- 1Department of Pharmacy, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences & Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
- 2School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- 3Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences and Sichuan People’s Hospital, Chengdu, China
- 4Cheng Fei Hospital, Chengdu, China
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a prevalent chronic respiratory disease characterized by high prevalence, mortality, and disease burden. Current understanding of COPD pathogenesis primarily focuses on airway inflammation, immune dysfunction, oxidative stress, and protease-antiprotease imbalance. Notably, recent studies have increasingly highlighted the role of metabolic reprogramming in COPD. Metabolic reprogramming refers to cellular adaptation through metabolic pathway alterations in response to environmental stress, enabling physiological or pathological state transitions. This review systematically summarizes COPD pathogenesis, with particular focus on metabolic reprogramming features (glucose, lipid, and amino acid metabolism) in immune cells from COPD experimental models. Furthermore, we analyze the interactions between these metabolic alterations and chronic inflammatory responses, providing new insights into COPD pathogenesis.
1 Introduction
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) constitutes a prevalent chronic respiratory disorder, characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow obstruction. It exhibits a higher incidence among the elderly and male populations, with concentrated prevalence in regions with high smoking rates and air pollution. Recent epidemiological data have documented that the prevalence of COPD among adults aged 40 years and older ranges from 9% to 10% (1, 2). According to the latest statistics from the World Health Organization (WHO), COPD ranks among the top five leading causes of global mortality—accounting for 3.5 million deaths in 2021, or approximately 5% of total global deaths—with its prevalence continuing on an upward trajectory. In urban areas of China, COPD ranks fourth in terms of mortality, while its hospitalization rate also exhibits a year-on-year increase (3, 4).
In addition to its direct harms to individual health, COPD imposes a substantial economic burden on families, healthcare systems, and society, driven by high medical expenditures and lost productivity (5). What makes the situation more complex is that COPD is often comorbid with cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, pneumonia, anxiety/depression, and other conditions. These comorbidities not only increase patients’ risk of hospitalization, prolong the length of hospital stay, and raise the readmission rate, but also further drive up medical costs, significantly increase the difficulty in disease management, and exacerbate the operational pressure on healthcare systems (1, 5, 6).
2 Risk factors for COPD
Tobacco smoking stands as the paramount risk factor precipitating COPD. According to research, smoking accounts for over 70% of COPD cases in high-income countries, whereas in low- and middle-income countries, this proportion ranges from 30% to 40% (3). Upon being inhaled into the human body, tobacco particles activate macrophages, neutrophils, lymphocytes, eosinophils, and dendritic cells, leading to pulmonary inflammatory cell infiltration, mucus hypersecretion, airway remodeling, and emphysema, which ultimately results in impairment of lung function (7). Epidemiological evidence further reveals that more than 15% of smokers develop chronic airway obstruction, while approximately 40% to 70% of heavy smokers progress to COPD (8, 9).
Beyond active smoking, other risk factors for COPD also encompass passive smoking, environmental and occupational exposures, infectious factors, an unhealthy diet, and individual factors (such as gender and age differences, as well as genetic factors) (10). Owing to their small particle size and hydrophobicity, persistent environmental particulate matter can easily penetrate terminal bronchioles and alveoli, evade mucociliary clearance, be phagocytosed by alveolar phagocytic cells, and persist in the pulmonary interstitium and epithelial cell membranes for a long time — a process that leads to the formation of carbon-laden macrophages and functional alterations, with these macrophages exhibiting increased volume and enhanced secretion of inflammatory factors (e.g., TNFα, CXCL8) (11). Additionally, particulate matter induces NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS production in macrophages and activates the macrophage-epithelial NF-κB/MAPK pathway, thereby sustaining pro-inflammatory gene transcription and perpetuating chronic inflammation (12). In parallel, external stimuli such as inflammation, infection, hypoxia, or hyperoxia can induce mitochondrial dysfunction, which in turn triggers oxidative stress, inflammasome activation, apoptosis, senescence, and metabolic reprogramming, exacerbating the progression of COPD (13, 14). For instance, hypoxia can drive the transformation of macrophages into the M1 pro-inflammatory phenotype by stabilizing hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), promote glycolytic reprogramming of activated naive B cells and naive T cells, and simultaneously inhibit the immunosuppressive function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) — thereby triggering and amplifying inflammatory responses. Additionally, HIF-1α upregulates the expression of glucose transporters (e.g., GLUT1) and key glycolytic enzymes (e.g., hexokinase, phosphofructokinase), enhancing cellular glucose uptake and utilization. Cells preferentially rely on glycolysis for energy supply under hypoxic conditions; under oxygen-replete environments, however, preferential glycolysis is only induced and mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) is inhibited when HIF-1α is abnormally activated via PI3K-AKT/oxidative stress and other non-hypoxic pathways. This ultimately exacerbates metabolic disorders and chronic inflammation in COPD, further promoting airway remodeling and progressive decline in lung function (15–17). Epidemiological and experimental evidence indicates that higher dietary fiber intake is associated with a reduced risk of COPD. Unhealthy dietary factors include insufficient dietary fiber intake, a lack of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), and other factors. Given that PUFAs possess antioxidant properties against oxidative stress, which may help alleviate airway inflammation, unhealthy diets may indirectly increase the risk of developing COPD by impairing the body’s antioxidant capacity and immune function (18). Meanwhile, gender differences may indirectly influence COPD development by modulating smoking history and occupational exposure patterns; with advancing age, pulmonary function naturally declines, rendering individuals more susceptible to COPD (19). Genetic and epigenetic factors—such as polymorphisms in the HHIP gene locus and α1-antitrypsin deficiency—also play pivotal roles in the onset and progression of COPD (20). Multidimensional key features of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)are shown in Figure 1.
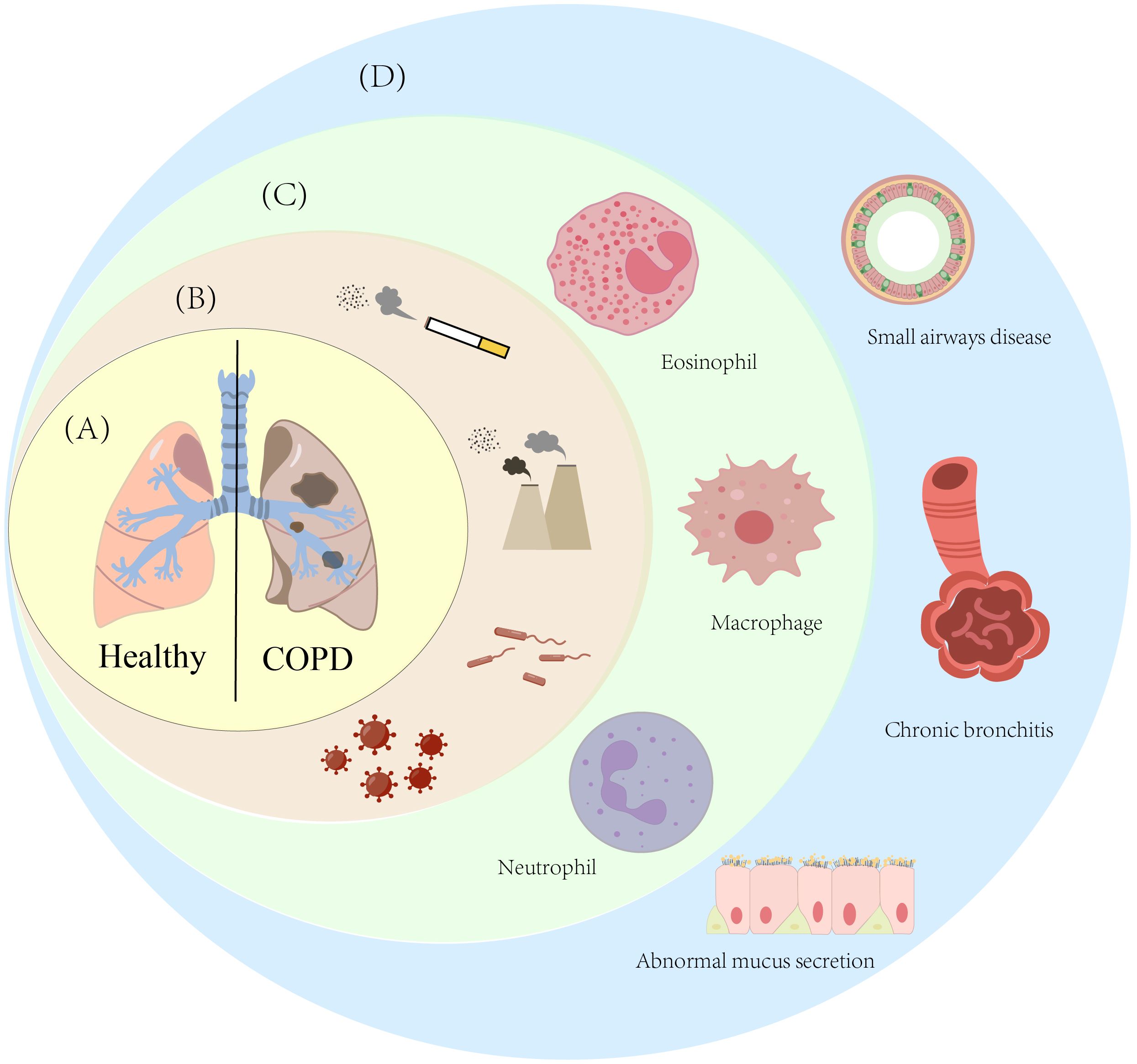
Figure 1. Multidimensional key features of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). (A) This diagram shows the comparison of lung tissue between healthy individuals and patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD); (B) This diagram lists the main risk factors for COPD, specifically including smoking, ambient smoke particles, bacterial infections, and viral infections; (C) This diagram presents the immune cells associated with COPD; (D) This diagram shows the pulmonary pathological changes caused by COPD, mainly including emphysema, airway stenosis, and abnormal mucus secretion by epithelial cells.
3 Phenotypes and endotypes of COPD
The clinical phenotype of COPD refers to one or more disease characteristics that reflect differences among COPD patients and correlate with clinical outcomes. COPD is traditionally classified into two types: the chronic bronchitis phenotype and the emphysema phenotype. With the advancement of research, the understanding of COPD etiology has expanded from “exposure to harmful gases/particles” to “multiple etiological types.” New classifications of COPD have emerged, including the pulmonary cachexia phenotype, COPD-bronchiectasis overlap phenotype, rapid progressive phenotype, non-smoking COPD phenotype, comorbidity/systemic phenotype, upper lobe-predominant emphysema phenotype, α1-antitrypsin deficiency phenotype, and early disease-related phenotypes (pre-COPD, early-onset COPD, preserved ratio impaired lung function) (21).
In contrast, an endotype represents the underlying biological or molecular mechanisms that produce these observable traits. Research on COPD endotypes is advancing rapidly, and several specific endotypes have been proposed or identified, including the T2-low endotype (neutrophil-predominant), T2-high endotype (eosinophil-predominant), genetic endotypes (α1-antitrypsin deficiency endotype, telomerase gene mutation endotype), pulmonary vascular endotype, and persistent inflammation/autoimmune endotype (22).
Phenotypes represent the external clinical manifestations of COPD, while endotypes provide mechanistic explanations behind these manifestations, thus linking clinical observations to molecular pathogenesis.
4 Key pathological features of COPD
COPD is defined by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation, with its pathological changes primarily manifesting in three domains: chronic bronchitis, small airway disease, and emphysema.
4.1 Chronic bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is pathologically characterized by hyperplasia of bronchial mucous glands, degeneration and necrosis of airway epithelial cells, squamous metaplasia, and concurrent infiltration of inflammatory cells (e.g., neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes) in the airway mucosa and submucosa. Clinical studies have confirmed that symptomatic chronic bronchitis—marked by chronic cough and sputum production—is associated with increased frequency of acute COPD exacerbations and accelerated decline in pulmonary function (1, 23).
