- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
- 2Liaoning Clinical Research Center for Laboratory Medicine, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
- 3Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery, Cancer Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
- 4Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery, Cancer Hospital of Dalian University of Technology, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
- 5Pancreatic Disease Center, Liaoning Cancer Hospital & Institute, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
Flavonoids are a vital class of dietary polyphenolic compounds that have attracted considerable attention owing to their powerful immunoregulatory and anti-inflammatory effects. This review summarizes recent advances in understanding the role of flavonoids in regulating immune cells and their therapeutic application in inflammatory diseases. We present an overview of the definition, classification, and dietary sources of flavonoids and detail their regulatory effects on multiple key immune cells, therapeutic potential of flavonoids in various inflammatory diseases, as well as discuss strategies to improve their bioavailability and targeting. Despite the promising immunoregulatory properties of flavonoids, their clinical utilization is impeded by issues such as low bioavailability, considerable interindividual variability, and the absence of high-quality randomized controlled trials. Future research needs to focus on elucidating the precise mechanisms of flavonoids, optimizing their pharmacokinetic properties, and conducting more standardized clinical trials to facilitate the transformation of these natural compounds into standardized immunomodulatory therapeutic agents.
1 Introduction
Inflammatory diseases have emerged as a significant global public health concern, encompassing inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), metabolic inflammatory disorders, neuroinflammatory conditions, respiratory inflammatory diseases, etc. Global data indicate that the prevalence of IBD ranges from 0.5% to 1% in Western nations and is increasing in emerging industrialized countries and may reach 1% in numerous regions by 2030 (1). RA affects approximately 0.5% to 1% of people worldwide (2). Metabolic inflammatory disorders, an inflammatory condition resulting from obesity and type 2 diabetes, collectively pose a substantial threat to human health (3). The shared pathological foundation of these diseases is immune system dysfunction, resulting in the overproduction of inflammatory mediators, inappropriate activation of immune cells, and ultimately causing tissue damage (4). The persistent presence of inflammation and the disruption of immune homeostasis are the primary mechanisms contributing to the chronic progression and treatment difficulties of these diseases.
Contemporary therapeutic approaches for inflammatory diseases include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologics (5). Although these therapies have effectively managed symptoms and decelerated disease progression, long-term use is often associated with severe adverse effects, including increased infection risk, osteoporosis, metabolic disorders, and the likelihood of malignant tumors (6, 7). Additionally, a considerable proportion of patients exhibit poor response to existing treatments or gradually lose responsiveness (8). Therefore, the development of secure and effective novel anti-inflammatory drugs or supplementary treatment strategies has become an urgent clinical need. In this context, flavonoid compounds derived from natural plants have attracted widespread attention owing to their broad immunomodulatory effects and minimal toxicity (9).
Flavonoids are a class of polyphenolic compounds characterized by a C6-C3-C6 fundamental structure, capable of regulating immune cell function through various mechanisms. However, their clinical application faces challenges. Their low bioavailability, short half-life in the body, and complex metabolic conversion make it difficult to achieve effective therapeutic concentrations (10). Furthermore, the immunoregulatory effects of flavonoids display dose-dependent and cell-specific characteristics, potentially exhibiting bidirectional regulatory effects, thereby complicating their clinical application (11, 12). Recent years have witnessed advancements in the research concerning the immunomodulatory effects of flavonoids. Advanced high-sensitivity analytical techniques enable researchers to identify flavonoids and their metabolites in vivo even when concentrations are extremely low, facilitating a more precise evaluation of their bioavailability (13). Studies on structure-activity relationships have identified crucial active domains, guiding the development of more efficient flavonoid derivatives (14). Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and non-RCT clinical trials have proved the therapeutic value of flavonoids in various diseases (15, 16).
Current reviews mainly focus on the impacts of particular subclasses of flavonoids or their effects within particular disease contexts, while a holistic perspective is absent. Many dietary components contain multiple flavonoids. Thus, traditional Chinese medicine, Tibetan medicine, and other ethnic medicines frequently consist of compound formulations containing diverse flavonoids. Furthermore, inflammatory diseases frequently coexist. It is of great significance to understand in detail the abundance of a specific flavonoid compound in a certain food or medicine and its therapeutic effects, mainly in different immune cells and various inflammatory diseases. We aimed to summarize how flavonoids regulate immune cells and their applications in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. By integrating the latest research evidence, we will provide a comprehensive understanding of the immunoregulatory capabilities of flavonoids and their rational application in the clinical treatment of inflammatory diseases.
2 Definition, classification, and dietary sources of flavonoids
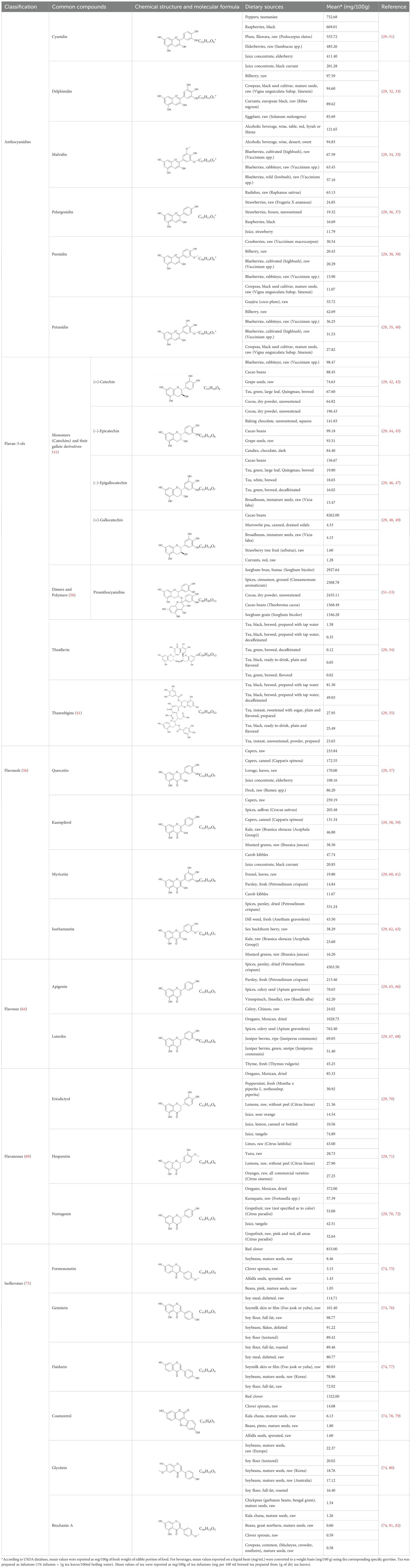
Flavonoids are a category of polyphenolic compounds that are commonly present in consumable plants and foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and nuts, primarily present in the form of β-glycosides (17). The fundamental structure of these compounds is constituted by a 15-carbon framework, which is comprised of two benzene rings (A and B) linked through a heterocyclic furan ring (C) (18). Currently, the identification of flavonoid compounds has exceeded 10, 000, with the figure continuing to increase (19). Flavonoids are classified according to their chemical structure into anthocyanins, flavan-3-ols, flavonols, flavones, flavanones, isoflavones, etc (Table 1). The physiological effects of flavonoids include anti-inflammatory properties, immune modulation, antioxidant activity, and regulation of gut microbiota (9, 20–22).
The absorption process of flavonoids is complicated and affected by their chemical structure, solubility, membrane permeability, and the metabolism of gut microbiota. Different classes of flavonoids possess distinct structural features, resulting in variations in their metabolic pathways and bioavailability within the body (23). However, the bioavailability of most flavonoids is limited due to their prevalence in glycoside forms, making them difficult for the digestive system to absorb (24). Flavonoid glycosides need to be hydrolyzed into aglycone forms so that they can pass through intestinal epithelial cells effectively (25). Additionally, some flavonoids are quickly broken down and become inactive by enzymes in the intestines and liver after ingestion, which, to some extent, reduces the amount of active compounds that reach the bloodstream (23). Recent research has developed drug delivery systems by adding flavonoids into carriers, such as nanoemulsions, metal-organic frameworks, and alginate-chitosan microspheres. These systems provided new approaches to improve the absorption and bioavailability of flavonoids (26–28).
3 The regulatory effect of flavonoids on immune cells
3.1 Macrophages
Macrophages are a type of innate immune cells with phagocytic and antigen-presenting functions, playing a crucial role in various diseases (83). Activated macrophages are generally categorized into two kinds: M1 macrophages, which participate in pro-inflammatory responses, and M2 macrophages, which engage in anti-inflammatory responses (84). In inflammatory conditions, a key therapeutic strategy is to promote the differentiation of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages into anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages. Flavonoids have been demonstrated to have the capacity to ameliorate inflammatory diseases by suppressing M1 polarization and enhancing M2 polarization in macrophages. Quercetin, puerarin, and luteolin can increase M2 markers (e.g., Arg1 and IL-10) via the PI3K/Akt, PPARγ, or AMPK pathways, thereby facilitating macrophage polarization towards M2 (85–87). In contrast, baicalin, Allium cepa L. peel extract, apigenin, and hesperidin can prevent macrophage polarization toward the M1 phenotype by blocking the JAK/STAT, MyD88/NF-κB, MAPK, direct kinase targets (IRAK4), or Jagged1/Notch1 pathways (88–91). Flavonoids have also been proven to influence macrophage polarization by regulating metabolic reprogramming. Phellodendrin has been shown to inhibit HIF-1α-regulated macrophage PI3K/Akt and glycolysis, restoring the M1/M2 macrophage balance in periodontitis, thereby reducing the pro-inflammatory effects and immune dysfunction caused by overactivated M1 macrophages (92).
NLRP3 inflammasome is a multiprotein complex existing in macrophages linked to a number of chronic inflammatory diseases. It can initiate the death of inflammatory cells and the release of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18 (93). It also serves as the main target for flavonoid compounds in regulating macrophages. Quercetin, luteolin, and apigenin can prevent NLRP3 inflammasome assembly, activate caspase-1, and cleave Gasdermin D (GSDMD) through reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging or Nrf2/HO-1 activation, thereby decreasing IL-1β secretion, inhibiting macrophage pyroptosis, and suppressing macrophage-driven inflammation (94–96).
New delivery systems have been developed to improve the effectiveness of flavonoid compounds targeting macrophages. Macrophage membrane-modified baicalin liposomes (MM-BA-LP), compared to conventional baicalin liposomes (BA-LP), offer better cerebral targeting, improved pharmacokinetics, and longer retention in the bloodstream (97). Zhang et al. constructed M2M@BANPs by loading baicalin onto poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles and encapsulating them within M2 macrophage membranes. Under the coating of M2M, M2M@BANPs can effectively target ischemic brain tissue and accumulate in microglia and neurons. This reprograms microglia from M1 to M2, significantly impacting therapeutic effects in ischemic stroke (98).
Although most flavonoids show their anti-inflammatory properties, certain studies have reported their pro-inflammatory effects. In the tumor microenvironment, vitexin has been observed to promote macrophage polarization towards the M1 phenotype via the VDR/PBLD pathway, thereby enhancing anticancer activity (99). In the mouse peritoneal infection model, intraperitoneal injection of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) significantly increased the quantity of monocytes/macrophages in both the peritoneal cavity and peripheral blood. EGCG can also induce pro-inflammatory responses in macrophages and promote phagocyte migration in co-culture systems containing macrophages, indicating that EGCG is an effective agent for preventing bacterial infections (100). The divergent regulatory effects of flavonoids on macrophage anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory responses indicate that their regulation is contingent upon environmental factors.
3.2 Neutrophil
Neutrophils are the most abundant type of leukocytes in the circulatory system. As effector cells of the innate immune system, they play a key role in the pathophysiological processes of inflammatory and autoimmune disorders (101, 102). Recent studies have shown that, beyond eliminating pathogens through traditional phagocytosis, neutrophils participate in anti-infective defense and inflammatory responses by releasing neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), secreting inflammatory mediators (e.g., cytokines, chemokines, and lipid mediators), and producing ROS (103, 104). However, excessive activation of neutrophils can result in tissue damage and the development of inflammatory diseases. Flavonoids have shown anti-inflammatory effects through the regulation of neutrophils.
NETs are network-like structures composed of chromatin and granular proteins released by activated neutrophils. Although these structures contribute to defense mechanisms by capturing pathogens, the excessive or abnormal NETs formation can contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. NETs can amplify localized inflammation and induce tissue damage. Accumulating evidence indicates that flavonoids exert anti-inflammatory effects by regulating neutrophil function and inhibiting NETs formation through multiple signaling pathways. For instance, quercetin inhibits NETs formation by targeting the P2X7R/P38MAPK/NOX2 signaling pathway (105), thereby alleviating oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in neutrophils. Astilbin suppresses NETs formation by regulating the purinergic P2Y6 receptor and the IL-8/CXCR2 pathway (106). Dihydromyricetin blocks NETs formation through the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway (107). Additionally, calycosin decreases NETs formation and neutrophil-mediated inflammation by acting on the TLR4/NF-κB pathway (108). Overall, these results show that flavonoids are effective inhibitors of NETs, potentially assisting in the reduction of inflammation and the development of autoimmune conditions.
ROS serve as critical effector molecules for neutrophil killing of pathogens, but excessive ROS may cause tissue damage. Research shows that luteolin can inhibit the production of ROS by regulating neutrophils, a process aided by the suppression of Raf1 activity (109). Flavonoids are capable of inhibiting overall ROS production; however, their effectiveness varies among different types. The condensation product of taxifolin with glyoxylic acid (DfTf) significantly decreases extracellular ROS levels with no effect on intracellular ROS. In contrast, naringin is more effective at inhibiting intracellular ROS (110). The role of ROS, intracellularly and extracellularly, varies in health and disease. Intracellular ROS has been shown to suppress IL-1β expression, thereby limiting neutrophil recruitment. In contrast, extracellular ROS appears to enhance IL-1β expression, promoting the recruitment of neutrophils to form collaborative clusters (111). The regulatory effects of flavonoids on intracellular and extracellular ROS show their divergent roles in different disease contexts.
3.3 Dendritic cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) are essential antigen-presenting cells that orchestrate immune responses by modulating T cell activation and differentiation, serving as a crucial connection between innate and adaptive immunity. Impairment of DCs has been demonstrated to play a role in the onset of inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. Recent studies indicate that flavonoids can exert immunomodulatory effects by further influencing T cells through the regulation of the immune response of DCs. Silibinin has been proven to inhibit the upregulation of co-stimulatory molecules and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules on lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulated mature DCs, while also suppressing the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-12, IL-23, and TNF-α, as well as CD4+ T cell proliferation and Th1/Th17 function, indicating strong immunosuppressive activity (112). RelB is a critical protein in the NF-κB pathway. Apigenin has been shown to inhibit RelB expression and nuclear translocation, affecting DC maturation and antigen presentation, which alters T cell responses from pro-inflammatory Th1/Th17 phenotypes to regulatory T cells (Tregs), thus alleviating inflammatory responses (113). Galangin and naringin have also been shown to contribute to this tolerance-inducing process. Treatment of DCs with galangin results in decreased expression of CD86 and MHC II molecules, with increased expression of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) and IL-10 secretion. This promotes T helper (Th) cells differentiation into Tregs, reducing inflammatory responses (114). Conversely, naringin has been shown to promote the differentiation and maturation of DCs through the KBP4/NR3C1/NRF2 axis, thus providing a novel therapeutic approach for NRF2-dependent autoinflammatory conditions (115).
3.4 T cells
T cells are a key immune cell of the adaptive immune system with the capacity of controlling immunological responses. CD4+ T cells, also known as Th cells, can differentiate into Th1, Th2, Th17, T follicular helper cells (Tfh), and Tregs, regulating immunological responses throughout the body collaboratively (116). Our previous study demonstrated that phloretin inhibits glucose uptake and proliferation in activated CD4+ T cells and modulates the Th17/Treg balance through AMPK signaling pathway (117). Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), also known as CD8+ T cells, are responsible for eliminating contaminated and cancer cells by releasing perforin and granzyme, leading to the initiation of apoptosis through interactions between Fas and Fas ligand (118). Dysfunction of T cell subsets and activities may cause the occurrence of autoimmune illnesses and tumor immune escape. Flavonoids can help restore immune homeostasis by regulating T cell differentiation. Apigenin is found to induce apoptosis in CD8+ T cells and decrease levels of inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, IFN-γ, and IL-17, by inhibiting the STAT3/IL-17 signaling pathway. This effectively downregulates CTLs activity and alleviates tissue damage (119). Naringin shows promise in the treatment of autoimmune hepatitis by regulating essential genes associated with T cell responses, such as IL-6 and TNF (120).
T cell exhaustion represents a considerable challenge in cancer treatment. The expression of immune checkpoint molecules, PD-L1 and indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase1 (IDO1), is responsible for this process (121). Tumor cells frequently enhance the expression of these molecules to evade immune detection. Flavonoids have been shown to have the ability to recover T cell function by regulating the status of immune checkpoints. Myricetin can reduce the expression of PD-L1 and IDO1 induced by IFN-γ in lung cancer cells, by targeting the JAK-STAT-IRF1 signal pathway. This reduction can help recover T cell proliferation and effector activity (122). Icariin has been demonstrated to directly induce ferroptosis in colorectal cancer cells while simultaneously promoting CD8+ T cell activation and IFN-γ secretion, thereby augmenting the therapeutic efficacy of programmed cell death protein1 (PD-1) checkpoint inhibitors (123). Baicalin has been shown to improve the CD8+ T cell/Treg ratio against resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy via modifying the composition of the gut microbiota (124). Furthermore, flavonoids can augment the immune system’s capacity to combat tumors by modulating T cell autophagy. Baicalin has been shown to promote the degradation of CD274 within autolysosomes, a process facilitated by increased interaction between CD274 and LC3, which shows the potential of baicalin to interfere as a CD274 inhibitor to tumors (125).
3.5 B cells
B cells are also a key part of the adaptive immune system, producing antibodies that fight infections, however, disorders may lead to autoimmune diseases and allergy. Flavonoids have been shown to have the capacity to regulate the balance and function of B cells. Baicalin can lower the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-17A, and TNF-α) and chemokines, by regulating the ratio of different types of B cells (decreasing the ratio of B220+ lymphocytes and increasing the ratio of memory B cells) and inhibiting TGF-β1 signaling, associated with fibrosis and immune regulation. This indicates that it might help prevent the growth of abnormal B cells and diminish immune system activation (126). Formononetin has been shown to suppress IgE production by B cells and mast cell activation by downregulating key signaling pathways, the JAK/STAT and PI3K/Akt pathways, suggesting that flavonoids may have a broader immunomodulatory role in allergy and IgE-related diseases (127).
In addition, flavonoids can also regulate mast cells, eosinophils, and other immune cells, thereby alleviating allergic reactions and autoimmune diseases (128, 129). Flavonoids can regulate multiple signaling pathways, which gives them the potential to exert a wide range of effects on different immune cells. Their roles as antioxidants, which is another common mechanism they act on, can directly eliminate ROS from macrophages and neutrophils or stimulate the body’s intrinsic antioxidant responses to alleviate inflammation. Additionally, they can modulate macrophages via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, inhibiting the dissemination of inflammatory signals. A notable observation is their capacity to trigger a transition in immune cells, including macrophages, dendritic cells, and T cells, from a pro-inflammatory to an anti-inflammatory state during periods of inflammation, which occurs irrespective of the specific cell type. However, in the presence of tumors, flavonoids have been observed to induce a pro-inflammatory transformation in immune cells.
