- 1State Key Laboratory of North China Crop Improvement and Regulation, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding, China
- 2Hebei Key Laboratory of Plant Physiology and Molecular Pathology, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding, China
Kynurenine monooxygenase, a vital rate-limiting enzyme in the kynurenine pathway metabolic branch, has shown promise as a drug target for treating human neurodegenerative diseases. However, the role of kynurenine monooxygenase in plant pathogens and its potential as a molecular target have received limited attention. In this study, we identified a novel kynurenine monooxygenase gene, BcKMOL, in Botrytis cinerea. By generating mutants of this gene, it was found that the deletion of BcKMOL affected the changes of key metabolites in the kynurenine pathway in vivo, and the △BcKMOL mutant exhibits reduced growth and fails to produce sclerotia. Additionally, changes were observed in the morphology of mycelium cells and spores, and the mutant’s pathogenicity was weakened. These findings indicate that BcKMOL positively regulates the growth, development, and pathogenic processes of B. cinerea. Furthermore, we screened two antibacterial peptides, CAMPQ3966 and CAMPQ4589, that target BcKMOL using MEGADOCK, HDOCK, and AlphaFold3. Both peptides effectively inhibited the pathogenicity of B. cinerea. These findings provide the foundation for developing novel drug targets for controlling gray mold.
1 Introduction
Botrytis cinerea, commonly known as the “gray mold fungus,” is responsible for causing significant pre- and post-harvest diseases in a wide range of plant species (Carrasco et al., 2017). As a typical necrotrophic plant pathogenic fungus, it can affect nearly a thousand different crops (Zhu et al., 2022). B. cinerea can form a black dormant structure called sclerotium during winter or under unfavorable conditions. Secondary inoculant sources include sclerotia, diseased straw, and infected seeds (Richardson et al., 2011). The fungus primarily spreads through conidia in humid environments with cool and optimal temperatures ranging from 15 to 23°C (Hua et al., 2018; Lecompte et al., 2017). The ubiquity of its conidia in the air leads to substantial losses (Plesken et al., 2021).
In recent years, various strategies have been proposed to manage B. cinerea infections and improve the postharvest management of fresh melons and fruits, thereby preventing quality degradation (Ceredi et al., 2009; Lichter et al., 2016; Sonker et al., 2016). Currently, the prevention and control of gray mold primarily rely on fungicides. However, the extensive use of fungicides has resulted in multiple drug-resistant strains of B. cinerea, which exhibit resistance to various fungicide groups (Yan et al., 2022). The overuse of fungicides significantly negatively impacts human health (Muri et al., 2009), soil microflora (Meena et al., 2020), and beneficial microorganisms in food and beverage fermentation (Pasquale et al., 2019). Therefore, it is crucial to delve deeper into the pathogenic mechanisms of B. cinerea and explore practical and safe long-term treatment options for this fungus.
The emergence of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) opens up a green, safe and new path for gray mold control. AMPs are a class of small molecular peptides ubiquitous in nature and an integral part of the innate immunity of almost all organisms (Li et al., 2022). Certain AMPs exert antifungal effects in fungi by inhibiting the synthesis of fungal cell wall components, such as glucan, chitin, and glycoprotein (Li et al., 2021). For instance, echinocandin, a glucan inhibitor, acts as a noncompetitive inhibitor of β-(1,3)-glucan synthase, affecting fungal cell wall synthesis. The cell wall is a promising target for AMPs to recognize microbial cells. AMPs targeting the cell wall primarily exert antibacterial effects by disrupting the synthesis and structure of cell wall components (Wasmann et al., 2018).
The kynurenine pathway is the primary route of tryptophan metabolism, profoundly influencing numerous biological processes within organisms (Davidson et al., 2022). A key terminal product of this pathway, NAD(P)+, serves as a crucial cofactor in redox reactions occurring in vivo. Notably, in certain microorganisms, the kynurenine pathway is the sole means of NAD+ biosynthesis (Lima et al., 2009), and it is closely related to many life processes such as energy metabolism, gene expression regulation, and secretion (Xie et al., 2020). In fungi and bacteria, siderophores are essential for synthesizing cytochromes and enzymes. Tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase (TDO), a key rate-limiting enzyme within the kynurenine pathway, is closely associated with synthesizing siderophores. Studies have shown that deletion of TDO in Pseudomonas affects siderophores synthesis, and exogenous addition of kynurenine can restore it (Matthijs et al., 2004). Further along the pathway, L-kynurenine is converted to 3-hydroxy-L-kynurenine by either flavinase or kynurenine monooxygenase. This compound serves as an essential precursor for the production of quinone antibiotics (Hirose et al., 2011). For instance, the actinomycin biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces chrysomallus includes the corresponding enzyme genes of the kynurenine pathway. The enzymes encoded by these genes facilitate the generation of an intermediate product via the kynurenine pathway, which subsequently provides the precursor 4-methyl-3-hydroxyanthranilic acid (4-MHA) for actinomycin biosynthesis (Keller et al., 2010).
Kynurenine monooxygenase (KMO) serves as a rate-limiting enzyme at the pivotal branch point within the kynurenine pathway, located on the outer membrane of mitochondria (Amaral et al., 2013; Giorgini et al., 2013; Wilson et al., 2014). It regulates the breakdown of the neuroactive metabolite kynurenine (KYNU) and 3-hydroxykynurenine (3-HK) synthesis. In recent years, KMOs have received considerable attention as drug targets in neurodegenerative diseases research. The crystal structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ScKMO was first elucidated in 2013 (Hughes et al., 2022). Subsequently, it was reported that PfKMO from Pseudomonas fluorescens is a soluble enzyme with a structure similar to that of ScKMO (Phillips et al., 2019). The C-terminal domain of PfKMO is crucial for substrate binding. In the absence of a substrate or inhibitor, PfKMO adopts an ‘open’ conformation, facilitating the rapid binding of substrates or inhibitors and the release of products. Upon binding, the C-terminal domain conforms to a ‘closed’ state, effectively inhibiting KMO activity (Gao et al., 2018; Wilkinson, 2013). The human-specific inhibitor UPF648 (Hughes et al., 2022) exploits this mechanism to inhibit KMO, redirecting kynurenine pathway metabolism to enhance the production of the neuroprotective compound kynurenic acid and ameliorate disease-related phenotypes (Amaral et al., 2013).
In this study, we identified the kynurenine monooxygenase gene BcMKOL in B. cinerea through bioinformatics analysis. We then elucidated the role of BcKMOL in growth, development, and pathogenicity by constructing knockout mutants of △BcMKOL. Furthermore, we utilized MEGADOCK, HDOCK, and AlphaFold3 to screen and identify antibacterial peptides that effectively inhibit the pathogenicity of B. cinerea. Our research findings provide valuable insights and innovative ideas for the green, safe, and sustainable prevention and control of gray mold.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Strains and cultural conditions
The wild-type strain B05.10 of B. cinerea was preserved in the Key Laboratory of Plant Physiology and Molecular Pathology of Hebei Province. Mycelia were inoculated in a PD medium (PDA medium without agar) and cultured at 25°C for 5 days for RNA and DNA extraction. For protoplast preparation, the wild-type strain was inoculated on PDA medium for 7–10 days, and the mycelium was scraped using Fries medium and cultured at 25°C to obtain a conidial suspension.
2.2 Bioinformatics analysis of kynurenine monooxygenase gene BcKMOL
The whole genome sequence of B05.10 was searched in the Ensembl fungi database using the amino acid sequence of human and mouse kynureninease. Multiple sequence alignment was performed to analyze the results, and the protein’s three-dimensional structure was predicted using the Swiss Model.1 Expression profile data of the B. cinerea infection process was obtained from the GEO2 database, and the expression data of the KMO gene at different times points were compared to the control (PRJNA628162). The log2 value were taken, and the expression level differences in each pathogen infection period were analyzed.
2.3 Construction of BcKMOL knockout mutants
Based on the restriction enzyme digestion site of the BcKMOL gene and the multiple cloning site of the pBS-pUC vector, Snapgene was used to find a suitable restriction enzyme digestion site. Gene-specific primers containing the restriction enzyme digestion site were designed (Table 1), and the target fragment was amplified. After digestion and ligation into the pMD19 cloning vector, positive clones with correct sequencing were ligated into pUC, and the positive clones were verified. The knockout mutant vector was used to obtain the knockout mutant △BcKMOL by protoplast transformation. DNA level analysis, Southern Blot, and qRT-PCR were performed to confirm the knockout.
The genomic DNA of B. cinerea B05.10 wild-type and knockout transformants △BcKMOL was extracted, and single enzyme digestion was performed using the restriction enzyme Xba I. The enzyme-digested genomic products were detected using 0.8% agarose gel to ensure that the enzyme digestion was sufficient. After purification, the purified product was separated by overnight electrophoresis with 0.8% agarose gel, transferred to the membrane, and the hygromycin resistance gene was labeled with digoxin (Zhang et al., 2025) to make a probe for overnight hybridization (Supplementary Table S1). The specific steps were performed according to the (Roche) kit.
