- 1Peking University People’s Hospital, Peking University Hepatology Institute, Infectious Disease and Hepatology Center of Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing Key Laboratory of Hepatitis C and Immunotherapy for Liver Diseases, Beijing International Cooperation Base for Science and Technology on NAFLD Diagnosis, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing, China
- 3Department of General Surgery, Integrated Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
- 4Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
- 5Laboratory of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University China, Guilin, Guangxi, China
- 6Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China
Introduction: Although the transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined with sintilimab and bevacizumab improves outcomes in unresectable HCC (uHCC), predictive tools are lacking. This study developed and validated a prognostic model for triple therapy efficacy.
Methods: A multicenter study enrolled uHCC patients receiving TACE-sintilimab-bevacizumab. Overall survival (OS) was the primary endpoint; a Cox model was developed and validated.
Results: This study enrolled 147 patients (training cohort: n = 92; validation cohort: n = 55). The optimal cutoff value for the fibrin degradation product-to-cholinesterase ratio*1000 (FCR) was determined as 0.8. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses identified FCR, AST, AFP, and PVTT as independent OS predictors. These variables were integrated to establish the FAAP scoring system, which demonstrated robust discriminative performance with AUC of 0.804 (95% CI: 0.703-0.893) and 0.799 (95% CI: 0.67-0.911) in the training and validation cohorts, respectively. Patients were stratified into three risk groups based on FAAP scores: low (FAAP < 0.7), intermediate (0.7 ≤ FAAP < 2.2), and high (FAAP ≥ 2.2). Kaplan-Meier analyses revealed significant prognostic stratification for both OS and progression-free survival (PFS) across groups. Subgroup analyses confirmed the prognostic relevance of FAAP scores in key clinical subsets, including age, gender, extrahepatic metastasis status, viral hepatitis etiology, PVTT presence, and Child-Pugh stage.
Conclusions: The FAAP scoring system effectively predicted survival outcomes in HCC patients receiving TACE-sintilimab-bevacizumab therapy, which suggests its clinical utility for prognostic prediction. Further large prospective studies are required for external validation.
1 Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related death worldwide (1), surgery and liver transplantation are considered curative treatments for HCC. However, due to the insidious onset of HCC, more than 60% of cases diagnosed too advanced for radical resection (2, 3). Patients with unresectable HCC (uHCC) face an unfavorable prognosis under conventional therapies, highlighting the critical need for innovative treatment strategies (4, 5).
The advent of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) targeting programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) and anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) agents has revolutionized systemic therapy for uHCC (6–9). In China, the combination of sintilimab and bevacizumab emerged as a first-line treatment following the landmark ORIENT-32 trial, which demonstrated superior progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) compared to sorafenib (10, 11). Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) provides a targeted locoregional approach by directly delivering chemotherapeutics and embolizing tumor-feeding vessels to effectively reduce tumor burden, which was widely used in Asian countries (12–16). CHANCE2201 studies report encouraging outcomes for TACE combined with ICIs and anti-VEGF triple therapy, triple therapy prolonged the median survival by 6.7 months compared with the control (17). However, how to predict the prognostic risk remain the huge research gap right now. To our knowledge, there are currently no prognostic models for uHCC patients receiving TACE, sintilimab and bevacizumab treatment.
To address this gap, we developed and validated the FAAP prognostic scoring system—a novel composite model integrating fibrin degradation product-to-cholinesterase ratio*1000 (FCR), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), AFP, and portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) to predict survival in uHCC patients undergoing TACE-sintilimab-bevacizumab therapy. This tool holds immediate clinical relevance for optimizing patient selection, guiding adaptive therapeutic escalation, and standardizing efficacy evaluation in trials exploring TACE-immunotherapy-antiangiogenesis combinations.
2 Methods
2.1 Patients
This is a multicenter retrospective study enrolled patients with uHCC who received TACE combined with sintilimab (anti-PD-1) plus bevacizumab (anti-VEGF) from Peking University People’s Hospital (n = 48, part of training cohort), Nanfang Hospital (n = 44, part of training cohort) and Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University (n = 55, validation cohort) between April 2021 and December 2023. Follow-up was closed on April 2025. Patients without the event were censored at the date of last contact or at end date, whichever occurred first. In accordance with the requirements of the Ethics Committee (18), the study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of each center and conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to initiating the combined therapy.
2.2 Diagnostic criteria and exclusion criteria
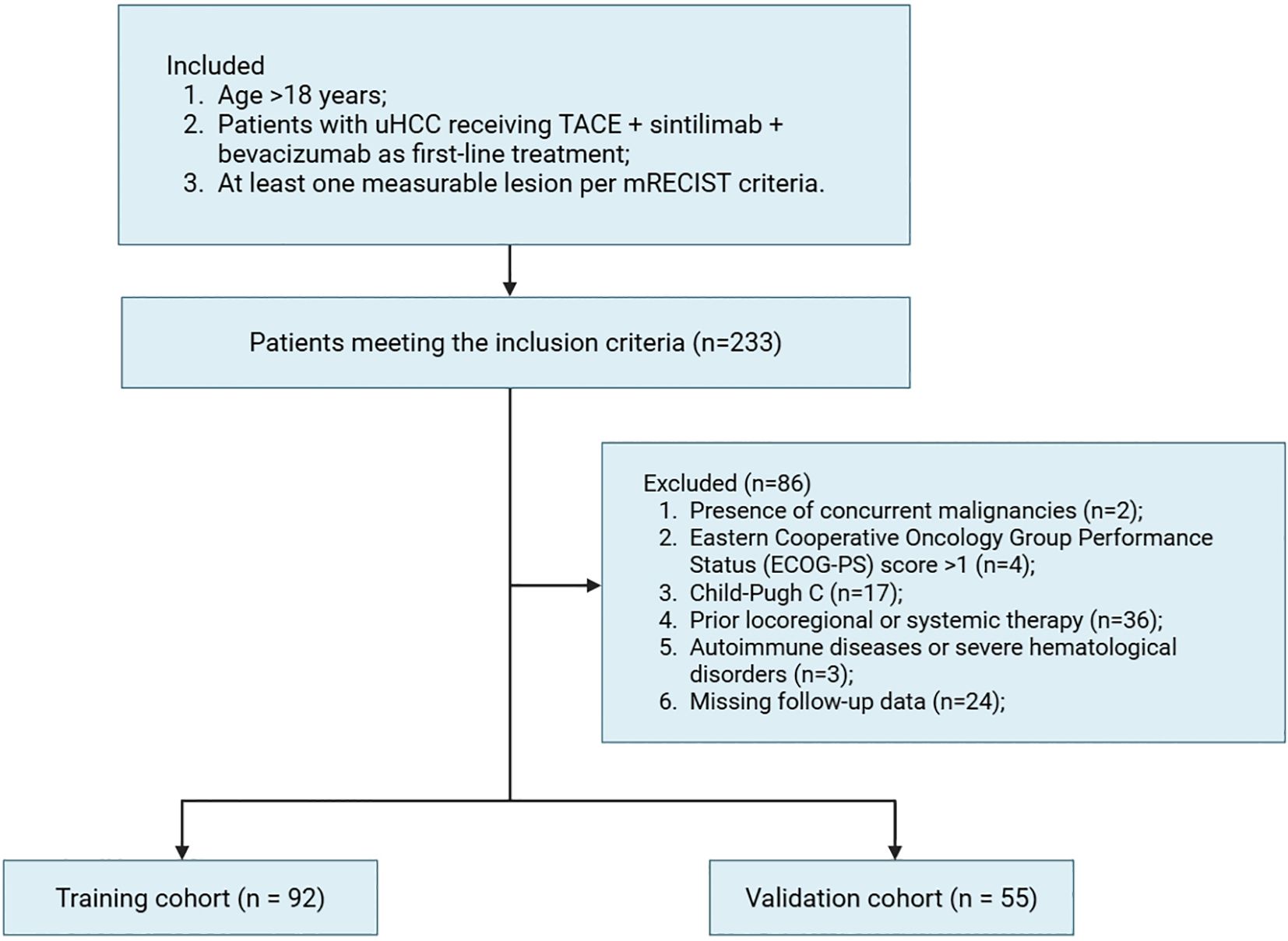
HCC diagnosis was established using non-invasive imaging criteria per the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) guidelines (19, 20). Tumor unresectability was defined by either advanced disease stage (e.g., multifocal lesions, vascular invasion, or extrahepatic spread) or insufficient post-resection liver remnant volume (< 40% for cirrhotic patients and < 30% for non-cirrhotic patients). Inclusion criteria were: 1) Age > 18 years; 2) Patients with unresectable HCC (uHCC) receiving first-line therapy with TACE, sintilimab and bevacizumab; 3) At least one measurable lesion per modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (mRECIST) (21). Exclusion criteria included: 1) Presence of concurrent malignancies; 2) Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG-PS) score > 1; 3) Child-Pugh C; 4) Prior locoregional or systemic therapy for HCC; 5) Active autoimmune diseases or severe hematological disorders; 6) Missing follow-up data.