4.1.1 Core cell types and their roles
As the main inflammatory cells infiltrating the airways, neutrophils disrupt the integrity of the airway epithelium by releasing elastase and matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-9), while secreting IL-8 and TNF-α to amplify the inflammatory cascade (24, 25). Activated alveolar macrophages secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α to mediate chronic airway inflammation; meanwhile, some studies have shown that oxidative stress can inhibit mitochondrial function and enhance glycolytic activity (26, 27). Recent data indicate the involvement of interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-22 in COPD pathophysiology — two cytokines crucial for regulating lung inflammation and infection. During disease initiation and progression, increased IL-17 secretion induces neutrophil recruitment, leading to chronic inflammation, airway obstruction, and emphysema. In the established phase of COPD, an impaired IL-22 response facilitates pathogen-associated infections and disease exacerbations (28). As the core of the airway barrier, damaged airway epithelial cells undergo mucous-secreting cell (goblet cell) hyperplasia, with excessive mucus secretion forming mucus plugs (29).
4.1.2 Key cytokines and regulatory networks
Chemokines (IL-8, CXCL1) are secreted by airway epithelial cells and macrophages to specifically recruit neutrophils to sites of airway inflammation, and their expression is regulated by transcription factors NF-κB and AP-1 (30). The pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α initiates the inflammatory cascade, induces the release of other cytokines, and promotes airway epithelial cell apoptosis; IL-6 promotes mucous gland hyperplasia and enhances mucus secretion via the JAK-STAT3 pathway. The reduced expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-10) fails to effectively inhibit pro-inflammatory factor production, resulting in sustained inflammatory imbalance (25, 30).
4.1.3 Regulatory roles of transcription factors
NF-κB is persistently activated in airway epithelial cells and macrophages, serving as a core transcription factor mediating chronic inflammation. By binding to the promoters of IL-8 and TNF-α genes, it promotes their expression; meanwhile, it regulates the expression of key glycolytic enzymes (e.g., HK2) to drive metabolic reprogramming (30). Composed of c-Jun and c-Fos, AP-1 is activated by ROS and synergizes with NF-κB to enhance pro-inflammatory factor transcription, while participating in the regulation of airway epithelial cell squamous metaplasia (27).
4.2 Emphysema
Emphysema represents another critical pathological hallmark of COPD, defined as “abnormal permanent enlargement of the airspaces distal to the terminal bronchioles, accompanied by destruction of alveolar walls and without significant fibrosis.” Clinically, two primary subtypes predominate: centrilobular emphysema and panlobular emphysema. Centrilobular emphysema, the most common subtype among smokers, predominantly affects the upper lobes of the lungs; panlobular emphysema, by contrast, is often linked to α1-antitrypsin deficiency and primarily involves the lower lobes. Destruction of alveolar walls in emphysematous regions leads to a reduction in the alveolar capillary bed, which diminishes lung elastic recoil—forming the core pathological basis for expiratory dyspnea in affected patients (16).
4.2.1 Core cell types and their roles
Macrophages are key effector cells in emphysema development, degrading elastic fibers of alveolar walls by secreting MMP-9 and MMP-12; meanwhile, macrophages may undergo M1-like metabolic reprogramming. A similar phenomenon has been observed in experimental models succinate accumulation activates HIF-1α, further enhancing glycolysis and pro-inflammatory factor release to accelerate alveolar destruction (27, 31). After infiltrating alveolar walls, neutrophils release elastase and proteinase 3 to degrade elastin and collagen, while producing ROS to damage alveolar epithelial cells; their enhanced glycolytic metabolism increases lactate production, further exacerbating oxidative stress (25). Fibroblasts exhibit decreased proliferative capacity and insufficient collagen synthesis, failing to repair damaged alveolar walls. Their metabolism is dominated by glycolysis, and studies suggest that the PTGES-AKT-HIF-1α pathway may be involved in fibroblast dysfunction, inhibiting their repair function (32).
4.2.2 Key cytokines and metabolic substrate abnormalities
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-9, MMP-12) are secreted by macrophages and neutrophils to directly degrade elastic fibers of alveolar walls; reduced expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP) fails to effectively inhibit MMP activity, leading to aggravated tissue destruction (31). Metabolomic studies have shown accumulation of TCA cycle intermediates (e.g., citrate, succinate, α-ketoglutarate) in alveolar tissue, impairing energy metabolism efficiency; decreased sphingomyelin (SM) levels damage mitochondrial membrane fluidity, inhibit OXPHOS, and indirectly promote glycolytic compensation (26, 33).
4.2.3 Regulatory roles of transcription factors
HIF-1α is highly expressed in emphysematous areas, activated by two pathways cigarette smoke-induced ROS and succinate accumulation. It upregulates key glycolytic enzymes (HK2, PKM2) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), promoting vascular remodeling and alveolar space enlargement, while inhibiting the proliferation and repair of alveolar epithelial cells (27, 34, 35). Nrf2 is a core transcription factor for antioxidant stress. Its reduced activity in COPD fails to effectively clear ROS, resulting in sustained oxidative damage and further exacerbation of alveolar wall destruction (30).
4.3 Small airway disease
Small airway disease, however, serves as the primary pathological driver of airflow limitation in COPD. This disorder affects small airways with a diameter < 2 mm, characterized by wall thickening (due to fibrosis and smooth muscle hyperplasia) and luminal narrowing or obstruction (resulting from mucus plug formation and accumulation of inflammatory exudates). Research has demonstrated a significant correlation between the severity of small airway disease and the degree of decline in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) (36, 37).
4.3.1 Core cell types and their roles
Airway smooth muscle cells (ASMCs) act as the core cells of airway remodeling, exhibiting typical Warburg-like metabolism with abnormal proliferation highly dependent on aerobic glycolysis; studies suggest that HHIP may mediate metabolic reprogramming via PKM2. Decreased HHIP expression relieves inhibition of PKM2, accelerating glycolysis and lactate production to promote cell proliferation (38). Damaged small airway epithelial cells undergo squamous metaplasia and increased mucus secretion; cigarette smoke exposure downregulates their α-enolase, reducing glycolytic efficiency, while activating FAO to produce ROS, exacerbating airway inflammation and fibrosis (39, 40). Lymphocytes B cells produce autoantibodies to participate in chronic inflammation; Th2 cells secrete IL-4 and IL-13 to induce ASMC proliferation and mucus secretion, with glycolysis-dominated metabolism further amplifying airway remodeling signals (7, 41).
4.3.2 Key cytokines and signaling pathways
IL-4 and IL-13 are secreted by Th2 cells and mast cells, activating the STAT6 pathway to promote ASMC proliferation and goblet cell mucus secretion, while upregulating PTGES expression to initiate the PTGES-AKT-HIF-1α pathway. Chemokines (CCL11, CCL24) recruit eosinophils and mast cells to small airways, releasing pro-inflammatory mediators to exacerbate airway narrowing and hyperreactivity. Fibrosis-related factors involve increased synthesis of collagen I and III, secreted by fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, leading to fibrotic thickening of the airway wall; their synthesis is coordinately regulated by TGF-β and HIF-1α.
4.3.3 Regulatory roles of transcription factors
STAT6, activated by IL-4 and IL-13, directly binds to the promoters of ASMC proliferation-related genes (e.g., cyclin D1) and mucus secretion genes (e.g., MUC5AC) to promote their expression, serving as a key transcription factor for small airway remodeling. Decreased activity of forkhead box protein O1 (FoxO1) may fail to inhibit ASMC proliferation and collagen synthesis; its function is regulated by phosphorylation via the AKT pathway, and sustained AKT activation in COPD leads to FoxO1 inactivation.HIF-1α is highly expressed in ASMCs, enhancing glucose uptake by upregulating GLUT1, inducing glycolytic enzyme expression, and inhibiting PDH activity to prevent pyruvate entry into the TCA cycle — providing energy and biosynthetic precursors for ASMC proliferation and myofibroblast differentiation (32, 35, 38).
5 Pathophysiological mechanisms of COPD
A complex, multi-dimensional network of mechanisms—among which chronic inflammation and immune response, oxidative stress, protease-antiprotease imbalance, and metabolic dysregulation are widely recognized as core drivers. Intricate crosstalk between these mechanisms collectively propels disease progression.
5.1 Chronic inflammation and immune response
Chronic inflammation constitutes a defining pathological feature of COPD, characterized by the infiltration and accumulation of key immune cells (e.g., neutrophils, macrophages, and T cells) in lung tissue and local airways. Concurrently, a spectrum of inflammatory mediators—including cytokines, chemokines, and proteases—is released, collectively establishing a persistent pro-inflammatory microenvironment that sustains disease progression (42). When the body is chronically exposed to harmful particles such as cigarette smoke, the immune response is activated: innate immune cells secrete pro-inflammatory mediators (e.g., tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α], interleukin-6 [IL-6], and interleukin-8 [IL-8]), triggering inflammatory reactions and inducing lung tissue damage (43, 44). Adaptive immune cells such as T cells then migrate to lesioned sites, further intensifying the local inflammatory milieu and driving disease progression (44). Throughout this process, the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway is activated—not only promoting the release of the aforementioned inflammatory factors and inducing local inflammation in the lungs and airways but also potentially contributing to a systemic inflammatory state (45).
In recent years, targeted studies have further unraveled the complex regulatory mechanisms of chronic inflammation in COPD, spanning molecular pathways, cellular effects, animal models, microecological balance, and immune defense.
From the perspective of molecular signaling pathway regulation, He et al. (45) combined clinical samples with animal experiments to demonstrate that the expression levels of microRNA-21 (miR-21), phosphorylated Smad2/3 (p-Smad2/3), and T helper 17 (Th17) cell-related cytokines (IL-17A, IL-6) are significantly upregulated in the lung tissue of COPD patients. When miR-21 was knocked out in mice, cigarette smoke (CS)-induced inflammatory responses were markedly attenuated, and pulmonary function damage was significantly alleviated. This finding clearly indicates that aberrant activation of the miR-21/Smad7/TGF-β signaling pathway promotes the differentiation and maturation of Th17 cells—emerging as a critical molecular mechanism underlying the initiation and persistence of chronic inflammation in COPD (45).
Focusing on the cellular effects of inflammation, a 2017 study by Huang et al. centered on neutrophils. Experiments confirmed that cigarette smoke selectively induces the infiltration and accumulation of neutrophils in lung tissue, while also prompting these cells to release matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9)—with MMP-9 expression levels increasing significantly with smoke exposure, ultimately triggering emphysematous lesions. Furthermore, the research team successfully recapitulated the pathological process of lung tissue destruction using an elastase-induced disease model, further validating that neutrophil-driven inflammatory responses constitute a core mechanism in the development and progression of emphysema (46).
Shifting to the perspective of airway microecology, a 2024 study by Li et al. was the first to investigate the association between the airway microbiome and COPD inflammation. Analysis of the airway microbiome in COPD patients revealed a significant reduction in α-diversity (microbial richness and evenness), alongside abnormal enrichment of potential pathogenic taxa such as Haemophilus and Pseudomonas. Further research identified synergistic interactions between fungi and bacteria in the airway, which collectively promote the release of pro-inflammatory mediators and exacerbate local inflammatory responses. This study suggests that airway microbiome dysbiosis not only serves as a key driver of chronic inflammation in COPD but may also be closely linked to the frequent occurrence of acute exacerbations (47). Airway microbiota dysbiosis can regulate the synergistic balance of host immunity and metabolism through a dual pathway of “direct metabolic interaction + indirect immune mediation,” driving the pathological progression of COPD. Firstly, the enrichment of pathogenic bacteria (e.g., Haemophilus) leads to the release of pro-inflammatory products such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which directly activate host TLR4 signaling pathways. On the one hand, this promotes the release of pro-inflammatory factors including IL-6 and TNF-α (48, 49); on the other hand, it induces enhanced glycolysis and suppressed fatty acid oxidation (FAO) via the phosphorylated AKT/HIF-1α pathway, disrupting glucose and lipid metabolic homeostasis (50, 51). Meanwhile, the reduction of beneficial bacteria (e.g., Bifidobacterium) results in insufficient production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which not only weakens their anti-inflammatory effects but also loses the inhibitory regulation on glycolysis, further breaking the balance (51, 52). Secondly, microbiota dysbiosis impairs the immune defense function of the airway mucosa, leading to increased bacterial colonization and triggering neutrophil infiltration as well as protease-antiprotease imbalance. Metabolic products such as lactate produced by neutrophils through aerobic glycolysis can reversely amplify macrophage M1 polarization and the release of pro-inflammatory mediators, forming a “immune infiltration - metabolic abnormality - inflammation amplification” feedback loop to indirectly promote metabolic reprogramming (48, 53, 54). Further studies have also found that synergistic interactions exist between fungi and bacteria in the airways, which can jointly promote the release of pro-inflammatory mediators and exacerbate local inflammatory responses. This study suggests that airway microbiota dysbiosis is not only an important driver of chronic inflammation and metabolic disorders in COPD but also closely associated with the frequent occurrence of acute exacerbations of the disease (50, 55).
