- University of Warsaw, Centre of New Technologies, Warsaw, Poland
Endolysins, bacteriophage-encoded peptidoglycan hydrolases, offer promising potential in antibacterial therapy, including treatments targeting gram-negative bacteria. While these enzymes naturally act primarily on gram-positive bacteria, their application against gram-negative pathogens is more challenging due to the presence of a dual-layer cell membrane, which acts as a protective barrier. However, innovative approaches, such as fusing endolysins with antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), have demonstrated increased efficacy against gram-negative bacteria. Modifying endolysins by introducing hydrophobic properties or positive charges or combining them with agents that disrupt the outer membrane enhances their bactericidal activity. Moreover, phage endolysins that exhibit activity against gram-negative bacteria are a promising source of membrane-active peptides. Identifying new peptide sequences derived from endolysins capable of penetrating the bacterial cell membrane represents a novel and increasingly explored research direction. Studying these innovative strategies had yielded promising results, though the field remains under active investigation and development. Ongoing efforts aim to optimize these approaches to improve their effectiveness against antibiotic-resistant gram-negative bacterial strains, which are particularly difficult to treat with conventional antibiotics. This review summarizes the latest advancements and solutions in the field, highlighting the potential of endolysins and membrane-active peptides as next-generation antibacterial agents.
1 Introduction
The emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria has become a global health threat (Salam et al., 2023). The World Health Organization (WHO) has prioritized the fight against drug resistance (World Health Organization, 2017, 2024). Antibiotics are becoming increasingly ineffective as resistance spreads worldwide, leading to infections that are becoming difficult to treat. There is an urgent need to develop more potent, non-toxic, and effective antimicrobials against MDR strains (Parmanik et al., 2022). The WHO published a list of antibiotic-resistant “priority pathogens,” which include carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, as well as extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBL)—producing Enterobacteriaceae (World Health Organization, 2017, 2024). These gram-negative bacteria, responsible for severe and often deadly infections, such as systemic infections and pneumonia. These bacteria resist many antibiotics, including carbapenems and third-generation cephalosporins, which are considered the drugs of last resort in treating gram-negative bacteria-related infections. Additionally, gram-negative bacteria are the most frequent cause of food spoilage and contamination in industrial systems (Wdowiak et al., 2023). A major challenge in developing effective antibiotics against these pathogens is the low permeability of the gram-negative bacteria cell envelopes (Cama et al., 2019). Their outer membrane is an exceptionally sophisticated macromolecular barrier, providing an extra layer of protection while regulating material exchange (Figure 1). Beneath this lies a thin periplasmic space with peptidoglycan (PG) layer and a phospholipid-based inner membrane, essential for transport, biosynthesis, and DNA anchoring (Breijyeh et al., 2020; Alegun et al., 2021). Because of its crucial role in bacterial survival, the bacterial envelope has become a primary target for researchers seeking new antibiotics. One promising alternative to conventional approaches is to disrupt the gram-negative bacterial cell membrane, distorting its integrity and causing bacterial lysis.

Figure 1. Schematic representation of the gram-negative cell wall and cleavage sites of bacteriophage endolysins in the peptidoglycan layer: MurNac, N-acetylmuramic acid; GlcNac, N-acetylglucosamine; m-DAP, diamino acid; L-Ala, L-alanine; D-Glu, D-glutamic acid; L-Lys; L-lysine; D-Ala, D-alanine; LPS, lipopolysaccharides.
Bacteriophages (phages) are the most abundant viruses on Earth and are natural antibacterial agents. Shortly after their discovery in 1919, phages were first used for therapeutic purposes in humans. One of their key advantages is their ability to evolve, allowing them to effectively combat multidrug-resistant pathogens and biofilms, combined with their specificity in targeting bacteria, which minimizes disruption to the host’s microbiota. However, a significant challenge to their therapeutic use is their rapid elimination by the human immune system, which limits their efficacy as antibiotics (Ghose and Euler, 2020; Rahman et al., 2021). One of the most promising approaches to overcome this obstacle is using phage-derived lytic enzymes, such as endolysins. These enzymes, responsible for bacterial lysis, are considered promising candidates for future antimicrobial therapies, particularly in combating antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Understanding their mechanisms of action could pave the way for their incorporation into commonly used disinfectants or therapeutic agents.
This review provides an integrated and up-to-date perspective on the engineering of endolysins for activity against gram-negative bacteria, with particular emphasis on membrane-targeting strategies. While several recent reviews have addressed individual aspects of endolysin activity, AMP fusion, or synergy with antibiotics, this manuscript offers a comprehensive synthesis of modular engineering approaches, including the use of synthetic linkers, lipid tails, nanocarriers, and Trojan-horse delivery designs. Additionally, it summarizes the development of peptides with outer membrane-disrupting activity derived from endolysin sequences. Recent advances in combinatorial design platforms such as VersaTile and the application of artificial intelligence tools to identify hidden antimicrobial motifs within lysin sequences are also highlighted. By integrating insights from endolysin biology and AMP engineering, this review outlines the current challenges and future directions in the development of endolysin-based therapeutics against multidrug-resistant gram-negative pathogens.
2 Endolysins—structure and activity
The term “endolysins” was first introduced in 1958 to describe bacteriophage-encoded peptidoglycan hydrolases (Jacob and Fuerst, 1958). These enzymes are synthesized within bacterial cells infected by a phage during the late stages of the phage replication cycle. Their primary function is to degrade the bacterial PG layer, facilitating host cell lysis and the subsequent release of newly assembled phage particles. Larger bacteriophages with a double-stranded DNA genome encode at least two lytic proteins necessary for bacterial cell lysis: holin and endolysin. Holin accumulates in the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane and, at a precisely programmed time, forms lethal pores that increase membrane permeability. This process allows endolysin to move from the cytoplasm into the bacterial periplasm, where it degrades the PG layer (Saier and Reddy, 2015; Cahill and Young, 2019; Bai et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2021; Pattnaik et al., 2024).
The endolysins of phages that infect gram-negative bacteria are typically simple, globular proteins of 15–20 kDa, consisting predominantly of an enzymatically active domain (EAD) (Rahman et al., 2021). However, some endolysins possess more than one EAD. Exceptions include two endolysins from P. aeruginosa phages KZ144 and EL188, which display a modular structure featuring an N-terminal cell wall binding domain (CBD) and a C-terminal EAD (Figure 2; Briers et al., 2007, 2009, 2011). Other endolysins with a modular structure (one CBD and one EAD), that target gram-negative bacteria, include Salmonella enterica bacteriophage endolysin Gp110 (Rodríguez-Rubio et al., 2016) and E. coli bacteriophage endolysin LysT84 (Figure 2; Love et al., 2022). The structure of endolysins may vary depending on the type of bacteria they target, e.g., the PlyC enzyme of bacteriophages targeting Streptococcus spp. is a holoenzyme consisting of nine subunits: one catalytic subunit with both glycosidase and endopeptidase activity and eight identical CBD subunits (Figure 2B; McGowan et al., 2012). This modular architecture was initially thought to be unique to endolysins from phages targeting gram-positive bacteria, where it is often arranged in the reverse orientation. Unlike gram-negative bacteria, gram-positive bacteria lack a protective outer membrane and have a thick, multi-layered PG cell wall adorned with surface carbohydrates, proteins, and wall teichoic acids (Rohde, 2019). This structural difference may explain the modular architecture of endolysins from gram-positive bacterial phages. In contrast, the presence of an outer membrane in gram-negative bacteria reduces the necessity for an additional CBD. Additionally, the thinner PG layer in gram-negative bacteria may not require as much enzymatic anchoring as the multilayered PG of gram-positive bacterial cell walls.
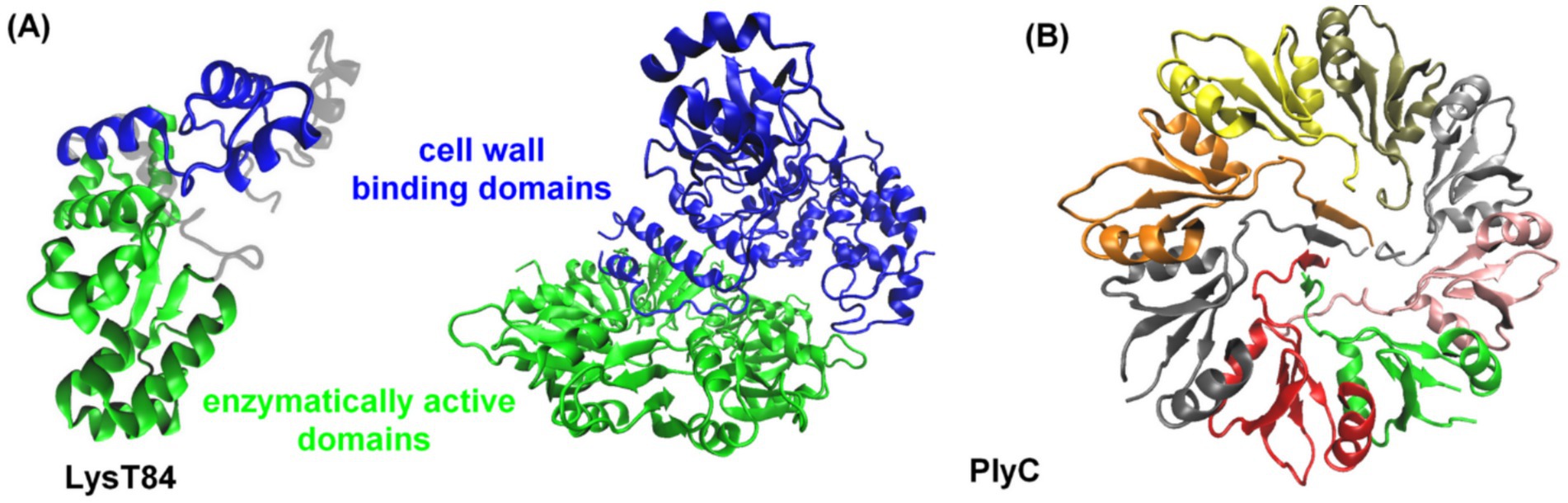
Figure 2. (A) Three-dimensional structures of the LysT84 (PDB code: 7RUM, Love et al., 2022) and PlyC (PDB code: 4F88, McGowan et al., 2012) endolysins. Enzymatically active domains are shown in green, while cell wall binding domains are depicted in blue. (B) Representation of the cell wall binding surface of PlyC endolysin, divided into eight domains. The proteins are displayed in a cartoon representation, using VMD (Humphrey et al., 1996).
Bacterial PG is composed of two major amino-sugar components: N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid, connected by a β-(1,4)-glycosidic bond. This polysaccharide lattice is stabilized by amino acid chains, whose composition differs between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Their common feature is the presence of L-alanine and D-alanine (Garde et al., 2021). Since this structure is highly conserved in both of these bacterial types, the number of covalent bonds that endolysins or other PG-digesting enzymes can target is inherently limited. The EAD of these enzymes specializes in cleaving one of the four primary bonds within the PG structure. Therefore, based on their activity, endolysins were classified into four main groups: glucosaminidase, amidases, endopeptidases, and muramidase (Figure 1; Gerstmans et al., 2018; Vázquez et al., 2018; Liu B. et al., 2023; Khan et al., 2024; Pattnaik et al., 2024; Zheng and Zhang, 2024). Glycosidases cleave bonds between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) in the carbohydrate chains of PG. They can be divided into two types: N-acetylglucosaminidases, which hydrolyze the β-1,4-glycosidic bond at the GlcNAc end, and N-acetylmuramidases, which target glycosidic bonds at the MurNAc end. The second group, amidohydrolases (amidases), cleaves the amide bond between MurNAc and the peptide residue (L-alanine) in bacterial PG. The third group, endopeptidases (or endoproteases), hydrolyzes peptide bonds within core peptides attached to MurNAc or those forming cross-links, disrupting PG structural integrity. The fourth group, lytic transglycosylases, like muramidases, digest β-1,4-glycosidic bonds between MurNAc and GlcNAc residues. Among the studied endolysins, most had been classified as amidases or muramidases (Gerstmans et al., 2018; Vázquez et al., 2018; Liu B. et al., 2023; Khan et al., 2024; Pattnaik et al., 2024; Zheng and Zhang, 2024).