2.3 The combination therapy
2.3.1 TACE
The conventional transarterial chemoembolization (C-TACE) procedures were performed by experienced interventional radiologists according to Chinese guidelines (22). Under local anesthesia, femoral artery access was obtained via the Seldinger technique, followed by selective angiography of the celiac trunk or hepatic artery to delineate vascular anatomy, tumor characteristics (number, size, location, vascular staining), and portal vein patency. A coaxial microcatheter (2.2-2.8F) was advanced superselectively into tumor-feeding segmental or subsegmental arterial branches. After angiographic confirmation of the target vessel, an emulsion of iodized oil (5–30 mL) and chemotherapeutic agents (e.g., Epirubicin 40–60 mg) was injected under fluoroscopic guidance until flow stasis or retrograde filling of peritumoral portal branches was observed. Subsequent embolization with polyvinyl alcohol embolization microspheres was performed to achieve complete occlusion of tumor-feeding arteries. Chemotherapy dosages were individualized based on body surface area, tumor burden, and functional status, while iodized oil volume (typically ≤ 20 mL per session) was adjusted according to tumor size, vascularity, and procedural objectives. Dynamic fluoroscopic imaging documenting iodized oil deposition patterns and superselective angiographic sequences were systematically archived for procedural validation and follow-up analysis. TACE was repeated when clinical benefit was anticipated, viable tumor or intrahepatic progression with acceptable liver function status, and withheld if liver function worsened, no treatable arterial target was available, or prespecified TACE-untreatable-progression criteria were met.
2.3.2 Sintilimab and bevacizumab administration
Sintilimab (200 mg) and bevacizumab (15 mg/kg) were administered via intravenous infusion every 3 weeks. The combination therapy cycle was maintained until disease progression or intolerable toxicities. Safety was assessed via treatment related adverse events (TRAEs), which were monitored and recorded in accordance with the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events Version 5.0.
2.4 Follow-up surveillance
Patients underwent clinical monitoring including laboratory testing and radiological examinations by contrast-enhanced MRI or CT every 4–8 weeks. PVTT was determined on contrast-enhanced CT/MRI. All baseline scans (within 4 weeks before treatment) were independently reviewed by two abdominal radiologists; discrepancies were resolved by consensus. PVTT was defined as solid intraluminal lesions within the portal vein that demonstrate partial arterial-phase enhancement and portal-phase filling defects on contrast-enhanced imaging. Treatment response was assessed by two independent radiologists by mRECIST criteria. The primary outcome was OS in this study, defined as the time span from the date when patients met the eligibility criteria and initiated the initial combination therapy until the occurrence of death from any cause, data censoring, or the end of follow-up, whichever occurred first. The secondary outcomes included PFS, defined as the time from treatment initiation until radiological progression or death from any cause. Objective response rate (ORR), incorporating complete response (CR, disappearance of arterial-enhancing targets) and partial response (PR, ≥ 30% reduction in enhancing lesion diameter).
2.5 Modeling and validation
Continuous clinical variables were dichotomized using established reference ranges or clinically validated cutoffs. Candidate predictors achieving significance (p < 0.05) in univariate Cox regression analyses advanced to multivariate modeling. The FAAP (Fibrin degradation product-to-cholinesterase ratio, Aspartate aminotransferase, Alpha-fetoprotein, and Portal vein tumor thrombosis) scoring system was derived from multivariate Cox regression. Each predictor was dichotomized, and regression coefficients (β) were used as weights to calculate the FAAP score as: FAAP = 0.891 × FCR (0/1) + 0.746 × AST (0/1) + 0.526 × AFP (0/1) + 0.528 × PVTT (0/1). Patients were stratified into risk groups according to X-tile determined cutoffs., weighting variables by their β coefficients. The model’s discriminative capacity was assessed in both training and validation cohorts using time-dependent receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, with optimal cutoffs determined via Youden’s index. Risk stratification based on FAAP scores enabled Kaplan-Meier survival curve generation, with between-strata comparisons performed through log-rank testing.
2.6 Statistical analysis
Categorical baseline characteristics were presented as frequencies with percentages. Between-group comparisons in training and validation cohorts were performed using Fisher’s exact test or Pearson’s chi-square test. Survival analyses were conducted through univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression models using the survival R package (v3.5-7). Kaplan-Meier curves with log-rank tests were generated using the survminer package (v0.4.9). Model discrimination was assessed via Harrell’s concordance index (C-index) calculated through bootstrap validation (1,000 resamples). Predictive performance was further evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves with area under the curve (AUC) quantification, implemented through timeROC package. Continuous variable distributions were visualized via violin plots created with ggplot2, incorporating Wilcoxon rank-sum tests for between-group comparisons. Subgroup analyses were performed through stratified Cox models, with results presented as forest plots generated using the forestploter and jstable packages. All tests were two-sided with statistical significance defined as p < 0.05. This integrated analytical workflow leveraged Python (v3.9.16) for data preprocessing and machine learning implementations, and R (v4.2.3) for survival analyses and advanced statistical visualizations.
3 Results
3.1 Patient characteristics
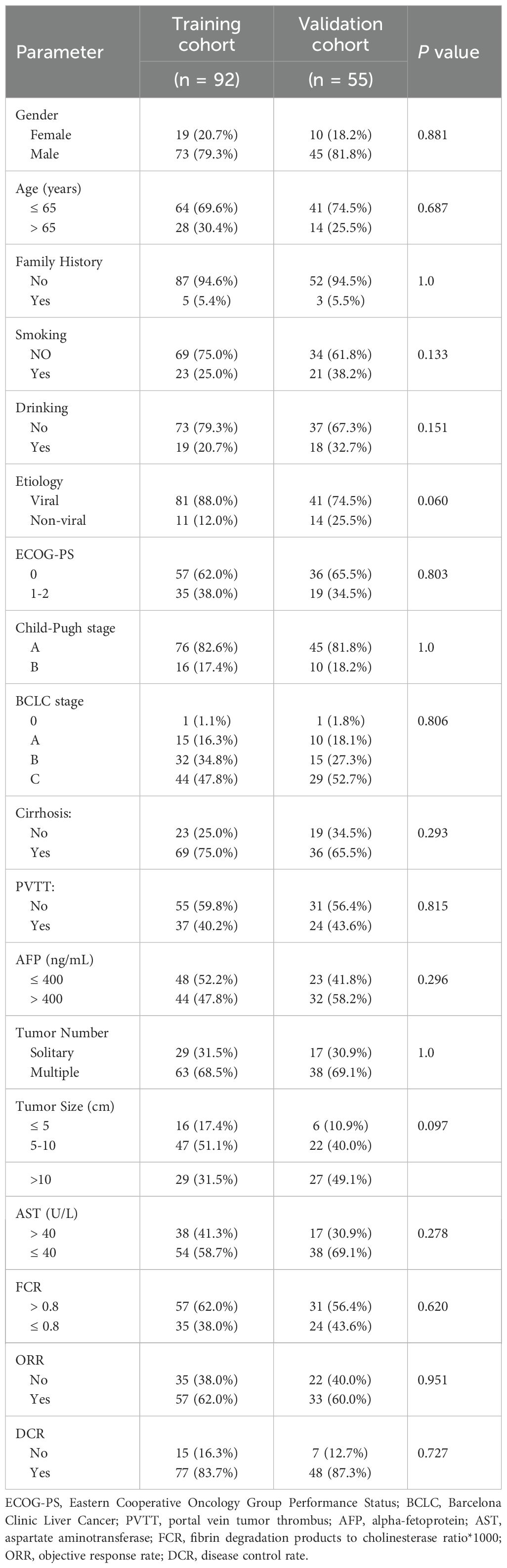
Among all 233 initially screened uHCC patients, 147 met eligibility criteria and were allocated to the training (n = 92) validation (n = 55) cohorts as shown in the Figure 1. Baseline characteristics were comparable between groups (Table 1). Most patients were male (~80%) and younger than 65 years (~70%), with viral hepatitis as the predominant etiology (88.0% vs. 74.5%). The majority had ECOG-PS 0–1 and Child-Pugh A liver function. Cirrhosis (75.0% vs. 65.5%) and portal vein tumor thrombosis (40.2% vs. 43.6%) were common. Approximately half had AFP >400 ng/mL, and most presented with multiple tumors, with tumor size >10 cm observed in 31.5% and 49.1% of patients. Treatment responses were similar, with ORR of 62.0% vs. 60.0% and DCR of 83.7% vs. 87.3%, confirming overall cohort comparability.
