- 1Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 2Shunyi Branch, Beijing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Beijing, China
- 3Beijing Research Institute of Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
Lipids orchestrate immune signaling beyond structure and energy. In autoimmune diseases (ADs), immune cells rewire fatty-acid and cholesterol pathways under microenvironmental pressures, creating pharmacologically actionable dependencies. This metabolic dysregulation is not merely a passive consequence of immune activation but is a key driver of disease progression. This review synthesizes evidence from human and preclinical studies to systematically outline the core regulatory networks of lipid metabolism. It further dissects the role of lipid metabolism in reshaping the functions of T cells, B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells, and delineates its organ-specific dysregulation in various ADs (e.g., synovium, skin, central nervous system, gut). Rather than blanket immunosuppression, we propose “immune-metabolic normalization”: titrating hyperactive nodes to physiological set-points while preserving host defense. We prioritize targets with high translational potential and evaluate corresponding targeted strategies, including drug repurposing, novel agents in clinical development, and innovative interventional concepts. Our work aims to bridge descriptive immunometabolic research with verifiable, patient-centered interventions, laying the groundwork for precision medicine in autoimmune diseases.
1 Introduction
Autoimmune diseases (ADs) are chronic inflammatory conditions characterized by a loss of immune tolerance to self-antigens, leading to immune-mediated attack on the body’s own tissues and organs (1). Affecting approximately 3-5% of the global population with rising incidence, ADs pose a significant public health challenge (2). Current clinical management primarily relies on glucocorticoids, broad-spectrum immunosuppressants, and biologics (3). However, these therapies often lack specificity; while suppressing aberrant immune responses, they concurrently impair normal host defense mechanisms, increasing the risk of infections and malignancies. Furthermore, many patients experience treatment resistance, disease relapse, or drug intolerance, highlighting the limitations of current strategies and underscoring the urgent need for more precise, safe, and durable interventions (3).
The emergence of the immunometabolism field has provided a revolutionary perspective for understanding and treating immune-mediated diseases. This discipline has revealed that cellular metabolism is not merely a passive process supplying energy post-activation (4) but is a decisive factor actively dictating immune cell fate and function (5, 6). Immune cells undergo precise metabolic reprogramming during different stages—quiescence, activation, differentiation, and memory formation—to meet specific bioenergetic and biosynthetic demands. For instance, effector T cells rely on glycolysis (7), whereas regulatory T cells (Tregs) and memory T cells prefer oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) (8). This tight coupling between metabolic signatures and cellular functions implies that metabolic pathways themselves can be targeted to modulate immune responses. By intervening at metabolic vulnerabilities specific to pathogenic immune cell subsets, it may be possible to selectively suppress deleterious immunity while sparing protective functions, enabling more precise immunomodulation.
Within the broad landscape of immunometabolism, lipid metabolism is moving from the background to the forefront. Traditionally viewed primarily as structural membrane components and energy stores, lipids are now recognized for their complex and central regulatory functions. They act as diverse signaling molecules (e.g., sphingosine-1-phosphate [S1P], specialized pro-resolving mediators [SPMs]) (9, 10), directly regulating cell survival, migration, and activation. They form the basis of key signaling platforms—lipid rafts—where minor compositional changes can influence the signaling efficiency of immune receptors like the T-cell receptor (TCR) and B-cell receptor (BCR) (11–13). Furthermore, lipid metabolites serve as substrates for post-translational modifications (e.g., palmitoylation) or ligands for nuclear receptors (e.g., Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors [PPARs], Liver X Receptors [LXRs]), thereby reshaping the gene expression profiles of immune cells at the transcriptional level (11, 14). Metaflammation represents a core link connecting metabolic dysregulation and autoimmunity (15). Growing evidence strongly indicates that lipid metabolic dysregulation is a central pathological feature of numerous ADs, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), multiple sclerosis (MS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and psoriasis (16). Metabolically derived harmful products can activate immune cells, while inflammatory cytokines released during immune responses exacerbate metabolic imbalance, creating a vicious cycle that drives AD pathogenesis (17).
This review aims to systematically elaborate on the role of immunocyte lipid metabolic reprogramming in ADs and its potential as a therapeutic target. We will first overview the fundamental biochemical processes, key regulatory networks, and organellar basis of lipid metabolism. Subsequently, we will detail how lipid metabolism finely regulates the differentiation and function of key immune cells, including T cells, B cells, and antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Then, we will delve into the specific manifestations and pathogenic mechanisms of lipid metabolic dysregulation in five representative ADs: SLE, RA, MS, IBD, and psoriasis. Finally, we will comprehensively evaluate therapeutic strategies targeting lipid metabolism. These strategies encompass drug repurposing, novel agents under clinical development, promising preclinical targets, and non-pharmacological interventions. This work is intended to provide a theoretical basis and direction for future research and clinical translation in this field.
2 Dual roles of lipid metabolism in immune regulation
Lipids are chemically and functionally diverse molecules, including fatty acids (FAs), triglycerides, cholesterol, and sphingolipids (18, 19). Their functions extend far beyond energy storage and biomembrane constitution (20–42; Supplementary Table 1). FAs are not only energy sources and precursors for complex lipids but also give rise to potent inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins (PGs) and leukotrienes (10). Sphingolipid metabolites, such as ceramide and S1P, are important second messengers regulating apoptosis, proliferation, and migration (43). Cholesterol is crucial for maintaining membrane fluidity and integrity and serves as a precursor for steroid hormones and bile acids (44). The dynamic balance among these molecules collectively determines cellular structural integrity, signaling efficiency, and metabolic status. This section outlines the core components of lipid metabolism to provide a foundation for understanding its cell-specific reprogramming in immune cells.
2.1 Coordination of key metabolic pathways and organelles
The fate and function of immune cells depend on the reprogramming of key lipid metabolic pathways, particularly the balance between de novo lipogenesis (DNL) and fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO) (Figure 1).
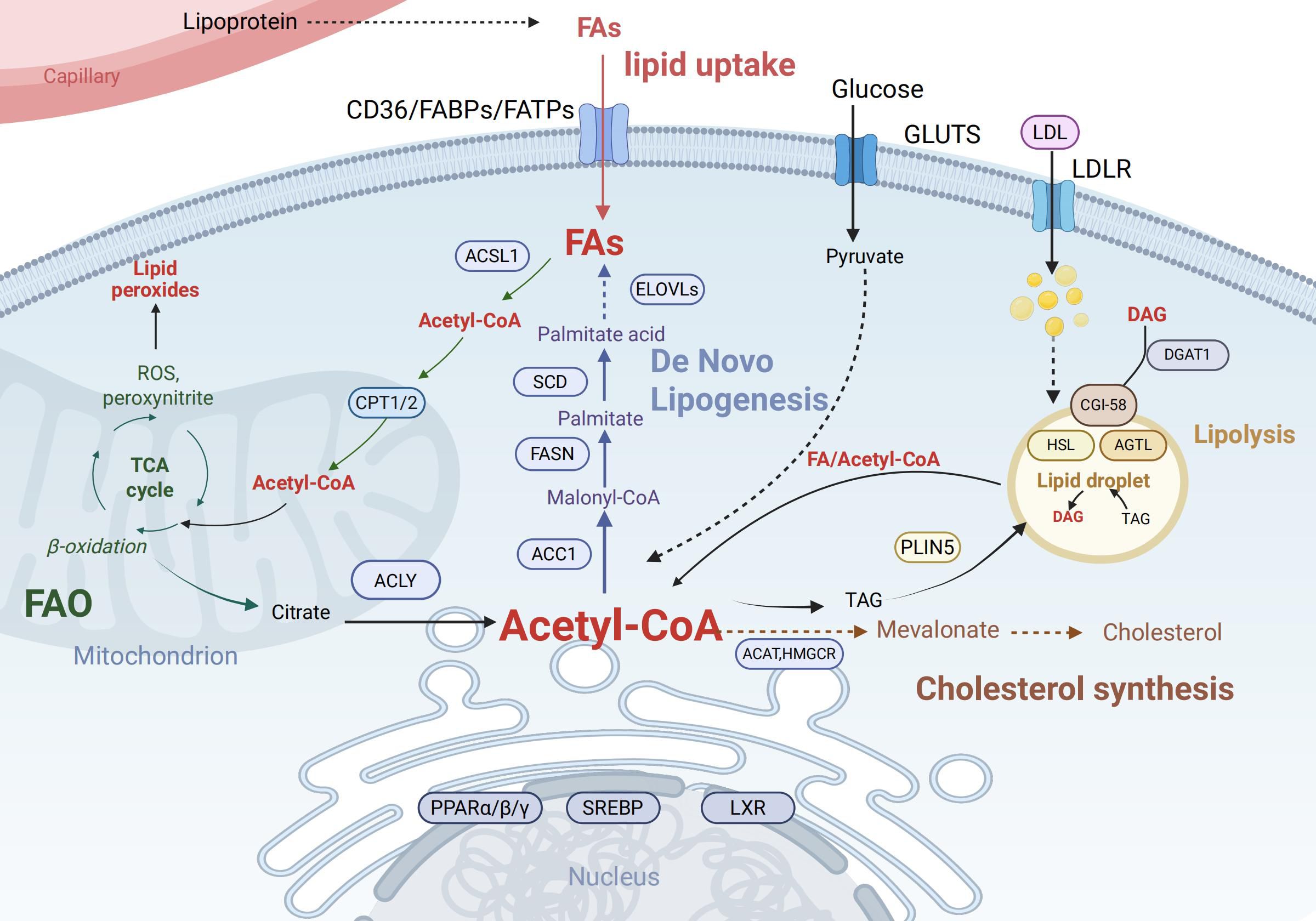
Figure 1. Key pathways of intracellular lipid metabolism. Cellular uptake of fatty acids (FAs) occurs via CD36, FABPs, and FATPs, while LDL enters through LDLR. Fas are activated to acyl-CoA by ACSL1 and can either undergo mitochondrial import via CPT1/2 for β-oxidation (producing acetyl-CoA, ATP, ROS, and citrate) or serve as substrates for de novo lipogenesis involving ELOVLs, SCD, and FASN to generate palmitate and triacylglycerol (TAG). Glucose-derived pyruvate also contributes to Acetyl-CoA production. TAG stored in lipid droplets is hydrolyzed by ATGL and HSL under PLIN5 regulation, releasing Diacylglycerol (DAG) and acyl-CoA, which may be re-esterified by DGAT1. Acetyl-CoA is also utilized for cholesterol synthesis via the mevalonate pathway (catalyzed by HMGCR). Key transcription factors including PPARs, Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Proteins (SREBPs), and Liver X Receptors (LXRs) coordinate these processes by regulating lipid metabolic genes. Created in BioRender. Yu, Y (2025). https://BioRender.com/havvjba Abbreviations: CD36,Cluster of Differentiation 36; FABPs, Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins; FATPs, Fatty Acid Transport Proteins; LDL, Low-Density Lipoprotein; LDLR, Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor; ACSL1, Acyl-CoA Synthetase Long-Chain Family Member 1; CPT1/2, Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 1 and 2; ROS, Reactive Oxygen Species; ELOVLs, Elongation of Very Long Chain Fatty Acids Proteins; SCD, Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase; FASN, Fatty Acid Synthase; TAG, Triacylglycerol; ATGL, Adipose Triglyceride Lipase; HSL, Hormone-Sensitive Lipase; PLIN5, Perilipin 5; DAG, Diacylglycerol; DGAT1, Diacylglycerol O-Acyltransferase 1;HMGCR, 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Reductase; PPARs, Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors.
Lipid metabolism depends on a highly coordinated network of organelles. DNL, which initiates from acetyl-CoA, occurs primarily in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (45, 46), whereas FAO takes place in mitochondria. Mitochondrial fitness—encompassing membrane potential, respiratory capacity, and dynamics (fusion and fission)—is critical for immune cell function (47, 48). Mitochondria also establish close contact with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) via structures known as mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs). These MAMs play a key role in multiple cellular processes: they mediate lipid transport, regulate calcium signaling, and help maintain cellular homeostasis (49). Furthermore, lipid droplets (LDs) store neutral lipids to buffer lipotoxicity and supply energy via lipolysis (50, 51). LDs also function as docking sites for signaling proteins and serve as platforms for the synthesis of inflammatory lipid mediators such as eicosanoids, thereby directly linking lipid storage to inflammatory responses (52, 53).
Different immune cells exhibit distinct preferences for metabolic pathways depending on their functional status. DNL supplies membrane constituents and modulates signaling in rapidly proliferating activated immune cells (54). In contrast, FAO serves as a crucial energy source required for the maintenance and survival of long-lived cells such as memory T cells and Tregs, thereby supporting their persistence and capacity for rapid responses (55). In these cells, fully functional mitochondria are indispensable (56, 57). FAO exerts diverse roles across immune cell types, and metabolic preferences evolve during cellular differentiation and in response to varying physiological contexts (55).
Cholesterol homeostasis is maintained through a balance of synthesis, uptake (via LDLR), and efflux (via ABCA1/ABCG1) (58). Together with sphingolipids, cholesterol forms specialized plasma membrane microdomains known as lipid rafts. These rafts act as signaling platforms that enrich the T-cell receptor (TCR), co-stimulatory molecules (e.g., CD28), and downstream signaling proteins (e.g., Lck). Upon antigen stimulation, lipid rafts facilitate the aggregation of these molecules, effectively initiating and amplifying TCR signaling (59, 60). Increased membrane cholesterol content lowers the activation threshold of T cells, a key mechanism underlying T cell hyperactivation in SLE patients (61, 62).
Under pathological conditions such as autoimmune disease, this precise metabolic coordination becomes disrupted. When immune cells encounter high protein synthesis demands (e.g., antibody secretion in plasma cells) or experience lipid imbalance, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is triggered, activating the unfolded protein response (UPR) (63). Although the UPR attempts to mitigate stress by upregulating lipid synthesis genes to expand ER membrane capacity, persistent ER stress disrupts lipid metabolism and can trigger inflammatory or apoptotic signaling (64). In activated immune cells such as macrophages and neutrophils, the number and size of LDs increase significantly, representing a hallmark feature of immunometabolic reprogramming (65).
2.2 The lipid regulatory network modulates immune functions
A sophisticated molecular network within cells senses lipid and energy status to adjust metabolic pathways and thereby regulate immune function. Key sensory and signaling pathways include:
2.2.1 Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins
SREBPs are master transcription factors regulated by cellular sterol levels (66). SREBP-2 primarily activates genes in the cholesterol synthesis pathway (e.g., HMG-CoA reductase [HMGCR], LDLR), while SREBP-1c mainly regulates genes involved in FA and triglyceride synthesis (e.g., acetyl-CoA carboxylase [ACC], fatty acid synthase [FASN]) (67). Studies have shown that the regulation of lipid synthesis can directly drive the functions of various effector immune cells. For instance, the SREBP signaling pathway in B cells is essential for antibody responses, as well as for the formation of germinal centers, memory B cells, and bone marrow plasma cells (68). In DCs, lipid metabolism regulates their antigen presentation and maturation processes (69).
2.2.2 Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors
PPARs are a family of nuclear receptors (PPARα, PPARβ/δ, PPARγ) acting as intracellular lipid sensors (70). PPARα and PPARβ/δ promote FAO and energy expenditure, whereas PPARγ drives lipogenesis and storage (71). PPARs play pivotal roles in integrating lipid metabolism with inflammation; for instance, PPARγ exerts potent anti-inflammatory effects and is a key determinant in the fate of Tregs, memory T cells, and M2 macrophages (72, 73). However, it is crucial to note this: PPARγ’s effects on immune cells are highly context-dependent (74). Additionally, they can vary substantially across species (75).
2.2.3 Liver X receptors
LXRs (LXRα and LXRβ) are nuclear receptors activated by oxysterols, sensing cholesterol levels (76). They promote cholesterol efflux by upregulating ABCA1/G1 to prevent cellular cholesterol overload. Additionally, LXRs possess significant anti-inflammatory functions, inhibiting the expression of inflammatory genes in macrophages (77) and modulating T cell and dendritic cell (DC) function, relevant to ADs (78–80).
2.2.4 AMPK/mTOR axis
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) are central kinases sensing cellular energy and nutrient status, exerting antagonistic yet coordinated effects on lipid metabolism (73). AMPK, an energy sensor, activates under low energy conditions (high AMP/ATP ratio). Activated AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits synthases like ACC. This action shuts down energy-consuming anabolic processes while promoting energy-producing catabolism, thereby reprogramming cellular energy metabolism to support cell function. In regulatory T cells (Tregs), this metabolic reprogramming combines with AMPK-mediated Foxp3 phosphorylation and stabilization. Together, they maintain the suppressive capacity of Tregs. Defects in this process can lead to autoimmune liver disease (81). mTORC1, a nutrient sensor, activates when signals like amino acids, glucose, and growth factors are abundant. Activated mTORC1 promotes anabolic processes necessary for growth and proliferation, including protein synthesis and lipid synthesis (partly via SREBP activation) (82). The balance of the AMPK/mTOR axis determines whether a cell is in an anabolic or catabolic mode, crucially influencing immune cell fate (83).
Cellular lipid metabolic status is determined not by a single pathway but by the interconnected network of these pathways at the organellar, metabolic, and signaling levels (84) (Supplementary Figure S1). For example, LXRs can induce SREBP-1c expression, forming a feed-forward loop connecting cholesterol clearance to FA synthesis, facilitating the esterification and storage of free cholesterol as cholesterol esters in LDs, which is vital for lipid homeostasis but can contribute to pathology when dysregulated (85). This networked regulation provides metabolic plasticity but also means dysfunction at any node can trigger cascades leading to complex metabolic disturbances. In ADs, persistent inflammatory signals and altered nutrient environments impact multiple nodes simultaneously, disrupting homeostasis and driving pathological metabolic reprogramming. We will now explore how these principles are implemented across different immune cell subsets. This metabolic programming ultimately shapes their unique immune functions.
3 Lipid metabolic preferences and functional remodeling in key immune cells
Building upon the foundational framework of lipid metabolism, we have observed that immune cells exhibit functionally specific lipid metabolic preferences (Figure 2), which directly shape the intensity and type of immune response (55). This section will provide an in-depth analysis of how key immune cells—such as T cells, B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells—leverage distinct lipid metabolic patterns to support their activation, differentiation, and functional execution (Table 1). Furthermore, it aims to elucidate the intrinsic link between metabolic reprogramming and the remodeling of immune functions.