Endolysins are fast-acting, potent, and inactive against eukaryotic cells. Combining phage lysins with antibiotics may enhance infection treatment efficacy compared to antibiotics alone. Bacterial resistance to lysins is considered unlikely because lysins target critical PG sites essential for bacterial viability (Ghose and Euler, 2020; Gondil et al., 2020; Gontijo et al., 2021; Rahman et al., 2021; Vázquez et al., 2021; Khan et al., 2023, 2024; Sisson et al., 2024b; Zheng and Zhang, 2024). Phage endolysin activity can induce lysis from the outside due to high intracellular osmotic pressure, which serves as a basis for exploring purified phage endolysins as antimicrobial agents against gram-positive pathogens (Liu H. et al., 2023; Vander Elst, 2024). However, in gram-negative bacteria, the outer membrane often prevents endolysin access, requiring surfactants or additional mechanisms for translocation. Nonetheless, some bacteriophage-derived endolysins exhibit antibacterial activity against gram-negative pathogens. In this review, endolysins were classified into two groups (Figure 3):
1. Endolysins that cannot penetrate the gram-negative bacterial cell wall.
2. Endolysins that can penetrate the gram-negative bacterial cell wall.
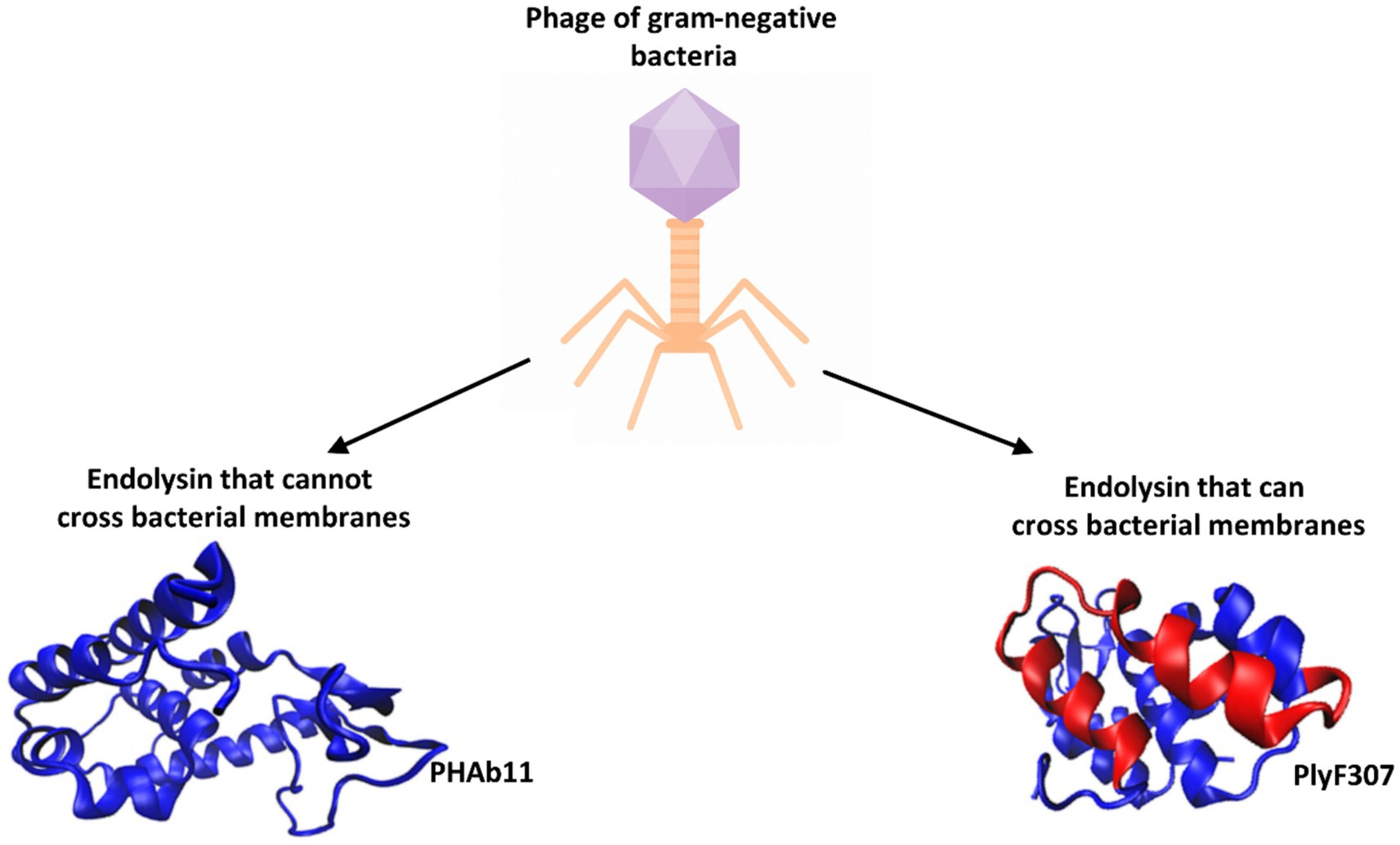
Figure 3. Endolysins derived from bacteriophages active against gram-negative bacteria are classified into two groups. An example of an endolysin belonging to the first group is PHAb11, which contains a single EAD domain with lysozyme activity (PDB code: 9KBS, Hu, 2024). An example of an endolysin capable of crossing bacterial membranes is PlyF307 (its structure was predicted using the I-TASSER program) (Yang and Zhang, 2015). The helical fragment isolated as an independent antibacterial peptide is marked in red.
In the following sections, existing methods for enhancing the activity of endolysins in the first group and present strategies proposed by various research groups for designing novel, membrane-active peptide sequences utilizing endolysins from the second group.
3 The use and limitations of endolysins in antibacterial therapies against gram-negative bacteria
Endolysins were initially considered ineffective against gram-negative bacteria due to the protective outer membrane of these organisms. However, various strategies had been developed to enhance their efficacy, including the use of outer membrane permeabilizers, fusion with membrane-active peptides, nanotechnology-based delivery methods, and liposome encapsulation. This review focuses on the key approaches for utilizing endolysins in therapies targeting gram-negative bacteria, specifically, it highlights methods involving membrane-permeabilizing agents and strategies that enhance endolysin activity through fusion with membrane-degrading peptides.
3.1 Combination of endolysins with outer membrane permeabilizes
Combining endolysins with outer membrane permeabilizers is a promising strategy to enhance their activity against gram-negative bacteria (Figure 4; Table 1). These permeabilizers disrupt the outer membrane by chelating divalent cations, making the peptidoglycan layer accessible to endolysins. The main approaches utilizing permeabilizers in combination with endolysins are outlined below.
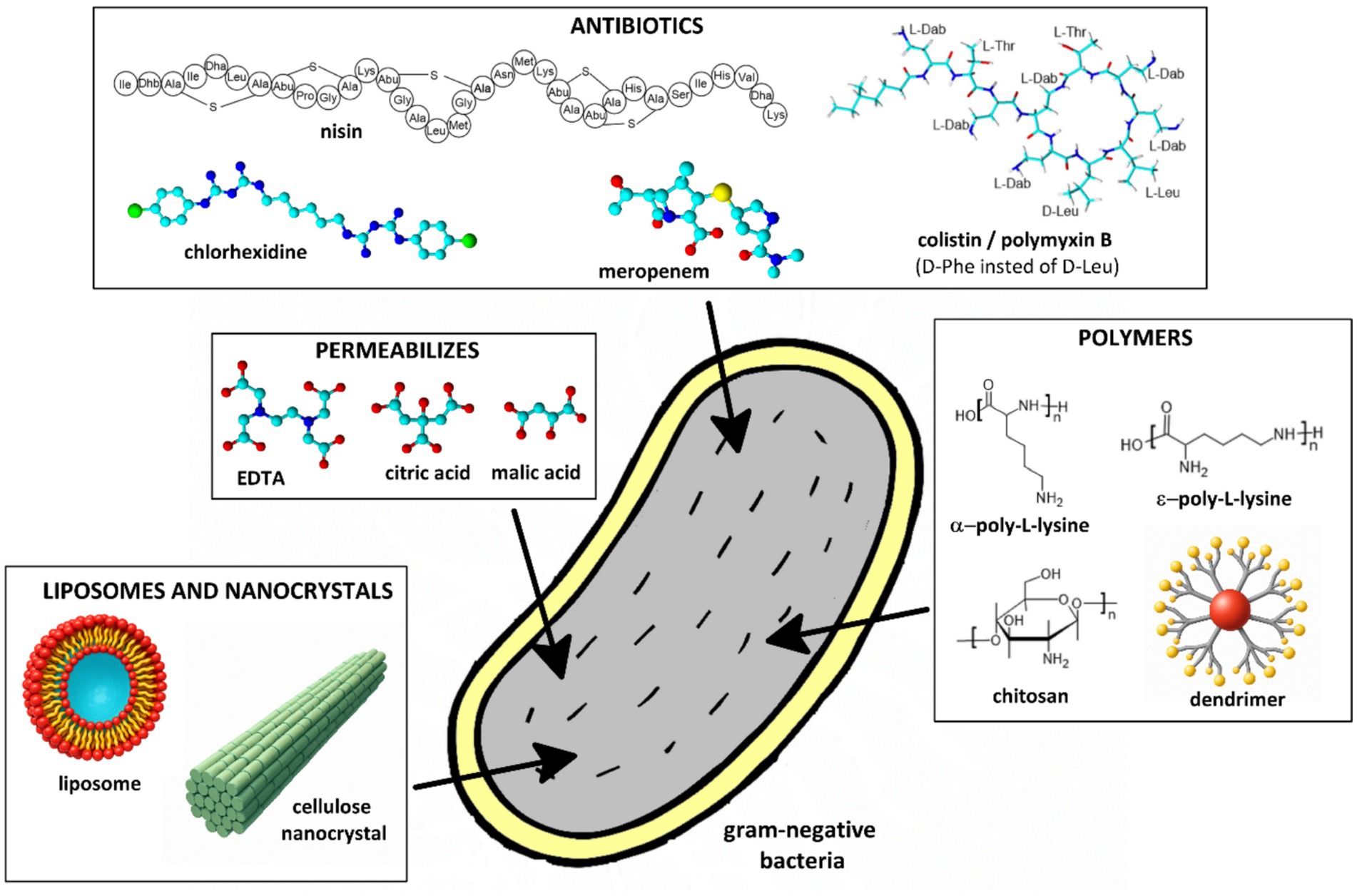
Figure 4. Schematic representation of selected outer membrane permeabilizers used to enhance the efficacy of endolysins against gram-negative bacteria.
3.1.1 Use of endolysins with chemical permeabilizes
Studies show that endolysins combined with permeabilizers such as ethylenediaminetetra acetic acid (EDTA) or organic acids lead to a notable increase in bacterial cell lysis (Figure 4). The combination of endolysin LysE and EDTA demonstrated a biofilm-preventive effect against Aeromonas hydrophila. EDTA enhanced the access of LysE to the bacterial cell wall, leading to a one-log reduction in A. hydrophila planktonic cells (Baliga et al., 2023). The endolysin SPN9CC, when used with EDTA, exhibited a significant bactericidal effect against E. coli. A combination of 300 μg/mL of endolysin with 1 mM EDTA resulted in a four-log reduction in bacterial counts—double the reduction observed with SPN9CC alone. EDTA alone did not significantly affect bacterial viability, indicating that its role was primarily to enhance endolysin access by disrupting the outer membrane (Lim et al., 2014). The endolysins OBPgp279, PVP-SE1gp146, 201φ2-1gp229, when combined with EDTA, showed increased antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa. This effect was attributed to EDTA’s ability to chelate divalent cations, destabilizing the outer membrane and allowing endolysin access (Walmagh et al., 2012). The combination of two endolysins (PsP3gp10 and K11gp3.5) with EDTA led to a 2.62-log reduction in P. aeruginosa PAO1 viability, demonstrating an effective strategy for enhancing endolysin-based antibacterial approaches. Briers et al. explored explored the use of outer membrane permeabilizers such as EDTA, citric acid, poly-L-lysine, and polymyxin B nonapeptide to enhance the antibacterial activity of the bacteriophage endolysin EL188 against P. aeruginosa. Among these, EDTA was found to be the most effective, significantly increasing bacterial permeability and enabling EL188 to reduce P. aeruginosa viability by up to 4 log units within 30 min. The study highlighted a strain-dependent effect, with higher-resistance strains requiring greater concentrations of EDTA for efficient permeabilization (Briers et al., 2011).
In addition to EDTA, other permeabilizers such as organic acids have been investigated for their ability to disrupt the outer membrane and potentiate the activity of endolysins (Oliveira et al., 2014, 2016; Plotka et al., 2015, 2019; Shen et al., 2023). Among them, citric acid and malic acid (Figure 4) have shown promising effects due to their capacity to acidify the microenvironment and destabilize the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) layer without relying on metal ion chelation. Unlike EDTA, which functions by sequestering divalent cations (Mg2+, Ca2+) and disrupting ionic bridges in the LPS structure, organic acids exert their activity primarily by reducing the pH and protonating phosphate groups within the outer membrane, leading to membrane destabilization. Oliveira et al. investigated the antibacterial potential of the thermostable Lys68 endolysin derived from an S. enterica phage. The study focused on how weak acids (EDTA, citric acid, malic acid) act as permeabilizers, enhancing the bactericidal activity of Lys68 against gram-negative pathogens. Weak acids disrupt the outer membrane, allowing Lys68 to hydrolyze the bacterial cell wall, leading to rapid bacterial lysis. Without permeabilizers, Lys68 alone showed limited activity, but in combination, it exhibited significantly enhanced bactericidal effects against S. enterica, E. coli, and K. pneumoniae. The permeabilizers also contributed to biofilm disruption, increasing overall antimicrobial efficacy. The study confirmed that Lys68 remains thermostable, retaining its activity under various temperature conditions, which could be advantageous for industrial and medical applications (Oliveira et al., 2014). The same authors (Oliveira et al., 2016) demonstrate that organic acids played a crucial role in enhancing the antibacterial efficacy of the endolysin ABgp46 against gram-negative bacteria. Citric acid and malic acid were tested as outer membrane permeabilizers, allowing ABgp46 to reach and degrade the bacterial cell wall, leading to effective bacterial lysis. The same permeabilizer improved the lytic activity of Ts2631 endolysin against MDR gram-negative pathogens, including P. aeruginosa and K. pneumoniae (Plotka et al., 2015, 2019). Other authors investigated the potential of combining a phage-derived endolysin with citric acid to enhance antibacterial efficacy against Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae (Psa), an important plant pathogen affecting kiwifruit. The research focuses on the endolysin PlyPa03, which, on its own, had limited activity against P. syringae due to the protective outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. However, the addition of citric acid as a permeabilizer destabilized the bacterial outer membrane, allowing PlyPa03 to access and degrade the peptidoglycan layer. Experimental results demonstrate that the combination significantly improves bacterial lysis compared to either agent alone, suggesting a promising biocontrol strategy for managing Psa infections in kiwifruit orchards (Sisson et al., 2024a).
Recent studies have demonstrated that combining citric or malic acid with phage-derived endolysins can significantly enhance bactericidal activity against Salmonella spp. under mildly acidic conditions (pH 5.0–6.0) (Oliveira et al., 2014, 2016). These combinations were particularly effective in reducing bacterial viability in food preservation and clinical isolate contexts, and represent an attractive alternative for situations where chelating agents such as EDTA are not desirable. Importantly, organic acids are generally regarded as safe and are already used in food and pharmaceutical formulations, which supports their potential in translational applications involving endolysin-based antimicrobials.
The use of chemical permeabilizers such as EDTA and weak acids improves the efficacy of endolysins against gram-negative bacteria. These combinations enhance bacterial cell wall penetration, leading to increased bactericidal activity, and biofilm disruption (Walmagh et al., 2012, 2013; Briers et al., 2014a; Lim et al., 2014; Yang et al., 2015; Defraine et al., 2016; Ni et al., 2021; Abdelkader et al., 2022; Baliga et al., 2023).