3.2 Treatment response and safety assessment
The objective response rates (ORR) were 62.0% and 60.0%, while the disease control rates (DCR) were 83.7% and 87.3% in the training and validation cohorts, respectively. Median OS were 19.0 and 18.0 months in the training and validation cohorts (Supplementary Figures S1 and S2), while median PFS were both 15 months in the training and validation cohorts (Supplementary Figures S3 and S4).
Among patients treated with the sintilimab and bevacizumab combination, treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) were frequent but largely manageable (Supplementary Table S1). In the training cohort, 84.8% of patients experienced any-grade TRAEs, with 60.9% being Grade 1-2, 19.6% Grade 3, and 4.3% Grade 4. Similarly, in the validation cohort, 83.6% reported any-grade TRAEs, including 60.0% Grade 1-2, 18.2% Grade 3, and 5.5% Grade 4. The most common any-grade adverse events across both cohorts were: Abnormal liver function (62.0% training, 61.8% validation) Fever (30.4% training, 29.1% validation) Hypertension (27.2% training, 25.5% validation) Fatigue (23.9% training, 23.6% validation). Most events were mild to moderate (Grade 1-2). Severe events (Grade ≥ 3) occurred in 19.6% (training) and 18.2% (validation) for Grade 3, and 4.3% (training) and 5.5% (validation) for Grade 4. No treatment-related deaths were reported, and most high-grade events were managed through dose adjustments or temporary therapy discontinuation.
3.3 Independent prognostic factors and modeling of FAAP scoring system
Fibrin degradation product-to-cholinesterase ratio (FCR) was determined as (FDP [mg/L]/CHE [U/L]) *1000, with an optimal cutoff value of 0.8 determined by X-tile analysis. Elevated FCR (> 0.8) demonstrated significant correlations with poor therapeutic outcomes (Figure 2): patients with high FCR showed reduced objective response rates (ORR: 28.6% vs. 63.2%; p < 0.001) and disease control rates (DCR: 64.3% vs. 89.5%; p = 0.003) compared to low-FCR patients. Violin plots revealed distinct FCR distributions across response categories (CR/PR/SD/PD), with progressive disease (PD) cases exhibiting median FCR values 2.3-fold higher than complete responders (CR) (p < 0.001).
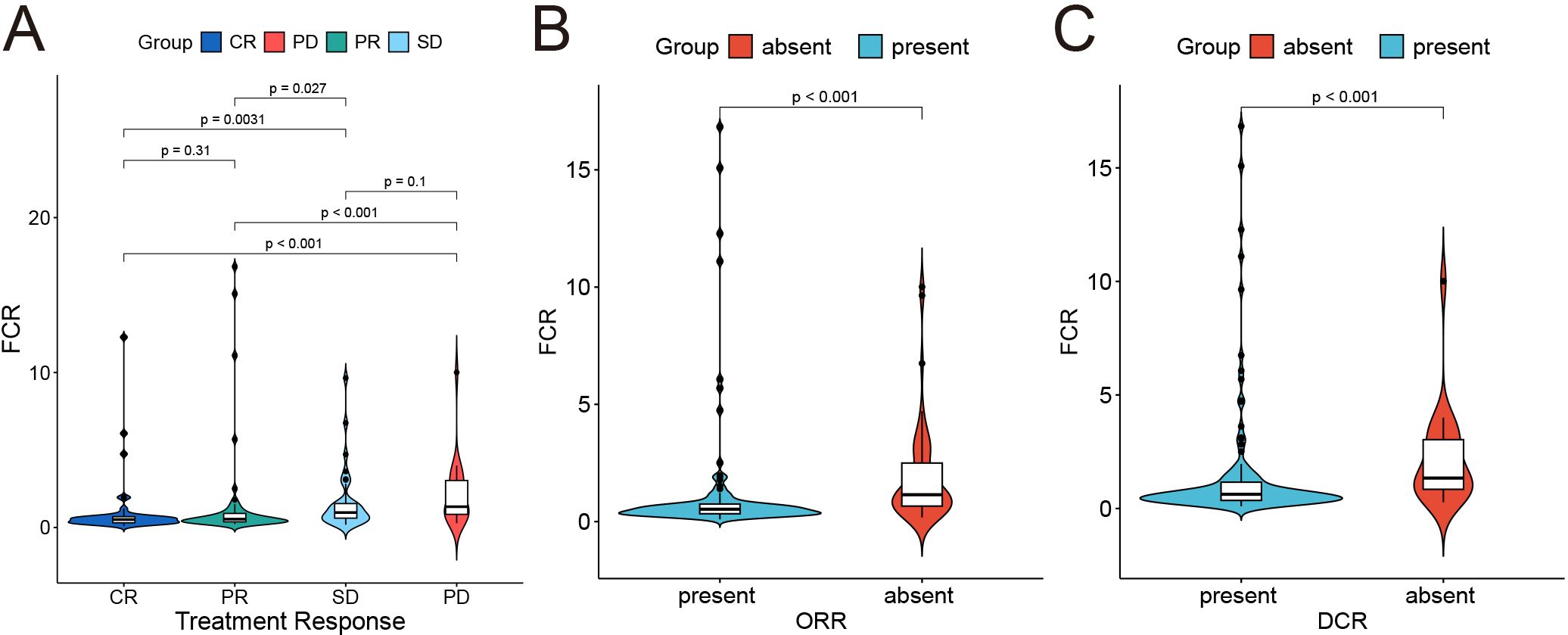
Figure 2. Correlation between fibrin degradation product-to-cholinesterase ratio*1000 (FCR) and treatment response. (A) Distribution of FCR across treatment response groups. (B, C) Binary classification of objective response rate (ORR) and DCR status (absent vs. present) and its association with FCR.
