- Laboratory of Molecular Immunology, Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Transplantation, Rega Institute, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
The resolution of inflammation is an active, tightly regulated process essential for restoring tissue homeostasis after an inflammatory process. While chemokines are classically recognized for their roles in leukocyte recruitment and immune cell positioning during the onset of inflammation, emerging evidence highlights their pivotal functions in orchestrating the resolution phase, as well. The chemokine system contributes to inflammation resolution through several complementary mechanisms, including the depletion of pro-inflammatory chemokines, the generation of autoantibodies, the promotion of neutrophil reverse migration, the recruitment and polarization of pro-resolving immune cells such as macrophages and regulatory T cells, and the induction of tissue repair and disease recovery. Modulating chemokine-receptor interactions, enhancing the activity of pro-resolving chemokines, or blocking detrimental chemokine signaling pathways represent promising strategies for the treatment of excessive inflammation or chronic inflammatory diseases. In addition, modulation of glycosaminoglycan interactions or chemokine-modifying enzymes, might also be useful in this context. In this review, we explore the roles of chemokines in resolution, with a focus on their mechanistic contributions to immune modulation and their potential as therapeutic targets for restoring immune balance.
Introduction
Resolution of inflammation
Resolution of inflammation is a highly coordinated process that restores tissue homeostasis after an inflammatory response. This process is not a passive stop of inflammation but involves a dynamic shift in cellular and molecular mechanisms to counterbalance the pro-inflammatory phase (1). Effective resolution requires the termination of inflammatory signaling, the removal of pro-inflammatory immune cells and debris, and the initiation of tissue repair pathways. Failure in the resolution of inflammation can lead to chronic inflammation, fibrosis, and/or autoimmunity (2). One of the first steps in resolution is the decrease in production of pro-inflammatory mediators, including cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6, as well as lipid mediators such as leukotrienes and prostaglandins. Simultaneously, neutrophil recruitment is ceased. Those neutrophils already present in inflamed tissues either go into apoptosis or may acquire anti-inflammatory properties, due to the production of vesicles that suppress complement activation, decreasing further neutrophil recruitment and reducing tissue damage (3). Eventually, apoptotic neutrophils in the tissue are cleared by macrophages in a process called efferocytosis, which not only removes cellular debris but also actively promotes the transition to a pro-resolving environment by triggering macrophage reprogramming toward an anti-inflammatory and tissue-repair phenotype (4–7). The subsequent cascade of pro-resolving responses involves a coordinated network of signaling events that collectively suppress inflammation and restore tissue homeostasis. Upon engulfing apoptotic neutrophils, macrophages undergo metabolic and transcriptional reprogramming characterized by increased production of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), as well as the downregulation of pro-inflammatory mediators (8, 9). This reprogramming not only limits further leukocyte recruitment but also fosters tissue regeneration by stimulating fibroblast activation, angiogenesis, and matrix remodeling (10, 11). In this way, the clearance of apoptotic neutrophils serves as a central turning point that transforms the inflammatory environment into one conducive to resolution and repair.
Among the cells involved in the resolution of inflammation, macrophages play an essential and multifaceted role. They originate from two major ontogenic sources: tissue-resident macrophages, arising from embryonic hematopoietic progenitors, and monocyte-derived macrophages, which develop from circulating monocytes during inflammation. This distinction is crucial, as tissue-resident macrophages are generally anti-inflammatory, maintaining homeostasis by constantly clearing apoptotic cells, which imprints a tolerogenic and anti-inflammatory phenotype (12, 13). In contrast, monocyte-derived macrophages are typically pro-inflammatory during the acute phase of inflammation, but can transition toward a pro-resolving phenotype as the inflammatory response subsides (14).
Besides the already mentioned efferocytosis, macrophages contribute to the production of pro-resolving mediators, including specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators (SPMs) such as resolvins, maresins, and protectins. Their synthesis can be stimulated by apoptotic bodies, extracellular vesicles from the microenvironment or through trans-cellular biosynthesis in cooperation with other cells. These mediators collectively facilitate the resolution of inflammation and promote tissue repair (4, 15–18). Additionally, by responding to signals from the environment, macrophages undergo polarization toward an anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving phenotype, commonly categorized as M2 macrophages (9, 19–21). A key feature of M2 macrophages is their expression of scavenger receptors such as CD163, CD206, and MerTK, which enhance their ability to clear apoptotic cells and diminish inflammation (4–6). Although the M1/M2 classification is widely used, it presents clear limitations. Transcriptomic analyses of murine macrophages revealed that macrophages associated with resolution exhibit a distinct genetic signature compared to conventional M2 macrophages. For instance, ccl5 transcripts are enriched, suggesting a specific role for this chemokine in the resolution process. This study also highlighted the differences between the cells polarized in vitro with defined cytokine stimuli and in situ macrophages (22). Thus, the proposed subdivision of M2 macrophages into additional subtypes remains controversial, and studies examining chemokines and their receptors in the context of macrophage polarization and resolution often fail to differentiate among various pro-resolving populations (23, 24). Therefore, we chose to maintain the simplified M1/M2 nomenclature, as further subdivision into M2 subtypes could introduce unnecessary complexity and potential confusion.
Besides macrophages, other cell types contribute to resolution of inflammation. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) secrete IL-10 and TGF-β, further dampening inflammation and supporting tissue repair. Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs), B cells and mesenchymal stromal cells also release pro-resolving mediators that modulate immune responses and prevent chronic inflammation (25–27). Additionally, endothelial cells and fibroblasts play a role in restoring vascular integrity and extracellular matrix homeostasis.
In summary, resolution of inflammation is a well-orchestrated process involving not only the cessation of pro-inflammatory responses but also the active engagement of cellular and molecular pathways that promote healing. The balance between pro-inflammatory and pro-resolving signals is crucial, making the study of resolution mechanisms highly relevant for the development of therapeutic strategies for treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
Chemokine system
Chemokines, or chemotactic cytokines, are a family of relatively small secreted proteins that signal through G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and are structurally characterized by the presence of four conserved cysteine residues (28, 29). The hallmark function of chemokines is to induce and guide the directional movement of cells, especially leukocytes. Additionally, chemokines trigger the activation of integrins and initiate effector functions in the target cells, e.g., the release of granules by polymorphonuclear cells, or influence cell survival (30). Therefore, chemokines are important in inflammation, but specific chemokines also act in homeostasis, angiogenesis, and embryogenesis (31–33). Based on the position of the cysteine residues in the N-terminal region of their sequence, chemokines are classified into 4 subfamilies (1): CC chemokines have two adjacent N-terminal cysteines (2), CXC chemokines present one amino acid between the two first cysteines (3), the CX3C chemokine has 3 amino acids between the two first cysteines, and (4) C chemokines possess only one of the usually conserved N-terminal cysteines. The CXC chemokine subfamily can be further subclassified into Glu-Leu-Arg (ELR)+ and ELR- CXC chemokines. The ELR+ CXC chemokines are associated with neutrophil recruitment, signal through chemokine receptors CXCR1 and/or CXCR2 and in humans include CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL5, CXCL6, CXCL7, and CXCL8 (34, 35).
Chemokine receptors
In addition to GPCRs, chemokines can bind to atypical chemokine receptors (ACKR) (36) and glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) (37). Chemokine-binding GPCRs are classified as CCR, CXCR, CX3CR, and XCR according to the cysteine motif in their ligands (38, 39). Interestingly, one chemokine sometimes binds different receptors and one receptor may transduce signals upon engagement of distinct ligands. These interactions elucidate apparent bias in the chemokine system, which allows us to understand how one chemokine might promote different responses in different contexts (40, 41). A GPCR consists of a single polypeptide chain that is folded into a globular shape and anchored in the cell’s membrane. These receptors possess seven transmembrane helices, three extra-cellular and three intra-cellular loops. Chemokines typically interact with two interaction sites on their receptors. One being the extracellular N-terminal part of the receptor and a second in a pocket more buried inside the receptor. The extracellular loops together with residues in the transmembrane domains form these chemokine binding pockets. Binding of chemokines in those pockets induces intracellular signaling by second messengers such as calcium, cyclic adenosine monophosphate, and GTPases (42, 43).
Currently, there are 20 identified conventional chemokine receptors, and they are widely expressed in leukocytes (Figure 1) (39, 44, 45). During inflammation, chemokines orchestrate leukocyte trafficking, guiding cells to sites of injury or infection. Although often discussed in simplified terms, most chemokine receptors exhibit pleiotropic and context-dependent functions that extend beyond mere recruitment. Briefly, CXCR1 and CXCR2 for instance, are predominantly associated with neutrophil recruitment and activation, yet they also participate in angiogenesis, epithelial regeneration, and tumor biology; CXCR3 is largely expressed on activated T cells and NK cells, where it mediates effector cell migration to inflamed tissues. However, the ligands of CXCR3 have been shown to downregulate angiogenic processes (46). CXCR4 plays multifaceted roles including progenitor cell retention in the bone marrow, T and B cell homing to secondary lymphoid organs, regulation of dendritic cell migration, and guidance of hematopoietic and endothelial precursors. Similarly, CXCR5 is critical for the positioning of B cells within germinal centers and for T follicular helper cell localization (34, 39).
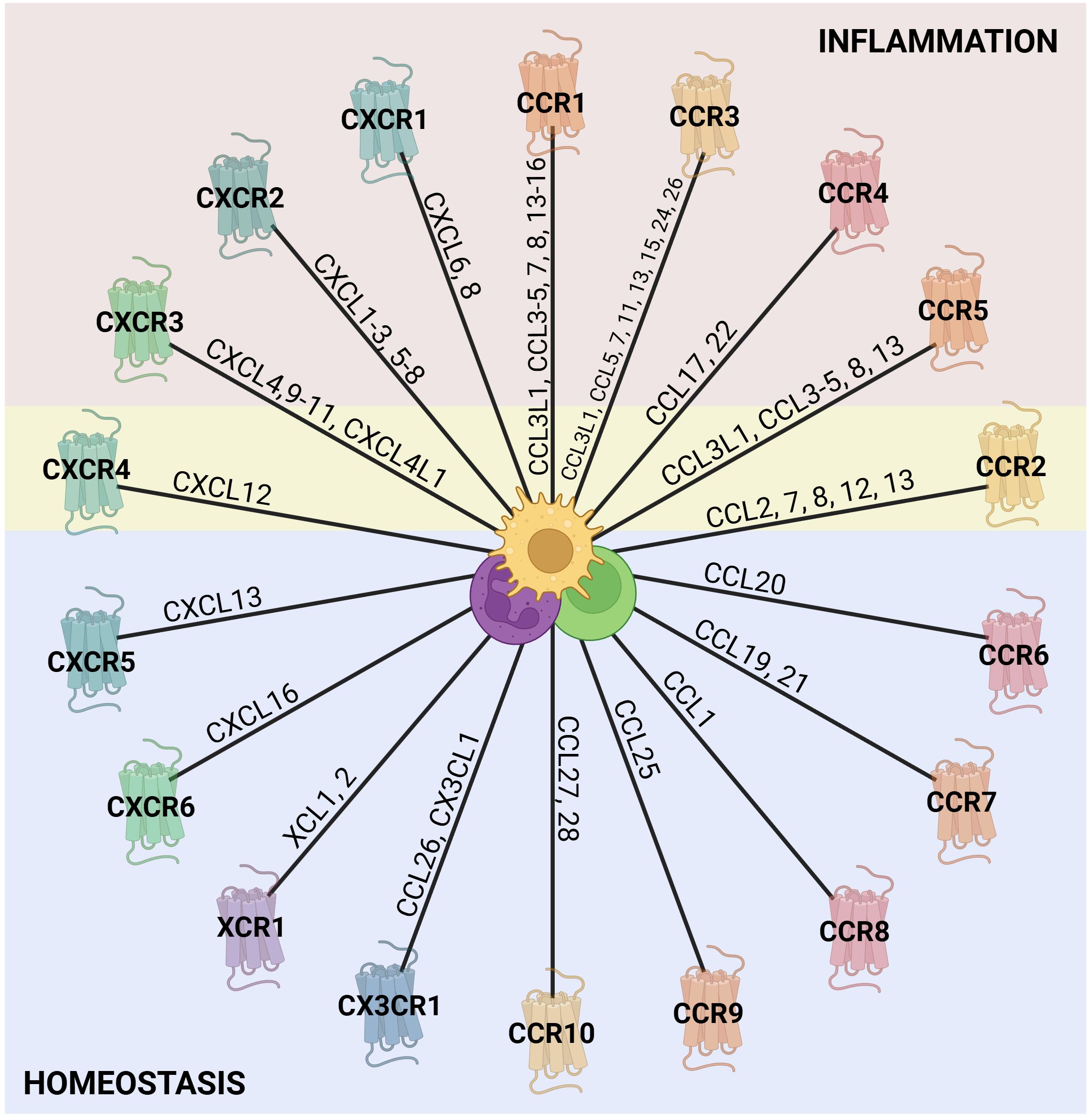
Figure 1. Chemokine receptors and their ligands. The outer ring of the wheel is composed of representations of the known chemokine receptors from each of the chemokine families (C, CC, CXC, and CX3C), with the chemokine agonists along the wheel spokes (39, 44, 45). The colors assigned to the receptors are arbitrary and serve to distinguish the families visually. Chemokine receptors are generally classified as either homeostatic or inflammatory based on their predominant roles. However, this distinction is not absolute, as their activity and function depend strongly on the cellular and inflammatory context. In the figure, receptors associated with inflammation are shaded in red, those linked to homeostasis in blue, and receptors with dual functionality in yellow. Notably, other inflammatory receptors may also contribute to homeostatic processes, given their role in tissue repair, although this remains to be further explored. In the center, there are some leukocytes that express chemokine receptors. Created in BioRender; Proost, P (2025).
CCR receptors are highly versatile and collectively govern the migration of monocytes, various lymphocyte subsets, NK cells, eosinophils, basophils, and dendritic cells. In particular, CCR2 and CCR7 are essential for monocyte egress from the bone marrow and dendritic cell trafficking to lymph nodes, respectively (28, 45). CX3CR1, on the other hand, mediates adhesion and migration of monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, T cells, and NK cells, contributing to both immune surveillance and tissue homeostasis (47).
As previously mentioned, chemokines and their receptors may have multiple functions or bind differently according to the context. Thus, it is important to notice that they can recruit other cells and can be involved in different processes (48). For instance, CCL3, CCL4, and CCL5 bind to CCR5 to recruit immune cells during inflammation, but also play a role in HIV suppression by competing with viral gp120 for binding to CCR5, resulting in reduction of viral entry in the target cells (49, 50). Similarly, CXCL12, which is essential for hematopoietic stem cell homing, is also exploited by tumor cells for metastasis and competes with HIV-1 gp120 for binding to CXCR4 (51). CXCL8, as main human neutrophil chemoattractant, directs neutrophil migration during acute inflammation, but also promotes tumor growth through stimulation of angiogenesis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (52). As shown in Figure 1, chemokines may be associated with general inflammation or homeostasis, but are not commonly described as being implicated in the resolution of inflammation. Nevertheless, evidences indicate that both their presence and absence can affect immune cell accumulation and activation during resolution.
