- 1Department of Pharmacy, Mianyang Central Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Mianyang, China
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Personalized Drug Research and Therapy Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
- 3School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Dysregulation of the homeostasis between regulatory T cell (Treg) and T helper 17 cell (Th17) is increasingly recognized as a pivotal mechanism in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Emerging evidence indicates that gut microbiota-derived metabolites, including short-chain fatty acids, secondary bile acids, and aromatic metabolites, modulate Treg/Th17 balance by shaping immune cell differentiation and function, thereby revealing novel therapeutic opportunities. This Review synthesizes recent clinical and preclinical findings on the influence of microbial communities and their metabolites on Treg/Th17 dynamics and examines the underlying mechanisms in representative autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Graves’ disease, autoimmune hepatitis, and myasthenia gravis. We critically evaluate current microbiome-targeted interventions and discuss their translational potential, highlighting both promises and challenges. Finally, we outline priorities for future research, focusing on multi-omic integration, the development of individualized therapeutic strategies, and rigorous clinical evaluation, to facilitate the development of safe and effective microbiota-based therapies for autoimmune diseases.
1 Introduction
Immune-cell imbalance — particularly the functional opposition and dysregulation between regulatory T cells (Treg) and T helper 17 cell (Th17) — has been widely recognized as a central driver of autoimmune disease pathogenesis (1, 2). Tregs are indispensable for maintaining immune homeostasis by suppressing excessive immune responses and preventing autoimmunity (3). In contrast, Th17 promote chronic inflammation and the development of autoimmune disorders through secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (4). Therefore, disruption of the Treg/Th17 equilibrium frequently precipitates the onset and progression of autoimmune disease (5, 6). Indeed, reduced Treg function accompanied by elevated Th17 activation is commonly observed in conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (7, 8).
The gut microbiota functions as a major regulator of host immunity, and microbial metabolites have emerged as key modulators of immune-cell differentiation and function (9). Accumulating clinical and preclinical studies indicate that gut microbes and their metabolic products influence autoimmune pathogenesis in part by shaping the Treg/Th17 balance (10). For example, microbial metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) have been reported to promote Treg differentiation while inhibiting Th17 activation (11, 12). Such regulatory mechanisms suggest novel therapeutic avenues for autoimmune disease.
Multiple studies further indicate that loss of microbial diversity and altered metabolite abundance correlate inversely with disease activity, and that restoring microbiome composition can rebalance Treg and Th17 populations and ameliorate disease severity (8, 13). Interventions targeting the gut microbiome — including probiotic administration, dietary modification, and fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) — have demonstrated potential to modulate immune responses and improve clinical outcomes in various settings (14, 15).
Identifying microbiota-derived metabolites that regulate immune homeostasis therefore provides new perspectives for therapeutic development and for prioritizing translational research. By synthesizing mechanistic insights and clinical evidence, this Review aims to delineate how gut microbial metabolites govern the Treg/Th17 axis, summarize disease-specific findings, and evaluate translational pathways toward microbiome-based therapies for autoimmune disease.
2 Interactions between gut microbiota and the immune system
2.1 Immunological functions of Treg and Th17 and mechanisms that maintain their balance
Treg and Th17 represent two principal CD4+ T-cell subsets that play opposing yet complementary roles in immune homeostasis and the regulation of immune responses (16). Treg cells restrain excessive immunity and maintain tolerance largely through the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and transforming growth TGF-β, thereby preventing autoimmune pathology (17). Numerous studies have documented quantitative and functional alterations in Treg populations across autoimmune disorders; impaired Treg function correlates closely with disease exacerbation in conditions such as RA and SLE (18, 19).
By contrast, Th17 promote inflammatory responses and contribute to autoimmune pathogenesis via secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines including IL-17 and IL-22 (20). Although Th17 cells are important for host defense against certain pathogens, their aberrant activation can drive tissue injury and autoimmunity (21). In many autoimmune diseases, the frequency or activity of Th17 is elevated while Treg numbers or suppressive capacity are reduced, producing a net shift toward inflammation and tissue damage (22, 23).
The lineage specification of Treg and Th17 is governed in part by the interplay between key transcriptional regulators: RORγt, the lineage-defining factor for Th17, and Foxp3, the master regulator of Treg identity and function (24). The balance between RORγt and Foxp3 is critical for immune equilibrium, and disruption of their reciprocal regulation can precipitate immune dysregulation and disease (25, 26).
In autoimmune settings, the Treg/Th17 balance is disrupted. For instance, RA patients exhibit elevated Th17 cells and often defective Treg function, leading to IL-17–mediated synovitis and osteoclast activation (27). Similarly, SLE patients show increased circulating Th17 frequency correlating with disease activity (28). These examples underscore that an overactive Th17 response concurrent with impaired Treg regulation underlies pathology in RA, SLE and other autoimmune diseases.
A range of extrinsic and intrinsic cues — including environmental signals, cytokine milieus and metabolic pathways — shape the differentiation trajectories of Treg versus Th17 (29). For example, cytokines such as IL-6 and IL-23 favor Th17 differentiation, whereas TGF-β promotes Treg induction under certain contexts (30). This dynamic interconversion and competitive differentiation between the two lineages underlies both immune tolerance and pathogenic inflammation, making restoration of the Treg/Th17 balance a promising strategy to modulate immune responses and treat autoimmune disease (31, 32).
2.2 Regulatory effects of the gut microbiota on the Treg/Th17 balance
The gut microbiota exerts profound influences on host immunity, particularly by shaping T-cell differentiation. Evidence indicates that microbial communities modulate the equilibrium between Treg and Th17 through diverse mechanisms, including the production of metabolites, antigen presentation, and regulation of mucosal immunity (33). Treg and Th17 are two major CD4+ T-cell subsets with opposing functions in immune regulation: Th17 drive inflammatory responses, whereas Treg cells suppress excessive immunity (34). Microbial metabolites such as SCFAs promote Treg differentiation while limiting Th17 proliferation, thereby sustaining both intestinal and systemic immune homeostasis (8). For example, Bacteroides fragilis polysaccharide Asignals via TLR2 to induce IL-10–producing Foxp3^+ Tregs (35), and segmented filamentous bacteria drive Th17 differentiation through antigen presentation and local DC-mediated cues (36). Collectively, these findings demonstrate that defined microbial species and their metabolites regulate Treg/Th17 polarization and cytokine production, maintaining immune balance within this axis (Figure 1) (33).
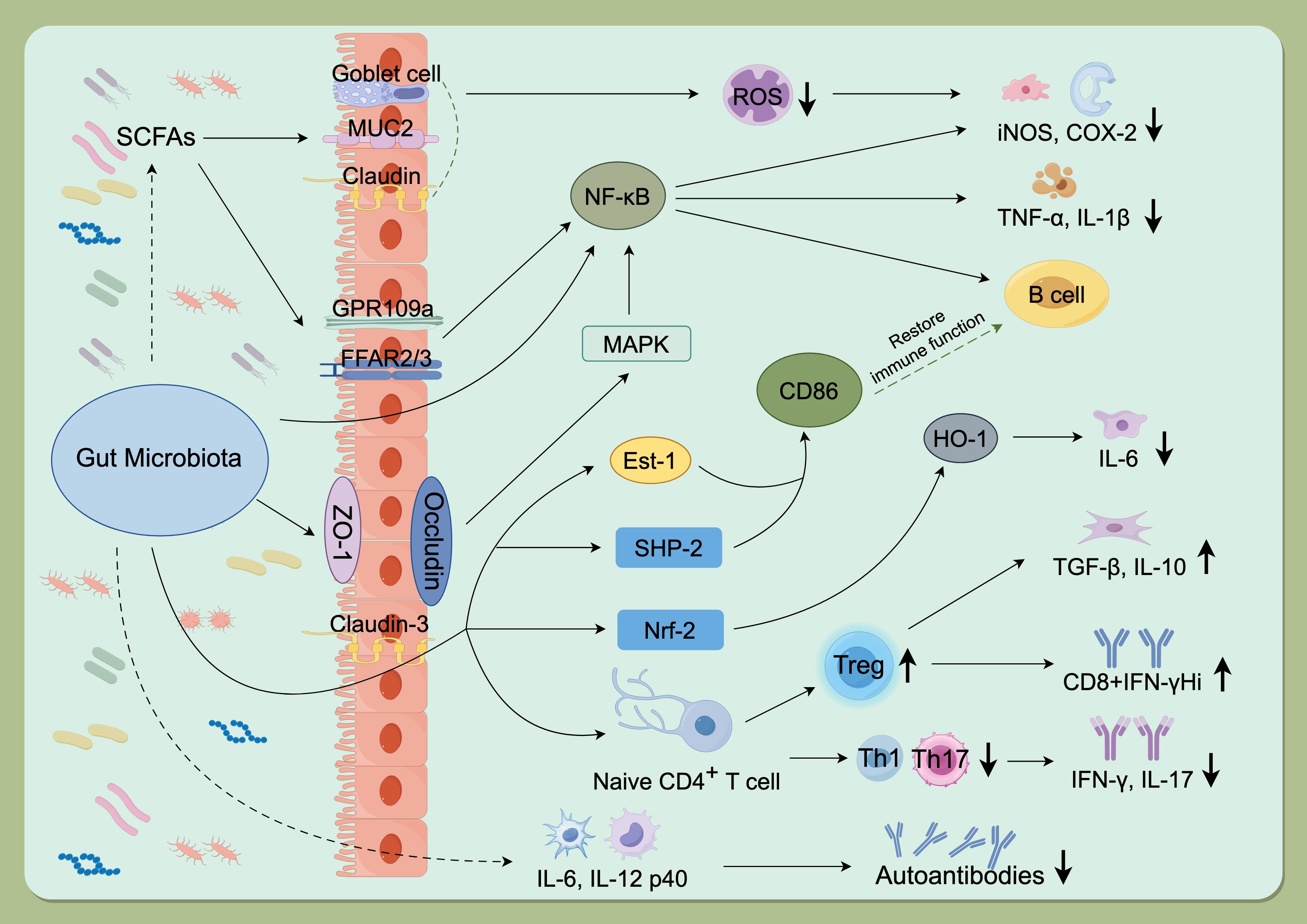
Figure 1. Mechanisms of gut microbiota involvement in autoimmune diseases. The gut microbiota promotes autoimmune pathogenesis by modulating key signaling pathways (NF-κB, Nrf-2), disrupting the Treg/Th1/Th17 balance, regulating the release of inflammatory factors, and producing microbial metabolites such as SCFAs. GPR109a, G protein-coupled receptor 109a; FFAR2/3, Recombinant Free Fatty Acid Receptor 2/3; SCFAs, Short chain fatty acids; MUC2, Recombinant Mucin 2; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; NF-kB, Nuclear factor kappa-B; COX-2, Cyclooxygenase 2; iNOS, Inducible nitric oxide synthase; ZO-1, Zona Occludens 1; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; IL-1b, Interleukin-1 beta; TNF-a, Tumor necrosis factor alpha; Est-1, Estrogen sulfotransferase-1; SHP-2, SH2 domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase-2; Nrf-2, NF-E2-related factor 2; HO-1, Recombinant Heme Oxygenase 1; IL-6, Interleukin-6; IL-10, Interleukin-10; TGF-b, Transforming growth factor beta; IFN-g, Interferon gamma; IL-17, Interleukin-17; IL-21/IL-22, Interleukin-21/Interleukin-22; IL-12 p40, Interleukin12 p40. (By Figdraw, ID: TWIOIab0ee).
Gut microbiota dysbiosis refers to an imbalance in gut microbial ecology that disrupts health. Formally, gut dysbiosis is defined as increased pathogens and pathobionts, reduced beneficial keystone taxa, and loss of overall diversity (37). Hallmarks include loss of SCFA-producing Firmicutes and bloom of Proteobacteria/enterobacteria (38). This is often accompanied by altered microbial metabolism: e.g. reduced butyrate synthesis and depleted anti-inflammatory metabolites. In elderly or diseased individuals, dysbiosis is manifested by narrowed richness and expansion of opportunistic bacteria (39). Functionally, dysbiosis predisposes to barrier dysfunction and inflammation: irreversible microbiome shifts associate with gut barrier breakdown and systemic disease (IBD, diabetes, etc.) (40, 41). Thus, we define dysbiosis as a loss of the “healthy” core microbiota (high diversity, stable SCFA producers) coupled with metabolite derangements. In this state, local and systemic immune tolerance is undermined.).