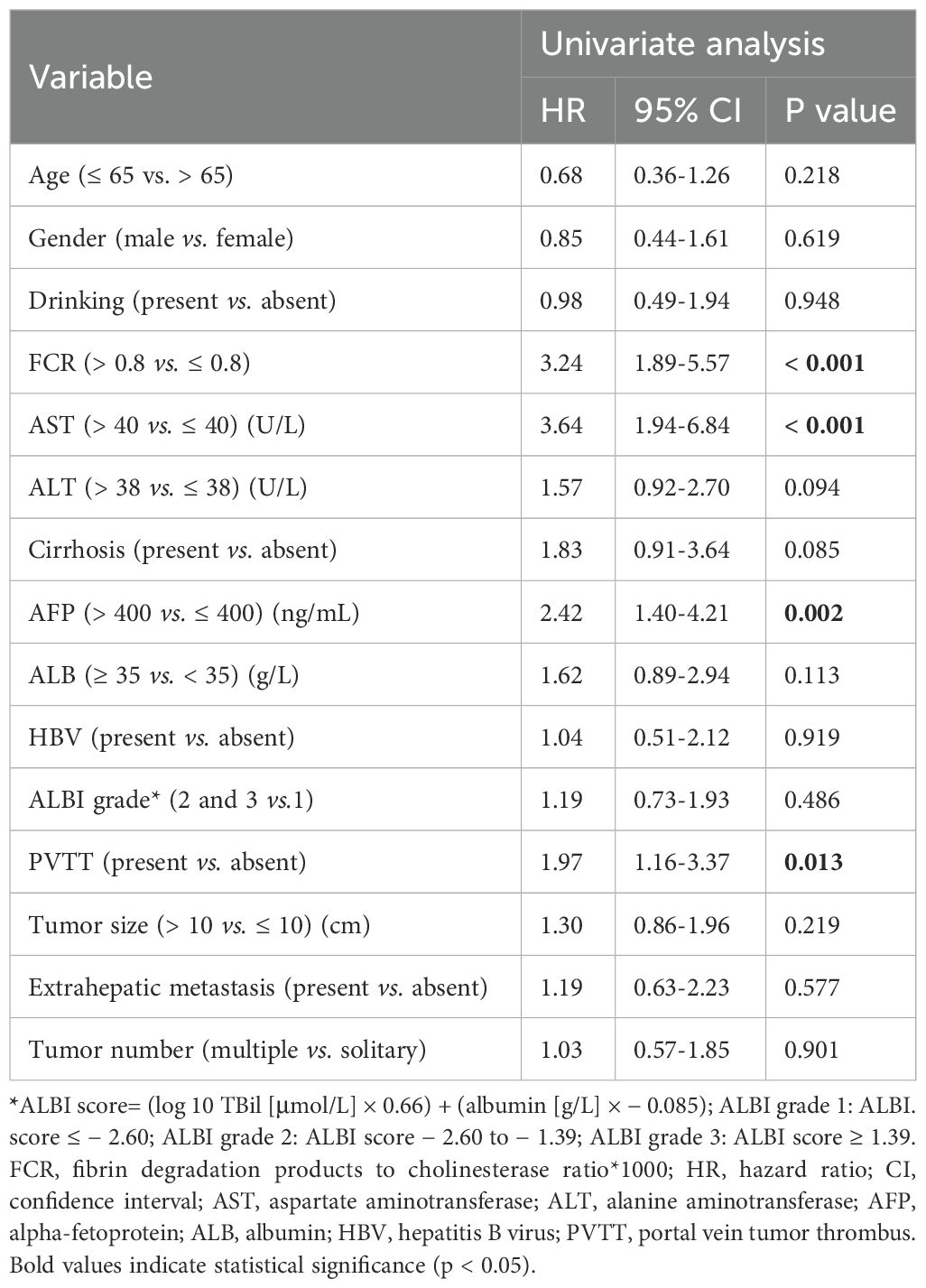
Univariable Cox regression identified four significant predictors of OS (Table 2): fibrin degradation product-to-cholinesterase ratio (FCR > 0.8: HR = 3.24, 95% CI: 1.89–5.57; p < 0.001), aspartate aminotransferase (AST > 40 U/L: HR = 3.64, 95% CI: 1.94–6.84; p < 0.001), alpha-fetoprotein (AFP > 400 ng/mL: HR = 2.42, 95% CI: 1.40–4.21; p = 0.002), and portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT: HR = 1.97, 95% CI: 1.16–3.37; p = 0.013). Variables including age, gender, drinking, ALBI grade, ALT, cirrhosis status, tumor number and tumor size showed no significant associations (p≥0.05). In the multivariable model (Figure 3), FCR retained the strongest predictive value (HR = 2.83, 95% CI: 1.61–4.96; p < 0.001), followed by AST (HR = 2.37, 95% CI: 1.22–4.63; p = 0.011), PVTT (HR = 1.87, 95% CI: 1.08–3.22; p = 0.025), and AFP (HR = 1.79, 95% CI: 1.01–3.20; p = 0.048).
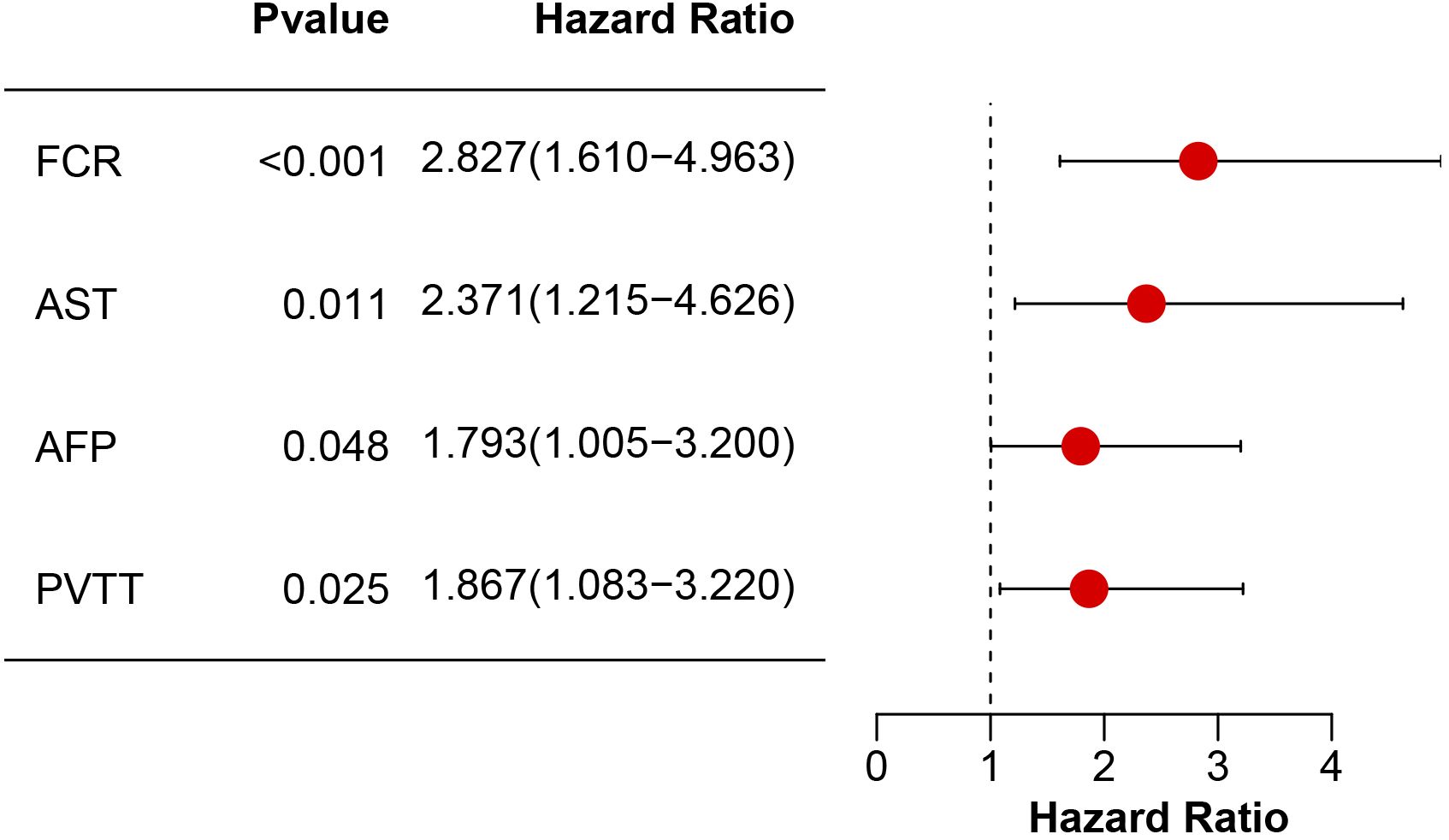
Figure 3. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards model analysis of prognostic factors. Hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) and corresponding p-values are shown for FCR, AST, AFP, and PVTT.