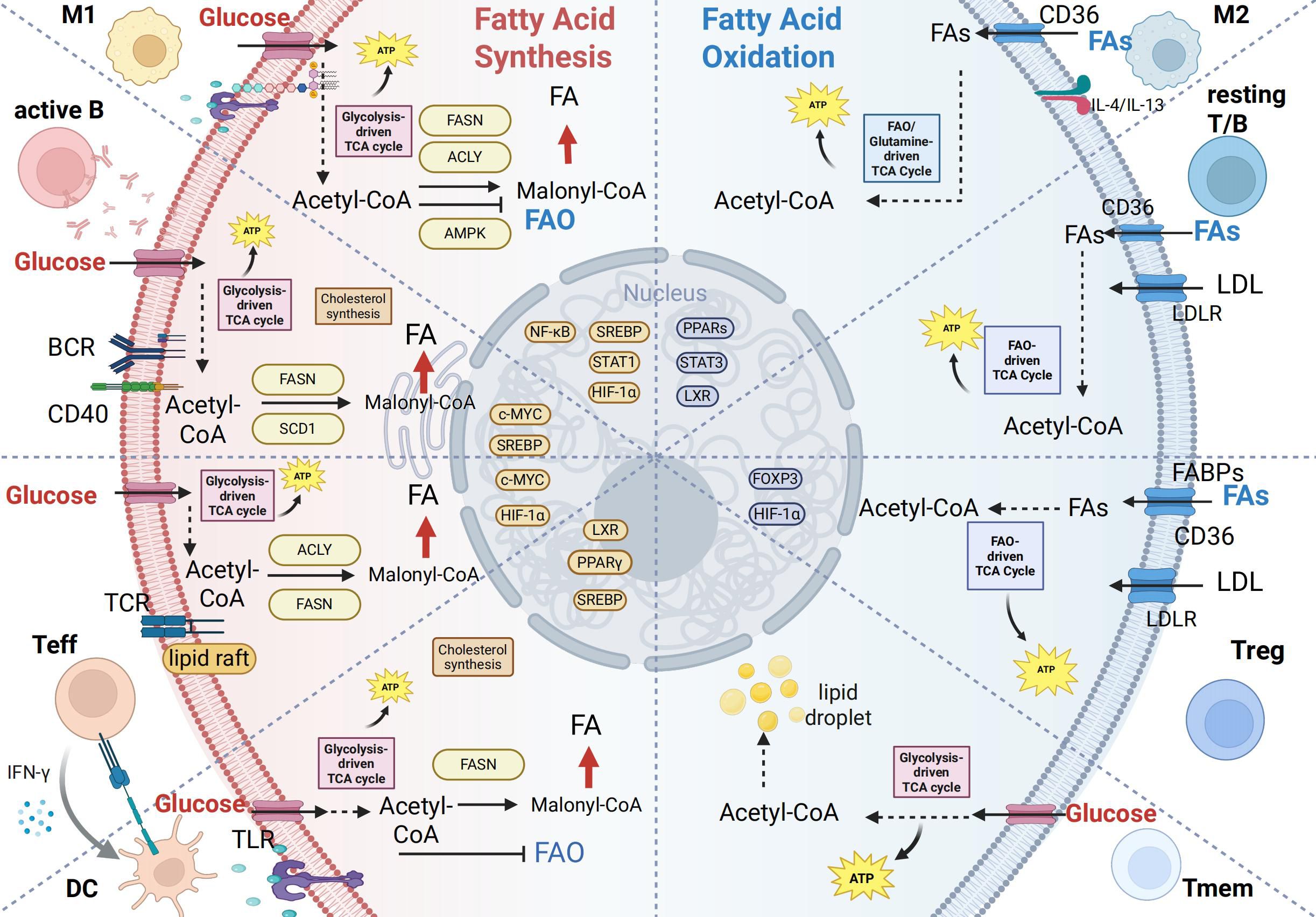
Figure 2. Lipid metabolic reprogramming in immune cell activation and differentiation. This figure summarizes lipid metabolic patterns across immune cell subsets, emphasizing the shift between fatty acid synthesis (FAS) and fatty acid oxidation (FAO) to meet functional demands. Left (Lipogenic phenotype – proliferating/effector cells): Rely on de novo lipogenesis (DNL) for membrane biogenesis and rapid growth.M1 macrophages: LPS/TLR4-induced HIF-1α enhances ACLY/FASN, promoting lipid synthesis and inflammation. Activated B cells: BCR/CD40 signaling activates SREBP/c-MYC, upregulating FASN/SCD1 to support antibody production. Effector T cells: TCR/mTOR-driven DNL facilitates proliferation and cytokine secretion. Dendritic cells: Glycolysis and DNL support antigen presentation structures. Right (FAO phenotype – regulatory/memory cells): Depend on fatty acid oxidation for long-term survival and regulatory functions.M2 macrophages: IL-4/IL-13 activate PPAR-γ/LXR, promoting FAO and anti-inflammatory activity. Resting T/B cells: Use exogenous lipids and FAO to maintain quiescence. Tregs: FAO-derived metabolites sustain Foxp3 and suppressive function. Memory cells: Rely on CD36 and FAO for rapid recall capacity. Transcriptional regulation: Key sensors (SREBP-1c, PPARs, HIF-1α/mTOR) integrate nutrient and immune signals to dynamically regulate metabolic genes, thereby coordinating immune cell function. Created in BioRender. yu, Y (2025). https://BioRender.com/yi5u4zy“.
3.1 T cells
As central players in adaptive immunity, T cell differentiation and function are tightly controlled by their metabolic state. Lipid metabolism acts as a checkpoint determining T cell fate (113, 114).
3.1.1 CD4+T cells
3.1.1.1Metabolic regulation of Th17/Treg balance
Upon antigen activation, naïve T cells rapidly initiate metabolic reprogramming, shifting to aerobic glycolysis to support rapid clonal expansion. Their eventual differentiation into different effector subsets is closely linked to lipid metabolic pathway choices. Pathogenic Th17 cells heavily rely on the DNL/fatty acid synthesis (FAS) pathway (involving enzymes like ATP-citrate lyase [ACLY], ACC, FASN) to convert glucose-derived carbons into FAs (115). Inhibiting ACC1 or FASN pharmacologically (e.g., with TOFA or soraphen A) or genetically can effectively block Th17 differentiation and promote Treg generation, ameliorating disease in autoimmune models (8, 115). Conversely, immunosuppressive Treg cells depend on FAO to maintain their stability and function (116, 117). Early studies using the carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a(CPT1a) inhibitor Etomoxir suggested that FAO is crucial for Treg cell function. This interpretation, however, was complicated by subsequent findings that questioned Etomoxir’s specificity and indicated CPT1a-independent effects (118). More definitive support comes from genetic studies. For example, disrupting the Acyl-CoA Synthetase Bubblegum Family Member 1(Acsbg1) gene in Treg cells has shown that their functional maintenance relies on intact mitochondrial fatty acid metabolism (119). This distinct metabolic preference makes the Th17/Treg axis an attractive therapeutic target; modulating the FAS/FAO balance may reshape immune responses and suppress autoimmune inflammation (113).
3.1.1.2 Metabolic profiles of Th1 and Th2 cells
The differentiation and function of Th1 and Th2 cells are regulated by distinct lipid metabolic pathways. In Th1 cells, the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway and its precursor mevalonate promote differentiation and enhance IFN-γ production (120). Consistent with this, inhibition of this pathway using statins selectively suppresses the production of IFN-γ and IL-10 without affecting cell viability, underscoring the specificity of metabolic regulation in Th1 function (121). Moreover, fatty acid metabolism profoundly influences Th1 functional states. For instance, loss of the monounsaturated fatty acid Scd2 activates type I interferon signaling in Th1 cells. This finding offers a novel metabolic–immune perspective for understanding the role of Th1 cells in antiviral defense and autoimmune inflammation (122).
In contrast, Th2 cell differentiation and function exhibit a stronger reliance on fatty acid metabolism. PPARγ is highly expressed during Th2 differentiation, and both PPARγ antagonism and inhibition of FAS significantly impair Th2 proliferation, differentiation, and secretion of signature cytokines such as IL-5 and IL-13 (123). Additionally, Th2 cells display high tolerance to lactate-rich environments, suggesting a metabolic preference for fatty acid oxidation(FAO) over glycolysis as an energy source (124, 125).
3.1.2 CD8+T cells
Lipid metabolism serves as a central regulator of CD8+ T cell fate and function, profoundly influencing their efficacy in antitumor immunity (126). To meet the demands of proliferation and effector functions, activated CD8+ T cells not only uptake exogenous lipids but also engage in de novo lipogenesis (DNL) to sustain optimal effector responses (127, 128).
However, in the tumor microenvironment (TME), cholesterol can upregulate Cluster of Differentiation 36(CD36) on CD8+ T cells, leading to intracellular lipid accumulation, lipid peroxidation, and ferroptosis. These changes ultimately impair cytotoxicity and promote tumor progression (129). Notably, targeting CD36 can restore cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) function and synergize with anti–PD-1 therapy (129).
On the other hand, memory CD8+ T cell (Tmem) persistence relies on highly efficient catabolic metabolism, particularly FAO, to maintain their quiescent state and metabolic flexibility. Similar to Treg cells, this process is independent of CPT1α (118, 130). Interestingly, Tmem cells depend less on extracellular fatty acid uptake. Instead, they utilize glucose taken up from the extracellular environment to support FAO and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) (131).
3.1.3 γδTcells
Beyond the previously emphasized Th17 cells, IL-17-producing γδ T (γδ T17) cells are increasingly recognized for their pivotal role in autoimmunity. As a major subset of innate-like lymphocytes, γδ T17 cells can rapidly and abundantly produce IL-17 within hours upon stimulation by IL-1β and IL-23, independent of conventional T cell receptor signaling (132). In various models, including experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), psoriasis, and arthritis, γδ T17 cells have been identified as a critical early source of IL-17, often preceding the activation of Th17 cells (133).
Recent studies reveal that the differentiation and function of γδ T17 cells are highly lipid-dependent. In inflammatory settings such as psoriasis, these cells shift toward aerobic glycolysis and lipogenesis. They also uptake free fatty acids, such as palmitate, via the CD36 receptor, which further stimulates IL-17A production (134). Importantly, inhibiting acetyl-CoA carboxylase ACC1 disrupts de novo fatty acid synthesis in γδ T17 cells, reducing their lipid storage and IL-17A secretion capacity. This metabolic intervention has been shown to markedly ameliorate inflammation in a psoriasis model (135).
3.2 B cells and plasma cells
B cell activation and proliferation also require substantial lipids for membrane expansion. Specifically, sterol (cholesterol) and fatty acid synthesis, regulated by the SREBP pathway, are crucial for B cell activation, germinal center (GC) formation, memory B cell generation, and ultimate differentiation into antibody-secreting plasma cells (PCs) (22, 68). Genetic deletion of SCAP, a key protein in the SREBP signaling pathway, in B cells abolishes effective proliferation and reduces lipid raft structures, indicating the necessity of SREBP-mediated lipogenesis for B cell responses (68). During the GC reaction, B cells undergo intense proliferation and affinity maturation, a process also dependent on mitochondrial metabolism and FAO for energy (23). Differentiated PCs significantly upregulate DNL and cholesterol synthesis to provide phospholipids and cholesterol needed for constructing the extensive ER membrane system required for high-rate antibody secretion (24). Inhibiting fatty acid synthesis severely impedes PC differentiation and antibody secretion capacity (166). Thus, lipid metabolic reprogramming is fundamental to the high antibody production function of PCs.
3.3 Dendritic cells
When DCs are activated via pattern recognition receptors such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs), they undergo metabolic reprogramming. This process upregulates glycolysis and de novo lipogenesis (DNL), leading to lipid droplet accumulation. These changes enhance their immunogenicity, enabling efficient initiation of immune responses (136).
Specifically, the maturation of cDC1s, their expression of co-stimulatory molecules, and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-12 are crucial for initiating Th1-type immune responses (136). Furthermore, membrane cholesterol enrichment in cDC1s is key for forming effective antigen presentation platforms. Impaired cholesterol efflux specifically enhances the immunogenicity of cDC1s (137). Conversely, LXR agonists inhibit the maturation of cDC2s by promoting cholesterol efflux (80). However, excessive lipid accumulation, such as that induced by a high-fat diet, impairs the antigen presentation capacity and lymph node migration of CD11b+ cDC2s. This shifts their function towards inducing immune tolerance rather than immune activation (138, 139).
3.4 Macrophages
Macrophages can polarize into pro-inflammatory M1 or anti-inflammatory M2 phenotypes, a balance often disrupted in ADs (140). The classical model posits that M1 macrophages are characterized by high aerobic glycolysis and a disrupted TCA cycle, coupled with FAS activation, while M2 macrophages rely on an intact TCA cycle and OXPHOS fueled by FAO. Activation of nuclear receptors like PPARγ and LXR is key for driving M2 polarization (141, 142). However, recent studies challenge this clear dichotomy, suggesting human M2 macrophages may also rely on glucose metabolism, and highlighting potential off-target effects of commonly used FAO inhibitors like etomoxir, indicating a more complex metabolic landscape for macrophages than previously thought (143–145).
It is evident that the lipid metabolic preferences of adaptive immune cells form the metabolic basis for their functional specialization. From FAS-dependent pathogenic Th17 cells to FAO-preferring Treg cells, and from plasma cells requiring extensive lipid synthesis to support antibody production to dendritic cells whose antigen-presenting capacity is influenced by lipid accumulation, metabolic characteristics directly determine the nature and intensity of immune responses. However, the metabolic programs of immune cells do not exist in isolation; they are profoundly shaped by their tissue microenvironment. Variations in lipid abundance and composition across different tissues shape distinct T cell communities. For instance, the intestinal environment, rich in dietary lipids and microbially derived bile acids, promotes the differentiation and functional maintenance of Treg cells to sustain immune tolerance (146). The skin, abundant in ceramides (CER), cholesterol (CHOL), and free fatty acids (FFA), serves as a key reservoir for resident memory T cells (147). Nevertheless, when this lipid environment undergoes quantitative or qualitative alterations, it can transform into a pathological foundation that drives chronic inflammation and autoimmunity (148, 149). In the following section, we will explore how lipid metabolism is altered in the pathological context of autoimmune diseases.
4 Landscape of lipid metabolic dysregulation in autoimmune diseases
Lipid metabolic dysregulation is a common pathological feature of various autoimmune diseases (16). However, distinct immune cell subsets and tissue microenvironments in different diseases exhibit unique patterns of lipid metabolic reprogramming (Figure 3). As previously discussed, this reprogramming is not merely a passive consequence but actively contributes to disease pathogenesis. In this section, we will systematically outline the specific landscape of lipid metabolic dysregulation in five representative autoimmune diseases: SLE, RA, MS, IBD, and psoriasis. Furthermore, we will clarify how unique patterns of metabolic disturbance in different disease contexts contribute to their specific immunopathological characteristics (Table 1).
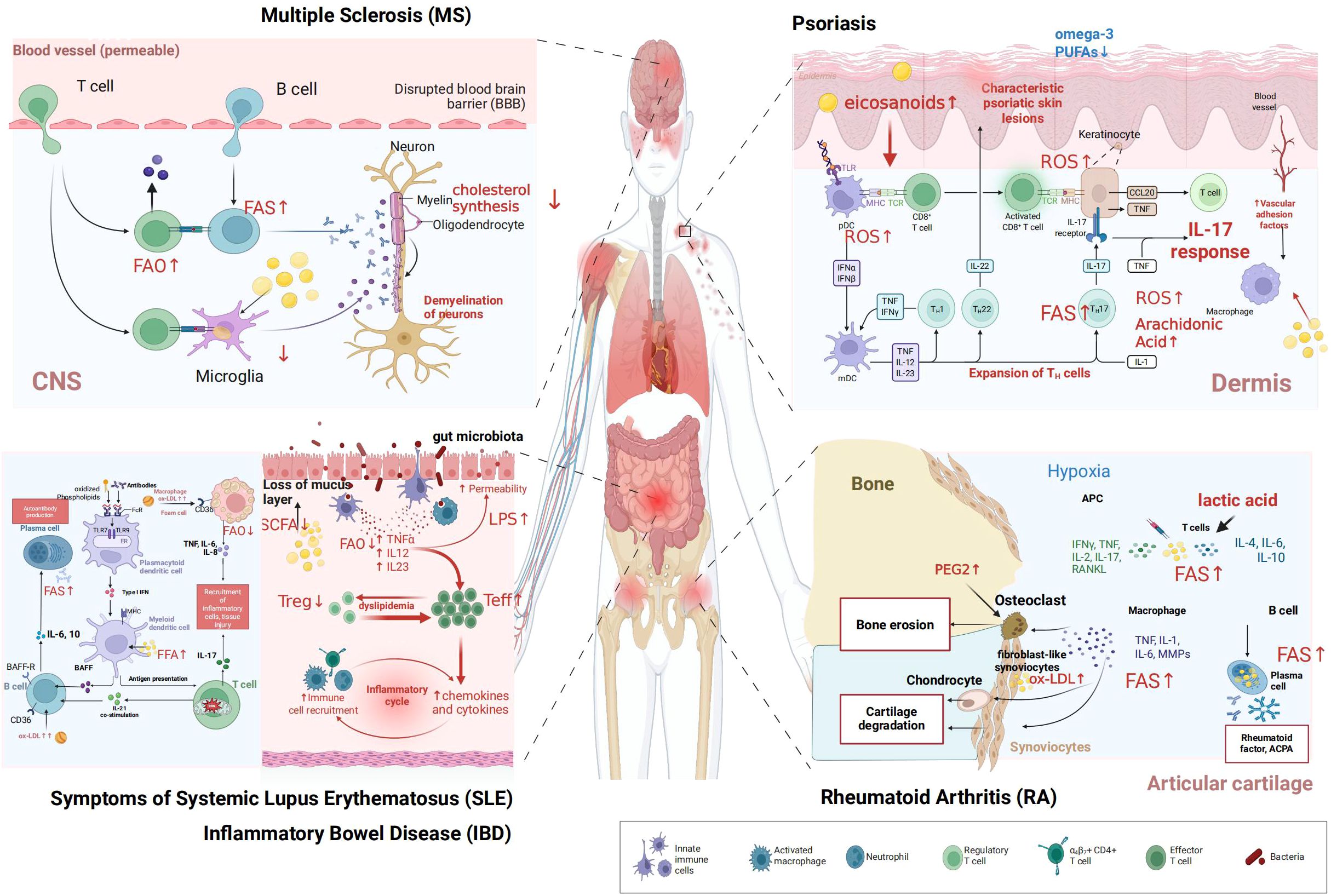
Figure 3. Dysregulated lipid metabolism in autoimmune diseases. This figure illustrates dysregulated lipid metabolism in key immune cells across five representative autoimmune diseases (1) MS: microglia, T cells, and B cells exhibit altered fatty acid oxidation (FAO), while oligodendrocytes show impaired cholesterol synthesis, contributing to neuronal demyelination (2) psoriasis: keratinocytes, T helper 17 (Th17) cells, plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), and macrophages display dysregulated arachidonic acid metabolism and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, with reduced omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), driving psoriatic skin lesion formation (3) SLE: autoreactive B cells, plasma cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages undergo abnormal FAO and interact with oxidized lipoproteins, facilitating autoantibody generation (4) IBD: effector T cells (Teff), regulatory T cells (Treg), and macrophages show disrupted FAO; coupled with gut microbiota dysbiosis (impacting short-chain fatty acids, SCFAs) and increased intestinal permeability, this fuels the inflammatory cycle (5) RA: fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS), osteoclasts, macrophages, T cells, and B cells exhibit dysregulated lipid metabolism (e.g., lactic acid accumulation, oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) involvement), leading to bone erosion and cartilage degradation. The legend depicts innate immune cells, activated macrophages, neutrophils, regulatory T cells, T helper subsets, effector T cells, and bacteria. ”Created in BioRender. yu, Y (2025). https://BioRender.com/21li3ok.