From the lens of immune defense mechanisms, Richmond et al. (56) focused on the protective role of secretory immunoglobulin A (SIgA). Experiments revealed that mice lacking SIgA exhibited impaired airway mucosal immune defense, leading to abnormal bacterial colonization in the airways and subsequent progressive emphysema. Concurrently, the expression levels of matrix metalloproteinase-12 (MMP-12) and neutrophil elastase were significantly elevated in the lung tissue of these mice—indicating that persistent bacterial colonization in the airways disrupts the “protease-antiprotease” balance in lung tissue, ultimately promoting COPD-like pathological changes. This work provides a novel perspective for understanding the immunoregulatory mechanisms of inflammation in COPD (56).
5.2 Oxidative stress
Oxidative stress represents a pivotal mechanism in COPD pathogenesis, defined as an imbalance between the body’s oxidative and antioxidant systems—either due to excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) or impaired antioxidant capacity. Free radicals (e.g., superoxide anions, hydroxyl radicals) present in tobacco smoke serve as direct sources of ROS, exerting direct damaging effects on lung tissue (57). Meanwhile, inflammatory cells such as neutrophils and macrophages—activated by stimuli like smoke particles and dust—produce large quantities of ROS, which in turn activate inflammatory factors such as IL-1β and TNF-α. This forms a positive feedback loop of “ROS—inflammatory factors—ROS” (58). Further compounding this scenario is mitochondrial dysfunction in COPD patients, which also contributes to excessive ROS generation (10, 59).
Oxidative stress directly damages biological macromolecules. ROS can induce oxidative inactivation of antiproteases such as α1-antitrypsin, while simultaneously depleting antioxidant substances like glutathione. This leads to the accumulation of oxidative stress products (e.g., 8-isoprostane), which exacerbates inflammation, damages airway epithelial cells and pulmonary macrophages, and impairs mucociliary clearance function (60, 61). Additionally, ROS activates transcription factors such as NF-κB and AP-1, promoting the release of inflammatory factors; it also regulates mucus-related genes (e.g., Muc5b, Muc5ac), increasing mucus secretion (57, 62).
Oxidative stress further suppresses the antioxidant system. Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) regulates the transcription of antioxidant genes; however, CS exposure reduces Nrf2 activity, leading to decreased expression of antioxidant genes and insufficient production of endogenous antioxidants. This impairment of the body’s self-protective mechanisms prevents effective clearance of ROS, ultimately exacerbating lung damage (19, 63).
5.3 Protease-antiprotease imbalance
Under physiological conditions, a dynamic balance is maintained between proteases (which degrade tissue components) and antiproteases (which inhibit protease activity) in lung tissue. In COPD, this balance is disrupted—primarily manifested as enhanced protease activity and diminished antiprotease activity (19, 64).
α1-antitrypsin (AAT) represents the most active antiprotease in the lungs, capable of binding to proteases such as neutrophil elastase (NE) at a 1:1 molar ratio to mitigate tissue damage. However, oxidants released by harmful gases (e.g., smoke, dust) induce oxidative inactivation of AAT—with oxidative stress further exacerbating this inactivation (7, 19). Concurrently, smoking disrupts the airway epithelial barrier, prompting activated inflammatory cells to release serine proteases (e.g., neutrophil elastase, proteinase-3) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). These enzymes degrade extracellular matrix proteins (e.g., elastin), leading to lung tissue damage such as collagen degradation (23, 65). Ultimately, antioxidant enzymes fail to effectively inhibit the activity of proteases such as NE and MMPs, resulting in protease-antiprotease imbalance and driving the pathological progression of COPD.
6 Metabolic reprogramming in COPD experimental models
6.1 Introduction to metabolic reprogramming
The process by which cells alter their metabolic pathways to meet their bioenergetic, biosynthetic, and redox needs in response to adverse environments such as hypoxia and nutrient deficiency is termed metabolic reprogramming (66). In recent years, the rise of metabolomics has provided new ideas and methods for exploring the pathogenesis of COPD (67). Metabolomic studies have revealed abnormalities in multiple metabolic pathways, including amino acid metabolism, lipid metabolism, and glucose metabolism, in COPD patients and experimental models such as cigarette smoke-exposed mice (51, 68), suggesting that metabolic reprogramming is a core component of the pathogenesis of COPD (69). Changes in metabolites are shown in Table 1. Underlying this metabolic reprogramming is the abnormal activation of core transcription factors such as HIF-1α and NF-κB, which regulate the expression of genes related to glycolysis, amino acid catabolism, and fatty acid oxidation, respectively (15, 70); epigenetic modifications including methylation and non-coding RNAs further modulate gene activity (66); ROS-mediated inflammatory pathways, microbiota-TLR4 pathways, and disrupted nutrient hormone signaling serve as upstream triggers, with multiple mechanisms synergistically driving the sustained abnormalities of metabolic pathways (51, 68).
6.2 Glucose metabolic reprogramming
Glucose metabolism encompasses three primary pathways: glycolysis, the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Glycolysis and the TCA cycle serve as core hubs for energy production, while the PPP primarily supplies the cell with NADPH (to maintain redox balance) and ribose-5-phosphate (for biosynthesis) (71). Glycolysis refers to the 10-step process by which glucose is converted into pyruvate (72). The PPP, by contrast, branches from glucose-6-phosphate, generating NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate (for nucleotide synthesis) (73). In the TCA cycle, pyruvate enters mitochondria and is converted to acetyl-CoA by pyruvate dehydrogenase; acetyl-CoA then enters the TCA cycle, where a series of reactions generate NADH and FADH2—substrates utilized in oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) (20).
Abnormal glucose metabolism in COPD patients is not driven by a single factor but rather reflects systemic dysregulation across the three core energy metabolic pathways: glycolysis, the PPP, and the TCA cycle. This dysregulation is driven by environmental factors such as cigarette smoke (CS) and amplified by dysregulated expression of molecules including prostaglandin E synthase (PTGES), Hedgehog-interacting protein (HHIP), and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α)—forming a vicious cycle of “environmental damage—metabolic reprogramming—pathological progression.”
Aberrant glycolysis in COPD patients serves as a critical metabolic basis for airway remodeling and persistent inflammation. At the systemic level, COPD patients exhibit compensatory enhancement of glycolytic activity even at rest: a study by Kao CC et al. demonstrated that compared to healthy controls, COPD patients display a significantly accelerated rate of whole-body glucose production and a concurrent increase in glucose clearance—indicating enhanced glucose uptake and utilization efficiency. This phenomenon was further corroborated by elevated concentrations of glycolytic metabolites in the vastus lateralis muscle (74). Under exercise stress, non-oxidative metabolism of pyruvate (lactate production) is significantly enhanced, with the magnitude of blood lactate elevation 1.5 to 2 times higher than in healthy individuals. This observation suggests that the TCA cycle cannot meet energy demands under stress, forcing cells to rely primarily on glycolysis for energy production (74). Using Seahorse technology to measure the extracellular acidification rate (ECAR)—a key indicator of glycolytic flux—Cloonan et al. found that human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to CS activate glycogenolysis and upregulate glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) expression via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway within 1.5 hours of rhinovirus infection. This further enhances glycolytic activity, providing essential energy and biosynthetic precursors for viral replication (75). Metabolomic studies have further revealed that serum levels of sphingomyelin (SM) and its hydroxylated form (SM [OH]) are significantly reduced in COPD patients, with SM C24:1 levels exhibiting a negative correlation with glucose clearance. Concurrently, levels of polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA)-containing phosphatidylcholine are decreased, while levels of lysophosphatidylcholine are increased. These phospholipid metabolic imbalances impair OXPHOS by disrupting mitochondrial membrane fluidity, indirectly forcing cells to rely on glycolysis for compensatory energy production (76).
At the cell-specific level, distinct lung tissue cells exhibit marked differences in glycolytic phenotypes. Airway smooth muscle cells (ASMCs)—core cells involved in airway remodeling—exhibit a typical Warburg-like metabolic profile, with their abnormal proliferation highly dependent on aerobic glycolysis (38). The differentiation of myofibroblasts also relies on glycolytic reprogramming: stimulation with IL-4, IL-13, or TNF-α upregulates PTGES expression in lung fibroblasts. PTGES then activates the AKT pathway to induce HIF-1α expression, which in turn upregulates the expression of key glycolytic enzymes (hexokinase 2 [HK2], pyruvate kinase M [PKM], and phosphoglycerate mutase 1 [PGAM1]). Treatment with a HIF-1α inhibitor (30 μM) or 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG, 8 mM) completely reverses the PTGES-induced increase in alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression—confirming that glycolysis constitutes an essential step in myofibroblast differentiation (32). Additionally, alveolar macrophages exposed to CS extract (CSE) exhibit suppressed OXPHOS and compensatory increases in glycolysis—a change associated with ROS generation. Treatment with N-acetylcysteine (a ROS scavenger) reverses glycolytic abnormalities and restores macrophage phagocytic function (2). Neutrophils, by contrast, exhibit insufficient glycogen reserves due to decreased expression of glycogen cycle-related enzymes (e.g., glycogen phosphorylase). Pro-inflammatory mediators (e.g., LPS) can induce increased glycolytic flux in neutrophils, with gluconeogenesis compensating for energy demands by generating glycolytic intermediates from non-glucose substrates such as lactate (77). By measuring ECAR and mitochondrial oxygen consumption rate, Malinska et al. observed increased glycolytic flux and OXPHOS damage in human bronchial epithelial cells following smoke exposure (78).
Notably, discrepancies emerge across studies: short-term CS exposure significantly inhibits glycolytic function in type II alveolar cells. CS induces S-glutathionylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), leading to its inactivation, reduced ECAR, decreased ATP production, and impaired pyruvate generation (40). A study by SuPing Zhang et al. found that cigarette smoke exposure downregulates alpha-enolase in rat lung tissue, suggesting that this may impair glycolytic efficiency. However, this conclusion lacks direct measurements of glycolytic flux, relying solely on inferences from the downregulation of a single enzyme (79).These different metabolic data also provide new insights for our research: whether abnormal metabolic changes are related to disease progression and the duration of external stimuli.
The core driver of aberrant glycolysis in COPD patients lies in the dysregulation of molecular regulatory networks. Key regulatory axes—including HIF-1α, HHIP-PKM2, PTGES-AKT-HIF-1α, and lactate/LDH-A (LDH5)-TGF-β—interact to collectively promote enhanced glycolysis and diminished oxidative metabolism, sustaining the pathological phenotype of the disease (80–82). Among these, HIF-1α serves as a central transcription factor integrating stress signals and glucose metabolism. Its expression is elevated in COPD lung tissue and can be activated via three pathways: CS-induced ROS activating the PI3K-AKT pathway, macrophage TCA cycle disruption leading to succinate accumulation, and the PTGES-AKT pathway (83, 84). Downstream, HIF-1α upregulates GLUT1 to enhance glucose uptake, induces the expression of glycolytic enzymes, and inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) activity via PDK1—preventing pyruvate from entering the TCA cycle. It also plays a central role in cross-cellular processes such as ASMC proliferation and myofibroblast differentiation (81, 85). The HHIP-PKM2 axis represents a critical link between genetic susceptibility and metabolic abnormalities: mRNA and protein levels of HHIP—a product of the COPD susceptibility gene (4q31 locus)—are reduced by 45% and 30%, respectively, in ASMCs. HHIP deficiency relieves its inhibitory effect on PKM2 catalytic activity and nuclear translocation (80). PKM2 not only accelerates cytoplasmic glycolysis (increasing lactate production by 22%) but also translocates to the nucleus to synergize with HIF-1α in upregulating glycolytic genes. Cigarette smoke further amplifies this effect by inducing PKM2 dimerization via ROS, while overexpression of HHIP reverses glycolytic abnormalities and excessive proliferation in COPD-derived ASMCs. The PTGES-AKT-HIF-1α axis constitutes a core pathway for inflammation-induced glycolysis: pro-inflammatory factors such as IL-4 and IL-13 upregulate PTGES, which catalyzes the conversion of PGH2 to PGE2 to activate the PI3K-AKT pathway downstream of G protein-coupled receptors (32). Activated AKT phosphorylates HIF-1α to inhibit its degradation and promote nuclear localization, ultimately upregulating the expression of glycolytic enzymes—providing energy and collagen precursors for myofibroblast differentiation. Inhibition of PTGES or AKT significantly reduces glycolysis and fibrotic phenotypes.
