- 1Inner Mongolia Academy of Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Sciences, Hohhot, China
- 2Inner Mongolia Normal University, Hohhot, China
- 3Hulunbuir Vocational Technical College, Hulunbuir, China
Introduction: L-methionine is nutritionally indispensable for humans and animals. It is widely applied to feed, livestock and poultry breeding, food, medicine, energy and chemical industries. Maize endosperm contains a stable protein called δ-zein, which is abundant in sulfur amino acids, including methionine. Candida utilis (C. utilis) has been utilized as a cell factory to express and produce recombinant products. However, there is limited information on its genetic background and expression regulatory elements.
Methods: In this study, we aimed to improve methionine yields in an engineered C. utilis harboring the δ-zein gene by identifying a strong promoter and optimal signal peptide. A C. utilis glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAP) promoter mutant library was constructed and screened to obtain a strong promoter. Subsequently, de novo sequencing of the C. utilis genome was performed using a combination of second-generation Illumina-Seq sequencing platform and third-generation nanopore sequencing technique. Endogenous signal peptides of C. utilis were analyzed by sequencing the C. utilis genome. Recombinant C. utilis strains with homologous integration expression vectors of different signal peptides were constructed and screened for C. utilis optimal signal peptides for secretion of δ-zein.
Results: Finally, a secretory expression system pGS-zein containing a strong promoter GP6 and an optimal signal peptide SP8 was constructed. In the food-grade engineered C. utilis C/pGS-zein methionine content increased by 21.09% compared with that of C/psP with the original promoter, and by 33.64% compared to wild-type C. utilis.
Discussion: This study demonstrates successful expression and secretion of δ-zein in C. utilis and establishes a foundation for enhanced methionine production of heterologous proteins in C. utilis. More importantly, these high-performance biological elements provide fundamental knowledge and technical knowhow for enhanced production of heterologous proteins in C. utilis.
1 Introduction
Methionine is an essential component of proteins and functional molecular precursors to support human and animal nutrition. Methionine is required for growth, immunity, metabolism and other biological processes with important physiological significance. It is widely used in food, animal feed, medicine and other fields (Jankowski et al., 2014). Numerous human and animal model studies have shown that methionine is involved in the regulation of several functions in vivo, including cellular protein synthesis in the immune system (Lin et al., 2023), methylation reactions, redox, polyamine synthesis and coupling of folate metabolism (Shen et al., 2023). Methionine is an essential feed additive in animal husbandry and breeding as it is the main sulfur-containing amino acid in poultry and ruminant diets (Sałek et al., 2020). Methionine cannot be synthesized by livestock and must be obtained from ingestion of external sources. Methionine supplementation in feed can promote sufficient feed intake, which in turn, stimulates livestock growth, thus, minimizing losses and reducing production costs (Lee et al., 2020). Cardoso et al. showed that the addition of microbial proteins and rumen amino acids, such as methionine and lysine, into cereal based diets for dairy cows, achieved higher milk production and protein content (Cardoso et al., 2021). Barido et al. demonstrated that Met/Lys supplementation resulted in higher protein scores, water holding capacity and lower shear force score. Lower shear force typically signifies that the product (e.g., meat) is more tender and requires less force when slicing or chewing. From a food quality perspective, products with this characteristic are often preferred for their improved taste profile (Barido et al., 2020). Accurate determination of livestock and poultry amino acid requirements can improve the efficiency of protein utilization by animals, thus reducing feed costs and increasing production efficiency (Awawdeh, 2022).
In recent years, limited supplementation of protein feed with the key restricted amino acids (methionine and lysine) and the high cost of breeding have hindered development of the feed industry and animal husbandry. One approach to solving these issues is the need to develop new protein feed resources. Currently, the production of methionine is undertaken predominantly by chemical synthesis. However, chemically synthesized products have several disadvantages including poor safety standards, serious environmental pollution and high costs. Recently, the biosynthesis of methionine via microbial fermentation has gained growing attention owing to certain advantages including less environmental damage and low cost of raw materials. With the continuous growth of the biotechnology field, new microbial strains are routinely being developed to construct microbial cell factories for the production of methionine. Zein (δ-zein) is a protein rich in sulfur-containing amino acids (20% methionine) present in the endosperm of maize (Kim and Krishnan, 2003). Kim et al. increased the methionine content in transgenic plants by expressing δ-zein in soybean (Kim and Krishnan, 2019).
C. utilis is a yeast approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use as a Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) food additive (Li et al., 2021). C. utilis, as a source of protein in concentrated feed for dairy cows, can be used as a substitute for soybean meal without affecting the quality of Norwegian Gouda-type cheeses (Olsen et al., 2021). Kieliszek et al. reported that C. utilis cells performed the biotransformation of inorganic selenium to organic derivatives (e.g., selenomethionine). It creates the possibility of obtaining selenium biocomplexes that can be used in the production of protein-selenium dietary supplements for animals and humans. C. utilis cellular biomass enriched with organic forms of selenium may be a protein source with high potential for application in the livestock and drug industries (Kieliszek et al., 2017). C. utilis has been used as a cell factory for protein expression of a wide range of recombinant products. The advantages of utilizing C. utilis include food safety and fast growth rates with an important role in the feed additives. However, limited studies on its genetic background and regulatory elements have been undertaken where this information will be key in improving the expression capacity of C. utilis.
As one of the basic elements for gene transcription, promoters play an important role in regulating gene expression and optimizing metabolic pathways (Nguyen et al., 2024). Constitutive promoters have a wide range of applications in metabolic engineering and synthetic biology. These types of promoters are independent of the host growth environment and growth stage and can maintain a relatively stable level of gene expression (Cui et al., 2016). The glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAP) promoter has been widely used as a constitutively strong promoter for high-level protein production. The strength of the GAP promoter is usually considered to be comparable to that of the methanol-induced AOX1 promoter (Vogl, 2022). Error-prone PCR (EP-PCR) is an approach commonly used in synthetic biology and directed evolution for integrating mutations across a wide range of genetic backgrounds (Feng et al., 2018; Myers, 2023). The imperfect fidelity of DNA polymerase is exploited to mismatch non-complementary dinucleotides during template mediated extension, followed by insertion of a mutation on the newly synthesized daughter strand, which is then inherited by the double-stranded progeny during replication. The obtained random mutant sequences are cloned into vectors to construct mutant libraries, and then suitable methods are used to screen promoter mutants that drive improved target protein expression (Feng et al., 2018). Qin et al. constructed promoter libraries by EP-PCR to screen for promoters of different strengths (Qin et al., 2011a). Hanson et al. developed a detailed method to construct a library of cloned mutants through EP-PCR and used the online program PEDEL-AA to analyze the diversity in the EP-PCR randomized library (Firth and Patrick, 2008). The advantage of the EP-PCR generated random mutants library is that, in contrast to targeted mutagenesis and rational design, EP-PCR is a highly stochastic process, and directed evolution utilizes Darwinian principles to identify proteins with novel or improved properties (Hanson-Manful and Patrick, 2013). Zhang et al. obtained promoters with different abilities to induce expression by modifying the maltose-inducible promoter Pglvc using EP-PCR. With green fluorescent protein expression as a readout, the study reported that the induced expression intensity from the promoter mutant was about 3.15-fold higher than that of the original promoter, proposing its potential application in metabolic engineering and synthetic biology (Zhang et al., 2022).
Signal peptides (SPs) are important regulatory elements that guide protein secretion. The majority of SPs are located at the N-terminus of secreted proteins with a small number found at the C-terminus or within the protein (Yiping Shi et al., 2014). SPs are a key factor that determines the optimal pathway of target proteins and how they are secreted across the cell membrane. The role of the SP is important to the production of soluble recombinant proteins, vaccine candidates and diagnostic proteins (Zhang et al., 2019). Different signal peptides can greatly affect the secretion levels of target proteins (Xue et al., 2023). The construction of signal peptide libraries in combination with high throughput screens enables identification of optimal signal peptides that drive different efficiencies of target protein secretion. This strategy has been used successfully to optimize the secretion efficiency of many proteins in heterologous hosts (Mori et al., 2015). In a recent study, Liu et al. identified a ferulic acid esterase with broad substrate specificity that is expressed and secreted by Bacillus subtilis. After codon optimization and signal peptide library screening, the secretion of feruloyl esterase by the strain was 10.2-fold higher than that of the parent strain. Hence, B. subtilis could improve secretion of heterologous enzymes by altering the protein sequences (Liu P. et al., 2022).