4.1 Systemic lupus erythematosus
SLE is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by abundant autoantibody production and multi-organ involvement (150, 151). Its pathogenesis involves dysfunction of various immune cells, including T cells, B cells, and APCs, closely linked to profound lipid metabolic abnormalities (152).
CD4+ T cells, central drivers in SLE, exhibit significant lipid metabolic abnormalities (153, 154). Given the crucial role of mTORC1-driven lipogenesis in promoting Th17 cell differentiation (82), its dysregulation is particularly relevant to the pathogenesis of SLE. Concurrently, the immunoregulatory function of Treg cells is suppressed (151–153). Studies have confirmed that activation of mTORC1 precedes the onset of SLE and related comorbidities, indicating that this metabolic reprogramming acts as a key upstream event driving T cell functional imbalance (86). Concurrently, T cells in SLE commonly exhibit mitochondrial dysfunction. This includes hyperpolarized mitochondrial membrane potential, increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), abnormal morphology (such as enlargement), and reduced ATP generation (155). These alterations impair energy supply and affect epigenetic modifications like DNA methylation, leading to aberrant expression of autoreactive genes. Reducing lipid peroxidation/ROS and inhibiting T cell oxidative stress can alleviate lupus nephritis (LN) (156–158). Furthermore, lipid rafts contribute to SLE pathogenesis (159). Increased synthesis of cholesterol and glycosphingolipids (GSLs) in SLE T cells leads to excessive lipid raft aggregation on the plasma membrane, enhancing TCR signaling and lowering the activation threshold for autoreactive T cells (160, 161). Downregulating the transcription factor FLI1 reduces GSL synthesis, affecting SLE progression (79, 87, 162, 163). Recent studies confirm increased CD38 expression in SLE CD4+ T cells correlates with increased lipid rafts, and targeting CD38 to modulate ganglioside GM2 distribution alleviates SLE pathology (161).
Autoreactive B cells in SLE upregulate the scavenger receptor CD36 to increase exogenous lipid uptake (164), enhancing mitochondrial OXPHOS to fuel B cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation, thereby exacerbating disease (165). B cell differentiation into PCs depends on SREBP-mediated lipogenesis to support massive ER expansion. Inhibiting fatty acid synthesis ameliorates disease in lupus-prone mice (166, 167). Conversely, regulatory B cells (Bregs) in SLE are reduced in number and functionally impaired, exhibiting metabolic abnormalities like mitochondrial depolarization and elevated ROS (168).
Macrophages and DCs also play significant roles in SLE, particularly LN (169). In LN models, renal macrophages exhibit impaired phagocytic function, failing to clear apoptotic cells and immune complexes effectively. Excess lipid peroxides can activate macrophage inflammation (170), while their phagocytic capacity is impaired due to downregulated CPT1α and reduced fatty acid metabolism (171, 172). Additionally, high levels of type I interferon persistently induce upregulation of the scavenger receptor SR-A1 on macrophages, promoting uptake of oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) and foam cell formation, accelerating atherosclerosis—a mechanism underlying the high cardiovascular risk in SLE patients (169). Research on DCs in SLE is less extensive. In LN, DCs infiltrate the kidney and amplify inflammation (173). Recent studies show that accumulated cholesterol metabolite farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) within DCs of SLE model mice promotes their activation via mitochondrial remodeling (174).
In summary, in SLE, mTOR-driven metabolic anomalies in T cells, excessive lipid uptake by B cells, and macrophage dysfunction drive premature immune cell activation, amplifying metabolic disturbances and providing the basis for autoantibody production and multi-organ inflammatory damage.
4.2 Rheumatoid arthritis
RA is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic synovial inflammation and joint cartilage/bone erosion (175).The pathological core lies in the pathogenic interaction between immune and stromal cells within the synovial microenvironment, wherein lipid metabolism serves a dual role as both an energy source and a signaling mechanism.
The inflamed RA synovium constitutes a unique metabolic microenvironment characterized by hypoxia and high lactate concentrations (176). High lactate is taken up by synovial CD4+ T cells via the transporter Solute Carrier Family 5 Member 12(SLC5A12), which inhibits their glycolysis and paradoxically drives FAS (177, 178). This lactate-induced increase in FAS is a key metabolic basis for T cell differentiation towards the pathogenic Th17 phenotype and IL-17 production. This mechanism directly links accumulated this local metabolite (lactate) to T cell pathogenicity (179, 180). Concurrently, excess FAs lead to LD deposition and upregulate T cell migration programs, facilitating immune cell infiltration and exacerbating synovitis and joint destruction (91, 176). Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) are major effectors of joint destruction in RA. RA-FLS exhibit upregulated FASN expression leading to fatty acid accumulation (181, 182). These excess FAs enhance phosphorylation of DRP1 protein, inducing mitochondrial fission, which increases ROS production and activates pro-inflammatory and pro-survival pathways like PI3K/mTOR/NF-κB, ultimately conferring the aggressive, cartilage-destructive phenotype to FLS (92). The RA synovium is infiltrated by numerous macrophages. Active RA is dominated by MerTK-negative (MerTK−) macrophages secreting pro-inflammatory cytokines, while remission phases enrich MerTK-positive (MerTK+) macrophages with repair functions (93). The latter can effectively produce SPMs (e.g., resolvins), inducing FLS repair responses and maintaining joint homeostasis (93). A hallmark pathological change in RA is bone erosion caused by excessive osteoclast activation. Osteoclast differentiation is regulated by cytokines like Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa-B Ligand(RANKL) (183). It is also closely linked to cholesterol metabolism (184). Statins, besides lowering lipids, can inhibit RANKL expression and inhibit osteoclast precursor differentiation, suggesting potential value for bone protection in RA (185). The hypoxic synovial microenvironment in RA initially induces lipid synthesis in T cells, and this metabolic reprogramming in turn drives their pathogenic phenotype and tissue infiltration capacity, illustrating the vicious cycle between metabolic abnormality and immune activation.
In the hypoxic joint microenvironment of RA, lactate accumulation drives lipid metabolic reprogramming in T cells and FLS. This reprogramming promotes the differentiation of pathogenic Th17 cells, enhances the invasiveness of FLS, and disrupts bone homeostasis, thereby synergistically exacerbating synovial inflammation and joint destruction. Hypoxia and lipid signaling act cooperatively within the RA joint microenvironment to jointly drive disease progression. Specifically, the hypoxic synovial milieu initially induces lipid synthesis in T cells, and this metabolic reprogramming in turn drives pathogenic T cell phenotypes and enhances tissue infiltration capacity. This process exemplifies a vicious cycle between metabolic dysregulation and immune activation.
4.3 Multiple sclerosis
MS is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic central nervous system (CNS) inflammation, demyelination, and neurodegeneration (186). Patients with MS exhibit significant alterations in lipid metabolism, including changes in levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), apolipoproteins, and oxysterols. These metabolic abnormalities correlate with clinical disease activity, although their causal relationship remains incompletely defined (187). Given that myelin itself is a lipid-rich structure, lipid metabolic disturbances occupy a central position in MS pathogenesis; lipid molecules are both targets of myelin destruction and inflammatory mediators affecting immune function.
Myelin, formed by extensions of oligodendrocyte membranes wrapping around axons, is rich in lipids (constituting ~70-80% of dry weight) (188). Therefore, oligodendrocytes must maintain high lipogenic capacity for myelination during development and effective remyelination after damage (189). The failure of remyelination in MS is partly due to impaired differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells into mature oligocytes. Consequently, these cells face a severe deficit in their lipid synthesis capacity, which is required for producing the vast amounts of lipids essential for myelin production (189). Altered myelin composition due to lipid dysmetabolism may affect its stability and increase its immunogenicity, potentially triggering immune attack (190). In MS demyelinating lesions, microglia and infiltrating macrophages phagocytose myelin debris, leading to lipid overload and foam cell formation (191). This lipid accumulation triggers sustained inflammation and inhibits transition to a pro-repair phenotype, hindering remyelination. The transcription factor Interferon Regulatory Factor 5(IRF5) is key for regulating myelin debris degradation and cholesterol homeostasis; IRF5 deficiency leads to inadequate degradation in lysosomes, causing abnormal accumulation of LDs and cholesterol crystals, exacerbating disease (191). Activity of the fatty acid elongase ELOVL6 has also been found to promote inflammatory foam cell formation (192). Changes in mitochondrial lipid metabolism have been identified in CD4+ T cells from MS patients (193). In the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mouse model, Treg cells infiltrating the CNS heavily rely on CPT1α-mediated FAO to maintain their function; enhancing Treg FAO capacity is considered a potential therapeutic strategy (194). Furthermore, the lipid mediator maresin-1 (MaR1) can reduce Th1 cells, increase Tregs, and suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines (98, 195), also reducing immune cell infiltration, accelerating inflammation resolution, and delaying disease progression in EAE models (102). CD4+ T cells from relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) patients exhibit dysregulated LXR-mediated lipid metabolism. While LXRβ expression is upregulated, downstream target gene expression is downregulated, leading to increased membrane cholesterol and decreased GSLs. This altered lipid raft composition is thought to enhance T cell reactivity, promote IL-17 production, and exacerbate neuroinflammation (99). Recently, a lipid kinase was found to promote Th17 differentiation via the mTORC1/STAT3 pathway, contributing to EAE progression (103). A clinical study profiling lipid metabolic reprogramming in immune cells of MS patients is ongoing (NCT04053374). Metabolic reprogramming endows pathogenic T cells with strong migratory and pathogenic capacity, enabling CNS invasion and inflammatory cytokine release; these cytokines, in turn, exacerbate lipid metabolic reprogramming in CNS immune cells and damaged cells, leading to myelin and neuronal injury.
4.4 Inflammatory bowel disease
IBD, including Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), involves a loss of tolerance to intestinal microbiota in genetically susceptible individuals, resulting in chronic gut inflammation. A nationwide study suggests abnormal lipid profiles in CD and UC patients (196). Lipid metabolism plays multifaceted roles in IBD, regulating intestinal barrier function, microbial homeostasis, and immune responses (197).
A healthy gut microbiota ferments dietary fiber to produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), notably butyrate (198). Butyrate is a primary energy source for colon epithelial cells and a potent histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor (199).Through this epigenetic mechanism, it promotes Treg cell differentiation while suppressing pro-inflammatory responses, ultimately maintaining intestinal immune tolerance (146). Patients with IBD commonly exhibit gut microbiota dysbiosis, characterized particularly by a reduction in butyrate-producing bacteria. This leads to decreased levels of butyrate, which is recognized as a key driver of inflammation in IBD (200). In ulcerative colitis, lipidomic analyses have revealed that alterations in triglyceride and phospholipid levels are closely linked to the pathogenesis, progression, and treatment response of the disease (201). CD patients exhibit a unique “creeping fat” phenomenon: mesenteric adipose tissue abnormally proliferates and wraps around the intestine (202). Creeping fat is infiltrated by immune cells and secretes high levels of adipokines like pro-inflammatory leptin. Interestingly, macrophages in CD creeping fat often exhibit M2 polarization promoting tissue remodeling, but the hyperplastic fat itself becomes a reservoir for inflammatory cells (203). Intestinal lamina propria macrophages are sentinels for mucosal immune homeostasis. In inflamed IBD gut, their metabolic reprogramming is characterized by significant downregulation of the anti-inflammatory nuclear receptor PPARγ and FAO pathways (204). This impairs their ability to polarize towards an M2 phenotype, preventing effective inflammation suppression and repair, thereby exacerbating gut damage. The probiotic Fecalibacterium prausnitzii can reprogram macrophage energy metabolism, guiding them towards M2 polarization and alleviating intestinal fibrosis in CD patients (205). Another study found Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 5(FABP5) upregulated in IBD macrophages, potentially exerting anti-inflammatory effects by preventing M1 polarization (206). IBD patients have impaired intestinal barrier function, associated with sphingolipid metabolism abnormalities, such as potentially elevated pro-inflammatory S1P and imbalances in ceramides necessary for barrier integrity (207). Furthermore, bile acids, synthesized by the liver and modified by microbiota, regulate intestinal immunity by activating receptors like Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) and Takeda G protein-coupled Receptor 5 (TGR5); their dysregulation also contributes to IBD pathogenesis (208, 209). In summary, immune cells in IBD exhibit significant metabolic reprogramming, including abnormalities in glucose/lipid metabolism and imbalanced microbiota-immune cell interactions, collectively driving and sustaining pathological gut inflammation.
4.5 Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by hyperproliferation of keratinocytes and immune cell infiltration (210). Its core pathological mechanism involves overactivation of the IL-23/Th17 axis (210). IL-17 production in psoriasis is not restricted to Th17 cells. Within psoriatic lesions, IL-17-producing skin γδ T cells are also pivotal in driving psoriasiform dermatitis. Moreover, the IL-36 signaling pathway plays a central and unique role in amplifying the IL-23/IL-17/IL-22 inflammatory axis and promoting disease progression (211). The pathogenesis of psoriatic lesions involves not only dysregulated immune-keratinocyte crosstalk but also cellular metabolic reprogramming. Critically, Th1/Th17 and Th2 cytokines exert divergent influences on lipid metabolism in differentiating keratinocytes. This metabolic influence is proposed as a key mechanism underlying the dysfunction of the skin barrier in psoriasis (212).Concurrently, cytokines from DCs prompt keratinocyte hyperproliferation and production of more chemokines/cytokines, further attracting immune cell infiltration, forming a vicious cycle (213, 214). Lipid metabolic abnormalities in psoriasis manifest at both local (skin) and systemic levels, accelerating disease progression by altering immune cell phenotypes and functions (215).
Healthy skin barrier function relies on a precise ratio of lipids (ceramides, cholesterol, free fatty acids) in the stratum corneum (108). Psoriatic lesions exhibit significant barrier defects and abnormal lipid profiles (216, 217), characterized by reduced levels of anti-inflammatory omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and elevated levels of pro-inflammatory arachidonic acid (AA). AA is the precursor for potent pro-inflammatory eicosanoids (e.g., prostaglandins, leukotrienes), which directly drive skin inflammation (218). Supplementing omega-3 PUFAs to modulate skin inflammation may have clinical significance (219, 220).
Moreover, psoriasis is a systemic inflammatory disease. A recent study suggests a significant association between elevated triglyceride levels and the risk of psoriasis (221). Furthermore, patients with psoriasis have a markedly increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis (109). A key link underlying this comorbidity is lipid metabolic dysregulation. Systemic inflammation causes dyslipidemia (222) and promotes monocyte/macrophage infiltration into vessel walls. In the inflammatory microenvironment, these macrophages avidly take up oxidized lipids, transforming into foam cells that initiate and accelerate atherosclerosis, a mechanism similar to that in SLE (223). Similarly, immune cells in psoriasis patients exhibit significant oxidative stress, leading to lipid peroxidation and the production of pro-inflammatory mediators (224, 225) (see Section 3.1). Moreover, these ROS-dependent lipid mediators activate pro-inflammatory signaling, promote Th1/Th17 differentiation, and stimulate keratinocytes (110). Simultaneously, Th17/Treg cells display a functional imbalance analogous to that observed in SLE, which disrupts a critical immunoregulatory equilibrium (88).Meanwhile, pathogenic Th17 cells favor aerobic glycolysis and lipogenesis, while Treg FAO is suppressed in the inflammatory environment, leading to insufficient immunosuppressive function (88).In psoriasis patients, levels of Th2-related cytokines or cell populations are reduced and negatively correlate with disease severity (226). Diagnostically, the combination of Th2+Treg cell ratio and adiponectin levels enables high-precision prediction of psoriasis (227). Mechanistically, recent research identifies Th2 immunity as a key tissue checkpoint that suppresses skin autoimmunity and maintains lipid homeostasis, conferring resistance to psoriasis by sustaining LXR/PPARγ-mediated fatty acid metabolism via STAT6 signaling (228).
A unifying theme across these diseases is the central role of “metaflammation” within target organs. In summary, although shared features of lipid metabolic dysfunction—such as hyperactive mTOR signaling and mitochondrial dysfunction—exist across autoimmune diseases, each disorder exhibits unique metabolic characteristics shaped by its specific tissue microenvironment. This spectrum ranges from lipid raft aggregation in T cells in SLE, to lactate-driven fatty acid synthesis in the RA synovium, and from imbalanced myelin lipid metabolism in MS to disrupted host-microbiota interactions in IBD. Critically, in affected tissues—be it the synovium in RA, the CNS in MS, the gut in IBD, or the skin and vasculature in psoriasis—the local metabolic milieu (e.g., lactate, lipids, and microbial metabolites) is not a passive backdrop but an active participant. It shapes the metabolic programs and functional phenotypes of immune cells, which in turn secrete inflammatory factors that further worsen the local metabolic environment, establishing a self-sustaining and amplifying pathological circuit (Table 2). This understanding underscores that effective therapeutic strategies may need to target not only the immune cells themselves but also strive to normalize the metabolic microenvironment of diseased tissues, thereby breaking this vicious cycle.