Abnormalities in the PPP are primarily manifested as oxidative stress-induced compensatory activation. As the rate-limiting enzyme of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) can promote the production of NADPH through increased activity, and together with PPP, it jointly participates in the regulation of glycolysis and redox balance. Specifically, in 3D bronchial tissues exposed to cigarette smoke, levels of key PPP intermediates (e.g., 6-phosphogluconate, erythrose-4-phosphate) are significantly elevated, while the activity of G6PD, which is the rate-limiting enzyme of the PPP, is enhanced. This directly confirms PPP activation, representing an adaptive cellular response to oxidative stress. However, excessive activation reduces the proportion of glucose entering glycolysis and the TCA cycle, impairing energy production efficiency (20, 86). Short-term CS exposure (4–8 weeks) induces upregulation of PPP-related gene expression in the lung tissue of A/J mice, enhancing PPP activity. This generates reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) to maintain cellular redox balance and compensate for CS-induced oxidative stress damage—with this change reversible upon cessation of CS exposure (83). These PPP abnormalities ultimately impact cellular function: for example, neutrophils in COPD patients primarily rely on glycolysis for energy, with both the PPP and glycolysis supplying energy and NADPH for the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Cigarette smoke can disrupt neutrophil function by enhancing these two pathways, contributing to the pathological progression of COPD (87, 88).
As the core of energy metabolism, the TCA cycle exhibits abnormalities primarily stemming from insufficient substrate supply and inhibited activity of key enzymes—ultimately leading to reduced energy production efficiency and dysregulation of metabolic intermediates (89). At the systemic level, pyruvate oxidation is usually reduced and lactate levels may be elevated in COPD subjects at rest; during exercise-induced stress, pyruvate non-oxidative metabolism increases disproportionately, and the magnitude of blood lactate elevation is greater than that observed in healthy individuals, which suggests insufficient oxidative reserve of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle that fails to meet the metabolic demands under stress conditions. Under exercise stress, however, non-oxidative metabolism of pyruvate is significantly enhanced, with blood lactate elevation exceeding that in healthy individuals. This indicates insufficient oxidative reserve of the TCA cycle, preventing it from meeting metabolic demands under stress (74, 90). Cigarette smoke (CS) further exacerbates this abnormality: it induces a 2-fold increase in IRP2 expression, leading to increased mitochondrial iron loading. Iron overload promotes ROS generation and inhibits the activity of aconitase—a key TCA enzyme—resulting in reduced cycle efficiency and citrate accumulation (2). Concurrently, molecular regulatory networks exacerbate substrate insufficiency: elevated LDH5 activity increases lactate production, reducing pyruvate influx into the TCA cycle; HIF-1α further blocks pyruvate entry into the cycle by upregulating PDK1 to inhibit PDH activity (85).
These TCA cycle abnormalities are further characterized by the accumulation of intermediates: in the lung tissue of COPD patients and smoke-exposed mice, TCA intermediates such as citrate, alpha-ketoglutarate, and succinate accumulate—with elevated alpha-ketoglutarate also detected in urine. Mitochondrial dysfunction in COPD patients leads to the accumulation of TCA intermediates (e.g., citrate, alpha-ketoglutarate), while smoke-exposed mice exhibit mitochondrial dysfunction and reduced TCA cycle rate (91–93). Additionally, fumarate and malate accumulate in the lung tissue of COPD patients—further indicators of impaired energy metabolism (93). Glutamic pyruvate transaminase 2 (GPT2) regulates citrate production, influencing the shift from glucose metabolism to lipid synthesis. In airway epithelial cells treated with CS, upregulated GPT2 induces citrate accumulation, promoting phospholipid synthesis and contributing to alveolar structural damage (94).
6.3 Lipid metabolic reprogramming
Normal lipid metabolism mainly consists of three core pathways: fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO, a catabolic process), fatty acid synthesis, and cholesterol synthesis (62). In the pathological microenvironment of COPD, lipid metabolism undergoes significant reprogramming, characterized by FAO abnormalities, dysregulated sphingolipid and glycerophospholipid metabolism, and imbalanced regulation of triacylglycerol (TAG) and phospholipid synthesis. Among these, the crosstalk between macrophage phenotypic polarization and FAO dysfunction is a key mechanism driving disease progression (20, 33, 95).
6.3.1 Macrophage phenotypic polarization in lipid metabolism of COPD
Macrophages are core cells regulating inflammation and metabolism in COPD lung tissue, and their phenotypic polarization is tightly coupled with FAO function (96). M1 macrophages are dominated by fatty acid synthesis, with significantly reduced FAO activity. They rely on the glycolytic pathway for energy supply, and even preferentially use glycolysis for energy production under oxygen-replete conditions, while continuously releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α to amplify local inflammatory responses (97, 98). M2 macrophages are characterized by FAO as the main metabolic feature, with enhanced FAO function tightly coupled to intact mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), efficiently generating energy to support the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and the function of pulmonary tissue repair.
The proportion of M1 macrophages is significantly increased in COPD lung tissue. Their FAO suppression leads to reduced fatty acid breakdown and lipid accumulation, forming “lipid-laden macrophages.” These macrophages have severely impaired phagocytic function and cannot effectively clear apoptotic cells, foreign bodies, and cigarette smoke particles, further exacerbating the stability of the inflammatory microenvironment; meanwhile, upregulated fatty acid synthesis promotes the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, continuously amplifying chronic inflammation and accelerating airway remodeling (99, 100).
In COPD, the number of M2 macrophages is reduced and their FAO function is insufficient, their anti-inflammatory and tissue repair capabilities are significantly inhibited. They cannot effectively antagonize the pro-inflammatory effects of M1 macrophages, nor can they repair alveolar structural damage and airway epithelial barrier disruption, ultimately promoting the formation of emphysema and progressive decline in lung function (101).
6.3.2 Abnormal fatty acid oxidation
It should be noted that FAO abnormalities have cell-type specificity — human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to short-term cigarette smoke (CS) or treated with cigarette smoke extract (CSE) show upregulated FAO and increased expression of carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A (CPT1A), the rate-limiting enzyme of FAO, thereby promoting FAO-mediated ROS production and cell death, and participating in the development of emphysema (33). Differences in FAO between immune cells and upper airway cells are shown in Table 2; while FAO suppression is the main feature in macrophages, and these cell-specific differences collectively constitute the complexity of lipid metabolic reprogramming in COPD.
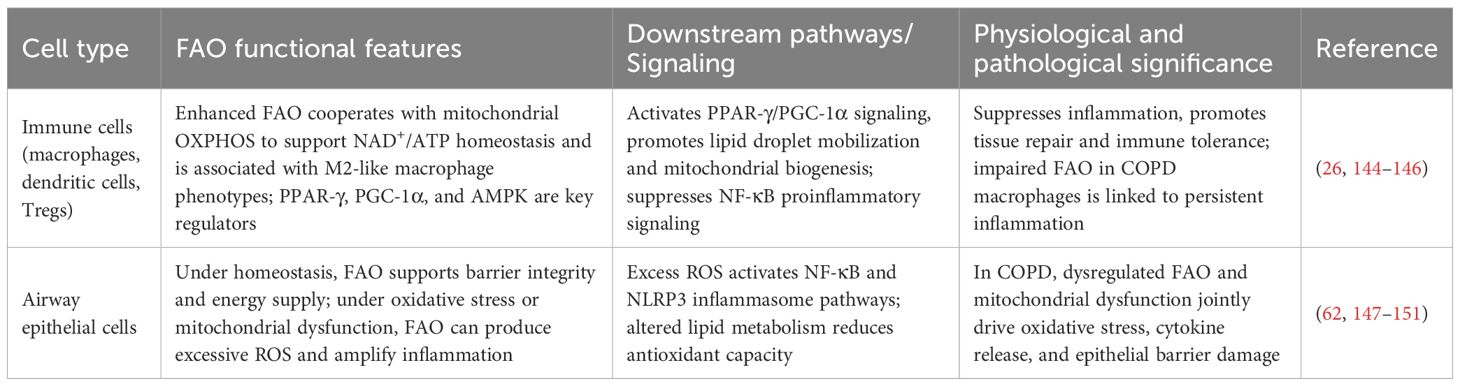
Table 2. Comparison table of fatty acid oxidation (FAO) between immune cells and airway epithelial cells.
6.3.3 Abnormal sphingolipid and glycerophospholipid metabolism
Plasma sphingomyelin (SM) levels are reduced in COPD patients with emphysema, while glycosphingolipids are associated with acute COPD exacerbations. Glycerophospholipid metabolic abnormalities correlate with airflow obstruction: lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) levels are elevated, and changes in phosphatidylcholine (PC) levels can distinguish between disease phenotypes (76, 102). Compared to healthy controls, COPD patients exhibit reduced plasma LPC and increased phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) levels (103).
6.3.4 Regulation of triacylglycerol and phospholipid synthesis
GPT2 regulates the synthesis of PC and TAG, participating in CS-induced lipid metabolic reprogramming in airway epithelial cells. Knockout of GPT2 inhibits CSE-induced PC and TAG abnormalities, alleviating lung damage. In smoking-induced lipid metabolic reprogramming, GPT2 regulates the expression of lipid metabolism-related genes (e.g., ACLY, CHPT1, DGAT1) (94). Plasma levels of lipids such as palmitoylethanolamide are abnormal in patients with advanced COPD, and combined detection of these lipids can improve diagnostic accuracy (104).
6.4 Amino acid metabolic reprogramming
Metabolic reprogramming in COPD also extends to amino acid metabolism, with abnormalities documented across multiple amino acid pathways (105).
6.4.1 Abnormal metabolism of branched-chain amino acids
Multiple metabolomic studies have indicated that plasma levels of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), namely leucine, isoleucine and valine, tend to decrease in some COPD patients, especially those with malnutrition or sarcopenia. This abnormality is associated with nutritional status and muscle metabolic disorders, and may reflect a pathological state of impaired protein catabolism and energy metabolism. However, evidence for a consistent association between BCAA levels and lung function parameters such as FEV1 and FEV1/FVC remains insufficient, requiring validation in larger-scale and longitudinal cohort studies (106).
In several animal studies of tobacco/smoke exposure, local or systemic amino acid profiles, including certain BCAAs or their metabolites, have been reported to be upregulated. This may reflect specific compensatory metabolic rearrangement or changes in protein metabolism in the early stage of smoking or in the models, but results between animal and human cohorts are not always consistent (93).
6.4.2 Abnormal tryptophan and kynurenine pathway
Tryptophan is the only essential amino acid containing an indole ring, and the kynurenine (KYN) pathway is its major metabolic route. A growing body of evidence has demonstrated that kynurenine pathway activity is generally increased in COPD and its acute exacerbations: the KYN/TRP ratio has been found to be elevated in peripheral blood or respiratory samples in several studies and is associated with inflammatory markers, suggesting a potential role of this pathway in the inflammation-metabolism crosstalk in COPD. In vitro and in vivo studies have also shown that the rate-limiting enzyme IDO1 can be induced in epithelial cells and immune cells, with its expression regulated by inflammatory signals such as IFN-γ, IL-6 and TNF. Additionally, experimental and review literatures have proposed that HIF-1α and oxidative stress may be involved in the regulation of IDO1, forming a complex interaction network, but complete evidence for each regulatory chain in human COPD airway tissues is still accumulating (107).
In terms of functional mechanisms, kynurenine and its downstream metabolites affect immune cell fate through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), including regulation of the Treg/Th17 balance. Moreover, certain downstream metabolites such as quinolinic acid can affect mitochondrial function and oxidative phosphorylation in vitro or model systems, thereby promoting metabolic reprogramming. These molecular mechanisms are supported by multiple reviews and experimental studies, but causal evidence in COPD patients needs further refinement (108).
