- Tianjin Key Laboratory of Risk Assessment and Control for Environment & Food Safety, State Key Laboratory of Pathogen and Biosecurity, Academy of Military Medical Sciences, Tianjin, China
In recent years, there has been an increase in the incidence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), its pathogenesis remains unknown, and there are no effective treatments available. Early identification of individuals at risk enables early targeted intervention, which improves outcomes. Through the integration of artificial intelligence and the medical field, researchers can establish a machine learning (ML) risk prediction model to estimate the risk of ASD. Currently, a variety of risk models have been developed using multiple factors, such as genetic background, gaze behavior, adverse conditions during pregnancy and childbirth, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, and intestinal microbial composition, to predict ASD. These ML prediction models have shown some reliability in predicting ASD risk. In the future, ML prediction models for ASD will present significant challenges and opportunities, potentially helping identify drug targets for developing novel therapies to alleviate ASD symptoms and enable precision medicine.
1 Introduction
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a common form of pervasive developmental disorder (PDD) characterized by neurodevelopmental abnormalities, resulting in communication difficulties, stereotyped actions, repetitive behaviors, and apathy (Matson et al., 2009, Santocchi et al., 2016). The incidence of ASD is high. According to the United States Centers for Disease Control (CDC) report in 2021, about 1 in 44 (2.3%) 8-year-old children were diagnosed with ASD by the Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network in 2018, with a prevalence rate 3.39 times higher than that in 2000 (Maenner et al., 2021). In 2022, the Development of the Autism Education and Rehabilitation Industry estimated that the number of ASD patients in China may exceed 10 million, with over 2 million being children aged 0–14 years and nearly 200,000 new cases per year (AERI, 2022). Zeidan et al. calculated a global prevalence rate of 1:100 for autism from 2012 to 2021 (Zeidan et al., 2022). In Australia, 0.74% of children under the age of 7 are diagnosed with ASD (Bent et al., 2015). Therefore, ASD has emerged as a global public health concern.
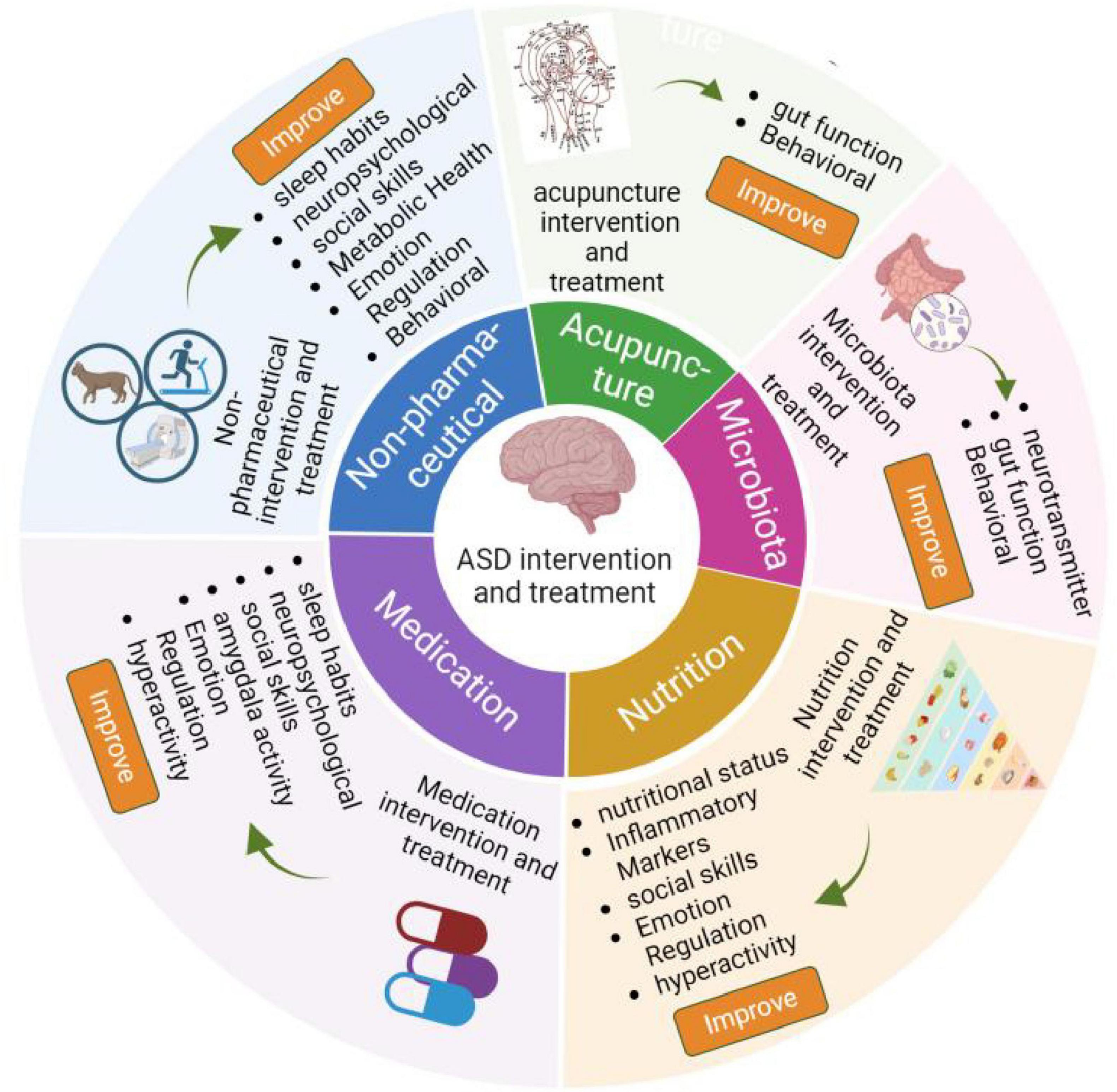
Nowadays, it is believed that ASD is a complex process driven by the accumulation of genetic, demographic, environmental, and adverse factors during pregnancy (Qin et al., 2024). However, the detailed pathogenesis of ASD is still poorly understood. Currently, ASD diagnosis is less than ideal, as it depends on interviews and questionnaires (Guthrie et al., 2012, Liu et al., 2019, Doi et al., 2022). Not only does it require a high level of diagnostic experience from physicians, but these methods also fail to detect child patients under 3 years old, who may have the highest detection rate due to their lack of typical autism characteristics. Failure to identify these children can disturb the development of their nervous system, resulting in lower efficacy in ASD management. Importantly, the intervention and treatment effects of ASD are also limited, which include non-pharmaceutical interventions, such as music therapy, exercise, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), equine-assisted activities, animal assisted therapy (Tse, 2020, Lopata et al., 2020, Rabeyron et al., 2020), targeting microbiota (Sanctuary et al., 2019, Kang et al., 2020, Wang et al., 2020), acupuncture (Chan et al., 2009, Wang et al., 2022), drug treatments (Golubchik et al., 2011, Harfterkamp et al., 2012, Scahill et al., 2015, Hendren et al., 2016, Ichikawa et al., 2016, Levine et al., 2016, Maras et al., 2018, Parker et al., 2019, Gabis et al., 2019, Ballester et al., 2019, Wichers et al., 2019, Mahdavinasab et al., 2019, Momtazmanesh et al., 2020, Soorya et al., 2021, McDougle et al., 2022, Le et al., 2022, Hacohen et al., 2022), nutrition supplements, such as tetrahydrobiopterin, resveratrol, vitamin D, omega-3, fatty acid, d-Cycloserine, folinic acid (Klaiman et al., 2013, Frye et al., 2016, Wink et al., 2017, Adams et al., 2018, Hendouei et al., 2019, Mazahery et al., 2019, Javadfar et al., 2020, Keim et al., 2022), as shown in Figure 1.
In recent years, machine learning (ML) has emerges as a key tool for early detection, diagnosis, and intervention of disease by analyzing large amounts of sample data to identify risk factors for disease. Duggan, M. R. (Duggan and Walker, 2024) utilized ML on plasma proteome data to predict 11 organ-specific aging diseases, including heart failure, cognitive decline, and Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). In addition, ML has been used to predict cardiovascular disease and breast cancer based on the human microbiome (Liu et al., 2024). In this review, we summarize the risk factors of ASD and the growing role of ML in predicting ASD, especially through the analysis of intestinal microbiome. Establishing an ML risk prediction model for ASD using gut microbiota and applying it to clinical practice may facilitate for the prediction and treatment of ASD in the future.
2 Risk factors of ASD
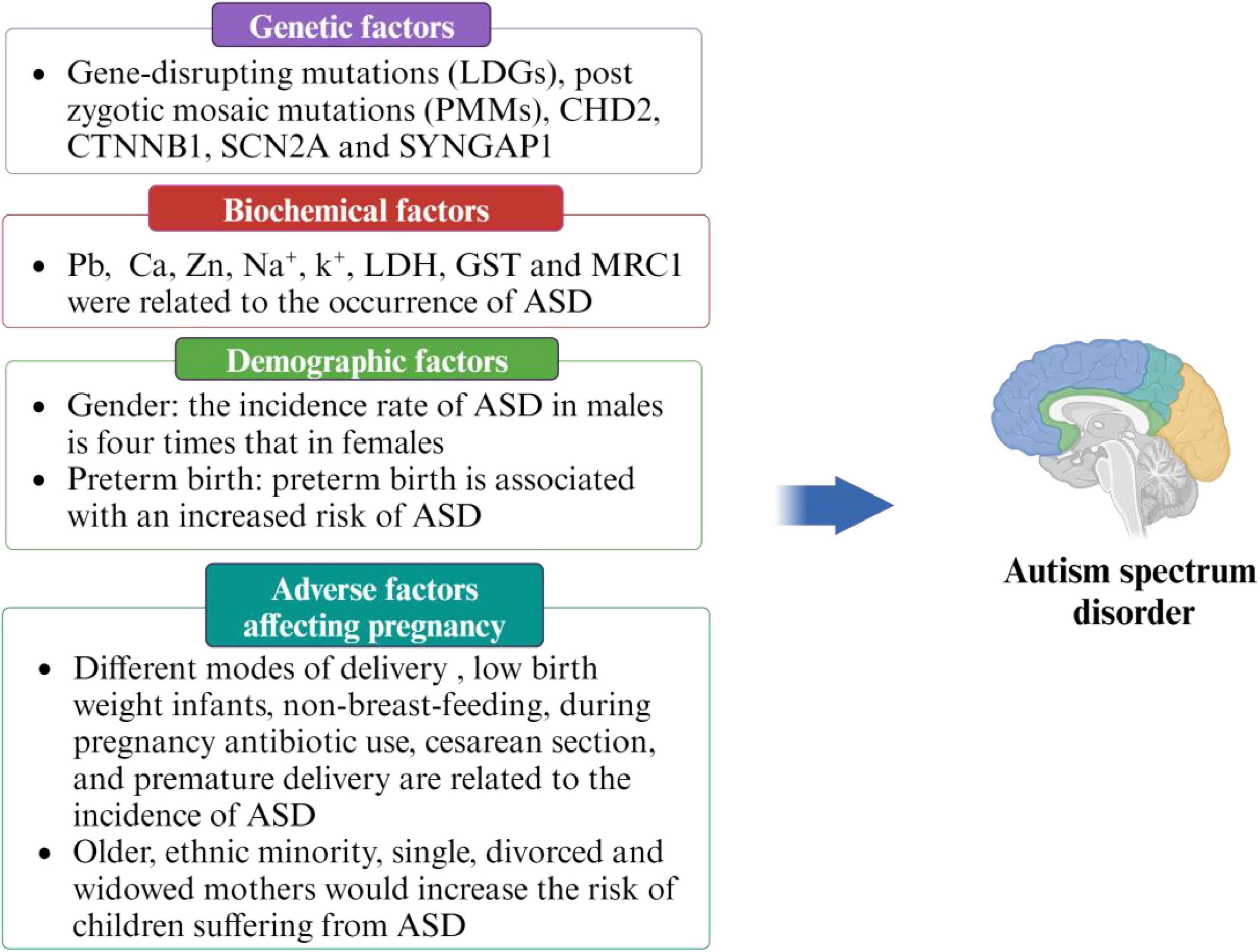
ASD may be a multifactorial disease, and a single factor alone is not sufficient to fully explain its onset. Therefore, it is crucial to identify and understand the various risk factors in order to prevent the occurrence of ASD. Previous studies have identified several high-risk factors related to ASD, including genetic factors (Zhang and Shen, 2016, Krupp et al., 2017), demographic factors (Perales-Marín et al., 2021, Crump et al., 2021, Faruk et al., 2023), adverse factors affecting pregnancy (Limperopoulos et al., 2008, Darcy-Mahoney et al., 2016, Al-Zalabani et al., 2019, Hamad et al., 2019, Axelsson et al., 2019, Madany et al., 2022a,b, Sousamli et al., 2024), and biochemical factors (Wu et al., 2018, Kim et al., 2019, Hassan et al., 2022, Zhang et al., 2022). Detailed information is provided in Figure 2.
