- 1Jiangxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Greenhouse Gas Accounting and Carbon Reduction, Institute of Energy Research, Jiangxi Academy of Sciences, Nanchang, China
- 2Jiangxi Carbon Neutalization Research Center, Nanchang, China
This study investigates how 0.8 V applied voltage modulates phenazine biosynthesis, quorum sensing (QS), and microbial interactions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1-inoculated microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) reactors. Voltage stimulation significantly enhanced phenazine derivatives (PYO: 8.65-fold; 1-OH-PHZ: 14.98-fold) and QS signals (C4-HSL: 2.88-fold; 3-OXO-C12-HSL: 2.21-fold), correlating with upregulated biosynthetic genes (phzG: 14.8-fold; rhlI: 15.2-fold). Electrical stimulation amplified QS cross-regulation, reinforcing Las-mediated positive feedback on Rhl/PQS systems while attenuating Rhl’s inhibition of PQS. Untargeted metabolomic analysis demonstrated significant alterations in bacterial metabolic activity under electrical stimulation, identifying 140 differential metabolites. Among these, indole, a signaling molecule with QS-like functionality, exhibited the highest VIP score as an upregulated metabolite, and another indole derivative, brassicanal A, was also elevated. KEGG pathway enrichment analysis highlighted that these metabolites were primarily associated with amino acid metabolism and transport, while anthranilic acid and L-tryptophan—key metabolites linked to both indole-related pathways and phenazine biosynthesis—were also identified. Correlation analysis between differential metabolites with microbial communities confirmed that Delftia and Burkholderiales were strongly associated with phenazine biosynthesis and QS activity in P. aeruginosa PAO1. These findings highlight voltage as a key driver of metabolic rewiring and microbial niche partitioning, optimizing MEC reactor performance for wastewater treatment. This work provides foundational insights into electro-stimulated biofilm engineering through targeted QS and metabolic pathway regulation.
1 Introduction
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a Gram-negative opportunistic pathogen, employs a sophisticated quorum sensing (QS) system to coordinate population-wide behaviors critical for virulence and environmental adaptation (Li et al., 2022; Shariati et al., 2024). In the medical field, researchers have attempted to suppress the survival capability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by quenching quorum sensing to treat wound infections caused by this pathogen (Rather et al., 2022; Rodriguez-Urretavizcaya et al., 2024). However, P. aeruginosa has also emerged as a pivotal microbial agent in wastewater nitrogen removal due to its unique metabolic versatility and engineering adaptability (Nie et al., 2020). Regulating its quorum sensing through specific methods can enhance its competitive advantage in water treatment systems, thereby achieving high-efficiency nitrogen removal.
In P. aeruginosa PAO1, the well-characterized QS systems with defined regulatory mechanisms are primarily the N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL)-based QS systems (Las and Rhl) and the PQS (Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal) system (Schuster and Greenberg, 2006; Vadakkan et al., 2024). The Las system is composed of the LasR protein (acting as a signal receptor) and the LasI protein (acting as a signal emitter). The LasI protein is primarily responsible for synthesizing the signaling molecule N-3-oxododecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (3-oxo-C12-HSL), which is then exported outside the cell membrane (de Oliveira Pereira et al., 2023). Free 3-oxo-C12-HSL molecules are detected by LasR proteins on neighboring cell membranes, forming a complex that activates the Las system and subsequently regulates the expression of downstream genes. This system mainly influences metabolic activities such as the synthesis of elastase, alkaline protease, proteolytic enzymes, toxin A, and the formation of pili and flagella. The Rhl system consists of the RhlR signal receptor protein and the RhlI signal synthase protein. The RhlI protein generates the signaling molecule N-butanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (C4-HSL) within the cell, which binds to RhlR to regulate downstream gene expression. This system primarily governs the synthesis of elastase and alkaline protease, and is also associated with the production of phenazine derivatives and rhamnolipids (Latifi et al., 1995; Pearson et al., 1997).The PQS system involves the operons pqsABCDE, phnAB, and pqsH, which form a genetic cluster controlling the synthesis of quorum-sensing PQS molecules. Upon activation, the PQS system regulates metabolic activities such as biofilm formation, phenazine derivative synthesis, and protease production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Gallagher et al., 2002; Rampioni et al., 2010; Winzer and Williams, 2001).
Phenazine derivatives are endogenous electron shuttles primarily secreted by Pseudomonas species, facilitating indirect extracellular electron transfer (IEET) (Franco et al., 2024; Saunders et al., 2020). In P. aeruginosa PAO1, two operons, phzA1B1C1D1E1F1G1 and phzA2B2C2D2E2F2G2, independently control the synthesis of simple phenazine compounds such as phenazine-1-carboxamide (PCN) without mutual interference (Cui et al., 2016; Sun et al., 2019). Subsequently, PCN and phenazine-1-carboxylic acid (PCA) are modified by proteins encoded by the phzS, phzM, and phzH genes into derivatives such as 1-hydroxyphenazine (1-OH-PHZ) and pyocyanin (PYO) (Huang et al., 2020; Qiao et al., 2015, 2017). P. aeruginosa utilizes these phenazine derivatives for electrogenic respiration by anchoring to MFC anode electrodes and enhances biofilm formation (Price-Whelan et al., 2006; Ramos et al., 2010). Previous studuy have demonstrated that exogenous supplementation of 3-oxo-C12-HSL can enhance phenazine derivatives secretion, biomass production, and denitrification activity during the early stages of P. aeruginosa PAO1 inoculation, thereby improving its competitive advantage in water treatment processes (Nie et al., 2021). In another study, electrical stimulation of P. aeruginosa PAO1 achieved similar outcomes (Nie et al., 2022). However, the research failed to establish a direct connection between the electrical stimulation and quorum sensing regulation.
This study aims to investigate the phenazine derivatives, quorum sensing signal molecules, and related gene expression of P. aeruginosa PAO1 in previously operated MEC reactors under conditions with and without 0.8V applied voltage. Through integration with untargeted metabolomics analysis, the work further seeks to identify metabolites closely associated with QS in the communities of P. aeruginosa PAO1 inoculated under electrical stimulation. Therefore, elucidating the relationship between the electroactivity of P. aeruginosa PAO1 and QS is critical for optimizing its application in wastewater treatment.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Samples
All samples in this experiment were derived from MEC reactors inoculated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 operating for 72 days under conditions of 0.8 V applied voltage (corresponds to anode potential) and non-electrified control in previous studies (Nie et al., 2021). For targeted metabolomic analysis of phenazine synthesis and quorum sensing: 50 mL of bacterial culture from this stage was centrifuged at 8,000 rpm for 5 min. The supernatant was collected for detecting phenazine derivatives and quorum sensing signal molecule concentrations, while the pellet (bacterial cells) was used for RNA extraction followed by reverse transcription and real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) analysis. For untargeted metabolomic analysis: 50 mL of the same bacterial culture was centrifuged at 8,000 rpm for 5 min to remove the supernatant. The remaining cell pellet was freeze-dried for 24 h and stored at −80°C for subsequent detection.