4 Flavonoids’ therapeutic applications in inflammatory diseases
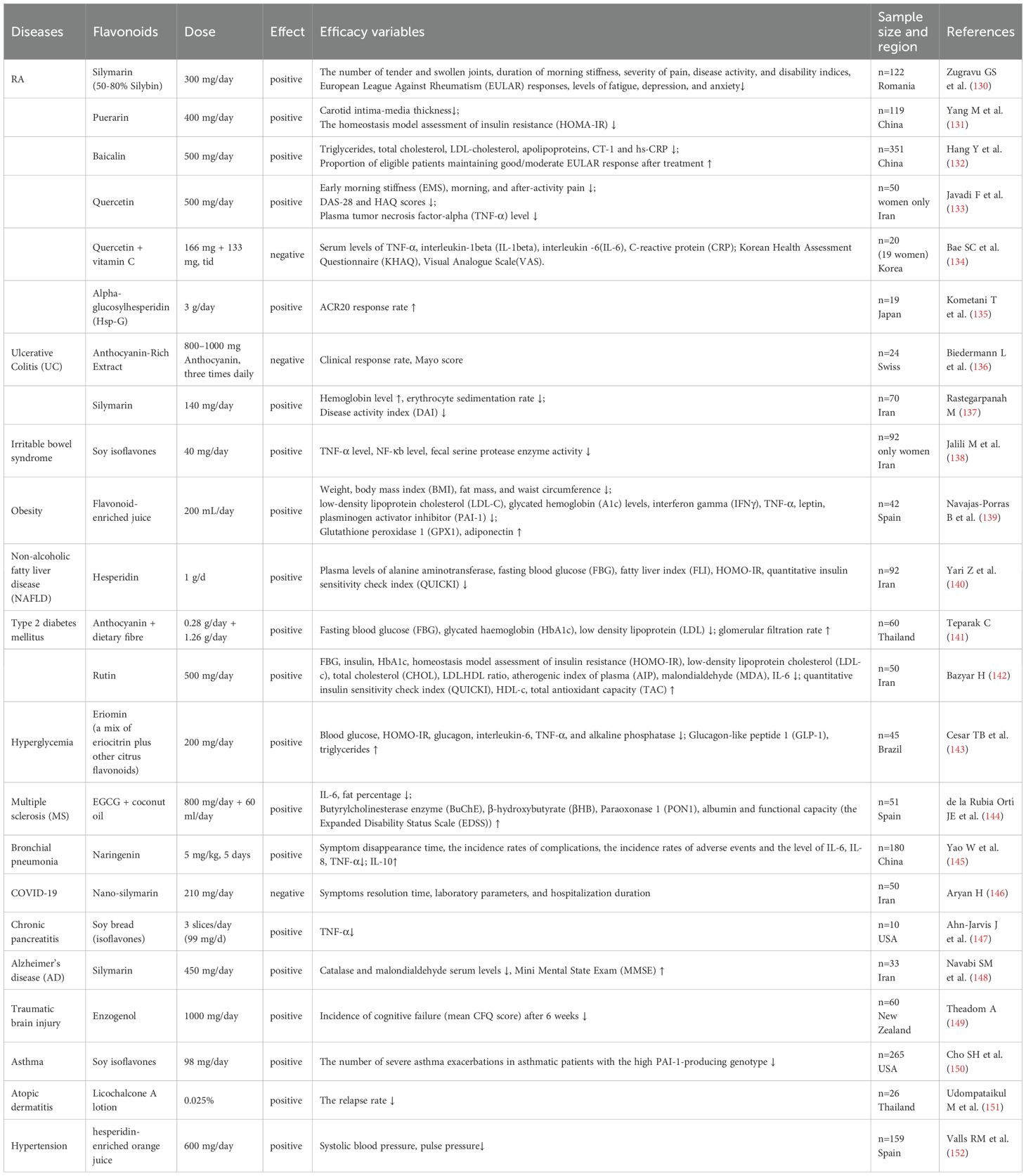
Flavonoids have been demonstrated to exert regulatory effects on immune cells and inflammatory factors. Accumulating evidence from existing RCTs indicates that flavonoids may serve as adjunctive therapies for inflammatory diseases (Table 2). The following section provides a detailed overview of the therapeutic mechanisms of flavonoids in inflammatory diseases.
4.1 Anti-inflammatory effects in inflammatory bowel disease
IBD is a chronic intestinal disorder closely linked to immune system dysfunction. Corticosteroids and 5-aminosalicylic acid are conventional IBD medications, but they sometimes have limited effectiveness and may cause side effects such as diabetes and kidney problems (153). Recent immunosuppressants and biologics have demonstrated efficacy for numerous patients; however, they also elevate the risk of severe cardiovascular complications, including thrombosis (154). Flavonoids are a relatively harmless type of medicine that may help treat IBD. Cohort studies have found a correlation between high intake of anthocyanins and quercetin and a lower risk of ulcerative colitis (UC) (155, 156). In patients with moderate to severe UC, treatment with anthocyanin-rich extracts has been shown to lower calprotectin levels, indicating therapeutic benefits. However, these extracts were less effective in patients with Crohn’s disease (136). Although studies have shown that anthocyanins do not have a significant benefit on Crohn’s disease, anthocyanin-rich maqui extract inhibited the NLRP3 inflammasome and mast cell activation in mice with TNBS-induced colitis (157). Therefore, further research is needed to understand the role of anthocyanins in Crohn’s disease. Flavonoids have been shown to have positive effects on colitis by modulating immune cell activity and preventing them from becoming pro-inflammatory. In a DSS mouse model of colonic lesions, puerarin has been found to directly inhibit M1 polarization of macrophages, while luteolin and formononetin have been demonstrated to regulate the M1/M2 balance of macrophages (87, 158, 159). Some flavonoids below have been reported to alleviate colitis through various mechanisms. EGCG can inhibit Th1 cell polarization, while hyperoside can regulate the Th17/Treg balance, hesperidin helping rebalancing Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg, and wogonin has been found to activate the AhR pathway, thereby preventing ILC3 from transforming into ILC1 (160–163). Flavonoids may also regulate the immune system and help prevent and treat inflammatory bowel disease by interacting with gut microbiota in bidirectional interactions. On one hand, following colon entry, flavonoid metabolites display gut microbiota-dependent characteristics, such as equol, a metabolite derived from soy isoflavones, which forms entirely dependent on the presence and composition of gut microbiota (164, 165). On the other hand, flavonoids entering the intestine also affect the composition of the gut microbiota (166). This effect not only directly influences the abundance of IBD-related gut microbiota but also helps gut microbiota to produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), regulators of T lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils, contributing to gut homeostasis (167–170). Taxifolin has been demonstrated to modify gut microbiota composition, which can lead to increased SCFAs production, thereby suppressing the production of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in colonic tissue, thus ameliorating DSS-induced colitis (171).
Flavonoids may also play a role in preventing the progression of UC to colorectal cancer. Glabridin has been demonstrated to inhibit STAT3 phosphorylation, regulate MMP1/3 activity, alleviate inflammation, reduce extracellular matrix degradation and decrease the occurrence of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions (172). Neohesperidin (NHP) can inhibit macrophage migration into target tissues and decrease pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and COX-2, at both mRNA and protein levels, exceeding that of mesalazine at similar concentrations (173). Vitexin has been shown to reduce the quantity of M1 phenotype macrophages in healthy tissue adjacent to tumors, enhance M1 macrophage polarization within tumor tissue, and impede the progression from ulcerative colitis to colorectal cancer (174).
4.2 Anti-inflammatory effects in rheumatoid arthritis
RA is a chronic inflammatory disease that causes persistent inflammation of the synovial membrane and joint damage, potentially resulting in disability (175). Although the use of traditional medications, DMARDs, and innovative biologic agents has collectively improved treatment outcomes, numerous patients exhibit insufficient responses to existing therapies or adverse side effects, highlighting the necessity for novel treatment strategies (176). Recent evidence from epidemiological and clinical studies suggests that dietary flavonoids may play an important role in RA treatment. A study from the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) indicated that adults in the US with elevated flavonoid consumption may exhibit a reduced likelihood of developing RA (177). Furthermore, individuals with active rheumatoid arthritis may experience alleviation of their condition and a reduction in inflammatory markers due to specific flavonoid compounds or flavonoid-rich extracts, such as silymarin and curcumin, with effects superior to those of DMARDs (130, 178).
Flavonoids may assist in the treatment of RA by regulating immune dysregulation in the synovial microenvironment. A key factor in RA development is the imbalance between pro-inflammatory effector T cells and anti-inflammatory Tregs, where flavonoids can directly correct and restore balance in the immune system. Naringin can inhibit the migration and polarization of CD4+ T lymphocytes in the synovium by regulating mitochondrial fission (179). In a collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model, kaempferol was found to reduce the quantity of pathogenic CD4+ effector memory T cells while increasing naïve T cells and Tregs, thereby ameliorating the condition (180), while berberine and rutin augment Treg activity to assist in the management of RA (181). Kurarinone inhibits the differentiation of pro-inflammatory Th1 and Th17 cells by directly activating the antioxidant Nrf2/KEAP-1 pathway, thus alleviating RA symptoms (182). Morin alleviates RA by inhibiting Th17 differentiation and fatty acid synthesis following PPARγ activation (183). Hesperidin alleviates RA by inhibiting Th17 activation, as well as reducing serum levels of TNF−α, IL−6, and IL−17A, ultimately improving joint pathology and clinical score (184). In the adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) rat model, Cyanidin enhances the outcomes of RA by reestablishing the Th17/Treg balance and suppressing the differentiation of Tfh cells via ROCK2 signaling (185). This targeted regulation of T cell subsets is crucial for attaining sustained remission of RA and is closely related to the control of autoreactive T cells (186). Macrophages also play an important role in coordinating RA synovitis and joint degradation (187). Flavonoids can prevent pro-inflammatory macrophages from functioning and promote their conversion into anti-inflammatory cells, thereby combating arthritis. Hesperidin inhibits macrophage infiltration into tissues by diminishing COX-2 expression (188). Acacetin binds specifically to the ATP domain of HSP90, causing HSP90 to detach from COX-2, which leads to COX-2 being ubiquitinated and broken down in macrophages, thereby reducing inflammatory reactions (189). Icariin, delivered via exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells, has been shown to convert pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages in synovial tissue into anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages, at the same time inhibiting glycolysis (190). Flavonoids can also prevent abnormal crosstalk between different immune cell groups that triggers the inflammatory cascade in RA (191). An adverse feedback loop exists between T cells and macrophages, wherein cytokines produced by T cells, such as IL-17A, diminish the function of synovial macrophages and worsen inflammation. Cyanidin has been shown to suppress this IL-17A-mediated impairment, thereby halting this intercellular inflammatory transmission (192). Neutrophils are essential in the pathogenesis of RA and represent an important target for therapeutic intervention, as they perpetuate inflammation through the secretion of cytokines, chemokines, and reactive oxygen species, in addition to forming NETs (193). Flavonoids can prevent these harmful processes to treat RA. Quercetin can inhibit neutrophil infiltration into tissues, induce apoptosis in active neutrophils, and obstruct NETs formation by interfering with autophagy (194). Rutin can obstruct neutrophil migration to joints and suppress the local synthesis of TNF-α (195). Refractory RA is when an individual with RA fails to respond to DMARDs treatment (196). The overexpression of the drug efflux pump P-glycoprotein (P-gp) in lymphocytes is regarded as a mechanism of DMARDs resistance (197). Nobiletin, functioning as a P-gp inhibitor, can suppress P-gp overexpression in lymphocytes in the AIA rat model when co-administered through a nanodelivery system, providing novel insights for refractory RA (26, 198). Flavonoid compounds may also exert beneficial effects on the overall integrity of joint structures. For instance, they can promote chondrocyte differentiation via the MAPK signalling pathway, inhibit synovial autophagy and fibroblast-like synoviocyte activation, making flavonoids even better candidates for comprehensive anti-arthritic agents (199–201).
4.3 Anti-inflammatory effects in metabolic disorders
Metabolic disorders, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes (T2DM), and atherosclerosis, are caused by a persistent low-grade inflammatory condition known as ‘metabolic inflammation’ (202). Metabolic stress activates immune cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, in metabolic organs, including adipose tissue, the liver, the pancreas, and blood vessels (203). These activated immune cells produce cytokines, contribute to cellular damage, and promote insulin resistance. Analysis of plasma samples from T2DM patients adhering to a Mediterranean diet for 12 weeks revealed an elevation in plasma concentrations of naringin, hesperetin and hesperidin, resulting in a reduction of inflammation and oxidative stress in individuals with T2DM (204). Flavonoids can regulate immune cells to inhibit the progression of metabolic inflammation.
4.3.1 Anti-inflammatory effects in obesity and fatty liver
Adipose tissue serves as the primary site of inflammation in metabolic inflammatory disorders. Flavonoids can reduce inflammation by regulating macrophage polarization, as the infiltration of macrophages and pro-inflammatory (M1) polarization are hallmark traits of obesity (205). In obese mice, dietary supplementation with kaempferol has demonstrated a reduction in intestinal inflammation and a decrease in the influx of immune cells into the intestines, thereby mitigating systemic metabolic issues (206). Apigenin, when delivered in nanoparticle delivery systems, promotes the transition of adipose tissue towards the M2 phenotype, thereby reducing obesity-related inflammation (207). 7, 8-Dihydroxyflavone and baicalin are two flavonoids with similar effects, blocking key inflammatory signaling pathways, including NF-κB and JNK, in macrophages, reducing insulin resistance in overweight individuals (208, 209). When metabolic inflammation extends to the liver, it may result in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition for which flavonoids demonstrate significant protective potential. Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, inhibits hepatic lipid accumulation and decelerates the progression of NAFLD by regulating M1/M2 macrophage polarization through enhanced autophagy and by suppressing the NLRP3 inflammasome, a critical contributor to inflammatory cell death (210). Hyperoside similarly promotes M2 macrophage polarization in an Nr4A1-dependent manner, contributing to the amelioration of NAFLD (211). Researchers have discovered that green tea extract, Theaphenon E (TE), protects the liver by diminishing lipid accumulation and preserving elevated CD4+ T cell counts (212).
4.3.2 Anti-inflammatory effects in diabetic vascular complications
Flavonoids can help prevent inflammation that may potentially harm the pancreatic beta cells. A study found that a flavonoid-rich diet, mixing cocoa powder and carob flour, may preserve β-cell mass in diabetic rats through preventing macrophages from infiltrating into the pancreatic islets and inhibiting NF-κB-mediated inflammation. This approach may help regulate insulin secretion and delay the development of T2DM (213). The persistent inflammation and hyperglycemia associated with diabetes inevitably have severe effects on blood vessels and tissues, leading to a series of serious complications (214). Flavonoids can alleviate these complications by regulating immune cell-mediated immune responses in affected tissues. Kaempferol mitigates diabetic retinopathy by targeting retinal microglia, which are the resident macrophages of the central nervous system. Kaempferol significantly diminishes the pro-inflammatory response of microglia and promotes an anti-inflammatory M2-like phenotype, thereby contributing to maintaining retinal integrity (215). Hyperoside may help treat diabetic nephropathy by regulating the T cell balance towards anti-inflammatory Th2 and Treg populations and by promoting macrophage polarization from the M1 to the M2 phenotype (216). Cardamonin inhibits diabetic cardiomyopathy by preventing M1 macrophages from infiltrating the cardiomyocyte and modifying their morphology. Meanwhile, cardamonin can activate KEAP1 to release the transcription factor NRF2, which activates a strong protective program that shields cardiomyocytes from damage by weakening inflammation and free radicals (217).
4.3.3 Anti-inflammatory effects in cardiovascular diseases
Inflammatory responses are key drivers of the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases. Immune cells contribute to pathological cardiovascular remodeling by inducing endothelial dysfunction, vascular remodeling, cardiomyocyte injury, and fibrotic changes (218, 219). Moreover, immunosenescence has emerged as an important contributor to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and hypertension (220). Flavonoids exert multiple protective effects in cardiovascular inflammatory conditions. In the vascular endothelium, flavonoids promote endothelial cell survival and function (221, 222). As for cardiomyocytes, they regulate autophagy and alleviate cellular swelling and fibrosis in heart failure conditions (222–224). Within vascular smooth muscle cells, flavonoids suppress their proliferation, migration, and inflammatory activation (225). Furthermore, by regulating the gut microbiota, flavonoids strengthen intestinal barrier integrity and thereby mitigate microbiota-driven cardiovascular pathology (226). Beyond their suppression of general inflammatory mediators, flavonoids can specifically target disease-relevant inflammatory markers, highlighting their therapeutic potential in managing cardiovascular inflammation (227).
Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory arterial disorder that may lead to strokes and myocardial infarctions. Flavonoids can not only inhibit cytokines but also regulate macrophage metabolic reprogramming, thereby preventing the formation of lipid-laden ‘foam cells’ that contribute to the development of atherosclerotic plaques (228). Wogonin, a flavonoid isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis, activates the PPARα-KLF11-YAP1 transcription complex, which redirects macrophage energy metabolism away from pro-inflammatory glycolysis towards protective fatty acid oxidation, thereby inhibiting foam cell formation and alleviating plaque inflammation (229). Quercetin can limit pyroptosis of macrophages by blocking the KEAP1/NRF2 interaction (230). Hawthorn leaf flavonoids can inhibit sPLA2-IIA in macrophages, thereby reducing macrophage inflammation (231). Both mechanisms have been shown to slow atherosclerosis progression in ApoE−/− mice fed a high-fat diet by targeting macrophages. In terms of reducing the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, biochanin A (BCA) promotes macrophage cholesterol efflux, while kaempferol suppresses macrophage inflammatory responses (232, 233). Elevated blood glucose levels prompt neutrophils to release NETs, resulting in vascular damage. Prenylchalcones may inhibit this process, indicating their potential as supplementary therapies for metabolic disorders (234).
Hypertension is also strongly associated with immune activation and chronic inflammation. Aberrant immune responses promote vascular inflammation, leading to endothelial dysfunction, vascular remodeling, and increased peripheral vascular resistance, which eventually drive blood pressure elevation (235, 236). Cohort studies indicate that flavonoids not only reduce the risk of developing hypertension but also prevent hypertension-related target organ damage and improve long-term clinical outcomes (237–240). The paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus, a bilateral structure adjacent to the third ventricle, plays a critical role in central blood pressure regulation. Beyond their anti-inflammatory effects, flavonoids can regulate immune and inflammatory processes within the PVN through actions on immune cells, thereby contributing to blood pressure control. Puerarin and anthocyanins attenuate blood pressure elevation in salt-induced prehypertensive rats by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation and ROS production in the PVN (241, 242). Similarly, luteolin ameliorates hypertension by inhibiting NF-κB-mediated inflammatory signaling and the PI3K/Akt pathway within the hypothalamic PVN (243).
4.4 Anti-inflammatory effects in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases
Neuroinflammation is characterized by immune cells in the central nervous system (CNS), mainly microglia and astrocytes, remaining persistently activated, which is regarded as a predominant mechanism in numerous neurodegenerative and neurological diseases (244). Microglia can exert neuroprotective effects by phagocytosing harmful protein aggregates; however, excessive phagocytosis of these aggregates may lead to neuronal damage and disease progression (245). In pathological conditions, peripheral immune cells, such as T cells and neutrophils, may also infiltrate the brain and spinal cord, further intensifying the inflammation (246, 247). Flavonoids can alleviate neuroinflammatory processes and decrease the progression of neurodegenerative diseases through their regulatory effects on immune cells, particularly microglia (248).
4.4.1 Anti-inflammatory effects in Alzheimer’s disease
In Alzheimer’s disease (AD), amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and tau protein tangles chronically activate microglia, causing a neurotoxic inflammatory state and impairing their phagocytic function (249). A study based on the NHANES database found that adults in the US population with higher flavonoid consumption exhibited a lower risk of AD-related mortality (250). Myricetin may aid in treating AD by blocking the p38 MAPK pathway and activating the NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia, thereby reducing Aβ accumulation (251). In addition to suppressing pathological processes, flavonoids can also enhance microglia’s protective ability. Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside (C3G) facilitates the transition of microglia from the M1 to the M2 phenotype by activating the PPARγ signal pathway and enhancing the phagocytosis of Aβ42 by upregulating TREM2, thereby facilitating the clearance of accumulated β-amyloid (252). Rutin has also been shown to help microglia uptake extracellular tau oligomers, thereby directly combating AD (253). Microglial senescence, a functional disorder state associated with aging and AD, can be mitigated through preventive measures, thereby alleviating neuroinflammation and cognitive decline (254). Studies suggest that delphinidin may decelerate this process through the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway, potentially mitigating cognitive deficits and pathological features of AD (255).