The prognostic model was designated as the FAAP score (FCR, AST, AFP, PVTT). Which is calculated as: FAAP Score = 0.891 × FCR (0 or 1) + 0.746 × AST (0 or 1) + 0.526 × AFP (0 or 1) + 0.528 × PVTT (0 or 1), where each variable is dichotomized using predefined thresholds (FCR > 0.8, AST > 40 U/L, AFP > 400 ng/mL, PVTT presence).
3.4 Performance of FAAP scoring system
The FAAP scoring system demonstrated favorable discriminative performance in both training and validation cohorts. As shown in Figures 4A, B, the FAAP score showed higher AUC values compared with established clinical parameters in the training cohort (AUC = 0.804, 95% CI: 0.703-0.893; FCR 0.660, AST 0.710, AFP 0.680, PVTT 0.612), while showing comparable accuracy in the validation cohort (AUC = 0.799, 95% CI: 0.672-0.911; FCR 0.717, AST 0.620, AFP 0.630, PVTT 0.607). The calibration curves for the training (Figure 4C) and validation (Figure 4D) cohorts demonstrated excellent agreement between the predicted survival probabilities and the observed survival fractions. The plots for 1-, 2-, and 3-year survival closely followed the diagonal reference line, indicating well-calibrated models without significant over- or under-estimation. These findings were supported by C-index analyses, with C-index values of 0.754 (95% CI: 0.691-0.813) and 0.722 (95% CI: 0.615-0.825) observed in the training and validation cohorts, respectively.
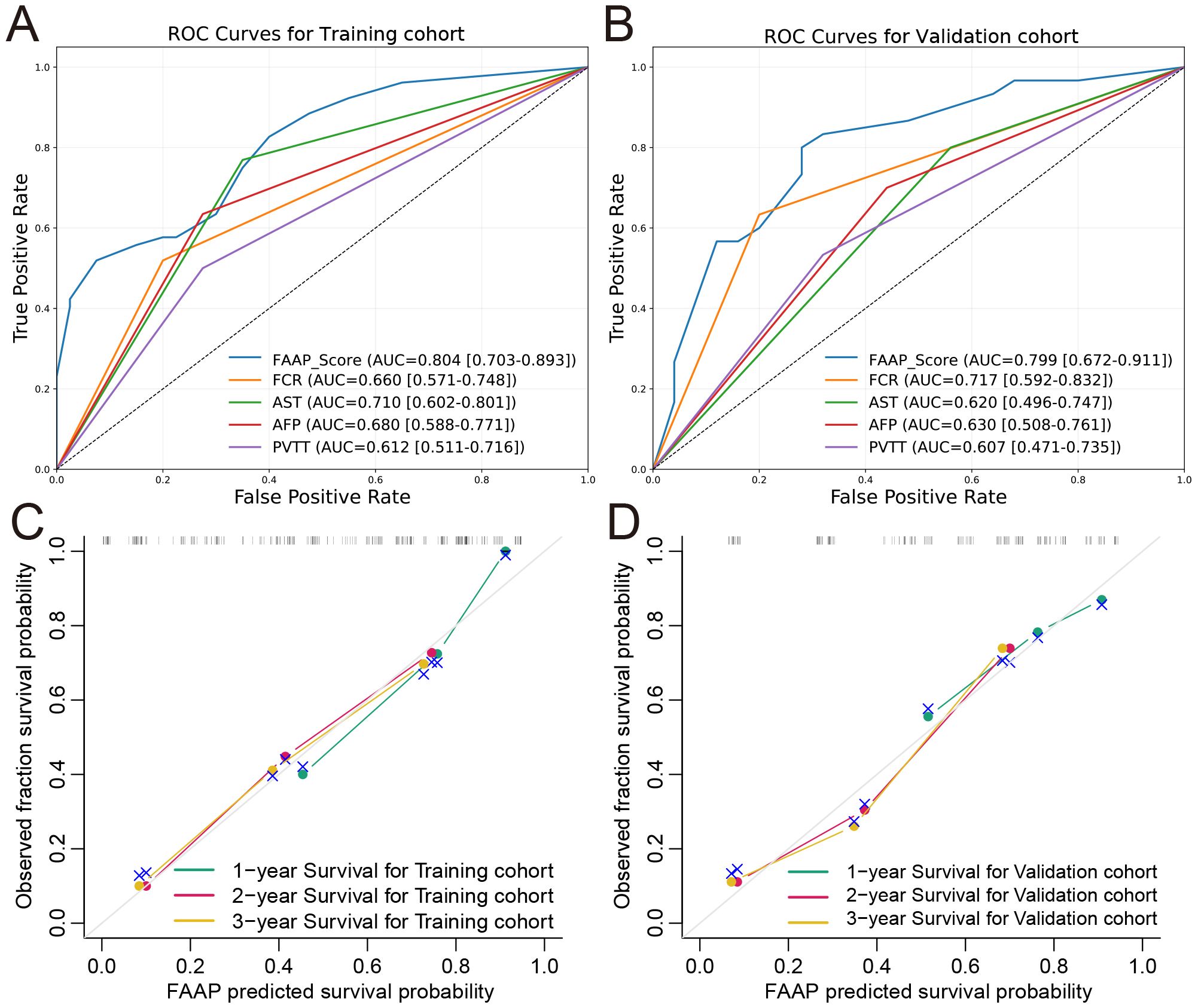
Figure 4. Predictive performance and calibration performance of the FAAP prognostic model. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for the predictive performance of the FAAP score in the training (A) and validation (B) cohorts. Observed versus predicted survival probabilities for one-year, two-year, and three-year survival in the training (C) and validation (D) cohorts, respectively.
3.5 Survival analysis of FAAP scoring system
The FAAP score was stratified into three different risk group using X-tile: low (FAAP < 0.7), intermediate (0.7 ≤ FAAP < 2.2), and high (FAAP ≥ 2.2). Kaplan–Meier survival analysis demonstrated significant differences in OS among patients classified into low, intermediate, and high FAAP groups in both cohorts (Figures 5A, B). The log-rank tests confirmed that these differences were statistically significant, reflecting the strong prognostic value of the FAAP score. In addition, progression-free survival (PFS) analysis showed that patients with higher FAAP scores had significantly shorter PFS compared to those with lower scores, as presented in Figures 5C, D. These findings collectively suggest that the FAAP scoring system effectively stratifies patients by risk and may serve as a reliable predictor of both overall and progression-free survival in HCC.
