and attenuates mechanical and thermal hypersensitivities in rats with complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced inflammatory pain. Neural Regener Res. (2023) 18:456–62. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.346547
10. Zhang X, Song T, Zhao M, Tao X, Zhang B, Sun C, et al. Sirtuin 2 alleviates chronic neuropathic pain by suppressing ferroptosis in rats. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:827016. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.827016
11. Zhang J-J, Du J, Kong N, Zhang G-Y, Liu M-Z, and Liu C. Mechanisms and pharmacological applications of ferroptosis: a narrative review. Ann Transl Med. (2021) 9:1503. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-1595
12. Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. (2012) 149:1060–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
13. Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, Yu Y, Huang J, Sun X, et al. Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ. (2016) 23:369–79. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.158
14. Yan H-F, Zou T, Tuo Q-Z, Xu S, Li H, Belaidi AA, et al. Ferroptosis: mechanisms and links with diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2021) 6:49. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00428-9
15. Deng L, He S, Guo N, Tian W, Zhang W, and Luo L. Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and relevance to inflammation. Inflammation Res. (2023) 72:281–99. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01672-1
16. Luo F and Huang C. New insight into neuropathic pain: the relationship between α7nAChR, ferroptosis, and neuroinflammation. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:6716. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126716
17. Guo C, Yue Y, Wang B, Chen S, Li D, Zhen F, et al. Anemoside B4 alleviates arthritis pain via suppressing ferroptosis-mediated inflammation. J Cell Mol Med. (2024) 28:e18136. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18136
18. Fang X, Ardehali H, Min J, and Wang F. The molecular and metabolic landscape of iron and ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2023) 20:7–23. doi: 10.1038/s41569-022-00735-4
19. Guo Y, Du J, Xiao C, Xiang P, Deng Y, Hei Z, et al. Inhibition of ferroptosis-like cell death attenuates neuropathic pain reactions induced by peripheral nerve injury in rats. Eur J Pain. (2021) 25:1227–40. doi: 10.1002/ejp.1737
20. Das UN. Saturated fatty acids, MUFAs and PUFAs regulate ferroptosis. Cell Chem Biol. (2019) 26:309–11. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.03.001
21. Hassannia B, Van Coillie S, and Vanden Berghe T. Ferroptosis: biological rust of lipid membranes. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2021) 35:487–509. doi: 10.1089/ars.2020.8175
22. Kagan VE, Mao G, Qu F, Angeli JPF, Doll S, Croix CS, et al. Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol. (2017) 13:81–90. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2238
23. Liang D, Minikes AM, and Jiang X. Ferroptosis at the intersection of lipid metabolism and cellular signaling. Mol Cell. (2022) 82:2215–27. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.03.022
24. Doll S and Conrad M. Iron and ferroptosis: A still ill-defined liaison. IUBMB Life. (2017) 69:423–34. doi: 10.1002/iub.1616
25. Doll S, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, Panzilius E, Kobayashi S, Ingold I, et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. (2017) 13:91–8. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2239
26. Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, and Tang D. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2021) 18:280–96. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-00462-0
27. Hu X, Bao Y, Li M, Zhang W, and Chen C. The role of ferroptosis and its mechanism in ischemic stroke. Exp Neurol. (2024) 372:114630. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114630
28. Kong Y, Li J, Lin R, Lu S, Rong L, Xue Y, et al. Understanding the unique mechanism of ferroptosis: a promising therapeutic target. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2024) 11:1329147. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1329147
29. Daher R, Manceau H, and Karim Z. Iron metabolism and the role of the iron-regulating hormone hepcidin in health and disease. Presse Med. (2017) 46:e272–8. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2017.10.006
30. Li Y, Jin C, Shen M, Wang Z, Tan S, Chen A, et al. Iron regulatory protein 2 is required for artemether -mediated anti-hepatic fibrosis through ferroptosis pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. (2020) 160:845–59. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.09.008
