- 1Department of Breast Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Tropical Translational Medicine of Ministry of Education, School of Basic Medicine and Life Sciences, Hainan Medical University, Haikou, China
- 3The Second People’s Hospital of Dongfang City, Dongfang, China
- 4Qunying Health Center of Lingshui Li Autonomous County, Lingshui, China
- 5Yongming Health Center of Ledong Li Autonomous County, Ledong, China
- 6Biotechnology and Biochemistry Laboratory, Hainan Medical University, Haikou, China
- 7Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Hainan Medical University, Haikou, China
A burgeoning corpus of evidence indicates that S24-7 is integral to human health, with links to obesity, inflammation, metabolism, and dietary interactions. In the present study, we conducted a comprehensive review of the S24-7 literature from the past 10 years, augmented by an evaluation of research trends using both quantitative and qualitative approaches. From the Web of Science (WoS) database, we retrieved 903 research articles and four review articles pertaining to S24-7, also known as Muribaculaceae, that were published between January 1, 2014, and January 1, 2024. Employing software tools such as R, Biblioshiny, VOSviewer, the Bibliometric Analysis Platform, and Pajek, we performed visual mapping and correlation analyses on the collected documents. Our analysis revealed China and the United States as the leading publishers in the field of S24-7 research. The top three academic journals for S24-7 family research are Food and Function, Frontiers in Microbiology, and Nutrition. Among individual contributors, Zhang Y stands out with 31 publications and an h-index of 13, representing 3.42% of the 907 articles analyzed. Jiangnan University leads in institutional output with 46 publications. Keyword analysis underscores that S24-7 research is concentrated on examining the family’s associations with obesity, inflammation, metabolism, and diet. This study highlights notable contributions from various countries, institutions, journals, and researchers, shedding light on the influence of the S24-7 family on human health. It serves to inform future research directions and clinical applications concerning the S24-7 flora.
1 Introduction
The human gut microbiota is teeming with billions of microbes that play a vital role in sustaining host health (Gomaa, 2020; Cryan and O'Mahony, 2011). Within this complex ecosystem, the S24-7 family, a prominent constituent of the Mycobacteriaceae phylum, holds significant relevance to human well-being. Saltzman and colleagues initially identified this family as part of the mouse intestinal microbiota (Seedorf et al., 2014). Later, Sidov et al. bestowed upon it the designation “S24-7” (Salzman et al., 2002). Ormerod et al. conducted a seminal study, sequencing the genomes of 30 S24-7 members and positioning them within the novel candidate family Candidatus Homeothermaceae (Ormerod et al., 2016). Genome analysis revealed that S24-7 spp. are functionally distinct from neighboring families and versatile with respect to complex carbohydrate degradation (Lagkouvardos et al., 2019). Bacteria belonging to the S24-7 constitute a predominant element of the mammalian gut microbiota.
Endowed with an expansive repertoire of carbohydrate-active enzymes, S24-7 members are adept at fermenting a diverse array of carbohydrates within the digestive tract. Moreover, S24-7 operates independently of T-cell-mediated immunity, fostering the production of Immunoglobulin A (IgA) (Bunker et al., 2015). This family also boasts an abundance of genes encoding enzymes that dismantle plant cell walls. Carbohydrate-active enzymes account for approximately 6% of the S24-7 coding sequence (Ormerod et al., 2016), with the GH13 family of glycoside hydrolases being particularly prevalent, chiefly comprising α-amylases. Trailing behind are the GH43 family, predominated by xylosidases and arabinosides. Subsequently, a gene pair analogous to susCD, integral to S24-7, was pinpointed at the genetic level, and susC/susD-like gene pairs typically form part of PUL clusters (Xu et al., 2003; Martens et al., 2009). These loci are defined by the structural components of the starch utilization system (Sus), which orchestrates the binding of starch and malt oligosaccharides to SusD and their translocation to the periplasmic space via SusC (Reeves et al., 1996; Reeves et al., 1997). Through the Sus system, the S24-7 exerts regulatory control over polysaccharide catabolism. Additionally, research has revealed that S24-7 exhibits a pronounced affinity for whole wheat grains (Garcia-Mazcorro et al., 2016). Furthermore, this family possesses a suite of genes encoding the electron transport chain and ATP-synthesizing enzymes, thereby contributing significantly to the acceleration of energy metabolism (Ormerod et al., 2016). Collectively, these attributes underscore S24-7’s pivotal role in intestinal functionality and health. Consequently, there is a compelling imperative to delve into the dynamics of the S24-7 in relation to health trends.
Bibliometrics, a discipline harnessing both qualitative and quantitative analytical techniques (Ninkov et al., 2022), employs the examination of recurrent keywords in extant literature to illuminate prevailing themes and burgeoning trends across the entire spectrum of research domains. Presently, there exists a dearth of bibliometric investigations concerning S24-7. Our endeavor aims to bridge this gap by elucidating the current research foci and forecasting prospective avenues for advancement in this area. This initiative is intended to furnish a foundation for more rigorous and focused explorations into the intricacies of gut microbiota, which in turn may yield novel diagnostic markers and innovative therapeutic strategies for a myriad of diseases.
2 Materials and methods
This study undertook a comprehensive review of the literature pertaining to S24-7, sourced from the Web of Science (WoS) database. The search spanned from January 1, 2014, to January 1, 2024, employing search terms inclusive of “S24-7” or “Muribaculaceae.” Original research articles and review papers were exclusively selected, while other forms of literature, including those from conferences and additional reviews, were excluded. The final dataset encompassed 907 articles relevant to the specified topic. For data analysis, a combination of statistical software R, its Biblioshiny extension, VOSviewer, the Bibliometric Analysis Platform, and Pajek were utilized to generate tabular datasets and visual representations. The R-based Biblioshiny application, accessible at https://bibliometrix.org/, facilitated the creation of bibliometric visualizations, including maps illustrating international collaborations, author productivity, and the corresponding impact factors (Hasan et al., 2023). VOSviewer, a web-based tool, specializes in the generation of maps based on bibliographic or textual data (van Eck and Waltman, 2010). It visually represents the co-occurrence of keywords, which is subsequently refined and optimized through the use of Pajek software. Additionally, the bibliometric analysis platform offered a detailed overview of the annual publication output per country.