Role of chemokines in resolution of inflammation
Depletion of inflammatory chemokines
One of the initial steps in resolving inflammation is to reduce neutrophil accumulation at the inflammatory site, mainly by abrogating their recruitment, but potentially also through stimulation of reverse migration (53). Therefore, the depletion of active inflammatory chemokines in the inflammation site is crucial to reduce the inflammatory response, facilitating tissue repair, and restoring homeostasis. Various mechanisms contribute to reducing levels of active chemokines, including enzymatic processing, capture by neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), and sequestration by receptors without activation of G proteins (Figure 2). Besides depletion, recent studies have shown that chemokines are neutralized by autoantibodies, and this may modulate inflammation and promote its resolution (54, 55).
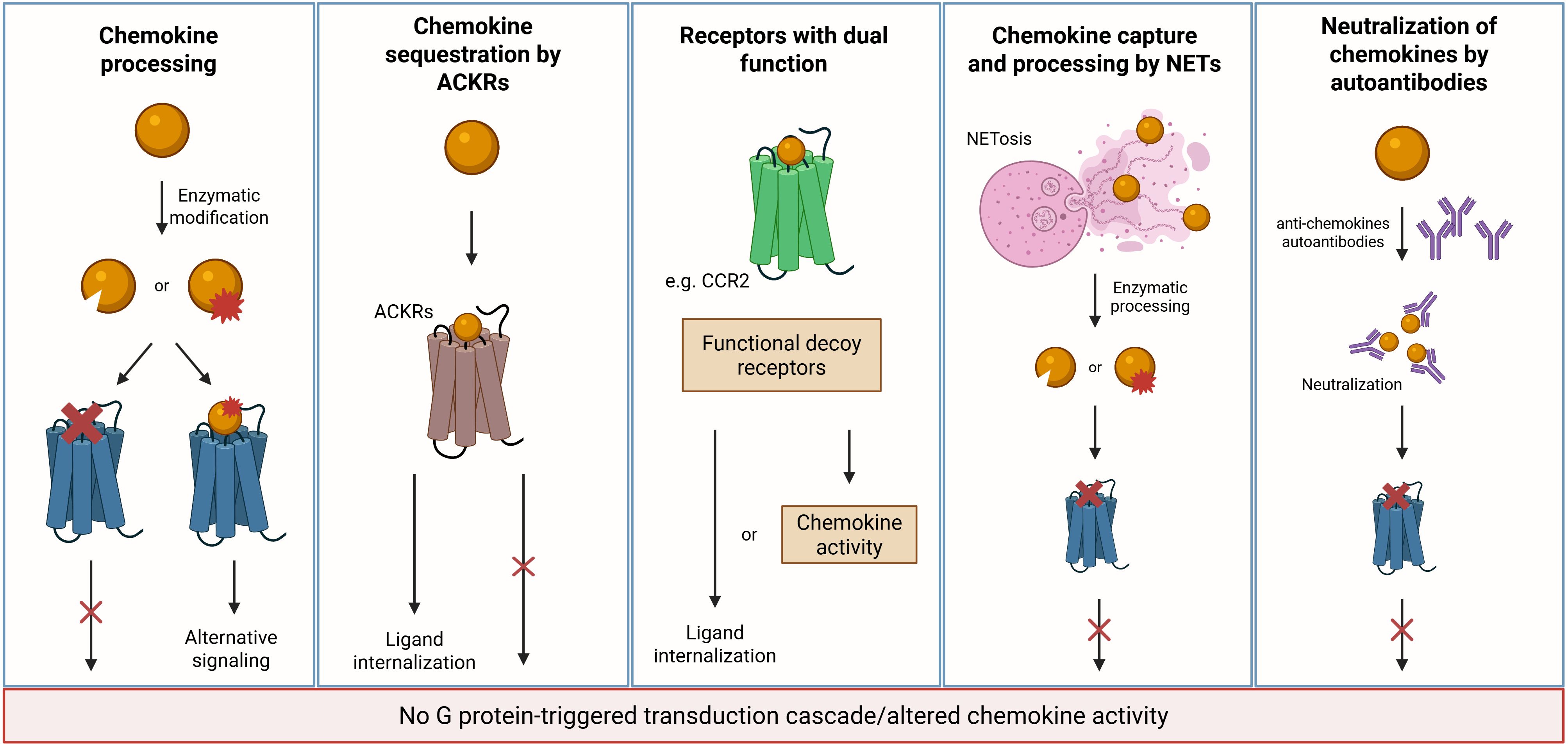
Figure 2. Mechanisms of chemokine depletion/inactivation during resolution. Multiple mechanisms contribute to the clearance or inactivation of chemokines as inflammation resolves. MMPs and other proteases cleave CC and CXC chemokines, generating inactive fragments or molecules with altered receptor specificity. ACKRs function as scavengers by internalizing chemokines without triggering G protein-coupled signaling but resulting in ligand internalization and degradation. Classical receptors may transiently adopt a decoy-like role under specific conditions. Specifically, CCR2 has been shown to act as a chemokine sink, internalizing excess CCL2 to limit inflammatory signaling and promote resolution. Additionally, NETs can capture and immobilize cytokines and chemokines, reducing their bioavailability and facilitating the transition toward resolution. Autoantibodies that neutralize chemokines can also contribute to their inactivation. Created in BioRender; Proost, P (2025).
Depletion of inflammatory chemokines by enzymatic processing
Different enzymes can affect the function of chemokines, inducing several post-translational modifications such as site specific proteolytic cleavage, citrullination, nitration and glycosylation. In this context, proteolytic processing has been shown, primarily in vitro, to play a crucial role in the activity regulation of chemokines. Several enzymes can cleave chemokines, including matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP4/CD26), and aminopeptidases such as aminopeptidase N (ANP/CD13) (29). These modifications can significantly influence the inflammatory response, not only by inactivating chemokines but also by producing more potent chemokines, altering their receptor specificity or modifying their chemotactic properties (56).
MMPs are a large family of calcium-dependent, zinc-containing endopeptidases that were initially identified through their role in degradation of extracellular matrix components. However, they participate in various biological and physiological processes (57–61). MMPs can cleave chemokines at their N- or C-terminus, modulating their activity and altering leukocyte recruitment. For instance, macrophage-secreted MMP-12 cleaves CXC chemokines at the ELR motif, which is essential for receptor binding, abolishing the ability to recruit neutrophils, and illustrating how chemokine processing can be a pro-resolving mechanism (62). Beyond neutrophils, MMP-processing modifies the activity of several CC-chemokines, thereby influencing the recruitment of a broader range of leukocytes, including monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, dendritic cells, and eosinophils. For example, MMP-2 and MMP-9 cleave CCL2 and CCL7, leading to the loss of their chemotactic activity for monocytes and lymphocytes (63, 64). The truncated CCL7 form retains the capacity to bind CCR1, CCR2, and CCR3, but without inducing migration, thus serving as a functional antagonist that dampens inflammation (62, 65). Similarly, MMP-processing of other CC-chemokines, such as CCL8, CCL13, CCL15, and CCL23, has been shown to alter their ability to attract leukocytes (62, 64, 66), further contributing to the fine-tuning of cell trafficking. Notably, although CC chemokines are involved in the recruitment of various leukocyte subsets, most studies have predominantly focused on their role in monocyte attraction, highlighting a knowledge gap that remains to be addressed.
Besides MMPs, CD26/DPP4 is present as a membrane-bound serine protease on various immune and non-immune cells, and also in a soluble shed form in plasma. This specific enzyme removes the two most N-terminal amino acids from a broad list of chemokines, including CCL3L1, CCL4, CCL5, CCL11, CCL14, CCL22, CXCL2, CXCL6, CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11, and CXCL12 (56). CD26/DPP4-mediated cleavage of chemokines often significantly impacts their activity, either enhancing or diminishing chemokine activity or altering the receptor specificity depending on the substrate. While some chemokines such as CCL3L1 are activated by CD26/DPP4, CCL5 becomes a specific CCR5 agonist and others including CXCL10, CXCL12, CCL11, and CCL22 are inactivated following truncation (67). For instance, CXCL12 cleavage by CD26/DPP4 decreases its affinity for CXCR4, significantly reduces downstream calcium signaling and CXCL12-driven cell migration (68, 69).
Aminopeptidase N (APN)/CD13 is another membrane-bound protease with a wide range of functions, including chemokine processing (70). Together with CD26/DPP4, APN/CD13 generates truncated forms of CXCL11 with reduced binding, signaling, and chemotactic properties. This proteolytic process dampens the immune response (71) and, consequently, promotes tissue repair. In contrast, CXCL8 appears to be resistant to cleavage by APN/CD13, highlighting the complexity of chemokine-protease interactions. This resistance emphasizes the need to investigate chemokine - protease interactions in different biological contexts, as their effects may vary depending on the specific chemokine and the tissue environment (71, 72).
In addition to proteolytic cleavage, citrullination, nitration and glycosylation may affect chemokine activity. For instance, citrullination of CXCL12 reduces its biological function, with fully citrullinated CXCL12 being inactive (73). Similarly, citrullinated CXCL8 displays reduced chemoattractant and signaling capacity through CXCR2, as well as reduced affinity for GAGs (74). Similar functional impairments have been reported for CXCL10 and CXCL11, which, despite maintaining their ability to bind CXCR3, show reduced signaling activity following citrullination (75). Nitration also reduces the activity of CCL2 (76), CXCL8 (77) and CXCL12 (78). Although glycosylation has been reported on only a few chemokines (e.g. on CCL2, CCL14 and CX3CL1) and may affect protein stability (as evidenced for CCL14), limited information is available on its biological effects. Reports up to now rather point towards fine tuning rather than abolishing chemokine activity. For instance, CX3CL1 is a membrane-bound and highly glycosylated chemokine and the extend of its glycosylation regulates the presentation of the chemokine domain to the receptor CX3CR1 (79). In addition, evidence is accumulating for a regulatory role for glycosylation and tyrosine sulfation of a large number, if not almost all chemokine receptors (80–86). However, the fact that glycosylation is regulated by about 200 glycosyltransferase enzymes of which the expression differs between cells and alters depending on the activation of cells further complicates the study of the impact of glycosylation (87).
Importantly, the spatial and temporal expression and activity of these chemokine and chemokine receptor processing enzymes is tightly regulated, ensuring that chemokine activity is fine-tuned according to the inflammatory stage and tissue environment (88–92). Dysregulation of this processing system has been associated with chronic inflammatory diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (93), cystic fibrosis (CF) (94), and rheumatoid arthritis (95). Furthermore, since a number of these enzymes also process cytokines, hormones, receptors, and/or extracellular matrix components, they participate in a broader regulatory network that coordinates immune responses and tissue remodeling.
Depletion of inflammatory chemokines by NETs
Another mechanism of chemokine depletion involves the release of NETs. These are net-like structures composed of DNA, histones and antimicrobial proteins. Notably, there are several enzymes associated to NETs that are released by activated neutrophils such as proteases and peptidylarginine deiminases that citrullinate proteins (96). These structures were first identified as a defense mechanism against pathogens, trapping and neutralizing bacteria, fungi, and viruses and facilitating their phagocytosis (97). It is known that recruited neutrophils release NETs to constrain the infection, but additionally to propagate the inflammation (98, 99). However, subsequent research has revealed that NETs also play a significant role in modulating inflammation. After the initial influx of neutrophils, the NETs aggregate, forming AggNETs, which sequester and degrade inflammatory mediators, dismantling chemokine and cytokine tissue gradients and inhibiting further neutrophil recruitment (100). This was demonstrated in a model of monosodium urate (MSU) crystal-induced gout, where NETs interrupt the inflammatory cycle by stimulating degradation of chemokines and proinflammatory cytokines, thus bringing recruitment of cells and NETosis to a halt and contributing to resolution of inflammation (101).
Depletion of inflammatory chemokines by decoy receptors
Chemokine receptors play a crucial role in regulating chemokine activity, and among them, atypical chemokine receptors (ACKRs) are especially important for fine-tuning chemokine availability. These seven-transmembrane spanning receptors differ from classical chemokine receptors in their broad ligand-binding profiles, and their inability to trigger conventional G protein-dependent signaling pathways (102, 103). Structurally and functionally diverse, the atypical chemokine receptor family includes five members: ACKR1, also called Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines (DARC); ACKR2, also called D6; ACKR3, also called CXCR7; ACKR4, previously called CCRL1 or Chemocentryx chemokine receptor (CCX-CKR); and ACKR5, also called GPR182 (36). These receptors have different roles and are mostly known to bind and constitutively internalize their ligands. Acting like decoy receptors, the ACKRs lack the DRY motif in the second intracellular loop, which is involved in coupling to G proteins and is essential to initiate these classical signaling cascades. While the receptor is recycled back to the plasma membrane, the ligand is directed toward lysosomal degradation. Notably, this internalization and recycling may occur independently of ligand presence. It is known that the absence of ACKRs leads to dysregulated accumulation of leukocytes and has different consequences (104, 105).
For instance, the absence of ACKR2 exacerbates inflammatory responses in several murine models. In the skin, ACKR2-deficient mice exhibit heightened inflammation following phorbol ester administration or complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) injection (105, 106). Similarly, these mice show increased sensitivity to carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury (107). In lung models, the absence of ACKR2 leads to increased recruitment of eosinophils and dendritic cells in allergic asthma (108), and, after Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, results in abnormal leukocyte accumulation in the lungs, kidneys, liver, and lymph nodes, eventually decreasing survival (109). In human disease, ACKR2 expression is found to be elevated in unaffected skin regions of patients with psoriasis (110) and in alveolar macrophages of individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (111), potentially due to a compensatory mechanism to excessive leukocyte recruitment (112). In another context, the lack of ACKR3 in murine embryos results in an increased number of natural killer and dendritic cells in the placenta, which in turn leads to an abnormal cytotoxic response and inefficient trophoblast invasion (113). Interestingly, reduced expression of ACKR3 has been observed in trophoblast cells from pregnancies affected by preeclampsia, suggesting a critical role for this receptor in placental development (114).