3.1.2 Combining endolysins with antibiotics
Combining endolysins with antibiotics that disrupt the outer membrane had also been shown to improve antibacterial activity (Figure 4). For instance, Thummeepak et al. investigated the antibacterial activity of the endolysin LysABP-01, derived from the A. baumannii bacteriophage ØABP-01. Their study demonstrated that LysABP-01 exhibited significant lytic activity against A. baumannii, particularly when combined with colistin—a last-resort antibiotic. Colistin disrupts the outer membrane, enhancing endolysin efficacy. The synergistic effect significantly increased bacterial killing, suggesting a promising strategy for treating multidrug-resistant A. baumannii infections (Thummeepak et al., 2016). Similarly, Blasco et al. tested the efficacy of combining colistin with the endolysins ElyA1 and ElyA2 against multidrug-resistant bacterial strains. Their study demonstrated enhanced antibacterial activity both in vitro and in vivo when endolysins were used in combination with colistin (Blasco et al., 2020). Another example involves Sitthisak et al. who developed recombinant endolysin LysAB-vT2 and its hydrophobic fusion variant LysAB-vT2-fusion. These endolysins exhibited a synergistic effect with polymyxin antibiotics (colistin, polymyxin B). The hydrophobic fusion variant improved bacterial lysis by enhancing the ability of the endolysin to interact with and disrupt the bacterial cell wall. The combination with polymyxins further potentiated their antimicrobial activity, providing a robust approach against drug-resistant gram-negative bacteria (Sitthisak et al., 2023). The research demonstrated that when used together, colistin and endolysins exhibit a synergistic effect, significantly improving bacterial killing compared to either agent alone. This combination therapy offers a promising strategy to combat infections caused by multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria (Zhang P. et al., 2024). The study presented by Oliveira et al. (2024) investigated a novel endolysin derived from the P. aeruginosa bacteriophage vB_PaeM_USP2. Biochemical assays demonstrated that rEnd2 possesses peptidoglycan-degrading activity, effectively targeting the bacterial cell wall. When combined with colistin, rEnd2 exhibited a synergistic antibacterial effect against P. aeruginosa (Oliveira et al., 2024). Tyagi et al. analyzed the interaction between bacteriophage endolysins (T7L, T4L) and antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) such as colistin, nisin, and polymyxin B to combat bacterial biofilms. Their study demonstrated that the combination provides a synergistic effect, significantly enhancing the eradication of bacterial biofilms compared to using either agent alone. This approach could be especially valuable for treating persistent bacterial infections protected by biofilms (Tyagi et al., 2024). The combination of endolysins and permeabilizers also presents a promising antibacterial strategy for food safety applications, helping to control S. enterica contamination in food products (Shen et al., 2023). The study (Shavrina et al., 2016) demonstrated that the bacteriophage T5 endolysin (EndoT5) showed significantly enhanced antibacterial activity against E. coli when combined with membrane-permeabilizing agents. The most effective permeabilizers included polymyxin B and chlorhexidine, which reduced bacterial counts by five orders of magnitude. Poly-L-lysine also contributed to a four-order reduction in CFUs (colony-forming units). The study highlighted a strong synergistic effect between EndoT5 and these agents, enabling efficient bacterial lysis (Shavrina et al., 2016).
A very interesting study prepared by Kim et al. (2023) explores the synergistic antibacterial activity of endolysin and depolymerase in combating S. enterica biofilms. While depolymerases break down biofilm exopolysaccharides, making bacteria more vulnerable to antimicrobial agents, the endolysins degrade the peptidoglycan layer in bacterial cells. The combination of phage-derived endolysin and depolymerase significantly enhanced biofilm disruption and bacterial killing compared to either enzyme alone. The dual-enzyme approach effectively reduced biofilm biomass and increased the susceptibility of biofilm-embedded S. typhimurium cells to lysis. This strategy presents a promising alternative to conventional antibiotics for controlling persistent S. enterica infections, especially in environments promoting the bacterial biofilm formation (Kim et al., 2023).
Sauve et al. investigated the efficacy of CF-370, an engineered lysin, against multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria, particularly P. aeruginosa. CF-370 demonstrated potent antimicrobial activity with minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for P. aeruginosa at 0.5 μg/mL. Notably, CF-370 exhibited bactericidal properties, effectiveness in human serum, low resistance development, anti-biofilm activity, and synergistic effects when combined with antibiotics. In a rabbit acute pneumonia model, combining CF-370 with meropenem significantly improved bacterial clearance from lung tissues compared to either agent alone, suggesting a promising therapeutic approach for antibiotic-resistant gram-negative bacteria (Sauve et al., 2024). Hong et al. demonstrated that combining EC340 with antibiotics such as colistin or meropenem significantly increased bactericidal effects against E. coli and other resistant gram-negative pathogens. The combinations allowed for lower antibiotic concentrations while maintaining or improving antimicrobial efficacy, which was crucial for preventing antibiotic resistance development. Additionally, the EC340-antibiotic combination effectively disrupted bacterial biofilms, which were often resistant to conventional treatments (Hong et al., 2022).
Baliga et al. explored alternative antimicrobial strategies against multidrug-resistant Aeromonas hydrophila, a gram-negative pathogen found in freshwater environments. The purified recombinant LysE protein showed substantial antimicrobial activity against A. hydrophila, particularly when combined with membrane-permeabilizing agents such as EDTA. LysE also reduced biofilm formation and exhibited synergistic effects with low concentrations of colistin. Importantly, cytotoxicity assays using Channa striatus kidney cell lines indicated that LysE was non-toxic to animal cells, highlighting its potential as an effective antimicrobial agent in aquaculture, food safety, and healthcare applications (Baliga et al., 2023).
3.1.3 Combination of endolysins with polymers
Polymer-based approaches, including the use of permeabilizers, dendrimers, liposomes, and enzyme immobilization, have been explored to enhance the efficacy of endolysins against gram-negative bacteria (Figure 4). Zhang et al. characterized S. enterica endolysin XFII, produced recombinantly in E. coli, evaluating its lytic activity, stability, and antibacterial efficacy. Additionally, the researchers explored combining XFII with chitosan, a natural antimicrobial agent, to enhance bacterial lysis. The combination of XFII and chitosan significantly improved antibacterial activity, offering a promising solution for treating gram-negative infections (Zhang et al., 2022). Another study investigated the impact of combining endolysin Lysqdvp001 with a permeabilizer ε-poly-lysine to enhance its antibacterial activity against Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its biofilms. The permeabilizer facilitated Lysqdvp001 penetration through the bacterial outer membrane, significantly improving its lytic efficiency and disrupting biofilms resistant to conventional antimicrobial agents (Ning H. Q. et al., 2021).
Dendrimers are highly branched, nano-sized macromolecules with a well-defined, symmetrical structure. Their unique architecture allows them to be monodisperse, meaning they have uniform size and structure, unlike conventional polymers. Due to their high functional group density, dendrimers exhibit exceptional properties such as high solubility, low toxicity, and the ability to form multivalent interactions. These characteristics make them particularly useful in biomedical applications, including drug delivery, gene therapy, diagnostic imaging, and antimicrobial treatments (Abbasi et al., 2014). The study Ciepluch et al. (2019) investigated the potential of combining phage-derived endolysins with cationic dendrimers to combat P. aeruginosa, a gram-negative bacterium notorious for antibiotic resistance. Cationic dendrimers, which carry a positive charge, can disrupt the bacterial outer membrane, enhancing the accessibility and activity of endolysins. Their study demonstrated that a specific phage endolysin combined with poly(propyleneimine) dendrimers resulted in significantly improved bacterial lysis compared to the endolysin alone. This suggests that cationic dendrimers aid in penetrating the outer membrane, enhancing the overall antibacterial efficacy of endolysins (Ciepluch et al., 2019). Quintana-Sanchez et al. studied PEGylated carbosilane dendrimers, which exhibited direct antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa by disrupting bacterial membranes. When combined with a phage-derived endolysin, the antibacterial effect was significantly enhanced, suggesting a synergistic interaction. The study demonstrated that dendrimers facilitated better access of endolysins to the bacterial peptidoglycan layer by compromising the outer membrane. This combination therapy was particularly effective against antibiotic-resistant strains, highlighting its potential as an alternative antimicrobial strategy (Quintana-Sanchez et al., 2022).
3.1.4 Liposomal and nanotechnology-based delivery systems
Another innovative approach explored the use of liposomes as delivery systems for endolysins to enhance their efficacy against gram-negative bacteria (Gondil and Chhibber, 2021). The researchers encapsulated endolysins within liposomes, which serve as carriers to facilitate their transport and release at the bacterial cell wall. The study involved formulating and characterizing cationic liposomes containing dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), cholesterol, and hexadecylamine, encapsulation BSP16Lys endolysin efficiency, and antimicrobial activity tests. The results demonstrated that liposome-encapsulated endolysins exhibited significantly improved antibacterial effects compared to free endolysins, particularly against multidrug-resistant gram-negative strains (Bai et al., 2019). Other authors, Morais et al. encapsulated newly identified prophage lysins (Pa7 and Pa119) within DMPC (dimirystoilofosfatydylocholina):DOPE (dioleoyl phosphatidylethanolamine):CHEMS (cholesteryl hemisuccinate) (4:4:2 molar ratio) liposomes to enhance their antibacterial efficacy against P. aeruginosa. The study demonstrated improved stability, bioavailability, and penetration of bacterial defenses. Evaluations both in vitro and in a P. aeruginosa infection model confirmed that liposome-encapsulated lysins exhibited enhanced antibacterial effects compared to free lysins (Morais et al., 2022). Encapsulation of phage lysin Lysqdvp001 in liposomes to enhance its stability and antibacterial activity against seafood-related pathogens was also tested. The liposomal formulation effectively inhibited the growth of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in live clams, reducing the risk of spoilage. The treatment showed no significant impact on the quality or viability of the clams, making it a promising alternative to traditional preservatives (Ning et al., 2023).
The immobilization of lysozymes (hen egg white lysozyme and T4 lysozyme) onto positively charged cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) was used to enhance their antibacterial activity and stability. Immobilization onto CNCs protected lysozymes from degradation and extended their functional lifespan. The modified lysozymes showed stronger antibacterial effects against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria compared to free enzymes. The immobilized enzymes provided a gradual and prolonged antibacterial effect, making them more effective in long-term applications (Abouhmad et al., 2017).
3.2 Modifications of endolysins for improving outer membrane penetration
Genetic engineering of endolysins to enhance their hydrophobic properties and positive charge has become a crucial strategy for improving their efficacy against gram-negative bacteria. These modifications help endolysins overcome the barrier posed by the negatively charged LPS in the outer membrane.
3.2.1 Fusion of endolysins with antimicrobial peptides
One of the most effective approaches involves fusing endolysins with membrane-active peptides to facilitate outer membrane penetration and enhance bactericidal activity (Table 2). A notable example is Artilysins®, developed by Lysando AG, which are engineered fusion proteins combining endolysins with antimicrobial or membrane-penetrating peptides (Schirmeier et al., 2018; Lysando, 2025). These hybrid molecules disrupt the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria, allowing the catalytic domain of the endolysin to access and degrade the PG layer (Carratalá et al., 2023). Examples of such constructs include the fusion of the cecropin A peptide (Figure 5) with OBPgp279W (Yang et al., 2015), AbEndolysin (Islam et al., 2022), and the LysMK34 endolysin (Abdelkader et al., 2022). In a study by Lim et al., researchers engineered the ST01 endolysin fused with cecropin A to target multidrug-resistant A. baumannii. This construct exhibited potent antimicrobial activity against clinical isolates. The fusion effectively disrupted bacterial membranes, leading to rapid cell death and significantly reduced bacterial counts in a mouse bacteremia model, highlighting its therapeutic potential (Lim et al., 2022a). Similarly, Jeong et al. (2023) characterized three distinct endolysins (Lys10-24(13), LysPBEC30, and LysPBEC56) and evaluated their bactericidal efficiency and structural properties. Their research demonstrated that fusing these endolysins with cecropin A enhanced their outer membrane penetration and antibacterial activity against E. coli, P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii, and K. pneumoniae (Jeong et al., 2023). Cho and You further demonstrated that fusing cecropin A to the endolysin mtEC340 significantly improved its interaction with LPS and increased its bactericidal activity against E. coli model (Figure 6). Their study emphasized that the cecropin A fusion accelerated bacterial membrane disruption, facilitating rapid cell death. This strategy also proved effective against bacterial strains with defects in their core oligosaccharides, underscoring the importance of LPS interaction in enhancing endolysin activity (Cho et al., 2024). LysAB2, derived from A. baumannii phage, was fused with the cecropin A (1-8) fragment, improving its penetration through the outer membrane and increasing its activity against multidrug-resistant A. baumannii (Chen et al., 2021).
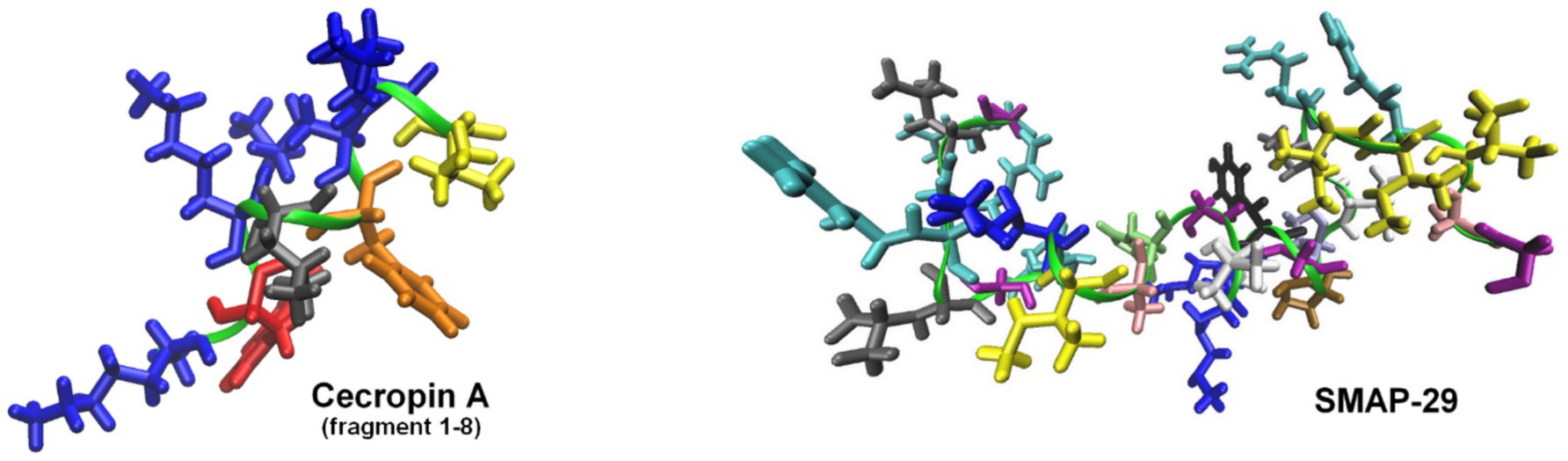
Figure 5. Structures of representative peptides fused with endolysins to enhance their antibacterial activity against gram-negative bacteria. The models of cecropin A (fragment 1-8) and SMAP-29 peptides were visualized based on the solution NMR structure with PDB codes: 1DYJ (Oh et al., 1999) and 1FRY (Tack et al., 2002), respectively. Peptides form helices marked as green ribbon, with the Lys side-chains shown in blue, Trp in red, Leu in gray, Phe in orange, Ile in yellow, Ala in pink, Arg in cyan, Gly in purple, His in lime, Pro in ochre, Thr in iceblue, Tyr in black, and Val in white. The figures were prepared with VMD (Humphrey et al., 1996).