2.2 Detection of phenazine derivatives
The concentrations of phenazine derivatives were determined using methods established in previous studies (Nie et al., 2021). For the extraction of 1-hydroxyphenazine (1-OH-PHZ) and pyocyanin (PYO), 5 mL of supernatant was transferred to a 10 mL centrifuge tube, mixed with 5 mL of chloroform, and vigorously vortexed for 5 min to fully dissolve 1-OH-PHZ and PYO into the chloroform phase. After centrifugation at 10,000 rpm for 5 min to separate the phases, the upper aqueous layer was discarded. A secondary extraction was then performed by adding 5 mL of pH 10 sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution for 1-OH-PHZ and pH 3 hydrochloric acid (HCl) solution for PYO, following the same vortexing and centrifugation steps. The final aqueous layer was retained, and absorbance was measured at 520 nm to determine concentrations based on standard curves. For phenazine-1-carboxylic acid (PCA) extraction, only a single-step chloroform extraction was performed using the same protocol, but the lower chloroform phase was directly analyzed by measuring absorbance at 252 nm. Standards for PCA and 1-OH-PHZ were purchased from Macklin Biochemical (Shanghai, China), and the PYO standard was obtained from Cayman Chemical (Ann Arbor, United States).
2.3 Detection of AHL-mediated QS signal molecules
The supernatant samples were mixed with an equal volume of ethyl acetate acidified with 0.1% formic acid. Two sequential extractions were performed to ensure complete recovery of target compounds. The combined ethyl acetate extracts were concentrated to 2 mL using a rotary evaporator at 40°C, followed by further evaporation to 400 μL under a nitrogen stream at 40°C. The aqueous phase was analyzed for C4-HSL, C6-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL, and 3-oxo-C12-HSL using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS; Thermo Scientific UltiMate 3000 UHPLC-Q Exactive system, Waltham, MA, United States) (Liu et al., 2024). AHLs standard samples were purchased from Yuanye Biotechnology (Shanghai, China).
2.4 RNA extraction and RT- qPCR
The samples were aliquoted into 50 mL centrifuge tubes and subjected to centrifugation at 8,000 rpm for 5 min to concentrate bacterial biomass (Liu et al., 2019). Total RNA was isolated from the pelleted cells using the RNAprep Bacteria Kit (Aidlab Biotechnologies, China), followed by DNase treatment with the DNA-free™ DNase Kit (New England Biolabs, United States) to eliminate genomic DNA contamination. RNA purity was verified by measuring A260/A280 ratios (2.08–2.12) using a NanoDrop™ UV spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, United States). To confirm the absence of residual DNA, RNA samples not subjected to reverse transcription were amplified by PCR using gene-specific primers employed in this study.
First-strand cDNA was synthesized from 1 μg of purified RNA using the THERMOscript™ 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Aidlab Biotechnologies, China) following the manufacturer’s protocol. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) was performed on a 7500 FAST Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, United States) with primers targeting denitrification-related genes, phenazine biosynthesis genes, quorum sensing genes and the reference genes proC (see Supplementary material). The qPCR conditions and cycling parameters were implemented as described by Nie et al. (2021), with cDNA serving as the template for amplification.
2.5 Untargeted metabolomics analysis
2.5.1 Samples treatment
For metabolomic extraction, 50 mg of cell pellets were weighed into a 2 mL centrifuge tube containing a 6-mm-diameter grinding bead. A 400 μL extraction solution (methanol:water = 4:1, v/v) spiked with 0.02 mg/mL internal standard (L-2-chlorophenylalanine) was added to the tube. The sample was homogenized in a frozen tissue grinder for 6 min at −10°C and 50 Hz, followed by low-temperature ultrasonic extraction for 30 min at 5°C and 40 kHz. The mixture was then incubated at −20°C for 30 min and centrifuged at 13,000 × g for 15 min (4°C). The supernatant was transferred to an autosampler vial with an insert for subsequent instrumental analysis. A quality control (QC) sample was prepared by mixing equal volumes of metabolites from all samples. During instrumental analysis, a QC sample was inserted every 3 samples to evaluate the reproducibility of the entire analytical process.
2.5.2 Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis
The LC-MS/MS analysis of the samples was performed using a Thermo Fisher Scientific UHPLC-Q Exactive HF-X system (Shanghai Majorbio Bio-pharm Technology Co., Ltd.). The samples were separated on an HSS T3 chromatographic column (100 mm × 2.1 mm i.d., 1.8 μm) with a mobile phase A consisting of 95% water + 5% acetonitrile (containing 0.1% formic acid) and mobile phase B consisting of 47.5% acetonitrile + 47.5% isopropanol + 5% water (containing 0.1% formic acid). The flow rate was 0.40 mL/min, and the column temperature was maintained at 40°C.
Mass spectrometry conditions: Data acquisition was performed in both positive and negative ion scanning modes with a mass scan range of 70–1,050 m/z. The sheath gas flow rate was set at 50 psi, auxiliary gas flow rate at 13 psi, and auxiliary gas heater temperature at 425°C. The ion spray voltage was set to 3,500 V in positive mode and −3500 V in negative mode. The ion transfer tube temperature was maintained at 325°C, and a stepped collision energy of 20–40–0 V was applied. The full scan mass spectra were acquired at a resolution of 60,000 (MS1) and 7,500 (MS2), respectively. Data-dependent acquisition (DDA) mode was employed for data collection.
2.5.3 Material identification and analysis
The LC-MS raw data were imported into the metabolomics processing software Progenesis QI (Waters Corporation, Milford, United States) for baseline filtering, peak identification, integration, retention time correction, and peak alignment. This process ultimately generated a data matrix containing retention time, mass-to-charge ratio (m/z), and peak intensity. The MS and MS/MS spectra were matched against public metabolite databases (HMDB; Metlin)1 and Majorbio’s in-house library to obtain metabolite annotations.
The annotated data matrix was then uploaded to the Majorbio Cloud Platform (https://cloud.majorbio.com/page/flow/index.html) for analysis. Data preprocessing included: (1) Applying the 80% rule to remove missing values, retaining variables with non-zero values in at least 80% of samples within any experimental group; (2) Filling remaining missing values with the minimum value from the original matrix; (3) Performing sum normalization to minimize technical variations from sample preparation and instrument instability, resulting in a log10-transformed normalized matrix; (4) Removing variables with relative standard deviation (RSD) > 30% in quality control (QC) samples; (5) Final log transformation to generate the processed matrix for downstream analysis.
Statistical analysis was performed using the R package ropls (Version 1.6.2) to conduct Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (OPLS-DA). Model robustness was evaluated through 7-fold cross-validation. Significantly differential metabolites were identified based on variable importance in projection (VIP) scores from OPLS-DA and Student’s t-test p-values, with thresholds set at VIP > 1 and p < 0.05.
