Abstract
Streptococcus suis (SS), particularly serotype 2 (SS2), is a significant zoonotic pathogen causing severe disease in swine and humans. High genetic diversity and antibiotic resistance complicate vaccine development. We firstly synthesize the pivotal advances in SS subunit vaccine design over the past ten years, thereby establishing a foundation for guiding future rational vaccine development. Promising candidates, including pS-Lpp-SaoA (delivered via OMVs), SaoA (via live vectors), IgA1 protease, rIde-10, rIde-14009-1, Enolase, 6-GPD, 38-BP-Enol, and multi-antigen formulations (MRP/GAPDH/DLD or SLY/Enolase/Sbp), elicit robust immune responses (high IgG/IgA titers) and confer up to 100% protection against lethal SS2 challenge in murine and porcine models. Cross-protection against heterologous serotypes (e.g., SaoA and Enolase delivered via S. Choleraesuis) is observed. Future efforts should prioritize: discovery of conserved antigens, optimization of delivery platforms/adjuvants, and translational validation in pigs to achieve broad, durable immunity.
1 Introduction
Streptococcus suis especially serotype 2 (SS2) is a globally distributed zoonotic pathogen causing significant economic losses in the swine industry and posing a threat to human health (1). Since its initial report in the Netherlands in 1951 (2), SS2 has been identified in humans, particularly in those who consumed contaminated pork in some Asian countries, leading to severe conditions such as sepsis, pneumonia, meningitis, and toxic shock (3, 4). Notably, outbreaks in China in 1998 and 2005 resulted in numerous fatalities (5). It is also a highly diverse pathogen with multiple serotypes circulating globally, making vaccine development challenging. In North America, SS2 and SS3 are dominant, while SS9 is more common in Europe, SS6,SS7 predominate in Australia (6) and SS2, SS7, and SS9 are frequently reported in human cases in Asia (7), as shown in Figure 1. This significant regional serotype diversity poses a major challenge for developing vaccines capable of providing broad cross-protection (8). Traditional inactivated vaccines offer limited cross-protection, with protection rates around 70% against homologous strains and lower against heterologous strains (9).
Figure 1
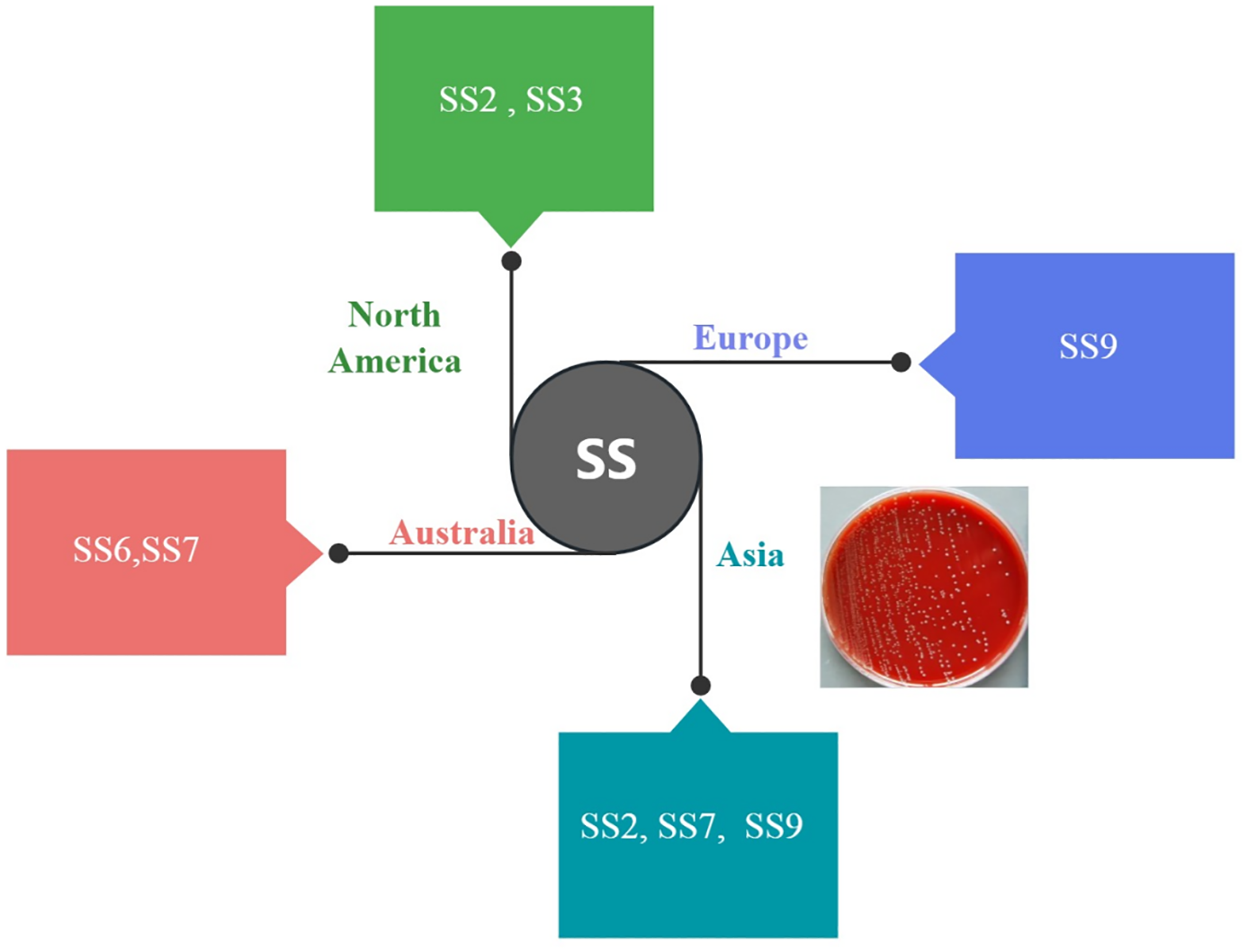
Global distribution of predominant Streptococcus suis serotypes in human infections. Pie charts illustrate the relative frequency of SS serotypes most commonly associated with human cases across major geographic regions. The notable regional variation in serotypes underscores the challenge in developing a universally effective vaccine.
SS2 exhibits varying antibiotic resistance patterns across regions, complicating control efforts. In Europe, resistance to lincosamides, macrolides, and tetracyclines is common, while β-lactams remain effective (10, 11). In Asia, resistance to these antibiotics is high and increasing, with emerging resistance to sulfonamides, aminoglycosides, and fluoroquinolones (12). North America shows similar resistance profiles to Europe but with lower resistance to β-lactams and amphenicols (13). From 2005 to 2021, sporadic human cases were consistently reported in Shenzhen, China, with strains showing resistance to multiple antibiotics (14). The high pathogenicity and multidrug resistance of SS2 pose a severe challenge to public health, highlighting the need for effective vaccines.
It employs a variety of virulence factors to infect pigs and humans (15–17), including adhesins (e.g., MRP, EF, FBPS, Lmb) (18), the toxin suilysin (SLY) (19), and immune evasion factors (e.g., IgdE, IdeSsuis, HP1022) (20). These virulence markers may contribute to its complex pathogenesis and ability to resist host defenses (21, 22). By 2015, despite extensive research, traditional SS vaccines (notably inconsistent bacterins and safety-challenged live-attenuated candidates) had largely failed to deliver reliable, cross-protective solutions against this economically devastating swine pathogen and emerging zoonotic threat (7). While subunit vaccines emerged as a promising alternative due to their safety profile and identification of numerous candidate antigens (21–23), critical barriers remained unresolved: efficacy was often limited to homologous strains, heavily dependent on specific adjuvants to induce essential opsonizing antibodies, and crucially lacked proven broad-spectrum protection across the pathogen’s highly diverse serotypes and sequence types.