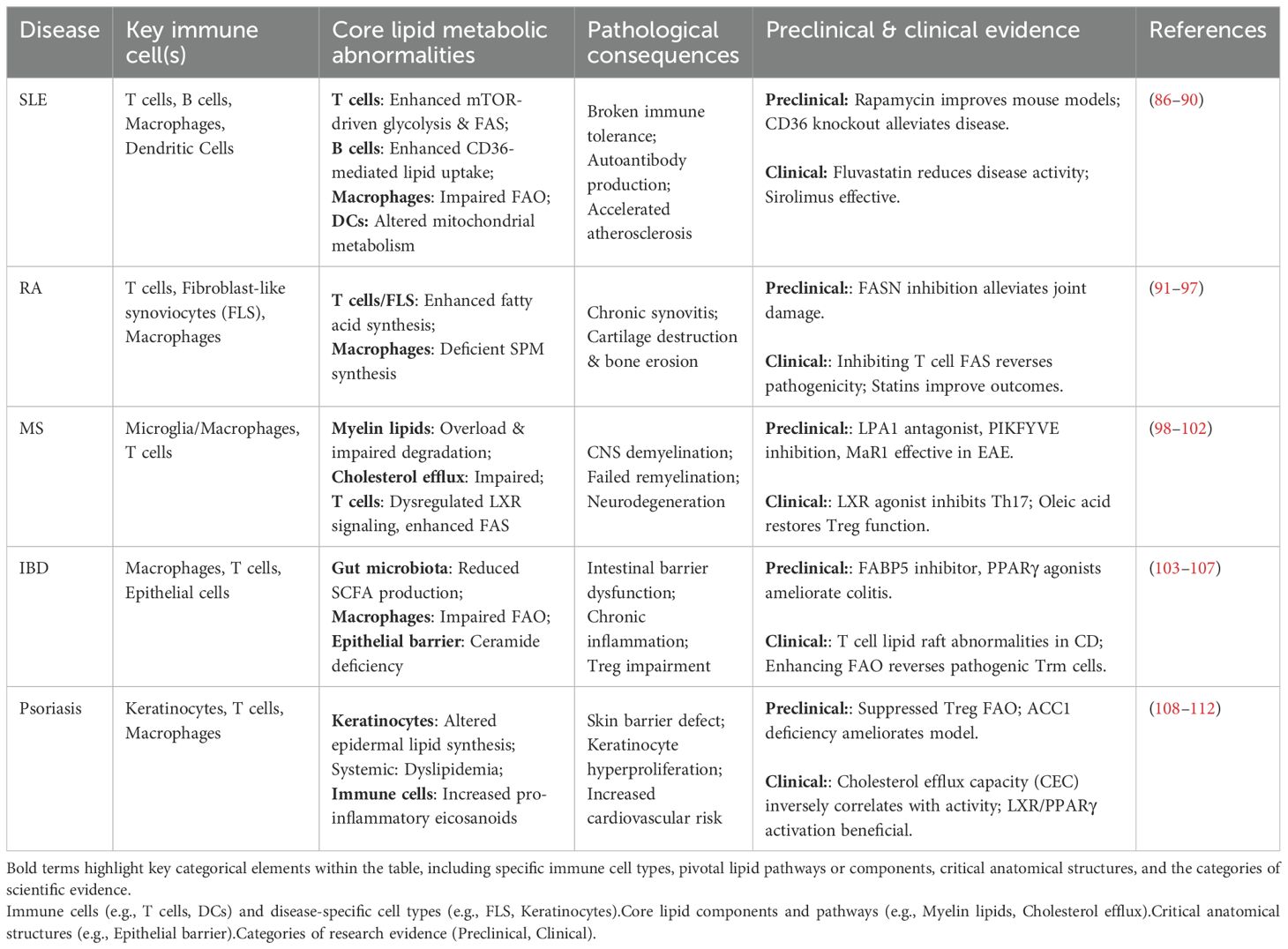
Table 2. Summary of dysregulated lipid metabolism in major autoimmune diseases. ① Preclinical: Studies conducted before human clinical trials (e.g., pharmacology, toxicology); ② Clinical: Trials in human subjects for safety and efficacy evaluation.
5 Therapeutic strategies targeting lipid metabolism: from drugs to clinic
Given the central driving role of lipid metabolism in ADs, targeting related pathways has become an highly attractive new therapeutic direction. Strategies can be broadly categorized into three groups: repurposing approved drugs for immunomodulatory effects, developing new drugs against emerging metabolic targets, and modulation via dietary and microbial interventions.
5.1 Novel immunomodulatory uses of marketed drugs
Some metabolic modulators already widely used in the clinic possess unexpected immunomodulatory effects, offering a promising path for “drug repurposing”.
5.1.1 Statins
Statins are HMGCR inhibitors primarily used for cholesterol lowering. However, their potential in treating ADs stems largely from pleiotropic anti-inflammatory effects (238). By inhibiting the mevalonate pathway, statins not only reduce cholesterol synthesis but, importantly, reduce the production of isoprenoid intermediates (e.g., FPP, GGPP). These intermediates are required for the prenylation of small GTPases (e.g., Rho, Ras), which are key nodes in inflammatory signaling pathways (239). Thus, statins can inhibit T cell activation, skew them from pro-inflammatory Th1/Th17 towards anti-inflammatory Th2 phenotypes (212), and inhibit DC maturation and antigen presentation capacity (240). In the realm of clinical trials, statins such as simvastatin (MS-STAT2 trial, NCT03896217) for MS and atorvastatin (NCT00356473, NCT04177173) for RA have demonstrated the potential to reduce disease activity and slow progression (241, 242). However, the results are inconsistent across studies, with some failing to observe significant beneficial effects (243). Efficacy in SLE is also debated. A retrospective study found adding atorvastatin to standard therapy improved immune function and disease activity indices in mild-to-moderate active SLE patients (244), while another found atorvastatin had no significant effect in MRL/lpr mice. However, in vitro experiments confirmed statins inhibit splenic B cell proliferation, suggesting potential for SLE (245). This indicates statin efficacy may be disease- and patient-specific.
5.1.2 S1P receptor modulators
Fingolimod, siponimod, and ozanimod are functional antagonists of S1P receptors (246). S1P binding to its receptor S1PR1 is necessary for lymphocyte egress from lymph nodes into circulation. These drugs, by binding S1PR1 and inducing its internalization and degradation, sequester lymphocytes in lymph nodes, preventing autoreactive lymphocytes from migrating to target organs like the CNS (43). Fingolimod, the first oral drug approved for MS, significantly reduces relapse rates and delays disability progression (247). Later-developed siponimod and ozanimod have higher receptor selectivity (248). Given their broad immunomodulatory effects, the potential of S1P receptor modulators in other ADs is being actively explored. For example, ozanimod is under investigation for UC (NCT05369832). Trial criteria sometimes mention RA and SLE, hinting at potential applications (249).
5.1.3 Fibrates
Fibrates like fenofibrate are PPARα agonists used primarily for hypertriglyceridemia. By activating PPARα, these agents drive metabolic reprogramming in T cells. This metabolic shift enhances FAO, thereby alleviating inflammation associated with ADs (250). Although research in ADs is early-stage, a trial plans to explore fenofibrate’s role in preventing chemotherapy-induced neuropathy (NCT07025005), indirectly suggesting potential utility in neuroinflammatory diseases like MS.
5.1.4 PPARγ agonists
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) like pioglitazone are potent PPARγ agonists. They promote macrophage polarization to the M2 anti-inflammatory phenotype, inhibit inflammatory pathways, and may improve skin barrier function, offering theoretical benefits in RA, IBD, and psoriasis. However, first-generation TZDs, affecting systemic lipid/glucose metabolism, have side effects (weight gain, edema) limiting use in non-diabetic populations (251). Research focuses on developing newer, more selective PPARγ agonists with better safety. A drug interaction study assessed pioglitazone pharmacokinetics in IBD patients (NCT02371603). Oral pioglitazone significantly improved clinical measures in secondary progressive MS patients without serious adverse events (NCT00242177) (252). Pioglitazone treatment in young female SLE patients significantly decreased inflammatory markers (NCT01322308) (253). In RA patients, pioglitazone significantly reduced disease activity and CRP levels, improved lipid profiles, and was well-tolerated (NCT00554853) (254), supported by other studies (NCT00763139; NCT02338899) (255, 256).
5.2 Emerging targets and drugs in clinical development
A range of new drugs targeting more specific nodes in immunometabolic pathways are under development, showing great therapeutic promise.
5.2.1 mTOR inhibitors
Sirolimus (rapamycin) and its analog everolimus are specific inhibitors of mTORC1. As mentioned, mTORC1 is hyperactivated in pathogenic T cells in SLE and RA. By inhibiting mTORC1, these drugs can reshape T cell balance: inhibiting Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation while promoting Treg cell expansion and function (257, 258). Several clinical trials are currently evaluating mTOR inhibitors. A Phase II trial (SIRIUS, NCT04582136) for active SLE is ongoing. Another early-phase trial at the US NIH explores sirolimus use in pediatric patients with autoimmune cytopenias related to SLE and RA, among others (NCT00392951). A Phase II trial for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD, NCT05746689) is not yet recruiting.
5.2.2 PCSK9 Inhibitors
PCSK9 is a key protein regulating cholesterol metabolism by mediating LDLR degradation. Initially developed for lipid lowering, PCSK9 inhibitors are being explored for ADs due to anti-inflammatory effects. A Mendelian randomization study suggested PCSK9 inhibition significantly lowers SLE risk but may increase asthma and CD risk, with effects differing from HMGCR inhibitors (245). A phase II trial is assessing PCSK9 inhibitor effects on islet function and inflammation markers (e.g., hs-CRP, IL-6) in type 1 diabetes (NCT05641753), results pending.
5.3 Frontier directions in preclinical research
At the basic research level, numerous novel lipid metabolic targets are being discovered and validated (Table 3).
5.3.1 Fatty acid synthesis inhibitors (FASN/ACC inhibitors)
Directly targeting the upregulated FAS pathway (e.g., FASN or ACC1) in pathogenic Th17 cells is a direct strategy to inhibit these cells (263). Various FASN and ACC inhibitors are in development, primarily for cancer and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). Inhibiting FASN-mediated lipid metabolism in B cells alleviates lupus in mice (166). The FASN inhibitor TVB-2640 can activate macrophages and DCs and significantly ameliorate imiquimod (IMQ)-induced lupus in mice (264), showing great potential, particularly in SLE.
5.3.2 Lipid uptake and transport modulators (CD36, FATP modulators)
Targeting the scavenger receptor CD36 may prevent lipid overload in macrophages and B cells, blocking key steps in SLE-related atherosclerosis and autoreactive B cell activation (164, 285). PPARγ activation can upregulate CD36-mediated FAO, enhancing Treg responses, potentially beneficial for treating inflammation and ADs (290). In the RA synovium, CD36 promotes pro-inflammatory macrophage polarization and IL-1β/TNF-α release via lipid uptake. An observational study is analyzing whether plasma from SLE/RA patients affects CD36 expression on monocytes (NCT01180361), providing basis for intervention studies. In EAE, CD36 is required for myelin debris uptake by macrophages/microglia; its pharmacological inhibition worsened neuroinflammation and disease severity (286).
5.3.3 Specialized pro-resolving mediators
SPMs, including resolvins, protectins, and maresins, are endogenous lipid mediators derived from omega-3 PUFAs. They do not passively suppress inflammation but actively initiate and coordinate the resolution of inflammation (10). SPMs restore tissue homeostasis by inhibiting neutrophil infiltration, enhancing macrophage clearance of apoptotic cells (efferocytosis), and promoting tissue repair (291). This “pro-resolution pharmacology” represents a novel therapeutic concept, shifting from anti-inflammatory to pro-resolving. Furthermore, SPM levels correlate with RA disease activity, and they directly inhibit pathogenic T cell proliferation by precisely regulating the Th17/Treg balance (254). This regulatory effect may involve the antagonism of key pro-inflammatory signals. For instance, in RA, γδ T cells represent a significant source of IL-17, and their function can conversely be enhanced by mediators such as prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) (267). This marks a transition in lipid metabolism research from correlative observation to functional target development. Exogenous administration of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) has demonstrated potent therapeutic efficacy in preclinical studies across various autoimmune disease models, including RA and MS, suggesting significant potential for clinical translation (98).
5.3.4 LXR agonists
LXR agonists effectively promote macrophage cholesterol efflux and exert potent anti-inflammatory effects, making them ideal candidates for inflammatory diseases like atherosclerosis (292). Targeting T cell LXRβ improved disease severity in an MS model (259). An LXR inverse agonist, SR9243, alleviated RA by modulating macrophage metabolism (260). However, a major challenge is that LXR agonists induce SREBP-1c, leading to increased hepatic lipogenesis and steatosis (293). This off-target effect hinders clinical translation. Research focuses on developing tissue-specific or pathway-selective LXR agonists to avoid liver side effects while retaining anti-inflammatory benefits (294). An LXR agonist, RGX-104, has undergone Phase I trials in advanced cancer (NCT02922764), proving druggability and providing experience for future AD applications.
5.4 Therapeutic potential of dietary and microbial interventions
5.4.1 Omega-3 PUFA supplementation
Dietary intervention is a direct means to modulate lipid metabolism. Diets rich in omega-3 PUFAs (e.g., EPA, DHA from fish oil) alter the body’s fatty acid profile, shifting eicosanoid synthesis from the pro-inflammatory omega-6 pathway towards producing anti-inflammatory or pro-resolving SPMs (295). Omega-3 supplementation modulates B cell differentiation in lupus-prone mice (296), reduces autoantibody production and immune complex deposition, and blocks interferon and chemokine gene expression in lupus (297, 298). Numerous clinical studies (including the large VITAL trial) have evaluated omega-3 supplements for preventing/treating RA, SLE, psoriasis, CD, etc., generally showing benefits in reducing disease activity (220, 299).
5.4.2 Gut microbiota modulation
Targeting the gut microbiota is another frontier for modulating host metabolism and immunity. Strategies like probiotics, prebiotics, or fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) can reshape gut microbial structure, increasing abundance of beneficial bacteria like butyrate producers, showing great promise in IBD treatment (300). Butyrate enhances gut barrier function and promotes Treg differentiation, significantly improving joint inflammation in the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model (301–303). Gut microbiota metabolites are key mediators linking nutrition and immunity: SCFAs promote Treg differentiation and enhance the gut immune barrier (304), while bacterially modified bile acids influence immune cell differentiation via receptor-mediated mechanisms (305–307). These findings promote integrated intervention strategies, e.g., using traditional Chinese medicine active components to modulate gut microbiota metabolism, potentially enabling multi-target immunometabolic regulation for chronic diseases.
5.5 Emerging therapeutic platforms and metabolic intersections
The convergence of emerging technologies with metabolic regulation is opening new avenues for modulating immunometabolic homeostasis to treat complex diseases. CAR-T therapy is being enhanced by metabolic reprogramming techniques to promote an FAO-dependent memory-like phenotype, preventing T cell exhaustion and enabling long-term survival/function in nutrient-poor, hypoxic environments, significantly improving efficacy. CAR-T cell therapy for ADs like SLE has entered clinical investigation (308). For example, CD19-CAR T cell therapy substantially inhibits key pathways in SLE, upregulating lipid metabolism-related pathways compared to rituximab and belimumab (309). In synthetic immunology, engineered probiotics designed to exploit APC metabolism, activating HIF-1α in DCs to produce lactate and inhibit autoreactive T cells, have been developed (310). In IBD models, pH-sensitive nanoparticle carriers can target butyrate delivery to inflamed gut areas, promoting Treg differentiation and barrier repair while reducing systemic side effects (311). These innovative cross-disciplinary technologies hold promise to revolutionize immunotherapy.
6 Conclusion
This review systematically elucidates the central role of lipid metabolism in immune regulation. The research paradigm has shifted from viewing lipids as passive structural and energy molecules to recognizing their active roles as signaling regulators and determinants of immune cell fate. Lipid reprogramming is a necessary condition for immune cell functional differentiation (80). It can also be induced by inflammatory factors (141). This forms a self-amplifying positive feedback loop, which acts as a core regulatory node driving disease initiation, progression, and chronicity. In ADs, distinct metabolic dysregulation—such as glycolytic hyperactivation in SLE, lactate-induced lipogenesis in RA, and myelin lipid overload in MS—characterizes each disorder. More importantly, these metabolic vulnerabilities present unprecedented opportunities for developing novel, more targeted therapeutic strategies. By reprogramming metabolism rather than using broad suppression, we can normalize immune function and restore homeostasis, representing a profound shift in the treatment philosophy for ADs.
A core paradox exists in targeting lipid metabolism for ADs: many effective drug targets (e.g., HMGCR, FASN) are essential for normal immune cell function (312). Why does inhibiting these pathways treat disease? Could it cause immunosuppression or metabolic toxicity? How to balance efficacy and safety? We posit that pathogenic immune cells in ADs exist in a state of metabolic hyperactivation, far exceeding normal homeostatic levels. The therapeutic goal is not complete pathway blockade but rather modulating runaway metabolic activity back to the normal homeostatic setpoint (313). The concept of “immunometabolic normalization” rather than “inhibition”—highlights the need for drugs with an appropriate therapeutic window. Such agents should effectively suppress pathological hyperactivation while avoiding excessive impairment of the normal metabolism essential for protective immunity.
Despite remarkable progress, challenges remain: while the association between lipid metabolic abnormalities and ADs is clear, precise causal chains need full elucidation. Determining the initiating factors and key nodes is crucial for identifying optimal intervention targets. Lipid metabolic regulation exhibits significant heterogeneity across diseases, patients, tissue microenvironments, and even cell subsets. For instance, inhibiting pathways like mTORC1 or FASN may affect both pathogenic and protective cells (103) or other tissue functions (314). AD metabolic dysregulation is systemic, involving interactions between tissue stromal cells (e.g., RA FLS) and distant organs (177, 178), adding complexity. Therefore, it is essential to move beyond one-size-fits-all suppression and toward tailored and personalized interventions. Cellular metabolic pathways are evolutionarily conserved and shared among nearly all cell types. This universality means metabolic interventions often have broad systemic effects. Translating basic findings into effective clinical therapies is challenging. Many drugs targeting core pathways (e.g., LXR agonists, ACC inhibitors) show efficacy preclinically but face limitations due to potential systemic side effects (e.g., hepatic steatosis with LXR agonists). Achieving targeted delivery to specific immune cells or tissues to improve efficacy and reduce off-target effects is a major bottleneck.
Future breakthroughs rely on multidisciplinary integration. Combining single-cell transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and lipidomics will enable mapping detailed metabolic landscapes of distinct immune cell subsets in disease states at unprecedented resolution. This will further aid in identifying disease-specific metabolic vulnerabilities, discovering novel targets, and stratifying patients for precision medicine trials based on their metabolic phenotypes. High-throughput lipidomics/metabolomics may yield biomarkers reflecting disease activity, predicting treatment response, or distinguishing patient subtypes, enabling early diagnosis, personalized therapy, and treatment monitoring. Developing novel drug delivery systems [e.g., based on liposomes, exosomes (311)] for targeted delivery of metabolic modulators to specific immune cells or inflamed tissues is key to overcoming off-target effects. Integrating metabolomic biomarkers with dietary (e.g., Omega-3 PUFAs, ketogenic diets) and gut microbiome (e.g., probiotics, FMT) interventions will help build multi-dimensional “metabolism-immune-microecology” regimens. Combining these agents with established immunotherapies promises synergistic effects. This includes pairing them with biologics (e.g., TNF-α or IL-17 inhibitors, B cell-depleting agents) or JAK inhibitors, which could lead to superior disease control, permit lower doses of individual drugs, and reduce treatment-related toxicity.
