- 1Norman Bethune College of Medicine, Jilin University, Changchun, China
- 2School and Hospital of Stomatology, Jilin University, Changchun, China
- 3College of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University, Changchun, China
- 4School of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, University of Bristol, Bristol, United Kingdom
- 5Department of Clinical Nutrition, Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 6School of Public Health, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 7Department of Immunobiology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, United States
- 8Center of Molecular and Cellular Oncology, Yale Cancer Center, Yale University, New Haven, CT, United States
- 9Department of Respiratory Medicine, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China
- 10Department of Experimental Orofacial Medicine, University of Marburg, Marburg, Germany
- 11Department of Biobank, China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are emerging as master regulators of the lung cancer tumor microenvironment (TME), where they reprogram immune cell functions, cytokine networks, and checkpoint signaling to create an immunosuppressive and therapy-resistant landscape. This review offers a comprehensive analysis of how lncRNAs mediate the interplay between tumor cells and immune components, underscoring their context-dependent roles as both oncogenic drivers and microenvironmental suppressors. It also highlights their clinical utility as liquid-biopsy biomarkers and their central role in conferring resistance to chemo- and radio-therapy. This review synthesizes current knowledge on the interplay between lncRNAs and the TME, highlighting the targeting of specific lncRNAs as a novel therapeutic strategy for precision lung cancer therapy.
1 Introduction
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, characterized by frequent late-stage diagnosis and a persistently poor prognosis for advanced disease (1–4). A major driver of this aggressiveness is the highly complex and dynamic tumor microenvironment (TME), which plays a fundamental role in promoting tumor progression, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance (5). Despite advances in surgery, targeted therapy, and radiation, survival for advanced disease remains unsatisfactory, largely due to immune evasion and treatment resistance (6).
While immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and adoptive cell therapies like chimeric antigen receptor T-cell immunotherapy (CAR-T) have revolutionized lung cancer treatment, their efficacy remains limited and heterogeneous (7). Objective response rates are often modest, and acquired resistance is common (8, 9). A fundamental barrier to the success of these immunotherapies is the profoundly immunosuppressive nature of the TME (10, 11). The TME comprises heterogeneous cellular components including tumor cells, diverse immune cells, cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), endothelial cells, and extracellular matrix that interact through complex signaling networks to create an immunosuppressive milieu promoting tumor growth and metastasis (12, 13). Immune cells within the TME display functional plasticity and often support tumor progression through cytokine dysregulation, checkpoint expression, metabolic competition, and effector cell suppression (12). Therefore, a comprehensive understanding and therapeutic targeting of the immunosuppressive TME is essential to overcome resistance and enhance the efficacy of therapeutic strategies (14).
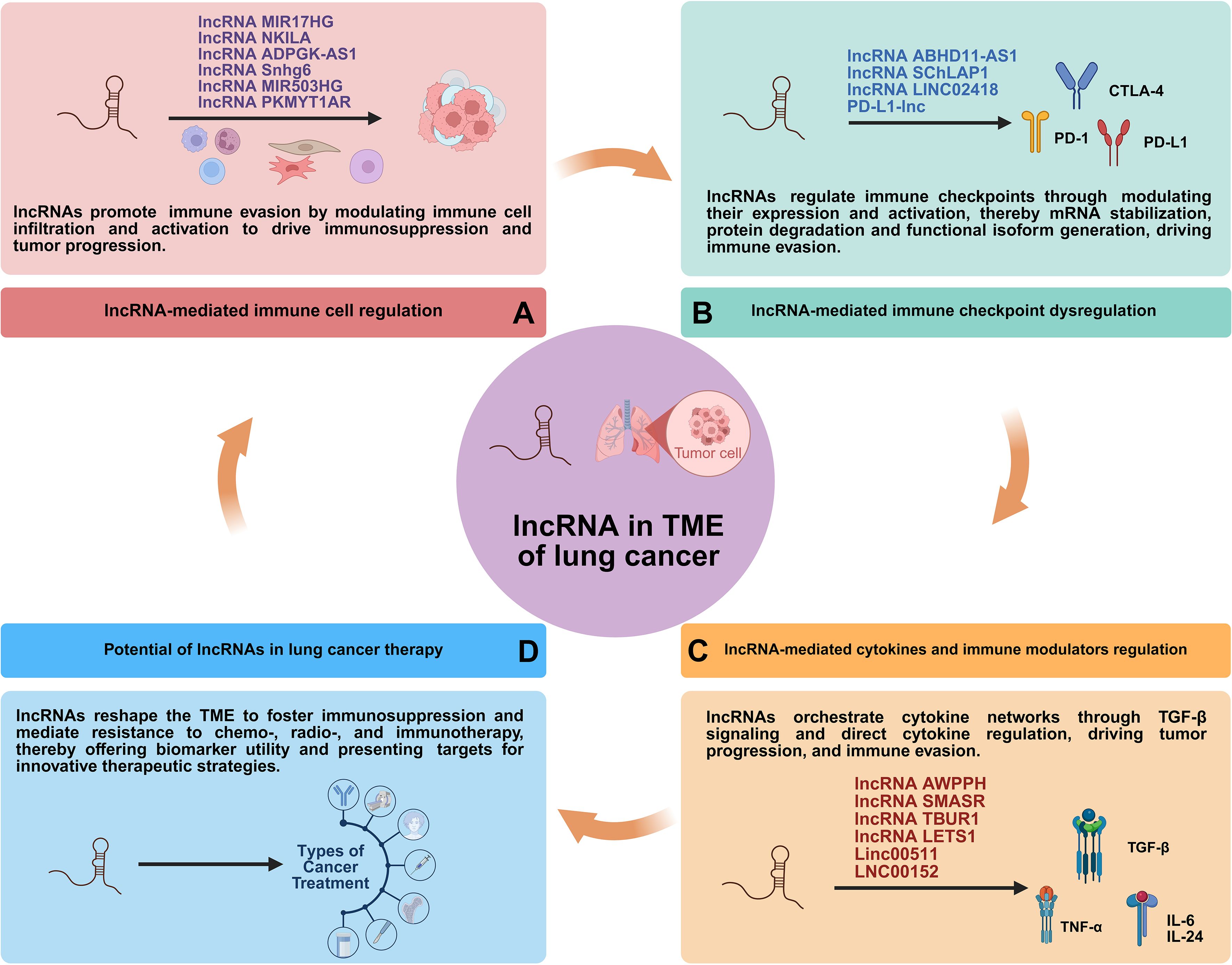
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are generally defined as RNA transcripts longer than 200 nucleotides with limited or no protein-coding potential (15). They have emerged as pivotal regulators of gene expression through diverse mechanisms, acting at transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and epigenetic levels (Figure 1) (15, 16). They modulate fundamental processes including proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, metastasis, metabolic reprogramming, and crucially, immune responses (17). Within the complex milieu of the lung cancer TME, lncRNAs emerge as critical mediators of intercellular communication and microenvironmental reprogramming (Figure 2) (18). By directly governing immune cell function and polarization, influencing the expression of immune-related genes and checkpoints, and modulating tumor-stromal interactions, lncRNAs collectively sculpt an immunosuppressive niche that promotes tumor growth, metastasis, and therapy resistance (19).
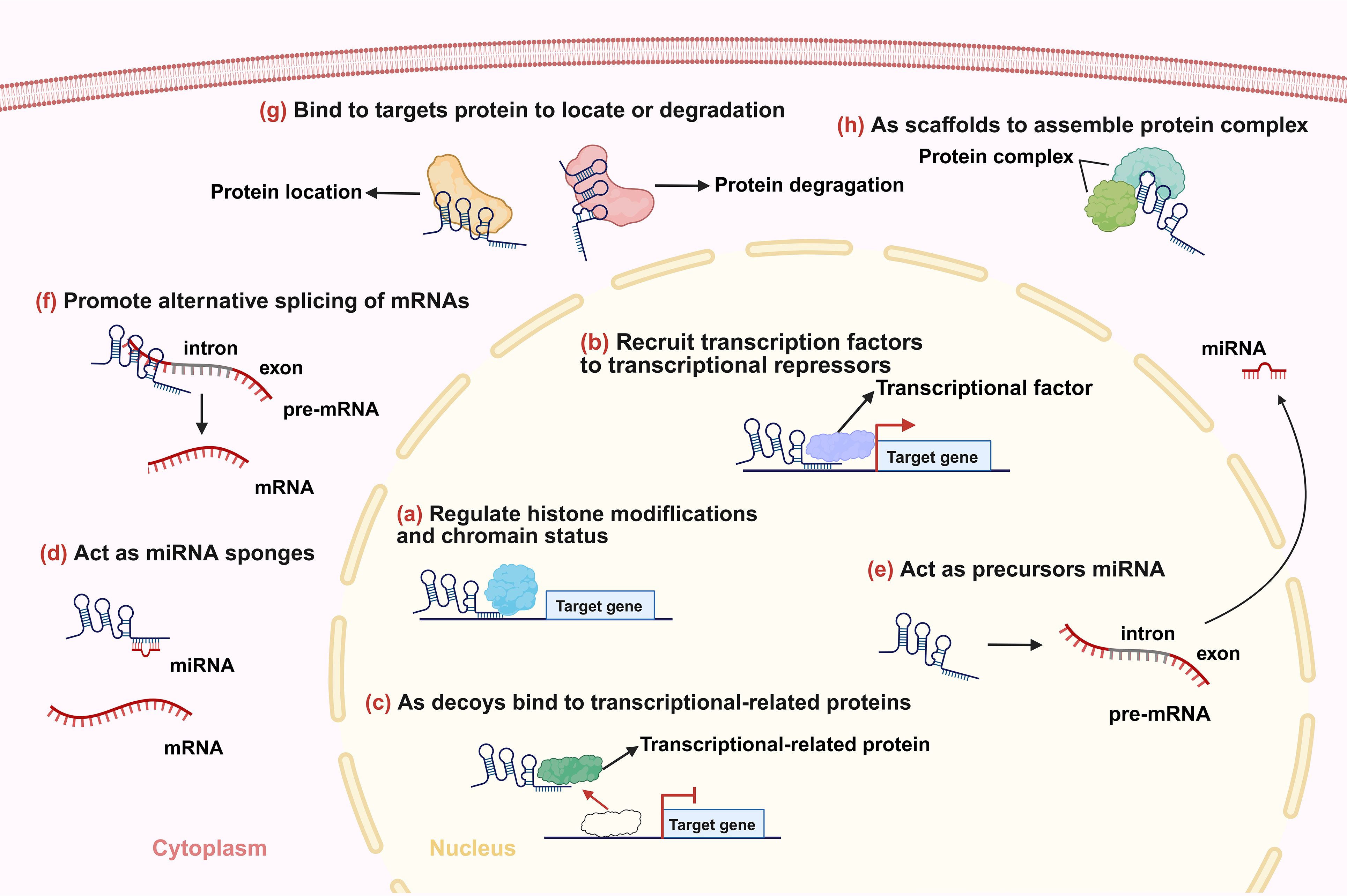
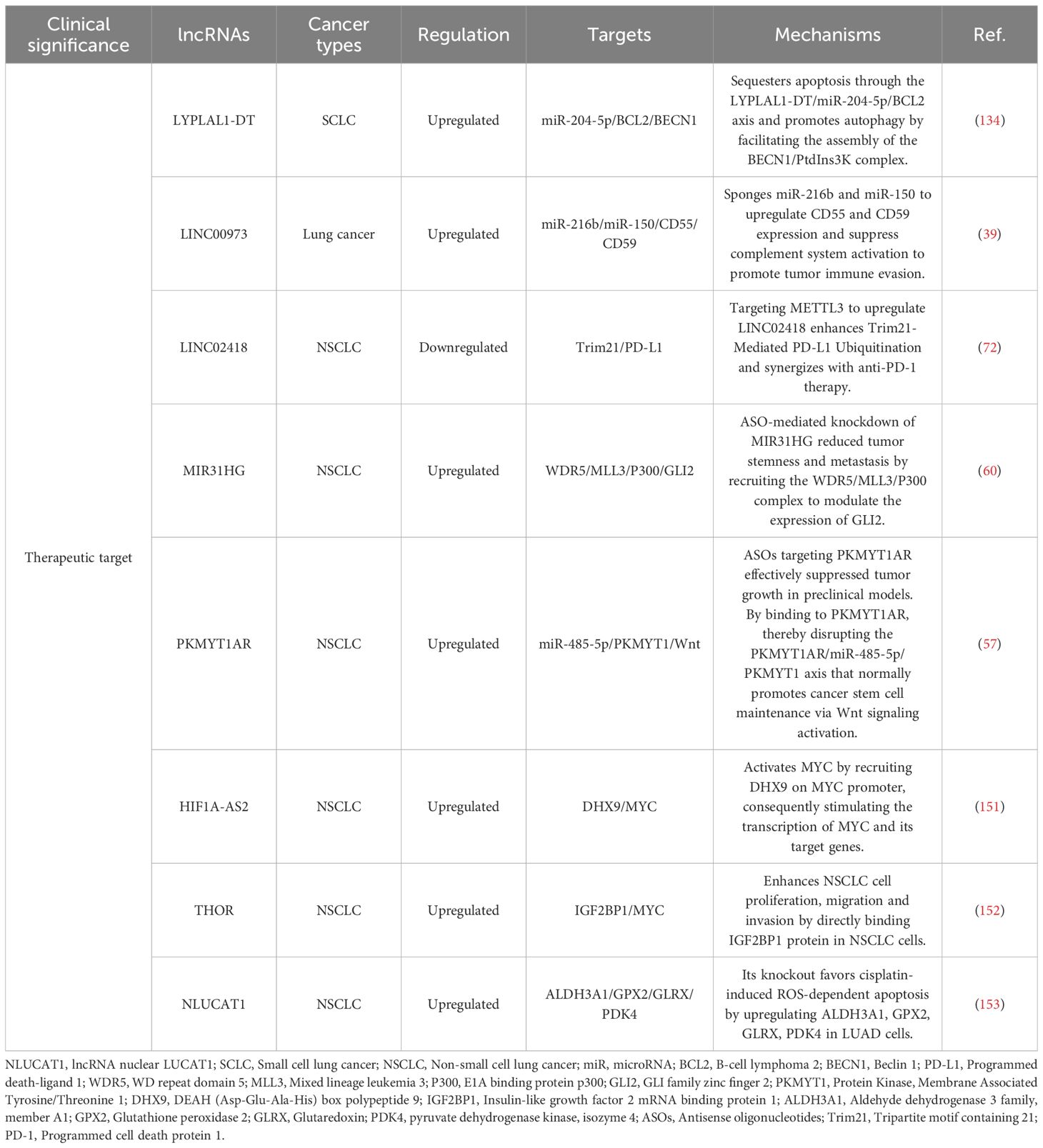
Figure 1. Main mechanisms of lncRNAs. (a) lncRNAs regulate histone modifications and/or chromatin status. (b) lncRNAs recruit transcription factors or transcriptional repressors to the promoters of their target genes to regulate transcription. (c) lncRNAs bind to transcriptional-related proteins as decoys preventing them from binding to their DNA targets. (d) lncRNAs function as miRNA sponges. (e) lncRNAs act as precursors of some small RNAs. (f) lncRNAs promote alternative splicing of mRNAs. (g) lncRNAs influence localization and degradation of targets proteins. (h) lncRNAs act as scaffolds to promote the formation of protein complexes.
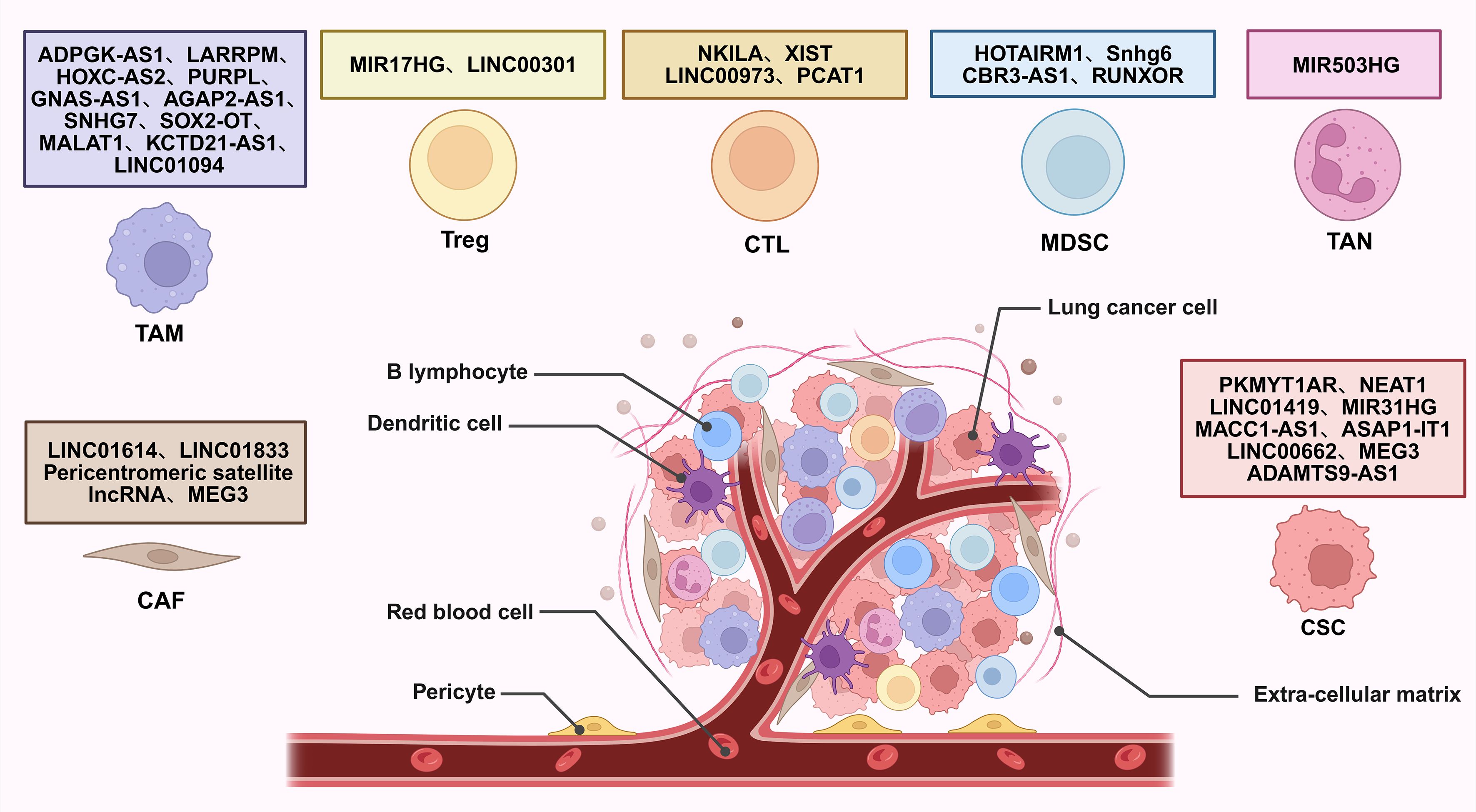
Figure 2. Interaction of lncRNAs with TME regulating lung cancer development. CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast; TAM, tumor-associated macrophage; Treg, regulatory T cell; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; TAN, tumor-associated neutrophil; CSC, cancer stem cell.
