- Department of Microbiology, JSS Medical College and Hospital, JSS Academy of Higher Education and Research, Mysuru, India
Background: Antimicrobial resistance [AMR] is a global health problem. It is important to train health care professionals on the rational use of antimicrobials to curb AMR.
Methods: This prospective interventional study was conducted with clinical practitioners, undergraduates [MBBS/Interns], postgraduates and pharmacy Students. A total of 50 participants were included in the study. The innovative games were administered for the management of infections of all the different systems of the body under the Indian Council Medical Research (ICMR) treatment guidelines of 2022 and the latest Infectious Disease Society of America (IDSA) guidelines involving different components. Pre-test and post-test questionnaires were administered and evaluated.
Results: After the intervention, the knowledge on the ability to differentiate between bacterial and viral symptoms in respiratory tract infections and gastroenteritis improved from 48 to 94%. The practice of using the right empirical choice of antimicrobials at the right dose for the right duration, on the basis of the severity of the infection, improved from 34 to 82%. The awareness/practice of using the right and rational combination of antibiotics improved from 44 to 84%. Knowledge of suspected multidrug-resistant gram-negative infections and other priority pathogens, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus [MRSA] and Candida infection, has improved from 32 to 78%. The practice of using certain antibiotics at specific infection sites based on the basis of their pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics improved from 20 to 76%. The knowledge of the intrinsic resistance of certain microorganisms to specific antimicrobial agents has improved from 15 to 80%.
Conclusion: The gamified intervention successfully improved participants’ knowledge and awareness of rational antimicrobial use. The substantial improvements in all the aforementioned components highlight the positive impact of the intervention in promoting optimal antimicrobial use and curbing AMR. Innovative gamified interventions create better and long-lasting awareness, ensuring the appropriate use of antimicrobials.
Introduction
Antimicrobial resistance [AMR] has become a serious global health problem. The World Health Organization [WHO] has identified AMR as one of the top ten public health concerns with the potential to kill 10 million people per year by 2050 (WHO policy guidance on integrated antimicrobial stewardship activities, 2023; Charani et al., 2021). Initially, penicillin revolutionized the treatment of infectious diseases. Healthcare and global development have transformed to reduce mortality. The continued introduction of various antimicrobial agents has enhanced healthcare, but their incorrect use at all levels of human, animal, and plant health has unleashed AMR repercussions (Jonas et al., 2017).
In the face of rising AMR, Lower middle income countries (LMICs) health and development policies aiming to eliminate severe poverty (living on less than $1.90 per day) by 2030 have proven impossible. According to the World Bank, the impact of AMR on healthcare expenses might vary from $300 billion to more than one trillion dollars by 2050 (Charani et al., 2021). In May 2015, the World Health Assembly established a global action plan for antibiotic resistance. This includes strategic objectives aimed at raising awareness and knowledge of antimicrobial resistance, as well as optimizing the use of these medications (WHO policy guidance on integrated antimicrobial stewardship activities, 2023). Continuous training is required both socially and professionally in various ways, such as through the use of media, conferences by specialists in the field, and antimicrobial optimization programs.
One of the most significant challenges in AMS programs is the amount of knowledge that students must master in a short period (Singh et al., 2021; Taneja and Sharma, 2019). AMR is a difficult concept to comprehend, and many people, including pharmacists and dentists, believe that the person develops resistance (Hsu, 2020; Woodhead and Finch, 2007). Up-to-date knowledge of optimal antimicrobial use appears to be quite poor in medical students and practitioners. Medical educators face a significant challenge in developing and implementing instructional approaches that promise to increase students’ knowledge of antimicrobial resistance and antimicrobial stewardship (Wutzke et al., 2007; Fuller et al., 2022; Mendelson et al., 2016).
Existing programs frequently exhibit mixed results in terms of effectiveness. The conventional method of teaching students [lectures] has not actively engaged the students. It is largely a passive strategy that has not been proven to increase long-term memory or understanding of AMR concepts. It has been suggested that games actively include participants in the AMR learning process, which helps address these constraints (Gautham et al., 2021; Azevedo et al., 2013).