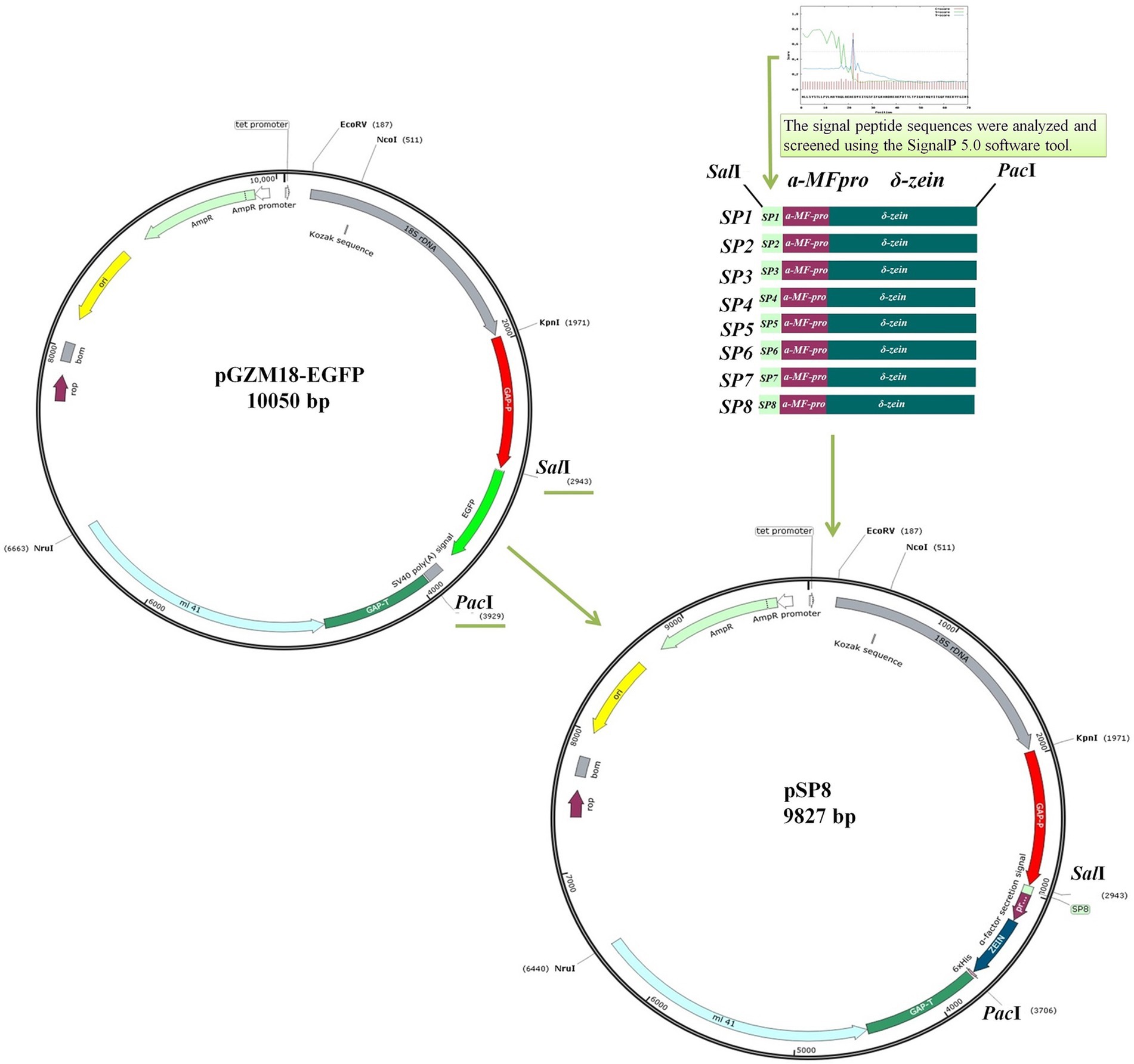
In this study, a C. utilis GAP promoter mutant library was constructed and screened to obtain a strong promoter. Subsequently, eight endogenous signal peptides from C. utilis were identified by sequencing the C. utilis genome. Finally, the strong promoter GP6 and an optimal signal peptide SP8 were utilized to enhance methionine production by overexpressing the δ-zein gene in a recombinant C. utilis. A schematic diagram of the overall strategy for enhancing methionine yields in an engineered C. utilis is shown in Figure 1.
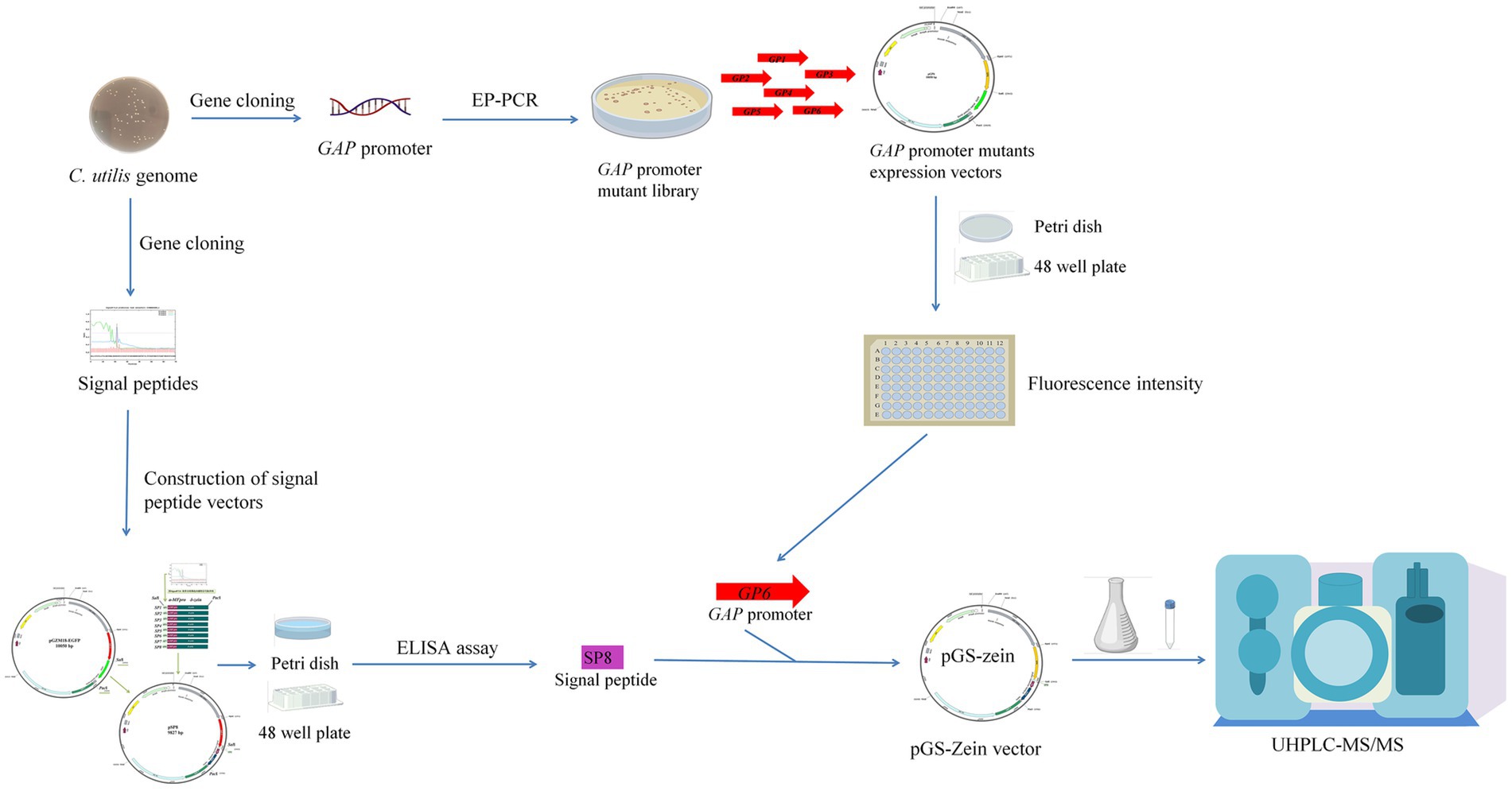
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the overall strategy for enhancing methionine yields in an engineered C. utilis. A C. utilis GAP promoter mutant library was constructed and screened to obtain a strong promoter. The endogenous signal peptides from C. utilis were identified by sequencing the C. utilis genome. The strong promoter and an optimal signal peptide were utilized to enhance methionine production by overexpressing δ-zein gene in a recombinant C. utilis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Construction of the reporter gene vector pGZM18-EGFP
All primer sequences used for strain construction and identification are listed in Supplementary Table S1. All plasmids and strains used in this study are listed in Supplementary Tables S2, S3. Escherichia coli cells were used for plasmid construction and cultured at 37°C in Luria Bertani (LB) medium. C. utilis cells were used as the host strain for target gene expression and cultivated at 28–30°C in Yeast Extract Peptone Dextrose (YPD) medium. If necessary, recombinant C. utilis YPD medium was supplemented with cycloheximide (CHX, 20 μg/ml).