In summary, targeting lipid metabolism opens a promising new avenue for treating ADs. Future research will strive to deepen our understanding of this complex regulatory network and translate this knowledge into precise metabolic intervention strategies that truly improve patients’ quality of life. This will require relentless exploration by basic scientists, as well as close collaboration among clinicians, pharmacologists, and the biotechnology industry. Such efforts will propel this exciting field from bench to bedside, ultimately enabling effective control and personalized management of ADs.
Author contributions
YC: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZF: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QZ: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HD: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HR: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82174314 to BL; No. 82305220 to ZD); Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (No.7244485 to WB).
Acknowledgments
Figures were created with BioRender.com.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1713148/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Schematic illustration of the regulatory network governing lipid metabolism. Fatty acids (FAs) enter cells via CD36-mediated lipid uptake. Subsequent intracellular signaling involves the PI3K/AKT pathway, which modulates activity of AMPK and mTOR1. AMPK functions as a central regulator: it influences peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα)-dependent transcriptional programs and modulates sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1) activity. Transcription factors SREBP1 and SREBP2 translocate to the nucleus to drive expression of genes for fatty acid synthesis (e.g., fatty acid synthase, FASN; acetyl-CoA carboxylase, ACC) and cholesterol synthesis (e.g., 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase, HMGCR; low-density lipoprotein receptor, LDLR), respectively. PPARα promotes fatty acid oxidation (FAO) by facilitating acetyl-CoA transport into mitochondria via carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1); within mitochondria, β-oxidation, the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and ATP production occur. Additionally, the liver X receptor (LXR) regulates cholesterol efflux via target genes such as ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) and G1 (ABCG1).Created in BioRender. yu, Y (2025). https://BioRender.com/havvjba
Supplementary Table 1 | Diverse lipids orchestrate immune cells in autoimmunity.
References
1. Davidson A and Diamond B. Autoimmune diseases. N Engl J Med. (2001) . 345:340–50. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200108023450506
2. Song Y, Li J, and Wu Y. Evolving understanding of autoimmune mechanisms and new therapeutic strategies of autoimmune disorders. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:263. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01952-8
3. Ramírez-Valle F, Maranville JC, Roy S, and Plenge RM. Sequential immunotherapy: towards cures for autoimmunity. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2024) . 23:501–24. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-00959-8
4. Xu R, He X, Xu J, Yu G, and Wu Y. Immunometabolism: signaling pathways, homeostasis, and therapeutic targets. MedComm (2020). (2024) . 5:e789. doi: 10.1002/mco2.789
5. Mathis D and Shoelson SE. Immunometabolism: an emerging frontier. Nat Rev Immunol. (2011) . 11:81. doi: 10.1038/nri2922
6. Murray PJ, Rathmell J, and Pearce E. SnapShot: immunometabolism. Cell Metab. (2015) . 22:190–190.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.06.014
7. Wang R, Dillon CP, Shi LZ, Milasta S, Carter R, Finkelstein D, et al. The transcription factor myc controls metabolic reprogramming upon T lymphocyte activation. Immunity. (2011) . 35:871–82. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.09.021
8. Berod L, Friedrich C, Nandan A, Freitag J, Hagemann S, Harmrolfs K, et al. De novo fatty acid synthesis controls the fate between regulatory T and T helper 17 cells. Nat Med. (2014) . 20:1327–33. doi: 10.1038/nm.3704
9. Li J, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Liu P, Liu M, Zhang M, et al. S1P/S1PR signaling pathway advancements in autoimmune diseases. Biomol Biomed. (2023) .23:922–35. doi: 10.17305/bb.2023.9082
10. Zhang Q, Wang Y, Zhu J, Zou M, Zhang Y, Wu H, et al. Specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators: a key player in resolving inflammation in autoimmune diseases. Sci Bull (Beijing). (2025) . 70:778–94. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2024.07.049
11. Bogie JFJ, Vanmierlo T, Vanmol J, Timmermans S, Mailleux J, Nelissen K, et al. Liver X receptor beta deficiency attenuates autoimmune-associated neuroinflammation in a T cell-dependent manner. J Autoimmun. (2021) . 124:102723. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102723
12. Li D, Liu Y, Lu Y, Gao S, and Zhang L. Palmitoylation of SARS-CoV-2 S protein is critical for S-mediated syncytia formation and virus entry. J Med Virol. (2022) . 94:342–8. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27339
13. Levental I, Levental KR, and Heberle FA. Lipid rafts: controversies resolved, mysteries remain. Trends Cell Biol. (2020) . 30:341–53. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.01.009
14. Leishman S, Aljadeed NM, Qian L, Cockcroft S, Behmoaras J, and Anand PK. Fatty acid synthesis promotes inflammasome activation through NLRP3 palmitoylation. Cell Rep. (2024) . 43:114516. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114516
15. Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature. (2017) . 542:177–85. doi: 10.1038/nature21363
16. Robinson G, Pineda-Torra I, Ciurtin C, and Jury EC. Lipid metabolism in autoimmune rheumatic disease: implications for modern and conventional therapies. J Clin Invest. (2022) . 132:e148552. doi: 10.1172/JCI148552
17. Stathopoulou C. Nikoleri,Dimitra, and bertsias G. Immunometabolism: Overview Ther Prospects Autoimmune Diseases. Immunother. (2019) . 11:813–29. doi: 10.2217/imt-2019-0002
18. Baker ES, Uritboonthai W, Aisporna A, Hoang C, Heyman HM, Connell L, et al. METLIN-CCS Lipid Database: An authentic standards resource for lipid classification and identification. Nat Metab. (2024) . 6:981–2. doi: 10.1038/s42255-024-01058-z
19. Fahy E, Subramaniam S, Brown HA, Glass CK, Merrill AH, Murphy RC, et al. A comprehensive classification system for lipids. J Lipid Res. (2005) . 46:839–61. doi: 10.1194/jlr.E400004-JLR200
20. DeBose-Boyd RA. Significance and regulation of lipid metabolism. Semin Cell Dev Biol. (2018) . 81:97. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.12.003
21. Steinberg GR and Hardie DG. New insights into activation and function of the AMPK. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2023) . 24:255–72. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00547-x
22. Unger Z, Kuklinski A, and Gomez-Casado C. Importance of SREBP signaling in controlling lipid metabolism and homeostasis in B cells for future vaccine design. Allergy. (2024) . 79:2885–7. doi: 10.1111/all.16134
23. Gracie CJ, Mitchell R, Johnstone JC, and Clarke AJ. The unusual metabolism of germinal center B cells. Trends Immunol. (2025) . 46:416–28. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2025.02.015
24. Lam WY and Bhattacharya D. Metabolic links between plasma cell survival, secretion, and stress. Trends Immunol. (2018) . 39:19–27. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2017.08.007
25. Yin Y, Choi SC, Xu Z, Perry DJ, Seay H, Croker BP, et al. Normalization of CD4+ T cell metabolism reverses lupus. Sci Transl Med. (2015) 7:274ra18. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa0835
26. Li W, Tang X, Zheng Y, Xu X, Zhao N, Tsao BP, et al. Phosphatidic acid promoting the generation of interleukin-17A producing double-negative T cells by enhancing mTORC1 signaling in lupus. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2024) . 76:1096–108. doi: 10.1002/art.42840
27. Zhang J, Guo Q, Dai D, Yu J, Wang L, Wu Z, et al. Rapamycin-encapsulated costimulatory ICOS/CD40L-bispecific nanoparticles restrict pathogenic helper T-B-cell interactions while in situ suppressing mTOR for lupus treatment. Biomaterials. (2022) . 289:121766. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121766
28. Huang N, Winans T, Wyman B, Oaks Z, Faludi T, Choudhary G, et al. Rab4A-directed endosome traffic shapes pro-inflammatory mitochondrial metabolism in T cells via mitophagy, CD98 expression, and kynurenine-sensitive mTOR activation. Nat Commun. (2024) . 15:2598. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46441-2
29. Katsuyama T, Li H, Comte D, Tsokos GC, and Moulton VR. Splicing factor SRSF1 controls T cell hyperactivity and systemic autoimmunity. J Clin Invest. (2019) . 129:5411–23. doi: 10.1172/JCI127949
30. Takeshima Y, Iwasaki Y, Nakano M, Narushima Y, Ota M, Nagafuchi Y, et al. Immune cell multiomics analysis reveals contribution of oxidative phosphorylation to B-cell functions and organ damage of lupus. Ann Rheum Dis. (2022) . 81:845–53. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221464
31. Xie W, Li J, Du H, and Xia J. Causal relationship between PCSK9 inhibitor and autoimmune diseases: a drug target Mendelian randomization study. Arthritis Res Ther. (2023) . 25:148. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03122-7
32. Lima SF, Gogokhia L, Viladomiu M, Chou L, Putzel G, Jin WB, et al. Transferable immunoglobulin A-coated odoribacter splanchnicus in responders to fecal microbiota transplantation for ulcerative colitis limits colonic inflammation. Gastroenterology. (2022) . 162:166–78. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.061
33. Park J, Wang Q, Wu Q, Mao-Draayer Y, and Kim CH. Bidirectional regulatory potentials of short-chain fatty acids and their G-protein-coupled receptors in autoimmune neuroinflammation. Sci Rep. (2019) . 9:8837. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45311-y
34. Frasca D, Romero M, Garcia D, Diaz A, and Blomberg BB. Obesity accelerates age-associated defects in human B cells through a metabolic reprogramming induced by the fatty acid palmitate. Front Aging. (2021) . 2:828697. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2021.828697
35. Hoxha M, Spahiu E, Prendi E, and Zappacosta B. A systematic review on the role of arachidonic acid pathway in multiple sclerosis. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. (2022) . 21:160–87. doi: 10.2174/1871527319666200825164123
36. Feng C, Li L, Li Q, Switzer K, Liu M, Han S, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid ameliorates autoimmune inflammation by activating GPR120 signaling pathway in dendritic cells. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) . 97:107698. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107698
37. Lin L, Hu M, Li Q, Du L, Lin L, Xue Y, et al. Oleic acid availability impacts thymocyte preprogramming and subsequent peripheral Treg cell differentiation. Nat Immunol. (2024) . 25:54–65. doi: 10.1038/s41590-023-01672-1
38. Grajchen E, Loix M, Baeten P, Côrte-Real BF, Hamad I, Vanherle S, et al. Fatty acid desaturation by stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 controls regulatory T cell differentiation and autoimmunity. Cell Mol Immunol. (2023) . 20:666–79. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-01011-2
39. Liao W, Hu R, Ji Y, Zhong Z, Huang X, Cai T, et al. Oleic acid regulates CD4+ T cells differentiation by targeting ODC1-mediated STAT5A phosphorylation in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease. Phytomedicine. (2025) . 141:156660. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156660
40. Srivastava N, Hu H, Peterson OJ, Vomund AN, Stremska M, Zaman M, et al. CXCL16-dependent scavenging of oxidized lipids by islet macrophages promotes differentiation of pathogenic CD8+ T cells in diabetic autoimmunity. Immunity. (2024) . 57:1629–1647.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.04.017
41. Zhang F, Zhang B, Ding H, Li X, Wang X, Zhang X, et al. The oxysterol receptor EBI2 links innate and adaptive immunity to limit IFN response and systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) . 10:e2207108. doi: 10.1002/advs.202207108
42. Kornilov SA, Price ND, Gelinas R, Acosta J, Brunkow ME, Gervasi-Follmar T, et al. Multi-Omic characterization of the effects of Ocrelizumab in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. (2024) . 467:123303. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2024.123303
43. Cartier A and Hla T. Sphingosine 1-phosphate: Lipid signaling in pathology and therapy. Science. (2019) 366:eaar5551. doi: 10.1126/science.aar5551
44. Ikonen E and Olkkonen VM. Intracellular cholesterol trafficking. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2023) 15:a041404. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041404
45. Xu L, Li J, Ma J, and Hasim A. Combined spatially resolved metabolomics and spatial transcriptomics reveal the mechanism of RACK1-mediated fatty acid synthesis. Mol Oncol. (2024) 19:1668–86. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13752
46. Tubbs E and Rieusset J. Metabolic signaling functions of ER-mitochondria contact sites: role in metabolic diseases. J Mol Endocrinol. (2017) . 58:R87–R106. doi: 10.1530/JME-16-0189
47. Spinelli JB and Haigis MC. The multifaceted contributions of mitochondria to cellular metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. (2018) . 20:745–54. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0124-1
48. Bahat A, MacVicar T, and Langer T. Metabolism and innate immunity meet at the mitochondria. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) . 9:720490. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.720490
49. Jacquemyn J, Cascalho A, and Goodchild RE. The ins and outs of endoplasmic reticulum-controlled lipid biosynthesis. EMBO Rep. (2017) . 18:1905–21. doi: 10.15252/embr.201643426
50. Najt CP, Adhikari S, Heden TD, Cui W, Gansemer ER, Rauckhorst AJ, et al. Organelle interactions compartmentalize hepatic fatty acid trafficking and metabolism. Cell Rep. (2023) . 42:112435. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112435
51. Cho CH, Patel S, and Rajbhandari P. Adipose tissue lipid metabolism: lipolysis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. (2023) . 83:102114. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2023.102114
52. Pilic J and Kleele T. An organelle tango controls lipid metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. (2024) . 26:1227–8. doi: 10.1038/s41556-024-01441-8
53. Jarc E and Petan T. A twist of FATe: Lipid droplets and inflammatory lipid mediators. Biochimie. (2020) . 169:69–87. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2019.11.016
54. Jin HR, Wang J, Wang ZJ, Xi MJ, Xia BH, Deng K, et al. Lipid metabolic reprogramming in tumor microenvironment: from mechanisms to therapeutics. J Hematol Oncol. (2023) . 16:103. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01498-2
55. Kemp F, Braverman EL, and Byersdorfer CA. Fatty acid oxidation in immune function. Front Immunol. (2024) . 15:1420336. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1420336
56. Chen X, Lin P, Lu Y, Zheng J, Lin Y, Zhou Z, et al. Mitochondrial regulation of CD8+ T cells: mechanisms and therapeutic modulation. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2025) . 12:e03095. doi: 10.1002/advs.202503095
57. Weinberg SE, Singer BD, Steinert EM, Martinez CA, Mehta MM, Martínez-Reyes I, et al. Mitochondrial complex III is essential for suppressive function of regulatory T cells. Nature. (2019) . 565:495–9. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0846-z
58. Lagunas-Rangel FA. Cholesterol effects on the tumor immune microenvironment: from fundamental concepts to mechanisms and implications. Front Oncol. (2025) . 15:1579054. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1579054
59. Zahid D, Zhang N, Fang H, Gu J, Li M, and Li W. Loss of core fucosylation suppressed the humoral immune response in Salmonella typhimurium infected mice. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. (2021) . 54:606–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.02.006
60. Luo C, Wang K, Liu DQ, Li Y, and Zhao QS. The functional roles of lipid rafts in T cell activation, immune diseases and HIV infection and prevention. Cell Mol Immunol. (2008) 5:1–7. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2008.1
61. Patsoukis N, Bardhan K, Chatterjee P, Sari D, Liu B, Bell LN, et al. PD-1 alters T-cell metabolic reprogramming by inhibiting glycolysis and promoting lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation. Nat Commun. (2015) . 6:6692. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7692
62. Mailer R KW, Gisterå A, Polyzos KA, Ketelhuth DFJ, and Hansson GK. Hypercholesterolemia enhances T cell receptor signaling and increases the regulatory T cell population. Sci Rep. (2017) . 7:15655. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15546-8
63. Celik C, Lee SYT, Yap WS, and Thibault G. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and lipids in health and diseases. Prog Lipid Res. (2023) . 89:101198. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2022.101198
64. Chen X and Cubillos-Ruiz JR. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signals in the tumor and its microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer. (2021) . 21:71–88. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-00312-2
65. Zhang W, Xu L, Zhu L, Liu Y, Yang S, and Zhao M. Lipid droplets, the central hub integrating cell metabolism and the immune system. Front Physiol. (2021) . 12:746749. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.746749
66. Shen S, Shen M, Kuang L, Yang K, Wu S, Liu X, et al. SIRT1/SREBPs-mediated regulation of lipid metabolism. Pharmacol Res. (2024) . 199:107037. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.107037
67. Xu X, Jin W, Chang R, and Ding X. Research progress of SREBP and its role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Front Immunol. (2024) . 15:1398921. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1398921
68. Luo W, Adamska JZ, Li C, Verma R, Liu Q, Hagan T, et al. SREBP signaling is essential for effective B cell responses. Nat Immunol. (2023) . 24:337–48. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01376-y
69. Plebanek MP, Xue Y, Nguyen YV, DeVito NC, Wang X, Holtzhausen A, et al. A lactate-SREBP2 signaling axis drives tolerogenic dendritic cell maturation and promotes cancer progression. Sci Immunol. (2024) 9:eadi4191. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adi4191
70. Toobian D, Ghosh P, and Katkar GD. Parsing the role of PPARs in macrophage processes. Front Immunol. (2021) . 12:783780. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.783780
71. Wahli W and Michalik L. PPARs at the crossroads of lipid signaling and inflammation. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2012) . 23:351–63. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.05.001
72. Montaigne D, Butruille L, and Staels B. PPAR control of metabolism and cardiovascular functions. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2021) . 18:809–23. doi: 10.1038/s41569-021-00569-6
73. Christofides A, Konstantinidou E, Jani C, and Boussiotis VA. The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) in immune responses. Metabolism. (2021) . 114:154338. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154338
74. Kökény G, Calvier L, and Hansmann G. PPARγ and TGFβ-major regulators of metabolism, inflammation, and fibrosis in the lungs and kidneys. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) . 22:10431. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910431
75. Garoche C, Boulahtouf A, Grimaldi M, Chiavarina B, Toporova L, den Broeder MJ, et al. Interspecies differences in activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ by pharmaceutical and environmental chemicals. Environ Sci Technol. (2021) . 55:16489–501. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.1c04318
76. Bilotta MT, Petillo S, Santoni A, and Cippitelli M. Liver X receptors: regulators of cholesterol metabolism, inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. Front Immunol. (2020) . 11:584303. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.584303
77. Repa JJ, Liang G, Ou J, Bashmakov Y, Lobaccaro JM, Shimomura I, et al. Regulation of mouse sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c gene (SREBP-1c) by oxysterol receptors, LXRalpha and LXRbeta. Genes Dev. (2000) . 14:2819–30. doi: 10.1101/gad.844900
