- 1Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China
- 2School of Clinical Medicine, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a growing public health concern due to its rising incidence and high rate of cancer-associated deaths. Emerging evidence suggests that gut microbiota and their metabolites are critically involved in the initiation and advancement of CRC. These metabolites, which originate from the breakdown of nutrients from food and host-related substances through microbial activity in the gut, can profoundly influence tumor formation. In addition to well-studied compounds such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), bile acids (BAs), tryptophan metabolites, and polyamines, this review highlights emerging metabolites—including hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) and formate—that have recently drawn attention for their roles in colorectal carcinogenesis. We also incorporate recent mechanistic insights, such as butyrate-induced ferroptosis and H2S-mediated protein persulfidation, to illustrate how microbial metabolites influence cancer cell metabolism. Moreover, the potential of microbial metabolites as biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis of CRC is discussed. Therapeutic strategies targeting microbial metabolites—such as dietary modulation, combination therapies, fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), and phage therapy—are also reviewed. By providing a comprehensive and up-to-date overview of microbial metabolic networks associated with CRC, this review underscores the critical functions of gut microbial metabolites in tumorigenesis, offering novel insights into their utility as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, as well as promising therapeutic targets.
1 Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most frequently identified cancers and ranks second in cancer-related mortality across genders, making it a significant public health concern (Song and Chan, 2019). Although the overall incidence of CRC has declined in recent years, particularly among older adults, an alarming rise in both incidence and mortality has been observed in younger populations. Most CRC cases are sporadic and progress from adenoma to carcinoma through multiple genetic and epigenetic alterations (Song et al., 2020). Among these alterations, gut microbiota dysbiosis, which characterized by disrupted microbial community, has attracted more and more attention in the field of CRC research (Zou et al., 2018; Chang et al., 2025; Sameni et al., 2025). This dysbiosis in the gut microbiota correlates with various disturbances, including reduced microbial diversity, depletion of beneficial bacteria, and overgrowth of pathogenic microorganisms, all of which contribute to colorectal tumorigenesis (Hanus et al., 2021; Feng et al., 2023). Recent advances in metabolomics and metagenomics technologies have revealed a complex relationship between microbial metabolites and CRC progression, particularly their impact on the tumor microenvironment (Gao et al., 2022; John Kenneth et al., 2023). Notably, specific metabolites such as propionate exhibit protective, anti-tumorigenic functions, while others like TMAO is associated with pro-carcinogenic activities (Wang and Hu, 2025). Beyond their mechanistic roles, microbial metabolites are gaining attention as promising non-invasive biomarkers for CRC screening and prognosis. They can be detected in stool, blood, urine, and even exhaled breath, providing insight into tumor-associated metabolic shifts (Alustiza et al., 2023). Furthermore, manipulating microbial metabolite profiles through dietary intervention, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), or phage therapy has demonstrated potential to enhance therapeutic outcomes and reduce treatment-related toxicity (Li S. et al., 2024; Abdeen et al., 2025).
This review provides a comprehensive synthesis of current knowledge on how gut microbial metabolites influence CRC onset and progression, highlights their diagnostic and prognostic value, and discusses emerging strategies targeting these metabolites for therapeutic benefit. By integrating metabolic, microbial, and clinical perspectives, this review aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of microbial metabolic networks involved in CRC and to explore emerging therapeutic strategies that target microbial metabolites.
2 Key gut microbial metabolites and their impact on CRC development
2.1 Short-chain fatty acids
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), notably butyrate, acetate, and propionate, are key metabolites generated during the microbial breakdown of dietary fiber in the colon. These metabolites are essential for sustaining gut homeostasis and have been extensively recognized for their protective influence on the gastrointestinal tract, especially in reducing the risk of CRC (Wang et al., 2019; Gomes et al., 2020).
Butyrate, in particular, is a key fatty acid known for its strong anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects. It serves as the primary metabolic fuel for colon epithelial cells and supports epithelial maturation while preserving cellular integrity (Zeng et al., 2020). A key mechanism of butyrate is the inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDACs), which activates the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, reverses the Warburg effect, and induces apoptosis in CRC cells. In addition, SCFAs have been found to modulate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, a key pathway in CRC development and progression. In mouse models, butyrate-generating microbes like Clostridium butyricum suppress intestinal tumor formation by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which highlights the promising application of SCFAs such as butyrate in CRC therapy. Butyrate also protects the intestinal mucosal barrier by activating the AMPK signaling pathway, inducing MUC2 secretion, and maintaining tight junctions (Chen and Vitetta, 2021). In addition, butyrate modulates antitumor immunity by affecting CD8 + T cell activity (He et al., 2021), which plays a significant role in immune surveillance against CRC. Furthermore, a recent study suggests that SCFAs can inhibit the development of CRC by regulating ferroptosis and immune responses (Cui W. et al., 2024). Butyrate, in particular, promotes ferroptosis by downregulating ferroptosis-related genes such as GPX4 and SLC7A11, enhancing the sensitivity of CRC cells to ferroptosis and inhibiting tumor growth.
Acetate, also known as acetic acid, is the most abundant SCFA in the colon, accounting for approximately 60%. It is primarily produced by Bacteroides bacteria in the gut through the fermentation of dietary fibers (Bishehsari et al., 2018; Zeng et al., 2020). Acetate can promote apoptosis in CRC cells by inducing changes in lysosomal membrane permeability, which leads to the release of lysosomal protease cathepsin D (CatD) into the cytoplasm, potentially contributing to its anti-cancer effects (Marques et al., 2013). In high-risk CRC populations, acetate concentrations are significantly lower, suggesting that acetate may have a potential protective role in the prevention of CRC. According to a systematic meta-analysis, acetate concentrations were significantly lower in high-risk individuals compared to healthy controls, with a standardized mean difference (SMD) of 2.02 (95% CI: 0.31–3.74, p = 0.02). Additionally, in the CRC incidence analysis, the concentration of acetate was significantly higher in healthy controls than in CRC patients, with a SMD of 0.61 (95% CI: 0.09–1.13, p = 0.02) (Alvandi et al., 2022).
Propionate, also primarily produced by Bacteroides, has been shown to exert potent anti-cancer effects in CRC. These protective effects are primarily mediated through the enhancement of intestinal barrier integrity and the modulation of immune responses. Specifically, propionate promotes the differentiation of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and suppresses the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby reducing intestinal inflammation and inhibiting CRC development (Wang et al., 2019). In addition, studies have shown that propionic acid promotes apoptosis of CRC cells through multiple mechanisms, including mitochondrial dysfunction, release of apoptosis-inducing factors, activation of caspase-3, down-regulation of PRMT1, and up-regulation of TNFAIP1 (Ryu et al., 2019; Gomes et al., 2020; Ryu et al., 2022).
Formate is another type of SCFA, but compared to other SCFAs, its concentration in the gut is relatively low. It is often considered a secondary intermediate in metabolic processes, but recent studies have revealed its important role in promoting CRC development (El Tekle and Garrett, 2023; Kulecka et al., 2024). Formic acid promotes CRC through a variety of mechanisms, the most obvious of which is through its induction of oxidative stress and DNA injury. Excessive accumulation of formic acid in the colorectal environment can promote reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation via the Fenton reaction, leading to DNA damage, genetic mutations in epithelial cells, and ultimately facilitating colorectal carcinogenesis (Ternes et al., 2022b). In addition, formic acid has been shown to activate several carcinogenic pathways, one of which is the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Aberrant Wnt signaling, a hallmark of CRC, governs epithelial homeostasis and cellular proliferation (Yin et al., 2023). The ability of formic acid to disrupt this pathway may further exacerbate tumorigenesis. The second is the NF-κB signaling pathway, which is activated by formic acid to trigger immune-related reactions, with chronic inflammation serving as a critical factor in driving CRC progression (Cao et al., 2024). Elevated levels of formic acid have been shown to disrupt the intestinal barrier by downregulating tight junction proteins, leading to increased intestinal permeability (Yu et al., 2018). This barrier dysfunction permits translocation of microbial products and inflammatory cytokines into deeper tissue layers, exacerbating inflammation and creating a microenvironment conducive to CRC progression. In summary, SCFAs are closely linked to the inhibition of CRC progression through their roles in maintaining intestinal barrier integrity and modulating immune homeostasis. However, under dysbiotic gut conditions, the production or function of SCFAs may be impaired, potentially diminishing their anti-tumorigenic effects and creating a microenvironment conducive to tumor progression (Bultman, 2017).
2.2 Bile acid
Bile acid (BAs), primarily synthesized in the liver from cholesterol, are essential for fat digestion (Di Ciaula et al., 2023). Beyond their digestive roles, however, BAs are gaining growing attention for their pivotal involvement in the development and advancement of CRC (Gou et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2025). While SCFAs predominantly exert their effects through anti-inflammatory pathways, BAs primarily activate host receptors to influence tumor growth (Ocvirk and O'Keefe, 2017; Ahmad et al., 2023). Within the colon, BAs are subjected to microbial transformation, converting initial BAs exemplified by chenodeoxycholic acid into secondary bile acids (SBAs), such as lithocholic acid (LCA) as well as deoxycholate acid (DCA) (Zeng et al., 2019). These SBAs exert diverse effects on colon cells, with some promoting cancer and others offering protective effects, depending on their concentration, metabolic pathways, and gut microbiota composition (Ridlon et al., 2016; Jiang et al., 2022). DCA, a well-established carcinogen, has been linked to CRC by inducing inflammation, DNA damage, and oxidative stress (Jia et al., 2018; Ternes et al., 2022a). Clinical trials have shown that elevated levels of DCA are particularly associated with an increased CRC risk in populations consuming high-fat, low-fiber diets (Reddy et al., 1989). The production of DCA is linked to disruptions in the gut microbial community, which promote the growth of microbes that transform primary bile acids (PBAs) into harmful SBAs (Ahmad et al., 2023). Conversely, certain BAs, such as lithocholic acid, have been shown to possess anti-cancer properties. LCA can induce apoptosis and inhibit cancer cell proliferation, thus providing a protective mechanism against CRC (Liu et al., 2022; Kouhzad et al., 2025). This dual role of BAs underscores their complex involvement in CRC progression. While SBAs like DCA promote tumorigenesis through inflammation and oxidative damage, other BAs like LCA counteract these effects by promoting cell death in cancer cells (Yang et al., 2025). The balance between these opposing actions is influenced by factors such as bile acid concentration, microbiome composition, and host genetics (Ahmad et al., 2023).
BAs regulate signaling pathways by binding to cellular receptors (Caliceti et al., 2022). One such receptor is the farnesoid X receptor (FXR), which plays a key role in maintaining bile acid homeostasis and exerts protective effects against inflammation. However, in CRC, FXR expression is often downregulated, and lower FXR levels are associated with poorer clinical outcomes (Sun et al., 2021; Yin et al., 2021). In contrast, another bile acid receptor, the G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 1 (TGR5), has been implicated in promoting inflammation, particularly in the context of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), a recognized risk factor for CRC. Upregulation of TGR5 in the inflamed intestinal mucosa suggests its contribution to the chronic inflammation that drives CRC development (Liu et al., 2021; Zhang H. et al., 2021). In addition to their receptor-mediated effects, BAs are hydrophobic and can directly interact with cell membranes, disrupting their integrity. These disruptions can induce cell cycle abnormalities, enhance invasiveness, and facilitate tumorigenesis (Payne et al., 2010; Zeng et al., 2019).
2.3 Amino metabolites
2.3.1 Tryptophan metabolites
Amino acid metabolites are key mediators of the interplay between the host and microbiota during the development of CRC, with their diverse metabolic products influencing cancer progression through different mechanisms. As a vital amino acid, tryptophan metabolites is widely present in dietary sources including meat, soy products, and seeds (Richard et al., 2009). It undergoes multiple metabolic routes, including kynurenine pathway, serotonin pathway, and indole pathway, predominantly by intestinal microbiota (Yan et al., 2024).
The majority of tryptophan metabolism in the gut occurs via the kynurenine and indole pathways, with the kynurenine pathway accounting for about 90–95% of the metabolism, and indole-related pathways processing around 5% (Wyatt and Greathouse, 2021). Indole and compounds derived from indole, including indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), indole-3-lactic acid, indole-3-propionic acid (IPA), and indole-3-aldehyde, are known for their bioactive properties and play important roles in regulating diverse physiological processes including immune modulation, inflammation, cellular homeostasis within the gut (Li M. et al., 2024; Huang et al., 2025). Indole derivatives, primarily produced through the metabolism of the amino acid tryptophan by gut microbiota, have garnered increasing attention in CRC.