Pathway annotation of differential metabolites was performed using the KEGG database2. Pathway enrichment analysis was conducted via the Python scipy.stats package, with statistically relevant biological pathways identified through Fisher’s exact test to reveal treatment-related metabolic mechanisms.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Phenazine synthesis and quorum sensing in MEC reactors with/without 0.8 V applied voltage
Phenazine derivatives and QS signal molecules were detected in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-inoculated MEC reactors on day 72 (Figure 1). In the MEC reactors with an applied voltage of 0.8 V, the production levels of PCA, 1-OH-PHZ, and PYO were 1. 38-, 14. 98-, and 8.65-fold higher, respectively, compared to those in the 0 V control reactors. The differences in QS signal molecules were primarily attributed to C4-HSL and 3-oxo-C12-HSL, which are secreted by P. aeruginosa, with increases of 2.88- and 2.21-fold, respectively. Additionally, trace amounts of other AHLs, including C6-HSL and C8-HSL, were detected at concentrations ranging from 34.23 to 39.41 μg/L and 12.14–23.15 μg/L, respectively. These AHLs may originate from other bacterial species within the microbial community.
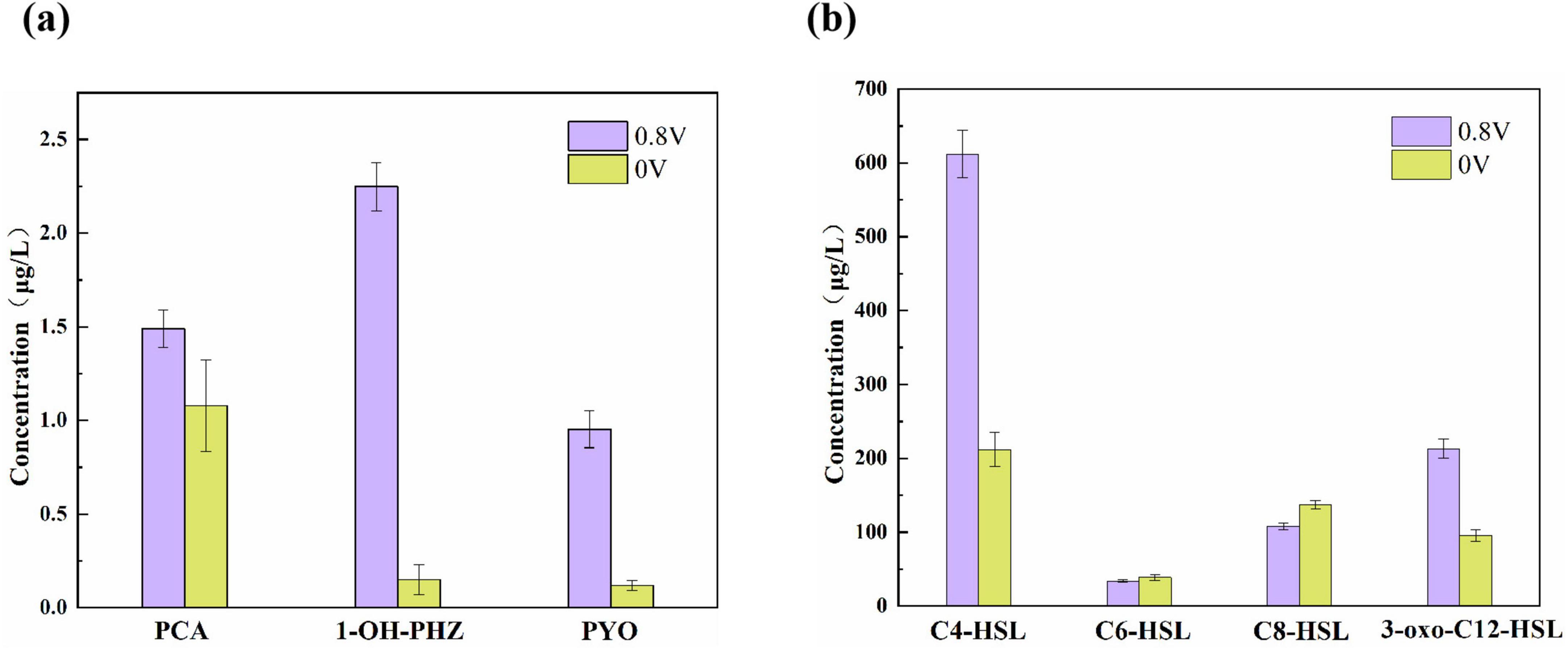
Figure 1. (a) Phenazine derivatives and (b) quorum sensing signal molecules detected in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-inoculated MEC reactors on day 72.
In the phenazine biosynthesis pathway of P. aeruginosa, the phzG gene is located upstream of all phenazine derivative synthesis pathways and participates in the production of the core intermediate PCA. Under an external voltage of 0.8 V, the expression level of phzG was upregulated by 14.8-fold (Figure 2); however, the production of PCA did not show a significant increase, likely because PCA, as an intermediate, is further metabolized by downstream regulatory genes. The genes phzH, phzS, and phzM regulate the conversion of PCA into PCN, PYO, and 1-OH-PHZ, respectively. Their expression levels were upregulated by 5. 38-, 2. 02-, and 3.69-fold, respectively (Figure 2). These expression changes exhibited a certain correlation with the altered production levels of their corresponding phenazine derivatives.
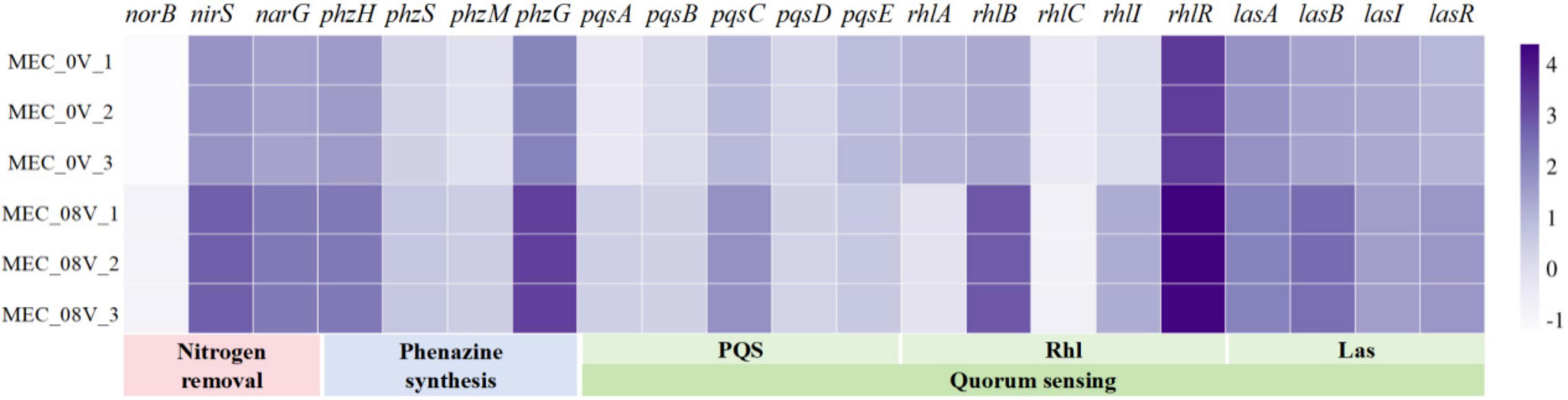
Figure 2. Relative expression of denitrification, phenazine synthesis, and quorum-sensing genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa with/without 0.8 V applied voltage. Relative expression abundance processed with log10.
