- 1College of Landscape Architecture and Horticulture, Southwest Forestry University, Kunming, China
- 2Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Life Sciences, China Medical University, Shenyang, China
- 3Yunnan Provincial Key Laboratory for Conservation and Utilization of In-forest Resource, Southwest Forestry University, Kunming, China
Introduction: The species of tree most appropriate for the cultivation of Sanqi in an understory environment is pine. Nevertheless, the precise type of pine that confers the greatest benefit to soil health during Sanqi cultivation has not been definitively established.
Methods: Herein, four distinct land use configurations were established, including the Pinus armandii, Pinus kesiya, Sanqi–Pinus armandii (SPA), and Sanqi–Pinus kesiya (SPK) systems. High-throughput sequencing technology and metabolomics analysis were used to comparatively evaluate variations in bacterial and fungal community structures and soil metabolites between the SPA and SPK systems.
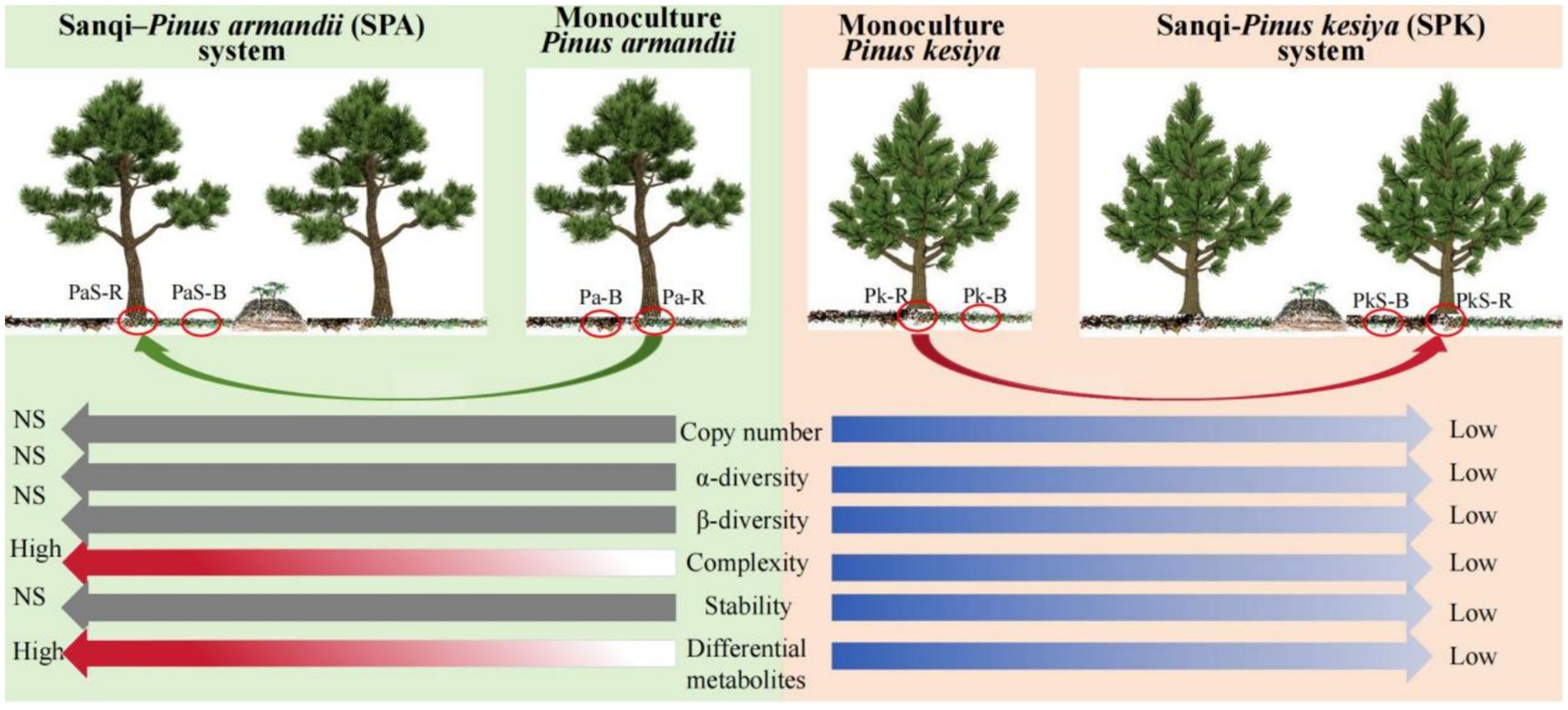
Results and discussion: After cultivating Sanqi, the content of total phosphorus, ammonium nitrogen, and total potassium as well as water content and soil pH were significantly increased in P. armandii soil. Moreover, the bacterial and fungal copy numbers, alpha- and beta-diversity, remained unchanged in the soil of P. armandii, but significantly decreased in the soil of P. kesiya following Sanqi planting. Moreover, Sanqi cultivation significant increased complexity of the microbial network in P. armandii rather than P. kesiya soil, while the network stability was maintained. Structural equation modeling indicated that soil enzymes, metabolites, and edaphic factors enhanced the complexity of the microbial network in P. armandii soil in SPA system. Additionally, the content of eight differentially accumulated metabolites (DAMs) was significantly increased in the rhizosphere and bulk soils of P. armandii. In conclusion, the cultivation of Sanqi benefits the microbiome and metabolites in P. armandii rather than P. kesiya soil, thus providing an important theoretical foundation for the sustainable development of Sanqi cultivation.
Highlights
• After cultivating Sanqi, bacterial and fungal copy numbers, α- and β- diversity were unchanged in P. armandii soil but significantly decreased in P. kesiya soil.
• Sanqi cultivation increased microbial network complexity in P. armandii rather than P. kesiya soil, while maintaining network stability.
• Differential metabolites increased significantly in the rhizosphere and bulk soil of P. armandii after Sanqi planting.
• After cultivating Sanqi, soil enzymes, metabolites, and edaphic factors increased the complexity of the microbial network in P. armandii soil.
1 Introduction
Sanqi (Panax notoginseng) is a perennial herbaceous plant that belongs to the family Araliaceae. The practice of artificial cultivation of Sanqi began in China four centuries ago, with Yunnan and Guangxi Provinces being the primary areas of cultivation (Chen et al., 2022). Sanqi has considerable therapeutic effects such as promoting blood circulation and resolving blood stasis, reducing swelling, and relieving pain (Hei et al., 2023). Furthermore, its root and flowers are key ingredients of several Chinese patent medicines (Li et al., 2024). A conventional management of Sanqi cultivation is associated with continuous cropping obstacles of considerable severity, with a 7–10-year interval typically required before replantation can be done (Tan et al., 2017). Conversely, Sanqi cultivation in the forest understory under organic management is associated with several benefits, including improvements in the quality of Sanqi (Li et al., 2024), mitigation of continuous cropping obstacles (Hei et al., 2023, 2024), enhancement of soil microbial diversity (Jia et al., 2022), alleviation of carbon limitation in pine soils (Rui et al., 2025), and increase in the content of differentially accumulated metabolites (DAMs) (He et al., 2025). Previous studies have revealed that suitable forest tree species for Sanqi cultivation include broadleaf (with trees such as walnut; Gong et al., 2016), coniferous (Pinus armandii, Pinus kesiya, and Pinus yunnanensis; Jia et al., 2022), and mixed (a combination of coniferous and broadleaf trees; Deng et al., 2020) forests. However, previous research has indicated that Sanqi cultivated under the pine trees can achieve better quality and higher yield (Shi et al., 2021). Therefore, the Sanqi–pine agroforestry system subjected to organic management has been widely promoted in Yunnan and covers an area of 666.67 hectares (Hei et al., 2023). Sanqi is a key plant species in the agroforestry system, and previous research on Sanqi has chiefly focused on the optimization of planting density (Liu et al., 2021), prevention and control of pests and diseases (Luo et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2023), quality analysis (Chen et al., 2022; Hei et al., 2023), identification of metabolites (Shi et al., 2022), and prevention as well as control of continuous cropping obstacles. Nonetheless, it is imperative to consider the sustainable development of both plant species within the agroforestry system. Consequently, undertaking research on the impact of Sanqi cultivation on soil health and its impact on the growth of pine trees is expected to aid the establishment of a robust theoretical foundation for the sustainable development of the Sanqi–pine agroforestry system.
Soil microbes are considered a key indicator of soil health in terrestrial ecosystems (Wilhelm et al., 2022), and they are significantly influenced by cropping patterns and ecological niches (Karoline and Jeroen, 2012; Qin et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2023). The conversion of land use pattern to agroforestry systems has had a significant impact on the abundance and community structure of soil microbes (Araujo et al., 2012; Beule et al., 2022). For example, the walnut–tea agroforestry system has been shown to notably enhance the abundance and structural composition of bacterial and fungal communities in the soil (Bai et al., 2022). Likewise, the mulberry–peanut agroforestry system has been observed to augment the diversity and richness of bacterial and fungal populations (Li M. N. et al., 2022). Conversely, a decline in the richness and diversity of soil microbes has been observed in other systems, including the ginkgo–metasequoia and ginkgo–rubber agroforestry systems (Wang et al., 2017; Guo et al., 2021). These varying outcomes may be attributed to a confluence of factors encompassing plant species (Mortimer et al., 2015) and growth environments (Guo et al., 2021). Furthermore, the conversion of pine forests into Sanqi–pine agroforestry systems facilitates the transfer of beneficial microbial communities from Sanqi to the pine trees, subsequently inducing an elevation in the alpha (α)–diversity of fungi in the soil where the pine trees grow. Conversely, the transfer of microbes from pine trees to Sanqi influences the microbial composition and endophytes associated with Sanqi (Jia et al., 2022). The cultivation of Sanqi has been shown to result in higher diversity of fungi compared to that of bacteria in the rhizosphere of pine trees, while the bacterial and fungal diversity in the soil of Sanqi remain consistent. Additionally, enhancements have been observed in the diversity, community structure, network complexity, and stability of carbon-fixing bacteria in the soil in which Sanqi and pine were grown (He et al., 2025), as well as in the diversity and network complexity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil in which Sanqi was cultivated (Zhao et al., 2025). This phenomenon is attributed to the differences in the types of root exudates produced by various plants (Ding et al., 2022) and the unique environmental conditions in the soil (Jiang et al., 2023).
Soil metabolites serve as biomarkers for changes in the community composition of soil microbes (Li et al., 2023), and the metabolite components are significantly influenced by different cultivation practices and ecological niches. The primary soil metabolites in pine forests include organic and phenolic acids (Shao et al., 2011). However, the cultivation of Sanqi in the forest understory leads to an increase in the content of organic acids such as phthalic and palmitic acids in the soil (Hei et al., 2023). An increase in the concentration of these organic acids beyond 150 mg/kg negatively affects plant growth, soil environment, and the interactions among the members of the microbial communities (Hei et al., 2023, 2024). This is attributed to the transport capacity of organic acids, despite the differences in the transport range among different plants. For instance, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid and vanillin cause significant autotoxicity within a 20-cm range of the Rehmannia glutinosa root system, and this effect weakens with increasing distance from the root system (Zhang et al., 2016). By contrast, benzoic acid shows strong allelopathic activity within a 6–10-cm zone of the Panax ginseng root system (Ren, 2016). On the one hand, organic acids can regulate soil metabolites via interactions with other organic and phenolic acids (Shen et al., 2020; Hei et al., 2024). Conversely, they influence the structure of microbial communities and thereby, indirectly affect soil metabolites (Zhou et al., 2023). Furthermore, ecological niches (rhizosphere and bulk) have a significant impact on soil metabolites (Zhalnina et al., 2018). Studies have shown that metabolites in the rhizosphere soil exhibit trends of increase (Song et al., 2020), decrease (Sun et al., 2022), or lack of significant changes (Chen et al., 2018) compared to bulk soil. These variations are attributed to differences in plant root morphology (Iannucci et al., 2021), root exudates (Bi et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2023), soil factors (Tian et al., 2022), and microbial community structure (Cheng et al., 2022). In summary, the soil metabolites released from one plant may exert either positive or negative effects on the growth of other plants in the environment (Wang et al., 2021).