78. Waddington KE, Robinson GA, Rubio-Cuesta B, Chrifi-Alaoui E, Andreone S, Poon KS, et al. LXR directly regulates glycosphingolipid synthesis and affects human CD4+ T cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2021) . 118:e2017394118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2017394118
79. Ito A, Hong C, Oka K, Salazar JV, Diehl C, Witztum JL, et al. Cholesterol accumulation in CD11c+ Immune cells is a causal and targeta ble factor in autoimmune disease. Immunity. (2016) . 45:1311–26. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.11.008
80. Bosteels V, Maréchal S, De Nolf C, Rennen S, Maelfait J, Tavernier SJ, et al. LXR signaling controls homeostatic dendritic cell maturation. Sci Immunol. (2023) 8:eadd3955. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.add3955
81. Zhu H, Liu Z, An J, Zhang M, Qiu Y, and Zou MH. Activation of AMPKα1 is essential for regulatory T cell function and autoimmune liver disease prevention. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) . 18:2609–17. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00790-w
82. Shimano H and Sato R. SREBP-regulated lipid metabolism: convergent physiology - divergent pathophysiology. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2017) . 13:710–30. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.91
83. Liu Y, Zhang D, and Liu X. mTOR signaling in T cell immunity and autoimmunity. Int Rev Immunol. (2015) . 34:50–66. doi: 10.3109/08830185.2014.933957
84. Han X. Lipidomics for studying metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2016) . 12:668–79. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.98
85. Wang Y, Xiao H, Lai L, and Zheng Z. Therapeutic strategies targeting SREBP transcription factors: an update to 2024. Acta Materia Medica. (2025) . 4:437–65. doi: 10.15212/AMM-2025-0001
86. Oaks Z, Winans T, Huang N, Banki K, and Perl A. Activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin in SLE: explosion of evidence in the last five years. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2016) . 18:73. doi: 10.1007/s11926-016-0622-8
87. Schutt SD, Wu Y, Kharel A, Bastian D, Choi HJ, Hanief Sofi M, et al. The druggable transcription factor Fli-1 regulates T cell immunity and tolerance in graft-versus-host disease. J Clin Invest. (2022) . 132:e143950. doi: 10.1172/JCI143950
88. Sarandi E, Krueger-Krasagakis S, Tsoukalas D, Sidiropoulou P, Evangelou G, Sifaki M, et al. Psoriasis immunometabolism: progress on metabolic biomarkers and targeted therapy. Front Mol Biosci. (2023) . 10:1201912. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1201912
89. Ruiz-Limon P, Barbarroja N, Perez-Sanchez C, Aguirre MA, Bertolaccini ML, Khamashta MA, et al. Atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: effects of in vivo statin treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. (2015) . 74:1450–8. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204351
90. Wang X, Ye L, Liu S, Zheng Y, Zhu L, Huang W, et al. FXR inhibition functions as a checkpoint blockade of the pathogenic Tfh cell response in lupus. Cell Mol Immunol. (2025) . 22:889–900. doi: 10.1038/s41423-025-01309-3
91. Weyand CM, Wu B, and Goronzy JJ. The metabolic signature of T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (2020) . 32:159–67. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000683
92. Yue S, Fan J, Xie D, Cao C, Wang Z, Huang J, et al. Unveiling the therapeutic potential: targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev Mol Med. (2025) . 27:e18. doi: 10.1017/erm.2025.11
93. Alivernini S, MacDonald L, Elmesmari A, Finlay S, Tolusso B, Gigante MR, et al. Distinct synovial tissue macrophage subsets regulate inflammation and remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med. (2020) . 26:1295–306. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0939-8
94. Frommer KW, Hasseli R, Schäffler A, Lange U, Rehart S, Steinmeyer J, et al. Free fatty acids in bone pathophysiology of rheumatic diseases. Front Immunol. (2019) . 10:2757. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02757
95. Lai ZW, Kelly R, Winans T, Marchena I, Shadakshari A, Yu J, et al. Sirolimus in patients with clinically active systemic lupus erythematosus resistant to, or intolerant of, conventional medications: a single-arm, open-label, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet. (2018) . 391:1186–96. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30485-9
96. Li N, Gong Z, Li X, Ma Q, Wu M, Liu D, et al. Betulinic acid inhibits the migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2019) . 67:186–93. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.11.042
97. Shen Y, Wen Z, Li Y, Matteson EL, Hong J, Goronzy JJ, et al. Metabolic control of the scaffold protein TKS5 in tissue-invasive, proinflammatory T cells. Nat Immunol. (2017) . 18:1025–34. doi: 10.1038/ni.3808
98. Sánchez-Fernández A, Zandee S, Mastrogiovanni M, Charabati M, Rubbo H, Prat A, et al. Administration of Maresin-1 ameliorates the physiopathology of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroinflammation. (2022) . 19:27. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02386-1
99. Martin-Gutierrez L, Waddington KE, Maggio A, Coelewij L, Oppong AE, Yang N, et al. Dysregulated lipid metabolism networks modulate T-cell function in people with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. (2024) . 217:204–18. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxae032
100. Ladakis DC, Pedrini E, Reyes-Mantilla MI, Sanjayan M, Smith MD, Fitzgerald KC, et al. Metabolomics of multiple sclerosis lesions demonstrates lipid changes linked to alterations in transcriptomics-based cellular profiles. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. (2024) . 11:e200219. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200219
101. Poon MM, Lorrain KI, Stebbins KJ, Edu GC, Broadhead AR, Lorenzana AO, et al. Discovery of a brain penetrant small molecule antagonist targeting LPA1 receptors to reduce neuroinflammation and promote remyelination in multiple sclerosis. Sci Rep. (2024) . 14:10573. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61369-9
102. Zahoor I, Nematullah M, Ahmed ME, Fatma M, Sajad M, Ayasolla K, et al. Maresin-1 promotes neuroprotection and modulates metabolic and inflammatory responses in disease-associated cell types in preclinical models of multiple sclerosis. J Biol Chem. (2025) . 301:108226. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108226
103. Prado DS, Cattley RT, Sonego AB, Sutariya P, Wu S, Lee M, et al. The phospholipid kinase PIKFYVE is essential for Th17 differentiation. J Exp Med. (2025) . 222:e20240625. doi: 10.1084/jem.20240625
104. Damjanovich L, Volkó J, Forgács A, Hohenberger W, and Bene L. Crohn’s disease alters MHC-rafts in CD4+ T-cells. Cytometry A. (2012) . 81:149–64. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.21173
105. Decara J, Rivera P, López-Gambero AJ, Serrano A, Pavón FJ, Baixeras E, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: experimental targeting for the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases. Front Pharmacol. (2020) . 11:730. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00730
106. Pompura SL, Wagner A, Kitz A, LaPerche J, Yosef N, Dominguez-Villar M, et al. Oleic acid restores suppressive defects in tissue-resident FOXP3 Tregs from patients with multiple sclerosis. J Clin Invest. (2021) . 131:e138519. doi: 10.1172/JCI138519
107. Suh JH and Saba JD. Sphingosine-1-phosphate in inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated colon cancer: the fat’s in the fire. Transl Cancer Res. (2015) . 4:469–83. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-676X.2015.10.06
108. Zeng C, Wen B, Hou G, Lei L, Mei Z, Jia X, et al. Lipidomics profiling reveals the role of glycerophospholipid metabolism in psoriasis. Gigascience. (2017) . 6:1–11. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/gix087
109. Piaserico S, Orlando G, and Messina F. Psoriasis and cardiometabolic diseases: shared genetic and molecular pathways. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) . 23:9063. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169063
110. Wroński A and Wójcik P. Impact of ROS-dependent lipid metabolism on psoriasis pathophysiology. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) . 23:12137. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012137
111. Kao YS, Mamareli P, Dhillon-LaBrooy A, Stüve P, Godoy GJ, Velasquez LN, et al. Targeting ACC1 in T cells ameliorates psoriatic skin inflammation. J Mol Med (Berl). (2023) . 101:1153–66. doi: 10.1007/s00109-023-02349-w
112. Liang G, Huang J, Chen J, Wen X, Li R, Xie H, et al. Fatty acid oxidation promotes apoptotic resistance and proinflammatory phenotype of CD4+ Tissue-resident memory T cells in crohn’s disease. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) . 17:939–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2024.02.014
113. Lim SA, Su W, Chapman NM, and Chi H. Lipid metabolism in T cell signaling and function. Nat Chem Biol. (2022) . 18:470–81. doi: 10.1038/s41589-022-01017-3
114. Buck MD, O’Sullivan D, and Pearce EL. T cell metabolism drives immunity. J Exp Med. (2015) . 212:1345–60. doi: 10.1084/jem.20151159
115. Young KE, Flaherty S, Woodman KM, Sharma-Walia N, and Reynolds JM. Fatty acid synthase regulates the pathogenicity of Th17 cells. J Leukoc Biol. (2017) . 102:1229–35. doi: 10.1189/jlb.3AB0417-159RR
116. Endo Y, Onodera A, Obata-Ninomiya K, Koyama-Nasu R, Asou HK, Ito T, et al. ACC1 determines memory potential of individual CD4+ T cells by regulating de novo fatty acid biosynthesis. Nat Metab. (2019) . 1:261–75. doi: 10.1038/s42255-018-0025-4
117. Cluxton D, Petrasca A, Moran B, and Fletcher JM. Differential regulation of human treg and th17 cells by fatty acid synthesis and glycolysis. Front Immunol. (2019) . 10:115. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00115
118. Raud B, Roy DG, Divakaruni AS, Tarasenko TN, Franke R, Ma EH, et al. Etomoxir actions on regulatory and memory T cells are independent of cpt1a-mediated fatty acid oxidation. Cell Metab. (2018) . 28:504–515.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.06.002
119. Kanno T, Nakajima T, Kawashima Y, Yokoyama S, Asou HK, Sasamoto S, et al. Acsbg1-dependent mitochondrial fitness is a metabolic checkpoint for tissue Treg cell homeostasis. Cell Rep. (2021) . 37:109921. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109921
120. Cai F, Jin S, and Chen G. The effect of lipid metabolism on CD4+ T cells. Mediators Inflamm. (2021) . 2021:6634532. doi: 10.1155/2021/6634532
121. Perucha E, Melchiotti R, Bibby JA, Wu W, Frederiksen KS, Roberts CA, et al. The cholesterol biosynthesis pathway regulates IL-10 expression in human Th1 cells. Nat Commun. (2019) . 10:498. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08332-9
122. Kanno T, Miyako K, Nakajima T, Yokoyama S, Sasamoto S, Asou HK, et al. SCD2-mediated cooperative activation of IRF3-IRF9 regulatory circuit controls type I interferon transcriptome in CD4+ T cells. Front Immunol. (2022) . 13:904875. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.904875
123. Angela M, Endo Y, Asou HK, Yamamoto T, Tumes DJ, Tokuyama H, et al. Fatty acid metabolic reprogramming via mTOR-mediated inductions of PPARγ directs early activation of T cells. Nat Commun. (2016) . 7:13683. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13683
124. Chakraborty S, Khamaru P, and Bhattacharyya A. Regulation of immune cell metabolism in health and disease: Special focus on T and B cell subsets. Cell Biol Int. (2022) . 46:1729–46. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11867
125. Schreiber S, Hammers CM, Kaasch AJ, Schraven B, Dudeck A, and Kahlfuss S. Metabolic interdependency of th2 cell-mediated type 2 immunity and the tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol. (2021) . 12:632581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.632581
126. Wang R, Liu Z, Fan Z, and Zhan H. Lipid metabolism reprogramming of CD8+ T cell and therapeutic implications in cancer. Cancer Lett. (2023) . 567:216267. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216267
127. Tang Y, Chen Z, Zuo Q, and Kang Y. Regulation of CD8+ T cells by lipid metabolism in cancer progression. Cell Mol Immunol. (2024) . 21:1215–30. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01224-z
128. Lee J, Walsh MC, Hoehn KL, James DE, Wherry EJ, and Choi Y. Regulator of fatty acid metabolism, acetyl coenzyme a carboxylase 1, controls T cell immunity. J Immunol. (2014) 192:3190–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302985
129. Ma X, Xiao L, Liu L, Ye L, Su P, Bi E, et al. CD36-mediated ferroptosis dampens intratumoral CD8+ T cell effector function and impairs their antitumor ability. Cell Metab. (2021) . 33:1001–1012.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.02.015
130. van der Windt GJW, Everts B, Chang CH, Curtis JD, Freitas TC, Amiel E, et al. Mitochondrial respiratory capacity is a critical regulator of CD8+ T cell memory development. Immunity. (2012) . 36:68–78. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.12.007
131. O’Sullivan D, van der Windt GJW, Huang SCC, Curtis JD, Chang CH, Buck MD, et al. Memory CD8(+) T cells use cell-intrinsic lipolysis to support the metabolic programming necessary for development. Immunity. (2014) . 41:75–88. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.005
132. Papotto PH, Reinhardt A, Prinz I, and Silva-Santos B. Innately versatile: γδ17 T cells in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun. (2018) . 87:26–37. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2017.11.006
133. Cua DJ and Tato CM. Innate IL-17-producing cells: the sentinels of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. (2010) . 10:479–89. doi: 10.1038/nri2800
134. Nah J, Lee Y, and Seong RH. PRDM16 regulates γδT17 cell differentiation via controlling type 17 program and lipid-dependent cell fitness. Front Immunol. (2023). 14:1332386. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1332386
135. Kao YS, Lauterbach M, Lopez Krol A, Distler U, Godoy GJ, Klein M, et al. Metabolic reprogramming of interleukin-17-producing γδ T cells promotes ACC1-mediated de novo lipogenesis under psoriatic conditions. Nat Metab. (2025) 7:966–84. doi: 10.1038/s42255-025-01276-z
136. You Z and Chi H. Lipid metabolism in dendritic cell biology. Immunol Rev. (2023) . 317:137–51. doi: 10.1111/imr.13215
137. Westerterp M, Gautier EL, Ganda A, Molusky MM, Wang W, Fotakis P, et al. Cholesterol accumulation in dendritic cells links the inflammasome to acquired immunity. Cell Metab. (2017) . 25:1294–1304.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.04.005
138. Liu X, Yu P, Xu Y, Wang Y, Chen J, Tang F, et al. Metformin induces tolerogenicity of dendritic cells by promoting metabolic reprogramming. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2023) . 80:283. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04932-3
139. Chen IC, Awasthi D, Hsu CL, Song M, Chae CS, Dannenberg AJ, et al. High-fat diet-induced obesity alters dendritic cell homeostasis by enhancing mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. J Immunol. (2022) . 209:69–76. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100567
140. Wu S, Zhao S, Hai L, Yang Z, Wang S, Cui D, et al. Macrophage polarization regulates the pathogenesis and progression of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. (2025) . 24:103820. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2025.103820
141. Huang SCC, Everts B, Ivanova Y, O’Sullivan D, Nascimento M, Smith AM, et al. Cell-intrinsic lysosomal lipolysis is essential for alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Immunol. (2014) . 15:846–55. doi: 10.1038/ni.2956
142. Zizzo G and Cohen PL. The PPAR-γ antagonist GW9662 elicits differentiation of M2c-like cells and upregulation of the MerTK/Gas6 axis: a key role for PPAR-γ in human macrophage polarization. J Inflammation (Lond). (2015) . 12:36. doi: 10.1186/s12950-015-0081-4
143. Wang F, Zhang S, Vuckovic I, Jeon R, Lerman A, Folmes CD, et al. Glycolytic stimulation is not a requirement for M2 macrophage differentiation. Cell Metab. (2018). 28:463–475.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.08.012
144. Nomura M, Liu J, Rovira II, Gonzalez-Hurtado E, Lee J, Wolfgang MJ, et al. Fatty acid oxidation in macrophage polarization. Nat Immunol. (2016) . 17:216–7. doi: 10.1038/ni.3366
145. Batista-Gonzalez A, Vidal R, Criollo A, and Carreño LJ. New insights on the role of lipid metabolism in the metabolic reprogramming of macrophages. Front Immunol. (2019) . 10:2993. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02993
146. Su F, Su M, Wei W, Wu J, Chen L, Sun X, et al. Integrating multi-omics data to reveal the host-microbiota interactome in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Microbes. (2025) . 17:2476570. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2476570
147. Bouwstra JA, Nădăban A, Bras W, McCabe C, Bunge A, and Gooris GS. The skin barrier: An extraordinary interface with an exceptional lipid organization. Prog Lipid Res. (2023) . 92:101252. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2023.101252
148. Chang MH, Levescot A, Nelson-Maney N, Blaustein RB, Winden KD, Morris A, et al. Arthritis flares mediated by tissue-resident memory T cells in the joint. Cell Rep. (2021) . 37:109902. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109902
149. Ayasoufi K, Wolf DM, Namen SL, Jin F, Tritz ZP, Pfaller CK, et al. Brain resident memory T cells rapidly expand and initiate neuroinflammatory responses following CNS viral infection. Brain Behav Immun. (2023) . 112:51–76. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.05.009
150. Hoi A, Igel T, Mok CC, and Arnaud L. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. (2024) . 403:2326–38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00398-2
151. Morand EF, Fernandez-Ruiz R, Blazer A, and Niewold TB. Advances in the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. BMJ. (2023) . 383:e073980. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2022-073980
152. Dai X, Fan Y, and Zhao X. Systemic lupus erythematosus: updated insights on the pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention and therapeutics. Sig Transduct Target Ther. (2025). 10:1–51. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02168-0
153. Hu C, Zhang J, Hong S, Li H, Lu L, Xie G, et al. Oxidative stress-induced aberrant lipid metabolism is an important causal factor for dysfunction of immunocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Free Radic Biol Med. (2021) . 163:210–9. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.12.006
154. Sharabi A and Tsokos GC. T cell metabolism: new insights in systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis and therapy. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2020) . 16:100–12. doi: 10.1038/s41584-019-0356-x
155. Gergely P, Grossman C, Niland B, Puskas F, Neupane H, Allam F, et al. Mitochondrial hyperpolarization and ATP depletion in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2002) . 46:175–90. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200201)46:1
156. Hisada R, Yoshida N, Orite SYK, Umeda M, Burbano C, Scherlinger M, et al. Role of glutaminase 2 in promoting CD4+ T cell production of interleukin-2 by supporting antioxidant defense in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2022) . 74:1204–10. doi: 10.1002/art.42112
157. Yi T, Zhang W, Hua Y, Xin X, Wu Z, Li Y, et al. Rutin alleviates lupus nephritis by inhibiting T cell oxidative stress through PPARγ. Chem Biol Interact. (2024) . 394:110972. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.110972
158. Al-Mazroua HA, Nadeem A, Attia SM, Bakheet SA, Ahmad A, Ansari MA, et al. The PPAR-α selective agonist WY14643 improves lupus nephritis via the downregulation of the RORγT/STAT3 signaling pathway in MRL/lpr mice. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) . 145:113787. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113787
159. Krishnan S, Nambiar MP, Warke VG, Fisher CU, Mitchell J, Delaney N, et al. Alterations in lipid raft composition and dynamics contribute to abnormal T cell responses in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. (2004) . 172:7821–31. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.12.7821
160. McDonald G, Deepak S, Miguel L, Hall CJ, Isenberg DA, Magee AI, et al. Normalizing glycosphingolipids restores function in CD4+ T cells from lupus patients. J Clin Invest. (2014) . 124:712–24. doi: 10.1172/JCI69571