4.4.2 Anti-inflammatory effects in demyelinating diseases
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune demyelinating disease in which both T cells and glial cells contribute to the progression of the disease (256, 257). Flavonoids have shown their potential for therapeutic applications in MS via regulating both the central and peripheral immune systems. In the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of MS, procyanidin B2 3, 3’’-di-O-gallate (PCB2DG) has been found to directly suppress the immune response of pathogenic CD4+ T cells, aiding in disease management. Glycolysis is crucial for T cell activation. PCB2DG exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by modulating glycolytic metabolism, consequently reducing the production of T cell-mediated inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ and IL-17, as well as their infiltration into the spinal cord. This mechanism has been proved effective for treating spinal cord injury (258). Baicalein and kaempferol have been demonstrated to alleviate demyelination and microglial activation caused by cuprizone poisoning by inhibiting the STAT3 and NF-κB signaling pathways (259). Agathisflavone has been shown to influence microglia activation through the estrogen receptor alpha, promoting myelin regeneration and alleviating symptoms of MS (260).
4.4.3 Anti-inflammatory effects in acute central nervous system injury
After acute injuries such as stroke and trauma, the activation of microglia and the infiltration of peripheral immune cells into ischemic tissues may trigger a robust and deleterious neuroinflammatory response (261). Flavonoids have been proven to have therapeutic potential in repairing such damage. Quercetin can regulate the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway, promoting a transition from a pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype to an anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype in microglia and macrophages, thereby effectively alleviating brain ischemia/reperfusion injury (85). In spinal cord injury models, alpinetin reduce neuroinflammation and enhance motor function recovery by inhibiting microglial activation (262). In an experimental intracerebral hemorrhage model, didymin has been found to improve cerebral function by reducing microglial activation and pyroptosis. Furthermore, this process also leads to a reduction of neutrophils infiltrating the perihematomal tissue, thereby helping to alleviate post-hemorrhagic neuroinflammation (263).
4.4.4 Anti-inflammatory effects in mental, stress and pain-related disorders
Neuroinflammation is considered a pathogenic factor in the development of depression and anxiety (264), while flavonoids have been demonstrated to exert therapeutic effects on depression and anxiety by reducing neuroinflammation induced by microglia. Luteolin can promote the Arg-1+ microglial phenotype in a chronic stress-induced depression model, which contributes to the suppression of microglial pro-inflammatory activity and ameliorates depressive-like behavior (265). Hyperoside has been demonstrated to ameliorate depressive-like behavior by promoting M2 polarization of microglia in the hippocampus (266), and quercetin can alleviate cognitive impairments in depressed mice by targeting HSP90 to inhibit the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia (267). In a mouse model of chronic unpredictable stress (CUS) depression, morin can relieve neuropathic pain by balancing M1/M2 microglial polarization and inhibiting neuroinflammation (268).
A major impediment in the treatment of neurological disorders is the blood-brain barrier, while delivery mechanisms can enhance the efficacy of flavonoids. Xu et al. formulated BDNF(brain-derived neurotrophic factor)-quercetin alginate nanogels and delivered them intranasally, resulting in a nearly 50-fold enhancement in the bioavailability of quercetin compared to oral treatment (269). Zhang et al. attached the blood-brain barrier-penetrating peptide (RVG29) to the surface of nanoparticles and included 4, 4’-dimethoxychalcone (DMC), referred to as RVG-nDMC. This delivery system successfully traversed the blood-brain barrier (BBB), improved the transport of DMC to dopaminergic neurons and microglia in the substantia nigra pars compacta of Parkinson’s disease (PD) mice, and intervened in PD (270).
4.5 Anti-inflammatory effects in respiratory tract diseases
When pathogens invade the respiratory tract, innate immune cells respond to the infection rapidly. However, excessive activation might result in inflammation and damage to the respiratory system (271). Consequently, in respiratory tract infections, it is essential for the immune system to maintain a balance between combating pathogens and minimizing host tissue damage (272). Flavonoids have shown potential in this condition by directly reducing pathogen replication and virulence while also regulating the host immune response, offering new prospects for the treatment of respiratory tract infections (RTI).
4.5.1 Anti-inflammatory effects in acute lung injury
Acute lung injury (ALI) and its more severe form, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), are serious conditions usually caused by sepsis, trauma, or severe infection. ALI is characterized by widespread pulmonary inflammation, alveolar edema, and progressive respiratory failure, with neutrophils and macrophages serving as key cellular mediators in this process (273, 274). Numerous flavonoids have demonstrated considerable therapeutic potential in experimental models of ALI and sepsis, particularly in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. In ALI, macrophages typically exhibit a pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype, secreting substantial quantities of cytokines and aggravating lung tissue damage. Flavonoids may counteract this pathological process by promoting the transition of macrophages toward the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype, thereby facilitating inflammation resolution and initiating tissue repair mechanisms. Wogonin and apigenin have been reported to ameliorate sepsis-induced ALI by regulating macrophage M1/M2 polarization (275, 276). Oroxylin A alleviates sepsis through the induction of “trained immunity”. It increases LC3-associated phagocytosis (LAP) in macrophages via activation of the Dectin-1-Syk signaling axis and the mTOR pathway, thereby enhancing macrophage capacity to combat infection and resist sepsis progression (277). Catechin hydrate directly inhibits macrophage RasGRP1, a pro-inflammatory gene in macrophages, thereby diminishing excessive inflammation and oxidative stress that contribute to numerous organ dysfunctions resulting from sepsis (278). Icariin II mitigates LPS-induced ALI by targeting the neutrophil receptor CXCR, hence reducing excessive neutrophil activation and the formation of NETs (279).
4.5.2 Anti-inflammatory effects in bacterial respiratory tract infections
With the continuous advancement of antibiotic therapies, bacterial pneumonia has been partially controlled. However, the emergence of drug resistance poses significant challenges to both clinical treatment and public health, particularly in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, during which the prevalence of multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) has increased rapidly (280, 281). Flavonoids provide a multi-target therapeutic strategy for bacterial pneumonia through various mechanisms, including direct antibacterial effects, suppression of bacterial pathogenicity, and regulation of the host’s immunological response to infection. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic Gram-negative bacterium frequently responsible for hospital-acquired pneumonia and may lead to severe and often multidrug-resistant infections (282). In a murine model of bacterial pneumonia, luteolin demonstrated the capacity to inhibit M1 macrophage polarization by suppressing the EGFR/PI3K/AKT/NF-κB and EGFR/ERK/AP-1 signaling pathways. It can simultaneously reduce lung permeability, neutrophil infiltration, pro-inflammatory cytokine synthesis, and pulmonary bacterial load, thereby improving the survival rate of mice (283). Phloretin exhibits direct antibacterial and anti-biofilm properties against non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi), Moraxella catarrhalis, and Streptococcus pneumoniae. In murine models, dietary supplementation with phloretin was found to decrease NTHi bacterial load and reduce levels of the neutrophil chemoattractant CXCL1, thereby ameliorating pneumonia (284). MgrA is a key regulatory factor in Staphylococcus aureus and plays a central role in regulating bacterial virulence and resistance. methylophiopogonanone can diminish the connection between MgrA and DNA in S. aureus, leading to reduced toxin expression, diminished bacterial adhesion, disruption of immune evasion mechanisms, and enhanced neutrophil chemotaxis, thereby preventing S. aureus-induced pneumonia in mice (285).
In addition to their therapeutic effects on existing infections, flavonoids also demonstrate preventive potential against bacterial infections. EGCG elicits an adjustable pro-inflammatory response in macrophages via the 67LR/p38/JNK signaling pathway, showing promise in the prevention of bacterial infections. Furthermore, it can also regulate macrophage-mediated immunity, stimulate phagocyte migration, and enhance the immune system’s capacity to respond more swiftly and effectively to subsequent bacterial assaults (100).
4.5.3 Anti-inflammatory effects in viral respiratory tract infections
Whether it’s seasonal influenza or the more recent COVID-19 pandemic, various viral respiratory infections can elicit immune responses, resulting in pulmonary damage. Flavonoids present a multi-targeted therapeutic approach that not only inhibits viral invasion and replication but also regulates the host’s inflammatory response, thereby offering therapeutic benefits (286, 287). In an experimental model of lung inflammation induced by the H1N1 subtype of influenza A virus, an RNA virus responsible for seasonal and pandemic influenza, 5-methoxyflavone was shown to suppress the recruitment of CD8+ T cells, attenuate inflammatory responses, and reduce ALI (288). In a mouse model of H9N2 viral infection, baicalin was found to directly inhibit viral replication, augment the expression of antiviral proteins Mx1 and PKR, equilibrate the CD4+/CD8+ T cell ratio, ultimately strengthening mucosal immunity against H9N2. Although the H9N2 avian influenza virus exhibits low pathogenicity in humans compared to other avian influenza subtypes, these findings suggest potential implications for the prevention of highly pathogenic avian influenza (289). Luteolin-7-O-glucoside (LUT-7G) has been demonstrated to ameliorate lung injury and inhibit respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) replication by preserving mitochondrial function in alveolar macrophages and promoting the production of protective interferon-β (290).
The presence of COVID-19 not only leads to severe pneumonia and associated sequelae but also significantly affects the epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance patterns of other respiratory pathogens (291, 292). The cytokine storm in COVID-19 is an exaggerated immune response characterized by the excessive synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines, potentially resulting in ARDS and multi-organ failure. It is closely associated with the rapid deterioration of COVID-19 and high mortality rates (293). An RCT has shown that a flavonoid-containing mouthwash can effectively reduce the viral load of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva (294). Lianhua Qingwen Capsules, which have been clinically validated for the treatment of COVID-19, contain forsythoside as a main active ingredient, which includes rutin, quercetin, and other flavonoids, confirming the therapeutic efficacy of flavonoids against COVID-19 infection indirectly (295). Diosmetin-7-O-β-D-pyran glucoside (DG) and kaempferol can modulate M1/M2 macrophage polarization, suppress endotoxin-induced cytokine storms, enhance mouse survival rates, and concurrently limit viral activity and replication (296, 297). Furthermore, the combination of quercetin and dasatinib has been found to reduce the infiltration of macrophages and neutrophils in pulmonary tissue, thereby mitigating the inflammatory response in the lungs of patients with COVID-19 (298). It is worth noting that hesperidin and its aglycone metabolite hesperetin demonstrated antiviral effects at multiple stages of COVID-19 infection. Hesperetin can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Spike -induced activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, thereby attenuating excessive inflammatory responses (299). Hesperidin interferes with the binding between the spike protein and human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2), thus suppressing intercellular transmission and immune evasion of SARS-CoV-2 (300). Furthermore, hesperetin can directly inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication (301). These findings indicate that hesperidin and hesperetin exert inhibitory effects across multiple phases of the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle. Moreover, hesperetin and hesperidin are reported to directly suppress viral replication in other pathogens such as RSV, zika virus (ZIKV), chikungunya virus (CHIKV), suggesting them as potential broad-spectrum antiviral agents with multi-target mechanisms (302, 303). These evidences highlight the therapeutic potential of hesperidin and hesperetin in managing viral infections and co-infections. Further investigation is warranted to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which hesperidin and hesperetin act at different stages of these viral infections.
Another important finding is that many flavonoids have been proven to significantly inhibit the release of elastase from neutrophils. Neutrophil elastase is a potent proteolytic enzyme secreted by neutrophils as part of the innate immune response to infection. However, overactivation can lead to structural damage to alveolar and vascular tissues, contributing to the pathogenesis of COVID-19 and other pulmonary disorders. The inhibition of elastase allows flavonoids to assume a protective function, improving clinical outcomes in multiple respiratory diseases (304).
4.6 Anti-inflammatory effects in asthma and allergic diseases
Asthma and allergic diseases are characterized by chronic inflammation and atypical immune responses, mediated through complex interactions among multiple immune cells, with both innate and adaptive immunity being essential. Asthma frequently co-occurs with other allergic diseases—such as allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, and food allergies—posing significant challenges to accurate diagnosis and effective management, ultimately influencing patients’ quality of life (305). An RCT indicated that oral quercetin supplementation can effectively mitigate symptoms associated with allergic rhinitis induced by pollen (306). Furthermore, epidemiological evidence from a cohort study indicated an inverse association between maternal dietary intake of flavonoids during pregnancy and the subsequent risk of childhood asthma development (307). Flavonoids can markedly inhibit the release of histamine and pro-inflammatory cytokines from mast cells, which are central mediators in allergic responses (308). Through their immunoregulatory properties, flavonoids contribute significantly to the alleviation and management of various asthma and allergic diseases.
4.6.1 Anti-inflammatory effects in asthma and allergic airway inflammation
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disorder, and recent years have witnessed significant progress in understanding the role of type 2 immunity in its pathogenesis. Type 2 immunity is an immune response driven by Th2 cells, resulting in the synthesis of allergen-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) and the activation of mast cells and basophils (309). Flavonoids exhibit diverse therapeutic potential in targeting airway hyperresponsiveness, inflammation, and tissue remodeling in asthma. They can modulate β-catenin to inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and thereby mitigate airway remodeling in asthma (310). Additionally, they are capable of regulating the Th1/Th2 immune balance. Research has found that tectorigenin can reestablish this equilibrium in asthmatic mice by upregulating the expression of Th1-associated factors while suppressing Th2 cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, consequently reducing serum IgE levels. This immunoregulatory effect has been linked to the activation of the antioxidant Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway (311). Tectochrysin and sophoraflavanone G have also been found to suppress Th2 responses and augment the antioxidant capacity of lung tissue, thus ameliorating allergic airway inflammation (312, 313). Flavonoids additionally regulate key intracellular signaling pathways in both immune and structural cells. Daphnetin exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting intracellular Ca²+ mobilization and suppressing the JAK/STAT6 signaling pathway—a critical axis involved in Th2 cytokine production—thereby alleviating allergic airway inflammation (314). Wogonoside can significantly reduce airway inflammation and excessive mucus production while enhancing airway remodeling by inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and STAT6 in lung tissue and bronchial epithelial cells, as well as decreasing Th2-related cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, IL-13) in lung tissue and serum IgE levels (315). Moreover, flavonoids can regulate immune cells implicated in asthma pathogenesis. Tilianin suppresses Th2 immune responses by down-regulating interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) in DCs, therefore mitigating house dust mite-induced allergic asthma (316).
4.6.2 Anti-inflammatory effects in atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic and recurrent inflammatory dermatosis that belongs to the spectrum of atopic diseases, which also includes asthma and food allergies. In atopic dermatitis, an exaggerated type 2 immune response, predominantly facilitated by Th2 cells, can induce skin inflammation and provoke neural sensitization, resulting in intense pruritus (317). Flavonoids have demonstrated efficacy in alleviating symptoms by regulating skin-infiltrating immune cells and restoring epidermal barrier integrity. Research on a ternary compound formula containing ginsenoside Rg1, tetrandrine, and icaritin (GTI) can mitigate atopic dermatitis-like symptoms by reducing the infiltration of eosinophils, mast cells, and CD4+ T cells in skin tissue, as well as reducing IgE-mediated reactions and inhibiting MAPK signaling activation. Furthermore, it enhances epidermal barrier function by promoting the expression of tight junction proteins (318). Emerging technologies are being developed to overcome the challenge of flavonoid delivery across the skin barrier. A microneedle-based delivery system incorporating epigallocatechin gallate and L-ascorbic acid-loaded poly-γ-glutamic acid has been found to substantially ameliorate atopic dermatitis symptoms in mice, significantly decrease serum IgE and histamine levels, and downregulate Th2-type immune responses, ultimately enhancing atopic dermatitis outcomes (319).
4.6.3 Anti-inflammatory effects in food allergy
Food allergy is a potentially life-threatening condition, triggered by IgE-mediated mast cell activation. These findings suggest that although mast cells are central to the classical allergic reaction pathway, other immune cells, like basophils and neutrophils, may also contribute. A range of flavonoids has demonstrated efficacy in mitigating food allergy. Formononetin, an isoflavone, not only inhibits degranulation of mast cells and basophils but also directly suppresses IgE production by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells through modulation of the JAK/STAT/PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, thereby attenuating allergic responses (127). In an ovalbumin-induced murine model of food allergy, nevadensin alleviates food allergy symptoms by inhibiting the c-Kit receptor, reducing the proliferation of bone marrow-derived mast cells, and promoting their apoptosis (320). Dihydromyricetin not only lowers the quantity of B cells and mast cells in the spleens of ovalbumin-allergic mice but also increases the population of Tregs, thereby ameliorating food hypersensitivity (321). Emerging evidence highlights the interplay between flavonoids, the immune system, and gut health as a promising avenue for alleviating allergic diseases. A comparative study has demonstrated that neohesperidin dihydrochalcone (NHDC), an artificially structurally modified flavonoid, exhibits superior efficacy in mitigating ovalbumin-induced food allergy in mice compared to its precursor compound, neohesperidin (NH). NHDC is more effective in restoring Th1/Th2 immune homeostasis and suppressing NOTCH/NF-κB signaling activation in the spleen. Both compounds can positively regulate the gut microbiota by enhancing the abundance of probiotic bacteria such as Lactobacillus, therefore ameliorating allergic symptoms. These findings underscore the potential of structural modifications to significantly enhance the anti-allergic properties of flavonoids (322).
5 Strategies to enhance the bioavailability of flavonoids
Although the immunoregulatory and anti-inflammatory properties of flavonoids have been demonstrated through in vitro and in vivo experiments as well as clinical studies, their therapeutic potential is constrained by low bioavailability. A major contributing factor is the low water solubility and limited membrane permeability exhibited by many flavonoids, which result in minimal gastrointestinal absorption (323). Fortunately, emerging technologies offer strategies to overcome these pharmacokinetic barriers, improving the clinical prospects of flavonoid therapies.
5.1 Nanotechnology
Studies have shown that nanotechnology and nanomaterials have successfully enhanced the water solubility and absorption of flavonoids. A notable example is naringenin, a hydrophobic flavonoid with limited aqueous solubility and stability. Electrospun pullulan nanofibers have been shown to rapidly disintegrate in artificial saliva and completely dissolve in water. When loaded with naringenin and sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin, these nanofibers significantly improve the aqueous solubility of naringenin, thereby enhancing its potential for oral absorption (324). The porous structure and plasticity exhibited by nanomaterials facilitate precise modulation of drug release profiles, enabling sustained, targeted, and stimuli-responsive delivery in therapeutic settings. Specially designed nanomaterials can effectively encapsulate poorly water-soluble drugs and regulate their release rate. In a mouse model of osteoarthritis, MXene-quercetin demonstrated superior effects in protective cartilage compared to free quercetin, highlighting the therapeutic advantages of nanodelivery systems (325). Topical drug delivery relies on passive diffusion, and prolonged drug retention helps improve efficacy. Nanocrystals can improve drug solubility and skin adhesion. Rutin nanocrystal gel exhibits more than 3 times higher permeability than conventional rutin gel, highlighting the substantial improvement enabled by nanotechnology (326). Nanomaterials can also help change the gastrointestinal absorption pathways of flavonoids. Lipid−based nanoparticles can encapsulate flavonoids and promote their integration into chylomicrons in the intestinal tract. These chylomicrons are then transported to the lymphatic vessels rather than the portal vein, thereby avoiding first−pass hepatic metabolism. This route helps increase systemic exposure and enhances the oral bioavailability of flavonoids (327).