In addition, genes related to QS all showed varying degrees of upregulation, including the PQS, Las, and Rhl systems (Figure 2). Among these, the genes in the Rhl system exhibited the most significant upregulation trend: the genes regulating C4-HSL synthesis, rhlB and rhlI, were upregulated by 36.29- and 15.2-fold, respectively, while the gene regulating C4-HSL-binding protein synthesis, rhlR, was upregulated by 9.15-fold. The Las system holds the highest priority among these three QS systems and can positively regulate the Rhl and PQS systems through feedback mechanisms (Miller and Bassler, 2001; Soukarieh et al., 2018). In contrast, the Rhl system exerts negative feedback regulation on the PQS system (Diggle et al., 2006). Under applied voltage, this negative feedback regulation may be attenuated due to the combined effects of Las-mediated positive feedback regulation and intrinsic enhancement of the PQS system.
3.2 Differential metabolites analysis in MEC reactors with/without 0.8 V applied voltage
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Orthogonal Partial Least Squares-Discriminant Analysis (OPLS-DA) were performed on the metabolomic profiles of MEC reactors under 0.8V applied voltage and non-electrified conditions. Notably, in both positive and negative ion modes, the electrified group exhibited clear separation from the control group along the first principal component (PC1), demonstrating that voltage application significantly altered the metabolic landscape (Figure 3). Among the 477 annotated metabolites detected, 69 differential metabolites were significantly upregulated (41 in positive ion mode and 28 in negative ion mode), and 71 were significantly downregulated (30 in positive ion mode and 41 in negative ion mode), as illustrated in the volcano plots (Figures 4a,b).
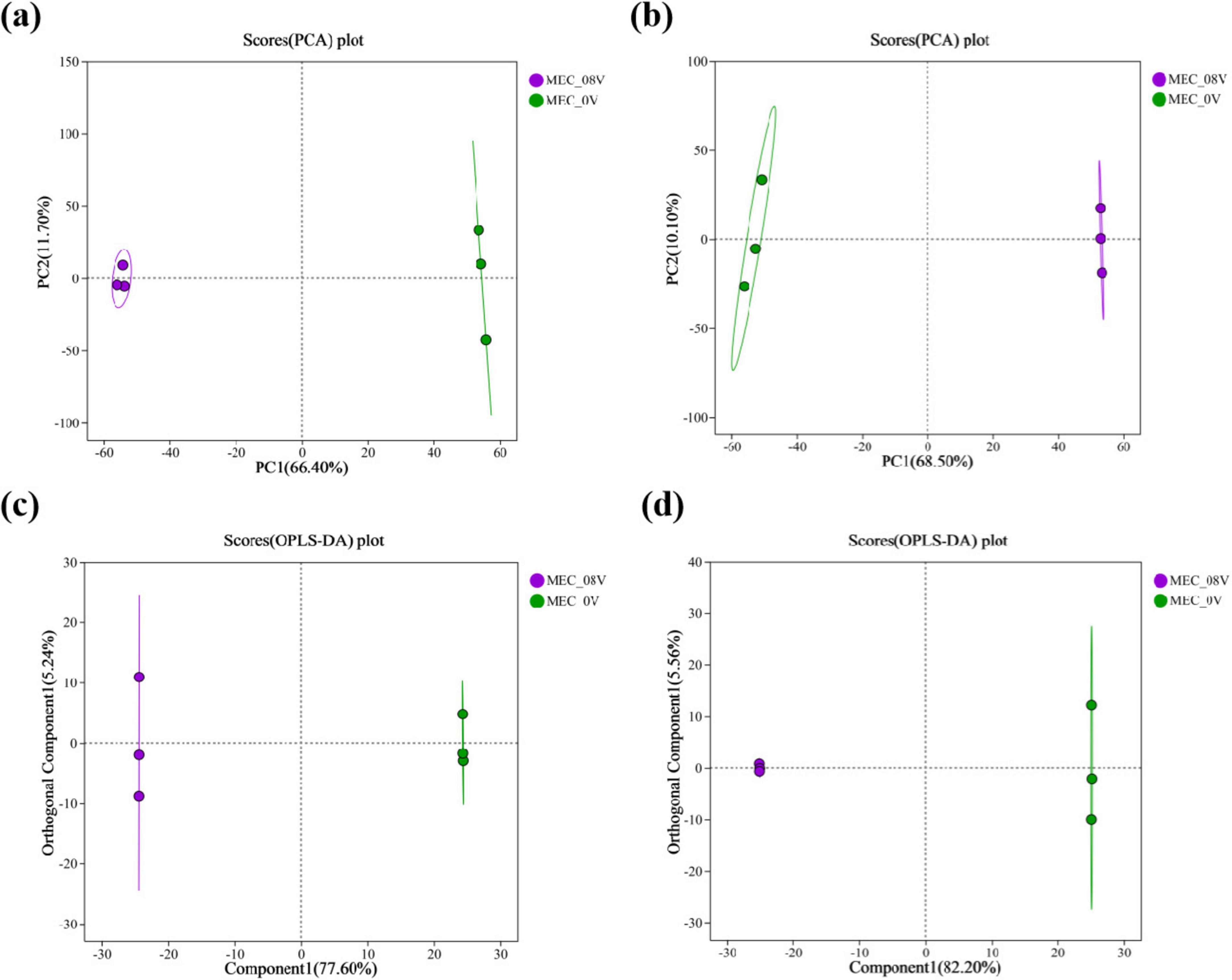
Figure 3. Score plot of principal component analysis (PCA) for metabolites in MEC reactors with/without 0.8 V applied voltage (a) positive ion mode (b) negative ion mode; score plot of orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) for metabolites in MEC reactors with/without 0.8 V applied voltage (c) positive ion mode (d) negative ion mode.

Figure 4. Volcano plots of differential metabolites in (a) positive ion mode; (b) negative ion mode. The x-axis represents the log2-transformed fold change (log2FC) of metabolite expression between groups, and the y-axis corresponds to the statistical significance of expression changes [-log10 (p-value)]. Each point denotes a specific metabolite, with size indicating VIP scores. Purple, green, and gray dots represent significantly upregulated, downregulated, and non-significant differential metabolites, respectively. (c) Bubble plot and relative expression heatmap of the top 30 VIP-ranked significant differential metabolites.
