- 1Department of Oncology, Suining Central Hospital, Suining, Sichuan, China
- 2Department of Systems Biology, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center Biomedical Research Center, Monrovia, CA, United States
- 3Department of Gastrointestinal Surgical Unit, Suining Central Hospital, Suining, Sichuan, China
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant internal RNA modification, orchestrated by writers, erasers, and readers. METTL14, a key component of the m6A methyltransferase complex, acts as a structural scaffold that ensures substrate recognition and modification precision. Beyond this canonical role, METTL14 regulates multiple biological processes, including chromatin remodeling, transcriptional activity, and senescence-associated signaling. Recent studies highlight its pivotal function in tumor immunity: METTL14 shapes T cell differentiation, CD8+ T cell activation, and the activity of macrophages and NK cells, thereby remodeling the tumor immune microenvironment. Moreover, METTL14 directly modulates immune checkpoint pathways by regulating PD-1 and PD-L1 expression, linking epitranscriptomic control with immune escape and therapeutic resistance. Aberrant METTL14 expression correlates with tumor progression and immune evasion, underscoring its potential as a predictive biomarker and therapeutic target. Targeting METTL14, alone or in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors, may provide novel strategies to enhance immunotherapy efficacy.
1 Introduction
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is one of the most prevalent internal modifications in eukaryotic mRNA and long non-coding RNA, dynamically regulated by “writers”, “erasers” and “readers” (1).” As a reversible post-transcriptional modification, m6A governs multiple aspects of RNA metabolism, including splicing, nuclear export, stability, and translational efficiency, thereby exerting profound effects on cell fate determination and environmental adaptation (2–4). In the immune system, m6A modification has been shown to regulate both innate and adaptive immune responses (5, 6). For instance, it modulates dendritic cell (DC) antigen presentation and macrophage polarization by influencing interferon signaling and cytokine expression downstream of pattern recognition receptors. At the same time, m6A controls the expression of transcription factors and signaling molecules critical for CD4+ T cell lineage commitment, CD8+ T cell activation and exhaustion, and the maintenance of regulatory T cell (Treg) suppressive functions, ultimately shaping the strength and durability of immune responses (7). Collectively, these findings underscore m6A modification as a pivotal layer connecting genomic information with immune plasticity, playing a central role in sculpting the tumor immune microenvironment.
Within the m6A writer complex, METTL14 serves as an indispensable core component. The complex primarily consists of a METTL3–METTL14 heterodimer, with auxiliary cofactors such as WTAP ensuring its nuclear localization (8). Although METTL14 itself possesses minimal catalytic activity, it provides critical RNA substrate recognition and structural stabilization, thereby dictating the site selectivity and substrate specificity of m6A deposition (9). In immune cells, the functions of METTL14 exhibit strong cell type– and context-dependent features. In Tregs, METTL14-mediated m6A modification is essential for sustaining immunosuppressive function and homeostasis (10). Conversely, in CD8+ T cells, METTL14 regulates the expression of genes associated with effector function, cytokine production, and exhaustion, thereby influencing antigen-specific immune responses and therapeutic efficacy. These findings position METTL14 not only as a structural scaffold within the m6A machinery but also as a critical regulatory node governing immune cell fate and functionality.
In recent years, the advent of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has revolutionized cancer therapy and markedly improved clinical outcomes across multiple malignancies (11). However, therapeutic responses remain highly heterogeneous, and only a subset of patients achieve durable benefit. The complexity and heterogeneity of the tumor immune microenvironment are recognized as major contributors to this variability (11). Against this backdrop, METTL14 and its mediated m6A modification have emerged as critical factors linking epigenetic regulation with tumor immunity. On one hand, METTL14 expression is closely associated with immune cell infiltration, immune-related gene expression, and patient prognosis, highlighting its potential as a predictive and prognostic biomarker (12). On the other hand, targeting METTL14 or modulating its downstream pathways may enhance the efficacy of ICIs and provide novel strategies to overcome therapeutic resistance (13). Notably, existing literature and reviews have largely focused on the role of METTL14 in tumorigenesis and cancer progression, while its contribution to tumor immune regulation remains relatively underexplored. Therefore, this review aims to systematically summarize the molecular mechanisms and biological functions of METTL14 in tumor immunity, and to further discuss its potential value and translational prospects in immunotherapy.
2 Biological functions and regulatory mechanisms of METTL14
To provide a foundation for understanding METTL14 impact on tumor immunity, this section will summarize its diverse biological functions and the multilayered regulatory mechanisms that govern its expression and activity, highlighting how these features position METTL14 as a central hub in cellular homeostasis and disease progression. METTL14 functions not only as a structural scaffold that maintains the stability and specificity of the m6A writer complex but also exerts a spectrum of m6A-independent roles (14). By regulating the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), chromatin states, and transcriptional activity, METTL14 critically influences cell fate decisions and homeostasis (15). Moreover, its expression and activity are subject to multilayered regulation, including epigenetic modifications, transcription factors, non-coding RNAs, and post-translational modifications, endowing METTL14 with remarkable dynamic plasticity across diverse physiological and pathological contexts. These molecular and network-level regulatory mechanisms not only underscore the multidimensional functionality of METTL14 but also establish its importance in tumorigenesis, immune modulation, and therapeutic resistance. Consequently, an in-depth exploration of its pathological roles and potential value in immunotherapy holds significant theoretical and translational relevance. In summary, METTL14 versatile functions and finely tuned regulatory mechanisms provide a mechanistic basis for its central role in immune regulation and tumor biology, setting the stage for a detailed examination of its specific molecular functions.
2.1 Role of METTL14 within the m6A writer complex
This section focuses on METTL14 role as a structural scaffold and substrate recognition factor within the m6A methyltransferase complex, emphasizing how these features underpin its influence on RNA metabolism and downstream immune modulation. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant internal modification in eukaryotic mRNAs and various non-coding RNAs, dynamically regulated by “writers”, “erasers” and “readers”. Among them, the m6A methyltransferase complex (MTC) constitutes the central catalytic unit, composed of both catalytic and auxiliary subunits (1). As an essential component, METTL14 acts in concert with METTL3, WTAP, and other cofactors. Structurally, METTL14 forms a stable heterodimer with METTL3. While METTL3 harbors canonical catalytic activity that transfers a methyl group from S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) to adenosine, METTL14 lacks independent enzymatic activity due to evolutionary alterations in key catalytic residues within its methyltransferase domain (8) (Figure 1). Instead, METTL14 provides an extended RNA-binding interface and stabilizes METTL3 conformation, thereby enhancing substrate recognition efficiency and modification specificity. Functionally, METTL14 ensures the precision of m6A deposition. Its ability to recognize consensus motifs (RRACH) facilitates the enrichment of m6A at intron–exon junctions, the 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR), and regions near stop codons. This distribution pattern directly influences downstream RNA splicing, nuclear export, stability, and translation (16). Furthermore, through cooperation with cofactors such as WTAP, VIRMA, and RBM15/15B, METTL14 participates in guiding the localization of m6A marks to specific RNA regions, reinforcing the spatial specificity of the modification (16). In summary, METTL14 functions not as a catalytic core but as a structural scaffold and substrate recognition factor, stabilizing the MTC and coordinating auxiliary subunits to ensure high efficiency and specificity of m6A deposition. These structural and functional attributes provide the molecular basis for its pivotal role in immune regulation and disease progression. Overall, METTL14 structural and functional contributions to the m6A writer complex ensure precise RNA modification, providing the molecular foundation for its regulatory impact on gene expression, immune function, and disease progression.
