- Department of Stomatology, China-Japan Union Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun, China
Periodontitis, a chronic inflammatory disease leading to irreversible tissue destruction, is a highly prevalent oral disease. The clinical management of periodontitis is challenging because conventional treatments like mechanical debridement and antibiotic therapy lack sufficient regenerative efficacy to achieve functional periodontal restoration. In recent years, exosomes have received widespread attention as cell-free therapeutic agents for periodontal tissue regeneration. This article reviews the dual role of exosomes in modulating immune response and promoting tissue repair, and briefly describes the exosome delivery systems studied so far. The aim of this review is to emphasize the important position occupied by cell-derived exosomes in the treatment of periodontitis as well as the main mechanisms, and to explore novel targets for the treatment of periodontitis.
1 Introduction
Periodontitis is a major global chronic inflammatory and destructive condition, the major cause of tooth loss worldwide (1–3) and a potential risk factor for a variety of systemic diseases. A large amount of evidence supports the association between periodontal disease and various systemic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes (4–6). For example, the risk of suffering an acute myocardial infarction has been shown to be two to four times higher in patients with moderate to severe periodontitis (7). Periodontitis is characterized by pathologic loss of periodontal attachment and progressive alveolar bone resorption (8). The ultimate goal of periodontal treatment is to control the infections and reconstruct the structure and function of periodontal tissues including cementum, alveolar bone, periodontal ligament (PDL) and gingival connective tissue. The routine treatment for periodontal disease mainly includes basic therapy, guided tissue regeneration (GTR), and guided bone regeneration (GBR). However, these approaches are associated with significant limitations. Non-surgical treatments, such as long-term antibiotic use, carry the risk of inducing bacterial resistance, while mechanical debridement alone fails to stimulate regeneration of lost bone tissue. Surgical interventions, including GTR and GBR, are constrained by inherent surgical risks, strict indication criteria, and technical challenges such as membrane exposure and inadequate vascularization (2, 9, 10). Consequently, current therapeutic strategies for periodontitis primarily aim to control infection but often fall short of reliably reconstructing the supporting structures and biological connections of periodontal tissues damaged by the disease. As a result, achieving predictable periodontal regeneration remains a major clinical challenge (11–13). Therefore, the current research trend has shifted towards developing tissue engineering and cell-based techniques for periodontal regeneration (14). Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy has been shown to have regenerative potential in the treatment of periodontal defects. However, the clinical application of exogenous cell therapy faces several challenges, including the requirement for large-scale cell expansion and specialized technical expertise, which substantially elevates treatment costs. Moreover, the efficacy of transplanted exogenous stem cells is highly dependent on donor-specific factors and the pathophysiological microenvironment of the recipient’s lesion (15). Additionally, cell-based therapies are associated with inherent risks such as immunogenic responses, potential disease transmission, limited cell survival, and tumorigenicity (16). Consequently, the therapeutic benefits of MSCs are increasingly attributed not to their direct differentiation capacity but rather to their paracrine functions, particularly mediated through the secretion of exosomes or small extracellular vesicles (17). Given these considerations, this review aims to synthesize current understanding of the therapeutic potential of exosomes in periodontal regeneration, emphasizing their dual roles in immunomodulation and tissue repair. This review comprehensively elucidates the cellular and molecular regulatory effects of exosomes on periodontitis-associated immune cells (such as neutrophils, macrophages, and T cells) and regenerative tissues (including gingival epithelium, alveolar bone, and periodontal ligament), providing robust evidence for the role of exosomes in promoting comprehensive periodontal regeneration. Furthermore, this review outlines recent advances in engineered exosome delivery systems and provides a forward-looking analysis of related clinical translation challenges and future research directions (Figure 1).
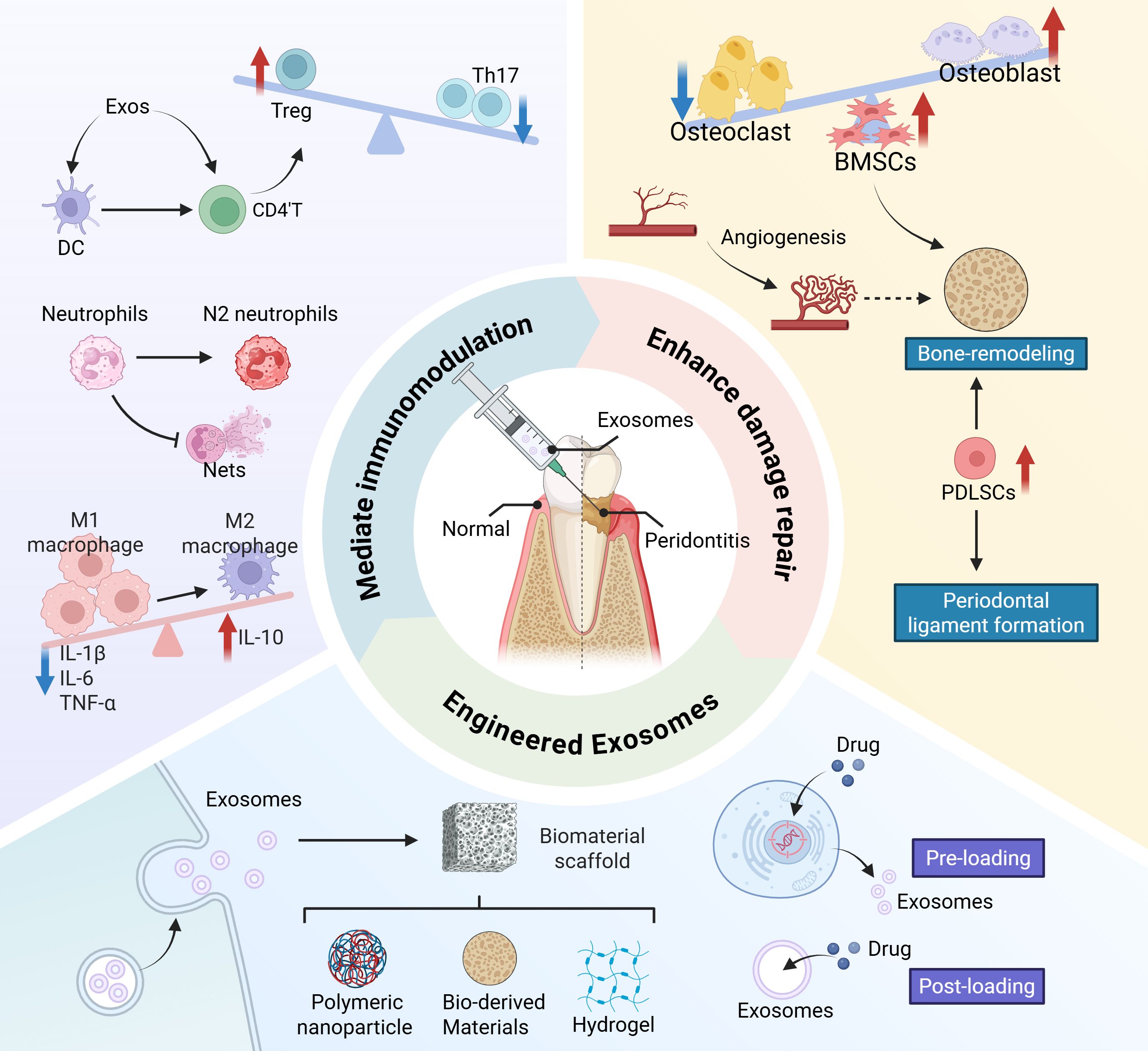
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of exosomes improving inflammatory microenvironment and promoting periodontal regeneration.
2 Exosomes
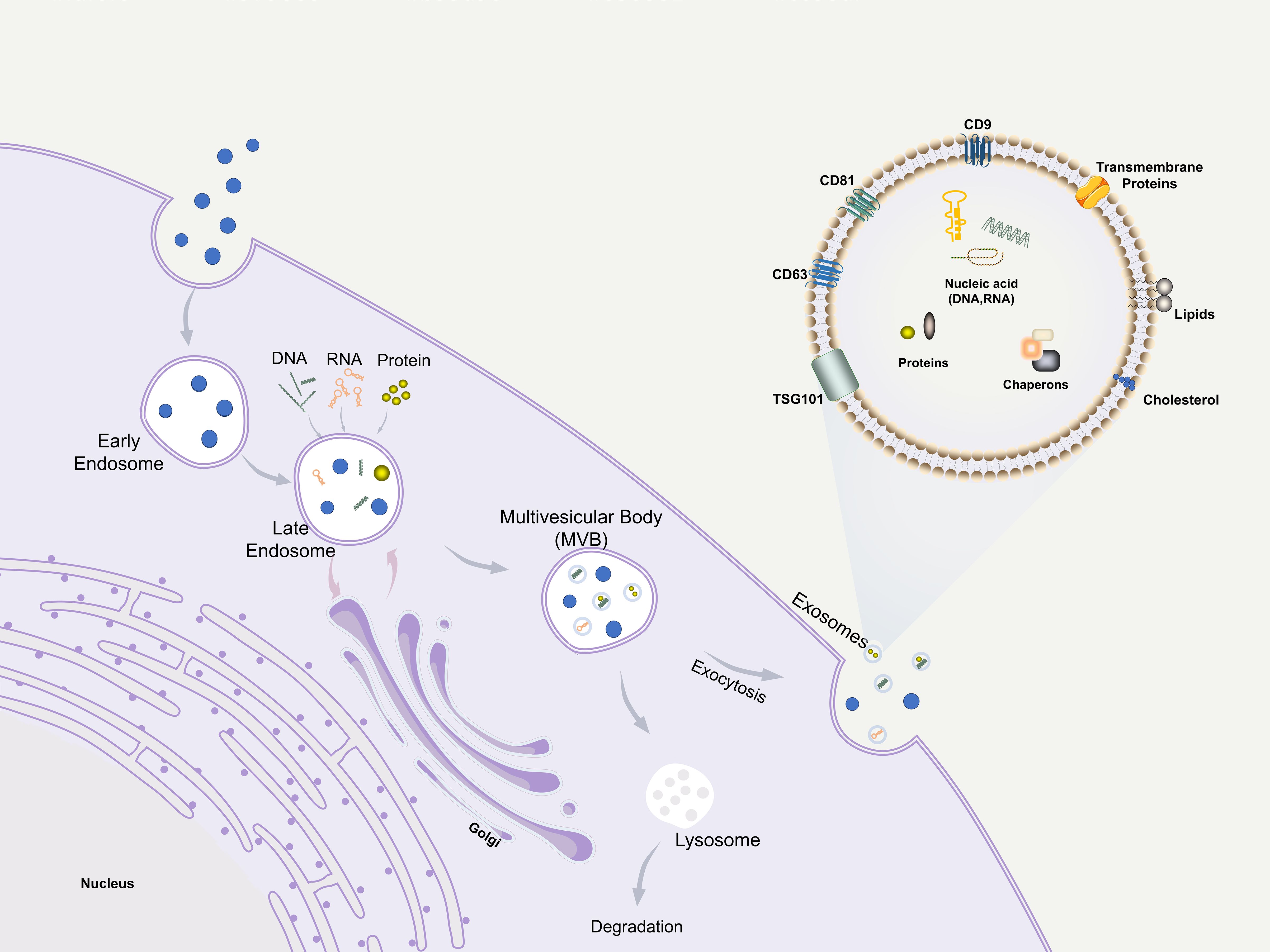
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane-bound particles released by cells into the extracellular environment, which are broadly classified into three major subtypes based on their biogenesis and size: exosomes, microvesicles, and apoptotic bodies (18, 19). Exosomes, the smallest among these EVs, range from 30 to 150 nm in diameter and possess a lipid bilayer structure. They are secreted by a wide variety of cell types and play a crucial role in intercellular communication by transferring bioactive molecules—such as proteins, lipids, and genetic materials including mRNA, miRNA, and snRNA—from donor to recipient cells (19–22). In terms of biogenesis, apoptotic bodies (800–5000 nm) and microvesicles (200–1000 nm) are generated through direct budding from the plasma membrane (23). In contrast, exosomes are derived from the endosomal pathway: they are formed as intraluminal vesicles via inward budding of the endosomal membrane within multivesicular bodies (MVBs) and are subsequently released into the extracellular space upon fusion of MVBs with the plasma membrane (24) (Figure 2). This distinct mode of formation underscores the unique molecular and functional identity of exosomes among EVs. Exosomes can directly fuse with the receptor cytoplasmic membrane and deliver information, being internalized through endocytosis or phagocytosis (25). Exosomes as important mediators of paracrine effects retain almost all advantages of source cells. In addition to their unique advantages of being cell-free, ready-to-use, easy to store, and easy to reformulate to support different routes of administration (26), exos have lower immunogenicity and better biocompatibility than cell-based therapies, resulting in lower post-transplantation immune-related adverse reactions (27–29). Moreover, the composition of the contents of exosomes from different types of cells is different, and even for cells of the same type, the exos they secrete are highly heterogeneous because of the different environments in which they are located (28). This heterogeneity, while presenting a challenge for standardization, also offers opportunities for sourcing exosomes with specific desired functions. Recent studies have shown that exosomes are effective in various animal models of tissue damage and have emerged as potential therapies for inflammatory diseases and tissue injuries (21). The potential of exosomes in periodontal regeneration has been demonstrated in recent years.