5.2 Liposome delivery
Phospholipids possess both hydrophilic and hydrophobic domains, enabling them to effectively encapsulate poorly water-soluble flavonoids. Moreover, the phospholipid bilayer membrane of liposomes exhibits high biocompatibility and membrane fluidity, making them helping to promote biological permeability and nutrient absorption. At equivalent dosing, liposomal hesperidin demonstrates superior therapeutic efficacy compared with the unformulated compound (328).
5.3 Chemical modification
Chemical modification can significantly improve the water solubility and stability of drugs, thereby improving their bioavailability. Glycosylation and methylation modification of flavonoids have emerged as promising strategies to overcome pharmacokinetic limitations. Rutin has exhibited diverse pharmacological activities, but its clinical utility is constrained by poor water solubility and low bioavailability. These limitations can be improved through glycosylation modification. In animal studies, glycosylated rutin demonstrated stronger hepatoprotective effects than the unmodified compound (329). Fisetin also faces challenges, including insufficient stability, low oral bioavailability, and poor absorption. Biocatalytic methylation using engineered methyltransferases enables efficient modification of fisetin, leading to improved solubility, chemical stability, and lipophilicity, thereby enhancing its development and application (330).
5.4 Adding cosolvents
The addition of cosolvents is one of the most effective strategies to promote the solubility of non-polar drug molecules. Cosolvents such as ethanol and propylene glycol can efficiently extract flavonoids from foods, fruits, or herbs and enhance the solubility of flavonoids in the digestive system, thereby increasing their bioavailability. Flavonoids dissolved in ethanol can be easily formulated into oral or injectable preparations, facilitating the realization of their therapeutic potential (331).
6 Discussion
This review provides a comprehensive overview of the regulatory effects of flavonoids on immune cell functions and their strategic applications in the management of inflammatory disorders (Figures 1 and 2). Studies have indicated that flavonoids regulate immune cell functioning through multi-target and multi-pathway mechanisms, exhibiting broad anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties across various inflammatory conditions. Structurally, the C6-C3-C6 backbone serves as the fundamental scaffold for the biological activities of flavonoids, while different subclasses, including flavones, flavonols, flavanones, and isoflavones, exhibit distinct functional characteristics due to variations in their molecular structures.
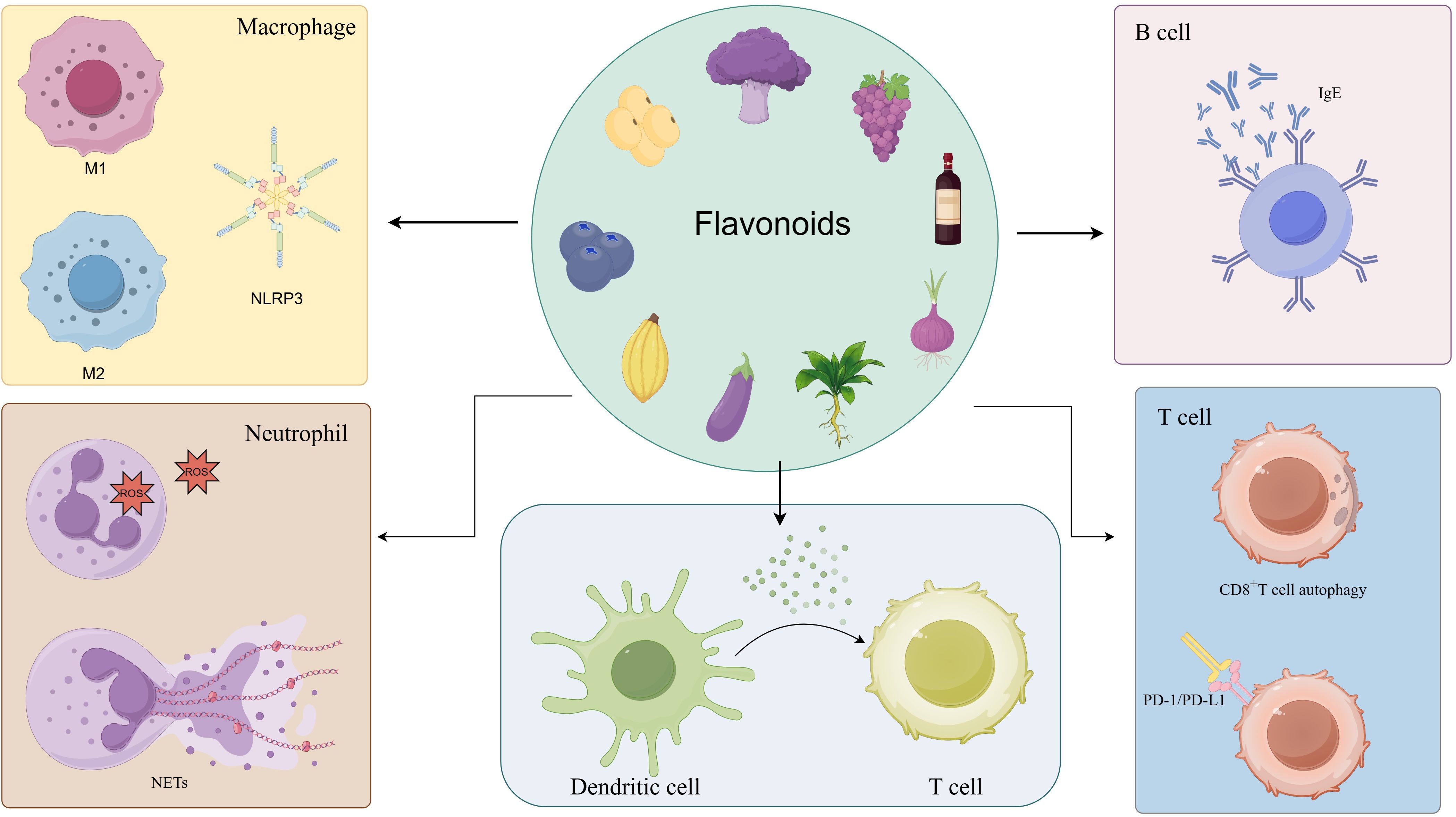
Figure 1. Flavonoids’ regulatory effects on key immune cells. Flavonoids can regulate immune cells including macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, T cells, and B cells: inhibiting the polarization of macrophages toward the pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype and facilitating their conversion to the anti-inflammatory M2 type; reducing neutrophil activation and NET formation; modulating dendritic cell maturation and antigen presentation; influencing T cell differentiation, particularly by modulating Th17/Treg balance; and suppressing B cell activation and autoantibody production.
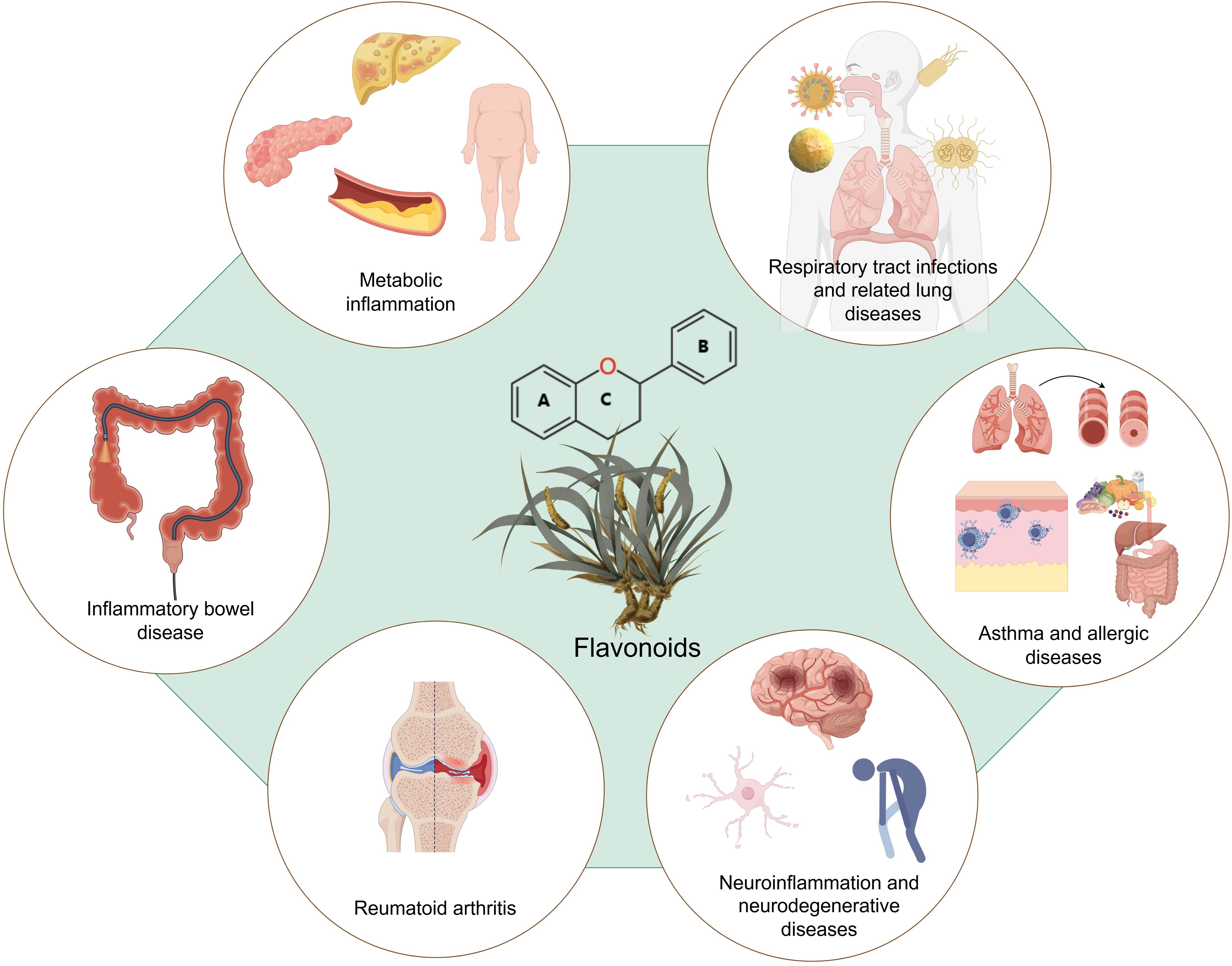
Figure 2. Flavonoids’ therapeutic applications in inflammatory diseases. Flavonoids show their therapeutic potential in inflammatory diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, metabolic inflammatory disorders, neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases, respiratory tract infections and related lung diseases, asthma and allergic diseases.
With respect to immune regulation, flavonoids exhibit substantial regulatory effects on both innate immune cells (macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells) and adaptive immune cells (T cells and B cells), highlighting their therapeutic relevance in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. In intestinal inflammatory diseases, they contribute to the reduction of gut inflammation by preserving intestinal barrier integrity and modulating gut microbiota composition. In RA, they suppress synovial inflammation and prevent bone erosion. In metabolic diseases, they improve insulin sensitivity and mitigate adipose tissue inflammation, thereby alleviating metabolic dysregulation. However, their in vivo efficacy is often constrained by their low bioavailability, influenced by physicochemical characteristics, intestinal absorption, hepatic metabolism, gut microbiota composition, etc. To overcome the challenge of limited bioavailability, emerging strategies such as nanodelivery systems, structural modifications, and prodrug formulations are being actively investigated to enhance the pharmacokinetic properties and clinical utility. Future studies could focus on optimizing the molecular structure of flavonoids, which may yield structurally modified derivatives with enhanced pharmacological potency. For inflammatory diseases such as pulmonary disorders, developing inhalable formulations may achieve higher drug concentrations at target sites. Furthermore, novel drug delivery systems, such as pH-responsive carriers and yeast encapsulation, offer promising strategies to enhance the permeability and intestinal absorption of flavonoids.
Despite considerable advancements in the investigation of the immunomodulatory properties of flavonoids, notable limitations persist in the current research. Firstly, the majority of studies have been conducted using in vitro cell models or animal models, with a lack of clinical investigations, particularly high-quality RCTs. As flavonoids are natural compounds, they face significant challenges in securing patent protection, which in turn discourages commercial investment and limits the feasibility of conducting large-scale RCTs. Existing clinical studies often suffer from single-center experiments, small sample sizes, short follow-up durations, and the absence of standardized endpoint measures, which challenge comparative analyses across studies and the establishment of conclusive evidence. Dietary prevalence of flavonoids may introduce confounding factors and compromise the internal validity of clinical studies. These limitations collectively undermine the robustness of current clinical evidence. Future clinical research on flavonoids should prioritize larger sample sizes, longer follow-up durations, and multi-center study designs to enhance statistical power and generalizability. Moreover, investigating the differential therapeutic responses to flavonoids across diverse racial and population groups warrants further exploration to support personalized treatment.
Secondly, the deficiencies in the research approach should not be ignored. The concentrations of flavonoids employed in in vitro research sometimes exceed those attainable in vivo. Moreover, variations in dosing regimens, administration routes, and animal models across studies contribute to inconsistencies and limit the comparability of findings. For example, in quercetin treatment for RA in mice, Shen et al. (332) administered quercetin orally using normal saline containing 0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose as solvent, with a maximum concentration of 100 mg/kg/day. While Yuan et al. (194) used intraperitoneal injection of a quercetin solution without reporting solvent, concentration, or dosage used. Most flavonoids exhibit poor water solubility, necessitating the use of cosolvents and solvents in experimental settings. However, the choice of such cosolvents and solvents can significantly influence the effective bioavailable concentration of the compound, thereby affecting pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic outcomes. Therefore, we recommend that studies involving flavonoids clearly report details of the administration protocol, including the compound concentration, the specific cosolvent and solvent used, the fasting status of experimental subjects, as well as the dosing frequency and route of administration. For studies employing multi-component formulations, the concentrations of individual flavonoids within the mixture should also be explicitly specified. Standardized reporting would enhance the reproducibility and facilitate robust meta-analyses to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of flavonoids. Furthermore, in vitro studies that aim to simulate oral drug exposure should verify whether the applied flavonoid concentrations are achievable through in vivo metabolism following oral intake.
Third, the investigation of molecular processes remains insufficient. While numerous signaling pathways regulated by flavonoids have been identified, investigations into broader regulatory networks, such as epigenetic regulation and immune metabolic reprogramming, are still in their infancy. Future research could focus on investigating the crosstalk among signaling pathways modulated by flavonoids, which would significantly enhance our understanding of their complex regulatory mechanisms. The potential of flavonoids as modulators of epigenetic regulators, such as TET2, is also worth investigating. Moreover, there is a lack of comprehensive pharmacokinetics and safety data for flavonoids. The absence of standardized analytical methodologies has led to considerable variability in reported bioavailability values across studies. Long-term safety evaluations of flavonoid supplementation remain insufficient, particularly for vulnerable populations such as pregnant women, children, and the elderly. Moreover, research on potential interactions between flavonoids and conventional pharmaceuticals is limited, further contributing to uncertainties regarding their clinical application. The potential for flavonoids to enhance metabolic effects through combination therapy with established pharmacological agents, such as statins, ACEI/ARB, and SGLT2/GLP-1 receptor agonists, warrants systematic investigation. Exploring synergistic interactions between flavonoids and these drug classes could reveal novel therapeutic strategies with improved efficacy.
Mechanistically, flavonoids act by concurrently modulating multiple interconnected signaling pathways, reshaping the immune network in a mild yet sustained manner rather than strongly suppressing a single pathway. This characteristic renders flavonoids particularly suitable as immunomodulatory agents for chronic inflammatory disorders, especially for long-term maintenance therapy during the early or remission phases of the disease. Future research should conceptualize flavonoids as “multi-target network regulators” rather than conventional single-target drugs and prioritize investigations into their complex mechanisms. As a broad-spectrum and multi-target therapeutic agent, flavonoids require more comprehensive and rigorous evaluation of their anti-inflammatory effects to prevent the risk of excessive immunosuppression, which may lead to increased susceptibility to infections and malignancies.
7 Conclusion
Flavonoids have demonstrated broad immunoregulatory and anti-inflammatory effects in both innate and adaptive immune cells, with evidence supporting therapeutic potential in RA, intestinal inflammatory diseases, metabolic disorders, CVD, respiratory diseases, etc. Their multi-target, network-based mechanisms appear to contribute to sustained immune regulation, indicating potential suitability for long-term management of chronic inflammatory diseases. However, key translational challenges remain, including poor bioavailability, methodological inconsistencies, and a scarcity of high-quality clinical evidence. To better understand the clinical utility of flavonoids and assess their potential as adjunctive therapies, the following areas need to be further investigated: structural optimization, drug targeting, and inhalation delivery systems, standardized research reporting, and multi-omics data integration, along with rigorous multicenter clinical trials and comprehensive safety evaluations.