Games have recently been increasingly employed in AMS programs, as games are more effective than conventional methods. Games can increase interest in a topic and reinforce previously provided information. They have been demonstrated to foster a competitive environment and boost student interaction. As a result, games could be viewed as a suitable supplement to existing healthcare initiatives, addressing the limitations of “conventional techniques” (Al-Amin et al., 2021; Collins et al., 2022). This study aimed to determine how games can increase knowledge about antibiotic prescription practices by creating an engaging learning environment.
Methodology
This prospective interventional study was conducted with clinical practitioners, undergraduates [MBBS/Interns], postgraduate and pharmacy students of JSS Medical College and JSS College of Pharmacy, Mysuru, South India. A total of 50 participants were included in the study. The participants were divided into 2 teams. The pretest questionnaire was first administered to each participant over a period of 20 min. The intervention was then conducted as follows:
1. Introduction about rational use of antibiotics, the importance of antimicrobial stewardship interventions in a tertiary hospital setting.
2. Playing innovative games designed for the management of infections of different systems [based on the latest ICMR antimicrobial treatment guidelines 2022 and the latest IDSA treatment guidelines].
3. A post-test Questionnaire was administered to assess the effectiveness of the intervention.
Questionnaire
A multiple-choice questionnaire covering all systemic infections was designed with 150 marks, with 30 questions, each with a weightage of 5 marks. The questions focused mainly on the empirical choice of the right antimicrobial agent at the right dose and duration for a particular infection, with antibiotics to be avoided under certain conditions on the basis of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics and intrinsic resistance. The participants answered the questionnaire independently for over 20 min without using reference materials, notes, or assistance. Thus, baseline knowledge was evaluated.
Game design
The innovative games were designed for the management of infections of all the different systems of the body under the ICMR-AMR treatment guidelines of 2022 and the latest IDSA guidelines, which focus on the following:
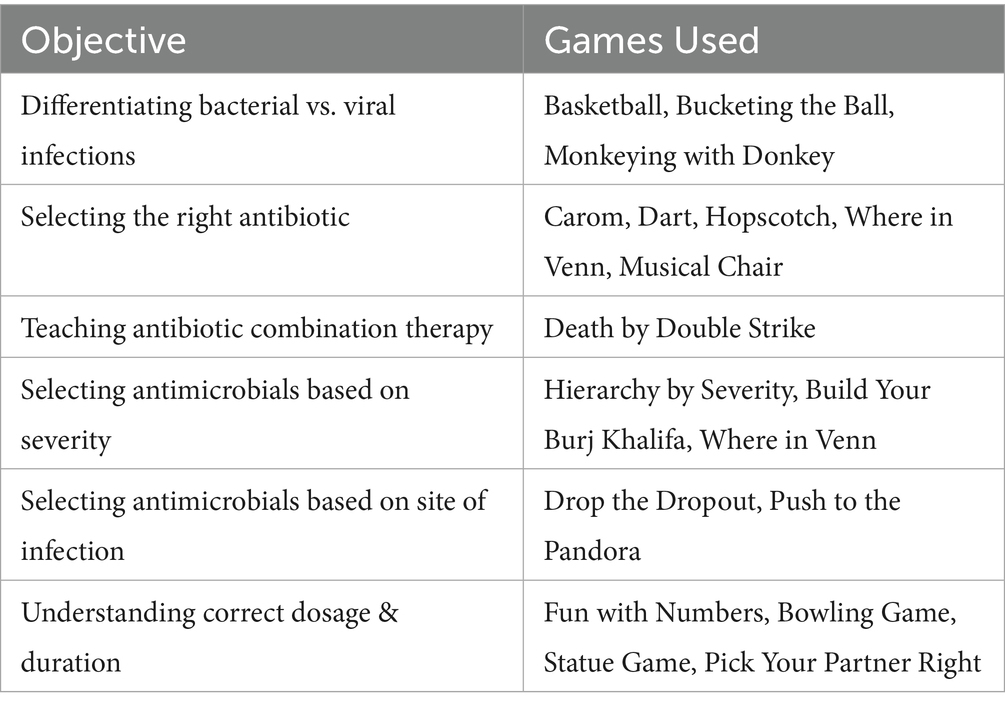
1. To differentiate between bacterial and viral features in common infections, such as respiratory tract infections and gastroenteritis, as most often these infections are caused by viruses, they are treated with antibiotics.