Addressing these gaps, this review synthesizes advances from the past decade in SS subunit vaccine development, focusing on antigen discovery, rational design for immune targeting, the optimization of delivery platforms (e.g., viral vectors, bacterial vectors, OMVs) (24) and adjuvant strategies. It serves as a foundation for accelerating novel vaccines that overcome historical limitations.
2 Single subunit vaccines
Subunit vaccines have become a key strategy against SS, as they can induce strong and specific immune responses against this pathogen. The core of these vaccines lies in utilizing highly immunogenic antigens derived from SS, produced through the single expression in systems such as E. coli or other engineered bacterial strains or viral expression systems. Nevertheless, it is critical to emphasize that these antigens must not only be highly immunogenic but also highly conserved across different SS strains to ensure broad protection.
2.1 Sao antigen
The Sao protein (Surface-anchored protein), a highly conserved antigen (>94.2% homology across major S. suis serotypes), has been a focal point in SS vaccine research (Table 1). Its immunogenicity, conversely, is critically dependent on the delivery platform and adjuvant formulation. Initial evaluation of recombinant Sao-L (rSao-L) produced in bioreactors established its immunogenicity, inducing robust antigen-specific antibodies and cellular responses (increased CD8+ and CD4+/CD8+ DP T cells) in pigs, conferring a 60% reduction in lesions upon heterologous challenge; otherwise, this level of protection, although statistically significant, indicated substantial room for improvement. Furthermore, the reliance on a water-in-oil-in-water (w/o/w) emulsion adjuvant raised potential safety concerns regarding granuloma formation at the injection site (25).
Table 1
| Adjuvant name | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Freund’s Complete/Incomplete Adjuvants | Strong enhancement of immune responses; high IgG levels | Potential for local inflammatory reactions; generally not suitable for human use |
| Quil-A | Enhances mucosal and systemic immune responses | Potential for local reactions; dose optimization needed |
| TiterMax Gold | Significant enhancement of IgG responses, especially for CPS | High cost; may require cold chain storage |
| Stimune | Enhances IgG responses; provides good protection | Dependent on antigen type; may need combination with other adjuvants |
| ISA 206 VG | Suitable for multi-epitope vaccines; provides good protection | Potential for local reactions; formulation optimization needed |
| Aluminum Hydroxide (AlOH) | Low cost; widely used | Limited immune enhancement; higher doses may be needed |
| Montanide ISA206 | Low cost; widely used | Limited immune enhancement; formulation optimization needed |
| Polygen™ | Low cost; widely used | Limited immune enhancement; formulation optimization needed |
Summary of adjuvants’ advantages and disadvantages.
In a subsequent refinement, a maternal vaccination strategy was employed: sows were immunized with a combination of recombinant Sao protein (rSao) and an inactivated bacterin. This approach significantly improved protection in piglets, demonstrating a 75-81% reduction in lesions upon challenge. This protection was mediated by the transfer of passive immunity from vaccinated sows to their offspring via colostrum. However, a limitation was observed, as the antibody titers in piglets waned by 6 weeks post-partum (26). A technologically advanced approach using engineered OMVs displaying lipidated SaoA (Lpp-SaoA fusion) leveraged intrinsic adjuvanticity, inducing superior, balanced immune responses and exceptional protection (up to 100% survival) in mice without external adjuvant, although porcine evaluation is pending (27). Live-attenuated Salmonella vectors (e.g., rSC0016, rSC0012) effectively delivered SaoA, inducing robust mucosal and systemic immunity and conferring strong homologous and heterologous (SS7) protection in pigs, with rSC0012 showing an improved safety profile (28, 29). The rSC0016 vector has been successfully utilized to deliver a variety of heterologous antigens, such as SaoA and Enolase from S. suis (28) and P42/P97 from Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, inducing protective immune responses in both murine and porcine models (30, 31). This underscores its potential as a versatile and effective vaccine platform for swine respiratory diseases. Paradoxically, despite inducing cross-reactive opsonophagocytic antibodies (OPA) against multiple serotypes (SS2, SS7, SS9, SS1/2) via the Salmonella vector, monovalent SaoA provided limited protection (e.g., only 20% survival against SS9 in mice). This disconnect between OPA titers and in vivo efficacy highlights the antigen’s formulation-dependent variability and suggests potential issues with antibody functionality or undiscovered serotype-specific epitope variations (32). Thus, while Sao protein shows promise as a conserved target, achieving consistent, broad cross-protection and optimal safety remains challenging, contingent on advanced delivery platforms, including significant challenges in biosafety, manufacturing scalability, and regulatory acceptance, which must be addressed before they can replace traditional bacterins in the field.
2.2 Capsular polysaccharide antigen
Capsular polysaccharide (CPS) from S. suis is a key virulence factor, but its poor immunogenicity has posed significant challenges for vaccine development. Calzas et al. (33) found that CPS-specific antibody responses in infected animals are often absent or only slightly elevated compared to non-infected animals, primarily consisting of low-titer IgM. In contrast, experimental infections using live virulent SS2 strains (such as the European P1/7 or North American 89-1591) consistently induced robust immune responses in both mice and pigs. These responses were characterized by strong, isotype-switched IgG antibodies targeting bacterial proteins and exhibited memory features upon re-challenge. While the antibody response directed against the CPS was markedly impaired. This anti-CPS response was weak or often undetectable, predominantly consisting of low-titer IgM. Critically, it showed no significant isotype switching to IgG in either animal model and elicited only a minimal memory boost upon re-exposure (33). This CPS-specific unresponsiveness was independent of the infecting strain’s geographic origin or TLR2 signaling, underscoring the inherent poor immunogenicity of S. suis CPS in vivo and directly explaining the limitations of traditional bacterins.
To address these challenges, researchers have explored CPS glycoconjugate vaccines. Goyette-Desjardins et al. demonstrated the successful development and protective efficacy of a SS2 capsular polysaccharide glycoconjugate vaccine. By coupling purified, depolymerized, and oxidized CPS to tetanus toxoid (TT) and formulating it with emulsifying adjuvants (Stimune or TiterMax Gold), they induced robust, T cell-dependent immune responses in mice and pigs. This included high levels of IgM and isotype-switched IgG antibodies (including IgG1, IgG2b, IgG2c, IgG3 in mice and IgG1 in pigs) specific to the CPS, which exhibited functional in vitro opsonophagocytic activity (64-98% bacterial killing in mice). Crucially, the conjugate vaccine provided significant protection (70% survival) against a lethal intraperitoneal challenge with virulent SS2 in pigs, comparable to a commercial bacterin vaccine (72% survival), and significantly reduced clinical signs (abnormal behavior, lameness) and bacterial recovery from joints (34). Additionally, serotype 3 CPS was shown to induce robust opsonizing IgG responses in mice when adjuvanted with TiterMax Gold, while CPS from other serotypes (7, 8, and 9) failed to elicit significant antibody responses (21).
2.3 IgA1 protease and IgM protease antigen
IgA1 protease and IgM protease have emerged as promising candidates for S. suis vaccines due to their roles in bacterial pathogenesis and immune evasion. Recombinant IgA1 protease (rIgAP) from SS2 has been shown to induce high levels of IgG antibodies and provide complete protection against lethal SS2 challenge in mice when combined with a Marcol 52-based adjuvant (35). This finding confirms that IgA1 protease is expressed on the bacterial surface, making it a potential surface protective antigen. Thus, its efficacy in pigs remains unconfirmed, highlighting the need for further research to evaluate its potential in relevant animal models (36). Similarly, the IgM protease Ide-S.suis, which disrupts the classical complement pathway by cleaving IgM, has been shown to provide protection against a highly virulent serotype 9 strain in pigs (37) showed that Ide-S.suis, an IgM protease, disrupts the classical complement pathway by cleaving IgM, aiding bacterial evasion in pigs. Vaccination with the recombinant IgM-degrading enzyme (rIde) induced specific IgG antibodies and reduced bacterial survival in blood, leading to 100% survival in vaccinated piglets challenged with a lethal dose of S. suis cps9 strain (38). But vaccinated pigs exhibited signs of morbidity, such as fever and lameness, indicating partial protection.