Indole derivatives have been shown to promote intestinal homeostasis by enhancing epithelial barrier function and supporting immune tolerance, which is critical for suppressing chronic inflammation, one of the known risk factors for CRC (Li M. et al., 2024). For example, germ-free mice lacking IPA-producing Clostridium mutants in one animal experiment showed increased intestinal permeability, inflammation, and immune cell infiltration (Krause et al., 2024). In addition, Indole-3-methanol, a derivative of indole present in cruciferous vegetables, has been shown to alleviate colitis in mice by upregulating interleukin-22 (IL-22), a cytokine that strengthens epithelial immunity and modulates intestinal inflammation (Nolan et al., 2021). Moreover, indoles may modulate the gut microbiome by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting pathogenic microbes (Zhao et al., 2019). A balanced microbiota is essential for maintaining intestinal homeostasis and preventing carcinogenesis. However, the role of indole derivatives in CRC is not a single stimulant (Ye et al., 2022). Other studies have found that although indole-3-acetaldehyde (IAAD) can induce apoptosis of CRC cells at low concentrations, it may promote epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) and cell invasiveness at high concentrations, potentially accelerating tumor progression (Dai et al., 2024). Interestingly, tryptophan metabolism is often altered in CRC patients, manifested by increased kynuretic production and decreased indole production (Sun et al., 2020). The indole pathway and its metabolites mostly protect the body in the fight against tumors, but kynurenine, as the main metabolite in the kynurenine pathway, is mostly associated with the pathogenesis of CRC (Platten et al., 2019). Kynurenine functions as an endogenous ligand of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and can directly bind to and activate this receptor. In colitis-associated CRC models, increased tumor formation was observed in mice lacking AhR, suggesting a potential tumor-suppressive role for AhR (Safe et al., 2013). However, kynurenine–AhR signaling has also been shown to promote an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Upon AhR activation, kynurenine can inhibit effector T cell function and promote Treg differentiation, thereby facilitating immune evasion and tumor progression (Liu et al., 2024).
Tryptophan can additionally be hydroxylated to produce serotonin (5-HT), a key neurotransmitter (Kuhn and Hasegawa, 2020). While most previous research focused on its role in mood regulation, sleep, and appetite control, recent studies have revealed its close association with the development of CRC. The study has been shown serotonin (5-HT) significantly promotes the clonal formation of CRC stem cells through the receptors HTR1B, HTR1D, and HTR1F, with higher concentrations leading to the formation of larger clones (Zhu et al., 2022). In mouse experiments, treatment with a serotonin synthesis inhibitor resulted in tumor shrinkage and a decreased proportion of CRC stem cells thereby impeding tumor growth (Zhu et al., 2022).
2.3.2 Polyamines
Comprising putrescine, spermine, spermidine, polyamines are low molecular weight amines produced by gut microbiota during their metabolic processes (Li et al., 2020). These polyamines are essential for multiple cellular functions, including cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. Dysregulated polyamine metabolism is associated with the advancement of several diseases, particularly CRC (Park and Igarashi, 2013). In CRC, polyamines are essential for promoting cell proliferation, stabilizing nucleic acids, regulating ion channels, and modulating protein functions—processes that collectively contribute to tumor growth (Wu et al., 2025). Studies have found that levels of polyamine metabolites such as cadaverine and putrescine in CRC stool samples are closely associated with increased tumor incidence and poor prognosis (Yang et al., 2019). Overgrowth of specific bacteria such as enterotoxin-producing fragile Bacteroides (ETBF) can lead to excessive production of polyamines (Goodwin et al., 2011), thereby increasing the probability of CRC. Polyamines have been shown to regulate matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), which play a key role in tumor migration, invasion, and metastasis (Soda, 2011). In addition, polyamines regulate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway through spermidine/spermidine-N (1) -acetyltransferase (SSAT) activity, further promoting tumor proliferation (Wang et al., 2017). Notably, ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), the rate-limiting enzyme in polyamine biosynthesis, regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis, and also promotes tumor angiogenesis through a pro-angiogenic mechanism independent of the conventional VEGF pathway (Holbert et al., 2024). Tumors with high ODC expression show stronger angiogenic ability which is very unfavorable to the control of CRC.
2.3.3 H2S
Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) in the human gut is produced by sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) and other gut microbes through the metabolism of sulfur-containing amino acids such as cysteine and taurine. Recent studies have identified a strong association between elevated levels of H₂S-producing bacteria—such as Bilophila wadsworthia and Desulfovibrio—and an increased risk of CRC, suggesting a close link between H₂S and CRC pathogenesis (Ai et al., 2019). Firstly, H₂S is essential for modulating the bioenergetic processes of CRC cells. H₂S exhibits a biphasic effect in cancer biology: at low concentrations, it enhances mitochondrial function and promotes glycolysis, thereby supporting cancer cell proliferation, whereas at high concentrations, it inhibits proliferation. For example, the slow-releasing H₂S donor GYY4137 has been shown to stimulate mitochondrial ATP production and enhance glycolysis in CRC cell lines such as HCT116. Low concentrations of GYY4137 (0.3 mM) promote cell proliferation by enhancing bioenergetics, whereas higher concentrations (1 mM) inhibit cancer cell growth (Untereiner et al., 2017). Secondly, H₂S can promote tumor progression through persulfidation—a post-translational modification in which a sulfur atom is added to the cysteine residue of a protein, converting –SH to –SSH. This modification enhances the activity of several pro-tumor signaling pathways, thereby promoting cancer cell proliferation, inhibiting apoptosis, and facilitating tumor growth. For instance, H₂S-mediated persulfidation activates the NF-κB pathway, which not only sustains chronic inflammation but also supports tumor angiogenesis and progression. At the same time, H₂S also activates the downstream mTOR signaling pathway by promoting the persulfidation and activation of AKT, which drives the metabolic reprogramming and rapid division of tumor cells (Wang et al., 2021). In addition, in CRC cells, H₂S regulates Sp1 transcription factors and promotes the activation of ATP citrate lyase (ACLY) genes, further triggering a series of biological effects that are conducive to tumor cell growth and metabolic reprogramming (Ascenção et al., 2021).
2.4 Trimethylamine n-oxide
Trimethylamine n-oxide (TMAO) is another compound formed through the combined activities of gut microbiota and liver enzymes. Foods rich in compounds containing trimethylamine groups, such as choline, betaine, and carnitine, found in fish, red meat, and poultry, serve as precursors for TMAO production (Liu and Dai, 2020). Although the majority of research has focused on the relationship between TMAO and cardiovascular diseases, recent studies suggest that TMAO may also play a role in the progression of CRC by promoting cell proliferation and angiogenesis. In vitro experiments have demonstrated that TMAO induces proliferation of CRC HCT-116 cells and increases the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA). In vivo, mice subjected to a long-term high-choline diet exhibited elevated circulating TMAO levels, increased tumor volume, enhanced angiogenesis, and upregulated expression of VEGFA and CD31 (Yang S. et al., 2022). These findings indicate a potential association between TMAO and CRC progression. Furthermore, a prospective study involving 761 CRC cases revealed that TMAO and its precursors are positively associated with the risk of distal colon cancer, while no significant association was found with the overall risk of rectal cancer (Byrd et al., 2024). This suggests that TMAO may influence CRC risk differently depending on the tumor’s anatomical location. However, the precise mechanisms underlying the relationship between TMAO and CRC remain unclear. Further research is necessary to elucidate the pathophysiological mechanisms and causal relationships between TMAO and CRC development.
3 Microbial metabolites as biomarkers for CRC diagnosis and prognosis
CRC is a highly heterogeneous disease, posing significant challenges for early detection and accurate prognostication in clinical oncology. Traditional diagnostic methods have many disadvantages, such as colonoscopy and histopathology are invasive and expensive, while biomarkers like carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and microsatellite instability (MSI) exhibit limitations in sensitivity and specificity, often leading to false-positive results. Therefore, as a valuable biomarker, the detection of microbial metabolites associated with colorectal tumors came into being. Microbial metabolic profiling provides a non-invasive method for the diagnosis and prognosis of CRC (Feng et al., 2023), which is expected to improve diagnostic accuracy and patient survival rates.
3.1 Identification of metabolites as diagnostic markers
Identification of microbial metabolites as diagnostic biomarkers for CRC has attracted considerable scientific interest. These gut microbial metabolites are detectable in various biological specimens, including stool, blood, tissue, urine, and exhaled breath (van Vorstenbosch et al., 2022). Notably, CRC patients exhibit dynamic shifts in microbial metabolite profiles, reflecting the complex interplay between the gut microbiome and tumor progression. Figure 1 provides an overview of the sample types and representative microbial metabolites used for CRC diagnosis.
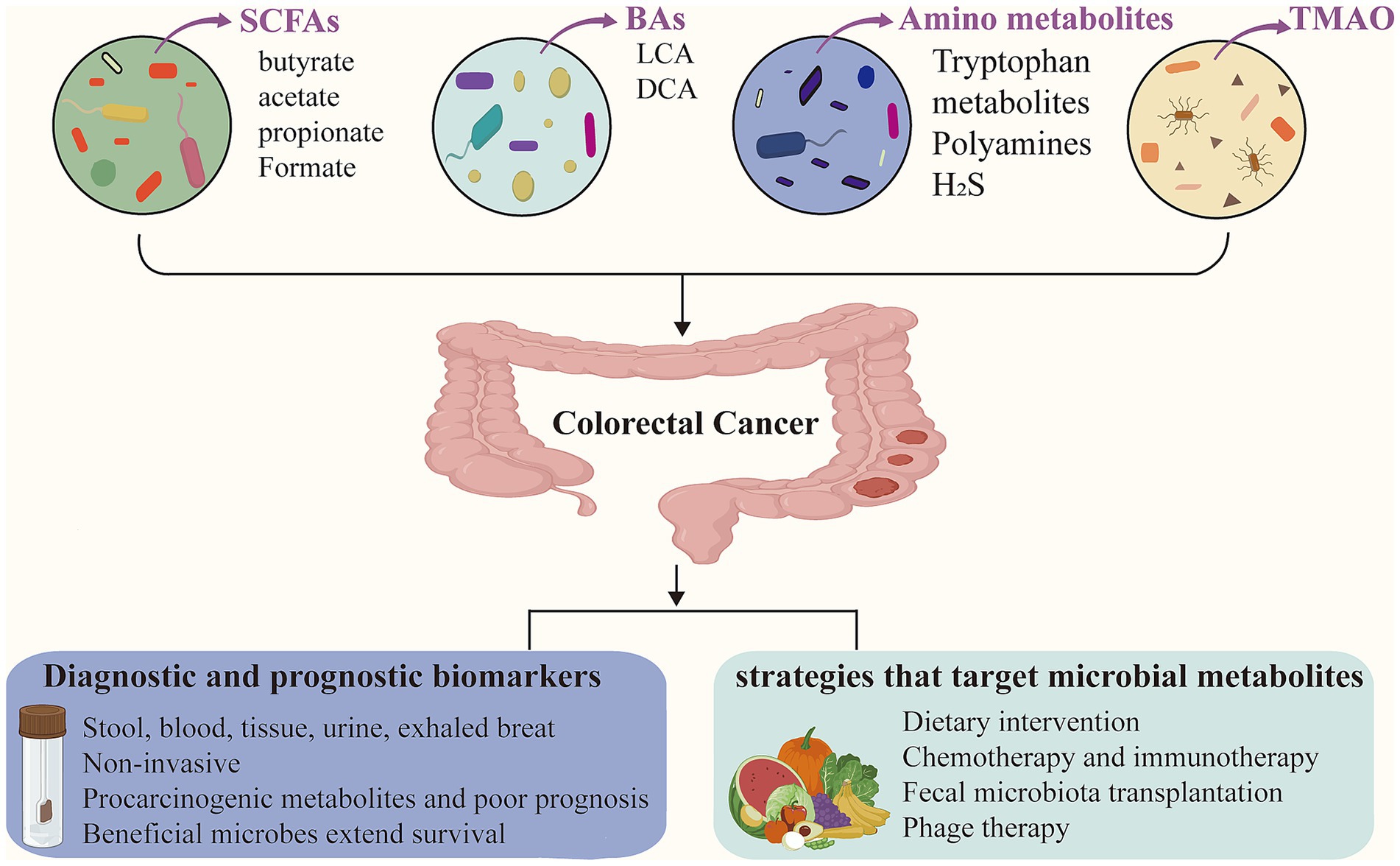
Figure 1. Gut microbial metabolites in colorectal cancer. Microbial metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), bile acids (BAs), amino acid derivatives, and trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), play important roles in the modulation of colorectal cancer (CRC). These metabolites can serve as non-invasive diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, detectable in stool, blood, tissue, urine, and exhaled breath. Furthermore, microbial metabolites offer emerging insights for guiding CRC treatment strategies.