2. To understand the right empirical choice of antimicrobials at the right dose for the right duration based on the severity of infection.
3. To use the right and rational combination of antibiotics.
4. To suspect multidrug-resistant gram-negative infections and other priority pathogens causing infections, such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Candida.
5. To highlight antibiotics that are not useful at certain infection sites based on the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the antibiotics.
6. Intrinsic resistance of some organisms to antimicrobial agents.
7. Miscellaneous- Dosage calculation based on renal functions, rational choice of investigations at different stages of infection, and choosing the right antibiotic based on the breakpoint minimum inhibitory concentration quotient [BMQ].
Table 1 highlights the innovative use of interactive games to enhance understanding of rational antimicrobial use. Each game is designed to target specific learning objectives, from differentiating bacterial and viral infections to selecting the right antibiotic, dosage, and duration.
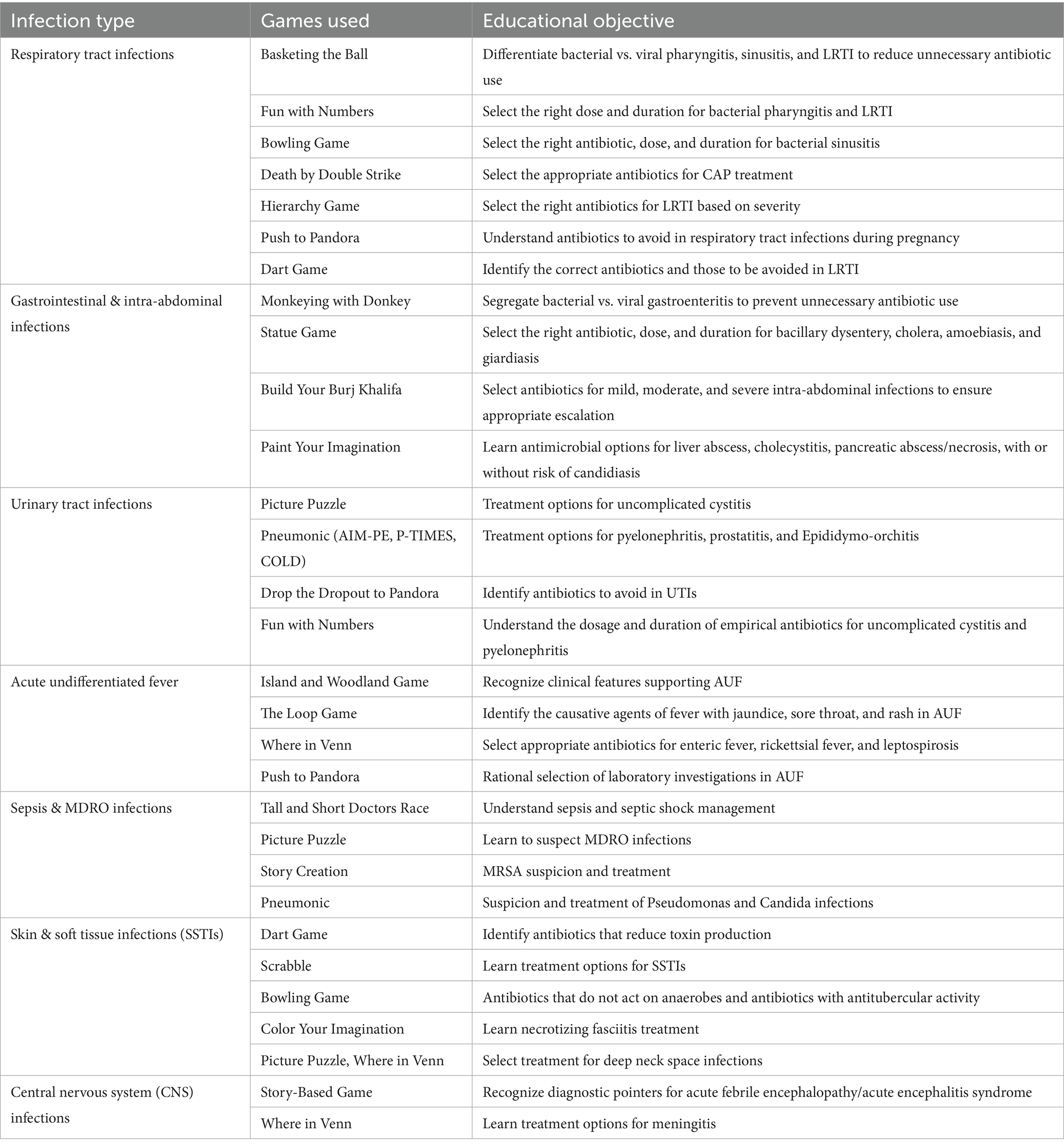
Table 2 presents a gamified educational strategy for rational antimicrobial use across various infections. Each game is designed to reinforce key learning objectives, such as differentiating bacterial and viral infections, selecting appropriate antibiotics based on severity and site, and understanding optimal dosage and duration.
Statistical analysis
Data analysis was carried out using SPSS software version 20.0. The effectiveness of the intervention was evaluated by comparing pre-test and post-test scores across six components among 50 participants. Confidence intervals for the mean percentages were calculated at a 95% confidence level. A two-tailed z-test for proportions was used to determine the statistical significance of the observed differences.
Results
The various components of rational antimicrobial use (as outlined in the methodology) were assessed pre-test and post-test.
Pre-test result analysis