Author contributions
YL: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. AJ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Cultivation fund project of National Natural Science Foundation, Liaoning Cancer Hospital, grant number 2021-ZLLH-11.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the contributions of all investigators whose research informed this study and FigDraw for figure support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Kaplan GG and Windsor JW. The four epidemiological stages in the global evolution of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 18:56–66. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-00360-x
2. Venetsanopoulou AI, Alamanos Y, Voulgari PV, and Drosos AA. Epidemiology and risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis development. Mediterr J Rheumatol. (2023) 34:404–13. doi: 10.31138/mjr.301223.eaf
3. Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature. (2017) 542:177–85. doi: 10.1038/nature21363
4. Furman D, Campisi J, Verdin E, Carrera-Bastos P, Targ S, Franceschi C, et al. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat Med. (2019) 25:1822–32. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0675-0
5. Smolen JS, Landewé RBM, Bergstra SA, Kerschbaumer A, Sepriano A, Aletaha D, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82:3–18. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223356
6. Li JX and Cummins CL. Fresh insights into glucocorticoid-induced diabetes mellitus and new therapeutic directions. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2022) 18:540–57. doi: 10.1038/s41574-022-00683-6
7. Pofi R, Caratti G, Ray DW, and Tomlinson JW. Treating the side effects of exogenous glucocorticoids; can we separate the good from the bad? Endocr Rev. (2023) 44:975–1011. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnad016
8. Dos-Santos R, Gomez-Vieites C, Fernández D, Fernández I, Vilas A, Pérez-Pampín E, et al. POS1306 treatment strategies in chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CMRO) or chronic non-bacterial osteomyelitis (cno): systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2021) 80:935. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-eular.1890
9. Martínez G, Mijares M, and De Sanctis J. Effects of flavonoids and its derivatives on immune cell responses. Recent Patents Inflammation Allergy Drug Discov. (2019) 13 2:84–104. doi: 10.2174/1872213X13666190426164124
10. Naeem A, Ming Y, Hu P-Y, Jie K, Yali L, Zhang H, et al. The fate of flavonoids after oral administration: a comprehensive overview of its bioavailability. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 62:6169–86. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1898333
11. Xiao Q, Huang J, Zhu X, Shi M, Chen L, Chen L, et al. Formononetin ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis via enhancing antioxidant capacity, promoting tight junction protein expression and reshaping M1/M2 macrophage polarization balance. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 142:113174. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113174
12. Han L, Fu Q, Deng C, Luo L, Xiang T, and Zhao H. Immunomodulatory potential of flavonoids for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and tumour. Scand J Immunol. (2021) 95:16–34. doi: 10.1111/sji.13106
13. Ottaviani JI, Fong R, Kimball J, Ensunsa JL, Britten A, Lucarelli D, et al. Evaluation at scale of microbiome-derived metabolites as biomarker of flavan-3-ol intake in epidemiological studies. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:9859. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28333-w
14. Shamsudin NF, Ahmed Q, Mahmood S, Shah SA, Khatib A, Mukhtar S, et al. Antibacterial effects of flavonoids and their structure-activity relationship study: A comparative interpretation. Mol (Basel Switzerland). (2022) 27:1149. doi: 10.3390/molecules27041149
15. Zhao H, Zhu W, Zhao X, Li X, Zhou Z, Zheng M, et al. Efficacy of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in preventing dermatitis in patients with breast cancer receiving postoperative radiotherapy: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. (2022) 158:779–86. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.1736
16. Ferdowsi S, Shidfar F, Heidari I, Kashi M, Sohouli MH, and Sarrafi Zadeh S. Effect of silymarin on lipid profile and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Phytother Res: PTR. (2024) 38:4667–74. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8273
17. Panche AN, Diwan AD, and Chandra SR. Flavonoids: an overview. J Nutr Sci. (2016) 5:e47. doi: 10.1017/jns.2016.41
18. Shen N, Wang T, Gan Q, Liu S, Wang L, and Jin B. Plant flavonoids: Classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. (2022) 383:132531. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132531
19. Ullah A, Munir S, Badshah SL, Khan N, Ghani L, Poulson BG, et al. Important flavonoids and their role as a therapeutic agent. Mol (Basel Switzerland). (2020) 25:5243. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225243
20. Li X, Chu L, Liu S, Zhang W, Lin L, and Zheng G. Smilax China L. flavonoid alleviates HFHS-induced inflammation by regulating the gut-liver axis in mice. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2021) 153728:153728. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153728
21. Zhao L, Yuan B-D, Zhao J-L, Jiang N, Zhang A, Wang G, et al. Amelioration of hexavalent chromium-induced bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, tight junction proteins and immune-related signaling factors by Allium mongolicum Regel flavonoids in Ctenopharyngodon idella. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2020) 106:99–1003. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2020.09.005
22. Chen S, Zhou Q, Chen L, Liao X, Li R, and Xie T. The Aurantii Fructus Immaturus flavonoid extract alleviates inflammation and modulate gut microbiota in DSS-induced colitis mice. Front Nutr. (2022) 9. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1013899
23. Gonzales G, Smagghe G, Grootaert C, Zotti M, Raes K, and Camp J. Flavonoid interactions during digestion, absorption, distribution and metabolism: a sequential structure–activity/property relationship-based approach in the study of bioavailability and bioactivity. Drug Metab Rev. (2015) 47:175–90. doi: 10.3109/03602532.2014.1003649
24. Zhao J, Yang J, and Xie Y. Improvement strategies for the oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble flavonoids: an overview. Int J Pharm. (2019) 118642:118642. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118642
25. Setchell KD, Brown NM, Zimmer-Nechemias L, Brashear WT, Wolfe BE, Kirschner AS, et al. Evidence for lack of absorption of soy isoflavone glycosides in humans, supporting the crucial role of intestinal metabolism for bioavailability. Am J Clin Nutr. (2002) 76:447–53. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/76.2.447
26. Qu B, Wang XL, Zheng DC, Mai CT, Liu ZQ, Zhou H, et al. Novel treatment for refractory rheumatoid arthritis with total glucosides of paeony and nobiletin codelivered in a self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system. Acta Pharmacol Sinica. (2022) 43:2094–108. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00801-6
27. Ge X, Jiang F, Wang M, Chen M, Li Y, Phipps J, et al. Naringin@Metal-organic framework as a multifunctional bioplatform. ACS Appl Mater Interf. (2023) 15:677–83. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c19904
28. Wang QS, Wang GF, Zhou J, Gao LN, and Cui YL. Colon targeted oral drug delivery system based on alginate-chitosan microspheres loaded with icariin in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Int J Pharm. (2016) 515:176–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.10.002
29. Bhagwat S and Haytowitz DB. USDA database for the flavonoid content of selected foods, Release 3.3 (March 2018). Beltsville, Maryland: US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Service (2022).
30. Dissanayake IH, Zak V, Kaur K, Jaye K, Ayati Z, Chang D, et al. Australian native fruits and vegetables: Chemical composition, nutritional profile, bioactivity and potential valorization by industries. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2023) 63:8511–44. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2057913
31. Cordeiro T, Fernandes I, Pinho O, Calhau C, Mateus N, and Faria A. Anthocyanin content in raspberry and elderberry: The impact of cooking and recipe composition. Int J Gastron Food Sci. (2021) 24:100316. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgfs.2021.100316
32. Husain A, Chanana H, Khan SA, Dhanalekshmi UM, Ali M, Alghamdi AA, et al. Chemistry and pharmacological actions of delphinidin, a dietary purple pigment in anthocyanidin and anthocyanin forms. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:746881. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.746881
33. Abebe BK and Alemayehu MT. A review of the nutritional use of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp) for human and animal diets. J Agric Food Res. (2022) 10:100383. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2022.100383
34. He F, Liang NN, Mu L, Pan QH, Wang J, Reeves MJ, et al. Anthocyanins and their variation in red wines I. Monomeric anthocyanins and their color expression. Mol (Basel Switzerland). (2012) 17:1571–601. doi: 10.3390/molecules17021571
35. Liu X, Zhang J, Di Y, Wan H, Wang K, and Nie J. Comprehensive evaluation of quality and antioxidant capacity of highbush blueberries (Vaccinium corymbosum). Foods (Basel Switzerland). (2025) 14:3251. doi: 10.3390/foods14183251
36. Davik J, Aaby K, Buti M, Alsheikh M, Šurbanovski N, Martens S, et al. Major-effect candidate genes identified in cultivated strawberry (Fragaria×ananassa Duch.) for ellagic acid deoxyhexoside and pelargonidin-3-O-malonylglucoside biosynthesis, key polyphenolic compounds. Hortic Res. (2020) 7:125. doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-00347-4
37. Burton-Freeman BM, Sandhu AK, and Edirisinghe I. Red raspberries and their bioactive polyphenols: cardiometabolic and neuronal health links. Adv Nutr (Bethesda Md). (2016) 7:44–65. doi: 10.3945/an.115.009639
38. Vaneková Z and Rollinger JM. Bilberries: curative and miraculous - A review on bioactive constituents and clinical research. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:909914. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.909914
39. Wang J, Zhao X, Zheng J, Herrera-Balandrano DD, Zhang X, Huang W, et al. In vivo antioxidant activity of rabbiteye blueberry (Vaccinium ashei cv. ‘Brightwell’) anthocyanin extracts. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. (2023) 24:602–16. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2200590
40. Venancio VP, Cipriano PA, Kim H, Antunes LM, Talcott ST, and Mertens-Talcott SU. Cocoplum (Chrysobalanus icaco L.) anthocyanins exert anti-inflammatory activity in human colon cancer and non-malignant colon cells. Food Funct. (2017) 8:307–14. doi: 10.1039/C6FO01498D
41. Knaze V, Zamora-Ros R, Luján-Barroso L, Romieu I, Scalbert A, Slimani N, et al. Intake estimation of total and individual flavan-3-ols, proanthocyanidins and theaflavins, their food sources and determinants in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) study. Br J Nutr. (2012) 108 6:1095–108. doi: 10.1017/S0007114511006386
42. Cornejal N, Pollack E, Kaur R, Persaud A, Plagianos M, Juliani HR, et al. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties of Theobroma cacao, Bourreria huanita, Eriobotrya japonica, and Elettaria cardamomum - Traditional Plants Used in Central America. J Medicinally Active Plants. (2023) 12:1–17. doi: 10.7275/wets-9869
43. Lyu W, Rodriguez D, Ferruzzi MG, Pasinetti GM, Murrough JW, Simon JE, et al. Chemical, manufacturing, and standardization controls of grape polyphenol dietary supplements in support of a clinical study: mass uniformity, polyphenol dosage, and profiles. Front Nutr. (2021) 8:780226. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.780226
44. González-Barrio R, Nuñez-Gomez V, Cienfuegos-Jovellanos E, García-Alonso FJ, and Periago-Castón MJ. Improvement of the flavanol profile and the antioxidant capacity of chocolate using a phenolic rich cocoa powder. Foods (Basel Switzerland). (2020) 9:189. doi: 10.3390/foods9020189
45. VanderWeide J, Del Zozzo F, Nasrollahiazar E, Kennedy JA, Peterlunger E, Rustioni L, et al. Influence of freezing and heating conditions on grape seed flavan-3-ol extractability, oxidation, and galloylation pattern. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:3838. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07925-7
46. Collings ER, Carmen Alamar M, Redfern S, Cools K, and Terry LA. Spatial changes in leaf biochemical profile of two tea cultivars following cold storage under two different vapour pressure deficit (VPD) conditions. Food Chem. (2019) 277:179–85. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.10.095
47. Fu H, Hu O, Xu L, Fan Y, Shi Q, Guo X, et al. Simultaneous recognition of species, quality grades, and multivariate calibration of antioxidant activities for 12 famous green teas using mid- and near-infrared spectroscopy coupled with chemometrics. J Anal Methods Chem. (2019) 2019:4372395. doi: 10.1155/2019/4372395
48. Ganesan K and Xu B. Polyphenol-rich dry common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and their health benefits. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18:2331. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112331
49. Bebek Markovinović A, Brčić Karačonji I, Jurica K, Lasić D, Skendrović Babojelić M, Duralija B, et al. Strawberry tree fruits and leaves (Arbutus unedo L.) as raw material for sustainable functional food processing: A review. Horticulturae. (2022) 8:881. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae8100881
50. Vogiatzoglou A, Mulligan A, Luben R, Lentjes M, Heiss C, Kelm M, et al. Assessment of the dietary intake of total flavan-3-ols, monomeric flavan-3-ols, proanthocyanidins and theaflavins in the European Union. Br J Nutr. (2013) 111:1463–73. doi: 10.1017/S0007114513003930
51. Haytowitz D, Wu X, and Bhagwat S. USDA Database for the proanthocyanidin content of selected foods Release 2.1. Beltsville, Maryland: US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Service (2018).
52. Ashley D, Marasini D, Brownmiller C, Lee JA, Carbonero F, and Lee SO. Impact of grain sorghum polyphenols on microbiota of normal weight and overweight/obese subjects during in vitro fecal fermentation. Nutrients. (2019) 11:217. doi: 10.3390/nu11020217
53. Mateos-Martín ML, Fuguet E, Quero C, Pérez-Jiménez J, and Torres JL. New identification of proanthocyanidins in cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum L.) using MALDI-TOF/TOF mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. (2012) 402:1327–36. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-5557-3
54. Glisan SL, Grove KA, Yennawar NH, and Lambert JD. Inhibition of pancreatic lipase by black tea theaflavins: Comparative enzymology and in silico modeling studies. Food Chem. (2017) 216:296–300. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.08.052
55. Yang CS, Chen G, and Wu Q. Recent scientific studies of a traditional chinese medicine, tea, on prevention of chronic diseases. J Tradit Complement Med. (2014) 4:17–23. doi: 10.4103/2225-4110.124326
56. Barreca D, Trombetta D, Smeriglio A, Mandalari G, Romeo O, Felice M, et al. Food flavonols: Nutraceuticals with complex health benefits and functionalities. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2021) 117:194–204. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.03.030
57. Xiong F, Zhang Y, Li T, Tang Y, Song SY, Zhou Q, et al. A detailed overview of quercetin: implications for cell death and liver fibrosis mechanisms. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1389179. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1389179
58. Wojdyło A, Nowicka P, Grimalt M, Legua P, Almansa MS, Amorós A, et al. Polyphenol compounds and biological activity of caper (Capparis spinosa L.) flowers buds. Plants (Basel Switzerland). (2019) 8:539. doi: 10.3390/plants8120539
59. Criado-Navarro I, Ledesma-Escobar CA, Pérez-Juan P, and Priego-Capote F. Distribution of main bioactive compounds from saffron species as a function of infusion temperature and time in an oil/water system. Mol (Basel Switzerland). (2024) 29:3080. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133080
60. Goulas V, Stylos E, Chatziathanasiadou MV, Mavromoustakos T, and Tzakos AG. Functional components of carob fruit: linking the chemical and biological space. Int J Mol Sci. (2016) 17:1875. doi: 10.3390/ijms17111875
61. Fusani P, Biazzi E, Mella M, Doria F, and Tava A. The flavonoids and oil composition of parsley [Petroselinum crispum (Mill) Nyman] fruits. J Food Compos Anal. (2025) 140:107288. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2025.107288
62. Wang Z, Zhao F, Wei P, Chai X, Hou G, and Meng Q. Phytochemistry, health benefits, and food applications of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.): A comprehensive review. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:1036295. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1036295
63. Lin LZ and Harnly JM. Phenolic component profiles of mustard greens, yu choy, and 15 other brassica vegetables. J Agric Food Chem. (2010) 58:6850–7. doi: 10.1021/jf1004786
64. Hostetler GL, Ralston RA, and Schwartz SJ. Flavones: food sources, bioavailability, metabolism, and bioactivity. Adv Nutr (Bethesda Md). (2017) 8:423–35. doi: 10.3945/an.116.012948
65. Poureini F, Mohammadi M, Najafpour GD, and Nikzad M. Comparative study on the extraction of apigenin from parsley leaves (Petroselinum crispum L.) by ultrasonic and microwave methods. Chem Papers. (2020) 74:3857–71. doi: 10.1007/s11696-020-01208-z
66. Singh A, Singh J, Parween G, Khator R, and Monga V. A comprehensive review of apigenin a dietary flavonoid: biological sources, nutraceutical prospects, chemistry and pharmacological insights and health benefits. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2025) 65:4529–65. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2024.2390550
67. Bautista-Hernández I, Aguilar CN, Martínez-Ávila GC, Torres-León C, Ilina A, Flores-Gallegos AC, et al. Mexican oregano (Lippia graveolens Kunth) as source of bioactive compounds: A review. Mol (Basel Switzerland). (2021) 26:5156. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175156
68. Olech M, Nowak R, Ivanova D, Tashev A, Boyadzhieva S, Kalotova G, et al. LC-ESI-MS/MS-MRM profiling of polyphenols and antioxidant activity evaluation of junipers of different origin. Appl Sci. (2020) 10:8921. doi: 10.3390/app10248921
69. Barreca D, Gattuso G, Bellocco E, Calderaro A, Trombetta D, Smeriglio A, et al. Flavanones: Citrus phytochemical with health-promoting properties. BioFactors. (2017) 43:495–506. doi: 10.1002/biof.1363
70. Cortés-Chitala M, Flores-Martínez H, Orozco-Ávila I, León-Campos C, Suárez-Jacobo Á, Estarrón-Espinosa M, et al. Identification and quantification of phenolic compounds from mexican oregano (Lippia graveolens HBK) hydroethanolic extracts and evaluation of its antioxidant capacity. Mol (Basel Switzerland). (2021) 26:702. doi: 10.3390/molecules26030702
71. Johnson JB, Hungerford NL, Sultanbawa Y, and Netzel ME. Unlocking the sublime: A review of native Australian citrus species. Foods (Basel Switzerland). (2025) 14:2425. doi: 10.3390/foods14142425
72. Ali MR, Ibrahim HH, and Salah-Eldin AA. Unveiling the chemical composition, bioactive profile and antioxidant capacity of dried Egyptian Jew’s mallow stems as a promising anticancer agent. Mol (Basel Switzerland). (2024) 29:1377. doi: 10.3390/molecules29061377
73. Danciu C, Avram Ş, Pavel I, Ghiulai R, Dehelean C, Ersilia A, et al. Main isoflavones found in dietary sources as natural anti-inflammatory agents. Curr Drug Targets. (2018) 19 7:841–53. doi: 10.2174/1389450118666171109150731
74. Bhagwat S and Haytowitz DB. USDA Database for the Isoflavone Content of Selected Foods, Release 2.1 (November 2015). Beltsville, Maryland: US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Service (2015).