Among the top 30 differential metabolites ranked by VIP value, Indole is the top-ranked upregulated metabolite (Figure 4c). Indole and its derivatives represent a class of microbial signaling molecules, with a notable example being indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), a classic plant growth hormone. Recent studies have also linked indole to quorum sensing, and its addition during water treatment has been shown to enhance biofilm growth in Burkholderia (Wu et al., 2024). Indole can also directly stimulate biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa and Streptococcus mutans (Inaba et al., 2020; Kim et al., 2015). Additionally, another upregulated metabolite identified among the top 30 VIP-ranked differential metabolites is brassicanal A, a metabolic derivative of indole that is closely associated with indole biosynthesis (Wang et al., 2023). However, the majority of other differential metabolites have only been identified in applications such as material synthesis and pharmaceutical synthesis, with no clear link established to microbial activities, particularly quorum sensing. Therefore, further analysis of the functional roles of differential metabolites with VIP values beyond the top 30 remains necessary.
Thirteen differential metabolites, including indole, L-ornithine, anthranilic acid, L-tryptophan, L-histidine, L-proline, spermidine, boldione, N2-succinyl-L-ornithine, 2-isopropylmalic acid, uric acid, inosine, and L-lysine, were annotated with KEGG among the 140 differential metabolites, and these exhibited enrichment across 18 metabolic pathways (Figure 5a). Nearly half of the differential metabolites were amino acids and their derivatives. Consequently, pathways related to amino acid synthesis and transport—including D-arginine and D-ornithine metabolism, phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis, aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, beta-Alanine metabolism, arginine and proline metabolism, and ABC transporters—exhibited high enrichment factors. Under electrical stimulation, granular sludge or biofilms show increased secretion of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), whose primary components are polysaccharides (PS) and proteins (PN) (Jiang et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2019). These components mediate material exchange between bacterial cells and the external environment, which may explain the observed hyperactivity in amino acid synthesis and transport metabolism. Another noteworthy observation is the pathways associated with indole, specifically phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis, and tryptophan metabolism, both of which are linked to L-tryptophan and anthranilic acid (Figure 5b). Anthranilic acid is associated with phenazine biosynthesis. Its precursor, chorismate, can simultaneously participate in the synthesis of phenazine derivatives and the conversion to anthranilic acid, ultimately generating the PQS signaling molecule. Under electrical stimulation, the upregulation of anthranilic acid may coincide with enhanced activation of the PQS system. Additionally, L-tryptophan, as a downregulated differential metabolite in this study, can be degraded by certain bacteria to produce anthranilic acid and indole. The observed reduction in its accumulation might result from intensified degradation processes.
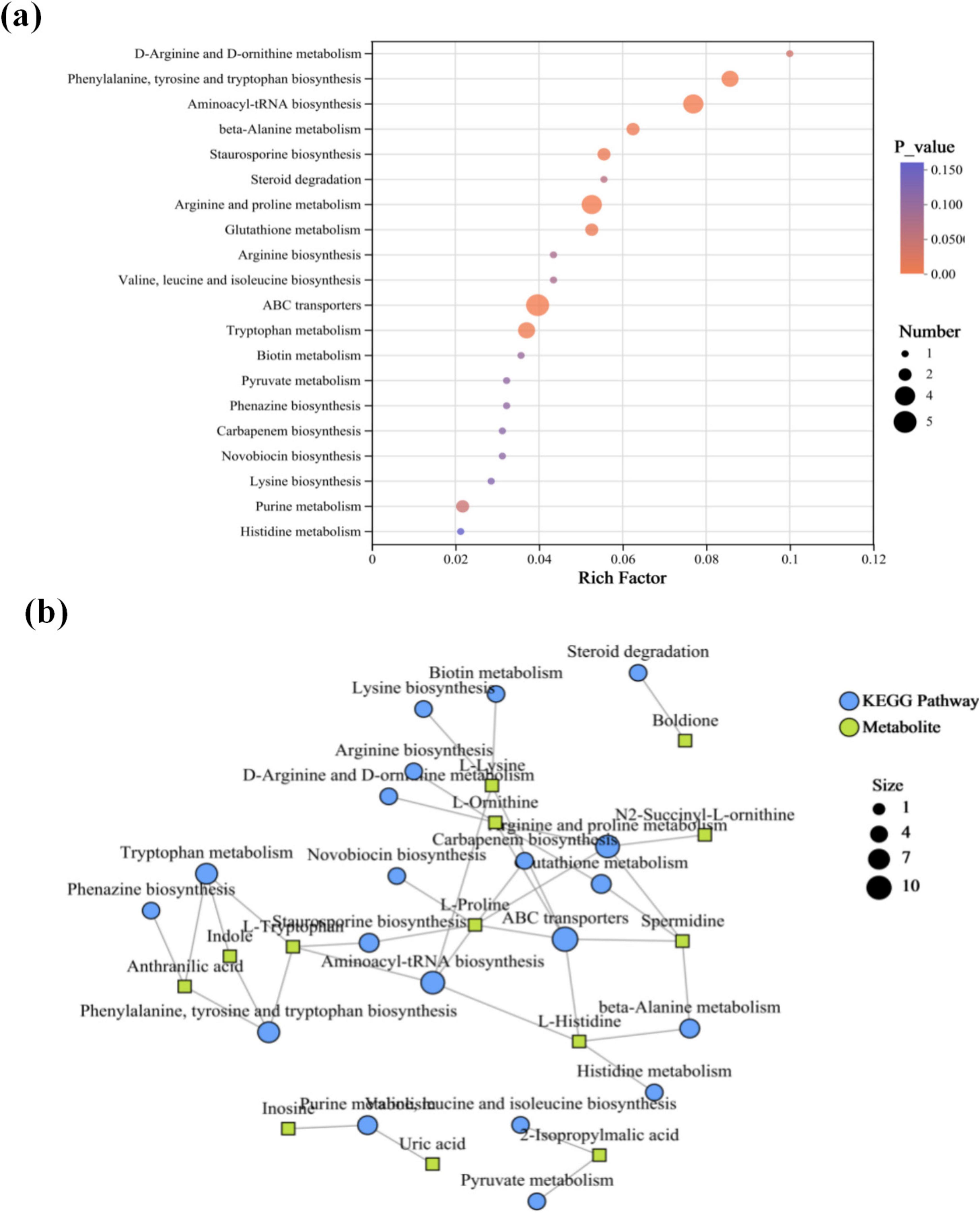
Figure 5. (a) KEGG enrichment bubble plot of differential metabolites. X-axis: Enrichment ratio (calculated as number in study group/number in population); Y-axis: KEGG pathways. Bubble size represents the number of metabolites enriched in each pathway; color indicates the enrichment significance [-log10 (p-value)]. (b) KEGG enrichment network diagram. Green square nodes denote metabolites; blue circular nodes represent KEGG pathways, with node size proportional to the number of associated metabolites.