161. Katsuyama E, Humbel M, Suarez-Fueyo A, Satyam A, Yoshida N, Kyttaris VC, et al. CD38 in SLE CD4 T cells promotes Ca2+ flux and suppresses interleukin-2 production by enhancing the expression of GM2 on the surface membrane. Nat Commun. (2024) . 15:8304. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52617-7
162. Vukelic M, Kono M, and Tsokos GC. T cell metabolism in lupus. Immunometabolism. (2020) . 2:e200009. doi: 10.20900/immunometab20200009
163. He YS, Yang XK, Hu YQ, Xiang K, and Pan HF. Emerging role of Fli1 in autoimmune diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) . 90:107127. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107127
164. Zeng Q, Wang S, Li M, Wang S, Guo C, Ruan X, et al. Spleen fibroblastic reticular cell-derived acetylcholine promotes lipid metabolism to drive autoreactive B cell responses. Cell Metab. (2023) . 35:837–854.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.03.010
165. Iwata S, Hajime Sumikawa M, and Tanaka Y. B cell activation via immunometabolism in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. (2023) . 14:1155421. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1155421
166. Xiao Y, Hu Y, Gao Y, Wang L, Zhang L, Ma Q, et al. IL-17B alleviates the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus by inhibiting FASN-mediated differentiation of B cells. JCI Insight. (2024) . 9:e181906. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.181906
167. Zhang Y, Gui M, Wang Y, Mani N, Chaudhuri S, Gao B, et al. Inositol-requiring enzyme 1α-mediated synthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids as a driver of B cell differentiation and lupus-like autoimmune disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2021) . 73:2314–26. doi: 10.1002/art.41883
168. Xiao J, Zhao Z, Zhou F, Xiong J, Yang Z, Gong B, et al. TM9SF1 expression correlates with autoimmune disease activity and regulates antibody production through mTOR-dependent autophagy. BMC Med. (2024) . 22:502. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03729-w
169. Wang C, Chen B, Yu X, and Guan X. Macrophages unmasked: their pivotal role in driving atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2025) . 68:10. doi: 10.1007/s12016-025-09025-6
170. Cheng Q, Mou L, Su W, Chen X, Zhang T, Xie Y, et al. Ferroptosis of CD163+ tissue-infiltrating macrophages and CD10+ PC+ epithelial cells in lupus nephritis. Front Immunol. (2023) . 14:1171318. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1171318
171. Játiva S, Torrico S, Calle P, Poch E, Muñoz A, García M, et al. The phagocytosis dysfunction in lupus nephritis is related to monocyte/macrophage CPT1a. Immunol Lett. (2024) . 266:106841. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2024.106841
172. Tang Y, Zhang Y, Li X, Xu R, Ji Y, Liu J, et al. Immune landscape and the key role of APOE+ monocytes of lupus nephritis under the single-cell and spatial transcriptional vista. Clin Transl Med. (2023) . 13:e1237. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1237
173. Maria NI and Davidson A. Renal macrophages and dendritic cells in SLE nephritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2017) . 19:81. doi: 10.1007/s11926-017-0708-y
174. Zhang X, Chen Y, Sun G, Fei Y, Zhu H, Liu Y, et al. Farnesyl pyrophosphate potentiates dendritic cell migration in autoimmunity through mitochondrial remodeling. Nat Metab. (2024) . 6:2118–37. doi: 10.1038/s42255-024-01149-x
175. Di Matteo A, Bathon JM, and Emery P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. (2023) . 402:2019–33. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01525-8
176. Qiu J, Wu B, Goodman SB, Berry GJ, Goronzy JJ, and Weyand CM. Metabolic control of autoimmunity and tissue inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2021) . 12:652771. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.652771
177. Pucino V, Certo M, Bulusu V, Cucchi D, Goldmann K, Pontarini E, et al. Lactate buildup at the site of chronic inflammation promotes disease by inducing CD4+ T cell metabolic rewiring. Cell Metab. (2019) . 30:1055–1074.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.10.004
178. Certo M, Tsai CH, Pucino V, Ho PC, and Mauro C. Lactate modulation of immune responses in inflammatory versus tumor microenvironments. Nat Rev Immunol. (2021) . 21:151–61. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0406-2
179. Jantz-Naeem N, Guvencli N, Böttcher-Loschinski R, Böttcher M, Mougiakakos D, and Kahlfuss S. Metabolic T-cell phenotypes: from bioenergetics to function. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2025) 328:C1062–75. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00478.2024
180. Kanno T, Miyako K, and Endo Y. Lipid metabolism: a central modulator of RORγt-mediated Th17 cell differentiation. Int Immunol. (2024) . 36:487–96. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxae031
181. Su J, Fan X, Zou Y, Fu G, Feng S, Wang X, et al. Inhibition of aberrant activated fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by leishmania peptide via the regulation of fatty acid synthesis metabolism. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2025) . 12:e2409154. doi: 10.1002/advs.202409154
182. Hu Z, Li Y, Zhang L, Jiang Y, Long C, Yang Q, et al. Metabolic changes in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: state of the art review. Front Immunol. (2024) . 15:1250884. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1250884
183. Kong YY, Feige U, Sarosi I, Bolon B, Tafuri A, Morony S, et al. Activated T cells regulate bone loss and joint destruction in adjuvant arthritis through osteoprotegerin ligand. Nature. (1999) 402:304–9. doi: 10.1038/46303
184. Kim H, Choi IA, Umemoto A, Bae S, Kaneko K, Mizuno M, et al. SREBP2 restricts osteoclast differentiation and activity by regulating IRF7 and limits inflammatory bone erosion. Bone Res. (2024) . 12:48. doi: 10.1038/s41413-024-00354-4
185. Xiao H, Li W, Qin Y, Lin Z, Qian C, Wu M, et al. Crosstalk between lipid metabolism and bone homeostasis: exploring intricate signaling relationships. Res (Wash D C). (2024) . 7:447. doi: 10.34133/research.0447
186. Noroozi R, Tsai HH, Yu K, Bronson P, Samuel K, Trinh K, et al. Metabolic and lipid alterations in multiple sclerosis linked to disease severity. Mult Scler. (2025) . 31:433–43. doi: 10.1177/13524585251325468
187. Lorincz B, Jury EC, Vrablik M, Ramanathan M, and Uher T. The role of cholesterol metabolism in multiple sclerosis: From molecular pathophysiology to radiological and clinical disease activity. Autoimmun Rev. (2022) . 21:103088. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2022.103088
188. Montani L. Lipids in regulating oligodendrocyte structure and function. Semin Cell Dev Biol. (2021) . 112:114–22. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.07.016
189. Klotz L, Antel J, and Kuhlmann T. Inflammation in multiple sclerosis: consequences for remyelination and disease progression. Nat Rev Neurol. (2023) . 19:305–20. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00801-6
190. López-Muguruza E and Matute C. Alterations of oligodendrocyte and myelin energy metabolism in multiple sclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) . 24:12912. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612912
191. Montilla A, Zabala A, Calvo I, Bosch-Juan M, Tomé-Velasco I, Mata P, et al. Microglia regulate myelin clearance and cholesterol metabolism after demyelination via interferon regulatory factor 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2025) . 82:131. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05648-2
192. Garcia Corrales AV, Verberk SGS, Haidar M, Grajchen E, Dehairs J, Vanherle S, et al. Fatty acid elongation by ELOVL6 hampers remyelination by promoting inflammatory foam cell formation during demyelination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2023) . 120:e2301030120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2301030120
193. Vergara D, D’Alessandro M, Rizzello A, De Riccardis L, Lunetti P, Del Boccio P, et al. A lipidomic approach to the study of human CD4(+) T lymphocytes in multiple sclerosis. BMC Neurosci. (2015) . 16:46. doi: 10.1186/s12868-015-0183-1
194. Han A, Peng T, Xie Y, Zhang W, Sun W, Xie Y, et al. Mitochondrial-regulated Tregs: potential therapeutic targets for autoimmune diseases of the central nervous system. Front Immunol. (2023) . 14:1301074. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1301074
195. Zahoor I and Giri S. Specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators: emerging therapeutic candidates for multiple sclerosis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2021) . 60:147–63. doi: 10.1007/s12016-020-08796-4
196. Soh H, Im JP, Han K, Park S, Hong SW, Moon JM, et al. Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are associated with different lipid profile disorders: a nationwide population-based study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2020) . 51:446–56. doi: 10.1111/apt.15562
197. Kayama H and Takeda K. Emerging roles of host and microbial bioactive lipids in inflammatory bowel diseases. Eur J Immunol. (2023) . 53:e2249866. doi: 10.1002/eji.202249866
198. Sharma A, Sharma G, and Im SH. Gut microbiota in regulatory T cell generation and function: mechanisms and health implications. Gut Microbes. (2025) . 17:2516702. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2516702
199. Li C, Gu S, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Wang J, Gao T, et al. Histone deacetylase in inflammatory bowel disease: novel insights. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. (2025) . 18:17562848251318833. doi: 10.1177/17562848251318833
200. Lavelle A and Sokol H. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as key actors in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) . 17:223–37. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0258-z
201. Yu T, Zhou Z, Liu S, Li C, Zhang ZW, Zhang Y, et al. The role of phosphatidylcholine 34:1 in the occurrence, development and treatment of ulcerative colitis. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2023) . 13:1231–45. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.09.006
202. Crohn BB and Ginzburgl OGD. Regional ileitis: A pathologic and clinical entity. J Am Med Assoc. (1932) . 99:1323–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.1932.02740680019005
203. Ha C WY, Martin A, Sepich-Poore GD, Shi B, Wang Y, Gouin K, et al. Translocation of viable gut microbiota to mesenteric adipose drives formation of creeping fat in humans. Cell. (2020) . 183:666–683.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.009
204. Quan T, Li R, and Gao T. The intestinal macrophage-intestinal stem cell axis in inflammatory bowel diseases: from pathogenesis to therapy. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) . 26:2855. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072855
205. Wang Y, Li L, Chen S, Yu Z, Gao X, Peng X, et al. Fecalibacterium prausnitzii-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate chronic colitis-related intestinal fibrosis by macrophage metabolic reprogramming. Pharmacol Res. (2024) . 206:107277. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107277
206. Xu J, Zheng B, Xie C, Zhao Y, Wu H, Wang Y, et al. Inhibition of FABP5 attenuates inflammatory bowel disease by modulating macrophage alternative activation. Biochem Pharmacol. (2024) . 219:115974. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115974
207. Kitsou K, Kokkotis G, Rivera-Nieves J, and Bamias G. Targeting the sphingosine-1-phosphate pathway: new opportunities in inflammatory bowel disease management. Drugs. (2024) . 84:1179–97. doi: 10.1007/s40265-024-02094-5
208. Baars A, Oosting A, Knol J, Garssen J, and van Bergenhenegouwen J. The gut microbiota as a therapeutic target in IBD and metabolic disease: A role for the bile acid receptors FXR and TGR5. Microorganisms. (2015) . 3:641–66. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms3040641
209. Attema B and Kuipers F. Microbiome-derived secondary bile acids promote repair of colonic mucosa after injury. EMBO Mol Med. (2025) . 17:863–5. doi: 10.1038/s44321-025-00218-2
210. Di Cesare A, Di Meglio P, and Nestle FO. The IL-23/th17 axis in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. (2009) . 129:1339–50. doi: 10.1038/jid.2009.59
211. Tortola L, Rosenwald E, Abel B, Blumberg H, Schäfer M, Coyle AJ, et al. Psoriasiform dermatitis is driven by IL-36-mediated DC-keratinocyte crosstalk. J Clin Invest. (2012) . 122:3965–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI63451
212. Cavallo A, Camera E, Maiellaro M, Bottillo G, Mosca S, Kovacs D, et al. Effects of Th1/Th17 and Th2 cytokines on lipid metabolism in differentiated keratinocytes. Front Physiol. (2025) . 16:1387128. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1387128
213. Kamata M and Tada Y. Dendritic cells and macrophages in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:941071. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.941071
214. Schett G, Rahman P, Ritchlin C, McInnes IB, Elewaut D, and Scher JU. Psoriatic arthritis from a mechanistic perspective. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2022) . 18:311–25. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00776-6
215. Ryu H, Kim J, Kim D, Lee JE, and Chung Y. Cellular and molecular links between autoimmunity and lipid metabolism. Mol Cells. (2019) . 42:747–54. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2019.0196
216. Butera A, Agostini M, Cassandri M, De Nicola F, Fanciulli M, D’Ambrosio L, et al. ZFP750 affects the cutaneous barrier through regulating lipid metabolism. Sci Adv. (2023) 9:eadg5423. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg5423
217. Tu Y, Gu H, Li N, Sun D, Yang Z, and He L. Identification of key genes related to immune-lipid metabolism in skin barrier damage and analysis of immune infiltration. Inflammation. (2024) 48:2051–68. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02174-4
218. Nowowiejska J, Baran A, and Flisiak I. Fatty acid-binding proteins in psoriasis-A review. Metabolites. (2022) . 12:833. doi: 10.3390/metabo12090833
219. Morin S, Tremblay A, Dumais E, Julien P, Flamand N, and Pouliot R. Eicosapentaenoic acid influences the lipid profile of an in vitro psoriatic skin model produced with T cells. Biomolecules. (2023) . 13:1413. doi: 10.3390/biom13091413
220. Sorokin AV, Arnardottir H, Svirydava M, Ng Q, Baumer Y, Berg A, et al. Comparison of the dietary omega-3 fatty acids impact on murine psoriasis-like skin inflammation and associated lipid dysfunction. J Nutr Biochem. (2023) . 117:109348. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109348
221. Greve AM, Wulff AB, Bojesen SE, and Nordestgaard BG. Elevated plasma triglycerides increase the risk of psoriasis: a cohort and Mendelian randomization study. Br J Dermatol. (2024) . 191:209–15. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae089
222. Ferraz-Amaro I, Hernández-Hernández MV, Armas-González E, Sánchez-Pérez H, MaChado JD, and Díaz-González F. HDL cholesterol efflux capacity is related to disease activity in psoriatic arthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol. (2020) . 39:1871–80. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-04961-4
223. Radić M, Belančić A, Đogaš H, Vučković M, Sener YZ, Sener S, et al. Cardiometabolic risk in psoriatic arthritis: A hidden burden of inflammation and metabolic dysregulation. Metabolites. (2025) . 15:206. doi: 10.3390/metabo15030206
224. Villarreal-Martinez A, Martinez-de-Villarreal LE, Gomez-Flores M, Chavez-Alvarez S, Cerda-Flores R, Ocampo-Candiani J, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction: The pathological link between psoriasis and insulin resistance? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2023) . 37:340–7. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18631
225. Wroński A, Gęgotek A, and Skrzydlewska E. Protein adducts with lipid peroxidation products in patients with psoriasis. Redox Biol. (2023) . 63:102729. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102729
226. Divyapriya D, Priyadarssini M, Indhumathi S, Rajappa M, Chandrashekar L, and Mohanraj PS. Evaluation of cytokine gene expression in psoriasis. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. (2021) . 38:858–65. doi: 10.5114/ada.2021.110109
227. Cataldi C, Mari NL, Lozovoy MAB, Martins LMM, Reiche EMV, Maes M, et al. Proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine profiles in psoriasis: use as laboratory biomarkers and disease predictors. Inflammation Res. (2019) . 68:557–67. doi: 10.1007/s00011-019-01238-8
228. Lee JE, Kim M, Ochiai S, Kim SH, Yeo H, Bok J, et al. Tonic type 2 immunity is a critical tissue checkpoint controlling autoimmunity in the skin. Cell Rep. (2024) . 43:114364. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114364
229. Damasceno LEA, Prado DS, Veras FP, Fonseca MM, Toller-Kawahisa JE, Rosa MH, et al. PKM2 promotes Th17 cell differentiation and autoimmune inflammation by fine-tuning STAT3 activation. J Exp Med. (2020) . 217:e20190613. doi: 10.1084/jem.20190613
230. Kanno T, Nakajima T, Miyako K, and Endo Y. Lipid metabolism in Th17 cell function. Pharmacol Ther. (2023) . 245:108411. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108411
231. Bommireddy R and Doetschman T. TGFbeta1 and Treg cells: alliance for tolerance. Trends Mol Med. (2007) . 13:492–501. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2007.08.005
232. Wang J, Zhao X, and Wan YY. Intricacies of TGF-β signaling in Treg and Th17 cell biology. Cell Mol Immunol. (2023) . 20:1002–22. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-01036-7
233. Nadeau S and Martins GA. Conserved and unique functions of blimp1 in immune cells. Front Immunol. (2021) . 12:805260. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.805260
234. Liu W, Wang J, Yang H, Li C, Lan W, Chen T, et al. The metabolite indole-3-acetic acid of bacteroides ovatus improves atherosclerosis by restoring the polarization balance of M1/M2 macrophages and inhibiting inflammation. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2025) . 12:e2413010. doi: 10.1002/advs.202413010
235. Peng Y, Zhou M, Yang H, Qu R, Qiu Y, Hao J, et al. Regulatory mechanism of M1/M2 macrophage polarization in the development of autoimmune diseases. Mediators Inflamm. (2023) . 2023:8821610. doi: 10.1155/2023/8821610
236. Hu W, Jain A, Gao Y, Dozmorov IM, Mandraju R, Wakeland EK, et al. Differential outcome of TRIF-mediated signaling in TLR4 and TLR3 induced DC maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2015) . 112:13994–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1510760112
237. Li W, Yu C, Zhang X, Gu Y, He X, Xu R, et al. Dendritic cells: understanding ontogeny, subsets, functions, and their clinical applications. Mol Biomed. (2025) . 6:62. doi: 10.1186/s43556-025-00300-8
238. Dehnavi S, Sohrabi N, Sadeghi M, Lansberg P, Banach M, Al-Rasadi K, et al. Statins and autoimmunity: state-of-the-art. Pharmacol Ther. (2020) . 214:107614. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107614
239. Liao JK. Isoprenoids as mediators of the biological effects of statins. J Clin Invest. (2002) . 110:285–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI16421
240. Yilmaz A, Reiss C, Tantawi O, Weng A, Stumpf C, Raaz D, et al. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors suppress maturation of human dendritic cells: new implications for atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. (2004) . 172:85–93. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2003.10.002
241. Blackstone J, Williams T, Nicholas JM, Bordea E, De Angelis F, Bianchi A, et al. Evaluating the effectiveness of simvastatin in slowing the progression of disability in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (MS-STAT2): protocol for a multicenter, randomized controlled, double-blind, phase 3 clinical trial in the UK. BMJ Open. (2024) . 14:e086414. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-086414
242. Sarabi ZS, Saeidi MG, Khodashahi M, Rezaie AE, Hashemzadeh K, Khodashahi R, et al. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory effects of atorvastatin on patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized clinical trial. Electron Physician. (2016) . 8:2700–6. doi: 10.19082/2700
243. Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Saad HM, and Batiha GES. The potential therapeutic effect of statins in multiple sclerosis: beneficial or detrimental effects. Inflammopharmacology. (2023) . 31:1671–82. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01240-x
244. Sun Y, Yuan L, Liu X, Yu W, and Li J. Effects of atorvastatin and Zishen Qingqi granules on immune function and liver function of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with mild and moderate activity. Pak J Pharm Sci. (2021) 34:2085–90.