While numerous individual lncRNAs have been characterized, a unifying perspective that integrates their roles across the entire immunosuppressive landscape is lacking. To bridge this knowledge gap, this review provides a comprehensive and contextualized analysis of lncRNAs as central orchestrators of the lung cancer TME. We focus on their coordinated regulation of immune components, stromal cells, and signaling networks. Furthermore, we critically evaluate their emerging roles as liquid biopsy biomarkers and therapeutic targets, thereby mapping a path from mechanistic understanding to clinical translation. Ultimately, this synthesis aims to highlight novel therapeutic targets and outline combinatorial approaches for overcoming resistance in lung cancer (Figure 3).
2 TME in lung cancer
TME is a pivotal determinant of cancer progression and therapeutic outcome, such as in lung cancer (20). It consists of malignant cells, diverse immune populations, stromal components, and molecular factors such as immune checkpoints and cytokines, all engaged in dynamic crosstalk. These interactions collectively promote immunosuppression, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance (21, 22). In lung cancer, the TME evolves with disease progression, adapting to therapeutic pressures and shaping clinical outcomes (22).
The cellular composition of the lung cancer TME includes a diverse array of immune and stromal cells. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and regulatory T cells (Tregs) play opposing roles. CTLs mediate antitumor responses, while Tregs suppress effector immunity through cytokines like interleukin 10 (IL-10) and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) (23, 24). Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) inhibit T-cell function via arginase-1 (Arg-1) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) (24). Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), particularly M2-polarized subsets, facilitate angiogenesis and tissue remodeling through vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) secretion (25). Tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) promote metastasis via neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (26). Additionally, cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and cancer stem cells (CSCs) contribute to extracellular matrix remodeling, growth factor release, and drug resistance, further reinforcing the immunosuppressive niche in lung cancer (27, 28).
Immune checkpoints constitute pivotal immunosuppressive mechanisms exploited by tumors to evade immunity within the TME. Programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) overexpression on tumor/stromal cells engages programmed death receptor 1 (PD-1) to exhaust T cells, while cytotoxic T lymphocyte associate protein-4 (CTLA-4) competitively blocks CD28 co-stimulation (29). Critically, tumor-intrinsic drivers synergistically reinforce immune evasion. These integrated mechanisms establish dominant resistance to cytotoxic lymphocytes, with checkpoint blockade demonstrating transformative efficacy in lung cancer (30).
Cytokines further shape the immune contexture of lung cancer. TGF-β promotes EMT and metastatic progression in lung cancer, while IL-6 activates signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling to support tumor cell survival and proliferation (31, 32). Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) contributes to cancer-related inflammation and angiogenesis through nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activation (33). These cytokines collectively enhance the recruitment and function of immunosuppressive cells while inhibiting effector immune responses, thereby sustaining a chronic inflammatory state that favors lung cancer progression.
The roles of lncRNAs in the differentiation and function of various immune cells, including T cells, TAMs, MDSCs and TANs, as well as other tumor associated cells are increasingly well understood (34). Critically, lncRNAs interface with cytokine signaling and immune checkpoint pathways, thereby serving as both biomarkers and actionable targets for immunotherapy potentiation of lung cancer.
3 lncRNA regulation of the TME in lung cancer
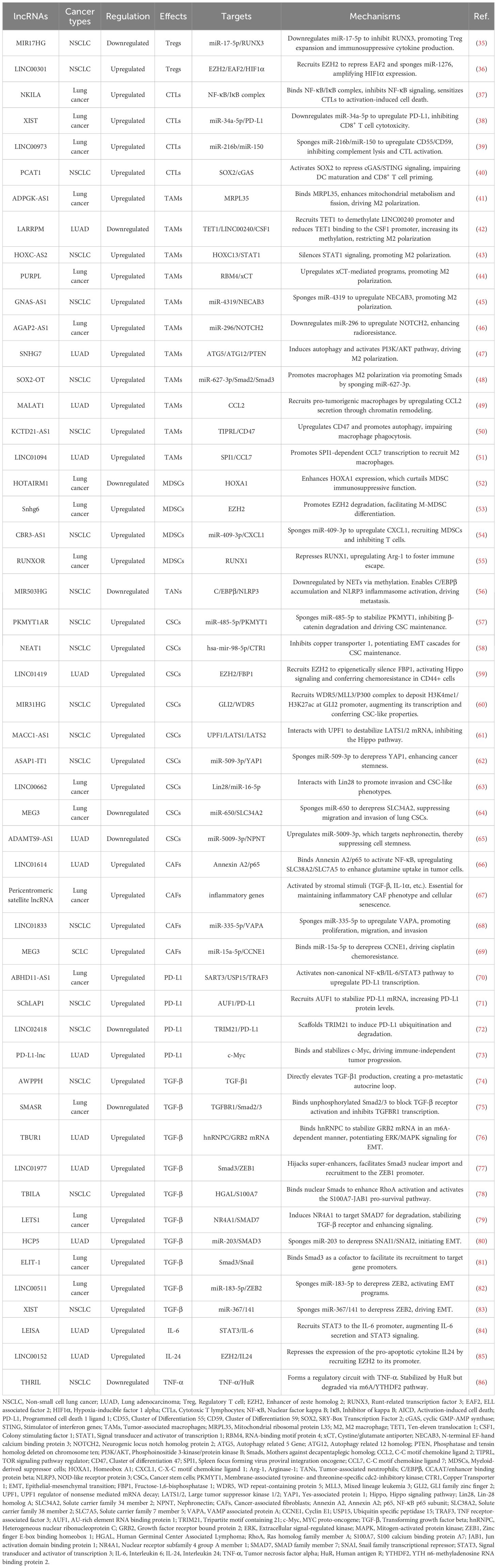
lncRNAs have been shown to play a crucial role in modulating TME in lung cancer through various mechanisms. They participate in the regulation of immune cell functions, cytokine production, and checkpoint expression, thereby influencing antitumor immunity and therapeutic efficacy. This section discusses the interplay between lncRNAs and different immune components in the context of lung cancer (Table 1).
3.1 Regulation of immune cells by lncRNAs in lung cancer
3.1.1 Adaptive immune cells
Adaptive immune cells, including B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes, mediate humoral and cellular immune responses. Current studies regarding lncRNAs in lung cancer and adaptive immunity have largely focused on T cells, especially Tregs and CTLs, due to limited evidence regarding B cell-related lncRNA mechanisms (Figure 4).
Figure 4. lncRNAs act as modulators between adaptive cells and tumor cells of lung cancer. +: promoting the tumor progression; -: inhibiting the tumor progression. Treg, regulatory T cell; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte.
3.1.1.1 Tregs
In the TME of lung cancer, Tregs inhibit the activity of effector T cells, limit the function of antigen-presenting cells, and secrete immunosuppressive cytokines like IL-10 and TGF-β. These actions collectively dampen the immune system’s ability to attack tumor cells, enabling tumors to evade immune surveillance and promoting their growth and progression. The presence of a large number of Tregs in tumor tissues is often associated with poor clinical prognosis (23). Emerging evidence indicates that lncRNAs critically regulate Treg differentiation, function, and immunosuppressive activity in lung cancer.
In the realm of tumor immunology, understanding how lncRNAs modulate Treg-mediated immune evasion has become a focal point. lncRNA miR-17-92a-1 cluster host gene (MIR17HG), upregulated in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), promotes Treg-mediated immunosuppression. Mechanistically, it serves as a precursor for miR-17-5p, which directly targets and downregulates runt-related transcription factor 3 (RUNX3). Consequently, RUNX3 deficiency amplifies Treg expansion and enhances immunosuppressive cytokine production (VEGF-A, TGF-β, IL-10), while suppressing interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) secretion. Critically, MIR17HG knockdown in vivo reduces Treg infiltration and suppresses tumor growth, highlighting its role as a pro-tumorigenic lncRNA (35). However, whether altering RUNX3 expression could affect the functions of MIR17HG and miR-17-5p in the tumorigenicity or Treg-mediated immune escape of NSCLC cells should be further investigated (35).
Beyond their role in immune evasion, lncRNAs also play a key role in shaping the immune-suppressive TME through their regulation of Tregs. For instance, LINC00301, transcriptionally activated by forkhead box C1 (FOXC1) and overexpressed in advanced NSCLC, orchestrates immunosuppression via dual-pathway potentiation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF1α). In the nucleus, LINC00301 directly binds enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2), recruiting it to deposit repressive trimethylated histone H3 at lysine 27 (H3K27me3) marks on the ELL associated factor 2 (EAF2) promoter. Consequently, EAF2 deficiency destabilizes von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) protein, leading to hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α) accumulation. In the cytoplasm, LINC00301 functions as a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) to sponge miR-1276, thereby relieving miR-1276-mediated suppression of HIF1α mRNA and further amplifying HIF1α expression (36). Notably, this study demonstrated that the primary oncogenic driver of LINC00301 is its nuclear role in binding EZH2, while the contribution of its cytoplasmic ceRNA function appears minimal. Thus, the proposed ceRNA mechanism warrants further validation (36).
Indeed, the lncRNA-Treg axis is a central driver of immune evasion in lung cancer. Pinpointing the few lncRNAs that sit at the crossroads of this axis may provide the missing leverage to restore anti-tumor immunity.
3.1.1.2 CTLs
CD8+ T cells kill tumors via cytotoxic granules, but the TME suppresses them through nutrient depletion and immunosuppressive cells (87). Recent studies reveal that lncRNAs disable these T cells in two ways: directly undermining their survival and effector signaling, and indirectly disrupting innate-immune priming and checkpoint control. Targeting these lncRNAs offers a route to reinvigorate CD8+ T cell responses.
Direct CTL functional regulation is exemplified by the lncRNA NKILA-mediated pathway which promotes tumor immune evasion by directly sensitizing CTLs to activation-induced cell death (AICD). NKILA is transcriptionally induced in tumor-infiltrating CTLs upon T-cell receptor stimulation. Research demonstrates that calcium influx activates calmodulin, which removes histone deacetylases (HDAC) from the NKILA promoter to enhance STAT1-mediated transcription. NKILA binds the NF-κB/inhibitor of kappa B (IκB) complex by directly interacting with p65, inhibiting IκBα phosphorylation and preventing its degradation and p65 nuclear translocation. This blockade suppresses Bcl-2-like 1 gene expression, thereby sensitizing CTLs to AICD. Accordingly, NKILA overexpression correlates with CTL apoptosis and poor survival in lung cancer, while its knockdown enhances tumor clearance in patient-derived xenografts (37). Thus, NKILA orchestrates direct CTL dysfunction by epigenetically tuning T-cell sensitivity to apoptotic signals within the immunosuppressive TME.
Beyond intrinsic regulation, immune checkpoint subversion represents a critical tumor escape paradigm. The lncRNA X inactive specific transcript (XIST), previously implicated in breast cancer immune evasion, orchestrates immunosuppression in lung cancer via the XIST/miR-34a-5p/PD-L1 axis. XIST-mediated downregulation of miR-34a-5p elevates PD-L1 expression, directly inhibiting CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity (38).
Concurrently, lncRNA-mediated crosstalk with innate immunity reshapes CTL responses through multifaceted mechanisms. LINC00973 mediates complement-dependent immune evasion. Upregulated by epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/the wingless-related integration site (Wnt) signaling, LINC00973 functions as a ceRNA to sequester miR-216b and miR-150, leading to elevated expression of complement inhibitors CD55 and CD59 on tumor cells. These surface proteins block complement-mediated tumor lysis and suppress IL-2/IFN-γ secretion required for CTL activation. Remarkably co-targeting LINC00973 and PD-1 triggers synergistic tumor regression in lung cancer models by reactivating complement-dependent cytotoxicity and CTL function (39). Besides, other lncRNAs like prostate cancer-associated ncRNA transcripts 1 (PCAT1) achieve immunosuppression through distinct pathways, notably by interfering with innate immune sensing. PCAT1 orchestrates immunosuppression via metabolic-immune crosstalk. Mechanistically, in NSCLC, PCAT1 activates the transcription factor SRY-Box transcription factor 2 (SOX2), which directly represses cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) promoter activity. Consequently, suppressed cGAS/STING signaling reduces type I interferon production, impairing dendritic cell maturation and CD8+ T cell priming. From a therapeutic perspective, PCAT1 inhibition restores radiotherapy-induced immune activation and synergizes with anti-PD-L1 in preclinical models (40). However, the unresolved mechanisms of optimally combining PCAT1 targeting with radiotherapy to modulate immunity represent a prime opportunity for exploring novel combinatorial immunotherapies (40).
In this regard, these findings demonstrate that lncRNA dysregulation promotes tumor immune evasion through both direct CTL functional regulation and multifaceted crosstalk with innate immunity, positioning them as promising targets for immunotherapy, particularly in combination with checkpoint blockade.
3.1.2 Innate immune cells
Innate immune cells include TAMs, MDSCs, and TANs. They interact with lncRNAs in the lung TME and affect the formation of immunosuppressive TME (Figure 5).
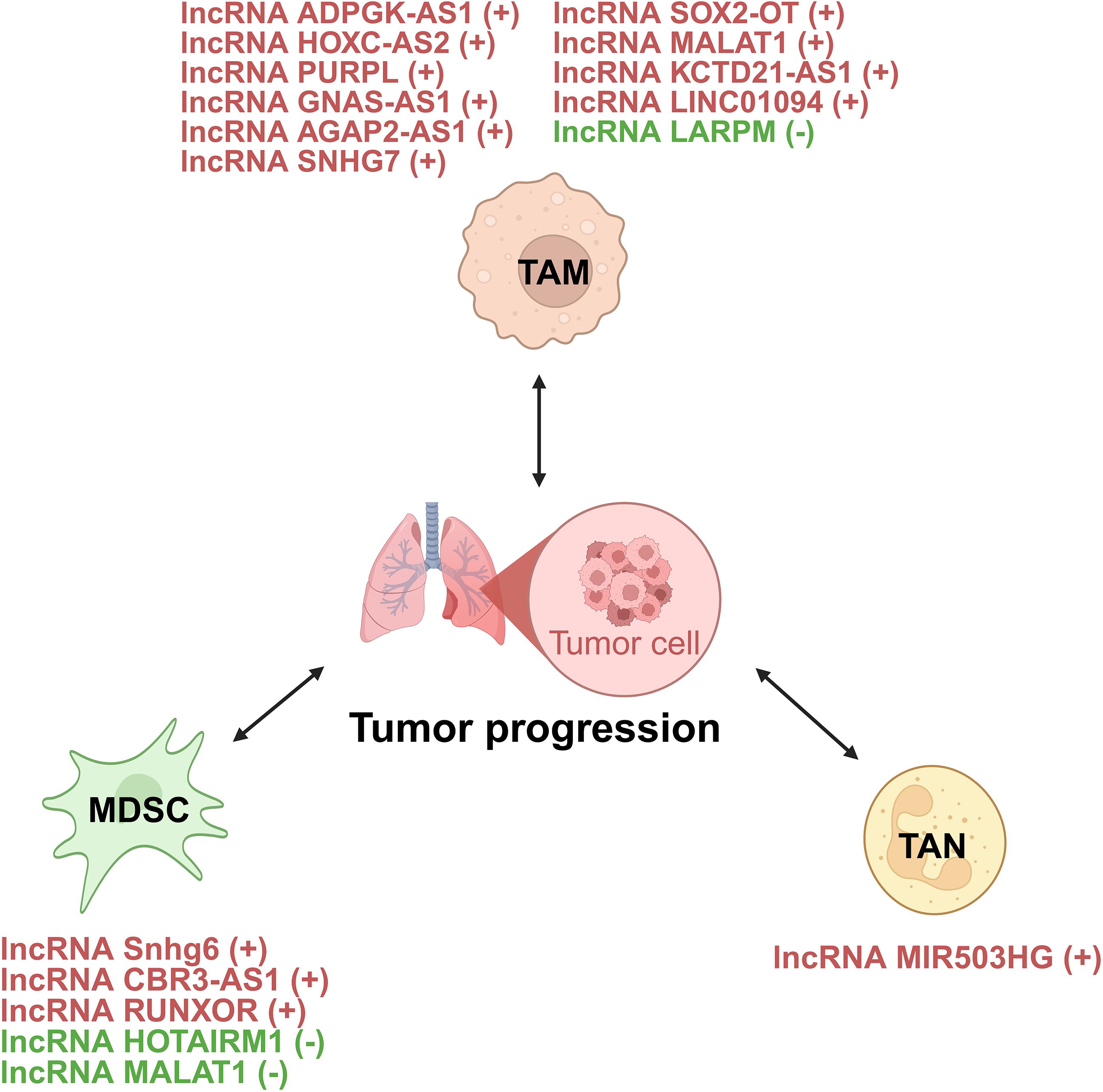
Figure 5. lncRNAs act as modulators between innate immune cells and tumor cells of lung cancer. +: promoting the tumor progression; -: inhibiting the tumor progression. TAM, tumor-associated macrophage; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; TAN, tumor-associated neutrophil.
3.1.2.1 TAMs
TAMs, key components of the TME, can both suppress and promote tumor progression (88). They show phenotypic plasticity, polarizing into proinflammatory (M1-like) or anti-inflammatory (M2-like) phenotypes based on stimuli. While TAMs may initially inhibit tumors, they often acquire an M2-like phenotype as tumors grow, supporting tumor progression (89). They are linked to processes like angiogenesis, immunosuppression, metastasis, and therapy resistance, but can also have antitumor effects via phagocytosis and immune promotion (89). lncRNAs critically regulate TAMs in lung cancer through directly controlling macrophage polarization states, mediating intercellular crosstalk via exosomal transfer, and orchestrating TAM recruitment, phagocytic capacity, and inflammatory reprogramming (90) (Figure 6).