2.4 Construction of BcKMOL revertant mutant
Snapgene was used to analyze the pEarleyGate104 expression vector and the CDS sequence of the BcKMOL gene. Specific primers (BcKMOL-pEarleyGate104-F/BcKMOL-pEarleyGate104-R; Table 1) were designed to amplify the full-length gene, and the correct positive clone was named pEarleyGate104-BcKMOL. BcKMOL-C transformants were obtained by ATMT transformation. PCR using the glufosinate gene on the vector and gene-specific primers was used to identify the transformants. Real-time PCR was performed to confirm the transformants, using the Tubulin gene as the internal reference.
2.5 Kynurenine pathway metabolites analysis of the gene BcKMOL gene mutants
The wild-type and mutant △BcKMOL were inoculated in a liquid PD medium, respectively, and grew for 10 days at 25°C in the dark. After treatment with a freeze-dryer, 80% methanol was mixed and placed in a 2 mL adapter. The liquid nitrogen was frozen for 5 min, repeated freezing and thawing twice, and 900 μL 10% methanol was added. The liquid nitrogen was repeatedly frozen and thawed and installed in a freeze grinder. Centrifuge at 4°C for 5 min at 12,000 rpm/min. 100 μL supernatant was added to 100 μL 20 ppb Trp-d5 solution and vortexed for 10 s. 150 μL supernatant was added to the detection bottle, and the contents of tryptophan, kynurenine, 3-hydroxy kynurenine and quinolinic acid, the key metabolites of kynurenine pathway, were determined by tryptophan targeted metabolic analysis.
2.6 Growth and development analysis of the BcKMOL gene mutants
The BcKMOL gene mutants were inoculated on the non-resistant PDA medium to observe the colony growth rate, recorded every 24 h. Conidia growth of the BcKMOL gene mutants were observed. Five-day-old mutant colonies were rinsed with 5 mL sterile ddH2O, and 10 μL was placed on a slide for microscopic observation. Mycelium morphology was observed under a fluorescence microscope after CFW staining, and cell length and width were counted.
2.7 Pathogenicity analysis of the BcKMOL gene mutants
Tobacco leaves were surface-disinfected with 75% alcohol for 3 min and washed with sterile water 2–3 times. Uniform fungal plates were made using an 8 mm puncher from 7-day-old mutant and wild-type strains. Colonies were inoculated on tobacco leaves using 50% Tween drops and moisturized under dark conditions at 25°C. Disease incidence was observed, and lesion areas were statistically analyzed using a multi-spectral scanner. Three replicates were set for each strain, and one-way ANOVA was performed using GraphPad software (significant: *: 0.01 < p ≤ 0.05; highly significant: **: p ≤ 0.01).
2.8 Analysis of pathogenic factors of the BcKMOL gene mutants
The BcKMOL gene mutants were inoculated on the non-resistant PDA medium, and infection pads were observed under the microscope. The number and size of the infection pads were statistically analyzed. The BcKMOL gene mutants and wild-type strains were inoculated on a PDA medium containing 0.05% bromothymol blue and incubated in complete darkness at 22°C for 7 days to assess acid secretion. Cell wall-degrading enzymes activity was determined using an enzyme activity detection kit after filtering the culture medium of 14-day-old liquid PD cultures. qRT-PCR analyzed the expression levels of cell wall-degrading enzyme-related genes in the BcKMOL gene mutants.
2.9 Screening of antimicrobial peptides targeting BcKMOL
The three-dimensional structure of BcKMOL was constructed, and docking software was used to analyze the target protein sequence. MEGADOCK was used to predict eigenvalues, and the protein–protein interaction data with antibacterial peptides were obtained. The top 200 protein groups were selected based on the MEGADOCK score and docked in batches using HDOCK docking software. The top 10 combinations were selected for AlphaFold3 interaction analysis.
2.10 Simulated molecular docking of BcKMOL and antimicrobial peptides
The protein three-dimensional structure of BcKMOL, CAMPQ3966, and CAMPQ4589 was established using Swiss-Model,3 and molecular simulation docking was performed using HDOCK SERVER.4 The results were imported into Pymol for in-depth analysis (Wang et al., 2024).
2.11 Induced expression and purification of antimicrobial peptides
The two antimicrobial peptides with the highest docking scores were selected as CAMPQ3966 and CAMPQ4589. After codon optimization, the prokaryotic expression vectors were constructed respectively, and the plasmids were extracted and transformed into E. coliBL21. The positive clones pET28a-CAMPQ3966 and pET28a-CAMPQ4589 were inoculated into 20 mL LB medium containing kanamycin sulfate and cultured overnight. The overnight culture broth was taken at a ratio of 1:20 and inoculated into LB medium preheated to 37°C and containing kanamycin sulfate. Conventional culture at 37°C for about 30–60 min or longer, until the OD600 of the bacterial solution reached 0.5–0.7; the pET28a-CAMPQ3966 strain was added with IPTG to a final concentration of 0.1 mM and induced at 16°C for 24 h. The pET28a-CAMPQ4589 strain was added with IPTG to a final concentration of 1 mM and induced at 28°C for 12 h. The bacterial liquid was collected into a centrifuge tube, centrifuged at 4°C, 15,000 g for 1 min, discarded the supernatant, and collected the precipitate; the supernatant was resuspended with Tris–HCL, added 5 × louding buffer, boiled for 10 min, centrifuged at 12,000 g for 3 min, and 20 μL of the supernatant was placed on 10% SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis, 80 V electrophoresis for 1 h, 100 V electrophoresis for 1 h, Coomassie brilliant blue staining for 15 min, washed with water, and observed protein induction.
The antimicrobial peptide CAMPQ3966 was induced to express at 16°C for 24 h, and CAMPQ4589 was induced to express at 28°C for 12 h. Antibacterial peptides CAMPQ3966 and CAMPQ4589 were induced in large quantities and purified using an AKTA protein purification instrument after ultrasonic lysis and centrifugation.
2.12 Effect of antimicrobial peptide on the growth and development of B. cinerea
The wild-type strain of B. cinerea and the BcKMOL mutants at the same growth period were inoculated on PDA solid plates. After 5 days of dark culture at 25°C, a bacterial plate with a diameter of 5 mm was punched with a sterile puncher for subsequent inoculation experiments. The same concentration of CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589 proteins were coated on the right side of the culture dish, and the same volume of protein eluent was coated on the left side of the culture dish as the control group. The wild-type strain of B. cinerea and the BcKMOL mutants were inoculated to observe the growth of the strain.
2.13 Effect of antimicrobial peptide on pathogenicity of B. cinerea
The wild-type strain B05.10 of B. cinerea was inoculated on a PDA solid plate and cultured for 5 days. A 5 mm diameter plate was punched for subsequent inoculation experiments. N. benthamiana plants at 4–5 weeks were selected. CAMPQ3966 and CAMPQ4589 proteins were applied to the right side of tobacco leaves, with soluble Elution Buffer applied to the left side as a control. Elution Buffer was prepared from 5.844 g NaCl, 4 mL 20 mM Tris–HCl, 100 mL 1 M Imidazole, and diluted to 200 mL. After 24 h, leaves were inoculated with B05.10, and plants were placed in a humid environment at 25°C for dark culture. Tobacco leaf disease incidence was observed and photographed after 2 days of inoculation. The same number of diseased leaves were taken and RNA was extracted. The Tublin gene was used as the reference gene of Botrytis cinerea, and the fungal biomass during the disease period was detected by qRT-PCR. The protein CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589 were mixed with Tween in equal proportions, and an appropriate amount was dropped on the surface of apples or pears. In the control group, the protein eluent was mixed with Tween in equal proportions, and an appropriate amount was added to the other side of the same apple or pear. The wild-type strain of B. cinerea at the same growth period was inoculated and placed in dark to observe the incidence.
2.14 qRT-PCR
RNA was extracted from the knockout transformants and wild-type strains, and reverse transcribed into cDNA. The expression of the target gene in the transformants was detected by Real-time PCR using Tubulin gene as an internal reference (Supplementary Table S1). The reaction system was: template (cDNA) 2.0 μL, Mix (5 U/μL) 10.0 μL, forward primer (10 μM) 0.4 μL, reverse primer (10 μM) 0.4 μL, ROX 1.0 μL, ddH2O 6.2 μL, the total system was 20 μL. The reaction procedure was carried out in strict accordance with the Takara fluorescence quantitative RT-PCR kit.
2.15 ELISA
The appropriate amount of mycelium or leaf lesion site was taken, grinded and crushed, diluted with PBS buffer solution with pH = 7.2, after repeated freezing and thawing, the ultrasonic crushing instrument was used for crushing. Centrifuging at 4°C, 2,000 rpm/min for 20 min, and the supernatant was carefully collected. The kynurenine monooxygenase activity of BcKMO protein was determined by the Human KMO ELISA kit (DLDEVELOP, Canada). The specific steps were carried out according to the instructions of the kit. The linear regression equation of the standard curve was calculated by using the concentration and OD value of the standard substance, and the OD value of the sample was substituted into the equation to calculate the enzyme activity of the sample.