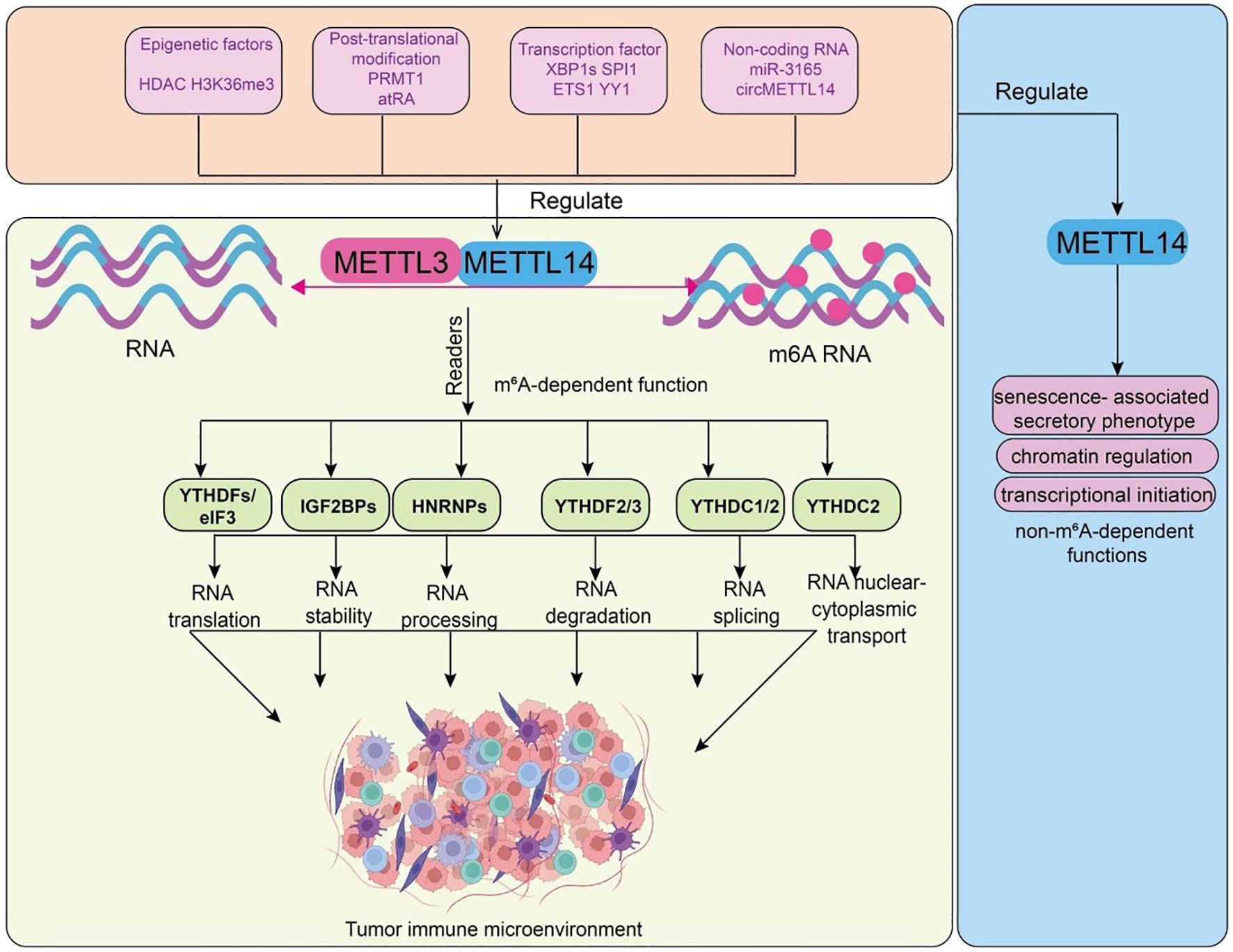
Figure 1. Functions and upstream regulatory mechanisms of METTL14. Epigenetic factors (HDAC, H3K36me3), post-translational modifications (PRMT1, atRA), transcription factors (XBP1s, SPI1, ETS1, YY1), and non-coding RNAs (miR-3165, circMETTL14) regulate the METTL3–METTL14 methyltransferase complex, leading to m6A RNA modification. m6A-modified RNAs are recognized by reader proteins, including YTHDFs/eIF3, IGF2BPs, HNRNPs, YTHDF2/3, YTHDC1/2, and YTHDC2, which regulate RNA translation, stability, processing, degradation, splicing, and nuclear–cytoplasmic transport. These events collectively reshape the tumor immune microenvironment. METTL14 non-m6A-dependent functions, including regulation of SASP, chromatin architecture, and transcriptional initiation, which contribute to its multifaceted influence on cell fate and disease.
2.2 m6A-independent functions of METTL14
Beyond its canonical role in m6A deposition, this section highlights METTL14 non-m6A-dependent functions, including regulation of SASP, chromatin architecture, and transcriptional initiation, which contribute to its multifaceted influence on cell fate and disease (Figure 1). Although METTL14 is best known as a key component of the m6A writer complex, recent studies have uncovered a range of biological functions independent of m6A modification, highlighting its multifunctionality. First, METTL14 regulates the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) in an m6A-independent manner, under conditions of without detectable changes in total m6A abundance (15). It upregulates the expression of SASP-related genes such as IL-6 and CXCL8, thereby promoting the secretion of cytokines by senescent cells (15). These secreted factors act in a paracrine manner to induce reprogramming or senescence in neighboring cells. For example, during the reprogramming of somatic cells into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), METTL14-driven SASP factor secretion by unsuccessfully reprogrammed cells enhances the reprogramming efficiency of adjacent cells (17). Second, METTL14 participates in chromatin regulation and transcriptional control, these chromatin regulatory effects were observed in cells expressing catalytically inactive METTL3, where global m6A levels remained unchanged. It binds to heterochromatic regions and recruits the histone demethylase KDM6B by recognizing the H3K27me3 mark, thereby reducing H3K27me3 levels and altering transcriptional activity. This function is critical for maintaining pluripotency and regulating differentiation in mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs), independent of its role in m6A modification (17). Together, these findings reveal that METTL14 possesses non-m6A-dependent roles in regulating SASP gene expression, remodeling chromatin architecture, and facilitating transcriptional initiation. These discoveries not only broaden our understanding of METTL14 biological versatility but also highlight its roles in cell fate determination, senescence, and disease development. Together, these findings illustrate METTL14 m6A-independent versatility, reinforcing its significance in cell senescence, differentiation, and pathological processes relevant to tumor immunity.
2.3 Upstream regulatory mechanisms of METTL14 expression
This section will examine the hierarchical and interconnected upstream mechanisms that regulate METTL14 expression and activity, demonstrating how epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and post-translational layers collectively fine-tune METTL14 function in physiological and pathological contexts (Figure 1). The expression and activity of METTL14 are finely tuned not only by its role within the m6A methyltransferase complex but also by multilayered upstream mechanisms, which ensure precise regulation across physiological and pathological contexts. These mechanisms encompass chromatin modifications, transcription factor regulation, non-coding RNA mediation, and post-translational modifications, collectively determining METTL14 transcription, translation, and protein stability. At the chromatin level, epigenetic modifications directly influence the accessibility and transcriptional activity of the METTL14 gene. In ocular melanoma, histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) markedly increase global m6A levels by restoring histone acetylation at the METTL14 promoter, reactivating its transcription (18). Upregulated METTL14 subsequently enhances FAT4 expression through an m6A-YTHDF1-dependent pathway, exerting tumor-suppressive effects (18). In pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), SETD2-mediated H3K36me3 modification upregulates METTL14 expression, leading to enhanced m6A deposition. Overexpressed METTL14 promotes pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell (PASMC) proliferation and exacerbates disease phenotypes in hypoxia-induced mouse models (19). Transcription factors also exert critical control. In breast cancer cells, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress induces XBP1s-dependent transcriptional activation of METTL3/METTL14, thereby elevating cellular m6A levels. In hematopoiesis, METTL14 is highly expressed in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) and certain acute myeloid leukemia (AML) subtypes (t(11q23), t(15;17), t(8;21)), but its expression declines during myeloid differentiation. Importantly, SPI1 negatively regulates METTL14, forming a SPI1–METTL14–MYB/MYC axis essential for normal hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis (20). In neuroblastoma, METTL14 expression is significantly elevated in high-risk patients and correlates with poor prognosis, with ETS1 and YY1 identified as upstream regulators (21). Non-coding RNAs further refine METTL14 regulation. MicroRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs modulate its expression either by directly targeting METTL14 mRNA or functioning as molecular sponges. For instance, miR-3165 suppresses METTL14 expression in bladder cancer, promoting tumor progression via the miR-3165–METTL14–USP38 axis (22). In vascular endothelial inflammation underlying atherosclerosis, circMETTL14(11)S is highly expressed upon TNF-α stimulation and positively regulates METTL14, exacerbating inflammatory responses in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) (23). Post-translational modifications (PTMs) also play a pivotal role. Phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and acetylation directly affect METTL14 stability, subcellular localization, and interactions within the MTC. For example, PRMT1-mediated arginine methylation (R255me) enhances METTL14 binding to WTAP and RNA substrates, stabilizing MTC function, maintaining global m6A levels, and promoting endodermal differentiation in embryonic stem cells (24). During ER stress, accumulated unfolded/misfolded proteins induce METTL14 expression. METTL14 then promotes CHOP mRNA degradation via m6A modification at its 3′UTR, thereby suppressing pro-apoptotic gene expression and facilitating cell adaptation to stress (25). Mechanistically, the unfolded protein response (UPR) competes with the HRD1-ERAD pathway to prevent METTL14 ubiquitination and degradation, stabilizing its protein levels (25). In palatogenesis, environmental teratogen all-trans retinoic acid (atRA) induces aberrant upregulation of METTL14, elevating m6A levels in palatal mesenchymal cells (26). This disrupts proliferation and cell cycle gene expression, promoting cleft palate formation, which can be partially alleviated by siRNA-mediated METTL14 knockdown or inhibition of the m6A methyltransferase complex with SAH. Collectively, the upstream regulation of METTL14 is hierarchical and interconnected. These multilayered regulatory mechanisms not only maintain METTL14 homeostasis under normal conditions but also enable its dynamic responses to inflammation, immune signaling, and tumor microenvironmental changes. Understanding these regulatory pathways will provide crucial insights into the central role of METTL14 in tumor immune modulation and lay the foundation for developing METTL14-targeted therapeutic strategies. Collectively, these multilayered regulatory mechanisms ensure METTL14 homeostasis and dynamic responsiveness to cellular stress, inflammation, and tumor microenvironmental cues, highlighting their critical importance for METTL14-mediated immune modulation and providing a rationale for therapeutic targeting.