To characterize the strengths of the C. utilis mutant promoters, a reporter gene vector pGZM18-EGFP was constructed using the expression vector pGZM18 and a reporter gene with enhanced green fluorescent protein (egfp). Plasmid pGZM18 carrying δ-zein gene was engineered in our previous work and deposited in our lab (He et al., 2018). The plasmid pGZM18 was used as a template to design primers for seamless cloning experiments, PCR amplification of the 18S rDNA gene fragment, GAP promoter, GAP terminator, and Large ribosomal subunit protein (mL41) gene. The egfp gene and SV40 poly (A) signal gene sequence were amplified by PCR from pCMV-C-EGFP plasmid (Beyotime, Shanghai, China). The pBR322 vector was subjected to EcoRV and NruI double digestion, and the product was recovered by gel electrophoresis. The 18S rDNA gene fragment, GAP promoter, egfp, GAP terminator, and mL41 gene were ligated with the linearized pBR322 vector at a particular molar ratio, gently mixed, and incubated at 50°C for 15 min. The recombinant products were placed on ice and cooled for transformation into E. coli. To construct the reporter strain C/pGP, plasmid pGZM18-EGFP was digested by NcoI and transformed into C. utilis. C. utilis competent cells were prepared according to the Yeastmaker™ Yeast Transformation System 2 User Manual (Takara, Beijing, Japan). Finally, the control vector with the original GAP promoter driven egfp gene expression was constructed as a reference.
2.2 Construction of recombinant C. utilis with GAP promoter mutants
The GAP promoter was mutated by error-prone PCR (EP-PCR). For the construction of the C. utilis GAP promoter mutants, the GAP promoter was amplified with primers QDZ-P2S and QDZ-P2AS (Supplementary Table S1) based on the reporter gene vector pGZM18-EGFP. EP-PCR was performed according to Diversify PCR Random Mutagenesis Kit standard protocols (Takara, Beijing, Japan). To increase mutational diversity and reach an appropriate error rate, four consecutive EP-PCRs were conducted. Directly ligating the obtained EP-PCR products into the C. utilis homologous integration expression vectors was relatively inefficient and resulted in only a small number of promoter mutants. Therefore, the EP-PCR products were first ligated into the pEASY-T1simple cloning vector and transformed into E. coli. After sequencing the promoter mutant DNA sequences, six promoter mutant sequences with the highest mutation rate were selected to screen and characterize strong promoters. Finally, six candidate promoter mutant sequences were inserted into pGZM18-EGFP cleaved with KpnI and SalI, respectively. Six GAP promoter mutant expression vectors were constructed and transformed individually into E. coli. The six expression plasmids were digested with NcoI and purified cleavage products were transformed into C. utilis to construct the GAP promoter mutant recombinant strains. Six GAP promoter mutant C. utilis strains were selected for further screening and characterization of strong GAP promoters.
2.3 Screening of GAP strong promoter
The GAP promoter mutant C. utilis strains that harbored egfp gene were screened based on the fluorescence signal. The GAP promoter mutant single colonies were selected and cultured into 1 ml YPD medium for 24 h. From each well of the YPD culture plates, 100 μl culture broth was taken and added to 900 μl of Buffered Minimal Dextrose (BMD, 0.2%) medium for 48 h. Then the 900 μl BMD medium (with 1% glucose) was cultured with a 100 μl culture from the BMD (0.2% glucose) plate and grown for 36 h (Qin et al., 2011b). The GAP promoter mutant C. utilis strains were cultured in 48 deep-well plates at 30°C, 220 r/min. The egfp gene expression intensity and strain concentration was measured by a multifunctional enzyme labeling instrument (BioTek, Vermont, USA). The culture broth was diluted with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) to a final OD600nm of around 1 and 200 μl of the diluted sample was transferred to a 96-well plate. Fluorescence intensity was measured under excitation light at 488 nm and emission light at 550 nm, and the OD600 nm was read.
The GAP promoter mutant single colonies were selected and cultured into 1 ml YPD medium for 48 h. The egfp gene transcript levels in different GAP promoter mutants were detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Total RNA samples were extracted from the cells using a total RNA extraction reagent (Takara, Beijing, Japan). Takara’s PrimeScriptTM RT Reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser was used to convert mRNA into cDNA by reverse transcription, which was used as a template for qRT-PCR. The qRT-PCR was performed according to Takara’s SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM instructions, and the relative transcript levels of egfp gene were analyzed by the 2-ΔΔCt method using the gapdh gene as an internal reference (Zhang et al., 2021; Guan et al., 2016). The relative activities of six GAP promoter mutants were characterized by comparison with those of the original GAP promoter.
2.4 Construction of recombinant C. utilis with different endogenous signal peptide vector
To analyze the usability of signal peptide vectors for recombinant protein production in C. utilis, the GAP promoter was selected to drive the production of δ-zein. To identify the target proteins, we added a His-tag to the C-terminus of δ-zein. The C. utilis whole genome sequence was analyzed using SignalP 5.0 (Sanaboyana and Elcock, 2024) to obtain endogenous signal peptide sequences with protein secretion potential. The C. utilis amino acid sequences were predicted and analyzed by entering them into the SignalP 5.0 software based on the C, Y, S and D scores assigned by the software (Almagro Armenteros et al., 2019). The C score gives an idea about the role of different amino acids in the shear site. Y score reflects the combined highest point of S and C scores. The S score indicates contribution of different amino acids in the signal peptide region. D score is the average of S and Y scores, which is important to distinguish if a protein is secreted (Yiping Shi et al., 2014). Amino acid sequences with a D score of more than 0.7 have a high likelihood of being a signal peptide. Therefore, 8 signal peptide sequences were screened from the genome data. Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae) α-mate-factor (a-MF) (Dai et al., 2024), as a widely used exogenous signal peptide with good secretion ability, was used as a signal peptide screening control vector to investigate the effect of C. utilis endogenous signal peptide on δ-zein secretion. A construct containing the S. cerevisiae α-MF signal peptide and δ-zein (C-terminal with His-tag) gene was synthesized (GenScript, Piscataway, USA). The synthesized construct was ligated to SalI, PacI double digested pGZM18-EGFP and pM-zein (C-terminal containing His-tag) vector was constructed as the experimental control vector for screening signal peptide sequences. α-MF signal peptide includes a pre-region and a pro-region. The α-MF pro-region was retained when the subsequent screening signal peptide vectors were constructed in the present study.
C. utilis genomic DNA was extracted by TIANamp Yeast DNA Kit (TIANGEN, Beijing, China) and was used as the template to amplify the signal peptides with the SP1-8F/SP1-8MR primers (Supplementary Table S1). α-MFpro-zein sequences were PCR amplified from pM-zein vector using the primers SP1-8MF/SPR. The amplified signal peptides and α-MFpro-zein sequences were used as nested PCR templates, and SP1-8F/SPR were used as primers to amplify eight different endogenous signal peptide sequences, respectively. The PCR products were digested with SalI and PacI, and cloned into pGZM18-EGFP that had been digested with the same enzymes to yield eight endogenous signal peptide expression vectors: pSP1, pSP2, pSP3, pSP4, pSP5, pSP6, pSP7 and pSP8. These vectors were transformed into E. coli. The signal peptide expression vectors as well as pM-zein were subsequently transformed into C. utilis, respectively.
2.5 Screening for optimized endogenous signal peptides
The content of His-tagged δ-zein protein in the supernatant of the fermentation broth of signal peptide recombinant C. utilis cultured for 48 h was detected using the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The His-Tag ELISA assay kit was used in accordance with the product’s instruction manual (GenScript, Piscataway, USA). Recombinant protein content in the samples was determined by spectrophotometry (OD450nm). All experiments were performed in triplicates. The data were analyzed using SPSS22.0 statistical software. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to determine significant differences among the results (means ± standard deviation).
2.6 Construction of engineered C. utilis with a strong promoter and optimized signal peptide
The vector pSP8 was digested with KpnI and SalI, and the GAP promoter mutant GP6 fragment was circularized using T4 DNA ligase to generate the constitutive vector. The δ-zein secretion expression vector containing the GAP promoter mutant GP6 and SP8 signal peptide sequence was constructed and the vector was subsequently transformed into E. coli. The vector bacterial DNA sequences from prokaryotic microorganisms, including the resistance screening marker Ampr, and prokaryotic replication regions, were later deleted by splicing overlap extension-PCR (SOE-PCR) to obtain a food-grade vector pGS-Zein, and the food-grade vector was transformed into C. utilis.