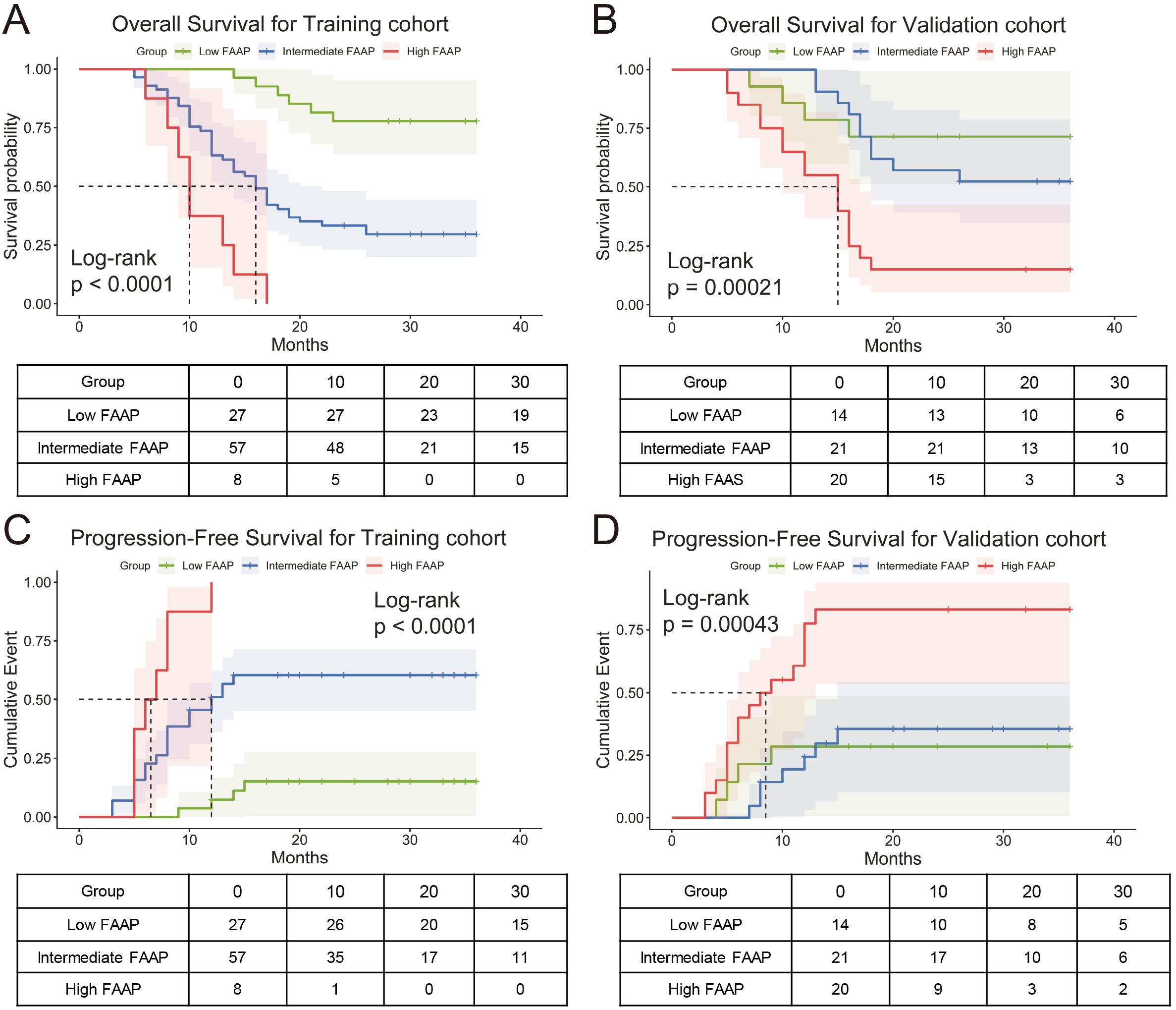
Figure 5. Prognostic stratification by FAAP score in training and validation cohorts. (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for overall survival (OS) in the training cohort, stratified into low, intermediate, and high FAAP score groups (Log-rank p < 0.0001). (B) Survival probability curves in validation cohort across FAAP subgroups (Log-rank p = 0.00021). (C, D) Progression-free survival (PFS) analysis for the training cohort (Log-rank p < 0.0001) and validation cohort (Log-rank p = 0.00043), respectively.
3.6 Subgroup analysis of FAAP prognostic efficacy
Subgroup analysis demonstrated consistent prognostic performance of the FAAP score across clinically relevant subgroups as shown in Figure 6. High-risk patients (FAAP ≥2.2) exhibited an increased mortality risk compared to low/intermediate-risk patients (95% CI: 2.25–10.89; p < 0.001). The association remained significant in male (HR = 4.32, p = 0.003) and female subgroups (HR = 7.33, p = 0.017), with amplified effects observed in elderly patients (> 65 years: HR = 11.34, p < 0.001). Notably, the FAAP score retained predictive validity regardless of portal vein tumor thrombosis status (PVTT-positive: HR = 3.82, p = 0.004) and Child-Pugh classification (Stage A: HR = 5.40, p < 0.001). Subgroup heterogeneity emerged in extrahepatic metastasis cohorts (metastasis-positive: HR = 3.47, p = 0.084), potentially reflecting limited sample size rather than biological variation. Viral hepatitis-negative patients showed no calculable risk due to complete early mortality (8/8 deaths) in the high-FAAP group.
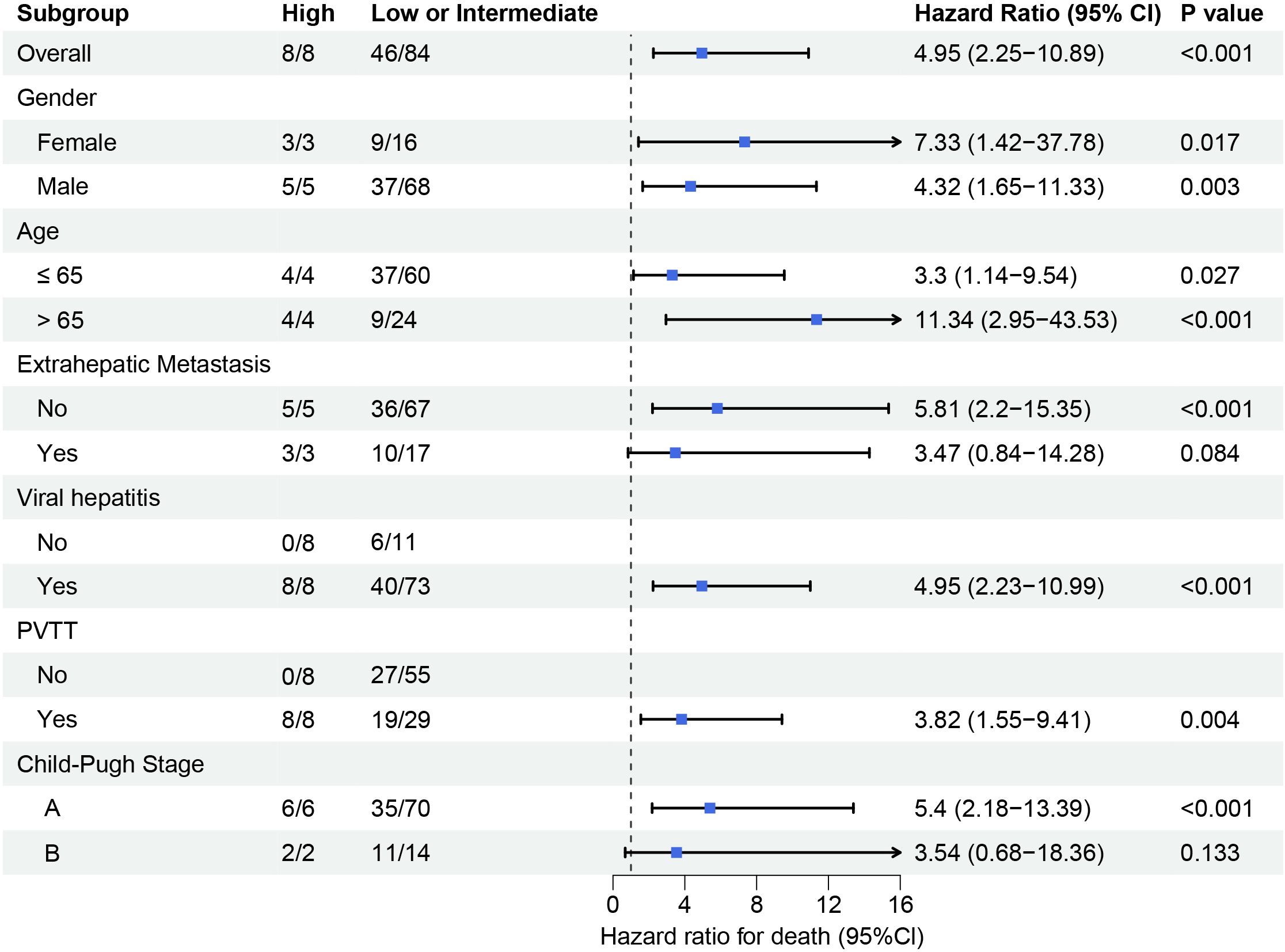
Figure 6. Subgroup analysis of survival outcomes stratified by clinical and pathological characteristics. Forest plot displays hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for mortality risk across different subgroups. High FAAP score subgroups (vs. low/intermediate) consistently exhibited elevated mortality risk.