In addition to structural decoy receptors, functional decoy receptors have been identified within the chemokine system (115, 116). These receptors are structurally identical to signaling chemokine receptors. However, under specific environmental conditions, they become uncoupled from intracellular signaling pathways and do not induce cellular activation or migration. Nonetheless, they still bind and sequester their ligands, effectively functioning as decoy receptors. The expression of chemokine receptors that naturally fail to trigger intracellular signaling has long been observed in several cell types, such as monocytes and dendritic cells (117). This is observed when the cells are simultaneously exposed to a classical inflammatory signal such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) together with the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. Under these conditions, IL-10 prevents the typical downregulation of CCR1, CCR2, and CCR5 that LPS induces in monocytes and dendritic cells. Despite high surface expression of these receptors, the cells are unable to migrate in response to chemokines such as CCL2, CCL3, CCL4, or CCL5 (116). Besides the silencing, the expression of these receptors can be increased in apoptotic neutrophils to sequester more chemokines and lead to chemokine depletion and resolution of inflammation (118). Notably, recent findings revealed that CCR2 can act as both a signaling and scavenging receptor, highlighting that even classical chemokine receptors may dynamically switch between these functions depending on the cellular context and inflammatory environment (119).
Neutralization of inflammatory chemokines by autoantibodies
Emerging evidence suggests that autoantibodies targeting chemokines may assist in the resolution of inflammation. These naturally occurring or infection-induced antibodies can selectively neutralize pro-inflammatory chemokines, thereby reducing leukocyte recruitment and dampening excessive immune activation. Elevated levels of such neutralizing antibodies have been observed in individuals recovering from COVID-19, where higher titers correlated with milder disease and faster recovery, supporting their protective, inflammation-limiting function (55, 120). In cancer and autoimmune contexts, they are increasingly recognized as endogenous regulators of inflammation, potentially contributing to immune homeostasis and preventing chronic inflammatory responses (54, 121, 122). Collectively, these findings reveal an additional regulatory layer within the chemokine network, suggesting that the adaptive immune system itself can aid in resolving inflammation through the generation of chemokine-specific autoantibodies.
Reverse migration
Besides the classical cell migration, chemokines may be involved in regulating the reverse migration of neutrophils, and this might be important for resolving inflammation. Neutrophils are typically the first responders recruited to an inflammatory site, and their prompt clearance from the tissue is vital to prevent excessive tissue damage. Although the apoptosis of neutrophils is considered a hallmark of resolution of inflammation, some studies have shown that neutrophils at the site of the inflammation may return to the main circulation and do not undergo apoptosis locally (53, 123, 124).
In the reverse migration process, the plasma levels of certain chemokines, such as CXCL1 and CXCL2, or other chemokine receptor ligands, are increased, creating a gradient from the inflammation site to the blood circulation, in other words, the classical chemotactic gradient is inverted. In turn, the endothelial cells capture these chemokines and present them to neutrophils in the inflammation site, inducing the reverse migration (125–127). It has been show that, in a murine air pouch model, neutrophils that regress to the blood vessels have increased expression of CCRL2 and the level of chemerin, a CCRL2 ligand, in plasma is increased in late stages of inflammation. In the same study, the neutralization of chemerin led to a reduction in reverse migration, suggesting that circulating chemerin attracts neutrophils to leave inflammatory sites by interacting with CCRL2 (128). In zebrafish, reverse migration has been shown to depend on CXCL8a and its receptor CXCR2. Within this model, CXCR2 regulates neutrophil behavior in inflamed tissues and contributes to the resolution of inflammation by limiting neutrophil accumulation at the wound site (129). After returning to the blood vessels, neutrophils can stay in circulation as a distinct population of long-lived cells, as observed in peripheral blood of patients with chronic inflammatory arthritis and atherosclerosis (130). Alternatively, neutrophils can return to the bone marrow (126) or migrate to remote organs, such as lungs, where they may have pathological effects (127). These findings highlight the dual nature of reverse migration: while it may contribute to the resolution of local inflammation, it might also lead to inflammatory responses in remote tissues. Despite its importance in experimental models, the clinical relevance of reverse migration in humans remains under investigation, as most of the current understanding is derived from murine and zebrafish studies (127–129, 131).
Together with the depletion of chemokines and the clearance of apoptotic cells by macrophages, the increase of chemokines in the blood circulation in late stages of inflammation leads to the reduction of local neutrophil accumulation and allows the return of homeostasis. Further studies are needed to explore the consequences of reverse migration and potential strategies to manipulate this process, in which the chemokine system plays a key role.
Recruitment and polarization of pro-resolving cells
The recruitment of pro-resolving leukocytes by chemokines is an essential step for transitioning from inflammation to tissue repair and homeostasis. This recruitment involves a shift in the type of cells present in the tissue, replacing pro-inflammatory cells with pro-resolving ones, such as pro-resolving macrophages, Tregs, ILCs, and others (1, 26). Certain chemokines, such as CCL2, CCL5, and CXCL12, are known to attract monocytes and macrophages to sites of inflammation, where they can contribute to the resolution process by clearing apoptotic cells and debris (132). Similarly, CCR4 and its ligands, CCL17 and CCL22, are essential for the recruitment of Tregs, that contribute to immune suppression by releasing anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and by directly interacting with other immune cells to dampen their activity (133–137). Interestingly, engulfment of apoptotic cells by CD169+ macrophages induces expression of CCL22 that, in turn, recruits Tregs via CCR4, showing once more how efferocytosis triggers several events linked to resolution (138). In addition to CCR4, Treg migration is regulated by several other chemokine receptors, including CCR7, which guides Tregs to lymph nodes in response to CCL19 and CCL21 (139), and CCR5, which facilitates their homing to inflamed tissues via CCL3 and CCL4 (140). CXCR3 has also been implicated in directing Tregs to sites of Th1-type inflammation through CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11 (141), while CCR8 and its ligand CCL1 have been shown to mediate Treg accumulation in tumor microenvironments (142).
In contrast, CCR2 plays a major role in monocyte recruitment but shows context-dependent roles. For instance, the recruitment of monocytes, or rather its reduction, does not affect the resolution of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) induced by either malaria (143) or LPS (144) in mice. Although the absence of monocytes does not directly affect disease progression or resolution, likely due to compensatory mechanisms such as alveolar macrophage proliferation (144), the lack of CCR2 might disrupt the restoration of homeostasis, since it impairs the reappearance of eosinophils and interstitial macrophages during recovery (143). Nonetheless, in a model of lung injury induced by infection with influenza A or treatment with bleomycin, as well as in a model of lung injury induced by acetaminophen, a subpopulation of macrophages, dependent on CCR2, was discovered and associated with tissue repair and regeneration (145). In a context of wound healing, CCR2 has also been described as essential given that, once the CCR2/CCL2 axis is disrupted by stimulator of interferon genes (STING) deficiency, the recruitment of monocytes and the accumulation of macrophages in the wound is significantly reduced. In other words, CCR2/CCL2 signaling, in particular, facilitates the recruitment of Ly6Chigh monocytes from the bone marrow and their migration to the wound site, which is essential for replacing neutrophils and promoting wound healing. In the absence of proper chemokine signaling, monocyte recruitment is impaired, leading to prolonged inflammation and delayed resolution (146).
The effects of chemokines on macrophages, however, goes beyond their recruitment. They also participate in the regulation of apoptosis and recognition and clearance of apoptotic cells. CCL1 signaling through its receptor CCR8 on lymphocytes inhibits apoptosis (30). On the other hand, CX3CL1 (fractalkine) functions as a “find-me” signal released by apoptotic cells, attracting phagocytes such as macrophages to the site of cell death and facilitating the initiation of efferocytosis (147). Also in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury models, the CX3CL1/CX3CR1 axis plays a regulatory role in macrophage-mediated recovery. Specifically, CX3CR1 signaling modulates the expression of MerTK, a receptor tyrosine kinase essential for efferocytosis. Interestingly, CX3CR1 deficiency enhances the capacity of macrophages to clear apoptotic cells and leads to compensatory upregulation of other chemokine receptors such as CCR1 and CCR5. This results in increased immigration of monocytes, that differentiate locally to macrophages to replenish the Kupffer cell population and contribute to tissue homeostasis (148).
Besides recruitment and modulation of macrophage activity, chemokines play a key role in guiding macrophage polarization toward either the pro-inflammatory M1 or the pro-resolving M2 phenotype (149). For instance, Li et al. (150) have demonstrated that knocking down CCR1 or CCR5 can impair CCL5-induced MAPK and NF-κB activation. This, in turn, decreases M1 polarization while simultaneously enhancing IL-4-induced M2 polarization. On the other hand, certain chemokines facilitate the polarization of macrophages into the M2 phenotype, which is associated with anti-inflammatory responses and tissue repair. Specifically, CCL22 has been shown to induce the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages into the M2 subtype in the context of cervical cancer. This process may significantly contribute to progression and increased aggressiveness of a tumor (151, 152). Also in the context of cancer, CXCL13 has been implicated in promoting M2 macrophage polarization and facilitating tumor progression in myeloma osteolytic disease. Similarly, but in other circumstances, CCL24 plays a fundamental role in angiotensin II-induced heart failure by promoting the polarization of macrophages toward the M2 phenotype (152). Taken together, these data indicate that chemokines play an important and multifaceted role in the context of the localization of specific subpopulations of macrophages, as they are not only involved in the selective recruitment of cells but also actively contribute to their polarization.
It is important to recognize that, while chemokines are considered important co-factors, they are not the primary drivers of macrophage polarization. Cytokines such as interferon (IFN)-γ and IL-4/IL-13 are well-established as crucial regulators in this process (23, 153). Thus, the interplay between chemokines and the production of these cytokine mediators must be taken into consideration when evaluating macrophage polarization.
In addition to macrophages, neutrophils have increasingly been recognized for their pro-resolving functions. The most studied role of neutrophils in resolution is that they become apoptotic and are cleared by macrophages, leading to a cascade of anti-inflammatory and tissue-repair responses. However, as already discussed, neutrophils contribute to resolution through mechanisms beyond their own death (154, 155). These cells may participate in dampening complement activation and inflammation (3), promote cytokine scavenging (101), remove tissue debris (156), induce matrix remodeling (157), and support angiogenesis and tissue regeneration (158, 159).
Although several studies highlight neutrophil phenotypic heterogeneity and functional plasticity, the link between different phenotypes and specific neutrophil subpopulations is not completely understood, particularly outside the context of cancer. Currently, neutrophils may be classified into N1, with pro-inflammatory or anti-tumor functions, and N2, with pro-resolving or pro-tumor functions. For instance, the number of N2 neutrophils is increased after myocardial infarction which may help to prevent further wall thinning of the ventricle (160). Moreover, a study about resolution of liver injury has shown that, following the phagocytosis of cellular debris, neutrophils underwent a shift in gene expression towards an anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving profile. This includes the upregulation of receptors such as CXCR2 and CXCR4, which mediate reverse migration and homing to the bone marrow, as well as the expression of anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving mediators such as IL-10 and annexin A1 (ANXA1) (161). Similarly, a pro-resolving population of neutrophils has been identified in late stages of mouse acute liver injury (162). This population was characterized by the downregulation of pro-inflammatory genes and is associated with modulation of macrophage activity and polarization, as well as promotion of angiogenesis. CXCR4, whose expression in neutrophils has been linked to angiogenesis and tissue repair, is among the surface markers of this subset (163, 164). In contrast, the pro-inflammatory neutrophil subpopulation expresses CXCR5, highlighting how the expression of specific chemokine receptors plays a pivotal role in guiding the recruitment of functionally distinct neutrophil subsets to the liver (162). Interestingly, another study has shown that the activation of the CCL20-CCR6 axis via TNF-α recruits proangiogenic VEGFA+ neutrophils to sites of ischemic injury leading to initiation of angiogenesis and tissue regeneration (165). More about the different subtypes of neutrophils in vivo and the role of the chemokine system in this process is yet to be discovered.
Promotion of disease recovery and tissue repair
Chemokines are traditionally known for their role in initiating and amplifying inflammatory responses, but growing evidence highlights their importance in resolving inflammation and promoting recovery across various pathological contexts. Once the inflammatory phase subsides, chemokines contribute to the restoration of tissue homeostasis by orchestrating the clearance of apoptotic cells, recruiting reparative leukocytes, and directing stromal, epithelial, and progenitor cells to damaged areas. This spatiotemporal regulation ensures that immune responses are terminated efficiently, preventing chronic inflammation and fibrosis.
In COVID-19, for instance, chemokines and their receptors modulate the mucosal immune response, promoting viral clearance while facilitating symptom resolution. According to Cass et al. (166), increased levels of the chemokines CCL13, CCL17, and CCL26 are associated with the development of a Th2-like immune response in the upper respiratory tract. These chemokines recruit and activate key immune players such as ILCs, B cells, and eosinophils, which contribute to virus control and tissue integrity recovery. Interestingly, therapeutic intervention with budesonide, a corticosteroid commonly used for asthma and early COVID-19 treatment (167), can enhance the expression of CCL17. This upregulation was associated with improved clinical outcomes, without a demonstrable direct antiviral effect (166).
Aberrant chemokine signaling can, however, impair resolution and delay healing. In WHIM (warts, hypogammaglobulinemia, infections, and myelokathexis) syndrome, gain-of-function mutations in CXCR4 prevent receptor desensitization, leading to immune cell retention in the bone marrow and contributing to osteopenia and defective tissue regeneration (168). In this context, diminishing CXCR4 activity is beneficial (169). Mice treated with plerixafor (AMD3100), a CXCR4 antagonist, showed a restored osteogenic capacity, highlighting the importance of a proper balance in the chemokine system (170, 171).
Besides leukocytes, chemokines regulate the migration of fibroblasts and endothelial cells, both of which are crucial for wound healing and tissue remodeling. Importantly, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis are not restricted to the resolution phase. They also occur during inflammation, where they contribute to leukocyte recruitment and nutrient supply to inflamed tissues (172). However, as inflammation resolves, these same processes become essential for tissue repair and restoration of homeostasis (173).
Chemokines such as CCL2 and CXCL8, as well as other CXCR2 ligands, recruit fibroblasts and endothelial cells to sites of injury, promoting extracellular matrix (ECM) production and angiogenesis (174–176). CCR7 and its ligands CCL19 and CCL21 also participate in fibroblast recruitment in inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis (177) and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (178). These fibroblasts display enhanced migration and proliferation capacities and secrete vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which further promotes angiogenesis (177). Beyond VEGF secretion, the CCR7/CCL21 axis influences macrophage polarization and Th17 cell differentiation, leading to osteoclast activation and subsequent vascular remodeling (179). Similarly, in skin wounds infected with Enterococcus faecalis, CXCL2 acts together with SPP1 (osteopontin) to coordinate pathogen control and tissue regeneration. In this context, CXCL2 not only recruits neutrophils to limit infection but also promotes angiogenesis, highlighting the dual role of certain chemokines in both inflammation and tissue repair (180, 181).