Expanding on these insights, the IgM protease vaccine based on the Ide-S.suis gene has been shown to induce serotype-independent protection in pigs against multiple S. suis strains expressing group A IgM protease (39). This vaccine was effective in both piglet and gilt vaccination studies, providing protection against various strains, including st1, st2, st9, and st14. No protection was observed against strains expressing group B IgM protease, highlighting the need for a more comprehensive antigenic coverage. The study also developed a qPCR test to classify S. suis strains based on their IgM protease groups, which could aid in predicting vaccine efficacy. Additionally, research by Dolbec et al. (40) has further explored the potential of IgM-targeting strategies in vaccine development, emphasizing the necessity of enhancing IgM-focused approaches to improve host defense against S. suis. While IgA, IgG, and IgM proteases have shown promise as vaccine candidates, several limitations remain, including serotype-specific efficacy and incomplete protection against certain strains. Further in vivo studies in relevant animal models are needed to improve cross-protection and confirm overall efficacy.
2.4 ABC transporter antigens
PstB was identified as a highly conserved protein with nearly 100% amino acid sequence identity across various S. suis isolates. Immunization with recombinant PstB (rPstB) induced high levels of IFN-γ and IL-4, indicating strong Th1 and Th2 immune responses. Mice immunized with rPstB showed significant protection against challenges with SS2 (87.5% survival), SS7 (62.5% survival), and SS9 (87.5% survival). A multi-epitope construct of PstB provided poor protection (12.5% survival) against all tested serotypes (41).
S-ABC was found to be highly conserved across multiple SS strains, with 97% amino acid sequence identity. Mice immunized with recombinant S-ABC (rS-ABC) exhibited strong antigen-specific antibody responses and significant production of IFN-γ and IL-4, indicating robust Th1 and Th2 immune responses. The vaccine conferred high levels of protection against challenges with SS2 (87.5% survival) and 9 (100% survival), and moderate protection against serotype 7 (50% survival). In contrast, a multi-epitope construct of S-ABC provided lower protection (25%-37.5%). These results demonstrate that full-length rS-ABC is a promising candidate for a universal subunit vaccine against multiple SS serotypes, though further research is needed to optimize its efficacy and explore its potential in broader serotype coverage (42).
Moreover, Zhang et al. (2021) (43) synthesized oligosaccharides resembling the CPS of S. suis serotypes 2, 3, 9, and 14, identifying lead antigens with the potential to elicit immune responses. While this work laid the groundwork for glycoconjugate vaccine development, it remains in the early stages, with no in vivo efficacy data yet available. Similarly, Singh et al. (2022) (44) reported the synthesis of oligosaccharides for S. suis serotype 18, overcoming challenges in synthesizing the penta-saccharide repeating unit. This research provides a foundation for future glycoconjugate vaccine development but has not yet evaluated the immunogenicity or protective efficacy of the synthesized antigens in vivo.
2.5 The enolase antigen
Recombinant S. suis Enolase (SsEno) and Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPPIV) subunit vaccines, although expressed by 86% and 88% of field strains respectively and inducing strong antibody responses in mice, failed to provide significant protection against a lethal serotype 2 challenge in an outbred (CD-1) mouse model (45). This lack of protection was consistent regardless of the adjuvant used (Quil-A®, Polygen™, Stimune®, or Montanide™ ISA 50 V2), demonstrating that adjuvant optimization alone could not confer efficacy to these antigens under these experimental conditions. However, a study by Li et al. using a recombinant S. Choleraesuis vector (rSC0016) carrying the enolase antigen achieved 100% protection against SS2 and SS9, and 80% protection against SS7 in mice. This study evaluated a live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis vector (rSC0016) delivering a conserved surface protein enolase as a potential universal vaccine against multiple serotypes of S. suis. The enolase, a highly conserved surface protein present in all S. suis serotypes, was expressed by the rSC0016(pS-Enolase) vaccine strain. The results showed that the vaccine strain effectively colonized the lymphatic tissues of mice and elicited strong mucosal, humoral, and cellular immune responses against enolase (46).
This study evaluated a live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis vector (rSC0016) delivering a conserved surface protein enolase as a potential universal vaccine against multiple serotypes of SS. The enolase, a highly conserved surface protein present in all SS serotypes, was expressed by the rSC0016(pS-Enolase) vaccine strain. The results showed that the vaccine strain effectively colonized the lymphatic tissues of mice and elicited strong mucosal, humoral, and cellular immune responses against enolase. These findings suggest that the rSC0016(pS-Enolase) vaccine is a promising candidate for a universal vaccine against multiple SS serotypes, offering a balance between host safety and immunogenicity.
Drawing from these observations, Li et al. (32) constructed a dual-antigen expression cassette using S. Choleraesuis, which provided broad protection against multiple S. suis serotypes (2, 7, 9, and 1/2) in mice, with protection rates ranging from 80% to 100%. This dual-antigen approach, combining Sao and Enolase, demonstrated the potential to enhance protective immunity by leveraging the strengths of multiple conserved antigens. The results highlight the importance of combining antigens to develop a universal vaccine against multiple S. suis serotypes, suggesting that a multi-antigen strategy may be more effective in providing broad-spectrum protection.
2.6 Other subunit antigens
Other subunit vaccines, such as 6-PGD, PDH, SsnA, EF-Tu, PrsA, and SBP2, have shown significant immunogenicity and varying degrees of protection in mice and rabbits.
Researchers developed a live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis vaccine vector (rSC0011), incorporating regulated delayed attenuation and regulated delayed antigen synthesis, to deliver the 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (6-PGD) protein from SS2. The vaccine strain rSC0011 exhibited significant attenuation and enhanced colonization in mice lymphoid tissues compared to the licensed vaccine strain C500. Mice immunized with rSC0011(pS6-PGD) developed strong immune responses, including high levels of serum IgG and mucosal IgA antibodies against 6-PGD and Salmonella antigens. The vaccine conferred 90% protection against intraperitoneal challenge with a lethal dose of SS2, demonstrating its potential as an effective vaccine candidate (47).
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), a biofilm-associated protein of SS, is also a subunit vaccine candidate. The recombinant PDH (rPDH) was expressed and purified from E. coli and used to immunize mice with the ISA206 adjuvant. Results showed that PDH had high sequence conservation among different S. suis serotypes and strong immunogenicity, inducing high levels of specific antibodies (up to 1:409,600 titer) and significant expression of immune-related genes (CD4, CD8, IFN-γ, and IL-6) in mice spleens. Mice immunized with rPDH or inactivated bacteria exhibited 70% and 60% survival rates, respectively, against a lethal dose of S. suis ZY05719, with reduced pathological damage in vital organs like liver, brain, and spleen. Additionally, PDH antiserum significantly inhibited S. suis growth and biofilm formation in vitro. Conversely, the study was limited to a single serotype 2, and its efficacy across other serotypes remains to be determined (48). Additionally, vaccines based on other proteins like SsnA (49), EF-Tu (50), PrsA (51), and SBP2 (52) have shown varying degrees of protection in mice and rabbits. In especial, the rSsnA + ALOH vaccine achieves a protection rate of 91.25% against SS in mice, significantly reducing mortality and bacterial counts. Some proteins, like PrsA and SBP2, have shown partial cross-protection against multiple serotypes. Nonetheless, most studies are limited to murine models, and their efficacy in natural hosts (e.g., pigs) remains untested.