31. Hu C, Zu D, Xu J, Xu H, Yuan L, Chen J, et al. Polyphyllin B suppresses gastric tumor growth by modulating iron metabolism and inducing ferroptosis. Int J Biol Sci. (2023) 19:1063–79. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.80324
32. Li J, Cao F, Yin H-L, Huang Z-J, Lin Z-T, Mao N, et al. Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:88. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2298-2
33. Kakhlon O and Cabantchik ZI. The labile iron pool: characterization, measurement, and participation in cellular processes(1). Free Radic Biol Med. (2002) 33:1037–46. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(02)01006-7
34. Xie L-H, Fefelova N, Pamarthi SH, and Gwathmey JK. Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and relevance to cardiovascular disease. Cells. (2022) 11:2726. doi: 10.3390/cells11172726
35. Chen J, Li X, Ge C, Min J, and Wang F. The multifaceted role of ferroptosis in liver disease. Cell Death Differ. (2022) 29:467–80. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-00941-0
36. Niu B, Liao K, Zhou Y, Wen T, Quan G, Pan X, et al. Application of glutathione depletion in cancer therapy: Enhanced ROS-based therapy, ferroptosis, and chemotherapy. Biomaterials. (2021) 277:121110. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121110
37. Yan R, Xie E, Li Y, Li J, Zhang Y, Chi X, et al. The structure of erastin-bound xCT-4F2hc complex reveals molecular mechanisms underlying erastin-induced ferroptosis. Cell Res. (2022) 32:687–90. doi: 10.1038/s41422-022-00642-w
38. Jiang X, Stockwell BR, and Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2021) 22:266–82. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8
39. Lewerenz J, Hewett SJ, Huang Y, Lambros M, Gout PW, Kalivas PW, et al. The cystine/glutamate antiporter system xc– in health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2013) 18:522–55. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4391
40. Liu L, Liu R, Liu Y, Li G, Chen Q, Liu X, et al. Cystine-glutamate antiporter xCT as a therapeutic target for cancer. Cell Biochem Funct. (2021) 39:174–9. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3581
41. Ursini F, Maiorino M, Valente M, Ferri L, and Gregolin C. Purification from pig liver of a protein which protects liposomes and biomembranes from peroxidative degradation and exhibits glutathione peroxidase activity on phosphatidylcholine hydroperoxides. Biochim Biophys Acta. (1982) 710:197–211. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90150-3
42. Su Y, Zhao B, Zhou L, Zhang Z, Shen Y, Lv H, et al. Ferroptosis, a novel pharmacological mechanism of anti-cancer drugs. Cancer Lett. (2020) 483:127–36. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.02.015
43. Kim KM, Cho SS, and Ki SH. Emerging roles of ferroptosis in liver pathophysiology. Arch Pharm Res. (2020) 43:985–96. doi: 10.1007/s12272-020-01273-8
44. Hassannia B, Wiernicki B, Ingold I, Qu F, Van Herck S, Tyurina YY, et al. Nano-targeted induction of dual ferroptotic mechanisms eradicates high-risk neuroblastoma. J Clin Invest. (2018) 128:3341–55. doi: 10.1172/JCI99032
45. Li L, Guo L, Gao R, Yao M, Qu X, Sun G, et al. Ferroptosis: a new regulatory mechanism in neuropathic pain. Front Aging Neurosci. (2023) 15:1206851. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1206851
46. Wang H, Huo X, Han C, Ning J, Chen H, Li B, et al. Ferroptosis is involved in the development of neuropathic pain and allodynia. Mol Cell Biochem. (2021) 476:3149–61. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04138-w
47. Qiu Y, Cao Y, Cao W, Jia Y, and Lu N. The application of ferroptosis in diseases. Pharmacol Res. (2020) 159:104919. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104919
48. Salvemini D, Little JW, Doyle T, and Neumann WL. Roles of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in pain. Free Radic Biol Med. (2011) 51:951–66. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.01.026
49. Woller SA and Hook MA. Opioid administration following spinal cord injury: implications for pain and locomotor recovery. Exp Neurol. (2013) 247:328–41. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.03.008
50. Meisner JG, Marsh AD, and Marsh DR. Loss of GABAergic interneurons in laminae I-III of the spinal cord dorsal horn contributes to reduced GABAergic tone and neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. (2010) 27:729–37. doi: 10.1089/neu.2009.1166
51. Mantyh PW. Bone cancer pain: from mechanism to therapy. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. (2014) 8:83–90. doi: 10.1097/SPC.0000000000000048
52. Daniele CA and MacDermott AB. Low-threshold primary afferent drive onto GABAergic interneurons in the superficial dorsal horn of the mouse. J Neurosci. (2009) 29:686–95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5120-08.2009