According to the statistical results of the WOS database, we used R Studio to generate the Biblioshiny application for related data such as institutions, journals, and authors. Additionally, a map of the number of publications by institutions and journals, the number of authors’ literature published and cited, and the distribution of maps using RStudio were generated. The bar charts of article publications by country for each year and country collaboration maps using the bibliometric analysis platform was generated. The keywords were analyzed for hotspots using VOSviewer, and then the data were saved as Pajek files and imported into Pajek software to draw a clearer cluster analysis of the hotspot words.
3 Results
3.1 Analysis of nations and institutions
Over the course of the 10-year investigation, publications pertaining to the S24-7 appeared across 53 countries. China emerged as the foremost contributor with 688 articles, accounting for 75.85% of the total 907 papers, closely followed by the United States with 128 papers (14.11%). Canada contributed 25 articles (2.76%), Japan 24 (2.65%), and South Korea 23 (2.54%) (Figure 1A). The collaborative network visualization map illustrated both the quantity of publications—with darker shades denoting higher numbers—and the connections indicating collaborative ties (Figures 1B,C).
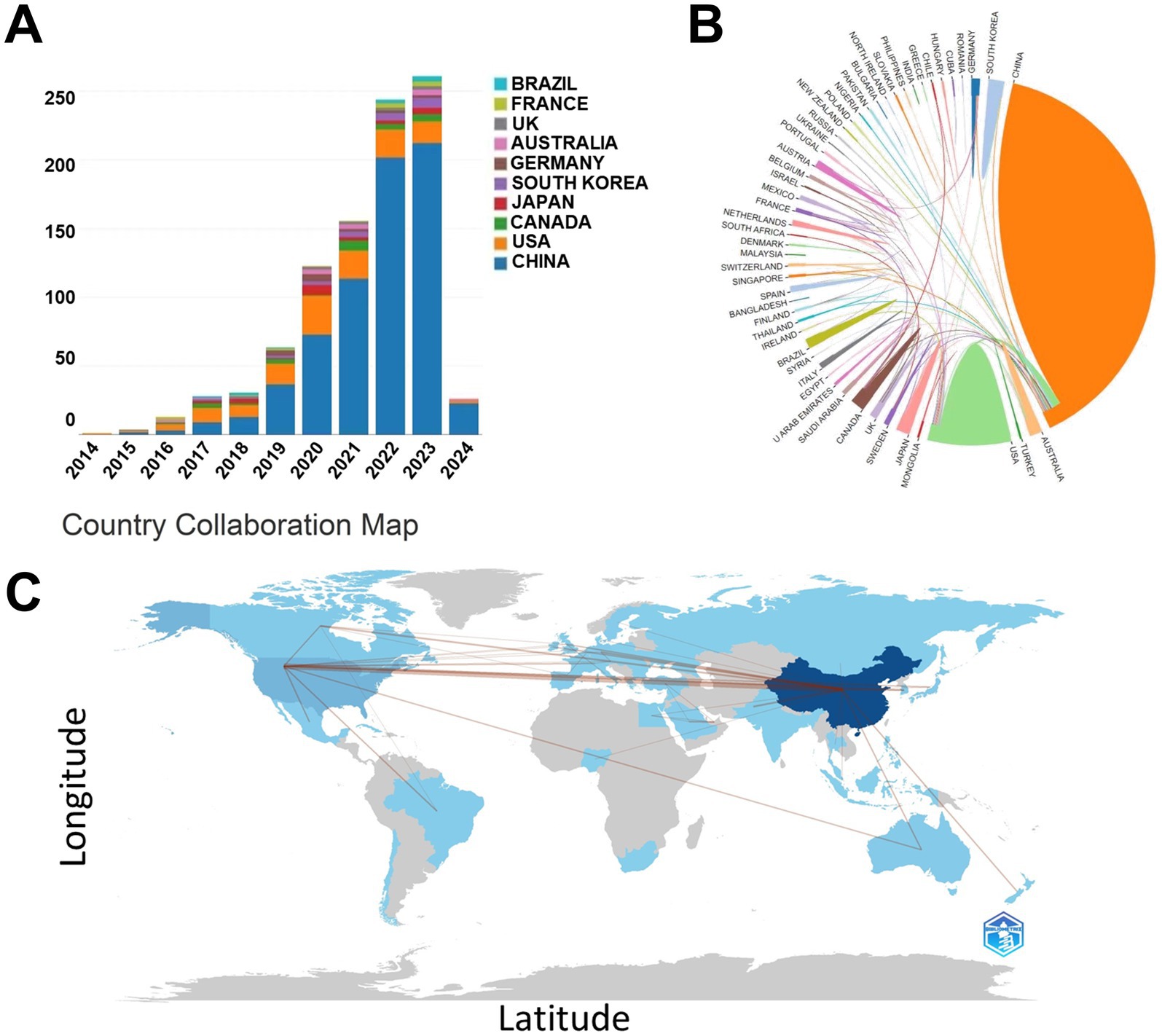
Figure 1. Article releases in the field by country. (A) Number of article releases in the field by country in different years. (B) The cooperation and (C) partnerships of countries in the field of S24-7 from 2014 to 2024.
In terms of institutional productivity, Jiangnan University was the most prolific with 46 publications, trailed by the University of California System with 41 and China Agricultural University with 36. Jiangnan University not only led in the number of publications but also stood out for its high degree of collaboration (Figure 2A). Moreover, Figure 2B presented a connectivity diagram showcasing the top 10 countries, institutions, and authors by volume of published work, reflecting robust inter-agency and cross-institutional cooperative efforts.