Sanqi thrives in the forests of P. armandii, P. kesiya, and P. yunnanensis understorey. Among these three pine species, the most extensive areas suitable for Sanqi cultivation are those of P. armandii and P. kesiya. Previous research has indicated that the microbiomes associated with Sanqi significantly influence the microbial communities related to P. armandii and P. kesiya (Jia et al., 2022). However, it remains unclear whether Sanqi cultivation affects the metabolites in pine soil. Additionally, microbiomes are closely linked to metabolites, and the metabolites of some medicinal plants can disperse over a distance (Zhang et al., 2016). Thus, four land use patterns, encompassing the P. armandii, P. kesiya, Sanqi–P. armandii (SPA), and Sanqi–P. kesiya (SPK) systems, were established. Bacterial and fungal communities, along with soil metabolites, were comparatively analyzed using high-throughput sequencing and LC–MS metabolomics approaches to explore the effects of Sanqi cultivation on the relationship between microbiomes and metabolites. The purpose of this study was: (1) To determine the effects of Sanqi cultivation on the soil microbiomes and metabolites of P. armandii and P. kesiya; (2) to investigate the changes in the relationship between soil microbiomes and metabolites.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study sites and Sanqi transplantation
The sites corresponding to the SPA and SPK systems are located in Lancang Lahu Autonomous County, Pu’er City, Yunnan Province (with coordinates 22.74°N and 99.82°E, elevation 1457.39 m, average annual temperature 19.2°C, and average annual precipitation 1008.6 mm) and Dadi Water Village, Xundian Hui Autonomous County, Kunming City (coordinates 25.47°N and 103.21°E, elevation 2247.81 m, average annual temperature 15.5°C, and average annual precipitation 1624.0 mm), respectively.
Plots under the SPA and SPK systems with slopes ranging from 5° to 15° were selected in December 2018. After the clearing of stones and vegetation from the soil surface, the soil was plowed to a depth of 20–30 cm, and its pH was adjusted using hydrated lime. A ridge of the following dimensions was constructed along the isoheight of each forest: 40-cm height with 120- and 80-cm width at the base and top, respectively. Subsequently, one-year-old Sanqi seedlings were transplanted in the ridges at a depth of 3–5 cm and with row spacing of (10–15) cm × (10–15) cm; they were then covered with 2–5 cm of soil. Following Sanqi transplantation, the surface of the soil was covered with pine needles of 3–5 cm thickness. The cultivation techniques and routine management practices for Sanqi in the forest understory were carried out as detailed previously (Hei et al., 2023, 2024).
2.2 Experimental design and soil sampling
To compare the effects of Sanqi plantation on the soils of P. armandii and P. kesiya, 24 plots each measuring 10 m × 10 m were established herein, including those with P. armandii and P. kesiya monocultures and SPA as well as SPK systems; the corresponding soils in these systems are hereafter referred to as Pa-R, Pa-B, Pk-R, Pk-B, PaS-R, PaS-B, PkS-R and PkS-B.
In November 2021, prior to Sanqi harvest, the rhizosphere and bulk soil from each plot were collected using a five-point method (Jia et al., 2024). The soil (0–2 mm) adhering to the root surfaces of P. armandii and P. kesiya was designated as rhizosphere soil, whereas the soil obtained at a depth of 0–20 cm and distance of 20 cm away from P. armandii and P. kesiya was considered bulk soil. A total of 24 soil samples were collected, specifically: 8 treatments × 3 replicates. All the soil samples were subsequently combined to form a composite sample, which was treated as a single replicate. The soil samples were passed through a 4-mm sieve and then segregated into three distinct portions that were subsequently preserved at 4°C and −80°C or air-dried in an indoor setting for subsequent analysis.
2.3 Analyses of physicochemical characteristics and multiple ecosystem functions
Soil water content (WC) was determined by subjecting the soil samples to drying at 100°C for 24 h. Soil pH was determined using a 1: 5 (w: v) soil slurry. The content of total phosphorus (TP), total nitrogen (TN), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−–N), and ammonium nitrogen (NH4+–N) in the soil matrix was measured using a continuous flow analyzer (Seal Auto Analyzer AA3, Germany). Total potassium (TK) was quantified employing a flame atomic absorption spectrophotometer (AA-6300C). The soil organic carbon (SOC) content was determined using the potassium dichromate oxidation method.
2.4 DNA extraction and qPCR analysis
The Power Soil DNA Isolation Kit (MoBio, USA) was utilized for extracting DNA from the soil samples (0.5 g). The quality and concentration of the isolated DNA were assessed using agarose gel (1%) electrophoresis and NanoDrop2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA), respectively. Absolute quantification of bacteria (16S rRNA) and fungi (ITS1) in the soil samples was performed using the LightCycler®480 II system (Roche, Switzerland). The sequences of the primers employed for the quantification of bacteria (338F/806R) and fungi (ITS1F/ITS2R), along with the protocols for qPCR, are presented in Supplementary Table S1. After determining the concentration of the plasmid DNA isolated using a plasmid extraction kit (Takara, China), a standard curve was generated by carrying out qPCR with 10-fold serial dilutions of the plasmid DNA. The amplification efficiencies of the 16S rRNA and ITS genes ranged from 95 to 103%, with R2 > 0.99. The Cp value for each sample was ascertained via comparison with the standard curve based on the initial copy number of the 16S rRNA and ITS genes, with three replicates employed for each sample.
2.5 Illumina sequencing
High-throughput sequencing of the purified amplicons was conducted at Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Company in Shanghai (China) utilizing the Illumina MiSeq PE300 platform (Illumina, USA). The sequence similarity threshold for operational taxonomic units was set at 0.97. The sequences associated with accession numbers PRJNA821648 (bacteria) and PRJNA821834 (fungi) have been archived in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive.
2.6 Metabolite profiling using rhizosphere soil samples
Samples of rhizosphere soil (1 g each) from Pa, Pk, PaS, and PkS were accurately weighed and mixed with 1 mL of extraction solution (4:1 [v/v] mixture of methanol: water). The samples were pulverized in a frozen tissue grinder at −10°C and 50 Hz, followed by incubation at −20°C for 30 min. After centrifuging for 15 min at 13,000 rpm and 4°C, 120 μL of a 1:1 (v/v) acetonitrile mixture: water was added, and the sample was extracted by ultrasonication at a low temperature (5°C, 40 kHz) for 5 min. Subsequently, the sample was subjected to another centrifugation step for 15 min. The supernatant was transferred to sample vials for subsequent liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis (Thermo Scientific, USA). The data were processed and annotated using Progenesis QI (Waters Corporation, USA) and various databases (HMDB, KEGG) for metabolite identification.
2.7 Statistical analysis
The sample data adhered to the assumptions of homogeneity and normal distribution, as evidenced by the Levene’s test (p > 0.05) and the Shapiro–Wilk test (p > 0.05). Then, the measured edaphic factors and microbial abundances were subjected to one-way analysis of variance utilizing SPSS 23 (SPSS Inc., USA). The α- (Chao and Shannon indices) and beta (β)–diversity were calculated using QIIME and the Bray–Curtis distance matrix, respectively. Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA) was executed using the vegan package (version 2.5–3). Microbial composition was evaluated using Circos software. The influence of soil characteristics on the microbial community was evaluated using Redundancy Analysis (RDA) (Hei et al., 2023). Before conducting the RDA analysis, and considering that the length of the first axis of the Detrended Correspondence Analysis (DCA) was less than 3, we determined that RDA is more suitable than CCA for analyzing soil characteristics and microbial communities (correlation coefficient > 0.7; Li N. et al., 2022). The topological coefficients were determined using the “igraph” R package to evaluate the network complexity. The greater the node, edge, and graph density, as well as the average degree and clustering coefficient, the lower the average path length and graph diameter, indicating a higher complexity of the network (Xu et al., 2023). We selected the top 200 OTUs with higher abundance to calculate the network stability of bacteria and fungi. Specifically, the network stability analysis was conducted using R software (version 4.2.2), and was measured by the remaining proportion of nodes (proportion of remaining nodes in the network after random removal some nodes) and robustness (proportion of remaining nodes in the network after random deletion of 50% of the nodes) (Wu et al., 2021). Generally, networks with a higher proportion of remaining nodes and robustness exhibit greater stability, with each error bar representing the standard deviation of 100 repeated simulations (Xu et al., 2023). Structural equation modeling (SEM) was employed for investigating the interconnections between α-diversity, soil edaphic factors, microbial abundance, soil enzyme activity, microbial community composition, soil metabolites, and network complexity as well as stability. The appropriateness of the model was evaluated using the goodness of fit index (>0.7), as proposed by Rosseel (2012).
3 Results
3.1 Analysis of the physicochemical properties of various soil samples
Significant increase in the content of TP, NH4+–N, WC, and TK as well as soil pH was observed in the PaS soil compared to that in the Pa soil, while the content of SOC and TN exhibited a significant decrease. Furthermore, all the assessed indicators in the PaS soil, except for WC and the content of TP and NH4+–N, exhibited higher concentrations in the rhizosphere soil compared to that in the bulk soil. Additionally, the content of SOC and NO3−–N was significantly higher in the PkS soil compared to that in the Pk soil, while the content of TN, NH4+–N, and TK as well as soil pH were significantly lower. Moreover, all the evaluated indicators in the PkS soil, except for WC and the content of SOC and TK, were higher in the rhizosphere soil compared to that in the bulk soil (Supplementary Table S2).
3.2 Variations in the copy number and α- as well as β-diversity of soil microbes
The copy numbers and α-diversity of bacteria and fungi, as evaluated using Shannon and Chao indices, were not significantly different in the PaS soil compared to that in the Pa soil. Moreover, the copy numbers of bacteria and fungi were highest in the rhizosphere soil; however, the α-diversity of bacteria and fungi did not significantly differ between the rhizosphere and bulk soils. In general, the copy numbers and α-diversity of bacteria and fungi were significantly reduced in the PkS soil compared to that in the Pk soil. Moreover, the highest values of these indicators were obtained in the rhizosphere soil (Figure 1; Supplementary Figure S1; Supplementary Table S3).