53. Cabungcal J-H, Steullet P, Morishita H, Kraftsik R, Cuenod M, Hensch TK, et al. Perineuronal nets protect fast-spiking interneurons against oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2013) 110:9130–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1300454110
54. Kann O. The interneuron energy hypothesis: Implications for brain disease. Neurobiol Dis. (2016) 90:75–85. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.08.005
55. Xiang Y, Song X, and Long D. Ferroptosis regulation through Nrf2 and implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Arch Toxicol. (2024) 98(3):579–615. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03660-8
56. Nashed MG, Balenko MD, and Singh G. Cancer-induced oxidative stress and pain. Curr Pain Headache Rep. (2014) 18:384. doi: 10.1007/s11916-013-0384-1
57. Angeli J, Schneider M, Proneth B, Tyurina Y, Tyurin V, Hammond V, et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol. (2014) 16(12):1180–91. doi: 10.1038/ncb3064
58. Chen L, Hambright WS, Na R, and Ran Q. Ablation of the ferroptosis inhibitor glutathione peroxidase 4 in neurons results in rapid motor neuron degeneration and paralysis. J Biol Chem. (2015) 290:28097–106. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.680090
59. Segelcke D, Reichl S, Neuffer S, Zapp S, Rüther T, Evers D, et al. The role of the spinal cyclooxygenase (COX) for incisional pain in rats at different developmental stages. Eur J Pain. (2020) 24:312–24. doi: 10.1002/ejp.1487
60. Vardeh D, Wang D, Costigan M, Lazarus M, Saper CB, Woolf CJ, et al. COX2 in CNS neural cells mediates mechanical inflammatory pain hypersensitivity in mice. J Clin Invest. (2009) 119:287–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI37098
61. Dilokthornsakul P, Valuck RJ, Nair KV, Corboy JR, Allen RR, and Campbell JD. Multiple sclerosis prevalence in the United States commercially insured population. Neurology. (2016) 86:1014–21. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002469
62. Filippini G, Minozzi S, Borrelli F, Cinquini M, and Dwan K. Cannabis and cannabinoids for symptomatic treatment for people with multiple sclerosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2022) 2022:CD013444. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013444.pub2
63. Costa I, Barbosa DJ, Benfeito S, Silva V, Chavarria D, Borges F, et al. Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and their involvement in brain diseases. Pharmacol Ther. (2023) 244:108373. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108373
64. Neema M, Arora A, Healy BC, Guss ZD, Brass SD, Duan Y, et al. Deep gray matter involvement on brain MRI scans is associated with clinical progression in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimaging. (2009) 19:3–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1552-6569.2008.00296.x
65. Hu C-L, Nydes M, Shanley KL, Pantoja IEM, Howard TA, and Bizzozero OA. Reduced expression of the ferroptosis inhibitor GPx4 in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurochem. (2019) 148:426–39. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14604
66. Jhelum P, Santos-Nogueira E, Teo W, Haumont A, Lenoël I, Stys PK, et al. Ferroptosis mediates cuprizone-induced loss of oligodendrocytes and demyelination. J Neurosci. (2020) 40:9327–41. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1749-20.2020
67. Weigel KJ, Lynch SG, and LeVine SM. Iron chelation and multiple sclerosis. ASN Neuro. (2014) 6:e00136. doi: 10.1042/AN20130037
68. Stephenson E, Nathoo N, Mahjoub Y, Dunn JF, and Yong VW. Iron in multiple sclerosis: roles in neurodegeneration and repair. Nat Rev Neurol. (2014) 10:459–68. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2014.118
69. Liu Y-J, Jia G-R, Zhang S-H, Guo Y-L, Ma X-Z, Xu H-M, et al. The role of microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: From the perspective of ferroptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2025). doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01560-4
70. Spaas J, van Veggel L, Schepers M, Tiane A, van Horssen J, Wilson DM, et al. Oxidative stress and impaired oligodendrocyte precursor cell differentiation in neurological disorders. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2021) 78:4615–37. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03802-0
71. GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. (2021) 20:795–820. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00252-0
72. Liampas A, Velidakis N, Georgiou T, Vadalouca A, Varrassi G, Hadjigeorgiou GM, et al. Prevalence and management challenges in central post-stroke neuropathic pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv Ther. (2020) 37:3278–91. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01388-w