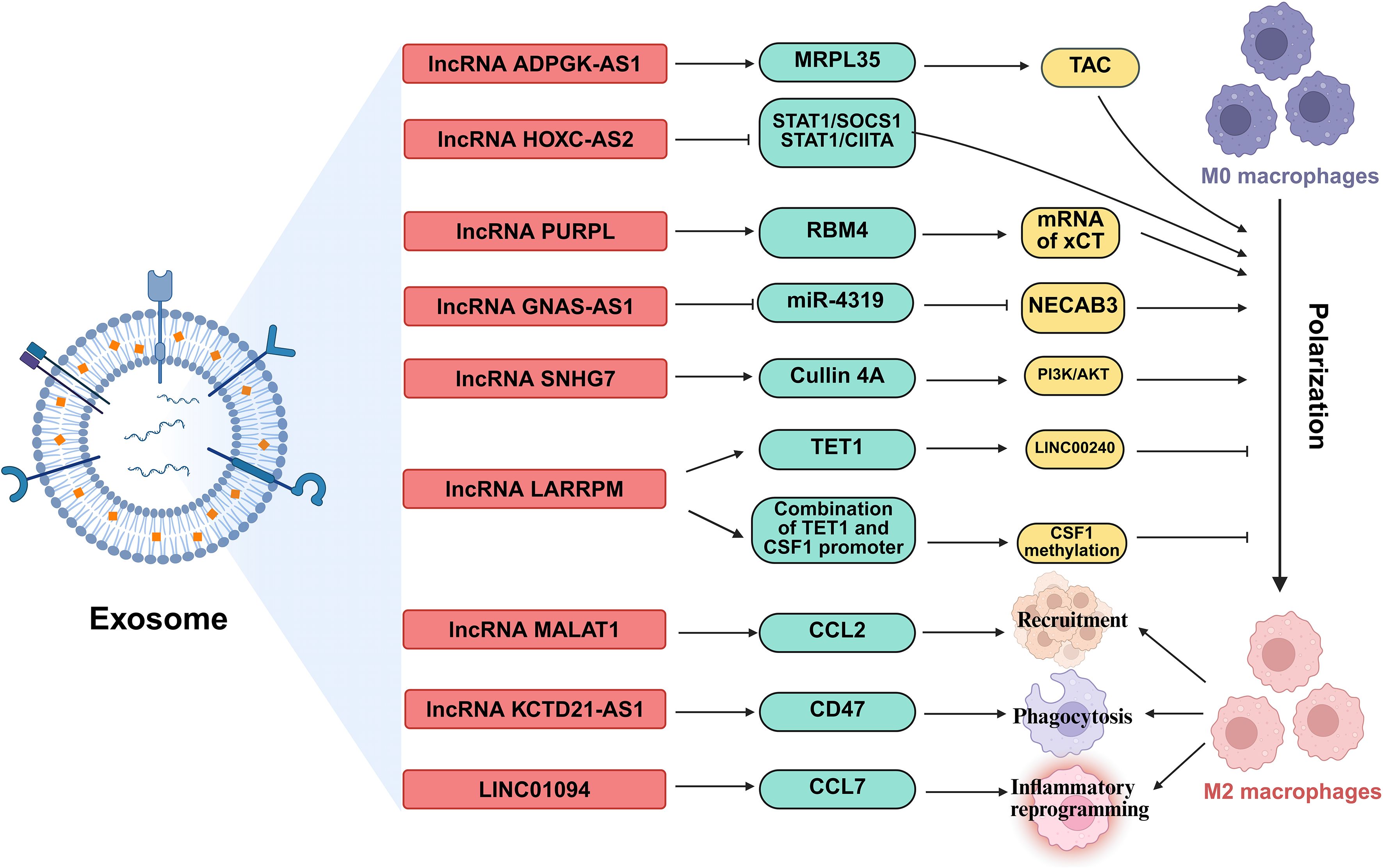
Figure 6. The regulatory roles of lncRNAs in TAMs. lncRNAs, shuttled via exosomes, are involved in regulation the polarization of TAMs, orchestrating TAM recruitment, phagocytic capacity, and inflammatory reprogramming. MRPL35, Mitochondrial ribosomal protein L35; STAT1, Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; SOCS1, Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1; CIITA, class II transactivator; RBM4, RNA-binding motif protein 4; TET1, Ten-eleven translocation 1; CSF1, Colony stimulating factor 1; CCL, C-C motif chemokine ligand; NECAB3, N-terminal EF-hand calcium binding protein 3.
lncRNAs orchestrate macrophage polarization in lung cancer, tipping the balance between anti-tumor M1 and pro-tumor M2 states (91). For instance, the lncRNA ADPGK antisense RNA 1 (ADPGK-AS1) is substantially upregulated in M2-like macrophages and TAMs. Mechanistically, ADPGK-AS1 localizes to mitochondria, binds mitochondrial ribosomal protein MRPL35, enhances the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TAC), and promotes mitochondrial fission. This metabolic shift drives a phenotypic switch toward tumor-promoting M2-like states, facilitating lung cancer growth. Significantly, macrophage-specific ADPGK-AS1 knockdown reverts cells to tumor-suppressive M1-like states, inhibiting tumor progression across preclinical models (41). In contrast, LINC00240 antisense RNA regulating promoter methylation (LARRPM) is downregulated in advanced lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and correlates with poor prognosis. At the molecular level, LARRPM recruits the DNA demethylase ten-eleven translocation methylcytosine dioxygenase 1 (TET1) to the promoter of its antisense gene LINC00240, reducing DNA methylation and activating LINC00240 transcription. Simultaneously, LARRPM decreases TET1 binding to the colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF1) promoter, increasing CSF1 methylation and repressing this key M2-polarization factor. Collectively, these epigenetic actions restrict M2 TAM polarization and LUAD progression (42). The potential influence of LARRPM on other TET1 targets remains unclear, underscoring the need to fully elucidate its context-specific regulatory mechanisms (42). Recently, additional lncRNAs skew macrophages toward M2. For example, lncRNA HOXC cluster antisense RNA 2 (HOXC-AS2) silences STAT1 signaling (43), lncRNA p53 upregulated regulator of p53 levels (PURPL) upregulates cystine glutamate reverse transporter (xCT)-mediated programs (44), and lncRNA GNAS antisense RNA 1 (GNAS-AS1) relieves miR-4319 repression of N-terminal EF-hand calcium binding protein 3 (NECAB3) (45). Together, these findings outline a druggable lncRNA network that governs TAM fate and tumor progression.
Exosomes serve as critical vehicles for lncRNA-mediated crosstalk between tumor cells and TAMs (92). As an example, M2 macrophage-derived exosomal lncRNA AGAP2 antisense RNA 1 (AGAP2-AS1) transferred to lung cancer cells. Upon delivery, AGAP2-AS1 functions as a ceRNA, sequestering miR-296 to derepress its target notch homolog protein 2 (NOTCH2). This axis ultimately enhances tumor cell radioresistance and dampens radiotherapy efficacy. Therapeutically, silencing exosomal AGAP2-AS1 restores radiation sensitivity, highlighting its role as an intercellular effector of treatment resistance (46). However, the functional relevance of this proposed ceRNA model for AGAP2-AS1 remains to be fully elucidated (46). Likewise, tumor-derived exosomal lncRNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 7 (SNHG7) promotes docetaxel resistance in LUAD. Mechanistically, exosomal SNHG7 is internalized by recipient cells where it recruits Human Antigen R (HuR) to stabilize autophagy genes autophagy related 5 (ATG5) and autophagy related 12 (ATG12), inducing protective autophagy, and activates the PI3K/AKT pathway by recruiting Cullin 4A to degrade the tumor suppressor phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), thereby driving M2 macrophage polarization. As a result, SNHG7 fosters a dual chemoresistance mechanism in tumor cells and their surrounding immune landscape (47). NSCLC cell-derived exosomal lncRNA SOX2 overlapping transcript (SOX2-OT) also induces M2 polarization, contributing to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) resistance (48). These findings revealed that tumor and TAMs use exosomal lncRNAs as “molecular messages” to jointly promote therapy resistance and immune suppression.
Beyond polarization and exosomes, lncRNAs directly orchestrate TAM recruitment, phagocytic capacity, and inflammatory reprogramming. A key regulator is the metastasis-associated lncRNA metastasis-associated LUAD transcript 1 (MALAT1), which is overexpressed in LUAD. Mechanistically, MALAT1 induces global chromatin remodeling, increasing accessibility at the CCL2 promoter. This action elevates CCL2 secretion, recruiting protumorigenic macrophages to the TME. Critically, MALAT1-driven metastasis is abrogated by CCL2 blockade or macrophage depletion in vivo, establishing its non-cell-autonomous role in shaping the immunosuppressive niche (49). However, whether MALAT1 overexpression during later stages of tumor development exerts the same potent pro-metastatic effect as during initiation remains to be determined (49). Furthermore, the N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-modified lncRNA KCTD21 antisense RNA 1 (KCTD21-AS1) impairs macrophage phagocytosis by upregulating the “don’t eat me” signal CD47 and promoting autophagy via TIP41-like protein (50). LINC01094 further exemplifies chemokine-mediated crosstalk, promoting SPI1-dependent chemokine ligand 7 (CCL7) transcription to recruit M2 macrophages and facilitate metastasis (51). Together, these lncRNAs act as central regulators that control where TAMs gather, how they function, and their role in supporting tumor growth.
Taken together, these findings demonstrate that lncRNAs critically orchestrate the pro-tumorigenic functions of TAMs in lung cancer through multifaceted mechanisms. These lncRNA-driven alterations profoundly contribute to tumor progression, immunosuppression, and treatment failure, positioning them as compelling therapeutic targets, potentially in combination with existing modalities.
3.1.2.2 MDSCs
MDSCs are heterogeneous cells from immature myeloid progenitors. They promote lung cancer progression by creating an immunosuppressive TME. These cells inhibit antitumor immune responses and promote tumor progression by facilitating tumor angiogenesis, tumor cell invasion, and premalignant niche formation. High levels of MDSCs are associated with poor clinical outcomes and increased resistance to chemotherapy and immunotherapy in lung cancer patients (24). Recent studies have highlighted the regulatory role of lncRNAs in the function and differentiation of MDSCs in lung cancer. These lncRNAs can either enhance or suppress the immunosuppressive activity of MDSCs, thereby influencing tumor progression and therapeutic outcomes (93).
Certain lncRNAs, such as HOXA transcript antisense RNA, myeloid-specific 1 (HOTAIRM1) and MALAT1, have been shown to suppress the immunosuppressive activity of MDSCs. Specifically, HOTAIRM1, a lncRNA crucial for myeloid cell differentiation, is significantly downregulated in MDSCs isolated from lung cancer patients. At the molecular level, HOTAIRM1 is associated with elevated expression of the transcription factor homeobox A1 (HOXA1). Intriguingly, elevated HOXA1 gene levels curtail the immunosuppressive function of MDSCs. However, the precise mechanism underlying this regulation in MDSCs remains to be fully elucidated (52). In a comparable manner, MALAT1, a widely studied lncRNA, exhibits downregulation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of lung cancer patients. Consistently, low MALAT1 expression correlates with a higher proportion of circulating MDSCs, and its experimental knockdown increases MDSC frequency, indicating a negative regulatory role for MALAT1 in MDSC accumulation (94). However, its regulatory mechanism needs to be further studied in future researches. All together, these lncRNAs act as endogenous brakes that constrain MDSC-mediated immunosuppression.
On the flip side, some lncRNAs contribute to MDSC-mediated immunosuppression. lncRNA SNHG6 is highly expressed in tumor-derived MDSCs within Lewis lung carcinoma models (53). Mechanistically, SNHG6 facilitates the differentiation of monocytic MDSCs (M-MDSCs) by promoting the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of EZH2, a key epigenetic regulator. While SNHG6 primarily influences M-MDSC differentiation without directly altering their established immunosuppressive function, its action enhances the plenty of immunosuppressive MDSCs within the TME, contributing to tumor progression (53). Another prominent example involves RNA binding motif protein 15 (RBM15) and the lncRNA CBR3 antisense RNA 1 (CBR3-AS1). Research demonstrates that RBM15, potentially through mediating m6A modification, stabilizes the lncRNA CBR3-AS1 (54). In terms of its functional role, lncRNA CBR3-AS1 acts as a ceRNA, sponging miR-409-3p. This sequestration relieves miR-409-3p-mediated repression of its target, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1 (CXCL1). Consequently, elevated CXCL1 expression recruits MDSCs to the tumor site. Critically, this RBM15/CBR3-AS1/miR-409-3p/CXCL1 axis not only recruits MDSCs but also inhibits T cell activity, thereby promoting radioresistance in NSCLC (54). While this work highlights a direct link between lncRNA-mediated MDSC regulation and therapeutic response, its clinical implications warrant further validation, particularly given the potential confounding effects of concurrent chemotherapy in the study cohort and the current absence of targeted inhibitors for this pathway (54). Similarly, lncRNA RUNX1 overlapping RNA (RUNXOR) is elevated in both the peripheral blood and MDSCs of lung cancer patients. By repressing its overlapping gene RUNX1, RUNXOR upregulates Arg-1, the signature immunosuppressive enzyme of MDSCs, and thereby fosters tumor immune escape (55). However, that the precise molecular mechanism by which RUNXOR regulates the RUNX1-Arg1 axis in MDSCs remains to be fully elucidated (55). Therefore, such lncRNAs function as molecular accelerators that drive MDSC-dependent immune evasion.
Collectively, these findings underscore lncRNAs as pivotal regulators of MDSC abundance and immunosuppressive function in the lung TME. However, it is noteworthy that for many of these lncRNAs, such as HOTAIRM1 and RUNXOR, the precise molecular mechanisms, including their exact binding partners or downstream effectors, remain incompletely characterized. A deeper mechanistic understanding will be crucial for evaluating their potential as therapeutic targets.
3.1.2.3 TANs
Neutrophils contribute to cancer progression by inducing oxidative DNA damage and promoting tumor cell proliferation in TME (95). A key mechanism underlying their pro-tumorigenic activity is the formation of NETs. These structures, composed of chromatin DNA and granule proteins, facilitate lung cancer metastasis by accumulating at distant sites, where their DNA component acts as a chemotactic factor to promote cancer cell adhesion and seeding (96). The role of lncRNAs in regulating NET in lung cancer is an emerging area of research (95). However, research on lncRNAs specifically regulating NETs in lung cancer remains scarce. The lncRNA MIR503 host gene (MIR503HG) serves as a prominent example, with studies demonstrating how TAN-derived NETs subvert its function to promote metastasis (56, 97, 98).
First establishing MIR503HG’s tumor-suppressive role, Lin et al. documented consistent downregulation of this lncRNA in NSCLC tissues and cell lines. Functional assays demonstrated that MIR503HG overexpression inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis, primarily through suppressing Wnt1 expression. Crucially, xenograft models confirmed reduced tumor growth, positioning MIR503HG as a metastasis suppressor (97). Based on this, Wang et al. discovered that NETs in the lung TME downregulate the MIR503HG. This downregulation was identified by lncRNA microarray analysis and confirmed by qRT-PCR. They found that NET exposure promotes metastasis by inducing EMT in NSCLC cells. Mechanistically, NET-mediated suppression of MIR503HG leads to hyperactivation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which in turn triggers the NLRP3 inflammasome axis. Ultimately, this signaling cascade drives lung cancer dissemination. Crucially, rescue experiments demonstrated that restoring MIR503HG expression effectively blocked NET-facilitated metastasis in mouse models (56). The precise mechanism by which NETs downregulate MIR503HG remains unclear. Further study by Ye et al. decoded the full TAN/NET-MIR503HG-NLRP3 axis driving NSCLC metastasis. NETs silence the lncRNA MIR503HG via promoter methylation. This prevents MIR503HG from facilitating ring finger protein 43 (RNF43)-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of the transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta (C/EBPβ). Accumulated C/EBPβ then activates the NLRP3 promoter, elevating inflammasome activity and metastasis. DNA methyltransferase inhibitors reversed this effect, restoring MIR503HG and suppressing metastasis (98). However, these mechanistic insights are primarily derived from in vitro models of NETs. These findings require validation in more physiologically relevant in vivo systems to fully capture the complexities of the intact TME (98).
Collectively, TANs release NETs that suppress MIR503HG expression. This silencing activates key pro-metastatic cascades like NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome hyperactivation, ultimately driving lung cancer dissemination (56, 97, 98). Furthermore, building upon this established axis, investigating whether other lncRNAs are similarly regulated by NETs, or whether TANs themselves export regulatory lncRNAs via extracellular vesicles to regulate other cells in the niche, represents a promising research direction.
3.1.3 Other tumor associated cells
3.1.3.1 CSCs
CSCs are vital in tumor biology, driving initiation, progression, metastasis, and therapy resistance. They self-renew and differentiate, initiating tumors and maintaining heterogeneity. CSCs proliferate to fuel growth, invade via EMT, and resist therapy through dormancy and drug efflux. They evade immunity by creating a suppressive microenvironment and reactivating post-treatment to cause recurrence (99). lncRNAs regulate lung cancer CSCs through multiple mechanisms to modulate their maintenance and stemness (Figure 7).
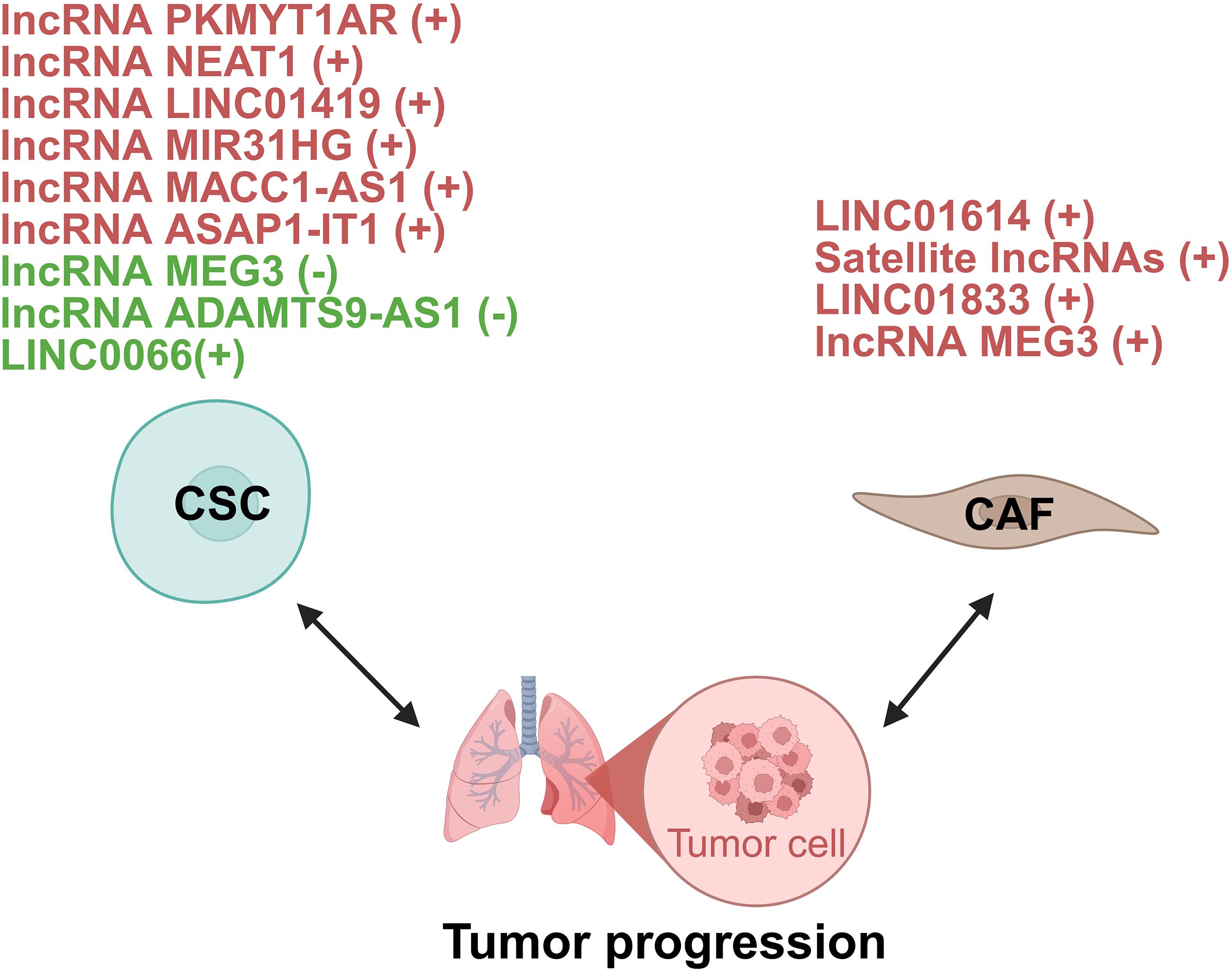
Figure 7. lncRNAs act as modulators between CSC/CAF and lung tumor cells. +: promoting the tumor progression; -: inhibiting the tumor progression. CSC, cancer stem cell; CAF, cancer-associated fibroblasts.