3 Results
3.1 BcKMOL encodes kynurenine monooxygenase in B. cinerea
Utilizing the amino acid sequence of kynurenine monooxygenase (KMO) from humans and yeast, a search was conducted in the Ensembl Fungi database for the corresponding sequence in B. cinerea B05.10 strain. The search revealed that Bcin01g01500, henceforth referred to as BcKMO-like or BcKMOL, exhibited high similarity to KMO in other species. The Swiss-Model website was used to analyze the advanced structure of BcKMOL and found that it was similar to the structure of other KMOs (Figure 1a). Multiple sequence alignment was performed using MEGA7.0 software, which highlighted several highly conserved sequences between BcKMOL, HsKMO (human KMO) and ScKMO (yeast KMO) (Figure 1b). By analyzing the expression profile data of the wild-type B. cinerea strain from the GEO database during its growth, development, and infection phases, it was observed that the expression level of the BcKMOL gene increased within the first 1–15 h post-inoculation (hpi) during pathogen growth and development. Notably, the expression level peaked at 16 hpi during pathogen infection but gradually declined thereafter (Figure 1c). These findings suggest that BcKMOL plays a role in the growth and development of B. cinerea. By detecting the activity of BcKMOL at 16 hpi, the enzyme activity of BcKMOL was significantly higher than that of uninfected (Supplementary Figure S3a).
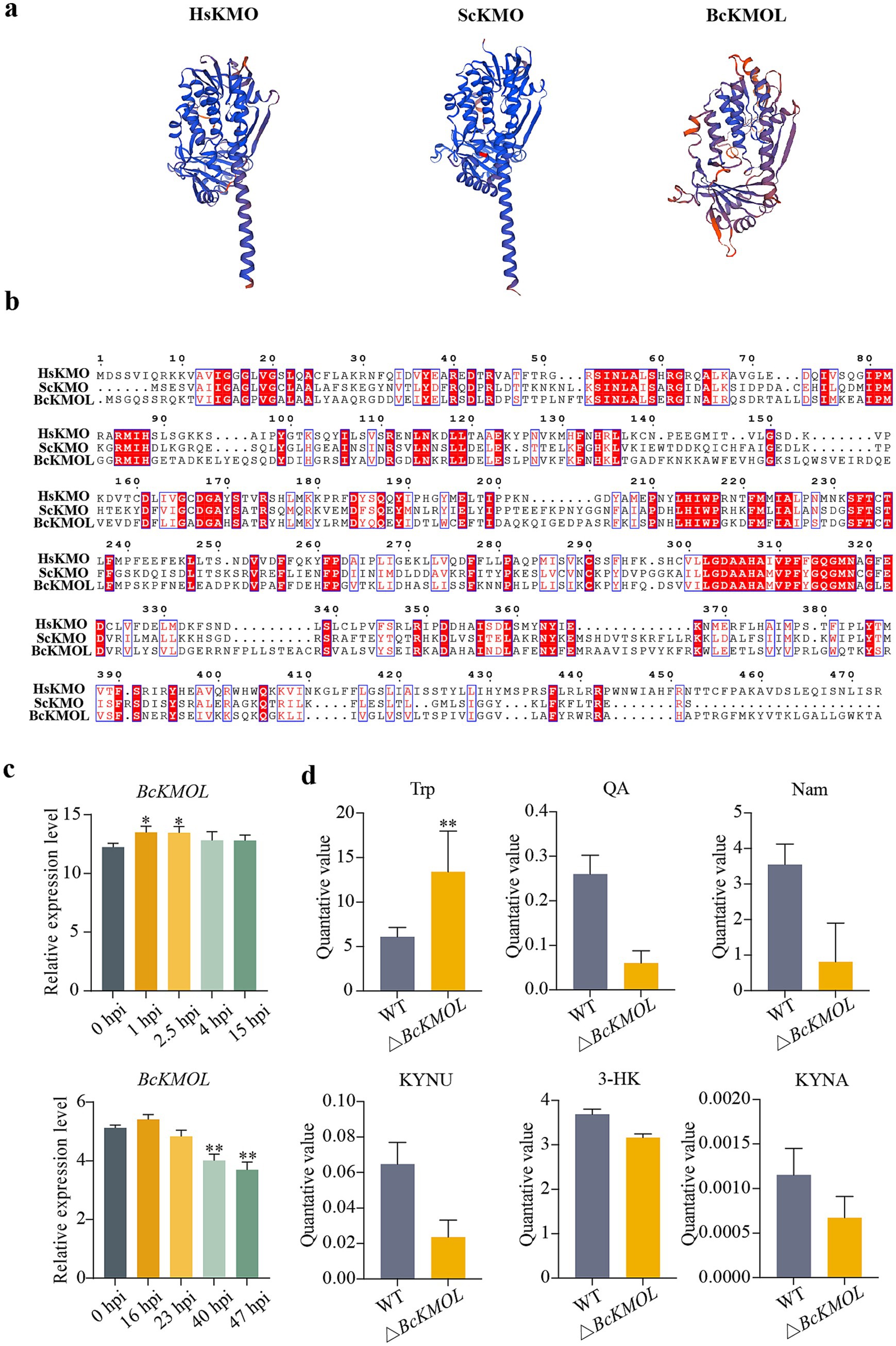
Figure 1. Bioinformatics analysis of kynurenine monooxygenase KMO. (a) Advanced structural analysis. A phylogenetic tree and domain of B. cinerea KMO and its human homologous were generated using the Swiss Model. (b) Multiple sequence alignment. Protein sequences of HsKMO (human), ScKMO (yeast), and BcKMOL (B. cinerea) were aligned using MEGA software. (c) The expression level of BcKMOL in each stage of conidial growth and infection of B. cinerea was analyzed. The expression level of BcKMOL during the growth and development of B. cinerea conidia was analyzed at 0 hpi. The expression level of BcKMOL during B. cinerea infection was analyzed at 0 hpi when tomato was infected. (d) Analysis of kynurenine pathway metabolites in BcKMOL mutants. △BcKMOL-1, △BcKMOL-2, and △BcKMOL-3 are three biological replicates. Each histogram represents the average SD from three biological replicates, and the asterisk indicates a significant difference from WT, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
To elucidate the impact of BcKMOL on growth and development of B. cinerea, we successfully generated knockout mutants and revertant strains of the BcKMOL gene (Supplementary Figures S1, S2). It was found that the deletion of BcKMOL affected the content of key metabolites of KP, in which the upstream product tryptophan was significantly accumulated, and the downstream metabolites 3-HK and QA were decreased. The content of other key metabolites such as KYNU, KYNA, and Nam also changed (Figure 1d). The contents of metabolites related to the other two pathways of tryptophan metabolism: the bacterial degradation pathway and the 5-hydroxytryptamine pathway also changed (Supplementary Figure S3b). It is speculated that BcKMOL encodes kynurenine monooxygenase and regulates the growth, development, and infection of B. cinerea.
3.2 BcKMOL affects the growth and development of B. cinerea
We then observed the colony morphology, mycelial morphology, and growth rate of these BcKMOL gene mutants (Figure 2). Our findings revealed that the knockout mutants of the BcKMOL gene failed to produce sclerotia, and their conidia exhibited an elongated morphology compared to the wild type. Furthermore, the mycelial cells of the mutants were significantly longer and considerably narrower than those of the wild type. Notably, the BcKMOL-C mutant exhibited a substantial restoration in sclerotium production, spore morphology, mycelial cell length, and growth rate when compared to the wild type. These results collectively suggest that mutations in the BcKMOL gene exert a specific influence on the growth and development of B. cinerea, thereby implicating the BcKMOL gene in the regulation of the growth and development processes in B. cinerea.