2.7 Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC–MS/MS) system analysis
Sample preparation was performed according to the following steps. The C.utilis culture solution was vortexed to ensure homogeneity. Ten microliters of the vortexed solution were then transferred into a microcentrifuge tube containing 490 μl of MS grade water. After vortexing to mix, 50 μl of the diluted sample was added to 200 μl of precipitation reagent containing mixed internal standards (acetonitrile: methanol = 1:1). After vortexing, the samples were incubated on ice for 30 min, centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C, and the supernatants were used for UHPLC–MS/MS analysis.
An ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC–MS/MS) system (ExionLC™ AD UHPLC-QTRAP 6500+, Boston, USA) was used to quantitate the production of methionine with different promoters in C. utilis harboring the δ-zein gene. Separation was performed on an ACQUITY UPLC BEH Amide column (2.1 × 100 mm, 1.7 μm) which was maintained at 50°C. The mobile phase, consisting of 0.1% formic acid in 5 mM Ammonium acetate (solvent A) and 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile (solvent B), was delivered at a flow rate of 0.30 mL/min. The solvent gradient was set as follows: initial 80% B, 0.5 min; 80–70% B, 2 min; 70–45% B, 4 min; 45–80% B, 6.01 min; 80% B, 9 min. The methionine content was determined in the three groups of samples: wild-type C. utilis (WT), C/pSP and C/pGS-zein. WT was used as control group 1, C/pSP engineered C. utilis containing original GAP promoter and δ-zein gene was used as control group 2, and optimized C/pGS-zein engineered C. utilis containing the δ-zein gene, GAP promoter mutant GP6, and signal peptide SP8 were used as the experimental group. The UHPLC–MS/MS system analysis was performed by Beijing Novozymes Technology Co. (China).
3 Results
3.1 Construction of GAP promoter mutants
The reporter gene vector pGZM18-EGFP was constructed and used to test the expression of the egfp gene under the control of the original GAP promoter in the recombinant strain C/pGP. A GAP promoter mutant library was generated by mutated GAP promoter variants obtained through four consecutive rounds of EP-PCR (Figure 2). Forty putative promoter mutants were sequenced following EP-PCR. The sequencing results demonstrated that the mutation rate ranged from 0.3 to 1.9%, and six promoter mutant sequences with the highest mutation rate were selected for construction of recombinant C. utilis with GAP promoter mutants. It has previously been reported that promoter sequences with mutation rates ranging from 1 to 5% are generally effective promoters. Six sequences with the highest mutation rates (1.2 to 1.9%) were selected, and subsequent screening was carried out. The constructed GAP promoter mutants were introduced into the C. utilis chromosome by homologous recombination to obtain the GAP promoter mutant C. utilis. The GAP promoter mutant recombinant vectors were digested and identified. The full length of the plasmid was 10,050 bp after SalI single digestion and KpnI+SalI double digestion resulted in a 970 bp fragment of the GAP promoter mutant and 9,080 bp for the remaining sequence of the vector. After single enzyme digestion of pGZM18-EGFP plasmid with SalI, a linear fragment of 10,050 bp was obtained. After double enzyme digestion with KpnI+SalI, the length of original GAP promoter was 970 bp, and the remaining sequence length of GAP promoter was 9,080 bp. The results showed that the GAP promoter mutants expression vectors were successfully constructed (Supplementary Figure S1).
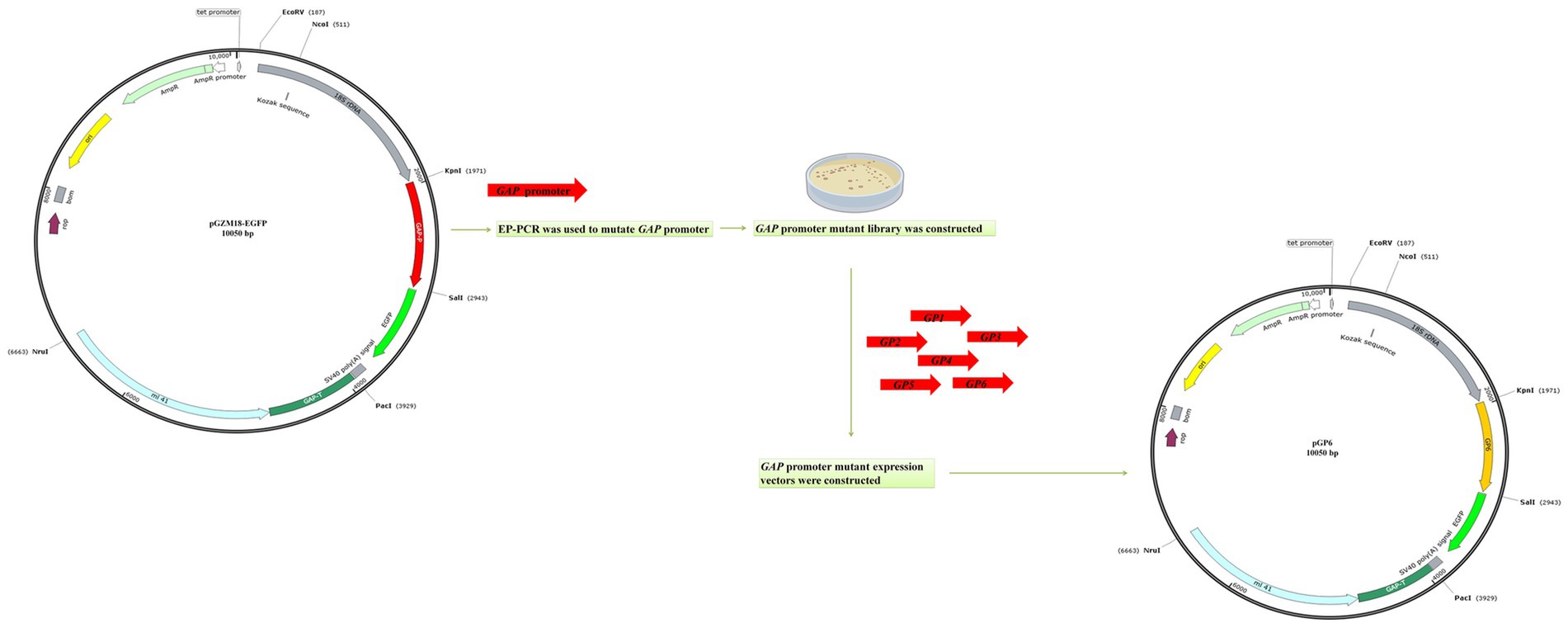
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of GAP promoter mutant expression vectors construction. A GAP promoter mutant library was generated by mutated GAP promoter variants obtained through EP-PCR. The six promoter mutant sequences with the highest mutation rate were selected for construction of recombinant C. utilis with GAP promoter mutants.
3.2 Characterization of different promoter mutants
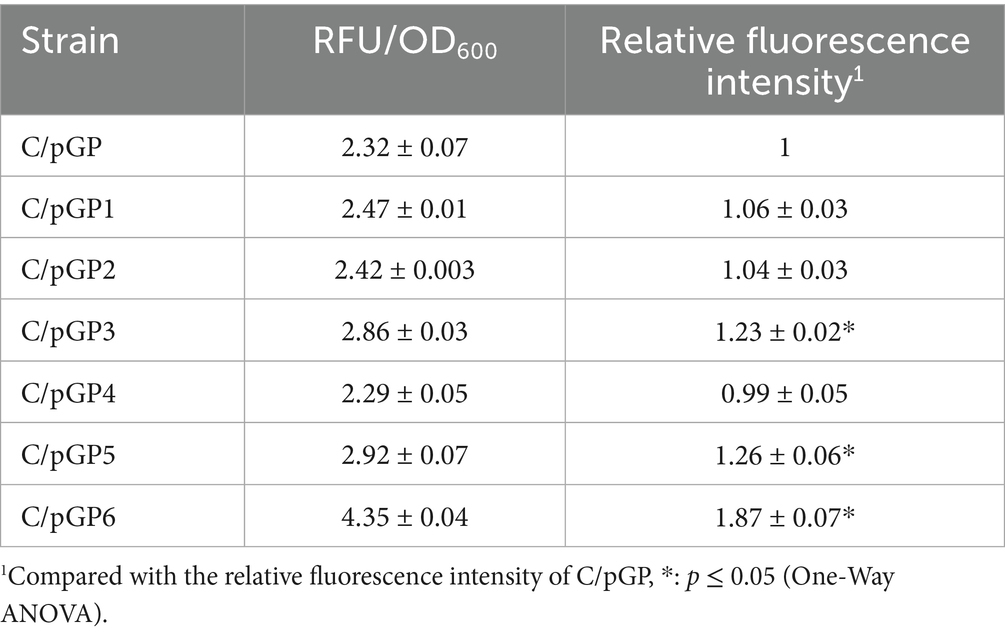
Gene expression under the control of six selected GAP promoter mutants was further investigated at the transcriptional level. The GAP promoter mutants recombinant C. utilis were cultured and promoter activity was represented by the fluorescence intensity of egfp gene reporter. A significant increase in fluorescence intensity of the GAP mutant recombinant C. utilis strains was observed compared to C. utilis with the original GAP promoter. The relative fluorescence intensities of three mutant recombinant C. utilis strains were significantly different from the original GAP promoter in the recombinant strain C/pGP (Table 1). The relative promoter activities were normalized to the activity obtained with the original GAP promoter. The relative fluorescence intensity of C/pGP6 was 1.87-fold higher than that of the control C/pGP and had the highest fluorescence intensity value, while the relative fluorescence intensities of C/pGP3 and C/pGP5 were 1.23-fold and 1.26-fold higher than those of the control C/pGP.