3.3 Correlation analysis between differential metabolites and microbial communities in MEC reactors
To clarify the association between differential metabolites and microbial communities in MEC reactors, a Mantel test-based correlation analysis was conducted (Figure 6). After 72 days of operation, four bacterial genera, Achromobacter, Delftia, Stenotrophomonas, and Burkholderiales, were identified in MEC reactors inoculated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Among these, the abundances of Pseudomonas, Delftia, and Burkholderiales were higher in reactors with an applied voltage of 0.8 V. The analysis revealed that the metabolites most strongly correlated with these genera were primarily QS-related compounds, such as anthranilic acid, phenazine derivatives, and QS signaling molecules. Additionally, amino acids involved in metabolic processes, including L-ornithine, L-tryptophan, and L-proline, exhibited significant correlations.
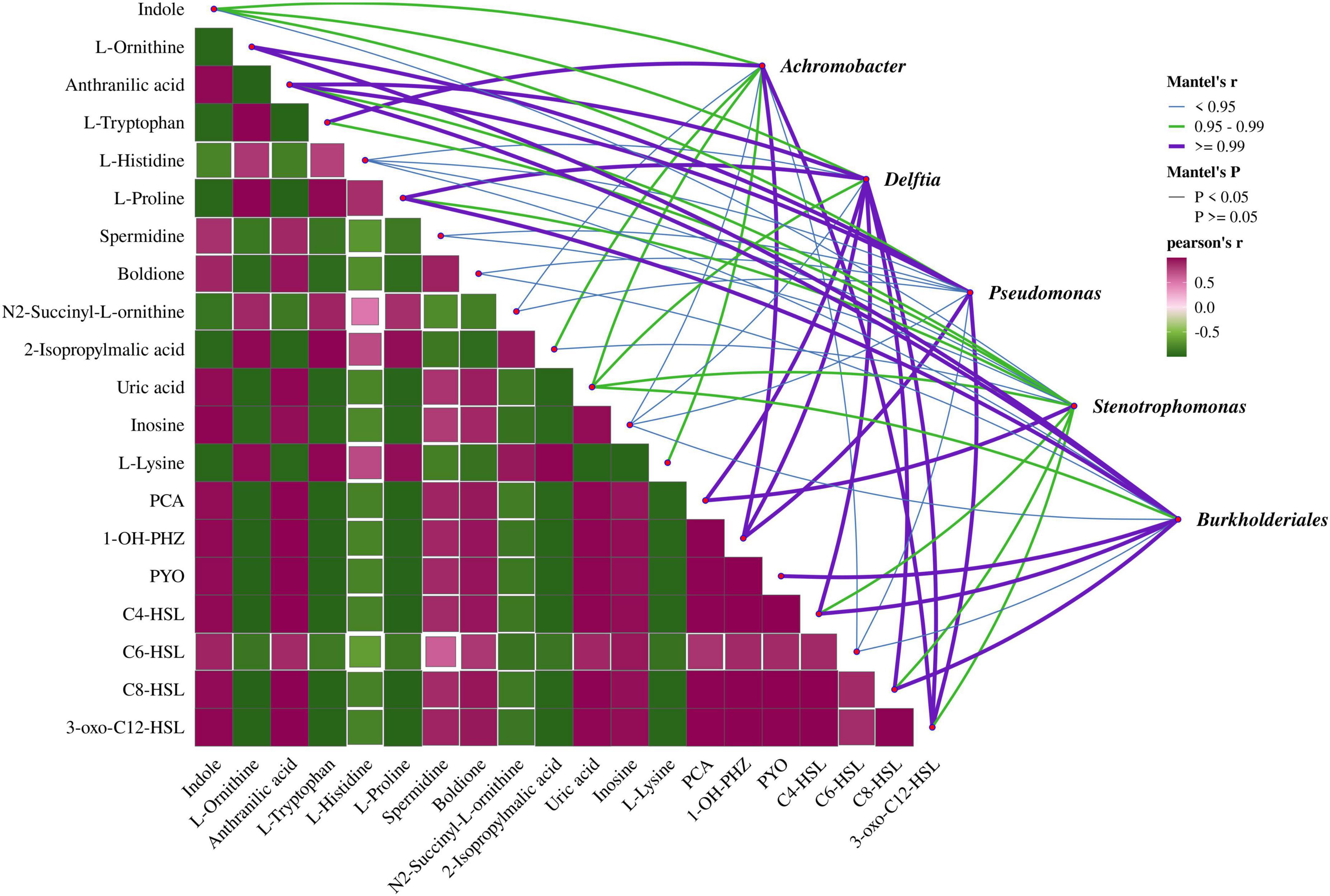
Figure 6. Correlation analysis of differential metabolites with microbial communities in MEC reactors. Analysis based on Pearson correlation coefficients; Mantel tests for correlations between metabolites and microbial communities. The line width and color represent the Mantel’s r statistic for the corresponding microbial community and environmental factor, while the line style indicates the significance of the statistical analysis.
The three genera whose abundances were enhanced by electrical stimulation, Pseudomonas, Delftia, and Burkholderiales, exhibited strong correlations with multiple metabolites. Delftia is recognized as a genus with quorum quenching (QQ) activity, enabling it to degrade AHLs and compete with QS bacteria like Pseudomonas aeruginosa in most environments (Singh et al., 2017; Xu et al., 2023). However, under electrical stimulation, P. aeruginosa released excessive AHLs, and the relatively low abundance of Delftia (7.14%) was insufficient to fully degrade these AHLs. This resulted in a transient synergistic relationship between P. aeruginosa and Delftia, leading to a close correlation between Delftia’s abundance and the levels of C4-HSL and 3-OXO-C12-HSL secreted by P. aeruginosa. In contrast, Burkholderiales was hypothesized to exhibit a QS-like system mediated by indole as a signaling molecule (Chunxiao et al., 2023; Wu et al., 2024). However, the correlation between indole and Burkholderiales was the weakest among all tested relationships. This may be attributed to the unclear biosynthetic origin of indole within the community structure of this study. In fact, indole synthesis is widespread among microbial genera; for example, Escherichia coli can synthesize indole via tryptophanase. However, within Burkholderiales, only a single Burkholderia sp. has been reported to produce indole (Lee and Lee, 2010), suggesting that it is unlikely derived from Burkholderiales itself.