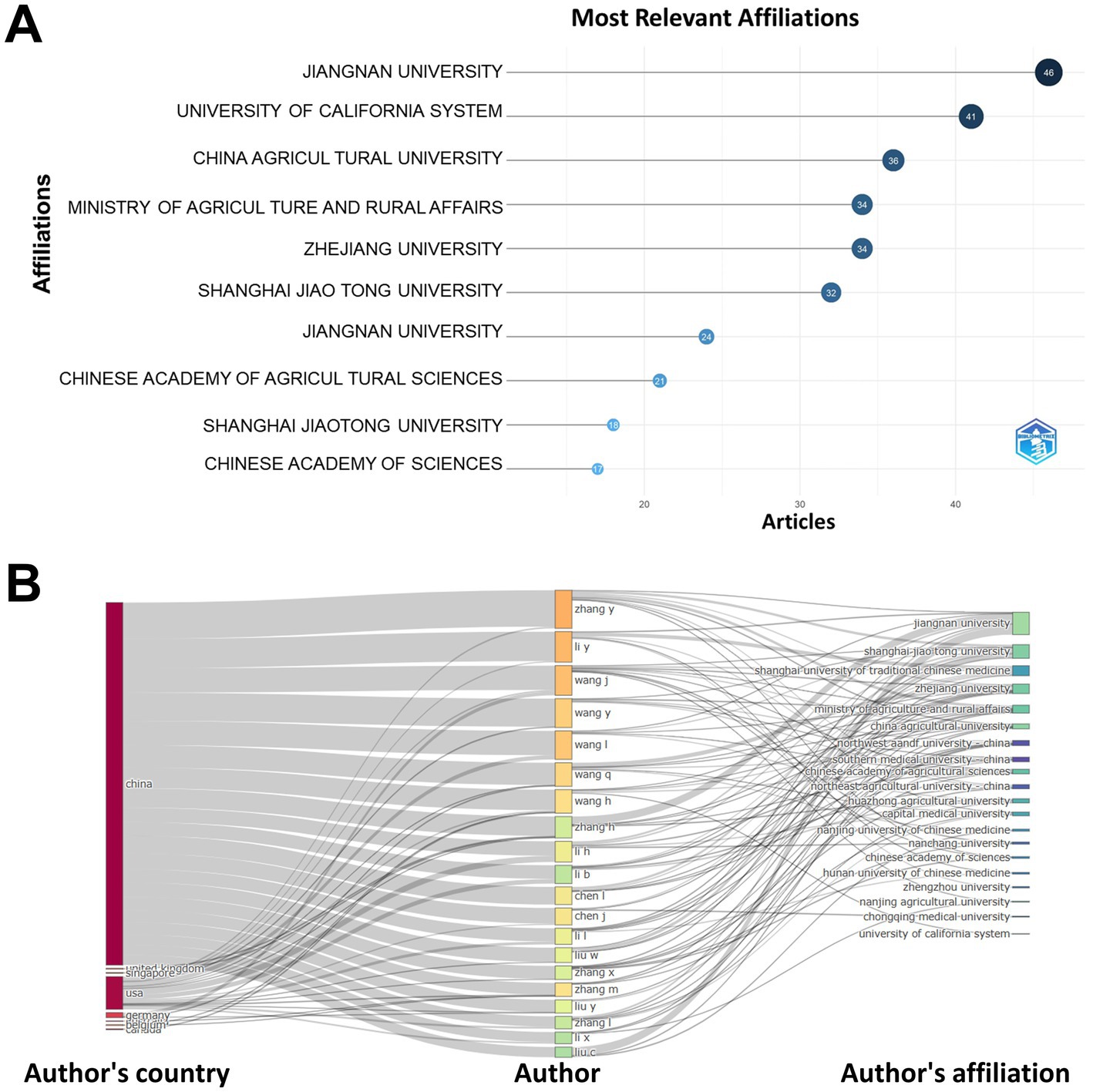
Figure 2. Institutional literature releases in the field. (A) Number of article releases in the field by institution. (B) Map of collaborative networks of countries, institutions and authors.
3.2 Analysis of journals
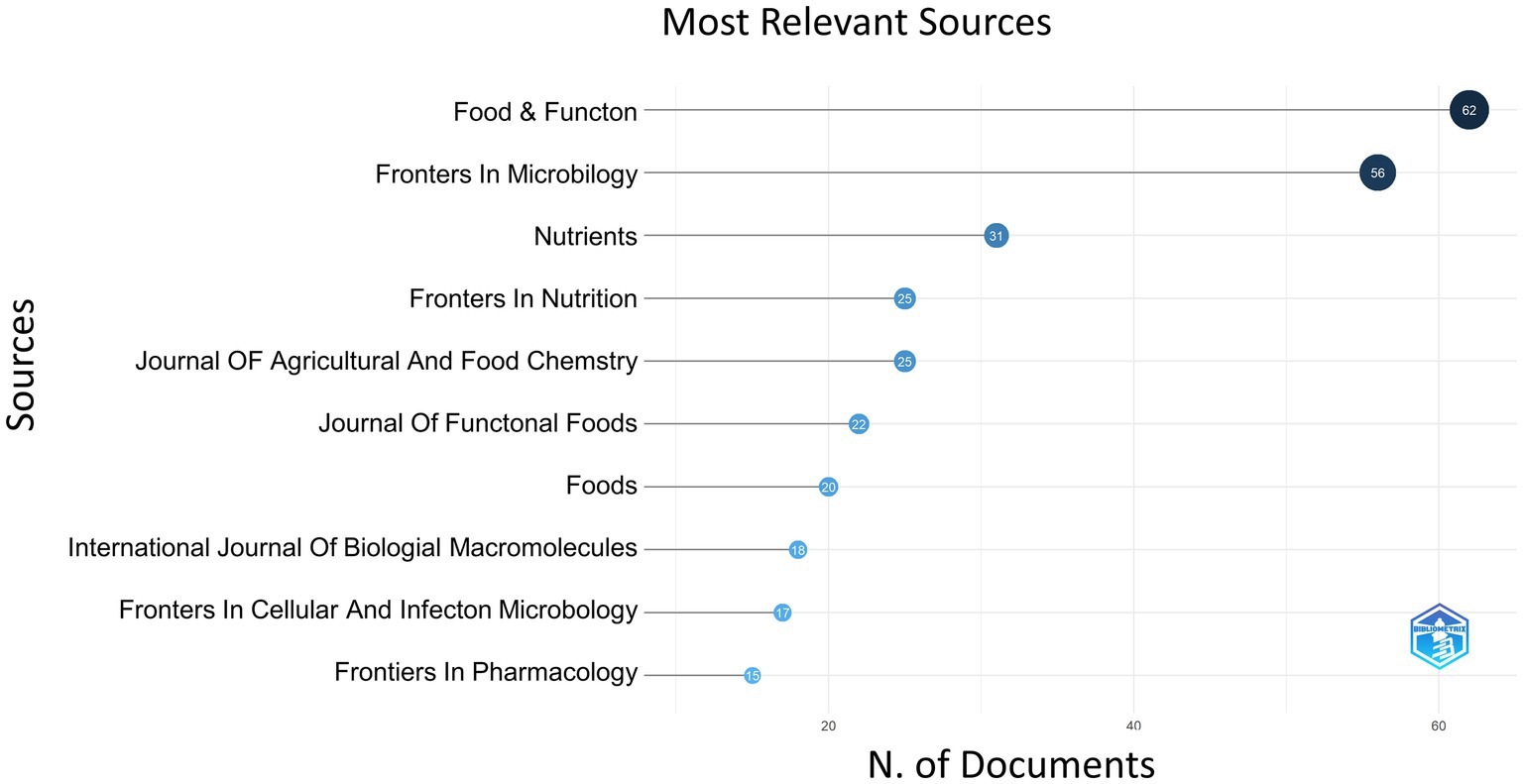
Publications on the S24-7 appeared in 299 distinct scientific journals, with Food and Function leading the list with 62 articles, representing 6.84% of the total. Frontiers in Microbiology came in second with 56 articles (6.17%); Nutrients published 31 articles (3.42%); Frontiers in Nutrition and Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry both contributed 25 articles each, accounting for 2.76%. Figure 3 detailed the top 10 journals ranked by the number of published papers. The average impact factor for the top five journals was approximately 6, and notably, the majority were categorized in Q1, highlighting the high caliber of the publishing venues.