To detect the level of expression from different promoter mutants, transcript levels of the egfp gene were detected by qRT-PCR using the 2-ΔΔCt method with the gapdh gene as an internal reference. Transcript levels of reporters were normalized to the value obtained with the original GAP promoter. The original promoter values were set to 1. The results showed that the relative expression of egfp mRNA in C/pGP3, C/pGP5 and C/pGP6 was higher than that in C/pGP, at 1.29-fold, 1.60-fold and 1.67-fold, respectively. The relative expression of egfp mRNA in C/pGP5 and C/pGP6 groups was significantly different from that in the C/pGP group (p ≤ 0.05). The relative egfp expression of C/pGP1, C/pGP2 and C/pGP4 was low, while the relative egfp expression of C/pGP6 was the highest. The trends of the qRT-PCR results and the fluorescence intensity results aligned well, both of which showed that GP6 had the strongest ability to induce expression (Figure 3).
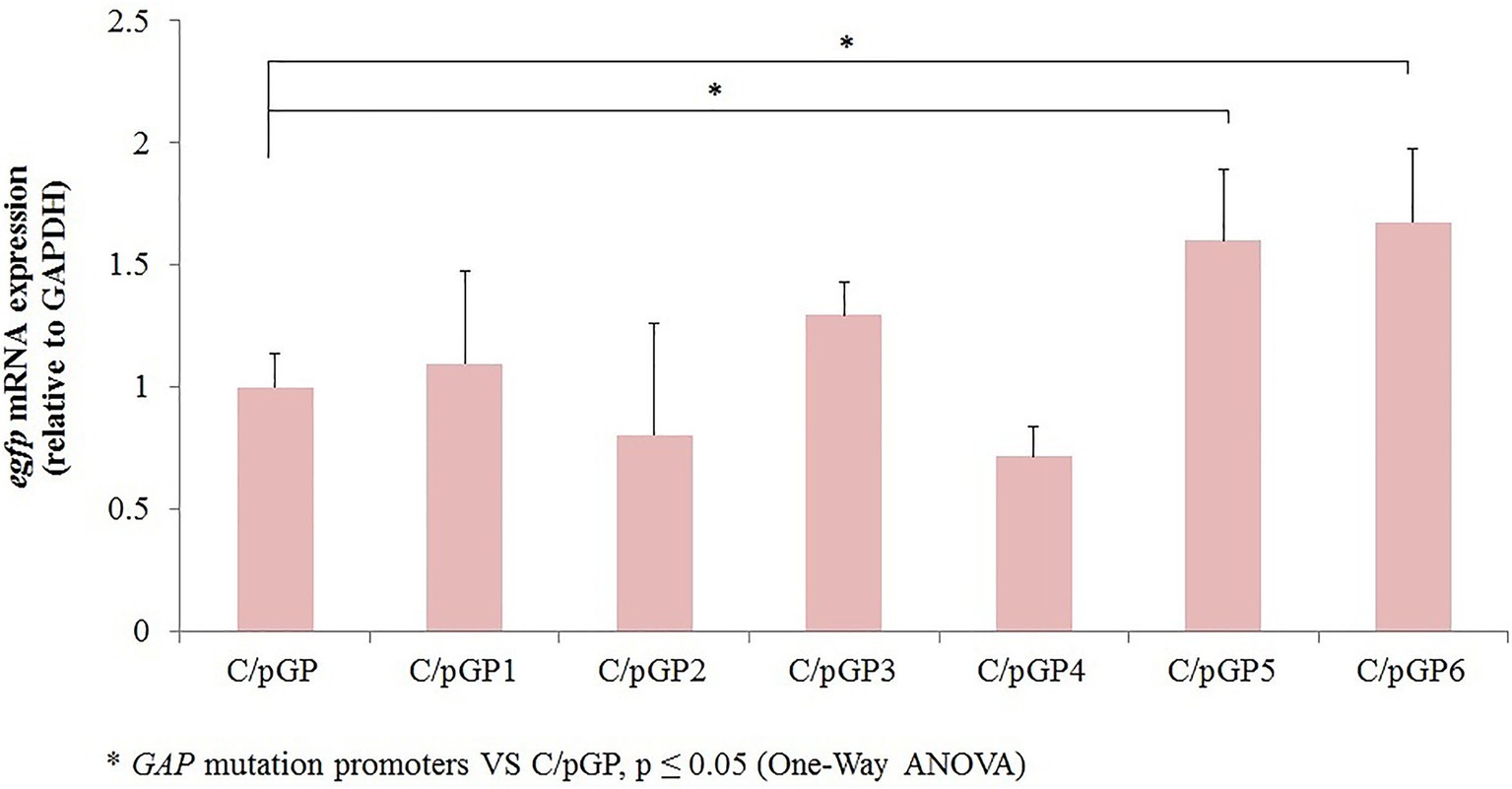
Figure 3. The relative transcription and protein expression level of recombinant C. utilis with GAP promoter mutants were determined by qRT-PCR. Detection of egfp transcription levels in recombinant* C. utilis with different GAP mutation promoters VS C/pGP, p ≤ 0.05 (One-Way ANOVA).
3.3 Construction and characterization of different endogenous signal peptide vectors
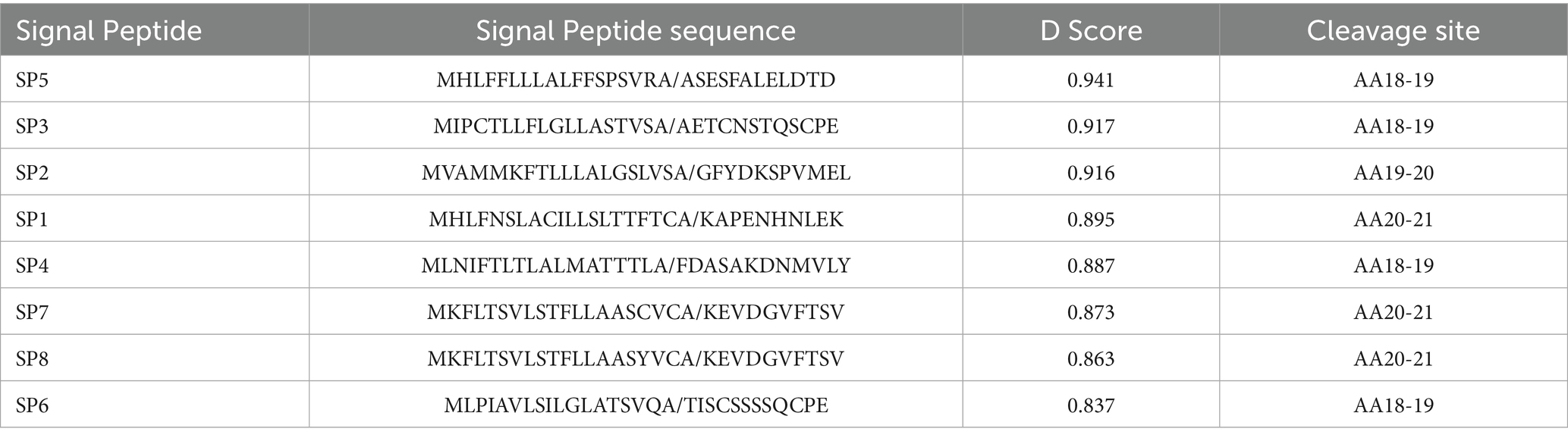
Signal peptides are important factors that can affect protein secretion and expression. The endogenous signal peptides of C. utilis were analyzed by sequencing the C. utilis genome. Candidate signal peptides SP1, SP2, SP3, SP4, SP5, SP6, SP7, and SP8 were analyzed and the respective D scores were all greater than 0.8 (Table 2), indicating that all of the signal peptide sequences were functional signal peptides. The selected signal peptide sequences were amplified from the C. utilis genome. The α-MFpro-zein sequences were amplified from pM-zein. The SPs and α-MFpro-zein were used as nested PCR templates, and SP1-8F/SPR (Supplementary Table S1) was used as primer to amplify eight sequences of SP1-SP8α-MFpro-zein (C-terminal with His-tag). The amplified signal peptide sequences were digested with SalI and PacI and the target gene of 764 bp was recovered. pGZM18-EGFP was digested with SalI+PacI and the vector fragment of 9,060 bp was recovered by gel electrophoresis. Different signal peptide expression vectors were constructed (Figure 4) and named pSP1, pSP2, pSP3, pSP4, pSP5, pSP6, pSP7 and pSP8 (Supplementary Table S2). These vectors were transformed into C. utilis and the efficiency of each signal peptide were indicated by the His-Tag ELISA assay kit to evaluate secretory efficiencies of signal peptides.