3 The role of METTL14 in the TME
With the rapid advancement of cancer immunotherapy, the TME has been increasingly recognized as a central determinant of therapeutic efficacy and resistance (27). As a core component of the m6A methyltransferase complex, METTL14 not only promotes tumor initiation and progression through post-transcriptional regulation of cancer cells, but also profoundly influences the differentiation, functional maintenance, and intercellular communication of immune cells. Accumulating evidence indicates that METTL14 exerts multi-level immune regulatory effects in the TME by modulating T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs), tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), and natural killer (NK) cells, thereby reshaping the immune landscape and regulating antitumor immunity. Together, these observations underscore METTL14 as a central hub linking epitranscriptomic regulation to tumor immune modulation, which is the core argument of this review. These findings not only deepen our understanding of tumor immune evasion mechanisms but also suggest that METTL14 may represent a promising target for improving immunotherapy sensitivity and overcoming immune resistance. As summarized in Table 1, METTL14 exhibits distinct targets, regulatory mechanisms, and functional effects across different tumors and immune cells.
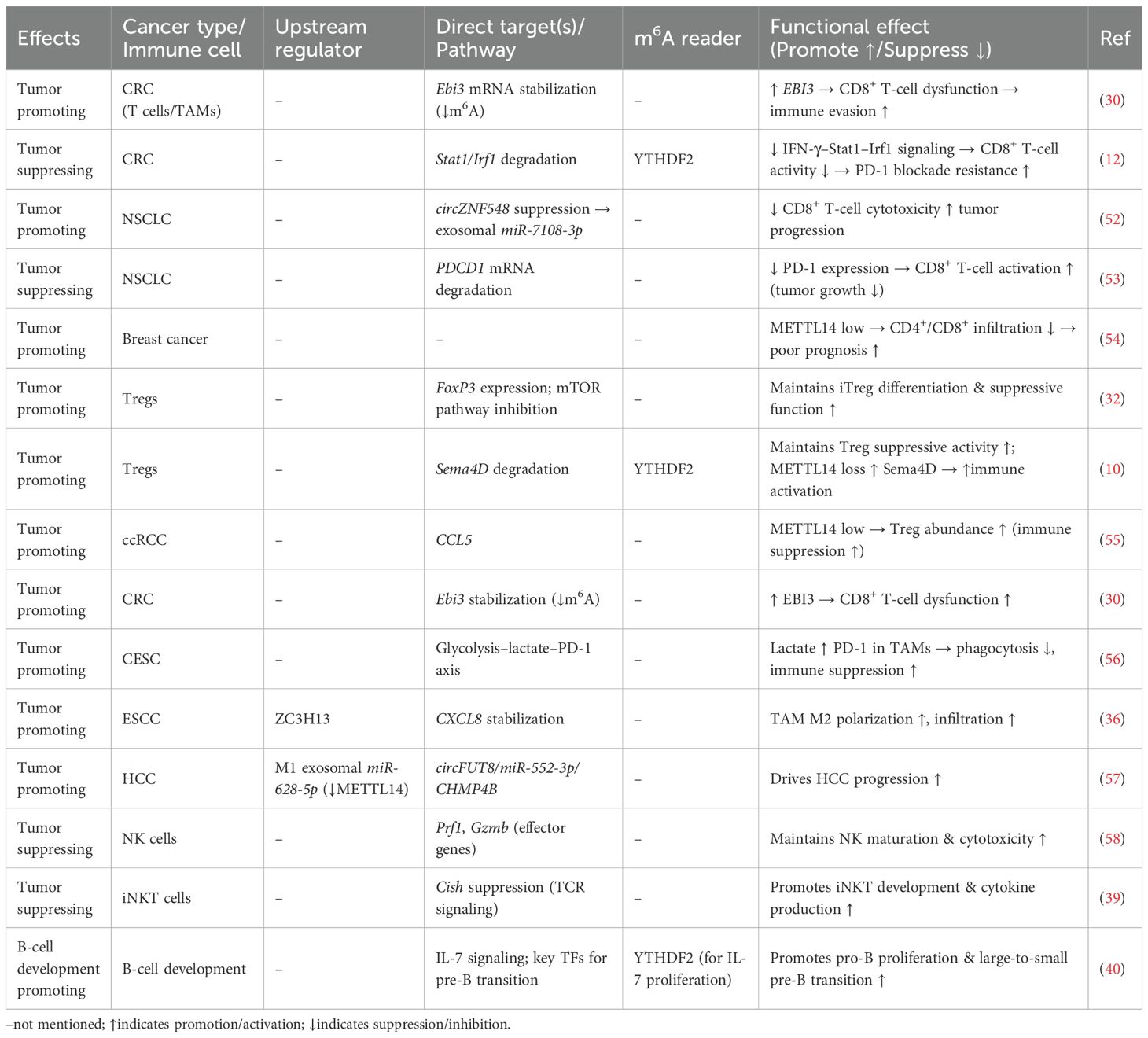
Table 1. Key targets, regulatory mechanisms, and functional effects of METTL14 in different tumors or immune cells.
3.1 Regulation of T-cell infiltration and function
T cells are the central executors of antitumor immunity, and their infiltration and cytotoxic activity are tightly regulated within the TME (28). This section illustrates how METTL14 directly modulates T-cell infiltration and cytotoxic function, highlighting its pivotal role as a mediator between m6A epitranscriptomic modification and adaptive antitumor immunity. Studies using CD4-Cre conditional knockout mice demonstrated that T cell–specific loss of Mettl14 leads to spontaneous colitis characterized by increased inflammatory infiltration, elevated colon weight/length ratio, and enhanced Th1/Th17 cytokine expression (29). Mechanistically, Mettl14 deficiency causes dysfunction of regulatory T cells (Tregs), marked by reduced RORγt expression and impaired iTreg differentiation, ultimately failing to suppress inflammatory responses (29). Rescue experiments confirmed that adoptive transfer of wild-type Tregs ameliorates colitis, while antibiotic treatment mitigates disease progression, highlighting the role of gut microbiota. In the tumor context, METTL14 plays a crucial role in TAMs. In T-cell-specific METTL14 knockout mice, alterations in CD8+ T-cell cytotoxicity were observed, indicating that METTL14 acts primarily within T cells to modulate antitumor immunity. Macrophage-specific deletion of METTL14 reduces m6A modification, thereby stabilizing Ebi3 mRNA and increasing EBI3 protein expression. Elevated EBI3 drives CD8+ T cells toward dysfunction, diminishing their cytotoxicity and fostering tumor immune evasion. Blocking EBI3 restores CD8+ T-cell activity and enhances antitumor immunity (30) (Figure 2). Consistently, clinical colorectal cancer samples show a negative correlation between METTL14 expression/m6A levels and T-cell dysfunction. In lung cancer, METTL14 stabilizes HSD17B6 mRNA through m6A modification, suppressing CD8+ T-cell infiltration and activation, ultimately facilitating tumor progression and impairing PD-1 blockade efficacy (Figure 2) (13). Similarly, in pMMR-MSI-L colorectal cancer, METTL14 promotes YTHDF2-dependent degradation of Stat1/Irf1 mRNA, dampening IFN-γ–Stat1–Irf1 signaling and limiting CD8+ T-cell activity, which restricts PD-1 immunotherapy response (Figure 2). Additional evidence shows that circZNF548, downregulated in NSCLC and associated with favorable prognosis, enhances CD8+ T-cell cytotoxicity via exosomal miR-7108-3p, while METTL14 reduces circZNF548 levels through m6A modification, thereby promoting tumor progression (Figure 2) (12). Interestingly, METTL14-mediated m6A-dependent degradation of PDCD1 mRNA reduces PD-1 expression, maintaining CD8+ T-cell activation and restraining tumor growth (12) (Figure 2). Conversely, METTL14 loss elevates PD-1 levels, impairs T-cell function, and induces immunotherapy resistance. In breast cancer, METTL14 is frequently downregulated, correlating with ER-/PR-/triple-negative subtypes, poor prognosis, and advanced progression. Importantly, low METTL14 levels are positively associated with reduced infiltration of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells as well as neutrophils, underscoring its pivotal role in modulating TME and antitumor immunity. In summary, these findings demonstrate that METTL14 regulation of T-cell activity is a key mechanism by which epitranscriptomic modifications influence antitumor immunity, supporting its role as a critical node in the TME.