A healthy gut microbiota can maintain the organism’s normal tolerance environment. Commensals induce intestinal DCs to produce retinoic acid and TGFβ, promoting peripheral Tregs (42). Dysbiosis increases epithelial permeability and translocation of microbial products (LPS, flagellin), triggering DC activation and IL-6/IL-23 production that favor Th17 differentiation (43). Indeed, irreversible dysbiotic changes associate with gut barrier defects and systemic inflammation (44, 45). Restoring commensal-derived signals (e.g. mucosal IgA, epithelial IL-10) is thus crucial to re-establish Treg-mediated tolerance (46, 47).
The gut ecosystem is shaped by numerous intrinsic and extrinsic factors, which in turn influence the Treg/Th17 balance. Intrinsic factors include age, sex, and genetics. For example, normal gut diversity increases during early life and plateaus in adulthood (48), but old age is associated with loss of microbial richness and depletion of SCFA-producers (49), possibly contributing to “inflammaging”. Host sex hormones also modulate the microbiota: in NOD mice, gut microbes elevated testosterone in males, protecting against autoimmunity, and transfer of male microbiota to females increased their testosterone and reduced disease (50). Such “microgenderome” effects likely contribute to the higher prevalence of autoimmune disorders in women, although the exact microbial taxa involved are still under study.
Extrinsic factors are major drivers of microbiota composition. Diet is paramount: cohorts across continents show that Western diets (high fat/sugar, low fiber) select for low-diversity communities, whereas rural or high-fiber diets support diverse, fiber-fermenting microbiota (51). For instance, a high-fat diet consistently increases the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio and reduces beneficial taxa (52). Changes can be rapid; immigrants adopt the gut microbiome of the host country within weeks of diet change (53). Conversely, lifelong Western diets can irreversibly erase key taxa (54). Geography and lifestyle also matter, stool surveys show distinct microbial signatures in Malawian and Amerindian children versus US children (51), reflecting diet, sanitation, and cultural habits. Antibiotics and drugs profoundly perturb the microbiota, even short courses cause sustained loss of diversity and expansion of resistant organisms (55).
Targeted microbial interventions — including probiotics, prebiotics, and FMT — have been shown to restore Treg/Th17 homeostasis and ameliorate immune-mediated disorders. For instance, plant-derived compounds such as phytosterols enhance SCFAs production, thereby promoting Treg differentiation, suppressing Th17 expansion, rebalancing gut microbial ecology, and attenuating inflammation (56).
Notably, the immunomodulatory influence of the gut microbiota extends beyond the intestinal tract to peripheral compartments such as the blood and spleen (33). This cross-compartment regulation underscores that microbial health impacts not only gastrointestinal physiology but also systemic immune homeostasis. Taken together, these insights highlight the substantial therapeutic potential of microbiota-based interventions in autoimmune disease, particularly through re-establishing the Treg/Th17 balance.
3 Molecular mechanisms by which gut microbial metabolites regulate the Treg/Th17 balance
3.1 SCFAs
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), principally acetate, propionate, and butyrate, are microbial metabolites generated through fermentation of dietary fibers in the gut (57). Accumulating evidence highlights their indispensable roles in intestinal health and immune regulation. The study found that SCFAs enhance the stability of Treg cells and suppress the activity of Th17 cells, thereby contributing to the maintenance of immune system homeostasis (58). SCFAs, particularly butyrate, function as a primary energy source for colonocytes. Simultaneously, they modulate host immunity by promoting regulatory T-cell differentiation and mucosal tolerance through mechanisms that include GPR43-mediated signaling and epigenetic regulation via histone deacetylase inhibition (59). One key pathway is engagement of SCFA-sensing G protein–coupled receptors: microbial acetate, propionate and butyrate activate FFAR2 (GPR43) and FFAR3 (GPR41) on mucosal cells and leukocytes. FFAR2 signaling is necessary for SCFA-driven expansion of colonic Foxp3^+ regulatory T cells and protection from T-cell-transfer colitis, while SCFAs additionally act via HDAC inhibition and mTOR–S6K modulation to stabilize Foxp3 expression and limit pro-inflammatory Th17 responses (Figure 2) (60). For instance, propionate activates the GPR43–cAMP/PKA–CREB signaling cascade, leading to expansion of Treg cells and increased secretion of IL-10 and TGF-β (8). In animal models of autoimmune disease such as RA, SCFAs supplementation significantly alleviates joint inflammation and tissue injury.
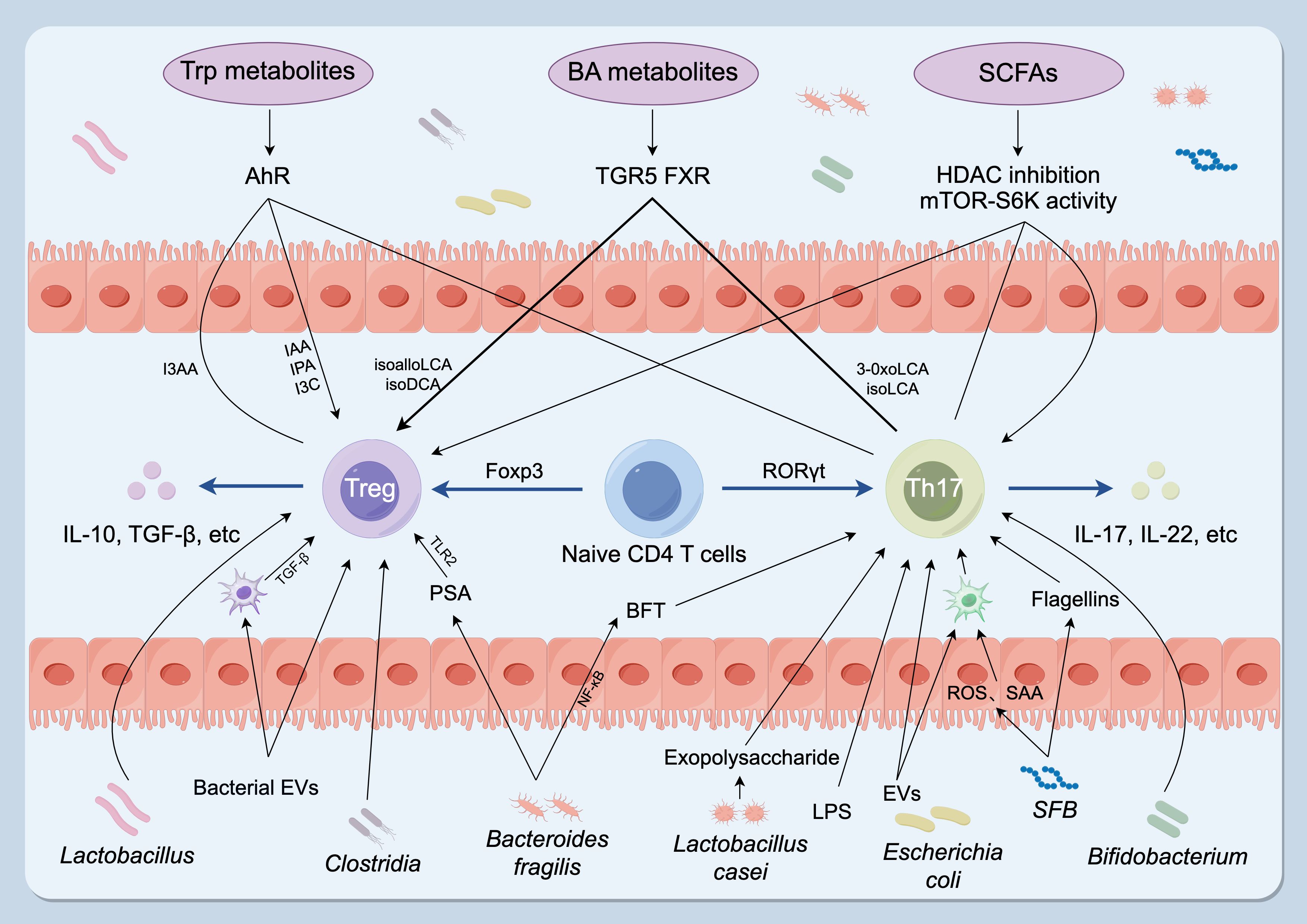
Figure 2. Gut microbiota and microbial metabolites regulate the Th17–Treg balance. Specific taxa influence T-cell fate: Clostridium, Bacteroides fragilis and Lactobacillus promote Treg development and function, whereas SFB, Bacteroides fragilis, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium stimulate Th17 differentiation and cytokine production. Microbial metabolites are key effectors: SCFAs (acetate, propionate, butyrate) act mainly via HDAC inhibition and modulation of the mTOR–S6K pathway; BA derivatives signal through TGR5 and FXR to promote Treg differentiation and/or suppress Th17 polarization; Trp-derived ligands (IAA, IPA, I3C) function as AhR agonists that favor Treg generation and restrain Th17 responses, whereas I3AA may antagonize AhR and impair Treg function. Microbial components and secreted factors — including LPS, flagellin (from SFB), exopolysaccharides (from Lactobacillus casei), EVs and BFT — promote Th17 differentiation. Conversely, EVs, PSA (from Bacteroides fragilis) and cell-surface β-glucan/galactan polysaccharides enhance Treg activity. Treg, regulatory T cell; Th17, T helper 17 cell; SFB, segmented filamentous bacteria; SCFAs, short-chain fatty acids; BA, bile acid; Trp, tryptophan; HDACs, histone deacetylases; TGR5, G-protein-coupled bile acid receptor; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; IAA, indole-3-acetic acid; IPA, indole-3-propionic acid; I3C, indole-3-carbinol; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; I3AA, indole-3-acetaldehyde; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; EVs, bacterial extracellular vesicles; BFT, Bacteroides fragilis toxin; PSA, polysaccharide A. (By Figdraw, ID: ATTYS1c1c0).
SCFAs also regulate immune function through inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDACs), thereby stabilizing the Treg phenotype (61). Butyrate, for example, promotes Foxp3 expression via HDAC inhibition, strengthening Treg suppressive capacity. This epigenetic mechanism contributes to the maintenance of tolerance and prevents excessive immune activation, thereby curbing autoimmune responses (62).
Moreover, SCFAs reinforce tolerance by balancing pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine production. They downregulate pro-inflammatory mediators such as IL-6 and IL-23 while enhancing IL-10 and TGF-β expression, a shift repeatedly observed across models of autoimmune disease (63, 64). These findings suggest that SCFAs hold substantial translational promise as immunoregulatory metabolites.
In vivo studies support this potential: supplementation with SCFAs attenuates clinical symptoms in models of RA and inflammatory bowel disease, while improving barrier integrity and reducing systemic inflammation (65). Taken together, SCFAs emerge as key microbial products that modulate the Treg/Th17 axis through convergent signaling and epigenetic pathways, thereby promoting tolerance and constraining autoimmune pathology. Their capacity to re-establish immune balance positions SCFAs as both mechanistic targets and therapeutic candidates for autoimmune disease (66, 67).
3.2 Secondary bile acids
The gut microbiota converts primary bile acids into secondary bile acids through a series of complex metabolic processes, exerting profound effects on the host immune system. Primary bile acids are synthesized in the liver and secreted into the intestine via bile, where microbial enzymatic reactions transform them into secondary bile acids such as deoxycholic acid (DCA) and lithocholic acid (LCA) (68, 69). These metabolites not only contribute to the composition of the bile acid pool but also regulate host metabolism and immune responses by binding to bile acid receptors expressed on host cells. Accumulating evidence indicates that the synthesis of secondary bile acid is tightly linked to the composition and functional state of the gut microbiota, with microbial diversity significantly shaping this metabolic process (70, 71). Moreover, secondary bile acids play crucial roles in maintaining intestinal barrier integrity, modulating immune responses, and mediating anti-inflammatory effects.