The content of His-tagged δ-zein fusion protein in the recombinant C. utilis supernatants was quantified. The content of His fusion δ-zein in the supernatant of C/pSP, C/pSP1, C/pSP2, C/pSP3, C/pSP4, C/pSP5, C/pSP6, C/pSP7 and C/pSP8 was 1181.70, 1326.87, 1436.52, 1270.40, 1007.00, 1159.97, 1122.09, 1517.57 and 2091.58 ng/mL, respectively. Protein content in C/pSP8 was significantly higher compared with the control group C/pSP (a-MF) (relative to the C/pSP group, p ≤ 0.01). Thus, signal peptide SP8 was selected as the optimal signal peptide to be used in the subsequent construction of optimized expression vectors (Figure 5).
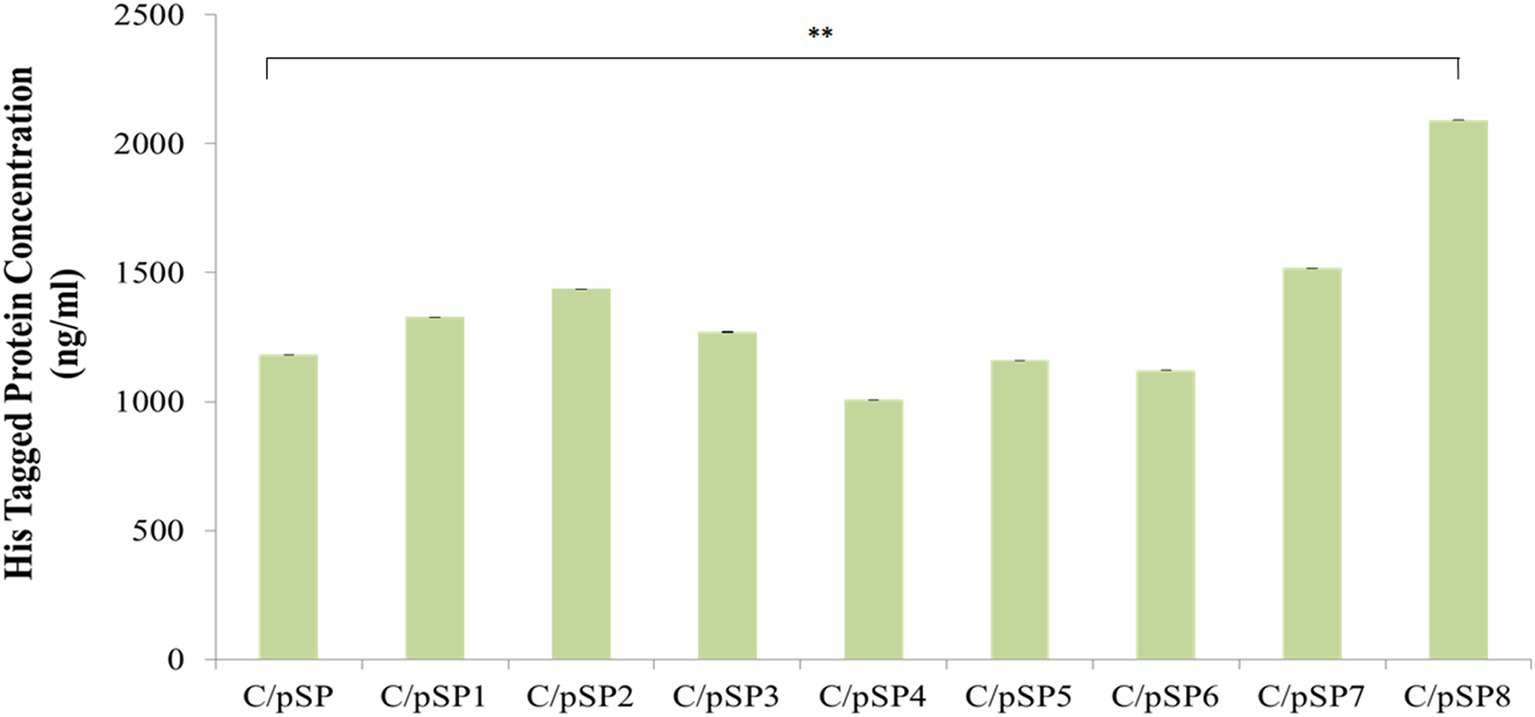
Figure 5. The effects of different signal peptides on δ-zein secretion were detected by ELISA. **: p ≤ 0.01 (One-Way ANOVA).
3.4 The effect of strong promoter and optimized signal peptide on C. utilis expression
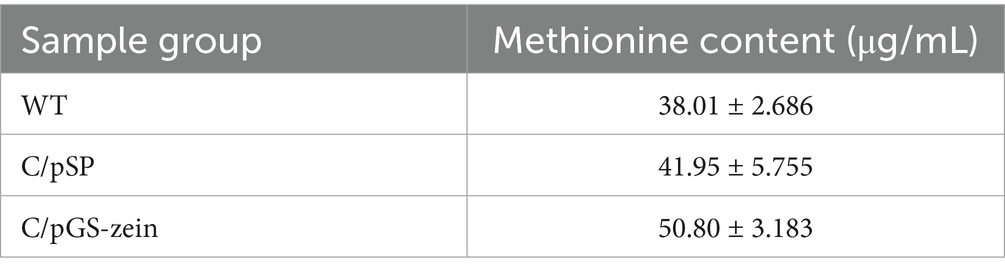
The optimized methionine-producing food grade engineered C. utilis were obtained by constructing expression vectors with the screened strong promoter GP6 and the optimal signal peptide pSP8. The methionine content in the engineered C. utilis C/pGS-zein increased by 21.09% compared to C/pSP engineered C. utilis containing original GAP promoter. In addition, the level of methionine content in C/pGS-zein was 33.64% more than that of the wild-type strain (Table 3). The results indicate that the system compromised of plasmid pGS-zein with promoter GP6 and signal peptide SP8 has tremendous potential for the overproduction of methionine by engineered C. utilis. This approach can be adapted to improve the production of heterologous proteins in C. utilis.
4 Discussion
L-Methionine is a sulfur-containing amino acid essential for human and animal nutrition, mainly used in the feed industry and is an indispensable additive in animal feed (Gong et al., 2023). Currently, research on the production of methionine by microbial fermentation mainly focuses on the cultivation of suitable strains through classical mutagenesis (Cai et al., 2023). In recent years, the research direction has shifted towards metabolic engineering of major hosts such as E. coli (Niu et al., 2023), Corynebacterium glutamicum (C. glutamicum) (Liu B. et al., 2022) and Bacillus cereus (B. cereus) (He et al., 2020). A more specific and targeted approach to improve methionine production in engineered strains is to understand and take advantage of the regulatory mechanisms used by the host (Schipp et al., 2020). C. utilis has properties such as amino acid diversity and protein content of about 50% of the weight of the cells, making it an ideal source of protein supplementation for animal feed (Buerth et al., 2011). C. utilis is a Crabtree negative yeast, which does not produce ethanol under aerobic culture conditions, and has high respiratory capacity, which allows it to be cultured at high density under efficient continuous culture conditions (Li et al., 2022). These growth conditions are conducive to large-scale culturing, which improves industrial productivity and reduces costs, and C. utilis can be used in various fields such as feed additives and biopharmaceuticals (Kunigo et al., 2013). Currently, research on C. utilis expression systems and regulatory components is limited and the best host vector system has yet to be established. This requires the development of an optimized gene expression system that necessitates selection of appropriate strains, expression vectors, promoters, and signal peptides. In this study, the genome and sequence analysis of C. utilis was performed to obtain the sequence of endogenous signal peptides, construct δ-zein expression vectors with different signal peptides and their recombinant yeast strains and screen for the optimal signal peptide of δ-zein. In addition, we used EP-PCR to mutate the C. utilis GAP promoter and construct a promoter mutant library. Using EGFP as a reporter protein, recombinant yeast was constructed and screened for strong GAP promoter mutants.