4 Discussion
This study established and validated the FAAP scoring system, a novel prognostic model integrating fibrin degradation product-to-cholinesterase ratio*1000 (FCR), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), and portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) to predict survival outcomes in uHCC patients receiving triple therapy with TACE, sintilimab and bevacizumab. The FAAP score demonstrated robust discriminative performance for stratifying patients into distinct risk groups, with significant prognostic relevance for both OS and PFS. By addressing the unmet need for predictive tools in this therapeutic context, our model provides clinicians with a practical framework to optimize treatment selection and prognosis evaluation.
Previous studies have reported that the combination of TACE and anti-PD-1 therapy achieves an ORR of approximately ≥ 50% (23, 24). In our study, the ORR was 61.96% in the training cohort and 60.00% in the validation cohort, with the addition of bevacizumab further improving the ORR. This underscores the critical role of antiangiogenic therapy in uHCC treatment. According to recent clinical trials or multicenter studies, anti-PD-1/PD-L1 plus anti-VEGF yields an ORR of 25%-31% (10, 25, 26). On this basis, our study incorporated TACE, significantly enhancing the ORR in uHCC patients and demonstrating the feasibility of this regimen. Additionally, in our study, the median OS and PFS in the training cohort were 19.0 and 15.0 months, respectively. Given the complexity of TACE procedures, as well as differences in follow-up duration, baseline characteristics, and sample size compared to the CHANCE2201 study, these outcomes are acceptable (17). Although clinical trial cohorts are often highly selected, our findings remain largely consistent with previous studies (6, 27). These results further indicate that TACE may provide complementary benefits to the combined therapy of sintilimab and bevacizumab.
When further analyzing treatment efficacy, safety and tolerability should also be considered. Although the combination therapy demonstrated a significant improvement in ORR, the associated adverse events and their management remain crucial. In our study, most patients tolerated the combination of bevacizumab, TACE, and anti-PD-1 therapy, with an adverse event profile consistent with previous reports (28, 29). This suggests that the regimen achieves a reasonable balance between efficacy and tolerability. Moreover, accumulating long-term follow-up data will allow for a more comprehensive assessment of the durability and potential survival benefits of this strategy. Future studies could explore response variations among patients with different baseline characteristics to optimize individualized treatment approaches and further improve outcomes in uHCC.
The FAAP model developed in this study integrates four variables: FCR (fibrinogen degradation product/cholinesterase ratio*1000), AST, AFP, and PVTT. First of all, FCR is an innovative composite biomarker, which simultaneously reflects coagulation-fibrinolysis activation (elevated FDP) and impaired hepatic synthetic function (decreased cholinesterase). Prior studies suggest that elevated FDP is associated with HCC and other malignancies, serving as a diagnostic biomarker to differentiate malignant from non-malignant ascites and correlating with liver dysfunction or cirrhosis (30–32). Meanwhile, decreased cholinesterase indicates compromised liver reservation function. FCR may more sensitively capture the synergistic effect between abnormal coagulation and liver dysfunction, However, the dual-dimensional characteristics of coagulation and metabolism of FCR are unique, even though this idea is similar to the recently proposed composite indicators such as systemic immune inflammation index (SII) (33). Second, AST, AFP, and PVTT are validated prognostic factors, but their weights in the context of combined treatment are worthy of exploration. AST is a marker of liver injury, which correlates with post-resection HCC recurrence, and its inclusion reflects the impact of local treatment-related hepatotoxicity on survival (34). AFP serves as a tumor biological marker, retains prognostic value in the era of immunotherapy, consistent with subgroup analyses from trials such as IMbrave150 (7). PVTT is a vascular invasion indicator, which directly affects TACE efficacy and systemic treatment response, with its prognostic significance repeatedly validated in studies combining TACE with immunotherapy (35, 36). Compared to other models (e.g., ALBI focusing on liver function, mRECIST emphasizing tumor burden), FAAP more precisely evaluates local-systemic interactions by incorporating PVTT. The similarities and differences with previous models deserve attention: (1) BCLC and CNLC remain the primary staging system for determining treatment methods, while FAAP serves as a complementary, biomarker-based prognostic tool that stratifies risk among patients managed with a similar treatment; (2) Unlike immunotherapy-specific models, Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) or PD-L1 expression, FAAP excludes direct immune parameters but may indirectly reflect tumor microenvironment. Additionally, while similar combination therapy studies (LEAP-012) often include ECOG performance status or tumor burden metrics, FAAP prioritizes liver function and tumor biology, highlighting divergent core prognostic factors across treatment modalities.
Briefly, the FAAP variables might distinguish prognosis in patients receiving TACE plus anti-VEGF and PD-1 blockade. FCR integrates fibrinolysis activity and hepatic synthetic reserve, both linked to ischemia–hypoxia, vascular remodeling, and systemic therapy tolerance. AST reflects baseline hepatocellular injury, which influences both TACE-related hepatic stress and the capacity to continue systemic therapy. AFP indicates tumor burden and aggressiveness. PVTT represents macrovascular invasion that limits locoregional control and alters perfusion/immune microenvironment. Together, these dimensions provide a biologically plausible, biomarker-based prognostic portrait for patients managed with the same triple-therapy rationale, while not implying prediction of treatment benefit across different therapies.
This study has several limitations. First, although standardization of TACE procedures within a single center offers advantages, inherent variability in TACE administration remains unavoidable. Second, Given the retrospective design and modest sample size, potential selection bias is inevitable. We will first expand the sample size and continue follow up, then initiate prospective or ambispective multicenter validation to confirm generalizability and clinical utility. Third, the follow-up time limits the assessment of long-term outcomes, particularly for patients receiving combination immunotherapy. Therefore, extended observation is still required to evaluate survival benefits and delayed toxicities. Finally, the clinical utility of the FAAP scoring system remains to be defined, including how dynamic parameter changes may influence its predictive performance.
In conclusion, the FAAP scoring system effectively stratifies uHCC patients undergoing TACE-sintilimab-bevacizumab therapy into distinct prognostic groups, offering a clinically accessible tool for personalized management. Its derivation from readily available parameters enhances translational applicability, though prospective validation is essential to confirm its generalizability and refine risk-adapted therapeutic strategies.
Data availability statement
The data analyzed in this study is subject to the following licenses/restrictions:The datasets used and analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Requests to access these datasets should be directed to Y2hlbmhvbmdzb25nMjk5OUAxNjMuY29t.