73. Rosner J, de Andrade DC, Davis KD, Gustin SM, Kramer JLK, Seal RP, et al. Central neuropathic pain. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2023) 9:73. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00484-9
74. Klit H, Finnerup NB, and Jensen TS. Central post-stroke pain: clinical characteristics, pathophysiology, and management. Lancet Neurol. (2009) 8:857–68. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70176-0
75. Shi Z-M, Jing J-J, Xue Z-J, Chen W-J, Tang Y-B, Chen D-J, et al. Stellate ganglion block ameliorated central post-stroke pain with comorbid anxiety and depression through inhibiting HIF-1α/NLRP3 signaling following thalamic hemorrhagic stroke. J Neuroinflamm. (2023) 20:82. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02765-2
76. Zhang X-Y, Han P-P, Zhao Y-N, Shen X-Y, and Bi X. Crosstalk between autophagy and ferroptosis mediate injury in ischemic stroke by generating reactive oxygen species. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e28959. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28959
77. Ma R, Sun X, Liu Z, Zhang J, Yang G, Tian J, et al. Ferroptosis in ischemic stroke and related traditional chinese medicines. Molecules. (2024) 29:4359. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184359
78. Wang Q, Xu S, Wang B, Qin Y, Ji Y, Yang Q, et al. Chemokine receptor 7 mediates miRNA-182 to regulate cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2022) 29:712–26. doi: 10.1111/cns.14056
79. Chai Z, Zheng J, and Shen J. Mechanism of ferroptosis regulating ischemic stroke and pharmacologically inhibiting ferroptosis in treatment of ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2024) 30:e14865. doi: 10.1111/cns.14865
80. Cui Y, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Shao L, Liu G, Sun C, et al. ACSL4 exacerbates ischemic stroke by promoting ferroptosis-induced brain injury and neuroinflammation. Brain Behav Immun. (2021) 93:312–21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2021.01.003
81. Tang L-J, Luo X-J, Tu H, Chen H, Xiong X-M, Li N-S, et al. Ferroptosis occurs in phase of reperfusion but not ischemia in rat heart following ischemia or ischemia/reperfusion. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. (2021) 394:401–10. doi: 10.1007/s00210-020-01932-z
82. She R, Liu D, Liao J, Wang G, Ge J, and Mei Z. Mitochondrial dysfunctions induce PANoptosis and ferroptosis in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: from pathology to therapeutic potential. Front Cell Neurosci. (2023) 17:1191629. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1191629
83. Wang J, Lv C, Wei X, and Li F. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for ferroptosis and cuproptosis in ischemic stroke. Brain Behav Immun Health. (2024) 40:100837. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100837
84. Zhang X, Gou Y-J, Zhang Y, Li J, Han K, Xu Y, et al. Hepcidin overexpression in astrocytes alters brain iron metabolism and protects against amyloid-β induced brain damage in mice. Cell Death Discov. (2020) 6:113. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-00346-3
85. Gill D, Monori G, Tzoulaki I, and Dehghan A. Iron status and risk of stroke. Stroke. (2018) 49:2815–21. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.022701
86. Schomberg D, Miranpuri G, Duellman T, Crowell A, Vemuganti R, and Resnick D. Spinal cord injury induced neuropathic pain: Molecular targets and therapeutic approaches. Metab Brain Dis. (2015) 30:645–58. doi: 10.1007/s11011-014-9642-0
87. Shi Z, Yuan S, Shi L, Li J, Ning G, Kong X, et al. Programmed cell death in spinal cord injury pathogenesis and therapy. Cell Prolif. (2021) 54:e12992. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12992
88. Burke D, Fullen BM, Stokes D, and Lennon O. Neuropathic pain prevalence following spinal cord injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Pain. (2017) 21:29–44. doi: 10.1002/ejp.905
89. Shiao R and Lee-Kubli CA. Neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury: challenges and research perspectives. Neurotherapeutics. (2018) 15:635–53. doi: 10.1007/s13311-018-0633-4
90. Bai X-Y, Liu X-L, Deng Z-Z, Wei D-M, Zhang D, Xi H-L, et al. Ferroptosis is a new therapeutic target for spinal cord injury. Front Neurosci. (2023) 17:1136143. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1136143
91. Chen Y-X, Zuliyaer T, Liu B, Guo S, Yang D-G, Gao F, et al. Sodium selenite promotes neurological function recovery after spinal cord injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. Neural Regener Res. (2022) 17:2702–9. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.339491