The knowledge on intrinsic resistance of certain microorganisms to specific antimicrobial agents [Component VI] was the least during the pre-test [15%]. The knowledge on suspecting multidrug-resistant gram-negative infections and other priority pathogens, such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus [MRSA] and Candida [Component IV], was also very low [32%]. The practice of using the right empirical choice of antibiotics for the right duration based on the severity of the infection [Component II] was satisfactory [34%]. The practice of using certain antibiotics in specific infection sites based on their pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics [Component V] was better when compared to the other five components [20%]. The awareness/practice of using the right and rational combination of antibiotics [Component III] was also better when compared to the other five components [44%]. The knowledge about differentiating between bacterial and viral symptoms in common infections like respiratory tract infections and gastroenteritis [Component I] was the best when compared to the other five components [48%].
Post-test result analysis
After the intervention, the knowledge about differentiating between bacterial and viral symptoms in common infections like respiratory tract infections and gastroenteritis improved from 48 to 94%. The practice of using the right empirical choice of antimicrobials in the right dose for the right duration, based on the severity of the infection, improved from 34 to 82%. The awareness/practice of using the right and rational combination of antibiotics improved from 44 to 84%. The knowledge on suspecting multidrug-resistant Gram-negative infections and other priority pathogens, such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus [MRSA] and Candida infection, improved from 32 to 78%. The practice of using certain antibiotics in specific infection sites based on their pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics improved from 20 to 76%. The knowledge of the intrinsic resistance of certain microorganisms to specific antimicrobial agents improved from 15 to 80%. Table 3 depicts the comparison between pre- and post-test results of six different components on the rational use of antibiotics.