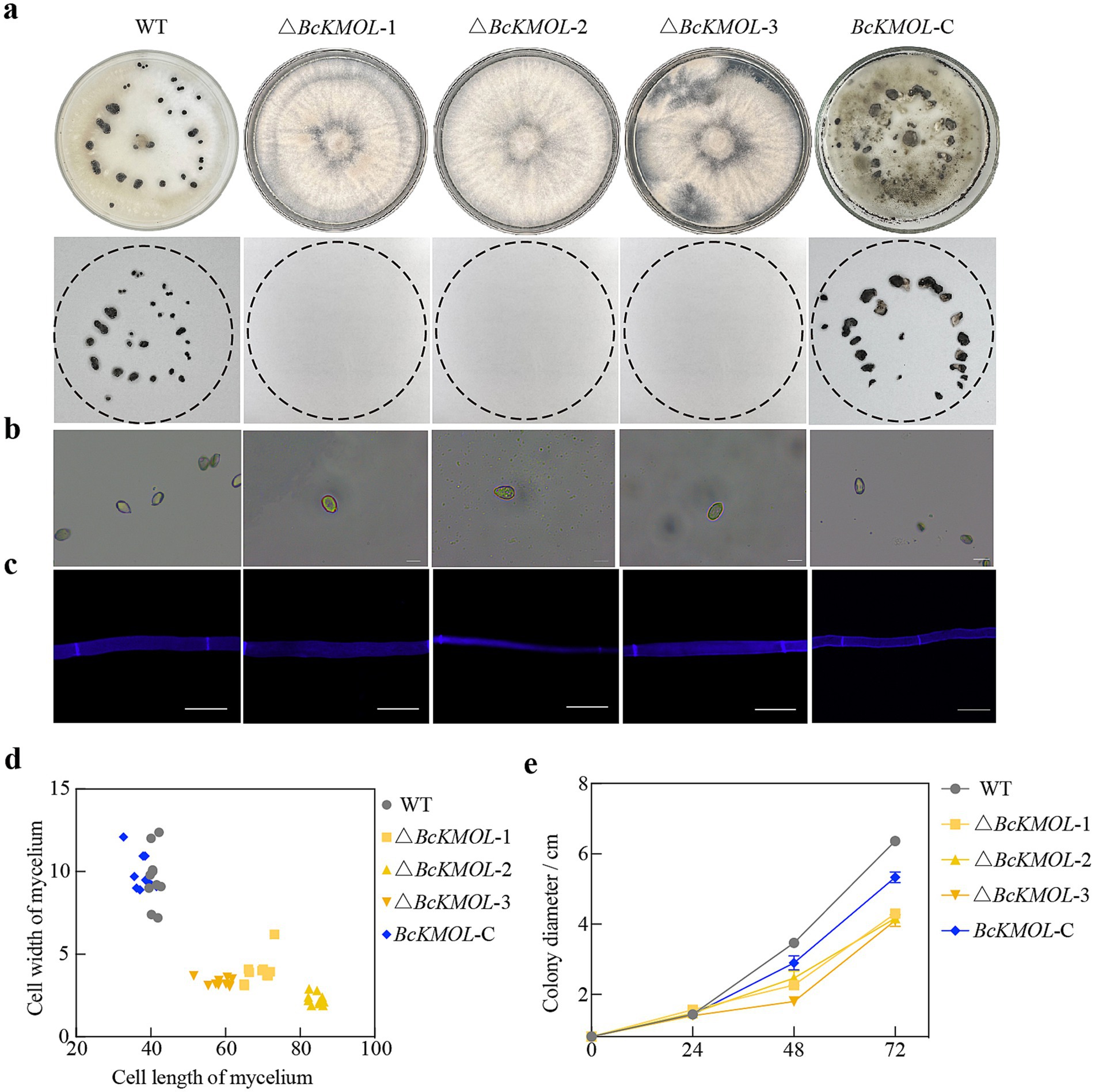
Figure 2. Role of the BcKMOL gene in B. cinerea growth and development. (a) Sclerotia growth of analysis. The growth of sclerotia in the BcKMOL gene mutants on the non-selective PDA medium was observed and recorded. (b) Spore morphological observation. Colonies were washed, filtered, and observed under a microscope. Scale bar: 10 μm. (c) Mycelial morphology observation. Mycelia stained with Calcofluor White (CFW) were observed under a fluorescence microscope. Scale bar: 20 μm. (d) Mycelial morphology analysis. A box plot representing the width and length of mycelial cells, used for growth rate analysis of the BcKMOL gene mutants. (e) Growth rate statistics of BcKMOL gene mutants. The BcKMOL gene mutants and wild type at the same growth stage were inoculated on PDA plates, and the colony diameter was recorded every 24 h.
3.3 BcKMOL positively regulates the pathogenicity in B. cinerea
To investigate the role of the BcKMOL gene in the pathogenesis of B. cinerea, we inoculated tobacco leaves with both the wild type and the BcKMOL gene mutants at the same growth stage. The results showed that while the △BcKMOL mutant was capable of producing visible lesions on tobacco leaves, the lesion area was significantly smaller compared to that caused by the wild type (Figure 3). Moreover, the pathogenicity of the BcKMOL-C revertant strain was restored, confirming that the BcKMOL gene exerts a positive regulatory effect on the pathogenesis of B. cinerea.
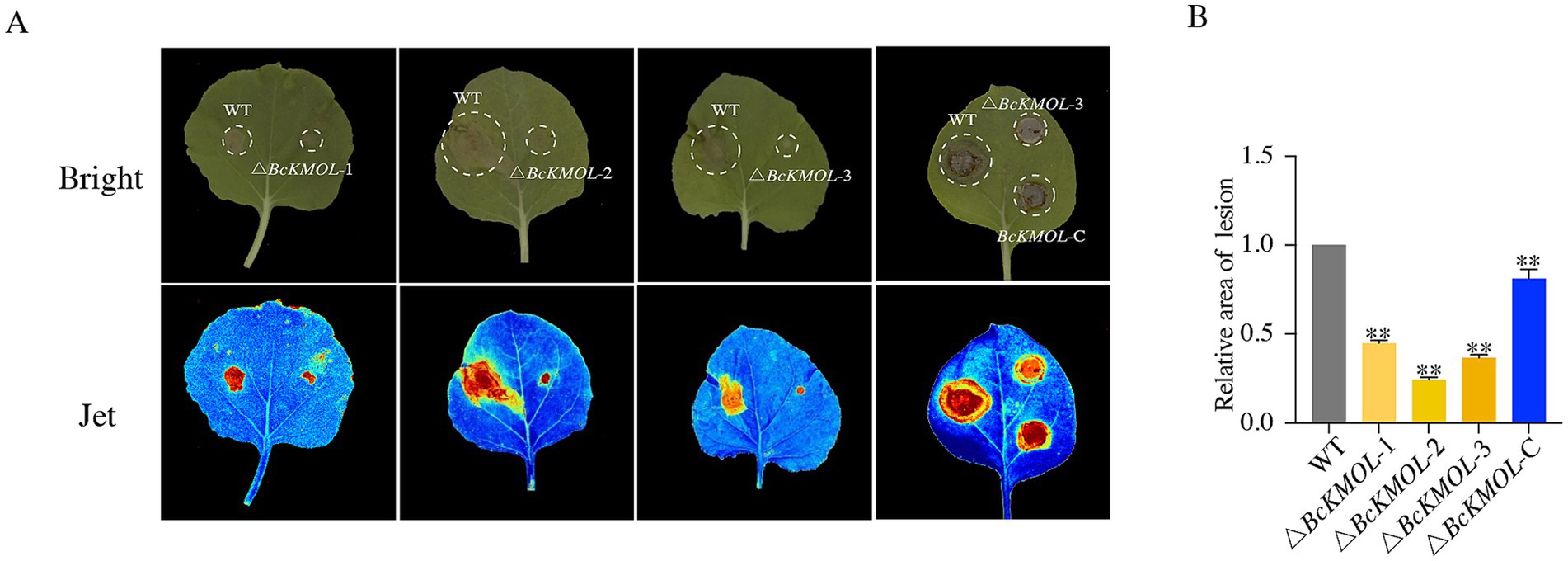
Figure 3. Pathogenicity analysis of the BcKMOL gene mutants. (A) Pathogenicity analysis. Tobacco leaves were inoculated with the BcKMOL gene mutants and wild-type strains of the same growth period. The mutants and wild type at the same growth stage were inoculated on tobacco leaves, placed in a humid environment at 25°C, and treated in the dark for 48 hpi to analyze the lesion area. Each group of treatments had three biological replicates. Bright denotes standard optical mode, and Jet denotes multi-spectral imaging mode. (B) Lesion area statistics. Error bars represent the standard deviation from three biological replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the wild type (WT) *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
3.4 BcKMOL impacts infection cushion formation and acid production in B. cinerea
As a necrotrophic plant pathogenic fungus, B. cinerea develops multicellular structures known as infection cushions specifically for plant penetration. To elucidate the role of the BcKMOL gene in the pathogenic process of this fungus, we analyzed the infection cushions and acid production capabilities of B. cinerea wild-type, along with BcKMOL gene mutants (Figure 4). The results showed that the number and size of the infection cushions of the △BcKMOL mutants were significantly different from those of the wild type and the revertant mutant (Figure 4). Although the colony color of the △BcKMOL mutants was largely similar to that of the wild type, we further assessed the colony’s pH value and found no significant difference between the BcKMOL mutant and the wild type. These results suggest that the BcKMOL gene negatively regulates the formation of infection cushion in B. cinerea.