92. Li F, Wang H, Chen H, Guo J, Dang X, Ru Y, et al. Mechanism of ferroptosis and its role in spinal cord injury. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:926780. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.926780
93. Feng Z, Min L, Chen H, Deng W, Tan M, Liu H, et al. Iron overload in the motor cortex induces neuronal ferroptosis following spinal cord injury. Redox Biol. (2021) 43:101984. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101984
94. Song Q-F, Cui Q, Wang Y-S, and Zhang L-X. Mesenchymal stem cells, extracellular vesicles, and transcranial magnetic stimulation for ferroptosis after spinal cord injury. Neural Regener Res. (2023) 18:1861–8. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.367838
95. Zhang Y, Fan B-Y, Pang Y-L, Shen W-Y, Wang X, Zhao C-X, et al. Neuroprotective effect of deferoxamine on erastininduced ferroptosis in primary cortical neurons. Neural Regener Res. (2020) 15:1539–45. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.274344
96. Mauceri D. Role of epigenetic mechanisms in chronic pain. Cells. (2022) 11:2613. doi: 10.3390/cells11162613
97. Lu K, Ma F, Yi D, Yu H, Tong L, and Chen D. Molecular signaling in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. (2022) 32:21–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2021.07.001
98. Katz JN, Arant KR, and Loeser RF. Diagnosis and treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis: A review. JAMA. (2021) 325:568–78. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.22171
99. Tong L, Yu H, Huang X, Shen J, Xiao G, Chen L, et al. Current understanding of osteoarthritis pathogenesis and relevant new approaches. Bone Res. (2022) 10:60. doi: 10.1038/s41413-022-00226-9
100. Li J, Zhang B, Liu W-X, Lu K, Pan H, Wang T, et al. Metformin limits osteoarthritis development and progression through activation of AMPK signalling. Ann Rheum Dis. (2020) 79:635–45. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216713
101. Li J, Wang Y, Chen D, and Liu-Bryan R. Oral administration of berberine limits post-traumatic osteoarthritis development and associated pain via AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in mice. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. (2022) 30:160–71. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2021.10.004
102. Cai C, Hu W, and Chu T. Interplay between iron overload and osteoarthritis: clinical significance and cellular mechanisms. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:817104. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.817104
103. Kennish L, Attur M, Oh C, Krasnokutsky S, Samuels J, Greenberg JD, et al. Age-dependent ferritin elevations and HFE C282Y mutation as risk factors for symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in males: a longitudinal cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2014) 15:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-8
104. Zhang X, Hou L, Guo Z, Wang G, Xu J, Zheng Z, et al. Lipid peroxidation in osteoarthritis: focusing on 4-hydroxynonenal, malondialdehyde, and ferroptosis. Cell Death Discov. (2023) 9:320. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01613-9
105. An F, Zhang J, Gao P, Xiao Z, Chang W, Song J, et al. New insight of the pathogenesis in osteoarthritis: the intricate interplay of ferroptosis and autophagy mediated by mitophagy/chaperone-mediated autophagy. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2023) 11:1297024. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1297024
106. Wang S, Li W, Zhang P, Wang Z, Ma X, Liu C, et al. Mechanical overloading induces GPX4-regulated chondrocyte ferroptosis in osteoarthritis via Piezo1 channel facilitated calcium influx. J Adv Res. (2022) 41:63–75. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.01.004
107. Miao Y, Chen Y, Xue F, Liu K, Zhu B, Gao J, et al. Contribution of ferroptosis and GPX4’s dual functions to osteoarthritis progression. EBioMedicine. (2022) 76:103847. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103847
108. Wang L, He T, Liu J, Tai J, Wang B, Zhang L, et al. Revealing the immune infiltration landscape and identifying diagnostic biomarkers for lumbar disc herniation. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:666355. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.666355
109. C Q, X W, J B, X M, G Z, Z G, et al. Differential proteomic analysis of fetal and geriatric lumbar nucleus pulposus: immunoinflammation and age-related intervertebral disc degeneration. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2020) 21(1):339. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03329-8