The immunomodulatory properties of secondary bile acids are particularly evident in the regulation of Treg and Th17 (72). FOXP3+ Tregs are key mediators of immune tolerance, and their dysfunction or depletion is closely associated with the pathogenesis of multiple autoimmune diseases (73). Studies have shown that secondary bile acids, particularly DCA and LCA, promote the differentiation of FOXP3+ Treg while suppressing Th17 cell development through specific signaling pathways (72, 74). In autoimmune disorders such as multiple sclerosis (MS), a deficiency of secondary bile acids correlates with reduced Treg abundance and increased Th17 responses, suggesting a critical role of bile acid metabolites in regulating CNS autoimmunity (75). Modulating gut microbial composition to enhance secondary bile acid production may therefore represent a novel therapeutic strategy for MS and related diseases.
In MS patients, the production of secondary bile acids is markedly reduced compared with healthy controls, paralleling impaired immune regulation. Specifically, microbial taxa responsible for secondary bile acid biosynthesis are diminished, leading to decreased intestinal levels of immunoregulatory metabolites such as DCA and LCA (72). This reduction compromises Treg function while enhancing Th17 differentiation, driving CNS inflammation and disease progression. Therapeutic strategies aimed at restoring bile acid balance have shown promise: supplementation with DCA or LCA in experimental MS models effectively restored immune homeostasis, reduced Th17 frequency, promoted Treg differentiation, and alleviated clinical symptoms (72, 74). These findings not only highlight the therapeutic potential of secondary bile acid supplementation but also deepen our understanding of microbiota–immune system crosstalk. Targeting bile acid metabolism may thus offer new treatment options for MS, improving both immune balance and patient outcomes.
3.3 Tryptophan and other aromatic metabolites
Tryptophan (Trp), an essential aromatic amino acid in humans, has emerged as a critical substrate for generating immunoregulatory metabolites such as indole and indole-3-propionic acid. Increasing evidence indicates that Trp-derived indole compounds modulate the balance between Treg and Th17 primarily through binding to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) (58). AhR is a ligand-activated transcription factor that governs diverse physiological processes, including immune regulation. Trp metabolism therefore not only shapes the local intestinal immune microenvironment but also exerts systemic immunomodulatory effects by directing T-cell differentiation and function (76). In murine models, indole compounds have been shown to promote Treg generation while suppressing Th17 differentiation, thereby sustaining immune tolerance and dampening inflammatory responses (77). These findings highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting Trp metabolism to reestablish Treg/Th17 homeostasis in autoimmune diseases.
Trp metabolism is a key microbiota–immune interface. Both host enzymes (IDO1/IDO2, TDO) and bacterial pathways convert Trp into bioactive compounds (9, 78). The host IDO-mediated kynurenine (Kyn) pathway generates metabolites that modulate T cells (79). Microbiota-derived indole and indole-derivatives (e.g. indole-3-aldehyde, indole propionic acid) act via AhR on immune cells and mucosal cells (80). These Trp metabolites generally promote Tregs and suppress Th17. For instance, Kyn and 3-HAA synergistically drive naïve CD4^+ T cells to Foxp3^+ Tregs in the presence of DCs (81). Indole derivatives from commensals activate AhR to induce IL-22 and IL-10, enhancing barrier function and Treg stability. Notably, RA patients show perturbations in Trp metabolism: serum kynurenic and xanthurenic acids (Treg-promoting) are decreased, while neurotoxic quinolinic acid is elevated (82). Experimental arthritis was improved by supplementing enzyme activities to boost Kyn metabolites. In SLE, increased IDO activity and high Kyn/Trp ratio correlate with disease and fatigue (83). These data link dysbiotic Trp metabolism to Th17/Treg imbalance in autoimmunity. Overall, Trp-derived metabolites constitute another axis by which gut microbiota shape T cell fate.
4 Advances in the study of gut microbial metabolites and Treg/Th17 balance in representative autoimmune diseases
4.1 Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder in which mounting evidence links the gut microbiome to disease onset and progression. Patients with RA frequently exhibit reduced microbial diversity, diminished levels of SCFAs, and an increased proportion of Th17, collectively contributing to aberrant immune activation and persistent inflammation (84, 85). Dysbiosis disrupts the delicate equilibrium between Treg and Th17, thereby fueling chronic inflammatory responses (8, 86). Table 1 summarizes mechanistic and clinical evidence for gut microbiota–derived metabolites in modulating the Treg/Th17 axis across representative autoimmune diseases.
Notably, SCFAs concentrations are significantly lower in RA patients compared with healthy controls (102). SCFAs not only sustain intestinal barrier integrity but also orchestrate immune regulation by promoting Treg differentiation and suppressing Th17 activation (103, 104). For instance, butyrate enhances Treg expansion and IL-10 secretion via GPR43 signaling while simultaneously attenuating Th17 polarization, underscoring its potential as a therapeutic target in RA (8, 105).
Current therapies such as methotrexate have been shown to partially restore gut microbial composition and increase SCFAs levels, thereby rebalancing Treg and Th17 populations. Clinical studies demonstrate that methotrexate treatment improves microbial diversity and structure in RA patients, accompanied by reduced inflammatory markers (106, 107). These findings suggest that targeting the gut microbiota to modulate immune responses may represent a promising adjunctive strategy for RA management.
Dysregulation of Trp metabolism has emerged as a critical link connecting the gut microbiota, host immunity, and disease activity in RA. Recent studies highlight its dual role: an imbalance in the host kynurenine pathway, characterized by decreased protective metabolites (e.g., kynurenic acid) and elevated pro-inflammatory metabolites (e.g., quinolinic acid), correlates with disease severity, and restoring this balance shows therapeutic potential in animal models (82, 108). Concurrently, gut microbiota-derived indole derivatives exert opposing effects. For instance, indole-3-propionic acid maintains immune homeostasis and alleviates arthritis by activating AhR (84), whereas unmodified indole promotes a pro-inflammatory Th17 response, exacerbating disease (109). This metabolic heterogeneity underscores that Trp metabolism is not only a source of robust biomarkers for RA but also a promising, yet complex, therapeutic target requiring precise modulation.
Probiotic interventions have also shown therapeutic promise. For example, Lactobacillus casei has been reported to alleviate arthritis by reshaping gut microbial communities and enhancing SCFAs production. Specifically, Lactobacillus casei CCFM1074 reduced Th17 cell proportions while expanding Treg populations, thereby ameliorating disease severity in RA mouse models (104, 110). Such evidence highlights the potential of probiotic supplementation as an adjunct therapy for RA, reinforcing the concept that gut microbiota modulation could be harnessed as a novel therapeutic avenue.
Collectively, these studies demonstrate that gut microbial metabolites play a pivotal role in regulating the Treg/Th17 balance in RA. Future research should aim to delineate the precise mechanisms through which microbial metabolites influence RA pathogenesis and explore their translational potential in clinical settings (111, 112).
4.2 Systemic lupus erythematosus
In systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), growing attention has been directed toward the regulatory effects of gut microbiota and their metabolites on immune homeostasis. SLE is a complex autoimmune disease characterized by an imbalance between Treg and Th17, leading to chronic inflammation and multi-organ damage (113). Experimental studies have revealed that specific microbial taxa are markedly reduced in SLE models, whereas supplementation with these key strains can effectively restore the Treg/Th17 balance and ameliorate disease severity (114).
In the MRL/lpr mouse model, species such as Eisenbergiella massiliensis, Lacrimispora saccharolytica, and Hungatella xylanolytica were significantly decreased following disease onset. Their depletion was closely associated with reduced levels of metabolites including 5-cholestenol, cholesterol, p-cresol, and indole (114). These metabolites are linked to immune regulation and may influence the Treg/Th17 axis. Restoration of these microbial populations was shown to improve SLE symptoms and contribute to re-establishing Treg/Th17 balance (114).
Supplementation with Bifidobacterium has also demonstrated beneficial effects in both clinical and preclinical studies. Multiple investigations have confirmed that the abundance of Bifidobacterium is significantly reduced in SLE patients, correlating with impaired Treg function and increased Th17 activity (10). Accordingly, Bifidobacterium and its metabolites not only correct gut dysbiosis but also restore Treg-mediated suppression, thereby reducing Th17-driven inflammation, alleviating clinical symptoms, and mitigating renal injury in SLE (115).
SCFAs, key metabolites derived from microbial fermentation of dietary fibers, also play a pivotal role in regulating the Treg/Th17 axis (116). SCFAs production is essential for gut health and modulates immune cell differentiation and function to restrain autoimmune responses (62). In SLE models, SCFAs deficiency has been directly linked to increased Th17 activity and Treg dysfunction (117). In addition, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a structural component of Gram-negative bacteria, exerts dual immunological effects: at low concentrations it stimulates appropriate immune activation, whereas at high concentrations it triggers excessive inflammation and immune dysregulation (118). In SLE and other autoimmune diseases, disruption in the balance of SCFAs and LPS has been implicated in disease pathogenesis (119). Hence, deciphering the roles of these microbial products provides an important foundation for developing novel immunotherapies.
4.3 Graves’ disease
In patients with Graves’ disease (GD), gut microbiota dysbiosis has been identified as a key contributing factor. Studies have demonstrated that supplementation with Bacteroides fragilis and its metabolite propionate can effectively modulate the Th17/Treg ratio, thereby attenuating inflammatory responses and improving immune homeostasis (120). Specifically, experimental evidence indicates that oral administration of Bacteroides fragilis or propionate markedly reduced levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, total thyroxine, and thyrotropin receptor antibodies in GD mouse models, while simultaneously decreasing the proportion of circulating Th17 and increasing the frequency of Treg (121). These immunological shifts not only alleviated systemic inflammation but also ameliorated hyperthyroid symptoms and diminished the autoimmune response against thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor.
Moreover, Bacteroides fragilis and propionate significantly reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines and the proportion of M1 macrophages in thyroid tissues, while enhancing Treg cells and M2 macrophages, collectively mitigating thyroid inflammation and hypertrophy. These findings highlight the pivotal role of gut microbes and their metabolites in GD pathogenesis and underscore their therapeutic potential.
Importantly, combining Bacteroides fragilis or propionate with the conventional drug methimazole significantly improved pathological changes in GD mice and allowed for a reduced methimazole dosage (121). This synergistic effect not only enhanced therapeutic efficacy but also minimized adverse drug reactions, providing a rationale for microbiota-based therapies as adjuncts to standard regimens. Such strategies may represent safer and more effective treatment paradigms for GD.
Additionally, analysis of the gut microbiota in 162 patients with mild and severe GD, compared with healthy controls, revealed significant taxonomic and functional alterations (122). These distinct microbial signatures hold promise as non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers for GD and provide a foundation for future clinical applications.
4.4 Autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic, immune-mediated liver disease characterized by the breakdown of immune tolerance and aberrant immune attacks against hepatic autoantigens (123). Increasing evidence indicates that gut microbiota and their metabolites play pivotal roles in the pathogenesis of AIH. Patients with AIH commonly exhibit gut dysbiosis, with markedly reduced microbial diversity compared with healthy individuals (124). Such alterations not only reshape the intestinal immune milieu but may also influence hepatic immunity via the gut–liver axis.
Changes in gut microbial composition have been shown to directly affect T cell function, particularly the balance between Treg and Th17 (125). Tregs are critical for maintaining immune tolerance and suppressing autoimmunity, whereas Th17 cells are strongly associated with pro-inflammatory responses. In AIH models, disruption of the Treg/Th17 balance exacerbates hepatic injury (126). For example, dysregulation of Trp metabolism can impair SCFAs production, resulting in diminished Treg function and enhanced Th17 activation (127).
Modulating gut microbiota composition and its metabolites has emerged as a promising strategy to restore Treg/Th17 homeostasis and attenuate liver injury. Studies have demonstrated that supplementation with specific probiotics enhances Treg proportions while suppressing Th17 activity in AIH mouse models (128, 129). For instance, Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis has shown therapeutic potential by strengthening intestinal barrier integrity and modulating hepatic immune cell responses (130).