Stool samples represent one of the most accessible and informative sources for microbial metabolite analysis, providing a direct reflection of gut microbial activity. A study involving 441 participants found that the fecal microbiota diversity of young CRC patients was significantly lower than that of healthy controls (p = 0.0074), and the abundance of butyrate-producing bacteria (such as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Eubacterium rectale) was significantly reduced (Kong et al., 2023). Additionally, stool metabolite analysis has revealed significant alterations in SBAs, which are produced by dysbiotic gut bacteria like Clostridium scindens. Increased fecal DCA levels correlate with tumorigenic changes in the colon, promoting carcinogenesis via DNA damage and FXR signaling disruption, making it a valuable biomarker for early CRC detection (Ma et al., 2022). Importantly, combining multiple metabolite markers - such as DCA/butyrate and polyamine/SCFA ratios has shown higher discriminatory power compared to single-metabolite measurements alone. Recent studies indicated that the ratio of butyrate to SBAs, such as DCA, offered superior diagnostic specificity in distinguishing early CRC from adenomas (AUC = 0.92). These findings supported the use of multi-metabolite panels to improve diagnostic accuracy and highlight the importance of combinatorial metabolite profiling (Coker et al., 2022).
In addition to stool analysis, other non-invasive methods such as urine and exhaled breath tests have also been employed clinically to detect alterations in gut microbial metabolites in patients with CRC. Certain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) produced by gut microbial metabolism can be excreted through urine and exhaled breath samples. Therefore, analyzing microbial-derived VOCs in urine and exhaled breath offers insights into gut microbiota activity and provides a novel direction for the early diagnosis and screening of CRC. A meta-analysis that included 11 CRC case studies evaluated the diagnostic potential of VOCs in breath and urine samples, identifying 14 microbial-related VOCs in CRC. The pooled sensitivity and specificity were 0.89 and 0.88, respectively, with an AUC of 0.95, indicating the strong diagnostic potential of VOCs for cancer screening (Zhou et al., 2024).
Microbial metabolites can be detected also in blood samples, particularly in serum or plasma, using metabolomics approaches such as liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS). A recent study by Hang et al. (2022) reported that higher plasma levels of the microbial metabolite phenylacetylglutamine (PAG) were associated with a lower risk of CRC precursors, including conventional adenomas and serrated polyps, in women. In line with this finding, another clinical trial analyzed plasma and fecal samples from 1,251 individuals which demonstrated significant differences in the metabolic profiles of patients with CRC and colorectal adenomas (CRA) compared to those in the normal control (NC) group. Notably, plasma from CRC patients exhibited a significant enrichment of oleic acid and a marked reduction in isodeoxycholic acid. Based on these metabolic changes, the study developed a diagnostic panel comprising 17 plasma metabolites, which achieved AUC values ranging from 0.848 to 0.987, highlighting the strong diagnostic potential of gut microbial metabolites (Sun et al., 2024). Gao’s work identified serum specific gut microbial metabolites, such as leucylalanine and linoleoylglycerol, which consistently distinguished CRC patients from healthy individuals across multiple cohorts. A diagnostic panel based on these metabolites achieved an AUC of 0.912 for colorectal adenomas (CRA) and 0.994 for CRC, indicating excellent diagnostic performance (Gao et al., 2022). These studies provided a basis for detecting intestinal microbial metabolites in blood samples to predict the progression of CRC. In addition, changing in plasma metabolites serves as an important indicator for determining whether a patient responds to chemotherapy to distinguish responders from non-responders. One study found significant differences in plasma metabolite profiles between chemotherapy responders and non-responders. By analyzing 17 specific plasma metabolites, the study established a diagnostic model with an AUC of 0.908, sensitivity of 86.4% and specificity of 83.3% (Sun et al., 2024).
The collection of tissue biopsy samples, like that of such as blood samples, is an invasive procedure (Cousins et al., 2019). Moreover, tissue biopsies may be limited by the representativeness of the sampling site. Tissue biopsies remain valuable in certain research contexts, particularly when direct analysis of the intratumoral microbiota and associated metabolites is required. Feng’s work compared cancerous lesions and surrounding non-tumorous tissues in CRC patients, along with corresponding stool samples, have revealed distinct microbial and metabolic profiles across these sample types (Feng et al., 2023). Additionally, another study investigated the characteristics of microbial communities and resistomes in biopsy specimens, underscoring the value of tissue samples in elucidating the complexity and dynamics of the gut microbiome (Yuan et al., 2021). When considering gut microbial metabolites as diagnostic biomarkers for CRC, selecting appropriate detection methods based on the clinical context is essential to ensure both clinical relevance and practical feasibility.
3.2 Prognostic value of microbial metabolites
Gut microbial metabolites profiling is important to the prognostic assessment of CRC. Alterations in specific gut microbial metabolites may serve as biomarkers for predicting CRC progression and patient outcomes. Several metabolites mentioned above, such as SBAs, TMAO, and H₂S, had been implicated in promoting CRC development by inducing chronic inflammation, DNA damage, and activation of oncogenic signaling pathways (Ajouz et al., 2014; Cheng et al., 2024). Accordingly, elevated levels of these metabolites in CRC patients often associated with poor prognosis. In contrast, specific SCFAs like butyrate are recognized for exerting anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects (Feitelson et al., 2023). Higher levels of butyrate in CRC patients are linked to improved prognostic outcomes. Several studies shown that the increased abundance of specific beneficial bacterial taxa and associated metabolites are significantly correlated with prolonged progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in cancer patients. This further supports the prognostic relevance of gut microbial metabolites (Zhu et al., 2024). In addition, Löser et al. demonstrated the potential value of polyamines as prognostic biomarkers for postoperative recurrence and disease progression in CRC patients (Löser et al., 1990). Although serum and urinary concentrations of several polyamines (e.g., total spermidine, acetylputrescine, and N1-acetylspermidine) were significantly elevated in CRC patients compared to healthy controls, similar elevations were also observed in certain non-malignant gastrointestinal conditions, limiting their diagnostic specificity. Thus, although polyamines exhibit high sensitivity, their utility as stand-alone diagnostic markers is limited, but their prognostic potential appears more promising. In patients who underwent curative surgery, polyamine levels returned to normal, whereas confirmed tumor recurrence or metastasis was associated with further increases. Moreover, polyamine levels were found to correlate positively with tumor size, although no significant associations were observed with Dukes staging, tumor location, or conventional tumor markers like CEA and CA19-9 (Löser et al., 1990). Overall the results indicate that polyamines may serve as auxiliary prognostic biomarkers for monitoring treatment response and detecting tumor recurrence. In conclusion, gut microbial metabolites show considerable promise as prognostic biomarkers in CRC. Before clinical application, large-scale cohort studies are required, and standardized protocols for sample preparation and metabolomic analysis are essential to ensure objective and accurate assessment of their prognostic utility.
4 Novel strategies based on gut microbial metabolites
4.1 Dietary intervention
Dietary intervention is crucial for regulating gut microbiota and its metabolites in the management of CRC. The effects of microbiota-targeted dietary treatments on CRC, based on microbial metabolite regulation are summarized in Table 1.
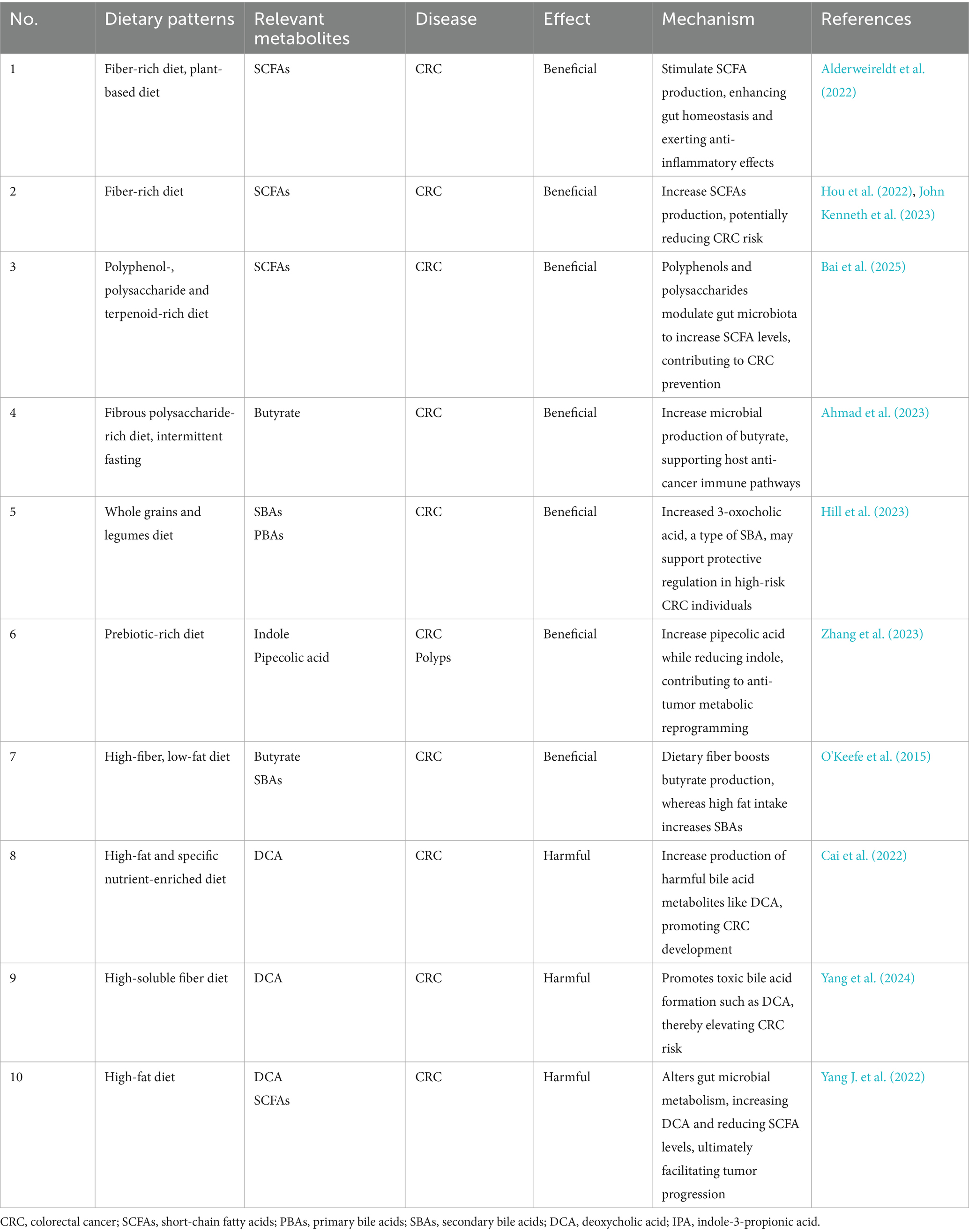
Table 1. Summary of dietary patterns targeting colorectal cancer through modulation of microbial metabolites.