In the viral vector domain, the BoHV-4/GMD vaccine achieved a protection rate of 71.4% against SS2 challenge, while BoHV-4/SLY provided only 12.5% protection. The study demonstrated that BoHV-4/GMD induced higher levels of antibody-mediated phagocytic activity against SS2, SS7, and SS9 compared to BoHV-4/SLY. Although the study provides promising results for BoHV-4/GMD as a potential vaccine candidate, the findings are limited by the use of a rabbit model, which may not fully replicate the immune response in pigs. Additionally, the study did not directly evaluate the protective efficacy against SS7 and SS9 due to the lack of a suitable rabbit model for these serotypes (53).
3 Multi-subunit vaccines
Multi-subunit vaccines have shown promise in providing broader protection against S. suis by combining multiple antigens to enhance immune responses and increase cross-protection across different serotypes (Figure 2). Initial efforts focused on membrane-associated proteins such as Ldh, Dldh, Pec, and Sbp, with Sbp showing the most promising results, eliciting strong humoral immune responses and providing protection against lethal challenges in mice (54). Subsequent studies identified additional proteins (SSU0185, SSU1215, SSU1355, SSU1773, SSU1915) through functional genomic screening, which induced robust immune responses, including IgG antibodies and cell-mediated immunity, and provided significant protection against virulent S. suis. The efficacy of these vaccines was highly dependent on the choice of adjuvants, with Carbopol-AddaVax and Emulsigen-D showing particular promise (55).
Figure 2
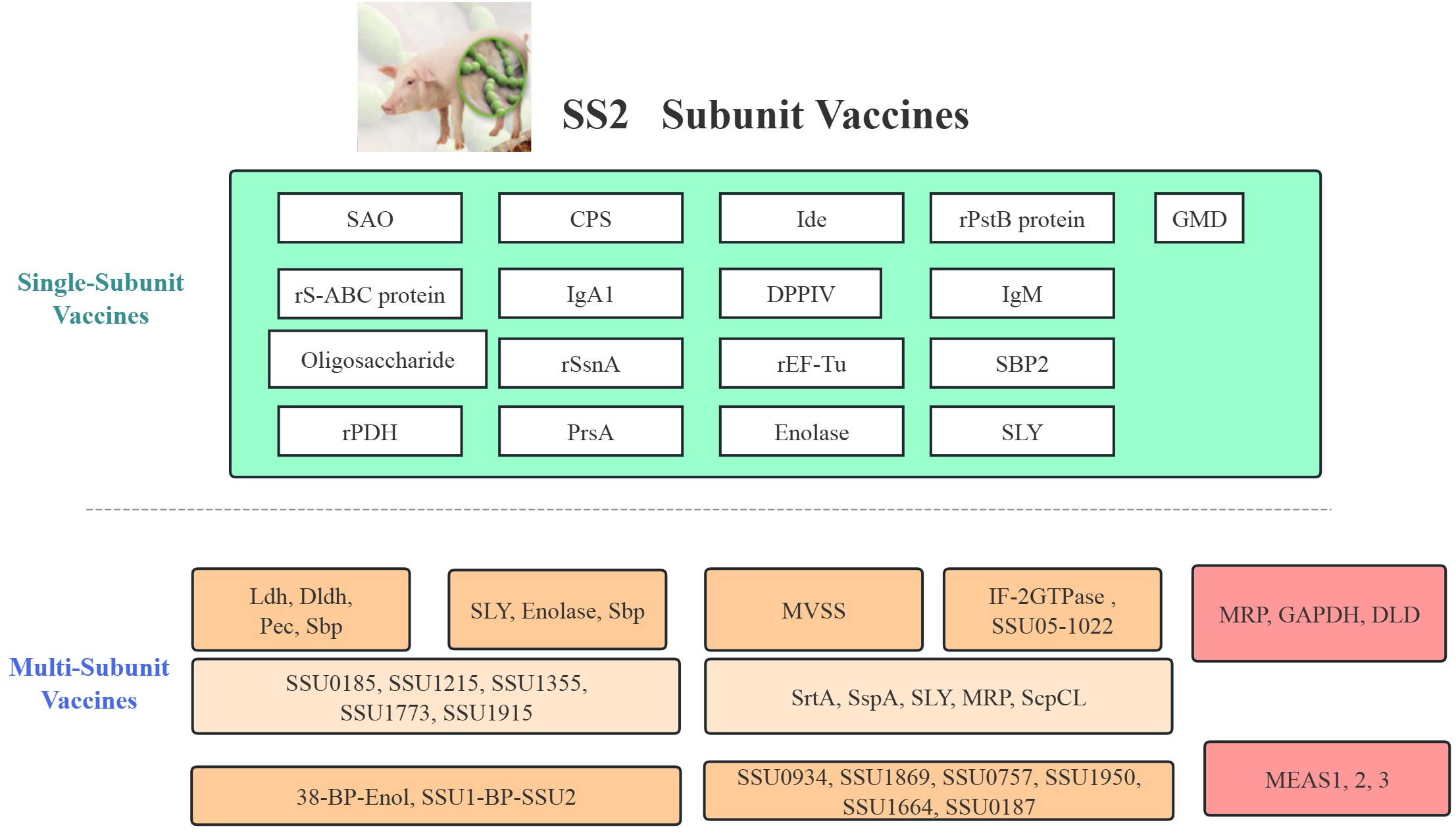
Comprehensive classification and evaluation of Streptococcus suis subunit vaccines and associated animal models. This figure summarizes various vaccine strategies including single antigen vaccines and multi-subunit formulations.
Innovative delivery methods have also shown potential. For instance, intranasal administration of the V5 multi-subunit vaccine, comprising SrtA, SspA, SLY (56), MRP, and ScpCL virulence factors with CpG ODN adjuvant, promoted robust mucosal immunity in mice, leading to significant clearance of S. suis from the nasopharynx and high homologous protection against systemic SS2 challenge (57). Despite these successes, some candidates like DPPIV and enolase (SsEno) failed to provide protection in mice, highlighting the need for further optimization (45). Proteomic and bioinformatic analyses identified 131 predicted surface proteins in S. suis human isolates, providing a resource for vaccine candidate testing, though in vivo immunogenicity and protective capacity were not evaluated (58).
Engineering approaches have shown potential in enhancing vaccine efficacy. BP formulations such as 38-BP-Enol and SSU1-BP-SSU2 induced significant antigen-specific humoral immune responses, with IgG titers reaching up to 1.0×107, and provided 100% survival in vaccinated mice compared to 70% in control groups (59). Similarly, proteins like IF-2 and 1022 provided cross-protection against lethal doses of SS2 and SS9, with high antibody titers and significant protection in challenge experiments (60). Yet, a multicomponent vaccine composed of six conserved immunogens failed to demonstrate significant protection in piglets challenged with S. suis cps14 (61). In contrast, a trivalent protein vaccine (JointS) combined with a TLR4 agonist (MPLA) provided complete protection against SS2 infection in mice and good protection in piglets (62). Additionally, an engineered E. coli strain secreting S. suis antigens using the Tat pathway showed higher survival rates and milder clinical symptoms in vaccinated mice (63). Yet, the risk of gene transfer and environmental contamination must be carefully assessed. Multi-epitope vaccines (e.g., MVSS) (64) and MEASs (65) have also shown strong immunogenicity and partial protection in mouse models, with some formulations demonstrating superior efficacy. These studies highlight the potential of multi-subunit vaccines but also underscore the need for further optimization to achieve broad-spectrum protection.