2.1 Demographic factors
Preterm birth and gender have been associated with an increased risk of ASD development in infants (Crump et al., 2021, Haghighat et al., 2022, Tartaglione et al., 2022). A national cohort study performed on 4,061,795 infants born in Sweden from 1973 to 2013 found that preterm birth is associated with a higher risk of ASD (Beggiato et al., 2017). This could be attributed to the neurological development of the fetus. Alfred et al. (Supekar et al., 2022) conducted a population-based case-control study involving 128 children diagnosed with ASD and 311 control subjects in Spain. The study utilized questionnaires to collect information and found a higher incidence of ASD among children born via cesarean section and male gender. The incidence rate of ASD in males is four times that in females (Wu et al., 2022). This disparity may be due to the underrecognition of ASD in girls by diagnostic tools and sex-related genetic factors (Wilfert et al., 2021). The brains functionally organized differently of females and males with ASD, such as motor, language and visuospatial attentional systems (Supekar et al., 2022), which shows that the different incidence rate of ASD between male and female may be related to brain function.
2.2 Pregnancy, delivery, and postpartum factors
Exposure to adverse risk factor during pregnancy can significantly impact the normal development of the fetus, leading to impaired neurodevelopment in children. Several factors, such as different modes of delivery, low birth weight, lack of breastfeeding, antibiotic use during pregnancy (Hamad et al., 2019, Madany et al., 2022a,b), cesarean section (Al-Zalabani et al., 2019, Axelsson et al., 2019), and premature delivery (Limperopoulos et al., 2008) has been linked to an higher incidence of ASD. A retrospective study analyzed 664 records of children treated at one of the largest ASD treatment centers in the United States from March 1, 2009, to December 10, 2010 found that children born to older mothers, as well as those from ethnic minority, or raised by single, divorced, or widowed mothers, had an elevated risk of developing ASD (Darcy-Mahoney et al., 2016). In addition, multicenter studies have shown that maternal exposure to the triclosan during pregnancy can cause ASD in offspring, significant male (Wu et al., 2022). Hamad et al. analyzed data from Manitoba’s population, including 214,834 children born in Manitoba, Canada, from April 1, 1998, to March 31, 2016 and found that children exposed to antibiotics during the second or third trimester of pregnancy had an elevated risk of developing ASD (Hamad et al., 2019).
2.3 Genetic factors
Genetic mutations related to ASD result in neurodevelopmental impairments (Wilfert et al., 2021). A recent study identified gene expression signatures in various neuronal cell types associated with genes containing likely gene-disrupting mutations (LGDs) in ASD patients and screened 117 risk genes (Zhang and Shen, 2016). The analysis of relevant gene subsets and genetic variations associated with non-syndromic ASD was conducted using databases such as the National library of medicine (ClinVar), autism research community focusing on genes implicated in autism susceptibility (SFARI Gene), and Autism informatics portal (AutDB). Through this analysis, a subset of twenty overlapping genes potentially specific to non-syndromic ASD was identified. These genes were found to be enriched in biological processes related to neuronal development and differentiation, synaptic function, and social behavior (An et al., 2018). Krupp et al. evaluated the potential role of post-zygotic mosaic mutations (PMMs) in ASD risk and identified the risk genes CHD2, CTNNB1, SCN2A, and SYNGAP1, as well as the candidate risk genes ACTL6B, BAZ2B, COL5A3, SSRP1, and UNC79, which may be involved in chromatin remodeling or neural development (Krupp et al., 2017). These findings highlight neurogenesis, chromatin modification, and synaptic functions as key potential mediators of genetic vulnerability. Furthermore, Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) of de novo and rare inherited single-nucleotide variants (SNVs), along with structural variations in genes previously linked to ASD and other neurodevelopmental disorders, revealed important insights. In one case, two ASD-affected siblings harbored distinct ASD-related mutations, rather than sharing a common risk variant. Interestingly, these siblings exhibited greater clinical variability compared to cases where siblings shared a common risk variant (Yuen et al., 2015). This suggests that variations in ASD-associated genetic factors may contribute to clinical heterogeneity, thereby complicating ASD identification.
2.4 Biochemical factors
A study tested the blood of 1,537 children in Xinjiang from September 2018 to September 2019 and found that Pb, Ca, and Zn were linked to the occurrence of ASD (Zhang et al., 2022). A meta-analysis encompassed 29 case-control studies involving a total of 2,504 children with ASD and 2,419 healthy controls. The analysis revealed that copper levels in hair were significantly lower in children with ASD compared to healthy controls. However, no significant difference was observed in blood copper levels between the ASD group and the control group (Liu et al., 2023). This indicates that copper has adverse effects on the accumulation sites in the body. Detection in the hair indicates a higher accumulation in the head, which can cause significant damage to the brain. In addition, vitamin D status in neonates was significantly associated with ASD and intellectual disabilities (Wu et al., 2018). In another study, Hassan et al. analyzed blood samples from 40 ASD patients and 40 healthy controls. Their findings revealed that sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH), Glutathione-S-Transferases (GST), and Mannose Receptor C Type 1 (MRC1) were all associated with ASD onset (Hassan et al., 2022). Blood contains various ions that play a role in the regulation of nervous system activities and exchanging nutrition substances with cells through a variety of ion channels.
Research has evaluated perinatal biomarkers associated with the subsequent development of ASD. Utilizing banked cord blood plasma samples and clinical data from the Iowa Maternal Fetal Tissue Bank, the study found elevated levels of homocysteine, myristic acid, and pentadecanoic acid in ASD samples. Conversely, levels of L-isoleucine, L-threonine, O-phosphoethanolamine, and 2-hydroxybutyric acid were reduced (Brandon et al., 2022). In cytokine levels, comparing those later diagnosed with ASD (n = 38) to typically developing (TD) (n = 103) infants at 3 years of age. The results showed elevated levels of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) and reduced levels of interleukin-1α (IL-1α), IL-1β, and IL-4 in the ASD group (Moreno et al., 2024). The Barwon Infant Study, which involved n = 1,074 mother-child pairs, identified a correlation between elevated cord blood acylcarnitine levels and increased Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)/ASD symptoms at age of two. This relationship appeared to be partially mediated by socioeconomic factors such as low income, low Apgar scores, and maternal inflammation (Vacy et al., 2024). A total of 567 children (92 with ASD and 475 neurotypical) from the Boston Birth Cohort study were enrolled at birth and prospectively monitored at the Boston Medical Center. Elevated levels of cord blood unmetabolized folic acid were linked to an increased risk of ASD among Black children (Raghavan et al., 2020), underscoring the need to consider ethnic-specific factors for prenatal folic acid supplementation.
ASD is characterized by a complex interplay of risk factors, including genetic predisposition, biochemical imbalances, prenatal complications, and gut microbiota dysbiosis. While progress has been made in understanding these contributing elements, substantial gaps remain. Future research should integrate multi-omics data, such as genomic, radiomic, and microbiome, with Artificial Intelligence (AI) analytics. This system-level approach could decode ASD heterogeneity through computational modeling, paving the way toward personalized diagnostics and therapies.