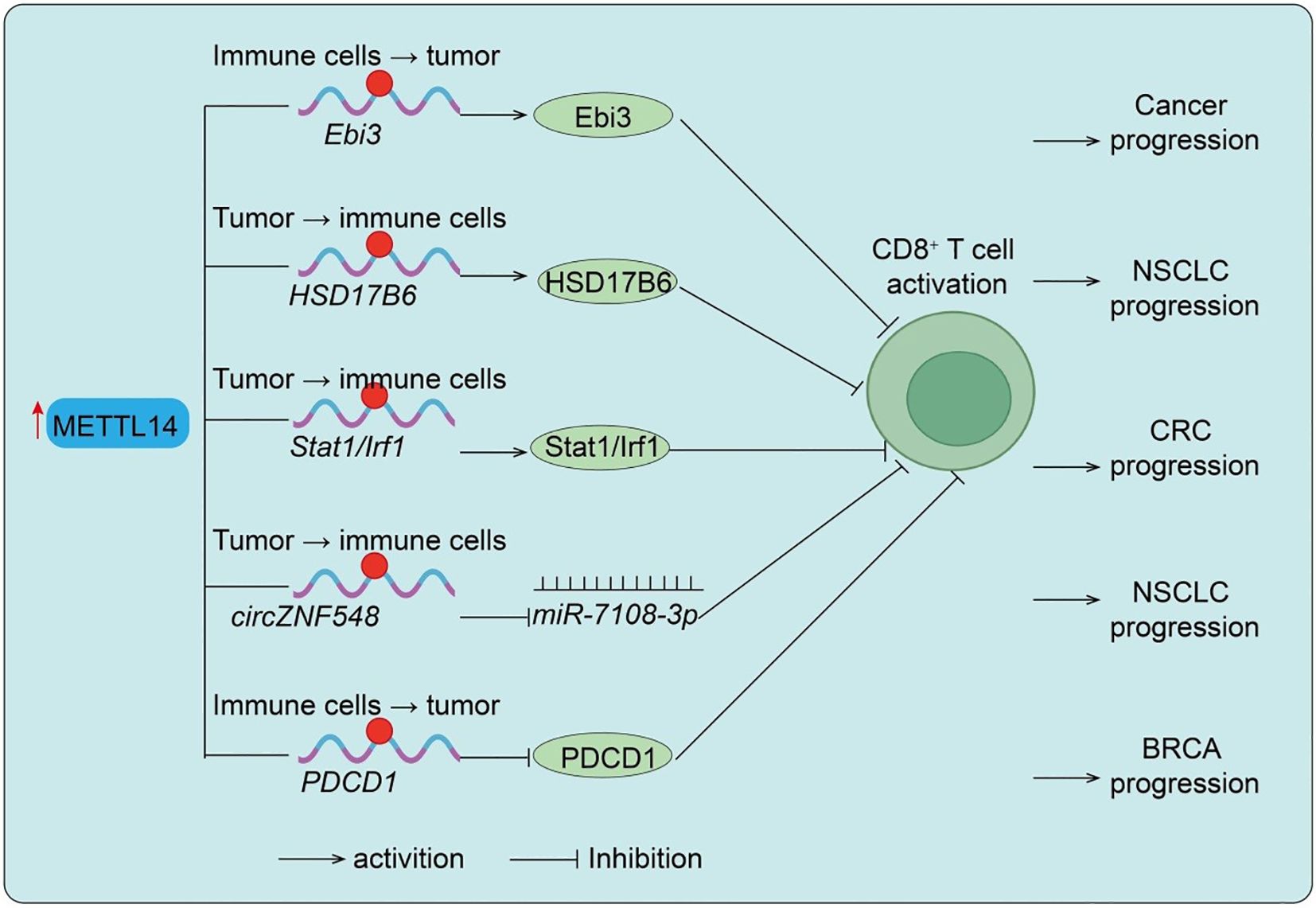
Figure 2. METTL14-mediated regulation of CD8+ T cell function in different cancers. Upregulation of METTL14 enhances m6A modification of target transcripts such as Ebi3, HSD17B6, Stat1/Irf1, and circZNF548, thereby modulating CD8+ T cell dysfunction, infiltration, activation, or killing capacity, ultimately influencing cancer progression in NSCLC and CRC. Conversely, reduced METTL14 expression leads to upregulation of PDCD1, suppressing CD8+ T cell activation and promoting BRCA progression. Tumor → immune cells indicate Tumor cell–initiated regulation of immune cells; Immune cells → tumor indicate Immune cell–intrinsic regulation of tumor cells.
3.2 Regulatory T cells (Tregs)
Tregs are indispensable for immune tolerance and play a dual role in suppressing antitumor immunity within the TME (31). Here, we show that METTL14 is essential for Treg differentiation and suppressive function, connecting its epitranscriptomic activity to the modulation of immune tolerance and tumor immune escape. In vitro studies revealed that METTL14 expression is markedly upregulated in induced Tregs (iTregs). Silencing METTL14 with siRNA reduced FoxP3 expression, impaired differentiation, and elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ and IL-17a. Functional assays confirmed that Mettl14 loss compromises iTreg suppressive capacity both in vivo (colitis mouse models) and in vitro (CFSE inhibition assays). Mechanistically, Mettl14 deficiency activates the mTOR pathway (elevated p-mTOR and p-p70S6K), disrupting iTreg stability and immunosuppressive function (32). Further studies demonstrated that Mettl14-mediated m6A modification is essential for Treg expansion and immunosuppressive cytokine production (IL-10, TGF-β). Treg-specific knockout of Mettl14 disrupts their suppressive capacity, leading to graft rejection, largely via SOCS pathway regulation (33). Moreover, Mettl14-YTHDF2–dependent degradation of Sema4D mRNA maintains Treg function, whereas METTL14 loss upregulates Sema4D (Figure 3), impairing immunosuppressive activity. Pharmacological inhibition of Sema4D restores Treg functionality and prolongs graft survival (10). Clinically, Sema4D expression negatively correlates with renal graft survival, supporting its role as a therapeutic target. In clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), METTL14 expression is inversely correlated with Treg abundance and positively associated with CCL5 levels, suggesting a METTL14/CCL5/Tregs axis that shapes the tumor immune landscape (34). Collectively, these findings underscore METTL14 as a central regulator of Treg-mediated immune suppression, reinforcing its function as a molecular link between RNA methylation and immune modulation in the TME.
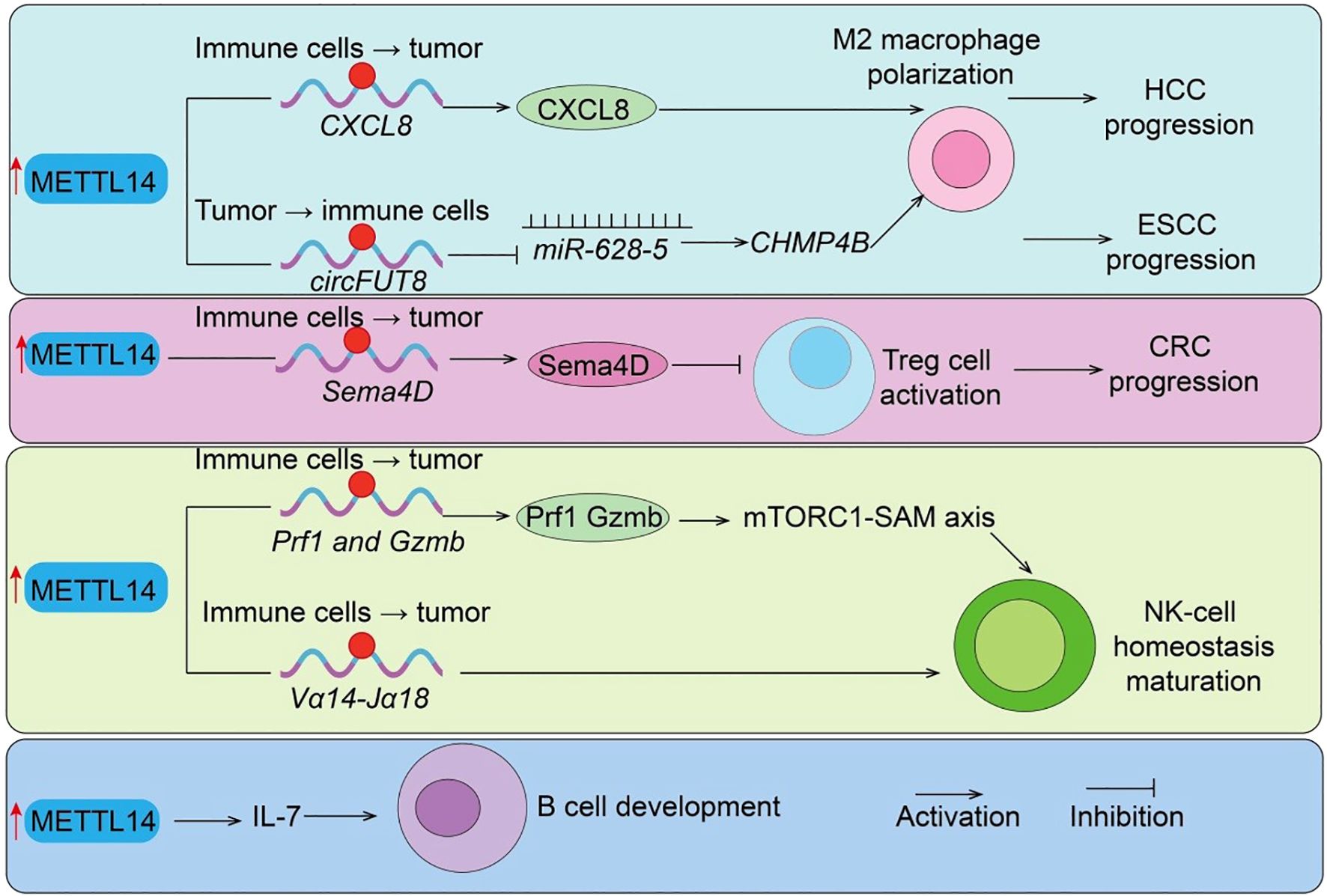
Figure 3. METTL14-mediated regulation of immunosuppressive cells and B cell development. METTL14 promotes tumor progression by regulating immune suppressive mechanisms: (i) Sema4D and circFUT8/miR-628–5 axis drive Treg cell activation and M2 macrophage polarization in CRC and HCC; (ii) CXCL8 induces M2 macrophage polarization in ESCC; (iii)Prf1/Gzmb/Mtorc1-SAM axis regulate NK cells function. (iiii) METTL14/IL7 axis regulate B cells development. Tumor → immune cells indicate Tumor cell–initiated regulation of immune cells; Immune cells → tumor indicate Immune cell–intrinsic regulation of tumor cells.