Promoters serve as crucial regulatory components within the genome, overseeing the spatial and temporal expression of genes as well as the levels at which they are expressed (Liu et al., 2019). In particular, strong promoters are essential in biotechnological applications and associated industrial sectors. Qin et al. constructed a GAP promoter library by mutagenesis and obtained GAP promoter mutants with activities ranging from 0.006 to 19.6 times the activity of the original GAP promoter (Qin et al., 2011a). Ata et al. constructed a library of GAP promoters with different regulatory properties and overexpressed or deleted selected transcription factor genes to understand their role in heterologous protein production. Overexpression in the range of 0.35 to 3.10-fold higher than the original GAP promoter was reported (Ata et al., 2017).
The SP plays a vital role in the successful directing of the translocation machinery and the subsequent movement from the cytoplasm into the culture medium. At present, research on the C. utilis endogenous signal peptide is limited. Therefore, further research on C. utilis is necessary to gain an in-depth understanding of the interaction between signal peptides and proteins to improve the secretion and expression efficiency of the target protein. This has significant consequences for future research and application of C. utilis in the field of biotechnology. Consequently, the effective extracellular production of target proteins would greatly benefit from a suitable SP. Mayer et al. created a library of signal peptides from Priestia megaterium (P. megaterium) to develop a simple and rapid cloning and screening system to identify signal peptides that are optimal for different proteins. The results showed a 1.6-fold increase in the secretion of the α-amylase AmyE, demonstrating the functionality of the entire library and suggesting that this approach contributes to the improved secretion of recombinant proteins from Bacillus (Mayer et al., 2022).
Most research on methionine production via microbial fermentation has hitherto focused on traditional mutagenesis or metabolic engineering of well-characterized hosts such as E. coli and C. glutamicum. Through analyzing the rate-limiting factors in the L-methionine synthesis pathway, Li optimized the biosynthetic pathway, significantly boosting methionine production in E. coli to 10 g/L via fermentation (Li, 2017). Gao performed metabolic engineering modifications using C. glutamicum as the parental strain, yielding two engineered strains with methionine production levels of 3.78 g/L and 4.32 g/L, 2.96-fold and 2.57-fold higher than the wild-type strain, respectively (Gao, 2022). It is worth noting that, compared with our study, these studies adopted different metabolic engineering modification methods and achieved very high methionine yields. In future research, we will optimize the fermentation processes of engineered strains and conduct metabolic engineering modifications targeting methionine synthesis-related pathways to further increase methionine yields. C. utilis, a type of single-cell protein (SCP), offers advantages such as a short production cycle, straightforward manufacturing process, high nutritional value, and low production cost (Krahulec et al., 2020). A significant hurdle in utilizing C. utilis for recombinant protein production and enhanced methionine synthesis is its poorly understood genetic background. This study is the first to construct a GAP promoter mutant library and analyze endogenous signal peptides by sequencing, thereby uncovering new C. utilis genetic resources. This expands the genetic toolkit for this yeast species while providing a foundation for further genetic engineering efforts, particularly for C. utilis-based methionine production. The overall strategy of improving methionine production in C. utilis through promoter and signal peptide optimization aligns with the growing demand for sustainable and cost effective production methods. Chemically synthesized methionine has drawbacks such as safety concerns, environmental pollution, and high costs. Microbial fermentation, especially using a food-grade organism like C. utilis, offers a more sustainable alternative. By optimizing genetic elements in C. utilis, this study paves the way for large-scale, efficient, and environmentally friendly methionine production. This approach can be extended to other heterologous protein production applications utilizing C. utilis, thereby contributing to the development of a more sustainable biotechnology industry.
5 Conclusion
The GAP promoter of C. utilis was studied for the first time. We constructed a mutant library of the GAP promoter in C. utilis, screened and obtained a strong promoter, GP6. The genome of C. utilis was sequenced and endogenous signal peptides were analyzed. Homologous integrated expression vectors of different signal peptides and their recombinant C. utilis were constructed. The signal peptide SP8 enabled the highest expression and secretion of δ-zein. The combination of the strong promoter GP6 and the optimal signal peptide SP8 resulted in the construction of an integrated expression vector and its food-grade engineered C. utilis C/pGS-zein. Methionine content in the engineered C. utilis C/pGS-zein increased by 21.09% compared with engineered C. utilis C/pSP containing the original GAP promoter and 33.64% compared to wild-type C. utilis. This strategy of identifying a strong promoter and optimal signal peptide acts as an effective method for enhanced production of methionine in C. utilis. Further modifications via metabolic engineering of methionine synthesis related pathways can be undertaken to improve methionine yield in engineered C. utilis.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary material.
Author contributions
QH: Project administration, Writing – original draft. SS: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. RA: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. LH: Writing – review & editing. XW: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MC: Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. GG: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Funds for Local Scientific and Technological Development under the Guidance of the Central Government (2024ZY0098); Inner Mongolia Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Innovation Fund (2022CXJJM09).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Hu He for his generous support in this study. The Figure 1 was partly generated using Biovisart (https://biovisart.com.cn).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1586229/full#supplementary-material
References
Almagro Armenteros, J. J., Tsirigos, K. D., Sønderby, C. K., Petersen, T. N., Winther, O., Brunak, S., et al. (2019). SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 420–423. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0036-z
Ata, Ö., Prielhofer, R., Gasser, B., Mattanovich, D., and Çalık, P. (2017). Transcriptional engineering of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter for improved heterologous protein production in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 114, 2319–2327. doi: 10.1002/bit.26363
Awawdeh, M. S. (2022). Effects of supplemental lysine and methionine on performance of nursing Awassi ewes fed two levels of dietary protein. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 54:61. doi: 10.1007/s11250-022-03070-5
Barido, F. H., Utama, D. T., Jeong, H. S., Kim, J., Lee, C. W., Park, Y. S., et al. (2020). The effect of finishing diet supplemented with methionine/lysine and methionine/α-tocopherol on performance, carcass traits and meat quality of Hanwoo steers. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 33, 69–78. doi: 10.5713/ajas.19.0209
Buerth, C., Heilmann, C. J., Klis, F. M., de Koster, C. G., Ernst, J. F., and Tielker, D. (2011). Growth-dependent secretome of Candida utilis. Microbiology (Reading) 157, 2493–2503. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.049320-0
Cai, M., Liu, Z., Zhao, Z., Wu, H., Xu, M., and Rao, Z. (2023). Microbial production of L-methionine and its precursors using systems metabolic engineering. Biotechnol. Adv. 69:108260. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2023.108260
Cardoso, F. F., Donkin, S. S., Pereira, M. N., Pereira, R. A. N., Peconick, A. P., Santos, J. P., et al. (2021). Effect of protein level and methionine supplementation on dairy cows during the transition period. J. Dairy Sci. 104, 5467–5478. doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-19181
Cui, W., Han, L., Cheng, J., Liu, Z., Zhou, L., Guo, J., et al. (2016). Engineering an inducible gene expression system for Bacillus subtilis from a strong constitutive promoter and a theophylline-activated synthetic riboswitch. Microb. Cell Factories 15:199. doi: 10.1186/s12934-016-0599-z
Dai, H., Zhang, C., Wu, J., Tang, Q., Xie, Y., Yu, Y., et al. (2024). Optimizing Pichia pastoris protein secretion: role of N-linked glycosylation on the α-mating factor secretion signal leader. J. Biotechnol. 391, 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2024.04.008
Feng, Y., Xie, Z., Jiang, X., Li, Z., Shen, Y., Wang, B., et al. (2018). The applications of promoter-gene-engineered biosensors. Sensors (Basel) 18:2823. doi: 10.3390/s18092823
Firth, A. E., and Patrick, W. M. (2008). GLUE-IT and PEDEL-AA: new programmes for analyzing protein diversity in randomized libraries. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, W281–W285. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn226
Gao, X. (2022). Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum to construct methionine biosynthesis engineering strain. Jilin agricultural university, MA thesis.