75. MaChado Dutra J, Espitia PJP, and Andrade Batista R. Formononetin: Biological effects and uses – A review. Food Chem. (2021) 359:129975. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129975
76. Jaiswal N, Akhtar J, Singh SP, and Ahsan F. An overview on genistein and its various formulations. Drug Res. (2019) 69:305–13. doi: 10.1055/a-0797-3657
77. Ahmad S, Ahsan F, Ansari JA, Mahmood T, Shamim A, Bano S, et al. A review on daidzein as food supplement: Exploring its phytopharmacological and preclinical status. eFood. (2024) 5:e70008. doi: 10.1002/efd2.70008
78. Malca-Garcia GR, Liu Y, Dong H, Nikolić D, Friesen JB, Lankin DC, et al. Auto-hydrolysis of red clover as “green” approach to (iso)flavonoid enriched products. Fitoterapia. (2021) 152:104878. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2021.104878
79. Chiriac ER, Chiţescu CL, Borda D, Lupoae M, Gird CE, Geană EI, et al. Comparison of the Polyphenolic Profile of Medicago sativa L. and Trifolium pratense L. Sprouts in Different Germination Stages Using the UHPLC-Q Exactive Hybrid Quadrupole Orbitrap High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Mol (Basel Switzerland). (2020) 25:2321. doi: 10.3390/molecules25102321
80. Klejdus B, Mikelová R, Petrlová J, Potesil D, Adam V, Stiborová M, et al. Evaluation of isoflavone aglycon and glycoside distribution in soy plants and soybeans by fast column high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a diode-array detector. J Agric Food Chem. (2005) 53:5848–52. doi: 10.1021/jf0502754
81. Feng ZJ and Lai WF. Chemical and biological properties of biochanin A and its pharmaceutical applications. Pharmaceutics. (2023) 15:1105. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041105
82. Sarfraz A, Javeed M, Shah MA, Hussain G, Shafiq N, Sarfraz I, et al. Biochanin A: A novel bioactive multifunctional compound from nature. Sci Total Environ. (2020) 722:137907. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137907
83. Park MD, Silvin A, Ginhoux F, and Merad M. Macrophages in health and disease. Cell. (2022) 185:4259–79. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.10.007
84. Yunna C, Mengru H, Lei W, and Weidong C. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur J Pharmacol. (2020) 877:173090. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173090
85. Li L, Jiang W, Yu B, Liang H, Mao S, Hu X, et al. Quercetin improves cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by promoting microglia/macrophages M2 polarization via regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 168:115653. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115653
86. Fang X, Lan X, Zhu M, He M, Sun M, Cao Y, et al. Puerarin induces macrophage M2 polarization to exert antinonalcoholic steatohepatitis pharmacological activity via the activation of autophagy. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:7187–202. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c09601
87. Yang S, Duan H, Zeng J, Yan Z, Niu T, Ma X, et al. Luteolin modulates macrophage phenotypic switching via the AMPK-PPARγ pathway to alleviate ulcerative colitis in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. (2025) 339:119157. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119157
88. Wang T, Wang S, Jia X, Li C, Ma X, Tong H, et al. Baicalein alleviates cardiomyocyte death in EAM mice by inhibiting the JAK-STAT1/4 signalling pathway. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2024) 128:155558. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155558
89. Lee HS, Kwon YJ, Seo EB, Kim SK, Lee H, Lee JT, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Allium cepa L. peel extracts via inhibition of JAK-STAT pathway in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. (2023) 317:116851. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116851
90. Gongpan P, Xu T, Zhang Y, Ji K, Kong L, Wang X, et al. Apigenin alleviates inflammation as a natural IRAK4 inhibitor. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2025) 139:156519. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156519
91. Zhao X, Tang Z, Yue C, Tan Z, and Huang B. Hesperidin regulates Jagged1/Notch1 pathway to promote macrophage polarization and alleviate lung injury in mice with bronchiolitis. Zhongguo yi xue ke xue yuan xue bao Acta Academiae Medicinae Sinicae. (2022) 44:777–84. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503x.14888
92. Zeng X, Li T, Yang K, Jiang Y, Chen S, Yang S, et al. Natural compound phloretin restores periodontal immune homeostasis via HIF-1α-regulated PI3K/Akt and glycolysis in macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 141:112933. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112933
93. Vande Walle L and Lamkanfi M. Drugging the NLRP3 inflammasome: from signalling mechanisms to therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2024) 23:43–66. doi: 10.1038/s41573-023-00822-2
94. Luo X, Bao X, Weng X, Bai X, Feng Y, Huang J, et al. The protective effect of quercetin on macrophage pyroptosis via TLR2/Myd88/NF-κB and ROS/AMPK pathway. Life Sci. (2022) 291:120064. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120064
95. Zou Y, Luo X, Feng Y, Fang S, Tian J, Yu B, et al. Luteolin prevents THP-1 macrophage pyroptosis by suppressing ROS production via Nrf2 activation. Chemico biol Interact. (2021) 345:109573. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109573
96. Weng X, Luo X, Dai X, Lv Y, Zhang S, Bai X, et al. Apigenin inhibits macrophage pyroptosis through regulation of oxidative stress and the NF-κB pathway and ameliorates atherosclerosis. Phytother Res: PTR. (2023) 37:5300–14. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7962
97. Long Y, Xiang Y, Liu S, Zhang Y, Wan J, Ci Z, et al. Macrophage membrane modified baicalin liposomes improve brain targeting for alleviating cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. Nanomedicine. (2022) 43:102547. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2022.102547
98. Zhang S, Li R, Song M, Han J, and Fan X. Exploration of M2 macrophage membrane as a biotherapeutic agent and strong synergistic therapeutic effects in ischemic stroke. J Controlled Release: Off J Controlled Release Society. (2025) 378:476–89. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.11.033
99. Chen Y, Liang J, Chen S, Lin N, Xu S, Miao J, et al. Discovery of vitexin as a novel VDR agonist that mitigates the transition from chronic intestinal inflammation to colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:196. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02108-6
100. Yang Y, Han X, Chen Y, Wu J, Li M, Yang H, et al. EGCG induces pro-inflammatory response in macrophages to prevent bacterial infection through the 67LR/p38/JNK signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem. (2021) 69:5638–51. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c01353
101. Xie X, Shi Q, Wu P, Zhang X, Kambara H, Su J, et al. Single-cell transcriptome profiling reveals neutrophil heterogeneity in homeostasis and infection. Nat Immunol. (2020) 21:1119–33. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0736-z
102. Li P, Jiang M, Li K, Li H, Zhou Y, Xiao X, et al. Glutathione peroxidase 4-regulated neutrophil ferroptosis induces systemic autoimmunity. Nat Immunol. (2021) 22:1107–17. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00993-3
103. Jia J, Wang M, Meng J, Ma Y, Wang Y, Miao N, et al. Ferritin triggers neutrophil extracellular trap-mediated cytokine storm through Msr1 contributing to adult-onset Still’s disease pathogenesis. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:6804. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34560-7
104. Yin C, Liu B, Li Y, Li X, Wang J, Chen R, et al. IL-33/ST2 induces neutrophil-dependent reactive oxygen species production and mediates gout pain. Theranostics. (2020) 10:12189–203. doi: 10.7150/thno.48028
105. Liu S, Wang Y, Ying L, Li H, Zhang K, Liang N, et al. Quercetin mitigates lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC)-induced neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) formation through inhibiting the P2X7R/P38MAPK/NOX2 pathway. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:9411. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179411
106. Li C, Huang Y, Wu C, Qiu Y, Zhang L, Xu J, et al. Astilbin inhibited neutrophil extracellular traps in gouty arthritis through suppression of purinergic P2Y6 receptor. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2024) 130:155754. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155754
107. Ma X, Li M, Wang X, Xu H, Jiang L, Wu F, et al. Dihydromyricetin ameliorates experimental ulcerative colitis by inhibiting neutrophil extracellular traps formation via the HIF-1α/VEGFA signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 138:112572. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112572
108. Cao W, Huang L, Yu H, Qian Y, Liu L, Xu M, et al. Calycosin extracted from Astragali Radix reduces NETs formation to improve renal fibrosis via TLR4/NF-κB pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. (2025) 342:119391. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119391
109. Yang SC, Chen PJ, Chang SH, Weng YT, Chang FR, Chang KY, et al. Luteolin attenuates neutrophilic oxidative stress and inflammatory arthritis by inhibiting Raf1 activity. Biochem Pharmacol. (2018) 154:384–96. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.06.003
110. Shubina VS, Kozina VI, and Shatalin YV. A comparative study of the inhibitory effect of some flavonoids and a conjugate of taxifolin with glyoxylic acid on the oxidative burst of neutrophils. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:15068. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015068
111. Warnatsch A, Tsourouktsoglou TD, Branzk N, Wang Q, Reincke S, Herbst S, et al. Reactive oxygen species localization programs inflammation to clear microbes of different size. Immunity. (2017) 46:421–32. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.02.013
112. Pagano MT, Fecchi K, Pierdominici M, Ortona E, and Peruzzu D. Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells are the pharmacological target of the immunosuppressant flavonoid silibinin. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:10417. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810417
113. Ginwala R, Bhavsar R, Moore P, Bernui M, Singh N, Bearoff F, et al. Apigenin modulates dendritic cell activities and curbs inflammation via relB inhibition in the context of neuroinflammatory diseases. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol: Off J Soc NeuroImmune Pharmacol. (2021) 16:403–24. doi: 10.1007/s11481-020-09933-8
114. Song HY, Kim WS, Han JM, Seo HS, Lim ST, and Byun EB. Galangin treatment during dendritic cell differentiation confers tolerogenic properties in response to lipopolysaccharide stimulation. J Nutr Biochem. (2021) 87:108524. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108524
115. Xiong H, Chen Z, Lin B, Xie B, Liu X, Chen C, et al. Naringenin regulates FKBP4/NR3C1/NRF2 axis in autophagy and proliferation of breast cancer and differentiation and maturation of dendritic cell. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:745111. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.745111
116. Zhu J, Yamane H, and Paul WE. Differentiation of effector CD4 T cell populations (*). Annu Rev Immunol. (2010) 28:445–89. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-030409-101212
117. Jiao AA-O, Yang Z, Fu X, and Hua XA-O. Phloretin modulates human Th17/Treg cell differentiation in vitro via AMPK signaling. BioMed research international. (2020) 2020:6267924. doi: 10.1155/2020/6267924
118. Harty JT, Tvinnereim AR, and White DW. CD8+ T cell effector mechanisms in resistance to infection. Annu Rev Immunol. (2000) 18:275–308. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.275
119. Liu J, Wang N, Wu Z, Gan Y, Ji J, Huang Z, et al. Apigenin ameliorates lupus nephritis by inhibiting SAT3 signaling in CD8(+) T cells. Food Funct. (2024) 15:10020–36. doi: 10.1039/D4FO02773F
120. Zhu Q, Jiang Y, Lin W, Gao M, Chen X, Li X, et al. Naringin as a natural candidate for anti-autoimmune hepatitis: Inhibitory potency and hepatoprotective mechanism. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2024) 129:155722. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155722
121. Deng J, Wang ES, Jenkins RW, Li S, Dries R, Yates K, et al. CDK4/6 inhibition augments antitumor immunity by enhancing T-cell activation. Cancer Discov. (2018) 8:216–33. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0915
122. Chen YC, He XL, Qi L, Shi W, Yuan LW, Huang MY, et al. Myricetin inhibits interferon-γ-induced PD-L1 and IDO1 expression in lung cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. (2022) 197:114940. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.114940
123. Haoyue W, Kexiang S, Shan TW, Jiamin G, Luyun Y, Junkai W, et al. Icariin promoted ferroptosis by activating mitochondrial dysfunction to inhibit colorectal cancer and synergistically enhanced the efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2025) 136:156224. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156224
124. Yu Z, Xiaojia L, Wei Z, Jian Z, Aiting W, Jing W, et al. Baicalin circumvents anti-PD-1 resistance by regulating the gut microbiota metabolite short-chain fatty acids. Pharmacol Res. (2024) 199:107033. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.107033
125. Hao B, Lin S, Liu H, Xu J, Chen L, Zheng T, et al. Baicalein tethers CD274/PD-L1 for autophagic degradation to boost antitumor immunity. Autophagy. (2025) 21:917–33. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2024.2439657
126. Peng B, Hu Q, He R, Hou H, Lian D, Chen Y, et al. Baicalein alleviates fibrosis and inflammation in systemic sclerosis by regulating B-cell abnormalities. BMC Complement Med Ther. (2023) 23:62. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03885-1
127. Musa I, Wang ZZ, Yang N, and Li XM. Formononetin inhibits IgE by huPlasma/PBMCs and mast cells/basophil activation via JAK/STAT/PI3-Akt pathways. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1427563. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1427563
128. Huang Y, Wang N, Ji X, Luo S, Gong L, Zhao C, et al. Apigenin ameliorates inflamed ulcerative colitis by regulating mast cell degranulation via the PAMP-MRGPRX2 feedback loop. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2025) 140:156564. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156564
129. Bai D, Sun T, Lu F, Shen Y, Zhang Y, Zhang B, et al. Eupatilin suppresses OVA-induced asthma by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK and activating Nrf2 signaling pathways in mice. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:1582. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031582
130. Zugravu GS, Pintilescu C, Cumpat CM, Miron SD, and Miron A. Silymarin supplementation in active rheumatoid arthritis: outcomes of a pilot randomized controlled clinical study. Med (Kaunas Lithuania). (2024) 60. doi: 10.3390/medicina60060999
131. Yang M, Luo Y, Liu T, Zhong X, Yan J, Huang Q, et al. The effect of puerarin on carotid intima-media thickness in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: ARandomized controlled trial. Clin Ther. (2018) 40:1752–64.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2018.08.014
132. Hang Y, Qin X, Ren T, and Cao J. Baicalin reduces blood lipids and inflammation in patients with coronary artery disease and rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lipids Health Dis. (2018) 17:146. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0797-2
133. Javadi F, Ahmadzadeh A, Eghtesadi S, Aryaeian N, Zabihiyeganeh M, Rahimi Foroushani A, et al. The effect of quercetin on inflammatory factors and clinical symptoms in women with rheumatoid arthritis: A double-blind, randomized controlled trial. J Am Coll Nutr. (2017) 36:9–15. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2016.1140093
134. Bae SC, Jung WJ, Lee EJ, Yu R, and Sung MK. Effects of antioxidant supplements intervention on the level of plasma inflammatory molecules and disease severity of rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Am Coll Nutr. (2009) 28:56–62. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2009.10719762
135. Kometani T, Fukuda T, Kakuma T, Kawaguchi K, Tamura W, Kumazawa Y, et al. Effects of alpha-glucosylhesperidin, a bioactive food material, on collagen-induced arthritis in mice and rheumatoid arthritis in humans. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. (2008) 30:117–34. doi: 10.1080/08923970701812688
136. Biedermann L, Doulberis M, Schreiner P, Nielsen OH, The FO, Brand S, et al. Efficacy and safety of anthocyanin-rich extract in patients with ulcerative colitis: A randomized controlled trial. Nutrients. (2024) 16:4197. doi: 10.3390/nu16234197
137. Rastegarpanah M, Malekzadeh R, Vahedi H, Mohammadi M, Elahi E, Chaharmahali M, et al. A randomized, double blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial of silymarin in ulcerative colitis. Chin J Integr Med. (2015) 21:902–6. doi: 10.1007/s11655-012-1026-x
138. Jalili M, Vahedi H, Poustchi H, and Hekmatdoost A. Soy isoflavones and cholecalciferol reduce inflammation, and gut permeability, without any effect on antioxidant capacity in irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr ESPEN. (2019) 34:50–4. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2019.09.003
139. Navajas-Porras B, Bosch-Sierra N, Valle CG, Salazar JD, Marqués-Cardete R, Sáez G, et al. Effects of a flavonoid-enriched orange juice on antioxidant capacity, lipid profile, and inflammation in obese patients: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Food Res Int (Ottawa Ont). (2025) 217:116759. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2025.116759
140. Yari Z, Cheraghpour M, Alavian SM, Hedayati M, Eini-Zinab H, and Hekmatdoost A. The efficacy of flaxseed and hesperidin on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an open-labeled randomized controlled trial. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2021) 75:99–111. doi: 10.1038/s41430-020-0679-3
141. Teparak C, Uriyapongson J, Phoemsapthawee J, Tunkamnerdthai O, Aneknan P, Tong-Un T, et al. Diabetes therapeutics of prebiotic soluble dietary fibre and antioxidant anthocyanin supplement in patients with type 2 diabetes: randomised placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nutrients. (2025) 17:1098. doi: 10.3390/nu17071098
142. Bazyar H, Moradi L, Zaman F, and Zare Javid A. The effects of rutin flavonoid supplement on glycemic status, lipid profile, atherogenic index of plasma, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), some serum inflammatory, and oxidative stress factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Phytother Res: PTR. (2023) 37:271–84. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7611
143. Cesar TB, Ramos FMM, and Ribeiro CB. Nutraceutical eriocitrin (Eriomin) reduces hyperglycemia by increasing glucagon-like peptide 1 and downregulates systemic inflammation: A crossover-randomized clinical trial. J Medicinal Food. (2022) 25:1050–8. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2021.0181
144. de la Rubia Ortí JE, Platero JL, Yang IH, Ceron JJ, Tvarijonaviciute A, Sabater PS, et al. Possible role of butyrylcholinesterase in fat loss and decreases in inflammatory levels in patients with multiple sclerosis after treatment with epigallocatechin gallate and coconut oil: A pilot study. Nutrients. (2021) 13:3230. doi: 10.3390/nu13093230
145. Yao W, Zhang X, Xu F, Cao C, Liu T, and Xue Y. The therapeutic effects of naringenin on bronchial pneumonia in children. Pharmacol Res Perspect. (2021) 9:e00825. doi: 10.1002/prp2.825
146. Aryan H, Farahani RH, Chamanara M, Elyasi S, Jaafari MR, Haddad M, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of oral nano-silymarin formulation in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytother Res: PTR. (2022) 36:3924–31. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7537
147. Ahn-Jarvis J, Lombardo E, Cruz-Monserrate Z, Badi N, Crowe O, Kaul S, et al. Reduction of inflammation in chronic pancreatitis using a soy bread intervention: A feasibility study. Pancreatol: Off J Int Assoc Pancreatol (IAP) [et al]. (2020) 20:852–9. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.04.018
148. Navabi SM, Elieh-Ali-Komi D, Afshari D, Goudarzi F, Mohammadi-Noori E, Heydari K, et al. Adjunctive silymarin supplementation and its effects on disease severity, oxidative stress, and inflammation in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Nutr Neurosci. (2024) 27:1077–87. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2023.2301163
149. Theadom A, Mahon S, Barker-Collo S, McPherson K, Rush E, Vandal AC, et al. Enzogenol for cognitive functioning in traumatic brain injury: a pilot placebo-controlled RCT. Eur J Neurol. (2013) 20:1135–44. doi: 10.1111/ene.12099
150. Cho SH, Jo A, Casale T, Jeong SJ, Hong SJ, Cho JK, et al. Soy isoflavones reduce asthma exacerbation in asthmatic patients with high PAI-1-producing genotypes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2019) 144:109–17.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.01.020
151. Udompataikul M and Srisatwaja W. Comparative trial of moisturizer containing licochalcone A vs. hydrocortisone lotion in the treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis: a pilot study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol: JEADV. (2011) 25:660–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03845.x
152. Valls RM, Pedret A, Calderón-Pérez L, Llauradó E, Pla-Pagà L, Companys J, et al. Effects of hesperidin in orange juice on blood and pulse pressures in mildly hypertensive individuals: a randomized controlled trial (Citrus study). Eur J Nutr. (2021) 60:1277–88. doi: 10.1007/s00394-020-02279-0
153. Al Sulais E, Louis E, Bokemeyer B, Gecse KB, Parkes GC, Parkes M, et al. Differences in the adverse event burden of corticosteroid use in inflammatory bowel disease as reported between adverse event reporting systems and a patient questionnaire. J Crohn’s Colitis. (2025) 19:jjae138. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjae138
154. Mease P, Charles-Schoeman C, Cohen S, Fallon L, Woolcott J, Yun H, et al. Incidence of venous and arterial thromboembolic events reported in the tofacitinib rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis development programmes and from real-world data. Ann Rheum Dis. (2020) 79:1400–13. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216761
155. Sun S, Wang D, Dan L, Fu T, Chen J, Zhang Y, et al. Dietary anthocyanin intake, genetic risk, and incident ulcerative colitis: A prospective cohort study. Phytother Res: PTR. (2024) 38:5782–92. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8341
156. Lu SY, Dan L, Sun S, Fu T, and Chen J. Dietary quercetin intake is associated with lower ulcerative colitis risk but not Crohn’s disease in a prospective cohort study and in vivo experiments. Food Funct. (2024) 15:6553–64. doi: 10.1039/D3FO05391A
157. Ortiz-Cerda T, Argüelles-Arias F, Macías-García L, Vázquez-Román V, Tapia G, Xie K, et al. Effects of polyphenolic maqui (Aristotelia Chilensis) extract on the inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome and activation of mast cells in a mouse model of Crohn’s disease-like colitis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1229767. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1229767
158. Tao Q, Liang Q, Fu Y, Qian J, Xu J, Zhu Y, et al. Puerarin ameliorates colitis by direct suppression of macrophage M1 polarization in DSS mice. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2024) 135:156048. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156048
159. Xiao Q, Luo L, Zhu X, Yan Y, Li S, Chen L, et al. Formononetin alleviates ulcerative colitis via reshaping the balance of M1/M2 macrophage polarization in a gut microbiota-dependent manner. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2024) 135:156153. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156153