Another important chemokine in the angiogenesis context is CXCL12. Although VEGF is the most studied and recognized factor for migration and proliferation of endothelial cells (182), CXCL12 coordinates the migration of endothelial cells through the spatially restricted activation of ACKR3 and CXCR4b (183), promoting angiogenesis. In ischemic injury, CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling promotes endothelial progenitor cell (EPC) recruitment and vascular regeneration, facilitating angiogenesis and restoring perfusion (184). Furthermore, CXCL12 is essential for promoting tissue regeneration in organs such as the lungs and liver by enhancing cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation (185, 186). Although CXCL12 classically binds CXCR4, it also interacts with ACKR3 that is involved in angiogenesis and cell proliferation (187, 188). Treatment with ACKR3 antagonists suppressed symptoms of collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice, reducing the number of blood vessels in inflamed joints. These findings suggest that disease suppression may be mediated, at least in part, by the inhibition of pathological angiogenesis. Consistently, strong expression of ACKR3 has been found on endothelial cells in the synovium of rheumatoid arthritis patients, suggesting a similar mechanism in human disease (112, 189).
Chemokines also promote lymphangiogenesis, a process essential during both inflammation and resolution. In inflamed tissues, lymphangiogenesis facilitates the drainage of edema and the trafficking of immune cells, whereas in the resolution phase, it contributes to clearing interstitial fluid, apoptotic cells, and inflammatory mediators. CCL21, via its receptor CCR7, promotes the formation of new lymphatic vessels, an essential step in resolving tissue edema and removing cellular debris (190). This has been demonstrated in patients with idiopathic diffuse alveolar damage, in which CCR7+ macrophages were found around the newly formed lymphatics, suggesting they may participate in lymphangiogenesis, facilitated by CCL19 from the lymphatic endothelium (191). This contributes to immune homeostasis and ensures that the inflammatory response resolves efficiently, preventing further tissue damage (173). Further along the resolution process, chemokines regulate the migration, retention, and activation of progenitor and stem cells, which are crucial for tissue regeneration and remodeling. For instance, CXCL12 plays a central role in maintaining hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) in the bone marrow niche via CXCR4 signaling, and its gradient guides the mobilization of these cells into peripheral tissues during repair (192, 193). Moreover, CCL11 regulates the trafficking of neural progenitor cells in models of brain injury, suggesting that chemokine-mediated progenitor mobilization extends beyond classical immune repair mechanisms (194).
In addition to the many chemokines implicated in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis, CCL5 produced by pro-resolving macrophages appears to contribute to tissue repair by promoting wound healing (195). This effect appears to be partially mediated through the recruitment of stromal cells via CCR1 (196). Other chemokines, such as CXCL12 and CCL2, play crucial roles by promoting stromal cell homing, proliferation, and differentiation within damaged tissues, thereby supporting angiogenesis and tissue remodeling (197, 198).
Importantly, the ability of chemokines to promote tissue repair appears to depend on the surrounding microenvironment. When acting alongside anti-inflammatory mediators, chemokines may support tissue regeneration and recovery, whereas their association with pro-inflammatory factors can hinder healing. In line with this, a pro-resolving macrophage secretome rich in anti-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines such as CCL5, CXCL2, and CCL22 has shown therapeutic efficacy in experimental models of inflammation (199–201). Conversely, increased CCL5 production together with type IFN-I has been associated with defective mucosal repair in Crohn’s disease (202).
The chemokine system as a therapeutic target
Several chemokines and their receptors are under investigation as therapeutic targets (203). In the context of cancer, the chemokine receptors CCR4 and CXCR4 have been extensively investigated. An anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody, mogamulizumab, has been approved for the treatment of mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome, and is under evaluation for use in other types of cancer (204–206). Given that CCR4 is highly expressed in effector Tregs but not in naïve Tregs, mogamulizumab selectively depletes effector Tregs without affecting naïve Tregs, which remain essential for autoimmune suppression (207). Due to its overexpression in multiple cancer types and its well-established role in tumor progression via the CXCR4/CXC12 axis, CXCR4 is another therapeutic target, with inhibitors such as plerixafor being used for autologous transplantation of bone marrow in patients with Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma or multiple myeloma and as a chemosensitizer (208, 209). Also other antagonists of CXCR4 are being explored in this context. Among them, the CXCR4 antagonist mavorixafor enhances CD8+ cell infiltration and decreases immunosuppressive cells in the tumor microenvironment (210).
In 2024 the FDA approved mavorixafor for patients from 12 years of age on with WHIM syndrome to increase the number of circulating mature neutrophils and lymphocytes, highlighting the clinical potential of chemokine receptor targeting beyond oncology (211). Additionally, CXCR4 blockade with plerixafor has shown promising results in controlling osteoporosis in WHIM syndrome, although these studies are still at the preclinical stage (170, 171). Furthermore, drugs targeting CCR5, such as maraviroc, have been approved for the treatment of HIV infection, demonstrating how chemokine receptor blockade can be translated into effective therapies for infectious diseases.
Regarding the resolution of inflammation, inhibitors of chemokine receptors are being developed to limit the recruitment of inflammatory cells to affected tissues in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease. For instance, CCR5 and CCR2 antagonists are being evaluated for their potential to reduce excessive immune cell infiltration and promote Treg cell generation in inflammatory conditions (212, 213). Moreover, given that chemokines play a role in tissue regeneration, modulating these pathways could promote repair of damaged tissue or prevent fibrosis (214). More specifically, the modulation of the CXCL12-CXCR4 axis is being vastly explored (52). Enhancing the effects of CXCL12 to promote stem cell differentiation and revascularization could be beneficial for organ repair and wound healing (215, 216). Conversely, in pathological conditions where angiogenesis is harmful, such as retinopathies and cancers, targeting and blocking CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling may have therapeutic advantages (217–219). Thus, the development of strategies aimed at either promoting or inhibiting CXCL12-driven pathways holds significant therapeutic potential but needs to be tailored to the specific context of interest (220). For instance, blocking CXCR4 with plerixafor has demonstrated pro-healing effects related to stem cell mobilization. In diabetic mice, a single topical application of plerixafor significantly accelerated wound healing by mobilizing bone marrow–derived endothelial progenitor cells and promoting fibroblast migration and proliferation (221).
Given its crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, various approaches are being explored to optimize the therapeutic use of CXCL12 while minimizing side effects, such as utilizing local administration to precisely target specific tissues (186, 216). In addition to directly targeting chemokine signaling, modulating chemokine degradation may also offer therapeutic opportunities, and both approaches can be combined, as demonstrated by Vågesjö and colleagues (222). In their study, the authors employed a CXCL12-delivering Lactobacillus strain that simultaneously lowered the local pH, thereby inhibiting CD26/DPP4, while producing CXCL12. This strategy significantly accelerated wound healing and the bacteria are currently in advanced stages of clinical testing as a therapeutic approach (223, 224). Furthermore, CD26/DPP4 is implicated in various inflammatory diseases due to its role in cleaving several chemokines. Therefore, inhibiting this enzyme could extend the lifespan of chemokines and, consequently, enhance their activity (225–227). In turn, the increase of chemokine activity might recruit specific cells with pro-resolving effects, such as Tregs (141). Nonetheless, despite its promise, modulation of CD26/DPP4 activity should be approached with caution, as this enzyme also processes neuropeptides, peptide hormones, vasoactive peptides, growth factors, and various cytokines (67).
Another promising therapeutic approach targeting the chemokine system is the use of glycosaminoglycan (GAG)-binding molecules. GAGs play a crucial role in the recruitment of immune cells by retaining chemokines on the endothelium and presenting them to circulating leukocytes, thereby facilitating the interaction between chemokines and their respective receptors (228, 229). Recent studies have highlighted the potential of GAG-binding peptides derived from chemokines, such as CXCL9 (74–103), as a therapeutic intervention. In murine models of inflammatory diseases, such as COVID-19 and antigen-induced arthritis, the administration of these peptides has been shown to reduce leukocyte recruitment to the sites of inflammation, likely due to the impairment of GAG-chemokine interactions (230–233). This reduction prevents excessive inflammatory responses and, as a result, tissue damage is decreased. While the specific impact on resolution of inflammation requires further investigation, it is reasonable to suggest that better regulation of leukocyte recruitment may contribute to a more effective resolution of inflammation.
Targeting the chemokine system is a promising strategy for both dampening inflammation and promoting resolution and tissue repair. Different approaches (Figure 3) have shown positive results in preclinical models. However, these outcomes are highly dependent on the specific context, including the tissue, disease stage, immune cell population, and timing of intervention. Despite the significant potential of molecules that target the chemokine network, the underlying mechanisms of this network and the effects of inhibiting or stimulating one member are not fully understood, and the therapeutic window remains to be explored. Much is yet to be discovered to ensure that chemokine-targeting therapeutic strategies are both effective and safe across different pathological settings.
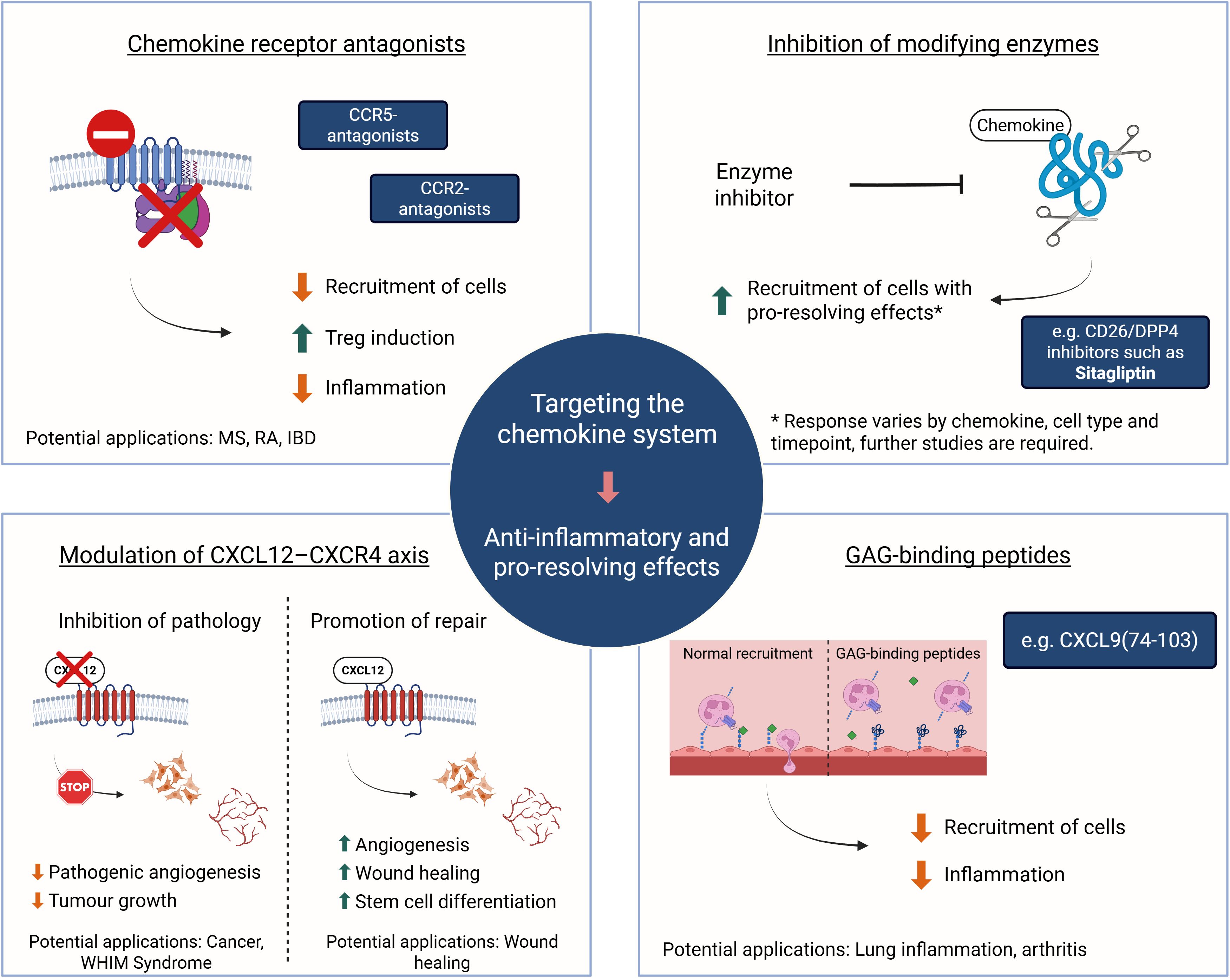
Figure 3. The chemokine system as a therapeutic target. Overview of current and emerging therapeutic strategies aimed at modulating chemokine activity. These include antagonizing chemokine receptors (e.g., CCR2, CCR5). Fine-tuning the CXCL12-CXCR4 axis may involve use of CXCR4 antagonists to reduce angiogenesis and tumor growth or to counteract gain-of-function mutations in WHIM syndrome. Alternatively, retaining CXCL12 signaling results in faster wound healing. Inhibiting the activity of chemokine modifying enzymes, such as DPP4/CD26, may stimulate recruitment of pro-resolving cells and disrupting interactions of inflammatory chemokines with GAGs through competition with potent GAG-binding peptides showed beneficial effects in preclinical models of lung and joint inflammation. Such interventions can modulate immune cell infiltration, promote inflammation resolution, and enhance tissue repair. The clinical outcomes of these strategies are highly context-dependent, varying with disease type, affected tissue, and timing of the intervention. Created in BioRender; Proost, P (2025).
Future directions
The chemokine system has emerged as a critical regulator not only of immune cell recruitment during inflammation but also of its resolution. In addition, chemokine receptors, being GPCRs, make chemokines and their receptors therapeutic targets (203). While most current strategies focus on inhibiting pro-inflammatory chemokine signaling to limit immune cell infiltration, future research must deepen our understanding of how chemokines contribute to the later phases of inflammation, particularly in driving its resolution and promoting tissue repair.
One promising direction lies in the selective modulation of chemokine pathways that actively promote resolution, such as those involved in neutrophil reverse migration, macrophage polarization, and recruitment of regulatory and tissue-repairing cells. Future interventions in the chemokine system may focus on modulating the activity or availability of chemokines also by targeting enzymes responsible for posttranslational modifications. Similarly, precise temporal control over chemokine inhibition or enhancement, targeting specific phases of the inflammatory response, could minimize tissue damage while preserving essential immune defense mechanisms. The CXCL12-CXCR4 axis exemplifies this dual potential, where both the enhancement and inhibition of signaling may yield therapeutic benefits depending on the timing and the specific disease context (186).
Moreover, targeting the interactions between chemokines and GAGs is an emerging strategy with potential to regulate immune cell recruitment and gradient formation without directly interfering with receptor signaling (230, 232). As studies already have shown how GAG-binding peptides can modulate leukocyte recruitment, further investigation is needed to clarify their role in supporting inflammation resolution and limiting fibrosis.