During digestion, gut microbes ferment nutrients such as dietary fiber to produce SCFAs, including butyrate, propionate, and acetate. These metabolites exhibit anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor properties, thereby contributing to intestinal health (John Kenneth et al., 2023). Dietary fiber serves as the essential substrate for the microbial production of SCFAs. A comparative study between African Americans and rural South Africans demonstrated that compared to a diet high in animal protein and fat, a high-fiber, low-fat diet significantly increases butyrate production, inhibits SBAs synthesis (such as DCA), and reduces inflammation and hyperplasia of the colon mucosa, which is associated with the prevention of CRC (O'Keefe et al., 2015). Compared to a diet rich in animal-based proteins and fats, a high-fiber diet particularly the Mediterranean diet, which enhances butyrate production and inhibits histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity through epigenetic mechanisms, thus preventing CRC cells proliferation. Evidence from another study demonstrated a strong association between dietary patterns and risk of distal colon cancer. Diets that promote the enrichment of SCFA-producing bacteria were linked to a reduced risk of distal colon cancer. Specifically, the study showed that for men, the hazard ratio (HR) was 0.65 (95% CI, 0.47–0.89), indicating a significant protective effect. For women, the HR was 0.77 (95% CI, 0.64–0.93), also indicating a significant reduction in risk. This further confirm that a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, low in processed meats, and low in sugary beverages has a protective effect in reducing CRC risk (Lo et al., 2021). Plant-based diets are generally more beneficial than animal-based diets because plant-based diets are rich in unsaturated fatty acids and dietary fiber, which help increase SCFAs production, reduce SBAs production, and lower the risk of CRC (Alderweireldt et al., 2022). Diets rich in polyphenols, polysaccharides, and terpenoids can also indirectly promote the production of SCFAs, thereby potentially reducing the risk of CRC (Bai et al., 2025). In addition, dietary interventions such as dietary fiber polysaccharide intake and intermittent fasting (such as Ramadan fasting) are able to alter the composition of the gut microbiota, promote the growth of beneficial microorganisms, and strengthen the host’s anti-cancer defenses (Ahmad et al., 2023). However, excessive soluble fiber intake may disrupt microbial community composition, favoring the growth of harmful microbes that produce toxic bile acid metabolites, such as DCA, thereby increasing CRC risk (Yang et al., 2024). Additionally, a high-fat diet has been found to reduce the production of beneficial SCFAs while promoting intestinal inflammation through the increased production of harmful bile acid metabolites. This diet also activates key signaling pathways, including Wnt/β-catenin and NF-kB, which contribute to tumor progression. Furthermore, a high-fat diet may elevate the production of harmful metabolites, such as ammonia and nitrites, which promote cancer risk by inducing DNA damage and amplifying inflammation (Yang J. et al., 2022). Studies also suggest that bile acid derivatives such as UDCA may regulate bile acid metabolism and potentially reduce the risk of colon cancer. However, gender differences in its efficacy require further investigation to clarify its therapeutic potential (Cai et al., 2022).
In addition, prebiotic foods can have a positive impact on the treatment of CRC by regulating the intestinal microbiota and its metabolites. The BE GONE trial results demonstrated that after consuming legumes as prebiotic foods, obese patients with a history of CRC or polyps exhibited an increase in blood levels of pipecolic acid, while indole levels decreased (Zhang et al., 2023). The increase in pipecolic acid may reduce the risk of cancer by regulating the inflammatory environment in the intestine and reducing chronic low-grade inflammation, while the decrease in indole levels can help maintain a healthy intestinal environment and reduce the risk of cancer caused by intestinal inflammation. In another study, researchers found that supplementation with a whole grains and legumes diet, such as rice bran and navy beans, had limited effects on SCFAs but led to an increase in 3-oxocholic acid, a type of SBAs, which may support protective regulation in individuals at high risk for CRC (Hill et al., 2023). Additionally, dry legumes as prebiotic foods can promote the growth of gas-producing Clostridium perfringens, Enterococcus faecalis, and Bifidobacterium. Legumes may exert significant therapeutic effects in high-risk populations for CRC by modulating the gut microbiota and its metabolites (Cai et al., 2022). A recent review further reported that gut microbes can convert isoflavones from soy and its products into active metabolites such as equol, which shows strong inhibitory effects on CRC cells. This further confirms the association between soybean consumption and a reduced risk of CRC (Wang et al., 2024).
4.2 Chemotherapy
Metabolites produced by the gut microbiota may significantly contribute to CRC chemotherapy by modulating tumor metabolism, enhancing drug sensitivity, and mitigating chemotherapy-induced toxicity (Li S. et al., 2024). Increasing evidence indicates that gut microbiota and their metabolites can substantially influence the pharmacokinetics and therapeutic efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents. For instance, Zimmermann et al. (2019) systematically evaluated the metabolic capacity of 76 human gut bacterial strains against 271 orally administered drugs and found that more than two-thirds of the drugs could be significantly metabolized by at least one strain. These findings highlight the extensive potential of gut microbiota and their metabolites in modulating drug metabolism across various diseases, including CRC. Notably, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a key chemotherapeutic for CRC, also shows strong antimicrobial activity against Fusobacterium nucleatum (Fn), a bacterium linked to poor prognosis and chemoresistance (LaCourse et al., 2022). This suggests that part of 5-FU’s efficacy may stem from targeting tumor-associated microbes, underscoring the importance of microbiota–drug interactions in CRC treatment.
In this context, specific microbial metabolites have been shown to influence drug efficacy through distinct molecular mechanisms. Among these, butyrate and indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) are well-characterized. Butyrate enhances the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents via two mechanisms: it inhibits tumor cell glycolysis (the “Warburg effect”), reducing energy supply and sensitizing cells to chemotherapy, and it activates the GPR109a–AKT pathway, inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, thereby increasing chemosensitivity (Geng et al., 2021). IAA, on the other hand, is oxidized by myeloperoxidase (MPO) in tumor-infiltrating neutrophils into cytotoxic derivatives in FOLFIRINOX-treated models. These byproducts elevate ROS levels and downregulate antioxidant enzymes such as GPX3 and GPX7, enhancing oxidative stress (Tintelnot et al., 2023). Simultaneously, IAA inhibits autophagy, further suppressing tumor proliferation. These synergistic effects have been shown to boost the antitumor efficacy of chemotherapy in CRC and other solid tumors (Kwon, 2023). Beyond enhancing cytotoxicity, microbial metabolites also modulate chemoresistance. For instance, butyrate enhances CRC cell sensitivity to irinotecan by promoting apoptosis and reducing chemoresistance-related protein expression (Encarnação et al., 2018). It also facilitates OXA-induced ferroptosis by downregulating SLC7A11 in a c-Fos-dependent manner, overcoming ferroptosis resistance and improving drug efficacy (He et al., 2023). In contrast, some metabolites promote chemoresistance. Bacteroides vulgatus boosts nucleotide biosynthesis and DNA repair in tumor cells, enhancing resistance to 5-FU (Teng et al., 2023). H₂S similarly enhances resistance by modulating apoptosis pathways. In CRC cell models, H₂S inhibited chemotherapy-induced apoptosis, contributing to treatment failure. Inhibition of H₂S production, such as through aminooxyacetic acid (AOAA), has been shown to restore chemosensitivity and enhance 5-FU-induced apoptosis (Lin et al., 2023).
In addition to influencing drug efficacy and resistance, gut microbial metabolites also affect chemotherapy-induced toxicities. Butyrate has been shown to promote the differentiation of Tregs, thereby alleviating excessive inflammatory responses induced by chemotherapy. In addition, SCFAs play a protective role in maintaining intestinal mucosal integrity by reducing epithelial cell apoptosis, which helps mitigate chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal mucosal injury and lowers the incidence of adverse effects such as diarrhea (Al-Qadami et al., 2022). Moreover, butyrate exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that contribute to the attenuation of other systemic toxicities associated with chemotherapy, including cardiotoxicity, by protecting cardiomyocytes from damage (Russo et al., 2019). Therefore, certain natural bioactive compounds that promote the production of SCFAs, such as purple rice bran anthocyanins (PRBA), have shown promising potential as adjunctive therapies in CRC through reshaping the gut microbial composition and boosting antitumor immunity (Chen T. et al., 2022). Building on this, increasing attention has been given to natural polysaccharides used in combination with chemotherapeutic agents (Chen M. et al., 2022). For instance, carboxymethylated pachyman (CMP) and Albuca bracteata polysaccharides have demonstrated the ability to stimulate the production of SCFAs as well as to improve gut microbiota composition (Qin et al., 2022). Taken together, the combination of these natural compounds with chemotherapeutic drugs like 5-FU not only helps alleviate chemotherapy-induced gut dysbiosis and toxicity, but may also enhance the overall therapeutic efficacy by improving the intestinal microenvironment and reinforcing immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. In contrast, some gut microbial metabolites may intensify the systemic toxicity of chemotherapy by interfering with host drug metabolism. For instance, it has been shown that gut microbiota can convert Brivudine into a toxic metabolite, BVU, which is absorbed and disrupts hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes, thereby increasing the systemic toxicity of agents such as 5-FU. This finding reveals the pivotal role of microbial metabolites in modulating gastrointestinal drug metabolism and shaping therapeutic outcomes and systemic toxicity profiles in distant, sterile sites. Interestingly, certain microbial metabolites may exert dual effects. For example, urolithin A, derived from polyphenol metabolism by the gut microbiota, has been shown to enhance cancer cell sensitivity to chemotherapy-induced stress by regulating oxidative stress and activating mitophagy (D'Amico et al., 2021). At the same time, it downregulates the expression of multiple drug efflux pumps in tumor cells, thereby reversing multidrug resistance (MDR) and increasing the intracellular accumulation and cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents such as cisplatin, paclitaxel, and 5-FU (Ghosh et al., 2022).
4.3 Immunotherapy
Treatment strategies for CRC are undergoing a major shift from traditional surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation to immunotherapy. Immunotherapy has become an important part of CRC treatment by enhancing the body’s immune response to identify and eliminate cancer cells. Immune checkpoint blocking (ICB) therapy is an emerging cancer immunotherapy strategy, which alleviates immune suppression and promotes antitumor immunity by blocking the immune checkpoint pathway between tumor cells and immune cells. In CRC, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) primarily act by blocking the interaction between programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L1, and also by inhibiting the function of cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) (Jiao et al., 2020). However, there are many limitations in the clinical application of treatment in patients with CRC. There are significant differences in response to ICB therapy among CRC patients, with studies showing that individuals exhibiting deficient mismatch repair (dMMR) or high levels of microsatellite instability (MSI-H) tend to respond more favorably to ICB treatment, while the efficacy is limited for patients with microsatellite stability (MSS) (Jin and Sinicrope, 2022). In addition, the application of ICB therapy in CRC is also facing the problem of drug resistance. Therefore, immunotherapy studies based on metabolites of gut microbiota provide a new direction to improve the effectiveness of CRC immunotherapy. To further illustrate the regulatory roles of microbial metabolites in immune checkpoint therapy, Table 2 summarizes the current evidence on how representative gut microbial metabolites affect the efficacy and mechanisms of ICIs in CRC.
Growing research highlights the significant influence of microbial metabolites in modulating cancer immunotherapy. For instance, SCFAs, in addition to the roles mentioned above, may also be associated with the effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors. One study by Hou et al. found that SCFAs exhibit bidirectional immunoregulatory functions and modulate the therapeutic response to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy. The study indicated SCFAs contribute to strengthening antitumor immune activity via modulation of the tumor immune microenvironment, thus improving the efficacy of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 treatment. However, excessively high levels of SCFAs may lead to increased immune tolerance (Hou et al., 2022). Another study also discovered that SCFA production was reduced in mice on a low-fiber diet, which could suppress the immune system, particularly by reducing the activity and number of cytotoxic T cells required for anti-PD-1 therapy. This may lead to a worse response of tumors to anti-PD-1 treatment (Spencer et al., 2021). Furthermore, another study showed that butyrate inhibited the upregulation of CD80/CD86 on dendritic cells and the expression of Inducible T-cell Co-Stimulator on T cells in a mouse model, thereby impairing the recruitment of effector and memory T cells targeting tumor antigens. These changes may weaken the efficacy of anti-CTLA-4 therapy (Coutzac et al., 2020). Clinical studies also support these findings, suggesting that high levels of butyrate and propionate may enhance the function of immunosuppressive cells, such as Treg cells, and alter the immune microenvironment, thereby limiting the effectiveness of CTLA-4 inhibitors (Coutzac et al., 2020). The dual role of SCFAs on ICIs highlights the complexity of the effects of gut microbiota metabolites on the host, emphasizing the importance of continued investigation to determine the specific mechanisms.
Inosine, produced by specific commensal bacteria such as Lactobacillus johnsonii, has been shown to enhance the efficacy of ICB therapy. Immunotherapy-induced disruption of intestinal barrier function facilitates the systemic translocation of inosine. Inosine promotes T-helper 1 (Th1) differentiation by engaging the adenosine A2A receptor on T cells, thereby facilitating the recruitment of IFN-γ–producing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells within the tumor microenvironment, which augments the antitumor response induced by both anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 therapies (Liu et al., 2023). Notably, the immunomodulatory effect of inosine is context-dependent and may require a pro-inflammatory tumor microenvironment to exert its full therapeutic potential.