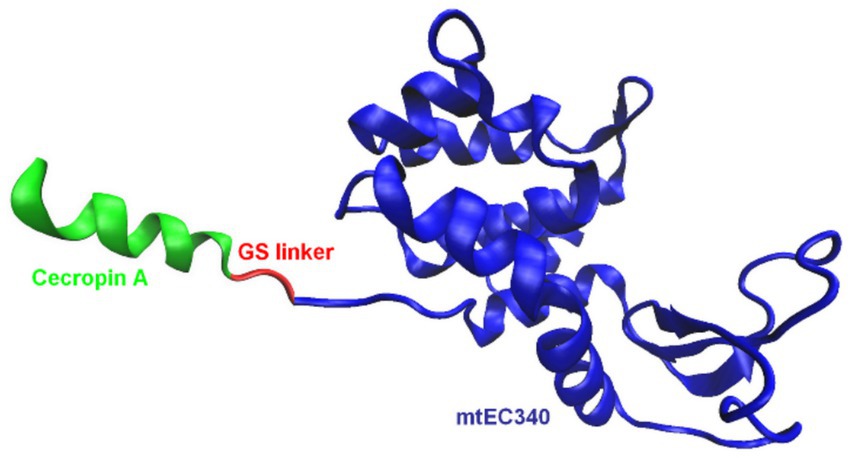
Figure 6. Schematic representation of an example of endolysin fusion with a peptide: LNT113 (Cho et al., 2024). The artilysin is composed of the Cecropin A peptide fused to the mtEC340 endolysin. The model of the mtEC340 endolysin was visualized based on the X-ray crystallography structure, PDB code: 8HP8 (Wang et al., 2023). The figure was prepared using VMD software (Humphrey et al., 1996).
Other studies described a conjugation of LysPA26 (Wang et al., 2021) and KZ144 (Briers et al., 2014a; Defraine et al., 2016) with antimicrobial peptide SMAP-29 (Figure 5). Art-085 and Art-175, derived from KZ144 fused with SMAP-29, exhibited enhanced bactericidal efficacy against pathogens like P. aeruginosa, E. coli (Briers et al., 2014a), and A. baumannii (Defraine et al., 2016). In another study, Antonova et al. explored how fusing different cationic and amphipathic peptides to the endolysin LysECD7 improved its bactericidal activity against gram-negative bacteria. This research demonstrated that specific peptide tags significantly enhanced the enzyme’s lytic efficiency (Antonova et al., 2020; Vasina et al., 2024). Sitthisak et al. further optimized endolysins by adding hydrophobic amino acids to the C-terminus of LysAB-vT2, increasing its lytic activity. These hydrophobic fusion constructs exhibited enhanced efficacy when combined with colistin and polymyxin B (Sitthisak et al., 2023). A particularly innovative fusion, Tha-PA90, developed by Lim et al. combined the antimicrobial peptide thanatin with the endolysin PA90. This fusion exhibited strong lytic activity against A. baumannii, including antibiotic-resistant strains, and effectively disrupted biofilms. In vivo studies using a mouse infection model confirmed that Tha-PA90 significantly reduced bacterial loads and improved survival rates, making it a promising alternative for treating A. baumannii infections (Lim et al., 2024). A polycationic nonapeptide (PCNP) had also been used as a carrier to deliver endolysins into gram-negative bacterial cells. One study demonstrated that PCNP effectively addressed a broad range of MDR gram-negative pathogens, making it a versatile tool for combating various bacterial infections (Briers et al., 2014b). Another study focused on Helicobacter pylori, emphasizing its role in gastrointestinal diseases (Xu et al., 2021).
Ma et al. engineered Lysep3 by inserting cationic peptides into its C-terminal region, increasing its interaction with the bacterial outer membrane and improving its antimicrobial activity (Ma et al., 2017). The same cationic peptides were fused to the Lysqdvp001 endolysin, significantly enhancing antimicrobial activity against V. parahaemolyticus strains (Ning H. et al., 2021). Similar results were achieved by Yan et al. who introduced hydrophobic amino acids to Lysep3, increasing its lytic efficacy under specific pH conditions (Yan et al., 2019). Another innovative approach involved combining endolysins with sensitizer peptides to improve their ability to penetrate the outer membrane. Son, Kim, and Ryu engineered Lys1S-L9P by fusing Lys1S with the sensitizer peptide KL-L9P, with enhanced bactericidal activity against MDR E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and A. baumannii (Son et al., 2023). Lim et al. fused the PA90 endolysin with a cell-penetrating peptide (CPP), DS4.3, demonstrated efficient bacterial eradication, biofilm disruption, and reduced cytotoxicity in vitro and in vivo (Lim et al., 2022b). Li et al. improved the antibacterial efficacy of LysECD7 by fusing it with LPS-interacting peptides and modifying it with fatty acid derivatization. These modifications significantly enhanced bacterial killing and infection clearance (Li et al., 2024). The novel recombinant endolysin (rEnd2), derived from P. aeruginosa phage vB_PaeM_USP2, particularly when combined with colistin. Further conjugation of rEnd2 with polycationic-polymer nanoparticles improved its stability and antimicrobial activity, suggesting promising potential for treating MDR bacterial infections (Oliveira et al., 2024).
In the study prepared by Siu et al. researchers constructed a chimeric endolysin library by inserting an oligonucleotide sequence of 20 repeated NNK codons upstream of the endolysin gene Bp7e. This library was expressed in E. coli and screened for variants exhibiting extracellular antibacterial activity. One engineered endolysin, named Art-Bp7e6, demonstrated significant bactericidal effects against E. coli. Further analysis revealed that the chimeric peptide depolarized the bacterial cell envelope, increased cell permeability, and facilitated enzyme access to degrade peptidoglycan, providing a novel platform for engineering and screening highly active endolysins (Sui et al., 2023). Other researchers engineered endolysins derived from a K. pneumoniae phage, fusing them with peptides ApoE23 and COG133 to create chimeric proteins. These engineered endolysins were tested in vitro against ESKAPEE pathogens (Enterococcus faecium, S. aureus, K. pneumoniae, A. baumannii, P. aeruginosa, Enterobacter spp., and E. coli). The results demonstrated that the chimeric endolysin ApoE23-Kp84B (CHU-1) achieved a reduction growth of A. baumannii, E. faecalis, and K. pneumoniae. Similarly, COG133-Kp84B (CHU-2) exhibited significant efficacy against S. aureus (Chen et al., 2024).
These studies highlight the substantial progress in engineering endolysins through genetic modifications and peptide fusions. These advancements enhance their ability to penetrate the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria, offering promising therapeutic options against MDR pathogens (Table 2).
The design of AMP–endolysin fusion constructs plays a critical role in determining their ability to penetrate the outer membrane and reach the periplasmic space, where the endolysin exerts its catalytic activity on the peptidoglycan layer. Naturally occurring endolysins that exhibit antibacterial activity often contain a positively charged peptide domain at their C-terminus, suggesting that C-terminal fusion with antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) might be the preferred strategy. However, current studies explore peptide conjugation at both the N- and C-termini of lysins. N-terminal fusion of AMPs such as SMAP-29 (Briers et al., 2014a; Wang et al., 2021) or cecropin A (Abdelkader et al., 2022; Islam et al., 2022; Lim et al., 2022a; Yang et al., 2015) facilitates initial interaction with and disruption of the bacterial outer membrane, thereby enhancing periplasmic accessibility. Conversely, C-terminal fusions may sterically hinder membrane interaction or result in suboptimal orientation of the AMP moiety, potentially limiting transport efficiency (Antonova et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2021; Ma et al., 2017). To date, no consensus has been reached regarding which terminus should be modified to achieve optimal antimicrobial performance. It seems that the nature of the AMP and its physicochemical properties—including charge, hydrophobicity, amphipathicity, and length—critically influence the antimicrobial potency of the fusion construct. For instance, Artilysins containing the short, highly cationic AMPs have demonstrated broad-spectrum activity and membrane-permeabilizing efficiency, while Lysocins employing longer bacteriocins like Colicin–Lysep3 hybrids (Yan et al., 2017) show higher activity against specific strains but may require optimized linker design for maximal efficacy.
The inclusion of linker sequences between endolysins and fused peptides plays a critical role in modulating the bactericidal activity of engineered fusion constructs. In the study by Antonova et al., three SMAP-29 peptide-fused variants of the LysECD7 endolysin were compared: one without a linker, one with a flexible Gly-Ser-rich linker, and one with a rigid alanine-rich helical linker. The variant lacking a linker (LysECD7-SMAP) exhibited the highest antibacterial activity under physiological conditions (PBS and serum) and against stationary-phase A. baumannii cells. In contrast, the rigid linker construct (LysECD7-rigid-SMAP) showed significantly reduced activity, suggesting that linker rigidity can hinder optimal positioning or membrane interaction of the AMP domain. The flexible linker variant (LysECD7-flex-SMAP) retained intermediate activity, indicating that linker flexibility supports more favorable domain orientation and function (Antonova et al., 2020). The studies by Wang et al. and Chen et al. strongly support that short, flexible linkers preserve the structural integrity and enhance the synergistic activity between AMP and endolysin domains. Overly long or rigid linkers may lead to misfolding or spatial disconnection between functional domains, reducing efficacy (Chen et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2021). These results suggest that linker design-particularly its length, flexibility, and composition-directly influences the spatial arrangement and synergistic activity of fused domains. Thus, systematic linker optimization is essential for enhancing the functional performance of endolysin–peptide fusion constructs, especially when targeting gram-negative pathogens. Rational selection of AMP partners, linker length, and orientation should therefore be guided by the intended target spectrum, membrane composition of the pathogen, and delivery context.
3.2.2 Modular fusion proteins
Modular fusion proteins are engineered biomolecules composed of distinct functional domains that are fused to create a single polypeptide with enhanced or novel properties. These proteins are designed by combining different modules, each responsible for a specific function, such as enzymatic activity, binding specificity, or signal transduction. The modular nature allows for precise customization, enabling fusion proteins to perform complex biological tasks efficiently. Fusion proteins can be designed for biomedical applications, including targeted drug delivery, immunotherapy, enzyme engineering, and synthetic biology. One common strategy in designing modular fusion proteins is the fusion of enzymatically active domains with cell-binding domains to improve specificity and efficacy, particularly in therapeutic applications (Lin and Liu, 2016; Yi et al., 2022).
The endolysin 1D10 was engineered as a fusion protein composed of four modules: catalytic domain—responsible for hydrolyzing the peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall, binding module—ensures specific binding to target bacteria, cationic peptide—cecropin A, which increases outer membrane permeability in gram-negative bacteria, and stabilizing domain—enhances thermal stability and resistance to proteolytic degradation. The modified lysin demonstrated increased thermal stability and proteolytic resistance, making it more effective under physiological conditions. Unlike traditional endolysins, which require membrane permeabilization, 1D10 exhibited direct bactericidal activity, degrading the bacterial cell wall even in the presence of an intact outer membrane. Studies confirmed that 1D10 activity depends on both the presence of cecropin A and the catalytic domain. Deletion analysis further defined the role of each module in the enzyme’s mechanism of action. The lysin effectively killed a range of MDR gram-negative bacteria, including P. aeruginosa and K. pneumoniae. Given its stability and unique killing mechanism, 1D10 represents a promising candidate for alternative antimicrobial therapies against antibiotic-resistant infections (Gerstmans et al., 2023).
In contrast, another study focused on the characterization and application of Plychap001, a single catalytic domain of the Lysqdvp001 endolysin, for controlling V. parahaemolyticus and its biofilms. Plychap001 effectively degraded V. parahaemolyticus cells, demonstrating strong bactericidal properties. The single endolysin domain reduced biofilm formation, highlighting its potential as an agent for biofilm-associated infections. The study emphasized Plychap001’s potential application in the food industry to combat Vibrio-related contamination (Wang et al., 2022). The addition of the D8 binding domain from the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens bacteriophage endolysin to E. coli bacteriophage endolysin Lysep3 significantly increased its ability to bind and degrade E. coli peptidoglycan. The modified Lysep3 exhibited stronger lytic activity against E. coli compared to the original enzyme (Wang et al., 2017). These studies suggest that fusion with specialized binding domains can enhance endolysin efficacy against gram-negative bacteria, offering a promising strategy for combating antibiotic-resistant infections.