3 Screening with ASD ML prediction model
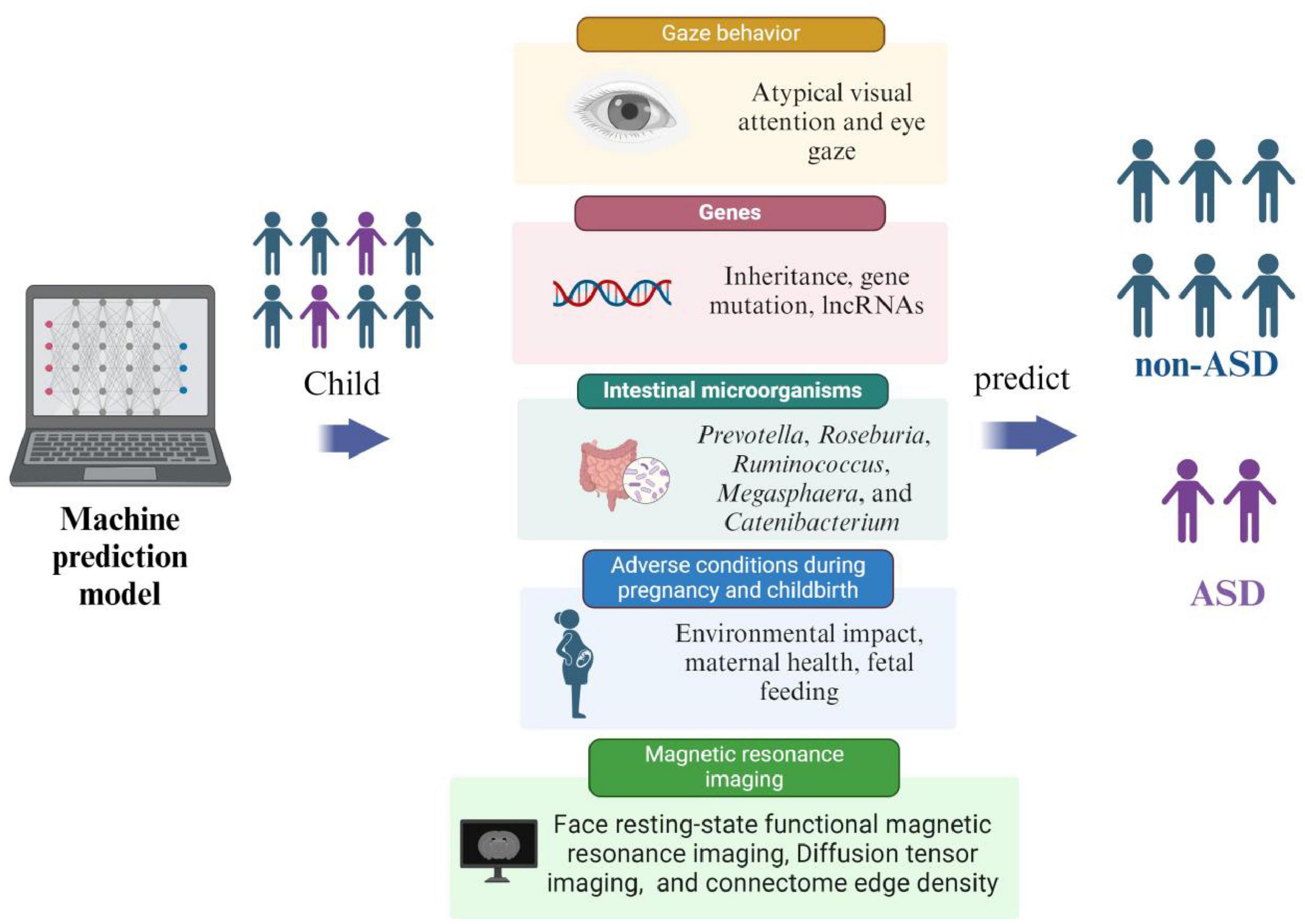
ASD is an irreversible mental development disorder. Its diagnosis relies on scales and behavioral tests, which can only identify patients with obvious symptoms. However, these tools often fail to accurately diagnose individuals with atypical or subtle presentations, limiting opportunities for early treatment and reducing intervention effectiveness. Early intervention can effectively prevent the onset of ASD, with a scientific and feasible risk prediction model serving as the foundation for predicting ASD. Rahman et al. (2020) used the electronic medical records (EMRs) system of the Israeli Health Maintenance Organization to extract data on ASD children and non-ASD children born from January 1, 1997 to December 31, 2008, and predicted ASD through an ML model. By incorporating parents’ sociodemographic information, medical history, and prescription medications data to train various ML algorithms, including Multiple Logistic Regression (MLR), Artificial Neural Network (ANN), and Random Forest (RF), they achieved a c statistic (the c statistic is mainly used to evaluate the prediction model’s accuracy; accuracy increases as the value gets closer to 1) of 0.709 for predicting ASD. The model demonstrated a sensitivity of 29.93%, specificity of 98.18%, accuracy of 95.62%, false positive rate of 1.81%, and positive predictive value of 43.35%. The study concluded that the ML algorithm, combined with EMR data, effectively identified ASD risk in early life and revealed previously unknown features associated with ASD risk. These methods can have the potential to enhance the accurate and effective detection of ASD in a large population of children. Currently, there is no universally accepted gold standard for ASD risk prediction models. Factors used for prediction include starting behavior (early behavioral indicators), magnetic resonance imaging, adverse factors affecting pregnancy, genetics, and gut microbiota. The development of ML-based risk prediction models for ASD is an ongoing area of research (Figure 3).
3.1 ASD ML prediction models based on genetic factors
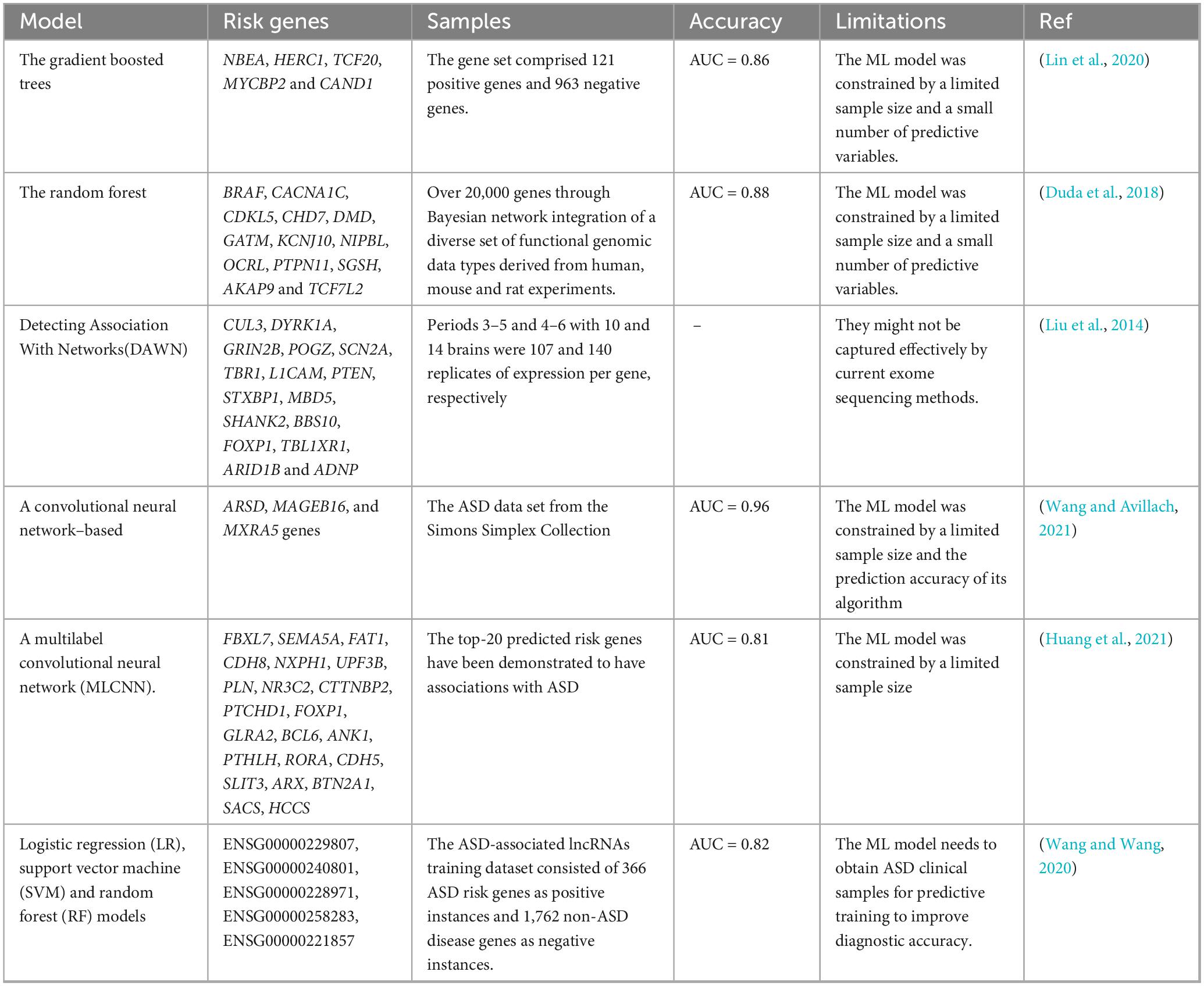
The development of ASD is linked to genetic factors. At present, ML prediction models are increasingly used for genetic risk prediction (Yao et al., 2021). A study used a method based on ML to predict ASD risk genes, analyzing human brain spatiotemporal gene expression patterns, gene level constraint indicators, and other gene variation characteristics to predict the risk of ASD (Lin et al., 2020). Duda et al. (2018) constructed an ML model to rank ASD risk genes across the entire genome using a brain-specific functional relationship network (FRN) of genes. They identified some key pathways in early neural development of ASD through functional enrichment analysis of candidate gene networks. A new algorithm, Detecting Association With Networks (DAWN), was developed to identify ASD using rare variations in exome sequencing and gene co-expression in the fetal middle prefrontal and motor somatosensory neocortex. The algorithm converts the integrated data into a hidden Markov random field, where the structure of the graph is determined by gene co-expression, and combines these interrelationships with node-specific observations, namely, gene identity, expression, and genetic data, to estimate risk. DAWN was used to study the emerging ASD sequence data and gene expression data from other brain regions and tissues (Liu et al., 2014). ASD is a complex brain disorder with polygenic etiology. Wang and Avillach (2021) used a deep learning gene classifier to diagnose ASD, performing chi-square test on the collected genome data to extract common variants that may be protective or pathogenic to ASD and designing a diagnostic classifier based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to predict ASD using the significant common variants identified. The deep learning model outperformed shallow ML models, achieving an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.955 and an 88% accuracy in identifying non-ASD individuals.
The prediction model develops constantly updated and developed. A new multi-label classification (MLC) model has been used to identify ASD risk genes and toxic chemicals on a large-scale dataset. First, the characteristic matrix and partial marker network of ASD risk genes and toxic chemicals were constructed from multiple heterogeneous biological databases. Based on global and local metrics, simulation results showed that the model has better classification performance than other MLC methods (Huang et al., 2021). This work will help promote the relationship discovery of ASD risk genes–environment interactions and aid in studying the gene–environment interactions in the future (genetic factors are internal, while environmental factors are external) to better understand the pathological mechanism of ASD. Wang and Wang (2020) developed a new ML method to predict candidate lncRNAs related to ASD. In the pre-training stage of model construction, an autoencoder network utilized gene expression data for representation learning, and random-forest-based feature selection was applied to the transcript-sequence-derived k-mers. The model includes LR, Support Vector Machine (SVM), and RF algorithms demonstrating the robustness of candidate priorities based on 10-fold cross-validation and hypothesis sites. These models are used to predict and prioritize a series of candidate lncRNAs (These lncRNAs demonstrate significant correlations with various ASD-related traits, such as sex differences, synapsin function, birth weight, and both intelligence and cognitive performance.), including some reported cis-regulators of known ASD risk genes. Gene mutations associated with ASD are polygenic, with a high frequency of gene mutations in humans. However, the relative contribution of each gene is small, hampering their identification. The details of the above ASD ML prediction models based on genetic factors are shown in Table 1.