In a recent study, supplementation with Lactobacillus johnsonii or its microbial metabolite IPA also significantly improved the therapeutic outcome of ICB therapy in mice (Jia et al., 2024). The study demonstrated that Lactobacillus johnsonii collaborates with Clostridium sporogenes to produce IPAs, which then promote the driness of CD8 + T cells by increasing H3K27 acetylation in the T cell factor 7(Tcf7) superenhancer region. This epigenetic modification regulates the memory and persistence of T cells to support a more robust and sustained immune response, thereby improving the effectiveness of immunotherapy. Therefore, IPA supplementation promotes the expansion of CD8 + T cells, a key population of anti-tumor immune response, which helps to improve the cytotoxic ability of T cells against tumor cells. Based on this, the study found that L. johnii and its metabolite IPA can improve ICB reactivity and significantly improve the therapeutic efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors such as anti-PD-1 antibodies (Jia et al., 2024).
Another gut microbiome derived metabolite, gallic acid (GA), produced by microbial metabolism of dietary polyphenols such as tannins, has been found to enhance the efficacy of ICIs (Deng et al., 2022). GA acts by interfering with the phosphorylation process of signal transduction and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). In this way, it leads to decreased expression of the ubiquitin-specific peptidase 21 (Usp21) gene. The subsequent reduction in Usp21 gene expression creates a chain reaction that results in decreased stability of FOXP3 and PD-L1 proteins. At the same time, FOXP3 and PD-L1 are closely related to the immunosuppressive function of Treg cells, and the weakening of their stability will cause Treg cells to reprogram to show a phenotype more similar to Th1, reducing their inhibitory activity. The researchers conducted further validation using a CRC mouse model, in which significant changes were observed when GA was combined with an PD-1 antibody. The expression levels of FOXP3 and PD-L1 in tumor infiltrating Treg cells were significantly decreased. At the same time, the production of IFN-γ in CD8 + T cells increases. In summary, GA can effectively improve the therapeutic effect of anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 antibodies.
Studies have shown that the exopolysaccharide EPS-R1, produced by Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. Bulgaricus OLL1073R-1, can stimulate the production of CCR6+ CD8+ T cells in both mice and humans (Kawanabe-Matsuda et al., 2022). Oral administration of EPS-R1 in mice increases the number of CCR6+ CD8+ T cells in Peyer’s patches. These cells are capable of migrating to CCL20-expressing tumor tissues, including CRC, and exhibit enhanced IFN-γ production, thereby improving the tumor microenvironment (Nandi et al., 2021). This immunomodulatory effect of EPS-R1 significantly enhances the efficacy of ICIs, including anti-PD-1, anti-PD-L1, and anti-CTLA-4 antibodies, in treating CCL20-expressing colorectal tumors. These findings suggest that dietary intake of Lactobacillus-derived products containing EPS-R1 may represent a promising strategy to modulate specific T cell subsets and optimize the tumor microenvironment, ultimately improving the outcomes of immunotherapy for CRC.
Building upon the contribution of microbial metabolites to the improvement of immunotherapeutic outcomes, another study demonstrated that Limosilactobacillus reuteri (LR) produces indole-3-aldehyde (I3A), a tryptophan-derived metabolite that activates the AHR, thereby promoting IFN-γ and enhancing anti-tumor immune responses. Based on this finding, researchers developed a nanotechnology-engineered LR strain (LR-S-CD/CpG@LNP), which is loaded with an immunoadjuvant (CpG) and carbon dots (CDs), endowing it with photothermal and photodynamic properties. Experimental results showed that oral administration of LR-S-CD/CpG@LNP in mice modulated gut microbial metabolism and enhanced the tryptophan metabolic pathway, leading to increased I3A production (Xu et al., 2025). This, in turn, improved intestinal immune activity and markedly boosted the therapeutic effectiveness of immunotherapy against CRC.
The potential therapeutic impact of gut microbial metabolites extends beyond the prevention of immunosuppression; it also encompasses the mitigation of immune-related adverse events (irAEs). Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota may lead to immune dysregulation and an increased risk of irAEs. Studies have shown that microbial imbalance is associated with the exacerbation of irAEs, such as colitis, dermatologic reactions, and hepatotoxicity—common side effects observed in patients undergoing ICI therapy (Tan et al., 2022). Bacteria with anti-inflammatory properties, such as Bifidobacterium, and their metabolites may help alleviate immune-related inflammation. Restoring a healthier microbial balance could potentially mitigate the intensity of these immune-related complications, consequently enhancing both the tolerability and effectiveness of cancer immunotherapy. However, further clinical and mechanistic studies are needed to elucidate the specific relationships between gut microbial metabolites and irAEs, providing a foundation for future therapeutic strategies.
4.4 Fecal microbiota transplantation
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is an emerging microbiota-centered intervention that that entails transferring a diverse and stable community of gut microbiota from the feces of a healthy donor into the gastrointestinal tract of a recipient (Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka et al., 2020). Initially developed for the treatment of recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection, FMT has gained increasing attention in recent years due to its potential in correcting gut microbiota dysbiosis in various diseases, including CRC (Baunwall et al., 2020). As a novel microecological intervention, FMT reconstructs a healthy gut microbiota and effectively modulates the metabolic landscape within the tumor microenvironment. In one study using a CRC mouse model, FMT significantly improved survival, with approximately 90% of mice in the FMT-treated group surviving, compared to only about 50% in the untreated group (Yu et al., 2023). FMT was shown to restore heterogeneity and richness in gut microbiota of CRC mouse models, notably increasing the abundance of beneficial bacteria and reducing the proportion of harmful taxa. Furthermore, FMT alleviated intestinal inflammation by upregulating the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 and reduced the accumulation of immunosuppressive Foxp3+ Tregs, thereby enhancing anti-tumor immune responses and suppressing CRC progression. In another study, researchers also applied FMT to CRC mouse models and found that FMT could restore both microbial composition and metabolic profiles, suggesting its therapeutic potential in CRC (Song et al., 2024). FMT significantly influenced the composition of microbial metabolites by increasing the production of beneficial SCFAs, particularly butyrate, while reducing the accumulation of carcinogenic SBAs. Moreover, FMT has been reported to enhance tumor sensitivity to conventional therapies such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy by reshaping the gut microbiota (Kang and Cai, 2021). As a promising adjunctive or standalone strategy, FMT offers a feasible and innovative approach to microbiota-targeted therapy in the management of CRC.
4.5 Phage therapy
The use of bacteriophages to target specific pathogenic bacteria and modulate their metabolic products has emerged as a potential therapeutic strategy in CRC management (Han et al., 2025). Studies have shown that phage therapy can selectively reduce the abundance of harmful bacteria and thus indirectly alter the composition of gut microbial metabolites. This modulation can influence host immune responses and inflammatory status, ultimately having a beneficial impact on the treatment of CRC. In a rather representative study, researchers loaded dextran based nanoparticles loaded with the chemotherapeutic drug irinotecan and combined them with engineered phages targeting the tumor-promoting bacterium Fn in experiments using phage-guided nanotechnology to modulate the gut microbiota in mouse models of CRC (Kannen et al., 2019). The experimental results are exciting, and these phage-guided nanoparticles not only cleverly promote the growth of beneficial Clostridium butyricum production, inject positive factors into the intestinal microecological environment, but also substantially enhance the anti-tumor effect of irinotecan and significantly improve the effectiveness of treatment. This example of research strongly demonstrates that phage therapy holds great potential in modulating the gut microbiota and its metabolites. Although bacteriophages have shown promising prospects in the field of modulating the gut microbiota and its metabolites, it is undeniable that their use in CRC therapy is still in its infancy (Liping et al., 2024). In the practical application process, there are still many urgent challenges to be solved. These include poor in vivo stability, limited targeting specificity, potential immunogenicity, and the lack of safe and effective delivery methods (Cui L. et al., 2024). Addressing these issues is essential for advancing phage-based interventions.
5 Conclusion and prospect
Gut microbiota metabolites are now recognized as key mediators in the pathogenesis of CRC, acting as biochemical messengers that link microbial dysbiosis to tumor initiation and progression. These small molecules span a wide range of types and collectively influence essential processes in the colorectal tumor microenvironment, including chronic inflammation, immune surveillance, epithelial cell proliferation, and apoptosis. Some metabolites exert tumor-suppressive effects, for instance, SCFAs help maintain intestinal barrier integrity and induce cancer cell apoptosis, while others promote carcinogenesis through mechanisms such as inducing genomic instability or modulating host cell signaling in favor of tumor progression. Therefore, the overall impact of the gut metabolic network on CRC depends on a delicate balance of these opposing effects, which can vary depending on factors such as dosage and context (Zhang W. et al., 2021).
Recent studies have highlighted the potential of microbial metabolites as diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers for CRC (Li et al., 2022). Since a majority of metabolites in feces and urine originate from the microbiota, metabolomic analysis offers a non-invasive window to monitor tumor-associated microbial activity. Integrative analyses combining metagenomics and metabolomics have identified several metabolite panels with high diagnostic accuracy. In addition to early detection, metabolite biomarkers also hold promise in prognostication, as well as in monitoring treatment responses and disease relapse. However, further validation in large cohorts and standardization of detection methods are needed to ultimately translate these findings into clinical practice. In terms of treatment, gut microbiota metabolites are being actively explored as targets and tools for CRC therapy. In addition to dietary modulation to alter the production of microbial metabolites, the combination of beneficial metabolites or microbiota modulators with chemotherapy or immunotherapy has also shown promising results. Furthermore, FMT to introduce beneficial microbiota and bacteriophage therapy targeting CRC-associated pathogens provide additional therapeutic options for CRC. Although these methods are still in the experimental stage, microbiome-based therapies are opening new dimensions in CRC treatment. By focusing on the tumor-supportive microbial ecosystem rather than just the cancer cells themselves, these innovative approaches hold the potential to enhance the effectiveness of CRC therapies. Despite strong evidence linking gut metabolites to the pathogenesis of CRC, several important limitations still impact our current understanding. First, findings across different studies are not always consistent. Variations in study design, sample types, and analytical techniques can lead to discrepancies in the metabolites identified as significant (Peng et al., 2021). It is increasingly clear that the lack of standardized protocols for sample collection, processing, and analysis hinders the reproducibility of results. Fecal, blood, or tissue samples may produce different metabolite profiles, and the outcomes can vary depending on the techniques used, such as gas chromatography–mass spectrometry or nuclear magnetic resonance. Therefore, there is an urgent need for larger cohorts and standardized sample preparation and metabolomic analysis methods to ensure the robustness of the identified biomarkers and mechanisms. Source attribution is another challenge. Many metabolites of interest, such as certain amino acid derivatives or vitamins, can be produced both by the microbiota and the host, or derived from the diet. Untangling the source of a metabolite detected in patients—whether microbial, host, or dietary—can often be challenging. Moreover, current research tends to focus on a relatively small subset of metabolites, leaving many compounds underexplored. The human gut metabolome contains thousands of molecules; however, most studies have concentrated on short-chain fatty acids, a few bile acids, and well-known toxins such as colibactin or H₂S. Many other bacterial products’ roles in CRC remain insufficiently studied. It is likely that within these metabolites lies crucial biological insight into cancer biology. Similarly, the gut mycobiome and virome have been relatively neglected. These interact with bacterial communities and hosts, producing metabolites that influence bacterial metabolism (El Haddad et al., 2022). Addressing these issues will require expanding our research perspective to consider the gut microbiota as a complex and diverse ecosystem, where each component may impact the development of CRC.
Looking ahead, integrating gut microbial metabolites into CRC management will require interdisciplinary and innovative research efforts. Incorporating host genomics, diet, and lifestyle factors into microbiome studies is crucial. The interaction between the host genome and microbiota may help explain why certain individuals are more sensitive to the pro-carcinogenic effects of microbial metabolites, thereby opening new avenues for personalized strategies aligned with an individual’s specific microbiome and metabolic characteristics. In terms of treatment, precision microbiome manipulation holds great promise. While traditional dietary and probiotic interventions remain relatively crude, engineered microbiota-based therapies are expected to emerge in the coming years. Synthetic biology enables bacteria to be genetically programmed to perform desired functions in the gut. In CRC, researchers can design probiotics to secrete anti-cancer compounds, neutralize carcinogenic metabolites, or deliver immune-modulating signals in the tumor microenvironment. These “designer probiotics” can be tailored to individual microbiomes, enhancing therapeutic specificity (Siguenza et al., 2024). Similarly, phage therapy can be bioengineered to improve efficacy and safety, targeting harmful bacteria and delivering gene-editing tools to knock out genes responsible for toxic metabolites. Additionally, developing small-molecule inhibitors to block microbial enzymes represents an attractive strategy for chemically modulating microbiome metabolism without eradicating microbes. In conclusion, gut microbial metabolites are critically involved in CRC by contributing to tumor development, serving as indicators of disease onset and progression, and offering novel therapeutic opportunities. Despite the challenges in decoding these complex biochemical interactions, the field is rapidly advancing. Continued interdisciplinary efforts and well-designed clinical trials will help uncover deeper insights into the relationship between CRC and gut microbial metabolites, offering new opportunities for more effective treatment strategies.