3.2.3 Innolysins: receptor-binding protein-endolysin fusions
Athina Zampara and her colleagues had conducted pioneering research on “Innolysins” engineered molecules designed to combat gram-negative bacteria by fusing bacteriophage endolysins with receptor-binding proteins (RBPs). This fusion enables endolysins to target specific bacteria, overcoming the outer membrane barrier that typically restricts access to the peptidoglycan layer. In their study, the researchers introduced the Innolysins concept by fusing the endolysin from bacteriophage T5 with its RBP, Pb5. Among the engineered constructs, Innolysin Ec6 demonstrated bactericidal activity against E. coli, reducing bacterial counts by approximately 1 log in bacterial counts. This antibacterial effect was dependent on the presence of the FhuA receptor, the specific target of Pb5 on E. coli cells. Furthermore, Innolysin Ec6 exhibited activity against other bacteria possessing FhuA homologs, such as Shigella sonnei and P. aeruginosa. Expanding the Innolysin approach, the researchers targeted Campylobacter jejuni, a leading cause of foodborne illnesses. The team identified an H-fiber from a CJIE1-like prophage in C. jejuni CAMSA2147, which functions as a novel RBP. By fusing this H-fiber to phage T5 endolysin, they created Innolysin Cj1, which exhibited antibacterial activity against various C. jejuni strains, achieving up to a 1.30 ± 0.21 log reduction in bacterial counts after 45 min of exposure at 20°C. Additionally, the application of Innolysin Cj1 on contaminated chicken skin at 5°C resulted in a 1.63 ± 0.46 log reduction of C. jejuni cells, demonstrating its potential for food safety applications (Zampara et al., 2021). The modular nature of Innolysins allows for customization by selecting different combinations of endolysins and RBPs, enabling the targeting of a broad spectrum of gram-negative pathogens. Zampara’s work represents a significant advancement in the development of novel antibacterial agents, offering a promising strategy to address the growing challenge of antibiotic-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections (Zampara et al., 2020, 2021).
3.2.4 Lysocins: bacteriocin-endolysin fusions
Another innovative study introduces “Lysocins,” a novel class of bioengineered antimicrobial molecules that fuse bacteriophage lysins with bacteriocins—bacterial toxins inhibiting the growth of related bacterial strains. The study utilizes bacteriocins as a delivery mechanism to transport lysins across the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. The engineered Lysocin PyS2-GN4, which combines the bacteriophage lysin GN4 with the P. aeruginosa bacteriocin Pyocin S2 (PS2), exhibited high lytic activity against P. aeruginosa. In vitro studies showed that Lysocins effectively killed P. aeruginosa, disrupted biofilms, and had minimal endotoxin release, making them superior to conventional antibiotics in human serum. In vivo experiments in a mouse model confirmed that Lysocins could significantly reduce bacterial infections, suggesting their potential as an alternative therapeutic strategy (Heselpoth et al., 2019). Yan et al. (2017) investigated how the N-terminal and central domains of Colicin A, a bacteriocin secreted by E. coli, enhance the extracellular lytic activity of a Lysep3 endolysin. The fusion of Colicin A domains with Lysep3 enabled the enzyme to bypass the outer membrane of E. coli, facilitating direct bacterial lysis. The N-terminal and central domains of bacteriocin were crucial for membrane disruption, allowing the phage lysin to reach the peptidoglycan layer. The engineered Colicin-Lysep3 fusion exhibited enhanced bactericidal activity, showing promise for antibiotic-free treatment strategies against E. coli. Domains of the same bacteriocin were conjugated to Campylobacter-derived lysins. Although this lysin was not derived from a bacteriophage, the study confirmed that conjugating lytic enzymes with bacteriocin domains significantly improves activity (Liu P. et al., 2023). By leveraging the specific receptor-binding properties of bacteriocins, Lysocins selectively target and kill certain gram-negative pathogens. The combination of lysins’ peptidoglycan-degrading ability and bacteriocins’ membrane-penetrating properties significantly enhances antimicrobial efficacy, positioning Lysocins as a promising next-generation antibacterial approach.
4 Use of endolysins that can penetrate the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria to design membrane-active peptides
Until recently, only a few endolysins with intrinsic antibacterial activity against gram-negative species were known (Lim et al., 2014; Thandar et al., 2016; Larpin et al., 2018; Sykilinda et al., 2018; Raz et al., 2019; Bai et al., 2020; Kim et al., 2020; Chu et al., 2022; Euler et al., 2023). The antibacterial efficacy of endolysins against gram-negative bacteria depends on two key properties: (i) enzymatic activity, which enables degradation of the PG layer and (ii) membrane permeabilization, which facilitates endolysin translocation into bacterial cells. Several natural features enabling outer membrane permeabilization have been identified in endolysins: many endolysins contain highly positively charged C-terminal segments. Some endolysins possess one or more amphipathic helices, the C-terminal fragments of these endolysins enhance outer membrane permeability. Researchers hypothesize that amphipathic helices competitively displace divalent cations, which stabilize the LPS layer, leading to local outer membrane disruption and allowing endolysin to translocate into gram-negative bacteria. Once inside, the PG layer is degraded, resulting in bacterial lysis.
Several cationic peptides with bactericidal properties had been successfully isolated from whole endolysin proteins (Düring et al., 1999; Thandar et al., 2016; Li et al., 2021; Heselpoth et al., 2022; Szadkowska et al., 2022; Vázquez et al., 2022a, 2022b). Their activity was summarized in Table 3.
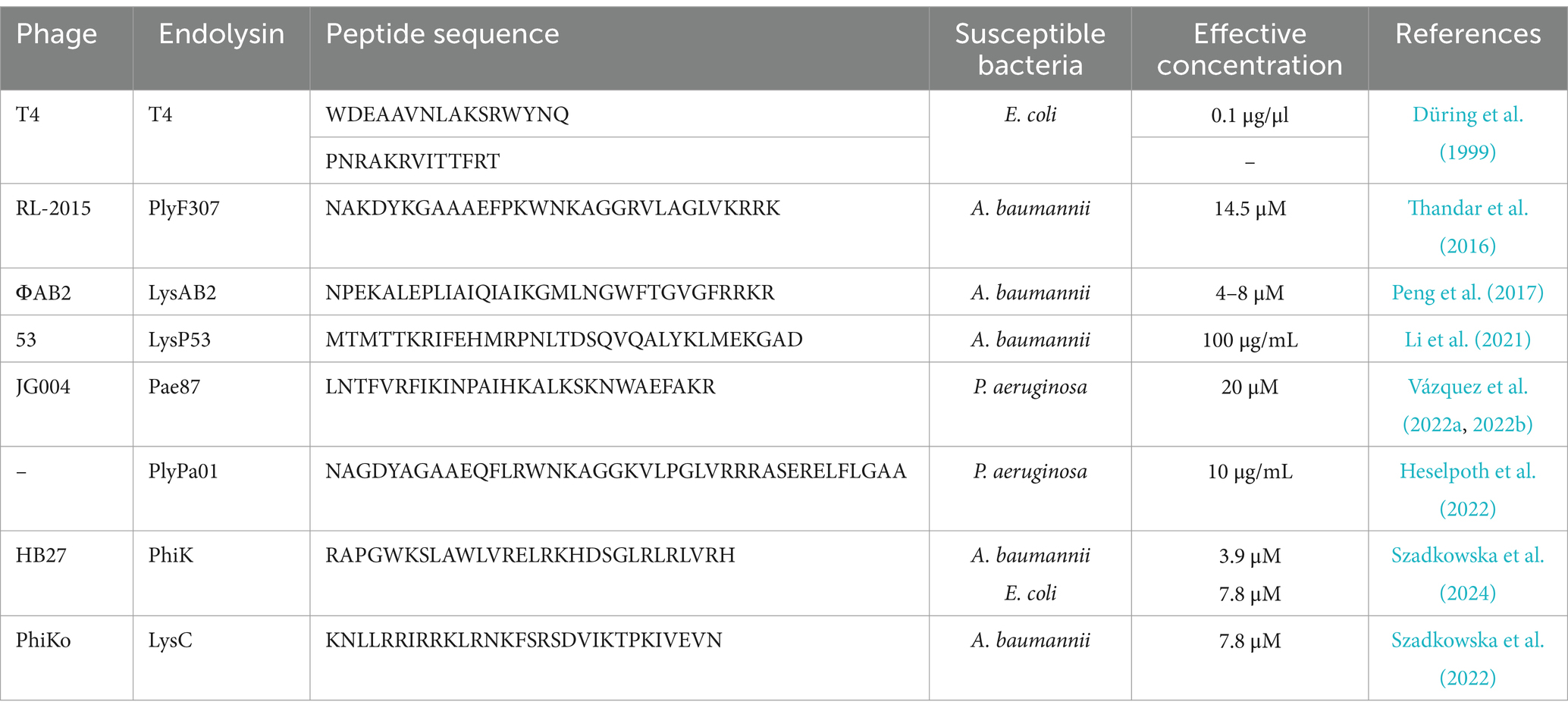
Table 3. Antimicrobial activity of peptides derived from phage endolysins of gram-negative bacteria.
Düring et al. (1999) investigated the non-enzymatic microbicidal activity of lysozymes, particularly the T4 lysozyme. The study showed that amphipathic helix in the C-terminal region play a crucial role in antibacterial and fungistatic activities, even after heat denaturation. Synthetic peptides imitating to the C-terminal amphipathic domains exhibited microbicidal activity by disrupting bacterial and fungal cell membranes. However, they did not induce hemolysis in mammalian cells, suggesting selective antimicrobial action. The findings indicate that these peptides act by destabilizing microbial membranes while remaining non-hemolytic to mammalian (Düring et al., 1999). This work had inspired other researchers, who had focused on extracting short, active peptides from the endolysin sequences.
Thandar et al. (2016) engineered peptides derived from PlyF307, a phage lysin, targeting A. baumannii. The study identified a highly cationic C-terminal domain, which, after modification, exhibited enhanced antibacterial potency (Figure 3). The engineered peptides showed strong bactericidal activity in vitro and in vivo, particularly in murine skin infection models (Thandar et al., 2016). Researchers Li et al. (2021) characterized LysP53, a novel endolysin from an A. baumannii phage. Its first 33 amino acids (P104) were identified as a potent antimicrobial peptide capable of killing multidrug-resistant gram-negative pathogens. The antimicrobial peptide P104 exhibited bactericidal activity comparable to full-length LysP53, demonstrating high efficacy against A. baumannii, P. aeruginosa, K. pneumoniae, and E. coli (Li et al., 2021).
The paper Vázquez et al. (2022b) explores the structural and functional properties of the endolysin Pae87 from P. aeruginosa phage JG004, which were promising alternatives to conventional antibiotics, particularly against antibiotic-resistant P. aeruginosa. The crystal structure of Pae87 was determined, revealing the C-terminal region of Pae87 containing a positively charged AMP-like sequence (P87). This peptide can directly disrupt bacterial outer membranes, providing an additional mechanism for bacterial killing beyond enzymatic lysis. When its catalytic activity was knocked out (via mutations), Pae87 retained bactericidal activity. This suggests that the P87 region alone can act as an antimicrobial agent by permeabilizing bacterial membranes. The same authors improved the antibacterial activity of the peptide P87 through sequence modifications, resulting in the engineered peptide P88 (Vázquez et al., 2022a). The modifications increased its net charge and hydrophobicity, improving membrane interactions. P88 maintained activity against a wide range of P. aeruginosa clinical isolates, including multidrug-resistant strains, indicating its potential as a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent and exhibited synergistic effects when combined with antibiotics like erythromycin, chloramphenicol, tetracycline, and azithromycin. P88 effectively reduced P. aeruginosa biofilms, although its activity against human A549 lung cells was higher compared to other antimicrobial peptides like melittin. The therapeutic index suggests potential for further optimization (Vázquez et al., 2022a).
PaP1 represents a highly potent, lysin-derived antimicrobial peptide with broad-spectrum activity, rapid bactericidal effects, and excellent biocompatibility. Derived from the C-terminal region of PlyPa01 endolysin, which naturally contains a cationic, amphipathic membrane-active region. Its topical use in treating chronic wound infections and biofilm-associated infections makes it a strong candidate for future clinical development. PaP1 permeabilizes the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria and also disrupts the cytoplasmic membrane, leading to bacterial death. This dual mode of action eliminates the need for enzymatic peptidoglycan degradation, which is typical for full-length lysins. PaP1 was effective against a wide range of gram-negative and gram-positive pathogens, including: P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, S. aureus (including methicillin-resistant S. aureus, MRSA), and Enterococcus faecium (including vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, VRE). The peptide was effective in a murine model of burn wound infections, reducing bacterial loads of MRSA and MDR P. aeruginosa, and the enhancement in the efficacy of standard topical antibiotics (e.g., mupirocin, gentamicin), suggested synergistic potential. Combined with low toxicity to human cells (no hemolysis and low cytotoxicity toward neutrophils), PaP1 lysin constituted a safer alternative to existing membrane-targeting antimicrobials like polymyxins (Heselpoth et al., 2022).
Another study explores Intestinalin (P30), a cryptic antimicrobial peptide derived from the LysC enzyme of Clostridium intestinale. Interestingly, the amino acid sequence was similar to the endolysins of phages targeting Thermus scotoductus, isolated from Icelandic hot springs. This peptide was discovered within the N-terminal region of LysC, and its antimicrobial properties surpass those of the full-length enzyme. P30 represents a promising blueprint for the development of novel peptide-based antibiotics, particularly for difficult-to-treat infections and biofilm-associated diseases (Szadkowska et al., 2022). The same authors investigated PhiKo endolysin, an enzyme derived from the phiKo bacteriophage that infects the extremophilic bacterium Thermus thermophilus HB27 (Szadkowska et al., 2024). The research also identifies RAP-29, a cryptic lytic peptide hidden within the C-terminal region of PhiKo. The study provides a comprehensive molecular characterization of the PhiKo endolysin and the cryptic peptide RAP-29. While PhiKo endolysin is highly thermostable but has limited mesophilic activity, RAP-29 emerges as a potent, broad-spectrum AMP. RAP-29 demonstrates strong antimicrobial properties against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, making it a promising candidate for novel antimicrobial therapies. The study validates the concept of cryptic antimicrobial peptides hidden within lysins and proves that bioinformatics-driven peptide discovery can lead to novel antibiotic candidates. Such a promising perspective encourages further modifications to optimize stability, selectivity, and in vivo efficacy (Szadkowska et al., 2024).
The isolated peptides frequently demonstrated comparable or superior antibacterial activity to their full-length endolysins. Moreover, these peptides were effective in vivo, successfully treating bacterial infections and accelerating wound healing in murine models. These findings validate cryptic antimicrobial peptides as a novel antimicrobial strategy, emphasizing the therapeutic potential of lysin-derived peptides for next-generation antibacterial therapies. However, to date, the discovery of AMPs has mostly been based on their similarities to already-known microbicidal molecules. Introducing bioinformatics methods, including machine learning-based predictions, has accelerated potential AMP screening.