3.3 Recruitment and function of tumor-associated macrophages
Macrophages are highly plastic immune cells that critically influence tumor progression, and METTL14 has emerged as a regulator of TAM recruitment and function. This section highlights METTL14 role in orchestrating TAM behavior, providing evidence that its m6A-mediated regulation contributes to immune suppression and tumor progression, further connecting epitranscriptomic modifications to tumor immunity. TAM-specific loss of METTL14 reduces global m6A levels, stabilizing Ebi3 mRNA and increasing immunosuppressive EBI3 expression. This drives CD8+ T-cell dysfunction and weakens antitumor responses, whereas EBI3 blockade restores cytotoxic T-cell activity (30). Clinically, METTL14 expression inversely correlates with CD8+ T-cell dysfunction in colorectal cancer. In cervical cancer, METTL14 is overexpressed and enhances tumor glycolysis, producing lactate that upregulates PD-1 expression in TAMs (30). This suppresses phagocytosis and promotes an immunosuppressive TME. Functional and in vivo studies confirm the glycolysis–lactate–PD-1 axis as a critical mechanism by which METTL14 drives TAM-mediated tumor progression, identifying it as a potential therapeutic target. In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), M1 macrophage–derived exosomes deliver miR-628-5p to suppress METTL14, reducing circFUT8 methylation and nuclear export (35). METTL14 otherwise promotes circFUT8/miR-552-3p/CHMP4B signaling, driving HCC progression (Figure 3), highlighting an interplay between macrophage exosomal miRNA and METTL14-mediated circRNA regulation (35). In esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), ZC3H13 modulates METTL14/METTL3 nuclear transport and stabilizes CXCL8 mRNA, driving M2 polarization and infiltration, thereby facilitating immune evasion (36). Taken together, these studies confirm that METTL14 modulates TAM recruitment, polarization, and immunosuppressive activity, illustrating another pathway by which epitranscriptomic regulation impacts antitumor immune responses.
3.4 NK cell function
Natural killer (NK) cells are innate lymphocytes essential for early antitumor responses (37). In this section, we demonstrate that METTL14-mediated m6A modification is crucial for NK and iNKT cell stability, maturation, and cytotoxic function, showing how epitranscriptomic regulation influences innate antitumor immunity. Short-term activation rapidly elevates m6A levels in NK cells, whereas this modification is suppressed within the TME (38). Single knockout of METTL3 or METTL14 has minimal effect, but double knockout profoundly impairs NK-cell homeostasis, maturation, and cytotoxic function, underscoring their cooperative role. Mechanistically, m6A directly modifies effector genes such as Prf1 and Gzmb, regulating their expression, while the mTORC1-SAM axis drives rapid NK activation via m6A-dependent mechanisms (Figure 3). Similarly, m6A modification is indispensable for invariant NKT (iNKT) cell development (39). In T cell–specific METTL14-deficient mice, increased apoptosis of double-positive thymocytes reduces Vα14-Jα18 rearrangement (Figure 3), resulting in decreased thymic and peripheral iNKT numbers (39). Residual iNKT cells exhibit increased apoptosis, impaired maturation, and weakened responses to IL-2/IL-15 and TCR stimulation. Knockdown of METTL14 in mature iNKT cells upregulates Cish, suppresses TCR signaling, and reduces cytokine production. Overall, METTL14 ensures effective innate immune surveillance through m6A-dependent mechanisms, reinforcing its central role as a molecular hub linking epitranscriptomic modification with tumor immunity.
3.5 B cell development
RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation, catalyzed by the METTL14 methyltransferase complex, plays a critical regulatory role in numerous biological processes (1). Studies have shown that deletion of Mettl14 significantly reduces mRNA m6A methylation levels in developing B cells and severely impairs B-cell development in mice (40). Loss of Mettl14 weakens interleukin-7 (IL-7)-induced pro-B cell proliferation and blocks the transition from large pre-B cells to small pre-B cells, while also causing abnormal expression of B-cell development–related genes (Figure 3). IL-7–induced pro-B cell proliferation depends on the cytoplasmic m6A reader YTHDF2, which suppresses a subset of transcripts, whereas the block in large-to-small pre-B cell transition is independent of either YTHDF1 or YTHDF2 and instead results from the failure to properly upregulate key transcription factors (40). Overall, this study highlights the essential regulatory roles of RNA m6A methylation and its reader proteins in early B-cell development.
4 METTL14 and immunotherapy
To provide a clear framework for the following sections, this part will highlight how METTL14, as a core component of the m6A “writer” complex, regulates immune checkpoint molecules and the tumor immune microenvironment, thus serving as a central node linking epitranscriptomic regulation to antitumor immunity. In recent years, the clinical application of tumor immunotherapies, particularly immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), has significantly improved the prognosis of certain cancer patients. However, their efficacy remains limited by immune evasion and resistance mechanisms. RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification, as a key layer of epitranscriptional regulation, has increasingly been recognized as a critical determinant of tumor immune microenvironment remodeling and immunotherapy response. As a core component of the m6A “writer” complex, METTL14 not only regulates the expression of immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-1 and PD-L1 to modulate T cell function and immune escape, but also interacts with multiple non-canonical signaling pathways, thereby profoundly influencing tumor sensitivity to immunotherapy. In summary, the mechanistic and therapeutic significance of METTL14 positions it as a pivotal link between epitranscriptomic regulation and tumor immune responses, setting the stage for a deeper discussion of its role in immunotherapy efficacy.
4.1 Regulation of immune checkpoint inhibitor efficacy
This section will focus on how METTL14 modulates PD-1/PD-L1 and related molecules to regulate T cell function and tumor immune evasion, emphasizing its critical role in immunotherapy efficacy. Evidence has shown that METTL14 promotes m6A-dependent degradation of PDCD1 mRNA, thereby downregulating PD-1 expression, sustaining CD8+ T cell activation, and suppressing tumor progression. Conversely, METTL14 deficiency results in elevated PD-1 levels, impaired T cell function, and resistance to immunotherapy. This highlights the METTL14–PD-1 axis as a critical regulatory pathway and suggests that targeting METTL14 in combination with PD-1 blockade may hold translational value. In glioblastoma (GBM), METTL14 is highly expressed and enhances PD-L1 stability by promoting its m6A modification. Knockdown of METTL14 significantly suppresses GBM proliferation, migration, and immune evasion while slowing tumor growth in murine models (41) (Figure 3). Mechanistically, METTL14-mediated m6A modification stabilizes PD-L1 mRNA in an IGF2BP2-dependent manner. Rescue experiments confirmed that PD-L1 overexpression reverses the inhibitory effect of METTL14 knockdown, underscoring PD-L1 as a key downstream effector (41). Thus, METTL14 drives GBM progression and immune escape by stabilizing PD-L1 via an IGF2BP2-dependent mechanism. In cholangiocarcinoma (CCA), an m6A–METTL14–Siah2–PD-L1 axis has been identified. METTL14 promotes m6A deposition on the 3′UTR of Siah2 mRNA, enhancing its YTHDF2-dependent degradation and ultimately upregulating Siah2 expression (42). Siah2 directly interacts with PD-L1, regulating its stability through K63-linked ubiquitination. Knockdown of Siah2 maintains PD-L1 expression in tumor cells, markedly impairing T cell proliferation and cytotoxicity (42) (Figure 3). Clinical analysis confirmed the presence of this axis in CCA tissues and demonstrated that patients with low Siah2 expression were more responsive to PD-1 blockade. Collectively, these findings reveal a novel mechanism whereby METTL14 regulates PD-L1 stability via Siah2, providing new therapeutic insight for CCA immunotherapy. In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), METTL14 plays a key role in immune escape. In orthotopic Hepa1–6 models, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation significantly upregulated PD-1 and PD-L1 expression. Mechanistic studies showed that LPS enhanced METTL14 expression, which in turn stabilized the lncRNA MIR155HG through m6A modification in an ELAVL1 (HuR)-dependent manner. MIR155HG acted as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) regulating the miR-223/STAT1 axis, thereby further increasing PD-L1 expression. This LPS–METTL14–MIR155HG–PD-L1 axis was validated in HepG2 xenografts and was particularly prominent in HCC with cirrhosis, suggesting a novel m6A-dependent lncRNA regulatory pathway contributing to HCC immune escape (43). In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), KCTD10 expression is significantly downregulated in tumor tissues. Functional assays revealed that KCTD10 overexpression effectively suppressed tumor progression both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, KCTD10 interacted with β-catenin via its BTB domain, promoting β-catenin K48-linked ubiquitination and degradation, thereby suppressing downstream PD-L1 expression (44). Importantly, combined KCTD10 overexpression and PD-1 blockade exhibited a pronounced synergistic effect in suppressing lung cancer progression and brain metastasis. Notably, METTL14 directly enhanced the stability of KCTD10 mRNA via m6A modification within its coding sequence in a YTHDF2-dependent manner (44). Taken together, KCTD10 suppresses lung cancer progression and immune escape via the β-catenin/PD-L1 axis, and its expression is tightly regulated by METTL14-dependent m6A modification, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target. Taken together, these findings underscore METTL14 as a master regulator of immune checkpoint signaling and tumor immune escape, providing a mechanistic rationale for targeting METTL14 to enhance immunotherapy responses.