Author contributions
QC: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MY: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MC: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Committee–College Joint Innovation Fund (number: WXLH202403006), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (number: 82274529), and the Hundred Talents Program for Improving Scientific Research Capacity (number: 20-B05).
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the funding agencies.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdeen, S. K., Mastandrea, I., Stinchcombe, N., Puschhof, J., and Elinav, E. (2025). Diet-microbiome interactions in cancer. Cancer Cell 43, 680–707. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2025.03.013
Ahmad, F., Saha, P., Singh, V., Wahid, M., Mandal, R. K., Nath Mishra, B., et al. (2023). Diet as a modifiable factor in tumorigenesis: focus on microbiome-derived bile acid metabolites and short-chain fatty acids. Food Chem. 410:135320. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135320
Ai, D., Pan, H., Li, X., Gao, Y., Liu, G., and Xia, L. C. (2019). Identifying gut microbiota associated with colorectal cancer using a zero-inflated lognormal model. Front. Microbiol. 10:826. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00826
Ajouz, H., Mukherji, D., and Shamseddine, A. (2014). Secondary bile acids: an underrecognized cause of colon cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 12:164. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-12-164
Alderweireldt, E., Grootaert, C., De Wever, O., and Van Camp, J. (2022). A two-front nutritional environment fuels colorectal cancer: perspectives for dietary intervention. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 33, 105–119. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2021.11.002
Al-Qadami, G. H., Secombe, K. R., Subramaniam, C. B., Wardill, H. R., and Bowen, J. M. (2022). Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids: impact on Cancer treatment response and toxicities. Microorganisms 10:2048. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10102048
Alustiza, M., Ripoll, L., Canals, A., Murcia, O., Martínez-Roca, A., García-Heredia, A., et al. (2023). A novel non-invasive colorectal cancer diagnostic method: volatile organic compounds as biomarkers. Clin. Chim. Acta 542:117273. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2023.117273
Alvandi, E., Wong, W. K. M., Joglekar, M. V., Spring, K. J., and Hardikar, A. A. (2022). Short-chain fatty acid concentrations in the incidence and risk-stratification of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 20:323. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02529-4
Ascenção, K., Dilek, N., Augsburger, F., Panagaki, T., Zuhra, K., and Szabo, C. (2021). Pharmacological induction of mesenchymal-epithelial transition via inhibition of H2S biosynthesis and consequent suppression of ACLY activity in colon cancer cells. Pharmacol. Res. 165:105393. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105393
Bai, X., Liu, B., Fan, D., Lu, Y., and Zhao, X. (2025). Modulating the gut microbiota: a novel perspective in colorectal cancer treatment. Cancer Lett. 612:217459. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217459
Baunwall, S. M. D., Lee, M. M., Eriksen, M. K., Mullish, B. H., Marchesi, J. R., Dahlerup, J. F., et al. (2020). Faecal microbiota transplantation for recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine 29-30:100642. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100642
Bishehsari, F., Engen, P. A., Preite, N. Z., Tuncil, Y. E., Naqib, A., Shaikh, M., et al. (2018). Dietary Fiber treatment corrects the composition of gut microbiota, promotes SCFA production, and suppresses Colon carcinogenesis. Genes (Basel) 9:102. doi: 10.3390/genes9020102
Bultman, S. J. (2017). Interplay between diet, gut microbiota, epigenetic events, and colorectal cancer. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 61, 97–106. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201500902
Byrd, D. A., Zouiouich, S., Karwa, S., Li, X. S., Wang, Z., Sampson, J. N., et al. (2024). Associations of serum trimethylamine N-oxide and its precursors with colorectal cancer risk in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial Cohort. Cancer 130, 1982–1990. doi: 10.1002/cncr.35219
Cai, J., Sun, L., and Gonzalez, F. J. (2022). Gut microbiota-derived bile acids in intestinal immunity, inflammation, and tumorigenesis. Cell Host Microbe 30, 289–300. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2022.02.004
Caliceti, C., Punzo, A., Silla, A., Simoni, P., Roda, G., and Hrelia, S. (2022). New insights into bile acids related signaling pathways in the onset of colorectal cancer. Nutrients 14:2964. doi: 10.3390/nu14142964
Cao, Y., Yi, Y., Han, C., and Shi, B. (2024). NF-κB signaling pathway in tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 15:1476030. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1476030
Chang, Y., Long, M., Shan, H., Liu, L., Zhong, S., and Luo, J. L. (2025). Combining gut microbiota modulation and immunotherapy: a promising approach for treating microsatellite stable colorectal cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 208:104629. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2025.104629
Chen, M., Lin, W., Li, N., Wang, Q., Zhu, S., Zeng, A., et al. (2022). Therapeutic approaches to colorectal cancer via strategies based on modulation of gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 13:945533. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.945533
Chen, T., Shen, M., Yu, Q., Chen, Y., Wen, H., Lu, H., et al. (2022). Purple red rice anthocyanins alleviate intestinal damage in cyclophosphamide-induced mice associated with modulation of intestinal barrier function and gut microbiota. Food Chem. 397:133768. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133768
Chen, J., and Vitetta, L. (2021). Intestinal dysbiosis in celiac disease: decreased butyrate production may facilitate the onset of the disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 118:e2113655118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2113655118
Cheng, W., Li, F., and Yang, R. (2024). The roles of gut microbiota metabolites in the occurrence and development of colorectal Cancer: multiple insights for potential clinical applications. Gastro Hep Adv. 3, 855–870. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2024.05.012
Coker, O. O., Liu, C., Wu, W. K. K., Wong, S. H., Jia, W., Sung, J. J. Y., et al. (2022). Altered gut metabolites and microbiota interactions are implicated in colorectal carcinogenesis and can be non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers. Microbiome 10:35. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01208-5
Cousins, S., Blencowe, N. S., and Blazeby, J. M. (2019). What is an invasive procedure? A definition to inform study design, evidence synthesis and research tracking. BMJ Open 9:e028576. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028576
Coutzac, C., Jouniaux, J. M., Paci, A., Schmidt, J., Mallardo, D., Seck, A., et al. (2020). Systemic short chain fatty acids limit antitumor effect of CTLA-4 blockade in hosts with cancer. Nat. Commun. 11:2168. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16079-x
Cui, W., Hao, M., Yang, X., Yin, C., and Chu, B. (2024). Gut microbial metabolism in ferroptosis and colorectal cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 35, 341–351. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2024.08.006
Cui, L., Watanabe, S., Miyanaga, K., Kiga, K., Sasahara, T., Aiba, Y., et al. (2024). A comprehensive review on phage therapy and phage-based drug development. Antibiotics (Basel) 13:870. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13090870
Dai, Z., Deng, K. L., Wang, X. M., Yang, D. X., Tang, C. L., and Zhou, Y. P. (2024). Bidirectional effects of the tryptophan metabolite indole-3-acetaldehyde on colorectal cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 16, 2697–2715. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2697
D'Amico, D., Andreux, P. A., Valdés, P., Singh, A., Rinsch, C., and Auwerx, J. (2021). Impact of the natural compound Urolithin a on health, disease, and aging. Trends Mol. Med. 27, 687–699. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2021.04.009
Deng, B., Yang, B., Chen, J., Wang, S., Zhang, W., Guo, Y., et al. (2022). Gallic acid induces T-helper-1-like T (reg) cells and strengthens immune checkpoint blockade efficacy. J. Immunother. Cancer 10:e004037. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-004037
Di Ciaula, A., Bonfrate, L., Khalil, M., and Portincasa, P. (2023). The interaction of bile acids and gut inflammation influences the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Intern. Emerg. Med. 18, 2181–2197. doi: 10.1007/s11739-023-03343-3
El Haddad, L., Mendoza, J. F., and Jobin, C. (2022). Bacteriophage-mediated manipulations of microbiota in gastrointestinal diseases. Front. Microbiol. 13:1055427. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1055427
El Tekle, G., and Garrett, W. S. (2023). Bacteria in cancer initiation, promotion and progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 23, 600–618. doi: 10.1038/s41568-023-00594-2
Encarnação, J. C., Pires, A. S., Amaral, R. A., Gonçalves, T. J., Laranjo, M., Casalta-Lopes, J. E., et al. (2018). Butyrate, a dietary fiber derivative that improves irinotecan effect in colon cancer cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 56, 183–192. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.02.018
Feitelson, M. A., Arzumanyan, A., Medhat, A., and Spector, I. (2023). Short-chain fatty acids in cancer pathogenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 42, 677–698. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10117-y
Feng, J., Gong, Z., Sun, Z., Li, J., Xu, N., Thorne, R. F., et al. (2023). Microbiome and metabolic features of tissues and feces reveal diagnostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Front. Microbiol. 14:1034325. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1034325
Gao, R., Wu, C., Zhu, Y., Kong, C., Zhu, Y., Gao, Y., et al. (2022). Integrated analysis of colorectal Cancer reveals cross-cohort gut microbial signatures and associated serum metabolites. Gastroenterology 163, 1024–1037.e9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.06.069
Geng, H. W., Yin, F. Y., Zhang, Z. F., Gong, X., and Yang, Y. (2021). Butyrate suppresses glucose metabolism of colorectal Cancer cells via GPR109a-AKT signaling pathway and enhances chemotherapy. Front. Mol. Biosci. 8:634874. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.634874
Ghosh, S., Singh, R., Vanwinkle, Z. M., Guo, H., Vemula, P. K., Goel, A., et al. (2022). Microbial metabolite restricts 5-fluorouracil-resistant colonic tumor progression by sensitizing drug transporters via regulation of FOXO3-FOXM1 axis. Theranostics 12, 5574–5595. doi: 10.7150/thno.70754
Gomes, S. D., Oliveira, C. S., Azevedo-Silva, J., Casanova, M. R., Barreto, J., Pereira, H., et al. (2020). The role of diet related short-chain fatty acids in colorectal Cancer metabolism and survival: prevention and therapeutic implications. Curr. Med. Chem. 27, 4087–4108. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180530102050
Goodwin, A. C., Destefano Shields, C. E., Wu, S., Huso, D. L., Wu, X., Murray-Stewart, T. R., et al. (2011). Polyamine catabolism contributes to enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis-induced colon tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 15354–15359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010203108
Gou, H., Zeng, R., Lau, H. C. H., and Yu, J. (2024). Gut microbial metabolites: shaping future diagnosis and treatment against gastrointestinal cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 208:107373. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107373
Han, Q., Li, J., Li, Z., Aishajiang, R., and Yu, D. (2025). Novel therapeutic strategies and recent advances in gut microbiota synergy with nanotechnology for colorectal cancer treatment. Mater. Today Bio 31:101601. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101601
Hang, D., Zeleznik, O. A., Lu, J., Joshi, A. D., Wu, K., Hu, Z., et al. (2022). Plasma metabolomic profiles for colorectal cancer precursors in women. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 37, 413–422. doi: 10.1007/s10654-021-00834-5
Hanus, M., Parada-Venegas, D., Landskron, G., Wielandt, A. M., Hurtado, C., Alvarez, K., et al. (2021). Immune system, microbiota, and microbial metabolites: the unresolved triad in colorectal Cancer microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 12:612826. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.612826
He, Y., Fu, L., Li, Y., Wang, W., Gong, M., Zhang, J., et al. (2021). Gut microbial metabolites facilitate anticancer therapy efficacy by modulating cytotoxic CD8(+) T cell immunity. Cell Metab. 33, 988–1000.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.03.002
He, Y., Ling, Y., Zhang, Z., Mertens, R. T., Cao, Q., Xu, X., et al. (2023). Butyrate reverses ferroptosis resistance in colorectal cancer by inducing c-Fos-dependent xCT suppression. Redox Biol. 65:102822. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102822
Hill, E. B., Baxter, B. A., Pfluger, B., Slaughter, C. K., Beale, M., Smith, H. V., et al. (2023). Plasma, urine, and stool metabolites in response to dietary rice bran and navy bean supplementation in adults at high-risk for colorectal cancer. Front. Gastroenterol. (Lausanne) 2:1087056. doi: 10.3389/fgstr.2023.1087056