Ultimately, translating chemokine-targeting therapies into effective clinical interventions requires a more nuanced understanding of their context-dependent roles in inflammation and the chemokine system redundancy. Integrating single-cell and spatial transcriptomics with functional studies may help identify precise chemokine signatures associated with resolution and repair across tissues and disease models. In parallel, expanding our knowledge on chemokine modifications, such as proteolytic modification, citrullination, glycosylation and nitration, and how they affect biological function may reveal new therapeutic opportunities, especially in the context of resolution (74, 77).
In summary, the next generation of chemokine-modulating therapies should move beyond inflammation suppression toward the fine-tuned orchestration of resolution. Exploring the full spectrum of chemokine functions and other molecules associated with that holds great promise for restoring immune balance and promoting recovery in inflammatory diseases.
Concluding remarks
The chemokine system plays a critical role in both the inflammatory and resolution phases. During inflammation, chemokines mediate cellular recruitment to inflammation sites, and later, during resolution, chemokine depletion is the first step for limiting inflammation (28). Proteolytic processing by enzymes such as MMPs and CD26/DPP4, and the activity of atypical chemokine receptors, play a major role in modulating chemokine levels and activity (62, 234). However, chemokines appear to have a more complex role in resolving the inflammatory response than previously understood.
One of the mechanisms through which chemokines promote the resolution of inflammation is by facilitating the recruitment and polarization of pro-resolving cells, such as M2 macrophages and Tregs (149). These cells play critical roles in clearing apoptotic cells and dampening the immune response, thereby contributing to the restoration of tissue homeostasis and the resolution of inflammation. Furthermore, certain chemokines, such as CXCL1 and CXCL2, are implicated in reverse migration of neutrophils back to the circulation, thus preventing excessive tissue damage (53, 125, 126). Finally, chemokines are also important for tissue repair by recruiting fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and progenitor cells to damaged tissue. This facilitates extracellular matrix production, angiogenesis, and tissue regeneration, ensuring effective recovery. Chemokines such as CXCL12 and CCL21 are particularly important for stem cell recruitment and lymphangiogenesis, highlighting their complex role in inflammation and homeostasis (186, 190, 220).
In conclusion, the chemokine system plays a crucial dual role in both promoting and resolving inflammation by modulating cell recruitment, polarization, and tissue repair. Regarding the clinical implications, there are several options for therapeutically targeting the chemokine system and some are already being explored (203). Nevertheless, despite its vast potential, challenges remain in terms of specificity and balancing immune modulation without compromising host defense mechanisms. Future research should focus on further elucidating the precise mechanisms by which chemokines regulate the resolution of inflammation, possibly leading to new therapeutic strategies for controlling inflammation and enhancing tissue repair.
Author contributions
VO: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PP: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. SS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors were supported by a C1 and a C3 research grant from KU Leuven (C14/23/143 and C3/22/054, respectively), an FWO Flanders project grant (G067123N), and received funding under the Horizon Europe programme through the MSCA-DN project B-ACTIVE (project number 101120187).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Buckley CD, Gilroy DW, Serhan CN, Stockinger B, and Tak PP. The resolution of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2013) 13:59–66. doi: 10.1038/nri3362
2. Schett G and Neurath MF. Resolution of chronic inflammatory disease: universal and tissue-specific concepts. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:3261. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05800-6
3. Hsu AY, Huang Q, Pi X, Fu J, Raghunathan K, Ghimire L, et al. Neutrophil-derived vesicles control complement activation to facilitate inflammation resolution. Cell. (2025) 188:1623–1641.e26. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.01.021
4. Dalli J and Serhan CN. Specific lipid mediator signatures of human phagocytes : microparticles stimulate macrophage efferocytosis and pro-resolving mediators. Blood (2012) 120:60–72. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-04-423525
5. Lichtnekert J, Kawakami T, Parks WC, and Duffield JS. Changes in macrophage phenotype as the immune response evolves. Curr Opin Pharmacol. (2013) 13:555–64. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2013.05.013
6. Sica A, Mantovani A, Sica A, and Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization : in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest (2012) 122:787–95. doi: 10.1172/JCI59643DS1
7. Savill JS, Wyllie AH, Henson JE, Walport MJ, Henson PM, and Haslett C. Macrophage phagocytosis of aging neutrophils in inflammation. Programmed cell death in the neutrophil leads to its recognition by macrophages. J Clin Invest. (1989) 83:865–75. doi: 10.1172/JCI113970
8. Voll RE, Herrmann M, Roth EA, Stach C, Kalden JR, and Girkontaite I. Immunosuppressive effects of apoptotic cells. Nature. (1997) 390:350–1. doi: 10.1038/37022
9. Sugimoto MA, Ribeiro ALC, Costa BRC, Vago JP, Lima KM, Carneiro FS, et al. Phagocytes, granulocytes, & myelopoiesis: Plasmin & plasminogen induce macrophage reprogramming & regulate key steps of inflammation resolution via annexin A1. Blood. (2017) 129:2896–907. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-742825
10. Wang L, Yang K, Xie X, Wang S, Gan H, Wang X, et al. Macrophages as multifaceted orchestrators of tissue repair: bridging inflammation, regeneration, and therapeutic innovation. J Inflammation Res. (2025) 18:8945–59. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S527764
11. Brown BN, Ratner BD, Goodman SB, Amar S, and Badylak SF. Macrophage polarization: an opportunity for improved outcomes in biomaterials and regenerative medicine. Biomaterials. (2012) 33:3792–802. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.02.034
12. Cummings RJ, Barbet G, Bongers G, Hartmann BM, Gettler K, Muniz L, et al. Different tissue phagocytes sample apoptotic cells to direct distinct homeostasis programs. Nature. (2016) 539:565–9. doi: 10.1038/nature20138
13. A-Gonzalez N, Quintana JA, García-Silva S, Mazariegos M, González De La Aleja A, Nicolás-Ávila JA, et al. Phagocytosis imprints heterogeneity in tissue-resident macrophages. J Exp Med. (2017) 214:1281–96. doi: 10.1084/jem.20161375
14. Lechner AJ, Driver IH, Lee J, Conroy CM, Nagle A, Locksley RM, et al. Recruited monocytes and type 2 immunity promote lung regeneration following pneumonectomy. Cell Stem Cell. (2017) 21:120–134.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2017.03.024
15. Krishnamoorthy N, Burkett PR, Dalli J, Abdulnour R-EE, Colas R, Ramon S, et al. Cutting edge: maresin-1 engages regulatory T cells to limit type 2 innate lymphoid cell activation and promote resolution of lung inflammation. J Immunol. (2015) 194:863–7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402534
16. Serhan CN. Pro-resolving lipid mediators are leads for resolution physiology. Nature. (2014) 510:92–101. doi: 10.1038/nature13479
17. Serhan CN, Hong S, Gronert K, Colgan SP, Devchand PR, Mirick G, et al. Resolvins : A family of bioactive products of omega-3 fatty acid transformation circuits initiated by aspirin treatment that counter proinflammation signals. J Exp Med (2002) 196:1025–37. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020760
18. Dalli J and Serhan CN. Pro-resolving mediators in regulating and conferring macrophage function. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:1400. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01400
19. Kaur M, Bell T, Salek-Ardakani S, and Hussell T. Macrophage adaptation in airway inflammatory resolution. Eur Respir Rev. (2015) 24:510–5. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0030-2015
20. Melo EM, Oliveira VLS, Boff D, and Galvão I. Pulmonary macrophages and their different roles in health and disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2021) 141:1060–95. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2021.106095
21. Nepal S, Tiruppathi C, Tsukasaki Y, Farahany J, Mittal M, Rehman J, et al. STAT6 induces expression of Gas6 in macrophages to clear apoptotic neutrophils and resolve inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2019) 116:16513–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821601116
22. Stables MJ, Shah S, Camon EB, Lovering RC, Newson J, Bystrom J, et al. Transcriptomic analyses of murine resolution-phase macrophages. Blood. (2011) 118:e192–208. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-04-345330
23. Murray PJ. Macrophage polarization. Annu Rev Physiol. (2017) 79:541–66. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034339
24. Pyonteck SM, Akkari L, Schuhmacher AJ, Bowman RL, Sevenich L, Quail DF, et al. CSF-1R inhibition alters macrophage polarization and blocks glioma progression. Nat Med. (2013) 19:1264–72. doi: 10.1038/nm.3337
25. Aggarwal NR, D’Alessio FR, Tsushima K, Sidhaye VK, Cheadle C, Grigoryev DN, et al. Regulatory T cell-mediated resolution of lung injury: Identification of potential target genes via expression profiling. Physiol Genomics. (2010) 41:109–19. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00131.2009
26. Rauber S, Luber M, Weber S, Maul L, Soare A, Wohlfahrt T, et al. Resolution of inflammation by interleukin-9-producing type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Nat Med. (2017) 23:938–44. doi: 10.1038/nm.4373
27. Wang L, Wang X, Tong L, Wang J, Dou M, Ji S, et al. Recovery from acute lung injury can be regulated via modulation of regulatory T cells and Th17 cells. Scand J Immunol. (2018) 88:1–13. doi: 10.1111/sji.12715
28. David BA and Kubes P. Exploring the complex role of chemokines and chemoattractants in vivo on leukocyte dynamics. Immunol Rev. (2019) 289:9–30. doi: 10.1111/imr.12757
29. Proost P, Struyf S, Van Damme J, Fiten P, Ugarte-Berzal E, and Opdenakker G. Chemokine isoforms and processing in inflammation and immunity. J Autoimmun. (2017) 85:45–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2017.06.009
30. Van Snick J, Houssiau F, Proost P, and Van Damme J. Renauld JC. I-309/T cell activation gene-3 chemokine protects murine T cell lymphomas against dexamethasone-induced apoptosis. J Immunol Baltim Md. (1996) 157:2570–6.
31. Kawaguchi N, Zhang T-T, and Nakanishi T. Involvement of CXCR4 in normal and abnormal development. Cells. (2019) 8:185. doi: 10.3390/cells8020185
32. Raman D, Sobolik-Delmaire T, and Richmond A. Chemokines in health and disease. Exp Cell Res. (2011) 317:575–89. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.01.005
33. Vilgelm AE and Richmond A. Chemokins modulate immune surveillance in tumorignesis, metastatsis, and response to immunotherapy. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:333. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00333
34. Griffith JW, Sokol CL, and Luster AD. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: positioning cells for host defense and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. (2014) 32:659–702. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032713-120145
35. Metzemaekers M, Malengier-Devlies B, Gouwy M, De Somer L, Cunha FDQ, Opdenakker G, et al. Fast and furious: The neutrophil and its armamentarium in health and disease. Med Res Rev. (2023) 43:1537–606. doi: 10.1002/med.21958
36. Chevigné A, Legler DF, Rot A, Sozzani S, Szpakowska M, and Thelen M. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CXVIII. Update on the nomenclature for atypical chemokine receptors, including ACKR5. Pharmacol Rev. (2025) 77:100012. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.124.001361
37. Crijns H, Vanheule V, and Proost P. Targeting chemokine—Glycosaminoglycan interactions to inhibit inflammation. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:483. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00483
38. Bachelerie F, Ben-Baruch A, Burkhardt AM, Combadiere C, Farber JM, Graham GJ, et al. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. LXXXIX. Update on the extended family of chemokine receptors and introducing a new nomenclature for atypical chemokine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. (2014) 66:1–79. doi: 10.1124/pr.113.007724
39. Hughes CE and Nibbs RJB. A guide to chemokines and their receptors. FEBS J. (2018) 285:2944–71. doi: 10.1111/febs.14466
40. Steen A, Larsen O, Thiele S, and Rosenkilde MM. Biased and G protein-independent signaling of chemokine receptors. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:277. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00277
41. Zweemer AJM, Toraskar J, Heitman LH, and IJzerman AP. Bias in chemokine receptor signalling. Trends Immunol. (2014) 35:243–52. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2014.02.004
42. Allen SJ, Crown SE, and Handel TM. Chemokine: receptor structure, interactions, and antagonism. Annu Rev Immunol. (2007) 25:787–820. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.24.021605.090529
43. Hilger D, Masureel M, and Kobilka BK. Structure and dynamics of GPCR signaling complexes. Nat Struct Mol Biol. (2018) 25:4–12. doi: 10.1038/s41594-017-0011-7
44. Ruytinx P, Proost P, and Struyf S. CXCL4 and CXCL4L1 in cancer. Cytokine. (2018) 109:65–71. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.02.022
45. White GE, Iqbal AJ, and Greaves DR. CC chemokine receptors and chronic inflammation—Therapeutic opportunities and pharmacological challenges. Pharmacol Rev. (2013) 65:47–89. doi: 10.1124/pr.111.005074
46. Metzemaekers M, Vanheule V, Janssens R, Struyf S, and Proost P. Overview of the mechanisms that may contribute to the non-redundant activities of interferon-inducible CXC chemokine receptor 3 ligands. Front Immunol. (2018) 8:1970. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01970
47. Lee M, Lee Y, Song J, Lee J, and Chang S-Y. Tissue-specific role of CX3CR1 expressing immune cells and their relationships with human disease. Immune Netw. (2018) 18:1–15. doi: 10.4110/in.2018.18.e5
48. Dyer DP, Medina-Ruiz L, Bartolini R, Schuette F, Hughes CE, Pallas K, et al. Chemokine receptor redundancy and specificity are context dependent. Immunity. (2019) 50:378–389.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.01.009
49. Cocchi F, DeVico AL, Garzino-Demo A, Arya SK, Gallo RC, and Lusso P. Identification of RANTES, MIP-1α, and MIP-1β as the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ T cells. Science. (1995) 270:1811–5. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5243.1811
50. Zhao W, Pahar B, Borda JT, Alvarez X, and Sestak K. A decline in CCL3–5 chemokine gene expression during primary simian-human immunodeficiency virus infection. PloS One. (2007) 2:e726. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000726
51. Janssens R, Struyf S, and Proost P. Pathological roles of the homeostatic chemokine CXCL12. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2018) 44:51–68. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2018.10.004
52. Cambier S, Gouwy M, and Proost P. The chemokines CXCL8 and CXCL12: molecular and functional properties, role in disease and efforts towards pharmacological intervention. Cell Mol Immunol. (2023) 20:217–51. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-00974-6
53. Xu Q, Zhao W, Yan M, and Mei H. Neutrophil reverse migration. J Inflammation. (2022) 19:22. doi: 10.1186/s12950-022-00320-z
54. Karin N. Autoantibodies to chemokines and cytokines participate in the regulation of cancer and autoimmunity. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:623. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00623
55. Wilhelm F, Cadamuro J, and Mink S. Autoantibodies in long COVID: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis. (2025) 303:S1473309925004116. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00411-6
56. Vanheule V, Metzemaekers M, Janssens R, Struyf S, and Proost P. How post-translational modifications influence the biological activity of chemokines. Cytokine. (2018) 109:29–51. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.02.026
57. Aguilera-Montilla N, Bailón E, Ugarte-Berzal E, Uceda-Castro R, Prieto-Solano M, García-Martínez E, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 induces a pro-angiogenic profile in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2019) 520:198–204. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.09.127
58. Grillet B, Pereira RVS, Van Damme J, Abu El-Asrar A, Proost P, and Opdenakker G. Matrix metalloproteinases in arthritis: towards precision medicine. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2023) 19:363–77. doi: 10.1038/s41584-023-00966-w