Gong, L., Mahmood, T., Mercier, Y., Xu, H., Zhang, X., Zhao, Y., et al. (2023). Dietary methionine sources and levels modulate the intestinal health status of broiler chickens. Anim. Nutr. 15, 242–255. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2023.07.004
Guan, Y., Huang, D., Chen, F., Gao, C., Tao, T., Shi, H., et al. (2016). Phosphorylation of Def regulates nucleolar p53 turnover and cell cycle progression through Def recruitment of Calpain3. PLoS Biol. 14:e1002555. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002555
Hanson-Manful, P., and Patrick, W. M. (2013). Construction and analysis of randomized protein-encoding libraries using error-prone PCR. Methods Mol. Biol. 996, 251–267. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-354-1_15
He, H., He, K., Chen, X., Hu, C., Yao, X., and Li, L. (2020). Construction of L-methionine genetically engineered strains. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 48, 37–43. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2020.22.006
He, Q., Wu, S., Su, S. F., Gong, G., Wang, Y. H., Liu, H. K., et al. (2018). Expression of methionine-rich zein protein in Candida utilis. AHFS 39, 16–23. doi: 10.16003/j.cnki.issn1672-5190.2018.11.004
Jankowski, J., Kubińska, M., and Zduńczyk, Z. (2014). Nutritional and immunomodulatory function of methionine in poultry diets – a review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 14, 17–32. doi: 10.2478/aoas-2013-0081
Kieliszek, M., Błażejak, S., and Kurek, E. (2017). Binding and conversion of selenium in Candida utilis ATCC 9950 yeasts in bioreactor culture. Molecules 22:352. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030352
Kim, W. S., and Krishnan, H. B. (2003). Allelic variation and differential expression of methionine-rich delta-zeins in maize inbred lines B73 and W23a1. Planta 217, 66–74. doi: 10.1007/s00425-002-0971-6
Kim, W. S., and Krishnan, H. B. (2019). Impact of co-expression of maize 11 and 18 kDa δ-zeins and 27 kDa γ-zein in transgenic soybeans on protein body structure and sulfur amino acid content. Plant Sci. 280, 340–347. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.12.016
Krahulec, J., Lišková, V., Boňková, H., Lichvariková, A., Šafranek, M., and Turňa, J. (2020). The ploidy determination of the biotechnologically important yeast Candida utilis. J. Appl. Genet. 61, 275–286. doi: 10.1007/s13353-020-00544-w
Kunigo, M., Buerth, C., Tielker, D., and Ernst, J. F. (2013). Heterologous protein secretion by Candida utilis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97, 7357–7368. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-4890-1
Lee, C. Y., Song, A. A., Loh, T. C., and Abdul Rahim, R. (2020). Effects of lysine and methionine in a low crude protein diet on the growth performance and gene expression of immunity genes in broilers. Poult. Sci. 99, 2916–2925. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.03.013
Li, H. (2017). Systematic metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for l-methionine production. Jiangnan University, PhD dissertation.
Li, H., Lin, X., Yu, L., Li, J., Miao, Z., Wei, Y., et al. (2022). Comprehensive characterization of the bacterial community structure and metabolite composition of food waste fermentation products via microbiome and metabolome analyses. PLoS One 17:e0264234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264234
Li, W., Song, Y. Y., Cao, P. H., and Zhao, L. M. (2021). Acclimation of copper absorption ability of Candida utilis. Anim. Biotechnol. 32, 454–460. doi: 10.1080/10495398.2020.1715418
Lin, G., Qi, H., Guo, X., Wang, W., Zhang, M., and Gao, X. (2023). ARID1B blocks methionine-stimulated mTOR activation to inhibit milk fat and protein synthesis in and proliferation of mouse mammary epithelial cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 114:109274. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109274
Liu, P., Guo, J., Miao, L., and Liu, H. (2022). Enhancing the secretion of a feruloyl esterase in Bacillus subtilis by signal peptide screening and rational design. Protein Expr. Purif. 200:106165. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2022.106165
Liu, Y., Shi, C., Li, D., Chen, X., Li, J., Zhang, Y., et al. (2019). Engineering a highly efficient expression system to produce BcaPRO protease in Bacillus subtilis by an optimized promoter and signal peptide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 138, 903–911. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.07.175
Liu, B., Sun, X., Liu, Y., Yang, M., Wang, L., Li, Y., et al. (2022). Increased NADPH supply enhances glycolysis metabolic flux and L-methionine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Food Secur. 11:1031. doi: 10.3390/foods11071031
Mayer, J., Knuuti, T., Baumgarten, L., Menke, E., Bischoff, L., Bunk, B., et al. (2022). Construction and application of a plasmid-based signal peptide library for improved secretion of recombinant proteins with Priestia megaterium. Microorganisms 10:777. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10040777
Mori, A., Hara, S., Sugahara, T., Kojima, T., Iwasaki, Y., Kawarasaki, Y., et al. (2015). Signal peptide optimization tool for the secretion of recombinant protein from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 120, 518–525. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2015.03.003
Myers, F. A. (2023). Random mutagenesis by PCR. Methods Mol. Biol. 2633, 81–86. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3004-4_7
Nguyen, L., Schmelzer, B., Wilkinson, S., and Mattanovich, D. (2024). From natural to synthetic: promoter engineering in yeast expression systems. Biotechnol. Adv. 77:108446. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2024.108446
Niu, K., Fu, Q., Mei, Z. L., Ge, L. R., Guan, A. Q., Liu, Z. Q., et al. (2023). High-level production of l-methionine by dynamic deregulation of metabolism with engineered nonauxotroph Escherichia coli. ACS Synth. Biol. 12, 492–501. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.2c00481
Olsen, M. A., Vhile, S. G., Porcellato, D., Kidane, A., and Skeie, S. B. (2021). Feeding concentrates with different protein sources to high-yielding, mid-lactation Norwegian red cows: effect on cheese ripening. J. Dairy Sci. 104, 4062–4073. doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-19226
Qin, X., Qian, J., Xiao, C., Zhuang, Y., Zhang, S., and Chu, J. (2011a). Reliable high-throughput approach for screening of engineered constitutive promoters in the yeast Pichia pastoris. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 52, 634–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2011.03051.x
Qin, X., Qian, J., Yao, G., Zhuang, Y., Zhang, S., and Chu, J. (2011b). GAP promoter library for fine-tuning of gene expression in Pichia pastoris. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 3600–3608. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02843-10
Sałek, P., Przybylski, W., Jaworska, D., Adamczak, L., Zielińska, D., and Głuchowski, A. (2020). The effects on the quality of poultry meat of supplementing feed with zinc-methionine complex. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 19, 73–82. doi: 10.17306/J.AFS.0756
Sanaboyana, V. R., and Elcock, A. H. (2024). Improving signal and transit peptide predictions using AlphaFold2-predicted protein structures. J. Mol. Biol. 436:168393. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168393
Schipp, C. J., Ma, Y., Al-Shameri, A., D'Alessio, F., Neubauer, P., Contestabile, R., et al. (2020). An engineered Escherichia coli strain with synthetic metabolism for in-cell production of translationally active methionine derivatives. Chembiochem 21, 3525–3538. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202000257
Shen, Z. Y., Wang, Y. F., Wang, L. J., Zhang, B., Liu, Z. Q., and Zheng, Y. G. (2023). Construction of exogenous methanol, formate, and betaine modules for methyl donor supply in methionine biosynthesis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11:1170491. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1170491
Vogl, T. (2022). Engineering of promoters for gene expression in Pichia pastoris. Methods Mol. Biol. 2513, 153–177. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2399-2_10
Xue, S., Liu, X., Pan, Y., Xiao, C., Feng, Y., Zheng, L., et al. (2023). Comprehensive analysis of signal peptides in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals features for efficient secretion. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 10:e2203433. doi: 10.1002/advs.202203433
Yiping Shi, X. Z., Hu, M., Lin, J., Tao, Y., and Huang, J. (2014). Effect of signal peptides on the expression of laccase in Pichia pastoris. Acta Microbiol Sin. 54, 1446–1452. doi: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.2014.12.007
Zhang, Y., Liu, H., Liu, Y., Huo, K., Wang, S., Liu, R., et al. (2021). A promoter engineering-based strategy enhances polyhydroxyalkanoate production in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 191, 608–617. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.142
Zhang, G., Teng, M., Liu, S., Zhou, J., Li, J., and DU, G. (2022). Directed evolution of maltose induced promoters with expanded gradient intensity. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 38, 2606–2617. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.220251
Keywords: Candida utilis, promoter, signal peptides, methionine, expression vector
Citation: He Q, Su S, Ao R, He L, Wang X, Chun M and Gong G (2025) An optimised promoter and signal peptide improves methionine production of a genetically engineered Candida utilis harboring the δ-zein gene. Front. Microbiol. 16:1586229. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1586229
Edited by:
Sung Sun Yim, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Republic of KoreaReviewed by:
Michael Benedik, Texas A&M University, United StatesPrem Pritam, University of Delaware, United States
Copyright © 2025 He, Su, Ao, He, Wang, Chun and Gong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gaowa Gong, Z2Fvd2EyMDA5Y0AxNjMuY29t
 Qiburi He
Qiburi He Shaofeng Su1
Shaofeng Su1