110. Shamji MF, Setton LA, Jarvis W, So S, Chen J, Jing L, et al. Proinflammatory cytokine expression profile in degenerated and herniated human intervertebral disc tissues. Arthritis Rheum. (2010) 62:1974–82. doi: 10.1002/art.27444
111. Ru Q, Li Y, Xie W, Ding Y, Chen L, Xu G, et al. Fighting age-related orthopedic diseases: focusing on ferroptosis. Bone Res. (2023) 11:12. doi: 10.1038/s41413-023-00247-y
112. Yang R-Z, Xu W-N, Zheng H-L, Zheng X-F, Li B, Jiang L-S, et al. Involvement of oxidative stress-induced annulus fibrosus cell and nucleus pulposus cell ferroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol. (2021) 236:2725–39. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30039
113. Wang W, Jing X, Du T, Ren J, Liu X, Chen F, et al. Iron overload promotes intervertebral disc degeneration via inducing oxidative stress and ferroptosis in endplate chondrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. (2022) 190:234–46. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.08.018
114. Li F-C, Zhang N, Chen W-S, and Chen Q-X. Endplate degeneration may be the origination of the vacuum phenomenon in intervertebral discs. Med Hypotheses. (2010) 75:169–71. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2010.02.012
115. Jing X, Du T, Li T, Yang X, Wang G, Liu X, et al. The detrimental effect of iron on OA chondrocytes: Importance of pro-inflammatory cytokines induced iron influx and oxidative stress. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25:5671–80. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16581
116. Jiang M, Jike Y, Liu K, Gan F, Zhang K, Xie M, et al. Exosome-mediated miR-144-3p promotes ferroptosis to inhibit osteosarcoma proliferation, migration, and invasion through regulating ZEB1. Mol Cancer. (2023) 22:113. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01804-z
117. Yang R, Yan L, Xu T, Zhang K, Lu X, Xie C, et al. Injectable bioadhesive hydrogel as a local nanomedicine depot for targeted regulation of inflammation and ferroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Biomaterials. (2024) 311:122706. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122706
118. Lin Z, Li Y, Wu Z, Liu Q, Li X, and Luo W. Eriodictyol-cisplatin coated nanomedicine synergistically promote osteosarcoma cells ferroptosis and chemosensitivity. J Nanobiotechnol. (2025) 23:109. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03206-3
119. Santos MCQ, da Silva TCB, da Silva FBO, Siebert C, Kroth A, Silveira EMS, et al. Effects of vitamin D administration on nociception and spinal cord pro-oxidant and antioxidant markers in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Braz J Med Biol Res. (2021) 54:e11207. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2021e11207
120. Zhang W, Yu S, Jiao B, Zhang C, Zhang K, Liu B, et al. Vitamin D3 attenuates neuropathic pain via suppression of mitochondria-associated ferroptosis by inhibiting PKCα/NOX4 signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2024) 30:e70067. doi: 10.1111/cns.70067
121. Song X and Long D. Nrf2 and ferroptosis: A new research direction for neurodegenerative diseases. Front Neurosci. (2020) 14:267. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00267
122. Guo X, Tao X, Tong Q, Li T, Dong D, Zhang B, et al. Impaired AMPK−CGRP signaling in the central nervous system contributes to enhanced neuropathic pain in high−fat diet−induced obese rats, with or without nerve injury. Mol Med Rep. (2019) 20:1279–87. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10368
123. Reichardt HM, Gold R, and Lühder F. Glucocorticoids in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Expert Rev Neurother. (2006) 6:1657–70. doi: 10.1586/14737175.6.11.1657
124. von Mässenhausen A, Zamora Gonzalez N, Maremonti F, Belavgeni A, Tonnus W, Meyer C, et al. Dexamethasone sensitizes to ferroptosis by glucocorticoid receptor-induced dipeptidase-1 expression and glutathione depletion. Sci Adv. (2022) 8:eabl8920. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl8920
125. H L, L Z, X W, Q Z, F Z, L Z, et al. Dexamethasone upregulates macrophage PIEZO1 via SGK1, suppressing inflammation and increasing ROS and apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol. (2024) 222:116050. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116050
126. Chen K, Liu Y, He J, Pavlos N, Wang C, Kenny J, et al. Steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head reveals enhanced reactive oxygen species and hyperactive osteoclasts. Int J Biol Sci. (2020) 16:1888–900. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.40917
127. Li Z, Zhang Y, Ji M, Wu C, Zhang Y, and Ji S. Targeting ferroptosis in neuroimmune and neurodegenerative disorders for the development of novel therapeutics. Biomed Pharmacother. (2024) 176:116777. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116777