3.3 Analysis of authors and references
Zhang stood out as the most prolific author in the S24-7 research domain, having authored 31 papers (3.42% of 907 total publications) (Figure 4). Wang followed closely behind with 23 publications (2.54%). Both individuals boast relatively high h-indices of 13 and 12, respectively. Notably, they both hail from China and have engaged in collaborations with numerous other authors and organizations.
3.4 Analysis of keywords
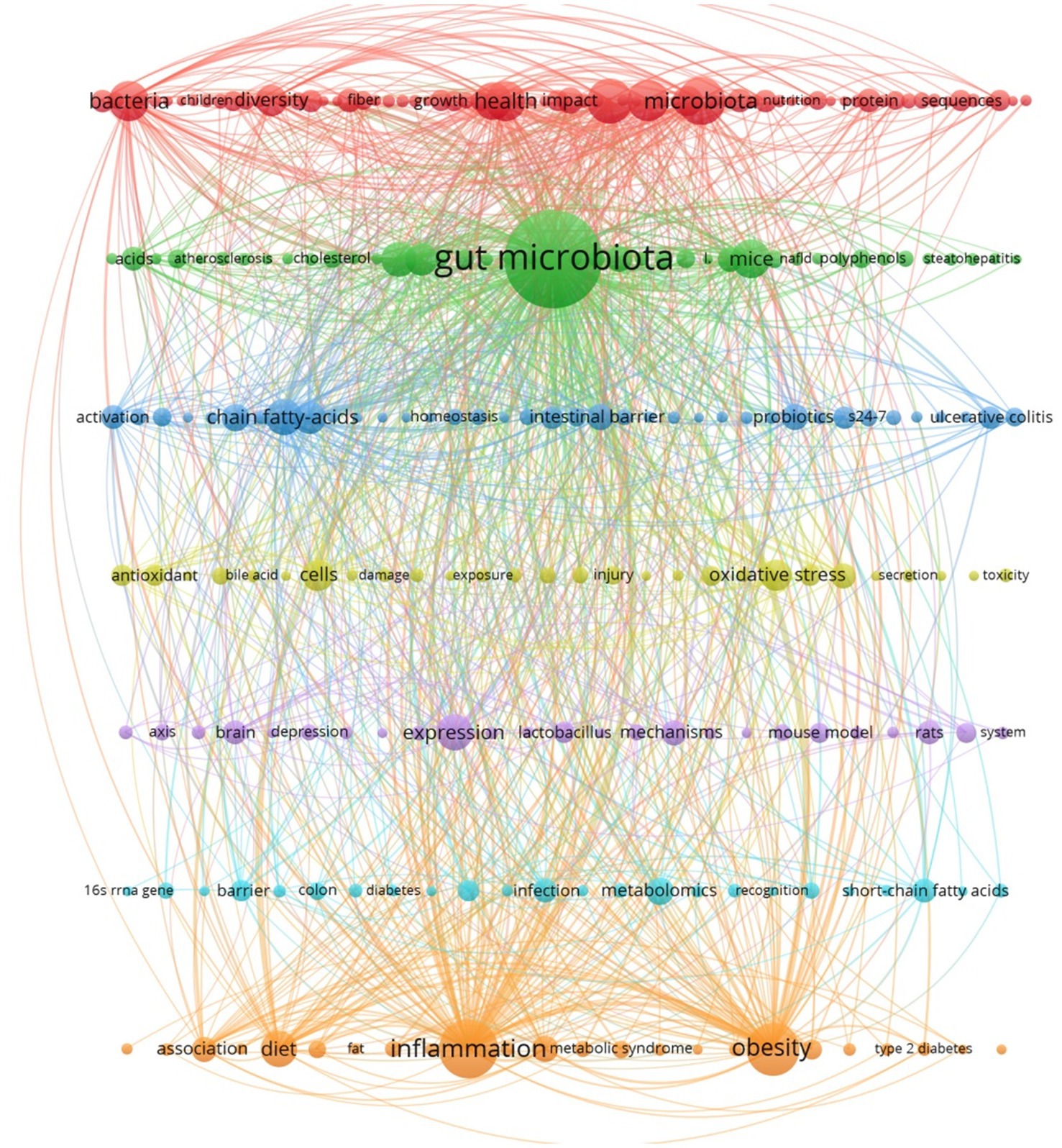
High-frequency keywords served as effective indicators of research focal points and trends. Through the use of VOSviewer, 3,848 keywords were extracted from a dataset of 907 articles, with those appearing at least six times designated as high-frequency keywords, totaling 253 (Figure 5). Common themes among these keywords included gut microbiota, inflammation, obesity, metabolism, health, and diet. Research trends suggested a focus on the implications of S24-7 abundance variations for human health, with specific interests in its role in obesity, inflammation, and metabolism, as well as the impact of dietary patterns on the prevalence of S24-7.