245. Sun J, Xu W, Wu Z, Cao C, Tan Y, Zhu M, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of atorvastatin on MRL/lpr mice. Adv Rheumatol. (2022) . 62:47. doi: 10.1186/s42358-022-00282-z
246. McGinley MP and Cohen JA. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulators in multiple sclerosis and other conditions. Lancet. (2021) . 398:1184–94. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00244-0
247. Brinkmann V, Billich A, Baumruker T, Heining P, Schmouder R, Francis G, et al. Fingolimod (FTY720): discovery and development of an oral drug to treat multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2010) . 9:883–97. doi: 10.1038/nrd3248
248. Kihara Y and Chun J. Molecular and neuroimmune pharmacology of S1P receptor modulators and other disease-modifying therapies for multiple sclerosis. Pharmacol Ther. (2023) . 246:108432. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108432
249. Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, D’Haens G, Wolf DC, Jovanovic I, Hanauer SB, et al. Ozanimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. (2021) . 385:1280–91. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2033617
250. Masuyama S, Mizui M, Morita M, Shigeki T, Kato H, Yamamoto T, et al. Enhanced fatty acid oxidation by selective activation of PPARα alleviates autoimmunity through metabolic transformation in T-cells. Clin Immunol. (2024) . 268:110357. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2024.110357
251. Briganti S, Mosca S, Di Nardo A, Flori E, and Ottaviani M. New insights into the role of PPARγ in skin physiopathology. Biomolecules. (2024) . 14:728. doi: 10.3390/biom14060728
252. Pershadsingh HA, Heneka MT, Saini R, Amin NM, Broeske DJ, and Feinstein DL. Effect of pioglitazone treatment in a patient with secondary multiple sclerosis. J Neuroinflammation. (2004) . 1:3. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-1-3
253. Juárez-Rojas JG, Medina-Urrutia AX, Jorge-Galarza E, Caracas-Portilla NA, Posadas-Sánchez R, Cardoso-Saldaña GC, et al. Pioglitazone improves the cardiovascular profile in patients with uncomplicated systemic lupus erythematosus: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. Lupus. (2012) . 21:27–35. doi: 10.1177/0961203311422096
254. Marder W, Khalatbari S, Myles JD, Hench R, Lustig S, Yalavarthi S, et al. The peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ pioglitazone improves vascular function and decreases disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Heart Assoc. (2013) . 2:e000441. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000441
255. Hasni S, Temesgen-Oyelakin Y, Davis M, Chu J, Poncio E, Naqi M, et al. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ agonist pioglitazone improves vascular and metabolic dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. (2022) . 81:1576–84. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-222658
256. Ormseth MJ, Oeser AM, Cunningham A, Bian A, Shintani A, Solus J, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ agonist effect on rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Res Ther. (2013) . 15:R110. doi: 10.1186/ar4290
257. Kato H and Perl A. Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 expands th17 and IL-4+ CD4–CD8– double-negative T cells and contracts regulatory T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. (2014) . 192:4134–44. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301859
258. Kato H and Perl A. Blockade of treg cell differentiation and function by the interleukin-21-mechanistic target of rapamycin axis via suppression of autophagy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2018) . 70:427–38. doi: 10.1002/art.40380
259. Bogie JFJ, Timmermans S, Huynh-Thu VA, Irrthum A, Smeets HJM, Gustafsson JÅ, et al. Myelin-derived lipids modulate macrophage activity by liver X receptor activation. PloS One. (2012) . 7:e44998. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044998
260. Zheng DC, Hu JQ, Mai CT, Huang L, Zhou H, Yu LL, et al. Liver X receptor inverse agonist SR9243 attenuates rheumatoid arthritis via modulating glycolytic metabolism of macrophages. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2024) . 45:2354–65. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01315-7
261. Hindinger C, Hinton DR, Kirwin SJ, Atkinson RD, Burnett ME, Bergmann CC, et al. Liver X receptor activation decreases the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurosci Res. (2006) . 84:1225–34. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21038
262. Xie Y, Feng SL, Mai CT, Zheng YF, Wang H, Liu ZQ, et al. Suppression of up-regulated LXRα by silybin ameliorates experimental rheumatoid arthritis and abnormal lipid metabolism. Phytomedicine. (2021) . 80:153339. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153339
263. Stüve P, Godoy GJ, Ferreyra FN, Hellriegel F, Boukhallouk F, Kao YS, et al. ACC1 is a dual metabolic-epigenetic regulator of Treg stability and immune tolerance. Mol Metab. (2025) . 94:102111. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2025.102111
264. Xiao Y, Gao Y, Hu Y, Zhang X, Wang L, Li H, et al. FASN contributes to the pathogenesis of lupus by promoting TLR-mediated activation of macrophages and dendritic cells. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 142:113136. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113136
265. Endo Y, Asou HK, Matsugae N, Hirahara K, Shinoda K, Tumes DJ, et al. Obesity drives th17 cell differentiation by inducing the lipid metabolic kinase, ACC1. Cell Rep. (2015) . 12:1042–55. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.07.014
266. Yamada H, Saegusa J, Sendo S, Ueda Y, Okano T, Shinohara M, et al. Effect of resolvin D5 on T cell differentiation and osteoclastogenesis analyzed by lipid mediator profiling in the experimental arthritis. Sci Rep. (2021) . 11:17312. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96530-1
267. Du B, Zhu M, Li Y, Li G, and Xi X. The prostaglandin E2 increases the production of IL-17 and the expression of costimulatory molecules on γδ T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol. (2020) . 91:e12872. doi: 10.1111/sji.12872
268. Lee EJ, Kwon JE, Park MJ, Jung KA, Kim DS, Kim EK, et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid attenuates experimental autoimmune arthritis by targeting Th17 and inducing pAMPK and transcriptional corepressor SMILE. Immunol Lett. (2017) . 188:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2017.05.011
269. Cheng T, Ding S, Liu S, Li X, Tang X, and Sun L. Resolvin D1 improves the treg/th17 imbalance in systemic lupus erythematosus through miR-30e-5p. Front Immunol. (2021) . 12:668760. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.668760
270. Murakami K. Potential of specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators against rheumatic diseases. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. (2016) . 39:155–63. doi: 10.2177/jsci.39.155
271. Kim JY, Lim K, Kim KH, Kim JH, Choi JS, and Shim SC. N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids restore Th17 and Treg balance in collagen antibody-induced arthritis. PloS One. (2018) . 13:e0194331. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194331
272. Jin S, Chen H, Li Y, Zhong H, Sun W, Wang J, et al. Maresin 1 improves the Treg/Th17 imbalance in rheumatoid arthritis through miR-21. Ann Rheum Dis. (2018) . 77:1644–52. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213511
273. Zhang K, Pace S, Jordan PM, Peltner LK, Weber A, Fischer D, et al. Beneficial modulation of lipid mediator biosynthesis in innate immune cells by antirheumatic tripterygium wilfordii glycosides. Biomolecules. (2021) . 11:746. doi: 10.3390/biom11050746
274. Derada Troletti C, Enzmann G, Chiurchiù V, Kamermans A, Tietz SM, Norris PC, et al. Pro-resolving lipid mediator lipoxin A4 attenuates neuro-inflammation by modulating T cell responses and modifies the spinal cord lipidome. Cell Rep. (2021) . 35:109201. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109201
275. Harbige LS, Layward L, Morris-Downes MM, Dumonde DC, and Amor S. The protective effects of omega-6 fatty acids in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in relation to transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta1) up-regulation and increased prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production. Clin Exp Immunol. (2000) . 122:445–52. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01399.x
276. Xu J, Guo S, Jia Z, Ma S, Li Z, and Xue R. Additive effect of prostaglandin E2 and adenosine in mouse experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. (2013) 100-101:30–5. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2012.11.004
277. Unoda K, Doi Y, Nakajima H, Yamane K, Hosokawa T, Ishida S, et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) induces peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. (2013) 256:7–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2012.12.003
278. Lopes Pinheiro MA, Kroon J, Hoogenboezem M, Geerts D, van Het Hof B, van der Pol SMA, et al. Acid Sphingomyelinase-Derived Ceramide Regulates ICAM-1 Function during T Cell Transmigration across Brain Endothelial Cells. J Immunol. (2016) . 196:72–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500702
279. Li FQ, Sempowski GD, McKenna SE, Laskowitz DT, Colton CA, and Vitek MP. Apolipoprotein E-derived peptides ameliorate clinical disability and inflammatory infiltrates into the spinal cord in a murine model of multiple sclerosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2006) . 318:956–65. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.103671
280. Wei J, Zheng M, Liang P, Wei Y, Yin X, Tang Y, et al. Apolipoprotein E and its mimetic peptide suppress Th1 and Th17 responses in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neurobiol Dis. (2013) . 56:59–65. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.04.009
281. Wang N, Zhao X, Huai J, Li Y, Cheng C, Bi K, et al. Arachidonic acid metabonomics study for understanding therapeutic mechanism of Huo Luo Xiao Ling Dan on rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. J Ethnopharmacol. (2018) . 217:205–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.02.027
282. Calder PC. Marine omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Effects, mechanisms and clinical relevance. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2015) . 1851:469–84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.08.010
283. Miyabe Y, Miyabe C, Iwai Y, Takayasu A, Fukuda S, Yokoyama W, et al. Necessity of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 for development of arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2013) . 65:2037–47. doi: 10.1002/art.37991
284. Ferret-Sena V, Capela C, Macedo A, Salgado AV, Derudas B, Staels B, et al. Fingolimod treatment modulates PPARγ and CD36 gene expression in women with multiple sclerosis. Front Mol Neurosci. (2022) . 15:1077381. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1077381
285. He C, Hua G, Liu Y, and Li S. Unveiling the hidden role of the interaction between CD36 and FcγRIIb: implications for autoimmune disorders. Cell Mol Biol Lett. (2024) . 29:76. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00593-7
286. Grajchen E, Wouters E, van de Haterd B, Haidar M, Hardonnière K, Dierckx T, et al. CD36-mediated uptake of myelin debris by macrophages and microglia reduces neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation. (2020) . 17:224. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01899-x
287. Lv F, He Y, Xu H, Li Y, Han L, Yan L, et al. CD36 aggravates podocyte injury by activating NLRP3 inflammasome and inhibiting autophagy in lupus nephritis. Cell Death Dis. (2022) . 13:729. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05179-9
288. Rawji KS, Young AMH, Ghosh T, Michaels NJ, Mirzaei R, Kappen J, et al. Niacin-mediated rejuvenation of macrophage/microglia enhances remyelination of the aging central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. (2020) . 139:893–909. doi: 10.1007/s00401-020-02129-7
289. Wen W, He M, Liang X, Shan GS, Zhou J, and Yi YZ. Accelerated transformation of macrophage-derived foam cells in the presence of collagen-induced arthritis mice serum is associated with dyslipidemia. Autoimmunity. (2016) . 49:115–23. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2015.1118761
290. Miao Y, Zhang C, Yang L, Zeng X, Hu Y, Xue X, et al. The activation of PPARγ enhances Treg responses through up-regulating CD36/CPT1-mediated fatty acid oxidation and subsequent N-glycan branching of TβRII/IL-2Rα. Cell Commun Signal. (2022) . 20:48. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00849-9
291. Karpurapu M, Yan J, Chung S, Pannu SR, Parinandi N, Berdyshev E, et al. Specialized pro-resolving mediator loaded extracellular vesicles mitigate pulmonary inflammation. bioRxiv. (2025) 2025:4.09.648009. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.09.648009
292. de la Aleja AG, Herrero C, Torres-Torresano M, Schiaffino MT, Del Castillo A, Alonso B, et al. Inhibition of LXR controls the polarization of human inflammatory macrophages through upregulation of MAFB. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2023) . 80:96. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04745-4
293. Zelcer N and Tontonoz P. Liver X receptors as integrators of metabolic and inflammatory signaling. J Clin Invest. (2006) . 116:607–14. doi: 10.1172/JCI27883
294. Cao E, Lindgren A, Martinsson S, Hu L, Lindfors L, Sigfridsson K, et al. Promoting intestinal lymphatic transport targets a liver-X receptor (LXR) agonist (WAY-252,623) to lymphocytes and enhances immunomodulation. J Control Release. (2019) . 296:29–39. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.01.002
295. Dyall SC, Balas L, Bazan NG, Brenna JT, Chiang N, da Costa Souza F, et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and fatty acid-derived lipid mediators: Recent advances in the understanding of their biosynthesis, structures, and functions. Prog Lipid Res. (2022) . 86:101165. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2022.101165
296. Sanchez HN, Moroney JB, Gan H, Shen T, Im JL, Li T, et al. B cell-intrinsic epigenetic modulation of antibody responses by dietary fiber-derived short-chain fatty acids. Nat Commun. (2020) . 11:60. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13603-6
297. Liu A, Li Z, Zeng J, Peng Y, Wang S, Bi X, et al. ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid alleviates systemic lupus erythematosus by suppressing autoimmunity in a murine model. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) . 126:111299. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111299
298. Kobayashi A, Ito A, Shirakawa I, Tamura A, Tomono S, Shindou H, et al. Dietary supplementation with eicosapentaenoic acid inhibits plasma cell differentiation and attenuates lupus autoimmunity. Front Immunol. (2021) . 12:650856. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.650856
299. Tao F, Xing X, Wu J, and Jiang R. Enteral nutrition modulation with n-3 PUFAs directs microbiome and lipid metabolism in mice. PloS One. (2021) . 16:e0248482. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248482
300. Pandey H, Jain D, Tang D WT, Wong SH, and Lal D. Gut microbiota in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and therapeutics of inflammatory bowel disease. Intest Res. (2024) . 22:15–43. doi: 10.5217/ir.2023.00080
301. Wang X, Pan L, Niu D, Zhou J, Shen M, Zeng Z, et al. Jingfang Granules alleviates the lipid peroxidation induced ferroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis rats by regulating gut microbiota and metabolism of short chain fatty acids. J Ethnopharmacology. (2025) . 339:119160. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119160
302. Hui W, Yu D, Cao Z, and Zhao X. Butyrate inhibit collagen-induced arthritis via Treg/IL-10/Th17 axis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2019) . 68:226–33. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.01.018
303. Cao S, Budina E, Raczy MM, Solanki A, Nguyen M, Beckman TN, et al. A serine-conjugated butyrate prodrug with high oral bioavailability suppresses autoimmune arthritis and neuroinflammation in mice. Nat BioMed Eng. (2024) . 8:611–27. doi: 10.1038/s41551-024-01190-x
304. Kim CH. Complex regulatory effects of gut microbial short-chain fatty acids on immune tolerance and autoimmunity. Cell Mol Immunol. (2023) . 20:341–50. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-00987-1
305. Bhargava P, Smith MD, Mische L, Harrington E, Fitzgerald KC, Martin K, et al. Bile acid metabolism is altered in multiple sclerosis and supplementation ameliorates neuroinflammation. J Clin Invest. (2020) . 130:3467–82. doi: 10.1172/JCI129401
306. Hu J, Wang C, Huang X, Yi S, Pan S, Zhang Y, et al. Gut microbiota-mediated secondary bile acids regulate dendritic cells to attenuate autoimmune uveitis through TGR5 signaling. Cell Rep. (2021) . 36:109726. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109726
307. Fiorucci S, Marchianò S, Urbani G, Di Giorgio C, Distrutti E, Zampella A, et al. Immunology of bile acids regulated receptors. Prog Lipid Res. (2024) . 95:101291. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2024.101291
308. Wang W, He S, Zhang W, Zhang H, DeStefano VM, Wada M, et al. BCMA-CD19 compound CAR T cells for systemic lupus erythematosus: a phase 1 open-label clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis. (2024) . 83:1304–14. doi: 10.1136/ard-2024-225785
309. Garantziotis P, Beretta L, Lindblom J, Moysidou GS, Nikolopoulos D, Grieshaber-Bouyer R, et al. Differential molecular signatures in response to CD19-CAR T cell therapy compared with conventional pharmacotherapy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. (2025) S0003-4967 :04187–1:25. doi: 10.1016/j.ard.2025.06.2132
310. Sanmarco LM, Rone JM, Polonio CM, Fernandez Lahore G, Giovannoni F, Ferrara K, et al. Lactate limits CNS autoimmunity by stabilizing HIF-1α in dendritic cells. Nature. (2023) . 620:881–9. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06409-6
311. Fan X, Zhang Z, Gao W, Pan Q, Luo K, He B, et al. An engineered butyrate-derived polymer nanoplatform as a mucosa-healing enhancer potentiates the therapeutic effect of magnolol in inflammatory bowel disease. ACS Nano. (2024) . 18:229–44. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c05732
312. King RJ, Singh PK, and Mehla K. The cholesterol pathway: impact on immunity and cancer. Trends Immunol. (2022) . 43:78–92. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2021.11.007
313. Liu H, Wang S, Wang J, Guo X, Song Y, Fu K, et al. Energy metabolism in health and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2025) . 10:69. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02141-x
Keywords: lipid metabolism, immunometabolism, autoimmune diseases, T cells, B cells, macrophages, targeted therapy
Citation: Cui Y, Feng Z, Zhao Q, Dai H, Zheng Y, Rui H and Liu B (2025) Immunocyte lipid metabolic reprogramming: a novel pathway for targeted intervention in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 16:1713148. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1713148
Received: 25 September 2025; Accepted: 22 October 2025;
Published: 06 November 2025.
Edited by:
Gareth S. D. Purvis, University of Oxford, United KingdomReviewed by:
Andras Perl, Upstate Medical University, United StatesHuiyang Yu, The University of Queensland, Australia
Copyright © 2025 Cui, Feng, Zhao, Dai, Zheng, Rui and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Baoli Liu, bGl1YmFvbGlAYmp6aG9uZ3lpLmNvbQ==; Hongliang Rui, cnVpaG9uZ2xpYW5nQGJqemhvbmd5aS5jb20=
 Yanyu Cui
Yanyu Cui Zhendong Feng
Zhendong Feng Qihan Zhao
Qihan Zhao Haoran Dai
Haoran Dai Yang Zheng
Yang Zheng Hongliang Rui
Hongliang Rui Baoli Liu
Baoli Liu