4 Animal models in SS vaccine
In the development of subunit vaccines for S. suis, a variety of animal models have been employed to evaluate efficacy, immunogenicity, and protection. These models include mice, pigs, rabbits, and zebrafish, each with distinct roles, advantages, and limitations, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3
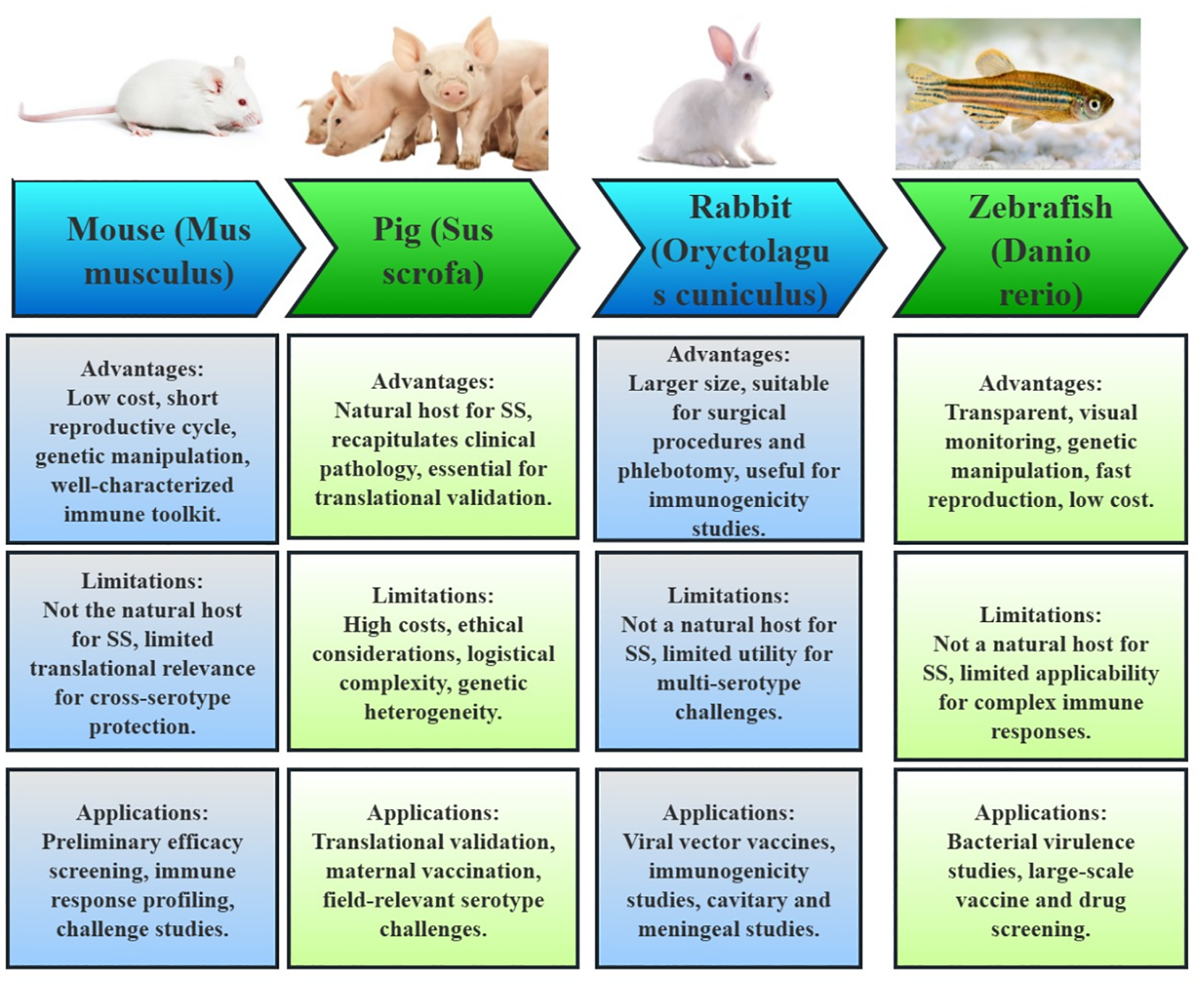
Animal models utilized in the development of Streptococcus suis subunit vaccines. The figure illustrates the key animal models employed to assess immunogenicity, protective efficacy, and safety of vaccine candidates. For each model, its advantages, limitations and applications are summarized, reflecting their distinct roles in vaccine evaluation.
Mice are the most prevalent model used for preliminary efficacy screening, immune response profiling (antibody titers, cytokine levels), and challenge studies (66). The advantages of using mice include their low cost, short reproductive cycle, and ease of genetic manipulation. Additionally, well-characterized immune toolkits, such as the BALB/c and C57BL/6 strains, facilitate high-throughput screening of antigens and adjuvants. For instance, studies involving OMVs and Salmonella vectors have benefited from the scalability and genetic tractability of mice. Still, mice are not the natural host for SS, and their pathophysiology may not accurately mirror the disease in swine or humans. This limitation is particularly evident in conditions like SS meningitis, which is poorly modeled in mice. Furthermore, vaccines optimized in mice often fail to translate effectively to pigs, highlighting the limited translational relevance for cross-serotype protection.
Pigs are critical for translational validation, especially in evaluating maternal vaccination and field-relevant serotype challenges. As the natural host for SS, pigs recapitulate clinical pathology, including sepsis and meningitis, making them essential for assessing passive immunity (e.g., sow-to-piglet antibody transfer) and the efficacy of field strains (67). On the other hand, the use of pigs is constrained by high costs, ethical considerations, and logistical complexity. Additionally, the genetic heterogeneity of pigs may introduce variability in vaccine responses, complicating the interpretation of results.
Rabbits have niche applications (68), particularly in the study of viral vector vaccines like BoHV-4. Their larger size facilitates surgical procedures and phlebotomy, making them useful for immunogenicity studies of human-zoonotic strains. Despite these advantages, rabbits are not natural hosts for SS, and their immune mechanisms may not reflect those of swine. Moreover, rabbits have limited utility for multi-serotype challenges, as there are no established rabbit models for certain serotypes like SS7 and SS9.
Zebrafish represent an emerging model for rapid in vivo screening, exemplified by studies involving the joints trivalent vaccine combined with a TLR4 agonist. The transparency of zebrafish enables real-time imaging of immune responses, and their high fecundity and genetic tractability make them suitable for large-scale screening (69). Conversely, their evolutionary distance from mammals and the lack of adaptive immunity complexity limit their applicability for SS pathology and cross-protection studies.
5 Adjuvants for SS vaccine
Adjuvants play a crucial role in enhancing the immunogenicity and efficacy of bacterial vaccines (70). Over the years, various adjuvants have been explored in the development of subunit vaccines of SS2, with some showing significant enhancement of immune responses, while others have demonstrated limited or no effect, as displayed in Table 1. Freund’s Complete and Incomplete Adjuvants have been widely used in experimental studies and have shown strong enhancement of immune responses. For example, in studies involving the Sao protein and CPS-TT conjugates (34), Freund’s adjuvants induced high levels of IgG antibodies and robust Th1/Th2 immune responses, leading to significant protection against lethal challenges in mice and pigs. Quil-A, a saponin-based adjuvant, has been effective in enhancing mucosal and systemic immune responses (45). In studies using recombinant SaoA delivered via a Salmonella vector, Quil-A significantly boosted IgG and IgA levels, providing strong protection against SS2 and SS7. TiterMax Gold has shown significant enhancement of opsonizing IgG responses, particularly in CPS-based vaccines. For instance, CPS3 adjuvanted with TiterMax Gold induced strong opsonic IgG responses in mice, highlighting its potential for enhancing vaccine efficacy (21). Stimune has also been used in CPS-TT conjugate vaccines, inducing high levels of IgG antibodies and providing significant protection against lethal challenges in pigs. ISA 206 VG has been effective in enhancing IgG responses in multi-epitope vaccines, providing significant protection against SS2 and SS9 in mice (48).
On the other hand, some adjuvants have shown limited or no effect. Aluminum Hydroxide (AlOH), while commonly used, has shown limited efficacy in enhancing immune responses in some studies. For example, in CPS-based vaccines, AlOH failed to induce significant antibody responses, highlighting its potential limitations (49). Montanide ISA206, in some studies involving enolase and other subunit vaccines, did not provide significant protection, despite inducing high IgG titers. Polygen™ has also shown limited enhancement of immune responses in some studies (45), particularly in subunit vaccines like rDPPIV, where it failed to provide significant protection against SS2 challenge. Future research should focus on optimizing adjuvant formulations and exploring novel adjuvants to improve vaccine efficacy and safety.