Moreover, metabolites such as SCFAs possess potent immunomodulatory properties, promoting Treg differentiation while inhibiting Th17 activation (127). In AIH, restoration of a healthy gut microbiota not only improves systemic immune regulation but also mitigates hepatic inflammation and tissue damage. By targeting gut microbial communities and their metabolic pathways to re-establish Treg/Th17 equilibrium, significant hepatoprotective effects can be achieved, offering novel therapeutic targets and translational strategies for AIH management (131, 132). Thus, interventions focused on gut microbes and their metabolites represent a promising avenue for AIH therapy.
4.5 Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is an acquired neuromuscular autoimmune disorder characterized by impaired signal transmission at the neuromuscular junction, resulting in muscle weakness and fatigability (133). Recent studies have implicated gut microbial dysbiosis in the onset and progression of MG, with evidence pointing to a concurrent functional imbalance between Treg and Th17 as a key pathogenic mechanism (134).
Compared with healthy controls, patients with MG exhibit reduced gut microbial diversity and abundance, notably a depletion of bacterial taxa that produce SCFAs, which is considered a contributor to immune dysregulation (135). For example, marked decreases in beneficial genera such as Faecalibacterium have been directly associated with impaired Treg function, a deficit that may permit excessive activation of Th17 and thereby exacerbate the pathological cascade of MG (136). These observations suggest that restoring microbial balance could ameliorate symptoms by re-establishing the equilibrium between Treg and Th17 and dampening autoreactive immune responses.
Modulating the gut microbiota and its metabolites has therefore been proposed as a novel therapeutic avenue. Several investigations report that supplementation with specific probiotics or with SCFAs improves clinical and immunological features of MG, promoting immune rebalancing (137). For instance, butyrate supplementation increases Treg numbers and suppresses Th17 activity, thereby restoring the Treg/Th17 balance and mitigating pathological manifestations in experimental models (137). In addition, certain phytochemicals such as curcumin have shown potential in MG mouse models, apparently acting via modulation of the gut microbiome and elevation of SCFA levels (138).
Together, these findings indicate that targeted interventions — including probiotic therapy and dietary or metabolite supplementation — may offer new treatment options for patients with MG. Such strategies aim not only to restore immune homeostasis but also to improve patient quality of life and reduce reliance on conventional immunosuppressants. Future clinical research should prioritize rigorous evaluation of diverse microbiome-modulating approaches to determine their safety, efficacy and translational potential in MG management.
5 Therapeutic translation of gut microbial metabolites in regulating Treg/Th17 balance
5.1 Microbial and metabolite supplementation therapies
Recent years have seen growing interest in the capacity of probiotics and their metabolites to shape the gut microbiome and modulate host immune responses. Evidence indicates that oral probiotic supplementation can ameliorate clinical features of various autoimmune disorders. For example, administration of Limosilactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 was reported to improve the balance between Treg and Th17, thereby slowing autoimmune progression driven by Treg deficiency (139). SCFAs, such as butyrate, are key microbial metabolites that suppress activation of Th17 while promoting proliferation of Treg, and have been shown to reduce intestinal inflammation in murine models (33).
Supplementation with particular strains, notably members of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, has produced marked benefits in preclinical and clinical studies. For instance, Bifidobacterium supplementation not only remodels gut community structure but also mitigates pathological changes in autoimmune hepatitis by modulating host immune responses (115).
Beyond probiotics and SCFAs, secondary bile acids and their derivatives exert important immunoregulatory effects. Secondary bile acids influence intestinal immunity and microbial ecology by engaging specific host receptors, and perturbations in bile acid pools have been linked to autoimmune disease pathogenesis via effects on barrier function and immune-cell activity (140).
FMT has emerged as a promising therapeutic modality: by transferring a healthy donor microbiome to a patient, FMT aims to restore microbial balance, improve immune function and reduce inflammatory burden. Multiple studies report significant effects of FMT in the treatment of autoimmune conditions, supporting its further investigation (141).
For example, studies in RA have shown that FMT can significantly improve clinical symptoms, which correlates with increased gut microbial diversity (142). Moreover, FMT has been found to rebalance Treg/Th17 ratios, counteracting immune dysregulation caused by gut microbiota disturbances (143).
Clinically, FMT has been applied in the treatment of several autoimmune diseases, particularly inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, with encouraging outcomes (144). By restoring microbial diversity, FMT not only alleviates gastrointestinal symptoms but also promotes systemic immune reconstitution (145). However, further research is needed to establish long-term efficacy and optimize procedural standards for clinical application.
5.2 Metabolite-targeted delivery systems and nanotechnology
The clinical application of microbial metabolites, which play a crucial role in modulating immune responses, is often limited by their low oral bioavailability. This is particularly true for polar small-molecule metabolites such as itaconate (IA), whose intracellular efficacy often requires high exogenous concentrations to achieve therapeutic effects (146). To address this challenge, nanotechnology-based delivery systems have been developed to enhance metabolite bioavailability by improving solubility and stability. For instance, polyester-based polymeric microparticles enable endogenous delivery of small-molecule metabolites via macrophage phagocytosis, significantly increasing their effective concentration within immune cells while exhibiting low cytotoxicity (147). Moreover, the design of nanocarriers allows for targeted delivery, enabling selective release to specific cells or tissues and maximizing therapeutic outcomes.
Stimuli-responsive release systems represent a principal application of contemporary nanotechnology, enabling precise therapeutic release under defined physiological conditions (148). Using this strategy, nanoparticle-based carriers (nanocarriers) can remain stable within the intestinal microenvironment while discharging their payloads in response to specific triggers — for example, changes in pH or temperature — thereby allowing tight control over both the gut microbiota and immune-cell function. For instance, multifunctional particles engineered by nanotechnology have been shown to adjust their release profiles according to physiological variations in the intestine, effectively reshaping local immune responses and offering new therapeutic avenues for autoimmune disease (149). Moreover, combining targeted delivery of microbial metabolites with stimuli-responsive release increases treatment selectivity and reduces systemic adverse effects, thereby strengthening the clinical potential of metabolite-based interventions.
By integrating advanced nanotechnologies with intelligent release modalities, researchers are accelerating the clinical translation of metabolite-centered therapies for autoimmune disorders; these platforms substantially improve the precision and efficacy of drug delivery and help address many of the current therapeutic challenges.
5.3 Dietary interventions and lifestyle modifications
High-fiber diets have garnered increasing research interest, particularly in the context of managing autoimmune diseases. Studies have shown that dietary fiber is fermented by gut microbiota to produce SCFAs — such as butyrate, propionate, and acetate — which play essential roles in regulating immune balance (150). High-fiber intake has been demonstrated to significantly improve the immune profile in mouse models of RA, particularly by modulating the balance between Th17 and Treg. For example, one study revealed that a diet rich in pectin and inulin markedly reduced the severity of collagen-induced arthritis in mice and corrected aberrant T-cell differentiation by enhancing SCFAs production, thereby ameliorating immune responses (85). SCFAs not only promote Treg expansion via activation of the GPR43 receptor but also inhibit Th17 polarization, contributing to improved autoimmune outcomes (8).
Furthermore, SCFAs are closely associated with intestinal barrier integrity. By enhancing tight junctions between intestinal epithelial cells and increasing the expression of mucin Muc2, SCFAs help maintain gut barrier function, thereby reducing systemic inflammation (151). Increased SCFAs levels have been correlated with elevated Treg frequencies and reduced populations of Th1 and Th17, further supporting their therapeutic potential in autoimmune conditions (152). Therefore, implementing high-fiber diets as an intervention strategy can not only reshape the gut microbial composition but also modulate immune responses through enhanced SCFAs production, offering a novel non-pharmacological approach to autoimmune disease management.
The design of personalized dietary regimens should take into account individual gut microbial compositions. Advances in microbiome research have revealed considerable interindividual variability in gut microbiota, suggesting that uniform dietary interventions may not be effective for all patients. Tailored nutritional strategies can more effectively improve an individual’s immune status and overall health. For instance, one study showed that different dietary compositions variably influenced gut microbiota, which in turn affected immune responses and disease progression in mice (153).
In the management of autoimmune diseases, designing diet plans based on an individual’s microbiome profile may help optimize SCFAs production. Certain individuals may respond more favorably to specific types of dietary fiber, which should be prioritized in their nutritional intake. Such personalized dietary interventions can enhance microbial diversity and modulate immune cell ratios — particularly the Treg/Th17 balance — thereby alleviating autoimmune responses (154, 155).
5.4 Combined pharmacotherapy strategies
In the treatment of autoimmune diseases, conventional immunosuppressants, though effective, are often associated with significant side effects and high relapse rates (156). Consequently, developing combined therapeutic strategies to enhance efficacy and reduce drug dosage has become a major research focus. Microecological modulators — particularly probiotics and their metabolites — have recently demonstrated considerable potential in modulating immune responses, offering novel avenues for the treatment of autoimmune disorders.
For instance, studies have shown that Bacteroides fragilis and its metabolite propionate can significantly ameliorate disease manifestations in a mouse model of GD by restoring the Treg/Th17 balance (121). Oral supplementation with Bacteroides fragilis effectively reduced inflammatory cytokine levels, increased the proportion of Treg, and decreased Th17 cell frequency, thereby attenuating systemic inflammation, hyperthyroidism, and autoimmune responses. More importantly, the combination of Bacteroides fragilis with the conventional immunosuppressant methimazole not only improved pathological outcomes but also substantially reduced the required dosage of methimazole, indicating a synergistic therapeutic effect between microecological modulators and traditional drugs (121).
Further studies support the efficacy of combining microbial modulators with immunosuppressants. In RA, for example, probiotic administration has been shown to modulate gut microbiota composition and promote the production of anti-inflammatory metabolites such as SCFAs, leading to improved immune function and alleviated disease symptoms. Clinical evidence indicates that probiotics can reduce the abundance of harmful bacteria, enhance Treg functionality, and suppress Th17 activity, ultimately contributing to effective RA management (157, 158).
Combining microbiome-directed interventions with conventional immunosuppressive agents can both potentiate therapeutic benefit and mitigate drug-related adverse effects, thereby improving patients’ quality of life. Such combination strategies open new avenues for managing autoimmune diseases; future work should continue to define the mechanisms of action of distinct microbiome modulators and determine their optimal pairings with standard drugs to enable personalized regimens and enhanced clinical efficacy.
In GD, co-administration of Bacteroides fragilis and methimazole has produced marked therapeutic effects. Experimental data indicate that Bacteroides fragilis not only attenuates disease manifestations by recalibrating immune-cell populations but also acts synergistically with methimazole to permit dose reduction and lower side-effect burden. Specifically, supplementation with Bacteroides fragilis significantly decreased serum levels of inflammatory mediators — including proinflammatory cytokines and thyroid-associated autoantibodies — while increasing the frequency of Treg and suppressing the activity of Th17, thereby reducing systemic inflammation and the degree of thyrotoxicosis (121).
The mechanistic basis for this synergy likely involves microbiota-driven restoration of intestinal ecology and enhanced production of SCFAs, metabolites that play important roles in shaping host immune responses. In addition, combined treatment with Bacteroides fragilis and methimazole has been shown to improve histopathological features and to allow clinically meaningful reductions in methimazole dosing, suggesting that adjunctive microbiome therapy can preserve efficacy while improving tolerability (121).
Future studies should evaluate the efficacy of Bacteroides fragilis or other microbial modulators in combination with a broader range of immunosuppressants, and systematically assess the impact of dose, timing and route of administration on therapeutic outcomes. In summary, integrating microbiome-directed agents with standard pharmacotherapy offers a promising strategy for autoimmune disease treatment and merits further mechanistic and clinical investigation.
6 Therapeutic perspectives
6.1 Integrating multi-omics technologies to decipher the gut–immune axis
Recent advances in multi-omics technologies have offered powerful new perspectives for dissecting the complex interplay between the gut microbiota and the host immune system, particularly in the dynamic regulation of Treg and Th17 (159). Integrative applications of metagenomics, metabolomics and transcriptomics show great promise for resolving how microbial communities and their biochemical products influence the differentiation, function and cross-talk of Treg and Th17 (160). For example, SCFAs — key metabolites produced by gut microbes — have been shown to promote the expansion of Treg via receptors such as GPR41 and GPR43 while concurrently restraining the differentiation of Th17, thereby contributing to the maintenance of immune homeostasis (161, 162).