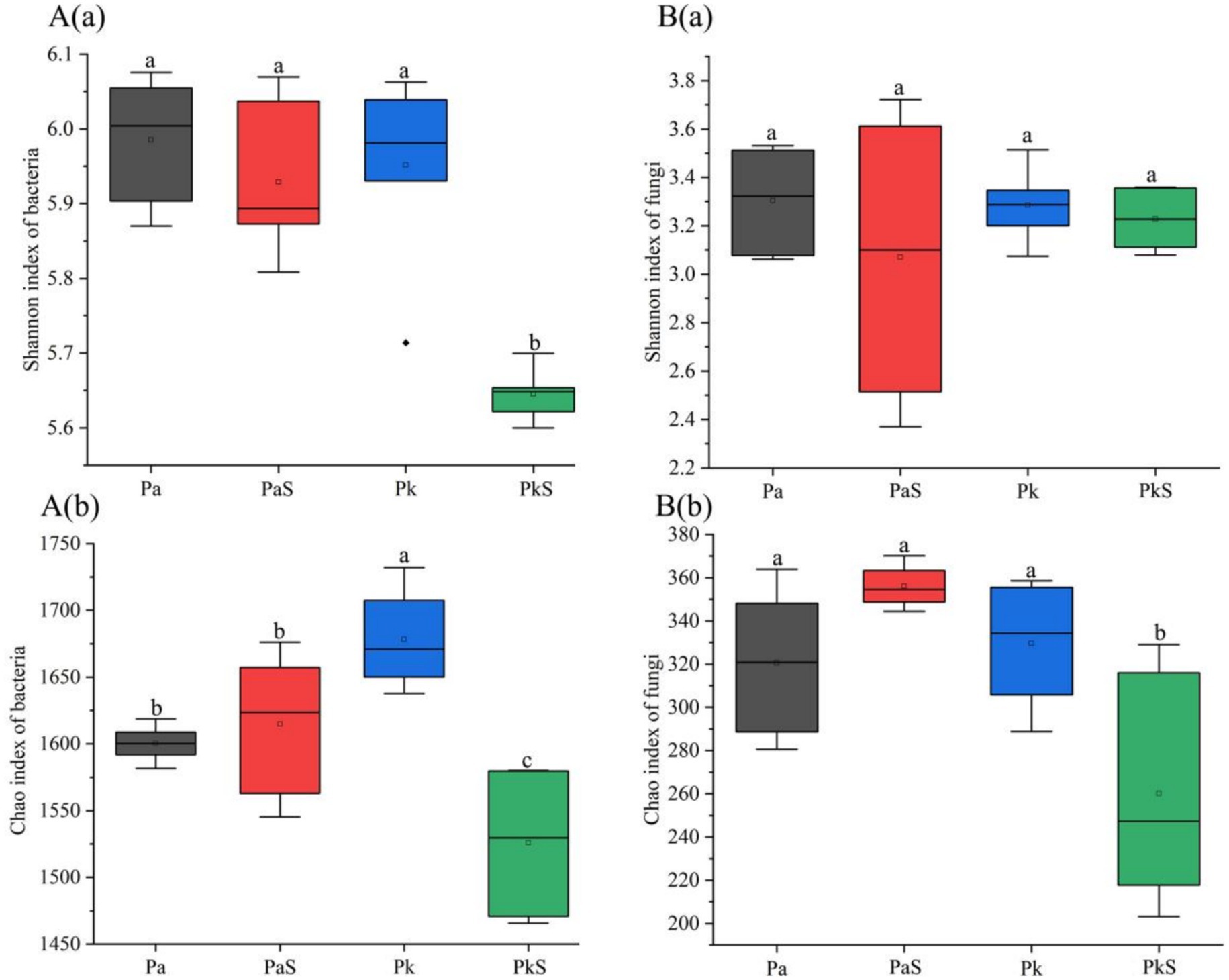
Figure 1. Shannon (a) and Chao (b) indices of bacteria (A) and fungi (B) under the various land use systems. a, b, and c indicate significant differences at p < 0.05, respectively.
3.3 Bacterial and fungal community structures
The results of PCoA indicate that the differences in bacterial (r = 0.9974, p = 0.001) and fungal (r = 0.9974, p = 0.001) communities among different treatments were both highly significant (Figure 2). ANOSIM analysis based on Bray-Curtis revealed that the influence of tree species on the community structures of bacteria (Bray-Curtis ANOSIM = 0.329, p = 0.004) and fungi (Bray-Curtis ANOSIM = 0.418, p = 0.007) was greater than that of Sanqi introduction on the community structures of bacteria (Bray-Curtis ANOSIM = 0.112, p = 0.04) and fungi (Bray-Curtis ANOSIM = 0.197, p = 0.02).
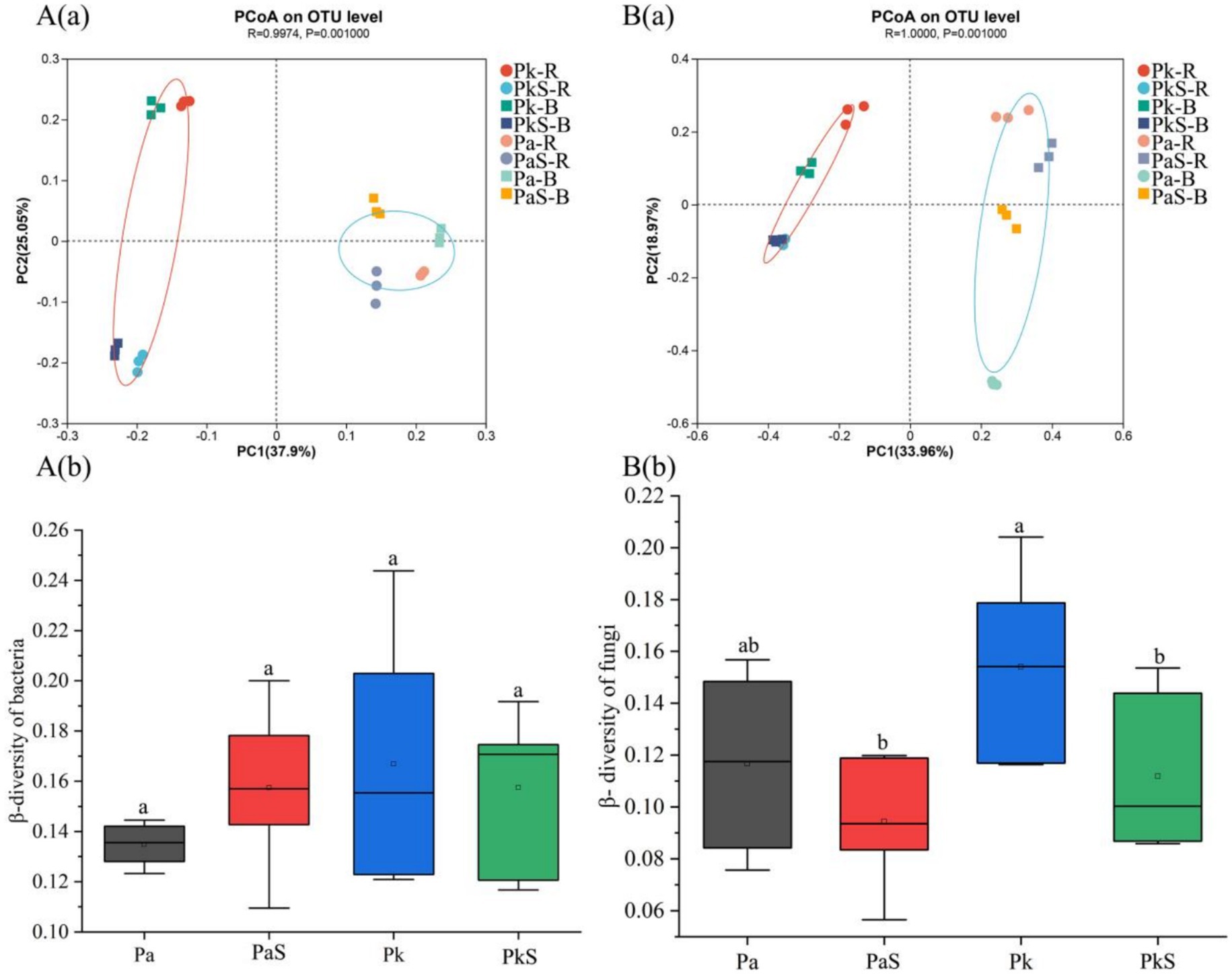
Figure 2. Community structures of soil bacteria (A) and fungi (B) in the various land use systems. a and b indicate significant differences at p < 0.05, respectively.
There was no significant difference in the community structure of bacteria (Bray-Curtis ANOSIM = 0.01, p = 0.78) and fungi (Bray-Curtis ANOSIM = 0.02, p = 0.56) between the rhizosphere and bulk soil. Additionally, greater changes were observed in the community structure of fungi (R = 1.0) than that of bacteria (Supplementary Table S4). Moreover, the values of β-diversity of both bacteria and fungi were not significantly different in the PaS soil (Figure 2), mirroring a similar absence of significant variation between the rhizosphere and bulk soils. In the case of PkS soil, the β-diversity of bacteria remained stable whereas that of fungi experienced a significant decline. Nonetheless, significant differences were not observed between the rhizosphere and bulk soils (Supplementary Table S5).
The dominant bacterial phyla included Proteobacteria (32.88%), Actinobacteria (19.95%), Acidobacteriota (18.68%), and Chloroflexi (14.84%), whereas the dominant fungal phyla were Ascomycota (47.06%), Basidiomycota (46.68%), and Mortierellomycota (7.72%; Figure 3). Moreover, the cultivation of Sanqi increased the abundance of Chloroflexi in PaS and soils while decreasing that of Actinobacteria. Additionally, the abundance of Ascomycota and Mortierellomycota increased significantly in the PaS but not PkS soil, whereas that of Proteobacteria, Acidobacteriota, and Basidiomycota decreased significantly (Figure 3).
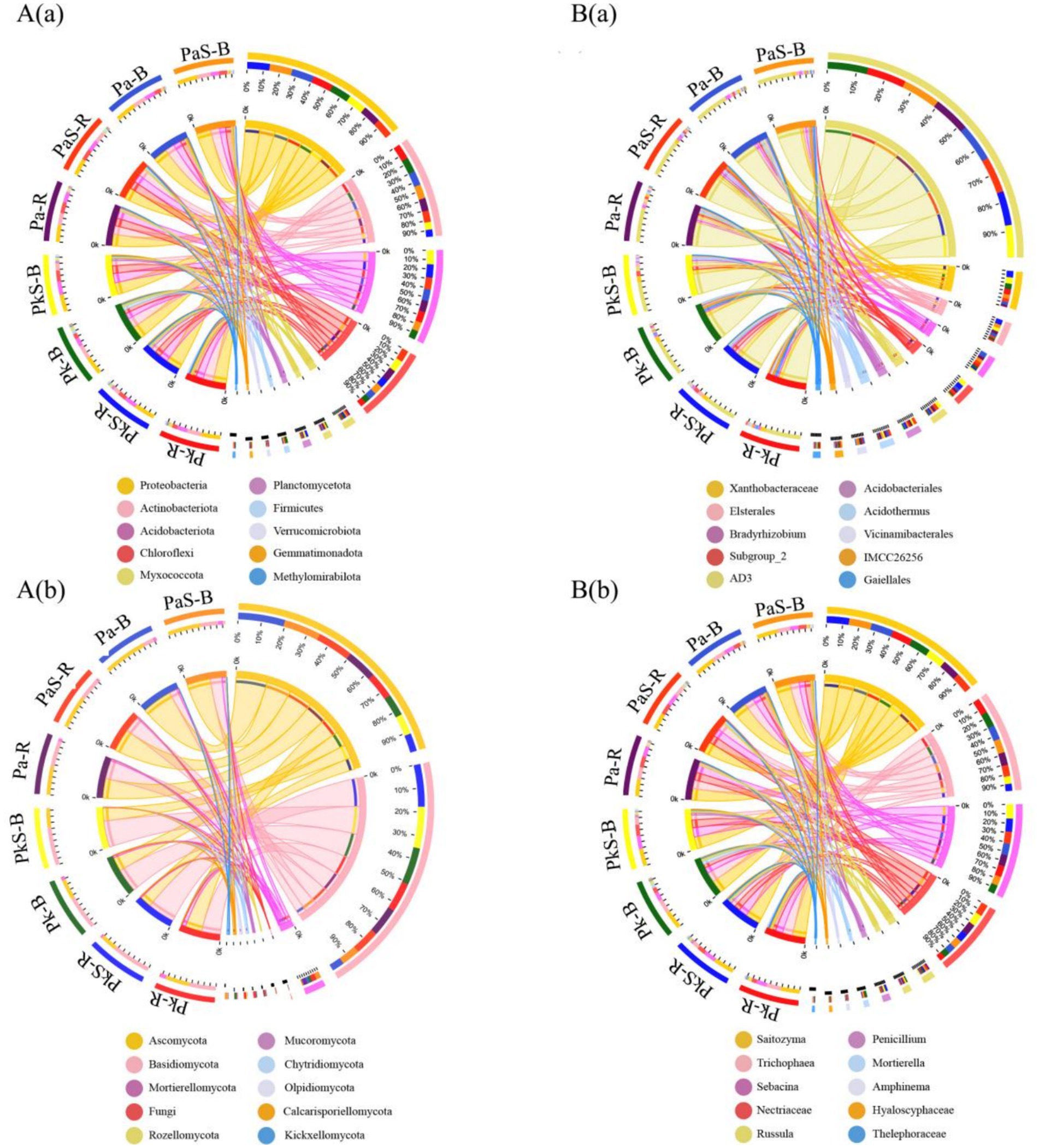
Figure 3. Relative abundance of bacteria (A) and fungi (B) at the level of (a) phylum and (b) genus.