4 Discussion
Numerous studies have underscored the critical role of the gut microbiome in human health (Milani et al., 2017). The S24-7 is closely tied to obesity, inflammation, metabolism, and dietary composition in mammals (Li et al., 2019). It is anticipated to become a key biomarker for diagnosing human diseases and guiding therapeutic strategies, thereby enhancing our understanding of naturally occurring therapeutic agents and disease prevention measures.
To delineate the research hotspots and trends within the S24-7 family, a bibliometric analysis was conducted on relevant articles spanning from 2014 to 2024. This yielded 907 S24-7-associated papers, with China being the leading contributor, followed by the United States. Among institutions, Jiangnan University led with 46 publications, closely followed by the University of California system with 41 and China Agricultural University with 36. These findings indicate a collaborative effort among the mentioned countries and organizations. The analysis revealed that within the past decade, a significant number of researchers and institutions have concentrated on examining the link between the S24-7 and human health. Specifically, there has been a surge in studies exploring the correlation between gut microbiota distribution and obesity, inflammation, and metabolism (Li et al., 2019; Lin et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2020). Moreover, experimental research has begun to investigate the impact of dietary structures on the abundance of the S24-7 (Zhao et al., 2019). The thematic development and research trends of the S24-7 have been elucidated through keyword hotspot distribution maps and development maps. Preeminent themes include the gut microbiota, obesity, inflammation, metabolism, and diet. Leveraging advanced technological capabilities and the establishment of sophisticated mammalian experimental models, future research is poised to delve deeper into the S24-7 family’s connection with human health.
Over the past decade, a growing number of scholars and countries have expressed increasing concern about the relationship between the S24-7 and obesity. As a significant public health issue, obesity has escalated into an epidemic (Hill et al., 2003). Raoult et al. posit that obesity is multifactorially influenced by environmental, genetic, neurological, and endocrine elements (Raoult, 2008). Alterations in the human gut microbiome are also implicated in obesity. Previous research indicates that obesity correlates with an expansion of thick-walled bacterial phyla and a reduction in bacillus-like phyla (Turnbaugh et al., 2006; Bäckhed et al., 2004). S24-7 exhibits a strong association with obesity, and a high-fat diet can markedly influence the microbiome composition, characterized by elevations in Sclerotinia, Proteobacteria, and Verrucomicrobia, along with diminished levels of mycobacterium-like organisms (the S24-7 family) and Candida arthritis (Tomas et al., 2016). Mechanistic investigations into the link between S24-7 and obesity often suggest that elevated levels of bacillus-like S24-7 contribute to increased butyric acid production, which subsequently impacts metabolism (Rose et al., 2018). Butyric acid plays a crucial role in regulating mitochondrial function, including enhancing oxidative phosphorylation and β-oxidation, thereby optimizing cellular metabolic processes. Furthermore, butyric acid stimulates genes involved in fat oxidation, attenuates glycolysis, and boosts fat metabolism (Mollica et al., 2017; Valvassori et al., 2013). Additional studies demonstrate that butyric acid facilitates mitochondrial fission, thereby augmenting NADH production, intensifying the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and ultimately fostering nutrient breakdown while curtailing metabolite accumulation (Mollica et al., 2017; Valvassori et al., 2013). In a murine model of obesity induced by a high-fat diet, Henagan et al. observed similar outcomes, noting that butyric acid amplifies mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, upregulates the expression of fatty acid oxidase and uncoupling protein (UCP) 69, and initiates the nuclear coding of mitochondrial genes, including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PGC1α), culminating in enhanced β-oxidation and improved insulin sensitivity (Henagan et al., 2015). Butyric acid also encourages the conversion of white adipose tissue (WAT) into brown adipose tissue (BAT), thereby increasing host energy expenditure (Li et al., 2019; Li et al., 2018; Montanari et al., 2017; Kajimura and Saito, 2014). Moreover, emerging evidence suggests that maternal obesity may disrupt placental oxidation and inflammatory responses by altering the gut microbiota composition (Hu et al., 2021). Future research endeavors may illuminate potential targets for elucidating the interplay between the S24-7 and obesity, potentially leading to novel strategies for obesity management.
A burgeoning body of research has established connections between the S24-7 and inflammation, particularly within the gastrointestinal tract. The S24-7 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), with notable alterations in the microbial ecosystem observed in ulcerative colitis (UC) characterized by an elevated Bacillus thickeniensis to Bacillus anthropophilus ratio (Meisel et al., 2017). Interleukin-15 (IL-15), an inflammatory cytokine that perturbs gut microbiota equilibrium, has been shown to diminish S24-7 abundance and butyric acid levels in both the gut and feces of mice, precipitating intestinal inflammation (Zou et al., 2020). Conversely, Li-Zhong Tang’s research demonstrated that enhancing the S24-7 in mice could modulate the MAPK pathway, restructure the gut microbiota, reduce inflammatory cell infiltration, attenuate tumor necrosis factor activity, and dampen the inflammatory response (Zou et al., 2020). Certain bioactive compounds, such as Ficus carica polysaccharide (FCPS), human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs), components derived from legumes, and cinnamon essential oil obtained from fig fruits, have been identified as capable of elevating S24-7 levels in mice. These substances play a pivotal role in regulating inflammatory responses, maintaining intestinal endothelial integrity, and producing bioactive molecules that promote intestinal health, including phenolic metabolites and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Their application holds promise for the prevention and treatment of IBD (Zou et al., 2020; Monk et al., 2016; Li et al., 2020). Additionally, supplementation with probiotics like Lactobacillus royale has been shown to diversify the gut microbiome, increase S24-7 abundance, enrich bacterial motility proteins, and ameliorate mucositis induced by the chemotherapeutic agent 5-FU, offering a novel approach to mitigating chemotherapy-induced bacterial injury (Yeung et al., 2020). Conversely, a low-fiber diet has been associated with reduced S24-7 levels in mouse models and is known to disturb the gut microbiome, potentially triggering underlying inflammatory processes that contribute to the exacerbation of inflammatory states (Makki et al., 2018). It has been shown that atherosclerosis and systemic inflammatory response were also reduced in the group using SGLT2 compared to the control group, with higher levels of S24-7 in the feces (Hao et al., 2023). Collectively, these findings underscore the intimate relationship between the S24-7 and intestinal inflammation, positioning it as a current focal point of research interest and laying the groundwork for future investigative efforts.