Furthermore, transcriptomic approaches have enabled the identification of specific gene expression profiles and signaling pathways associated with Treg/Th17 balance (163). These studies not only illustrate how microbial metabolites modulate immune responses by altering the host transcriptome but also reveal potential therapeutic targets. For example, certain microbial metabolites can influence the secretion of cytokines such as IL-10 and IL-17, further modulating the Treg/Th17 ratio and thereby affecting the progression of autoimmune diseases (164, 165).
Constructing a cross-tissue regulatory network model of the “gut–immune–target organ” axis is essential for understanding how gut microbiota influence systemic immunity and organ function. Through the integration of multi-omics data, it is possible to map the complex interaction networks among the gut, immune system, and target organs (e.g., liver, lungs) (166). For instance, in chronic inflammatory diseases, gut microbial composition and metabolites can influence the immune status of distant organs via systemic circulation, forming feedback loops along the gut–immune–target organ axis.
Emerging evidence indicates that gut dysbiosis not only triggers local inflammation but may also initiate or exacerbate systemic autoimmune diseases by altering overall immune status. In conditions such as SLE and RA, alterations in gut microbiota and their metabolites are closely associated with disease progression. By establishing cross-tissue regulatory network models, researchers can identify key regulatory factors and their mechanisms, providing a theoretical foundation for precision medicine (167, 168).
6.2 Development of personalized microecological therapeutics
The development of individualized microbiome-based therapeutic regimens is a complex but essential undertaking that seeks to design precise interventions by accounting for interindividual variation in gut microbial composition and metabolic output. Studies have shown that the structure of the gut microbiota closely correlates with an individual’s health status, disease susceptibility and therapeutic responsiveness; notably, specific bacterial taxa have been directly linked to the development of metabolic disorders such as obesity and type 2 diabetes (169). Accordingly, tailoring treatments to a patient’s microbiome profile has the potential both to enhance efficacy and to reduce adverse effects.
A first prerequisite for personalized microbiome therapy is the construction of patient-specific gut microbiome databases using high-throughput sequencing to characterize microbial community composition and functional capacity (170, 171). Comparative analyses between healthy subjects and patients enable identification of microbial taxa that are associated with disease states (172). These data can inform predictive models of treatment response and support longitudinal monitoring to permit timely adjustment of therapeutic strategies.
Therapeutic options for microbiome modulation include administration of probiotics, provision of prebiotics, and FMT, among other approaches (173). For example, particular probiotic strains have been reported to increase microbial diversity and bolster immune competence, thereby improving clinical outcomes (174). Dietary interventions likewise exert a demonstrable effect on the intestinal microbiota; specific dietary components can selectively promote the growth of beneficial microbes and thereby contribute to overall health (33).
Finally, successful implementation of individualized microbiome therapies depends on multidisciplinary collaboration among clinicians, microbiologists and nutrition scientists. Integrating mechanistic insights into the “microbiome–metabolite–host” axis will support more finely tuned, patient-centered interventions that enhance therapeutic benefit and improve quality of life for patients (175).
6.3 Clinical translation and multicenter large-scale trials
The contributions of the gut microbiota and their metabolites to the study and treatment of autoimmune diseases have attracted growing attention. Recent studies indicate that alterations of the gut microbiota can promote the onset and progression of diverse autoimmune disorders (176). For example, dysbiosis observed in patients with MG is closely associated with an imbalance between Treg and Th17, providing a rationale for microbiota-directed approaches to restore immune equilibrium (177). To facilitate clinical translation of microbiome-based therapies, stronger integration of fundamental research and clinical practice is essential so that mechanistic insights can be reliably converted into effective interventions.
Furthermore, the clinical development of microbiome therapeutics requires well-designed, multicenter, large-scale trials that include geographically and demographically diverse populations to ensure broad applicability and robust evidence. For instance, investigations into postmenopausal osteoporosis have demonstrated that the gut microbiota and its metabolites modulate bone metabolism via the gut–bone axis and the gut–brain axis (178). Systematic evaluation of therapeutic efficacy and safety, together with exploration of applications across different autoimmune conditions, will be critical to inform future clinical practice.
7 Limitations and future directions
As our understanding of the gut microbiota and its metabolites deepens, their central role in regulating the balance between Treg and Th17 has become increasingly evident. Treg and Th17 operate as opposing forces within immune networks, and microbial-derived signals that shift their equilibrium provide fresh mechanistic insight into autoimmune disease pathogenesis. A growing body of experimental and clinical evidence shows that restoring a healthy microbial ecology and correcting metabolite profiles can re-establish immune homeostasis and ameliorate disease manifestations across multiple autoimmune disorders. These observations underscore that the integrity of the gut microbiome closely informs systemic immune stability and thereby influences both disease onset and progression.
Building on these mechanistic insights, a range of translational strategies targeting microbial metabolites has emerged. Approaches span direct metabolite supplementation, targeted delivery platforms (including nano-formulations), microbiome-informed personalized regimens, and rational combinations with conventional immunosuppressive agents. Such multidimensional strategies aim to improve therapeutic efficacy while minimizing adverse effects, and individualized treatment programs in particular hold promise for tailoring interventions to patients’ distinct microbiome and immune profiles.
Despite this promise, significant heterogeneity and limitations remain across the literature. Conflicting results often reflect small cohort sizes, divergent study designs, variable analytical pipelines, and limited longitudinal follow-up. These constraints impede causal inference and the identification of robust, generalizable biomarkers. Addressing these gaps will require rigorously powered studies with standardized methods and transparent reporting.
Looking ahead, advancing precision therapies that harness microbial metabolites to recalibrate immune function will depend on tighter integration with clinical practice. Systematic application of multi-omics platforms combined with deep clinical phenotyping can reveal mechanistic links and predictive signatures suitable for clinical translation. Equally important are large-scale, well-controlled clinical trials and long-term follow-up studies to establish safety, efficacy, and durability of microbiome-targeted interventions.
In summary, the gut microbiota and its metabolic products are pivotal determinants of the Treg/Th17 axis and thus of autoimmune disease biology. Modulating microbial communities and their metabolites offers a compelling avenue to restore immune balance and develop innovative treatments. Future efforts that combine multidisciplinary science, rigorous clinical evaluation, and patient-centered design are essential to realize safe, effective, and personalized microbiome-based therapies for autoimmune disease.
Author contributions
GL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft. YX: Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. ZL: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. QY: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. SL: Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. JX: Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. SZ: Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. DY: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YY: Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JY: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2025ZNSFSC0718), Talent Introduction Research Project of Mianyang Central Hospital (2025RCYJ-008), and Incubation Project of Mianyang Central Hospital (2024FH013).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support from Mianyang Central Hospital, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, and Southwest Medical University. And thank Yong Yang for his contribution to the paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Honing DY, Luiten RM, and Matos TR. Regulatory T cell dysfunction in autoimmune diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:7171. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137171
2. Sprouse ML, Bates NA, Felix KM, and Wu H-JJ. Impact of gut microbiota on gut-distal autoimmunity: a focus on T cells. Immunology. (2019) 156:305–18. doi: 10.1111/imm.13037
3. Sambucci M, Gargano F, Guerrera G, Battistini L, and Borsellino G. One, no one, and one hundred thousand: T regulatory cells’ Multiple identities in neuroimmunity. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2947. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02947
4. Hassan T, Zakaria M, Diaa A, Abdalla AELS, Ahmed ALSMS, Abdelmonem DM, et al. Contribution of T helper 17 cells and interleukin-17 to the pathogenesis of primary immune thrombocytopenia in Egyptian children. Eur J Pediatr. (2023) 182:5673–9. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-05242-3
5. Tang F, Zhou Z, Huang K, Deng W, Lin J, Chen R, et al. MicroRNAs in the regulation of Th17/Treg homeostasis and their potential role in uveitis. Front Genet. (2022) 13:848985. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.848985
6. Kargar M, Torabizadeh M, Purrahman D, Zayeri ZD, and Saki N. Regulatory factors involved in Th17/Treg cell balance of immune thrombocytopenia. Curr Res Transl Med. (2023) 71:103389. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2023.103389
7. Wang Z, Liu Z, Zheng J, Huang L, Jin R, Wang X, et al. The effects of low-dose IL-2 on Th17/Treg cell imbalance in primary biliary cholangitis mouse models. BMC Gastroenterol. (2024) 24:87. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03176-0
8. Lv J, Hao P, Zhou Y, Liu T, Wang L, Song C, et al. Role of the intestinal flora-immunity axis in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis-mechanisms regulating short-chain fatty acids and Th17/Treg homeostasis. Mol Biol Rep. (2025) 52:617. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10714-w
9. Wang J, Zhu N, Su X, Gao Y, and Yang R. Gut-microbiota-derived metabolites maintain gut and systemic immune homeostasis. Cells. (2023) 12:793. doi: 10.3390/cells12050793
10. Lian F-P, Zhang F, Zhao C-M, Wang X-X, Bu Y-J, Cen X, et al. Gut microbiota regulation of T lymphocyte subsets during systemic lupus erythematosus. BMC Immunol. (2024) 25:41. doi: 10.1186/s12865-024-00632-0
11. Mortezaee K. Microbiota interaction with Tregs: a target for colitis. Clin Transl Oncol. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s12094-025-03974-2
12. Tian N, Yang C, Du Y, Chen M, Li B, Li D, et al. Cannabinoid receptor 2 selective agonist ameliorates adjuvant-induced arthritis by modulating the balance between Treg and Th17 cells. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:1532518. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1532518
13. Chen J, Pan Q, Lu L, Huang X, Wang S, Liu X, et al. Atg5 deficiency in basophils improves metabolism in lupus mice by regulating gut microbiota dysbiosis. Cell Commun Signal. (2025) 23:40. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02041-1
14. Ge J, Zhang X, Tang F, and Liu Y. SIRT7 ameliorates Th17/Treg imbalance by desuccinylation of STAT3 to improve immune thrombocytopenia. Clin Transl Immunol. (2025) 14:e70048. doi: 10.1002/cti2.70048
15. Yin T, Zhang X, Xiong Y, Li B, Guo D, Sha Z, et al. Exploring gut microbial metabolites as key players in inhibition of cancer progression: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Microbiol Res. (2024) 288:127871. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2024.127871
16. Brescia C, Audia S, Pugliano A, Scaglione F, Iuliano R, Trapasso F, et al. Metabolic drives affecting Th17/Treg gene expression changes and differentiation: impact on immune-microenvironment regulation. APMIS. (2024) 132:1026–45. doi: 10.1111/apm.13378
17. Fisher MS and Sennikov SV. T-regulatory cells for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1511671. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1511671
18. Gao P, Luo YP, Li JF, Chen I, and Mao XR. Effects of hepatitis B virus on Th17, Treg and Th17/Treg ratio in different alanine aminetransferase stages. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. (2022) 54:272–7. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.02.012
19. Gautam S, Kumar S, and Dada R. Transcription factor analysis to investigate immunosenescence in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Methods Mol Biol. (2025) 2857:79–87. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4128-6_7