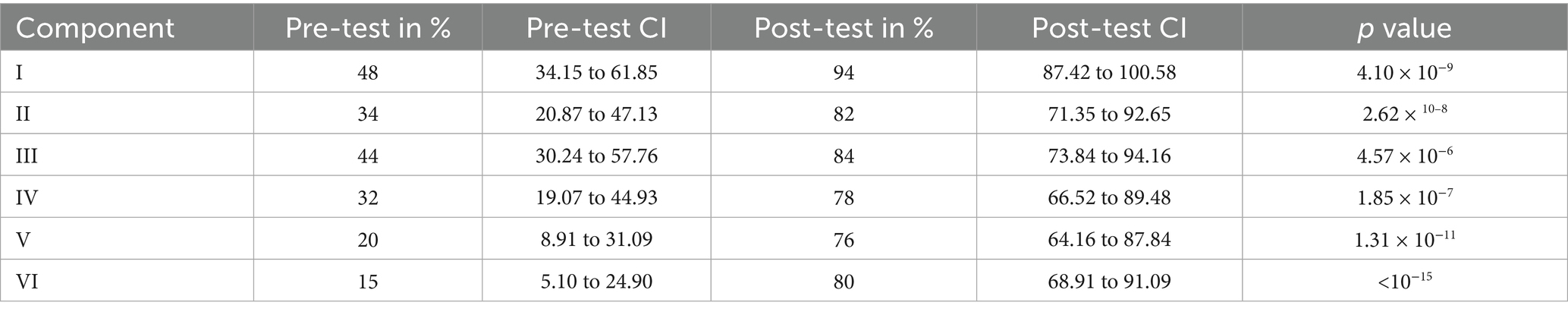
Table 3. Depicts the comparison between pre- and post-test results of six different components on the rational use of antibiotics.
Discussion
The findings of this study show that a gamified intervention is an effective strategy for improving knowledge and awareness of the rational use of antimicrobials. Observed improvements across all six components suggest that gamified educational strategies can significantly influence participants’ comprehension of complex antimicrobial stewardship principles. Using gamification as a teaching tool engages learners and makes learning interactive, which is particularly important for addressing antimicrobial resistance (AMR), a global health challenge. This approach allows learners to actively participate in scenarios that mimic real-life decision-making, fostering greater comprehension of the topic.
The intervention enabled participants to distinguish bacterial symptoms from viral symptoms in common infections, highlighting how gamified methods can deliver targeted education. This study demonstrated an improvement from 48 to 94%, resonating with findings reported by Azevedo et al. (2013). They also demonstrated that educational activities significantly improved knowledge regarding the correct use of antibiotics for bacterial infections rather than viral infections. According to Gyssens (2018), gamified educational strategies were more effective than traditional methods in improving healthcare professionals’ knowledge of AMR-related concepts. These results highlight gamification’s ability to equip individuals with the knowledge needed to make informed choices about antimicrobial use, thereby reducing inappropriate antibiotic prescriptions.
Another impact of the intervention was the improvement in participants’ understanding of antimicrobial selection based on the severity of the infection. Gamified platforms, as highlighted by Gorbanev et al. (2018), are valuable for teaching clinical decision-making. Gamification simulates real-life scenarios, enhancing learners’ ability to apply theoretical knowledge to practice (Gorbanev et al., 2018). This process bridges the gap between education and clinical application. The intervention also improved awareness of rational antibiotic combinations by emphasizing synergy and minimizing resistance development. Previous studies, such as Molina et al. (2020), have shown that interactive and gamified educational settings significantly improve participants’ comprehension of pharmacological principles, making the learning process more impactful.
In the context of AMR, the intervention’s focus on detecting multidrug-resistant pathogens was particularly notable. Calik et al. (2022) demonstrated that gamified interventions helped learners diagnose and prepare to address drug-resistant infections. This improvement translates into better infection control practices and more targeted antimicrobial therapy, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Similarly, a better understanding of the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of antibiotics for site-specific infections highlights the intervention’s success in imparting critical knowledge for effective treatment. Zainuddin et al. (2020) noted that gamification fosters dynamic educational settings that facilitate the retention of complex information, supporting the findings of this study.
The improved understanding of certain organisms’ intrinsic resistance to specific antimicrobials demonstrates the intervention’s substantial impact. This understanding is crucial for combating AMR by avoiding irrational antimicrobial use. Nowbuth et al. (2023) emphasized the role of gamification in antimicrobial stewardship education, demonstrating its ability to transform knowledge into practice by reinforcing key stewardship principles through engaging and memorable experiences.
Gamified interventions in healthcare education are increasingly recognized for their relevance and efficacy. This study contributes to the growing body of literature by addressing the limitations of traditional didactic approaches, which often fail to sustain learners’ interest or promote active participation. Contemporary educational strategies prioritize interactive and experiential learning, and gamified interventions align perfectly with these priorities.