A closer look revealed that the dominant bacteria belonged to Xanthobacteraceae (7.92%), Elsterales (5.30%), Bradyrhizobium (5.00%), Subgroup_2 (4.74%), AD3 (3.94%), Acidobacteriales (3.58%), Acidothermus (3.53%), Vicinamibacterales (2.56%), IMCC26256 (2.38%), and Gaiellales (2.24%). Similarly, the dominant fungi belonged to Saitozyma (11.41%), Trichophaea (10.30%), Sebacina (9.24%), Nectriaceae (8.35%), Russula (6.13%), Penicillium (4.81%), Mortierella (4.67%), Amphinema (3.55%), Hyaloscyphaceae (3.52%), and Thelephoraceae (2.68%; Figure 3). Overall, the cultivation of Sanqi resulted in an increase in the abundance of Xanthobacteraceae, AD3, Acidobacteriales, Trichophaea, Nectriaceae, and Russula in the PaS and PkS soils. By contrast, the abundance of Bradyrhizobium, Saitozyma, Penicillium, Hyaloscyphaceae, Thelephoraceae, and Vicinamibacterales decreased. Additionally, the abundance of IMCC26256, Gaiellales, Mortierella, and Amphinema significantly increased while that of Elsterales, Subgroup_2, Acidothermus, and Sebacina significantly decreased in the PaS soil compared to that observed in the PkS soil.
RDA was employed for investigating the correlations between soil factors and microbial communities at the level of genera. The results revealed that the bacterial and fungal community was significantly impacted by the content of TK (r2 = 0.8662, p = 0.002) and TN (r2 = 0.4125, p = 0.0055) in the Pa soil and by pH (r2 = 0.8778, p = 0.001) and NO3−–N (r2 = 0.959, p = 0.001) content in the Pk soil, WC (r2 = 0.8885, p = 0.001; r2 = 0.7301, p = 0.001) in the PaS soil and by NO3−–N (r2 = 0.4652, p = 0.001) content and SOC (r2 = 0.9195, p = 0.001) in the PkS soil (Supplementary Figure S2).
3.4 Analysis of bacterial and fungal network complexity and stability
Compared to that observed in the Pa soil, the complexity of the bacterial and fungal networks in the PaS soil exhibited a significant increase in the numbers of nodes and connecting edges, graph density, average degree, and average clustering coefficient, while the average path length and graph diameter exhibited a significant decrease. This indicates that the cultivation of Sanqi increased the complexity of the bacterial and fungal networks in the pine soil. Conversely, the complexity of the bacterial and fungal networks in the PkS soil was significantly reduced compared to that observed in the Pk soil (Figure 4, Supplementary Table S6). Moreover, the bacterial and fungal networks in the PaS soil exhibited good stability, with the highest stability observed in the rhizosphere soil following Sanqi cultivation. By contrast, the stability of the bacterial and fungal networks declined in the PkS soil, although the differences between the rhizosphere and bulk soils were not significant (Figure 5; Supplementary Table S7).
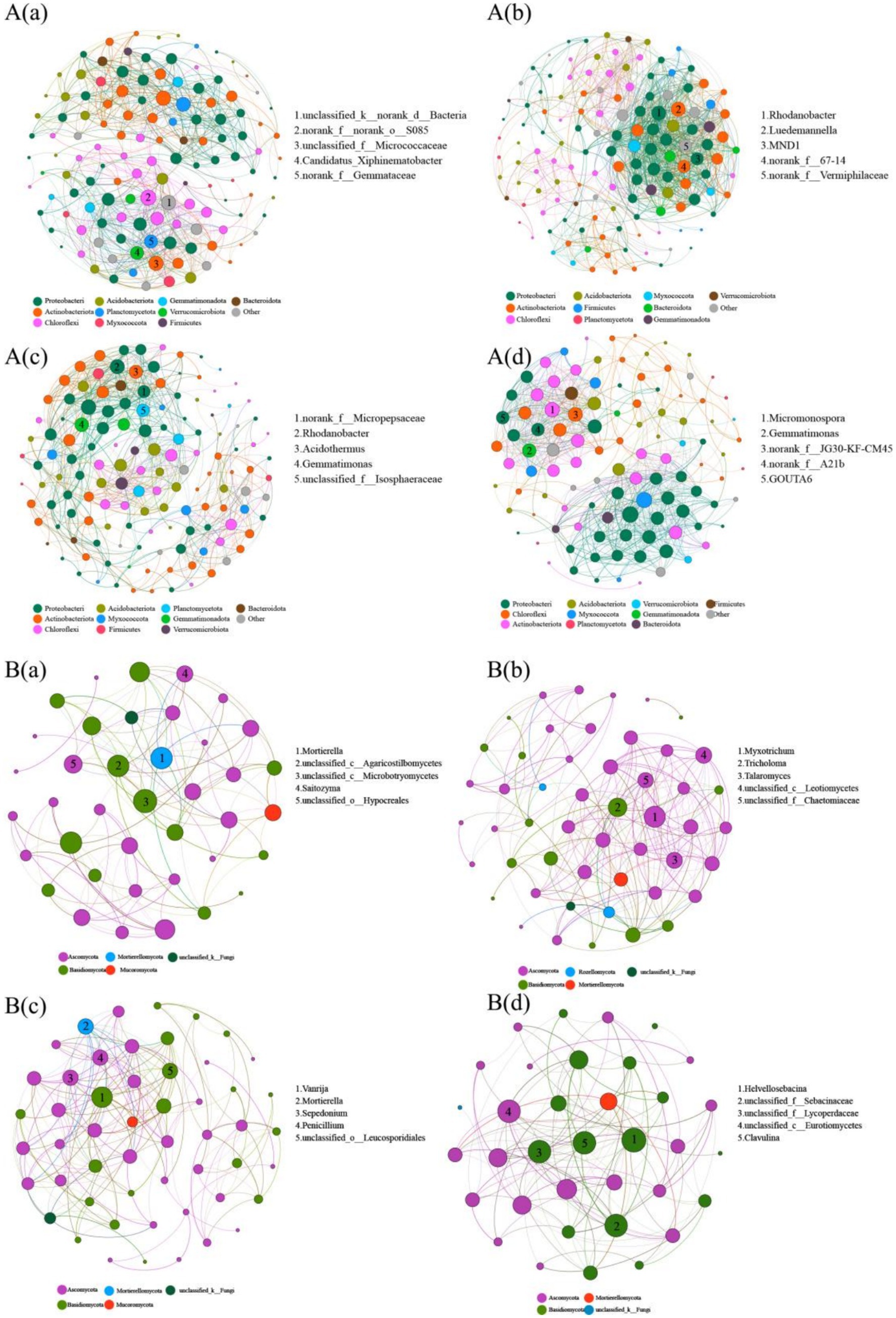
Figure 4. Bacterial (A) and fungal (B) network complexity in different land use systems. (a) Pa, (b) PaS, (c) Pk, and (d) PkS soils. Different colored dots denote distinct phyla to which the genera are affiliated. The figures within the nodes signify pivotal genera within the network.
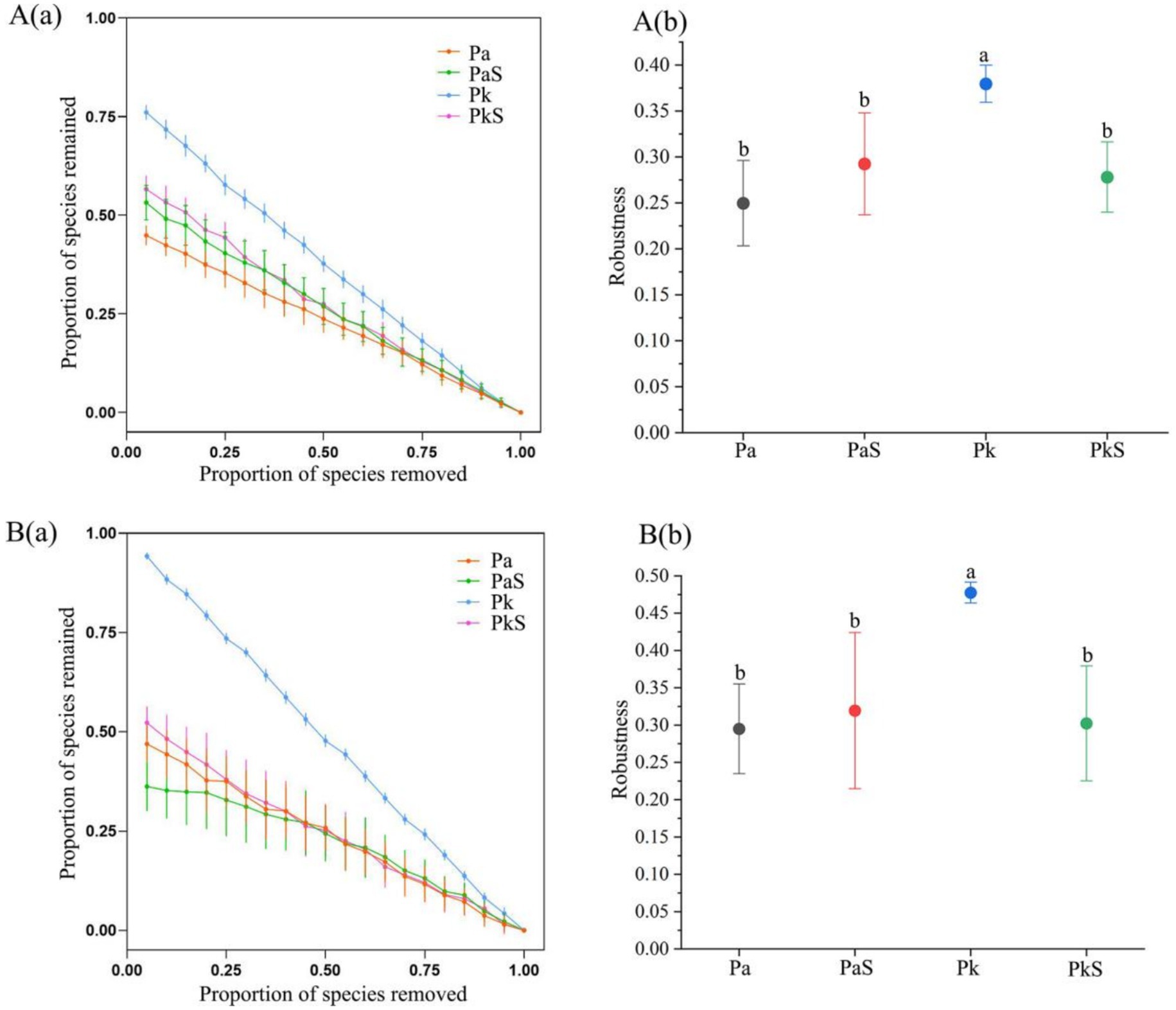
Figure 5. Bacterial (A) and fungal (B) network stability in different land use systems. The proportion of remaining nodes in the network after the random removal of some (a) and 50% (b) of the nodes. a and b indicate significant differences at p < 0.05, respectively.