20. Bisoendial R and Lubberts E. A mechanistic insight into the pathogenic role of interleukin 17A in systemic autoimmune diseases. Mediators Inflammation. (2022) 2022:6600264. doi: 10.1155/2022/6600264
21. Schnell A, Littman DR, and Kuchroo VK. TH17 cell heterogeneity and its role in tissue inflammation. Nat Immunol. (2023) 24:19–29. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01387-9
22. Zhu X, Wang P, Zhan X, Zhang Y, Sheng J, He S, et al. USP1-regulated reciprocal differentiation of Th17 cells and Treg cells by deubiquitinating and stabilizing TAZ. Cell Mol Immunol. (2023) 20:252–63. doi: 10.1038/s41423-022-00969-9
23. Kubick N, Paszkiewicz J, Bieńkowska I, Ławiński M, Horbańczuk JO, Sacharczuk M, et al. Investigation of mutated in colorectal cancer (MCC) gene family evolution history indicates a putative role in Th17/Treg differentiation. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:11940. doi: 10.3390/ijms241511940
24. Zhou L and Littman DR. Transcriptional regulatory networks in Th17 cell differentiation. Curr Opin Immunol. (2009) 21:146–52. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2009.03.001
25. Su Y, Zhang F, Wu L, Kuang H, Wang Q, and Cheng G. Total withanolides ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation. J Ethnopharmacol. (2022) 285:114895. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114895
26. Siracusa F, Muscate F, and Perez LG. Murine T-helper cell differentiation and plasticity. Methods Mol Biol. (2021) 2285:65–75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1311-5_5
27. Shahrara S, Huang Q, Mandelin AM, and Pope RM. TH-17 cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2008) 10:R93. doi: 10.1186/ar2477
28. Chen M, Chen X, and Wan Q. Altered frequency of Th17 and Treg cells in new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Eur J Clin Invest. (2018) 48:e13012. doi: 10.1111/eci.13012
29. Zhang W, Liu X, Zhu Y, Liu X, Gu Y, Dai X, et al. Transcriptional and posttranslational regulation of Th17/Treg balance in health and disease. Eur J Immunol. (2021) 51:2137–50. doi: 10.1002/eji.202048794
30. Zhang S, Gang X, Yang S, Cui M, Sun L, Li Z, et al. The alterations in and the role of the Th17/Treg balance in metabolic diseases. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:678355. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.678355
31. Wang J, Zhao X, and Wan YY. Intricacies of TGF-β signaling in Treg and Th17 cell biology. Cell Mol Immunol. (2023) 20:1002–22. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-01036-7
32. Zhang S, Zhong R, Tang S, Chen L, and Zhang H. Metabolic regulation of the Th17/Treg balance in inflammatory bowel disease. Pharmacol Res. (2024) 203:107184. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107184
33. Wang J, Hou Y, Mu L, Yang M, and Ai X. Gut microbiota contributes to the intestinal and extraintestinal immune homeostasis by balancing Th17/Treg cells. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 143:113570. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113570
34. Thomas R, Qiao S, and Yang X. Th17/Treg imbalance: implications in lung inflammatory diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:4865. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054865
35. Mazmanian SK, Round JL, and Kasper DL. A microbial symbiosis factor prevents intestinal inflammatory disease. Nature. (2008) 453:620–5. doi: 10.1038/nature07008
36. Goto Y, Panea C, Nakato G, Cebula A, Lee C, Diez MG, et al. Segmented filamentous bacteria antigens presented by intestinal dendritic cells drive mucosal Th17 cell differentiation. Immunity. (2014) 40:594–607. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.03.005
37. Hrncir T. Gut microbiota dysbiosis: triggers, consequences, diagnostic and therapeutic options. Microorganisms. (2022) 10:578. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10030578
38. Safarchi A, Al-Qadami G, Tran CD, and Conlon M. Understanding dysbiosis and resilience in the human gut microbiome: biomarkers, interventions, and challenges. Front Microbiol. (2025) 16:1559521. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1559521
39. An R, Wilms E, Masclee AAM, Smidt H, Zoetendal EG, and Jonkers D. Age-dependent changes in GI physiology and microbiota: time to reconsider? Gut. (2018) 67:2213–22. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-315542
40. Das B and Nair GB. Homeostasis and dysbiosis of the gut microbiome in health and disease. J Biosci. (2019) 44:117. doi: 10.1007/s12038-019-9926-y
41. Wang L, Alammar N, Singh R, Nanavati J, Song Y, Chaudhary R, et al. Gut microbial dysbiosis in the irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies. J Acad Nutr Diet. (2020) 120:565–86. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2019.05.015
42. Coombes JL, Siddiqui KRR, Arancibia-Cárcamo CV, Hall J, Sun C-M, Belkaid Y, et al. A functionally specialized population of mucosal CD103+ DCs induces Foxp3+ regulatory T cells via a TGF-beta and retinoic acid-dependent mechanism. J Exp Med. (2007) 204:1757–64. doi: 10.1084/jem.20070590
43. Kinnebrew MA, Buffie CG, Diehl GE, Zenewicz LA, Leiner I, Hohl TM, et al. Interleukin 23 production by intestinal CD103(+)CD11b(+) dendritic cells in response to bacterial flagellin enhances mucosal innate immune defense. Immunity. (2012) 36:276–87. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.12.011
44. Brenchley JM, Price DA, Schacker TW, Asher TE, Silvestri G, Rao S, et al. Microbial translocation is a cause of systemic immune activation in chronic HIV infection. Nat Med. (2006) 12:1365–71. doi: 10.1038/nm1511
45. Mudd JC and Brenchley JM. Gut mucosal barrier dysfunction, microbial dysbiosis, and their role in HIV-1 disease progression. J Infect Dis. (2016) 214:S58–66. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw258
46. Bunker JJ, Erickson SA, Flynn TM, Henry C, Koval JC, Meisel M, et al. Natural polyreactive IgA antibodies coat the intestinal microbiota. Science. (2017) 358:eaan6619. doi: 10.1126/science.aan6619
47. Zheng L, Kelly CJ, Battista KD, Schaefer R, Lanis JM, Alexeev EE, et al. Microbial-derived butyrate promotes epithelial barrier function through IL-10 receptor-dependent repression of claudin-2. J Immunol. (2017) 199:2976–84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700105
48. Bäckhed F, Roswall J, Peng Y, Feng Q, Jia H, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, et al. Dynamics and stabilization of the human gut microbiome during the first year of life. Cell Host Microbe. (2015) 17:852. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.05.012
49. Rampelli S, Soverini M, D’Amico F, Barone M, Tavella T, Monti D, et al. Shotgun metagenomics of gut microbiota in humans with up to extreme longevity and the increasing role of xenobiotic degradation. mSystems. (2020) 5:e00124–20. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00124-20
50. Markle JGM, Frank DN, Mortin-Toth S, Robertson CE, Feazel LM, Rolle-Kampczyk U, et al. Sex differences in the gut microbiome drive hormone-dependent regulation of autoimmunity. Science. (2013) 339:1084–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1233521
51. Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ, Trehan I, Dominguez-Bello MG, Contreras M, et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature. (2012) 486:222–7. doi: 10.1038/nature11053
52. Hildebrandt MA, Hoffmann C, Sherrill-Mix SA, Keilbaugh SA, Hamady M, Chen Y-Y, et al. High-fat diet determines the composition of the murine gut microbiome independently of obesity. Gastroenterology. (2009) 137:1716–24.e1–2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.08.042
53. David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN, Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE, et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature. (2014) 505:559–63. doi: 10.1038/nature12820
54. Sonnenburg ED, Smits SA, Tikhonov M, Higginbottom SK, Wingreen NS, and Sonnenburg JL. Diet-induced extinctions in the gut microbiota compound over generations. Nature. (2016) 529:212–5. doi: 10.1038/nature16504
55. Palleja A, Mikkelsen KH, Forslund SK, Kashani A, Allin KH, Nielsen T, et al. Recovery of gut microbiota of healthy adults following antibiotic exposure. Nat Microbiol. (2018) 3:1255–65. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0257-9
56. Wen S, He L, Zhong Z, Zhao R, Weng S, Mi H, et al. Stigmasterol restores the balance of Treg/Th17 cells by activating the butyrate-PPARγ Axis in colitis. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:741934. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.741934
57. Mukhopadhya I and Louis P. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and their role in human health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2025) 23:635–651. doi: 10.1038/s41579-025-01183-w
58. Debnath N, Kumar R, Kumar A, Mehta PK, and Yadav AK. Gut-microbiota derived bioactive metabolites and their functions in host physiology. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. (2021) 37:105–53. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2021.1989847
59. Donohoe DR, Garge N, Zhang X, Sun W, O’Connell TM, Bunger MK, et al. The microbiome and butyrate regulate energy metabolism and autophagy in the mammalian colon. Cell Metab. (2011) 13:517–26. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.02.018
60. Smith PM, Howitt MR, Panikov N, Michaud M, Gallini CA, Bohlooly- YM, et al. The microbial metabolites, short chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science. (2013) 341. doi: 10.1126/science.1241165
61. Saadh MJ, Allela OQB, Ballal S, Mahdi MS, Chahar M, Verma R, et al. The effects of microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids on T lymphocytes: From autoimmune diseases to cancer. Semin Oncol. (2025) 52:152398. doi: 10.1016/j.seminoncol.2025.152398
62. Liu X-F, Shao J-H, Liao Y-T, Wang L-N, Jia Y, Dong P-J, et al. Regulation of short-chain fatty acids in the immune system. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1186892. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1186892
63. Chen X, Wei J, Zhang L, Wang H, Zhang Y, Li Z, et al. Association between plasma short-chain fatty acids and inflammation in human immunodeficiency virus-associated neurocognitive disorder: a pilot study. Lipids Health Dis. (2025) 24:66. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02477-x
64. Qin X, Sun J, Xu Y, Lu L, Ma Y, Lou F, et al. Short-chain fatty acids are potential biomarkers of immune regulation in diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. (2025) 66:23. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.6.23
65. Ventura I, Chomon-García M, Tomás-Aguirre F, Palau-Ferré A, Legidos-García ME, Murillo-Llorente MT, et al. Therapeutic and immunologic effects of short-chain fatty acids in inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:10879. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010879
66. Huang H, Yang C, Li S, Zhan H, Tan J, Chen C, et al. Lizhong decoction alleviates experimental ulcerative colitis via regulating gut microbiota-SCFAs-Th17/Treg axis. J Ethnopharmacol. (2025) 349:119958. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119958
67. Pang S, Ren Z, Ding H, and Chan P. Short-chain fatty acids mediate enteric and central nervous system homeostasis in Parkinson’s disease: Innovative therapies and their translation. Neural Regener Res. (2026) 21:938–56. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-01265
68. Biagioli M, Di Giorgio C, Massa C, Marchianò S, Bellini R, Bordoni M, et al. Microbial-derived bile acid reverses inflammation in IBD via GPBAR1 agonism and RORγt inverse agonism. BioMed Pharmacother. (2024) 181:117731. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117731
69. Biagioli M, Marchianò S, Carino A, Di Giorgio C, Santucci L, Distrutti E, et al. Bile acids activated receptors in inflammatory bowel disease. Cells. (2021) 10:1281. doi: 10.3390/cells10061281
70. Tyagi A and Kumar V. The gut microbiota-bile acid axis: a crucial regulator of immune function and metabolic health. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. (2025) 41:215. doi: 10.1007/s11274-025-04395-7
71. Zhao M, Zhao J, Yang H, Ouyang Z, Lv C, Geng Z, et al. The bile acid-gut microbiota axis: A central hub for physiological regulation and a novel therapeutic target for metabolic diseases. BioMed Pharmacother. (2025) 188:118182. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118182
72. Antonini Cencicchio M, Montini F, Palmieri V, Massimino L, Lo Conte M, Finardi A, et al. Microbiota-produced immune regulatory bile acid metabolites control central nervous system autoimmunity. Cell Rep Med. (2025) 6:102028. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102028
73. Gootjes C, Zwaginga JJ, Roep BO, and Nikolic T. Defining human regulatory T cells beyond FOXP3: the need to combine phenotype with function. Cells. (2024) 13:941. doi: 10.3390/cells13110941
74. Yang Z, Zhou F, Zhan D, Li P, and Pan J. Levels of bile acid metabolism are associated with alterations of gut microbes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. (2025) 64:543–51. doi: 10.1002/mc.23869
75. Urbani G, Rondini E, Distrutti E, Marchianò S, Biagioli M, and Fiorucci S. Phenotyping the chemical communications of the intestinal microbiota and the host: secondary bile acids as postbiotics. Cells. (2025) 14:595. doi: 10.3390/cells14080595
76. Stone TW and Williams RO. Modulation of T cells by tryptophan metabolites in the kynurenine pathway. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2023) 44:442–56. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2023.04.006
77. Cao Y, Xiao S, He B, Shi X, Xiao N, Liu X, et al. Chronic exposure to fluxapyroxad exacerbated susceptibility to colitis in mice via a gut microbiota-indole derivatives-Th17/Treg cell balance axis. J Agric Food Chem. (2025) 73:10172–85. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5c02749