3 Modulating the inflammatory and immune response
Extensive research on cellular and animal models has begun to unravel the complex immunopathogenesis of periodontitis. Recent studies have shown that the progression of periodontitis is an organized cellular response, with tissue-resident dendritic cells (DCs), B cells, plasma cells, macrophage, T cells. Neutrophils respond early and rapidly to subgingival pathogens, producing associated enzymes to kill the pathogens and releasing cytokines and chemokines, which attract immune cells such as macrophages, T cells, and DCs to the site, participating in the periodontal immune response. This section will explore the effects of exosomes on the modulation of immune responses in various immune cells within the periodontal tissues.
3.1 Neutrophils
Neutrophils are polymorphonuclear leukocytes, the most prevalent immune cells in the human body, constituting 60-70% of all circulating leukocytes, and the proportion of neutrophils in the oral mucosa is significantly higher than that in other barrier tissues (30). Neutrophils are the first line of defense of the innate immune system against pathogens (31) and the balance between their activity and apoptosis plays a crucial role in maintaining periodontal homeostasis. In periodontitis, this balance is disrupted; overactive neutrophils triggers excessive release of proteolytic enzymes, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Recent clinical evidence has demonstrated that elevated levels of NETs (32) and ROS (33) in gingival tissues and gingival crevicular fluid of periodontitis patients are positively correlated with the severity of periodontitis and the degree of tissue destruction. Studies have indicated that NETs not only contribute directly to tissue damage, but may also perpetuate inflammation by promoting cytokine release and activating other immune pathways (34). This pathological accumulation of cytotoxic mediators creates a self-perpetuating cycle of inflammation that drives progressive destruction of periodontal structures (35).
The therapeutic potential of exosomes lies in their ability to recalibrate this dysregulated neutrophil response. Studies found that MSCs-exos could reduce tissue damage by inhibiting NETs, increasing anti-inflammatory cytokines, and reducing immune responses (36, 37) Exosomes can suppress the destructive NETosis process, as mechanistically demonstrated by Morishima et al., who identified exosomal miR-125a-3p as a direct mediator of this inhibition (38). Furthermore, they can induce neutrophil apoptosis, thereby facilitating the clearance of these cells, shifting macrophages toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype, and accelerating inflammation resolution (39). Another facet of their function is the induction of N2 polarization in neutrophils, which promotes the release of pro-angiogenic factors like BV8, thereby stimulating angiogenesis and tissue repair (40). Conversely, other studies present a seemingly paradoxical effect: exosomes may prolong neutrophil lifespan (41) and enhance phagocytosis via anti-apoptotic miRNAs (e.g., let-7 family, IL-6 mRNA) (42). This evidence raises a critical question: do exosomes primarily eliminate overactive neutrophils or reprogram them to enhance their phagocytic function?
This apparent contradiction likely underscores the context-dependent duality of exosome therapy, rather than representing mutually exclusive actions. The effect on neutrophils is probably determined by variables such as the specific exosomal cargo (which is influenced by the cellular source and preconditioning), the local inflammatory microenvironment, and the temporal stage of the disease. This duality demonstrates the strategic potential of applying exosomes to achieve tailored therapeutic outcomes—by eliminating pathological neutrophils or reprogramming their reparative functions during different stages of inflammation. However, translating this promise into reality faces significant hurdles. Therefore, a central consideration for future therapeutic development will be striking a precise balance between suppressing detrimental neutrophil functions and preserving or enhancing their beneficial roles.
3.2 Macrophages
As an important component of innate immunity, macrophages exhibit remarkable diversity and plasticity, playing critical roles in inflammatory responses. Functionally, within local tissue microenvironments, macrophages are broadly categorized into classically activated (M1), alternatively activated (M2), and unactivated (M0) states (43, 44). M1 macrophages are induced by Th1 cytokines like Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) or microbial products like lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and mediate pro-inflammatory responses through the production of cytokines such as IL-1β, Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and IL-6. In contrast, M2 macrophages are induced by cytokines IL-4 and IL-13, characterized by their secretion of anti-inflammatory mediators, including IL-10, Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), and Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) (45).
In periodontal tissues, macrophages play a key role in mobilizing host defense against microbial infection and maintaining tissue homeostasis. However, excessive activation towards the M1 phenotype can lead to periodontal tissue destruction and aggravate periodontitis (46, 47). Therefore, a timely and appropriate phenotypic transition from pro-inflammatory (M1) to anti-inflammatory (M2) macrophages is critical for resolving inflammation and treating periodontitis (48).
Through RNA sequencing and gene ontology analysis, Yue et al. found that the most significant biological activities of macrophages affected by exosome treatment were metabolic processes and cell differentiation (49). MSC-derived exosomes can significantly alter macrophage M1 to M2 phenotypes (50). Current studies have shown that Gingival mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes (GMSCs-exos) (25), human periodontal ligament cells-derived exosomes (hPDLCs-exos) (51), dental pulp stem cells-derived exosome (DPSC-exos) (52), M2 macrophage-derived exosome (M2-exos) (48), and adipose mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes (ADSC-exos) (53) can positively promote the conversion of M1 macrophages to M2 macrophages, reduce the production of pro-inflammatory factors and stimulate the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, inhibiting periodontal bone loss and treating periodontitis. Moreover, it has been demonstrated that macrophage-derived exosomes can effectively clear MRSA/E. coli (54).
Several studies have shown that exosomes contain miRNAs such as miR-223 (53), miR-1246 (52), miR-21-5p (55) and miR-182 (56), which play important roles in regulating macrophage phenotypes. This regulation may be mediated through multiple signaling pathways: Zhang et al. identified Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) suppression by exosomes as a key driver (56); miR-23a-3p in MSCs-exos inhibits IRF1 expression and the NF-κB signaling pathway to promote M2 phenotypes; Exo-181b was shown to significantly down-regulate PRKCD expression, thereby enhancing p-AKT, polarizing macrophages to M2 (57); And ADSCs-exos regulate macrophages via miR-451a/MIF (58). Additionally, Cmklr1 (ChemR23), the receptor for Resolvin E1, was significantly increased in macrophages by exosomes, which is conducive to the suppression of periodontal tissue inflammation and the reduction of bone loss (49). Furthermore, pretreatment of cells enhances this immunomodulatory capacity of exosomes. Wang et al. proposed that under conditions of circulating tensile stress, PDLCs-exos can Suppress IL-1β Production through the Inhibition of the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in LPS-stimulated Macrophages, which contribute to the maintenance of periodontal immune/inflammatory homeostasis (59). Nakao et al. demonstrated that Exosomes from TNF-α-treated human gingiva-derived MSCs(Exo-TNF) have a greater ability to convert macrophage phenotype from M1 to M2 by examining the expression of M1 (CD86) and M2 markers (CD206), and it was further demonstrated that high CD73 expression of Exo-TNF is important for M2 macrophage polarization (Figure 3) (51).
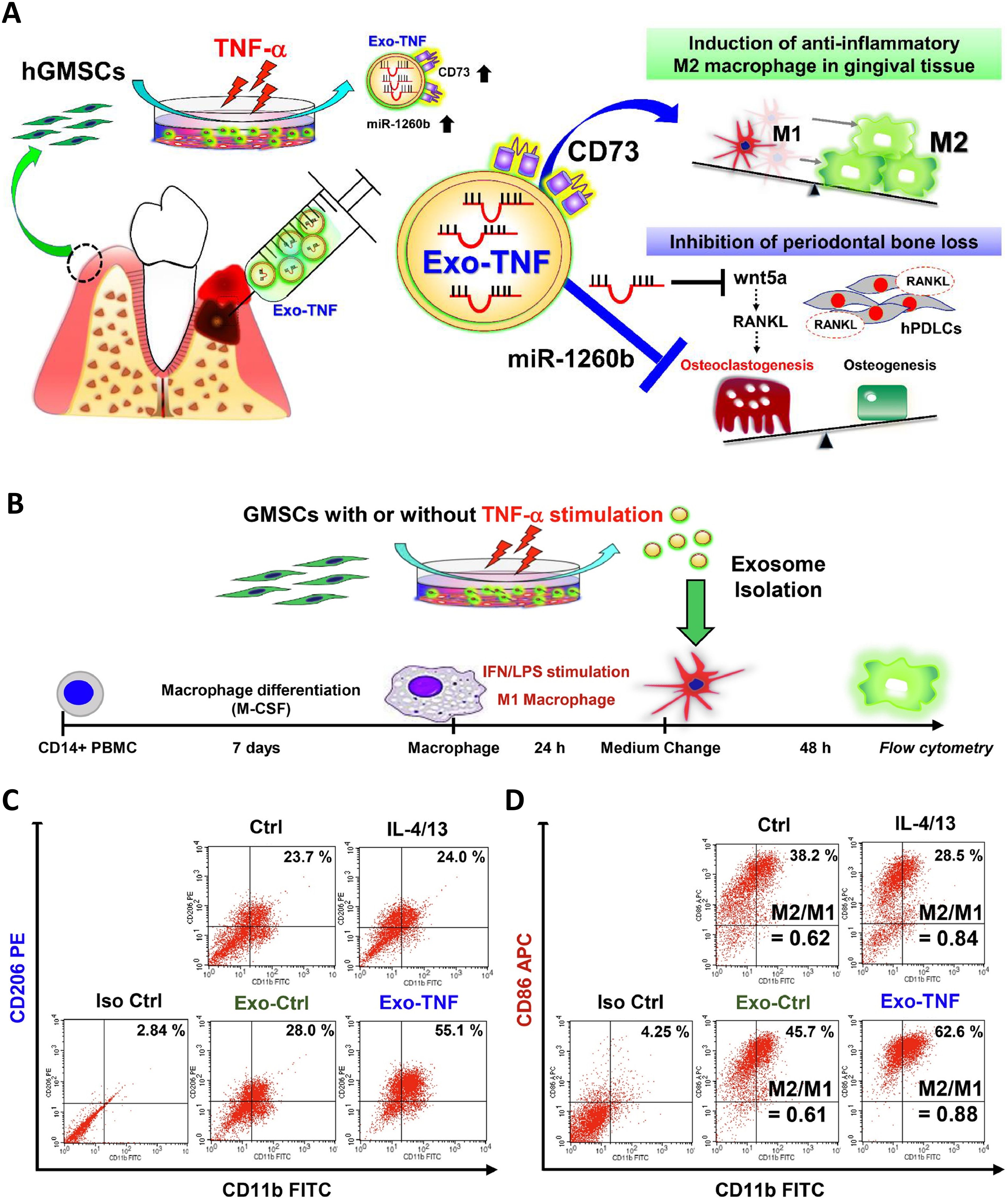
Figure 3. Effect of TNF-α-treated GMSC-derived exosomes on macrophage polarization. (A) Mechanism diagram of Exo-TNF treatment of periodontitis. (B) Strategy diagram to validate the capacity of exosomes to promote M1 to M2 macrophages. (C) Effects exosomes on CD86 expression in M1 macrophages. The percentage of double-positive cells (CD11b+ CD206+) was analyzed to represent the ratio of M2 macrophages. (D) The percentage of double positive cells (CD11b+ CD86+) was analyzed to represent M1 macrophages. M2/M1 balance was expressed by the ratio of (CD11b+ CD206+)/(CD11b+ CD86+) macrophage populations (51). © 2020 Acta Materialia Inc.
However, the functional consequences of exosome-induced M2 polarization are not uniformly straightforward. While M2 macrophages are typically associated with the release of regenerative factors such as Bone Morphogenetic Protein type 2 (BMP-2) and VEGF, which promote osteogenesis (60), studies have shown that the M2 phenotype can also elevate the expression of markers for osteoclastogenesis and enhance osteoclast differentiation (61–63). Exosomes have been found to promote this pro-osteoclastogenic effect (64), thereby presenting a more complex picture. This apparent paradox—whereby the M2 polarization that aids in resolving inflammation may also inadvertently facilitate bone resorption—highlights the insufficiency of the simplistic M1/M2 dichotomy in capturing the functional heterogeneity of macrophage subsets in periodontal healing. The therapeutic outcome is likely determined by the specific M2 subpopulation induced, the timing of polarization, and the integrated signals from the surrounding microenvironment. Consequently, achieving precise induction and control over these complex macrophage responses emerges as a central challenge in developing exosome-based therapies for periodontitis.