The other two genera, Achromobacter and Stenotrophomonas, showed higher abundances under non-electrostimulated conditions. Achromobacter exhibited the strongest negative correlation with 3-OXO-C12-HSL. As a heterotrophic nitrifier and aerobic denitrifier, Achromobacter has been reported to enhance its growth activity and denitrification capacity when co-cultured with strains secreting C8-HSL (Zhao et al., 2022). However, since C8-HSL levels in the system were extremely low, Achromobacter’s dominance (46.4% abundance without electrical stimulation) may stem from its inherent competitive advantage over P. aeruginosa. Under electrical stimulation, P. aeruginosa’s growth was upregulated by 3-OXO-C12-HSL, suppressing Achromobacter’s abundance to 12.9%. Additionally, certain strains of the genus Achromobacter, such as Achromobacter sp. strain N2, have been reported to harbor metabolic pathways for synthesizing IAA and are capable of forming symbiotic relationships with plants (Corsini et al., 2018). Therefore, the indole detected in the system may originate from direct electrochemical conversion. Stenotrophomonas displayed the weakest correlation with differential metabolites among the five genera. This is likely because Stenotrophomonas primarily employs the diffusible signal factor (DSF) system for QS, and its ecological niche depends on the cooperative and competitive dynamics of the other four genera (Coves et al., 2023; Zhuang et al., 2023).
4 Conclusion
This study demonstrates that applying 0.8 V voltage significantly enhances phenazine synthesis and quorum sensing (QS) activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 within MEC reactors. Key phenazine derivatives (e.g., PYO, 1-OH-PHZ) and QS signaling molecules (C4-HSL, 3-OXO-C12-HSL) increased by 8.65–14.98-fold and 2.21–2.88-fold, respectively, accompanied by upregulation of biosynthesis genes (phzG, rhlI). Electrical stimulation amplified QS network interactions by reinforcing Las-mediated positive feedback on Rhl/PQS systems while weakening Rhl’s inhibitory effect on PQS. Metabolomics revealed differential metabolites (e.g., indole, anthranilic acid) enriched in amino acid and indole-related pathways, linked to upregulated extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) secretion and substrate competition under voltage. Microbial community analysis indicated voltage-driven enrichment of Pseudomonas, Delftia, and Burkholderiales. Delftia formed transient synergism with PAO1 due to incomplete AHL degradation, while Burkholderiales showed weak indole correlation, likely due to non-indigenous origin. In contrast, Achromobacter dominance (46.4% without voltage) was suppressed (12.9% with voltage) by PAO1’s 3-OXO-C12-HSL-mediated growth advantage. These findings highlight that voltage reshapes metabolic networks and microbial interactions, optimizing functional community structure and metabolic efficiency in MEC reactors, providing insights for electro-stimulated biofilm engineering.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
LW: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YL: Formal Analysis, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. JD: Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SG: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing. HN: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 52300046), the Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (grant no. 20232BAB213085), the Key Research and Development Program of Jiangxi Province (grant no. 20223BBG71016), and Introduction of Doctor Program of Jiangxi Academy of Sciences (grant no. 2023YYB02).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1621417/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
Chunxiao, D., Ma, F., Wu, W., Li, S., Yang, J., Chen, Z., et al. (2023). Metagenomic analysis reveals indole signaling effect on microbial community in sequencing batch reactors: Quorum sensing inhibition and antibiotic resistance enrichment. Environ. Res. 229:115897. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115897
Corsini, A., Colombo, M., Gardana, C., Zecchin, S., Simonetti, P., and Cavalca, L. (2018). Characterization of As(III) oxidizing Achromobacter sp strain N2: Effects on arsenic toxicity and translocation in rice. Ann. Microbiol. 68, 295–304. doi: 10.1007/s13213-018-1338-y
Coves, X., Bravo, M., Huedo, P., Conchillo-Solé, Ò, Gómez, A.-C., Esteve-Codina, A., et al. (2023). A Stenotrophomonas maltophilia TetR-like transcriptional regulator involved in fatty acid metabolism is controlled by quorum sensing signals. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 89:e00635-23. doi: 10.1128/aem.00635-23
Cui, Q., Lv, H., Qi, Z., Jiang, B., Xiao, B., Liu, L., et al. (2016). Cross-regulation between the phz1 and phz2 operons maintain a balanced level of phenazine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. PLoS One 11:e0144447. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144447
de Oliveira Pereira, T., Groleau, M.-C., and Deziel, E. (2023). Surface growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa reveals a regulatory effect of 3-oxo-C12-homoserine lactone in the absence of its cognate receptor, LasR. mBio 14:e0092223. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00922-23
Diggle, S., Cornelis, P., Williams, P., and Cámara, M. (2006). 4-quinolone signalling in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Old molecules, new perspectives. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 296, 83–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2006.01.038
Franco, A., Chukwubuikem, A., Meiners, C., and Rosenbaum, M. A. (2024). Exploring phenazine electron transfer interaction with elements of the respiratory pathways of Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioelectrochemistry 157:8636. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2023.108636
Gallagher, L. A., McKnight, S. L., Kuznetsova, M. S., Pesci, E. C., and Manoil, C. (2002). Functions required for extracellular quinolone signaling by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 184, 6472–6480. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.23.6472-6480.2002
Huang, L., Huang, Y., Lou, Y., Qian, H., Xu, D., Ma, L., et al. (2020). Pyocyanin-modifying genes phzM and phzS regulated the extracellular electron transfer in microbiologically-influenced corrosion of X80 carbon steel by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Corros. Sci. 164:108355. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2019.108355
Inaba, T., Obana, N., Habe, H., and Nomura, N. (2020). Biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans is enhanced by indole via the quorum sensing pathway. Microbes Environ. 35:ME19164. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME19164
Jiang, Z., Yu, Q., Zhao, Z., Song, X., and Zhang, Y. (2023). Reason for the increased electroactivity of extracellular polymeric substances with electrical stimulation: Structural change of α-helix peptide of protein. Water Res. 238:119995. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2023.119995
Kim, S.-K., Park, H.-Y., and Lee, J.-H. (2015). Anthranilate deteriorates the structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms and antagonizes the biofilm-enhancing indole effect. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81, 2328–2338. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03551-14
Latifi, A., Winson, M. K., Foglino, M., Bycroft, B. W., Stewart, G. S., Lazdunski, A., et al. (1995). Multiple homologues of LuxR and LuxI control expression of virulence determinants and secondary metabolites through quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Mol. Microbiol. 17, 333–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.mmi_17020333.x
Lee, J.-H., and Lee, J. (2010). Indole as an intercellular signal in microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 34, 426–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00204.x
Li, Q., Mao, S., Wang, H., and Ye, X. (2022). The molecular architecture of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing inhibitors. Mar. Drugs 20:488. doi: 10.3390/md20080488
Liu, Y., Zhu, Y., Deng, J., Yan, B., Zhan, J., Wei, Y., et al. (2024). In situ enrichment of anammox bacteria from pig farm anoxic sludge through co-cultivation with a quorum-sensing functional strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Ferment.-basel 10:548. doi: 10.3390/fermentation10110548