Holbert, C. E., Casero, R. A. Jr., and Stewart, T. M. (2024). Polyamines: the pivotal amines in influencing the tumor microenvironment. Discov. Oncol. 15:173. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01034-9
Hou, H., Chen, D., Zhang, K., Zhang, W., Liu, T., Wang, S., et al. (2022). Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and colorectal cancer: ready for clinical translation? Cancer Lett. 526, 225–235. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.11.027
Huang, R., Shen, Z. Y., Huang, D., Zhao, S. H., Dan, L. X., Wu, P., et al. (2025). Microbiota-indole-3-propionic acid-heart axis mediates the protection of leflunomide against αPD1-induced cardiotoxicity in mice. Nat. Commun. 16:2651. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58107-8
Jia, D., Wang, Q., Qi, Y., Jiang, Y., He, J., Lin, Y., et al. (2024). Microbial metabolite enhances immunotherapy efficacy by modulating T cell stemness in pan-cancer. Cell 187, 1651–1665.e21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.02.022
Jia, W., Xie, G., and Jia, W. (2018). Bile acid-microbiota crosstalk in gastrointestinal inflammation and carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 15, 111–128. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.119
Jiang, X., Jiang, Z., Cheng, Q., Sun, W., Jiang, M., and Sun, Y. (2022). Cholecystectomy promotes the development of colorectal cancer by the alternation of bile acid metabolism and the gut microbiota. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 9:1000563. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1000563
Jiao, Q., Ren, Y., Ariston Gabrie, A. N., Wang, Q., Wang, Y., Du, L., et al. (2020). Advances of immune checkpoints in colorectal cancer treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 123:109745. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109745
Jin, Z., and Sinicrope, F. A. (2022). Mismatch repair-deficient colorectal Cancer: building on checkpoint blockade. J. Clin. Oncol. 40, 2735–2750. doi: 10.1200/jco.21.02691
John Kenneth, M., Tsai, H. C., Fang, C. Y., Hussain, B., Chiu, Y. C., and Hsu, B. M. (2023). Diet-mediated gut microbial community modulation and signature metabolites as potential biomarkers for early diagnosis, prognosis, prevention and stage-specific treatment of colorectal cancer. J. Adv. Res. 52, 45–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.12.015
Kang, Y. B., and Cai, Y. (2021). Faecal microbiota transplantation enhances efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors therapy against cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 27, 5362–5375. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i32.5362
Kannen, V., Parry, L., and Martin, F. L. (2019). Phages enter the fight against colorectal Cancer. Trends Cancer 5, 577–579. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.08.002
Kawanabe-Matsuda, H., Takeda, K., Nakamura, M., Makino, S., Karasaki, T., Kakimi, K., et al. (2022). Dietary Lactobacillus-derived exopolysaccharide enhances immune-checkpoint blockade therapy. Cancer Discov. 12, 1336–1355. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-21-0929
Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka, K., Daca, A., Fic, M., van de Wetering, T., Folwarski, M., and Makarewicz, W. (2020). Therapeutic methods of gut microbiota modification in colorectal cancer management - fecal microbiota transplantation, prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics. Gut Microbes 11, 1518–1530. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1764309
Kong, C., Liang, L., Liu, G., Du, L., Yang, Y., Liu, J., et al. (2023). Integrated metagenomic and metabolomic analysis reveals distinct gut-microbiome-derived phenotypes in early-onset colorectal cancer. Gut 72, 1129–1142. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327156
Kouhzad, M., Götz, F., Navidifar, T., Taki, E., Ghamari, M., Mohammadzadeh, R., et al. (2025). Carcinogenic and anticancer activities of microbiota-derived secondary bile acids. Front. Oncol. 15:1514872. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1514872
Krause, F. F., Mangold, K. I., Ruppert, A. L., Leister, H., Hellhund-Zingel, A., Lopez Krol, A., et al. (2024). Clostridium sporogenes-derived metabolites protect mice against colonic inflammation. Gut Microbes 16:2412669. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2412669
Kuhn, D. M., and Hasegawa, H. (2020). “Chapter 12- tryptophan hydroxylase and serotonin synthesis regulation” in Handbook of behavioral neuroscience. eds. C. P. Müller and K. A. Cunningham (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 239–256.
Kulecka, M., Czarnowski, P., Bałabas, A., Turkot, M., Kruczkowska-Tarantowicz, K., Żeber-Lubecka, N., et al. (2024). Microbial and metabolic gut profiling across seven malignancies identifies fecal Faecalibacillus intestinalis and formic acid as commonly altered in Cancer patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25:8026. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158026
Kwon, B. (2023). A metabolite of the gut microbiota: a facilitator of chemotherapy efficacy in cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 8:238. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01506-4
LaCourse, K. D., Zepeda-Rivera, M., Kempchinsky, A. G., Baryiames, A., Minot, S. S., Johnston, C. D., et al. (2022). The cancer chemotherapeutic 5-fluorouracil is a potent Fusobacterium nucleatum inhibitor and its activity is modified by intratumoral microbiota. Cell Rep. 41:111625. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111625
Li, M., Ding, Y., Wei, J., Dong, Y., Wang, J., Dai, X., et al. (2024). Gut microbiota metabolite indole-3-acetic acid maintains intestinal epithelial homeostasis through mucin sulfation. Gut Microbes 16:2377576. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2377576
Li, J., Meng, Y., Wu, X., and Sun, Y. (2020). Polyamines and related signaling pathways in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 20:539. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01545-9
Li, J., Zhang, A. H., Wu, F. F., and Wang, X. J. (2022). Alterations in the gut microbiota and their metabolites in colorectal Cancer: recent Progress and future prospects. Front. Oncol. 12:841552. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.841552
Li, S., Zhu, S., and Yu, J. (2024). The role of gut microbiota and metabolites in cancer chemotherapy. J. Adv. Res. 64, 223–235. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.11.027
Lin, H., Yu, Y., Zhu, L., Lai, N., Zhang, L., Guo, Y., et al. (2023). Implications of hydrogen sulfide in colorectal cancer: mechanistic insights and diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Redox Biol. 59:102601. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102601
Liping, Z., Sheng, Y., Yinhang, W., Yifei, S., Jiaqun, H., Xiaojian, Y., et al. (2024). Comprehensive retrospect and future perspective on bacteriophage and cancer. Virol. J. 21:278. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02553-1
Liu, Y., and Dai, M. (2020). Trimethylamine N-oxide generated by the gut microbiota is associated with vascular inflammation: new insights into atherosclerosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 4634172–4634115. doi: 10.1155/2020/4634172
Liu, Y., Lau, H. C., Cheng, W. Y., and Yu, J. (2023). Gut microbiome in colorectal Cancer: clinical diagnosis and treatment. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 21, 84–96. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2022.07.002
Liu, L., Yang, M., Dong, W., Liu, T., Song, X., Gu, Y., et al. (2021). Gut Dysbiosis and abnormal bile acid metabolism in colitis-associated Cancer. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2021, 6645970–6645912. doi: 10.1155/2021/6645970
Liu, X., Yang, M., Xu, P., Du, M., Li, S., Shi, J., et al. (2024). Kynurenine-AhR reduces T-cell infiltration and induces a delayed T-cell immune response by suppressing the STAT1-CXCL9/CXCL10 axis in tuberculosis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 21, 1426–1440. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01230-1
Liu, Y., Zhang, S., Zhou, W., Hu, D., Xu, H., and Ji, G. (2022). Secondary bile acids and tumorigenesis in colorectal cancer. Front. Oncol. 12:813745. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.813745
Lo, C.-H., Mehta, R. S., Nguyen, L. H., Wang, Y., Ma, W., Wang, K., et al. (2021). Empirical dietary pattern associated with short-chain fatty acid-producing BACTERIA in relation to colorectal CANCER risk. Gastroenterology 160, S-165–S-166. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(21)01147-1
Löser, C., Fölsch, U. R., Paprotny, C., and Creutzfeldt, W. (1990). Polyamines in colorectal cancer. Evaluation of polyamine concentrations in the colon tissue, serum, and urine of 50 patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer 65, 958–966. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19900215)65:4<958::aid-cncr2820650423>3.0.co;2-z
Ma, Y., Zhang, Y., Qu, R., Zhou, X., Sun, L., Wang, K., et al. (2022). Promotion of deoxycholic acid effect on colonic Cancer cell lines in vitro by altering the mucosal microbiota. Microorganisms 10:2486. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10122486
Marques, C., Oliveira, C. S., Alves, S., Chaves, S. R., Coutinho, O. P., Côrte-Real, M., et al. (2013). Acetate-induced apoptosis in colorectal carcinoma cells involves lysosomal membrane permeabilization and cathepsin D release. Cell Death Dis. 4:e507. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.29
Nandi, B., Del Valle, J. P., Samur, M. K., Gibbons, A. J., Prabhala, R. H., Munshi, N. C., et al. (2021). CCL20 induces colorectal cancer neoplastic epithelial cell proliferation, migration, and further CCL20 production through autocrine HGF-c-met and MSP-MSPR signaling pathways. Oncotarget 12, 2323–2337. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28131
Nolan, L. S., Mihi, B., Agrawal, P., Gong, Q., Rimer, J. M., Bidani, S. S., et al. (2021). Indole-3-Carbinol-dependent aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling attenuates the inflammatory response in experimental necrotizing Enterocolitis. Immunohorizons 5, 193–209. doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.2100018
Ocvirk, S., and O'Keefe, S. J. (2017). Influence of bile acids on colorectal Cancer risk: potential mechanisms mediated by diet-gut microbiota interactions. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 6, 315–322. doi: 10.1007/s13668-017-0219-5
O'Keefe, S. J., Li, J. V., Lahti, L., Ou, J., Carbonero, F., Mohammed, K., et al. (2015). Fat, fibre and cancer risk in African Americans and rural Africans. Nat. Commun. 6:6342. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7342
Park, M. H., and Igarashi, K. (2013). Polyamines and their metabolites as diagnostic markers of human diseases. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 21, 1–9. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2012.097
Payne, C. M., Crowley-Skillicorn, C., Bernstein, C., Holubec, H., Moyer, M. P., and Bernstein, H. (2010). Hydrophobic bile acid-induced micronuclei formation, mitotic perturbations, and decreases in spindle checkpoint proteins: relevance to genomic instability in colon carcinogenesis. Nutr. Cancer 62, 825–840. doi: 10.1080/01635581003695756
Peng, Y., Nie, Y., Yu, J., and Wong, C. C. (2021). Microbial metabolites in colorectal cancer: basic and clinical implications. Meta 11:159. doi: 10.3390/metabo11030159
Platten, M., Nollen, E. A. A., Röhrig, U. F., Fallarino, F., and Opitz, C. A. (2019). Tryptophan metabolism as a common therapeutic target in cancer, neurodegeneration and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 18, 379–401. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0016-5
Qin, Z., Yuan, X., Liu, J., Shi, Z., Cao, L., Yang, L., et al. (2022). Albuca Bracteata polysaccharides attenuate AOM/DSS induced Colon tumorigenesis via regulating oxidative stress, inflammation and gut microbiota in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 13:833077. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.833077
Reddy, B., Engle, A., Katsifis, S., Simi, B., Bartram, H. P., Perrino, P., et al. (1989). Biochemical epidemiology of colon cancer: effect of types of dietary fiber on fecal mutagens, acid, and neutral sterols in healthy subjects. Cancer Res. 49, 4629–4635
Richard, D. M., Dawes, M. A., Mathias, C. W., Acheson, A., Hill-Kapturczak, N., and Dougherty, D. M. (2009). L-tryptophan: basic metabolic functions, behavioral research and therapeutic indications. Int. J. Tryptophan. Res. 2, 45–60. doi: 10.4137/ijtr.s2129
Ridlon, J. M., Wolf, P. G., and Gaskins, H. R. (2016). Taurocholic acid metabolism by gut microbes and colon cancer. Gut Microbes 7, 201–215. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2016.1150414
Russo, M., Guida, F., Paparo, L., Trinchese, G., Aitoro, R., Avagliano, C., et al. (2019). The novel butyrate derivative phenylalanine-butyramide protects from doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 21, 519–528. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1439
Ryu, T. Y., Kim, K., Han, T. S., Lee, M. O., Lee, J., Choi, J., et al. (2022). Human gut-microbiome-derived propionate coordinates proteasomal degradation via HECTD2 upregulation to target EHMT2 in colorectal cancer. ISME J. 16, 1205–1221. doi: 10.1038/s41396-021-01119-1
Ryu, T. Y., Kim, K., Son, M. Y., Min, J. K., Kim, J., Han, T. S., et al. (2019). Downregulation of PRMT1, a histone arginine methyltransferase, by sodium propionate induces cell apoptosis in colon cancer. Oncol. Rep. 41, 1691–1699. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6938