3.3 T cells
Within CD4+ T lymphocyte populations, the balance between T helper 17 (Th17) and regulatory T (Treg) cells critically influences periodontitis pathogenesis (65). It was found that Th17 were up-regulated or Treg were down-regulated respectively in peripheral blood and periodontal tissues of patients with periodontitis (66). Emerging evidence further positions Tregs as central mediators of tissue repair, suppressing the inflammatory response by producing anti‐inflammatory cytokines such as IL‐10, TGF‐β, and IL‐35 (67, 68), with their local presence demonstrably attenuating experimental periodontitis severity and limiting alveolar bone destruction (69–71). Zheng et al. demonstrated that Periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSC)-exosomes can be taken up by CD4+ T cells, which in turn regulate Th17/Treg balance (Figure 4) (66). In addition, this immune imbalance is orchestrated by DCs, the principal conductors of T cell differentiation (72). At oral lymphoid foci, DCs direct naïve T cell fate determination, selectively promoting either pro-inflammatory Th17 or reparative Treg dominance (73).
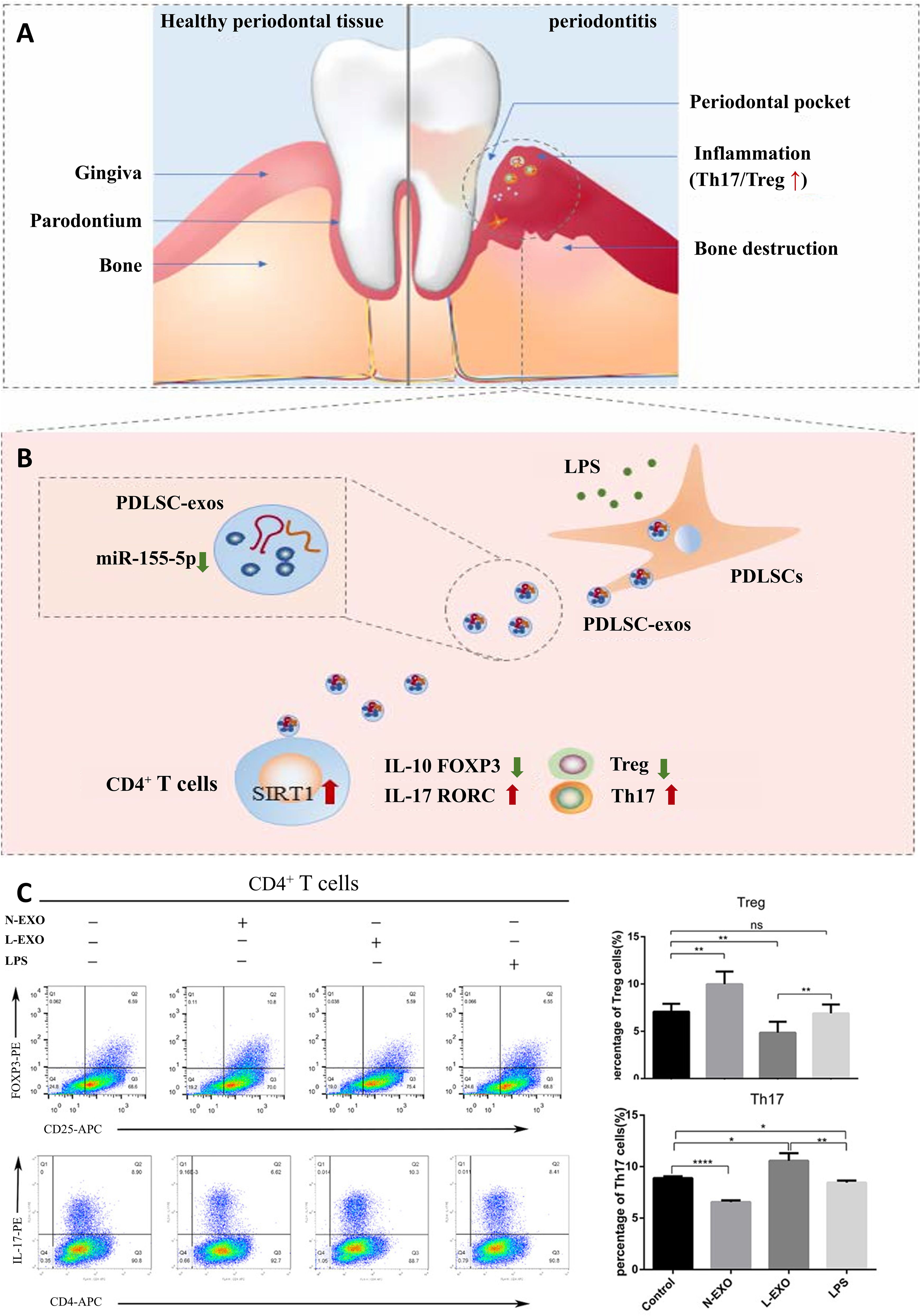
Figure 4. PDLSC-exos improves Th17/Treg balance in periodontitis. (A) Th17/Treg imbalance in periodontal tissues. (B) PDLSC-exos ameliorate the inflammatory microenvironment through the Th17/Treg/miR-155-5p/SIRT1 regulatory network. (C) After 72hr of exosome treatment of CD4+ T cells, the amount of Th17 (CD4+IL-17+) and Treg (CD4+CD25+FOXP3+) was detected by flow cytometry. ns, no significant difference; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p<0.0001. N-EXO, exosomes from the normal PDLSCs; L-EXO, exosomes from the PDLSCs stimulated with 1 ug/ml LPS (66). © 2019 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Dendritic cell (DC)-derived exosomes demonstrate targeted immunomodulatory effects in inflammatory bone loss contexts (74), with regulatory DC exosomes exhibiting enhanced retention within inflamed gingival tissues (73). These exosomes concurrently impair recipient DC maturation, suppress Th17 effector induction, and promote Treg recruitment, ultimately attenuating alveolar bone destruction by reducing bone-resorptive cytokines (73, 74). This regulatory network is amplified through reciprocal exosomal crosstalk: Treg-derived exosomes reprogram DCs toward anti-inflammatory phenotypes (characterized by increasing IL-10/decreasing IL-6 production) (75), while delivering miRNAs (e.g., Let-7d) that inhibit Th1 proliferation and IFN-γ secretion in vitro and in vivo (76). Aiello et al. found that Engineered dnIKK2-Treg-EVs further enhance immunomodulation by suppressing IFN-γ+ T cells and inducing IL-10 expression (75). Crucially, exosomal miRNAs orchestrate Th17/Treg rebalancing through distinct pathways—PDLSC-derived miR-155-5p targets Sirtuin-1 to suppress Th17 differentiation while expanding Treg populations (66), and 3D-cultured MSC-exosomes restore immune equilibrium in periodontitis via the miR-1246/NFAT5 axis (77). Complementing these mechanisms, PD-L1-engineered HUVEC-exosomes bind PD-1 on T cells to suppress activation and promote osteogenesis (78), collectively establishing exosomes as multifaceted immunotherapeutic agents.
4 Repairing and regenerating periodontal tissues
4.1 Gingival epithelial barrier regeneration
The gingival epithelium serves as the primary barrier against pathogenic microbial invasion into periodontal tissues, functioning as both a physical shield preventing microbial components from penetrating deeper connective tissues and a key component of nonspecific immunity in periodontal inflammation (79). Compromised integrity of this epithelial barrier is strongly associated with the pathogenesis of periodontal diseases (80). Therapeutic strategies targeting epithelial barrier restoration and immunomodulation have demonstrated efficacy in preventing or ameliorating periodontitis in preclinical studies (81–84).
In rat models of experimental periodontitis, DPSC-exos significantly promote gingival epithelial healing by suppressing the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway, thereby reducing inflammatory cell infiltration, mitigating tissue damage, and attenuating periodontal inflammation (85). Similarly, ADSC-exos enhance gingival repair by improving human gingival fibroblast migration and collagen synthesis through IL-1RA-mediated anti-inflammatory actions (86, 87). Despite these promising findings, research on exosome-mediated mechanisms within the gingival epithelium remains limited, and their precise regulatory functions require further elucidation. This represents a significant gap in the literature, as effective barrier restoration is fundamental to treating periodontitis.
4.2 Bone regeneration
Periodontitis is characterized by progressive inflammation and alveolar osteolysis that eventually leads to tooth loss, fundamentally driven by disrupted osteoblast-osteoclast homeostasis (88). Therapeutic strategies must therefore stabilize the immune microenvironment, activate mesenchymal stem cells (bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, BMSCs/PDLSCs), and enhance osteogenic differentiation (20). Recently, exosomes derived from various types of cells have been reported to inhibit periodontal bone loss and promote tissue regeneration (26, 51). Currently, there is evidence that exosomes can promote the repair of experimental periodontitis in rats through anti-inflammatory as well as modulation of stem cell proliferation and osteogenesis (Figure 5) (85).
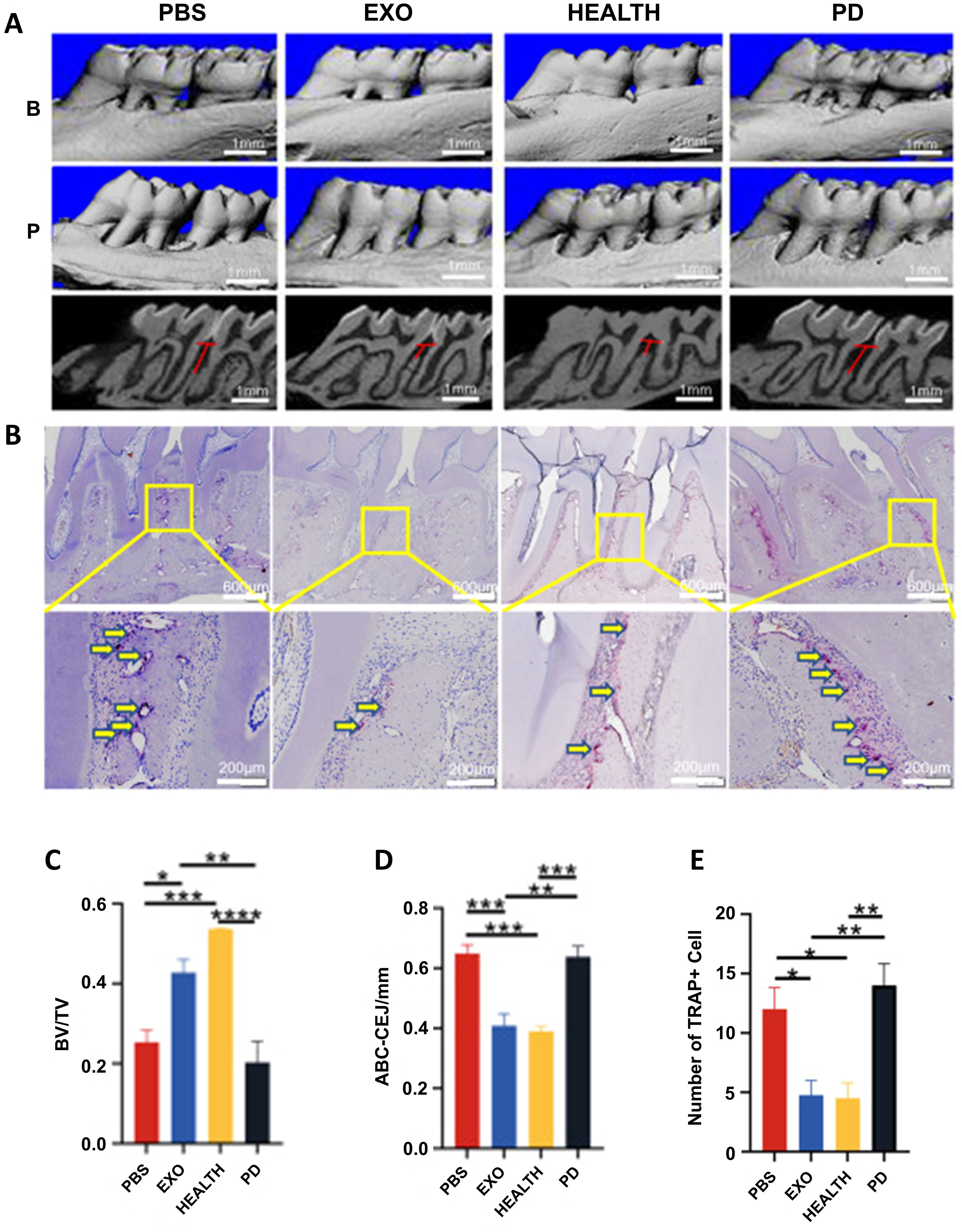
Figure 5. The therapeutic effect of DPSC-EXO on periodontitis in rats. (A) Sagittal view of a micro CT scan of the maxillary molars. The red line corresponds to the ABC-CEJ distance. (B) The extent of osteoclast infiltration in TRAP-stained sections of periodontal tissue. (C, D) BV/TV measurements and distance from ABC to CEJ. (E) Quantitative analysis of osteoclasts between the first and second molars *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p<0.0001. (85). © 2023 Qiao et al.