160. Che S, Qin B, Wu K, Zhu M, Hu H, Peng C, et al. EGCG drives gut microbial remodeling-induced epithelial GPR43 activation to lessen Th1 polarization in colitis. Redox Biol. (2024) 75:103291. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103291
161. Liu Y, Sun Q, Xu X, Li M, Gao W, Li Y, et al. Platycodon grandiflorus polysaccharides combined with hesperidin exerted the synergistic effect of relieving ulcerative colitis in mice by modulating PI3K/AKT and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways. Chin J Natural Med. (2025) 23:848–62. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(25)60913-7
162. Cheng C, Zhang W, Zhang C, Ji P, Wu X, Sha Z, et al. Hyperoside ameliorates DSS-induced colitis through MKRN1-mediated regulation of PPARγ Signaling and Th17/Treg balance. J Agric Food Chem. (2021) 69:15240–51. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c06292
163. Ye Q, Huang S, Wang Y, Chen S, Yang H, Tan W, et al. Wogonin improves colitis by activating the AhR pathway to regulate the plasticity of ILC3/ILC1. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2024) 128:155425. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155425
164. Yokoyama Y, Sakuraba H, Iino C, Chinda D, Shimoyama T, Fukuda S, et al. Daidzein intake is associated with equol producing status through an increase in the intestinal bacteria responsible for equol production. Nutrients. (2019) 11:433. doi: 10.3390/nu11020433
165. Zhong Q, Guo Y, Fang X, Zhang J, Wang L, Zhao L, et al. Colonization potential to reconstitute a microbe community in pseudo germ-free mice after fecal microbe transplant from equol producer. Front Microbiol. (2020) 11. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01221
166. Sun WL, Yang JW, Dou HY, Li GQ, Li XY, Shen L, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of luteolin is related to the changes in the gut microbiota and contributes to preventing the progression from simple steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Bioorg Chem. (2021) 112:104966. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104966
167. Zeng SL, Li SZ, Xiao PT, Cai YY, Chu C, Chen BZ, et al. Citrus polymethoxyflavones attenuate metabolic syndrome by regulating gut microbiome and amino acid metabolism. Sci Adv. (2020) 6:eaax6208. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax6208
168. Sun M, Wu W, Chen L, Yang W, Huang X, Ma C, et al. Microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids promote Th1 cell IL-10 production to maintain intestinal homeostasis. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:3555. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05901-2
169. Schulthess J, Pandey S, Capitani M, Rue-Albrecht KC, Arnold I, Franchini F, et al. The short chain fatty acid butyrate imprints an antimicrobial program in macrophages. Immunity. (2019) 50:432–45.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.12.018
170. Li G, Lin J, Zhang C, Gao H, Lu H, Gao X, et al. Microbiota metabolite butyrate constrains neutrophil functions and ameliorates mucosal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Microbes. (2021) 13:1968257. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1968257
171. Li W, Zhang L, Xu Q, Yang W, Zhao J, Ren Y, et al. Taxifolin alleviates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by acting on gut microbiome to produce butyric acid. Nutrients. (2022) 14:1069. doi: 10.3390/nu14051069
172. Li R, Chi H, Liao X, Cen S, and Zou Y. The glabridin from huangqin decoction prevents the development of ulcerative colitis into colitis-associated colorectal cancer by modulating MMP1/MMP3 activity. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 135:112262. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112262
173. Cao X, Li L, Hu J, Zhu S, Song S, Kong S, et al. Neohesperidin protects against colitis-associated colorectal cancer in mice via suppression of the NF-κB/p65 and MAPK pathways. J Nutr Biochem. (2025) 136:109804. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2024.109804
174. Chen Y, Wang B, Yuan X, Lu Y, Hu J, Gao J, et al. Vitexin prevents colitis-associated carcinogenesis in mice through regulating macrophage polarization. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2021) 83:153489. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153489
175. Smolen JS, Aletaha D, and McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet (London England). (2016) 388:2023–38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8
176. Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A, Burmester GR, Emery P, Firestein GS, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2018) 4:18001. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2018.1
177. Chen Y, Tang H, Luo N, Liang X, Yang P, Zhang X, et al. Association between flavonoid intake and rheumatoid arthritis among US adults. J Nutr Biochem. (2024) 131:109673. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2024.109673
178. Kou H, Huang L, Jin M, He Q, Zhang R, and Ma J. Effect of curcumin on rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1121655. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1121655
179. Jiang YP, Wen JJ, Zhao XX, Gao YC, Ma X, Song SY, et al. The flavonoid naringenin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis through curbing the migration and polarization of CD4(+) T lymphocyte driven by regulating mitochondrial fission. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 24:279. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010279
180. He X, Wu T, He H, Chen L, Han K, Zheng J, et al. Study of kaempferol in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis through modulation of the NLRP3/CASP1/GSDMD axis and T-cell activation: Based on network pharmacology, single-cell analysis, and experimental validation. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 143:113357. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113357
181. Sharma A, Tirpude NV, Bhardwaj N, Kumar D, and Padwad Y. Berberis lycium fruit extract and its phytoconstituents berberine and rutin mitigate collagen-CFA-induced arthritis (CIA) via improving GSK3β/STAT/Akt/MAPKs/NF-κB signaling axis mediated oxi-inflammation and joint articular damage in murine model. Inflammopharmacology. (2022) 30:655–66. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-00941-z
182. Tang KT, Lin CC, Lin SC, Wang JH, and Tsai SW. Kurarinone attenuates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th1/Th17 cell responses and oxidative stress. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:4002. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084002
183. Miao Y, Wu X, Xue X, Ma X, Yang L, Zeng X, et al. Morin, the PPARγ agonist, inhibits Th17 differentiation by limiting fatty acid synthesis in collagen-induced arthritis. Cell Biol Toxicol. (2023) 39:1433–52. doi: 10.1007/s10565-022-09769-3
184. Babu V, Binwal M, Ranjana, Kumari R, Sen S, Kumar A, et al. Hesperidin-rich ethanol extract from waste peels of Citrus limetta mitigates rheumatoid arthritis and related complications. Phytother Res: PTR. (2021) 35:3325–36. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7053
185. Samarpita S and Rasool M. Cyanidin restores Th17/Treg balance and inhibits T follicular helper cell differentiation via modulation of ROCK2 signaling in an experimental model of rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 101:108359. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108359
186. Huang YS, Tseng WY, Clanchy FIL, Topping LM, Ogbechi J, McNamee K, et al. Pharmacological modulation of T cell immunity results in long-term remission of autoimmune arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2021) 118:e2100939118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2100939118
187. Boutet MA, Courties G, Nerviani A, Le Goff B, Apparailly F, Pitzalis C, et al. Novel insights into macrophage diversity in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Autoimmun Rev. (2021) 20:102758. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102758
188. Li YS, Zhang J, Tian GH, Shang HC, and Tang HB. Kirenol, darutoside and hesperidin contribute to the anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of Siegesbeckia pubescens makino by inhibiting COX-2 expression and inflammatory cell infiltration. J Ethnopharmacol. (2021) 268:113547. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113547
189. Wang W, Zhai S, Yang W, Gao H, Chang N, Zhang M, et al. Acacetin alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by targeting HSP90 ATPase domain to promote COX-2 degradation. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2024) 135:156171. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156171
190. Yan Q, Liu H, Sun S, Yang Y, Fan D, Yang Y, et al. Adipose-derived stem cell exosomes loaded with icariin alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by modulating macrophage polarization in rats. J Nanobiotechnol. (2024) 22:423. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02711-1
191. McInnes IB and Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. (2007) 7:429–42. doi: 10.1038/nri2094
192. Samarpita S, Srivastava S, Srikanth M, Miriam Jose A, Rithvik A, and Rasool M. IL-17A/IL-17RA interaction blockade sensitizes synovial macrophages to efferocytosis and PD-L1 signaling via rewiring STAT-3/ADAM17/MERTK axis in rheumatoid arthritis animal model. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 136:112343. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112343
193. Wright HL, Moots RJ, and Edwards SW. The multifactorial role of neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2014) 10:593–601. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.80
194. Yuan K, Zhu Q, Lu Q, Jiang H, Zhu M, Li X, et al. Quercetin alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting neutrophil inflammatory activities. J Nutr Biochem. (2020) 84:108454. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108454
195. Teixeira FM, Coelho MN, José-Chagas FDN, Malvar DDC, Kanashiro A, Cunha FQ, et al. Oral treatments with a flavonoid-enriched fraction from Cecropia hololeuca and with rutin reduce articular pain and inflammation in murine zymosan-induced arthritis. J Ethnopharmacol. (2020) 260:112841. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112841
196. Buch MH, Eyre S, and McGonagle D. Persistent inflammatory and non-inflammatory mechanisms in refractory rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2021) 17:17–33. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-00541-7
197. Tsujimura S, Saito K, Nawata M, Nakayamada S, and Tanaka Y. Overcoming drug resistance induced by P-glycoprotein on lymphocytes in patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2008) 67:380–8. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.070821
198. Liu R, Song Y, Li C, Zhang Z, Xue Z, Huang Q, et al. The naturally occurring flavonoid nobiletin reverses methotrexate resistance via inhibition of P-glycoprotein synthesis. J Biol Chem. (2022) 298:101756. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101756
199. Chang TK, Ho TL, Lin YY, Thuong LHH, Lai KY, Tsai CH, et al. Ugonin P facilitates chondrogenic properties in chondrocytes by inhibiting miR-3074-5p production: implications for the treatment of arthritic disorders. Int J Biol Sci. (2025) 21:1378–90. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.108789
200. Yang G, Xia X, Zhong H, Shen J, and Li S. Protective effect of tangeretin and 5-hydroxy-6, 7, 8, 3’, 4’-pentamethoxyflavone on collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting autophagy via activation of the ROS-AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem. (2021) 69:259–66. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c06801
201. Cao D, Fan Q, Li Z, Chen M, Jiang Y, Lin R, et al. Transcriptomic profiling revealed the role of apigenin-4’-O-α-L-rhamnoside in inhibiting the activation of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via MAPK signaling pathway. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2022) 102:154201. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154201
202. Tall AR and Yvan-Charvet L. Cholesterol, inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. (2015) 15:104–16. doi: 10.1038/nri3793
203. Peiseler M, Schwabe R, Hampe J, Kubes P, Heikenwälder M, and Tacke F. Immune mechanisms linking metabolic injury to inflammation and fibrosis in fatty liver disease - novel insights into cellular communication circuits. J Hepatol. (2022) 77:1136–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.06.012
204. Al-Aubaidy HA, Dayan A, Deseo MA, Itsiopoulos C, Jamil D, Hadi NR, et al. Twelve-week Mediterranean diet intervention increases citrus bioflavonoid levels and reduces inflammation in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutrients. (2021) 13:1133. doi: 10.3390/nu13041133
205. Prieur X, Mok CY, Velagapudi VR, Núñez V, Fuentes L, Montaner D, et al. Differential lipid partitioning between adipocytes and tissue macrophages modulates macrophage lipotoxicity and M2/M1 polarization in obese mice. Diabetes. (2011) 60:797–809. doi: 10.2337/db10-0705
206. Bian Y, Lei J, Zhong J, Wang B, Wan Y, Li J, et al. Kaempferol reduces obesity, prevents intestinal inflammation, and modulates gut microbiota in high-fat diet mice. J Nutr Biochem. (2022) 99:108840. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2021.108840
207. Mohaghegh N, Iyer A, Wang E, Balajam NZ, Kang H, Akbari M, et al. Apigenin-loaded nanoparticles for obesity intervention through immunomodulation and adipocyte browning. J Controlled Release: Off J Controlled Release Society. (2025) 382:113670. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.113670
208. Shin YE, Choi JW, Park YI, and Kim HK. 7, 8-dihydroxyflavone attenuates inflammatory response and insulin resistance induced by the paracrine interaction between adipocytes and macrophages. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:3520. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043520
209. Zhu Z, Yu M, Xu M, Ji X, Zong X, Zhang Z, et al. Baicalin suppresses macrophage JNK-mediated adipose tissue inflammation to mitigate insulin resistance in obesity. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 332:118355. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118355
210. Yang X, Deng Y, Tu Y, Feng D, and Liao W. Nobiletin mitigates NAFLD via lipophagy and inflammation. Food Funct. (2022) 13:10186–99. doi: 10.1039/D2FO01682F
211. Sun B, Zhang R, Liang Z, Fan A, and Kang D. Hyperoside attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through targeting Nr4A1 in macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 94:107438. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107438
212. Coia H, Ma N, Hou Y, Permaul E, Berry DL, Cruz MI, et al. Theaphenon E prevents fatty liver disease and increases CD4+ T cell survival in mice fed a high-fat diet. Clin Nutr (Edinburgh Scotland). (2021) 40:110–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.04.033
213. Gallardo-Villanueva P, Fernández-Marcelo T, Villamayor L, Valverde AM, Ramos S, Fernández-Millán E, et al. Synergistic effect of a flavonoid-rich cocoa-carob blend and metformin in preserving pancreatic beta cells in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Nutrients. (2024) 16:273. doi: 10.3390/nu16020273
214. Zheng Y, Ley SH, and Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2018) 14:88–98. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.151
215. Albalawi FE, Alsharif I, Moawadh MS, Alkhoshaiban A, Falah Alshehri F, Albalawi AE, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of Kaempferol on microglial and Macrophage cells during the progression of diabetic retinopathy. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 133:112021. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112021
216. Liu J, Zhang Y, Sheng H, Liang C, Liu H, Moran Guerrero JA, et al. Hyperoside suppresses renal inflammation by regulating macrophage polarization in mice with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:733808. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.733808
217. Nan W, Yin J, Hao W, Meng H, Wu J, Yin X, et al. Cardamonin protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy by activating macrophage NRF2 signaling through molecular interaction with KEAP1. Food Funct. (2024) 15:11083–95. doi: 10.1039/D4FO03543G
218. Wang X and He B. Endothelial dysfunction: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. MedComm. (2024) 5:e651. doi: 10.1002/mco2.651
219. Wang X, Chen L, Wei J, Zheng H, Zhou N, Xu X, et al. The immune system in cardiovascular diseases: from basic mechanisms to therapeutic implications. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2025) 10:166. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02220-z
220. Barbé-Tuana F, Funchal G, Schmitz CRR, Maurmann RM, and Bauer ME. The interplay between immunosenescence and age-related diseases. Semin Immunopathol. (2020) 42:545–57. doi: 10.1007/s00281-020-00806-z
221. Prananda AT, Halim P, and Syahputra RA. Targeting miRNA with flavonoids: unlocking novel pathways in cardiovascular disease management. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:1532986. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1532986
222. Singh S, Ahuja A, and Varshney M. Potential therapeutic effects of flavonoids in cardiovascular disorders: review. Curr Hypertens Rev. (2025). doi: 10.2174/0115734021373759250730062326
223. L’Abbate S and Kusmic C. The protective effect of flavonoids in the diet on autophagy-related cardiac impairment. Nutrients. (2024) 16:2207. doi: 10.3390/nu16142207
224. Zhang Q, Hu L, Chen L, Li H, Wu J, Liu W, et al. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, the major green tea catechin, regulates the desensitization of β1 adrenoceptor via GRK2 in experimental heart failure. Inflammopharmacology. (2018) 26:1081–91. doi: 10.1007/s10787-017-0429-x
225. Fardoun MM, Maaliki D, Halabi N, Iratni R, Bitto A, Baydoun E, et al. Flavonoids in adipose tissue inflammation and atherosclerosis: one arrow, two targets. Clin Sci (London England: 1979). (2020) 134:1403–32. doi: 10.1042/CS20200356
226. Mansour H, Slika H, Nasser SA, Pintus G, Khachab M, Sahebkar A, et al. Flavonoids, gut microbiota and cardiovascular disease: Dynamics and interplay. Pharmacol Res. (2024) 209:107452. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107452
227. Zhou P, Ma YY, Zhao XN, and Hua F. Phytochemicals as potential target on thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Inflammopharmacology. (2023) 31:207–20. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-01130-8
228. Liu X, Guo JW, Lin XC, Tuo YH, Peng WL, He SY, et al. Macrophage NFATc3 prevents foam cell formation and atherosclerosis: evidence and mechanisms. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42:4847–61. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab660
229. Ma C, Hua Y, Yang S, Zhao Y, Zhang W, Miao Y, et al. Wogonin attenuates atherosclerosis via KLF11-mediated suppression of PPARα-YAP1-driven glycolysis and enhancement of ABCA1/G1-mediated cholesterol efflux. Advanced Sci (Weinheim Baden-Wurttemberg Germany). (2025) 12:e2500610. doi: 10.1002/advs.202500610
230. Luo X, Weng X, Bao X, Bai X, Lv Y, Zhang S, et al. A novel anti-atherosclerotic mechanism of quercetin: Competitive binding to KEAP1 via Arg483 to inhibit macrophage pyroptosis. Redox Biol. (2022) 57:102511. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102511
231. Bai X, Wang S, Shu L, Cao Q, Hu H, Zhu Y, et al. Hawthorn leaf flavonoids alleviate the deterioration of atherosclerosis by inhibiting SCAP-SREBP2-LDLR pathway through sPLA2-IIA signaling in macrophages in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 327:118006. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118006
232. Yu XH, Chen JJ, Deng WY, Xu XD, Liu QX, Shi MW, et al. Biochanin A mitigates atherosclerosis by inhibiting lipid accumulation and inflammatory response. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2020) 2020:8965047. doi: 10.1155/2020/8965047
233. Chu T, Wang Y, Wang S, Li J, Li Z, Wei Z, et al. Kaempferol regulating macrophage foaming and atherosclerosis through Piezo1-mediated MAPK/NF-κB and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. J Adv Res. (2025) 75:635–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.11.016
234. Sousa A, Lucas M, Ribeiro D, Correia CM, Silva VLM, Silva AMS, et al. Chalcones as modulators of neutrophil oxidative burst under physiological and high glucose conditions. J Nat Prod. (2020) 83:3131–40. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c00728
235. Mikołajczyk T and Guzik T. Adaptive immunity in hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. (2019) 21:68. doi: 10.1007/s11906-019-0971-6
236. Zhang Z, Zhao L, Zhou X, Meng X, and Zhou X. Role of inflammation, immunity, and oxidative stress in hypertension: New insights and potential therapeutic targets. Front Immunol. (2023) 13. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1098725
237. Niu Y, Chen X, Xiao L, Li W, Feng L, and Aierken A. The relationship between dietary flavonoid intake and hypertension: a cross-sectional study from NHANES. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2025) 12:1518549. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1518549
238. Jennings A, Thompson AS, Tresserra-Rimbau A, O’Neill JK, Hill C, Bondonno NP, et al. Flavonoid-rich foods, dementia risk, and interactions with genetic risk, hypertension, and depression. JAMA Netw Open. (2024) 7:e2434136. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.34136
239. Zheng Y, Fang Y, Li L, Wang H, Zhang S, Zhu Y, et al. Quercetin supplementation prevents kidney damage and improves long-term prognosis in hypertensive patients. Phytother Res: PTR. (2024) 38:5376–88. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8306
240. Lin X, Zhao J, Ge S, Lu H, Xiong Q, Guo X, et al. Dietary polyphenol intake and risk of hypertension: an 18-y nationwide cohort study in China. Am J Clin Nutr. (2023) 118:264–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.05.001
241. Gao HL, Yang Y, Tian H, Xu SL, Li BW, Fu LY, et al. Puerarin alleviates blood pressure via inhibition of ROS/TLR4/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of salt-induced prehypertensive rats. Nutrients. (2024) 16:2580. doi: 10.3390/nu16162580
242. Xu C, Zhu J, Gong G, Guo L, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, et al. Anthocyanin attenuates high salt-induced hypertension via inhibiting the hyperactivity of the sympathetic nervous system. Clin Exp Hypertens (New York NY: 1993). (2023) 45:2233717. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2023.2233717
243. Gao HL, Yu XJ, Feng YQ, Yang Y, Hu HB, Zhao YY, et al. Luteolin attenuates hypertension via inhibiting NF-κB-mediated inflammation and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Nutrients. (2023) 15:502. doi: 10.3390/nu15030502
244. Kwon HS and Koh SH. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: the roles of microglia and astrocytes. Trans Neurodegeneration. (2020) 9:42. doi: 10.1186/s40035-020-00221-2
245. Gao C, Jiang J, Tan Y, and Chen S. Microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: mechanism and potential therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:359. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01588-0
246. DeMaio A, Mehrotra S, Sambamurti K, and Husain S. The role of the adaptive immune system and T cell dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuroinflamm. (2022) 19:251. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02605-9
247. Chou ML, Babamale AO, Walker TL, Cognasse F, Blum D, and Burnouf T. Blood-brain crosstalk: the roles of neutrophils, platelets, and neutrophil extracellular traps in neuropathologies. Trends Neurosci. (2023) 46:764–79. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2023.06.005
248. Spagnuolo C, Moccia S, and Russo GL. Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids in neurodegenerative disorders. Eur J Medicinal Chem. (2018) 153:105–15. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.09.001