6.4.3 Glutamine and glutamate metabolic imbalance
The importance of glutaminolysis in lung diseases is increasingly recognized. Multiple cellular and animal studies have shown that upregulation of glutaminase (GLS) is associated with metabolic reprogramming and profibrotic phenotypes of lung fibroblasts and macrophages. In pro-inflammatory macrophages (M1), glycolysis is predominant; glutaminolysis can assist in the production of succinate and itaconate, but energy supply still mainly relies on glycolysis. In M2 macrophages, the pathway of glutaminolysis → α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) → complete TCA cycle/oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) is a decisive metabolic feature that supports their anti-inflammatory function. Recent studies have indicated that glutamate-pyruvate transaminase 2 (GPT2) expression in smoking/smoke-exposed airway epithelial cells is associated with metabolic reprogramming. Glutamate levels are elevated in CSE-treated airway epithelial cells. Glutamate-pyruvate transaminase 2 (GPT2, also known as ALT2) regulates glutamate metabolism by catalyzing the conversion of pyruvate and glutamate into alanine and α-ketoglutarate (α-KG). Its effect on citrate production is a downstream indirect effect, and it also participates in the lipid synthesis pathway to regulate smoking-induced metabolic abnormalities in airway epithelial cells, thereby affecting energy homeostasis. Preliminary evidence from cellular, animal, transcriptomic and metabolomic studies for the specific pathological contribution of GPT2 in COPD airway structural cells has emerged in recent years, but more clinical samples and functional validations are needed to establish its strength of action in patients and feasibility as a therapeutic target (109).
6.4.4 Other amino acid abnormalities
In the serum of some COPD patients, arginine and proline levels are decreased—correlating with metabolic phenotypes (76). Elevated levels of glycine, aspartate, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) have been detected in the lung tissue of COPD patients, while elevated arginine levels are observed in mouse models—with these changes linked to inflammation and oxidative stress Glutamine levels exhibit variability across COPD cohorts but are generally associated with oxidative stress and nitrogen balance regulation (67). Hypoxanthine—related to purine metabolism—represents a potential biomarker for COPD (110).
7 Crosstalk between metabolic reprogramming and inflammatory responses
Metabolic reprogramming and inflammatory responses exhibit intimate crosstalk, with oxidative stress serving as a critical hub connecting the two. ROS generated during metabolic reprogramming (e.g., enhanced glycolysis, mitochondrial dysfunction) can amplify inflammatory signals, while inflammation further exacerbates metabolic dysregulation—forming a vicious cycle of “metabolic abnormalities—inflammation—immune dysregulation” (2, 111). Differences between the metabolism of healthy cells and that of COPD cells are shown in Table 3.
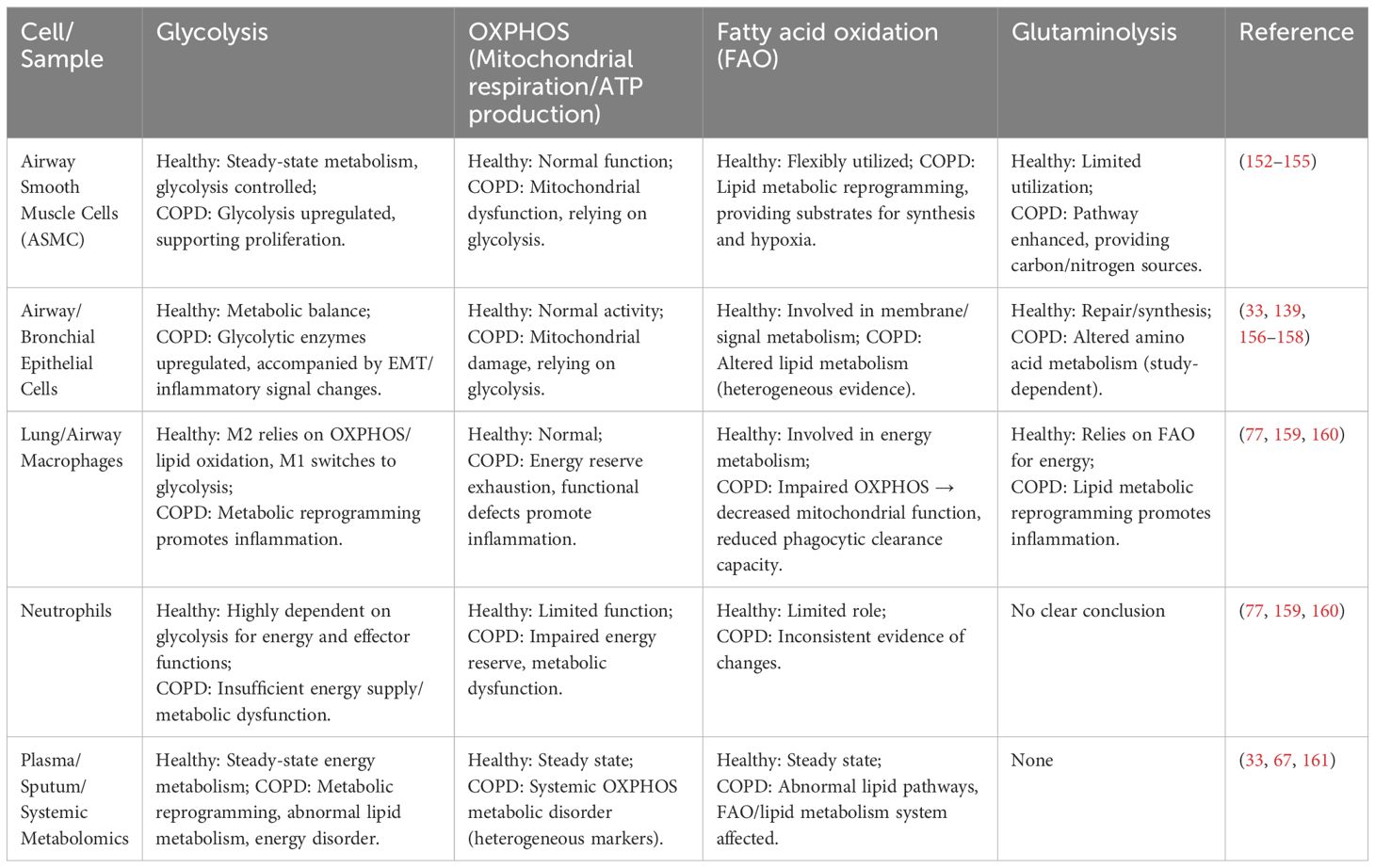
Table 3. Comparison of glycolysis, OXPHOS, fatty acid oxidation, and glutaminolysis metabolic pathways in different cells/samples between healthy and diseased states in COPD.
7.1 Crosstalk between metabolites and inflammatory signaling pathways
Metabolic reprogramming induces cells such as airway smooth muscle cells and epithelial cells to enhance aerobic glycolysis, producing large quantities of lactate. As a core metabolic product, lactate may promote the release of inflammatory mediators (e.g., IL-6, TNF-α) by activating the TGF-β signaling pathway, while enhancing NF-κB pathway activity to exacerbate local inflammatory infiltration in lung tissue — but this direct activation has not been demonstrated in COPD airway cells. Conversely, while inflammatory mediators can induce metabolic reprogramming, the fundamental driver of persistent inflammation lies in metabolic reprogramming—with metabolites such as lactate sustaining and amplifying inflammatory states to form a pathological loop (112, 113).
Metabolic reprogramming induces lipid metabolic dysregulation, increasing free fatty acid production and activating the TLR4 signaling pathway—directly exacerbating inflammatory responses. Concurrently, lipid metabolic reprogramming induces the synthesis of lipid mediators such as prostaglandin E2, further promoting the production of pro-inflammatory factors like IL-6 and aggravating respiratory inflammation. Additionally, lipid-laden macrophages have been observed in COPD patients, and their core functional abnormalities are mainly manifested by impaired phagocytic function and altered cell survival rate. Notably, the association between lipid accumulation and reactive oxygen species (ROS) is indirect; to date, no clear evidence has been found that it directly induces ROS production, and the amplification effect of related inflammatory damage may need to be mediated through other downstream pathways (114).
Metabolic reprogramming can regulate the expression of metabolism-related genes (e.g., thioredoxin reductase 1, TXNRD1), which exerts redox/antioxidant regulatory functions and participates in COPD-related metabolic disturbance processes by regulating redox balance (115). Concurrently, metabolic reprogramming induces high expression of MMP-9 (supported by increased synthetic precursors from enhanced glycolysis), which activates TGF-β1—contributing to both elastin degradation and fibrosis. This establishes a “metabolically driven link” between inflammation and tissue damage (113).
7.2 Metabolic reprogramming and immune cell function
Metabolic reprogramming shifts macrophage metabolism toward aerobic glycolysis, directly promoting M1-type pro-inflammatory polarization. M1 macrophages rely on glycolysis to rapidly generate ATP and pro-inflammatory factors (e.g., IL-1β, TNF-α), while simultaneously producing large quantities of ROS. Disruption of metabolic reprogramming (e.g., glycolysis inhibition) significantly attenuates M1 polarization and alleviates inflammatory responses. Cigarette smoke can exacerbate the pro-inflammatory function of macrophages by inducing metabolic reprogramming (enhanced glycolysis)—forming a cascade of “metabolic remodeling—macrophage activation—inflammation enhancement” (2, 116).
Metabolic reprogramming regulates lipid metabolic pathways, directly influencing the differentiation balance of T cell subsets. By modulating fatty acid oxidation (FAO) and lipid synthesis, metabolic reprogramming can promote the differentiation of either anti-inflammatory Treg cells or pro-inflammatory Th17 cells: a shift toward FAO enhances Treg cell differentiation, alleviating inflammation; conversely, a bias toward lipid synthesis increases Th17 cell differentiation, exacerbating inflammation. This metabolically regulated imbalance in T cell differentiation represents a key contributor to immune dysregulation in COPD (117).
Metabolic reprogramming reduces the expression of glycogen cycle-related enzymes in neutrophils, leading to insufficient glycogen reserves—directly impairing their bactericidal capacity and survival time. While pro-inflammatory mediators can induce neutrophils to generate glycolytic intermediates from non-glucose substrates via gluconeogenesis (a compensatory mechanism of metabolic reprogramming), this compensation fails to reverse functional deficits. Ultimately, this impairs the ability of neutrophils to clear pathogens in COPD patients, perpetuating inflammation (77).
8 Discussion and prospects
In recent years, with the rapid advancement of technologies such as metabolomics and single-cell sequencing, research on COPD has shifted beyond traditional focus on three classic mechanisms—chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and protease-antiprotease imbalance. Increasing attention has been directed toward metabolic reprogramming and its complex crosstalk with inflammation and immune dysregulation. It is increasingly recognized that metabolic abnormalities across multiple pathways (e.g., glucose, lipid, and amino acid metabolism) are not merely coincidental manifestations of disease phenotypes but potential drivers of disease maintenance and progression. This paradigm shift has transformed COPD research from a focus on isolated pathological processes to a systemic, multi-dimensional integrative perspective.
Despite the comprehensive review of COPD-related metabolic changes and the complex interactions between metabolic reprogramming, immunity, and inflammation presented herein, several limitations remain. Many theoretical foundations are derived from animal models or small-scale clinical cohorts; metabolic characteristic differences across species may limit the generalizability of conclusions. Additionally, some mechanistic inferences are based on observational data of metabolite levels or single-gene regulation, lacking causal validation via interventional experiments.
Based on the metabolic reprogramming mechanisms elaborated in this review, multiple potential therapeutic directions can be derived. Regarding metabolic inhibitors: HIF-1α inhibitors (e.g., PX-478) can specifically inhibit the enhancement of glycolysis and reduce the release of inflammatory factors (118, 119); inhibitors of key glycolytic enzymes (e.g., HK2, PKM2) may suppress airway smooth muscle cell proliferation and airway remodeling (120); fatty acid oxidation (FAO) modulators (e.g., PPAR-γ agonists) can correct macrophage metabolic imbalance and promote M2 polarization (121, 122). For dietary interventions: branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) supplementation can improve malnutrition and sarcopenia in COPD patients while regulating the mTOR signaling pathway; increased intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids (e.g., Omega-3) can ameliorate lipid metabolism disorders and alleviate inflammatory responses (123–125). In terms of immunomodulators: neutralizing antibodies or receptor antagonists targeting metabolic products (e.g., lactate, kynurenine) can block the “metabolic abnormality-inflammation” vicious cycle (107, 126, 127); regulation of the airway microbiota (e.g., probiotic supplementation) can improve host metabolic and immune imbalances (128, 129). These strategies provide new insights into the precise treatment of COPD, but their safety and efficacy still need to be verified by large-scale clinical trials.