In NSCLC, lncRNAs function as master regulators of CSC plasticity by modulating developmental signaling pathways. Central to Wnt/β-catenin hyperactivation is the human-specific PKMYT1 associated lncRNA (PKMYT1AR) which is induced by Yin Yang 1 factor (YY1). It sequesters tumor-suppressive miR-485-5p to stabilize PKMYT1, thereby inhibiting β-catenin degradation and driving CSC maintenance. Crucially, antisense oligonucleotide (ASO)-mediated PKMYT1AR silencing suppresses xenograft tumorigenesis, underscoring its therapeutic promise (57). However, the molecular function of PKMYT1 itself appears to be highly context-dependent, as it stabilizes β-catenin through distinct mechanisms in different cancers (57). Simultaneously, lncRNA nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) amplifies this Wnt-driven axis by inhibiting copper transporter 1 and potentiating EMT cascades (58). Beyond Wnt signaling, LINC01419 recruits EZH2 to epigenetically silence fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 (FBP1), activating Hippo signaling in CD44+ LUAD cells and conferring chemoresistance (59).
Epigenetic reprogrammers mediate CSC plasticity through chromatin remodeling. MIR31HG is elevated in NSCLC patient sera and correlates with poor prognosis. Mechanistically, MIR31 host gene (MIR31HG) recruits the WD repeat-containing protein 5 (WDR5)/mixed lineage leukemia 3 (MLL3)/P300 complex to deposit activating histone marks including histone H3 lysine 4 mono-methylation (H3K4me1) and histone H3 acetylated lysine 27 (H3K27ac) at the GLI2 promoter, augmenting transcription of this Hedgehog pathway effector. Functionally, this confers CSC-like properties including chemoresistance and metastasis. Intriguingly, in vivo ASOs targeting of MIR31HG attenuates metastasis, positioning it as a diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target (60). Further research is needed to define the genomic targeting scope of MIR31HG and to overcome the translational challenge posed by its lack of a murine homolog.
Another group of lncRNAs enhance CSC stemness through RNA interactions. For instance, lncRNA MACC1 antisense RNA 1 (MACC1-AS1) contributes to CSC stemness by interacting with up-frameshift 1 (UPF1) to destabilize large tumor suppressor kinase (LATS) 1/2 mRNA, further regulating the Hippo signaling pathway (61). In addition, lncRNA ASAP1 intronic transcript 1 (ASAP1-IT1) sponges miR-509-3p to derepress yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1), thus activating the Hippo pathway effector and enhancing cancer stemness in NSCLC (62). Moreover, LINC00662 promotes lung cancer cell invasion and CSC-like phenotypes by interacting with Lin28, highlighting its potential as a diagnostic and therapeutic target (63). Collectively, these studies demonstrate that lncRNA-mediated RNA interactions represent a versatile mechanism sustaining cancer stemness properties.
On the other hand, some lncRNAs act as suppressors of CSC characteristics. MEG3, downregulated in lung cancer stem cells (LCSCs), suppresses migration and invasion by sponging miR-650, which targets solute carrier family 34 member 2 (64). lncRNA ADAMTS9 antisense RNA 1 (ADAMTS9-AS1) is downregulated in LUAD and linked to better survival. It suppresses LUAD cell stemness by upregulating miR-5009-3p, which targets nephronectin. Overexpressing ADAMTS9-AS1 curbs LUAD progression in vitro (65).
lncRNAs orchestrate CSC plasticity through multi-tiered regulation, including signaling pathway activation, epigenetic reprogramming, and RNA interactions. This integrated network sustains stemness and immunosuppression, positioning lncRNAs as master regulators of CSC resilience.
3.1.3.2 CAFs
CAFs are key players in the TME, interacting with cancer and stromal cells to promote tumor progression, metastasis, and chemoresistance. Their significant heterogeneity and plasticity, stemming from diverse origins, necessitates understanding their diversity for effective therapies (100). The functional output of CAFs is critically regulated by lncRNAs, which act as master switches controlling their activation and matrix-remodeling capabilities. These lncRNAs operate through several core mechanisms, such as driving glycolytic reprogramming to trigger fibronectin secretion (101), stabilizing key cytokines to sustain an autocrine loop that maintains CAFs in an activated state (102), and directly hyperactivating signaling pathways like AKT (103) to orchestrate the transcriptional program for collagen deposition and stromal stiffening. In lung cancer, lncRNAs act as critical regulators of CAF functions, modulating tumor metabolism and transcriptional programs (Figure 7).
Emerging evidence highlights lncRNAs within CAFs as key orchestrators of metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells. A prime example identified in LUAD is the CAF-specific lncRNA LINC01614, which drives glutamine metabolic reprogramming. Mechanistically, LINC01614 is packaged into CAF exosomes and transferred to tumor cells, where it binds annexin A2 (ANXA2) and p65 to activate NF-κB signaling. This reprograms glutamine metabolism by upregulating transporters solute carrier family 38 member 2 (SLC38A2) and solute carrier family 7 member 5 (SLC7A5), boosting glutamine uptake to fuel tumor growth. Critically, tumor-derived cytokines further induce LINC01614 in CAFs, creating a feedforward loop. Blocking exosomal transfer suppresses glutamine addiction and tumor progression (66). This study highlights the therapeutic potential of targeting a CAF-specific lncRNA to inhibit glutamine utilization and cancer progression in LUAD.
Beyond specific metabolites, CAFs can induce broad transcriptional changes via satellite lncRNAs. Pericentromeric satellite lncRNAs are robustly induced in CAFs within the LUAD TME. These lncRNAs are transcriptionally activated in response to diverse stromal stimuli, including TGF-β, IL-1α, increased matrix stiffness, direct contact with tumor cells, and exposure to chemotherapeutic drugs. Following their induction, satellite lncRNAs are localized not only within the CAF nucleus and cytoplasm but are also packaged into extracellular vesicles (EVs) for secretion. Functionally, knockdown experiments revealed that these satellite lncRNAs are essential for maintaining an inflammatory CAF phenotype. Depleting satellite transcripts attenuates cellular senescence in CAFs and disrupts their ability to adopt a pro-tumorigenic, immunosuppressive state. This impairment consequently inhibits the pro-tumorigenic functions of CAFs (67). These findings position pericentromeric satellite lncRNAs as novel regulators of CAF activation and mediators of intercellular communication within the TME, presenting potential biomarkers or targets.
Similar mechanisms of CAF-derived exosomal lncRNAs driving tumor progression exist. For instance, exosomal LINC01833 from CAFs promotes NSCLC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by acting as a ceRNA for miR-335-5p, leading to increased VAMP associated protein A (VAPA) expression (68). Likewise, CAF-derived exosomal lncRNA maternally expressed 3 (MEG3) binds miR-15a-5p in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cells, derepressing cyclin E1 (CCNE1) to drive cisplatin chemoresistance and tumor progression (69).
In summary, CAF-derived exosomal lncRNAs mediate tumor-stroma communication to control cancer metabolism and transcriptional programs, critically driving lung cancer progression.
3.2 lncRNAs in immune checkpoint regulation
Immune checkpoints regulate immune activity and can be exploited by tumors to evade attack, creating an immunosuppressive microenvironment. Key checkpoints like PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 are critical targets. Tumor-intrinsic factors and oncogenic pathways further enable immune evasion (29). Critically, lncRNAs are emerging as master regulators of these checkpoints, particularly PD-L1, in lung cancer. Their control spans two key levels, including PD-L1 transcription and mRNA stability, PD-L1 protein stability and isoform generation.
Transcriptional control by lncRNAs constitutes a pivotal mechanism exploited by environmental carcinogens to drive oncogenesis. Hexavalent chromium [Cr (VI)], a potent lung carcinogen, triggers overexpression of the lncRNA ABHD11 antisense RNA 1 (ABHD11-AS1) in lung epithelial cells. Functionally, ABHD11-AS1 recruits the deubiquitinase ubiquitin specific peptidase 15 (USP15) to degrade tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3), thereby activating the non-canonical NF-κB pathway. Consequently, this cascade amplifies IL-6/STAT3 signaling and robustly upregulates PD-L1 transcription. Critically, ABHD11-AS1-driven PD-L1 elevation suppresses T cell infiltration and accelerates lung carcinogenesis in murine models, positioning this lncRNA as a molecular bridge between environmental exposure and immune evasion (70). Once PD-L1 mRNA is made, its half-life can be prolonged by lncRNA SWI/SNF complex antagonist associated with prostate cancer 1 (SChLAP1), which recruits AU-rich element RNA-binding factor 1 (AUF1) to the 3′-UTR and shields the transcript from degradation, thereby elevating steady-state protein levels and fueling tumor growth (71). These studies indicate that CAF-derived lncRNAs emerge as direct transcriptional regulators of pro-tumorigenic programs.
Beyond transcriptional regulation, lncRNAs critically govern PD-L1 protein stability and generate functionally diversified isoforms through distinct pathways. In NSCLC, the m6A-modified lncRNA LINC02418 directly controls PD-L1 protein stability by scaffolding tripartite motif containing 21 (TRIM21) to induce PD-L1 ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Silencing of this tumor suppressor elevates PD-L1 abundance, while its restoration enhances anti-PD-L1 therapy efficacy (72). The PD-L1 gene also expresses a long non-coding splice variant (PD-L1-lnc). Upon IFN-γ induction, this lncRNA promotes LUAD progression by directly enhancing c-Myc transcriptional activity (73). Targeting PD-L1-lnc holds exceptional therapeutic promise by simultaneously disrupting dual oncogenic-immune pathways.
These studies collectively delineate lncRNAs as central orchestrators of immune evasion pathways in lung cancer, operating through diverse mechanisms that converge on suppressing anti-tumor immunity.
3.3 lncRNAs in cytokines and immune modulators
lncRNAs serve as pivotal regulators of cytokine networks within TME, fine-tuning immune responses and stromal activation (104, 105). Among the cytokines and immune modulators influenced by lncRNAs, the TGF-β is the most extensively studied in lung cancer. We will therefore focus on TGF-β, while also noting other cytokine modulations by lncRNAs.
3.3.1 lncRNAs in regulation of TGF-β
TGF-β plays a complex dual role in lung carcinogenesis (106). In early-stage NSCLC, it acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting epithelial cell proliferation. However, in advanced disease, TGF-β becomes a potent driver of tumor progression through multiple mechanisms (107). It is the primary inducer of EMT in NSCLC cells, enhancing migratory and invasive capacities while conferring anti-apoptotic properties and chemoresistance (108). This process is markedly amplified by oncogenic kirsten ratsarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS) signaling (109). Beyond direct cancer cell effects, TGF-β critically shapes TME by activating CAFs, thereby promoting extracellular matrix remodeling and tissue stiffening (110). It also facilitates angiogenesis and orchestrates immune evasion through Treg induction, polarization of tumor-associated immune cells, and exclusion of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. In SCLC, TGF-β signaling is frequently disrupted, particularly in classic subtypes lacking TGFβR-II expression. This inactivation derepresses the neuroendocrine master regulator achaete-scute family bHLH transcription factor 1 (ASCL1), contributing to SCLC pathogenesis by maintaining the neuroendocrine phenotype and potentially enhancing cell survival (111).
Lung cancer-associated lncRNAs execute sequential control of TGF-β signal transduction, coordinating molecular events from extracellular ligand engagement to nuclear transcriptional activation (Figure 8).
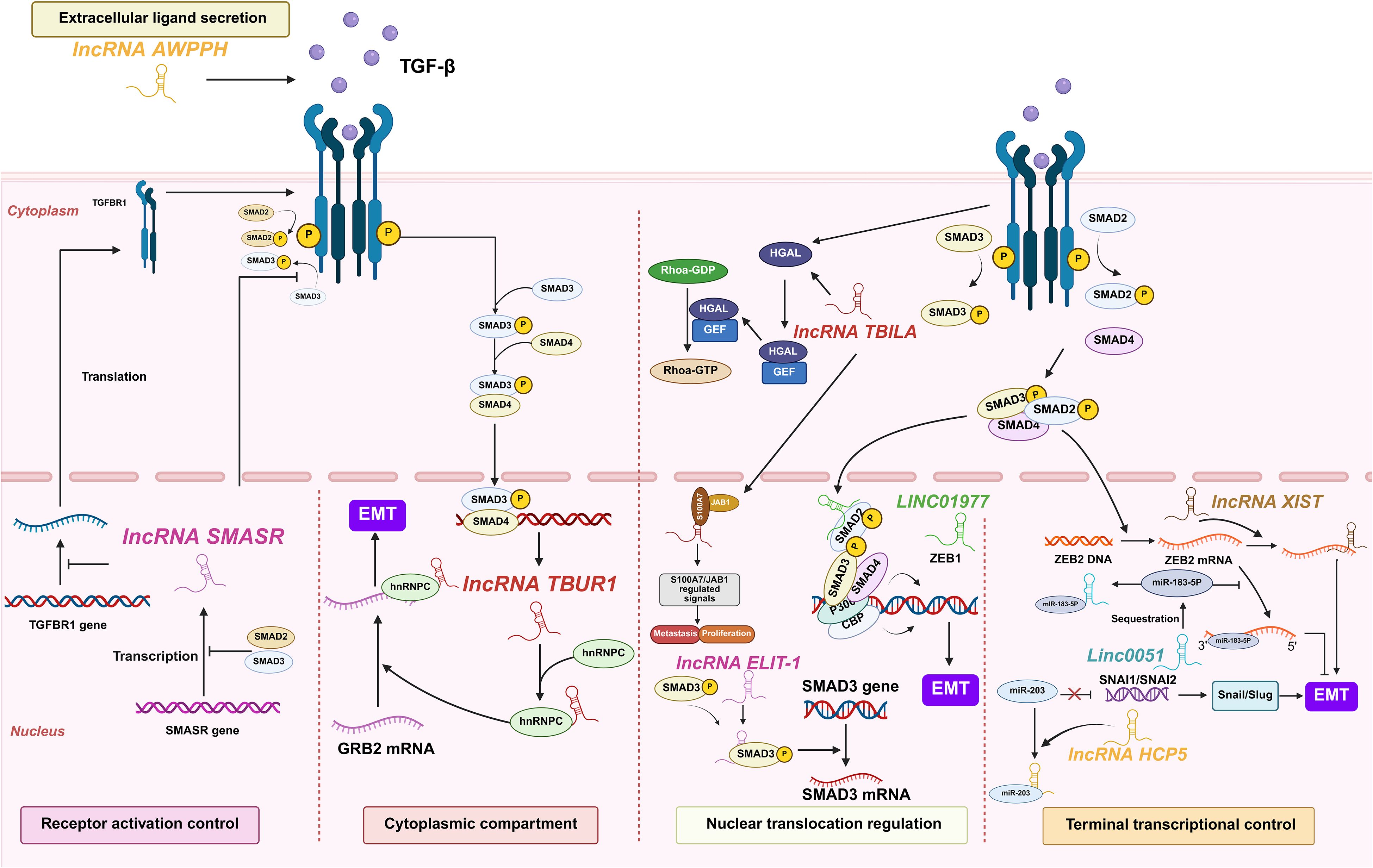
Figure 8. lncRNAs act as modulators of TGF-β in lung cancer. Lung cancer-associated lncRNAs exert sequential control over TGF-β signaling, coordinating five regulatory tiers from extracellular ligand engagement to nuclear transcriptional activation, collectively promoting tumor progression and immune evasion.
3.3.1.1 Extracellular ligand engagement
At the extracellular ligand secretion level, lncRNA associated with poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (AWPPH) directly elevates TGF-β1 production in resected NSCLC tumors. Clinical evidence reveals that blood AWPPH levels are positively correlated with TGF-β1 mRNA in distant recurrence patients, and AWPPH overexpression experimentally upregulates TGF-β1 protein expression. This establishes an autocrine feedforward loop that drives postoperative metastasis through sustained TGF-β1 secretion (74). However, the precise mechanism by which AWPPH upregulates TGF-β1 remains unknown.
3.3.1.2 Receptor activation control
For receptor activation control, SMAD3 associated lncRNA (SMASR) suppresses TGF-β receptor activation through binding unphosphorylated SMAD2/3 to block their phosphorylation while concurrently inhibiting TGFBR1 transcription. This negative feedback circuit is initiated by TGF-β itself, which downregulates SMASR expression via SMAD2/3, thereby constraining signal initiation at the plasma membrane (75). However, these proposed mechanisms require further validation. Key unresolved questions include identifying the specific SMAD domains critical for SMASR binding and exploring its potential non-transcriptional functions in the cytoplasm (75).
3.3.1.3 Cytoplasmic signal transduction
Within the cytoplasmic compartment, lncRNAs critically amplify TGF-β signaling through stabilizing core pathway components. TGF-β/SMAD3/4-activated TGF-β-upregulated lncRNA 1 amplifies cytoplasmic signal propagation by binding heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (hnRNPC) to stabilize growth factor receptor bound protein 2 (GRB2) mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner. This stabilization potentiates ERK phosphorylation and downstream MAPK signaling, thereby driving EMT initiation, enhancing LUAD cell migration/invasion in vitro, and promoting metastasis in vivo. Critically, TBUR1 overexpression correlates with poor clinical prognosis in LUAD, positioning it as both a metastasis driver and actionable therapeutic target (76).
3.3.1.4 Nuclear translocation regulation
Nuclear translocation regulation involves LINC01977-mediated hijacking of super-enhancer elements, which facilitates SMAD3 nuclear import and recruits CBP/P300 to the zinc finger e-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) promoter (77). TGF-beta induced lncRNA (TBILA), induced by TGF-β, binds nuclear SMAD complexes to enhance RhoA activation via cis-regulating human germinal center-associated lymphoma (HGAL) expression. Concurrently, it activates the S100A7-JAB1 pro-survival pathway by interacting with nuclear S100A7, facilitating NSCLC metastasis (78). Nuclear-localized lncRNA enforcing TGF-β signaling 1 (LETS1) potentiates TGF-β-SMAD signaling by stabilizing cell surface TβRI. Specifically, LETS1 binds nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT5) and induces expression of orphan nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1 (NR4A1), which targets SMAD7 for degradation in a destruction complex. This mechanism inhibits SMAD7-mediated polyubiquitination of TβRI, extending receptor half-life and enhancing TGF-β signal transduction. Crucially, TGF-β transcriptionally induces LETS1 expression, creating a nuclear-originated positive feedback loop that promotes EMT and cancer cell extravasation (79).