4.2 Potential of METTL14 inhibitors in combination immunotherapy
This section will explore the therapeutic potential of targeting METTL14 with inhibitors, emphasizing how modulating METTL14 activity can synergize with immune checkpoint blockade and overcome resistance, further demonstrating METTL14 role as a key link between epitranscriptomic regulation and antitumor immunity. With the rapid development of RNA epigenetic therapeutics, the METTL14-centered m6A methyltransferase complex has emerged as a novel druggable target. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that pharmacological inhibition of METTL14 reduces global m6A levels, destabilizes oncogenic transcripts, and suppresses malignant tumor progression. More importantly, because METTL14-mediated m6A modification enhances PD-L1 expression and promotes an immunosuppressive microenvironment, inhibition of METTL14 may not only directly impair tumor proliferation but also downregulate PD-L1 expression to improve T cell–mediated antitumor immunity. Therefore, combining METTL14 inhibitors with PD-1/PD-L1 ICIs offers synergistic therapeutic potential and may help overcome resistance to monotherapy in subsets of patients. Interestingly, viral infection studies provide additional mechanistic insights. During early HSV-1 infection, the immediate-early protein ICP0 interacts with METTL14 and targets it for ubiquitination at K156 and K162, leading to proteasomal degradation and reduced cellular m6A levels (45). Normally, METTL14 stabilizes ISG15 mRNA via IGF2BP3, contributing to antiviral defense. By degrading METTL14, HSV-1 suppresses this pathway to facilitate immune evasion (45). Remarkably, METTL14 inhibition enhances the efficacy of oncolytic HSV-1 (oHSV-1) in glioma, suggesting that the METTL14–ISG15 axis is both a viral immune checkpoint and a therapeutic target to potentiate oHSV-1 antitumor activity. In endometrial carcinoma, PRMT3 regulates METTL14 through arginine methylation. Pharmacological inhibition of PRMT3 (e.g., SGC707) relieves this repression, enhances METTL14 expression and m6A–YTHDF2–dependent modification, destabilizes GPX4 mRNA, and induces lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis (46). Functionally, PRMT3 inhibition sensitizes endometrial cancer cells to PD-1 blockade, cisplatin, and radiotherapy, highlighting PRMT3 as a novel therapeutic target that indirectly modulates METTL14 activity to enhance ferroptosis and immunotherapy efficacy. Moreover, combined inhibition of METTL3/METTL14 with paclitaxel (PTX) demonstrated potent synergistic antitumor effects in breast cancer cells and xenograft models. Mechanistic studies revealed that METTL14 stabilizes E2F1 mRNA through an m6A–IGF2BP2–dependent mechanism, contributing to resistance against CDK4/6 inhibitors (CDK4/6i) (47). A novel small-molecule inhibitor, WKYMVM, effectively reversed CDK4/6i resistance and significantly enhanced therapeutic efficacy when delivered via liposomal formulations. As shown in Figure 4, the combination of METTL14 inhibitors with PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies synergistically remodels the tumor immune microenvironment, enhancing antitumor immunity and effectively suppressing cancer progression. This highlights the potential of targeting METTL14 as a strategy to improve immunotherapeutic efficacy (Figure 4). Overall, these studies highlight METTL14-centered therapeutic strategies as a promising avenue to overcome immunotherapy resistance and potentiate antitumor immunity, reinforcing METTL14 central position at the intersection of epitranscriptomic regulation and immune modulation.
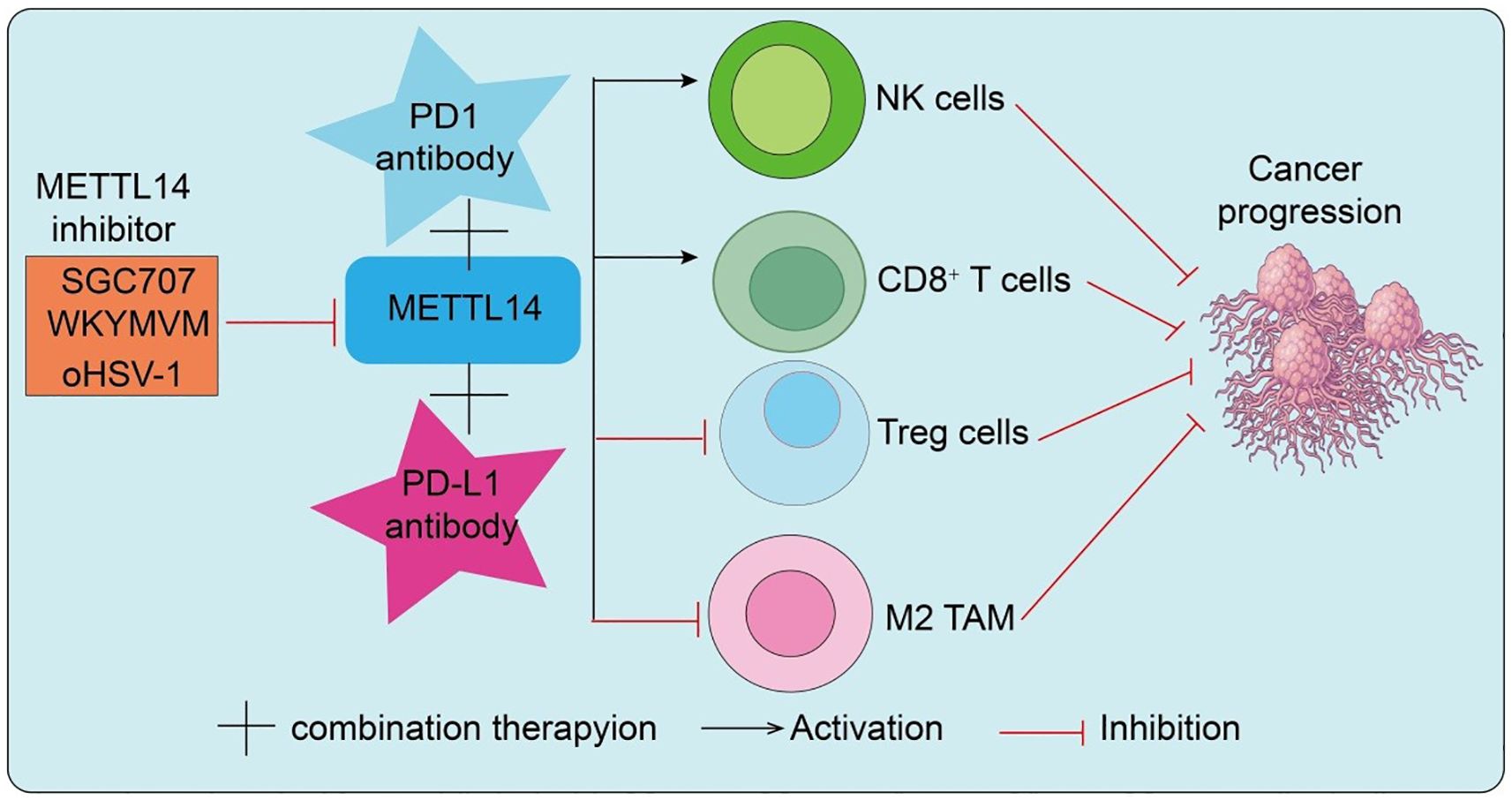
Figure 4. METTL14 inhibitors synergize with PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies to remodel the tumor immune microenvironment and suppress cancer progression.
5 Clinical significance and perspectives
With growing evidence of the immunoregulatory role of m6A modification, the multifaceted functions of METTL14 within the tumor immune microenvironment (TME) are being progressively unraveled, underscoring its translational value. As a core component of the m6A writer complex, METTL14 expression and activity are tightly associated with immune cell function and may critically determine patient responsiveness to immunotherapy, thereby holding great promise in precision oncology (48, 49). First, METTL14 may serve as a predictive biomarker for immunotherapy. Multiple studies demonstrate that m6A modification levels are closely linked to the efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade and other ICIs. METTL14 expression may influence immune cell infiltration, antigen presentation, and cytotoxic lymphocyte activity. Thus, assessing METTL14 status could provide a valuable indicator for predicting therapeutic response and prognosis. Second, targeting METTL14 or its downstream signaling pathways offers novel therapeutic opportunities. Direct modulation via small-molecule inhibitors, RNA interference, or genome editing—or indirect targeting of pathways such as T cell activation and dendritic cell function—could enhance immunotherapy sensitivity and improve clinical outcomes. Importantly, METTL14 exhibits “context-dependent” and “double-edged sword” characteristics: while it may potentiate antitumor immunity in some settings, it could promote immune suppression in others. This duality poses significant challenges for clinical translation and highlights the need for context-specific therapeutic strategies.