Looking ahead, the field of COPD metabolism holds vast potential for exploration. Focusing on “dynamic associations between metabolism and disease stages,” longitudinal metabolomic cohort studies can track changes in metabolic profiles of patients from early asymptomatic stages to stable and acute exacerbation phases—identifying core metabolic characteristics at different disease stages and addressing gaps in the current understanding of correlations between disease staging and metabolic abnormalities. On the other hand, integrating metabolomics with genomics to construct molecular subtypes of COPD will better align with the demands of personalized medicine in the modern era. In summary, with advancements in technical methodologies and strengthened interdisciplinary collaboration, substantial breakthroughs in precise subtyping, early diagnosis, and personalized treatment of COPD are anticipated—propelling COPD management into a new paradigm.
Author contributions
SZ: Writing – original draft. YZ: Writing – original draft. SL: Writing – original draft. ZL: Writing – original draft. PL: Writing – original draft. JX: Writing – original draft. JZ: Writing – original draft. LX: Writing – review & editing. YY: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers 72574038); Association for Promoting Sichuan Development by Sci-Tech and Education (Grant numbers KJXC24-0201); Research Project on High quality Development of Hospital Pharmacy, National Institute of Hospital Administration, NHC, China (Grant numbers NIHAYSZX2520).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Li C-L and Liu S-F. Exploring molecular mechanisms and biomarkers in COPD: an overview of current advancements and perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:7347. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137347
2. Li L, Yang DC, and Chen C-H. Metabolic reprogramming: A driver of cigarette smoke-induced inflammatory lung diseases. Free Radical Biol Med. (2021) 163:392–401. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.12.438
3. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-(copd) (Accessed August 18, 2025).
4. Wang L, Tang Y, Liu S, Mao S, Ling Y, Liu D, et al. Metabonomic profiling of serum and urine by 1H NMR-based spectroscopy discriminates patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and healthy individuals. PLoS One. (2013) 8:e65675. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065675
5. Mannino DM, Higuchi K, Yu T-C, Zhou H, Li Y, Tian H, et al. Economic burden of COPD in the presence of comorbidities. Chest. (2015) 148:138–50. doi: 10.1378/chest.14-2434
6. Ng T-P, Niti M, Tan W-C, Cao Z, Ong K-C, and Eng P. Depressive symptoms and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: effect on mortality, hospital readmission, symptom burden, functional status, and quality of life. Arch Intern Med. (2007) 167:60–7. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.1.60
7. Xu J, Zeng Q, Li S, Su Q, and Fan H. Inflammation mechanism and research progress of COPD. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1404615. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1404615
8. Raherison C and Girodet P-O. Epidemiology of COPD. Eur Respir Rev. (2009) 18:213–21. doi: 10.1183/09059180.00003609
9. Julio D, Antuni MD, and Peter J. Barnes DM. Evaluation of individuals at risk for COPD: beyond the scope of the global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: J COPD Foundation. 3:653–67. doi: 10.15326/jcopdf.3.3.2016.0129
10. Michaeloudes C, Bhavsar PK, Mumby S, Xu B, Hui CKM, Chung KF, et al. Role of metabolic reprogramming in pulmonary innate immunity and its impact on lung diseases. J Innate Immun. (2020) 12:31–46. doi: 10.1159/000504344
11. Baker J, Booth S, Dungwa J, Higham A, Singh D, and Lea S. Alveolar macrophage carbon is associated with COPD severity. ERJ Open Res. (2025) 11:00933–2024. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00933-2024
12. Daniel S, Phillippi D, Schneider LJ, Nguyen KN, Mirpuri J, and Lund AK. Exposure to diesel exhaust particles results in altered lung microbial profiles, associated with increased reactive oxygen species/reactive nitrogen species and inflammation, in C57Bl/6 wildtype mice on a high-fat diet. Part Fibre Toxicol. (2021) 18:3. doi: 10.1186/s12989-020-00393-9
13. Zhou W, Qu J, Xie S, Sun Y, and Yao H. Mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic respiratory diseases: implications for the pathogenesis and potential therapeutics. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2021) 2021:5188306. doi: 10.1155/2021/5188306
14. Prakash YS, Pabelick CM, and Sieck GC. Mitochondrial dysfunction in airway disease. Chest. (2017) 152:618–26. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2017.03.020
15. Corcoran SE and O’Neill LAJ. HIF1α and metabolic reprogramming in inflammation. J Clin Invest. 126:3699–707. doi: 10.1172/JCI84431
16. Kierans SJ and Taylor CT. Regulation of glycolysis by the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF): implications for cellular physiology. J Physiol. (2021) 599:23–37. doi: 10.1113/JP280572
17. Roth-Walter F, Berni Canani R, O’Mahony L, Peroni D, Sokolowska M, Vassilopoulou E, et al. Nutrition in chronic inflammatory conditions: Bypassing the mucosal block for micronutrients. Allergy. (2024) 79:353–83. doi: 10.1111/all.15972
18. Choi H and Kim T. Polyunsaturated fatty acids, lung function, and health-related quality of life in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Yeungnam Univ J Med. (2020) 37:194–201. doi: 10.12701/yujm.2020.00052
19. Guo P, Li R, Piao TH, Wang CL, Wu XL, and Cai HY. Pathological mechanism and targeted drugs of COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2022) 17:1565–75. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S366126
20. Ran N, Pang Z, Gu Y, Pan H, Zuo X, Guan X, et al. An updated overview of metabolomic profile changes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Metabolites. (2019) 9:111. doi: 10.3390/metabo9060111
21. Corlateanu A, Mendez Y, Wang Y, Garnica R de JA, Botnaru V, and Siafakas N. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and phenotypes: a state-of-the-art. Pulmonology. (2020) 26:95–100. doi: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2019.10.006
22. Xie C, Wang K, Yang K, Zhong Y, Gul A, Luo W, et al. Toward precision medicine in COPD: phenotypes, endotypes, biomarkers, and treatable traits. Respir Res. (2025) 26:274. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03356-w
23. Hogg JC and Timens W. The pathology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Annu Rev Pathol. (2009) 4:435–59. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092145
24. Sng JJ, Prazakova S, Thomas PS, and Herbert C. MMP-8, MMP-9 and neutrophil elastase in peripheral blood and exhaled breath condensate in COPD. COPD. (2017) 14:238–44. doi: 10.1080/15412555.2016.1249790
25. Jasper AE, McIver WJ, Sapey E, and Walton GM. Understanding the role of neutrophils in chronic inflammatory airway disease. F1000Res. (2019) 8:F1000 Faculty Rev–557. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.18411.1
26. Ogger PP and Byrne AJ. Macrophage metabolic reprogramming during chronic lung disease. Mucosal Immunol. (2021) 14:282–95. doi: 10.1038/s41385-020-00356-5
27. Chen S, Saeed AFUH, Liu Q, Jiang Q, Xu H, Xiao GG, et al. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Sig Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:207. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01452-1
28. Rouzic OL, Pichavant M, Frealle E, Guillon A, Si-Tahar M, and Gosset P. Th17 cytokines: novel potential therapeutic targets for COPD pathogenesis and exacerbations. Eur Respir J. (2017) 50:1602434. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02434-2016
29. Kapellos TS, Conlon TM, Yildirim AÖ, and Lehmann M. The impact of the immune system on lung injury and regeneration in COPD. Eur Respir J. (2023) 62:2300589. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00589-2023
30. Mumby S and Adcock IM. Recent evidence from omic analysis for redox signalling and mitochondrial oxidative stress in COPD. J Inflammation. (2022) 19:10. doi: 10.1186/s12950-022-00308-9
31. Gharib SA, Manicone AM, and Parks WC. Matrix metalloproteinases in emphysema. Matrix Biol. (2018) 73:34–51. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.01.018
32. Lin M, Lee Y, Liao J, Chou C, and Yang Y. PTGES is involved in myofibroblast differentiation via HIF-1α-dependent glycolysis pathway. J Cell Mol Med. (2024) 28:e70157. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70157
33. Liang Q, Wang Y, and Li Z. Lipid metabolism reprogramming in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Mol Med. (2025) 31:129. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01191-9
34. Woods PS, Kimmig LM, Sun KA, Meliton AY, Shamaa OR, Tian Y, et al. HIF-1α induces glycolytic reprograming in tissue-resident alveolar macrophages to promote cell survival during acute lung injury. eLife. (2022) 11:e77457. doi: 10.7554/eLife.77457
35. Tan L, Yang X, Zhang J, and Zhou K. Correlation between HIF1-A expression and airway remodeling in COPD. COPD. (2024) 19:921–31. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S447256
36. Hogg JC, Chu F, Utokaparch S, Woods R, Elliott WM, Buzatu L, et al. The nature of small-airway obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. (2004) 350:2645–53. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa032158
37. Barnes PJ, Shapiro SD, and Pauwels RA. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: molecular and cellular mechanisms. Eur Respir J. (2003) 22:672–88. doi: 10.1183/09031936.03.00040703
38. Li Y, Zhang L, Polverino F, Guo F, Hao Y, Lao T, et al. Hedgehog interacting protein (HHIP) represses airway remodeling and metabolic reprogramming in COPD-derived airway smooth muscle cells. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:9074. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88434-x
39. Bourdin A, Burgel P-R, Chanez P, Garcia G, Perez T, and Roche N. Recent advances in COPD: pathophysiology, respiratory physiology and clinical aspects, including comorbidities. Eur Respir Rev. (2009) 18:198–212. doi: 10.1183/09059180.00005509
40. Agarwal AR, Yin F, and Cadenas E. Short-term cigarette smoke exposure leads to metabolic alterations in lung alveolar cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2014) 51:284–93. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0523OC
41. Lange P, Ahmed E, Lahmar ZM, Martinez FJ, and Bourdin A. Natural history and mechanisms of COPD. Respirology. (2021) 26:298–321. doi: 10.1111/resp.14007
42. Jones B, Donovan C, Liu G, Gomez HM, Chimankar V, Harrison CL, et al. Animal models of COPD: What do they tell us? Respirology. (2017) 22:21–32. doi: 10.1111/resp.12908
43. Strzelak A, Ratajczak A, Adamiec A, and Feleszko W. Tobacco smoke induces and alters immune responses in the lung triggering inflammation, allergy, asthma and other lung diseases: A mechanistic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2018) 15:1033. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15051033
44. Vlahos R and Bozinovski S. Recent advances in pre-clinical mouse models of COPD. Clin Sci (Lond). (2014) 126:253–65. doi: 10.1042/CS20130182
45. He S, Sun S, Lu J, Chen L, Mei X, Li L, et al. The effects of the miR-21/SMAD7/TGF-β pathway on Th17 cell differentiation in COPD. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:6338. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85637-0
46. Huang G, Xu X-C, Zhou J-S, Li Z-Y, Chen H-P, Wang Y, et al. Neutrophilic inflammation in the immune responses of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: lessons from animal models. J Immunol Res. (2017) 2017:7915975. doi: 10.1155/2017/7915975
47. Li R, Li J, and Zhou X. Lung microbiome: new insights into the pathogenesis of respiratory diseases. Sig Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:1–27. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01722-y
48. Wang Z, Maschera B, Lea S, Kolsum U, Michalovich D, Van Horn S, et al. Airway host-microbiome interactions in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Res. (2019) 20:113. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1085-z
49. Moghaddam SJ, Ochoa CE, Sethi S, and Dickey BF. Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and lung cancer. Int J Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Dis. (2011) 6:113. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S15417
50. Katsoulis O, Pitts OR, and Singanayagam A. The airway mycobiome and interactions with immunity in health and chronic lung disease. Oxf Open Immunol. (2024) 5:iqae009. doi: 10.1093/oxfimm/iqae009
51. Shukla SD, Walters EH, Simpson JL, Keely S, Wark PAB, O’Toole RF, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor and bacterial infections in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respirology. (2020) 25:53–63. doi: 10.1111/resp.13722
52. Ney L-M, Wipplinger M, Grossmann M, Engert N, Wegner VD, and Mosig AS. Short chain fatty acids: key regulators of the local and systemic immune response in inflammatory diseases and infections. Open Biol. (2023) 13:230014. doi: 10.1098/rsob.230014
53. Sin DD. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and the airway microbiome: what respirologists need to know. Tuberculosis Respir Dis. (2023) 86:166. doi: 10.4046/trd.2023.0015
54. Zhou H-C, Yu W-W, Yan X-Y, Liang X-Q, Ma X-F, Long J-P, et al. Lactate-driven macrophage polarization in the inflammatory microenvironment alleviates intestinal inflammation. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1013686. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1013686
55. Garaci E, Pariano M, Nunzi E, Costantini C, Bellet MM, Antognelli C, et al. Bacteria and fungi of the lung: allies or enemies? Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1497173. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1497173