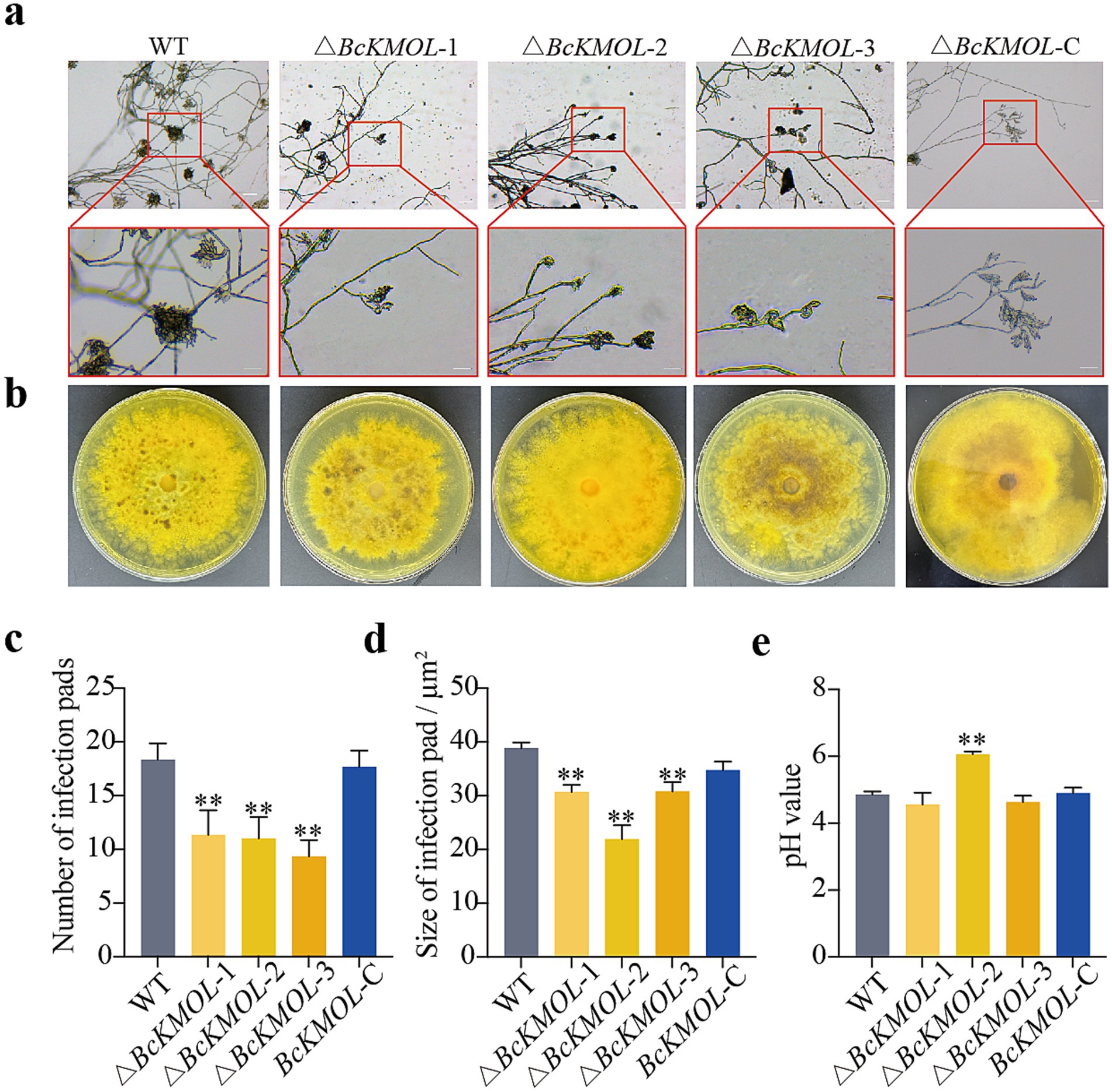
Figure 4. Infection cushion formation and acid production ability. (a) Infection cushion observation. Infection cushion formed during the same growth period were examined by microscopy. Scale bar: 10 μm. (b) Acid production analysis. Mutants were inoculated on the medium containing bromothymol blue to observe color change, indicating pH changes due to acid production. (c) The number of infection cushions of BcKMOL gene mutants. (d) The statistics of BcKMOL gene mutant’s infection cushion size. (e) The pH value of BcKMOL gene mutants. Each histogram represents the average SD from three biological replicates, and the asterisk indicates a significant difference from WT, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Error bars represent the standard deviation from three biological replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the wild type (WT); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
3.5 BcKMOL influences the activity of cell wall degrading enzymes in B. cinerea
The host infection by fungi primarily depends on cell wall permeability and integrity, which are governed by the activity of cell wall degrading enzymes (Zhang et al., 2009). Consequently, we assessed the extracellular pectinase and cellulase activities in the △BcKMOL mutants. Our results indicated that the deletion of BcKMOL led to a marked reduction in the extracellular pectinase and cellulase activities of the pathogen, whereas these activities were restored in the BcKMOL-C strain (Figure 5a). Additionally, we examined the expression levels of genes associated with cell wall degradation enzyme activity (Table 1). We observed significant down-regulation in the expression of BccutB, Bcpgx1, Bcpg3, Bcpme2, BccutA, Bcpme1, Bcams, Bcpg5, and Bcpg4. Conversely, only the expression levels of Bcpg1, Bcmns, and Bcmnl were up-regulated (Figure 5b).
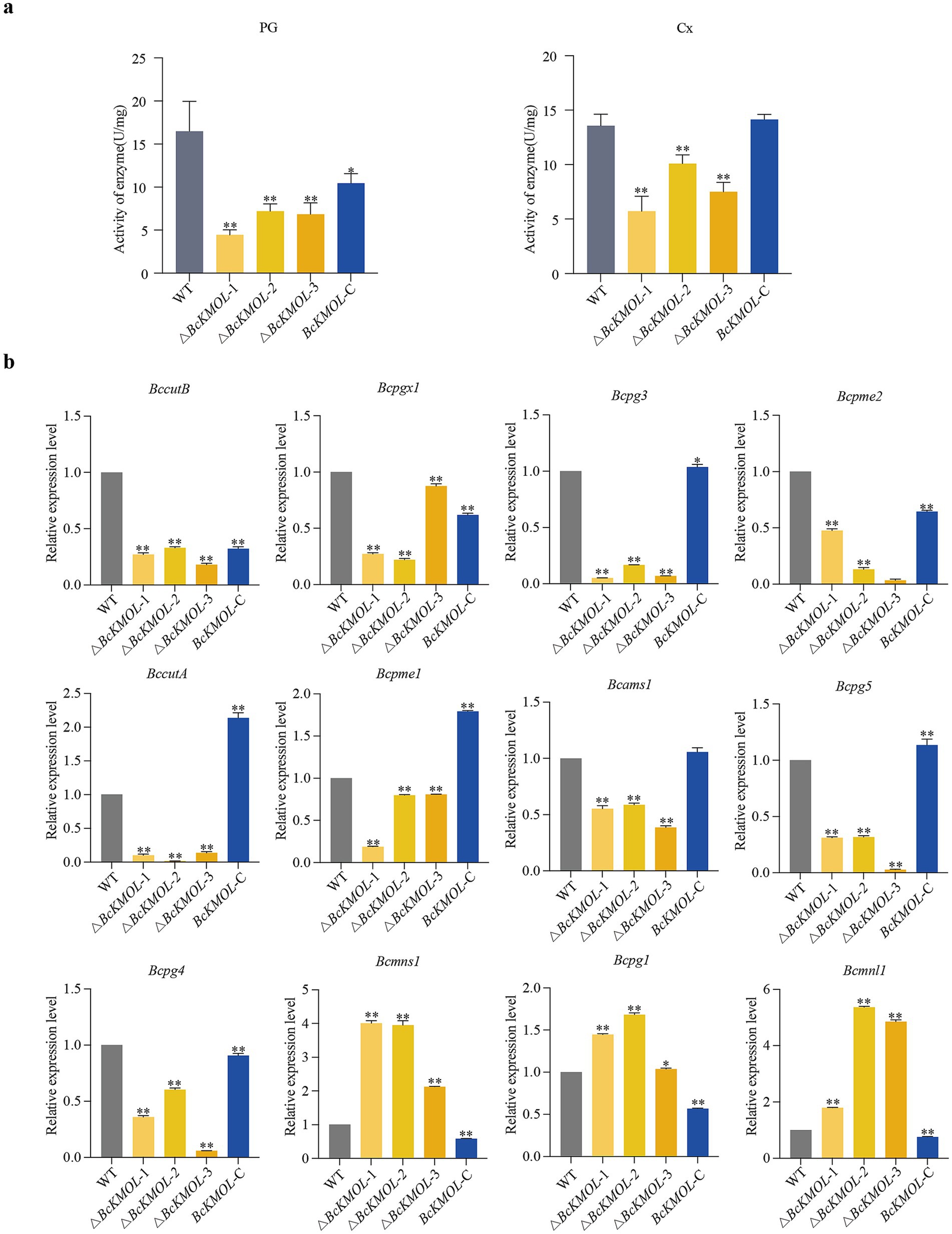
Figure 5. Analysis of pathogenic factors. (a) Extracellular enzyme activities. Pectinase (PG) and cellulase (Cx) activities were determined in the BcKMOL gene mutants and wild-type strains after 14 days of growth in liquid PD medium. (b) Analysis of expression levels of cell wall degrading enzyme-related genes. The BcKMOL gene mutants and wild-type strains at the same growth period were taken, and the cDNA was extracted. The cell wall degrading enzyme-related genes were detected by qRT-PCR. Tubulin served as the internal reference gene. Error bars represent the standard deviation from three biological replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the wild type (WT); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
3.6 Antibacterial peptide targeting BcKMOL can effectively suppress the pathogenicity of B. cinerea
We utilized BcKMOL as the bait protein and employed a multi-step screening process involving MEGADOCK for rough screening, HDOCK for fine screening, and AlphaFold3 for one-to-one nuanced analysis. This approach allowed us to identify 20 potential candidates. Notably, the iptm + ptm values for the bait protein and the library proteins with IDs of CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589 exceeded 0.75. Remarkably, the iptm + ptm value for the CAMPQ3966 protein reached 1.49, suggesting a very high probability of interaction with the bait protein (Table 2).