Specifically, immune cell-derived exosomes can enhance periodontal bone regeneration through targeted molecular delivery. Myeloid dendritic cell exosomes deliver miR-335 to BMSCs to stimulate proliferation and osteogenic differentiation (89), while LPS-stimulated monocyte exosomes upregulate expression of osteogenic genes in MSCs to facilitate bone regeneration (90). Exosomes from different types of macrophages have been shown to have different functional effects on osteogenesis, Macrophage-derived exosomes of types M0 and M2 have all been reported to contribute to osteogenesis (91, 92). M2-exosomes, in particular, induce BMSC differentiation into osteoblasts by targeting salt-inducible kinases 2 and 3 via miRNA-5106 (93) and inhibit osteoclastogenesis by releasing miR-1227-5p (94), delivering CYLD to inactivate STAT3 (95), and regulating the Pyruvate kinase (PK)M2/Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α) signaling axis (96). Furthermore, reparative M2-exosomes further deliver IL-10 mRNA to activate the IL-10/IL-10R pathway, simultaneously upregulating IL-10 expression in BMSCs and bone marrow-derived macrophage, which drives BMSC osteogenesis and inhibits osteoclast formation in periodontitis mice (20).
Periodontitis-associated bone loss primarily involves the RANKL/RANK pathway (97, 98), and the Wnt and TGF-β signaling pathways further participate in the pathogenesis of periodontitis through their roles in periodontal tissue development, including fibrinogenesis promotion, and osteogenesis regulation (99, 100). Exosomes play pivotal roles in counteracting this destruction, they promote bone formation by activating and enhancing the specific osteogenic differentiation of key mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs and PDLSCs) through the delivery of specific cargoes (85, 101–105). Li et al. found that vascular endothelial cell-derived exosomes facilitated the osteogenic differentiation and inhibited adipogenic differentiation of BMSCs by inhibiting STAT1 via miR-5p-72106_14 (106). Chen et al. found that miR-184 was down-regulated in the exosome of LPS-pretreated DFSCs, which attenuates oxidative stress, reduces inflammatory responses, and promotes osteogenic differentiation by targeting PPARα inhibition, activating the Akt pathway, and inhibiting the JNK pathway in PDLSCs (107). Likewise, Liu et al. demonstrated that exosomal lncRNA HCP5 promotes osteogenic differentiation of hPDLSCs through the miR-24-3p/HO1/P38/ELK1 pathway, thereby promoting bone regeneration (108). Mechanistically, exosomes inhibit Axin1 expression while upregulating β-catenin (109), and modulate Wnt (110) and RANKL (51) pathways to promote osteoblast generation and suppress osteoclast formation. Moreover, certain exosome subtypes carry surface-bound Wnt and TGF-β molecules that directly activate osteogenic pathways (111, 112), collectively enhancing bone repair and regeneration.
Beyond this direct osteogenic stimulation, exosomes critically ensure the success of bone regeneration by orchestrating a supportive vascular niche (113). They effectively promote angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo, even under hyperglycemic conditions, with the extent of neovascularization demonstrating a positive correlation with exosome concentration (114). Spatiotemporal coupling with angiogenesis (i.e., the precise coordination of where and when new blood vessels form) is essential for functional regeneration. An adequate vascular network supports the growth of cells associated with tissue production by delivering nutrient and oxygen, and removing metabolic waste (115). H-vessels, in particular, regulate bone vascularization, recruit osteoblasts and combine osteogenesis with angiogenesis (116). Exosomes establish vascularized bone niches by stimulating endothelial cells (ECs) proliferation/migration and upregulating VEGF/HIF-1α (117, 118). Notably, a self-amplifying circuit between BMSCs and ECs is triggered by EC-exosomes, which upregulate ZBTB16 in BMSCs to promote osteoprogenitor conversion; these osteoprogenitors reciprocally enhance H-type vessel formation via HIF-1α activation (119). Molecularly, exosomes may positively regulate angiogenesis and osteogenesis by mediating SOX2 (120), OTULIN (121) and other factors to regulate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, while activating the HIF-1α/VEGF and BMP-2/Smad1/RUNX2 signaling pathways (117). Additionally, Behera et al. proposed that the exosomal lnc-H19 uptakes endogenous miR-106 and regulates the expression of the angiogenic factor Angpt1, thereby activating lnc-H19/Tie2-NO signaling in mesenchymal and ECs, exerting angiogenic effects and promoting osteogenesis (115).
In conclusion, bone regeneration and repair is a complex physiological process that involves the synergistic action of many different cell types, such as MSCs, osteoblasts, osteoclasts, vascular endothelial cells and immune cells (122). Exosomes extracted from a variety of the above cells have been reported to promote bone repair by facilitating cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation, inhibiting osteoclast formation, promoting blood vessel formation, and modulating immunity.
4.3 Periodontal ligament regeneration
PDLSCs are considered to be the main functional cells for periodontal repair and regeneration because of their multipotent differentiation capacity (osteogenic, chondrogenic, adipogenic) and immunomodulatory properties, enabling reconstruction of osteoid/PDL-like tissues and alveolar bone. However, under inflammatory conditions, PDLSCs exhibit significantly impaired regenerative potential (123, 124).
In vivo studies confirm superior periodontal regeneration in exosome-treated rats, including newly formed bone and PDL formation (26). MSC-exos rescue this PDLSCs dysfunction through synergistic mechanisms: They suppress TNF-α/LPS-induced inflammation in human PDLSCs by inhibiting NF-κB activation—reducing apoptosis and osteogenic impairment while enhancing proliferation/differentiation (125–127)—with GMSC-exos specifically attenuating inflammation via NF-κB/Wnt5a axis modulation (128). Concurrently, exosomal biomolecules engage TLR to regulate immune responses (129–131), and by blocking the TLR4/NF-κB axis (a key driver of periodontitis-associated osteogenic suppression), MSC-exos mitigate inflammatory damage (21). Furthermore, exosomes can influence cellular function by regulating cellular energy metabolism. MSC-exos deliver glycolytic enzymes and other Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-generating enzymes (e.g., adenylate kinase, nucleoside-diphosphate kinase) that elevate ATP production via anaerobic metabolism (132–134), providing energy for cell survival and activating CD73-mediated adenosine receptor signaling to trigger pro-survival AKT/ERK pathways, thereby enhancing PDLSC migration and proliferation (26). M2-exos promotes aerobic glycolysis-mediated osteogenic differentiation of hPDLSCs by targeting TRIM26-induced PKM ubiquitination through significantly elevated miR-6879-5p (135).
5 Engineered exosomes
Exosomes have the capacity to load multiple bioactive components involved in the regulation of cellular communication and function in a paracrine manner. Consequently, their potential is amplified through two primary strategic paradigms: integration with biomaterial scaffolds to control spatiotemporal release, and direct engineering of the vesicles themselves to enhance targeting and therapeutic payload.
Exosomes have been combined with cells and materials, including hydrogels, biomaterials, and nanomaterials, to establish active tissue engineering complexes, which represent a promising future treatment for injured or defective tissues (136). Compared to free exosomes, combining exosomes with tissue-engineered scaffolds were suitable for stable and sustained exosome release, and may be advantageous for osteogenic induction and tissue repair. Moreover, exosomes often co-modify the scaffold surface with other pro-tissue-forming factors and anti-inflammatory factors to repair tissue damage. For example, Ti6Al4V scaffolds functionalized with engineered Smurf1-Exosome from BMSCs activate BMP/Smad signaling pathway in BMSCs and induce macrophage M2 polarization to promote osseointegration (137), while acellular fish scale scaffolds loaded with BMSC-exos enhance BMSC adhesion, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation in vitro, accelerating bone regeneration in vivo (138).
Beyond native vesicles, exosomes function as engineered delivery systems for therapeutic cargo (proteins, nucleic acids, lipids), leveraging their lipid bilayer structure for efficient intracellular transfer alongside lower immunogenicity and superior stability compared to synthetic nanoparticles (139, 140). Distinct from manufactured liposomal carriers, exosomes are endogenously assembled in cells, packaging a complex of biomolecules (e.g., targeting moieties, adhesion proteins) into their lipid bilayer that confers multifunctional properties (141). Since their composition reflects the donor cell’s phenotype, exosomes from specific sources possess inherent functional tendencies; immune cell-derived exosomes, for example, strongly modulate immunity (142). This intrinsic targeting capability makes them ideal for achieving precise drug delivery and enhanced therapeutic outcomes when loaded with therapeutic cargo. At present, there are two primary strategies to load exogenous drugs into exosomes (1): Pre-loading via genetic modification of parent cells to produce inherently functionalized exosomes (2); Post-loading through direct cargo incorporation into isolated exosomes. For example, BMSC-exos loaded with miR-26a via immunomodulatory peptide (DP7-C), activating the mTOR pathway to stimulate osteogenesis and suppress periodontitis (143); exosomes overexpressing miR-181b (Exo-181b) that inhibit PRKCD/AKT signaling to promote M2 macrophage polarization and bone formation (57). Moreover, the application of exosomes is undergoing a paradigm shift from serving as generic carriers to functioning as “precision-guided molecular therapeutics.” This advanced strategy synergistically leverages the inherent homing capabilities of exosomes by integrating exogenous targeting ligands with highly specific cargo (e.g., siRNA, miRNA), thereby achieving multi-faceted therapeutic outcomes. A example is bone-targeting exosome system (Bt-Exo-siShn3), an engineered exosome delivery system, which was constructed from iMSC-derived exosomes loaded with siShn3 via electroporation and conjugated to a bone-targeting peptide. This complex specifically delivers siRNA to osteoblasts, mediating Shn3 gene silencing to enhance osteogenic differentiation, promote H-type vessel formation, and inhibit osteoclastogenesis—collectively facilitating bone regeneration (Figure 6) (144).
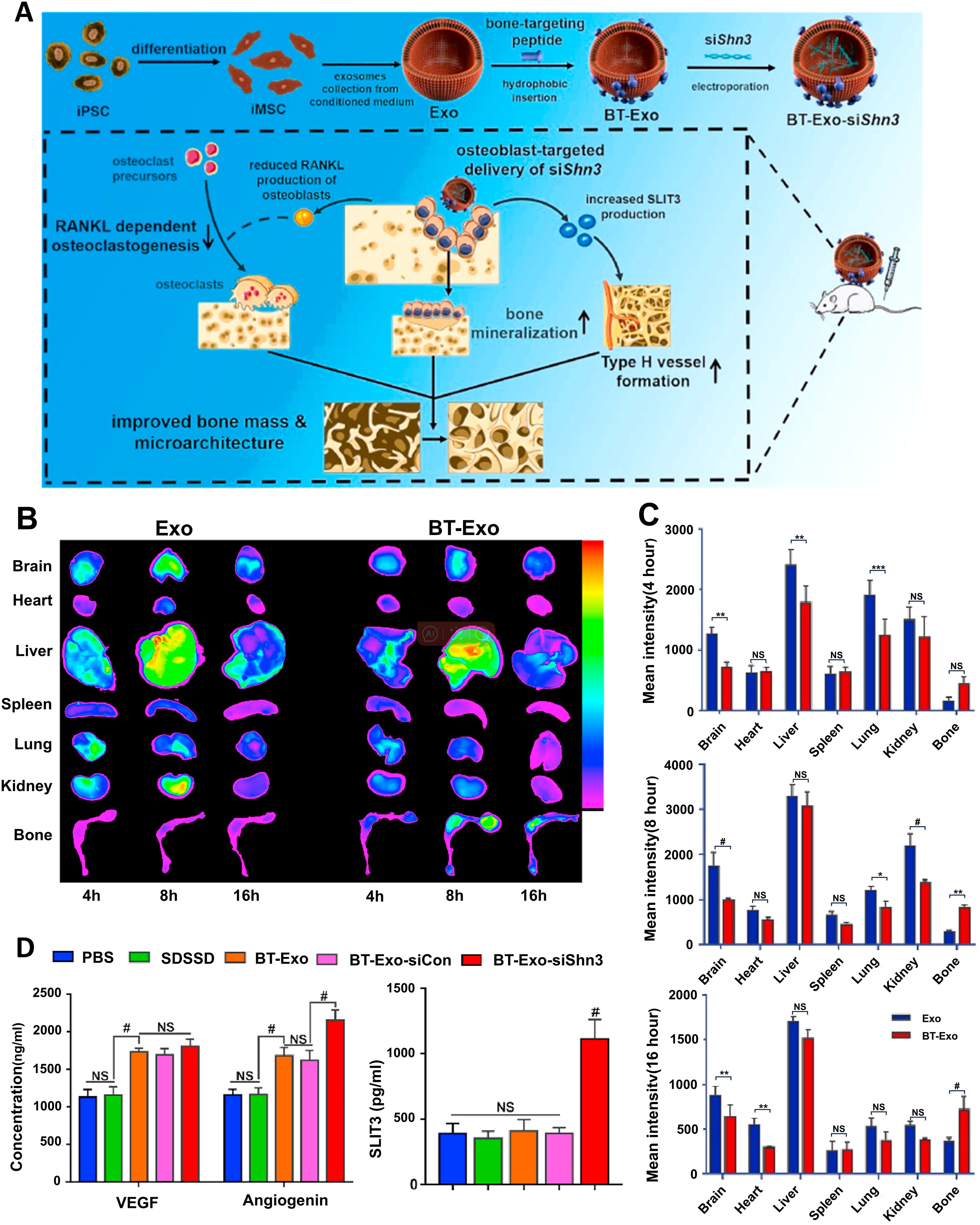
Figure 6. Bt-Exo-siShn3 promotes bone regeneration. (A) Preparation of BT-Exo-siShn3 and its therapeutic mechanism. (B) Biodistribution of DiR-labeled Exo in mouse. (C) Fluorescence intensity of DiR-labeled Exo in different organs. (D) Expression levels of VEGF, angiopoietin and SLIT3 in the co-culture system after different treatments. NS, no significant difference; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; #p<0.0001. (144). Adapted from Cui et al., 2022, © 2021 The Authors.