6 Conclusions
Over the past decade, as depicted in Figure 2 and Table 2, the evaluation of subunit vaccines for SS has identified several antigens that provide complete (100%) protection against lethal SS2 challenge in mouse and piglet models. Notably, only three antigens, SaoA, Ide r10, and Ide r10049, have demonstrated 100% protection in piglets, while other promising candidates like pS-Lpp-SaoA (delivered via OMVs), IgA1 protease, rIde-14009-1, Enolase, 6-GPD, 38-BP-Enol, and various combinations (e.g., MRP/GAPDH/DLD or SLY/Enolase/Sbp) have shown 100% protection in mice. However, most of these candidates have yet to achieve 100% protection in pigs. To bridge the efficacy gap between murine models and natural hosts, future research needs to focus intently on validation in pigs using physiologically relevant challenge models and route of immunization. Identifying immune correlates of protection, such as opsonic antibodies or mucosal IgA responses, in swine will be essential for guiding rational vaccine design and adjuvant selection. Future efforts should focus on identifying new immunogenic proteins and adjuvants to develop vaccines that can provide broader protection in target species such as swine.
Table 2
| Antigen | Dose | No. of immunizations | Route | Adjuvant | Antibody response | Animal model | Challenge Dose/ Route | Protection Rate (SS2) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pS-Lpp-SaoA (OMVs) |
10 µg | 2x | Intraperitoneal (i.p.) |
None | Highest IgG,IgG1,IgG2a; Balanced Th1/Th2; Strong Th17 |
BALB/c mice | 8×LD50, i.p. |
100% | (27) |
| SaoA | 1x 109 CFU |
2x | Oral | Live vector (rSC0016) | Strong serum IgG, mucosal IgA, High IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-17A |
BALB/c mice,Piglets | 3x108, i.p. |
100% | (28) |
| SaoA | 1 × 109 CFU |
2x | Oral | Attenuated S. Choleraesuis vector | High IgG/IgA ;Th1-biased (IgG2a > IgG1) -Induced cross-reactive OPA against SS2, SS7, SS9, SS1/2 |
BALB/c mice | 10 × LD50 of SS2, SS7, SS9, SS1/2, i.p. |
SS2: 100% SS7: 70% SS9: 60% SS1/2:60% |
(32) |
| IgA1 protease | 30 μg | 2x | i.p. | Marcol 52 | High IgG titers (IgG1/IgG2a) | BALB/c mice | 2 × 109, i.p. |
100% | (32) |
| rIde-10 (Group A) |
120 μg | 2x | Intramuscular | X-Solve | IgG | Piglets | 1×109, intratracheal | 100% | (39) |
| rIde-14009-1 (Group A) |
50 μg | 2x | Intramuscular | X-Solve | High IgG titers | Piglets | 4×109, intratracheal | 100% | (39) |
| rS-ABC (full-length) |
50 μg | 2x | Subcutaneous injection | Freund’s adjuvant/ Incomplet adjuvant |
Strong IgG response; IFN-γ/ IL-4 |
BALB/c mice | 2-6×108, i.p. |
87.5%(SS2), 100% (SS9), 50% (SS7) |
(42) |
| Enolase (via S.choleraesuis) |
1×109 CFU | 2x | Oral | None | IgG/IgA, (Th1-dominant) |
BALB/c mice | 10×LD50 (SS2: 1.2×108; SS7/SS9/SS1/2: varied), i.p. | 100% (SS2), 80% (SS7), 100% (SS9) |
(46) |
| 6-GPD | 1 ± 0.3 × 109 CFU | 2x | Oral | None | IgG, IgA | BALB/c mice | 1.3 × 108 or 2.6 × 108 CFU, i.p. | 100% | (47) |
| 38-BP-Enol | 6 μg | 2x | Subcutaneous | Quil-A® | Ig>107, IgG: >105 | C57BL/6 mice | 8×107 CFU, i.p. | 100% | (59) |
| MRP, GAPDH,DLD |
50 µg | 3x | Subcutaneous | MPLA | High IgG titers | BALB/c mice | 5×108 CFU, i.p. | 100% | (62) |
| SLY, Enolase,Sbp |
1018 CFU | 2x | Oral gavage | None | Not measured | Kunming Mice | 1.5×109, i.p. | 100% | (63) |
Summary of antigens conferring 100% protection against SS2 and evaluation of immune protection in the full text.
Statements
Author contributions
LF: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NJ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Scientific Research Projects of Medical and Health Institutions of Longhua District, Shenzhen NO. 2024027 and Guangdong Natural Science Foundation NO. 2025A1515011062, and the Sanming project of Shenzhen Longhua District Hospital.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Professor Weihuan Fang from Zhejiang University for his careful review and insightful suggestions on the draft of this paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Haas B Grenier D . Understanding the virulence of Streptococcus suis: A veterinary, medical, and economic challenge. Med Maladies Infectieuses. (2018) 48:159–66. doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2017.10.001
2
Segura M Fittipaldi N Calzas C Gottschalk M . Critical streptococcus suis virulence factors: are they all really critical? Trends Microbiol. (2017) 25:585–99.
3
Bleuzé M Gottschalk M Segura M . Neutrophils in streptococcus suis infection: from host defense to pathology. Microorganisms. (2021) 9. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9112392
4
Viana PB Penedos C Medeiros R Monte R . Streptococcus suis meningitis in a COVID-19 patient: A case report. Saudi J Anaesthesia. (2023) 17:281–3. doi: 10.4103/sja.sja_722_22
5
Dong X Chao Y Zhou Y Zhou R Zhang W Fischetti VA et al . The global emergence of a novel Streptococcus suis clade associated with human infections. EMBO Mol Med. (2021) 13:e13810. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202013810
6
Groves MD Jordan D Chapman TA Jassim RA . Multilocus sequence typing of Australian Streptococcus suis type 2 by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry analysis of PCR amplicons. Veterinary Microbiol. (2015) 177:394–7. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.03.006
7
Segura M . Streptococcus suis vaccines: candidate antigens and progress. Expert Rev Vaccines. (2015) 14:1587–608. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2015.1101349
8
Zhang W Lu CP . Immunoproteomic assay of membrane-associated proteins of Streptococcus suis type 2 China vaccine strain HA9801. Zoonoses Public Health. (2007) 54:253–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1863-2378.2007.01056.x
9
Wisselink HJ Stockhofe-Zurwieden N Hilgers LA Smith HE . Assessment of protective efficacy of live and killed vaccines based on a non-encapsulated mutant of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Veterinary Microbiol. (2002) 84:155–68. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1135(01)00452-7
10
Ji L Chen Z Li F Hu Q Xu L Duan X et al . Epidemiological and genomic analyses of human isolates of Streptococcus suis between 2005 and 2021 in Shenzhen, China. Front Microbiol. (2023) 14:1118056. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1118056
11
Ágoston Z Terhes G Hannauer P Gajdács M Urbán E . Fatal case of bacteremia caused by Streptococcus suis in a splenectomized man and a review of the European literature. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hungarica. (2020) 67:148–55. doi: 10.1556/030.2020.01123
12
Dechêne-Tempier M Jouy E Bayon-Auboyer MH Bougeard S Chauvin C Libante V et al . Antimicrobial resistance profiles of Streptococcus suis isolated from pigs, wild boars, and humans in France between 1994 and 2020. J Clin Microbiol. (2023) 61:e0016423. doi: 10.1128/jcm.00164-23
13
Segura M . Streptococcus suis research: progress and challenges. Pathog (Basel Switzerland). (2020) 9. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9090707
14
Rieckmann K Pendzialek SM Vahlenkamp T Baums CG . A critical review speculating on the protective efficacies of autogenous Streptococcus suis bacterins as used in Europe. Porcine Health Management. (2020) 6:12. doi: 10.1186/s40813-020-00150-6
15
Zhao C Jia X Pan Y Liao S Zhang S Ji C et al . Thioredoxin A of streptococcus suis serotype 2 contributes to virulence by inhibiting the expression of pentraxin 3 to promote survival within macrophages. J Microbiol (Seoul Korea). (2023) 61:433–48. doi: 10.1007/s12275-023-00038-4
16
Ji C Pan Y Liu B Liu J Zhao C Nie Z et al . Thioredoxin C of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 contributes to virulence by inducing antioxidative stress and inhibiting autophagy via the MSR1/PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway in macrophages. Veterinary Microbiol. (2024) 298:110263. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2024.110263
17
Baums CG Valentin-Weigand P . Surface-associated and secreted factors of Streptococcus suis in epidemiology, pathogenesis and vaccine development. Anim Health Res Rev. (2009) 10:65–83. doi: 10.1017/S146625230999003X
18
de Greeff A Buys H Verhaar R Dijkstra J van Alphen L Smith HE . Contribution of fibronectin-binding protein to pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Infect Immun. (2002) 70:1319–25. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.3.1319-1325.2002
19
Jacobs AA van den Berg AJ Loeffen PL . Protection of experimentally infected pigs by suilysin, the thiol-activated haemolysin of Streptococcus suis. Veterinary Rec. (1996) 139:225–8. doi: 10.1136/vr.139.10.225
20
Busque P Higgins R Caya F Quessy S . Immunization of pigs against Streptococcus suis serotype 2 infection using a live avirulent strain. Can J Vet Res. (1997) 61:275–9.