128. Hail N, Chen P, Kepa JJ, Bushman LR, and Shearn C. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase is required for N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide-induced reactive oxygen species production and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. (2010) 49:109–16. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.04.006
129. Martín-Montañez E, Pavia J, Valverde N, Boraldi F, Lara E, Oliver B, et al. The S1P mimetic fingolimod phosphate regulates mitochondrial oxidative stress in neuronal cells. Free Radic Biol Med. (2019) 137:116–30. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.04.022
130. Yan N, Xu Z, Qu C, and Zhang J. Dimethyl fumarate improves cognitive deficits in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats by alleviating inflammation, oxidative stress, and ferroptosis via NRF2/ARE/NF-κB signal pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 98:107844. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107844
131. Bao Z, Liu Y, Chen B, Miao Z, Tu Y, Li C, et al. Prokineticin-2 prevents neuronal cell deaths in a model of traumatic brain injury. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:4220. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24469-y
132. Wei N, Lu T, Yang L, Dong Y, and Liu X. Lipoxin A4 protects primary spinal cord neurons from Erastin-induced ferroptosis by activating the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. FEBS Open Bio. (2021) 11:2118–26. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13203
133. Liu X, Du Y, Liu J, Cheng L, He W, and Zhang W. Ferrostatin-1 alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through activation of the AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway. Brain Res Bull. (2023) 193:146–57. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.12.009
134. Shi Y, Han L, Zhang X, Xie L, Pan P, and Chen F. Selenium alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating oxidative stress, mitochondrial fusion and ferroptosis. Neurochem Res. (2022) 47:2992–3002. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03643-8
135. Liu W, Wang L, Liu C, Dai Z, Li T, and Tang B. Edaravone ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by downregulating ferroptosis via the nrf2/FPN pathway in rats. Biol Pharm Bull. (2022) 45:1269–75. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b22-00186
136. Guan X, Li Z, Zhu S, Cheng M, Ju Y, Ren L, et al. Galangin attenuated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibition of ferroptosis through activating the SLC7A11/GPX4 axis in gerbils. Life Sci. (2021) 264:118660. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118660
137. Ko G, Kim J, Jeon Y-J, Lee D, Baek H-M, and Chang K-A. Salvia miltiorrhiza alleviates memory deficit induced by ischemic brain injury in a transient MCAO mouse model by inhibiting ferroptosis. Antioxid (Basel). (2023) 12:785. doi: 10.3390/antiox12040785
138. Yang L, Ding W, Dong Y, Chen C, Zeng Y, Jiang Z, et al. Electroacupuncture attenuates surgical pain-induced delirium-like behavior in mice via remodeling gut microbiota and dendritic spine. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:955581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.955581
139. Wan K, Jia M, Zhang H, Lan Y, Wang S, Zhang K, et al. Electroacupuncture alleviates neuropathic pain by suppressing ferroptosis in dorsal root ganglion via SAT1/ALOX15 signaling. Mol Neurobiol. (2023) 60:6121–32. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03463-z
140. Mobarra N, Shanaki M, Ehteram H, Nasiri H, Sahmani M, Saeidi M, et al. A review on iron chelators in treatment of iron overload syndromes. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. (2016) 10:239–47.
141. Maggio A, Kattamis A, Felisi M, Reggiardo G, El-Beshlawy A, Bejaoui M, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of deferiprone compared with deferasirox in paediatric patients with transfusion-dependent haemoglobinopathies (DEEP-2): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. (2020) 7:e469–78. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30100-9
142. Deugnier Y, Turlin B, Ropert M, Cappellini MD, Porter JB, Giannone V, et al. Improvement in liver pathology of patients with β-thalassemia treated with deferasirox for at least 3 years. Gastroenterology. (2011) 141:1202–11. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.06.065
143. Wood JC, Kang BP, Thompson A, Giardina P, Harmatz P, Glynos T, et al. The effect of deferasirox on cardiac iron in thalassemia major: impact of total body iron stores. Blood. (2010) 116:537–43. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-250308