78. Agus A, Planchais J, and Sokol H. Gut microbiota regulation of tryptophan metabolism in health and disease. Cell Host Microbe. (2018) 23:716–24. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2018.05.003
79. Yang W and Cong Y. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites in the regulation of host immune responses and immune-related inflammatory diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) 18:866–77. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00661-4
80. Rooks MG and Garrett WS. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. (2016) 16:341–52. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.42
81. Gargaro M, Vacca C, Massari S, Scalisi G, Manni G, Mondanelli G, et al. Engagement of nuclear coactivator 7 by 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid enhances activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in immunoregulatory dendritic cells. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1973. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01973
82. Moulin D, Millard M, Taïeb M, Michaudel C, Aucouturier A, Lefèvre A, et al. Counteracting tryptophan metabolism alterations as a new therapeutic strategy for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2024) 83:312–23. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-224014
83. Åkesson K, Pettersson S, Ståhl S, Surowiec I, Hedenström M, Eketjäll S, et al. Kynurenine pathway is altered in patients with SLE and associated with severe fatigue. Lupus Sci Med. (2018) 5:e000254. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2017-000254
84. Jiang Z-M, Zeng S-L, Huang T-Q, Lin Y, Wang F-F, Gao X-J, et al. Sinomenine ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis by modulating tryptophan metabolism and activating aryl hydrocarbon receptor via gut microbiota regulation. Sci Bull (Beijing). (2023) 68:1540–55. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2023.06.027
85. Lou Y, Wen X, Song S, Zeng Y, Huang L, Xie Z, et al. Dietary pectin and inulin: A promising adjuvant supplement for collagen-induced arthritis through gut microbiome restoration and CD4+ T cell reconstitution. J Nutr Biochem. (2024) 133:109699. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2024.109699
86. Qi P, Chen X, Tian J, Zhong K, Qi Z, Li M, et al. The gut homeostasis-immune system axis: novel insights into rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis and treatment. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1482214. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1482214
87. Cao S, Budina E, Raczy MM, Solanki A, Nguyen M, Beckman TN, et al. A serine-conjugated butyrate prodrug with high oral bioavailability suppresses autoimmune arthritis and neuroinflammation in mice. Nat BioMed Eng. (2024) 8:611–27. doi: 10.1038/s41551-024-01190-x
88. Cao Y, Chen J, Xiao J, Hong Y, Xu K, and Zhu Y. Butyrate: a bridge between intestinal flora and rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1475529. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1475529
89. Cao S, Budina E, Wang R, Sabados M, Mukherjee A, Solanki A, et al. Injectable butyrate-prodrug micelles induce long-acting immune modulation and prevent autoimmune arthritis in mice. J Control Release. (2024) 372:281–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.06.027
90. Wang C, Yang J, Xie L, Saimaier K, Zhuang W, Han M, et al. Methyl butyrate alleviates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and regulates the balance of effector T cells and regulatory T cells. Inflammation. (2022) 45:977–91. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01596-8
91. Al KF, Craven LJ, Gibbons S, Parvathy SN, Wing AC, Graf C, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation is safe and tolerable in patients with multiple sclerosis: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Mult Scler J Exp Transl Clin. (2022) 8:20552173221086662. doi: 10.1177/20552173221086662
92. Paik D, Yao L, Zhang Y, Bae S, D’Agostino GD, Zhang M, et al. Human gut bacteria produce TH17-modulating bile acid metabolites. Nature. (2022) 603:907–12. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04480-z
93. Seo S-K and Kwon B. Immune regulation through tryptophan metabolism. Exp Mol Med. (2023) 55:1371–9. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01028-7
94. Hezaveh K, Shinde RS, Klötgen A, Halaby MJ, Lamorte S, Ciudad MT, et al. Tryptophan-derived microbial metabolites activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in tumor-associated macrophages to suppress anti-tumor immunity. Immunity. (2022) 55:324–40.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.01.006
95. Harris DMM, Szymczak S, Schuchardt S, Labrenz J, Tran F, Welz L, et al. Tryptophan degradation as a systems phenomenon in inflammation – an analysis across 13 chronic inflammatory diseases. eBioMedicine. (2024) 102. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105056
96. Li S. Modulation of immunity by tryptophan microbial metabolites. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1209613. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1209613
97. Kim TK, Lee J-C, Im S-H, and Lee M-S. Amelioration of autoimmune diabetes of NOD mice by immunomodulating probiotics. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1832. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01832
98. Jacob N, Jaiswal S, Maheshwari D, Nallabelli N, Khatri N, Bhatia A, et al. Butyrate induced Tregs are capable of migration from the GALT to the pancreas to restore immunological tolerance during type-1 diabetes. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:19120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76109-y
99. Bell KJ, Saad S, Tillett BJ, McGuire HM, Bordbar S, Yap YA, et al. Metabolite-based dietary supplementation in human type 1 diabetes is associated with microbiota and immune modulation. Microbiome. (2022) 10:9. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01193-9
100. Huang J, Pearson JA, Peng J, Hu Y, Sha S, Xing Y, et al. Gut microbial metabolites alter IgA immunity in type 1 diabetes. JCI Insight. (2020) 5. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.135718
101. Li W, Hang S, Fang Y, Bae S, Zhang Y, Zhang M, et al. A bacterial bile acid metabolite modulates Treg activity through the nuclear hormone receptor NR4A1. Cell Host Microbe. (2021) 29:1366–77.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.07.013
102. Martinsson K, Dürholz K, Schett G, Zaiss MM, and Kastbom A. Higher serum levels of short-chain fatty acids are associated with non-progression to arthritis in individuals at increased risk of RA. Ann Rheum Dis. (2022) 81:445–7. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221386
103. Belvončíková P, Macáková K, Tóthová N, Babál P, Tarabčáková L, and Gardlík R. Investigating the role of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis and progression of rheumatoid arthritis in a collagen-induced arthritis mouse model. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26:5099. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115099
104. Fan Z, Ross RP, Stanton C, Hou B, Zhao J, Zhang H, et al. Lactobacillus casei CCFM1074 Alleviates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats via Balancing Treg/Th17 and Modulating the Metabolites and Gut Microbiota. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:680073. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.680073
105. Inayat N, Zahir A, Hashmat AJ, Khan A, Ahmad A, Sikander M, et al. Gut microbiota as a key modulator of chronic disease: implications for diabetes, autoimmunity, and cancer. Cureus. (2025) 17:e84687. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84687
106. Zhu X, Lu H, Li W, Niu S, Xue J, Sun H, et al. Ferroptosis Induces gut microbiota and metabolic dysbiosis in Collagen-Induced arthritis mice via PAD4 enzyme. Gene. (2025) 936:149106. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.149106
107. Marazzato M, Iannuccelli C, Guzzo MP, Nencioni L, Lucchino B, Radocchia G, et al. Gut microbiota structure and metabolites, before and after treatment in early rheumatoid arthritis patients: A pilot study. Front Med. (2022) 9:921675. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.921675
108. Wu R, Li B, Su R, Liu X, Gao A, Luo J, et al. Serum tryptophan-kynurenine metabolites served as biomarkers of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis and linked to immune imbalance. Arthritis Res Ther. (2025) 27:136. doi: 10.1186/s13075-025-03596-7
109. Seymour BJ, Trent B, Allen BE, Berlinberg AJ, Tangchittsumran J, Jubair WK, et al. Microbiota-dependent indole production stimulates the development of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Clin Invest. (2023) 134:e167671. doi: 10.1172/JCI167671
110. Shimokawa C. The gut microbiome-helminth-immune axis in autoimmune diseases. Parasitol Int. (2025) 104:102985. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2024.102985
111. Feng W, Wan X, Fan S, Liu C-Z, Zheng X-X, Liu Q-P, et al. Mechanism underlying the action of Duanteng-Yimu Tang in regulating Treg/Th17 imbalance and anti-rheumatoid arthritis. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e15867. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15867
112. Cai X, Ren F, and Yao Y. Gut microbiota and their metabolites in the immune response of rheumatoid arthritis: Therapeutic potential and future directions. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 147:114034. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114034
113. Huang J, Li X, Zhu Q, Wang M, Xie Z, and Zhao T. Imbalance of Th17 cells, Treg cells and associated cytokines in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1425847. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425847
114. Ahn J-S, Lee Y-B, Han E-J, Choi Y-J, Kim D-H, Kwok SK, et al. Identification of specific gut microbes and their therapeutic potential in ameliorating systemic lupus erythematosus in a mouse model. Life Sci. (2025) 374:123684. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2025.123684
115. Wu L, Guan Z, Zhang X, Liu Y, Chi S, Duan X, et al. Bifidobacterium ameliorates lupus nephritis and modulates aberrant differentiation of lymphocyte subsets. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2025) 64:5518–5528. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaf271
116. Kim CH. Complex regulatory effects of gut microbial short-chain fatty acids on immune tolerance and autoimmunity. Cell Mol Immunol. (2023) 20:341–50. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-00987-1
117. Golpour F, Abbasi-Alaei M, Babaei F, Mirzababaei M, Parvardeh S, Mohammadi G, et al. Short chain fatty acids, a possible treatment option for autoimmune diseases. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 163:114763. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114763
118. Mytych J, Romerowicz-Misielak M, and Koziorowski M. Long-term culture with lipopolysaccharide induces dose-dependent cytostatic and cytotoxic effects in THP-1 monocytes. Toxicol In Vitro. (2017) 42:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2017.03.009
119. Rodríguez-Carrio J, López P, Sánchez B, González S, Gueimonde M, Margolles A, et al. Intestinal dysbiosis is associated with altered short-chain fatty acids and serum-free fatty acids in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:23. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00023
120. Shimizu J, Kubota T, Takada E, Takai K, Fujiwara N, Arimitsu N, et al. Propionate-producing bacteria in the intestine may associate with skewed responses of IL10-producing regulatory T cells in patients with relapsing polychondritis. PloS One. (2018) 13:e0203657. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203657
121. Zhang X, Pan Q, Yao G, Kong D, Chen H, Zhang Q, et al. Bacteroides fragilis and propionate synergize with low-dose methimazole to treat Graves’ disease. Microbiol Spectr. (2025) 13:e0318624. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03186-24
122. Zhu Q, Hou Q, Huang S, Ou Q, Huo D, Vasquez-Baeza Y, et al. Compositional and genetic alterations in Graves’ disease gut microbiome reveal specific diagnostic biomarkers. ISME J. (2021) 15:3399–3411. doi: 10.1038/s41396-021-01016-7
123. Preti M, Schlott L, Lübbering D, Krzikalla D, Müller A-L, Schuran FA, et al. Failure of thymic deletion and instability of autoreactive Tregs drive autoimmunity in immune-privileged liver. JCI Insight. (2021) 6:e141462. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.141462
124. Wu Q, Ge Z, Lv C, and He Q. Interacting roles of gut microbiota and T cells in the development of autoimmune hepatitis. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1584001. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1584001
125. Liu Y-J, Tang B, Wang F-C, Tang L, Lei Y-Y, Luo Y, et al. Parthenolide ameliorates colon inflammation through regulating Treg/Th17 balance in a gut microbiota-dependent manner. Theranostics. (2020) 10:5225–41. doi: 10.7150/thno.43716
126. Qian Q, He W, Tang R, and Ma X. Implications of gut microbiota in autoimmune liver diseases. Minerva Gastroenterol (Torino). (2023) 69:95–106. doi: 10.23736/S2724-5985.21.02860-9
127. Zhang W, Mackay CR, and Gershwin ME. Immunomodulatory effects of microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids in autoimmune liver diseases. J Immunol. (2023) 210:1629–39. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300016
128. Ji W, Wang W, Li P, Liu Y, Zhang B, and Qi F. sFgl2 gene-modified MSCs regulate the differentiation of CD4+ T cells in the treatment of autoimmune hepatitis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2023) 14:316. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03550-x
129. Liu Q, Tian H, Kang Y, Tian Y, Li L, Kang X, et al. Probiotics alleviate autoimmune hepatitis in mice through modulation of gut microbiota and intestinal permeability. J Nutr Biochem. (2021) 98:108863. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2021.108863