21
Goyette-Desjardins G Auger JP Dolbec D Vinogradov E Okura M Takamatsu D et al . Comparative study of immunogenic properties of purified capsular polysaccharides from streptococcus suis serotypes 3, 7, 8, and 9: the serotype 3 polysaccharide induces an opsonizing igG response. Infect Immun. (2020) 88.
22
Kralova N Stepanova H Gebauer J Norek A Matiaskova K Zouharova M et al . Vaccine against Streptococcus suis Infection in Pig Based on Alternative Carrier Protein Conjugate. Vaccines. (2022) 10. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10101620
23
Wisselink HJ Vecht U Stockhofe-Zurwieden N Smith HE . Protection of pigs against challenge with virulent Streptococcus suis serotype 2 strains by a muramidase-released protein and extracellular factor vaccine. Veterinary Rec. (2001) 148:473–7. doi: 10.1136/vr.148.15.473
24
Kamble NS Thomas S Madaan T Ehsani N Sange S Tucker K et al . Engineered bacteria as an orally administered anti-viral treatment and immunization system. Gut Microbes. (2025) 17:2500056. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2500056
25
Hsueh KJ Lee JW Hou SM Chen HS Chang TC Chu CY . Evaluation on a Streptococcus suis vaccine using recombinant sao-l protein manufactured by bioreactors as the antigen in pigs. Transboundary Emerg Dis. (2014) 61:e35–43. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12067
26
Hsueh KJ Cheng LT Lee JW Chung YC Chung WB Chu CY . Immunization with Streptococcus suis bacterin plus recombinant Sao protein in sows conveys passive immunity to their piglets. BMC Vet Res. (2017) 13:15. doi: 10.1186/s12917-016-0937-8
27
Li Q Zhou G Fei X Tian Y Wang S Shi H . Engineered bacterial outer membrane vesicles with lipidated heterologous antigen as an adjuvant-free vaccine platform for streptococcus suis. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2023) 89:e0204722. doi: 10.1128/aem.02047-22
28
Li YA Ji Z Wang X Wang S Shi H . Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis vector delivering SaoA antigen confers protection against Streptococcus suis serotypes 2 and 7 in mice and pigs. Veterinary Res. (2017) 48:89. doi: 10.1186/s13567-017-0494-6
29
Li YA Chen Y Du YZ Guo W Chu D Fan J et al . Live-attenuated Salmonella enterica serotype Choleraesuis vaccine with regulated delayed fur mutation confer protection against Streptococcus suis in mice. BMC Vet Res. (2020) 16:129. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02340-4
30
Zhou G Tian J Tian Y Ma Q Li Q Wang S et al . Recombinant-attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis vector expressing the PlpE protein of Pasteurella multocida protects mice from lethal challenge. BMC Vet Res. (2023) 19:128. doi: 10.1186/s12917-023-03679-0
31
Zhou G Tian Y Tian J Ma Q Huang S Li Q et al . Oral Immunization with Attenuated Salmonella Choleraesuis Expressing the P42 and P97 Antigens Protects Mice against Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Challenge. Microbiol Spectrum. (2022) 10:e0236122.
32
Li YA Sun Y Fu Y Zhang Y Li Q Wang S et al . Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis vector delivering a dual-antigen expression cassette provides mouse cross-protection against Streptococcus suis serotypes 2, 7, 9, and 1/2. Veterinary Res. (2022) 53:46. doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01062-9
33
Calzas C Lemire P Auray G Gerdts V Gottschalk M Segura M . Antibody response specific to the capsular polysaccharide is impaired in Streptococcus suis serotype 2-infected animals. Infect Immun. (2015) 83:441–53. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02427-14
34
Goyette-Desjardins G Calzas C Shiao TC Neubauer A Kempker J Roy R et al . Protection against Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Infection Using a Capsular Polysaccharide Glycoconjugate Vaccine. Infect Immun. (2016) 84:2059–75. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00139-16
35
Fu L Zhao J Lin L Zhang Q Xu Z Han L et al . Characterization of IgA1 protease as a surface protective antigen of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Microbes Infect. (2016) 18:285–9. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2015.12.005
36
Spoerry C Hessle P Lewis MJ Paton L Woof JM von Pawel-Rammingen U . Novel igG-degrading enzymes of the igdE protease family link substrate specificity to host tropism of streptococcus species. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0164809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164809
37
Seele J Beineke A Hillermann LM Jaschok-Kentner B von Pawel-Rammingen U Valentin-Weigand P et al . The immunoglobulin M-degrading enzyme of Streptococcus suis, IdeSsuis, is involved in complement evasion. Veterinary Res. (2015) 46:45. doi: 10.1186/s13567-015-0171-6
38
Rieckmann K Seydel A Klose K Alber G Baums CG Schütze N . Vaccination with the immunoglobulin M-degrading enzyme of Streptococcus suis, Ide (Ssuis), leads to protection against a highly virulent serotype 9 strain. Vaccine: X. (2019) 3:100046.