In summary, engineered exosomes successfully integrate the biological properties of natural vesicles with the precision and controllability of synthetic nanotechnology. While inheriting the inherent advantages of natural exosomes—such as low immunogenicity, high biocompatibility, and excellent biological barrier penetration—they have been further optimized through targeted modifications to effectively reduce off-target effects and enhance therapeutic precision and efficacy. As a result, engineered exosomes demonstrate significant potential in the treatment of periodontitis, offering the prospect of overcoming the limitations of conventional delivery systems and providing a more efficient and safe strategy for disease intervention.
6 Clinical challenges and future directions
Exosomes hold considerable promise for the treatment of periodontitis; however, several significant challenges remain, and their translation into clinical practice remains distant.
1. Challenges in large-scale production, storage, and transportation continue to limit the clinical application of exosomes (145). Current exosome yields remain low, and common methods such as ultracentrifugation are time-consuming and costly (146). Furthermore, exosomes require strict storage conditions. Studies have demonstrated that storage at 4°C can lead to aggregation and structural damage, while storage at –80°C—though it preserves particle size and concentration—may compromise certain functional properties of EVs (147). The use of cryoprotectants such as trehalose and the development of lyophilization techniques represent potential strategies to improve storage stability (148).
2. Lack of unified and efficient standards for production, isolation, and purification. Unlike synthetic carriers, exosomes are formed through intracellular assembly. Their molecular composition and biological functions depend not only on the cell type but are also susceptible to variations in culture conditions—such as bioreactor type, culture medium, duration, and cell confluence—which may alter their biological characteristics. Studies indicate that exosomes derived from the same parental cells can still exhibit heterogeneity (149). Moreover, different isolation methods yield exosomes with considerable variability in size, cargo, and function, resulting in poor batch-to-batch consistency and challenges in achieving reproducible production. This complicates comparative studies and treatment standardization (150). Quality control (QC) is essential to ensure the reproducibility of exosomes in research and to verify the purity, homogeneity, and integrity of exosome-based products prior to therapeutic use. Although the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles (ISEV) has issued guidelines recommending QC assessments, the processes for exosome isolation, optimization, and purification still lack universal standardization (151). Therefore, establishing unified protocols spanning isolation, characterization, and production, along with developing stable, controllable, and cost-effective large-scale manufacturing processes, is imperative for clinical translation.
3. Technical immaturity in therapeutic cargo loading and insufficient understanding of surface modification impacts. First, current methods for encapsulating therapeutic molecules—such as nucleic acids and proteins—into exosomes (including physical, chemical, and biological approaches) often compromise the integrity and functionality of the phospholipid membrane and surface proteins. In addition, lipid insertion strategies may introduce cytotoxicity (150, 152, 153). Second, although natural exosomes exhibit low immunogenicity, engineering modifications—particularly the introduction of exogenous proteins or chemical molecules—may alter their immunogenic profile and provoke unintended immune responses.
4. Evidence for exosome therapy in periodontitis remains insufficient. Current research remains largely confined to in vitro and animal models, with a notable lack of large-scale clinical trials validating their safety and efficacy. Some studies suggest that long-term use and genetically modified exosomes may pose unknown side effects (154). Moreover, as previously mentioned, the immune microenvironment in periodontitis is highly dynamic, and exosomes play a dual role in this context. Their regulatory networks remain poorly defined, and translating these complex—and at times contradictory—immunomodulatory effects into safe, predictable, and effective clinical treatments for periodontitis remains a major hurdle. Although certain substances within exosomes have been found to exert beneficial effects on immune regulation and tissue regeneration in periodontal inflammation, the composition of exosomal cargo remains highly complex. Within the specific pathological environment of periodontitis, our understanding of the cargo carried by exosomes from different cellular sources and their comprehensive effects on target cells remains limited.
In summary, critical obstacles—including challenges in scalable production, lack of standardized quality control, and immature engineering technologies—hinder the translation of exosome-based therapies into clinical products. From a current perspective, exosome-based treatment for periodontitis remains at a preliminary stage, and the associated costs for translational research and clinical application are expected to be substantial (155).
7 Conclusions
Exosomes, secreted by nearly all cell types, function as key mediators of intercellular communication by carrying and delivering bioactive molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. This enables them to exert the primary functions of their parent cells. Owing to their low immunogenicity, capacity for delivery across biological barriers, and multifaceted regulatory roles, exosomes have emerged as significant vectors for “cell-free therapeutics”. Their applications in disease diagnosis and treatment are consequently receiving increasing attention.
This review systematically elaborates on the therapeutic potential of exosomes in overcoming the limitations of traditional periodontal regeneration strategies. This potential is realized primarily through modulating the inflammatory immune microenvironment and directly promoting the repair of diverse periodontal tissues. Furthermore, engineered modifications of exosomes or their integration with biocompatible scaffolds can significantly enhance their targeting specificity and regenerative efficacy.
Although experimental studies have confirmed the therapeutic effects of exosomes against periodontitis (Table 1), their clinical translation faces several challenges. These include low yield, a lack of standardized protocols for isolation and characterization, difficulties in controlling heterogeneity, and inadequate assessment of long-term safety. Therefore, future efforts necessitate exploring large-scale, standardized production technologies and advancing engineering designs to enhance their yield and purity, thereby expanding the frontiers of their application in precision medicine. Additionally, more comprehensive and in-depth investigations are required to elucidate the detailed mechanisms and establish the definitive therapeutic efficacy of exosomes for the diagnosis and treatment of periodontitis.
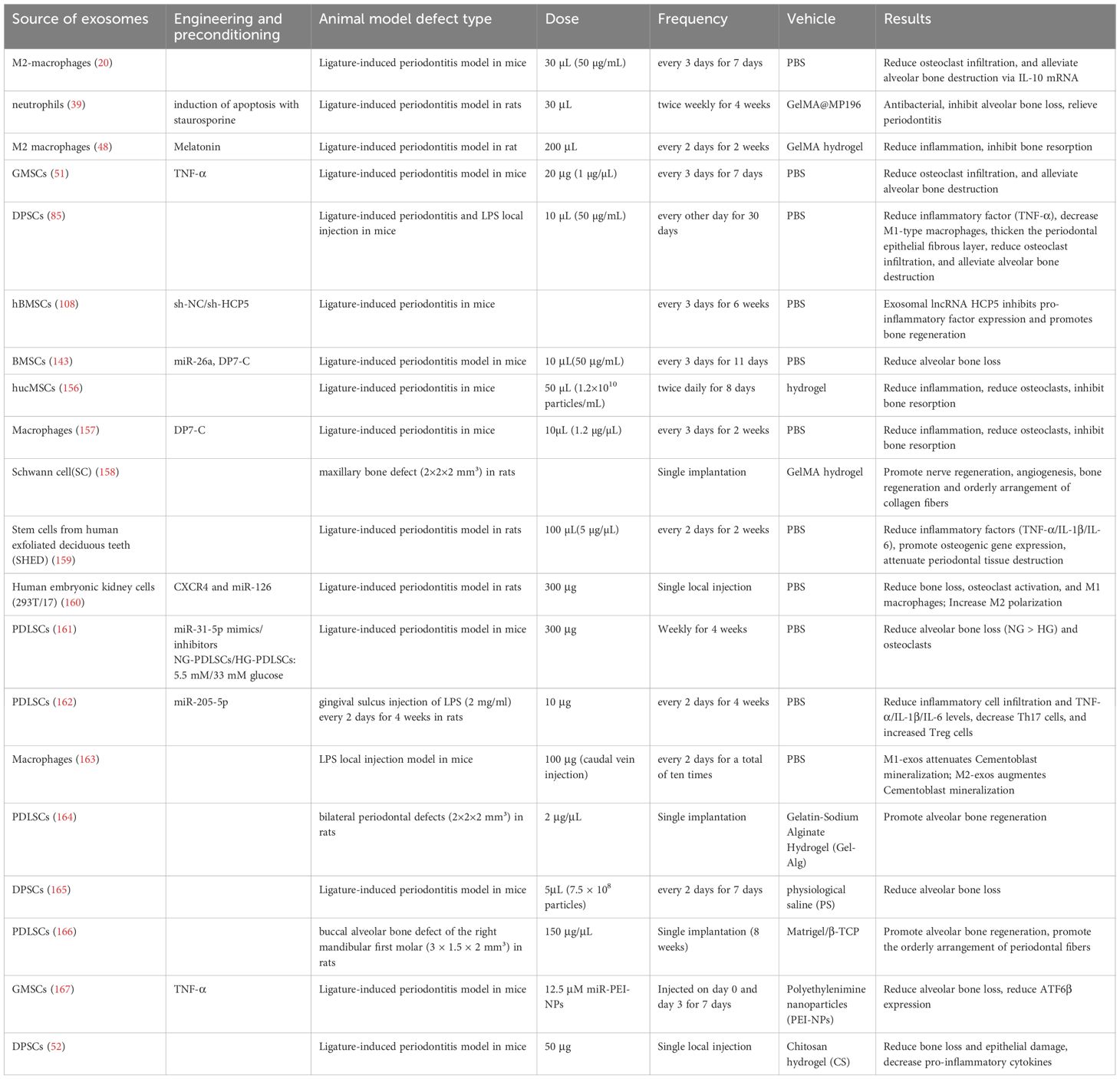
Table 1. Lists the characteristics and application scenarios published over the past 5 years regarding the use of cell-derived exosomes for periodontal regeneration in vivo.
In conclusion, compared to conventional therapies, exosomes represent a transformative cell-free therapeutic vector, offering a novel paradigm for periodontal treatment and demonstrating immense potential for clinical application.
Author contributions
SY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CH: Validation, Writing – original draft. QW: Validation, Writing – original draft. YA: Writing – original draft. DW: Writing – original draft. WS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Jilin Province Health Research Talent Special Project (2024SCZ22), International Cooperation Project of Jilin Department of Science and Technology (20240402011GH).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support received from the Jilin Province Health Research Talent Special Project (2024SCZ22), International Cooperation Project of Jilin Department of Science and Technology (20240402011GH). In addition, thanks to the partners for their mutual advice and support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
ADSCs, Adipose-derived stem cells; ATP, Adenosine triphosphate; BMP, Bone morphogenetic protein; BMP-2, Bone Morphogenetic Protein type 2; BMSCs, Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; DCs, Dendritic cells; DPSCs, Dental pulp stem cells; ECs, endothelial cells; EVs, Extracellular vesicles; GBR, Guided bone regeneration; GelMA, Gelatin methacryloyl; GMSCs, Gingival mesenchymal stem cells; GTR, Guided tissue regeneration; HIF-1α, Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; HucMSCs, Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; IFN-γ, Interferon-γ; LPS, Lipopolysaccharide; MSCs, Mesenchymal stem cells; MVBs, Multivesicular bodies; NETs, Neutrophil extracellular traps; PDL, Periodontal ligament; PDLCs, periodontal ligament cells; PDLSCs, Periodontal ligament stem cells; PK, Pyruvate kinase; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; SHED, Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth; TGF-β, Transforming growth factor beta; Th17, T helper 17; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TNF-α, Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; Treg, Regulatory T cells; VEGF, Vascular endothelial growth factor.