Liu, Z., Sun, D., Tian, H., Yan, L., Dang, Y., and Smith, J. A. (2019). Enhancing biotreatment of incineration leachate by applying an electric potential in a partial nitritation-anammox system. Bioresour. Technol. 285:121311. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121311
Miller, M. B., and Bassler, B. L. (2001). Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 55, 165–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.165
Nie, H., Dang, Y., Yan, H., Sun, D., and Holmes, D. E. (2021). Enhanced recovery of nitrous oxide from incineration leachate in a microbial electrolysis cell inoculated with a nosZ-deficient strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioresour. Technol. 333:125082. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125082
Nie, H., Liu, X., Dang, Y., and Sun, D. (2022). Early activated quorum sensing enhanced a nosZ-deficient strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for stably recovering nitrous oxide from incineration leachate in microbial electrolysis cell. Bioresour. Technol. 360:127394. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127394
Nie, H., Liu, X., Dang, Y., Ji, Y., Sun, D., Smith, J. A., et al. (2020). Efficient nitrous oxide recovery from incineration leachate by a nosZ-deficient strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioresour. Technol. 297:122371. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122371
Pearson, J. P., Pesci, E. C., and Iglewski, B. H. (1997). Roles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa las and rhl quorum-sensing systems in control of elastase and rhamnolipid biosynthesis genes. J. Bacteriol. 179, 5756–5767. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.18.5756-5767.1997
Price-Whelan, A., Dietrich, L., and Newman, D. (2006). Rethinking ‘secondary’ metabolism: Physiological roles for phenazine antibiotics. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2, 71–78. doi: 10.1038/nchembio764
Qiao, Y., Qiao, Y.-J., Zou, L., Ma, C.-X., and Liu, J.-H. (2015). Real-time monitoring of phenazines excretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa microbial fuel cell anode using cavity microelectrodes. Bioresour. Technol. 198, 1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.09.002
Qiao, Y.-J., Qiao, Y., Zou, L., Wu, X.-S., and Liu, J.-H. (2017). Biofilm promoted current generation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa microbial fuel cell via improving the interfacial redox reaction of phenazines. Bioelectrochemistry 117, 34–39. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2017.04.003
Ramos, I., Dietrich, L. E. P., Price-Whelan, A., and Newman, D. K. (2010). Phenazines affect biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in similar ways at various scales. Res. Microbiol. 161, 187–191. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2010.01.003
Rampioni, G., Pustelny, C., Fletcher, M. P., Wright, V. J., Bruce, M., Rumbaugh, K. P., et al. (2010). Transcriptomic analysis reveals a global alkyl-quinolone-independent regulatory role for PqsE in facilitating the environmental adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to plant and animal hosts. Environ. Microbiol. 12, 1659–1673. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02214.x
Rather, M. A., Saha, D., Bhuyan, S., Jha, A. N., and Mandal, M. (2022). Quorum quenching: A drug discovery approach against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Res. 264:127173. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2022.127173
Rodriguez-Urretavizcaya, B., Vilaplana, L., and Marco, M.-P. (2024). Strategies for quorum sensing inhibition as a tool for controlling Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 64:107323. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2024.107323
Saunders, S. H., Tse, E. C. M., Yates, M. D., Otero, F. J., Trammell, S. A., Stemp, E. D. A., et al. (2020). Extracellular DNA promotes efficient extracellular electron transfer by pyocyanin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Cell 182:919. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.07.006
Schuster, M., and Greenberg, E. (2006). A network of networks: Quorum-sensing gene regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 296, 73–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2006.01.036
Shariati, A., Noei, M., Askarinia, M., Khoshbayan, A., Farahani, A., and Chegini, Z. (2024). Inhibitory effect of natural compounds on quorum sensing system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A helpful promise for managing biofilm community. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1350391. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1350391
Singh, V. K., Mishra, A., and Jha, B. (2017). Anti-quorum sensing and anti-biofilm activity of Delftia tsuruhatensis extract by attenuating the quorum sensing-controlled virulence factor production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 7:337. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00337
Soukarieh, F., Williams, P., Stocks, M. J., and Camara, M. (2018). Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing systems as drug discovery targets: Current position and future perspectives. J. Med. Chem. 61, 10385–10402. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00540
Sun, L., Chi, X., Feng, Z., Wang, K., Kai, L., Zhang, K., et al. (2019). phz1 contributes much more to phenazine-1-carboxylic acid biosynthesis than phz2 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa rpoS mutant. J. Basic Microbiol. 59, 914–923. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201900165
Vadakkan, K., Ngangbam, A. K., Sathishkumar, K., Rumjit, N. P., and Cheruvathur, M. K. (2024). A review of chemical signaling pathways in the quorum sensing circuit of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 254:127861. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127861
Wang, Q., Xu, K., Cai, X., Wang, C., Cao, Y., and Xiao, J. (2023). Rosmarinic acid restores colonic mucus secretion in colitis mice by regulating gut microbiota-derived metabolites and the activation of inflammasomes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71, 4571–4585. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c08444
Winzer, K., and Williams, P. (2001). Quorum sensing and the regulation of virulence gene expression in pathogenic bacteria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 291, 131–143. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00110
Wu, W., Jing, J., Chen, Z., Guo, X., and Qu, Y. (2024). Indole signaling enhances biofilm formation and quorum sensing in sequencing biofilm batch reactors. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 12:112494. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2024.112494
Xu, F., Liao, J., Hu, J., Feng, Y., Huang, Y., Feng, X., et al. (2023). Biofouling mitigation and microbial community dynamics in the membrane bioreactor by the indigenous quorum quenching bacterium Delftia sp, JL5. Bioresour. Technol. 388:129753. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129753
Zhao, L., Fu, G., Tang, J., Wu, J., Pang, W., and Guo, Z. (2022). Efficient nitrogen removal of mangrove constructed wetlands: Enhancing heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification microflora through quorum sensing. Chem. Eng. J. 430:133048. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.133048
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, quorum sensing, phenazine derivative, microbial electrolysis cell, untargeted metabolomic analysis
Citation: Wu L, Liu Y, Deng J, Gui S and Nie H (2025) Integrated analysis of electrical stimulation effects on Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 inoculated denitrifying community: targeted and untargeted metabolomic analysis of phenazine biosynthesis and quorum sensing. Front. Microbiol. 16:1621417. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1621417
Received: 01 May 2025; Accepted: 16 May 2025;
Published: 13 June 2025.
Edited by:
Dandan Liang, Harbin Institute of Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Xinying Liu, Beijing Forestry University, ChinaJunhui Zhang, Kunming University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Liu, Deng, Gui and Nie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shuanglin Gui, Z3NsNTAzQDE2My5jb20=; Hanbing Nie, bmllaGFuYmluZzIyMUAxMjYuY29t
 Li Wu1,2
Li Wu1,2 Hanbing Nie
Hanbing Nie