3.5 Soil metabolomics analysis
Non-targeted metabolomics techniques were employed for determining the types and contents of metabolites in the various soil samples. A total of 602 metabolites were identified across all soil samples, including lipid and lipid-like molecules (48.0%), organic acids and derivatives (7.3%), organic heterocyclic compounds (6.8%), phenylpropanoids and polyketides (6.1%), organic oxygen compounds (5.1%), aromatic compounds (5.0%), nucleosides, nucleotides, and their analogs (2.6%), organic nitrogen compounds (0.8%), hydrocarbons (0.3%), lignans, neolignans, and related compounds (0.2%), as well as homonuclear nonmetallic compounds (0.2%). Among these, the content of 223 and 379 metabolites exhibited an increase and decrease, respectively, in the PaS soil. Similarly, the content of 257 and 345 metabolites displayed an increase and decrease, respectively, in the PkS soil.
Principal Component Analysis and volcano plot analysis revealed a significant impact of Sanqi cultivation on soil metabolites across various types of pine trees (Supplementary Figure S3). KEGG pathway enrichment analysis indicated that these differential metabolites were significantly enriched in multiple pathways, including ABC transporters, protein digestion and absorption, central carbon metabolism in cancer, biosynthesis of plant secondary metabolites, aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, arginine biosynthesis, alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism, and proximal tubular bicarbonate reclamation (Supplementary Figure S4). Furthermore, the following differential metabolites with roles in metabolic pathways were identified: L-glutamic acid (C5H9NO4), L-aspartic acid (C4H7NO4), L-glutamine (C5H10N2O3), L-asparagine (C4H8N2O3), L-arginine (C6H14N4O2), L-proline (C5H9NO2), malic acid (C4H6O5), beta-sitostenone (C29H48O), isocitrate (C6H8O7), L-tyrosine (C9H11NO3), and N2-acetyl-L-ornithine (C7H14N2O3; Supplementary Figure S5). Additionally, a metabolic pathway network comprising 11 differential metabolites was constructed herein (Figure 6). In summary, the levels of eight metabolites (L-aspartic acid, L-asparagine, L-tyrosine, malic acid, isocitric acid, L-proline, N2-acetyl-L-ornithine, and L-glutamic acid) exhibited a significant upward trend in the PaS soil, while that of beta-sitostenone displayed a marked decrease. Moreover, these differential metabolites exhibited positive correlation with the abundance of Gaiellales and Thelephoraceae, but negative correlation with that of Penicillium and Mortierella (Supplementary Figure S6).
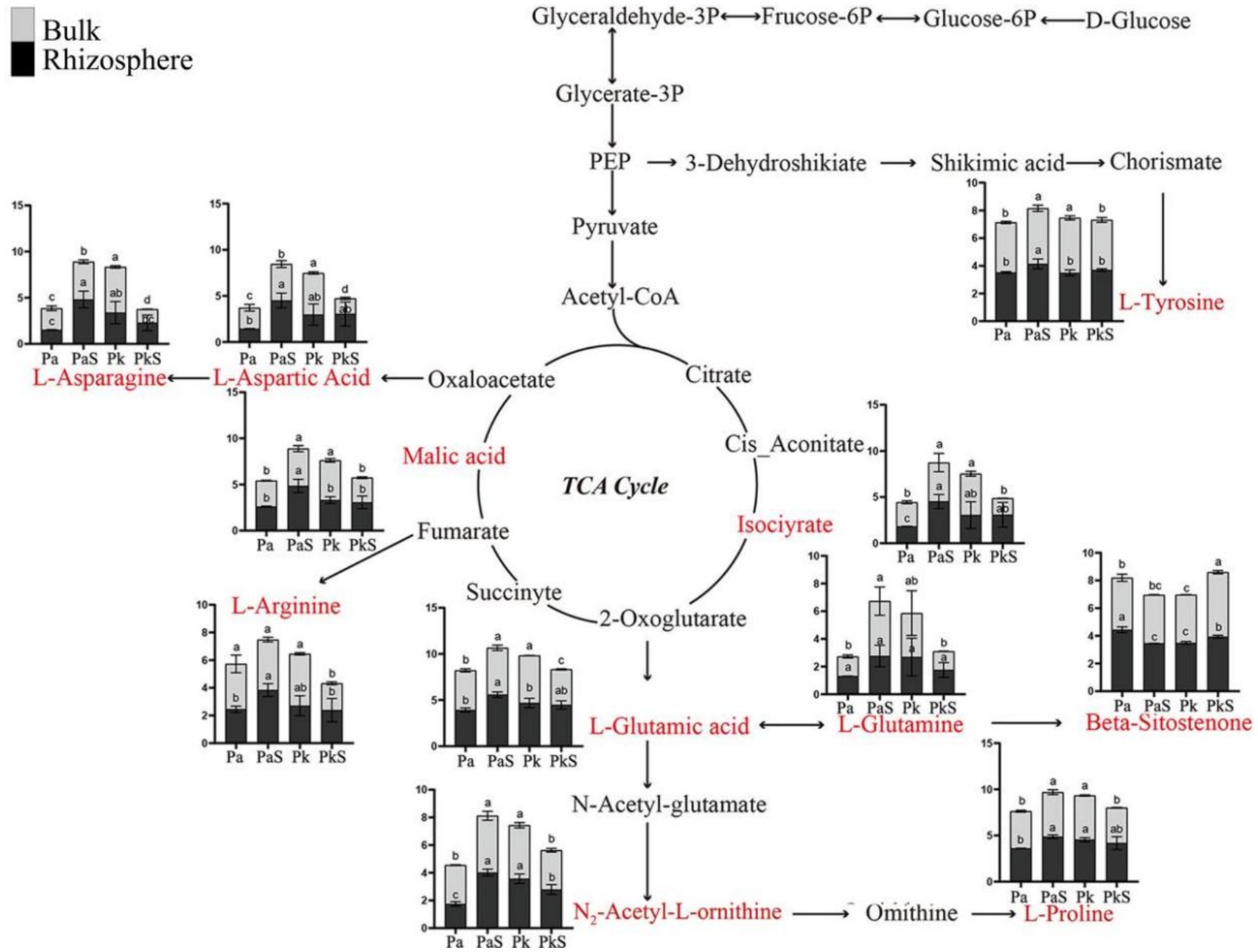
Figure 6. Identification of 11 differential metabolites and the associated metabolic pathways. a, b, and c indicate significant differences at p < 0.05, respectively.
3.6 SEM analysis
The results of SEM analysis revealed the direct and indirect factors that impact the complexity and stability of the bacterial and fungal networks in Pa and PaS soils. The physicochemical characteristics of the soil can further affect the complexity of the networks via effects on microbial community composition. Notably, soil enzymes and metabolites can also directly impact the complexity of the bacterial and fungal networks. Additionally, the abundance of bacteria and fungi in the PaS and Pa soils has a significant bearing on the stability of the corresponding microbial networks (Figure 7).
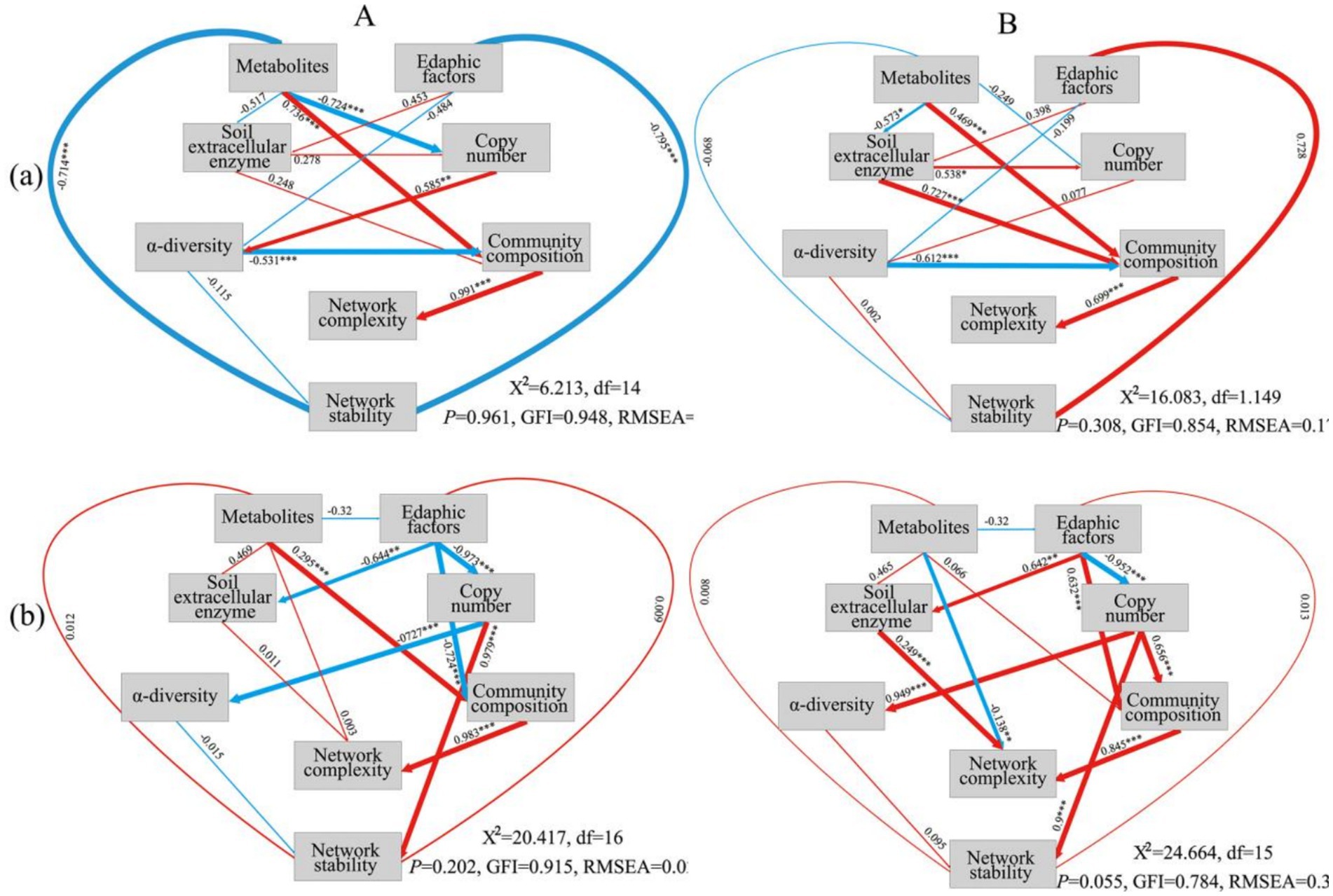
Figure 7. SEM analysis for soil bacteria (A) and fungi (B). Blue: negative correlation. Red: positive correlation. (a): Pa soil. (b) PaS soil.