3.3.1.5 Nuclear transcriptional activation
Terminal transcriptional control executes TGF-β signaling through the following lncRNA mechanisms. Human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen complex p5 (HCP5) achieves this control by sequestering miR-203 via direct binding, lifting SNAI1/SNAI2 repression to elevate Snail/Slug for EMT initiation (80). Concurrently, EMT-associated lncRNA induced by TGFβ1 (ELIT-1) binds to SMAD3 in nucleus upon TGFβ-stimulation, promoting the transcription of SMAD-target genes by facilitating SMAD3 recruitment to their respective promoters as a SMAD3 cofactor, enforcing terminal control (81). LINC00511 executes terminal transcriptional control by sponging miR-183-5p to derepress zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 (ZEB2), directly activating EMT transcription programs and matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) expression, thereby irreversibly committing TGF-β-driven metastasis (82). As a master terminal regulator, lncRNA XIST enforces irreversible EMT execution by ceRNA-mediated ZEB2 derepression, driving TGF-β-dependent transcriptional reprogramming and in vivo metastatic colonization, thus locking cells in a pro-metastatic state (83).
Collectively, these findings position lncRNAs as master regulators that exert precise control over the entire TGF-β signaling cascade in lung cancer. Their governance spans from initial ligand availability to the final transcriptional output, critically enforcing the pathway’s switch to a pro-tumorigenic state. Consequently, targeting these specific lncRNA-TGF-β axes presents a promising therapeutic strategy to inhibit TGF-β-mediated tumor progression and immunosuppression.
3.3.2 lncRNAs in regulation of other cytokines and immune regulatory factors
Beyond TGF-β, lncRNAs interact with diverse cytokines and immune regulatory factors including IL-6, IL24 and TNF-α. lncRNA enhancing IL-6/STAT3 signaling activation (LEISA) recruits transcription factor STAT3 to the IL-6 promoter, establishing a feedforward loop that augments IL-6 secretion and STAT3 phosphorylation to promote tumor proliferation and chemotherapy resistance (84). Equally critical for immune evasion, LINC00152 recruits EZH2 to deposit repressive H3K27me3 marks on the IL24 promoter, epigenetically silencing this pro-apoptotic cytokine and enabling uncontrolled tumor growth (85). For TNF-α signaling, TNF-α and heterogenous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L related immunoregulatory lncRNA (THRIL) forms a self-regulatory circuit where TNF-α induces fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO)-mediated m6A demethylation of THRIL, triggering YTH n6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2)-dependent degradation to suppress NSCLC proliferation. Conversely, THRIL stabilizes TNF-α mRNA via HuR complex formation, establishing a bistable loop that amplifies inflammatory responses while enabling tumor-suppressive feedback at high cytokine concentrations (86).
In summary, lncRNAs exert multifaceted control over the cytokine landscape of the TME, targeting key immune mediators such as IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α. Future studies should aim to decipher the precise molecular mechanisms through which these lncRNAs govern cytokine networks. Key questions include how they achieve spatial and temporal control over cytokine production and whether their functions are specific to certain cell types. Elucidating these intricate regulatory circuits will be crucial for developing novel therapeutic strategies that target lncRNAs to normalize the immunosuppressive TME and potentially overcome resistance to current immunotherapies.
4 The clinical significance of lncRNAs in lung cancer
4.1 lncRNAs as clinically stratified biomarkers in TME
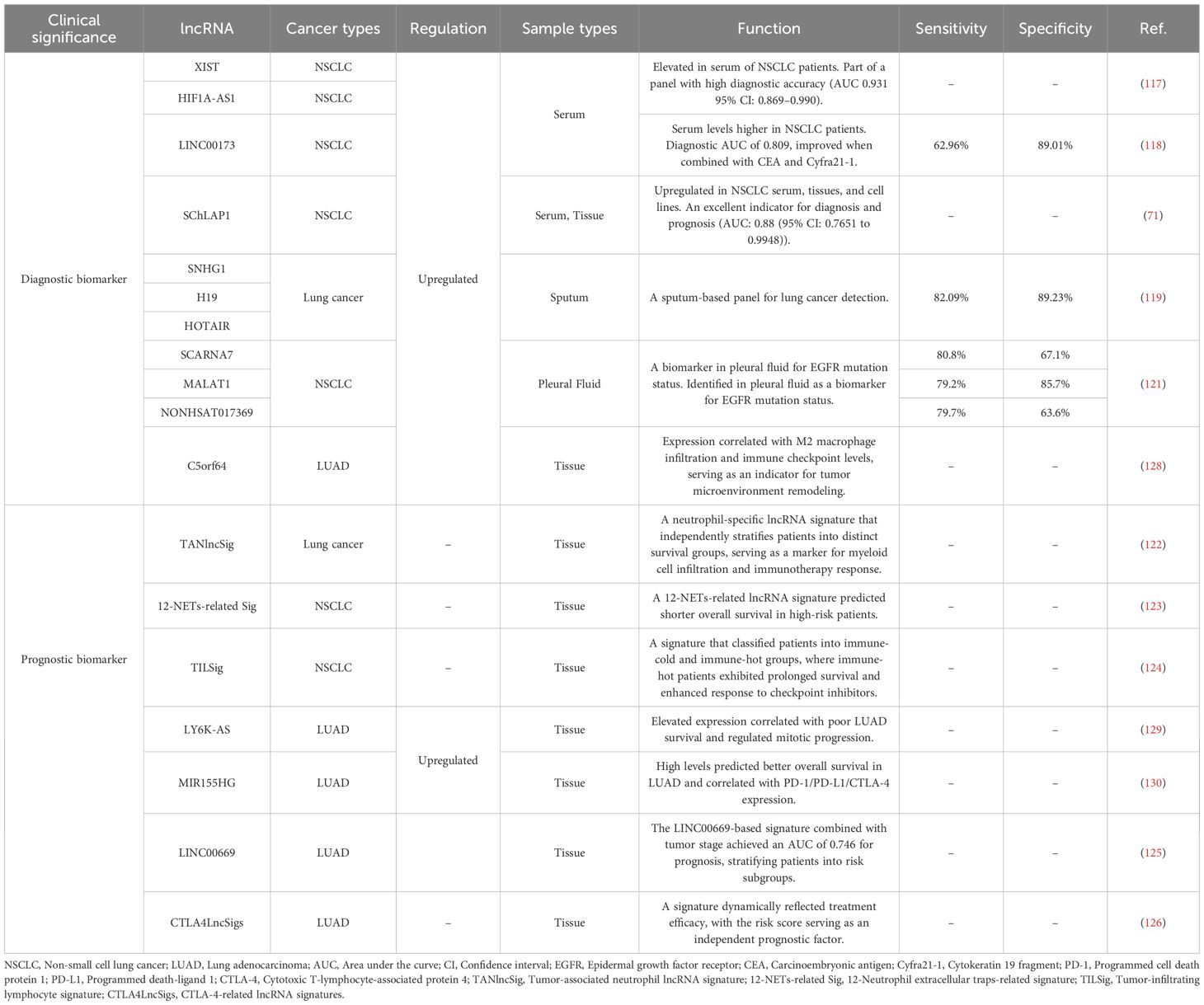
lncRNAs are emerging as powerful, clinically stratified biomarkers with significant diagnostic and prognostic utility in lung cancer (112). Crucially, their expression profiles within the TME and detection across diverse, accessible biofluids (including serum, sputum, urine, and pleural effusion) offer unprecedented opportunities for non-invasive diagnosis, precise risk stratification, and microenvironmental assessment (113, 114). Advanced detection techniques enable the robust quantification of these circulating and tissue-derived lncRNAs, solidifying their potential to guide personalized lung cancer management beyond conventional methods (115, 116).
lncRNAs demonstrate significant diagnostic potential across diverse body fluids in lung cancer detection. In serum, elevated levels of XIST and HIF1A antisense RNA 1 (HIF1A-AS1) were consistently observed in NSCLC patients. The combined detection of these lncRNAs demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy, outperforming individual markers (117). Similarly, serum LINC00173 levels were higher in 108 NSCLC patients than in healthy donors and benign pulmonary disease cases. Its combination with carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and cytokeratin 19 fragment (Cyfra 21-1) further improved diagnostic accuracy (118). SChLAP1 was significantly upregulated in NSCLC cell lines, serum and tissues, which was identified as an excellent indicator for the diagnosis and prognosis of NSCLC (71). Beyond blood samples, sputum analysis revealed that a panel of SNHG1, H19, and HOTAIR provided high sensitivity and specificity, surpassing conventional sputum cytology for lung cancer detection (119). For urine-based testing, exosomal analysis identified six differentially expressed lncRNAs (70 upregulated and 570 downregulated) through microarray screening, with QT-PCR validation confirming their diagnostic utility (120). Regarding effusion samples, pleural fluid analysis identified small cajal body-specific RNA 7 (SCARNA7), MALAT1, and NONHSAT017369 as biomarkers for EGFR mutation status, with consistent upregulation observed in plasma of EGFR-mutant patients (121). Collectively, these findings firmly establish lncRNAs as clinically actionable biomarkers detectable in serum, sputum, urine, and pleural effusion. Clinical translation now necessitates standardized assays and prospective validation to advance these lncRNAs into routine diagnostic and immunotherapeutic guidance.
lncRNAs demonstrate significant prognostic utility through multidimensional signatures in lung cancer management. Computational frameworks identified TANlncSig, a neutrophil-specific lncRNA signature that independently stratifies patients into distinct survival groups (HR >1, P<0.0001), serving as a marker for myeloid cell infiltration and immunotherapy response (122). Similarly, a 12-NETs-related lncRNA signature predicted shorter overall survival in high-risk patients (P<0.0001), with three adverse lncRNAs validated to increase post-NETs stimulation in tumor cells (123). For TME assessment, the TILSig signature (seven immune infiltration-associated lncRNAs) robustly classified patients into immune-cold and immune-hot groups, where immune-hot patients exhibited prolonged survival and enhanced response to checkpoint inhibitors (124). The LINC00669-based signature combined with tumor stage demonstrated significant prognostic value, stratifying patients into risk subgroups with distinct immune microenvironments and therapy responses (125). For therapy monitoring, CTLA4LncSigs (19 CTLA-4-related lncRNAs) dynamically reflected treatment efficacy, with the risk score serving as an independent prognostic factor (126). Collectively, these signatures enable precise risk stratification, immunotherapy response prediction, and real-time treatment efficacy monitoring beyond conventional imaging methods.
Despite their considerable promise, the clinical translation of lncRNA biomarkers faces several key challenges. A primary limitation is the need for completely noninvasive detection methods, which currently suffer from insufficient sensitivity to reliably detect low-abundance lncRNAs in liquid biopsies. This is compounded by the lack of standardized diagnostic panels with established reference values. Addressing these issues is essential to resolve the pressing question of clinical utility, such as whether these biomarkers can accurately distinguish malignant from benign pulmonary nodules (127).
In summary, lncRNAs demonstrate immense potential as clinically actionable tools for non-invasive diagnosis and multidimensional prognostication in lung cancer. The key biomarkers and signatures discussed above are systematically summarized in Table 2.
4.2 lncRNAs as modulators of therapy resistance in lung cancer
While systemic therapies such as chemotherapy provide substantial benefits for patients of advanced lung cancer in both preoperative and postoperative settings, the high initial response rates are frequently followed by the development of therapeutic resistance and disease recurrence. This resistance remains a major obstacle to improving long-term survival, driven by complex molecular adaptations within the TME. Accumulating evidence indicates that lncRNAs function as critical regulators of these adaptive processes, mediating resistance through diverse mechanisms (Figure 9) (115, 116).
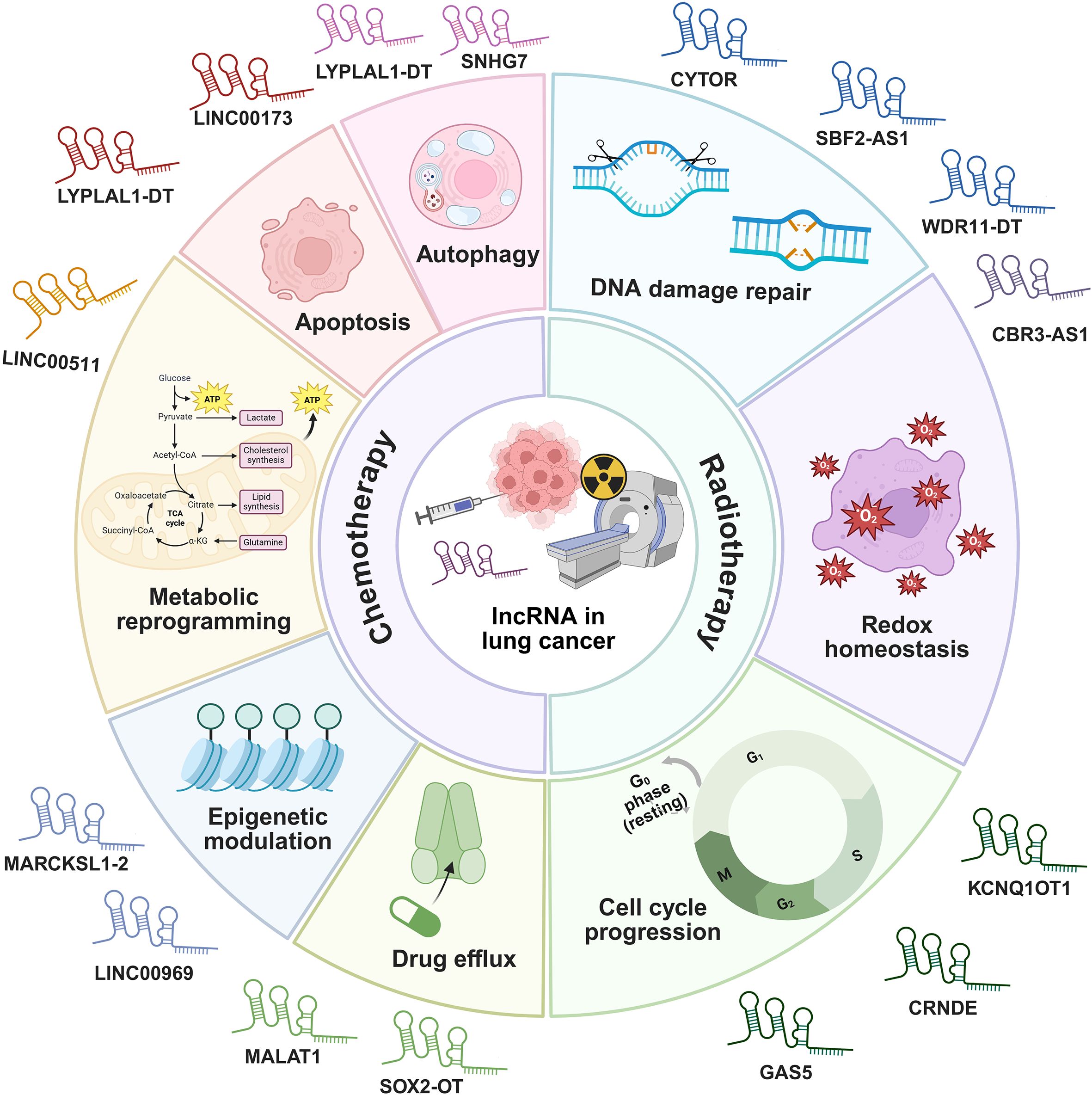
Figure 9. The mechanisms of lncRNAs regulating chemotherapy and radiotherapy responses in lung cancer.
4.2.1 lncRNAs in modulating chemotherapy resistance
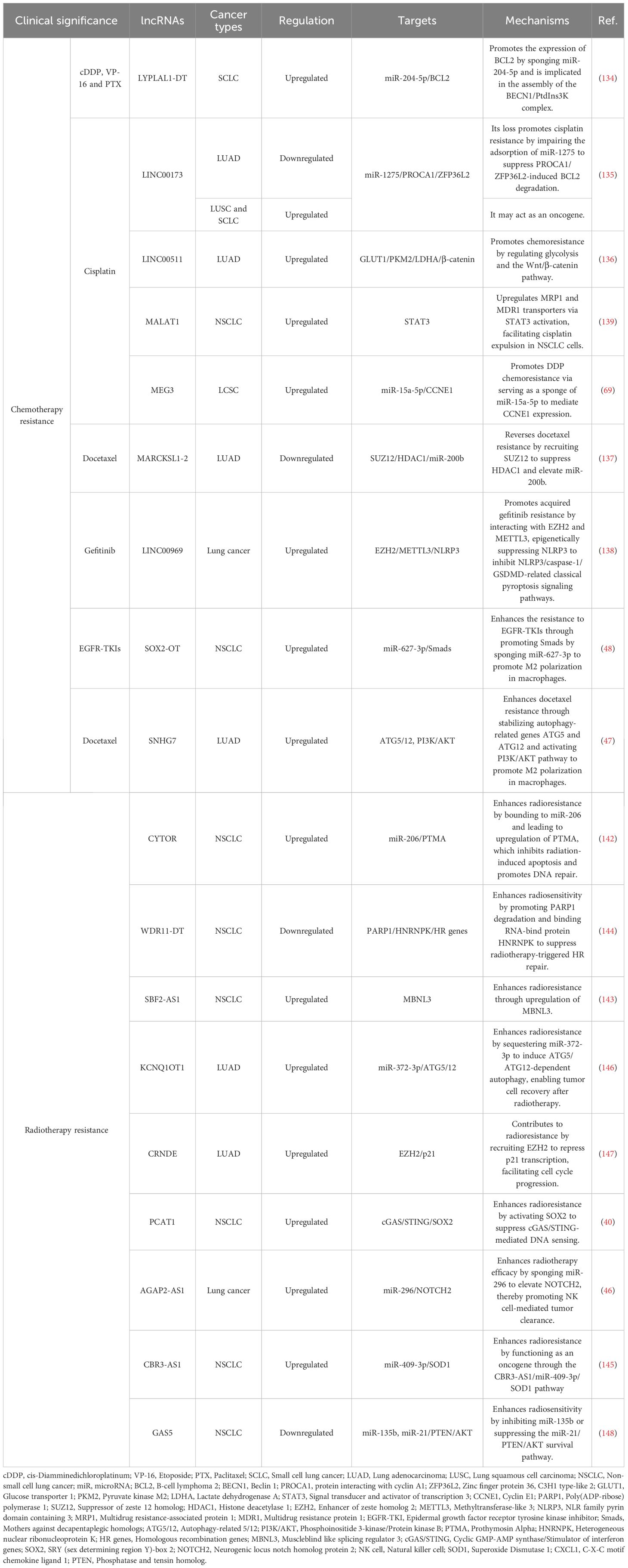
Chemotherapy regimens, primarily involving agents such as cisplatin, etoposide, and paclitaxel, remain a cornerstone first-line treatment for advanced NSCLC and are also extensively used in SCLC (131). Despite initial efficacy, the majority of patients inevitably develop therapeutic resistance to these chemotherapeutic drugs. This chemotherapy resistance poses a paramount clinical challenge. Intrinsic and acquired resistance significantly curtail the long-term benefits of chemotherapy, highlighting an urgent need to decipher its molecular drivers and develop novel strategies to circumvent it (132). lncRNAs have emerged as pivotal regulators of these complex resistance mechanisms, offering new insights and therapeutic avenues (133). Chemotherapy resistance in lung cancer is orchestrated by lncRNAs through four molecular mechanisms including regulation of autophagy and apoptosis, metabolic reprogramming, epigenetic modulation, and control of drug efflux.