130. Zhang H, Liu M, Liu X, Zhong W, Li Y, Ran Y, et al. Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. Lactis 420 Mitigates Autoimmune Hepatitis Through Regulating Intestinal Barrier and Liver Immune Cells. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:569104. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.569104
131. Han A, Oo YH, and Perera MTPR. Regulatory T-cell therapy in liver transplantation and chronic liver disease. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:719954. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.719954
132. Zhang X, Wan L, Zheng Y, and Ai Y. Gut barrier, microbial metabolites, and immune homeostasis in autoimmune hepatitis: from molecular mechanisms to strategies. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). (2025) 30:27747. doi: 10.31083/FBL27747
133. Verschuuren JJ, Palace J, Murai H, Tannemaat MR, Kaminski HJ, and Bril V. Advances and ongoing research in the treatment of autoimmune neuromuscular junction disorders. Lancet Neurol. (2022) 21:189–202. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00463-4
134. Kang Y, Li L, Kang X, Zhao Y, and Cai Y. Gut microbiota and metabolites in myasthenia gravis: Early diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic strategies. Clin Immunol. (2022) 245:109173. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2022.109173
135. Wu N, Li X, Ma H, Zhang X, Liu B, Wang Y, et al. The role of the gut microbiota and fecal microbiota transplantation in neuroimmune diseases. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1108738. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1108738
136. Ding X-J, Li H-Y, Wang H, Zhang X-H, Song M, Jiang X-H, et al. Altered gut microbiota and metabolites in untreated myasthenia gravis patients. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1248336. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1248336
137. Sun J, Xie Q, Sun M, Zhang W, Wang H, Liu N, et al. Curcumin protects mice with myasthenia gravis by regulating the gut microbiota, short-chain fatty acids, and the Th17/Treg balance. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e26030. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26030
138. Chang C-C, Liu T-C, Lu C-J, Chiu H-C, and Lin W-N. Explainable machine learning model for identifying key gut microbes and metabolites biomarkers associated with myasthenia gravis. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2024) 23:1572–83. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.04.025
139. Liu Y, Hoang TK, Taylor CM, Park ES, Freeborn J, Luo M, et al. Limosilactobacillus reuteri and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG differentially affect gut microbes and metabolites in mice with Treg deficiency. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. (2021) 320:G969–81. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00072.2021
140. Lv Y, Ge C, Wu L, Hu Z, Luo X, Huang W, et al. Hepatoprotective effects of magnolol in fatty liver hemorrhagic syndrome hens through shaping gut microbiota and tryptophan metabolic profile. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. (2024) 15:120. doi: 10.1186/s40104-024-01074-9
141. Bi Y, Cheng B, Zou B, Liu S, and Cui Z. The current landscape of fecal microbiota transplantation in treating inflammatory bowel disease. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2025) 10:55. doi: 10.21037/tgh-24-138
142. Furst A and Gill T. Exploring the role of gut microbes in spondyloarthritis: Implications for pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. (2024) 38:101961. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2024.101961
143. Zhang D, Dong B, Chen J, Zhang Z, Zeng W, Liao L, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation modulates Th17/Treg balance via JAK/STAT pathway in ARDS rats. Adv Biol (Weinh). (2025) 9:e00028. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202500028
144. Fehily SR, Wright EK, Basnayake C, Wilson-O’Brien AL, Stanley A, Marks EP, et al. Faecal microbiota transplantation in Crohn’s disease: an Australian randomised placebo-controlled trial protocol. BMJ Open. (2025) 15:e094714. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-094714
145. Harrington K and Shah K. Harmonizing the gut microbiome and cellular immunotherapies: the next leap in cancer treatment. Cells. (2025) 14:708. doi: 10.3390/cells14100708
146. Woodworth KE, Froom ZSCS, Osborne ND, Rempe CN, Wheeler B, Medd K, et al. Development of itaconate polymers microparticles for intracellular regulation of pro-inflammatory macrophage activation. Adv Healthc Mater. (2025) 14:e2405257. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202405257
147. Woodworth KE, Froom ZSCS, Osborne ND, Rempe CN, Wheeler B, Medd K, et al. Development of itaconate polymer microparticles for intracellular regulation of pro-inflammatory macrophage activation. bioRxiv. (2025) 14:e2405257. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.30.635692
148. Saravanan C, Gopinath NK, Ganesan R, and Thirumurugan D. Challenges and limitations in using bacterial metabolites as immunomodulators. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2025) 15:1535394. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1535394
149. Gong Y, Chen A, Zhang G, Shen Q, Zou L, Li J, et al. Cracking brain diseases from gut microbes-mediated metabolites for precise treatment. Int J Biol Sci. (2023) 19:2974–2998. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.85259
150. Luu M, Monning H, and Visekruna A. Exploring the molecular mechanisms underlying the protective effects of microbial SCFAs on intestinal tolerance and food allergy. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1225. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01225
151. Deleu S, Arnauts K, Deprez L, Machiels K, Ferrante M, Huys GRB, et al. High acetate concentration protects intestinal barrier and exerts anti-inflammatory effects in organoid-derived epithelial monolayer cultures from patients with ulcerative colitis. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:768. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010768
152. Sun Q, Li B-R, Li D-H, Wang X-Y, Wang Q-Y, Jiang Z-M, et al. WKB ameliorates DSS-induced colitis through inhibiting enteric glial cells activation and altering the intestinal microbiota. J Transl Med. (2025) 23:93. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06085-2
153. Ma J, Yu J, Jia Y, Luo Z, Yang X, Li H, et al. Fermented apple juice reduces the susceptibility of offspring mice to food allergy exacerbated by maternal high-fat diet. Nutrients. (2025) 17:1927. doi: 10.3390/nu17111927
154. Gao S, Yu Y, Shu J, Yang B, Zhang B, Xu J, et al. Black tea rich in polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides inhibits osteoporosis in ovariectomized mice through immune regulation and gut microbiota suppression. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:20701. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08827-0
155. Singh K and Bhadauriya AS. Effect of microbial dysbiosis on autoimmune associated inflammation. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. (2025) 395:1–22. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2024.12.016
156. Harrison L and Gleeson D. Stopping immunosuppressive treatment in autoimmune hepatitis (AIH): Is it justified (and in whom and when)? Liver Int. (2019) 39:610–20. doi: 10.1111/liv.14051
157. Liao R, Hsu JY, Aboelella NS, McKeever JA, Thomas-Toth AT, Koh AS, et al. Venetoclax induces BCL-2-dependent Treg to TH17 plasticity to enhance the antitumor efficacy of anti-PD-1 checkpoint blockade. Cancer Immunol Res. (2024) 12:1074–89. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-23-0344
158. Abebaw D, Akelew Y, Adugna A, Tegegne BA, Teffera ZH, Belayneh M, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of the gut microbiome: diagnostic and therapeutic potential for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Med. (2025) 25:226. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01777-x
159. Zhi Y, Li M, and Lv G. Into the multi-omics era: Progress of T cells profiling in the context of solid organ transplantation. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1058296. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1058296
160. Shen Y, Fan N, Ma S-X, Cheng X, Yang X, and Wang G. Gut microbiota dysbiosis: pathogenesis, diseases, prevention, and therapy. MedComm (2020). (2025) 6:e70168. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70168
161. Abeltino A, Hatem D, Serantoni C, Riente A, De Giulio MM, De Spirito M, et al. Unraveling the gut microbiota: implications for precision nutrition and personalized medicine. Nutrients. (2024) 16:3806. doi: 10.3390/nu16223806
162. Pei T, Li W, Zhou Z, Zhang Q, Yu G, Yin S, et al. The relationship between tryptophan metabolism and gut microbiota: Interaction mechanism and potential effects in infection treatment. Microbiol Res. (2025) 298:128211. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2025.128211
163. Höllbacher B, Duhen T, Motley S, Klicznik MM, Gratz IK, and Campbell DJ. Transcriptomic profiling of human effector and regulatory T cell subsets identifies predictive population signatures. Immunohorizons. (2020) 4:585–96. doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.2000037
164. Dawson SL, Todd E, and Ward AC. The interplay of nutrition, the gut microbiota and immunity and its contribution to human disease. Biomedicines. (2025) 13:329. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020329
165. Zhang M, Ma L, Luo J, Ren T, Liu S, Pan L, et al. Low-medium polarity ginsenosides from wild ginseng improves immunity by activating the AhR/MAPK pathway through tryptophan metabolism driven by gut microbiota. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:26142–54. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c06019
166. Mai Z, Han Y, Liang D, Mai F, Zheng H, Li P, et al. Gut-derived metabolite 3-methylxanthine enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis via dopamine receptor D1 in a mouse model of ovarian cancer. mSystems. (2024) 9:e0130123. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01301-23
167. Sun P, Liu J, Chen G, and Guo Y. The role of G protein-coupled receptors in the regulation of orthopaedic diseases by gut microbiota. Nutrients. (2025) 17:1702. doi: 10.3390/nu17101702
168. Wu Y, Zhang W, Liao Y, Sun T, Liu Y, and Liu Y. Immune cell aberrations in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: navigating the targeted therapies toward precision management. Cell Mol Biol Lett. (2025) 30:73. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00749-z
169. Sehgal K and Khanna S. Gut microbiota: a target for intervention in obesity. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 15:1169–79. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2021.1963232
170. Feng W, Liu J, Ao H, Yue S, and Peng C. Targeting gut microbiota for precision medicine: Focusing on the efficacy and toxicity of drugs. Theranostics. (2020) 10:11278–301. doi: 10.7150/thno.47289
171. Yin J, Ma H, Qi Y, Zhao Q, Zeng S, Li F, et al. MDIPID: Microbiota-drug interaction and disease phenotype interrelation database. Imeta. (2025) 4:e70019. doi: 10.1002/imt2.70019
172. Qusty N, Sarhan A, Taha M, Alshanqiti A, Almuteb AM, Alfaraidi AT, et al. The role of gut microbiota in the efficacy and side effect profile of biologic therapies for autoimmune diseases. Cureus. (2024) 16:e71111. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71111
173. Sorbara MT and Pamer EG. Microbiome-based therapeutics. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2022) 20:365–80. doi: 10.1038/s41579-021-00667-9
174. Addissouky TA, Wang Y, Sayed IETE, Naser NA, and Jalal AlAhmed M. Probiotics and diet modifications: A holistic approach to tackling helicobacter pylori with the help of the gut microbiota. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s12602-025-10706-z
175. Hu J, Feng T, Zhang L, Zhou Q, and Zhu L. Leveraging gut microbiota for enhanced immune checkpoint blockade in solid tumor therapy. Chin Med J (Engl). (2025). doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003687
176. Hou K, Wu Z-X, Chen X-Y, Wang J-Q, Zhang D, Xiao C, et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:135. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00974-4
177. Chen P and Tang X. Gut microbiota as regulators of Th17/Treg balance in patients with myasthenia gravis. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:803101. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.803101
Keywords: gut microbiota, microbial metabolites, Treg/Th17 balance, autoimmune diseases, immune regulation, therapeutic targets
Citation: Li G, Xiong Y, Li Z, Yu Q, Li S, Xie J, Zeng S, Yu D, Yang Y and Yu J (2025) Gut microbiota-derived metabolites modulate Treg/Th17 balance: novel therapeutic targets in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 16:1710733. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1710733
Received: 22 September 2025; Accepted: 28 October 2025;
Published: 10 November 2025.
Edited by:
Caio Cesar Souza Alves, Universidade Federal dos Vales do Jequitinhonha e Mucuri, BrazilReviewed by:
Jacy Gameiro, Juiz de Fora Federal University, BrazilRuihe Wu, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Li, Xiong, Li, Yu, Li, Xie, Zeng, Yu, Yang and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiangping Yu, NDcwNDA4MzIxQHFxLmNvbQ==; Yong Yang, eXl4cG93ZXJAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Dongke Yu, a2t5Z3JhY2UyNEAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work and share last authorship
 Guolin Li
Guolin Li Yu Xiong
Yu Xiong Zhimin Li
Zhimin Li Qin Yu3
Qin Yu3 Shiran Li
Shiran Li Jingxian Xie
Jingxian Xie Siyu Zeng
Siyu Zeng Yong Yang
Yong Yang