249. Leng F and Edison P. Neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: where do we go from here? Nat Rev Neurol. (2021) 17:157–72. doi: 10.1038/s41582-020-00435-y
250. Zong Z, Cheng X, Yang Y, Qiao J, Hao J, and Li F. Association between dietary flavonol intake and mortality risk in the U.S. adults from NHANES database. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:4572. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55145-y
251. Liu P, Zhou Y, Shi J, Wang F, Yang X, Zheng X, et al. Myricetin improves pathological changes in 3×Tg-AD mice by regulating the mitochondria-NLRP3 inflammasome-microglia channel by targeting P38 MAPK signaling pathway. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2023) 115:154801. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154801
252. Sanjay, Shin JH, Park M, and Lee HJ. Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside regulates the M1/M2 polarization of microglia via PPARγ and Aβ42 phagocytosis through TREM2 in an Alzheimer’s disease model. Mol Neurobiol. (2022) 59:5135–48. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02873-9
253. Sun XY, Li LJ, Dong QX, Zhu J, Huang YR, Hou SJ, et al. Rutin prevents tau pathology and neuroinflammation in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflamm. (2021) 18:131. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02182-3
254. Wei L, Yang X, Wang J, Wang Z, Wang Q, Ding Y, et al. H3K18 lactylation of senescent microglia potentiates brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease through the NFκB signaling pathway. J Neuroinflamm. (2023) 20:208. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02879-7
255. Liu Y, Hong T, Lv M, Guo X, Zhang P, Yan A, et al. Delphinidin attenuates cognitive deficits and pathology of Alzheimer’s disease by preventing microglial senescence via AMPK/SIRT1 pathway. Alzheimer’s Res Ther. (2025) 17:138. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01783-x
256. Kaskow BJ and Baecher-Allan C. Effector T cells in multiple sclerosis. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med. (2018) 8:a029025. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a029025
257. Baecher-Allan C, Kaskow BJ, and Weiner HL. Multiple sclerosis: mechanisms and immunotherapy. Neuron. (2018) 97:742–68. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.01.021
258. Endo K, Sawa T, Tanaka Y, Saiki T, Haga H, Rizeq L, et al. Oral administration of procyanidin B2 3, 3”-di-O-gallate ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through immunosuppressive effects on CD4(+) T cells by regulating glycolysis. Eur J Pharmacol. (2023) 954:175879. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175879
259. Liu L, Zhao Y, Bu J, Peng S, Li Y, Su P, et al. Baicalin and kaempferol alleviates cuprizone-induced demyelination and microglial activation by inhibiting the STAT3 and NF-κB signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 154:114592. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114592
260. de Almeida MMA, Pieropan F, de Mattos Oliveira L, Dos Santos Junior MC, David JM, David JP, et al. The flavonoid agathisflavone modulates the microglial neuroinflammatory response and enhances remyelination. Pharmacol Res. (2020) 159:104997. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104997
261. Candelario-Jalil E, Dijkhuizen RM, and Magnus T. Neuroinflammation, stroke, blood-brain barrier dysfunction, and imaging modalities. Stroke. (2022) 53:1473–86. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.122.036946
262. Xiao S, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Li A, Tong W, Xiong X, et al. Alpinetin inhibits neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis via targeting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in spinal cord injury. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2023) 29:1094–108. doi: 10.1111/cns.14085
263. Gu L, Sun M, Li R, Zhang X, Tao Y, Yuan Y, et al. Didymin suppresses microglia pyroptosis and neuroinflammation through the Asc/Caspase-1/GSDMD pathway following experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:810582. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.810582
264. Walker AK, Kavelaars A, Heijnen CJ, and Dantzer R. Neuroinflammation and comorbidity of pain and depression. Pharmacol Rev. (2014) 66:80–101. doi: 10.1124/pr.113.008144
265. Yuan NJ, Zhu WJ, Ma QY, Huang MY, Huo RR, She KJ, et al. Luteolin ameliorates chronic stress-induced depressive-like behaviors in mice by promoting the Arginase-1(+) microglial phenotype via a PPARγ-dependent mechanism. Acta Pharmacol Sinica. (2025) 46:575–91. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01402-9
266. Zhao K, Zhou F, Lu Y, Gao T, Wang R, Xie M, et al. Hyperoside alleviates depressive-like behavior in social defeat mice by mediating microglial polarization and neuroinflammation via TRX1/NLRP1/Caspase-1 signal pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 145:113731. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113731
267. Du L, Fan X, Yang Y, Wu S, and Liu Y. Quercetin ameliorates cognitive impairment in depression by targeting HSP90 to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Mol Neurobiol. (2024) 61:6628–41. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-03926-x
268. Shao Y, Chen Y, Lan X, Lu J, Tang G, Tang S, et al. Morin Regulates M1/M2 Microglial Polarization via NF-κB p65 to Alleviate Vincristine-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Drug Design Dev Ther. (2024) 18:3143–56. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S459757
269. Xu D, Gao LN, Song XJ, Dong QW, Chen YB, Cui YL, et al. Enhanced antidepressant effects of BDNF-quercetin alginate nanogels for depression therapy. J Nanobiotechnol. (2023) 21:379. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02150-4
270. Zhang W, Chen H, Ding L, Gong J, Zhang M, Guo W, et al. Trojan horse delivery of 4, 4’-dimethoxychalcone for parkinsonian neuroprotection. Advanced Sci (Weinheim Baden-Wurttemberg Germany). (2021) 8:2004555. doi: 10.1002/advs.202004555
271. Iwasaki A, Foxman EF, and Molony RD. Early local immune defences in the respiratory tract. Nat Rev Immunol. (2017) 17:7–20. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.117
272. Newton AH, Cardani A, and Braciale TJ. The host immune response in respiratory virus infection: balancing virus clearance and immunopathology. Semin Immunopathol. (2016) 38:471–82. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0558-0
273. Grommes J and Soehnlein O. Contribution of neutrophils to acute lung injury. Mol Med (Cambridge Mass). (2011) 17:293–307. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2010.00138
274. Wang L, Wang D, Zhang T, Ma Y, Tong X, and Fan H. The role of immunometabolism in macrophage polarization and its impact on acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1117548. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1117548
275. Ge J, Yang H, Yu N, Lin S, and Zeng Y. Wogonin alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by modulating macrophage polarization through the SIRT1-FOXO1 pathways. Tissue Cell. (2024) 88:102400. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2024.102400
276. Geng J, Zheng Z, Li L, Ren Z, Tian G, Qin J, et al. Apigenin attenuated sepsis induced acute lung injury via polarizing macrophage towards M2 by blocking miR-146a →TLR7 interaction. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 152:114446. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114446
277. Yin L, Bing Z, Zheng Y, Pan Y, Dong Y, Wang J, et al. Oroxylin A-induced trained immunity promotes LC3-associated phagocytosis in macrophage in protecting mice against sepsis. Inflammation. (2024) 47:2196–214. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02033-2
278. Li Z, Yu Y, Bu Y, Liu C, Liu E, Jin J, et al. Targeting macrophagic RasGRP1 with catechin hydrate ameliorates sepsis-induced multiorgan dysfunction. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2024) 130:155733. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155733
279. Li X, Wang Y, Chen Y, Lu Z, Sun Y, Zhong C, et al. Icariside II alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting lung epithelial inflammatory and immune responses mediated by neutrophil extracellular traps. Life Sci. (2024) 346:122648. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122648
280. Murray Ikuta CJl KS, Sharara F, Swetschinski L, Aguilar GR, and Gray A. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet (London England). (2022) 399:629–55. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02724-0
281. Lai CC, Chen SY, Ko WC, and Hsueh PR. Increased antimicrobial resistance during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Antimicrob Agents. (2021) 57:106324. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2021.106324
282. Qin S, Xiao W, Zhou C, Pu Q, Deng X, Lan L, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: pathogenesis, virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:199. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01056-1
283. Gu M and Pang Z. Luteolin inhibits inflammation and M1 macrophage polarization in the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced acute pneumonia through suppressing EGFR/PI3K/AKT/NF-κB and EGFR/ERK/AP-1 signaling pathways. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2025) 141:156663. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156663
284. Birru RL, Bein K, Bondarchuk N, Wells H, Lin Q, Di YP, et al. Antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activity of apple polyphenol phloretin on respiratory pathogens associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2021) 11:652944. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.652944
285. Guo X, Wang L, Zhang J, Liu Q, Wang B, Liu D, et al. Thwarting resistance: MgrA inhibition with methylophiopogonanone a unveils a new battlefront against S. aureus. NPJ Biofilms Microb. (2024) 10:15. doi: 10.1038/s41522-024-00485-w
286. Imanishi N, Tuji Y, Katada Y, Maruhashi M, Konosu S, Mantani N, et al. Additional inhibitory effect of tea extract on the growth of influenza A and B viruses in MDCK cells. Microbiol Immunol. (2002) 46:491–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2002.tb02724.x
287. Choi HJ, Song JH, Park KS, and Kwon DH. Inhibitory effects of quercetin 3-rhamnoside on influenza A virus replication. Eur J Pharm Sci: Off J Eur Fed Pharm Sci. (2009) 37:329–33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2009.03.002
288. Yang S, Wang L, Pan X, Liang Y, Zhang Y, Li J, et al. 5-Methoxyflavone-induced AMPKα activation inhibits NF-κB and P38 MAPK signaling to attenuate influenza A virus-mediated inflammation and lung injury in vitro and in vivo. Cell Mol Biol Lett. (2022) 27:82. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00381-1
289. Liu Z, Guo H, Zhi Y, Jiang X, and Zhang Q. Baicalin enhances respiratory mucosal immunity by modulating antiviral protein expression and T-cell homeostasis during H9N2 infection. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1593691. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1593691
290. Li W, Wang X, Chen Y, Ding Y, Ling X, Yuan B, et al. Luteolin-7-O-glucoside promotes macrophage release of IFN-β by maintaining mitochondrial function and corrects the disorder of glucose metabolism during RSV infection. Eur J Pharmacol. (2024) 963:176271. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176271
291. Baker MA, Sands KE, Huang SS, Kleinman K, Septimus EJ, Varma N, et al. The impact of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) on healthcare-associated infections. Clin Infect Dis. (2022) 74:1748–54. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab688
292. Patel A. Tackling antimicrobial resistance in the shadow of COVID-19. mBio. (2021) 12:e0047321. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00473-21
293. Jiang Y, Rubin L, Peng T, Liu L, Xing X, Lazarovici P, et al. Cytokine storm in COVID-19: from viral infection to immune responses, diagnosis and therapy. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:459–72. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.59272
294. Carrouel F, Valette M, Gadea E, Esparcieux A, Illes G, Langlois ME, et al. Use of an antiviral mouthwash as a barrier measure in the SARS-CoV-2 transmission in adults with asymptomatic to mild COVID-19: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind controlled trial. Clin Microbiol Infect. (2021) 27:1494–501. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028
295. Hu K, Guan WJ, Bi Y, Zhang W, Li L, Zhang B, et al. Efficacy and safety of Lianhuaqingwen capsules, a repurposed Chinese herb, in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A multicenter, prospective, randomized controlled trial. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2021) 85:153242. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153242
296. Xu YL, Li XJ, Cai W, Yu WY, Chen J, Lee Q, et al. Diosmetin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside from Pogostemonis Herba alleviated SARS-CoV-2-induced pneumonia by reshaping macrophage polarization and limiting viral replication. J Ethnopharmacol. (2025) 336:118704. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118704
297. Sun Y, Tao Q, Cao Y, Yang T, Zhang L, Luo Y, et al. Kaempferol has potential anti-coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) targets based on bioinformatics analyses and pharmacological effects on endotoxin-induced cytokine storm. Phytother Res: PTR. (2023) 37:2290–304. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7740
298. Lee S, Yu Y, Trimpert J, Benthani F, Mairhofer M, Richter-Pechanska P, et al. Virus-induced senescence is a driver and therapeutic target in COVID-19. Nature. (2021) 599:283–9. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03995-1
299. Arjsri P, Srisawad K, Mapoung S, Semmarath W, Thippraphan P, Umsumarng S, et al. Hesperetin from Root Extract of Clerodendrum petasites S. Moore Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 Subunit-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome in A549 Lung Cells via Modulation of the Akt/MAPK/AP-1 Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:10346. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810346
300. Kumara D, Harsan HS, Septisetyani EP, Prasetyaningrum PW, Paramitasari KA, Syaifudin M, et al. Inhibitory effects of citrus-derived flavonoids hesperidin and hesperetin on SARS-CoV-2 spike-mediated syncytia formation using in vitro cell model. Adv Pharm Bull. (2025) 15:416–27. doi: 10.34172/apb.44060
301. Fang J, Wu Q, Ye F, Cai C, Xu L, Gu Y, et al. Network-based identification and experimental validation of drug candidates toward SARS-CoV-2 via targeting virus-host interactome. Front Genet. (2021) 12:728960. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.728960
302. Sá JM, Piloto JV, Cilli EM, Tasic L, Fossey MA, Almeida FCL, et al. Hesperetin targets the hydrophobic pocket of the nucleoprotein/phosphoprotein binding site of human respiratory syncytial virus. J Biomol Struct Dyn. (2022) 40:2156–68. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1835717
303. Eberle RJ, Olivier DS, Pacca CC, Avilla CMS, Nogueira ML, Amaral MS, et al. In vitro study of Hesperetin and Hesperidin as inhibitors of zika and chikungunya virus proteases. PloS One. (2021) 16:e0246319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246319
304. Jakimiuk K, Gesek J, Atanasov AG, and Tomczyk M. Flavonoids as inhibitors of human neutrophil elastase. J Enzyme Inhibition Medicinal Chem. (2021) 36:1016–28. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2021.1927006
305. Julia V, Macia L, and Dombrowicz D. The impact of diet on asthma and allergic diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. (2015) 15:308–22. doi: 10.1038/nri3830
306. Yamada S, Shirai M, Inaba Y, and Takara T. Effects of repeated oral intake of a quercetin-containing supplement on allergic reaction: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind parallel-group study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2022) 26:4331–45. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202206_29072
307. Roy A, Goetz ME, Gebretsadik T, Kocak M, Adgent M, Zhao Q, et al. Maternal dietary flavonoid intake and child wheeze and asthma in the Conditions Affecting Neurocognitive Development and Learning in Early Childhood (CANDLE) cohort. Pediatr Allergy Immunol: Off Publ Eur Soc Pediatr Allergy Immunol. (2025) 36:e70052. doi: 10.1111/pai.70052
308. Mlcek J, Jurikova T, Skrovankova S, and Sochor J. Quercetin and its anti-allergic immune response. Mol (Basel Switzerland). (2016) 21:623. doi: 10.3390/molecules21050623
309. Ogulur I, Mitamura Y, Yazici D, Pat Y, Ardicli S, Li M, et al. Type 2 immunity in allergic diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. (2025) 22:211–42. doi: 10.1038/s41423-025-01261-2
310. Quan J, Xie D, Li Z, Yu X, Liang Z, Chen Y, et al. Luteolin alleviates airway remodeling in asthma by inhibiting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via β-catenin regulation. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2024) 135:156090. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156090
311. Jiang Y, Nguyen TV, Jin J, Yu ZN, Song CH, and Chai OH. Tectorigenin inhibits oxidative stress by activating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in Th2-mediated allergic asthmatic mice. Free Radical Biol Med. (2024) 212:207–19. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.12.031
312. Fang L, Yan Y, Xu Z, He Z, Zhou S, Jiang X, et al. Tectochrysin ameliorates murine allergic airway inflammation by suppressing Th2 response and oxidative stress. Eur J Pharmacol. (2021) 902:174100. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174100
313. Wang MC, Huang WC, Chen LC, Yeh KW, Lin CF, and Liou CJ. Sophoraflavanone G from sophora flavescens ameliorates allergic airway inflammation by suppressing Th2 response and oxidative stress in a murine asthma model. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:6104. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116104
314. Park JY, Lee JW, Oh ES, Song YN, Kang MJ, Ryu HW, et al. Daphnetin alleviates allergic airway inflammation by inhibiting T-cell activation and subsequent JAK/STAT6 signaling. Eur J Pharmacol. (2024) 979:176826. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176826
315. Yu X, Cai B, Yu L, Li N, Wu C, Hu Z, et al. Wogonoside ameliorates airway inflammation and mucus hypersecretion via NF-κB/STAT6 signaling in ovalbumin-induced murine acute asthma. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:7033–42. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c04082
316. Park SJ, Lee K, Kang MA, Kim TH, Jang HJ, Ryu HW, et al. Tilianin attenuates HDM-induced allergic asthma by suppressing Th2-immune responses via downregulation of IRF4 in dendritic cells. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2021) 80:153392. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153392
317. Guttman-Yassky E, Renert-Yuval Y, and Brunner PM. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet (London England). (2025) 405:583–96. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)02519-4
318. Wu Y, Wang XQ, Wu JY, Chen YJ, Bai JX, Li AS, et al. A tri-compound formula comprising Ginsenoside Rg1, tetrandrine and icariin alleviates atopic dermatitis symptoms in a mouse model. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2025) 141:156737. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156737
319. Chiu YH, Wu YW, Hung JI, and Chen MC. Epigallocatechin gallate/L-ascorbic acid-loaded poly-γ-glutamate microneedles with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Acta Biomaterialia. (2021) 130:223–33. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.05.032
320. Zhang YF, Shu ZD, Liu QM, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Liu H, et al. Nevadensin relieves food allergic responses and passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in mice through inhibiting the expression of c-Kit receptors. Food Funct. (2020) 11:10375–85. doi: 10.1039/D0FO02398A
321. Zhang YF, Liu QM, Liu B, Shu ZD, Han J, Liu H, et al. Dihydromyricetin inhibited ovalbumin-induced mice allergic responses by suppressing the activation of mast cells. Food Funct. (2019) 10:7131–41. doi: 10.1039/C9FO01557D
322. Liu X, Wang C, Tang S, Wang G, Huang Y, Yang F, et al. Comparative study on the alleviating effect of neohesperidin dihydrochalcones and its synthetic precursor neohesperidin on ovalbumin-induced food allergy. Food Res Int (Ottawa Ont). (2025) 212:116436. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2025.116436
323. Naeem A, Ming Y, Pengyi H, Jie KY, Yali L, Haiyan Z, et al. The fate of flavonoids after oral administration: a comprehensive overview of its bioavailability. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2022) 62:6169–86. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1898333
324. Khan N, Yadav SK, and Saneja A. Development of electrospun pullulan nanofibers encapsulating naringenin/sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex for rapid dissolution and antioxidant activity. Int J Biol Macromol. (2025) 330:147961. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.147961
325. Gan K, Li J, Zhang X, Feng Z, Liu J, and Zhao F. MXene-mediated nanocarrier delivery enhances the chondroprotective effects of quercetin in experimental osteoarthritis. Int J Nanomed. (2025) 20:11553–67. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S540035
326. Li J, Ni W, Aisha M, Zhang J, and Sun M. A rutin nanocrystal gel as an effective dermal delivery system for enhanced anti-photoaging application. Drug Dev Ind Pharmacy. (2021) 47:429–39. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2021.1890113
327. Abdi Syahputra R, Dalimunthe A, Utari ZD, Halim P, Sukarno MA, Zainalabidin S, et al. Nanotechnology and flavonoids: Current research and future perspectives on cardiovascular health. J Funct Foods. (2024) 120:106355. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2024.106355
328. Otarkhani M, Hatami H, Panahi Y, Jammal AA, Sadeghian R, and Yavari S. Niosomal hesperidin ameliorates depression-induced behavioral, histological, and molecular alterations in the rat hippocampus. Biomed Pharmacother. (2025) 191:118473. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118473
329. Tian J, Zhao Y, Li F, Xu Y, Yi W, Jiang S, et al. Enzymatic synthesis and mechanistic insights into the hepatoprotective effects of α-monoglucosyl rutin against cyclophosphamide-induced liver injury: a multi-omics approach. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 163:115265. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.115265
330. Shen T, Wang X, Zhang X, Pei J, Wang Z, Li Q, et al. Engineering of flavonoid 3’-O-methyltransferase for improved biomodification of fisetin in Escherichia coli. J Agric Food Chem. (2025) 73:11132–45. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c12864
331. Kadi RH, Alqahtani NK, Abdulfattah AM, Alsulaimani F, Basri AM, Algheshairy RM, et al. Anticancer potential of ethanolic sidr leaf extracts against MCF-7 breast cancer cells: phytochemical, nutritional, and antimicrobial profile comparisons of different plant parts. PeerJ. (2025) 13:e19858. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19858
Keywords: flavonoids, immunoregulators, immune cells, inflammatory diseases, molecular mechanism
Citation: Liu Y and Jiao A (2025) Flavonoids as Immunoregulators: Molecular Mechanisms in Regulating Immune Cells and Their Therapeutic Applications in Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 16:1703672. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1703672
Received: 12 September 2025; Accepted: 17 October 2025;
Published: 31 October 2025.
Edited by:
Kosuke Nishi, Ehime University, JapanReviewed by:
Abdullah Shaito, Qatar University, QatarRezvan Yazdian-Robati, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Liu and Jiao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ao Jiao, amlhb2Fvb3Jlb0BxcS5jb20=
 Yingshu Liu
Yingshu Liu Ao Jiao
Ao Jiao