Regarding the regulation of autophagy and apoptosis, lncRNA LYPLAL1 divergent transcript (LYPLAL1-DT) is highly upregulated in multi-drug resistant SCLC and promotes resistance to cisplatin, etoposide, and paclitaxel by enhancing autophagy and suppressing apoptosis. It acts by sponging miR-204-5p to elevate BCL2 expression and facilitates the assembly of the beclin 1/PtdIns3K autophagy complex. Notably, combining venetoclax with hydroxychloroquine effectively counteracts this form of resistance in preclinical models (134). Another regulator of cell survival, LINC00173, plays a context-dependent role. It is downregulated in cisplatin-resistant LUAD, where its loss promotes resistance through the miR-1275/protein interacting with cyclin A1 (CCNA1)/zinc finger protein 36 like 2 (ZFP36L2) axis, increasing BCL2 mRNA stability and inhibiting apoptosis. Interestingly, it has also been reported as an oncogenic factor in SCLC and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC), underscoring its subtype-specific functions (135).
lncRNAs also drive chemoresistance by reprogramming cellular metabolism. LINC00511 is downregulated by β-elemene, leading to inhibited expression of key glycolytic enzymes such as glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1), pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2), and lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), as well as β-catenin, thereby reversing chemoresistance (136).
Beyond transcriptional and metabolic reprogramming, epigenetic modulation represents another critical layer of lncRNA-mediated chemoresistance. MARCKS like 1-2 (MARCKSL1-2) reverses docetaxel resistance by recruiting suppressor of zeste 12 homolog (SUZ12) to suppress histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) transcription via H3K27me3 modification, resulting in elevated miR-200b expression and restored drug sensitivity (137). Similarly, LINC00969 promotes gefitinib resistance through its interaction with EZH2 and methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3), which leads to the epigenetic suppression of NLRP3. This process involves both H3K27me3 mediated transcriptional silencing and m6A-dependent mRNA decay, effectively inhibiting NLRP3 dependent pyroptosis and thereby facilitating drug resistance in lung cancer (138).
Furthermore, a key mechanism of resistance involves the lncRNA-mediated control of drug efflux. For instance, MALAT1 contributes to resistance by upregulating drug transporter genes, leading to increased efflux of chemotherapeutic agents and reduced intracellular drug accumulation (139). Other lncRNAs including SOX2-OT (48), SNHG7 (47), and MEG3 (69) have also been implicated in promoting chemotherapy resistance through above mechanisms.
4.2.2 lncRNAs in modulating radiosensitivity
Radiotherapy is a pivotal and potentially curative modality for locally advanced lung cancer, both as a definitive treatment and in combination with chemotherapy or immunotherapy (140). However, radioresistance is a major impediment to achieving durable local control and survival. The biological basis of radioresistance involves a complex interplay of cellular processes designed to mitigate the cytotoxic effects of ionizing radiation. Key mechanisms include DNA damage repair, redox homeostasis, and cell cycle progression. Overcoming radioresistance is crucial for improving the therapeutic ratio of radiotherapy in lung cancer (141). Dysregulation of specific lncRNAs has been closely linked to these radioresistant phenotypes, positioning them as key therapeutic targets to enhance radiotherapeutic efficacy (133). Radiotherapy resistance in lung cancer is orchestrated by lncRNAs through above mechanisms (141).
DNA repair capacity is a key determinant of radiosensitivity. In this regard, lncRNA cytoskeleton regulator RNA (CYTOR) confers resistance by acting as a molecular sponge for miR-206, leading to upregulation of prothymosin α (PTMA), a protein that inhibits radiation-induced apoptosis and promotes DNA repair machinery (142). Similarly, lncRNA SBF2 antisense RNA 1 (SBF2-AS1) enhances radioresistance through the miR-302a/MBNL3 axis, where MBNL3 knockdown sensitizes tumor cells to DNA damage (143). In contrast, lncRNA WDR11 divergent transcript (WDR11-DT) is a radiation-induced lncRNA that is downregulated in NSCLC and associated with poor prognosis post-radiotherapy. It enhances radiosensitivity by promoting poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) degradation via thyroid hormone receptor interactor 12 (TRIP12), impairing single-strand break repair, and binding heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (HNRNPK) to reduce the stability of homologous recombination genes (144).
Besides DNA repair capacity, the maintenance of redox homeostasis is another crucial determinant of radiosensitivity. This is well-illustrated by lncRNA CBR3-AS1, which is overexpressed in NSCLC and confers radioresistance by acting as a ceRNA for miR-409-3p, thereby upregulating superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1). This alleviates radiation-induced oxidative stress and enhances DNA repair, whereas its knockdown increases γH2AX foci, ROS levels, and apoptosis (145). This model, supported by canonical validation, exemplifies the need to determine if such ceRNA activity represents the lncRNA’s primary function, while also highlighting that other potential mechanisms remain to be explored.
For autophagy-mediated survival, lncRNA KCNQ1 opposite strand/antisense transcript 1 (KCNQ1OT1) sequesters miR-372-3p to induce ATG 5/12-dependent autophagy, enabling tumor cell recovery after stereotactic radiotherapy (146). Additionally, lncRNA colorectal neoplasia differentially expressed (CRNDE) is upregulated in radioresistant LUAD cells and contributes to resistance by recruiting EZH2 to repress p21 transcription, facilitating G1/S transition and reducing apoptosis (147). Notably, tumor-suppressive lncRNAs like GAS5 can counteract resistance by inhibiting miR-135b or suppressing the miR-21/PTEN/AKT survival pathway to enhance radiosensitivity (148). Additionally, certain lncRNAs such as PCAT1 (40), AGAP2-AS1 (46), and CBR3-AS1 (54) are involved in immune escape by modulating immune cell activity. Their mechanism has been described previously.
Collectively, these findings position lncRNAs as master regulators of radiotherapy response through the mechanisms discussed above, offering promising targets for novel therapeutic strategies. Table 3 summarizes the role of specific lncRNAs as key regulators of resistance to diverse treatment modalities.
4.3 lncRNAs as therapeutic targets
The strategic disruption of oncogenic lncRNAs is increasingly recognized as a powerful approach to enhance the efficacy of standard cancer therapies (149). This is achieved through a multi-pronged strategy, from re-sensitizing tumors to conventional chemotherapy and augmenting immune checkpoint blockade, to employing advanced molecular tools like ASOs for targeted inhibition (Table 4). Ultimately, these strategies all share the same goal to circumvent resistance mechanisms and achieve superior antitumor outcomes through combination therapy (150).
4.3.1 Overcoming chemoresistance and improving immunotherapy by targeting lncRNAs
A primary focus has been on overcoming chemoresistance by targeting key oncogenic lncRNAs. For example, the lncRNA LYPLAL1 divergent transcript (LYPLAL1-DT) is significantly upregulated in multi-drug resistant SCLC. It contributes to therapy resistance through mechanisms involving apoptosis inhibition and pro-survival autophagy. Importantly, the synergistic combination of venetoclax and hydroxychloroquine effectively reversed this type of resistance in both cell line-derived and patient-derived xenograft models. This combination offers a promising therapeutic strategy to overcome lncRNA-mediated drug resistance (134).
Beyond their role in chemoresistance, lncRNAs represent compelling targets for modulating immunotherapy response. Efforts to overcome immune checkpoint blockade resistance have focused on lncRNAs that regulate PD-L1 expression. For instance, targeting the RNA-modifying enzyme METTL3 to upregulate the tumor-suppressive lncRNA LINC02418, which promotes PD-L1 degradation and synergizes with anti-PD-1 therapy (72). Additionally, targeting the downstream effectors CD55 and CD59 with neutralizing antibodies, which are upregulated via EGFR/Wnt signaling and LINC00973, activates the complement system and synergizes with anti-PD-1 therapy to achieve a robust antitumor response (39).
4.3.2 Novel therapeutic strategies directly targeting lncRNAs
The development of therapeutic strategies directly targeting lncRNAs is a promising avenue for lung cancer treatment, with major approaches including ASOs, the CRISPR/Cas9 system, and engineered exosomes (Figure 10).
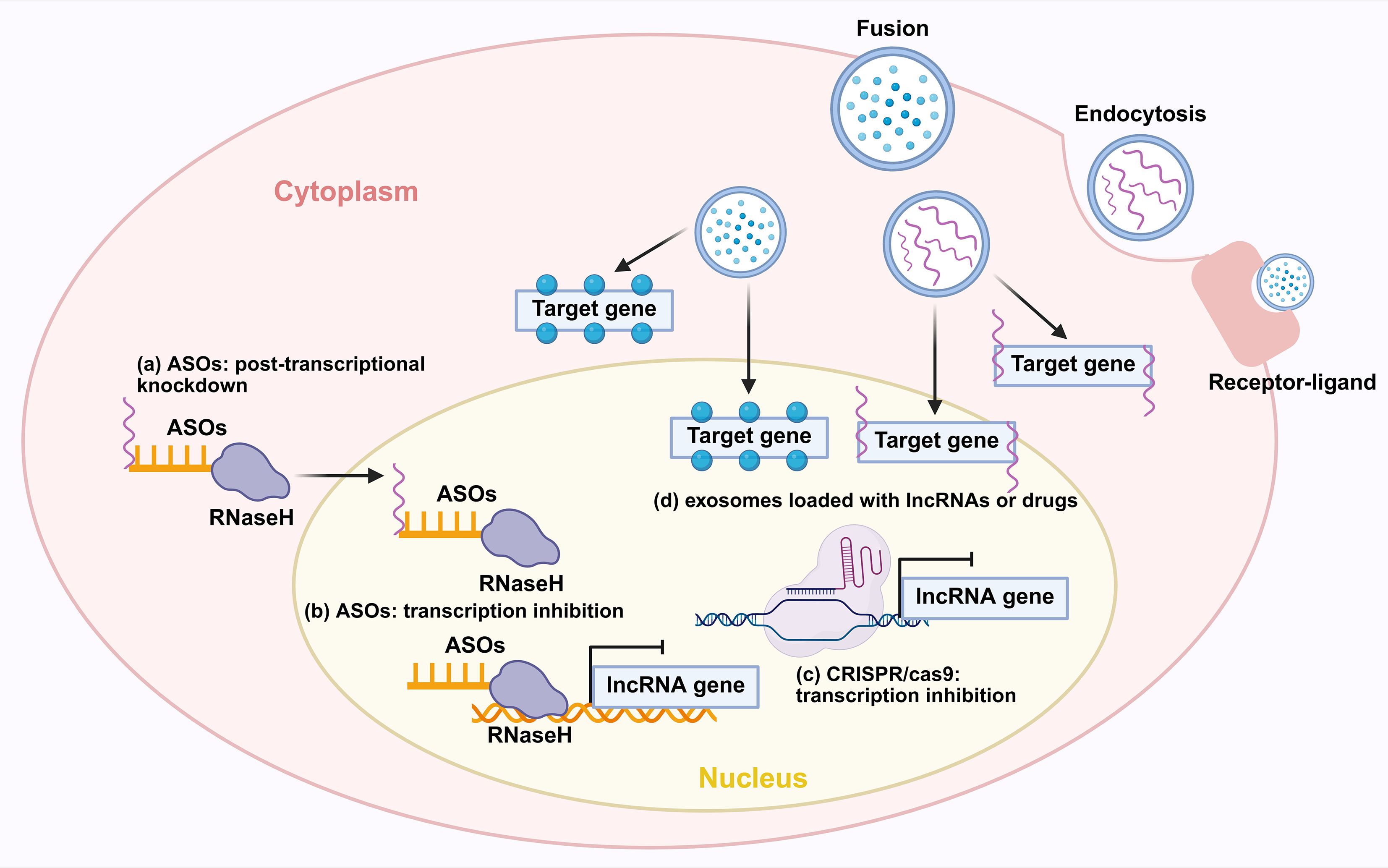
Figure 10. Novel therapeutic strategies for targeting lncRNAs. (a) ASOs exert effects through post-transcriptional knockdown via RNase H-mediated degradation of target lncRNAs. (b) ASOs inhibit transcription by interfering with the transcription of lncRNA genes. (c) CRISPR-Cas9 achieves transcriptional inhibition of lncRNA genes. (d) Exosomes loaded with lncRNAs or drugs can deliver therapeutic cargos. Exosomes can also be internalized into cells via receptor-ligand mediated endocytosis to modulate target genes. ASO, antisense oligonucleotide; RNaseH, Ribonuclease H.
ASOs represent a promising therapeutic strategy for targeting oncogenic lncRNAs. They function by binding to complementary RNA sequences through Watson-Crick base pairing, which subsequently recruits RNase H to degrade the target transcript. This mechanism offers high specificity and minimal off-target effects compared to conventional approaches. Furthermore, ongoing advancements are continuously improving the stability and delivery efficiency of ASO-based drugs (154). For instance, ASO-mediated knockdown of the oncogenic lncRNA MIR31HG reduces Treg-mediated immunosuppression and suppresses tumor growth (60). ASOs targeting the oncogenic lncRNA PKMYT1AR effectively suppressed tumor growth by modulating downstream signaling pathways (57). Similarly, ASO-mediated knockdown of ADPGK-AS1 reverses its pro-tumorigenic metabolic reprogramming of macrophages, shifting them from an M2 to a tumor-suppressive M1 phenotype and inhibiting lung tumor growth in vivo (41). Furthermore, by targeting the lncRNA HIF1A-AS2 with LNA GapmeR ASOs, researchers disrupted its double-positive feedback loop with MYC in KRAS-driven lung cancer. This intervention significantly inhibited tumor growth and enhanced the efficacy of both MYC inhibitors and cisplatin in patient-derived xenograft and transgenic mouse models (151). Currently, ASO-based therapeutics in lung cancer necessitate further exploration. However, with ongoing advancements in antisense oligonucleotide technology, research into their clinical application for lung cancer is anticipated to accelerate rapidly.
The CRISPR/Cas9 system offers a potent and definitive approach to target oncogenic lncRNAs in NSCLC. A key demonstration of this is the successful knockout (KO) of lncRNA THOR, which was achieved using a specific sgRNA in Cas9-expressing lung cancer cells. This genetic ablation disrupted the lnc-THOR/IGF2BP1 oncogenic axis, leading to the downregulation of key target mRNAs, and resulted in significantly suppressed tumor cell proliferation, migration, and increased apoptosis (152). In parallel, CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion of the hypoxia-regulated lncRNA nuclear LUCAT1 (NLUCAT1) robustly inhibited tumor aggressiveness. The knockout of NLUCAT1 not only attenuated cancer cell proliferation and invasion but also heightened oxidative stress and sensitized cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis, underscoring its role in regulating the cellular response to chemotherapy (153). Collectively, these studies demonstrate that CRISPR/Cas9 provides a precise and irreversible means to inactivate oncogenic lncRNAs, presenting a promising gene-editing approach for lung cancer therapy. However, notwithstanding its precision, the clinical translation of CRISPR/Cas9 is tempered by concerns over potential off-target effects, which could lead to unintended genomic alterations and serious consequences. Addressing these limitations is crucial for the safe and effective application of this technology in future cancer treatments (155).
Beyond direct RNA targeting, exosomes, which are nanoscale extracellular vesicles secreted by various cells, have emerged as a novel and promising delivery system for therapeutic agents. They function as natural mediators of intercellular communication by shuttling functional molecules, including proteins, lipids, mRNAs, and non-coding RNAs such as lncRNAs and miRNAs, and play pivotal roles in tumor pathogenesis and progression (156). Critically, exosomes exhibit higher safety and superior bioavailability compared to traditional synthetic vectors, making them an attractive platform for targeted therapy (157). Consequently, engineering exosomes to deliver specific drugs or therapeutic lncRNAs represents a highly promising frontier for developing next-generation targeted therapies in lung cancer.
The clinical potential of lncRNA modulation will likely be realized through its integration into multi-targeted regimens (158). Combining lncRNA-directed agents with immune checkpoint blockade, cellular therapies, or conventional treatments offers a pathway to disrupt synergistic immunosuppressive mechanisms and prevent adaptive resistance. Key to this approach will be a deeper mechanistic understanding of lncRNA function in the TME and the development of biomarkers to identify responsive patient populations (39). A critical aspect of this understanding involves deciphering the complex ceRNA networks, where lncRNAs function as molecular sponges to sequester miRNAs, thereby modulating the expression of downstream target genes involved in tumor progression and therapy resistance (159). Ultimately lncRNA modulation will enable more durable and adaptive treatment responses.
5 Conclusion and future perspectives
This review has synthesized current knowledge on the critical roles of lncRNAs in remodeling the TME of lung cancer. We have discussed how lncRNAs regulate the function and polarization of key immune cells including T cells, TAMs, MDSCs, TANs, as well as stromal components such as CAFs and CSCs. Additionally, we highlighted their influence on immune checkpoint expression, cytokine signaling, and chemokine activity, collectively shaping an immunosuppressive landscape that promotes tumor progression and therapy resistance. Furthermore, we explored the clinical applicability of these findings, emphasizing the potential of lncRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, as well as novel therapeutic targets to enhance the therapy efficacy in lung cancer.
While considerable progress has been made, future research should prioritize the following directions: (i) It is crucial to address fundamental questions in the field, including whether the emergence of oncogenic lncRNAs is a stochastic process and how to establish definitive causal relationships between lncRNAs and tumor progression (160). (ii) Elucidating the mechanisms governing lncRNA biogenesis, subcellular localization, and degradation, and critically reevaluating the prevalent ceRNA mechanism in light of insufficient stoichiometric relationships between lncRNAs and miRNAs (161, 162). (iii) Overcoming clinical obstacles, such as developing non-invasive detection methods, differentiating malignant from benign nodules, and identifying standardized lncRNA panels with reliable reference values (163). (iv) Leveraging advanced ex-vivo models like patient-derived organoids and engineered immune co-cultures to better dissect lncRNA functions in a humanized context, and exploring lncRNA-immune crosstalk to uncover novel combinatorial immunotherapies. (v) Exploring the crosstalk between lncRNAs and the immune system may uncover novel combinatorial immunotherapies that overcome resistance to existing checkpoint inhibitors.
Sustained research efforts are critical for unraveling the functional complexities of lncRNAs and translating these discoveries into effective clinical applications. Successful clinical implementation of lncRNA-based approaches will create new opportunities for precision medicine and ultimately yield improved therapeutic benefits against cancer.
Author contributions
XL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YR: Visualization, Writing – original draft. HH: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YJ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. BC: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. KZ: Writing – review & editing. YSJ: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. GC: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. ZH: Conceptualization, Investigation, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Open access funding provided by the Open Access Publishing Fund of Philipps-Universität Marburg.