The gamified approach adopted in this study is a significant step forward in antimicrobial stewardship education, offering a replicable model for broader implementation. As Mansen (2023) suggested, integrating gamification into healthcare education not only improves knowledge retention but also cultivates critical thinking and problem-solving skills. The results of this study strongly indicate that gamified interventions can be scaled across varied clinical and educational settings, contributing meaningfully to the global fight against AMR.
Conclusion
The gamified interventions employed in this study successfully improved participants’ knowledge and awareness of the rational use of antimicrobials. These improvements are a step ahead in curbing AMR and optimizing patient outcomes by reducing unnecessary antimicrobial prescriptions. Continued efforts to enhance the knowledge and create awareness on the rational use of antimicrobials are the need of the hour for combating the global challenge of AMR and preserving the efficacy of the antimicrobial agents for future generations. Innovative gamified interventions create better and long-lasting awareness, promoting rational use of antimicrobials to curb the growing AMR.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
MS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. SRS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YM: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. GM: Writing – review & editing. VG: Writing – review & editing. CE: Writing – review & editing. SSS: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study did not receive any funding to conduct the study, but publication charges will be provided by JSS Academy of Higher Education and Research, Mysuru, India.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Reference
Al-Amin, S., Hassan, M. Z., Saif-Ur-Rahman, K. M., Chowdhury, M. A., Morrison, S. D., Donevant, S. B., et al. (2021). Pattern of antibiotic use for acute respiratory infections among out-patients in south Asian region: protocol for a systematic review. Medicine 100:e22398. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022398
Azevedo, M. M., Pinheiro, C., Yaphe, J., and Baltazar, F. (2013). Assessing the impact of a school intervention to promote students’ knowledge and practices on correct antibiotic use. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 10, 2920–2931. doi: 10.3390/ijerph10072920
Calik, A., Cakmak, B., Kapucu, S., and Inkaya, B. (2022). The effectiveness of serious games designed for infection prevention and promotion of safe behaviours of senior nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic. Am. J. Infect. Control 50, 1360–1367. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2022.02.025
Charani, E., McKee, M., Ahmad, R., Balasegaram, M., Bonaconsa, C., Merrett, G. B., et al. (2021). Optimising antimicrobial use in humans–review of current evidence and an interdisciplinary consensus on key priorities for research. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 7:100161. doi: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100161
Collins, J. P., King, L. M., Collier, S. A., Person, J., Gerdes, M. E., Crim, S. M., et al. (2022). Antibiotic prescribing for acute gastroenteritis during ambulatory care visits—United States, 2006–2015. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 43, 1880–1889. doi: 10.1017/ice.2021.522
Fuller, W. L., Hamzat, O. T., Aboderin, A. O., Gahimbare, L., Kapona, O., Yahaya, A. A., et al. (2022). National action plan on antimicrobial resistance: an evaluation of implementation in the World Health Organization Africa region. J. Public Health Africa. 13:2000. doi: 10.4081/jphia.2022.2000
Gautham, M., Spicer, N., Chatterjee, S., and Goodman, C. (2021). What are the challenges for antibiotic stewardship at the community level? An analysis of the drivers of antibiotic provision by informal healthcare providers in rural India. Soc. Sci. Med. 275:113813. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.113813
Gorbanev, I., Agudelo-Londoño, S., González, R. A., Cortes, A., Pomares, A., Delgadillo, V., et al. (2018). A systematic review of serious games in medical education: quality of evidence and pedagogical strategy. Med. Educ. Online 23:1438718. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2018.1438718
Gyssens, I. C. (2018). Role of education in antimicrobial stewardship. Med. Clin. North Am. 102, 855–871. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2018.05.011
Hsu, J. (2020). How covid-19 is accelerating the threat of antimicrobial resistance. BMJ :369. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1983
Jonas, O. B., Irwin, A., Berthe, F. C., Le Gall, F. G., and Marquez, P. V. (2017). Drug-resistant infections: a threat to our economic future. World Bank Rep. 2, 1–32.