The binding sites of CAMPQ3966 and CAMPQ4589 to BcKMOL were subjected to further analysis using HDOCK and Pymol (Figure 6a). Specifically, the binding sites of CAMPQ3966 to BcKMOL encompassed THR (82)–THR (469), THR (85)–SER (466), SER (148)–ILE (472), and SER (184)–TRP (483). For CAMPQ4589 binding to BcKMOL2, the sites included ASN (8)–VAL (467), ASN (27)–LEU (419), SER (31)–GLY (463), GLY (56)–ARG (429), and GLN (143)–SER (470). Expression studies revealed that CAMPQ3966 could be produced in abundance at 16°C, while CAMPQ4589 was expressed in large quantities at 28°C and subsequently purified using an AKTA protein purification instrument (Supplementary Figures S4a,b). The wild type and BcKMOL mutants were treated with antimicrobial peptides, and it was found that the wild type and BcKMOL-C were sensitive to the antimicrobial peptides CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589, and the growth was significantly inhibited, while the growth of △BcKMOL did not change significantly (Figures 6b,c), which indicated that the antimicrobial peptides CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589 acted on BcKMOL.
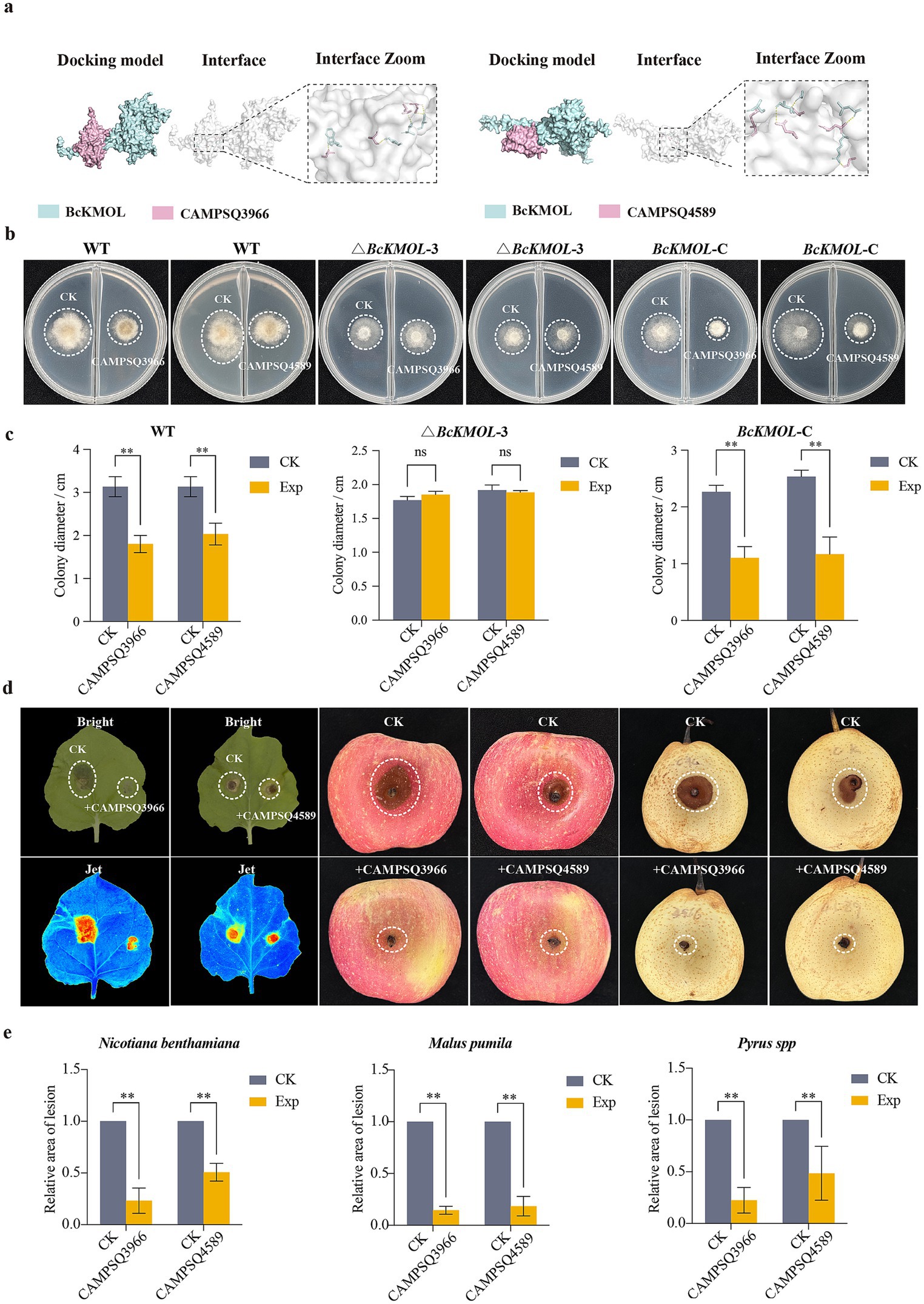
Figure 6. Screening and disease resistance analysis of antimicrobial peptides targeting BcKMOL. (a) Molecular docking simulation. Three-dimensional structures of BcKMOL, CAMPQ3966, and CAMPQ4589 were modeled using the Swiss-Model, and docking was performed using HDOCK. Results were analyzed in Pymol for interaction sites. (b) The binding analysis of antimicrobial peptides CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589 with BcKMOL. The antibacterial peptides CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589 of the same concentration were evenly coated on the right side of the culture dish, and the left side was coated with an equal volume of protein eluent as a control group. Wild type, △BcKMOL, and BcKMOL-C were inoculated, respectively. (c) The growth statistics of BcKMOL mutant colonies treated with antibacterial peptides CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589. The diameter of colony growth at 48 hpi was recorded. (d) The disease resistance analysis of antimicrobial peptides CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589. The protein concentration of CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589 was adjusted to be consistent. The protein elution buffer was applied to the left side of the tobacco, and the proteins CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589 were applied to the right side of the tobacco leaves, respectively. After dark treatment for 12 hpi, the wild-type strain of Botrytis cinerea at the same growth period was inoculated; the proteins CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589 were mixed with Tween in equal proportions, and the protein eluent was mixed with Tween in equal proportions in the control group. The wild-type strains of Botrytis cinerea at the same growth period were inoculated and placed in the dark to observe the incidence. The statistics of lesion area after treatment of crops with antimicrobial peptides CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589. Each histogram represents the average SD from three biological replicates, and the asterisk indicates a significant difference from WT, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
The purified antimicrobial peptides CAMPSQ396 and CAMPSQ4589 were applied to the right side of the tobacco leaves, and the blank control was set on the left side. The results showed that the leaves smeared with CAMPSQ3966 or CAMPSQ4589 had a significant inhibitory effect on the infection of B. cinerea. After treatment with antimicrobial peptides, the lesion area of the same apple or pear was significantly lower than that of the control group (Figures 6d,e), and the biomass of B. cinerea at the lesion of the leaves was detected. It was found that the biomass of B. cinerea was significantly reduced after treatment with CAMPSQ3966 or CAMPSQ4589 (Supplementary Figure S4c). It is indicated that the antibacterial peptides CAMPSQ396 and CAMPSQ4589 can inhibit the growth of B. cinerea and inhibit the pathogenicity of the pathogen.
4 Discussion
Kynurenine monooxygenase KMO, as a key rate-limiting enzyme in the kynurenine pathway (Xue et al., 2023), has become an important target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases in the human body. During the metabolic process, it can produce a series of neurotoxic substances such as kynurenine, 3-hydroxykynurenine and the neuroprotective substance kynurenic acid, and the imbalance of these metabolite levels is the key to the occurrence of the disease (Schwarcz et al., 2012). For example, it has been reported that KMO activity is up-regulated in the brain region of Huntington’s disease model mice (Sathyasaikumar et al., 2010). By inhibiting KMO activity, KP metabolic imbalance can be normalized, which can improve disease-related phenotypes (Bondulich et al., 2021). In this study, we detected the accumulation of tryptophan Trp content and the decrease of neurotoxic substances kynurenine KYNU, 3-hydroxykynurenine 3-HK, and quinolinic acid QA after the deletion of the BcKMOL gene in Botrytis cinerea. We speculated that the changes in these metabolite levels affected the growth and development and pathogenic process of the pathogen. Therefore, we analyzed the growth and development of BcKMOL gene knockout mutants. The most obvious is that the mutant △BcKMOL does not produce sclerotia, while the sclerotium structure of Botrytis cinerea is composed of compact vegetative mycelium cells and nutrients. It belongs to asexual resting structure (Elad et al., 2007; Richardson et al., 2011). Sclerotia can survive under various harsh conditions, such as low temperature or high temperature, drying and extreme lack of nutrients (Bolton et al., 2006). The pathogenicity of the mutant △BcKMOL was weakened. We analyzed the factors affecting the pathogenicity of the pathogen, such as the growth of the infection pad and the acid production ability of the pathogen. The size and number of the infection pad of the BcKMOL mutants were significantly affected, while Botrytis cinerea mainly penetrates the epidermis directly through the infection pad (Backhouse and Willets, 1987; Kunz et al., 2006; Sharman and Heale, 1977) or infects plants through wounds (Williamson et al., 2007). At the same time, several studies have shown that the main factors affecting the host ‘s resistance to fungal infection are cell wall permeability and integrity, which are maintained by the activity of cell wall degrading enzymes (Zhang et al., 2009). After knocking out the BcKMOL gene, we found that the activities of pectinase and cellulase were significantly down-regulated, and the expression levels of most genes related to cell wall degrading enzymes were down-regulated. Therefore, we can determine that BcKMOL plays an important role in the growth, development and pathogenicity of the pathogen. It is speculated that the BcKMOL gene deletion mutant of Botrytis cinerea may be due to changes in the level of kynurenine pathway metabolites affecting the growth, development, and infection structure of the pathogen, thereby affecting the pathogenic process of the pathogen. In the BcKMOL deletion mutant, we not only detected a decrease in neurotoxic substances but also a decrease in the neuroprotective substance KYNA. Therefore, the next step we will focus on the dynamic balance of the key metabolites of the kynurenine pathway and the ratio of key metabolites to help us better intervene in the pathway.