Safe, S., Lee, S. O., and Jin, U. H. (2013). Role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in carcinogenesis and potential as a drug target. Toxicol. Sci. 135, 1–16. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft128
Sameni, F., Elkhichi, P. A., Dadashi, A., Sadeghi, M., Goudarzi, M., Eshkalak, M. P., et al. (2025). Global prevalence of Fusobacterium nucleatum and Bacteroides fragilis in patients with colorectal cancer: an overview of case reports/case series and meta-analysis of prevalence studies. BMC Gastroenterol. 25:71. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03664-x
Siguenza, N., Brevi, A., Zhang, J. T., Pabani, A., Bhushan, A., Das, M., et al. (2024). Engineered bacterial therapeutics for detecting and treating CRC. Trends Cancer 10, 588–597. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2024.04.001
Soda, K. (2011). The mechanisms by which polyamines accelerate tumor spread. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 30:95. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-30-95
Song, M., and Chan, A. T. (2019). Environmental factors, gut microbiota, and colorectal Cancer prevention. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 17, 275–289. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.07.012
Song, M., Chan, A. T., and Sun, J. (2020). Influence of the gut microbiome, diet, and environment on risk of colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 158, 322–340. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.06.048
Song, Q., Gao, Y., Liu, K., Tang, Y., Man, Y., and Wu, H. (2024). Gut microbial and metabolomics profiles reveal the potential mechanism of fecal microbiota transplantation in modulating the progression of colitis-associated colorectal cancer in mice. J. Transl. Med. 22:1028. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05786-4
Spencer, C. N., McQuade, J. L., Gopalakrishnan, V., McCulloch, J. A., Vetizou, M., Cogdill, A. P., et al. (2021). Dietary fiber and probiotics influence the gut microbiome and melanoma immunotherapy response. Science 374, 1632–1640. doi: 10.1126/science.aaz7015
Sun, L., Cai, J., and Gonzalez, F. J. (2021). The role of farnesoid X receptor in metabolic diseases, and gastrointestinal and liver cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 18, 335–347. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-00404-2
Sun, Y., Zhang, X., Hang, D., Lau, H. C., Du, J., Liu, C., et al. (2024). Integrative plasma and fecal metabolomics identify functional metabolites in adenoma-colorectal cancer progression and as early diagnostic biomarkers. Cancer Cell 42, 1386–1400.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2024.07.005
Sun, X. Z., Zhao, D. Y., Zhou, Y. C., Wang, Q. Q., Qin, G., and Yao, S. K. (2020). Alteration of fecal tryptophan metabolism correlates with shifted microbiota and may be involved in pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 26, 7173–7190. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7173
Tan, B., Liu, Y. X., Tang, H., Chen, D., Xu, Y., Chen, M. J., et al. (2022). Gut microbiota shed new light on the management of immune-related adverse events. Thorac. Cancer 13, 2681–2691. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14626
Teng, H., Wang, Y., Sui, X., Fan, J., Li, S., Lei, X., et al. (2023). Gut microbiota-mediated nucleotide synthesis attenuates the response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer. Cancer Cell 41, 124–138.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.11.013
Ternes, D., Tsenkova, M., Pozdeev, V. I., Meyers, M., Koncina, E., Atatri, S., et al. (2022). The gut microbial metabolite formate exacerbates colorectal cancer progression. Nat. Metab. 4, 458–475. doi: 10.1038/s42255-022-00558-0
Tintelnot, J., Xu, Y., Lesker, T. R., Schönlein, M., Konczalla, L., Giannou, A. D., et al. (2023). Microbiota-derived 3-IAA influences chemotherapy efficacy in pancreatic cancer. Nature 615, 168–174. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05728-y
Untereiner, A. A., Oláh, G., Módis, K., Hellmich, M. R., and Szabo, C. (2017). H (2)S-induced S-sulfhydration of lactate dehydrogenase a (LDHA) stimulates cellular bioenergetics in HCT116 colon cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 136, 86–98. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.03.025
van Vorstenbosch, R., Cheng, H. R., Jonkers, D., Penders, J., Schoon, E., Masclee, A., et al. (2022). Systematic review: contribution of the gut microbiome to the volatile metabolic fingerprint of colorectal neoplasia. Meta 13:55. doi: 10.3390/metabo13010055
Wang, X., Chen, B., Fang, X., Zhong, Q., Liao, Z., Wang, J., et al. (2024). Soy isoflavone-specific biotransformation product S-equol in the colon: physiological functions, transformation mechanisms, and metabolic regulatory pathways. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64, 5462–5490. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2154744
Wang, R. H., Chu, Y. H., and Lin, K. T. (2021). The hidden role of hydrogen sulfide metabolism in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:6562. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126562
Wang, X., and Hu, Y. (2025). High-dose sodium propionate contributes to tumor immune escape through the IGF2BP3/PD-L1 axis in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 29:303. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.15049
Wang, C., Ruan, P., Zhao, Y., Li, X., Wang, J., Wu, X., et al. (2017). Spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase regulates cell growth and metastasis via AKT/β-catenin signaling pathways in hepatocellular and colorectal carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 8, 1092–1109. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13582
Wang, G., Yu, Y., Wang, Y. Z., Wang, J. J., Guan, R., Sun, Y., et al. (2019). Role of SCFAs in gut microbiome and glycolysis for colorectal cancer therapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 234, 17023–17049. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28436
Wu, J. Y., Zeng, Y., You, Y. Y., and Chen, Q. Y. (2025). Polyamine metabolism and anti-tumor immunity. Front. Immunol. 16:1529337. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1529337
Wyatt, M., and Greathouse, K. L. (2021). Targeting dietary and microbial tryptophan-indole metabolism as therapeutic approaches to colon cancer. Nutrients 13:1189. doi: 10.3390/nu13041189
Xu, H., Wang, Y., Liu, G., Zhu, Z., Shahbazi, M. A., Reis, R. L., et al. (2025). Nano-armed Limosilactobacillus reuteri for enhanced photo-immunotherapy and microbiota tryptophan metabolism against colorectal Cancer. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 12:e2410011. doi: 10.1002/advs.202410011
Yan, J., Chen, D., Ye, Z., Zhu, X., Li, X., Jiao, H., et al. (2024). Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic significance of tryptophan metabolism and signaling in cancer. Mol. Cancer 23:241. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02164-y
Yang, S., Dai, H., Lu, Y., Li, R., Gao, C., and Pan, S. (2022). Trimethylamine N-oxide promotes cell proliferation and angiogenesis in colorectal Cancer. J Immunol Res 2022, 7043856–7043857. doi: 10.1155/2022/7043856
Yang, Y., Misra, B. B., Liang, L., Bi, D., Weng, W., Wu, W., et al. (2019). Integrated microbiome and metabolome analysis reveals a novel interplay between commensal bacteria and metabolites in colorectal cancer. Theranostics 9, 4101–4114. doi: 10.7150/thno.35186
Yang, S., Wang, Y., Sheng, L., Cui, W., and Ma, C. (2025). The effect of fecal bile acids on the incidence and risk-stratification of colorectal cancer: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 15:740. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84801-6
Yang, J., Wei, H., Lin, Y., Chu, E. S. H., Zhou, Y., Gou, H., et al. (2024). High soluble Fiber promotes colorectal tumorigenesis through modulating gut microbiota and metabolites in mice. Gastroenterology 166, 323–337.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.012
Yang, J., Wei, H., Zhou, Y., Szeto, C. H., Li, C., Lin, Y., et al. (2022). High-fat diet promotes colorectal tumorigenesis through modulating gut microbiota and metabolites. Gastroenterology 162, 135–149.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.08.041
Ye, X., Li, H., Anjum, K., Zhong, X., Miao, S., Zheng, G., et al. (2022). Dual role of indoles derived from intestinal microbiota on human health. Front. Immunol. 13:903526. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.903526
Yin, Y., Wan, J., Yu, J., and Wu, K. (2023). Molecular pathogenesis of colitis-associated colorectal Cancer: immunity, genetics, and intestinal microecology. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 29, 1648–1657. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izad081
Yin, Y., Wang, M., Gu, W., and Chen, L. (2021). Intestine-specific FXR agonists as potential therapeutic agents for colorectal cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 186:114430. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114430
Yu, H., Li, X. X., Han, X., Chen, B. X., Zhang, X. H., Gao, S., et al. (2023). Fecal microbiota transplantation inhibits colorectal cancer progression: reversing intestinal microbial dysbiosis to enhance anti-cancer immune responses. Front. Microbiol. 14:1126808. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1126808
Yu, M., Wang, Q., Ma, Y., Li, L., Yu, K., Zhang, Z., et al. (2018). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation modulates intestinal epithelial barrier function by maintaining tight junction integrity. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 14, 69–77. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.22259
Yuan, Y., Chen, Y., Yao, F., Zeng, M., Xie, Q., Shafiq, M., et al. (2021). Microbiomes and Resistomes in biopsy tissue and intestinal lavage fluid of colorectal Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9:736994. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.736994
Zeng, H., Hamlin, S. K., Safratowich, B. D., Cheng, W. H., and Johnson, L. K. (2020). Superior inhibitory efficacy of butyrate over propionate and acetate against human colon cancer cell proliferation via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis: linking dietary fiber to cancer prevention. Nutr. Res. 83, 63–72. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2020.08.009
Zeng, H., Umar, S., Rust, B., Lazarova, D., and Bordonaro, M. (2019). Secondary bile acids and short chain fatty acids in the Colon: a focus on colonic microbiome, cell proliferation, inflammation, and cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:1214. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051214
Zhang, W., An, Y., Qin, X., Wu, X., Wang, X., Hou, H., et al. (2021). Gut microbiota-derived metabolites in colorectal cancer: the bad and the challenges. Front. Oncol. 11:739648. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.739648
Zhang, X., Irajizad, E., Hoffman, K. L., Fahrmann, J. F., Li, F., Seo, Y. D., et al. (2023). Modulating a prebiotic food source influences inflammation and immune-regulating gut microbes and metabolites: insights from the BE GONE trial. EBioMedicine 98:104873. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104873
Zhang, H., Xu, H., Zhang, C., Tang, Q., and Bi, F. (2021). Ursodeoxycholic acid suppresses the malignant progression of colorectal cancer through TGR5-YAP axis. Cell Death Discov. 7:207. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00589-8
Zhao, Z. H., Xin, F. Z., Xue, Y., Hu, Z., Han, Y., Ma, F., et al. (2019). Indole-3-propionic acid inhibits gut dysbiosis and endotoxin leakage to attenuate steatohepatitis in rats. Exp. Mol. Med. 51, 1–14. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0304-5
Zhou, M., Wang, Q., Lu, X., Zhang, P., Yang, R., Chen, Y., et al. (2024). Exhaled breath and urinary volatile organic compounds (VOCs) for cancer diagnoses, and microbial-related VOC metabolic pathway analysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 110, 1755–1769. doi: 10.1097/js9.0000000000000999
Zhu, P., Lu, T., Chen, Z., Liu, B., Fan, D., Li, C., et al. (2022). 5-hydroxytryptamine produced by enteric serotonergic neurons initiates colorectal cancer stem cell self-renewal and tumorigenesis. Neuron 110, 2268–2282.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.04.024
Zhu, C., Wang, Y., Zhu, R., Wang, S., Xue, J., Zhang, D., et al. (2024). Gut microbiota and metabolites signatures of clinical response in anti-PD-1/PD-L1 based immunotherapy of biliary tract cancer. Biomark. Res. 12:56. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00607-8
Zimmermann, M., Zimmermann-Kogadeeva, M., Wegmann, R., and Goodman, A. L. (2019). Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature 570, 462–467. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1291-3
Keywords: colorectal cancer, gut microbiota, microbial metabolites, biomarkers, therapeutic strategies
Citation: Cao Q, Yang M and Chen M (2025) Metabolic interactions: how gut microbial metabolites influence colorectal cancer. Front. Microbiol. 16:1611698. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1611698
Edited by:
Mingsong Kang, Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA), CanadaReviewed by:
Markus Tschurtschenthaler, Technical University of Munich, GermanyBahman Mirzaei, Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Cao, Yang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Min Chen, Y21AY2R1dGNtLmVkdS5jbg==
 Qinhan Cao
Qinhan Cao Meiju Yang
Meiju Yang Min Chen
Min Chen