Ethics statement
The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of each center (Peking University People’s Hospital: 2023PHB387; Nanfang Hospital, NFEC-202305-K32-02; Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University: 2021WJWZC14) and conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to initiating the combined therapy. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
LR: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Software. DC: Writing – original draft, Validation, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Software. XZ: Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Writing – original draft. SS: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. RF: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. XC: Resources, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. SM: Writing – review & editing, Methodology. YZ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. JG: Validation, Writing – review & editing. WL: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Data curation, Project administration. HC: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by the National Key Sci-Tech Special Project of China (No. 2018ZX10302207), the Beijing Nova Program (No.20250484965), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 7222191), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (NO. 7244426), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Peking University (PKU2024XGK005), the Peking University Medicine Seed Fund for Interdisciplinary Research (No. BMU2021MX007, BMU2022MX001), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1692632/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Zhong J-H, Ke Y, Gong W-F, Xiang B-D, Ma L, Ye X-P, et al. Hepatic resection associated with good survival for selected patients with intermediate and advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. (2014) 260:329–40. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000236
3. Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. (2016) 66:115–32. doi: 10.3322/caac.21338
4. Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J Hepatol. (2022) 76:681–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.018
5. Zhou J, Sun H, Wang Z, Cong W, Zeng M, Zhou W, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer (2022 edition). Liver Cancer. (2023) 12:405–44. doi: 10.1159/000530495
6. Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, Galle PR, Ducreux M, Kim T-Y, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382:1894–905. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1915745
7. Galle PR, Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, Zhu AX, Kim T-Y, et al. Patient-reported outcomes with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sorafenib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (IMbrave150): an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22:991–1001. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00151-0
8. Cheng A-L, Qin S, Ikeda M, Galle PR, Ducreux M, Kim T-Y, et al. Updated efficacy and safety data from IMbrave150: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab vs. sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. (2022) 76:862–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.030
9. Sangro B, Sarobe P, Hervás-Stubbs S, and Melero I. Advances in immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 18:525–43. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00438-0
10. Ren Z, Xu J, Bai Y, Xu A, Cang S, Du C, et al. Sintilimab plus a bevacizumab biosimilar (IBI305) versus sorafenib in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (ORIENT-32): a randomised, open-label, phase 2–3 study. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22:977–90. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00252-7
11. Sun H-C, Zhu X-D, Wang Z-Y, Gao Q, Ji Y, Shi Y-H, et al. Sintilimab plus bevacizumab followed by resection in intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase Ib clinical trial with biomarker analysis. BMJ Oncol. (2024) 3:e000578. doi: 10.1136/bmjonc-2024-000578
12. Lencioni R, De Baere T, Soulen MC, Rilling WS, and Geschwind J-FH. Lipiodol transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review of efficacy and safety data. Hepatology. (2016) 64:106–16. doi: 10.1002/hep.28453
13. Park J-W, Chen M, Colombo M, Roberts LR, Schwartz M, Chen P-J, et al. Global patterns of hepatocellular carcinoma management from diagnosis to death: the BRIDGE Study. Liver Int. (2015) 35:2155–66. doi: 10.1111/liv.12818
14. Lu J, Zhao M, Arai Y, Zhong B-Y, Zhu H-D, Qi X-L, et al. Clinical practice of transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: consensus statement from an international expert panel of International Society of Multidisciplinary Interventional Oncology (ISMIO). Hepatobil Surg Nutr. (2021) 10:661–71. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-21-260
15. Yang D-L, Ye L, Zeng F-J, Liu J, Yao H-B, Nong J-L, et al. Multicenter, retrospective GUIDANCE001 study comparing transarterial chemoembolization with or without tyrosine kinase and immune checkpoint inhibitors as conversion therapy to treat unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Survival benefit in intermediate or advanced, but not early, stages. Hepatology. (2025) 82. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000001229
16. Moris D, Martinino A, Schiltz S, Allen PJ, Barbas A, Sudan D, et al. Advances in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: An overview of the current and evolving therapeutic landscape for clinicians. CA Cancer J Clin. (2025) 75. doi: 10.3322/caac.70018
17. Jin Z-C, Chen J-J, Zhu X-L, Duan X-H, Xin Y-J, Zhong B-Y, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors and anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody/tyrosine kinase inhibitors with or without transarterial chemoembolization as first-line treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CHANCE2201): a target trial emulation study. EClinicalMedicine. (2024) 72:102622. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102622
18. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA. (2013) 310:2191–4. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.281053
19. Singal AG, Llovet JM, Yarchoan M, Mehta N, Heimbach JK, Dawson LA, et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. (2023) 78:1922–65. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000466
20. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. (2025) 82:315–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.08.028
21. Lencioni R and Llovet JM. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. (2010) 30:52–60. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1247132
22. Zhou J, Sun H, Wang Z, Cong W, Wang J, Zeng M, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (2019 edition). Liver Cancer. (2020) 9:682–720. doi: 10.1159/000509424
23. Zuo M, Wei R, Li D, Li W, and An C. The AFCRPLITY score for predicting the prognosis of immunotherapy combined with local-regional therapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2024) 16:17588359241297080. doi: 10.1177/17588359241297080
24. Li L, Xu X, Wang W, Huang P, Yu L, Ren Z, et al. Safety and efficacy of PD-1 inhibitor (sintilimab) combined with transarterial chemoembolization as the initial treatment in patients with intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma beyond up-to-seven criteria. J Immunother Cancer. (2025) 13:e010035. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010035
25. Scheiner B, Pomej K, Kirstein MM, Hucke F, Finkelmeier F, Waidmann O, et al. Prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with immunotherapy - development and validation of the CRAFITY score. J Hepatol. (2022) 76:353–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.09.035
26. Gairing SJ, Mildenberger P, Gile J, Artusa F, Scheiner B, Leyh C, et al. Evaluation of prognostic scores in patients with HCC undergoing first-line immunotherapy with atezolizumab and bevacizumab. JHEP Rep. (2025) 7:101295. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2024.101295
27. Qin S, Chan SL, Gu S, Bai Y, Ren Z, Lin X, et al. Camrelizumab plus rivoceranib versus sorafenib as first-line therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (CARES-310): a randomised, open-label, international phase 3 study. Lancet. (2023) 402:1133–46. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00961-3
28. Li S, Wu J, Wu J, Fu Y, Zeng Z, Li Y, et al. Prediction of early treatment response to the combination therapy of TACE plus lenvatinib and anti-PD-1 antibody immunotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Multicenter retrospective study. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1109771. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1109771
29. Zeng Z-X, Wu J-Y, Wu J-Y, Li Y-N, Fu Y-K, Zhang Z-B, et al. The TAE score predicts prognosis of unresectable HCC patients treated with TACE plus lenvatinib with PD-1 inhibitors. Hepatol Int. (2024) 18:651–60. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10613-x
30. Kołodziejczyk J and Ponczek MB. The role of fibrinogen, fibrin and fibrin(ogen) degradation products (FDPs) in tumor progression. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). (2013) 17:113–9. doi: 10.5114/wo.2013.34611
31. VanDewater L, Carr JM, Aronson D, and McDonagh J. Analysis of elevated fibrin(ogen) degradation product levels in patients with liver disease. Blood. (1986) 67:1468–73. doi: 10.1182/blood.V67.5.1468.1468
32. Kim SY, Kim J-E, Kim HK, Kim I, Yoon S-S, and Park S. Higher prognostic value of soluble fibrin complexes than D-dimer and fibrin degradation product for disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients with liver cirrhosis. Blood Coagul Fibrinol. (2013) 24:150–6. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0b013e32835aef6b
33. Hu B, Yang X-R, Xu Y, Sun Y-F, Sun C, Guo W, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2014) 20:6212–22. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0442
34. Lu J, Wang F, Zhang W, Ren Y, Yang T, Ratti F, et al. Perioperative changes in serum transaminases levels predicts long-term survival following liver resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. (2025) 32:2446–55. doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-16705-8
35. Lei Z, Chai H, Liu X, and Jiang Y. Key prognostic factors in transarterial chemoembolization combined with sorafenib treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Am J Cancer Res. (2025) 15:517–32. doi: 10.62347/SXMJ5155
36. Zhou T-Y, Tao G-F, Zhou G-H, Zhang Y-L, Zhu T-Y, Chen S-Q, et al. Comparison of drug-eluting bead with conventional transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: a randomized clinical trial. Int J Surg. (2024) 110:5527–37. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001691
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, immunotherapy, transcatheter arterial chemoembolization, prognostic model, FAAP score
Citation: Ren L, Chen D, Zhang X, She S, Fei R, Cong X, Mu S, Zhou Y, Gao J, Liao W and Chen H (2025) Development and validation of the FAAP model for prognostic stratification in HCC patients treated with TACE, sintilimab plus bevacizumab: a multicenter study. Front. Immunol. 16:1692632. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1692632
Received: 27 August 2025; Accepted: 06 November 2025; Revised: 29 October 2025;
Published: 25 November 2025.
Edited by:
Yan Yan, Mayo Clinic Florida, United StatesReviewed by:
Zhongbao Tan, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, ChinaShucheng (Bangli) Cao, McGill University, Canada
Copyright © 2025 Ren, Chen, Zhang, She, Fei, Cong, Mu, Zhou, Gao, Liao and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongsong Chen, Y2hlbmhvbmdzb25nMjk5OUAxNjMuY29t; Weijia Liao, bGlhb3dlaWppYTI4OEAxNjMuY29t; Jie Gao, Z2FvamllXzExMzFAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Yuchen Zhou, eXVjaGVuemhvdUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Liying Ren
Liying Ren Dongbo Chen1†
Dongbo Chen1† Xue Zhang
Xue Zhang Shaoping She
Shaoping She Ran Fei
Ran Fei Jie Gao
Jie Gao Weijia Liao
Weijia Liao Hongsong Chen
Hongsong Chen