Mansen, B. (2023). Exploring the use of new media in the study of communicative skills in off-classroom spaces: A case study (Cape Coast, Ghana: University of Cape Coast Repository).
Mendelson, M., Røttingen, J. A., Gopinathan, U., Hamer, D. H., Wertheim, H., Basnyat, B., et al. (2016). Maximising access to achieve appropriate human antimicrobial use in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet 387, 188–198. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00547-4
Molina, J. A., Lorenzo, C., and Chacón-Cervera, J. A. (2020). Serious games for teaching pharmacology principles in higher education. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 58, 534–551.
Nowbuth, A. A., Asombang, A. W., Alaboud, K., Souque, C., Dahu, B. M., Pather, K., et al. (2023). Gamification as an educational tool to address antimicrobial resistance: a systematic review. JAC Antimicrob Resist. 5, 1–13. doi: 10.1093/jacamr/dlad130
Singh, S., Charani, E., Devi, S., Sharma, A., Edathadathil, F., Kumar, A., et al. (2021). A road-map for addressing antimicrobial resistance in low-and middle-income countries: lessons learnt from the public private participation and co-designed antimicrobial stewardship programme in the state of Kerala, India. Antimicrob. Resist. Infec. Control 10, 1–9. doi: 10.1186/s13756-020-00873-9
Taneja, N., and Sharma, M. (2019). Antimicrobial resistance in the environment: the Indian scenario. Indian J. Med. Res. 149, 119–128. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_331_18
WHO policy guidance on integrated antimicrobial stewardship activities. (2023). Available online at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240025530
Woodhead, M., and Finch, R. (2007). Public education—a progress report. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 60, i53–i55. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkm158
Wutzke, S. E., Artist, M. A., Kehoe, L. A., Fletcher, M., Mackson, J. M., and Weekes, L. M. (2007). Evaluation of a national programme to reduce inappropriate use of antibiotics for upper respiratory tract infections: effects on consumer awareness, beliefs, attitudes and behaviour in Australia. Health Promot. Int. 22, 53–64. doi: 10.1093/heapro/dal034
Keywords: gamified intervention, tackling AMR, rational use of antimicrobials, ICMR antimicrobial treatment guidelines 2022, antimicrobial stewardship (AMS)
Citation: Sumana MN, Shettar SR, Maheshwarappa YD, Megha GK, GS V, Eshwarappa CS and SC SS (2025) Gamified interventions to educate healthcare professionals on the rational use of antimicrobials. Front. Microbiol. 16:1577005. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1577005
Edited by:
Takashi Azuma, Osaka Medical College, JapanReviewed by:
Jayshree Shriram Dawane, Bharati Vidyapeeth University Medical College, IndiaLetícia Massaud-Ribeiro, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Sumana, Shettar, Maheshwarappa, Megha, GS, Eshwarappa and SC. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mahadevaiah Neelambike Sumana, bW5zdW1hbmFAanNzdW5pLmVkdS5pbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share third authorship
‡ORCID: Mahadevaiah Neelambike Sumana, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8877-0602
Supreeta R Shettar, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4121-6054
Yogeesh D. Maheshwarappa, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5434-6387
G. K. Megha, https://orcid.org/0009-0003-7192-6791
Veerabhadraswamy G. S., https://orcid.org/0009-0009-1817-3501
Chinchana Shylaja Eshwarappa, https://orcid.org/0009-0007-3722-8374
Shruthi Shree S. C., https://orcid.org/0009-0002-5392-4883
 Mahadevaiah Neelambike Sumana
Mahadevaiah Neelambike Sumana Supreeta R. Shettar
Supreeta R. Shettar Yogeesh D. Maheshwarappa
Yogeesh D. Maheshwarappa G. K. Megha
G. K. Megha Veerabhadraswamy G. S.
Veerabhadraswamy G. S. Chinchana Shylaja Eshwarappa
Chinchana Shylaja Eshwarappa Shruthi Shree S. C.‡
Shruthi Shree S. C.‡