Gut microbes engage in co-metabolic processes with their hosts, furnishing them with essential enzymes that they cannot produce autonomously (Tremaroli and Bäckhed, 2012). Research has indicated that fluctuations in the abundance of the S24-7 correlate with lipid metabolism. Specifically, Chai Gui Tang and its principal constituents have been shown to mitigate spontaneous hypertension through the dual regulation of lipid metabolism and the maintenance of gut microbiota equilibrium, thereby contributing to the attenuation of this condition (Zhu et al., 2023). Expanding on this, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SC06 has been identified as a potent modulator of mammalian obesity. It achieves this by reshaping the composition of the gut microbiota and modulating bile acid metabolism via the FXR signaling pathway (Zeng et al., 2022). Additionally, enzymes produced by the S24-7 contribute to the breakdown of bile acids, which in turn influences bile acid metabolism, alters hepatic gene expression, and governs liver regeneration (Liu et al., 2016). An increased ratio of Bacillus thickeniensis to Bacillus anthropophilus has been linked to the progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in mouse models (Goodman et al., 2011; Pedersen et al., 2016). Conversely, the presence of the S24-7 appears to confer protection against obesity-induced insulin resistance (Louis and Flint, 2009). Given the intricate relationships between the S24-7 and various facets of metabolism, it is evident that targeted research on this microbial entity could serve as a valuable reference for future drug development initiatives aimed at metabolic disorders. By delving deeper into the mechanisms underpinning the interactions between the S24-7 and host metabolism, scientists may uncover new avenues for therapeutic intervention in metabolism-related diseases.
Dietary components precipitate shifts in the levels of S24-7 within the gut microbiota (Kurup et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2020). Notably, under conditions of a low-protein diet, the abundance of S24-7 experiences a substantial increase (Shen et al., 2016). The incorporation of pectin has been observed to elevate the relative abundance of the S24-7 group relative to a sugar-free diet control group (Wang et al., 2020). Furthermore, preliminary studies suggest that a combination of wasabi stems and rhizomes may exert a beneficial influence on cardiovascular health by modulating the abundance of the S24-7 population. Investigating the metabolic impact of two cinnamon bark extracts rich in polyphenols and grape pomace on mice fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, Van Hul M et al. reported that the introduction of sugars diminished the prevalence of S24-7, whereas a higher intake of fermentable fiber had the opposite effect, augmenting S24-7 levels (Van Hul et al., 2018). In synthesis, the dynamic between S24-7 and dietary intake may be partially attributable to its responsiveness to dietary fiber and protein. Given that the human genome lacks a comprehensive array of carbohydrate-active enzymes, dietary fiber escapes digestion in the stomach and small intestine and instead undergoes fermentation in the colon by the resident gut microbiota (Angelakis et al., 2012). While much of the current understanding regarding the dietary determinants of S24-7 abundance stems from mouse model studies, the translation of these insights into strategies for regulating S24-7 populations in humans for health benefits requires further elucidation.
4.1 Strengths and limitations
The bibliometric analysis and visualization methodology employed in this investigation to gage the volume and quality of research concerning the S24-7 inherently possess certain constraints. Initially, the analysis was confined to a solitary database for literature search, which may have limited the scope of the findings. Additionally, the search was restricted to article titles, potentially omitting relevant works that might not have been indexed under the specified search terms. Despite these caveats, our study presents the inaugural visual bibliometric analysis within this domain. Our findings offer an empirical overview of the foremost nations, institutions, publishing outlets, researchers, and keywords that have shaped the field over the past 10 years. This data paints a vivid portrait of the current landscape and prevailing trends in S24-7 research. Our analysis contributes meaningfully to the characterization of the S24-7 and sets a foundation for future investigations. Even with its acknowledged limitations, the insights gained from this study can catalyze a more profound understanding of the S24-7 within the scientific community.
5 Conclusion
The current research hotspot and trend revolve around the intricate associations between the S24-7 and human conditions such as obesity, inflammation, metabolism, and diet. With deepening insights into the S24-7, the landscape of disease diagnostics and targeted therapies is continuously reshaped. This progression not only enhances our understanding of naturally occurring therapeutic agents but also paves the way for innovative strategies in disease prevention. In light of these developments, the demand for sustained research efforts and conclusive findings is paramount to propel the field forward.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
FangmG: Software, Writing – original draft. FW: Data curation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. DW: Data curation, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. GD: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. FangfG: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank CiteSpace and VOSviewer for free access by researchers.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Angelakis, E., Armougom, F., Million, M., and Raoult, D. (2012). The relationship between gut microbiota and weight gain in humans. Future Microbiol. 7, 91–109. doi: 10.2217/fmb.11.142
Bäckhed, F., Ding, H., Wang, T., Hooper, L. V., Koh, G. Y., Nagy, A., et al. (2004). The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 15718–15723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407076101
Bunker, J. J., Flynn, T. M., Koval, J. C., Shaw, D. G., Meisel, M., McDonald, B. D., et al. (2015). Innate and adaptive humoral responses coat distinct commensal Bacteria with immunoglobulin a. Immunity 43, 541–553. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.08.007
Cryan, J. F., and O'Mahony, S. M. (2011). The microbiome-gut-brain axis: from bowel to behavior. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 23, 187–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2010.01664.x
Garcia-Mazcorro, J. F., Ivanov, I., Mills, D. A., and Noratto, G. (2016). Influence of whole-wheat consumption on fecal microbial community structure of obese diabetic mice. PeerJ 4:e1702. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1702