59. Opdenakker G, Vermeire S, and Abu El-Asrar A. How to place the duality of specific MMP-9 inhibition for treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases into clinical opportunities? Front Immunol. (2022) 13:983964. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.983964
60. Opdenakker G, Van Den Steen PE, Dubois B, Nelissen I, Van Coillie E, Masure S, et al. Gelatinase B functions as regulator and effector in leukocyte biology. J Leukoc Biol. (2001) 69:851–9. doi: 10.1189/jlb.69.6.851
61. Ugarte-Berzal E, Boon L, Martens E, Rybakin V, Blockmans D, Vandooren J, et al. MMP-9/gelatinase B degrades immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:538. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00538
62. Dean RA, Cox JH, Bellac CL, Doucet A, Starr AE, and Overall CM. Macrophage-specific metalloelastase (MMP-12) truncates and inactivates ELR+ CXC chemokines and generates CCL2, -7, -8, and -13 antagonists: potential role of the macrophage in terminating polymorphonuclear leukocyte influx. Blood. (2008) 112:3455–64. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-12-129080
63. Denney H, Clench MR, and Woodroofe MN. Cleavage of chemokines CCL2 and CXCL10 by matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9: Implications for chemotaxis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2009) 382:341–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.02.164
64. Young D, Das N, Anowai A, and Dufour A. Matrix metalloproteases as influencers of the cells’ Social media. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:3847. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163847
65. McQuibban GA, Gong J-H, Wong JP, Wallace JL, Clark-Lewis I, and Overall CM. Matrix metalloproteinase processing of monocyte chemoattractant proteins generates CC chemokine receptor antagonists with anti-inflammatory properties in vivo. Blood. (2002) 100:1160–7. doi: 10.1182/blood.V100.4.1160.h81602001160_1160_1167
66. Starr AE, Dufour A, Maier J, and Overall CM. Biochemical analysis of matrix metalloproteinase activation of chemokines CCL15 and CCL23 and increased glycosaminoglycan binding of CCL16. J Biol Chem. (2012) 287:5848–60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.314609
67. Mortier A, Gouwy M, Van Damme J, Proost P, and Struyf S. CD26/dipeptidylpeptidase IV-chemokine interactions: double-edged regulation of inflammation and tumor biology. J Leukoc Biol. (2016) 99:955–69. doi: 10.1189/jlb.3mr0915-401r
68. Ohtsuki T, Hosono O, Kobayashi H, Munakata Y, Souta A, Shioda T, et al. Negative regulation of the anti-human immunodeficiency virus and chemotactic activity of human stromal cell-derived factor 1α by CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV. FEBS Lett. (1998) 431:236–40. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00763-7
69. Proost P, Struyf S, Schols D, Durinx C, Wuyts A, Lenaerts J-P, et al. Processing by CD26/dipeptidyl-peptidase IV reduces the chemotactic and anti-HIV-1 activity of stromal-cell-derived factor-1α. FEBS Lett. (1998) 432:73–6. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00830-8
70. Wulfaenger J, Niedling S, Riemann D, and Seliger B. Aminopeptidase N (APN)/CD13-dependent CXCR4 downregulation is associated with diminished cell migration, proliferation and invasion. Mol Membr Biol. (2008) 25:72–82. doi: 10.1080/09687680701551855
71. Proost P, Mortier A, Loos T, Vandercappellen J, Gouwy M, Ronsse I, et al. Proteolytic processing of CXCL11 by CD13/aminopeptidase N impairs CXCR3 and CXCR7 binding and signaling and reduces lymphocyte and endothelial cell migration. Blood. (2007) 110:37–44. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-10-049072
72. Kehlen A, Egbert I, Thiele K, Fischer K, Riemann D, and Langner J. Increased expression of interleukin-8 and aminopeptidase N by cell-cell contact: interleukin-8 is resistant to degradation by aminopeptidase N/CD13. Eur Cytokine Netw. (2001) 12:316–24.
73. Struyf S, Noppen S, Loos T, Mortier A, Gouwy M, Verbeke H, et al. Citrullination of CXCL12 differentially reduces CXCR4 and CXCR7 binding with loss of inflammatory and anti-HIV-1 activity via CXCR4. J Immunol. (2009) 182:666–74. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.1.666
74. Proost P, Loos T, Mortier A, Schutyser E, Gouwy M, Noppen S, et al. Citrullination of CXCL8 by peptidylarginine deiminase alters receptor usage, prevents proteolysis, and dampens tissue inflammation. J Exp Med. (2008) 205:2085–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.20080305
75. Loos T, Mortier A, Gouwy M, Ronsse I, Put W, Lenaerts J-P, et al. Citrullination of CXCL10 and CXCL11 by peptidylarginine deiminase: a naturally occurring posttranslational modification of chemokines and new dimension of immunoregulation. Blood. (2008) 112:2648–56. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-04-149039
76. Barker CE, Thompson S, O’Boyle G, Lortat-Jacob H, Sheerin NS, Ali S, et al. CCL2 nitration is a negative regulator of chemokine-mediated inflammation. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:44384. doi: 10.1038/srep44384
77. Thompson S, Pang CY, Sepuru KM, Cambier S, Hellyer TP, Scott J, et al. Nitration of chemokine CXCL8 acts as a natural mechanism to limit acute inflammation. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2023) 80:35. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04663-x
78. Janssens R, Mortier A, Boff D, Vanheule V, Gouwy M, Franck C, et al. Natural nitration of CXCL12 reduces its signaling capacity and chemotactic activity in vitro and abrogates intra-articular lymphocyte recruitment in vivo. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:62439–59. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11516
79. Ostuni MA, Guellec J, Hermand P, Durand P, Combadière C, Pincet F, et al. CX3CL1, a chemokine finely tuned to adhesion: critical roles of the stalk glycosylation and the membrane domain. Biol Open. (2014) 3:1173–82. doi: 10.1242/bio.20149845
80. Hauser MA, Kindinger I, Laufer JM, Späte A-K, Bucher D, Vanes SL, et al. Distinct CCR7 glycosylation pattern shapes receptor signaling and endocytosis to modulate chemotactic responses. J Leukoc Biol. (2016) 99:993–1007. doi: 10.1189/jlb.2VMA0915-432RR
81. Huskens D, Princen K, Schreiber M, and Schols D. The role of N-glycosylation sites on the CXCR4 receptor for CXCL-12 binding and signaling and X4 HIV-1 viral infectivity. Virology. (2007) 363:280–7. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.01.031
82. Jørgensen AS, Brandum EP, Mikkelsen JM, Orfin KA, Boilesen DR, Egerod KL, et al. The C-terminal peptide of CCL21 drastically augments CCL21 activity through the dendritic cell lymph node homing receptor CCR7 by interaction with the receptor N-terminus. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2021) 78:6963–78. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03930-7
83. Kiermaier E, Moussion C, Veldkamp CT, Gerardy-Schahn R, De Vries I, Williams LG, et al. Polysialylation controls dendritic cell trafficking by regulating chemokine recognition. Science. (2016) 351:186–90. doi: 10.1126/science.aad0512
84. Pan X, Naruse C, Matsuzaki T, Ishibashi O, Sugihara K, Asada H, et al. Critical role of the potential O -linked glycosylation sites of CXCR4 in cell migration and bone marrow homing of hematopoietic stem progenitor cells. Stem Cells. (2025) 43:sxaf025. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxaf025
85. Verhallen L, Lackman JJ, Wendt R, Gustavsson M, Yang Z, Narimatsu Y, et al. Glyco-sulfo barcodes” regulate chemokine receptor function. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS. (2023) 80:55. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04697-9
86. Xu T, Schou AS, Lackman JJ, Barrio-Calvo M, Verhallen L, Goth CK, et al. Chemokine receptor N-terminus charge dictates reliance on post-translational modifications for effective ligand capture and following boosting by defense peptides. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:10854. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910854
87. Schjoldager KT, Narimatsu Y, Joshi HJ, and Clausen H. Global view of human protein glycosylation pathways and functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2020) 21:729–49. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-00294-x
88. Abu El-Asrar AM, Nawaz MI, Ahmad A, De Zutter A, Siddiquei MM, Blanter M, et al. Evaluation of proteoforms of the transmembrane chemokines CXCL16 and CX3CL1, their receptors, and their processing metalloproteinases ADAM10 and ADAM17 in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Front Immunol. (2021) 11:601639. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.601639
89. Bernaerts E, Ahmadzadeh K, De Visscher A, Malengier-Devlies B, Häuβler D, Mitera T, et al. Human monocyte-derived macrophages shift subcellular metalloprotease activity depending on their activation state. iScience. (2024) 27:111171. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111171
90. Chakraborti S, Mandal M, Das S, Mandal A, and Chakraborti T. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases: An overview. Mol Cell Biochem. (2003) 253:269–85. doi: 10.1023/A:1026028303196
91. Metzemaekers M, Van Damme J, Mortier A, and Proost P. Regulation of chemokine activity – A focus on the role of dipeptidyl peptidase IV/CD26. Front Immunol. (2016) 7:483. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00483
92. Opdenakker G, Van Den Steen PE, and Van Damme J. Gelatinase B: a tuner and amplifier of immune functions. Trends Immunol. (2001) 22:571–9. doi: 10.1016/S1471-4906(01)02023-3
93. Ostridge K, Williams N, Kim V, Bennett M, Harden S, Welch L, et al. Relationship between pulmonary matrix metalloproteinases and quantitative CT markers of small airways disease and emphysema in COPD. Thorax. (2016) 71:126–32. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2015-207428
94. Gaggar A, Hector A, Bratcher PE, Mall MA, Griese M, and Hartl D. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in cystic fibrosis lung disease. Eur Respir J. (2011) 38:721–7. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00173210
95. Mueller A-L, Payandeh Z, Mohammadkhani N, Mubarak SMH, Zakeri A, Alagheband Bahrami A, et al. Recent advances in understanding the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: new treatment strategies. Cells. (2021) 10:3017. doi: 10.3390/cells10113017
96. Yu K and Proost P. Insights into peptidylarginine deiminase expression and citrullination pathways. Trends Cell Biol. (2022) 109:1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2022.01.014
97. Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C, Fauler B, Uhlemann Y, Weiss DS, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science. (2004) 303:1532–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1092385
98. Luo H, Guo H, Zhou Y, Fang R, Zhang W, and Mei Z. Neutrophil extracellular traps in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: friend and foe. Curr Neuropharmacol. (2023) 21:2079–96. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666230308090351
99. Poto R, Shamji M, Marone G, Durham SR, Scadding GW, and Varricchi G. Neutrophil extracellular traps in asthma: friends or foes? Cells. (2022) 11:3521. doi: 10.3390/cells11213521
100. Hahn J, Schauer C, Czegley C, Kling L, Petru L, Schmid B, et al. Aggregated neutrophil extracellular traps resolve inflammation by proteolysis of cytokines and chemokines and protection from antiproteases. FASEB J. (2019) 33:1401–14. doi: 10.1096/fj.201800752R
101. Schauer C, Janko C, Munoz LE, Zhao Y, Kienhöfer D, Frey B, et al. Aggregated neutrophil extracellular traps limit inflammation by degrading cytokines and chemokines. Nat Med. (2014) 20:511–7. doi: 10.1038/nm.3547
102. Comerford I and McColl SR. Atypical chemokine receptors in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. (2024) 24:753–69. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-01025-5
103. Ulvmar MH, Hub E, and Rot A. Atypical chemokine receptors. Exp Cell Res. (2011) 317:556–68. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.01.012
104. Dawson TC, Lentsch AB, Wang Z, Cowhig JE, Rot A, Maeda N, et al. Exaggerated response to endotoxin in mice lacking the Duffy antigen/receptor for chemokines (DARC). Blood. (2000) 96:1681–4. doi: 10.1182/blood.V96.5.1681
105. Jamieson T, Cook DN, Nibbs RJB, Rot A, Nixon C, Mclean P, et al. The chemokine receptor D6 limits the inflammatory response in vivo. Nat Immunol. (2005) 6:403–11. doi: 10.1038/ni1182
106. De La Torre YM, Locati M, Buracchi C, Dupor J, Cook DN, Bonecchi R, et al. Increased inflammation in mice deficient for the chemokine decoy receptor D6. Eur J Immunol. (2005) 35:1342–6. doi: 10.1002/eji.200526114
107. Berres M-L, Trautwein C, Zaldivar MM, Schmitz P, Pauels K, Lira SA, et al. The chemokine scavenging receptor D6 limits acute toxic liver injury in vivo. bchm. (2009) 390:1039–45. doi: 10.1515/BC.2009.119
108. Whitehead GS, Wang T, DeGraff LM, Card JW, Lira SA, Graham GJ, et al. The chemokine receptor D6 has opposing effects on allergic inflammation and airway reactivity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2007) 175:243–9. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200606-839OC
109. Di Liberto D, Locati M, Caccamo N, Vecchi A, Meraviglia S, Salerno A, et al. Role of the chemokine decoy receptor D6 in balancing inflammation, immune activation, and antimicrobial resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Exp Med. (2008) 205:2075–84. doi: 10.1084/jem.20070608
110. Singh MD, King V, Baldwin H, Burden D, Thorrat A, Holmes S, et al. Elevated expression of the chemokine-scavenging receptor D6 is associated with impaired lesion development in psoriasis. Am J Pathol. (2012) 181:1158–64. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.06.042
111. Bazzan E, Saetta M, Turato G, Borroni EM, Cancellieri C, Baraldo S, et al. Expression of the atypical chemokine receptor D6 in human alveolar macrophages in COPD. Chest. (2013) 143:98–106. doi: 10.1378/chest.11-3220
112. Nibbs RJB and Graham GJ. Immune regulation by atypical chemokine receptors. Nat Rev Immunol. (2013) 13:815–29. doi: 10.1038/nri3544
113. Quinn KE, Matson BC, and Caron KM. Deletion of atypical chemokine receptor 3 (ACKR3) increases immune cells at the fetal-maternal interface. Placenta. (2020) 95:18–25. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2020.04.007
114. Lu J, Zhou W-H, Ren L, and Zhang Y-Z. CXCR4, CXCR7, and CXCL12 are associated with trophoblastic cells apoptosis and linked to pathophysiology of severe preeclampsia. Exp Mol Pathol. (2016) 100:184–91. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2015.12.013
115. Bonecchi R, Garlanda C, Mantovani A, and Riva F. Cytokine decoy and scavenger receptors as key regulators of immunity and inflammation. Cytokine. (2016) 87:37–45. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.06.023
116. D’Amico G, Frascaroli G, Bianchi G, Transidico P, Doni A, Vecchi A, et al. Uncoupling of inflammatory chemokine receptors by IL-10: generation of functional decoys. Nat Immunol. (2000) 1:387–91. doi: 10.1038/80819
117. Mantovani A, Locati M, Vecchi A, Sozzani S, and Allavena P. Decoy receptors: a strategy to regulate inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Trends Immunol. (2001) 22:328–36. doi: 10.1016/S1471-4906(01)01941-X
118. Ariel A, Fredman G, Sun Y-P, Kantarci A, Van Dyke TE, Luster AD, et al. Apoptotic neutrophils and T cells sequester chemokines during immune response resolution through modulation of CCR5 expression. Nat Immunol. (2006) 7:1209–16. doi: 10.1038/ni1392
119. Shroka TM, Kufareva I, Salanga CL, and Handel TM. The dual-function chemokine receptor CCR2 drives migration and chemokine scavenging through distinct mechanisms. Sci Signal. (2023) 16:eabo4314. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abo4314
120. Muri J, CecChinato V, Cavalli A, Shanbhag AA, Matkovic M, Biggiogero M, et al. Autoantibodies against chemokines post-SARS-CoV-2 infection correlate with disease course. Nat Immunol. (2023) 24:604–11. doi: 10.1038/s41590-023-01445-w
121. Loberg RD, Ying C, Craig M, Day LL, Sargent E, Neeley C, et al. Targeting CCL2 with systemic delivery of neutralizing antibodies induces prostate cancer tumor regression in vivo. Cancer Res. (2007) 67:9417–24. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1286
122. Cameron MJ, Arreaza GA, Grattan M, Meagher C, Sharif S, Burdick MD, et al. Differential expression of CC chemokines and the CCR5 receptor in the pancreas is associated with progression to type I diabetes. J Immunol. (2000) 165:1102–10. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.2.1102
123. Hamza B, Wong E, Patel S, Cho H, Martel J, and Irimia D. Retrotaxis of human neutrophils during mechanical confinement inside microfluidic channels. Integr Biol. (2014) 6:175–83. doi: 10.1039/C3IB40175H
124. Hughes J, Johnson RJ, Mooney A, Hugo C, Gordon K, and Savill J. Neutrophil fate in experimental glomerular capillary injury in the rat. Emigration exceeds in situ clearance by apoptosis. Am J Pathol. (1997) 1:223–34.