4 Discussion
4.1 Sanqi cultivation affects the abundance and α-diversity of bacteria and fungi in the PaS and PkS soils
The microbiome serves as a critical indicator of the healthy development of Sanqi–pine agroforestry systems. Previous research has revealed that the transformation of monoculture pine forests to Sanqi–pine agroforestry systems causes significant alterations in the diversity rather than community structure of pine-associated fungi (Jia et al., 2022). However, the current study revealed that the cultivation of Sanqi significantly reduced the abundance and α-diversity of bacteria and fungi in the soil of PkS rather than PaS, which is inconsistent with the results of previous studies. As reported previously, the abundance and diversity of soil microbes can remain unchanged (for instance, in the walnut–tea system), increase (mulberry–peanut system), or decrease (ginkgo–fir system) following the conversion of the land use pattern to agroforestry systems (Guo et al., 2021; Bai et al., 2022; Li M. N. et al., 2022). The factors responsible for the variations in microbial community dynamics across diverse agroforestry systems are primarily ascribed to the soil environment (Zou et al., 2023), the introduction of plant species (Mortimer et al., 2015), and the tree species involved (Xu et al., 2023). These factors exert a substantial influence on the abundance and α-diversity of soil microbes. For instance, the microbial abundance and α-diversity in the Pk soil exhibited positive correlation with the content of TN and NH4+–N but a significant negative correlation with SOC (Supplementary Table S8). Previous studies have indicated that the increase in microbial diversity is significantly influenced by an increase in SOC (wheat–nut agroforestry system) and the content of NH4+–N (Sanqi-pine agroforestry system) and TN (peanut–millet intercropping system) (Yang et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2024; Rui et al., 2024). This is because elevated levels of SOC, NH4+–N, and TN provide essential nutrients for soil microorganisms, thereby directly stimulating their growth and reproduction (Jia et al., 2024; Chandan et al., 2025). Therefore, we speculate that the decrease in NH4+–N and TN levels led to a reduction in microbial abundance and α-diversity in PkS soil.
4.2 Sanqi cultivation reduces the β-diversity of fungi in the soil of P. Kesiya rather than P. armandii soil
The cultivation of Sanqi significantly affects the β-diversity of fungi rather than bacteria in the pine soil and is mainly influenced by the pine species followed by the cultivation of Sanqi. These findings are in line with those of previous studies, which also emphasized the significant impact of ecological niches, Sanqi cultivation, and pine genotypes on the pine-associated microbial communities (Jia et al., 2022). Nevertheless, the cultivation of Sanqi resulted in a substantial reduction in β-diversity in the soil of P. kesiya rather than P. armandii, which may be attributed to variance in the pine species, climate, and soil characteristics. In the Sanqi–pine agroforestry systems, the genotype of the pine tree significantly influences the community structure of fungi (Jia et al., 2022); this is because pine typically forms ectomycorrhizal symbiotic associations with various fungi, whose characteristics are largely determined by the genotype of the pine tree (Peršoh, 2013; Huo et al., 2023). The results of RDA revealed that the microbial community was predominantly influenced by the content of WC in the PaS soil and by NO3−–N content and SOC in the PkS soil. The soil water content has been shown to exhibit correlation with the microbial community structure (Bao et al., 2020). Additionally, SOC has been shown to exert a substantial impact on fungal diversity, as it is one of the key factors driving the evolution of the fungal community structure (Feng et al., 2025). The cultivation of Sanqi has been postulated to influence the response of the soil microbial community to SOC and NO3−–N content in P. kesiya forests. This influence is likely to be intricately linked to the growth attributes of the pine trees, their root exudates, and their adaptability to the soil milieu (He et al., 2025). Therefore, SOC and NO3−–N content are pivotal factors that contribute to the decline in the diversity of soil fungal communities in P. kesiya forests.
4.3 Sanqi cultivation enhances the abundance of beneficial microorganisms and their network complexity in the soil of P. armandii
The main bacterial phyla in the soil of pine trees were determined to be Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Acidobacteriota, and Chloroflexi, while the main fungal phyla were Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, and Mortierellomycota. This finding is consistent with those of a previous study (Jia et al., 2022). The cultivation of Sanqi significantly increased the abundance of Ascomycota, Mortierellomycota (notably Mortierella), Gaiellales, and Amphinema in the soil of P. armandii; these fungi are responsible for the decomposition of lignin and organic matter in the soil (Zhong et al., 2022), breakdown of carbohydrates and polysaccharides (Fu et al., 2020), increase in soil nutrient content and enzyme activity (Wang et al., 2024), and nitrogen fixation (Jörgensen et al., 2024). Therefore, the increased abundance of these beneficial microorganisms is conducive to improving the ecological environment of the soil in P. armandii. This stable microbial ecosystem can also better provide suitable soil conditions for the growth of Sanqi, forming a virtuous ecological cycle.
The cultivation of Sanqi significantly enhanced the complexity of the microbial network in the soil of P. armandii, which is attributable to the direct effects of factors such as soil metabolites and extracellular enzymes on microbial complexity. Moreover, edaphic factors can indirectly influence the complexity of the microbial network by affecting the microbial community. Soil metabolites have a direct impact on the diversity and community structure of bacteria and fungi in the soil in which Sanqi is cultivated (Hei et al., 2024). This is because soil metabolites may exert inhibitory or promoting effects on microorganisms, thereby affecting microbial community dynamics (Sui et al., 2023). Extracellular enzymes in the soil are key indicators of soil quality and the metabolic activities of soil microbes, with changes in the enzyme activities directly reflecting alterations in soil ecology. Previous studies have shown that Sanqi cultivation reduces the activities of extracellular enzymes and alleviates carbon limitation for soil microbes in the soil of P. armandii (Rui et al., 2025). Furthermore, changes in edaphic factors can affect not only the growth rate of microbes but also alter the types of soil metabolites, thereby influencing the structure of soil microbial communities (Cao et al., 2019; Sui et al., 2023). Previous studies have revealed that Sanqi cultivation has a significant impact on soil characteristics in the SPA system (Rui et al., 2024, 2025), which is consistent with the findings of the current study. Nevertheless, variations in edaphic factors in the SPA and SPK agroforestry systems may be a contributing factor for the increased complexity of the microbial network in the soil of P. armandii. In Pa and PaS soils, microbial communities have a direct impact on the complexity of the microbial network. This occurs because alterations in the microbial community engender shifts in the interactions among microbes, which subsequently modify the topological structure of the microbial network (Dong et al., 2024). Furthermore, the cultivation of Sanqi significantly reduced the stability of the microbial network in PkS rather than PaS soil, which is attributable to the direct impact of the abundance of various bacteria and fungi on the stability of the microbial network. The abundance of soil microbes can promote aggregate formation and improve soil structure, thereby enhancing the stability of the microbial network (Feng et al., 2023). The cultivation of Sanqi resulted in a decrease in the abundance of bacteria and fungi in the PkS soil, with no alterations observed in the PaS soil; this may explain the reduced stability of the microbial network in the PkS soil.
4.4 Sanqi cultivation enhances the concentration of DAMs in the rhizosphere and bulk soils associated with P. armandii
The metabolites found in pine soil were primarily lipids (48.0%) followed by organic acids (7.3%), which is inconsistent with the results of previous studies (Shao et al., 2011). As per the previous study, organic (63.82 and 71.05%) and phenolic (27.80 and 16.30%) acids were the main soil metabolites found in monoculture forests of Pinus tabuliformis and Ostryopsis davidiana, respectively (Shao et al., 2011). Several factors encompassing plant species, soil environmental conditions (Wang et al., 2018), cultivation methodologies, ecological niches, and root exudates exert significant influence on the soil metabolites of pine trees (He et al., 2025). The cultivation of Sanqi may account for the elevated lipid content in PaS and PyS soils; this is because lipids are highly abundant (35.48%) in the soils associated with Sanqi cultivated in the forest understory (Hei et al., 2024) and can be transferred to the soil through various channels to stabilize soil structure and enhance microbial activity (Zhang et al., 2016; Nasir et al., 2024).
Organic acids constitute the second most significant soil metabolite and are notably abundant in PaS and PyS soils. They exert a pivotal influence on the forest soil and ecosystem, primarily due to their potential deleterious impacts on the growth of Sanqi and soil quality (Hei et al., 2023, 2024). Previous studies have revealed a disparity in the composition of organic acids in the soils associated with organically and conventionally managed Sanqi (Wu et al., 2014; Hei et al., 2023). A high concentration (>150 mg/kg) of organic acids in the soil associated with Sanqi cultivation in the forest understory can adversely impact the interplay between plant growth, soil environment, and microbial communities (Hei et al., 2023, 2024). Additionally, a considerable accumulation of heavy metal elements such as cadmium in the pine soil (Yang et al., 2023) has been shown to significantly correlate with the presence of organic acids (Wang et al., 2022). These observations have prompted the hypothesis that pine roots exude organic acids and the organic acids originating from Sanqi may also be transferred to the pine soil, which explains the higher organic acid content of the pine soil. Additionally, organic acids are capable of modulating soil metabolites via interactions with other organic and phenolic acids (Shen et al., 2020; Hei et al., 2024). They also indirectly influence soil metabolites by shaping the structure of the microbial community (Zhou et al., 2023) and engaging in nutrient cycling (Khangaroat et al., 2020). In essence, investigating the distribution patterns of lipids and organic acids in the soil of the Sanqi–pine agroforestry systems is expected to facilitate an in-depth understanding of the intricate relationship between Sanqi cultivation and the ecological dynamics of pine tree soil. In turn, this is expected to provide a scientific foundation for refining the management strategies of agroforestry systems.
The metabolic network of differential metabolites is predominantly centered on the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Notably, the content of eight differential metabolites was substantially increased in the rhizosphere and bulk soils of PaS but significantly reduced in the PkS soil. Previous studies have shown that the metabolites in Sanqi-associated soil are affected by the cultivation patterns (He et al., 2025), which is consistent with the results obtained herein. The TCA cycle is the central pathway of cellular energy metabolism (Sultana and McClure, 2023), and the results obtained herein may indicate heightened efficiency of energy metabolism and enhanced environmental adaptability in P. armandii upon cocultivation with Sanqi. The differential metabolites identified herein play a crucial role in the soil ecosystem. For instance, L-glutamate and N-acetylcholine are involved in the urea cycle (Meena et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020), while L-aspartate and L-asparagine participate in the nitrogen cycle (Patra et al., 2017). Moreover, L-tyrosine can enhance the rate of decomposition of organic matter in the soil (Wang et al., 2022). Furthermore, malate and isocitrate can regulate soil pH and promote phosphorus uptake by plants (Wang et al., 2022). Additionally, the current study revealed higher concentrations of most soil metabolites in the rhizosphere soil of P. armandii compared to that in the bulk soil, suggesting that the metabolites secreted by plant roots may exert a dominant influence on the composition of metabolites in the rhizosphere soil (Zhang et al., 2020). This observation aligns with the outcomes of preceding research endeavors (Liu et al., 2023). This is because the microbes occupying different ecological niches can utilize different energy sources, which affects the concentration of metabolites (Bajić et al., 2021). Correlation analysis indicated that these differential metabolites were positively correlated with beneficial microbes (such as members of Gaiellales and Thelephoraceae) and negatively correlated with pathogenic microbes (such as Penicillium and Mortierella; Hei et al., 2024). However, given that soil microbes are significant executors of metabolic activities in the soil, the composition of the microbial community governs the types and abundance of soil metabolites to a certain extent (Cheng et al., 2022). Therefore, regulating the structure of soil microbial communities allows the optimization of the types and abundance of soil metabolites, thereby promoting the growth and improving the quality of Sanqi.