3.2 ASD ML prediction model based on staring behavior
ASD is typically associated with atypical visual attention, and eye gaze data can be collected at a very young age. An automatic screening tool based on eye gaze data can identify the risk of ASD, which provides an opportunity to intervene before all symptoms manifest (Jiang et al., 2020, Tsuchiya et al., 2021). Using collected videos of Bangladeshi children from Dhaka Shishu Children’s Hospital and utilizing ML raters to determine the “risk score” of children’s ASD, this study improved the practicality and performance of the model. This was achieved by developing and applying a powerful new adaptive aggregation technology and establishing two classification layers. In the first layer, typical and atypical behavior are distinguished, while in the second layer, ASD and non-ASD are distinguished. Each layer utilizes a unique rater weighting scheme to summarize their classification scores based on the professional knowledge of different raters. Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was used to measure the accuracy of the model. The AUC of the first layer was 0.76, and that of the second layer was 0.85 (Tariq et al., 2019).
In addition, Liaqat et al. proposed two ML methods, the synthetic saccade method and the image-based method, to automatically classify children’s eye gaze data collected from natural image tasks. The first method uses the synthetic saccade pattern generation model to represent the baseline scan-path of a typical non-ASD individual. It combines this with the real scan-path and other auxiliary data as input for the depth learning classifier. The second method employs a more comprehensive image-based method, where the input image and a series of fixation maps are fed into a convolutional or recurrent neural network. In this experiment, the accuracy of ASD prediction in the validation dataset reached 62.13% (Liaqat et al., 2021). The details of the above ASD ML prediction models based on staring behavior are shown in Table 2.
3.3 ASD ML prediction model based on risk factor exposure during pregnancy and childbirth
The incidence of ASD is linked to certain risk factors during pregnancy. Grossi et al. (2016) evaluated 27 potential risk factors related to postpartum and pregnancy. They collected data by interviewing the mothers of 45 ASD children and 68 typically developing children. After selecting 16 variables from the initial 27 variables through a TWIST dataset (input selection and test training) system, special artificial neural networks (ANNs) differentiated between ASD and control subjects, with an overall accuracy of 80.19%. The study suggests that exposure to adverse factors during gestation may induce gene mutations in offspring.
To identify newborns at risk of ASD and detect potential biomarkers shortly after birth, a retrospective study was conducted comparing biological measurements and ultrasound data from infants later diagnosed with ASD to those from Neurotypical (NT) infants. These data were originally collected during routine prenatal and postnatal care. A supervised ML algorithm incorporating cross-validation was employed to classify NT and ASD infants. When optimizing for a low false-positive rate, the model correctly identified 96% of NT infants and 41% of ASD infants, yielding a positive predictive value of 77%. The study identified several biomarkers associated with ASD, including sex, autoimmune diseases in maternal family, cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection, IgG CMV levels, timing of fetal head rotation, femur length during the third trimester, white blood cell count during the third trimester, fetal heart rate during labor, neonatal feeding patterns, and differences in body temperature at birth and the following day. Statistical analysis revealed that 38% of ASD-risk infants had significantly larger fetal head circumference compared to age-matched NT infants (Caly et al., 2021). Maternal stress and immune influence fetal brain development, highlighting the importance of the mother’s physical health during pregnancy for optimal fetal development. The details of the above ASD ML prediction models based on adverse conditions during pregnancy and childbirth are shown in Table 3.
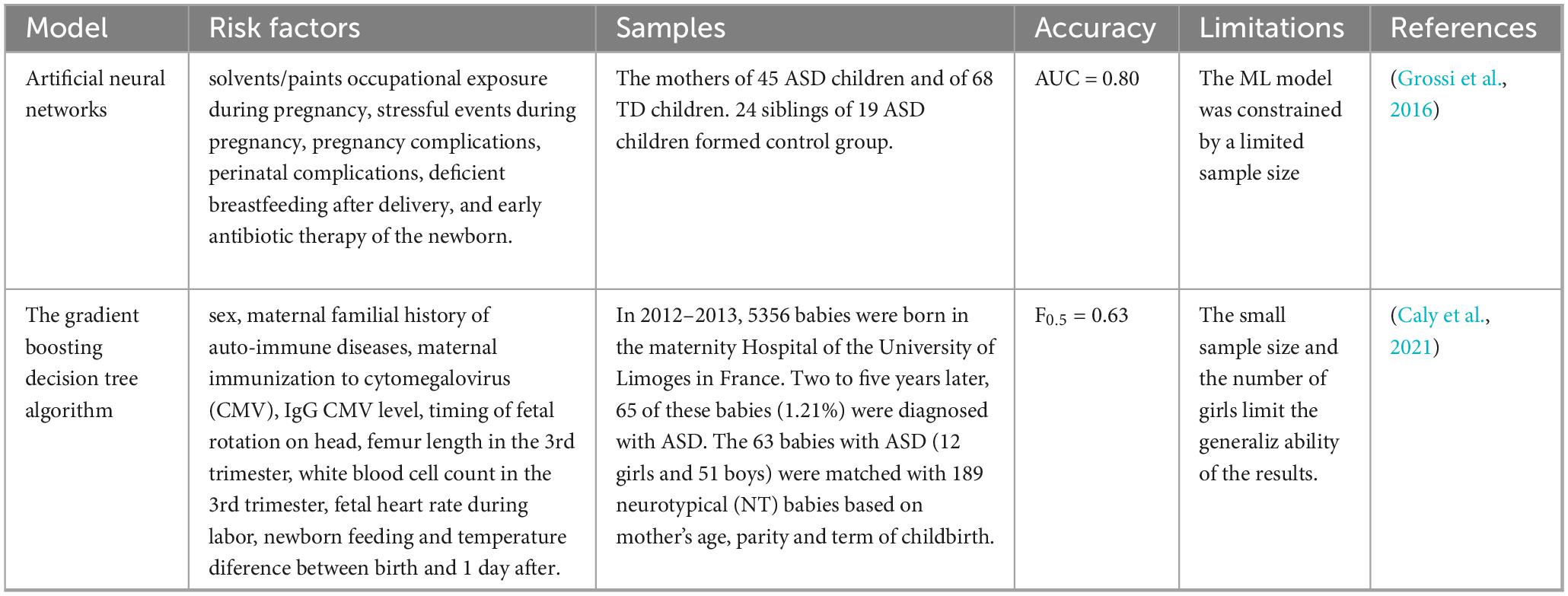
Table 3. ASD ML prediction models based on adverse conditions during pregnancy and childbirth comparative table.
3.4 ASD ML prediction model based on brain MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive detection method with high spatial resolution and high density resolution, which can effectively reflect brain lesions. With the advancement of computer technology and medical imaging technology, the “risk prediction model” based on medical imaging big data has emerged. The occurrence of infantile autism was predicted using the segmentation and segmentation maps of sMRI, with a peak sensitivity of 73.1% and a peak specificity of 75.9% (Gao et al., 2021). Liu et al. (2020) attempted to construct a reproducible and robust ASD neural patterns using heterogeneous multi-site brain imaging datasets. Brain connectivity was assessed using face resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data from the CC200 atlas based on the Extra-Trees algorithm. Through a cross-validation strategy, the mean classification accuracy of this method was found to be 72.2% (sensitivity, 68.6%; specificity, 75.4%). It improves the accuracy of ASD prediction by about 2% and the specificity by 3.2%. The connectivity analysis of the optimal model highlights the brain regions that play a significant role in social cognition and interaction, revealing that the correlation between the anterior and posterior default mode networks (DMNs) of individuals with ASD is lower than that of the control group. This observation is consistent with previous studies, which enables this method to effectively identify individuals with ASD risk. In addition, utilizing a hierarchical structure, deep ML models can identify ASD based on interactions within hierarchical functional brain networks (FBNs) inferred from fMRI, achieving a classification accuracy of 82.1% (Qiang et al., 2023).
There is evidence that microstructural disorders and the disruptions in the connectome of white matter (WM) are related to the onset of ASD. The influence of age on the microstructure of WM was evaluated using Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) and connectome Edge Density (ED) in ASD and control patients of different age groups. Fractional anisotropy (FA), Mean Diffusivity (MD), Radial Diffusivity (RD), Axial Diffusivity (AD), and ED maps were created for each subject. Voxel-wise and tract-based analysis was conducted using different combinations of improved ML classifiers and dimension reduction algorithms. The results showed that changes in the corpus callosum and connectome are related to ASD and are not present in infants and toddlers, but become more apparent in adolescents and young adults (Weber et al., 2022).