125. De Oliveira S, Rosowski EE, and Huttenlocher A. Neutrophil migration in infection and wound repair: going forward in reverse. Nat Rev Immunol. (2016) 16:378–91. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.49
126. Hind LE and Huttenlocher A. Neutrophil reverse migration and a chemokinetic resolution. Dev Cell. (2018) 47:404–5. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.11.004
127. Owen-Woods C, Joulia R, Barkaway A, Rolas L, Ma B, Nottebaum AF, et al. Local microvascular leakage promotes trafficking of activated neutrophils to remote organs. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:2301–18. doi: 10.1172/JCI133661
128. Ji J, Zhong H, Wang Y, Liu J, Tang J, and Liu Z. Chemerin attracts neutrophil reverse migration by interacting with C–C motif chemokine receptor-like 2. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:425. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06820-5
129. Powell D, Tauzin S, Hind LE, Deng Q, Beebe DJ, and Huttenlocher A. Chemokine signaling and the regulation of bidirectional leukocyte migration in interstitial tissues. Cell Rep. (2017) 19:1572–85. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.04.078
130. Buckley CD, Ross EA, McGettrick HM, Osborne CE, Haworth O, Schmutz C, et al. Identification of a phenotypically and functionally distinct population of long-lived neutrophils in a model of reverse endothelial migration. J Leukoc Biol. (2005) 79:303–11. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0905496
131. Mathias JR, Perrin BJ, Liu T-X, Kanki J, Look AT, and Huttenlocher A. Resolution of inflammation by retrograde chemotaxis of neutrophils in transgenic zebrafish. J Leukoc Biol. (2006) 80:1281–8. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0506346
132. Nahrendorf M, Pittet MJ, and Swirski FK. Monocytes: Protagonists of infarct inflammation and repair after myocardial infarction. Circulation. (2010) 121:2437–45. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.916346
133. Maeda S, Murakami K, Inoue A, Yonezawa T, and Matsuki N. CCR4 blockade depletes regulatory T cells and prolongs survival in a canine model of bladder cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. (2019) 7:1175–87. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0751
134. Marshall LA, MArubayashi S, Jorapur A, Jacobson S, Zibinsky M, Robles O, et al. Tumors establish resistance to immunotherapy by regulating T reg recruitment via CCR4. J Immunother Cancer. (2020) 8:e000764. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000764
135. Yuan Q, Bromley SK, Means TK, Jones KJ, Hayashi F, Bhan AK, et al. CCR4-dependent regulatory T cell function in inflammatory bowel disease. J Exp Med. (2007) 204:1327–34. doi: 10.1084/jem.20062076
136. Gobert M, Treilleux I, Bendriss-Vermare N, Bachelot T, Goddard-Leon S, Arfi V, et al. Regulatory T cells recruited through CCL22/CCR4 are selectively activated in lymphoid infiltrates surrounding primary breast tumors and lead to an adverse clinical outcome. Cancer Res. (2009) 69:2000–9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2360
137. Liu W, Wei X, Li L, Wu X, Yan J, Yang H, et al. CCR4 mediated chemotaxis of regulatory T cells suppress the activation of T cells and NK cells via TGF-β pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 488:196–203. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.05.034
138. Ravishankar B, Shinde R, Liu H, Chaudhary K, Bradley J, Lemos HP, et al. Marginal zone CD169+ macrophages coordinate apoptotic cell-driven cellular recruitment and tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2014) 111:4215–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1320924111
139. Schneider MA, Meingassner JG, Lipp M, Moore HD, and Rot A. CCR7 is required for the in vivo function of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Exp Med. (2007) 204:735–45. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061405
140. Ward ST, Li KK, Hepburn E, Weston CJ, Curbishley SM, Reynolds GM, et al. The effects of CCR5 inhibition on regulatory T-cell recruitment to colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. (2015) 112:319–28. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.572
141. Moreno Ayala MA, Campbell TF, Zhang C, Dahan N, Bockman A, Prakash V, et al. CXCR3 expression in regulatory T cells drives interactions with type I dendritic cells in tumors to restrict CD8+ T cell antitumor immunity. Immunity. (2023) 56:1613–1630.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.06.003
142. Kuehnemuth B, Piseddu I, Wiedemann GM, Lauseker M, Kuhn C, Hofmann S, et al. CCL1 is a major regulatory T cell attracting factor in human breast cancer. BMC Cancer. (2018) 18:1278. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5117-8
143. Pollenus E, Pham T-T, Vandermosten L, Possemiers H, Knoops S, Opdenakker G, et al. CCR2 is dispensable for disease resolution but required for the restoration of leukocyte homeostasis upon experimental malaria-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome. Front Immunol. (2021) 11:628643. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.628643
144. De Oliveira VLS, Pollenus E, Berghmans N, Queiroz-Junior CM, Blanter M, Mattos MS, et al. Absence of CCR2 promotes proliferation of alveolar macrophages that control lung inflammation in acute respiratory distress syndrome in mice. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:12920. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112920
145. Ruscitti C, Abinet J, Maréchal P, Meunier M, De Meeûs C, Vanneste D, et al. Recruited atypical Ly6G+ macrophages license alveolar regeneration after lung injury. Sci Immunol. (2024) 9:eado1227. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.ado1227
146. Chen C, Cai X, Liu Z, Zhang W, Yang J, Tang Y, et al. STING coordinates resolution of inflammation during wound repair by modulating macrophage trafficking through STAT3. J Leukoc Biol. (2025) 117:qiae175. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiae175
147. Truman LA, Ford CA, Pasikowska M, Pound JD, Wilkinson SJ, Dumitriu IE, et al. CX3CL1/fractalkine is released from apoptotic lymphocytes to stimulate macrophage chemotaxis. Blood. (2008) 112:5026–36. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-06-162404
148. Zhang H, You G, Yang Q, Jin G, Lv G, Fan L, et al. CX3CR1 deficiency promotes resolution of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating homeostatic function of liver infiltrating macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA - Mol Basis Dis. (2024) 1870:167130. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167130
149. Ruytinx P, Proost P, Van Damme J, and Struyf S. Chemokine-induced macrophage polarization in inflammatory conditions. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1930. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01930
150. Li M, Sun X, Zhao J, Xia L, Li J, Xu M, et al. CCL5 deficiency promotes liver repair by improving inflammation resolution and liver regeneration through M2 macrophage polarization. Cell Mol Immunol. (2020) 17:753–64. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0279-0
151. Little AC, Pathanjeli P, Wu Z, Bao L, Goo LE, Yates JA, et al. IL-4/IL-13 stimulated macrophages enhance breast cancer invasion via rho-GTPase regulation of synergistic VEGF/CCL-18 signaling. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:456. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00456
152. Wang Q, Sudan K, Schmoeckel E, Kost BP, Kuhn C, Vattai A, et al. CCL22-polarized TAMs to M2a macrophages in cervical cancer in vitro model. Cells. (2022) 11:2027. doi: 10.3390/cells11132027
153. Orecchioni M, Ghosheh Y, Pramod AB, and Ley K. Macrophage polarization: Different gene signatures in M1(Lps+) vs. Classically and M2(LPS-) vs. Alternatively activated macrophages. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1084. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01084
154. Rizo-Téllez SA and Filep JG. Beyond host defense and tissue injury: the emerging role of neutrophils in tissue repair. Am J Physiol-Cell Physiol. (2024) 326:C661–83. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00652.2023
155. Wang J. Neutrophils in tissue injury and repair. Cell Tissue Res. (2018) 371:531–9. doi: 10.1007/s00441-017-2785-7
156. Forbes SJ and Rosenthal N. Preparing the ground for tissue regeneration: from mechanism to therapy. Nat Med. (2014) 20:857–69. doi: 10.1038/nm.3653
157. Harty MW, Muratore CS, Papa EF, Gart MS, Ramm GA, Gregory SH, et al. Neutrophil depletion blocks early collagen degradation in repairing cholestatic rat livers. Am J Pathol. (2010) 176:1271–81. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090527
158. Nishio N, Okawa Y, Sakurai H, and Isobe K. Neutrophil depletion delays wound repair in aged mice. AGE. (2008) 30:11–9. doi: 10.1007/s11357-007-9043-y
159. Paris AJ, Liu Y, Mei J, Dai N, Guo L, Spruce LA, et al. Neutrophils promote alveolar epithelial regeneration by enhancing type II pneumocyte proliferation in a model of acid-induced acute lung injury. Am J Physiol-Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2016) 311:L1062–75. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00327.2016
160. Ma Y, Yabluchanskiy A, Iyer RP, Cannon PL, Flynn ER, Jung M, et al. Temporal neutrophil polarization following myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. (2016) 110:51–61. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvw024
161. Vandendriessche S, Mattos MS, Bialek EL, Schuermans S, Proost P, and Marques PE. Complement activation drives the phagocytosis of necrotic cell debris and resolution of liver injury. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1512470. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1512470
162. Maali Y, Flores Molina M, Khedr O, Abdelnabi MN, Dion J, Hassan GS, et al. Two transcriptionally and functionally distinct waves of neutrophils during mouse acute liver injury. Hepatol Commun. (2024) 8:e0459. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000459
163. Capucetti A, Albano F, and Bonecchi R. Multiple roles for chemokines in neutrophil biology. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1259. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01259
164. Tulotta C, Stefanescu C, Chen Q, Torraca V, Meijer AH, and Snaar-Jagalska BE. CXCR4 signaling regulates metastatic onset by controlling neutrophil motility and response to Malignant cells. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:2399. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38643-2
165. Lörchner H, Cañes Esteve L, Góes ME, Harzenetter R, Brachmann N, Gajawada P, et al. Neutrophils for revascularization require activation of CCR6 and CCL20 by TNFα. Circ Res. (2023) 133:592–610. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.323071
166. Cass SP, Nicolau DV, Baker JR, Mwasuku C, Ramakrishnan S, Mahdi M, et al. Coordinated nasal mucosa-mediated immunity accelerates recovery from COVID-19. ERJ Open Res. (2024) 10:00919–2023. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00919-2023
167. Ramakrishnan S, Nicolau DV, Langford B, Mahdi M, Jeffers H, Mwasuku C, et al. Inhaled budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): a phase 2, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. (2021) 9:763–72. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00160-0
168. McDermott DH and Murphy PM. WHIM syndrome: Immunopathogenesis, treatment and cure strategies. Immunol Rev. (2019) 287:91–102. doi: 10.1111/imr.12719
169. McDermott DH, Pastrana DV, Calvo KR, Pittaluga S, Velez D, Cho E, et al. Plerixafor for the treatment of WHIM syndrome. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380:163–70. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1808575
170. Anginot A, Nguyen J, Abou Nader Z, Rondeau V, Bonaud A, Kalogeraki M, et al. WHIM Syndrome-linked CXCR4 mutations drive osteoporosis. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:2058. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37791-4
171. McDermott DH, Lopez J, Deng F, Liu Q, Ojode T, Chen H, et al. AMD3100 is a potent antagonist at CXCR4R334X, a hyperfunctional mutant chemokine receptor and cause of WHIM syndrome. J Cell Mol Med. (2011) 15:2071–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01210.x
172. Kim H, Kataru RP, and Koh GY. Inflammation-associated lymphangiogenesis: a double-edged sword? J Clin Invest. (2014) 124:936–42. doi: 10.1172/JCI71607
173. Renò F and Sabbatini M. Breaking a vicious circle: lymphangiogenesis as a new therapeutic target in wound healing. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:656. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030656
174. Bernardini G, Ribatti D, Spinetti G, Morbidelli L, Ziche M, Santoni A, et al. Analysis of the role of chemokines in angiogenesis. J Immunol Methods. (2003) 273:83–101. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1759(02)00420-9
175. Heil M, Ziegelhoeffer T, Wagner S, Fernández B, Helisch A, Martin S, et al. Collateral artery growth (Arteriogenesis) after experimental arterial occlusion is impaired in mice lacking CC-chemokine receptor-2. Circ Res. (2004) 94:671–7. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000122041.73808.B5
176. Martins-Green M, Petreaca M, and Wang L. Chemokines and their receptors are key players in the orchestra that regulates wound healing. Adv Wound Care. (2013) 2:327–47. doi: 10.1089/wound.2012.0380
177. Brühl H, Mack M, Niedermeier M, Lochbaum D, Schölmerich J, and Straub RH. Functional expression of the chemokine receptor CCR7 on fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology. (2008) 47:1771–4. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken383
178. Pierce EM, Carpenter K, Jakubzick C, Kunkel SL, Evanoff H, Flaherty KR, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis fibroblasts migrate and proliferate to CC chemokine ligand 21. Eur Respir J. (2007) 29:1082–93. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00122806
179. Van Raemdonck K, Umar S, and Shahrara S. The pathogenic importance of CCL21 and CCR7 in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2020) 55:86–93. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.05.007
180. Celik C, Lee STT, Tanoto FR, Veleba M, Kline K, and Thibault G. Decoding the complexity of delayed wound healing following Enterococcus faecalis infection. eLife. (2024) 13:RP95113. doi: 10.7554/eLife.95113
181. Russo RC and Ryffel B. The chemokine system as a key regulator of pulmonary fibrosis: converging pathways in human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and the bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis model in mice. Cells. (2024) 13:2058. doi: 10.3390/cells13242058