5 Using machine learning to design endolysins active against gram-negative bacteria
Computational methods and artificial intelligence are increasingly used to design and optimize endolysins for improved antibacterial activity. These approaches enable rapid modifications, functional predictions, and structural optimizations to enhance the efficacy of lysins against gram-negative bacteria. For example, VersaTile is an innovative modular synthetic biology platform designed to accelerate the engineering and optimization of lysins for antibacterial applications (Gerstmans et al., 2020). This platform allows for rapid assembly and screening of engineered lysins by combining different functional modules, such as cell wall-binding domains and enzymatic cleavage domains. The VersaTile platform created a diverse library of lysin variants, tested for antimicrobial activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The study identified promising lysin candidates with enhanced stability, specificity, and bactericidal activity. For example, engineered variants targeting S. aureus and K. pneumoniae retained activity in serum and under high salt conditions, highlighting their therapeutic potential. VersaTile enables rapid hit-to-lead development, streamlining the discovery of highly effective engineered lysins for potential therapeutic applications (Gerstmans et al., 2020; Duyvejonck et al., 2021; Vander Elst et al., 2023).
The researchers (Tresnak and Hackel, 2023) conducted a comprehensive sequence–function analysis of lysins, evaluating their bactericidal efficiency, thermostability, and structural integrity. Using mutational scanning, they identified key amino acid residues responsible for optimal enzymatic activity and bacterial cell wall degradation. This study provided valuable insights into the structural determinants of lysin function, guiding the rational design of improved lysins with enhanced stability and potency. The findings contribute to the development of engineered lysins with broader antimicrobial activity and enhanced therapeutic potential (Tresnak and Hackel, 2023). The researchers (Zhang Y. et al., 2024) utilized machine learning and deep learning models to analyze large datasets of phage genomes and predict lysins with potential antibacterial activity. This artificial intelligence (AI)-driven approach enabled the discovery of previously unknown lysins, expanding the repertoire of phage-derived antimicrobial agents. Identified lysins were experimentally validated, demonstrating bactericidal activity against various bacterial pathogens, including antibiotic-resistant strains. The study highlights the power of AI in accelerating lysin discovery, offering a more efficient alternative to traditional experimental screening (Zhang Y. et al., 2024). The in silico design and development of novel chimeric lysins with high selectivity against Salmonella were tested. Using a computer-aided design approach, researchers engineered chimeric lysins by fusing different endolysins with antimicrobial peptides to enhance bacterial targeting and lytic activity. Various Salmonella-targeting endolysins were selected and modified through fusion with antimicrobial peptides to improve their binding affinity and lysis efficiency. Computational modeling predicted structural stability and binding interactions of the chimeras with Salmonella peptidoglycan. Molecular docking confirmed that the engineered lysins had a higher binding affinity to the Salmonella cell wall. The fusion peptides improved bacterial membrane interaction, suggesting potential for in vitro and in vivo applications. This study highlights the power of computational tools in designing novel chimeric lysins with enhanced antibacterial properties, paving the way for further experimental validation and therapeutic development (Nie et al., 2021).
The minireview by Bałdysz et al. (2024) provides a comprehensive overview of bioinformatic tools and databases relevant to lysin discovery, characterization, and engineering. The authors assessed the strengths and limitations of existing bioinformatics platforms used for predicting lysin structures, enzymatic functions, and bacterial targets. The study identified gaps in current computational tools, emphasizing the need for more specialized resources tailored to lysin research. Recommendations were provided on improving sequence annotation, structural modeling, and functional predictions to accelerate lysin-based antimicrobial development. The work stresses the importance of integrating computational and experimental approaches for better lysin optimization and therapeutic applications (Bałdysz et al., 2024).
An important consideration in machine learning-based lysin design is the selection of training datasets. Most current approaches rely exclusively on curated endolysin sequence databases, which offer domain-specific features relevant to muralytic activity. While this strategy ensures model focus and minimizes noise from unrelated protein classes, it also constrains the design space to variations within natural endolysin families. Expanding the training set to include non-endolysin proteins that also target peptidoglycan, such as bacteriocins, autolysins, or peptidoglycan-binding antimicrobial peptides, could enable the discovery of novel domain combinations and activity-enhancing motifs. These heterologous proteins may contribute unique structural elements or binding strategies that are not represented in phage-derived endolysins. However, inclusion of such diverse sequences would require careful curation, consistent functional annotation, and normalization of sequence features to prevent overfitting or functional ambiguity. A hybrid approach that incorporates well-characterized muralytic proteins from multiple biological sources may ultimately improve the robustness and generalizability of predictive models for engineered lysins.
The integration of AI-driven computational methods had revolutionized lysin engineering by enabling rapid modifications, functional predictions, and structural optimizations. Approaches such as machine learning, deep mutational scanning, and modular synthetic biology platforms like VersaTile have accelerated the discovery of engineered lysins with improved stability, specificity, and bactericidal activity. These advancements streamline antimicrobial development and open new therapeutic avenues for targeting antibiotic-resistant gram-negative bacteria.
6 Conclusions, challenges, and future directions
The main advantage of endolysins over conventional antibiotics is their high specificity against particular bacterial strains. Unlike broad-spectrum antibiotics, endolysins selectively target bacterial peptidoglycan, reducing collateral damage to the host microbiota or the induce in gene transduction. While research continues, studies on several endolysins, such as Tha-PA90 (Lim et al., 2024), ElyA1 and ElyA2 (Blasco et al., 2020), PA90 fused with DS4.3 (Lim et al., 2022b) have demonstrated no major toxicity or adverse effects in vivo, even at high concentrations. Recent preclinical and clinical evaluations further support the safety of endolysin-based therapeutics (ClinicalTrials.gov., 2017; Watson et al., 2019). The lysin CF-301 (exebacase) exhibited an excellent safety profile in animal models and early-phase clinical trials, with no cytotoxicity observed toward human cells or significant adverse events. Similarly, SAL200, a recombinant endolysin targeting S. aureus, was evaluated in a phase I clinical trial and found safe and well-tolerated in healthy volunteers (Jun et al., 2017). These findings highlight the strong potential of endolysins as safe antibacterial agents, although continued monitoring in advanced clinical phases is warranted. This feature makes them an attractive alternative to traditional antibiotics, particularly in an era of escalating antimicrobial resistance. Endolysins act significantly faster than traditional antibiotics, effectively lysing bacterial cells within minutes. Moreover, they function effectively in biofilms and mucosal environments, where conventional antibiotics tend to fail. However, the therapeutic application of endolysins against gram-negative bacteria remains a major challenge due to the presence of an impermeable outer membrane that limits access to the peptidoglycan layer. Various strategies had been developed to overcome this barrier, including fusion with AMPs, combination with outer membrane permeabilizers, and encapsulation within nanocarriers. While these approaches demonstrated promising results, further optimization is necessary to enhance their stability, reduce immunogenicity, and ensure targeted delivery in vivo.
One of the most significant breakthroughs in recent years had been the identification of membrane-active peptides hidden within endolysin sequences. These peptides exhibit independent antimicrobial activity, enabling them to permeabilize bacterial membranes and act synergistically with enzymatic lysis. The discovery of such cryptic AMPs had opened new avenues for the rational design of next-generation peptide-based therapeutics. Further research responds to the challenge of: (i) Optimizing peptide modifications to enhance stability, selectivity, and resistance to proteolytic degradation. (ii) Investigating structure–function relationships of cryptic AMPs to understand their interactions with bacterial membranes. (iii) Evaluating in vivo efficacy and safety profiles in clinically relevant animal models. (iv) Developing combination therapies where endolysin-derived peptides are paired with existing antibiotics or other antimicrobial agents to combat MDR pathogens.
Additionally, synthetic biology and AI-driven approaches are becoming increasingly valuable for optimizing endolysin-derived peptides. Machine learning models can predict peptide activity, stability, and toxicity, accelerating the design of novel antimicrobial agents. These AI-driven methods can also be applied to identify previously unrecognized antimicrobial sequences within lysin databases.
Endolysin-derived peptides represent a promising frontier in antimicrobial therapy, offering potent activity against MDR gram-negative bacteria. Future research should focus on refining their structure, improving delivery mechanisms, and ensuring safety and efficacy in clinical settings. With continued advancements in protein engineering and AI-assisted peptide design, these molecules have the potential to revolutionize the treatment of bacterial infections and provide a much-needed alternative to conventional antibiotics.
Author contributions
MW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by the National Science Centre, Poland (Sonata BIS UMO-2023/50/E/NZ1/00346) and the Excellence Initiative-Research University (2020-2026) New Ideas, a program of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author declares that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Chat GPT 4.0 was used to help with English correction and generate some elements of the figures.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abbasi, E., Aval, S. F., Akbarzadeh, A., Milani, M., Nasrabadi, H. T., Joo, S. W., et al. (2014). Dendrimers: synthesis, applications, and properties. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 9:247. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-9-247
Abdelkader, K., Gutiérrez, D., Tamés-Caunedo, H., Ruas-Madiedo, P., Safaan, A., Khairalla, A. S., et al. (2022). Engineering a lysin with Iintrinsic antibacterial activity (LysMK34) by Cecropin a fusion enhances its antibacterial properties against Acinetobacter baumannii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 88:e0151521. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01515-21
Abouhmad, A., Dishisha, T., Amin, M. A., and Hatti-Kaul, R. (2017). Immobilization to positively charged cellulose nanocrystals enhances the antibacterial activity and stability of hen egg white and T4 lysozyme. Biomacromolecules 18, 1600–1608. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.7b00219
Alegun, O., Pandeya, A., Cui, J., Ojo, I., and Wei, Y. (2021). Donnan potential across the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria and its effect on the permeability of antibiotics. Antibiotics 10:701. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10060701
Antonova, N., Vasina, D., Rubalsky, E., Fursov, M., Savinova, A., Grigoriev, I., et al. (2020). Modulation of endolysin LysECD7 bactericidal activity by different peptide tag fusion. Biomol. Ther. 10:440. doi: 10.3390/biom10030440
Bai, J., Lee, S., and Ryu, S. (2020). Identification and in vitro characterization of a novel phage endolysin that targets gram-negative bacteria. Microorganisms 8:447. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8030447
Bai, J., Yang, E., Chang, P. S., and Ryu, S. (2019). Preparation and characterization of endolysin-containing liposomes and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities against gram-negative bacteria. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 128, 40–48. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2019.05.006
Bałdysz, S., Nawrot, R., and Barylski, J. (2024). “Tear down that wall”—a critical evaluation of bioinformatic resources available for lysin researchers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 90:e0236123. doi: 10.1128/aem.02361-23
Baliga, P., Goolappa, P. T., Shekar, M., and Kallappa, G. S. (2023). Cloning, characterization, and antibacterial properties of endolysin LysE against planktonic cells and biofilms of Aeromonas hydrophila. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 15, 646–654. doi: 10.1007/s12602-021-09880-7
Blasco, L., Ambroa, A., Trastoy, R., Bleriot, I., Moscoso, M., Fernández-Garcia, L., et al. (2020). In vitro and in vivo efficacy of combinations of colistin and different endolysins against clinical strains of multi-drug resistant pathogens. Sci. Rep. 10:7163. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64145-7
Breijyeh, Z., Jubeh, B., and Karaman, R. (2020). Resistance of gram-negative bacteria to current antibacterial agents and approaches to resolve it. Molecules 25:1340. doi: 10.3390/molecules25061340
Briers, Y., Schmelcher, M., Loessner, M. J., Hendrix, J., Engelborghs, Y., Volckaert, G., et al. (2009). The high-affinity peptidoglycan binding domain of Pseudomonas phage endolysin KZ144. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 383, 187–191. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.03.161
Briers, Y., Volckaert, G., Cornelissen, A., Lagaert, S., Michiels, C. W., Hertveldt, K., et al. (2007). Muralytic activity and modular structure of the endolysins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophages φKZ and EL. Mol. Microbiol. 65, 1334–1344. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05870.x
Briers, Y., Walmagh, M., Grymonprez, B., Biebl, M., Pirnay, J. P., Defraine, V., et al. (2014a). Art-175 is a highly efficient antibacterial against multidrug-resistant strains and persisters of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58, 3774–3784. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02668-14
Briers, Y., Walmagh, M., and Lavigne, R. (2011). Use of bacteriophage endolysin EL188 and outer membrane permeabilizers against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 110, 778–785. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04931.x
Briers, Y., Walmagh, M., Van Puyenbroeck, V., Cornelissen, A., Cenens, W., Aertsen, A., et al. (2014b). Engineered endolysin-based “Artilysins” to combat multidrug-resistant gram-negative pathogens. mBio 5:e01379-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01379-14
Cahill, J., and Young, R. (2019). “Phage lysis: multiple genes for multiple barriers” in Advances in virus research (Academic Press Inc.), 33–70.
Cama, J., Henney, A. M., and Winterhalter, M. (2019). Breaching the barrier: quantifying antibiotic permeability across gram-negative bacterial membranes. J. Mol. Biol. 431, 3531–3546. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.03.031
Carratalá, J. V., Arís, A., Garcia-Fruitós, E., and Ferrer-Miralles, N. (2023). Design strategies for positively charged endolysins: insights into Artilysin development. Biotechnol. Adv. 69:108250. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2023.108250
Chen, W., Han, L.-M., Chen, X.-Z., Yi, P.-C., Li, H., Ren, Y.-Y., et al. (2024). Engineered endolysin of Klebsiella pneumoniae phage is a potent and broad-spectrum bactericidal agent against “ESKAPEE” pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 15:1397830. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1397830
Chen, X., Liu, M., Zhang, P., Leung, S. S. Y., and Xia, J. (2021). Membrane-permeable antibacterial enzyme against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. ACS Infect. Dis. 7, 2192–2204. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00222
Cho, J., Hong, H.-W., Park, K., Myung, H., and Yoon, H. (2024). Unveiling the mechanism of bactericidal activity of a cecropin A-fused endolysin LNT113. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 260:129493. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129493
Chu, J. J. K., Poh, W. H., Hasnuddin, N. T. B., Hew, E. Y., Dam, L. C., Sahili, A.El, et al. (2022). Novel phage Lysin Abp013 against Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics 11:169. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11020169
Ciepluch, K., Maciejewska, B., Gałczyńska, K., Kuc-Ciepluch, D., Bryszewska, M., Appelhans, D., et al. (2019). The influence of cationic dendrimers on antibacterial activity of phage endolysin against P. aeruginosa cells. Bioorg. Chem. 91:103121. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103121
ClinicalTrials.gov.. (2017). Safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetics of CF-301 vs. placebo in addition to antibacterial therapy for treatment of S. aureus bacteremia. Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03163446.