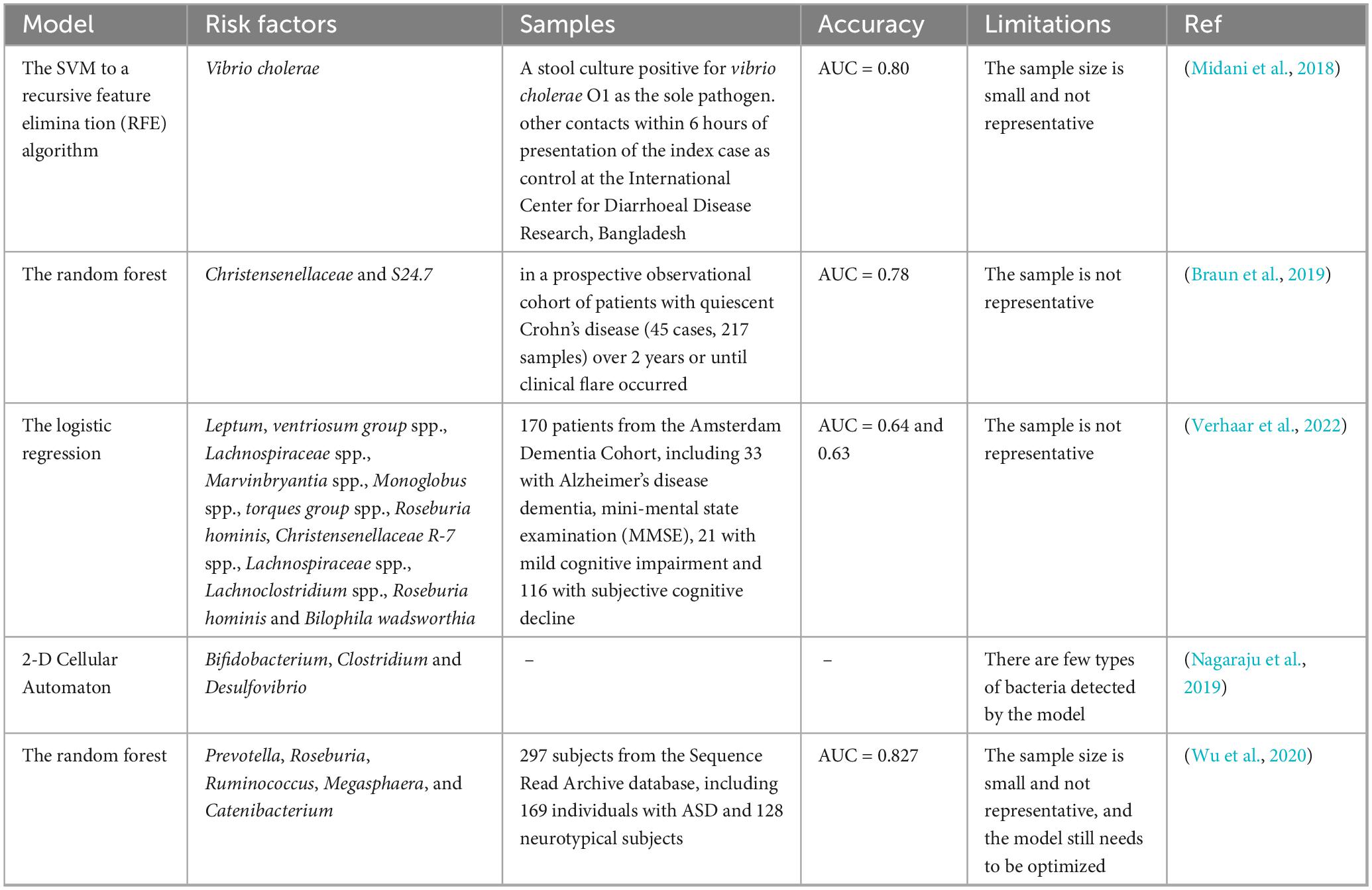
3.5 ASD ML prediction model based on intestinal microorganisms
There is a large number of bacteria, viruses, and fungi present in the human intestine, collectively known as gut microbiota. The normal human intestinal microorganisms are found in a state of dynamic equilibrium. When these microorganisms are disturbed, it can lead to disturbances in the normal functions of the digestive system, respiratory system, immune system, nervous system, and other bodily systems (Bose et al., 2020, Wastyk et al., 2021, Fu et al., 2021, Liu et al., 2022, Sun et al., 2024). Although the pathogenesis of ASD is not clear, individuals with ASD often experience gastrointestinal (GI) co-morbidities, such as irritable bowel syndrome, diarrhea, and chronic constipation, and the severity of these symptoms is linked to the degree of GI microbiota dysbiosis (Sanctuary et al., 2019, Harris et al., 2021). In addition, imbalances in intestinal microbiota is associated with the onset and progression of ASD (Dan et al., 2020, Fouquier et al., 2021, Li et al., 2022). Intestinal microbiota of ASD patients exhibit a reduction in alpha diversity (Lou et al., 2021). The abundance of Bifidobacterium spp. in the intestine of children with ASD is lower (Jendraszak et al., 2021). In a mouse model of ASD induced by SHANK gene deletion, changes in intestinal microbiota were observed, with an increase in Firmicutes and a decrease in Proteobacteria and Verrucomicrobia, as well as the presence of Deferriactors, Tenericites, and Chlamydiae (Sauer et al., 2019). Aseptic mice transplanted with intestinal microbiota from ASD patients exhibited increased repetitive behavior, decreased movement, and reduced communication (Sharon et al., 2019). Microbial transfer therapy has shown significant improvement in gastrointestinal and behavioral symptoms (Arnold et al., 2019, Kang et al., 2019, Kang et al., 2020, Li et al., 2021). In addition, supplementation with probiotics, such as Lactobacillus (L.) reuteri has been shown to improve social behavior in ASD mice through the vagus nerve (Sgritta et al., 2019).
Intestinal microbiota has shown significant predictive ability in disease prediction models. ML modeling of the human microbiome has the potential to identify microbial biomarkers and aid in the diagnosis of various diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes, and colorectal cancer (Topçuoğlu et al., 2020). Midani et al. (2018) developed an ML model based on intestinal microbiota that, along with known clinical and epidemiological risk factors, can predict vibrio cholerae infection. Braun et al. (2019) analyzed a study on Crohn’s disease (CD) using a binary/ternary/ratio (BTR) model and found that the microbial richness of patients with CD in clinical, biomarker, and mucosal remission was significantly reduced, while the ecological imbalance index was significantly increased. Verhaar et al. (2022) used an ML model to study the relationship between intestinal microbiota composition and AD biomarkers in patients with AD, mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and subjective cognitive decline (SCD). Microbiota composition showed the best performance in predicting amyloid and p-tau levels using ML, with AUC values of 0.64 and 0.63, respectively. Intestinal microbiota is not only associated with many gastrointestinal diseases but also affects other parts of the body, as evidenced by its role in ASD. Although it has been demonstrated that the number and structure of intestinal microbiota may be closely related to ASD, there are few models based on intestinal microbiota to predict ASD. A recent study used a two-dimensional cellular automatic mechanism to build a mathematical model to simulate the growth rate and intestinal nutrients of bifidobacteria, clostridium, and desulfovibrio, as well as the growth rate and interaction after lysozyme was introduced into the intestine. The model simulation revealed that altering the number of Clostridium in the intestine could cause changes in the intestinal microbiota, potentially affecting the risk of ASD (Nagaraju et al., 2019). In a study by Wu et al. (2020), 297 subjects from the sequence read archive database were evaluated, including 169 ASD patients and 128 neurotypical subjects. Various analyses were conducted, including α-diversity, phylogenetic profiles, and functional profiles. Principal component analysis (PCA) showed that ASD and neurotypical subjects could be distinguished based on unweighted UniFrac distance. Through linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe) evaluation and random forest analysis, Prevotella, Roseburia, Ruminococcus, Megasphaera, and Catenibacterium were identified as potential biomarkers of ASD. Functional analysis revealed six significant pathways distinguishing ASD and neurotypical subjects, including oxidative phosphorylation, nucleotide excision repair, peptidoglycan biosynthesis, photosynthesis, photosynthesis proteins, and two-component system. Based on these changes in the intestinal microbiota of ASD subjects, four ML models were developed: RF, MLP, kernelized Support Vector Machines (SVMs) with the RBF kernel, and Decision Tree (DT). Among them, the RF model demonstrated the best performance achieving an F1 score (a measure of a model’s precision and recall) of 0.74 and an AUC of 0.827, indicating both reliability and generalizability. The details of the above ASD ML prediction models based on intestinal microorganisms are shown in Table 4.
4 Conclusion and perspectives
The research outlined above has demonstrated the effectiveness of the ML model in predicting ASD using genetic background, gaze behavior, adverse perinatal conditions, brain MRI data, and intestinal microbiota. These approaches play a crucial role in forecasting the onset and progression of ASD. However, several improvements are required for enhancing the ML prediction model: (1) expanding the sample size and predicting factors for ML; (2) unifying the selection of prediction factors and detection methods; (3) continuously optimizing, training, and testing ML models to improve prediction accuracy; and (4) conducting a crowd cohort study in order to verify the accuracy and feasibility of the machine model.
The integration and development of ML and prediction models have been increasingly applied in the medical field (Lee et al., 2022, Ben-Yacov et al., 2023). ML prediction models for ASD have also been developed both domestically and internationally (Qiu et al., 2020, Zhu et al., 2022). This approach presents great challenges and potential for more effective screening, diagnosis, and treatment in clinical practice.
ML models discussed in the literature primarily serve two key purposes:
(1) Feature selection, involving the extraction of the most discriminative features from the data to be used in prediction or as a foundation for training ML models
(2) Classification of ASD and control groups, enabling the identification of differential features between both populations and facilitating the detection of ASD-related characteristics in previously unknown samples.
Most of the presented studies employed traditional ML techniques, such as SVM, LR, RF, and DT. Among these techniques, RF was the most frequently utilized due to its superior performance compared to the other techniques and its relatively low computational complexity during training. However, neural network models were solely used, with only classic architectures such as convolutional neural networks, multilabel convolutional neural networks, and artificial neural networks, being applied. It is evident that the discussed intestinal microbiota prediction models mainly rely on conventional ML algorithms, including RF, SVM, recursive feature elimination algorithm, and LR. However, AUC values for these models range from 0.64 to 0.83, indicating that they have not yet reached optimal performance. To improve model performance, experience-based algorithms incorporating meta-heuristic techniques can be employed for intelligent parameter optimization during model tuning. This approach not only improves predictive accuracy but also effectively mitigates the risk of overfitting, especially when considering small sample sizes. Future research will focus on exploring interpretable AI models and validating the proposed methods on additional ASD datasets as they become available, before being applied in clinical settings.
Currently, there is limited research on artificial intelligence in predicting ASD risk through intestinal microbiota analysis, and a comprehensive system has not been established yet. The main problem with ML is the small sample size and the lack of inclusion of key high-risk factors, which limits the diversity and accuracy of predictive factors. It is hoped that further research on ML models, especially the combination of laboratory research and population cohort studies, can achieve the following goals:
(1) Establishing a library of ASD intestinal microbiota samples, identifying the target bacteria in the microbiota as biomarkers using machine models, determining disease risk through screening these bacteria, and establishing a prediction model for early disease detection.
(2) Screening high-risk bacteria through ML prediction models, formulating standardized, refined, and intelligent treatment measures tailored to the characteristics of ASD patients, establishing more precise diagnostic standards and medication guidelines, and providing insights for precision medical treatment.
(3) Utilizing artificial intelligence to predict intestinal microbiota patterns as a guide for the prediction and treatment of ASD, providing a reference for the development of targeted drugs to regulate microbiota, and reducing the time and cost of drug development.
(4) Recognizing the deficiencies in underdeveloped countries medical services within the broader context of global healthcare disparities, particularly the low professional standards of doctors, which reflect systemic challenges in resource allocation, education, and infrastructure development in underserved regions worldwide. This issue underscores the need for a more equitable and inclusive approach to healthcare that addresses both local and global inequities, ensuring that all individuals, regardless of their geographic location, have access to quality medical care and professional expertise.
Early prediction, diagnosis, and treatment of ASD are crucial for enhancing neurodevelopmental outcomes in children. Gut microbiota plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of ASD through various mechanisms, including the regulation of metabolites, modulation of immune responses, and activation of neural signaling pathways. The dynamic variations in gut microbiota present potential targets for early prediction and intervention in ASD. However, the translation of basic research into clinical practice encounters several challenges, such as methodological limitations, data integrity issues, and ethical considerations. Addressing privacy, data deficiency and ethical issues in population surveys is not a matter of a single technical approach, but a systematic project that runs through the entire research life cycle and integrates legal compliance, technical safeguards, ethical principles and scientific rigor. Always placing the rights, dignity and well-being of participants at the core is the cornerstone of ensuring that research is scientifically effective and responsible. Moreover, the integration of multidisciplinary technologies, including single-cell omics and AI analytics, is essential for explaining the complex networks involved in gut-brain interactions.