Acknowledgments
The figures were created by the authors using BioRender.com under academic license.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Thai AA, Solomon BJ, Sequist L, Gainor JF, and Heist RS. Lung cancer. Lancet. (2021) 398:535–54. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00312-3
2. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca-a Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
3. Nicholson AG, Tsao MS, Beasley MB, Borczuk AC, Brambilla E, Cooper WA, et al. The 2021 WHO classification of lung tumors: impact of advances since 2015. J Thorac Oncol. (2022) 17:362–87. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.11.003
4. Detterbeck FC, Ostrowski M, Hoffmann H, Rami-Porta R, Osarogiagbon RU, Donnington J, et al. The international association for the study of lung cancer lung cancer staging project: proposals for revision of the classification of residual tumor after resection for the forthcoming (Ninth) edition of the TNM classification of lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. (2024) 19:1052–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2024.03.021
5. Mansouri S, Heylmann D, Stiewe T, Kracht M, and Savai R. Cancer genome and tumor microenvironment: Reciprocal crosstalk shapes lung cancer plasticity. Elife. (2022) 11:e79895. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79895
6. Grant C, Hagopian G, and Nagasaka M. Neoadjuvant therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2023) 190:104080. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2023.104080
7. Reck M, Remon J, and Hellmann MD. First-line immunotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:586–+. doi: 10.1200/jco.21.01497
8. Rizvi NA, Mazieres J, Planchard D, Stinchcombe TE, Dy GK, Antonia SJ, et al. Activity and safety of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor, for patients with advanced, refractory squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 063): a phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol. (2015) 16:257–65. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(15)70054-9
9. Chatterjee M, Turner DC, Felip E, Lena H, Cappuzzo F, Horn L, et al. Systematic evaluation of pembrolizumab dosing in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. (2016) 27:1291–8. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw174
10. Li G, Guo J, Zheng Y, Ding W, Han Z, Qin L, et al. CXCR5 guides migration and tumor eradication of anti-EGFR chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Mol Therapy-Oncolytics. (2021) 22:507–17. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.07.003
11. Jin M-Z and Jin W-L. The updated landscape of tumor microenvironment and drug repurposing. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2020) 5:166. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00280-x
12. Xiao Y and Yu D. Tumor microenvironment as a therapeutic target in cancer. Pharmacol Ther. (2021) 221:107753. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107753
13. Li T and Qiao T. Unraveling tumor microenvironment of small-cell lung cancer: Implications for immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol. (2022) 86:117–25. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.09.005
14. Wu T and Dai Y. Tumor microenvironment and therapeutic response. Cancer Lett. (2017) 387:61–8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.01.043
15. Chen B, Dragomir MP, Yang C, Li Q, Horst D, and Calin GA. Targeting non-coding RNAs to overcome cancer therapy resistance. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2022) 7:121. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00975-3
16. Nemeth K, Bayraktar R, Ferracin M, and Calin GA. Non-coding RNAs in disease: from mechanisms to therapeutics. Nat Rev Genet. (2024) 25:211–32. doi: 10.1038/s41576-023-00662-1
17. Chen L-L and Kim VN. Small and long non-coding RNAs: Past, present, and future. Cell. (2024) 187:6451–85. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.10.024
18. Dai S, Liu T, Liu YY, He Y, Liu T, Xu Z, et al. Long non-coding RNAs in lung cancer: the role in tumor microenvironment. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:795874. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.795874
19. Zhou L, Zhu Y, Sun D, and Zhang Q. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNAs in the tumor microenvironment. Int J Biol Sci. (2020) 16:2094–103. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.44420
20. Zhu L, Wu J, Gao H, Wang T, Xiao G, Hu C, et al. Tumor immune microenvironment-modulated nanostrategy for the treatment of lung cancer metastasis. Chin Med J (Engl). (2023) 136:2787–801. doi: 10.1097/cm9.0000000000002525
21. Sorin M, Rezanejad M, Karimi E, Fiset B, Desharnais L, Perus LJM, et al. Single-cell spatial landscapes of the lung tumour immune microenvironment. Nature. (2023) 614:548–+. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05672-3
22. Altorki NK, Markowitz GJ, Gao D, Port JL, Saxena A, Stiles B, et al. The lung microenvironment: an important regulator of tumour growth and metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. (2019) 19:9–31. doi: 10.1038/s41568-018-0081-9
23. Tanaka A and Sakaguchi S. Regulatory T cells in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. (2017) 27:109–18. doi: 10.1038/cr.2016.151
24. Yang Z, Guo J, Weng L, Tang W, Jin S, and Ma W. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells-new and exciting players in lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol. (2020) 13:10. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-0843-1
25. Aegerter H, Lambrecht BN, and Jakubzick CV. Biology of lung macrophages in health and disease. Immunity. (2022) 55:1564–80. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.08.010
26. Quail DF, Amulic B, Aziz M, Barnes BJ, Eruslanov E, Fridlender ZG, et al. Neutrophil phenotypes and functions in cancer: A consensus statement. J Exp Med. (2022) 219:e20220011. doi: 10.1084/jem.20220011
27. Rowbotham SP, Goruganthu MUL, Arasada RR, Wang WZ, Carbone DP, and Kim CF. Lung cancer stem cells and their clinical implications. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med. (2022) 12:a041270. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041270
28. Zhang H, Jiang H, Zhu L, Li J, and Ma S. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in non-small cell lung cancer: Recent advances and future perspectives. Cancer Lett. (2021) 514:38–47. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.05.009
29. Kalbasi A and Ribas A. Tumour-intrinsic resistance to immune checkpoint blockade. Nat Rev Immunol. (2020) 20:25–39. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0218-4
30. Konen JM, Wu H, and Gibbons DL. Immune checkpoint blockade resistance in lung cancer: emerging mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2024) 45:520–36. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2024.04.006
31. Essogmo FE, Zhilenkova AV, Tchawe YSN, Owoicho AM, Rusanov AS, Boroda A, et al. Cytokine profile in lung cancer patients: anti-tumor and oncogenic cytokines. Cancers. (2023) 15:5383. doi: 10.3390/cancers15225383
32. Khilwani R and Singh S. Systems biology and cytokines potential role in lung cancer immunotherapy targeting autophagic axis. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:2706. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102706
33. Wu Y and Zhou BP. TNF-α/NF-κB/Snail pathway in cancer cell migration and invasion. Br J Cancer. (2010) 102:639–44. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605530
34. Xu Z, Chen Y, Ma L, Chen Y, Liu J, Guo Y, et al. Role of exosomal non-coding RNAs from tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor microenvironment. Mol Ther. (2022) 30:3133–54. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.01.046
35. Zheng G, Ye H, Bai J, and Zhang X. Downregulation of lncRNA MIR17HG reduced tumorigenicity and Treg-mediated immune escape of non-small-cell lung cancer cells through targeting the miR-17-5p/RUNX3 axis. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. (2024) 38:e23715. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23715
36. Sun C-C, Zhu W, Li S-J, Hu W, Zhang J, Zhuo Y, et al. FOXC1-mediated LINC00301 facilitates tumor progression and triggers an immune-suppressing microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating the HIF1α pathway. Genome Med. (2020) 12:77. doi: 10.1186/s13073-020-00773-y
37. Huang D, Chen J, Yang L, Ouyang Q, Li J, Lao L, et al. NKILA lncRNA promotes tumor immune evasion by sensitizing T cells to activation-induced cell death. Nat Immunol. (2018) 19:1112–+. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0207-y
38. Li J, Che L, Xu C, Lu D, Xu Y, Liu M, et al. XIST/miR-34a-5p/PDL1 axis regulated the development of lung cancer cells and the immune function of CD8(+) T cells. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. (2022) 42:469–78. doi: 10.1080/10799893.2021.2019274
39. Shao F, Gao Y, Wang W, He H, Xiao L, Geng X, et al. Silencing EGFR-upregulated expression of CD55 and CD59 activates the complement system and sensitizes lung cancer to checkpoint blockade. Nat Cancer. (2022) 3:1192–+. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00444-4
40. Gao Y, Zhang N, Zeng Z, Wu Q, Jiang X, Li S, et al. LncRNA PCAT1 activates SOX2 and suppresses radioimmune responses via regulating cGAS/STING signalling in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Transl Med. (2022) 12:e792. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.792
41. Karger A, Mansouri S, Leisegang MS, Weigert A, Guenther S, Kuenne C, et al. ADPGK-AS1 long noncoding RNA switches macrophage metabolic and phenotypic state to promote lung cancer growth. EMBO J. (2023) 42:e111620. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022111620
42. Li Y, Chen C, Liu H-L, Zhang Z-F, and Wang C-L. LARRPM restricts lung adenocarcinoma progression and M2 macrophage polarization through epigenetically regulating LINC00240 and CSF1. Cell Mol Biol Lett. (2022) 27:91. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00376-y
43. Yin C, Li J, Li S, Yang X, Lu Y, Wang C, et al. LncRNA-HOXC-AS2 regulates tumor-associated macrophage polarization through the STAT1/SOCS1 and STAT1/CIITA pathways to promote the progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Signalling. (2024) 115:111031. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.111031
44. Guo J, Gong C, and Wang H. PURPL promotes M2 macrophage polarization in lung cancer by regulating RBM4/xCT signaling. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. (2024) 34:59–68. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2024052788
45. Li Z, Feng C, Guo J, Hu X, and Xie D. GNAS-AS1/miR-4319/NECAB3 axis promotes migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells by altering macrophage polarization. Funct Integr Genomics Jan. (2020) 20:17–28. doi: 10.1007/s10142-019-00696-x
46. Zhang F, Sang Y, Chen D, Wu X, Wang X, Yang W, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomal long non-coding RNA AGAP2-AS1 enhances radiotherapy immunity in lung cancer by reducing microRNA-296 and elevating NOTCH2. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:467. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03700-0
47. Zhang K, Chen J, Li C, Yuan Y, Fang S, Liu W, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of SNHG7 enhances docetaxel resistance in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. (2022) 526:142–54. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.10.029
48. Zhou DB, Xia Z, Xie MX, Gao Y, Yu Q, and He BM. Exosomal long non-coding RNA SOX2 overlapping transcript enhances the resistance to EGFR-TKIs in non-small cell lung cancer cell line H1975. Hum Cell. (2021) 34:1478–89. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00572-6
49. Martinez-Terroba E, Plasek-Hegde LM, Chiotakakos I, Li V, de Miguel FJ, Robles-Oteiza C, et al. Overexpression of Malat1 drives metastasis through inflammatory reprogramming of the tumor microenvironment. Sci Immunol. (2024) 9:eadh5462. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adh5462
50. Liang D-M, Li Y-J, Zhang J-X, Shen H-H, Wu C-X, Xie N, et al. m6A-methylated KCTD21-AS1 regulates macrophage phagocytosis through CD47 and cell autophagy through TIPR. Commun Biol. (2024) 7:215. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-05854-x
51. Wu Z, Bai X, Lu Z, Liu S, and Jiang H. LINC01094/SPI1/CCL7 axis promotes macrophage accumulation in lung adenocarcinoma and tumor cell dissemination. J Immunol Res. (2022) 2022:6450721. doi: 10.1155/2022/6450721
52. Tian X, Ma J, Wang T, Tian J, Zhang Y, Mao L, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOXA transcript antisense RNA myeloid-specific 1-HOXA1 axis downregulates the immunosuppressive activity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in lung cancer. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:473. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00473
53. Lu W, Cao F, Feng L, Song G, Chang Y, Chu Y, et al. LncRNA Snhg6 regulates the differentiation of MDSCs by regulating the ubiquitination of EZH2. J Hematol Oncol. (2021) 14:196. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01212-0
54. Hu S, Zhan N, Li J, Wang L, Liu Y, Jin K, et al. RBM15 recruits myeloid-derived suppressor cells via the m6A-IGF2BP3/CBR3-AS1/miR-409-3p/CXCL1 axis, facilitating radioresistance in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Trans Med. (2025) 23:191. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06205-y
55. Tian X, Ma J, Wang T, Tian J, Zheng Y, Peng R, et al. Long non-coding RNA RUNXOR accelerates MDSC-mediated immunosuppression in lung cancer. BMC Cancer. (2018) 18:660. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4564-6
56. Wang Y, Liu F, Chen L, Fang C, Li S, Yuan S, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) promote non-small cell lung cancer metastasis by suppressing lncRNA MIR503HG to activate the NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:867516. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.867516
57. He Y, Jiang X, Duan L, Xiong Q, Yuan Y, Liu P, et al. LncRNA PKMYT1AR promotes cancer stem cell maintenance in non-small cell lung cancer via activating Wnt signaling pathway. Mol Cancer. (2021) 20:156. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01469-6
58. Jiang P, Chen A, Wu X, Zhou M, Ul Haq I, Mariyam Z, et al. NEAT1 acts as an inducer of cancer stem cell-like phenotypes in NSCLC by inhibiting EGCG-upregulated CTR1. J Cell Physiol. (2018) 233:4852–63. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26288
59. Chen Z, Tang W, Zhou Y, and He Z. The role of LINC01419 in regulating the cell stemness in lung adenocarcinoma through recruiting EZH2 and regulating FBP1 expression. Biol Direct. (2022) 17:23. doi: 10.1186/s13062-022-00336-8
60. Chen W, Wang F, Yu X, Qi J, Dong H, Cui B, et al. LncRNA MIR31HG fosters stemness Malignant features of non-small cell lung cancer via H3K4me1- and H3K27Ace-mediated GLI2 expression. Oncogene. (2024) 43:1328–40. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02883-4
61. Wang X, Yu X, Wei W, and Liu Y. Long noncoding RNA MACC1-AS1 promotes the stemness of nonsmall cell lung cancer cells through promoting UPF1-mediated destabilization of LATS1/2. Environ Toxicol. (2020) 35:998–1006. doi: 10.1002/tox.22936
62. Liu Y, Yang Y, Zhang L, Lin J, Li B, Yang M, et al. LncRNA ASAP1-IT1 enhances cancer cell stemness via regulating miR-509-3p/YAP1 axis in NSCLC. Cancer Cell Int. (2021) 21:572. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02270-7
63. Gong W, Su Y, Liu Y, Sun P, and Wang X. Long non-coding RNA Linc00662 promotes cell invasion and contributes to cancer stem cell-like phenotypes in lung cancer cells. J Biochem. (2018) 164:461–9. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvy078
64. Zhao Y, Zhu Z, Shi S, Wang J, and Li N. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 regulates migration and invasion of lung cancer stem cells via miR-650/SLC34A2 axis. BioMed Pharmacother. (2019) 120:109457. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109457
65. Wang P, Zhang Y, Lv X, Zhou J, Cang S, and Song Y. LncRNA ADAMTS9-AS1 inhibits the stemness of lung adenocarcinoma cells by regulating miR-5009-3p/NPNT axis. Genomics. (2023) 115:110596. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2023.110596
66. Liu T, Han C, Fang P, Ma Z, Wang X, Chen H, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-specific lncRNA LINC01614 enhances glutamine uptake in lung adenocarcinoma. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:141. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01359-4
67. Enukashvily NII, Ponomartsev NVV, Ketkar A, Suezov R, Chubar AVV, Prjibelski ADD, et al. Pericentromeric satellite lncRNAs are induced in cancer-associated fibroblasts and regulate their functions in lung tumorigenesis. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:19. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05553-1
68. Chen J, Sun J-J, Ma Y-W, Zhu M-Q, Hu J, Lu Q-J, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts derived exosomal LINC01833 promotes the occurrence of non-small cell lung cancer through miR-335-5p-VAPA axis. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. (2024) 38:e23769. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23769
69. Sun Y, Hao G, Zhuang M, Lv H, Liu C, and Su K. MEG3 LncRNA from exosomes released from cancer-associated fibroblasts enhances cisplatin chemoresistance in SCLC via a MiR-15a-5p/CCNE1 axis. Yonsei Med J. (2022) 63:229–40. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2022.63.3.229
70. Wang PS, Liu Z, Sweef O, Saeed AF, Kluz T, Costa M, et al. Hexavalent chromium exposure activates the non-canonical nuclear factor kappa B pathway to promote immune checkpoint protein programmed death-ligand 1 expression and lung carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. (2024) 589:216827. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216827
71. Du Z, Niu S, Wang J, Wu J, Li S, and Yi X. SChLAP1 contributes to non-small cell lung cancer cell progression and immune evasion through regulating the AUF1/PD-L1 axis. Autoimmunity. (2021) 54:225–33. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2021.1913582
72. Sun Z, Mai H, Xue C, Fan Z, Li J, Chen H, et al. Hsa-LINC02418/mmu-4930573I07Rik regulated by METTL3 dictates anti-PD-L1 immunotherapeutic efficacy via enhancement of Trim21-mediated PD-L1 ubiquitination. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11:e007415. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007415
73. Qu S, Jiao Z, Lu G, Yao B, Wang T, Rong W, et al. PD-L1 lncRNA splice isoform promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression via enhancing c-Myc activity. Genome Biol. (2021) 22:104. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02331-0
74. Tang L, Wang T, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Zhao H, Wang H, et al. Long non-coding RNA AWPPH promotes postoperative distant recurrence in resected non-small cell lung cancer by upregulating transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1). Med Sci Monitor. (2019) 25:2535–41. doi: 10.12659/msm.912876
75. Xu L, Liu W, Li T, Hu Y, Wang Y, Huang L, et al. Long non-coding RNA SMASR inhibits the EMT by negatively regulating TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in lung cancer. Oncogene. (2021) 40:3578–92. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01760-2
76. Huang L, Liu X, Chen Q, Yang J, Zhang D, Zhao Y, et al. TGF-β-induced lncRNA TBUR1 promotes EMT and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma via hnRNPC-mediated GRB2 mRNA stabilization. Cancer Lett. (2024) 600:217153. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217153
77. Zhang T, Xia W, Song X, Mao Q, Huang X, Chen B, et al. Super-enhancer hijacking LINC01977 promotes Malignancy of early-stage lung adenocarcinoma addicted to the canonical TGF-β/SMAD3 pathway. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:114. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01331-2
78. Lu Z, Li Y, Che Y, Huang J, Sun S, Mao S, et al. The TGFβ-induced lncRNA TBILA promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression in vitro and in vivo via cis-regulating HGAL and activating S100A7/JAB1 signaling. Cancer Lett. (2018) 432:156–68. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.06.013
79. Fan C, González-Prieto R, Kuipers TB, Vertegaal ACO, van Veelen PA, Mei H, et al. The lncRNA LETS1 promotes TGF-β-induced EMT and cancer cell migration by transcriptionally activating a TβR1-stabilizing mechanism. Sci Signal. (2023) 16:eadf1947. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.adf1947
80. Jiang L, Wang R, Fang L, Ge X, Chen L, Zhou M, et al. HCP5 is a SMAD3-responsive long non-coding RNA that promotes lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via miR-203/SNAI axis. Theranostics. (2019) 9:2460–74. doi: 10.7150/thno.31097
81. Sakai S, Ohhata T, Kitagawa K, Uchida C, Aoshima T, Niida H, et al. Long noncoding RNA ELIT-1 acts as a Smad3 cofactor to facilitate TGFβ/Smad signaling and promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. (2019) 79:2821–38. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-18-3210
82. Jiang L, Xie X, Bi R, Ding F, and Mei J. Knockdown of Linc00511 inhibits TGF-β-induced cell migration and invasion by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and down-regulating MMPs expression. BioMed Pharmacother. (2020) 125:109049. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109049