Defraine, V., Schuermans, J., Grymonprez, B., Govers, S. K., Aertsen, A., Fauvart, M., et al. (2016). Efficacy of artilysin art-175 against resistant and persistent acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60, 3480–3488. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00285-16
Düring, K., Porsch, P., Mahn, A., Brinkmann, O., and Gieffers, W. (1999). The non-enzymatic microbicidal activity of lysozymes. FEBS Lett. 449, 93–100. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00405-6
Duyvejonck, L., Gerstmans, H., Stock, M., Grimon, D., Lavigne, R., and Briers, Y. (2021). Rapid and high-throughput evaluation of diverse configurations of engineered lysins using the VersaTile technique. Antibiotics 10:293. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10030293
Euler, C. W., Raz, A., Hernandez, A., Serrano, A., Xu, S., Andersson, M., et al. (2023). PlyKp104, a novel phage lysin for the treatment of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and other gram-negative ESKAPE pathogens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 67:e0151922. doi: 10.1128/aac.01519-22
Garde, S., Chodisetti, P. K., and Reddy, M. (2021). Peptidoglycan: structure, synthesis, and regulation. EcoSal Plus 9:eESP-0010-2020. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0010-2020
Gerstmans, H., Criel, B., and Briers, Y. (2018). Synthetic biology of modular endolysins. Biotechnol. Adv. 36, 624–640. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.12.009
Gerstmans, H., Duyvejonck, L., Vázquez, R., Staes, I., Borloo, J., Abdelkader, K., et al. (2023). Distinct mode of action of a highly stable, engineered phage lysin killing gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol. Spectr. 11:e0181323. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01813-23
Gerstmans, H., Grimon, D., Gutiérrez, D., Lood, C., Rodríguez, A., van Noort, V., et al. (2020). A VersaTile-driven platform for rapid hit-to-lead development of engineered lysins. Sci. Adv. 6:eaaz1136. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz1136
Ghose, C., and Euler, C. W. (2020). Gram-negative bacterial lysins. Antibiotics 9:74. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9020074
Gondil, V. S., and Chhibber, S. (2021). Bacteriophage and endolysin encapsulation systems: a promising strategy to improve therapeutic outcomes. Front. Pharmacol. 12:675440. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.675440
Gondil, V. S., Harjai, K., and Chhibber, S. (2020). Endolysins as emerging alternative therapeutic agents to counter drug-resistant infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 55:105844. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2019.11.001
Gontijo, M. T. P., Jorge, G. P., and Brocchi, M. (2021). Current status of endolysin-based treatments against gram-negative bacteria. Antibiotics 10:1143. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10101143
Heselpoth, R. D., Euler, C. W., and Fischetti, V. A. (2022). PaP1, a broad-spectrum lysin-derived cationic peptide to treat polymicrobial skin infections. Front. Microbiol. 13:817228. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.817228
Heselpoth, R. D., Euler, C. W., Schuch, R., and Fischetti, V. A. (2019). Lysocins: bioengineered antimicrobials that deliver lysins across the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 63:e00342-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00342-19
Hong, H.-W., Kim, Y. D., Jang, J., Kim, M. S., Song, M., and Myung, H. (2022). Combination effect of engineered endolysin EC340 with antibiotics. Front. Microbiol. 13:821936. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.821936
Hu, F. (2024). Crystal structure of PHAb11, another peptidoglycan hydrolase with thermal stability and broad-spectrum. PDB. doi: 10.2210/pdb9kbs/pdb
Islam, M. M., Kim, D., Kim, K., Park, S.-J., Akter, S., Kim, J., et al. (2022). Engineering of lysin by fusion of antimicrobial peptide (cecropin a) enhances its antibacterial properties against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 13:988522. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.988522
Jacob, F., and Fuerst, C. R. (1958). The mechanism of lysis by phage studied with defective lysogenic bacteria. J. Gen. Microbiol. 18, 518–526. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-2-518
Jeong, T.-H., Hong, H.-W., Kim, M. S., Song, M., and Myung, H. (2023). Characterization of three different endolysins effective against gram-negative bacteria. Viruses 15:679. doi: 10.3390/v15030679
Jun, S. Y., Jang, I. J., Yoon, S., Jang, K., Yu, K. S., Cho, J. Y., et al. (2017). Pharmacokinetics and tolerance of the phage endolysin-based candidate drug SAL200 after a single intravenous administration among healthy volunteers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 61:e02629-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02629-16
Khan, F. M., Chen, J.-H., Zhang, R., and Liu, B. (2023). A comprehensive review of the applications of bacteriophage-derived endolysins for foodborne bacterial pathogens and food safety: recent advances, challenges, and future perspective. Front. Microbiol. 14:1259210. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1259210
Khan, F. M., Rasheed, F., Yang, Y., Liu, B., and Zhang, R. (2024). Endolysins: a new antimicrobial agent against antimicrobial resistance. Strategies and opportunities in overcoming the challenges of endolysins against gram-negative bacteria. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1385261. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1385261
Kim, S., Lee, D. W., Jin, J. S., and Kim, J. (2020). Antimicrobial activity of LysSS, a novel phage endolysin, against Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 22, 32–39. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2020.01.005
Kim, J., Wang, J., and Ahn, J. (2023). Combined antimicrobial effect of phage-derived endolysin and depolymerase against biofilm-forming Salmonella Typhimurium. Biofouling 39, 763–774. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2023.2265817
Larpin, Y., Oechslin, F., Moreillon, P., Resch, G., Entenza, J. M., and Mancini, S. (2018). In vitro characterization of PlyE146, a novel phage lysin that targets gram-negative bacteria. PLoS One 13:e0192507. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192507
Li, C., Jiang, M., Khan, F. M., Zhao, X., Wang, G., Zhou, W., et al. (2021). Intrinsic antimicrobial peptide facilitates a new broad-spectrum lysin LysP53 to kill Acinetobacter baumannii in vitro and in a mouse burn infection model. ACS Infect. Dis. 7, 3336–3344. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00497
Li, X., Shangguan, W., Yang, X., Hu, X., Li, Y., Zhao, W., et al. (2024). Influence of lipopolysaccharide-interacting peptides fusion with endolysin LysECD7 and fatty acid derivatization on the efficacy against Acinetobacter baumannii infection in vitro and in vivo. Viruses 16:760. doi: 10.3390/v16050760
Lim, J., Hong, J., Jung, Y., Ha, J., Kim, H., Myung, H., et al. (2022a). Bactericidal effect of cecropin a fused endolysin on drug-resistant gram-negative pathogens. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32, 816–823. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2205.05009
Lim, J., Jang, J., Myung, H., and Song, M. (2022b). Eradication of drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii by cell-penetrating peptide fused endolysin. J. Microbiol. 60, 859–866. doi: 10.1007/s12275-022-2107-y
Lim, J., Myung, H., Lim, D., and Song, M. (2024). Antimicrobial peptide thanatin fused endolysin PA90 (Tha-PA90) for the control of Acinetobacter baumannii infection in mouse model. J. Biomed. Sci. 31:36. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01027-4
Lim, J. A., Shin, H., Heu, S., and Ryu, S. (2014). Exogenous lytic activity of SPN9CC endolysin against gram-negative Bacteria. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24, 803–811. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1403.03035
Lin, C. Y., and Liu, J. C. (2016). Modular protein domains: an engineering approach toward functional biomaterials. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 40, 56–63. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2016.02.011
Liu, P., Dong, X., Cao, X., Xie, Q., Huang, X., Jiang, J., et al. (2023). Identification of three Campylobacter lysins and enhancement of their anti-Escherichia coli efficacy using colicin-based translocation and receptor-binding domain fusion. Microbiol. Spectr. 11:e0451522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04515-22
Liu, B., Guo, Q., Li, Z., Guo, X., and Liu, X. (2023). Bacteriophage endolysin: e powerful weapon to control bacterial biofilms. Protein J. 42, 463–476. doi: 10.1007/s10930-023-10139-z
Liu, H., Hu, Z., Li, M., Yang, Y., Lu, S., and Rao, X. (2023). Therapeutic potential of bacteriophage endolysins for infections caused by gram-positive bacteria. J. Biomed. Sci. 30:29. doi: 10.1186/s12929-023-00919-1
Love, M. J., Coombes, D., Ismail, S., Billington, C., and Dobson, R. C. J. (2022). The structure and function of modular Escherichia coli O157:H7 bacteriophage FTBEc1 endolysin, LysT84: defining a new endolysin catalytic subfamily. Biochem. J. 479, 207–223. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20210701
Lysando, A. G. (2025). Are You concerned about the threat antibiotic-resistant bacteria pose? Available online at: https://www.lysando.com/technology/ (Accessed January 30, 2025).
Ma, Q., Guo, Z., Gao, C., Zhu, R., Wang, S., Yu, L., et al. (2017). Enhancement of the direct antimicrobial activity of Lysep3 against Escherichia coli by inserting cationic peptides into its C terminus. Anton. Leeuw. Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 110, 347–355. doi: 10.1007/s10482-016-0806-2
McGowan, S., Buckle, A. M., Mitchell, M. S., Hoopes, J. T., Gallagher, D. T., Heselpoth, R. D., et al. (2012). X-ray crystal structure of the streptococcal specific phage lysin PlyC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 109, 12752–12757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1208424109
Morais, D., Tanoeiro, L., Marques, A., Gonçalves, T., Duarte, A., Matos, A., et al. (2022). Liposomal delivery of newly identified prophage lysins in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:10143. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710143
Ni, P., Wang, L., Deng, B., Jiu, S., Ma, C., Zhang, C., et al. (2021). Characterization of a lytic bacteriophage against Pseudomonas syringae pv. Actinidiae and its indolysin. Viruses 13:631. doi: 10.3390/v13040631
Nie, T., Meng, F., Zhou, L., Lu, F., Bie, X., Lu, Z., et al. (2021). In silico development of novel chimeric lysins with highly specific inhibition against Salmonella by computer-aided design. J. Agric. Food Chem. 69, 3751–3760. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c07450
Ning, H., Cong, Y., Lin, H., and Wang, J. (2021). Development of cationic peptide chimeric lysins based on phage lysin Lysqdvp001 and their antibacterial effects against Vibrio parahaemolyticus: a preliminary study. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 358:109396. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2021.109396
Ning, H.-Q., Lin, H., and Wang, J.-X. (2021). Synergistic effects of endolysin Lysqdvp001 and ε-poly-lysine in controlling Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its biofilms. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 343:109112. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2021.109112
Ning, H., Zhang, J., Zhao, Q., Lin, H., and Wang, J. (2023). Development of the phage lysin-loaded liposomes as preservatives for live clams. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 387:110059. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.110059
Oh, D., Shin, S. Y., Kang, J. H., Hahm, K. S., Kim, K. L., and Kim, Y. (1999). NMR structural characterization of cecropin a(1-8) - magainin 2(1-12) and cecropin a(1-8) - melittin(1-12) hybrid peptides. J. Pept. Res. 53, 578–589. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3011.1999.00067.x
Oliveira, V. C., Rosa-Garzon, N. G., Rocha, A. C. S. D., Monteiro, R. M., Gonçalves, Y. G., Kravicz, M., et al. (2024). Characterization of a peptidoglycan-degrading protein: biochemical and antimicrobial characteristics, antibiotic synergism, and delivery system innovation. Probiot. Antimicrob. Proteins. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10374-5
Oliveira, H., Thiagarajan, V., Walmagh, M., Sillankorva, S., Lavigne, R., Neves-Petersen, M. T., et al. (2014). A thermostable Salmonella phage endolysin, Lys68, with broad bactericidal properties against gram-negative pathogens in presence of weak acids. PLoS One 9:e108376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108376
Oliveira, H., Vilas Boas, D., Mesnage, S., Kluskens, L. D., Lavigne, R., Sillankorva, S., et al. (2016). Structural and enzymatic characterization of ABgp46, a novel phage endolysin with broad anti-gram-negative bacterial activity. Front. Microbiol. 7:208. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00208
Parmanik, A., Das, S., Kar, B., Bose, A., Dwivedi, G. R., and Pandey, M. M. (2022). Current treatment strategies against multidrug-resistant bacteria: a review. Curr. Microbiol. 79:388. doi: 10.1007/s00284-022-03061-7
Pattnaik, A., Pati, S., and Samal, S. K. (2024). Bacteriophage as a potential biotherapeutics to combat present-day crisis of multi-drug resistant pathogens. Heliyon 10:e37489. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37489
Peng, S. Y., You, R. I., Lai, M. J., Lin, N. T., Chen, L. K., and Chang, K. C. (2017). Highly potent antimicrobial modified peptides derived from the Acinetobacter baumannii phage endolysin LysAB2. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11832-7
Plotka, M., Kaczorowska, A.-K., Morzywolek, A., Makowska, J., Kozlowski, L. P., Thorisdottir, A., et al. (2015). Biochemical characterization and validation of a catalytic site of a highly thermostable Ts2631 endolysin from the thermus scotoductus phage vB_Tsc2631. PLoS One 10:e0137374. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137374
Plotka, M., Kapusta, M., Dorawa, S., Kaczorowska, A.-K., and Kaczorowski, T. (2019). Ts2631 endolysin from the Extremophilic Thermus scotoductus bacteriophage vB_Tsc2631 as an antimicrobial agent against gram-negative multidrug-resistant bacteria. Viruses 11:657. doi: 10.3390/v11070657
Quintana-Sanchez, S., Gómez-Casanova, N., Sánchez-Nieves, J., Gómez, R., Rachuna, J., Wąsik, S., et al. (2022). The antibacterial effect of PEGylated carbosilane dendrimers on P. aeruginosa alone and in combination with phage-derived Endolysin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:1873. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031873
Rahman, M., Wang, W., Sun, Q., Shah, J. A., Li, C., Sun, Y., et al. (2021). Endolysin, a promising solution against antimicrobial resistance. Antibiotics 10:1277. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10111277