Future research should focus on the development of microbiota-based diagnostic tools and precision therapeutic strategies that selectively target specific microbial communities. Such approaches hold significant promise for improving neurodevelopmental outcomes for individuals with ASD.
Author contributions
WX: Writing – original draft. HL: Writing – review & editing. JL: Writing – review & editing. MJ: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82273588).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adams, J., Audhya, T., Geis, E., Gehn, E., Fimbres, V., Pollard, E., et al. (2018). Comprehensive nutritional and dietary intervention for autism spectrum disorder-a randomized, controlled 12-month trial. Nutrients 10, 369–369. doi: 10.3390/nu10030369
AERI. (2022). Report on the Development of Autism Education and Rehabilitation Industry in China.pdf. Beijing: Guangming Daily.
Al-Zalabani, A., Al-Jabree, A., and Zeidan, Z. (2019). Is cesarean section delivery associated with autism spectrum disorder? Neurosciences 24, 11–15. doi: 10.17712/nsj.2019.1.20180303
An, J., Lin, K., Zhu, L., Werling, D., Dong, S., Brand, H., et al. (2018). Genome-wide de novo risk score implicates promoter variation in autism spectrum disorder. Science 362:eaat6576. doi: 10.1126/science.aat6576
Arnold, L., Luna, R., Williams, K., Chan, J., Parker, R., Wu, Q., et al. (2019). Probiotics for gastrointestinal symptoms and quality of life in Autism: A placebo-controlled pilot trial. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 29, 659–669. doi: 10.1089/cap.2018.0156
Axelsson, P., Clausen, T., Petersen, A., Hageman, I., Pinborg, A., Kessing, L., et al. (2019). Relation between infant microbiota and autism?: Results from a National Cohort Sibling Design Study. Epidemiology 30, 52–60. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0000000000000928
Ballester, P., Martínez, M., Inda, M., Javaloyes, A., Richdale, A., Muriel, J., et al. (2019). Evaluation of agomelatine for the treatment of sleep problems in adults with autism spectrum disorder and co-morbid intellectual disability. J. Psychopharmacol. 33, 1395–1406. doi: 10.1177/0269881119864968
Beggiato, A., Peyre, H., Maruani, A., Scheid, I., Rastam, M., Amsellem, F., et al. (2017). Gender differences in autism spectrum disorders: Divergence among specific core symptoms. Autism Res. 10, 680–689. doi: 10.1002/aur.1715
Bent, C., Dissanayake, C., and Barbaro, J. (2015). Mapping the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders in children aged under 7 years in Australia, 2010-2012. Med. J. Aust. 202, 317–320. doi: 10.5694/mja14.00328
Ben-Yacov, O., Godneva, A., Rein, M., Shilo, S., Lotan-Pompan, M., Weinberger, A., et al. (2023). Gut microbiome modulates the effects of a personalised postprandial-targeting (PPT) diet on cardiometabolic markers: A diet intervention in pre-diabetes. Gut 72, 1486–1496. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-329201
Bose, D., Saha, P., Mondal, A., Fanelli, B., Seth, R., Janulewicz, P., et al. (2020). Obesity worsens gulf war illness symptom persistence pathology by linking altered gut microbiome species to long-term gastrointestinal, hepatic, and neuronal inflammation in a mouse model. Nutrients 12, 1–28. doi: 10.3390/nu12092764
Brandon, M. S., Serena, B. G., Donna, A. S., and Mark, K. S. (2022). Cord blood metabolomics and autism spectrum disorder. FASEB J. 36, 1–11. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2022.36.S1.R5837
Braun, T., Di Segni, A., BenShoshan, M., Neuman, S., Levhar, N., Bubis, M., et al. (2019). Individualized dynamics in the gut microbiota precede Crohn’s disease flares. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 114, 1142–1151. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000136
Caly, H., Rabiei, H., Coste-Mazeau, P., Hantz, S., Alain, S., Eyraud, J., et al. (2021). Machine learning analysis of pregnancy data enables early identification of a subpopulation of newborns with ASD. Sci. Rep. 11, 1–15. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86320-0
Chan, A., Cheung, M., Sze, S., and Leung, W. (2009). Seven-star needle stimulation improves language and social interaction of children with autistic spectrum disorders. Am. J. Chin. Med. 37, 495–504. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X09007004
Crump, C., Sundquist, J., and Sundquist, K. (2021). Preterm or early term birth and risk of autism. Pediatrics 148:e2020032300. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-032300
Dan, Z., Mao, X., Liu, Q., Guo, M., Zhuang, Y., Liu, Z., et al. (2020). Altered gut microbial profile is associated with abnormal metabolism activity of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Gut Microbes 11, 1246–1267. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1747329
Darcy-Mahoney, A., Minter, B., Higgins, M., Guo, Y., Zauche, L., and Hirst, J. (2016). Maternal and neonatal birth factors affecting the age of ASD diagnosis. Newborn Infant Nurs. Rev. 16, 340–347. doi: 10.1053/j.nainr.2016.09.033
Doi, H., Iijima, N., Furui, A., Soh, Z., Yonei, R., Shinohara, K., et al. (2022). Prediction of autistic tendencies at 18 months of age via markerless video analysis of spontaneous body movements in 4-month-old infants. Sci. Rep. 12:18045. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21308-y
Duda, M., Zhang, H., Li, H., Wall, D., Burmeister, M., and Guan, Y. (2018). Brain-specific functional relationship networks inform autism spectrum disorder gene prediction. Transl. Psychiatry 8, 1–9. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0098-6
Duggan, M., and Walker, K. (2024). Organ-specific aging in the plasma proteome predicts disease. Trends Mol. Med. 30, 423–424. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2024.01.005
Faruk, M., Rahman, M., Rana, M., Mahmud, S., Al-Neyma, M., Karim, M., et al. (2023). Socioeconomic and demographic risk factors of autism spectrum disorder among children and adolescents in Bangladesh: Evidence from a cross-sectional study in 2022. PLoS One 18:e0289220. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289220
Fouquier, J., Moreno Huizar, N., Donnelly, J., Glickman, C., Kang, D., Maldonado, J., et al. (2021). The gut microbiome in Autism: Study-site effects and longitudinal analysis of behavior change. mSystems 6:e00848-20. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00848-20
Frye, R., Slattery, J., Delhey, L., Furgerson, B., Strickland, T., Tippett, M., et al. (2016). Folinic acid improves verbal communication in children with autism and language impairment: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Mol. Psychiatry 23, 247–256. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.168
Fu, R., Li, Z., Zhou, R., Li, C., Shao, S., and Li, J. (2021). The mechanism of intestinal flora dysregulation mediated by intestinal bacterial biofilm to induce constipation. Bioengineered 12, 6484–6498. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1973356
Gabis, L., Ben-Hur, R., Shefer, S., Jokel, A., and Shalom, D. (2019). Improvement of language in children with autism with combined donepezil and choline treatment. J. Mol. Neurosci. 69, 224–234. doi: 10.1007/s12031-019-01351-7
Gao, K., Sun, Y., Niu, S., and Wang, L. (2021). Unified framework for early stage status prediction of autism based on infant structural magnetic resonance imaging. Autism Res. 14, 2512–2523. doi: 10.1002/aur.2626
Golubchik, P., Sever, J., and Weizman, A. (2011). Low-dose quetiapine for adolescents with autistic spectrum disorder and aggressive behavior: Open-label trial. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 34, 216–219. doi: 10.1097/WNF.0b013e31823349ac
Grossi, E., Veggo, F., Narzisi, A., Compare, A., and Muratori, F. (2016). Pregnancy risk factors in autism: A pilot study with artificial neural networks. Pediatr. Res. 79, 339–347. doi: 10.1038/pr.2015.222
Guthrie, W., Swineford, L., Nottke, C., and Wetherby, A. (2012). Early diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder: Stability and change in clinical diagnosis and symptom presentation. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 54, 582–590. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12008
Hacohen, M., Stolar, O., Berkovitch, M., Elkana, O., Kohn, E., Hazan, A., et al. (2022). Children and adolescents with ASD treated with CBD-rich cannabis exhibit significant improvements particularly in social symptoms: An open label study. Transl. Psychiatry 12, 1–24. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-02104-8
Haghighat, H., Mirzarezaee, M., Araabi, B., and Khadem, A. (2022). A sex-dependent computer-aided diagnosis system for autism spectrum disorder using connectivity of resting-state fMRI. J. Neural Eng. 19, 1–19. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac86a4
Hamad, A., Alessi-Severini, S., Mahmud, S., Brownell, M., and Kuo, I. (2019). Prenatal antibiotics exposure and the risk of autism spectrum disorders: A population-based cohort study. PLoS One 14:e0221921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221921
Harfterkamp, M., van de Loo-Neus, G., Minderaa, R., van der, G. R., Escobar, R., Schacht, A., et al. (2012). A randomized double-blind study of atomoxetine versus placebo for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in children with autism spectrum disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 51, 733–741. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2012.04.011
Harris, H., Micali, N., Moll, H., van Berckelaer-Onnes, I., Hillegers, M., and Jansen, P. (2021). The role of food selectivity in the association between child autistic traits and constipation. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 54, 981–985. doi: 10.1002/eat.23485
Hassan, W., Al-Dbass, A., Al-Ayadhi, L., Bhat, R., and El-Ansary, A. (2022). Discriminant analysis and binary logistic regression enable more accurate prediction of autism spectrum disorder than principal component analysis. Sci. Rep. 12, 1–13. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07829-6
Hendouei, F., Sanjari Moghaddam, H., Mohammadi, M., Taslimi, N., Rezaei, F., and Akhondzadeh, S. (2019). Resveratrol as adjunctive therapy in treatment of irritability in children with autism: A double-blind and placebo-controlled randomized trial. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 45, 324–334. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13076
Hendren, R., James, S., Widjaja, F., Lawton, B., Rosenblatt, A., and Bent, S. (2016). Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of Methyl B12 for children with autism. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 26, 774–783. doi: 10.1089/cap.2015.0159
Huang, Z., Zhang, J., Zhu, Z., Wu, E., and Tan, K. (2021). Identification of autistic risk candidate genes and toxic chemicals via multilabel learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32, 3971–3984. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3016357
Ichikawa, H., Mikami, K., Okada, T., Yamashita, Y., Ishizaki, Y., Tomoda, A., et al. (2016). Aripiprazole in the treatment of irritability in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder in Japan: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 48, 796–806. doi: 10.1007/s10578-016-0704-x
Javadfar, Z., Abdollahzad, H., Moludi, J., Rezaeian, S., Amirian, H., Foroughi, A., et al. (2020). Effects of vitamin D supplementation on core symptoms, serum serotonin, and interleukin-6 in children with autism spectrum disorders: A randomized clinical trial. Nutrition 7:110986. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2020.110986