Gomaa, E. Z. (2020). Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: a review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 113, 2019–2040. doi: 10.1007/s10482-020-01474-7
Goodman, A. L., Kallstrom, G., Faith, J. J., Reyes, A., Moore, A., Dantas, G., et al. (2011). Extensive personal human gut microbiota culture collections characterized and manipulated in gnotobiotic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 6252–6257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102938108
Hao, H., Li, Z., Qiao, S. Y., Qi, Y., Xu, X. Y., Si, J. Y., et al. (2023). Empagliflozin ameliorates atherosclerosis via regulating the intestinal flora. Atherosclerosis 371, 32–40. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2023.03.011
Hasan, M., Abedin, M. Z., Amin, M. B., Nekmahmud, M., and Oláh, J. (2023). Sustainable biofuel economy: a mapping through bibliometric research. J. Environ. Manag. 336:117644. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117644
Henagan, T. M., Stefanska, B., Fang, Z., Navard, A. M., Ye, J., Lenard, N. R., et al. (2015). Sodium butyrate epigenetically modulates high-fat diet-induced skeletal muscle mitochondrial adaptation, obesity and insulin resistance through nucleosome positioning. Br. J. Pharmacol. 172, 2782–2798. doi: 10.1111/bph.13058
Hill, J. O., Wyatt, H. R., Reed, G. W., and Peters, J. C. (2003). Obesity and the environment: where do we go from here? Science 299, 853–855. doi: 10.1126/science.1079857
Hu, C., Yan, Y., Ji, F., and Zhou, H. (2021). Maternal obesity increases oxidative stress in placenta and it is associated with intestinal microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 11:671347. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.671347
Kajimura, S., and Saito, M. (2014). A new era in brown adipose tissue biology: molecular control of brown fat development and energy homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 76, 225–249. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021113-170252
Kurup, K., Matyi, S., Giles, C. B., Wren, J. D., Jones, K., Ericsson, A., et al. (2021). Calorie restriction prevents age-related changes in the intestinal microbiota. Aging (Albany NY) 13, 6298–6329. doi: 10.18632/aging.202753
Lagkouvardos, I., Lesker, T. R., Hitch, T. C. A., Gálvez, E. J. C., Smit, N., Neuhaus, K., et al. (2019). Sequence and cultivation study of Muribaculaceae reveals novel species, host preference, and functional potential of this yet undescribed family. Microbiome 7:28. doi: 10.1186/s40168-019-0637-2
Li, Y., Cui, Y., Hu, X., Liao, X., and Zhang, Y. (2019). Chlorophyll supplementation in early life prevents diet-induced obesity and modulates gut microbiota in mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 63:e1801219. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201801219
Li, T., Gao, J., Du, M., and Mao, X. (2019). Bovine α-lactalbumin hydrolysates ameliorate obesity-associated endotoxemia and inflammation in high-fat diet-fed mice through modulation of gut microbiota. Food Funct. 10, 3368–3378. doi: 10.1039/C8FO01967C
Li, B., Li, L., Li, M., Lam, S. M., Wang, G., Wu, Y., et al. (2019). Microbiota depletion impairs thermogenesis of Brown adipose tissue and Browning of white adipose tissue. Cell Rep. 26, 2720–37.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.015
Li, A. L., Ni, W. W., Zhang, Q. M., Li, Y., Zhang, X., Wu, H. Y., et al. (2020). Effect of cinnamon essential oil on gut microbiota in the mouse model of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. Microbiol. Immunol. 64, 23–32. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12749
Li, Z., Yi, C. X., Katiraei, S., Kooijman, S., Zhou, E., Chung, C. K., et al. (2018). Butyrate reduces appetite and activates brown adipose tissue via the gut-brain neural circuit. Gut 67, 1269–1279. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314050
Lin, Y. C., Chen, Y. T., Li, K. Y., and Chen, M. J. (2020). Investigating the mechanistic differences of obesity-inducing Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens M1 and anti-obesity Lactobacillus mali APS1 by Microbolomics and metabolomics. Front. Microbiol. 11:1454. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01454
Liu, H. X., Rocha, C. S., Dandekar, S., and Wan, Y. J. (2016). Functional analysis of the relationship between intestinal microbiota and the expression of hepatic genes and pathways during the course of liver regeneration. J. Hepatol. 64, 641–650. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.09.022
Louis, P., and Flint, H. J. (2009). Diversity, metabolism and microbial ecology of butyrate-producing bacteria from the human large intestine. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 294, 1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01514.x
Makki, K., Deehan, E. C., Walter, J., and Bäckhed, F. (2018). The impact of dietary Fiber on gut microbiota in host health and disease. Cell Host Microbe 23, 705–715. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2018.05.012
Martens, E. C., Koropatkin, N. M., Smith, T. J., and Gordon, J. I. (2009). Complex glycan catabolism by the human gut microbiota: the Bacteroidetes Sus-like paradigm. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 24673–24677. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R109.022848
Meisel, M., Mayassi, T., Fehlner-Peach, H., Koval, J. C., O'Brien, S. L., Hinterleitner, R., et al. (2017). Interleukin-15 promotes intestinal dysbiosis with butyrate deficiency associated with increased susceptibility to colitis. ISME J. 11, 15–30. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2016.114
Milani, C., Duranti, S., Bottacini, F., Casey, E., Turroni, F., Mahony, J., et al. (2017). The first microbial colonizers of the human gut: composition, activities, and health implications of the infant gut microbiota. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 81:e00036-17. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00036-17
Mollica, M. P., Mattace Raso, G., Cavaliere, G., Trinchese, G., De Filippo, C., Aceto, S., et al. (2017). Butyrate regulates liver mitochondrial function, efficiency, and dynamics in insulin-resistant obese mice. Diabetes 66, 1405–1418. doi: 10.2337/db16-0924
Monk, J. M., Lepp, D., Zhang, C. P., Wu, W., Zarepoor, L., Lu, J. T., et al. (2016). Diets enriched with cranberry beans alter the microbiota and mitigate colitis severity and associated inflammation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 28, 129–139. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.10.014
Montanari, T., Pošćić, N., and Colitti, M. (2017). Factors involved in white-to-brown adipose tissue conversion and in thermogenesis: a review. Obes. Rev. 18, 495–513. doi: 10.1111/obr.12520
Ninkov, A., Frank, J. R., and Maggio, L. A. (2022). Bibliometrics: methods for studying academic publishing. Perspect. Med. Educ. 11, 173–176. doi: 10.1007/s40037-021-00695-4
Ormerod, K. L., Wood, D. L., Lachner, N., Gellatly, S. L., Daly, J. N., Parsons, J. D., et al. (2016). Genomic characterization of the uncultured Bacteroidales family S24-7 inhabiting the guts of homeothermic animals. Microbiome 4:36. doi: 10.1186/s40168-016-0181-2