In recent years, soluble KMOs involved in kynurenine pathway metabolism have been identified in many bacteria, such as P. fluorescens (Kurnasov et al., 2003), Cytophaga hutchinsonii (Crozier and Moran, 2007) and Ralstonia metallidurans (Kurnasov et al., 2003). With the clarification of KMO crystal structure and detailed kinetic studies, the development of KMO inhibitors has been accelerated (Amaral et al., 2013), and a series of new compounds leading to the inhibition of KMO activity have been identified (Zhang et al., 2021) For example, the elevation of 3-hydroxykynurenine in mice can cause death from acute pancreatitis, and blocking the pathway with KMO-specific inhibitor GSK898 can reduce the critical phenotype and death (Hayes et al., 2023); oral administration of Ro61-8048 in mice can inhibit KMO and increase the concentration of kynurenic acid KYNA in the brain (Zwilling et al., 2011). KMO can be used as the basis for virtual screening by using the data of structure and ligand interaction, and combined with prodrug strategy to develop permeable KMO inhibitors (Zhang et al., 2019). After determining that BcKMOL positively regulates the growth, development and pathogenicity of B. cinerea, we used MEGADOCK, HDOCK, and AlphaFold3 to screen the potential antifungal peptides of BcKMOL. The results showed that the antifungal peptides CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589 could effectively inhibit the growth and pathogenesis of B. cinerea. In recent years, the abuse of fungicides against Botrytis cinerea has led to increased crop resistance and increasingly serious pesticide residues. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are considered to be a new generation of antibiotics, which have strong antibacterial activity against various bacteria, fungi, and viruses (Chung and Khanum, 2017; Mygind et al., 2005). In addition, AMP also has the functions of anti-biofilm and immune regulation (Luo and Song, 2021), and AMP has the advantages of low toxicity, strong thermal stability, high solubility, low molecular weight and no resistance to eukaryotic cells (Li et al., 2019). It has been reported in the literature that the soybean peptide sequence with high anti-inflammatory effect has been successfully identified, and it has been determined that the sequence of the antibacterial peptide with high activity is characterized by hydrophobic amino acids at the N-terminus and alkaline amino acids at the C-terminus (Liu et al., 2025). In this study, the antibacterial peptides obtained by purification and screening were found by pathogenicity test. CAMPSQ3966 and CAMPSQ4589, the antibacterial peptides of BcKMOL2, can effectively inhibit the pathogenicity of Botrytis cinerea. It provides a valuable exploration path for the follow-up study of the mechanism of KMO regulating the kynurenine pathway and thus affecting the pathogenicity of the pathogen. However, the length of the antimicrobial peptide CAMPQ3966 is 222 amino acids, and the length of CAMPQ4589 is 148 amino acids. Due to the length of the peptide and the cumbersome process of prokaryotic expression and purification, it is impossible to achieve its industrial production. However, in the future, we can combine the molecular docking results with the KMO crystal structure to analyze the key sites of the antimicrobial peptide and the target protein BcKMOL, and determine the active core region of the antimicrobial peptide, which provides a new idea for the safe, effective and long-term prevention and treatment of gray mold.
5 Conclusion
BcKMOL, which encodes kynurenine monooxygenase, lays a crucial role in the growth, development, and pathogenicity of B. cinerea. The BcKMOL mutation affects the metabolites of the kynurenine pathway and regulates the pathogenic process of the pathogen by regulating the formation of sclerotia, mycelial and spore morphology, infection cushion development, acid production capacity and cell wall degradation enzyme activity. In this study, we screened two antimicrobial peptides, CAMPQ3966 and CAMPQ4589, that effectively inhibit the pathogenicity of B. cinerea. These findings establish a foundation for the functional analysis of the kynurenine pathway in B. cinerea and offer novel insights into exploring new drug targets for the safe prevention and control of gray mold.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
BL: Validation, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft. XL: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. JZ: Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Supervision. HC: Software, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Project administration. HS: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Project administration. KZ: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Data curation, Project administration, Funding acquisition. JX: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition. JD: Project administration, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972217) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei province (C2022204040).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1595008/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
1. ^https://swissmodel.expasy.org
2. ^https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/
References
Amaral, M., Levy, C., Heyes, D. J., Lafite, P., Outeiro, T. F., Giorgini, F., et al. (2013). Structural basis of kynurenine 3-monooxygenase inhibition. Nature 496, 382–385. doi: 10.1038/nature12039
Backhouse, D., and Willets, H. J. (1987). Development and structure of infection cushions of Botrytis cinerea. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 89, 89–95. doi: 10.1016/S0007-1536(87)80062-1
Bolton, M. D., Thomma, B. P., and Nelson, B. D. (2006). Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (lib.) de Bary: biology and molecular traits of a cosmopolitan pathogen. Mol. Plant Pathol. 7, 1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2005.00316.x
Bondulich, M. K., Fan, Y., Song, Y., Giorgini, F., and Bates, G. P. (2021). Ablation of kynurenine 3-monooxygenase rescues plasma inflammatory cytokine levels in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington's disease. Sci. Rep. 11:5484. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84858-7
Carrasco, H., Robles-Kelly, C., Rubio, J., Olea, A. F., Martinez, R., and Silva-Moreno, E. (2017). Antifungal effect of polygodial on Botrytis cinerea, a fungal pathogen affecting table grapes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18:2251. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112251
Ceredi, G. A. L., Montuschi, C., and De Paoli, E. (2009). Ten years of field trials on grey mold control on strawberries. Acta Hortic. 842, 327–330. doi: 10.17660/actahortic.2009.842.60
Chung, P. Y., and Khanum, R. (2017). Antimicrobial peptides as potential anti-biofilm agents against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 50, 405–410. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2016.12.005
Crozier, K. R., and Moran, G. R. (2007). Heterologous expression and purification of kynurenine-3-monooxygenase from Pseudomonas fluorescens strain 17400. Protein Expr. Purif. 51, 324–333. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2006.07.024
Davidson, M., Rashidi, N., Nurgali, K., and Apostolopoulos, V. (2022). The role of tryptophan metabolites in neuropsychiatric disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:9968. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179968
Elad, Y., Williamson, B., and Tudzynski, P. (2007). Botrytis spp and diseases they cause in agricultural systems an introduction. Botrytis: Biology, Pathology and Control, 1–8. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-2626-3_1
Gao, J., Yao, L., Xia, T., Liao, X., Zhu, D., and Xiang, Y. (2018). Biochemistry and structural studies of kynurenine 3-monooxygenase reveal allosteric inhibition by Ro 61-8048. FASEB J. 32, 2036–2045. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700397RR
Giorgini, F., Huang, S. Y., Sathyasaikumar, K. V., Notarangelo, F. M., Thomas, M. A., Tararina, M., et al. (2013). Targeted deletion of kynurenine 3-monooxygenase in mice: a new tool for studying kynurenine pathway metabolism in periphery and brain. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 36554–36566. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.503813
Hayes, A. J., Zheng, X., O'Kelly, J., Neyton, L. P. A., Bochkina, N. A., Uings, I., et al. (2023). Kynurenine monooxygenase regulates inflammation during critical illness and recovery in experimental acute pancreatitis. Cell Rep. 42:112763. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112763
Hirose, Y., Watanabe, K., Minami, A., Nakamura, T., Oguri, H., and Oikawa, H. (2011). Involvement of common intermediate 3-hydroxy-L-kynurenine in chromophore biosynthesis of quinomycin family antibiotics. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 64, 117–122. doi: 10.1038/ja.2010.142
Hua, L., Yong, C., Zhanquan, Z., Boqiang, L., Guozheng, Q., and Shiping, T. (2018). Pathogenic mechanisms and control strategies of Botrytis cinerea causing post-harvest decay in fruits and vegetables. Food Qual. Saf. 2, 111–119. doi: 10.1093/fqsafe/fyy016
Hughes, T. D., Güner, O. F., Iradukunda, E. C., Phillips, R. S., and Bowen, J. P. (2022). The kynurenine pathway and kynurenine 3-monooxygenase inhibitors. Molecules 27:273. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010273
Keller, U., Lang, M., Crnovcic, I., Pfennig, F., and Schauwecker, F. (2010). The actinomycin biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces chrysomallus: a genetic hall of mirrors for synthesis of a molecule with mirror symmetry. J. Bacteriol. 192, 2583–2595. doi: 10.1128/JB.01526-09