39
Jacobs AAC Grommen AWF Badbanchi S van Hout AJ van Kasteren-Westerneng TJ Morales LG et al . Serotype independent protection induced by a vaccine based on the IgM protease of Streptococcus suis and proposal for a new immunity-based classification system. Porcine Health Management. (2024) 10:41. doi: 10.1186/s40813-024-00398-2
40
Dolbec D Lehoux M de Beauville AA Zahn A Di Noia JM Segura M . Unmutated but T cell dependent IgM antibodies targeting Streptococcus suis play an essential role in bacterial clearance. PloS Pathogens. (2024) 20:e1011957. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011957
41
Yan Z Yao X Pan R Zhang J Ma X Dong N et al . Subunit Vaccine Targeting Phosphate ABC Transporter ATP-Binding Protein, PstB, Provides Cross-Protection against Streptococcus suis Serotype 2, 7, and 9 in Mice. Veterinary Sci. (2023) 10. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10010048
42
Yan Z Pan R Zhang J Sun J Ma X Dong N et al . Immunogenicity and Protective Capacity of Sugar ABC Transporter Substrate-Binding Protein against Streptococcus suis Serotype 2, 7 and 9 Infection in Mice. Vaccines. (2024) 12. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12050544
43
Zhang S Sella M Sianturi J Priegue P Shen D Seeberger PH . Discovery of Oligosaccharide Antigens for Semi-Synthetic Glycoconjugate Vaccine Leads against Streptococcus suis Serotypes 2, 3, 9 and 14*. Angewandte Chem (Int ed English). (2021) 60:14679–92. doi: 10.1002/anie.202103990
44
Singh RK Sianturi J Seeberger PH . Synthesis of oligosaccharides resembling the streptococcus suis serotype 18 capsular polysaccharide as a basis for glycoconjugate vaccine development. Org Lett. (2022) 24:2371–5. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c00596
45
Dumesnil A Martelet L Grenier D Auger JP Harel J Nadeau E et al . Enolase and dipeptidyl peptidase IV protein sub-unit vaccines are not protective against a lethal Streptococcus suis serotype 2 challenge in a mouse model of infection. BMC Vet Res. (2019) 15:448. doi: 10.1186/s12917-019-2196-y
46
Li Q Lv Y Li YA Du Y Guo W Chu D et al . Live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis vector delivering a conserved surface protein enolase induces high and broad protection against Streptococcus suis serotypes 2, 7, and 9 in mice. Vaccine. (2020) 38:6904–13. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.08.062
47
Ji Z Shang J Li Y Wang S Shi H . Live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis vaccine vector displaying regulated delayed attenuation and regulated delayed antigen synthesis to confer protection against Streptococcus suis in mice. Vaccine. (2015) 33:4858–67. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.07.063
48
Yi L Fan Q Wang Y Mao C Li J Jin M et al . Evaluation of immune effect of Streptococcus suis biofilm-associated protein PDH. Veterinary Microbiol. (2021) 263:109270. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2021.109270
49
Gómez-Gascón L Cardoso-Toset F Amarilla PS Tarradas C Carrasco L Olaya-Abril A et al . A new recombinant SsnA protein combined with aluminum hydroxide protects mouse against Streptococcus suis. Vaccine. (2014) 32:6992–9. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.10.019
50
Xia XJ Wang L Cheng LK Shen ZQ Li SG Wang JL . Expression and immunological evaluation of elongation factor Tu of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Polish J Vet Sci. (2017) 20:277–84. doi: 10.1515/pjvs-2017-0033
51
Jiang X Yang Y Zhou J Liu H Liao X Luo J et al . Peptidyl isomerase PrsA is surface-associated on Streptococcus suis and offers cross-protection against serotype 9 strain. FEMS Microbiol Lett. (2019) 366.
52
Guo G Kong X Wang Z Li M Tan Z Zhang W . Evaluation of the immunogenicity and protective ability of a pili subunit, SBP2’, of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Res Vet Sci. (2021) 137:201–7. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2021.05.006
53
Dong N Nichols H Sun Q Chen X Zheng J Guan Z et al . Bovine Herpesvirus-4 Based Vaccine Provides Protective Immunity against Streptococcus suis Disease in a Rabbit Model. Vaccines. (2023) 11. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11051004
54
Zhou Y Wang Y Deng L Zheng C Yuan F Chen H et al . Evaluation of the protective efficacy of four novel identified membrane associated proteins of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Vaccine. (2015) 33:2254–60. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.03.038
55
Brockmeier SL Loving CL Nicholson TL Wang J Peters SE Weinert L et al . Use of Proteins Identified through a Functional Genomic Screen To Develop a Protein Subunit Vaccine That Provides Significant Protection against Virulent Streptococcus suis in Pigs. Infect Immun. (2018) 86. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00559-17
56
Du H Huang W Xie H Ye C Jing H Ren Z et al . The genetically modified suilysin, rSLY(P353L), provides a candidate vaccine that suppresses proinflammatory response and reduces fatality following infection with Streptococcus suis. Vaccine. (2013) 31:4209–15. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.07.004
57
Xing X Bi S Fan X Jin M Liu W Wang B . Intranasal vaccination with multiple virulence factors promotes mucosal clearance of streptococcus suis across serotypes and protects against meningitis in mice. J Infect Dis. (2019) 220:1679–87. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz352
58
Prados de la Torre E Rodríguez-Franco A Rodríguez-Ortega MJ . Proteomic and bioinformatic analysis of streptococcus suis human isolates: combined prediction of potential vaccine candidates. Vaccines. (2020) 8. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8020188
59
Gonzaga ZJC Chen S Lehoux M Segura M Rehm BHA . Engineering Antigens to Assemble into Polymer Particle Vaccines for Prevention of Streptococcus suis Infection. Vaccines. (2021) 9. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9121386
60
Chen T Wang C Hu L Lu H Song F Zhang A et al . Evaluation of the immunoprotective effects of IF-2 GTPase and SSU05–1022 as a candidate for a Streptococcus suis subunit vaccine. Future Microbiol. (2021) 16:721–9. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2020-0232
61
Weiße C Dittmar D Jakóbczak B Florian V Schütze N Alber G et al . Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a Streptococcus suis vaccine composed of six conserved immunogens. Veterinary Res. (2021) 52:112. doi: 10.1186/s13567-021-00981-3
62
Wang Z Guo M Kong L Gao Y Ma J Cheng Y et al . TLR4 agonist combined with trivalent protein jointS of streptococcus suis provides immunological protection in animals. Vaccines. (2021) 9. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9020184
63
Li W Yin F Bu Z Liu Y Zhang Y Chen X et al . An Engineered Outer Membrane-Defective Escherichia coli Secreting Protective Antigens against Streptococcus suis via the Twin-Arginine Translocation Pathway as a Vaccine. J Microbiol Biotechnol. (2022) 32:278–86. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2107.07052
64
Liang S Zhang S Bao Y Zhang Y Liu X Yao H et al . Combined Immunoinformatics to Design and Evaluate a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Candidate against Streptococcus suis Infection. Vaccines. (2024) 12. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12020137
65
Liu J Zhang Z Pu W Pan X Li P Bai Q et al . A multi-epitope subunit vaccine providing broad cross-protection against diverse serotypes of Streptococcus suis. NPJ Vaccines. (2024) 9:216. doi: 10.1038/s41541-024-01015-7
66
Fang L Zhou J Fan P Yang Y Shen H Fang W . A serine/threonine phosphatase 1 of Streptococcus suis type 2 is an important virulence factor. J Vet Sci. (2017) 18:439–47. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.4.439
67
Zou G Zhou J Xiao R Zhang L Cheng Y Jin H et al . Effects of environmental and management-associated factors on prevalence and diversity of streptococcus suis in clinically healthy pig herds in China and the United Kingdom. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2018) 84. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02590-17
68
Fang L Shen H Tang Y Fang W . Superoxide dismutase of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 plays a role in anti-autophagic response by scavenging reactive oxygen species in infected macrophages. Veterinary Microbiol. (2015) 176:328–36. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.02.006
69
Zaccaria E Cao R Wells JM van Baarlen P . A zebrafish larval model to assess virulence of porcine streptococcus suis strains. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0151623. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151623
70
Zhang Y Xu JC Hu ZD Fan XY . Advances in protein subunit vaccines against tuberculosis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1238586. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1238586
Summary
Keywords
Streptococcus suis , subunit vaccines, adjuvants, cross-protection, vaccine delivery
Citation
Fang L and Ning J (2025) Decadal advances and future prospects in subunit vaccine development against Streptococcus suis infection. Front. Immunol. 16:1680732. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1680732
Received
06 August 2025
Accepted
02 September 2025
Published
19 September 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Victor C. Huber, University of South Dakota, United States
Reviewed by
Nitin Kamble, University of Cincinnati Medical Center, United States
Guodong Zhou, Liao Cheng University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Fang and Ning.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lihua Fang, fanglihuarc@163.com; Jie Ning, jiening919@gmail.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.