56. Richmond BW, Brucker RM, Han W, Du R-H, Zhang Y, Cheng D-S, et al. Airway bacteria drive a progressive COPD-like phenotype in mice with polymeric immunoglobulin receptor deficiency. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:11240. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11240
57. Albano GD, Gagliardo RP, Montalbano AM, and Profita M. Overview of the mechanisms of oxidative stress: impact in inflammation of the airway diseases. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022) 11:2237. doi: 10.3390/antiox11112237
58. Domej W, Oettl K, and Renner W. Oxidative stress and free radicals in COPD – implications and relevance for treatment. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2014) 9:1207–24. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S51226
59. Huang Q, Hu D, Wang X, et al. The modification of indoor PM2.5 exposure to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Chinese elderly people: A meet-in-metabolite analysis. Environ Int. (2018) 121:1243–52. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.10.046
60. Celikbas E, Penque D, and Zoidakis J. Systematic review on recent potential biomarkers of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Expert Rev Mol Diagnostics. (2019) 19:37–45. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2018.1559054
61. Yan X, Song Y, Shen C, Xu W, Chen L, Zhang J, et al. Mucoactive and antioxidant medicines for COPD: consensus of a group of Chinese pulmonary physicians. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2017) 12:803–12. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S114423
62. Taniguchi A, Tsuge M, Miyahara N, and Tsukahara H. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidative defense in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Antioxidants. (2021) 10:1537. doi: 10.3390/antiox10101537
63. Upadhyay P, Wu C-W, Pham A, Zeki AA, Royer CM, Kodavanti UP, et al. Animal models and mechanisms of tobacco smoke-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. (2023) 26:275–305. doi: 10.1080/10937404.2023.2208886
64. MacNee W. Pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc. (2005) 2:258–66. doi: 10.1513/pats.200504-045SR
65. Dey T, Kalita J, Weldon S, and Taggart CC. Proteases and their inhibitors in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Clin Med. (2018) 7:244. doi: 10.3390/jcm7090244
66. Zhao H, Dennery PA, and Yao H. Metabolic reprogramming in the pathogenesis of chronic lung diseases, including BPD, COPD, and pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2018) 314:L544–54. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00521.2017
67. Wu W, Li Z, Wang Y, Huang C, Zhang T, and Zhao H. Advances in metabolomics of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chin Med J Pulmonary Crit Care Med. (2023) 01:223–30. doi: 10.1016/j.pccm.2023.10.001
68. Gao J, Shen Y, and Chen Z. Novel insights into the pathological features of COPD: Focus on oxidative stress and mitophagy. Clin Trans Discov. (2024) 4:e343. doi: 10.1002/ctd2.343
69. Gharib AR, Jensen PN, Psaty BM, Hoofnagle AN, Siscovick D, Gharib SA, et al. Plasma sphingolipids, lung function and COPD: the Cardiovascular Health Study. ERJ Open Res. (2023) 9:346. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00346-2022
70. Zhang H-X, Yang J-J, Zhang S-A, Zhang S-M, Wang J-X, Xu Z-Y, et al. HIF-1α promotes inflammatory response of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by activating EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2018) 22:6077–84. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201809_15946
71. Zou W and Al-Rubeai M. Understanding central carbon metabolism of rapidly proliferating mammalian cells based on analysis of key enzymatic activities in GS-CHO cell lines. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. (2016) 63:642–51. doi: 10.1002/bab.1409
72. Bian X, Jiang H, Meng Y, Li Y, Fang J, and Lu Z. Regulation of gene expression by glycolytic and gluconeogenic enzymes. Trends Cell Biol. (2022) 32:786–99. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2022.02.003
73. Bertels L-K, Fernández Murillo L, and Heinisch JJ. The pentose phosphate pathway in yeasts–more than a poor cousin of glycolysis. Biomolecules. (2021) 11:725. doi: 10.3390/biom11050725
74. Kao CC, Hsu JW-C, Bandi V, Hanania NA, Kheradmand F, and Jahoor F. Glucose and pyruvate metabolism in severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Appl Physiol. (2012) 112:42–7. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00599.2011
75. Cloonan SM, Glass K, Laucho-Contreras ME, Bhashyam AR, Cervo M, Pabón MA, et al. Mitochondrial iron chelation ameliorates cigarette smoke-induced bronchitis and emphysema in mice. Nat Med. (2016) 22:163–74. doi: 10.1038/nm.4021
76. Kilk K, Aug A, Ottas A, Soomets U, Altraja S, and Altraja A. Phenotyping of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease based on the integration of metabolomes and clinical characteristics. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:666. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030666
77. Sadiku P, Willson JA, Ryan EM, Sammut D, Coelho P, Watts ER, et al. Neutrophils fuel effective immune responses through gluconeogenesis and glycogenesis. Cell Metab. (2021) 33:411–423.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.016
78. Malinska D, Szymański J, Patalas-Krawczyk P, Michalska B, Wojtala A, Prill M, et al. Assessment of mitochondrial function following short- and long-term exposure of human bronchial epithelial cells to total particulate matter from a candidate modified-risk tobacco product and reference cigarettes. Food Chem Toxicol. (2018) 115:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.02.013
79. Zhang S, Xu N, Nie J, Dong L, Li J, and Tong J. Proteomic alteration in lung tissue of rats exposed to cigarette smoke. Toxicol Lett. (2008) 178:191–6. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.03.014
80. Luo F, Liu X, Yan N, Li S, Cao G, Cheng Q, et al. Hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1α promotes hypoxia-induced A549 apoptosis via a mechanism that involves the glycolysis pathway. BMC Cancer. (2006) 6:26. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-26
81. Polosukhin VV, Cates JM, Lawson WE, Milstone AP, Matafonov AG, Massion PP, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 signalling promotes goblet cell hyperplasia in airway epithelium. J Pathol. (2011) 224:203–11. doi: 10.1002/path.2863
82. Liu Y, Kong H, Cai H, Chen G, Chen H, and Ruan W. Progression of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1238782. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1238782
83. Michaeloudes C, Bhavsar PK, Mumby S, Chung KF, and Adcock IM. Dealing with stress: defective metabolic adaptation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease pathogenesis. Ann Am Thorac Soc. (2017) 14:S374–82. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201702-153AW
84. Daijo H, Hoshino Y, Kai S, Suzuki K, Nishi K, Matsuo Y, et al. Cigarette smoke reversibly activates hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in a reactive oxygen species-dependent manner. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:34424. doi: 10.1038/srep34424
85. Kottmann RM, Kulkarni AA, Smolnycki KA, Lyda E, Dahanayake T, Salibi R, et al. Lactic Acid Is Elevated in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Induces Myofibroblast Differentiation via pH-Dependent Activation of Transforming Growth Factor-β. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2012) 186:740–51. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201201-0084OC
86. Stojkov D, Gigon L, Peng S, Lukowski R, Ruth P, Karaulov A, et al. Physiological and pathophysiological roles of metabolic pathways for NET formation and other neutrophil functions. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:826515. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.826515
87. Yipeng Z, Chao C, Ranran L, Tingting P, and Hongping Q. Metabolism: a potential regulator of neutrophil fate. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1500676. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1500676
88. Morán G, Uberti B, and Quiroga J. Role of cellular metabolism in the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps in airway diseases. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:850416. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.850416
89. Borkum JM. The tricarboxylic acid cycle as a central regulator of the rate of aging: implications for metabolic interventions. Advanced Biol. (2023) 7:2300095. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202300095
90. Engelen MP, Schols AM, Does JD, Gosker HR, Deutz NE, and Wouters EF. Exercise-induced lactate increase in relation to muscle substrates in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2000) 162:1697–704. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.162.5.9910066
91. Lu X, Zhang A, Wang H, Xu X, Chen L, and Luo L. Emerging role of the TCA cycle and its metabolites in lung disease. Front Physiol. (2025) 16:1621013. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1621013
92. Kim H-Y, Lee H-S, Kim I-H, Kim Y, Ji M, Oh S, et al. Comprehensive targeted metabolomic study in the lung, plasma, and urine of PPE/LPS-induced COPD mice model. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:2748. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052748
93. Feng Y, Xie M, Liu Q, Weng J, Wei L, Chung KF, et al. Changes in targeted metabolomics in lung tissue of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Thorac Dis. (2023) 15:2544–58. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-1731
94. Yan F, Zhang L, Duan L, Li L, Liu X, Liu Y, et al. Roles of glutamic pyruvate transaminase 2 in reprogramming of airway epithelial lipidomic and metabolomic profiles after smoking. Clin Trans Med. (2024) 14:e1679. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1679
95. Liu D, Meister M, Zhang S, Vong C-I, Wang S, Fang R, et al. Identification of lipid biomarker from serum in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Res. (2020) 21:242. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01507-9
96. Kim G-D, Lim EY, and Shin HS. Macrophage polarization and functions in pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:5631. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115631
97. Kotlyarov S and Kotlyarova A. Molecular mechanisms of lipid metabolism disorders in infectious exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:7634. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147634
98. Fujii W, Kapellos TS, Baßler K, Händler K, Holsten L, Knoll R, et al. Alveolar macrophage transcriptomic profiling in COPD shows major lipid metabolism changes. ERJ Open Res. (2021) 7:915. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00915-2020
99. Wang M, Wu D, Liao X, Hu H, Gao J, Meng L, et al. CPT1A-IL-10-mediated macrophage metabolic and phenotypic alterations ameliorate acute lung injury. Clin Transl Med. (2024) 14:e1785. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1785
100. Calle P, Muñoz A, Sola A, and Hotter G. CPT1a gene expression reverses the inflammatory and anti-phagocytic effect of 7-ketocholesterol in RAW264.7 macrophages. Lipids Health Dis. (2019) 18:215. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1156-7
101. El Kharbili M, Aviszus K, Sasse SK, Zhao X, Serban KA, Majka SM, et al. Macrophage programming is regulated by a cooperative interaction between fatty acid binding protein 5 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ. FASEB J. (2022) 36:e22300. doi: 10.1096/fj.202200128R
102. Paige M, Burdick MD, Kim S, Xu J, Lee JK, and Michael Shim Y. Pilot analysis of the plasma metabolite profiles associated with emphysematous Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease phenotype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2011) 413:588–93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.09.006
103. Zhou J, Li Q, Liu C, Pang R, and Yin Y. Plasma metabolomics and lipidomics reveal perturbed metabolites in different disease stages of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2020) 15:553–65. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S229505
104. Zhang Z, Wang J, Li Y, Liu F, Chen L, He S, et al. Proteomics and metabolomics profiling reveal panels of circulating diagnostic biomarkers and molecular subtypes in stable COPD. Respir Res. (2023) 24:73. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02349-x
105. Godbole S and Bowler RP. Metabolome features of COPD: A scoping review. Metabolites. (2022) 12:621. doi: 10.3390/metabo12070621
106. Pinson MR, Deutz NEP, Harrykissoon R, Zachria AJ, and Engelen MPKJ. Disturbances in branched-chain amino acid profile and poor daily functioning in mildly depressed chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. BMC Pulm Med. (2021) 21:351. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01719-9
107. Pamart G, Gosset P, Le Rouzic O, Pichavant M, and Poulain-Godefroy O. Kynurenine pathway in respiratory diseases. Int J Tryptophan Res. (2024) 17:11786469241232871. doi: 10.1177/11786469241232871
108. Gulcev M, Reilly C, Griffin TJ, Broeckling CD, Sandri BJ, Witthuhn BA, et al. Tryptophan catabolism in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2016) 11:2435–46. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S107844
109. Liu G and Summer R. Cellular metabolism in lung health and disease. Annu Rev Physiol. (2019) 81:403–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-020518-114640
110. Ying L, Yan GX, Chun C, Xu Z, Juan W, and Ting LT. Metabolomic profiling differences among asthma, COPD, and healthy subjects: A LC-MS-based metabolomic analysis. BES. (2019) 32:659–72. doi: 10.3967/bes2019.085