5 Conclusion
The current study revealed that the cultivation of Sanqi increased the content of TP, NH4+–N, and TK as well as WC and pH in PaS soil but only that of NO3−–N and SOC in PkS soil. Moreover, the copy numbers as well as α- and β-diversity of bacteria and fungi were stably maintained in PaS soil but declined in PkS soil. PCoA analysis revealed that the tree species mainly influenced the changes in the community structure of bacteria and fungi. Additionally, microbial network complexity increased significantly in PaS but not PkS soil, while network stability was maintained. SEM analysis revealed that the combined effects of soil enzymes, metabolites, and physicochemical properties resulted in an increase in microbial network complexity in PaS soil. Further investigations revealed that the soil metabolites in PaS and PkS soils mainly comprised lipids (48.0%) and organic acids (7.3%). The content of eight differential metabolites was significantly higher in the rhizosphere and bulk soils of PaS. In summary, P. armandii significantly contributes to the robust growth of P. notoginseng and the overall sustainability of the agroforestry system. This discovery provides an important theoretical foundation for optimizing Sanqi cultivation practices, thereby improving both its quality and yield.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, PRJNA821648 (bacteria) and PRJNA821834 (fungi).
Author contributions
JH: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft, Methodology. YL: Software, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. RR: Writing – original draft, Software, Data curation. NF: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Investigation. JP: Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. BW: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. SW: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Software. XH: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Project administration, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (202501BD070001-087; 202501BD070001-023; 202401BD070001-122), Yunnan Provincial Key Laboratory (202402AN360005), Yunnan Province Innovation Team (202405AS350027), Yunnan Ten Thousand People Plan Youth Top Talent Project (YNWRQNBJ-2019-028), China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-21-05B), Major Science and Technology Project of Kunming Science and Technology Bureau (2021JH002), and Academician (Expert) Workstations (202305AF150058).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the members of our group for their joint efforts.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1616266/full#supplementary-material
References
Araujo, A. S. F., Leite, L. F. C., Iwata, B. D. F., Lira, M. D. A., Xavier, G. R., and Figueiredo, M. D. V. B. (2012). Microbiological process in agroforestry systems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 32, 215–226. doi: 10.1007/s13593-011-0026-0
Bai, Y. C., Li, B. X., Xu, C. Y., Raza, M., Wang, Q., Wang, Q. Z., et al. (2022). Intercropping walnut and tea: effects on soil nutrients, enzyme activity, and microbial communities. Front. Microbiol. 13:852342. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.852342
Bajić, D., Rebolleda-Gómez, M., Muñoz, M. M., and Sánchez, Á. (2021). The macroevolutionary consequences of niche construction in microbial metabolism. Front. Microbiol. 12:718082. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.718082
Bao, T. L., Gao, L. Q., Wang, S. S., Yang, X. Q., Ren, W., and Zhao, Y. G. (2020). Moderate disturbance increases the PLFA diversity and biomass of the microbial community in biocrusts in the loess plateau region of China. Plant Soil 451, 499–513. doi: 10.1007/s11104-020-04554-9
Beule, L., Anna, V., and Virna, E. (2022). Abundance, diversity, and function of soil microorganisms in temperate alley-cropping agroforestry systems: a review. Microorganisms 10:616. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10030616
Bi, B. Y., Wang, K., Zhang, H., Wang, Y., Fei, H. Y., Pan, R. P., et al. (2021). Plants use rhizosphere metabolites to regulate soil microbial diversity. Land Degrad. Dev. 32, 5267–5280. doi: 10.1002/ldr.4107
Cao, X. Y., Hamilton, J., and Venturelli, O. S. (2019). Understanding and engineering distributed biochemical pathways in microbial communities. Biochemistry 58, 94–107. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01006
Chandan, S., Vivek, S., Kumar, P. A., Shashi, S., Mohil, K., and Kumar, S. R. (2025). The role of soil microbiome in enhancing plant nutrition and promoting soil health. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 37, 62–68. doi: 10.9734/ijpss/2025/v37i25302
Chen, Y., Lv, G. H., and Li, Y. (2018). Soil microbial functional diversity of rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere of three dominant herbaceous plants in the Dushanzi District. Acta Ecol. Sinica 38, 3110–3117. doi: 10.5846/stxb201703070382
Chen, S. Y., Rui, R., Wang, S., and He, X. H. (2022). Comparative analysis of the floral fragrance compounds of Panax notoginseng flowers under the Panax notoginseng-pinus agroforestry system using SPME-GC-MS. Molecules 27:3565. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113565
Cheng, H. Y., Yuan, M. S., Tang, L., Shen, Y. F., Yu, Q., and Li, S. Q. (2022). Integrated microbiology and metabolomics analysis reveal responses of soil microorganisms and metabolic functions to phosphorus fertilizer on semiarid farm. Sci. Total Environ. 817:152878. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152878
Deng, L. M., Yang, L., Zhang, J. X., Zi, B. X., Gong, J. S., Mei, X. Y., et al. (2020). Isolation and selection of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F. H. Chen growth-promoting antagonistic bacterial from different forest soils in Yunnan. J. South. Agric. 51, 115–122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2020.01.015
Ding, N., Lin, H., Zhang, X. H., He, Y., and Yu, G. (2022). Interaction mechanism between root secretion and rhizosphere microorganisms: a review. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 53, 1212–1219. doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2022010201
Dong, Z. H., Zhang, J. H., He, J., Wang, J. Y., Li, Y. Y., Ji, Y. B., et al. (2024). Soil microbial network complexity predicts the multifunctionality of afforestation restoration ecosystems on the loess plateau. Acta Ecol. Sinica. 44, 2544–2560. doi: 10.20103/J.S.TX.202302020174
Feng, H. L., Hao, X. Z., Lu, X. C., Chen, X., Yan, J., and Zou, W. X. (2023). Research progress on the formation and stability of soil aggregates by organic fertilization. Soils Crops. 12, 393–400. doi: 10.11689/sc.2023032801
Feng, Z., Kong, T., Zhang, X. Y., Zhao, W. Q., and Kou, Y. P. (2025). Community differences and driving factors of soil fungi of subalpine Picea asperata forests at two altitudes. Acta Ecol. Sin. 45, 1987–1998. doi: 10.20103/j.stxb.202406121365
Fu, H. P., Zhou, P. Q., Wang, Y. J., Mo, Z. D., Li, Z. H., Ma, Q. P., et al. (2020). Effects of intercropping different green manures on fungal community characteristics in rhizosphere soil of tea plant. J. Tea Communic. 47, 406–415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-525X.2020.03.007
Gong, Z., Luo, X. Q., Peng, J., and Gong, F. W. (2016). Pana xnotoginseng F.H.Chen: cultivation techniques under different forests. J. Agric. 6, 41–44. doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas16040029
Guo, J., Wu, Y. Q., Wu, X. H., Ren, Z., and Wang, G. B. (2021). Soil bacterial community composition and diversity response to land conversion is depth-dependent. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 32:e01923. doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2021.e01923
He, S., Rui, R., Hei, J. Y., Li, Y., Faisal, N., Wang, B., et al. (2025). Organically managed Sanqi alters the soil C metabolism and purine metabolism pathway through metagenomic and metabolomic analyses. Plant Soil 25, 1–7. doi: 10.1007/s11104-025-07396-5
Hei, J. Y., Li, Y., Wang, Q., Wang, S., and He, X. H. (2024). Effects of exogenous organic acids on the soil metabolites and microbial communities of Panax notoginseng from the forest understory. Agronomy 14:601. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14030601
Hei, J. Y., Wang, S., and He, X. H. (2023). Effects of exogenous organic acids on the growth, edaphic factors, soil extracellular enzymes, and microbiomes predict continuous cropping obstacles of Panax notoginseng from the forest understorey. Plant Soil 503, 105–122. doi: 10.1007/s11104-023-06044-0
Huo, X. Y., Ren, C. J., Wang, D. X., Wu, R. Q., Wang, Y. S., Li, Z. F., et al. (2023). Microbial community assembly and its influencing factors of secondary forests in Qinling Mountains. Soil Biol. Biochem. 184:109075. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2023.109075
Iannucci, A., Canfora, L., Nigro, F., Vita, P. D., and Beleggia, R. (2021). Relationships between root morphology, root exudate compounds and rhizosphere microbial community in durum wheat. Appl. Soil Ecol. 158:103781. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103781
Jia, W. J., Hei, J. Y., He, X. H., and Wang, S. (2024). Altitude rather than season and slope aspect has the greatest effect on the bacterial communities in subtropical forests in Yunnan, China. Plant Soil 501, 57–74. doi: 10.1007/s11104-023-06319-6
Jia, W. J., Wang, S., He, X. H., and Zhao, X. Y. (2022). Different factors drive the assembly of pine and Panax notoginseng-associated microbiomes in Panax notoginseng-pine agroforestry systems. Front. Microbiol. 13:1018989. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1018989
Jiang, Q. P., Yu, J. M., Wang, J. F., Liu, D. Y., Gong, J., Jiang, L. Q., et al. (2023). Soil properties affect bacterial community assembly and co-occurrence network in tobacco rhizosphere. Acta Microbiol Sin. 63, 1168–1184. doi: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20220540
Jörgensen, K., Clemmensen, K. E., Wallander, H., and Lindahl, B. D. (2024). Ectomycorrhizal fungi are more sensitive to high soil nitrogen levels in forests exposed to nitrogen deposition. New Phytol. 242, 1725–1738. doi: 10.1111/nph.19509
Karoline, F., and Jeroen, R. (2012). Microbial interactions: from networks to models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 10, 538–550. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2832
Khangaroat, M. S., Thomas, T., and David, A. A. (2020). Effect of different level of NPK and biochar on soil physico - chemical properties, yield and attributes of green gram (Vigna radiata L.) Var.–RMG 975 (Keshwanand mung 1). Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 8, 1302–1307. doi: 10.22271/chemi.2020.v8.i5r.10483
Li, S. M., Fan, W., Xu, G., Cao, Y., Zhao, X., Hao, S. W., et al. (2023). Bio-organic fertilizers improve Dendrocalamus farinosus growth by remolding the soil microbiome and metabolome. Front. Microbiol. 14:1117355. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1117355
Li, Y., Hei, J. Y., Wang, B., Wang, S., and He, X. H. (2024). Unraveling the molecular mechanisms of flavonoid biosynthesis in Panax notoginseng flowers across planting patterns and developmental stages using integrated metabolomics and transcriptomics analyses. Sci. Hortic. 335:113362. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2024.113362
Li, N., Wang, B. R., Huang, Y. M., Huang, Q., Jiao, F., and An, S. S. (2022). Response of cbbL-harboring microorganisms to precipitation changes in a naturally-restored grassland. Sci. Total Environ. 838:156191. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156191
Li, M. Z., Wei, Y. W., Yin, Y., Ding, H., Zhu, W. X., and Zhou, Y. B. (2022). The effect of intercropping mulberry (Morus alba L.) with peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.), on the soil rhizosphere microbial community. Forests 13:1757. doi: 10.3390/f13111757
Liu, H. J., Gu, H. R., Ye, C., Guo, C. W., Zhu, Y. F., and Huang, H. H. (2021). Planting density affects Panax notoginseng growth and ginsenoside accumulation by balancing primary and secondary metabolism. Front. Plant Sci. 12:628294. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.628294
Liu, Z., Nan, Z. W., Lin, S. M., Meng, W. W., Xie, L. Y., Yu, H. Q., et al. (2024). Peanut-based intercropping systems altered soil bacterial communities, potential functions, and crop yield. PeerJ 12:e16907. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16907
Liu, J. P., Tang, Y. J., Bao, J. S., Wang, H. K., Chen, M. Y., and Peng, F. R. (2023). Integrated microbiome and metabolomics analysis reveal a closer relationship between soil metabolites and bacterial community than fungal community in pecan plantations. Land Degrad. Dev. 34, 2812–2824. doi: 10.1002/ldr.4649
Luo, L. F., Zhang, J. X., Ye, C., Li, S., Duan, S. S., Wang, Z. P., et al. (2022). Foliar pathogen infection manipulates soil health through root exudate-modified rhizosphere microbiome. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e02418–e02422. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02418-2220
Meena, M., Divyanshu, K., Kumar, S., Swapnil, P., Zehra, A., Shukla, V., et al. (2019). Regulation of L-proline biosynthesis, signal transduction, transport, accumulation and its vital role in plants during variable environmental conditions. Heliyon 5:e02952. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02952
Mortimer, P. E., Gui, H., Xu, J., Zhang, C., Barrios, E., and Hyde, K. D. (2015). Alder trees enhance crop productivity and soil microbial biomass in tea plantations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 96, 25–32. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2015.05.012
Nasir, S., Andalibi, B., Tavakoli, A., Delavar, M. A., El-Keblawy, A., and Mastinu, A. (2024). Jasmonates improve drought tolerance of Hordeum vulgare L. after biochar treatment. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 24, 2008–2022. doi: 10.1007/s42729-024-01692-2
Patra, A., Sharma, V. K., Purakayastha, T., and Barman, M. (2017). Effect of integrated nutrient Management in Rice on nitrogen availability, L-asparaginase and L-glutaminase activity in acidic soil. Int. J Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 6, 3777–3783. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.466
Peršoh, D. (2013). Factors shaping community structure of endophytic fungi evidence from the Pinus-Viscum-system. Fungal Divers. 60, 55–69. doi: 10.1007/s13225-013-0225-x
Qin, X. M., Wei, C. Z., Li, J. T., Chen, Y. Q., Chen, H. S., Zheng, Y., et al. (2017). Changes in soil microbial community structure and functional diversity in the rhizosphere surrounding tea and soybean. J. Agric. Sci. 12, 1–13. doi: 10.4038/jas.v12i1.8201
Ren, J. (2016). The research of allelopathic activity and environmental behavior of organic acid of ginseng rhizosphere. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University.