Future directions warrant particular attention. (i) The role of METTL14 in phase separation may regulate RNA–protein condensate assembly, influencing transcriptional and translational efficiency in immune cells. Recent studies suggest that liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) serves as a key mechanism for the spatial and temporal organization of biomolecules, including RNA, proteins, and chromatin-associated factors. In the context of immunity, LLPS can facilitate the formation of membrane-less condensates such as immunological synapses, transcriptional hubs, or stress granules, thereby concentrating signaling molecules and enhancing the efficiency of immune responses (50). For instance, phase-separated condensates may regulate T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling by clustering key kinases and adaptor proteins, promoting rapid phosphorylation cascades and downstream cytokine production. Similarly, LLPS can modulate the localization and activity of RNA-binding proteins or m6A readers/writers like METTL14, affecting mRNA stability and translation of immune-related genes (51). Collectively, these observations indicate that phase separation provides an additional layer of epitranscriptomic and signaling regulation, enabling precise control of innate and adaptive immune functions within the tumor microenvironment. (ii) Its involvement in chromatin modification and 3D genome architecture suggests functions beyond canonical RNA methylation, potentially linking METTL14 to super-enhancer–mediated regulation of immune gene activity. The three-dimensional organization of the genome is increasingly recognized as a critical determinant of gene expression and cellular identity, including in immune cells. Chromatin looping, topologically associating domains (TADs), and enhancer–promoter contacts can dynamically regulate immune gene accessibility and transcriptional programs. For example, spatial proximity between interferon-stimulated gene clusters and super-enhancers can potentiate rapid antiviral or antitumor responses. Similarly, the 3D genome may influence T-cell differentiation or regulatory T-cell function by modulating long-range interactions that control cytokine or transcription factor loci, such as FoxP3 or Stat1. Moreover, epitranscriptomic modifiers, including METTL14 (51), may interact with specific chromatin regions to coordinate m6A deposition with 3D chromatin architecture, thereby linking RNA modification to gene regulatory landscapes in immune cells. These insights highlight 3D genomics as a forward-looking mechanism for fine-tuning immune responses and shaping tumor-immune interactions. (iii) Preclinical and clinical studies combining METTL14 knockdown or inhibition with ICIs or other immunotherapies could yield synergistic effects, paving the way for innovative combination strategies. In conclusion, research on METTL14 in tumor immunity remains in rapid evolution. As both a biomarker and therapeutic target, METTL14 presents exciting opportunities alongside complex challenges. Future mechanistic studies and large-scale clinical validation will be essential to bridge the gap from bench to bedside and to realize the full potential of METTL14 in cancer immunotherapy.
6 Limitations and context-dependent roles of METTL14 in tumor immunity
Despite extensive evidence highlighting the pivotal role of METTL14 in regulating tumor progression and immune cell function, several limitations must be acknowledged to provide a balanced perspective. First, the functions of METTL14 are highly context-dependent, varying across tumor types, immune cell subsets, and microenvironmental conditions. For instance, METTL14 may promote CD8+ T-cell dysfunction in colorectal cancer through stabilization of Ebi3 mRNA, yet enhance T-cell activation in other contexts by facilitating PDCD1 mRNA degradation (30). Similarly, its regulatory effects on Tregs, TAMs, and NK cells are influenced by local cytokine milieu, metabolic conditions, or epigenetic landscapes. These differences may arise from heterogeneous expression of m6A readers (e.g., YTHDF2, IGF2BP2), co-factors, and signaling intermediates, as well as the interplay between m6A-dependent and -independent functions such as chromatin remodeling or transcriptional regulation. Second, experimental limitations exist in many studies. Most mechanistic insights are derived from murine models or in vitro systems, which may not fully recapitulate the human tumor microenvironment. Additionally, global manipulation of METTL14 (e.g., knockout or knockdown) may obscure cell-type-specific effects, making it challenging to delineate precise molecular mechanisms. Contextual variables such as tumor stage, mutational burden, and microbiome composition may further modulate METTL14 functions, yet remain underexplored in current research.
Third, these context-dependent roles pose significant challenges for clinical translation. The dual and sometimes opposing functions of METTL14 across tumors and immune cell types complicate its application as a universal biomarker or therapeutic target. Systemic targeting of METTL14 could inadvertently disrupt immune homeostasis or impair anti-tumor immunity in specific contexts. Therefore, patient stratification based on tumor type, immune cell composition, and METTL14 expression patterns, along with the development of cell-type-specific delivery systems, will be critical for safe and effective therapeutic interventions. Moreover, the integration of emerging concepts such as phase separation and 3D genome architecture may provide additional layers of regulatory insight, potentially guiding more precise manipulation of METTL14 in the tumor immune microenvironment. Collectively, while METTL14 represents a promising target in cancer immunotherapy, future studies should carefully consider its context-dependent functions, mechanistic complexity, and translational constraints to fully realize its therapeutic potential.
Author contributions
CL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2025ZNSFSC1926).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. An Y and Duan H. The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer metabolism. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:14. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01500-4
2. Zou Z, Sepich-Poore C, Zhou X, Wei J, and He C. The mechanism underlying redundant functions of the YTHDF proteins. Genome Biol. (2023) 24:17. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-02862-8
3. Zou Z and He C. Splice epitranscriptomics and DNA damage repair together: ALKBH5-m(6)A-SF3B1 regulation in leukemic transformation. Mol Cell. (2023) 83:1022–3. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.02.019
4. Jiang X, Liu B, Nie Z, Duan L, Xiong Q, Jin Z, et al. The role of m6A modification in the biological functions and diseases. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2021) 6:74. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00450-x
5. Gao Z, Zha X, Li M, Xia X, and Wang S. Insights into the m(6)A demethylases FTO and ALKBH5: structural, biological function, and inhibitor development. Cell Biosci. (2024) 14:108. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01286-6
6. Zou Z, Dou X, Li Y, Zhang Z, Wang J, Gao B, et al. RNA m(5)C oxidation by TET2 regulates chromatin state and leukaemogenesis. Nature. (2024) 634:986–94. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07969-x
7. Mu S, Zhao K, Zhong S, and Wang Y. The role of m6A methylation in tumor immunity and immune-associated disorder. Biomolecules. (2024) 14. doi: 10.3390/biom14081042
8. Lin Z, Hsu PJ, Xing X, Fang J, Lu Z, Zou Q, et al. Mettl3-/Mettl14-mediated mRNA N(6)-methyladenosine modulates murine spermatogenesis. Cell Res. (2017) 27:1216–30. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.117
9. Pomaville M, Chennakesavalu M, Wang P, Jiang Z, Sun HL, Ren P, et al. Small-molecule inhibition of the METTL3/METTL14 complex suppresses neuroblastoma tumor growth and promotes differentiation. Cell Rep. (2024) 43:114165. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114165
10. Liu Y, Fu Q, Yang M, Xu J, Zhou Z, Chen X, et al. Downregulation of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation of Sema4D mRNA contributes to Treg dysfunction and allograft rejection. Am J Transplantation: Off J Am Soc Transplant Am Soc Transplant Surgeons. (2025) 25:930–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ajt.2025.01.017
11. Wang SJ, Dougan SK, and Dougan M. Immune mechanisms of toxicity from checkpoint inhibitors. Trends Cancer. (2023) 9:543–53. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2023.04.002
12. Wang L, Hui H, Agrawal K, Kang Y, Li N, Tang R, et al. m(6) A RNA methyltransferases METTL3/14 regulate immune responses to anti-PD-1 therapy. EMBO J. (2020) 39:e104514. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020104514
13. Sun C, Wang J, Li H, Liu L, Lin Y, Zhang L, et al. METTL14 regulates CD8(+)T-cell activation and immune responses to anti-PD-1 therapy in lung cancer. World J Surg Oncol. (2024) 22:128. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03402-9
14. Chen X, Xu M, Xu X, Zeng K, Liu X, Pan B, et al. METTL14-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of SOX4 mRNA inhibits tumor metastasis in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. (2020) 19:106. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01220-7
15. Liu P, Li F, Lin J, Fukumoto T, Nacarelli T, Hao X, et al. m(6)A-independent genome-wide METTL3 and METTL14 redistribution drives the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. Nat Cell Biol. (2021) 23:355–65. doi: 10.1038/s41556-021-00656-3
16. Patil DP, Chen CK, Pickering BF, Chow A, Jackson C, Guttman M, et al. m(6)A RNA methylation promotes XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature. (2016) 537:369–73. doi: 10.1038/nature19342
17. Mu M, Li X, Dong L, Wang J, Cai Q, Hu Y, et al. METTL14 regulates chromatin bivalent domains in mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell Rep. (2023) 42:112650. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112650
18. Zhuang A, Gu X, Ge T, Wang S, Ge S, Chai P, et al. Targeting histone deacetylase suppresses tumor growth through eliciting METTL14-modified m(6) A RNA methylation in ocular melanoma. Cancer Commun (London England). (2023) 43:1185–206. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12471
19. Yao MZ, Ge XY, Liu T, Huang N, Liu H, Chen Y, et al. MEIS1 regulated proliferation and migration of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Life Sci. (2020) 255:117822. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117822