References
1. Eke PI, Thornton-Evans G, Dye B, and Genco R. Advances in surveillance of periodontitis: the centers for disease control and prevention periodontal disease surveillance project. J Periodontol. (2012) 83:1337–42. doi: 10.1902/jop.2012.110676
2. Kwon T, Lamster IB, and Levin L. Current concepts in the management of periodontitis. Int Dent J. (2021) 71:462–76. doi: 10.1111/idj.12630
3. Petersen PE and Yamamoto T. Improving the oral health of older people: the approach of the who global oral health programme. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. (2005) 33:81–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0528.2004.00219.x
4. Sanz M, Marco Del Castillo A, Jepsen S, Gonzalez-Juanatey JR, D’Aiuto F, Bouchard P, et al. Periodontitis and cardiovascular diseases: consensus report. J Clin Periodontol. (2020) 47:268–88. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13189
5. Kaur S, White S, and Bartold M. Periodontal disease as a risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. JBI Libr Syst Rev. (2012) 10:1–12. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-288
6. Genco RJ and Sanz M. Clinical and public health implications of periodontal and systemic diseases: an overview. Periodontol 2000. (2020) 83:7–13. doi: 10.1111/prd.12344
7. Gomes-Filho IS, Coelho JMF, Miranda SS, Cruz SS, Trindade SC, Cerqueira EMM, et al. Severe and moderate periodontitis are associated with acute myocardial infarction. J Periodontol. (2020) 91:1444–52. doi: 10.1002/jper.19-0703
8. Slots J. Periodontitis: facts, fallacies and the future. Periodontol 2000. (2017) 75:7–23. doi: 10.1111/prd.12221
9. Yu S, Liu J, Ma X, Wei Z, Ye H, Zou L, et al. Artesunate carbon dots for attenuating periodontal inflammation and promoting bone regenerationviaactivation of ampk. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. (2025) 254:114873. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2025.114873
10. Li C, Yue X, Gao H, Meng Q, Qu J, Chen Y, et al. Injectable composite hydrogels based on minocycline and nir photothermal therapy for antimicrobial and bone regeneration. Biomater Adv. (2025) 177:214397. doi: 10.1016/j.bioadv.2025.214397
11. Hynes K, Menicanin D, Gronthos S, and Bartold PM. Clinical utility of stem cells for periodontal regeneration. Periodontol 2000. (2012) 59:203–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2012.00443.x
12. Nuñez J, Vignoletti F, Caffesse RG, and Sanz M. Cellular therapy in periodontal regeneration. Periodontol 2000. (2019) 79:107–16. doi: 10.1111/prd.12250
13. Liu J, Ruan J, Weir MD, Ren K, Schneider A, Wang P, et al. Periodontal bone-ligament-cementum regeneration via scaffolds and stem cells. Cells. (2019) 8:537. doi: 10.3390/cells8060537
14. Lin H, Chen H, Zhao X, Chen Z, Zhang P, Tian Y, et al. Advances in mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium-mediated periodontal tissue regeneration. J Transl Med. (2021) 19:456. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03125-5
15. Zheng C, Chen J, Liu S, and Jin Y. Stem cell-based bone and dental regeneration: A view of microenvironmental modulation. Int J Oral Sci. (2019) 11:23. doi: 10.1038/s41368-019-0060-3
16. Deng J, Zhang Y, Xie Y, Zhang L, and Tang P. Cell transplantation for spinal cord injury: tumorigenicity of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cells Int. (2018) 2018:5653787. doi: 10.1155/2018/5653787
17. Dostert G, Mesure B, Menu P, and Velot É. How do mesenchymal stem cells influence or are influenced by microenvironment through extracellular vesicles communication? Front Cell Dev Biol. (2017) 5:6. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2017.00006
18. Wang X, He L, Huang X, Zhang S, Cao W, Che F, et al. Recent progress of exosomes in multiple myeloma: pathogenesis, diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutic strategies. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:1635. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071635
19. Raposo G and Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. (2013) 200:373–83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201211138
20. Chen X, Wan Z, Yang L, Song S, Fu Z, Tang K, et al. Exosomes derived from reparative M2-like macrophages prevent bone loss in murine periodontitis models via il-10 mrna. J Nanobiotechnology. (2022) 20:110. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01314-y
21. Liu J, Chen T, Lei P, Tang X, and Huang P. Exosomes released by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuate lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia reperfusion via the tlr4/nf-κb pathway. Int J Med Sci. (2019) 16:1238–44. doi: 10.7150/ijms.35369
22. Chen W, Huang Y, Han J, Yu L, Li Y, Lu Z, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stromal cells-derived exosome. Immunol Res. (2016) 64:831–40. doi: 10.1007/s12026-016-8798-6
23. He C, Zheng S, Luo Y, and Wang B. Exosome theranostics: biology and translational medicine. Theranostics. (2018) 8:237–55. doi: 10.7150/thno.21945
24. Lin H, Chen H, Zhao X, Ding T, Wang Y, Chen Z, et al. Advances of exosomes in periodontitis treatment. J Transl Med. (2022) 20:279. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03487-4
25. Wang R, Ji Q, Meng C, Liu H, Fan C, Lipkind S, et al. Role of gingival mesenchymal stem cell exosomes in macrophage polarization under inflammatory conditions. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 81:106030. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106030
26. Chew JRJ, Chuah SJ, Teo KYW, Zhang S, Lai RC, Fu JH, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance periodontal ligament cell functions and promote periodontal regeneration. Acta Biomater. (2019) 89:252–64. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.03.021
27. Garbern JC and Lee RT. Cardiac stem cell therapy and the promise of heart regeneration. Cell Stem Cell. (2013) 12:689–98. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2013.05.008
28. Yan XZ, Yang F, Jansen JA, De Vries RB, and Van Den Beucken JJ. Cell-based approaches in periodontal regeneration: A systematic review and meta-analysis of periodontal defect models in animal experimental work. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. (2015) 21:411–26. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2015.0049
29. Liang X, Ding Y, Zhang Y, Tse HF, and Lian Q. Paracrine mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy: current status and perspectives. Cell Transplant. (2014) 23:1045–59. doi: 10.3727/096368913x667709
30. Williams DW, Greenwell-Wild T, Brenchley L, Dutzan N, Overmiller A, Sawaya AP, et al. Human oral mucosa cell atlas reveals a stromal-neutrophil axis regulating tissue immunity. Cell. (2021) 184:4090–104.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.013
31. Cohn ZA and Hirsch JG. The influence of phagocytosis on the intracellular distribution of granule-associated components of polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. (1960) 112:1015–22. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.1015
32. Kim TS, Silva LM, Theofilou VI, Greenwell-Wild T, Li L, Williams DW, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps and extracellular histones potentiate il-17 inflammation in periodontitis. J Exp Med. (2023) 220:e20221751. doi: 10.1084/jem.20221751
33. Mousa AO, Al Hussaini AHA, and Hussein HM. The potential role of reactive oxygen species produced by low-density neutrophils in periodontitis. Eur J Dent. (2024) 18:1142–8. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1782211
34. Shan Y, Zhong J, Sun Q, Gao W, Zhang C, Chen H, et al. Dual nanozymes-loaded core-shell microneedle patches with antibacterial and nets-degradation bifunctional properties for periodontitis treatment. Bioact Mater. (2025) 53:161–77. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.07.003
35. Vitkov L, Klappacher M, Hannig M, and Krautgartner WD. Extracellular neutrophil traps in periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. (2009) 44:664–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2008.01175.x
36. Kaspi H, Semo J, Abramov N, Dekel C, Lindborg S, Kern R, et al. Msc-ntf (Nurown®) exosomes: A novel therapeutic modality in the mouse lps-induced ards model. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2021) 12:72. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02143-w
37. Chen L, Liu Y, Wang Z, Zhang L, Xu Y, Li Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles protect against abdominal aortic aneurysm formation by inhibiting net-induced ferroptosis. Exp Mol Med. (2023) 55:939–51. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-00986-2
38. Morishima Y, Kawabori M, Yamazaki K, Takamiya S, Yamaguchi S, Nakahara Y, et al. Intravenous administration of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome alleviates spinal cord injury by regulating neutrophil extracellular trap formation through exosomal mir-125a-3p. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:2406. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042406
39. Zhuo H, Zhang S, Wang H, Deng J, and Zhang X. Gelatin methacryloyl @Mp196/exos hydrogel induced neutrophil apoptosis and macrophage M2 polarization to inhibit periodontal bone loss. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. (2025) 248:114466. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2024.114466
40. Yang J, Xie Y, Xia Z, Ji S, Yang X, Yue D, et al. Hucmsc-exo induced N2 polarization of neutrophils: implications for angiogenesis and tissue restoration in wound healing. Int J Nanomedicine. (2024) 19:3555–75. doi: 10.2147/ijn.S458295
41. Taghavi-Farahabadi M, Mahmoudi M, Rezaei N, and Hashemi SM. Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells exosomes and conditioned media increased neutrophil lifespan and phagocytosis capacity. Immunol Invest. (2021) 50:1042–57. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2020.1801720
42. Mahmoudi M, Taghavi-Farahabadi M, Rezaei N, and Hashemi SM. Comparison of the effects of adipose tissue mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes with conditioned media on neutrophil function and apoptosis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2019) 74:105689. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105689
43. Zhou S, Zhu Y, Wu Y, Zhang X, Kong X, Zhao X, et al. New insights on metabolic reprogramming in macrophage plasticity. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 157:114797. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114797
44. Wynn TA and Vannella KM. Macrophages in tissue repair, regeneration, and fibrosis. Immunity. (2016) 44:450–62. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.02.015
45. Gordon S and Martinez FO. Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity. (2010) 32:593–604. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.05.007
46. Sun X, Gao J, Meng X, Lu X, Zhang L, and Chen R. Polarized macrophages in periodontitis: characteristics, function, and molecular signaling. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:763334. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.763334
47. Yang J, Zhu Y, Duan D, Wang P, Xin Y, Bai L, et al. Enhanced activity of macrophage M1/M2 phenotypes in periodontitis. Arch Oral Biol. (2018) 96:234–42. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2017.03.006
48. Cui Y, Hong S, Xia Y, Li X, He X, Hu X, et al. Melatonin engineering M2 macrophage-derived exosomes mediate endoplasmic reticulum stress and immune reprogramming for periodontitis therapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) 10:e2302029. doi: 10.1002/advs.202302029
49. Yue C, Cao J, Wong A, Kim JH, Alam S, Luong G, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cell exosomes ameliorate periodontitis. J Dent Res. (2022) 101:1110–8. doi: 10.1177/00220345221084975
50. Hu P, Liang L, Li B, and Xia W. Heterocoagulation between coal and quartz particles studied by the mineral heterocoagulation quantifying system. Minerals Eng. (2019) 138:7–13. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2019.04.029
51. Nakao Y, Fukuda T, Zhang Q, Sanui T, Shinjo T, Kou X, et al. Exosomes from tnf-α-treated human gingiva-derived mscs enhance M2 macrophage polarization and inhibit periodontal bone loss. Acta Biomater. (2021) 122:306–24. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.12.046
52. Shen Z, Kuang S, Zhang Y, Yang M, Qin W, Shi X, et al. Chitosan hydrogel incorporated with dental pulp stem cell-derived exosomes alleviates periodontitis in mice via a macrophage-dependent mechanism. Bioactive Materials. (2020) 5:1113–26. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.07.002
53. Lo Sicco C, Reverberi D, Balbi C, Ulivi V, Principi E, Pascucci L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as mediators of anti-inflammatory effects: endorsement of macrophage polarization. Stem Cells Transl Med. (2017) 6:1018–28. doi: 10.1002/sctm.16-0363
54. Chen Y, Dong J, Li J, Li J, Lu Y, Dong W, et al. Engineered macrophage-derived exosomes via click chemistry for the treatment of osteomyelitis. J Mater Chem B. (2024) 12:10593–604. doi: 10.1039/d4tb01346h
55. Shen D and He Z. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes regulate the polarization and inflammatory response of macrophages via mir-21-5p to promote repair after myocardial reperfusion injury. Ann Transl Med. (2021) 9:1323. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-3557
56. Zhao J, Li X, Hu J, Chen F, Qiao S, Sun X, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes attenuate myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury through mir-182-regulated macrophage polarization. Cardiovasc Res. (2019) 115:1205–16. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz040
57. Liu W, Yu M, Chen F, Wang L, Ye C, Chen Q, et al. A novel delivery nanobiotechnology: engineered mir-181b exosomes improved osteointegration by regulating macrophage polarization. J Nanobiotechnology. (2021) 19:269. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01015-y
58. Li R, Li D, Wang H, Chen K, Wang S, Xu J, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells regulate M1/M2 macrophage phenotypic polarization to promote bone healing via mir-451a/mif. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2022) 13:149. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02823-1