Rosseel, Y. (2012). Iavaan: an R package for structural equation modelling. J. Stat. Softw. 7, 1–36. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041967
Rui, R., Hei, J. Y., Li, Y., Al Farraj, D. A., Noor, F., Wang, S., et al. (2024). Effects of humic acid fertilizer on the growth and microbial network stability of Panax notoginseng from the forest understorey. Sci. Rep. 14:17816. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68949-9
Rui, R., Hei, J., Li, Y., Wan, X. L., Wang, S., and He, X. (2025). Alleviating microbial carbon limitation in Pinus armandii forests through Panax notoginseng cultivation. Forests 16:158. doi: 10.3390/f16010158
Shao, D. H., Ren, Q., Ning, X. Z., and Bai, S. L. (2011). Root exudate constituents and allelopathic effects from forests of Pinus tabulaeformis, Ostryopsis davidiana, and a mixed forest. J. Zhejiang A&F Univ. 28, 333–338. doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2011.02.026
Shen, H., Yan, W. H., Yang, X. Y., He, X. H., Wang, X., Zhang, Y. T., et al. (2020). Co-occurrence network analyses of rhizosphere soil microbial PLFAs and metabolites over continuous cropping seasons in tobacco. Plant Soil 452, 119–135. doi: 10.1007/s11104-020-04560-x
Shi, R., Gu, H. Y., He, S., Xiong, B. J., Huang, Y. G., and Horowitz, A. R. (2021). Comparative metagenomic and metabolomic profiling of rhizospheres of Panax notoginseng grown under forest and field conditions. Agronomy 11:2488. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11122488
Shi, R., Wang, S., Xiong, B. J., Gu, H. Y., Wang, H. L., Ji, C., et al. (2022). Application of bioorganic fertilizer on Panax notoginseng improves plant growth by altering the rhizosphere microbiome structure and metabolism. Microorganisms 10:275. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020275
Song, Y., Li, X. N., Yao, S., Yang, X. L., and Jiang, X. (2020). Correlations between soil metabolomics and bacterial community structures in the pepper rhizosphere under plastic greenhouse cultivation. Sci. Total Environ. 728:138439. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138439
Sui, J. K., Yang, J. Y., Li, C. Y., and Zhang, L. X. (2023). Effects of a microbial restoration substrate on plant growth and rhizosphere bacterial community in a continuous tomato cropping greenhouse. Microorganisms 11:486. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020486
Sultana, S., and McClure, J. (2023). Intermediary metabolism. Anaesth. Intens. Care Med. 24, 139–147. doi: 10.1016/j.mpaic.2022.12.005
Sun, X., Zhang, X. K., Zhang, G. S., Miao, Y. J., Zeng, T. X., Zhang, M., et al. (2022). Environmental response to root secondary metabolite accumulation in Paeonia lactiflora: insights from rhizosphere metabolism and root-associated microbial communities. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e02800–e02822. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02800-22
Tan, Y., Cui, Y. S., Li, H. Y., Kuang, A. X., Li, X. R., Wei, Y. L., et al. (2017). Rhizospheric soil and root endogenous fungal diversity and composition in response to continuous Panax notoginseng cropping practices. Microbiol. Res. 194, 10–19. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2016.09.009
Tian, Y., Liu, Y., Yue, L., Uwaremwe, C., Zhao, X., Zhou, Q., et al. (2022). Bacterial inoculant and sucrose amendments improve the growth of Rheum palmatum L. by reprograming its metabolite composition and altering its soil microbial community. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:1694. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031694
Wang, Y., Feng, F. Y., Ge, J., Li, Y., and Yu, X. Y. (2022). Effects and mechanisms of plant root exudates on soil remediation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 42, 829–842. doi: 10.5846/stxb202101030011
Wang, N. Q., Kong, C. H., Wang, P., and Meiners, S. J. (2021). Root exudate signals in plant–plant interactions. Plant Cell Environ. 44, 1044–1058. doi: 10.1111/pce.13892
Wang, J. C., Ren, C. Q., Cheng, H. T., Zhou, Y. K., Bujhio, M. A., and Li, Q. F. (2017). Conversion of rainforest into agroforestry and monoculture plantation in China: consequences for soil phosphorus forms and microbial community. Sci. Total Environ. 595, 769–778. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.012
Wang, Y. F., Wang, J. F., Xu, Z. M., She, S. H., Yang, J. Q., and Li, Q. S. (2020). L-glutamic acid induced the colonization of high-efficiency nitrogen-fixing strain Ac63 (Azotobacter chroococcum) in roots of Amaranthus tricolor. Plant Soil 451, 357–370. doi: 10.1007/s11104-020-04531-2
Wang, Z. H., Wang, W. P., Yang, K., Ye, C., Wu, W. T., Wang, C. Y., et al. (2023). Adult-plant resistance of Panax notoginseng to nematodes and interspecific facilitation with pine trees. J. Pest. Sci. 96, 1271–1286. doi: 10.1007/s10340-023-01601-z
Wang, W. B., Yang, Y. Y., Li, J. G., Bu, P. T., Lu, A. J., Wang, H., et al. (2024). Consecutive fertilization-promoted soil nutrient availability and altered rhizosphere bacterial and bulk fungal community composition. Forests 15:514. doi: 10.3390/f15030514
Wang, Y., Zong, N., He, N. P., Zhang, J. J., Tian, J., and Li, L. T. (2018). Soil microbial functional diversity patterns and drivers along an elevation gradient on Qinghai-Tibet, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 38, 5837–5845. doi: 10.5846/stxb201707261343
Wilhelm, R. C., van Es, H. M., and Buckley, D. H. (2022). Predicting measures of soil health using the microbiome and supervised machine learning. Soil Biol. Biochem. 164:108472. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108472
Wu, M. H., Chen, S. Y., Chen, J. W., Xue, K., Chen, S. L., Wang, X. M., et al. (2021). Reduced microbial stability in the active layer is associated with carbon loss under alpine permafrost degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 118:2025321118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2025321118
Wu, L. J., Liu, J., Wang, W. Y., Dai, D., Cheng, X. Y., Zhang, Z. L., et al. (2014). Identification and content determination of phenolic acids of rhizosphere soil of Panax notoginseng. World Sci. Technol. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. 16, 825–829. doi: 10.11842/wst.2014.04.026
Xu, Z. Y., Hu, Z. H., Jiao, S., Xu, Q., Ma, L. L., and Chen, J. (2023). Depth-dependent effects of tree species identity on soil microbial community characteristics and multifunctionality. Sci. Total Environ. 878:162972. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162972
Yang, K., Wang, H. L., Luo, L. F., Zhu, S. S., Huang, H. P., Wei, Z. X., et al. (2023). Effects of different soil moisture on the growth, quality, and root rot disease of organic Panax notoginseng cultivated under pine forests. J. Environ. Manag. 329:117069. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117069
Zhalnina, K., Louie, K. B., Hao, Z., Mansoori, N., da Rocha, U. N., Shi, S. J., et al. (2018). Dynamic root exudate chemistry and microbial substrate preferences drive patterns in rhizosphere microbial community assembly. Nat. Microbiol. 3, 470–480. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0129-3
Zhang, H. L., Huang, M., Zhang, W. H., Gardea-Torresdey, J. L., White, J. C., Ji, R., et al. (2020). Silver nanoparticles alter soil microbial community compositions and metabolite profiles in unplanted and cucumber-planted soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 3334–3342. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b07562
Zhang, B., Li, X. Z., Wang, F. Q., Li, M. J., Zhang, J. Y., Gu, L., et al. (2016). Assaying the potential autotoxins and microbial community associated with Rehmannia glutinosareplant problems based on its “autotoxic circle”. Plant Soil 407, 307–322. doi: 10.1007/s11104-016-2885-2
Zhao, X. Y., He, S., Rui, R., Hei, J. Y., He, X. H., and Wang, S. (2025). Introduction of Panax notoginseng into pine forests significantly enhances the diversity, stochastic processes, and network complexity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil. Front. Microbiol. 16:1531875. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1531875
Zhong, Y. M., Zhang, A., Qin, X. W., Yu, H., Ji, X. Z., He, S. Z., et al. (2022). Effects of intercropping Pandanus amaryllifolius on soil properties and microbial community composition in Areca Catechu plantations. Forests 13:1814. doi: 10.3390/f13111814
Zhou, X. G., Zhang, J. Y., Rahman, M. K., Gao, D. M., Wei, Z., Wu, F. Z., et al. (2023). Interspecific plant interaction via root exudates structures the disease suppressiveness of rhizosphere microbiomes. Mol. Plant 16, 849–864. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2023.03.009
Keywords: Sanqi cultivation, microbial community, differential metabolites, network complexity, network stability
Citation: Hei J, Li Y, Rui R, Faisal N, Peng J, Wang B, Wang S and He X (2025) The cultivation of Panax notoginseng enhances the metabolites and microbial network complexity in the soil of Pinus armandii rather than Pinus kesiya. Front. Microbiol. 16:1616266. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1616266
Edited by:
Tofazzal Islam, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Agricultural University, BangladeshReviewed by:
Kaoping Zhang, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaYang Ye, Kunming University of Science and Technology, China
Wenbo Wang, University of Jinan, China
Copyright © 2025 Hei, Li, Rui, Faisal, Peng, Wang, Wang and He. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Biao Wang, d2FuZ2JpYW9AY211LmVkdS5jbg==; Shu Wang, d2FuZ3NodUBzd2Z1LmVkdS5jbg==; Xiahong He, aHhoQHN3ZnUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jingying Hei
Jingying Hei Yue Li1†
Yue Li1† Biao Wang
Biao Wang Shu Wang
Shu Wang