20. Weng H, Huang H, Wu H, Qin X, Zhao BS, Dong L, et al. METTL14 Inhibits Hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor Differentiation and Promotes Leukemogenesis via mRNA m(6)A Modification. Cell Stem Cell. (2018) 22:191–205.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2017.11.016
21. Wang J, Yin H, Li G, Wu D, Xu Y, Chen Y, et al. METTL14 promotes neuroblastoma formation by inhibiting YWHAH via an m6A-YTHDF1-dependent mechanism. Cell Death Discov. (2024) 10:186. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01959-8
22. Huang J, Zhou W, Hao C, He Q, and Tu X. The feedback loop of METTL14 and USP38 regulates cell migration, invasion and EMT as well as metastasis in bladder cancer. PloS Genet. (2022) 18:e1010366. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010366
23. Kang P and Dong P. CircMETTL14(11)S upregulated METTL14 and induced CXCR4 to aggravate endothelial inflammation and atherosclerosis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 126:110979. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110979
24. Liu X, Wang H, Zhao X, Luo Q, Wang Q, Tan K, et al. Arginine methylation of METTL14 promotes RNA N(6)-methyladenosine modification and endoderm differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:3780. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24035-6
25. Wang J, Fan P, Shen P, Fan C, Zhao P, Yao S, et al. XBP1s activates METTL3/METTL14 for ER-phagy and paclitaxel sensitivity regulation in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. (2024) 596:216846. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216846
26. Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Jiang Y, Cai H, Liang J, Li H, et al. Retinoic acid upregulates METTL14 expression and the m(6)A modification level to inhibit the proliferation of embryonic palate mesenchymal cells in cleft palate mice. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084538
27. Bejarano L, Jordāo MJC, and Joyce JA. Therapeutic targeting of the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Discov. (2021) 11:933–59. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1808
28. Ashby KM and Hogquist KA. A guide to thymic selection of T cells. Nat Rev Immunol. (2024) 24:103–17. doi: 10.1038/s41577-023-00911-8
29. Lu TX, Zheng Z, Zhang L, Sun HL, Bissonnette M, Huang H, et al. A new model of spontaneous colitis in mice induced by deletion of an RNA m(6)A methyltransferase component METTL14 in T cells. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 10:747–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2020.07.001
30. Dong L, Chen C, Zhang Y, Guo P, Wang Z, Li J, et al. The loss of RNA N(6)-adenosine methyltransferase Mettl14 in tumor-associated macrophages promotes CD8(+) T cell dysfunction and tumor growth. Cancer Cell. (2021) 39:945–957.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.04.016
31. Shafabakhsh R, Pourhanifeh MH, Mirzaei HR, Sahebkar A, Asemi Z, and Mirzaei H. Targeting regulatory T cells by curcumin: A potential for cancer immunotherapy. Pharmacol Res. (2019) 147:104353. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104353
32. Liu Y, Yuan Y, Zhou Z, Jiang X, He S, Wei F, et al. Mettl14 sustains FOXP3 expression to promote the differentiation and functions of induced-regulatory T cells via the mTOR signaling pathway. Immunol Lett. (2023) 258:35–44. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2023.04.008
33. Liu Y, Yuan Y, Zhou Z, Cui Y, Teng Y, Huang H, et al. Mettl14-mediated m6A modification enhances the function of Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells and promotes allograft acceptance. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1022015. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1022015
34. Chen Y, Lv G, Du X, Yang F, and Zhao Z. Fentanyl promoted the growth of placenta trophoblast cells through regulating the METTL14 mediated CCL5 levels. Biol Pharm Bull. (2023) 46:1797–804. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b23-00531
35. Wang L, Yi X, Xiao X, Zheng Q, Ma L, and Li B. Exosomal miR-628-5p from M1 polarized macrophages hinders m6A modification of circFUT8 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cell Mol Biol Lett. (2022) 27:106. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00406-9
36. Yan Q, Xu C, Gong L, Liang D, Yang J, Zheng Y, et al. The role of ZC3H13 in promoting M2 macrophage infiltration via m6A methylation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tumor progression. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1612041. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1612041
37. Tang J, Zhu Q, Li Z, Yang J, and Lai Y. Natural killer cell-targeted immunotherapy for cancer. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. (2022) 17:513–26. doi: 10.2174/1574888X17666220107101722
38. Aghaee F, Abedinpour M, Anvari S, Saberi A, Fallah A, and Bakhshi A. Natural killer cells in multiple sclerosis: foe or friends? Front Cell Neurosci. (2025) 19:1500770.
39. Cao L, Morgun E, Genardi S, Visvabharathy L, Cui Y, Huang H, et al. METTL14-dependent m(6)A modification controls iNKT cell development and function. Cell Rep. (2022) 40:111156. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111156
40. Zheng Z, Zhang L, Cui XL, Yu X, Hsu PJ, Lyu R, et al. Control of early B cell development by the RNA N(6)-methyladenosine methylation. Cell Rep. (2020) 31:107819. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107819
41. Zhang Z, Guo X, Qi T, Wang C, Zhai X, and Wang M. METTL14/IGF2BP2-mediated m6A modification of PD-L1 promotes proliferation, metastasis, and immune escape in high-grade gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. (2025). doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlaf090
42. Zheng H, Zheng WJ, Wang ZG, Tao YP, Huang ZP, Yang L, et al. Decreased expression of programmed death ligand-L1 by seven in absentia homolog 2 in cholangiocarcinoma enhances T-cell-mediated antitumor activity. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:845193. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.845193
43. Peng L, Pan B, Zhang X, Wang Z, Qiu J, Wang X, et al. Lipopolysaccharide facilitates immune escape of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via m6A modification of lncRNA MIR155HG to upregulate PD-L1 expression. Cell Biol Toxicol. (2022) 38:1159–73. doi: 10.1007/s10565-022-09718-0
44. Yin Z, Long S, Zhou H, Ouyang M, Wang Q, He J, et al. KCTD10 inhibits lung cancer metastasis and angiogenesis via ubiquitin-mediated β-catenin degradation. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1630311. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1630311
45. Chen Y, Bian S, Zhang J, Luan Y, Yin B, Dai W, et al. HSV-1-induced N6-methyladenosine reprogramming via ICP0-mediated suppression of METTL14 potentiates oncolytic activity in glioma. Cell Rep. (2024) 43:114756. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114756
46. Wang Y, Wang C, Guan X, Ma Y, Zhang S, Li F, et al. PRMT3-mediated arginine methylation of METTL14 promotes Malignant progression and treatment resistance in endometrial carcinoma. Adv Sci (Weinheim Baden-Wurttemberg Germany). (2023) 10:e2303812. doi: 10.1002/advs.202303812
47. Liu C, Fan D, Sun J, Li G, Du R, Zuo X, et al. Inhibition of METTL14 overcomes CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance driven by METTL14-m6A-E2F1-axis in ERα-positive breast cancer. J Nanobiotechnol. (2025) 23:3. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-03021-2
48. Li R, Yin YH, Ji XL, Liu X, Li JP, and Qu YQ. Pan-cancer prognostic, immunity, stemness, and anticancer drug sensitivity characterization of N6-methyladenosine RNA modification regulators in human cancers. Front Mol Biosci. (2021) 8:644620. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.644620
49. Kahraman S, De Jesus DF, Wei J, Brown NK, Zou Z, Hu J, et al. m(6)A mRNA methylation by METTL14 regulates early pancreatic cell differentiation. EMBO J. (2024) 43:5445–68. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00213-2
50. Xiao Q, McAtee CK, and Su X. Phase separation in immune signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. (2022) 22:188–99. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00572-5
51. Liu D, Yang J, and Cristea IM. Liquid-liquid phase separation in innate immunity. Trends Immunol. (2024) 45:454–69. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2024.04.009
52. Zhao YL, Li YJ, Wu CX, Xie N, Li XY, Cao DC, et al. m6A-modified circZNF548 regulates exosomal miR-7108-3p to activate CD3(+)CD8(+) T cells and suppress NSCLC growth by JMY. BMC Biol. (2025) 23:257. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02355-z
53. Huang C, Wang X, Gu Y, Ren K, Zang H, Zhang Y, et al. METTL14 Enhances Anti-Tumor Immunity through m6A-dependent loss of PD-1. Cancer Res. (2025). doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-25-0065
54. Gong PJ, Shao YC, Yang Y, Song WJ, He X, Zeng YF, et al. Analysis of N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase reveals METTL14 and ZC3H13 as tumor suppressor genes in breast cancer. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:578963. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.578963
55. Xu T, Gao S, Ruan H, Liu J, Liu Y, Liu D, et al. METTL14 acts as a potential regulator of tumor immune and progression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Front Genet. (2021) 12:609174. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.609174
56. Wang B, Mao Z, Ye J, Jiao X, Zhang T, Wang Q, et al. Glycolysis induced by METTL14 is essential for macrophage phagocytosis and phenotype in cervical cancer. J Immunol (Baltimore Md: 1950). (2024) 212:723–36. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300339
57. Yang W, Zha J, Tang Y, Wang K, He H, Zeng C, et al. Bladder cancer growth is inhibited by upregulating circFUT8 through the METTL14/FMR1 signaling pathway. Cell Biochem Biophysics. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01794-3
Keywords: METTL14, m6A methylase, tumor microenvironment, immune checkpoint, cancer immunotherapy
Citation: Li C, Jiang X, Yuan Y and Wang Q (2025) METTL14 in tumor immunity: epitranscriptomic regulation and therapeutic potential. Front. Immunol. 16:1709742. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1709742
Received: 20 September 2025; Accepted: 01 October 2025;
Published: 14 October 2025.
Edited by:
Diwei Zheng, Chinese Academy of Sciences, ChinaReviewed by:
Lin Che, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center (SYSUCC), ChinaCopyright © 2025 Li, Jiang, Yuan and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qiang Wang, d2FuZ3FpYW5nOTAyNDk3QDEyNi5jb20=
 Chunhong Li
Chunhong Li Xiulin Jiang
Xiulin Jiang Yixiao Yuan2
Yixiao Yuan2 Qiang Wang
Qiang Wang