59. Wang Z, Maruyama K, Sakisaka Y, Suzuki S, Tada H, Suto M, et al. Cyclic stretch force induces periodontal ligament cells to secrete exosomes that suppress il-1β Production through the inhibition of the nf-κb signaling pathway in macrophages. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1310. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01310
60. Yuan X, Cao H, Wang J, Tang K, Li B, Zhao Y, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of calcium and strontium co-doped titanium oxides on osteogenesis. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:1196. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01196
61. Wu H, Li L, Ma Y, Chen Y, Zhao J, Lu Y, et al. Regulation of selective pparγ Modulators in the differentiation of osteoclasts. J Cell Biochem. (2013) 114:1969–77. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24534
62. Yamaguchi T, Movila A, Kataoka S, Wisitrasameewong W, Ruiz Torruella M, Murakoshi M, et al. Proinflammatory M1 macrophages inhibit rankl-induced osteoclastogenesis. Infect Immun. (2016) 84:2802–12. doi: 10.1128/iai.00461-16
63. Yang J, Park OJ, Kim J, Kwon Y, Yun CH, and Han SH. Modulation of macrophage subtypes by irf5 determines osteoclastogenic potential. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:23033–42. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28863
64. Bai X, Wang Y, Ma X, Yang Y, Deng C, Sun M, et al. Periodontal ligament cells-derived exosomes promote osteoclast differentiation via modulating macrophage polarization. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:1465. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52073-9
65. Wang L, Wang J, Jin Y, Gao H, and Lin X. Oral administration of all-trans retinoic acid suppresses experimental periodontitis by modulating the th17/treg imbalance. J Periodontol. (2014) 85:740–50. doi: 10.1902/jop.2013.130132
66. Zheng Y, Dong C, Yang J, Jin Y, Zheng W, Zhou Q, et al. Exosomal microrna-155-5p from pdlscs regulated th17/treg balance by targeting sirtuin-1 in chronic periodontitis. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:20662–74. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28671
67. Proto JD, Doran AC, Gusarova G, Yurdagul A Jr., Sozen E, Subramanian M, et al. Regulatory T cells promote macrophage efferocytosis during inflammation resolution. Immunity. (2018) 49:666–77.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.07.015
68. Li B and Zheng SG. How regulatory T cells sense and adapt to inflammation. Cell Mol Immunol. (2015) 12:519–20. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2015.65
69. Wang R, Liang Q, Zhang Q, Zhao S, Lin Y, Liu B, et al. Ccl2-induced regulatory T cells balance inflammation through macrophage polarization during liver reconstitution. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2024) 11:e2403849. doi: 10.1002/advs.202403849
70. Garlet GP, Cardoso CR, Mariano FS, Claudino M, De Assis GF, Campanelli AP, et al. Regulatory T cells attenuate experimental periodontitis progression in mice. J Clin Periodontol. (2010) 37:591–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01586.x
71. Zhang Y, Guo J, and Jia R. Treg: A promising immunotherapeutic target in oral diseases. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:667862. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.667862
72. Kadowaki N. Dendritic cells: A conductor of T cell differentiation. Allergol Int. (2007) 56:193–9. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.R-07-146
73. Elashiry M, Elashiry MM, Elsayed R, Rajendran M, Auersvald C, Zeitoun R, et al. Dendritic cell derived exosomes loaded with immunoregulatory cargo reprogram local immune responses and inhibit degenerative bone disease in vivo. J Extracell Vesicles. (2020) 9:1795362. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2020.1795362
74. El-Awady AR, Elashiry M, Morandini AC, Meghil MM, and Cutler CW. Dendritic cells a critical link to alveolar bone loss and systemic disease risk in periodontitis: immunotherapeutic implications. Periodontol 2000. (2022) 89:41–50. doi: 10.1111/prd.12428
75. Aiello S, Rocchetta F, Longaretti L, Faravelli S, Todeschini M, Cassis L, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from T regulatory cells suppress T cell proliferation and prolong allograft survival. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:11518. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08617-3
76. Okoye IS, Coomes SM, Pelly VS, Czieso S, Papayannopoulos V, Tolmachova T, et al. Microrna-containing T-regulatory-cell-derived exosomes suppress pathogenic T helper 1 cells. Immunity. (2014) 41:89–103. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.05.019
77. Zhang Y, Chen J, Fu H, Kuang S, He F, Zhang M, et al. Exosomes derived from 3d-cultured mscs improve therapeutic effects in periodontitis and experimental colitis and restore the th17 cell/treg balance in inflamed periodontium. Int J Oral Sci. (2021) 13:43. doi: 10.1038/s41368-021-00150-4
78. Lin Z, Xiong Y, Meng W, Hu Y, Chen L, Chen L, et al. Exosomal pd-L1 induces osteogenic differentiation and promotes fracture healing by acting as an immunosuppressant. Bioact Mater. (2022) 13:300–11. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.10.042
79. Rivera A, Siracusa MC, Yap GS, and Gause WC. Innate cell communication kick-starts pathogen-specific immunity. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:356–63. doi: 10.1038/ni.3375
80. Bosshardt DD. The periodontal pocket: pathogenesis, histopathology and consequences. Periodontol 2000. (2018) 76:43–50. doi: 10.1111/prd.12153
81. Lv J, Liu Y, Jia S, Zhang Y, Tian H, Li J, et al. Carbon monoxide-releasing molecule-3 suppresses tumor necrosis factor-α- and interleukin-1β-induced expression of junctional molecules on human gingival fibroblasts via the heme oxygenase-1 pathway. Mediators Inflammation. (2020) 2020:6302391. doi: 10.1155/2020/6302391
82. Galenko-Yaroshevsky PA, Slavinskiy AА, Todorov SS, Popkov VL, Shelemekh OV, Lebedeva SA, et al. The effect of zinc complex of N-isopropenylimidazole on the morphological characteristics of gum tissues in experimental endodontic-periodontal lesions in rats. Res Results Pharmacol. (2023) 9:1–12. doi: 10.18413/rrpharmacology.9.10040
83. Tiwari S, Mahale SA, Walvekar AK, Patil RD, Harish S, Mehta A, et al. Efficacy of colloidal nanosilver tooth gel in the management of orodental conditions: A prospective, randomized, triple arm, parallel, double-blind controlled interventional clinical study. J Oral Health Community Dentistry. (2023) 17:49–56. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10062-0166
84. Takeuchi H, Nakamura E, Yamaga S, and Amano A. Porphyromonas gingivalis infection induces lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan penetration through gingival epithelium. Front Oral Health. (2022) 3:845002. doi: 10.3389/froh.2022.845002
85. Qiao X, Tang J, Dou L, Yang S, Sun Y, Mao H, et al. Dental pulp stem cell-derived exosomes regulate anti-inflammatory and osteogenesis in periodontal ligament stem cells and promote the repair of experimental periodontitis in rats. Int J Nanomedicine. (2023) 18:4683–703. doi: 10.2147/ijn.S420967
86. Zheng Y, Dong X, Wang X, Wang J, Chen S, He Y, et al. Exosomes derived from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells prevent medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw through il-1ra. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:8694. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108694
87. Kou X, Xu X, Chen C, Sanmillan ML, Cai T, Zhou Y, et al. The fas/fap-1/cav-1 complex regulates il-1ra secretion in mesenchymal stem cells to accelerate wound healing. Sci Transl Med. (2018) 10:eaai8524. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aai8524
88. Zhou R, Shen L, Yang C, Wang L, Guo H, Yang P, et al. Periodontitis may restrain the mandibular bone healing via disturbing osteogenic and osteoclastic balance. Inflammation. (2018) 41:972–83. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0751-5
89. Cao Z, Wu Y, Yu L, Zou L, Yang L, Lin S, et al. Exosomal mir-335 derived from mature dendritic cells enhanced mesenchymal stem cell-mediated bone regeneration of bone defects in athymic rats. Mol Med. (2021) 27:20. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00268-5
90. Ekström K, Omar O, Granéli C, Wang X, Vazirisani F, and Thomsen P. Monocyte exosomes stimulate the osteogenic gene expression of mesenchymal stem cells. PloS One. (2013) 8:e75227. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075227
91. Kang M, Huang CC, Lu Y, Shirazi S, Gajendrareddy P, Ravindran S, et al. Bone regeneration is mediated by macrophage extracellular vesicles. Bone. (2020) 141:115627. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115627
92. Xia Y, He XT, Xu XY, Tian BM, An Y, and Chen FM. Exosomes derived from M0, M1 and M2 macrophages exert distinct influences on the proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. PeerJ. (2020) 8:e8970. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8970
93. Xiong Y, Chen L, Yan C, Zhou W, Yu T, Sun Y, et al. M2 macrophagy-derived exosomal mirna-5106 induces bone mesenchymal stem cells towards osteoblastic fate by targeting salt-inducible kinase 2 and 3. J Nanobiotechnology. (2020) 18:66. doi: 10.1186/s12951-020-00622-5
94. Chen S, Liu J, and Zhu L. M2-like macrophage-derived exosomes inhibit osteoclastogenesis via releasing mir-1227-5p. Immunobiology. (2025) 230:152861. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2024.152861
95. Guo ZY, Yin NN, Li XF, Wang MM, Sui XN, Jiang CD, et al. Exosomes secreted from M2-polarized macrophages inhibit osteoclast differentiation via cyld. Tissue Cell. (2025) 93:102645. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2024.102645
96. Zhang Y, Liang Y, and Zhou Y. M2 polarization of raw264.7-derived exosomes inhibits osteoclast differentiation and inflammation via pkm2/hif-1α Axis. Immunol Invest. (2025) 54:1–15. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2025.2525896
97. Tsukasaki M, Komatsu N, Nagashima K, Nitta T, Pluemsakunthai W, Shukunami C, et al. Host defense against oral microbiota by bone-damaging T cells. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:701. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03147-6
98. Hajishengallis G, Chavakis T, and Lambris JD. Current understanding of periodontal disease pathogenesis and targets for host-modulation therapy. Periodontol 2000. (2020) 84:14–34. doi: 10.1111/prd.12331
99. Kuznetsova AV, Popova OP, Danilova TI, Latyshev AV, Yanushevich OO, and Ivanov AA. Effects of ecm components on periodontal ligament stem cell differentiation under conditions of disruption of wnt and tgf-β Signaling pathways. J Funct Biomater. (2025) 16:94. doi: 10.3390/jfb16030094
100. Wei X, Liu Q, Guo S, and Wu Y. Role of wnt5a in periodontal tissue development, maintenance, and periodontitis: implications for periodontal regeneration (Review). Mol Med Rep. (2021) 23:167. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11806
101. Narayanan R, Huang CC, and Ravindran S. Hijacking the cellular mail: exosome mediated differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. (2016) 2016:3808674. doi: 10.1155/2016/3808674
102. Gao J and Wu Z. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes enable osteogenic differentiation and inhibit inflammation in human periodontal ligament stem cells through promotion of cxcl12 expression. BMC Oral Health. (2024) 24:1070. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04831-4
103. Deng Y, Xiao J, Huang X, and Cao Z. Macrophage-derived exosomes rescue the tnf-α-suppressed osteo-/cementogenic differentiation of hpdlcs. Oral Dis. (2024) 30:5232–42. doi: 10.1111/odi.14947
104. Wang M, Li J, Ye Y, Chen D, and Song J. Shed-derived exosomes improve the repair capacity and osteogenesis potential of hpdlcs. Oral Dis. (2023) 29:1692–705. doi: 10.1111/odi.14153
105. Liu Y, Zeng L, Wang W, Yang Y, Wang Z, Liu J, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosome-derived mir-335-5p promotes osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells to alleviate periodontitis by downregulating dkk1. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. (2023) 43:420–7. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.03.12
106. Li H, Wang J, Xie X, Chen Y, Zheng Q, He J, et al. Exosome-derived mir-5p-72106_14 in vascular endothelial cells regulates fate determination of bmscs. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. (2024) 482:116793. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2023.116793
107. Chen L, Zhang J, Yu J, Guo S, and Tian W. Lps pretreated dental follicle stem cell derived exosomes promote periodontal tissue regeneration via mir-184 and pparα-akt-jnk signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2025) 16:347. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04462-8
108. Liu Y, Zhu J, Wang WH, Zeng L, Yang YL, Wang Z, et al. Exosomal lncrna hcp5 derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves chronic periodontitis by mir-24-3p/ho1/P38/elk1 pathway. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e34203. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34203
109. Cui Y, Luan J, Li H, Zhou X, and Han J. Exosomes derived from mineralizing osteoblasts promote st2 cell osteogenic differentiation by alteration of microrna expression. FEBS Lett. (2016) 590:185–92. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12024
110. Zhang D, Xiao W, Liu C, Wang Z, Liu Y, Yu Y, et al. Exosomes derived from adipose stem cells enhance bone fracture healing via the activation of the wnt3a/β-catenin signaling pathway in rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:4852. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054852
111. Gross JC, Chaudhary V, Bartscherer K, and Boutros M. Active wnt proteins are secreted on exosomes. Nat Cell Biol. (2012) 14:1036–45. doi: 10.1038/ncb2574
112. Webber J, Steadman R, Mason MD, Tabi Z, and Clayton A. Cancer exosomes trigger fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation. Cancer Res. (2010) 70:9621–30. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-10-1722
113. Sunartvanichkul T, Arayapisit T, Sangkhamanee SS, Chaweewannakorn C, Iwasaki K, Klaihmon P, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes from human exfoliated deciduous teeth promote angiogenesis in hyperglycemic-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Appl Oral Sci. (2023) 31:e20220427. doi: 10.1590/1678-7757-2022-0427