111. Rajendrasozhan S, Yang S-R, Edirisinghe I, Yao H, Adenuga D, and Rahman I. Deacetylases and NF-κB in redox regulation of cigarette smoke induced lung inflammation: implications in pathogenesis of COPD. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2008) 10:799–811. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1938
112. Manosalva C, Quiroga J, Hidalgo AI, Alarcón P, Ansoleaga N, Hidalgo MA, et al. Role of lactate in inflammatory processes: friend or foe. Front Immunol. (2022) 12:808799. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.808799
113. Yu Q and Stamenkovic I. Cell surface-localized matrix metalloproteinase-9 proteolytically activates TGF-β and promotes tumor invasion and angiogenesis. Genes Dev. (2000) 14:163–76. doi: 10.1101/gad.14.2.163
114. Rogero MM and Calder PC. Obesity, inflammation, toll-like receptor 4 and fatty acids. Nutrients. (2018) 10:432. doi: 10.3390/nu10040432
115. Huang Q, Peng M, Gu Y, Wu J, Zhan Y, Deng Z, et al. Metabolism-related gene TXNRD1 regulates inflammation and oxidative stress induced by cigarette smoke through the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in the small airway epithelium. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:7067623. doi: 10.1155/2022/7067623
116. Viola A, Munari F, Sánchez-Rodríguez R, Scolaro T, and Castegna A. The metabolic signature of macrophage responses. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1462. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01462
117. Norris PC and Dennis EA. Omega-3 fatty acids cause dramatic changes in TLR4 and purinergic eicosanoid signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2012) 109:8517–22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1200189109
118. Petraroia I, Ghidotti P, Bertolini G, Pontis F, Roz L, Balsamo M, et al. Extracellular vesicles from subjects with COPD modulate cancer initiating cells phenotype through HIF-1α shuttling. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:681. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06212-1
119. Xu Y, Wang A, and Li Y. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha is a driving mechanism linking chronic obstructive pulmonary disease to lung cancer. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:984525. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.984525
120. Jain M, Dhanesha N, Doddapattar P, Nayak MK, Guo L, Cornelissen A, et al. Smooth muscle cell–specific PKM2 (Pyruvate kinase muscle 2) promotes smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching and neointimal hyperplasia. Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis Vasc Biol. (2021) 41:1724–37. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.316021
121. He S, Tian R, Zhang X, Yao Q, Chen Q, Liu B, et al. PPARγ inhibits small airway remodeling through mediating the polarization homeostasis of alveolar macrophages in COPD. Clin Immunol. (2023) 250:109293. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2023.109293
122. Yu L, Gao Y, Aaron N, and Qiang L. A glimpse of the connection between PPARγ and macrophage. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1254317. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1254317
123. van de Bool C, Rutten EPA, van Helvoort A, Franssen FME, Wouters EFM, and Schols AMWJ. A randomized clinical trial investigating the efficacy of targeted nutrition as adjunct to exercise training in COPD. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2017) 8:748–58. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12219
124. Hu Y, Shao X, Xing L, Li X, Nonis GM, Koelwyn GJ, et al. Single-cell sequencing of lung macrophages and monocytes reveals novel therapeutic targets in COPD. Cells. (2023) 12:2771. doi: 10.3390/cells12242771
125. Yu H, Su X, Lei T, Zhang C, Zhang M, Wang Y, et al. Effect of omega-3 fatty acids on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2021) 16:2677–86. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S331154
126. Yang K, Xu J, Fan M, Tu F, Wang X, Ha T, et al. Lactate suppresses macrophage pro-inflammatory response to LPS stimulation by inhibition of YAP and NF-κB activation via GPR81-mediated signaling. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:587913. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.587913
127. Hoque R, Farooq A, Ghani A, Gorelick F, and Mehal WZ. Lactate reduces organ injury in toll-like receptor- and inflammasome-mediated inflammation via GPR81-mediated suppression of innate immunity. Gastroenterology. (2014) 146:1763–74. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.03.014
128. Su Z, Ma C, Ru X, Zhang S, Wu C, Huang Y, et al. Effects of probiotic treatment on patients and animals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2024) 14:1411222. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1411222
129. Shen H-T, Fang Y-T, Tsai W-H, Chou C-H, Huang M-S, Yeh Y-T, et al. A lactobacillus combination ameliorates lung inflammation in an elastase/LPS—induced mouse model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Probiotics Antimicro Prot. (2025) 17:3416–28. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10300-9
130. Kim J, Suresh B, Lim MN, Hong S-H, Kim K-S, Song HE, et al. Metabolomics reveals dysregulated sphingolipid and amino acid metabolism associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Dis. (2022) 17:2343. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S376714
131. Jiang C, Peng M, Dai Z, and Chen Q. Screening of lipid metabolism-related genes as diagnostic indicators in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2023) 18:2739–54. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S428984
132. Piao Z, Chai B, Wu Y, Diao H, He Q, Zheng Q, et al. The association between polyunsaturated fatty acids and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a meta-analysis. Food Funct. (2024) 15:5929–5941. doi: 10.1039/d3fo04675c
133. Zhang Y, Liang X, Luo S, Zhang Z, Zhou P, Zhou Z, et al. Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acid intake and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with COPD. Nutr Metab. (2025) 22:108. doi: 10.1186/s12986-025-01006-y
134. Zhou Q, Chen Y, Liang Y, and Sun Y. The role of lysophospholipid metabolites LPC and LPA in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Metabolites. (2024) 14:317. doi: 10.3390/metabo14060317
135. Gupte RS, Rawat DK, Chettimada S, Cioffi DL, Wolin MS, Gerthoffer WT, et al. Activation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase promotes acute hypoxic pulmonary artery contraction. J Biol Chem. (2010) 285:19561. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.092916
136. Gong J, Feng Z, Peterson AL, Carr JF, Lu X, Zhao H, et al. The pentose phosphate pathway mediates hyperoxia-induced lung vascular dysgenesis and alveolar simplification in neonates. JCI Insight. (2021) 6:e137594. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.137594
137. McDonald MI, Polkinghorne KR, McDonald CJ, Leong P, Hamza K, Kathriachchige G, et al. Elevated blood lactate in COPD exacerbations associates with adverse clinical outcomes and signals excessive treatment with β2 -agonists. Respirology (Carlton Vic). (2023) 28:860–868. doi: 10.1111/resp.14534
138. Wang H, Cho PSP, Kouritas V, and Feng L. Three key factors predicting the severity of exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: T lymphocytes, lactate, and prealbumin. J Thorac Dis. (2025) 17:2386. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2025-416
139. Gea J, Enríquez-Rodríguez CJ, Agranovich B, and Pascual-Guardia S. Update on metabolomic findings in COPD patients. ERJ Open Res. (2023) 9:180. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00180-2023
140. Chang C, Guo Z, He B, and Yao W. Metabolic alterations in the sera of Chinese patients with mild persistent asthma: a GC-MS-based metabolomics analysis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2015) 36:1356–66. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.102
141. Adamko DJ, Nair P, Mayers I, Tsuyuki RT, Regush S, and Rowe BH. Metabolomic profiling of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A pilot study differentiating diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2015) 136:571–580. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.05.022
142. Holz O, DeLuca DS, Roepcke S, Illig T, Weinberger KM, Schudt C, et al. Smokers with COPD show a shift in energy and nitrogen metabolism at rest and during exercise. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2020) 15:1–13. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S217474
143. Guo Z and Yan F. Targeting glutamate metabolism in chronic lung diseases. Clin Trans Discov. (2024) 4:e294. doi: 10.1002/ctd2.294
144. Wculek SK, Dunphy G, Heras-Murillo I, Mastrangelo A, and Sancho D. Metabolism of tissue macrophages in homeostasis and pathology. Cell Mol Immunol. (2022) 19:384–408. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00791-9
145. Nomura M, Liu J, Rovira II, Gonzalez-Hurtado E, Lee J, Wolfgang MJ, et al. Fatty acid oxidation in macrophage polarization. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:216–7. doi: 10.1038/ni.3366
146. Batista-Gonzalez A, Vidal R, Criollo A, and Carreño LJ. New insights on the role of lipid metabolism in the metabolic reprogramming of macrophages. Front Immunol. (2020) 10:2993. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02993
147. Crotta S, Villa M, Major J, Finsterbusch K, Llorian M, Carmeliet P, et al. Repair of airway epithelia requires metabolic rewiring towards fatty acid oxidation. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:721. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36352-z
148. Chen H, Li Z, Dong L, Wu Y, Shen H, and Chen Z. Lipid metabolism in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2019) 14:1009–18. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S196210
149. Li F, Xu M, Wang M, Wang L, Wang H, Zhang H, et al. Roles of mitochondrial ROS and NLRP3 inflammasome in multiple ozone-induced lung inflammation and emphysema. Respir Res. (2018) 19:230. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0931-8
150. Chung K-P, Cheng C-N, Chen Y-J, Hsu C-L, Huang Y-L, Hsieh M-S, et al. Alveolar epithelial cells mitigate neutrophilic inflammation in lung injury through regulating mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:7241. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51683-1
151. Cloonan SM, Kim K, Esteves P, Trian T, and Barnes PJ. Mitochondrial dysfunction in lung ageing and disease. Eur Respir Rev. (2020) 29:200165. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0165-2020
152. Michaeloudes C, Kuo C-H, Haji G, Finch DK, Halayko AJ, Kirkham P, et al. Metabolic re-patterning in COPD airway smooth muscle cells. Eur Respir J. (2017) 50:1700202. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00202-2017
153. Hiemstra PS and van der Does AM. Reprogramming of cellular metabolism: driver for airway remodelling in COPD? Eur Respir J. (2017) 50:1702197. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02197-2017
154. Gan PXL, Zhang S, and Fred Wong WS. Targeting reprogrammed metabolism as a therapeutic approach for respiratory diseases. Biochem Pharmacol. (2024) 228:116187. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116187
155. Li Z, Chen S-X, Jiang S, Yang Y-N, and Yan X-C. Unlocking the secrets of glucose metabolism reprogramming: the role in pulmonary diseases. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:1551452. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1551452
156. He Q, Li P, Han L, Yang C, Jiang M, Wang Y, et al. Revisiting airway epithelial dysfunction and mechanisms in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the role of mitochondrial damage. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2024) 326:L754–69. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00362.2023
157. Zhou K, Wen Q, Zuo Y, Bai G, and Sun R. Pathogenic cell in COPD: mechanisms of airway remodeling, immune dysregulation, and therapeutic implications. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2025) 20:2925–43. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S523519
158. Liu Y-B, Hong J-R, Jiang N, Jin L, Zhong W-J, Zhang C-Y, et al. The role of mitochondrial quality control in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lab Invest. (2024) 104:100307. doi: 10.1016/j.labinv.2023.100307
159. Morrison T, Watts ER, Sadiku P, and Walmsley SR. The emerging role for metabolism in fueling neutrophilic inflammation. Immunol Rev. (2023) 314:427–41. doi: 10.1111/imr.13157
160. Maldarelli ME and Noto MJ. The emerging role for neutrophil mitochondrial metabolism in lung inflammation. Immunometabolism (Cobham). (2024) 6:e00036. doi: 10.1097/IN9.0000000000000036
Keywords: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, metabolic reprogramming, inflammation, oxidative stress, airway remodeling, immunometabolism
Citation: Zeng S, Zhang Y, Li S, Li Z, Li P, Xie J, Zhang J, Xie L and Yang Y (2025) From metabolic alterations to chronic inflammation: mechanisms and immunoregulation of metabolic reprogramming in COPD. Front. Immunol. 16:1698832. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1698832
Received: 04 September 2025; Accepted: 13 November 2025; Revised: 03 November 2025;
Published: 02 December 2025.
Edited by:
Fernanda Degobbi Tenorio Quirino dos Santos Lopes, University of São Paulo, BrazilReviewed by:
Franziska Roth-Walter, University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna, AustriaThayse Bruggemann, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, United States
Copyright © 2025 Zeng, Zhang, Li, Li, Li, Xie, Zhang, Xie and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yong Yang, eXl4cG93ZXJAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Liling Xie, OTQwMzg0ODIyQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Siyu Zeng
Siyu Zeng Yanqiu Zhang
Yanqiu Zhang Shiran Li
Shiran Li Zhimin Li
Zhimin Li Pengfei Li1
Pengfei Li1 Jingxian Xie
Jingxian Xie Jiao Zhang
Jiao Zhang Yong Yang
Yong Yang