Jendraszak, M., Gałȩcka, M., Kotwicka, M., Regdos, A., Pazgrat-Patan, M., and Andrusiewicz, M. (2021). Commercial microbiota test revealed differences in the composition of intestinal microorganisms between children with autism spectrum disorders and neurotypical peers. Sci. Rep. 11:24274. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03794-8
Jiang, M., Francis, S., Tseng, A., Srishyla, D., DuBois, M., Beard, K., et al. (2020). Predicting core characteristics of ASD through facial emotion recognition and eye tracking in youth. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2020, 871–875. doi: 10.1109/EMBC44109.2020.9176843
Kang, D., Adams, J., Coleman, D., Pollard, E., Maldonado, J., McDonough-Means, S., et al. (2019). Long-term benefit of Microbiota Transfer Therapy on autism symptoms and gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 9:5821. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42183-0
Kang, D., Adams, J., Vargason, T., Santiago, M., Hahn, J., and Krajmalnik-Brown, R. (2020). Distinct fecal and plasma metabolites in children with autism spectrum disorders and their modulation after microbiota transfer therapy. mSphere 5:e00314-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00314-20
Keim, S., Jude, A., Smith, K., Khan, A., Coury, D., Rausch, J., et al. (2022). Randomized controlled trial of omega-3 and -6 fatty acid supplementation to reduce inflammatory markers in children with autism spectrum disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 52, 5342–5355. doi: 10.1007/s10803-021-05396-9
Kim, J., Son, M., Son, C., Radua, J., Eisenhut, M., Gressier, F., et al. (2019). Environmental risk factors and biomarkers for autism spectrum disorder: An umbrella review of the evidence. Lancet Psychiatry 6, 590–600. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(19)30181-6
Klaiman, C., Huffman, L., Masaki, L., and Elliott, G. (2013). Tetrahydrobiopterin as a treatment for autism spectrum disorders: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 23, 320–328. doi: 10.1089/cap.2012.0127
Krupp, D., Barnard, R., Duffourd, Y., Evans, S., Mulqueen, R., Bernier, R., et al. (2017). Exonic mosaic mutations contribute risk for autism spectrum disorder. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 101, 369–390. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.07.016
Le, J., Zhang, L., Zhao, W., Zhu, S., Lan, C., Kou, J., et al. (2022). Infrequent intranasal oxytocin followed by positive social interaction improves symptoms in autistic children: A pilot randomized clinical trial. Psychother. Psychosom. 91, 335–347. doi: 10.1159/000524543
Lee, S., Kung, H., Huang, J., Hsu, C., Wang, C., Wu, Y., et al. (2022). The clinical application of machine learning-based models for early prediction of hemorrhage in trauma intensive care units. J. Pers. Med. 12, 1–10. doi: 10.3390/jpm12111901
Levine, S., Kodesh, A., Goldberg, Y., Reichenberg, A., Furukawa, T., Kolevzon, A., et al. (2016). Initial severity and efficacy of risperidone in autism: Results from the RUPP trial. Eur. Psychiatry 32, 16–20. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2015.11.004
Li, J., Wang, H., Qing, W., Liu, F., Zeng, N., Wu, F., et al. (2022). Congenitally underdeveloped intestine drives autism-related gut microbiota and behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 105, 15–26. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2022.06.006
Li, N., Chen, H., Cheng, Y., Xu, F., Ruan, G., Ying, S., et al. (2021). Fecal microbiota transplantation relieves gastrointestinal and autism symptoms by improving the gut microbiota in an open-label study. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 11:759435. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.759435
Liaqat, S., Wu, C., Duggirala, P., Cheung, S., Chuah, C., Ozonoff, S., et al. (2021). Predicting ASD diagnosis in children with synthetic and image-based eye gaze data. Signal Process. Image Commun. 94:116198. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2021.116198
Limperopoulos, C., Bassan, H., Sullivan, N., Soul, J., Robertson, R., Moore, M., et al. (2008). Positive screening for autism in ex-preterm infants: Prevalence and risk factors. Pediatrics 121, 758–765. doi: 10.1542/peds.2007-2158
Lin, Y., Afshar, S., Rajadhyaksha, A., Potash, J., and Han, S. A. (2020). Machine learning approach to predicting autism risk genes: Validation of known genes and discovery of new candidates. Front. Genet. 11, 1–11. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.500064
Liu, G., Yu, Q., Tan, B., Ke, X., Zhang, C., Li, H., et al. (2022). Gut dysbiosis impairs hippocampal plasticity and behaviors by remodeling serum metabolome. Gut Microbes 14:2104089. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2104089
Liu, H., Huang, M., and Yu, X. (2023). Blood and hair copper levels in childhood autism spectrum disorder: A meta-analysis based on case-control studies. Rev. Environ. Health 39, 511–517. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2022-0256
Liu, L., Lei, J., Sanders, S., Willsey, A., Kou, Y., Cicek, A., et al. (2014). DAWN: A framework to identify autism genes and subnetworks using gene expression and genetics. Mol Autism. 5, 1–18. doi: 10.1186/2040-2392-5-22
Liu, Y., Fachrul, M., Inouye, M., and Méric, G. (2024). Harnessing human microbiomes for disease prediction. Trends Microbiol. 32, 707–719. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2023.12.004
Liu, Y., Liong, M., Chung, Y., Huang, H., Peng, W., Cheng, Y., et al. (2019). Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 on children with autism spectrum disorder in Taiwan: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrients 11, 1–16. doi: 10.3390/nu11040820
Liu, Y., Xu, L., Li, J., Yu, J., and Yu, X. (2020). Attentional connectivity-based prediction of autism using heterogeneous rs-fMRI Data from CC200 Atlas. Exp. Neurobiol. 29, 27–37. doi: 10.5607/en.2020.29.1.27
Lopata, C., Thomeer, M., Rodgers, J., Donnelly, J., and Booth, A. (2020). RCT of a comprehensive outpatient treatment for children with autism spectrum disorder. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 50, 796–810. doi: 10.1080/15374416.2020.1790380
Lou, M., Cao, A., Jin, C., Mi, K., Xiong, X., Zeng, Z., et al. (2021). Deviated and early unsustainable stunted development of gut microbiota in children with autism spectrum disorder. Gut 71, 1588–1599. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325115
Madany, A., Hughes, H., and Ashwood, P. (2022a). Antibiotic treatment during pregnancy alters offspring gut microbiota in a sex-dependent manner. Biomedicines 10, 1–23. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051042
Madany, A., Hughes, H., and Ashwood, P. (2022b). Prenatal maternal antibiotics treatment alters the gut microbiota and immune function of post-weaned prepubescent offspring. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:12879. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112879
Maenner, M., Shaw, K., Bakian, A., Bilder, D., Durkin, M., Esler, A., et al. (2021). Prevalence and characteristics of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years - autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 Sites, United States, 2018. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 70, 1–16. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7011a1
Mahdavinasab, S., Saghazadeh, A., Motamed-Gorji, N., Vaseghi, S., Mohammadi, M., Alichani, R., et al. (2019). Baclofen as an adjuvant therapy for autism: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 28, 1619–1628. doi: 10.1007/s00787-019-01333-5
Maras, A., Schroder, C., Malow, B., Findling, R., Breddy, J., Nir, T., et al. (2018). Long-term efficacy and safety of pediatric prolonged-release melatonin for insomnia in children with autism spectrum disorder. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 28, 699–710. doi: 10.1089/cap.2018.0020
Matson, J., Dempsey, T., and Fodstad, J. (2009). Stereotypies and repetitive/restrictive behaviours in infants with autism and pervasive developmental disorder. Dev. Neurorehabil. 12, 122–127. doi: 10.1080/17518420902936730
Mazahery, H., Conlon, C., Beck, K., Mugridge, O., Kruger, M., Stonehouse, W., et al. (2019). A randomised controlled trial of vitamin D and omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in the treatment of irritability and hyperactivity among children with autism spectrum disorder. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 187, 9–16. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.10.017
McDougle, C., Thom, R., Ravichandran, C., Palumbo, M., Politte, L., Mullett, J., et al. (2022). A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot trial of mirtazapine for anxiety in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 47, 1263–1270. doi: 10.1038/s41386-022-01295-4
Midani, F., Weil, A., Chowdhury, F., Begum, Y., Khan, A., Debela, M., et al. (2018). Human gut microbiota predicts susceptibility to Vibrio cholerae infection. J. Infect. Dis. 218, 645–653. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiy192
Momtazmanesh, S., Amirimoghaddam-Yazdi, Z., Moghaddam, H., Mohammadi, M., and Akhondzadeh, S. (2020). Sulforaphane as an adjunctive treatment for irritability in children with autism spectrum disorder: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 74, 398–405. doi: 10.1111/pcn.13016
Moreno, R., Rose, D., Tancredi, D., Schmidt, R., Ozonoff, S., and Ashwood, P. (2024). Cord blood cytokine profiles in children later diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder: Results from the prospective MARBLES study. Brain Behav. Immun. 122, 339–344. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2024.08.036
Nagaraju, K., Sudeep, K., and Kurhekar, M. P. (2019). A cellular automaton model to find the risk of developing autism through gut-mediated effects. Comput. Biol. Med. 110, 207–217. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.05.015
Parker, K., Oztan, O., Libove, R., Mohsin, N., Karhson, D., Sumiyoshi, R., et al. (2019). A randomized placebo-controlled pilot trial shows that intranasal vasopressin improves social deficits in children with autism. Sci. Transl. Med. 11:eaau7356. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aau7356
Perales-Marín, A., Peraita-Costa, I., Cervera-Boada, P., Tellez de Meneses, M., Llopis-González, A., Marí-Bauset, S., et al. (2021). Perinatal and obstetric predictors for autism spectrum disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 51, 3908–3916. doi: 10.1007/s10803-020-04846-0
Qiang, N., Gao, J., Dong, Q., Li, J., Zhang, S., Liang, H., et al. (2023). A deep learning method for autism spectrum disorder identification based on interactions of hierarchical brain networks. Behav. Brain Res. 452:114603. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114603
Qin, L., Wang, H., Ning, W., Cui, M., and Wang, Q. (2024). New advances in the diagnosis and treatment of autism spectrum disorders. Eur. J. Med. Res. 29, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01916-2
Qiu, N., Tang, C., Zhai, M., Huang, W., Weng, J., Li, C., et al. (2020). Application of the still-face paradigm in early screening for high-risk autism spectrum disorder in infants and toddlers. Front. Pediatr. 8:290. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.00290