Raz, A., Serrano, A., Hernandez, A., Euler, C. W., and Fischetti, V. A. (2019). Isolation of phage lysins that effectively kill Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mouse models of lung and skin infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 63:e00024-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00024-19
Rodríguez-Rubio, L., Gerstmans, H., Thorpe, S., Mesnage, S., Lavigne, R., and Briers, Y. (2016). DUF3380 domain from a Salmonella phage endolysin shows potent N-acetylmuramidase activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 82, 4975–4981. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00446-16
Rohde, M. (2019). The gram-positive bacterial cell wall. Microbiol. Spectr. 7:10.1128/microbiolspec.gpp3-0044-2018. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0044-2018
Saier, M. H., and Reddy, B. L. (2015). Holins in bacteria, eukaryotes, and archaea: multifunctional xenologues with potential biotechnological and biomedical applications. J. Bacteriol. 197, 7–17. doi: 10.1128/JB.02046-14
Salam, M. A., Al-Amin, M. Y., Salam, M. T., Pawar, J. S., Akhter, N., Rabaan, A. A., et al. (2023). Antimicrobial resistance: a growing serious threat for global public health. Healthcare 11:1946. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11131946
Sauve, K., Watson, A., Oh, J. T., Swift, S., Vila-Farres, X., Abdelhady, W., et al. (2024). The engineered Lysin CF-370 is active against antibiotic-resistant gram-negative pathogens in vitro and synergizes with meropenem in experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 230, 309–318. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae027
Schirmeier, E., Zimmermann, P., Hofmann, V., Biebl, M., Gerstmans, H., Maervoet, V. E. T., et al. (2018). Inhibitory and bactericidal effect of Artilysin® Art-175 against colistin-resistant mcr-1-positive Escherichia coli isolates. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 51, 528–529. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2017.08.027
Shavrina, M. S., Zimin, A. A., Molochkov, N. V., Chernyshov, S. V., Machulin, A. V., and Mikoulinskaia, G. V. (2016). In vitro study of the antibacterial effect of the bacteriophage T5 thermostable endolysin on Escherichia coli cells. J. Appl. Microbiol. 121, 1282–1290. doi: 10.1111/jam.13251
Shen, K., Shu, M., Zhong, C., Zhao, Y., Bao, S., Pan, H., et al. (2023). Characterization of a broad-spectrum endolysin rLysJNwz and its utility against Salmonella in foods. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 107, 3229–3241. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12500-9
Sisson, H. M., Fagerlund, R. D., Jackson, S. A., Briers, Y., Warring, S. L., and Fineran, P. C. (2024a). Antibacterial synergy between a phage endolysin and citric acid against the gram-negative kiwifruit pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. Actinidiae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 90:e0184623. doi: 10.1128/aem.01846-23
Sisson, H. M., Jackson, S. A., Fagerlund, R. D., Warring, S. L., and Fineran, P. C. (2024b). Gram-negative endolysins: overcoming the outer membrane obstacle. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 78:102433. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2024.102433
Sitthisak, S., Manrueang, S., Khongfak, S., Leungtongkam, U., Thummeepak, R., Thanwisai, A., et al. (2023). Antibacterial activity of vB_AbaM_PhT2 phage hydrophobic amino acid fusion endolysin, combined with colistin against Acinetobacter baumannii. Sci. Rep. 13:7470. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33822-8
Son, S. M., Kim, J., and Ryu, S. (2023). Development of sensitizer peptide-fused endolysin Lys1S-L9P acting against multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 14:1296796. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1296796
Sui, B., Wang, X., Zhao, T., Zhen, J., Ren, H., Liu, W., et al. (2023). Design, screening, and characterization of engineered phage endolysins with extracellular antibacterial activity against gram-negative bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 89:e0058123. doi: 10.1128/aem.00581-23
Sykilinda, N., Nikolaeva, A., Shneider, M., Mishkin, D., Patutin, A., Popov, V., et al. (2018). Structure of an Acinetobacter broad-range prophage endolysin reveals a C-terminal α-helix with the proposed role in activity against live bacterial cells. Viruses 10:309. doi: 10.3390/v10060309
Szadkowska, M., Kocot, A. M., Sowik, D., Wyrzykowski, D., Jankowska, E., Kozlowski, L. P., et al. (2024). Molecular characterization of the PhiKo endolysin from Thermus thermophilus HB27 bacteriophage phiKo and its cryptic lytic peptide RAP-29. Front. Microbiol. 14:1303794. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1303794
Szadkowska, M., Olewniczak, M., Kloska, A., Jankowska, E., Kapusta, M., Rybak, B., et al. (2022). A novel cryptic clostridial peptide that kills bacteria by a cell membrane permeabilization mechanism. Microbiol. Spectr. 10:e0165722. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01657-22
Tack, B. F., Sawai, M. V., Kearney, W. R., Robertson, A. D., Sherman, M. A., Wang, W., et al. (2002). SMAP-29 has two LPS-binding sites and a central hinge. Eur. J. Biochem. 269, 1181–1189. doi: 10.1046/j.0014-2956.2002.02751.x
Thandar, M., Lood, R., Winer, B. Y., Deutsch, D. R., Euler, C. W., and Fischetti, V. A. (2016). Novel engineered peptides of a phage lysin as effective antimicrobials against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60, 2671–2679. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02972-15
Thummeepak, R., Kitti, T., Kunthalert, D., and Sitthisak, S. (2016). Enhanced antibacterial activity of Acinetobacter baumannii bacteriophage ØABP-01 endolysin (LysABP-01) in combination with Colistin. Front. Microbiol. 7:1402. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01402
Tresnak, D. T., and Hackel, B. J. (2023). Deep antimicrobial activity and stability analysis inform lysin sequence-function mapping. ACS Synth. Biol. 12, 249–264. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.2c00509
Tyagi, J. L., Gupta, P., Ghate, M. M., Kumar, D., and Poluri, K. M. (2024). Assessing the synergistic potential of bacteriophage endolysins and antimicrobial peptides for eradicating bacterial biofilms. Arch. Microbiol. 206:272. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04003-6
Vander Elst, N. (2024). Bacteriophage-derived endolysins as innovative antimicrobials against bovine mastitis-causing streptococci and staphylococci: a state-of-the-art review. Acta Vet. Scand. 66:20. doi: 10.1186/s13028-024-00740-2
Vander Elst, N., Bert, J., Favoreel, H., Lavigne, R., Meyer, E., and Briers, Y. (2023). Development of engineered endolysins with in vitro intracellular activity against streptococcal bovine mastitis-causing pathogens. Microb. Biotechnol. 16, 2367–2386. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14339
Vasina, D. V., Antonova, N. P., Gushchin, V. A., Aleshkin, A. V., Fursov, M. V., Fursova, A. D., et al. (2024). Development of novel antimicrobials with engineered endolysin LysECD7-SMAP to combat gram-negative bacterial infections. J. Biomed. Sci. 31:75. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01065-y
Vázquez, R., Doménech-Sánchez, A., Ruiz, S., Sempere, J., Yuste, J., Albertí, S., et al. (2022a). Improvement of the antibacterial activity of phage lysin-derived peptide P87 through maximization of physicochemical properties and assessment of its therapeutic potential. Antibiotics 11:1448. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11101448
Vázquez, R., García, E., and García, P. (2018). Phage lysins for lighting bacterial respiratory infections: a new generation of antimicrobials. Front. Immunol. 9:2252. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02252
Vázquez, R., García, E., and García, P. (2021). Sequence-function relationships in phage-encoded bacterial cell wall lytic enzymes and their implications for phage-derived product design. J. Virol. 95:e0032121. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00321-21
Vázquez, R., Seoane-Blanco, M., Rivero-Buceta, V., Ruiz, S., van Raaij, M. J., and García, P. (2022b). Monomodular Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage JG004 lysozyme (Pae87) contains a bacterial surface-active antimicrobial peptide-like region and a possible substrate-binding subdomain. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 78, 435–454. doi: 10.1107/S2059798322000936
Walmagh, M., Boczkowska, B., Grymonprez, B., Briers, Y., Drulis-Kawa, Z., and Lavigne, R. (2013). Characterization of five novel endolysins from gram-negative infecting bacteriophages. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97, 4369–4375. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4294-7
Walmagh, M., Briers, Y., dos Santos, S. B., Azeredo, J., and Lavigne, R. (2012). Characterization of modular bacteriophage endolysins from myoviridae phages OBP, 201φ2-1 and PVP-SE1. PLoS One 7:e36991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036991
Wang, S., Gu, J., Lv, M., Guo, Z., Yan, G., Yu, L., et al. (2017). The antibacterial activity of E. coli bacteriophage lysin lysep3 is enhanced by fusing the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens bacteriophage endolysin binding domain D8 to the C-terminal region. J. Microbiol. 55, 403–408. doi: 10.1007/s12275-017-6431-6
Wang, L., Ju, X., Cong, Y., Lin, H., and Wang, J. (2022). A single catalytic endolysin domain Plychap001: characterization and application to control Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its biofilm directly. Food Secur. 11:1578. doi: 10.3390/foods11111578
Wang, J.-M., Seok, S.-H., Yoon, W.-S., Kim, J.-H., and Seo, M.-D. (2023). Crystal structure of the engineered endolysin mtEC340M. Acta Crystallogr. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 79, 105–110. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X23002583
Wang, T., Zheng, Y., Dai, J., Zhou, J., Yu, R., and Zhang, C. (2021). Design SMAP29-LysPA26 as a highly efficient artilysin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa with bactericidal and qntibiofilm activity. Microbiol. Spectr. 9:e0054621. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00546-21
Watson, A., Oh, J. T., Sauve, K., Bradford, P. A., Cassino, C., and Schuch, R. (2019). Antimicrobial activity of exebacase (Lysin CF-301) against the most common causes of infective endocarditis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 63:e01078-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01078-19
Wdowiak, M., Mierzejewski, P. A., Zbonikowski, R., Bończak, B., and Paczesny, J. (2023). Congo red protects bacteriophages against UV irradiation and allows for the simultaneous use of phages and UV for membrane sterilization. Environ. Sci. (Camb.) 9, 696–706. doi: 10.1039/d2ew00913g
World Health Organization (2017). WHO publishes list of bacteria for which new antibiotics are urgently needed. Available online at: https://www.who.int/news/item/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-for-which-new-antibiotics-are-urgently-needed (Accessed December 5, 2024).
World Health Organization (2024). Antimicrobial resistance. Available online at: https://www.who.int/europe/news-room/fact-sheets/item/antimicrobial-resistance (Accessed December 5, 2024).
Xu, D., Zhao, S., Dou, J., Xu, X., Zhi, Y., and Wen, L. (2021). Engineered endolysin-based “artilysins” for controlling the gram-negative pathogen Helicobacter pylori. AMB Express 11:63. doi: 10.1186/s13568-021-01222-8
Yan, G., Liu, J., Ma, Q., Zhu, R., Guo, Z., Gao, C., et al. (2017). The N-terminal and central domain of colicin a enables phage lysin to lyse Escherichia coli extracellularly. Anton. Leeuw. Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 110, 1627–1635. doi: 10.1007/s10482-017-0912-9
Yan, G., Yang, R., Fan, K., Dong, H., Gao, C., Wang, S., et al. (2019). External lysis of Escherichia coli by a bacteriophage endolysin modified with hydrophobic amino acids. AMB Express 9:106. doi: 10.1186/s13568-019-0838-x
Yang, H., Wang, M., Yu, J., and Wei, H. (2015). Antibacterial activity of a novel peptide-modified lysin against Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 6:1471. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01471
Yang, J., and Zhang, Y. (2015). I-TASSER server: new development for protein structure and function predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, W174–W181. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv342
Yi, J., Liu, Q., Zhang, Q., Chew, T. G., and Ouyang, H. (2022). Modular protein engineering-based biomaterials for skeletal tissue engineering. Biomaterials 282:121414. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121414
Zampara, A., Sørensen, M. C. H., Gencay, Y. E., Grimon, D., Kristiansen, S. H., Jørgensen, L. S., et al. (2021). Developing Innolysins against campylobacter jejuni using a novel prophage receptor-binding protein. Front. Microbiol. 12:619028. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.619028
Zampara, A., Sørensen, M. C. H., Grimon, D., Antenucci, F., Vitt, A. R., Bortolaia, V., et al. (2020). Exploiting phage receptor binding proteins to enable endolysins to kill gram-negative bacteria. Sci. Rep. 10:12087. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68983-3
Zhang, S., Chang, Y., Zhang, Q., Yuan, Y., Qi, Q., and Lu, X. (2022). Characterization of Salmonella endolysin XFII produced by recombinant Escherichia coli and its application combined with chitosan in lysing gram-negative bacteria. Microb. Cell Factories 21:171. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01894-2
Zhang, Y., Li, R., Zou, G., Guo, Y., Wu, R., Zhou, Y., et al. (2024). Discovery of antimicrobial lysins from the “dark matter” of uncharacterized phages using artificial intelligence. Adv. Sci. 11:e2404049. doi: 10.1002/advs.202404049
Zhang, P., Zeng, P., Lai, C. K. C., Ip, M., To, K. K. W., Zuo, Z., et al. (2024). Synergism of colistin and globular endolysins against multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 278:134670. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134670
Keywords: endolysins, peptides, antimicrobial peptides, bacteriophage, antibiotics, gram-negative bacteria, antimicrobial agents
Citation: Wojciechowska M (2025) Endolysins and membrane-active peptides: innovative engineering strategies against gram-negative bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 16:1603380. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1603380
Edited by:
Nuno F. Azevedo, University of Porto, PortugalReviewed by:
Duolong Zhu, Baylor College of Medicine, United StatesReshma Rudraraju, Rutgers University, Newark, United States
Dai Thien Nhan Tram, National University of Singapore, Singapore
Copyright © 2025 Wojciechowska. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Monika Wojciechowska, bS53b2pjaWVjaG93c2thQGNlbnQudXcuZWR1LnBs
Monika Wojciechowska, orcid.org/0000-0002-6255-6421
 Monika Wojciechowska
Monika Wojciechowska