Pedersen, H. K., Gudmundsdottir, V., Nielsen, H. B., Hyotylainen, T., Nielsen, T., Jensen, B. A., et al. (2016). Human gut microbes impact host serum metabolome and insulin sensitivity. Nature 535, 376–381. doi: 10.1038/nature18646
Raoult, D. (2008). Obesity pandemics and the modification of digestive bacterial flora. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 27, 631–634. doi: 10.1007/s10096-008-0490-x
Reeves, A. R., D'Elia, J. N., Frias, J., and Salyers, A. A. (1996). A Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron outer membrane protein that is essential for utilization of maltooligosaccharides and starch. J. Bacteriol. 178, 823–830. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.3.823-830.1996
Reeves, A. R., Wang, G. R., and Salyers, A. A. (1997). Characterization of four outer membrane proteins that play a role in utilization of starch by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. J. Bacteriol. 179, 643–649. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.3.643-649.1997
Rose, S., Bennuri, S. C., Davis, J. E., Wynne, R., Slattery, J. C., Tippett, M., et al. (2018). Butyrate enhances mitochondrial function during oxidative stress in cell lines from boys with autism. Transl. Psychiatry 8:42. doi: 10.1038/s41398-017-0089-z
Salzman, N. H., de Jong, H., Paterson, Y., Harmsen, H. J. M., Welling, G. W., and Bos, N. A. (2002). Analysis of 16S libraries of mouse gastrointestinal microflora reveals a large new group of mouse intestinal bacteria. Microbiology (Reading) 148, 3651–3660. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-11-3651
Seedorf, H., Griffin, N. W., Ridaura, V. K., Reyes, A., Cheng, J., Rey, F. E., et al. (2014). Bacteria from diverse habitats colonize and compete in the mouse gut. Cell 159, 253–266. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.008
Shen, T. C., Chehoud, C., Ni, J., Hsu, E., Chen, Y. Y., Bailey, A., et al. (2016). Dietary regulation of the gut microbiota engineered by a minimal defined bacterial consortium. PLoS One 11:e0155620. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155620
Tomas, J., Mulet, C., Saffarian, A., Cavin, J. B., Ducroc, R., Regnault, B., et al. (2016). High-fat diet modifies the PPAR-γ pathway leading to disruption of microbial and physiological ecosystem in murine small intestine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 113, E5934–E5943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1612559113
Tremaroli, V., and Bäckhed, F. (2012). Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 489, 242–249. doi: 10.1038/nature11552
Turnbaugh, P. J., Ley, R. E., Mahowald, M. A., Magrini, V., Mardis, E. R., and Gordon, J. I. (2006). An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444, 1027–1031. doi: 10.1038/nature05414
Valvassori, S. S., Calixto, K. V., Budni, J., Resende, W. R., Varela, R. B., de Freitas, K. V., et al. (2013). Sodium butyrate reverses the inhibition of Krebs cycle enzymes induced by amphetamine in the rat brain. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 120, 1737–1742. doi: 10.1007/s00702-013-1056-3
van Eck, N. J., and Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84, 523–538. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
Van Hul, M., Geurts, L., Plovier, H., Druart, C., Everard, A., Ståhlman, M., et al. (2018). Reduced obesity, diabetes, and steatosis upon cinnamon and grape pomace are associated with changes in gut microbiota and markers of gut barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 314, E334–E352. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00107.2017
Wang, B., Gao, R., Wu, Z., and Yu, Z. (2020). Functional analysis of sugars in modulating bacterial communities and metabolomics profiles of Medicago sativa silage. Front. Microbiol. 11:641. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00641
Wang, Y., Tang, C., Tang, Y., Yin, H., and Liu, X. (2020). Capsaicin has an anti-obesity effect through alterations in gut microbiota populations and short-chain fatty acid concentrations. Food. Nutr. Res. 64:64. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v64.3525
Xu, J., Bjursell, M. K., Himrod, J., Deng, S., Carmichael, L. K., Chiang, H. C., et al. (2003). A genomic view of the human-Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron symbiosis. Science 299, 2074–2076. doi: 10.1126/science.1080029
Xu, C., Liu, J., Gao, J., Wu, X., Cui, C., Wei, H., et al. (2020). Combined soluble Fiber-mediated intestinal microbiota improve insulin sensitivity of obese mice. Nutrients 12:351. doi: 10.3390/nu12020351
Yeung, C. Y., Chiang Chiau, J. S., Cheng, M. L., Chan, W. T., Chang, S. W., Chang, Y. H., et al. (2020). Modulations of probiotics on gut microbiota in a 5-fluorouracil-induced mouse model of mucositis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 35, 806–814. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14890
Zeng, Z., Zhou, Y., Xu, Y., Wang, S., Wang, B., Zeng, Z., et al. (2022). Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SC06 alleviates the obesity of Ob/Ob mice and improves their intestinal microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Food Funct. 13, 5381–5395. doi: 10.1039/D1FO03170H
Zhao, R., Khafipour, E., Sepehri, S., Huang, F., Beta, T., and Shen, G. X. (2019). Impact of Saskatoon berry powder on insulin resistance and relationship with intestinal microbiota in high fat-high sucrose diet-induced obese mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 69, 130–138. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.03.023
Zhu, H., Xu, C., Dong, Y., Lu, S., and Guo, L. (2023). Chai-Gui decoction and its representative components ameliorate spontaneous hypertension rats by modulating lipid metabolism and gut microbiota. J. Ethnopharmacol. 305:116116. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.116116
Zou, J., Shen, Y., Chen, M., Zhang, Z., Xiao, S., Liu, C., et al. (2020). Lizhong decoction ameliorates ulcerative colitis in mice via modulating gut microbiota and its metabolites. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 104, 5999–6012. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10665-1
Keywords: S24-7 , gut microbiota, research hotspots, bibliometric analysis, health
Citation: Gao F, Wang F, Wang D, Du G and Gao F (2025) Bibliometric analysis of the S24-7 family and its association with health. Front. Microbiol. 16:1571883. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1571883
Edited by:
Lucas De Paula Ramos, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, FranceReviewed by:
Joseph Atia Ayariga, Alabama State University, United StatesLorenzo Drago, University of Milan, Italy
Nazia Saiyed, Beaumont Health, United States
Copyright © 2025 Gao, Wang, Wang, Du and Gao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guankui Du, ZHVndWFua3VpQDE2My5jb20=; Fangfang Gao, MTQzODQ4NjQzMkBxcS5jb20=
 Fangmei Gao1,2,3
Fangmei Gao1,2,3 Guankui Du
Guankui Du Fangfang Gao
Fangfang Gao