144. Pennell DJ, Porter JB, Cappellini MD, Chan LL, El-Beshlawy A, Aydinok Y, et al. Deferasirox for up to 3 years leads to continued improvement of myocardial T2* in patients with β-thalassemia major. Haematologica. (2012) 97:842–8. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2011.049957
145. Zhang J, Hu W, Ding C, Yao G, Zhao H, and Wu S. Deferoxamine inhibits iron-uptake stimulated osteoclast differentiation by suppressing electron transport chain and MAPKs signaling. Toxicol Lett. (2019) 313:50–9. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.06.007
146. Casale M, Citarella S, Filosa A, De Michele E, Palmieri F, Ragozzino A, et al. Endocrine function and bone disease during long-term chelation therapy with deferasirox in patients with β-thalassemia major. Am J Hematol. (2014) 89:1102–6. doi: 10.1002/ajh.23844
147. Z W, K Y, Q Z, Jj G, H Y, and F Z. Antioxidant PDA-PEG nanoparticles alleviate early osteoarthritis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and angiogenesis in subchondral bone. J Nanobiotechnol. (2022) 20(1):479. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01697-y
148. Zhou X, Zheng Y, Sun W, Zhang Z, Liu J, Yang W, et al. D-mannose alleviates osteoarthritis progression by inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis in a HIF-2α-dependent manner. Cell Prolif. (2021) 54:e13134. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13134
149. Ruan H, Zhu T, Wang T, Guo Y, Liu Y, and Zheng J. Quercetin modulates ferroptosis via the SIRT1/nrf–2/HO–1 pathway and attenuates cartilage destruction in an osteoarthritis rat model. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:7461. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137461
150. He Q, Lin Y, Chen B, Chen C, Zeng J, Dou X, et al. Vitamin K2 ameliorates osteoarthritis by suppressing ferroptosis and extracellular matrix degradation through activation GPX4’s dual functions. Biomed Pharmacother. (2024) 175:116697. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116697
151. Liu Y, Xu T, Ma Z, Zhang C, Xu M, Li Q, et al. Cartilage protective and anti-edema effects of JTF in osteoarthritis via inhibiting NCOA4-HMGB1-driven ferroptosis and aquaporin dysregulation. Phytomedicine. (2024) 129:155593. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155593
152. Hu Z, Chen L, Zhao J, Zhang W, Jin Z, Sun Y, et al. Lipoxin A4 ameliorates knee osteoarthritis progression in rats by antagonizing ferroptosis through activation of the ESR2/LPAR3/Nrf2 axis in synovial fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Redox Biol. (2024) 73:103143. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103143
153. Zeng L, Liu Y, Wang Q, Wan H, Meng X, Tu P, et al. Botulinum toxin A attenuates osteoarthritis development via inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis through SLC7Al1/GPX4 axis. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Basis Dis. (2024) 1870:167215. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167215
154. Lv Z, Wang P, Li W, Xie Y, Sun W, Jin X, et al. Bifunctional TRPV1 targeted magnetothermal switch to attenuate osteoarthritis progression. Res (Wash D C). 7:316. doi: 10.34133/research.0316
155. Li W, Lv Z, Wang P, Xie Y, Sun W, Guo H, et al. Near infrared responsive gold nanorods attenuate osteoarthritis progression by targeting TRPV1. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2024) 11:2307683. doi: 10.1002/advs.202307683
156. Gao T, Xu G, Ma T, Lu X, Chen K, Luo H, et al. ROS-responsive injectable hydrogel loaded with SLC7A11-modRNA inhibits ferroptosis and mitigates intervertebral disc degeneration in rats. Adv Healthc Mater. 13(27):e2401103. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202401103
157. Wu J, Han W, Zhang Y, Li S, Qin T, Huang Z, et al. Glutamine mitigates oxidative stress-induced matrix degradation, ferroptosis, and pyroptosis in nucleus pulposus cells via deubiquitinating and stabilizing nrf2. Antioxid Redox Signaling. (2024) 41:278–95. doi: 10.1089/ars.2023.0384
Keywords: ferroptosis, pain, lipid peroxidation, iron dyshomeostasis, oxidative stress
Citation: Yan Q, Wang F, Liu M, Mao J, Zhao Z and Wang B (2025) Ferroptosis in pain: evidence, challenges, and opportunities. Front. Immunol. 16:1673783. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1673783
Received: 26 July 2025; Accepted: 14 August 2025;
Published: 03 September 2025.
Edited by:
Matheus Mattos, KU Leuven, BelgiumReviewed by:
Marcos Edgar Herkenhoff, Santa Catarina State University, BrazilFangping Bao, Zhejiang University, China
Copyright © 2025 Yan, Wang, Liu, Mao, Zhao and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zihao Zhao, enpoMjAyMEB6enUuZWR1LmNu; Bo Wang, a2luZ3dhdmVAc2N1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Qianqian Yan1,2†
Qianqian Yan1,2† Bo Wang
Bo Wang