Rabeyron, T., Robledo Del Canto, J., Carasco, E., Bisson, V., Bodeau, N., Vrait, F., et al. (2020). A randomized controlled trial of 25 sessions comparing music therapy and music listening for children with autism spectrum disorder. Psychiatry Res. 293:113377. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113377
Raghavan, R., Selhub, J., Paul, L., Ji, Y., Wang, G., Hong, X., et al. (2020). A prospective birth cohort study on cord blood folate subtypes and risk of autism spectrum disorder. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 112, 1304–1317. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqaa208
Rahman, R., Kodesh, A., Levine, S., Sandin, S., Reichenberg, A., and Schlessinger, A. (2020). Identification of newborns at risk for autism using electronic medical records and machine learning. Eur. Psychiatry 63:e22. doi: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2020.17
Sanctuary, M., Kain, J., Chen, S., Kalanetra, K., Lemay, D., Rose, D., et al. (2019). Pilot study of probiotic/colostrum supplementation on gut function in children with autism and gastrointestinal symptoms. PLoS One 14:e0210064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210064
Santocchi, E., Guiducci, L., Fulceri, F., Billeci, L., Buzzigoli, E., Apicella, F., et al. (2016). Gut to brain interaction in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A randomized controlled trial on the role of probiotics on clinical, biochemical and neurophysiological parameters. BMC Psychiatry 16:183. doi: 10.1186/s12888-016-0887-5
Sauer, A., Bockmann, J., Steinestel, K., Boeckers, T., and Grabrucker, A. (2019). Altered intestinal morphology and microbiota composition in the autism spectrum disorders associated SHANK3 mouse model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:2134. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092134
Scahill, L., McCracken, J., King, B., Rockhill, C., Shah, B., Politte, L., et al. (2015). Extended-release guanfacine for hyperactivity in children with autism spectrum disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 172, 1197–1206. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15010055
Sgritta, M., Dooling, S., Buffington, S., Momin, E., Francis, M., Britton, R., et al. (2019). Mechanisms underlying microbial-mediated changes in social behavior in mouse models of autism spectrum disorder. Neuron 101, 246–259.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.11.018
Sharon, G., Cruz, N., Kang, D., Gandal, M., Wang, B., Kim, Y., et al. (2019). Human gut microbiota from autism spectrum disorder promote behavioral symptoms in mice. Cell 177, 1600–1618.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.004
Soorya, L., Fogg, L., Ocampo, E., Printen, M., Youngkin, S., Halpern, D., et al. (2021). Neurocognitive outcomes from memantine: A pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in children with autism spectrum disorder. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 31, 475–484. doi: 10.1089/cap.2021.0010
Sousamli, A., Dragioti, E., Metallinou, D., Lykeridou, A., Dourou, P., Athanasiadou, C., et al. (2024). Perinatal and demographic risk factors associated with autism spectrum disorder: A National survey of potential predictors and severity. Healthcare 12:2057. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12202057
Sun, M., Lu, F., Yu, D., Wang, Y., Chen, P., and Liu, S. (2024). Respiratory diseases and gut microbiota: Relevance, pathogenesis, and treatment. Front. Microbiol. 15:1358597. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1358597
Supekar, K., de Los Angeles, C., Ryali, S., Cao, K., Ma, T., and Menon, V. (2022). Deep learning identifies robust gender differences in functional brain organization and their dissociable links to clinical symptoms in autism. Br. J. Psychiatry 220, 202–209. doi: 10.1192/bjp.2022.13
Tariq, Q., Fleming, S., Schwartz, J., Dunlap, K., Corbin, C., Washington, P., et al. (2019). Detecting developmental delay and autism through machine learning models using home videos of Bangladeshi children: Development and validation study. J. Med. Internet Res. 21:e13822. doi: 10.2196/13822
Tartaglione, A., Villani, A., Ajmone-Cat, M., Minghetti, L., Ricceri, L., Pazienza, V., et al. (2022). Maternal immune activation induces autism-like changes in behavior, neuroinflammatory profile and gut microbiota in mouse offspring of both sexes. Transl. Psychiatry 12, 1–10. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-02149-9
Topçuoğlu, B., Lesniak, N., Ruffin, M. IV, Wiens, J., and Schloss, P. (2020). A framework for effective application of machine learning to microbiome-based classification problems. MBio 11:e00434-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00434-20
Tse, A. (2020). Brief Report: impact of a Physical Exercise Intervention on Emotion Regulation and Behavioral Functioning in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J Autism Dev Disord. 50, 4191–4198. doi: 10.1007/s10803-020-04418-2
Tsuchiya, K., Hakoshima, S., Hara, T., Ninomiya, M., Saito, M., Fujioka, T., et al. (2021). Diagnosing autism spectrum disorder without expertise: A pilot study of 5- to 17-year-old individuals using Gazefinder. Front. Neurol. 11:603085. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.603085
Vacy, K., Thomson, S., Moore, A., Eisner, A., Tanner, S., Pham, C., et al. (2024). Cord blood lipid correlation network profiles are associated with subsequent attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder symptoms at 2 years: A prospective birth cohort study. EBioMedicine 100:104949. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104949
Verhaar, B., Hendriksen, H., de Leeuw, F., Doorduijn, A., van Leeuwenstijn, M., Teunissen, C., et al. (2022). Gut microbiota composition is related to AD pathology. Front. Immunol. 12:794519. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.794519
Wang, H., and Avillach, P. (2021). Retracted: Diagnostic classification and prognostic prediction using common genetic variants in autism spectrum disorder: Genotype-based deep learning. JMIR Med. Inform. 9:e24754. doi: 10.2196/24754
Wang, J., Liu, Y., Huang, H., Wu, J., and Wang, W. (2022). [Influence of acupuncture on the clinical manifestations and gastrointestinal symptoms of children with autism spectrum disorder]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 42, 1373–1376. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20220111-0004
Wang, J., and Wang, L. (2020). Prediction and prioritization of autism-associated long non-coding RNAs using gene expression and sequence features. BMC Bioinformatics 21:505. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03843-5
Wang, Y., Li, N., Yang, J., Zhao, D., Chen, B., Zhang, G., et al. (2020). Probiotics and fructo-oligosaccharide intervention modulate the microbiota-gut brain axis to improve autism spectrum reducing also the hyper-serotonergic state and the dopamine metabolism disorder. Pharmacol. Res. 157, 1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104784
Wastyk, H., Fragiadakis, G., Perelman, D., Dahan, D., Merrill, B., Yu, F., et al. (2021). Gut-microbiota-targeted diets modulate human immune status. Cell 184, 4137–4153.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.019
Weber, C., Lake, E., Haider, S., Mozayan, A., Mukherjee, P., Scheinost, D., et al. (2022). Age-dependent white matter microstructural disintegrity in autism spectrum disorder. Front. Neurosci. 16:957018. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.957018
Wichers, R., Findon, J., Jelsma, A., Giampietro, V., Stoencheva, V., Robertson, D., et al. (2019). Modulation of brain activation during executive functioning in autism with citalopram. Transl. Psychiatry 9, 1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0641-0
Wilfert, A., Turner, T., Murali, S., Hsieh, P., Sulovari, A., Wang, T., et al. (2021). Recent ultra-rare inherited variants implicate new autism candidate risk genes. Nat. Genet. 53, 1125–1134. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00899-8
Wink, L., Minshawi, N., Shaffer, R., Plawecki, M., Posey, D., Horn, P., et al. (2017). d-Cycloserine enhances durability of social skills training in autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Autism 8, 1–8. doi: 10.1186/s13229-017-0116-1
Wu, D., Wen, X., Han, X., Wang, S., Wang, Y., Shen, M., et al. (2018). Relationship between neonatal vitamin D at birth and risk of autism spectrum disorders: The NBSIB Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 33, 458–466. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3326
Wu, Q., Yang, T., Chen, L., Dai, Y., Wei, H., Jia, F., et al. (2022). Early life exposure to triclosan from antimicrobial daily necessities may increase the potential risk of autism spectrum disorder: A multicenter study in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 247:114197. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114197
Wu, T., Wang, H., Lu, W., Zhai, Q., Zhang, Q., Yuan, W., et al. (2020). Potential of gut microbiome for detection of autism spectrum disorder. Microb Pathog. 149:104568. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104568
Yao, F., Zhang, K., Feng, C., Gao, Y., Shen, L., Liu, X., et al. (2021). Protein biomarkers of autism spectrum disorder identified by computational and experimental methods. Front. Psychiatry 12:554621. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.554621
Yuen, R., Thiruvahindrapuram, B., Merico, D., Walker, S., Tammimies, K., Hoang, N., et al. (2015). Whole-genome sequencing of quartet families with autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Med. 21, 185–191. doi: 10.1038/nm.3792
Zeidan, J., Fombonne, E., Scorah, J., Ibrahim, A., Durkin, M., Saxena, S., et al. (2022). Global prevalence of autism: A systematic review update. Autism Res. 15, 778–790. doi: 10.1002/aur.2696
Zhang, C., and Shen, Y. A. (2016). Cell type-specific expression signature predicts haploinsufficient autism-susceptibility genes. Hum. Mutat. 38, 204–215. doi: 10.1002/humu.23147
Zhang, Y., Maimaiti, R., Lou, S., Abula, R., Abulaiti, A., and Kelimu, A. (2022). Risk prediction of autism spectrum disorder behaviors among children based on blood elements by nomogram: A cross-sectional study in Xinjiang from 2018 to 2019. J. Affect. Disord. 318, 1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.08.130
Zhu, Y., Nakatani, H., Yassin, W., Maikusa, N., Okada, N., Kunimatsu, A., et al. (2022). Application of a machine learning algorithm for structural brain images in chronic schizophrenia to earlier clinical stages of psychosis and autism spectrum disorder: A multiprotocol imaging dataset study. Schizophr. Bull. 48, 563–574. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbac030
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder, machine learning, risk prediction model, intestinal microbiome, biomarkers
Citation: Xu W, Li H, Li J and Jin M (2025) Age of machine learning: new trends in autism spectrum disorder prediction. Front. Microbiol. 16:1492484. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1492484
Received: 07 September 2024; Accepted: 12 June 2025;
Published: 11 July 2025.
Edited by:
Nebojsa Bacanin, Singidunum University, SerbiaReviewed by:
FengLong Yang, Fujian Medical University, ChinaDiego Armando Esquivel Hernandez, Metropolitan Autonomous University, Mexico
Miodrag Zivkovic, Singidunum University, Serbia
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Li, Li and Jin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Min Jin, amlubWluemhAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Weihong Xu
Weihong Xu Haibei Li
Haibei Li Junwen Li
Junwen Li Min Jin
Min Jin