114. Qi X, Zhang J, Yuan H, Xu Z, Li Q, Niu X, et al. Exosomes secreted by human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells repair critical-sized bone defects through enhanced angiogenesis and osteogenesis in osteoporotic rats. Int J Biol Sci. (2016) 12:836–49. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.14809
115. Behera J, Kumar A, Voor MJ, and Tyagi N. Exosomal lncrna-H19 promotes osteogenesis and angiogenesis through mediating angpt1/tie2-no signaling in cbs-heterozygous mice. Theranostics. (2021) 11:7715–34. doi: 10.7150/thno.58410
116. Kusumbe AP, Ramasamy SK, and Adams RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. (2014) 507:323–8. doi: 10.1038/nature13145
117. Zhang L, Jiao G, Ren S, Zhang X, Li C, Wu W, et al. Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhance fracture healing through the promotion of osteogenesis and angiogenesis in a rat model of nonunion. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 11:38. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-1562-9
118. Zhang Y, Hao Z, Wang P, Xia Y, Wu J, Xia D, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance fracture healing through hif-1α-mediated promotion of angiogenesis in a rat model of stabilized fracture. Cell Prolif. (2019) 52:e12570. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12570
119. Liu L, Zhou N, Fu S, Wang L, Liu Y, Fu C, et al. Endothelial cell-derived exosomes trigger a positive feedback loop in osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling via up-regulating zinc finger and btb domain containing 16 in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell. J Nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22:721. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-03002-5
120. Wu F, Song C, Zhen G, Jin Q, Li W, Liang X, et al. Exosomes derived from bmscs in osteogenic differentiation promote type H blood vessel angiogenesis through mir-150-5p mediated metabolic reprogramming of endothelial cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2024) 81:344. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05371-4
121. Luo Z, Peng W, Xu Y, Xie Y, Liu Y, Lu H, et al. Exosomal otulin from M2 macrophages promotes the recovery of spinal cord injuries via stimulating wnt/β-catenin pathway-mediated vascular regeneration. Acta Biomater. (2021) 136:519–32. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.09.026
122. Ho-Shui-Ling A, Bolander J, Rustom LE, Johnson AW, Luyten FP, and Picart C. Bone regeneration strategies: engineered scaffolds, bioactive molecules and stem cells current stage and future perspectives. Biomaterials. (2018) 180:143–62. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.07.017
123. Ikeda H, Sumita Y, Ikeda M, Ikeda H, Okumura T, Sakai E, et al. Engineering bone formation from human dental pulp- and periodontal ligament-derived cells. Ann BioMed Eng. (2011) 39:26–34. doi: 10.1007/s10439-010-0115-2
124. Lee JS, Yi JK, An SY, and Heo JS. Increased osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells on polydopamine film occurs via activation of integrin and pi3k signaling pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2014) 34:1824–34. doi: 10.1159/000366381
125. Zhang W, Jia L, Zhao B, Xiong Y, Wang YN, Liang J, et al. Quercetin reverses tnf−α Induced osteogenic damage to human periodontal ligament stem cells by suppressing the nf−κb/nlrp3 inflammasome pathway. Int J Mol Med. (2021) 47:39. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4872
126. Guo L, Sun H, and Pu J. Gnai3 mediated by lin28a regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and osteogenic differentiation in periodontal stem cells by mediating the nf-κb/nlrp3 inflammasome pathway. Arch Oral Biol. (2024) 163:105974. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2024.105974
127. Jiang J, Zhang N, Song H, Yang Y, Li J, and Hu X. Oridonin alleviates the inhibitory effect of lipopolysaccharide on the proliferation and osteogenic potential of periodontal ligament stem cells by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and nf-κb/nlrp3 inflammasome signaling. BMC Oral Health. (2023) 23:137. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-02827-0
128. Sun J, Wang Z, Liu P, Hu Y, Li T, Yang J, et al. Exosomes derived from human gingival mesenchymal stem cells attenuate the inflammatory response in periodontal ligament stem cells. Front Chem. (2022) 10:863364. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.863364
129. Liu J, Jiang M, Deng S, Lu J, Huang H, Zhang Y, et al. Mir-93-5p-containing exosomes treatment attenuates acute myocardial infarction-induced myocardial damage. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2018) 11:103–15. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.01.010
130. Kojima M, Gimenes-Junior JA, Chan TW, Eliceiri BP, Baird A, Costantini TW, et al. Exosomes in postshock mesenteric lymph are key mediators of acute lung injury triggering the macrophage activation via toll-like receptor 4. FASEB J. (2018) 32:97–110. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700488R
131. Seo W, Eun HS, Kim SY, Yi HS, Lee YS, Park SH, et al. Exosome-mediated activation of toll-like receptor 3 in stellate cells stimulates interleukin-17 production by Γδ T cells in liver fibrosis. Hepatology. (2016) 64:616–31. doi: 10.1002/hep.28644
132. Lai RC, Yeo RWY, Tan SS, Zhang B, Yin Y, Sze NSK, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes: the future msc-based therapy? In: Chase LG and Vemuri MC, editors. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ (2013). p. 39–61.
133. Lai RC, Yeo RW, Tan KH, and Lim SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosome ameliorates reperfusion injury through proteomic complementation. Regener Med. (2013) 8:197–209. doi: 10.2217/rme.13.4
134. Lai RC, Yeo RWY, and Lim SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. (2015) 40:82–8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.03.001
135. Liao X, Yang Z, Li Y, Cui Y, Ma L, Liang C, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosome facilitates aerobic glycolysis and osteogenic differentiation of hpdlscs by regulating trim26-induced pkm ubiquitination. Free Radic Biol Med. (2025) 237:88–100. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2025.05.425
136. Kim HD, Amirthalingam S, Kim SL, Lee SS, Rangasamy J, and Hwang NS. Biomimetic materials and fabrication approaches for bone tissue engineering. Adv Healthc Mater. (2017) 6. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700612
137. Xu H, Chai Q, Xu X, Li Z, Bao W, Man Z, et al. Exosome-functionalized ti6al4v scaffolds promoting osseointegration by modulating endogenous osteogenesis and osteoimmunity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. (2022) 14:46161–75. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c11102
138. Wang Y, Kong B, Chen X, Liu R, Zhao Y, Gu Z, et al. Bmsc exosome-enriched acellular fish scale scaffolds promote bone regeneration. J Nanobiotechnology. (2022) 20:444. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01646-9
139. Lou P, Liu S, Wang Y, Lv K, Zhou X, Li L, et al. Neonatal-tissue-derived extracellular vesicle therapy (Next): A potent strategy for precision regenerative medicine. Adv Mater. (2023) 35:e2300602. doi: 10.1002/adma.202300602
140. Ferguson SW and Nguyen J. Exosomes as therapeutics: the implications of molecular composition and exosomal heterogeneity. J Control Release. (2016) 228:179–90. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.02.037
141. Mathivanan S, Ji H, and Simpson RJ. Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteomics. (2010) 73:1907–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2010.06.006
142. Sun D, Zhuang X, Xiang X, Liu Y, Zhang S, Liu C, et al. A novel nanoparticle drug delivery system: the anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin is enhanced when encapsulated in exosomes. Mol Ther. (2010) 18:1606–14. doi: 10.1038/mt.2010.105
143. Lai S, Deng L, Liu C, Li X, Fan L, Zhu Y, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes loaded with mir-26a through the novel immunomodulatory peptide dp7-C can promote osteogenesis. Biotechnol Lett. (2023) 45:905–19. doi: 10.1007/s10529-023-03376-w
144. Cui Y, Guo Y, Kong L, Shi J, Liu P, Li R, et al. A bone-targeted engineered exosome platform delivering sirna to treat osteoporosis. Bioact Mater. (2022) 10:207–21. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.09.015
145. Ye Y, Zhang X, Xie F, Xu B, Xie P, Yang T, et al. An engineered exosome for delivering sgrna: cas9 ribonucleoprotein complex and genome editing in recipient cells. Biomater Sci. (2020) 8:2966–76. doi: 10.1039/d0bm00427h
146. Schwarz G, Ren X, Xie W, Guo H, Jiang Y, and Zhang J. Engineered exosomes: A promising drug delivery platform with therapeutic potential. Front Mol Biosci. (2025) 12:1583992. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1583992
147. Lőrincz ÁM, Timár CI, Marosvári KA, Veres DS, Otrokocsi L, Kittel Á, et al. Effect of storage on physical and functional properties of extracellular vesicles derived from neutrophilic granulocytes. J Extracell Vesicles. (2014) 3:25465. doi: 10.3402/jev.v3.25465
148. Frank J, Richter M, de Rossi C, Lehr CM, Fuhrmann K, and Fuhrmann G. Extracellular vesicles protect glucuronidase model enzymes during freeze-drying. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:12377. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30786-y
149. Li S, Xu J, Qian J, and Gao X. Engineering extracellular vesicles for cancer therapy: recent advances and challenges in clinical translation. Biomater Sci. (2020) 8:6978–91. doi: 10.1039/d0bm01385d
150. Chen H, Wang L, Zeng X, Schwarz H, Nanda HS, Peng X, et al. Exosomes, a new star for targeted delivery. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:751079. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.751079
151. Witwer KW, Buzás EI, Bemis LT, Bora A, Lässer C, Lötvall J, et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J Extracell Vesicles. (2013) 2:2. doi: 10.3402/jev.v2i0.20360
152. Kim MS, Haney MJ, Zhao Y, Yuan D, Deygen I, Klyachko NL, et al. Engineering macrophage-derived exosomes for targeted paclitaxel delivery to pulmonary metastases: in vitro and in vivo evaluations. Nanomedicine. (2018) 14:195–204. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2017.09.011
153. Li L, Hu S, and Chen X. Non-viral delivery systems for crispr/cas9-based genome editing: challenges and opportunities. Biomaterials. (2018) 171:207–18. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.04.031
154. Zhang J, Zhang Y, Khanal S, Cao D, Zhao J, Dang X, et al. Synthetic grna/cas9 ribonucleoprotein targeting hbv DNA inhibits viral replication. J Med Virol. (2023) 95:e28952. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28952
155. Li YJ, Wu JY, Liu J, Xu W, Qiu X, Huang S, et al. Artificial exosomes for translational nanomedicine. J Nanobiotechnology. (2021) 19:242. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00986-2
156. Li K, Gu X, Zhu Y, Guan N, Wang J, and Wang L. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes attenuates experimental periodontitis in mice partly by delivering mirnas. Int J Nanomedicine. (2025) 20:2879–99. doi: 10.2147/ijn.S502192
157. Lai S, Tang N, Guo J, Deng L, Yuan L, Zeng L, et al. Immunomodulatory peptide dp7-C mediates macrophage-derived exosomal mir-21b to promote bone regeneration via the socs1/jak2/stat3 axis. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. (2025) 253:114709. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2025.114709
158. Cui Y, Li X, He X, Zhou X, Wang X, Lin K, et al. Schwann cell-derived exosomes accelerate periodontal bone regeneration with osteogenesis, angiogenesis, and neurogenesis. J Mater Chem B. (2025) 13:4020–9. doi: 10.1039/d4tb02601b
159. Yu T, Mi N, Song Y, and Xie W. Exosomes mir-92a-3p from human exfoliated deciduous teeth inhibits periodontitis progression via the klf4/pi3k/akt pathway. J Periodontal Res. (2024) 59:771–82. doi: 10.1111/jre.13262
160. Luo H, Chen D, Li R, Li R, Teng Y, Cao Y, et al. Genetically engineered cxcr4-modified exosomes for delivery of mir-126 mimics to macrophages alleviate periodontitis. J Nanobiotechnology. (2023) 21:116. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01863-w
161. Lu J, Yu N, Liu Q, Xie Y, and Zhen L. Periodontal ligament stem cell exosomes key to regulate periodontal regeneration by mir-31-5p in mice model. Int J Nanomedicine. (2023) 18:5327–42. doi: 10.2147/ijn.S409664
162. Kang L, Miao Y, Jin Y, Shen S, and Lin X. Exosomal mir-205-5p derived from periodontal ligament stem cells attenuates the inflammation of chronic periodontitis via targeting xbp1. Immun Inflammation Dis. (2023) 11:e743. doi: 10.1002/iid3.743
163. Zhao Y, Huang Y, Liu H, Tan K, Wang R, Jia L, et al. Macrophages with different polarization phenotypes influence cementoblast mineralization through exosomes. Stem Cells Int. (2022) 2022:4185972. doi: 10.1155/2022/4185972
164. Zhao Y, Gong Y, Liu X, He J, Zheng B, and Liu Y. The experimental study of periodontal ligament stem cells derived exosomes with hydrogel accelerating bone regeneration on alveolar bone defect. Pharmaceutics. (2022) 14:2189. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102189
165. Shimizu Y, Takeda-Kawaguchi T, Kuroda I, Hotta Y, Kawasaki H, Hariyama T, et al. Exosomes from dental pulp cells attenuate bone loss in mouse experimental periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. (2022) 57:162–72. doi: 10.1111/jre.12949
166. Lei F, Li M, Lin T, Zhou H, Wang F, and Su X. Treatment of inflammatory bone loss in periodontitis by stem cell-derived exosomes. Acta Biomater. (2022) 141:333–43. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.12.035
Keywords: periodontitis, exosomes, immunomodulation, immune cells, periodontal tissue regeneration, alveolar bone regeneration
Citation: Yang S, Han C, Wang Q, Ai Y, Wang D and Song W (2025) Therapeutic potential of exosomes in periodontal regeneration: Immunomodulatory and tissue-repair mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 16:1675707. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1675707
Received: 29 July 2025; Accepted: 14 November 2025; Revised: 01 November 2025;
Published: 28 November 2025.
Edited by:
Kunal Bhattacharya, Patanjali Research Institute, IndiaCopyright © 2025 Yang, Han, Wang, Ai, Wang and Song. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenzhi Song, c29uZ3d6QGpsdS5lZHUuY24=
 Shuang Yang
Shuang Yang Chunyu Han
Chunyu Han Qihui Wang
Qihui Wang Wenzhi Song
Wenzhi Song