Kunz, C., Vandelle, E., Rolland, S., Poinssot, B., Bruel, C., Cimerman, A., et al. (2006). Characterization of a new, nonpathogenic mutant of Botrytis cinerea with impaired plant colonization capacity. New Phytol. 170, 537–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01682.x
Kurnasov, O., Goral, V., Colabroy, K., Gerdes, S., Anantha, S., Osterman, A., et al. (2003). NAD biosynthesis: identification of the tryptophan to quinolinate pathway in bacteria. Chem. Biol. 10, 1195–1204. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2003.11.011
Lecompte, F., Nicot, P. C., Ripoll, J., Abro, M. A., Raimbault, A. K., Lopez-Lauri, F., et al. (2017). Reduced susceptibility of tomato stem to the necrotrophic fungus Botrytis cinerea is associated with a specific adjustment of fructose content in the host sugar pool. Ann. Bot. 119, 931–943. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcw240
Li, T., Li, L., Du, F., Sun, L., Shi, J., Long, M., et al. (2021). Activity and mechanism of action of antifungal peptides from microorganisms: a review. Molecules 26:3438. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113438
Li, T., Liu, Q., Wang, D., and Li, J. (2019). Characterization and antimicrobial mechanism of CF-14, a new antimicrobial peptide from the epidermal mucus of catfish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 92, 881–888. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.07.015
Li, X., Zuo, S., Wang, B., Zhang, K., and Wang, Y. (2022). Antimicrobial mechanisms and clinical application prospects of antimicrobial peptides. Molecules 27:2675. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092675
Lichter, A., Kaplunov, T., and Zutahy, Y. (2016). Unique techniques developed in Israel for short- and long-term storage of table grapes. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 63, 2–6. doi: 10.1080/07929978.2016.1151289
Lima, W. C., Varani, A. M., and Menck, C. F. (2009). NAD biosynthesis evolution in bacteria: lateral gene transfer of kynurenine pathway in Xanthomonadales and Flavobacteriales. Mol. Biol. Evol. 26, 399–406. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msn261
Liu, W., Han, Y., An, J., Yu, S., Zhang, M., Li, L., et al. (2025). Alternation in sequence features and their influence on the anti-inflammatory activity of soy peptides during digestion and absorption in different enzymatic hydrolysis conditions. Food Chem. 471:142824. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.142824
Luo, Y., and Song, Y. (2021). Mechanism of antimicrobial peptides: antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antibiofilm activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:11401. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111401
Matthijs, S., Baysse, C., Koedam, N., Tehrani, K. A., Verheyden, L., Budzikiewicz, H., et al. (2004). The Pseudomonas siderophore quinolobactin is synthesized from xanthurenic acid, an intermediate of the kynurenine pathway. Mol. Microbiol. 52, 371–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.03999.x
Meena, R., Kumar, S., Datta, R., Lal, R., Vijayakumar, V., Brtnicky, M., et al. (2020). Impact of agrochemicals on soil microbiota and management: a review. Land 9:34. doi: 10.3390/land9020034
Muri, S. D., van der Voet, H., Boon, P. E., van Klaveren, J. D., and Bruschweiler, B. J. (2009). Comparison of human health risks resulting from exposure to fungicides and mycotoxins via food. Food Chem. Toxicol. 47, 2963–2974. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2009.03.035
Mygind, P. H., Fischer, R. L., Schnorr, K. M., Hansen, M. T., Sonksen, C. P., Ludvigsen, S., et al. (2005). Plectasin is a peptide antibiotic with therapeutic potential from a saprophytic fungus. Nature 437, 975–980. doi: 10.1038/nature04051
Pasquale, R., Carmen, B., Cristina De, C., Francesco, G., Giuseppe, S., and Vittorio, C. (2019). Pesticide residues and stuck fermentation in wine: new evidences indicate the urgent need of tailored regulations. Fermentation 5:3309. doi: 10.3390/fermentation5010023
Phillips, R. S., Iradukunda, E. C., and Hughes, T. (2019). Modulation of enzyme activity in the kynurenine pathway by kynurenine monooxygenase inhibition. Front. Mol. Biosci. 6:3. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00003
Plesken, C., Pattar, P., and Reiss, B. (2021). Genetic diversity of Botrytis cinerea revealed by multilocus sequencing, and identification of b. cinerea populations showing genetic isolation and distinct host adaptation. Front. Plant Sci. 12:e663027. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.663027
Richardson, P. M., Amselem, J., Cuomo, C. A., van Kan, J. A. L., Viaud, M., Benito, E. P., et al. (2011). Genomic analysis of the necrotrophic fungal pathogens Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. PLoS Genet. 7:e1002230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002230
Sathyasaikumar, K. V., Stachowski, E. K., Amori, L., Guidetti, P., Muchowski, P. J., and Schwarcz, R. (2010). Dysfunctional kynurenine pathway metabolism in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington's disease. J. Neurochem. 113, 1416–1425. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06675.x
Schwarcz, R., Bruno, J. P., Muchowski, P. J., and Wu, H. Q. (2012). Kynurenines in the mammalian brain: when physiology meets pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 13, 465–477. doi: 10.1038/nrn3257
Sharman, S., and Heale, J. B. (1977). Penetration of carrot roots by the grey mould fungus Botrytis cinerea Pers. ex Pers. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 10, 63–71. doi: 10.1016/0048-4059(77)90008-X
Sonker, N., Pandey, A. K., and Singh, P. (2016). Strategies to control post-harvest diseases of table grape: a review. J. Wine Res. 27, 105–122. doi: 10.1080/09571264.2016.1151407
Wang, Y., Guo, S., Sun, W., Tu, H., Tang, Y., Xu, Y., et al. (2024). Synthesis of 4H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one hydrazine derivatives as a potential inhibitor for the self-assembly of TMV particles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72, 2879–2887. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05334
Wasmann, R. E., Muilwijk, E. W., Burger, D. M., Verweij, P. E., Knibbe, C. A., and Bruggemann, R. J. (2018). Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of micafungin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 57, 267–286. doi: 10.1007/s40262-017-0578-5
Wilkinson, M. (2013). Structural dynamics and ligand binding in kynurenine 3-monooxygenase. (Doctor): The University of Edinburgh.
Williamson, B., Tudzynski, B., and Tudzynski, P. (2007). Botrytis cinerea: the cause of grey mould disease. Mol. Plant Pathol. 8, 561–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2007.00417.x
Wilson, K., Mole, D. J., Binnie, M., Homer, N. Z., Zheng, X., Yard, B. A., et al. (2014). Bacterial expression of human kynurenine 3-monooxygenase: solubility, activity, purification. Protein Expr. Purif. 95, 96–103. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2013.11.015
Xie, N., Zhang, L., Gao, W., Huang, C., Huber, P. E., Zhou, X., et al. (2020). NAD(+) metabolism: pathophysiologic mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 5:227. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00311-7
Xue, C., Li, G., Zheng, Q., Gu, X., Shi, Q., Su, Y., et al. (2023). Tryptophan metabolism in health and disease. Cell Metab. 35, 1304–1326. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.06.004
Yan, X., Chen, S., Sun, W., Zhou, X., Yang, D., Yuan, H., et al. (2022). Primary mode of action of the novel sulfonamide fungicide against botrytis cinerea and field control effect on tomato gray mold. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:1526. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031526
Zhang, S., Collier, M. E. W., Heyes, D. J., Giorgini, F., and Scrutton, N. S. (2021). Advantages of brain penetrating inhibitors of kynurenine-3-monooxygenase for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 697:108702. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108702
Zhang, S., Sakuma, M., and Deora, G. S. (2019). A brain-permeable inhibitor of the neurodegenerative disease target kynurenine 3-monooxygenase prevents accumulation of neurotoxic metabolites. Commun. Biol. 2:271. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0520-5
Zhang, S., Sun, L., and Kragler, F. (2009). The phloem-delivered RNA pool contains small noncoding RNAs and interferes with translation. Plant Physiol. 150, 378–387. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.134767
Zhu, W., Yu, M., Xu, R., Bi, K., Yu, S., Xiong, C., et al. (2022). Botrytis cinerea BcSSP2 protein is a late infection phase, cytotoxic effector. Environ. Microbiol. 24, 3420–3435. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15919
Zhang, Y., Liu, X., Luo, J., Liu, H., Li, Y., Liu, J., et al. (2025). Dual recombinase polymerase amplification system combined with lateral flow immunoassay for simultaneous detection of Staphylococcus aureus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 255:116621. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2024.116621
Keywords: Botrytis cinerea , kynurenine pathway, kynurenine monooxygenase, growth and pathogenesis, antimicrobial peptides
Citation: Li B, Liu X, Zang J, Cao H, Si H, Zhang K, Xing J and Dong J (2025) Kynurenine monooxygenase BcKMOL: a key regulator of growth, pathogenicity, and disease control in Botrytis cinerea. Front. Microbiol. 16:1595008. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1595008
Edited by:
Hector Mora Montes, University of Guanajuato, MexicoCopyright © 2025 Li, Liu, Zang, Cao, Si, Zhang, Xing and Dong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jihong Xing, eGluZ2ppaG9uZzIwMDBAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Jingao Dong ZG9uZ2ppbmdhb0AxMjYuY29t
 Bai Li
Bai Li Xiaoying Liu2
Xiaoying Liu2 Hongzhe Cao
Hongzhe Cao Kang Zhang
Kang Zhang Jihong Xing
Jihong Xing Jingao Dong
Jingao Dong