182. Lamalice L, Le Boeuf F, and Huot J. Endothelial cell migration during angiogenesis. Circ Res. (2007) 100:782–94. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000259593.07661.1e
183. Valentin G, Haas P, and Gilmour D. The chemokine SDF1a coordinates tissue migration through the spatially restricted activation of cxcr7 and cxcr4b. Curr Biol. (2007) 17:1026–31. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.05.020
184. Ceradini DJ, Kulkarni AR, Callaghan MJ, Tepper OM, Bastidas N, Kleinman ME, et al. Progenitor cell trafficking is regulated by hypoxic gradients through HIF-1 induction of SDF-1. Nat Med. (2004) 10:858–64. doi: 10.1038/nm1075
185. Aghi M, Cohen KS, Klein RJ, Scadden DT, and Chiocca EA. Tumor stromal-derived factor-1 recruits vascular progenitors to mitotic neovasculature, where microenvironment influences their differentiated phenotypes. Cancer Res. (2006) 66:9054–64. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3759
186. Pereira RVS, EzEldeen M, Ugarte-Berzal E, Vandooren J, Martens E, Gouwy M, et al. Protection of stromal cell-derived factor-1 SDF-1/CXCL12 against proteases yields improved skin wound healing. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1359497. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1359497
187. Cuesta-Margolles G, Schlecht-Louf G, and Bachelerie F. ACKR3 in skin homeostasis, an overlooked player in the CXCR4/CXCL12 axis. J Invest Dermatol. (2025) 145:1039–49. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2024.08.022
188. Wang G, Pang Y, Li N, Hui Y, and Jin D. CXCR7 promoted proliferation, migration and invasion in HCC Cells by inactivating Hippo-YAP signaling. Discov Oncol. (2025) 16:561. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02324-6
189. Watanabe K, Penfold MET, Matsuda A, Ohyanagi N, Kaneko K, Miyabe Y, et al. Pathogenic role of CXCR7 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. (2010) 62:3211–20. doi: 10.1002/art.27650
190. Tutunea-Fatan E, Majumder M, Xin X, and Lala PK. The role of CCL21/CCR7 chemokine axis in breast cancer-induced lymphangiogenesis. Mol Cancer. (2015) 14:35. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0306-4
191. Yamashita M, Iwama N, Date F, Shibata N, Miki H, Yamauchi K, et al. Macrophages participate in lymphangiogenesis in idiopathic diffuse alveolar damage through CCL19-CCR7 signal. Hum Pathol. (2009) 40:1553–63. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2009.03.021
192. Lapidot T and Petit I. Current understanding of stem cell mobilization. Exp Hematol. (2002) 30:973–81. doi: 10.1016/S0301-472X(02)00883-4
193. Sugiyama T, Kohara H, Noda M, and Nagasawa T. Maintenance of the hematopoietic stem cell pool by CXCL12-CXCR4 chemokine signaling in bone marrow stromal cell niches. Immunity. (2006) 25:977–88. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.10.016
194. Wang F, Baba N, Shen Y, Yamashita T, Tsuru E, Tsuda M, et al. CCL11 promotes migration and proliferation of mouse neural progenitor cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2017) 8:26. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0474-9
195. Savitri C, Kwon JW, Drobyshava V, Ha SS, and Park K. M2 macrophage-derived concentrated conditioned media significantly improves skin wound healing. Tissue Eng Regener Med. (2022) 19:617–28. doi: 10.1007/s13770-021-00414-4
196. Kauts M-L, Pihelgas S, Orro K, Neuman T, and Piirsoo A. CCL5/CCR1 axis regulates multipotency of human adipose tissue derived stromal cells. Stem Cell Res. (2013) 10:166–78. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2012.11.004
197. Filer A, Raza K, Salmon M, and Buckley CD. The role of chemokines in leucocyte-stromal interactions in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Biosci J Virtual Libr. (2008) 13:2674–85. doi: 10.2741/2874
198. Zhuang Y, Chen X, Xu M, Zhang L, and Xiang F. Chemokine stromal cell-derived factor 1/CXCL12 increases homing of mesenchymal stem cells to injured myocardium and neovascularization following myocardial infarction. Chin Med J (Engl). (2009) 122:183–7. doi: 10.3901/jme.2009.07.183
199. Bonnefoy F, Gauthier T, Vallion R, Martin-Rodriguez O, Missey A, Daoui A, et al. Factors produced by macrophages eliminating apoptotic cells demonstrate pro-resolutive properties and terminate ongoing inflammation. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2586. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02586
200. Saas P, Vetter M, Maraux M, Bonnefoy F, and Perruche S. Resolution therapy: Harnessing efferocytic macrophages to trigger the resolution of inflammation. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1021413. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1021413
201. Gauthier T, Martin-Rodriguez O, Chagué C, Daoui A, Ceroi A, Varin A, et al. Amelioration of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by in vivo reprogramming of macrophages using pro-resolving factors. J Neuroinflamm. (2023) 20:307. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02994-5
202. Jain U, Ver Heul AM, Xiong S, Gregory MH, Demers EG, Kern JT, et al. Debaryomyces is enriched in Crohn’s disease intestinal tissue and impairs healing in mice. Science. (2021) 371:1154–9. doi: 10.1126/science.abd0919
203. Lai WY and Mueller A. Latest update on chemokine receptors as therapeutic targets. Biochem Soc Trans. (2021) 49:1385–95. doi: 10.1042/BST20201114
204. Choi I, Yoshimitsu M, Kusumoto S, Shimokawa M, Utsunomiya A, Suehiro Y, et al. A phase 2 trial of CHOP with anti-CCR4 antibody mogamulizumab for elderly patients with CCR4-positive adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:7504–4. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2023.41.16_suppl.7504
205. Fujikawa K, Saito T, Kurose K, Kojima T, Funakoshi T, Sato E, et al. Integrated analysis of phase 1a and 1b randomized controlled trials; Treg-targeted cancer immunotherapy with the humanized anti-CCR4 antibody, KW-0761, for advanced solid tumors. PloS One. (2023) 18:e0291772. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291772
206. Kasamon YL, Chen H, De Claro RA, Nie L, Ye J, Blumenthal GM, et al. FDA approval summary: mogamulizumab-kpkc for mycosis fungoides and sézary syndrome. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. (2019) 25:7275–80. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2030
207. Ono S, Suzuki S, Kondo Y, Okubo I, Goto M, Ogawa T, et al. Trametinib improves Treg selectivity of anti-CCR4 antibody by regulating CCR4 expression in CTLs in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:21678. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22773-1
208. De Clercq E. Mozobil® (Plerixafor, AMD3100), 10 years after its approval by the US Food and Drug Administration. Antivir Chem Chemother. (2019) 27:204020661982938. doi: 10.1177/2040206619829382
209. Sahin Z, Tahirovic YA, Geng J, Wilson LJ, and Liotta DC. Small molecule and peptide CXCR4 antagonists. A patent review from 2019 to 2024. Expert Opin Ther Pat. (2025) 35:357–69. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2025.2462848
210. Rueda A, Serna N, Mangues R, Villaverde A, and Unzueta U. Targeting the chemokine receptor CXCR4 for cancer therapies. Biomark Res. (2025) 13:68. doi: 10.1186/s40364-025-00778-y
211. FDA. FDA approval for XOLREMDI™ (2024). Available online at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2024/218709s000lbl.pdf (Accessed October 21, 2025).
212. Madan U, Verma B, and Awasthi A. Cenicriviroc, a CCR2/CCR5 antagonist, promotes the generation of type 1 regulatory T cells. Eur J Immunol. (2024) 54:2350847. doi: 10.1002/eji.202350847
213. Song X, Jiang C, Yu M, Lu C, and He X. CCR2/CCR5 antagonist cenicriviroc reduces colonic inflammation and fibrosis in experimental colitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 39:1597–605. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16622
214. Sahin H and Wasmuth HE. Chemokines in tissue fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA - Mol Basis Dis. (2013) 1832:1041–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.11.004
215. Badillo AT, Chung S, Zhang L, Zoltick P, and Liechty KW. Lentiviral gene transfer of SDF-1α to wounds improves diabetic wound healing. J Surg Res. (2007) 143:35–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2007.03.051
216. Zheng Y, Wu G, Chen L, Zhang Y, Luo Y, Zheng Y, et al. Neuro-regenerative imidazole-functionalized GelMA hydrogel loaded with hAMSC and SDF-1α promote stem cell differentiation and repair focal brain injury. Bioact Mater. (2021) 6:627–37. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.08.026
217. Pablos JL, Santiago B, Galindo M, Torres C, Brehmer MT, Blanco FJ, et al. Synoviocyte-derived CXCL12 is displayed on endothelium and induces angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. (2003) 170:2147–52. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.4.2147
218. Shi Y, Riese DJ, and Shen J. The role of the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 chemokine axis in cancer. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:574667. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.574667
219. Wei F, Moore DC, Li Y, Zhang G, Wei X, Lee JK, et al. Attenuation of osteoarthritis via blockade of the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. (2012) 14:R177. doi: 10.1186/ar3930
220. Petit I, Jin D, and Rafii S. The SDF-1–CXCR4 signaling pathway: a molecular hub modulating neo-angiogenesis. Trends Immunol. (2007) 28:299–307. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2007.05.007
221. Nishimura Y, Ii M, Qin G, Hamada H, Asai J, Takenaka H, et al. CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 accelerates impaired wound healing in diabetic mice. J Invest Dermatol. (2012) 132:711–20. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.356
222. Vågesjö E, Öhnstedt E, Mortier A, Lofton H, Huss F, Proost P, et al. Accelerated wound healing in mice by on-site production and delivery of CXCL12 by transformed lactic acid bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2018) 115:1895–900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1716580115
223. Öhnstedt E, Vågesjö E, Fasth A, Lofton Tomenius H, Dahg P, Jönsson S, et al. Engineered bacteria to accelerate wound healing: an adaptive, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, first-in-human phase 1 trial. eClinicalMedicine. (2023) 60:102014. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102014
224. Öhnstedt E, Lofton Tomenius H, Frank P, Roos S, Vågesjö E, and Phillipson M. Accelerated wound healing in minipigs by on-site production and delivery of CXCL12 by transformed lactic acid bacteria. Pharmaceutics. (2022) 14:229. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020229
225. Shao S, Xu Q, Yu X, Pan R, and Chen Y. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors and their potential immune modulatory functions. Pharmacol Ther. (2020) 209:107503. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107503
226. Tian Y, Kong L, Li Y, Liao Z, Cai X, Deng S, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibition sensitizes radiotherapy by promoting T cell infiltration. OncoImmunology. (2023) 12:2268257. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2023.2268257
227. Ziff OJ, Bromage DI, Yellon DM, and Davidson SM. Therapeutic strategies utilizing SDF-1α in ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res. (2018) 114:358–67. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvx203
228. Graham GJ, Handel TM, and Proudfoot AEI. Leukocyte adhesion: reconceptualizing chemokine presentation by glycosaminoglycans. Trends Immunol. (2019) 40:472–81. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2019.03.009
229. Metzemaekers M, Mortier A, Janssens R, Boff D, Vanbrabant L, Lamoen N, et al. Glycosaminoglycans regulate CXCR3 ligands at distinct levels: Protection against processing by dipeptidyl peptidase IV/CD26 and interference with receptor signaling. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18:1513. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071513
230. Boff D, Russo RC, Crijns H, De Oliveira VLS, Mattos MS, Marques PE, et al. The Therapeutic Treatment with the GAG-Binding Chemokine Fragment CXCL9(74–103) Attenuates Neutrophilic Inflammation and Lung Dysfunction during Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection in Mice. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:6246. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116246
231. Boff D, Crijns H, Janssens R, Vanheule V, Menezes GB, Macari S, et al. The chemokine fragment CXCL9(74-103) diminishes neutrophil recruitment and joint inflammation in antigen-induced arthritis. J Leukoc Biol. (2018) 104:413–22. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3MA1217-502R
232. Oliveira VLS, Queiroz-Junior CM, Hoorelbeke D, Santos FRDS, Chaves IDM, Teixeira MM, et al. The glycosaminoglycan-binding chemokine fragment CXCL9(74–103) reduces inflammation and tissue damage in mouse models of coronavirus infection. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1378591. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1378591
233. Vanheule V, Boff D, Mortier A, Janssens R, Petri B, Kolaczkowska E, et al. CXCL9-derived peptides differentially inhibit neutrophil migration in vivo through interference with glycosaminoglycan interactions. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:530. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00530
Keywords: chemokines, chemokine receptors, resolution of inflammation, immune modulation, leukocyte recruitment
Citation: Oliveira VLS, Proost P and Struyf S (2025) Chemokines in the resolution of inflammation: key players and targets for therapeutic modulation. Front. Immunol. 16:1717666. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1717666
Received: 02 October 2025; Accepted: 31 October 2025;
Published: 19 November 2025.
Edited by:
Philippe Saas, Etablissement Français du Sang AuRA, FranceReviewed by:
Valentina Cecchinato, Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB), SwitzerlandNestor Ruben Lago, University of Buenos Aires, Argentina
Copyright © 2025 Oliveira, Proost and Struyf. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Vivian Louise Soares Oliveira, dml2aWFuLm9saXZlaXJhQGt1bGV1dmVuLmJl; Sofie Struyf, c29maWUuc3RydXlmQGt1bGV1dmVuLmJl
 Vivian Louise Soares Oliveira
Vivian Louise Soares Oliveira Paul Proost
Paul Proost Sofie Struyf
Sofie Struyf