83. Li C, Wan L, Liu Z, Xu G, Wang S, Su Z, et al. Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating miR-367/141-ZEB2 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. (2018) 418:185–95. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.01.036
84. Wu S, Liu B, Zhang Y, Hong R, Liu S, Xiang T, et al. Long non-coding RNA LEISA promotes progression of lung adenocarcinoma via enhancing interaction between STAT3 and IL-6 promoter. Oncogene. (2021) 40:3449–59. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01769-7
85. Chen QN, Chen X, Chen ZY, Nie FQ, Wei CC, Ma HW, et al. Long intergenic non-coding RNA 00152 promotes lung adenocarcinoma proliferation via interacting with EZH2 and repressing IL24 expression. Mol Cancer. (2017) 16:17. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0581-3
86. Dong Y, Sun N, Qiang Y, Wang Y, Yuan Y, and Li M. TNF-α inhibites non-small cell lung cancer cells proliferation by targeting THRIL in an FTO-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Arch Biochem Biophys. (2025) 770:110438. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2025.110438
87. Reina-Campos M, Scharping NE, and Goldrath AW. CD8+ T cell metabolism in infection and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. (2021) 21:718–38. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00537-8
88. Li W, Wang X, Li C, Chen T, and Yang Q. Exosomal non-coding RNAs: Emerging roles in bilateral communication between cancer cells and macrophages. Mol Ther. (2022) 30:1036–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.12.002
89. Li M, Yang Y, Xiong L, Jiang P, Wang J, and Li C. Metabolism, metabolites, and macrophages in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. (2023) 16:80. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01478-6
90. Karger A, Nandigama R, Stenzinger A, Grimminger F, Pullamsetti SS, Seeger W, et al. Hidden treasures: macrophage long non-coding RNAs in lung cancer progression. Cancers. (2021) 13:4127. doi: 10.3390/cancers13164127
91. Qiao X, Ding Y, Wu D, Zhang A, Yin Y, Wang Q, et al. The roles of long noncoding RNA-mediated macrophage polarization in respiratory diseases. Front Immunol. (2023) 13:1110774. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1110774
92. Lai X, Zhong J, Zhang B, Zhu T, and Liao R. Exosomal non-coding RNAs: novel regulators of macrophage-linked intercellular communication in lung cancer and inflammatory lung diseases. Biomolecules. (2023) 13:536. doi: 10.3390/biom13030536
93. Liu Y, Han Y, Zhang Y, Lv T, Peng X, and Huang J. LncRNAs has been identified as regulators of Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in lung cancer. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1067520. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1067520
94. Zhou Q, Tang X, Tian X, Tian J, Zhang Y, Ma J, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 negatively regulates MDSCs in patients with lung cancer. J Cancer. (2018) 9:2436–42. doi: 10.7150/jca.24796
95. Hedrick CC and Malanchi I. Neutrophils in cancer: heterogeneous and multifaceted. Nat Rev Immunol. (2022) 22:173–87. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00571-6
96. Cools-Lartigue J, Spicer J, Najmeh S, and Ferri L. Neutrophil extracellular traps in cancer progression. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2014) 71:4179–94. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1683-3
97. Lin H, Li P, Zhang N, Cao L, Gao YF, and Ping F. Long non-coding RNA MIR503HG serves as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer mediated by wnt1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2019) 23:10818–26. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201912_19785
98. Ye X, Fang C, Hong W, Qian X, Yu B, Zhou B, et al. LncRNA MIR503HG regulates NETs-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation and NSCLC metastasis by enhancing the ubiquitination of C/EBPβ. Clin Trans Med. (2025) 15:e70342. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70342
99. Chu X, Tian W, Ning J, Xiao G, Zhou Y, Wang Z, et al. Cancer stem cells: advances in knowledge and implications for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:170. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01851-y
100. Yang D, Liu J, Qian H, and Zhuang Q. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: from basic science to anticancer therapy. Exp Mol Med. (2023) 55:1322–32. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01013-0
101. Zhao L, Ji G, Le X, Wang C, Xu L, Feng M, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00092 acts in cancer-associated fibroblasts to drive glycolysis and progression of ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:1369–82. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-16-1615
102. Ding L, Ren J, Zhang D, Li Y, Huang X, Hu Q, et al. A novel stromal lncRNA signature reprograms fibroblasts to promote the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma via LncRNA-CAF/interleukin-33. Carcinogenesis. (2018) 39:397–406. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgy006
103. Lin A, Hu Q, Li C, Xing Z, Ma G, Wang C, et al. The LINK-A lncRNA interacts with PtdIns(3,4,5)P(3) to hyperactivate AKT and confer resistance to AKT inhibitors. Nat Cell Biol. (2017) 19:238–51. doi: 10.1038/ncb3473
104. Yang P, Ding J, Bian Y, Ma Z, Wang K, and Li J. Long non-coding RNAs and cancer mechanisms: Immune cells and inflammatory cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. Med Oncol. (2022) 39:108. doi: 10.1007/s12032-022-01680-5
105. Papoutsoglou P and Moustakas A. Long non-coding RNAs and TGF-β signaling in cancer. Cancer Sci. (2020) 111:2672–81. doi: 10.1111/cas.14509
106. Li J, Shen C, Wang X, Lai Y, Zhou K, Li P, et al. Prognostic value of TGF-β in lung cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. (2019) 19:691. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5917-5
108. Lai XN, Li J, Tang LB, Chen WT, Zhang L, and Xiong LX. MiRNAs and lncRNAs: dual roles in TGF-β Signaling-regulated metastasis in lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:1193. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041193
109. Aftabi S, Behrooz AB, Cordani M, Rahiman N, Sadeghdoust M, Aligolighasemabadi F, et al. Therapeutic targeting of TGF-β in lung cancer. FEBS J. (2025) 292:1520–57. doi: 10.1111/febs.17234
110. Casey TM, Eneman J, Crocker A, White J, Tessitore J, Stanley M, et al. Cancer associated fibroblasts stimulated by transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta 1) increase invasion rate of tumor cells: a population study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2008) 110:39–49. doi: 10.1007/s10549-007-9684-7
111. Saito A, Horie M, and Nagase T. TGF-β Signaling in lung health and disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:2460. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082460
112. Suri C, Swarnkar S, Bhaskar L, and Verma HK. Non-coding RNA as a biomarker in lung cancer. Noncoding RNA. (2024) 10:50. doi: 10.3390/ncrna10050050
113. Cao Z, Oyang L, Luo X, Xia L, Hu J, Lin J, et al. The roles of long non-coding RNAs in lung cancer. J Cancer. (2022) 13:174–83. doi: 10.7150/jca.65031
114. Li W, Liu J-B, Hou L-K, Yu F, Zhang J, Wu W, et al. Liquid biopsy in lung cancer: significance in diagnostics, prediction, and treatment monitoring. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:25. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01505-z
115. Arbour KC and Riely GJ. Systemic therapy for locally advanced and metastatic non-small cell lung cancer A review. Jama-Journal Am Med Assoc. (2019) 322:764–74. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.11058
116. Liu W, Zuo B, Liu W, Huo Y, Zhang N, and Yang M. Long non-coding RNAs in non-small cell lung cancer: implications for preventing therapeutic resistance. Biochim Et Biophys Acta-Reviews Cancer. (2023) 1878:188982. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188982
117. Tantai J, Hu D, Yang Y, and Geng J. Combined identification of long non-coding RNA XIST and HIF1A-AS1 in serum as an effective screening for non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2015) 8:7887–95.
118. Yang Q, Kong S, Zheng M, Hong Y, Sun J, Ming X, et al. Long intergenic noncoding RNA LINC00173 as a potential serum biomarker for diagnosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Biomarkers. (2020) 29:441–51. doi: 10.3233/cbm-201616
119. Gupta C, Su J, Zhan M, Stass SA, and Jiang F. Sputum long non-coding RNA biomarkers for diagnosis of lung cancer. Cancer Biomarkers. (2019) 26:219–27. doi: 10.3233/cbm-190161
120. Lin Q, Xie D, Pan L, Lou Y, and Shi M. Urinary exosomal long noncoding RNAs serve as biomarkers for early detection of non-small cell lung cancer. Biosci Rep. (2021) 41:BSR20210908. doi: 10.1042/bsr20210908
121. Lv P, Yang S, Liu W, Qin H, Tang X, Wu F, et al. Circulating plasma lncRNAs as novel markers of EGFR mutation status and monitors of epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Thorac Cancer. (2020) 11:29–40. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13216
122. Tang Z, Wang Q, Chen P, Guo H, Shi J, Pan Y, et al. Computational recognition of LncRNA signatures in tumor-associated neutrophils could have implications for immunotherapy and prognostic outcome of non-small cell lung cancer. Front Genet. (2022) 13:1002699. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1002699
123. Fang C, Liu F, Wang Y, Yuan S, Chen R, Qiu X, et al. A innovative prognostic symbol based on neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs)-related lncRNA signature in non-small-cell lung cancer. Aging (Albany NY). (2021) 13:17864–79. doi: 10.18632/aging.203289
124. Sun J, Zhang Z, Bao S, Yan C, Hou P, Wu N, et al. Identification of tumor immune infiltration-associated lncRNAs for improving prognosis and immunotherapy response of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2020) 8:e000110. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000110
125. Zhu J, Cao K, Zhang P, and Ma J. LINC00669 promotes lung adenocarcinoma growth by stimulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:9005–23. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5604
126. Shan H, Wang X, Yin F, Zhou Y, Mao L, Zhu X, et al. Combination of transcriptome and Mendelian inheritance reveals novel prognostic biomarker of CTLA-4-related lncRNAs and protective role of nitrogen metabolism pathway in lung adenocarcinoma development. BMC Cancer. (2024) 24:1009. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12777-7
127. Ao YQ, Gao J, Jiang JH, Wang HK, Wang S, and Ding JY. Comprehensive landscape and future perspective of long noncoding RNAs in non-small cell lung cancer: it takes a village. Mol Ther. (2023) 31:3389–413. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.09.015
128. Pang Z, Chen X, Wang Y, Wang Y, Yan T, Wan J, et al. Long non-coding RNA C5orf64 is a potential indicator for tumor microenvironment and mutation pattern remodeling in lung adenocarcinoma. Genomics. (2021) 113:291–304. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.12.010
129. Ali MM, Di Marco M, Mahale S, Jachimowicz D, Kosalai ST, Reischl S, et al. LY6K-AS lncRNA is a lung adenocarcinoma prognostic biomarker and regulator of mitotic progression. Oncogene. (2021) 40:2463–78. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01696-7
130. Peng L, Chen Z, Chen Y, Wang X, and Tang N. MIR155HG is a prognostic biomarker and associated with immune infiltration and immune checkpoint molecules expression in multiple cancers. Cancer Med. (2019) 8:7161–73. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2583
131. Herzog BH, Devarakonda S, and Govindan R. Overcoming chemotherapy resistance in SCLC. J Thorac Oncol. (2021) 16:2002–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.07.018
132. Rotow J and Bivona TG. Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat Rev Cancer. (2017) 17:637–58. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.84
133. Ge X, Shen Z, and Yin Y. Comprehensive review of LncRNA-mediated therapeutic resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell Int. (2024) 24:369. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03549-1
134. Li S, Lv J, Li Z, Zhang Q, Lu J, Huo X, et al. Overcoming multi-drug resistance in SCLC: a synergistic approach with venetoclax and hydroxychloroquine targeting the lncRNA LYPLAL1-DT/BCL2/BECN1 pathway. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:243. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02145-1
135. Tao X, Li Y, Fan S, Wu L, Xin J, Su Y, et al. Downregulation of Linc00173 increases BCL2 mRNA stability via the miR-1275/PROCA1/ZFP36L2 axis and induces acquired cisplatin resistance of lung adenocarcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 42:12. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02560-6
136. Zhang W, Li L, Yang G, Li C, Deng X, Huang X, et al. Investigating the mechanism of β-elemene-mediated LINC00511 modulation to suppress cisplatin resistance in lung cancer. J Vis Exp. (2025) (222):10.3791/68825. doi: 10.3791/68825
137. Jiang M, Qi F, Zhang K, Zhang X, Ma J, Xia S, et al. MARCKSL1–2 reverses docetaxel-resistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells by recruiting SUZ12 to suppress HDAC1 and elevate miR-200b. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:150. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01605-w
138. Dai J, Qu T, Yin D, Cui Y, Zhang C, Zhang E, et al. LncRNA LINC00969 promotes acquired gefitinib resistance by epigenetically suppressing of NLRP3 at transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels to inhibit pyroptosis in lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:312. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05840-x
139. Fang Z, Chen W, Yuan Z, Liu X, and Jiang H. LncRNA-MALAT1 contributes to the cisplatin-resistance of lung cancer by upregulating MRP1 and MDR1 via STAT3 activation. BioMed Pharmacother. (2018) 101:536–42. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.130
140. Horinouch H. Precision radiotherapy for patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the era of immunotherapy and precision medicine. Trans Lung Cancer Res. (2018) 7:S146–8. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2018.03.13
141. Barker HE, Paget JTE, Khan AA, and Harrington KJ. The tumour microenvironment after radiotherapy: mechanisms of resistance and recurrence. Nat Rev Cancer. (2015) 15:409–25. doi: 10.1038/nrc3958
142. Jiang G, Yu H, Li Z, and Zhang F. lncRNA cytoskeleton regulator reduces non-small cell lung cancer radiosensitivity by downregulating miRNA-206 and activating prothymosin α. Int J Oncol. (2021) 59:88. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5268
143. Yu Z, Wang G, Zhang C, Liu Y, Chen W, Wang H, et al. LncRNA SBF2-AS1 affects the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer via modulating microRNA-302a/MBNL3 axis. Cell Cycle. (2020) 19:300–16. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1708016
144. Yang Y, Li Z, Yu X, Zheng Y, Yu Y, Yang M, et al. WDR11-DT enhances radiosensitivity via promoting PARP1 degradation and homologous recombination deficiency. Cancer Lett. (2025) 625:217757. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217757
145. Liu S, Zhan N, Gao C, Xu P, Wang H, Wang S, et al. Long noncoding RNA CBR3-AS1 mediates tumorigenesis and radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer through redox and DNA repair by CBR3-AS1/miR-409-3p/SOD1 axis. Cancer Lett. (2022) 526:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.11.009
146. He H, Song X, Yang Z, Mao Y, Zhang K, Wang Y, et al. Upregulation of KCNQ1OT1 promotes resistance to stereotactic body radiotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma by inducing ATG5/ATG12-mediated autophagy via miR-372-3p. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:883. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03083-8
147. Zhang M, Gao C, Yang Y, Li G, Dong J, Ai Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA CRNDE/PRC2 participated in the radiotherapy resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma through targeting p21 expression. Oncol Res. (2018) 26:1245–55. doi: 10.3727/096504017x14944585873668
148. Xue Y, Ni T, Jiang Y, and Li Y. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 inhibits tumorigenesis and enhances radiosensitivity by suppressing miR-135b expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Res. (2017) 25:1305–16. doi: 10.3727/096504017x14850182723737
149. Coan M, Haefliger S, Ounzain S, and Johnson R. Targeting and engineering long non-coding RNAs for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Genet. (2024) 25:578–95. doi: 10.1038/s41576-024-00693-2
150. Bridges MC, Daulagala AC, and Kourtidis A. LNCcation: lncRNA localization and function. J Cell Biol. (2021) 220:e202009045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202009045
151. Yang K, Zhang W, Zhong L, Xiao Y, Sahoo S, Fassan M, et al. Long non-coding RNA HIF1A-As2 and MYC form a double-positive feedback loop to promote cell proliferation and metastasis in KRAS-driven non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Differ Jun. (2023) 30:1533–49. doi: 10.1038/s41418-023-01160-x
152. Jiao PF, Tang PJ, Chu D, Li YM, Xu WH, and Ren GF. Long non-coding RNA THOR depletion inhibits human non-small cell lung cancer cell growth. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:756148. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.756148
153. Leon LM, Gautier M, Allan R, Ilié M, Nottet N, Pons N, et al. The nuclear hypoxia-regulated NLUCAT1 long non-coding RNA contributes to an aggressive phenotype in lung adenocarcinoma through regulation of oxidative stress. Oncogene. (2019) 38:7146–65. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-0935-y
154. Chen YY, Li ZJ, Chen XG, and Zhang S. Long non-coding RNAs: From disease code to drug role. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2021) 11:340–54. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.10.001
155. Wang S-W, Gao C, Zheng Y-M, Yi L, Lu J-C, Huang X-Y, et al. Current applications and future perspective of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing in cancer. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:57. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01518-8
156. Wang R, Xu Y, Tong L, Zhang X, and Zhang S. Recent progress of exosomal lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in lung cancer: implication for clinical application. Front Mol Biosci. (2024) 11:1417306. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1417306
157. Xu K, Zhang C, Du T, Gabriel ANA, Wang X, Li X, et al. Progress of exosomes in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 134:111111. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111111
158. Esposito R, Polidori T, Meise DF, Pulido-Quetglas C, Chouvardas P, Forster S, et al. Multi-hallmark long noncoding RNA maps reveal non-small cell lung cancer vulnerabilities. Cell Genomics. (2022) 2:100171. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2022.100171
159. Wang XW, Guo QQ, Wei Y, Ren KM, Zheng FS, Tang J, et al. Construction of a competing endogenous RNA network using differentially expressed lncRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs in non−small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep. (2019) 42:2402–15. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7378
160. Sholl LM, Hirsch FR, Hwang D, Botling J, Lopez-Rios F, Bubendorf L, et al. The promises and challenges of tumor mutation burden as an immunotherapy biomarker: A perspective from the international association for the study of lung cancer pathology committee. J Thorac Oncol. (2020) 15:1409–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2020.05.019
161. Seo D, Kim D, Chae Y, and Kim W. The ceRNA network of lncRNA and miRNA in lung cancer. Genomics Inform. (2020) 18:e36. doi: 10.5808/GI.2020.18.4.e36
162. Zhang C, Zhou Y, Zhang B, Sheng Z, Sun N, Yuan B, et al. Identification of lncRNA, miRNA and mRNA expression profiles and ceRNA Networks in small cell lung cancer. BMC Genomics. (2023) 24:217. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09306-4
Keywords: long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), lung cancer, tumor microenvironment (TME), biomarkers, therapy resistance
Citation: Li X, Ren Y, Hao H, Jin Y, Chen B, Zhao K, Ji Y, Chen G and He Z (2025) Long non-coding RNAs as key orchestrators of the tumor microenvironment in lung cancer. Front. Immunol. 16:1716180. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1716180
Received: 30 September 2025; Accepted: 18 November 2025; Revised: 06 November 2025;
Published: 02 December 2025.
Edited by:
Radu Pîrlog, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Iuliu Hatieganu, RomaniaReviewed by:
Noha Mousaad Elemam, University of Sharjah, United Arab EmiratesHuacheng Luo, The Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Copyright © 2025 Li, Ren, Hao, Jin, Chen, Zhao, Ji, Chen and He. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhenglin He, bGlvdXNoZUAxMjYuY29t; Guanyu Chen, Z3Vhbnl1LmNoZW5AdW5pLW1hcmJ1cmcuZGU=
 Xuechao Li1,2
Xuechao Li1,2 Yifei Ren
Yifei Ren Kai Zhao
Kai Zhao Guanyu Chen
Guanyu Chen Zhenglin He
Zhenglin He