- 1Institute of Zoonosis, College of Public Health, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Maternal & Child Health and Exposure Science of Guizhou Higher Education Institutes, Zunyi, China
- 3Qingdao Municipal Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Qingdao, China
- 4China Animal Health and Epidemiology Center, Qingdao, China
Autophagy is the process by which cells degrade and recycle damaged organelles and macromolecules by forming autophagosomes. This process is closely related to the maintenance of cellular homeostasis, ontogeny, and the occurrence and development of various diseases. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are a class of RNA molecules that do not encode proteins but play crucial roles in regulating gene expression. Numerous studies have demonstrated that ncRNAs are involved in regulating autophagy, and accumulating scientific evidence suggests that ncRNAs play an essential role in virus-induced cellular autophagy. ncRNAs affect autophagy by participating in the autophagy regulatory network, mediating the transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of autophagy-related genes. This review aims to explore the role of ncRNAs in autophagy induced by viral infection and analyze the relevant molecular regulatory mechanisms underlying autophagy. By examining the content above, we speculate that targeted regulation of ncRNAs can affect autophagy induced upon viral infection, thereby achieving antiviral effects and host cell protection.
Highlights
• ncRNAs play a key role in regulating viral infection-induced autophagy, influencing cellular homeostasis and viral replication via critical signaling pathways.
• ncRNAs can both promote and inhibit autophagy during viral infections, with effects varying by virus type and host cell context.
• Emerging research reveals ncRNAs’ dual role in autophagy and viral replication, offering potential targets for antiviral drug development.
• Targeted ncRNA regulation may provide novel therapeutic strategies to modulate autophagy, control viral infections, and protect host cells.
1 Introduction
Autophagy is recognized as a cyclic degradation mechanism that removes protein aggregates, damaged organelles, and intracellular pathogens to control cell damage. It is essential for the survival of eukaryotic cells and mammals, playing a key role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, development, tumorigenesis, and viral infections (Levine and Kroemer, 2009, 2019; Ghafouri-Fard et al., 2022). Autophagy is a complex cellular process that involves the delivery of cellular contents to lysosomes for degradation and the subsequent recycling of macromolecules formed from this degradation (Chang, 2020). The three primary forms of autophagy—microautophagy, macroautophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy—differ in their physiological functions and mechanisms of lysosomal delivery. Among these, macroautophagy is the most critical and widely studied form Wu et al. (2023). Macroautophagy engulfs cytoplasmic contents, including protein aggregates, damaged organelles, and intracellular pathogens, into double-membrane autophagosomes. These autophagosomes fuse with lysosomes to form autolysosomes, where their contents are degraded, and the resulting macromolecules are recycled for cellular reuse (Ueno and Komatsu, 2017). The autophagy process is regulated by a variety of cellular regulators, which play a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. Genetic or functional defects may lead to autophagy disorders, which in turn affect cell homeostasis and physiological balance in vivo (Füllgrabe et al., 2016; Lee, 2018; Gómez-Virgilio et al., 2022). In addition, autophagy defects can influence the pathogenesis of various diseases, and their abnormalities are associated with the onset and progression of multiple diseases. For example, the single allelic deletion of the autophagy-related gene Beclin-1 in various human cancers reduces autophagy activity, thereby increasing the risk of cancer (Li et al., 2010; Tang et al., 2015). Autophagy is crucial in viral infections, and defects in autophagy-related genes can affect the host’s antiviral immune response and viral lifecycle. For instance, the deletion of the autophagy-related gene ATG5 can increase interferon production against RNA viruses such as VSV, thereby inhibiting viral replication (Choi et al., 2018). In contrast, another study has shown that ATG5 deficiency can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction, induce a large amount of ROS synthesis, upregulate the RLR signaling pathway, and trigger the excessive secretion of IFN-α and IL-6, resulting in host cell damage (Kim et al., 2010). Moreover, viral infection can activate or inhibit autophagy in host cells, thereby affecting virus replication and spread. For example, infection with SARS-CoV-2 activates ULK-1-Atg13 and VPS34-VPS15-BECN1 pathways, promoting autophagosome formation and inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 replication (Zhou et al., 2023). It is worth noting that viruses have evolved mechanisms to combat autophagy. For example, SARS-CoV-2’s ORF3a inhibits autophagosome-lysosome fusion by blocking SNARE complex assembly, mediated by the HOPS complex, thereby reducing autophagic flux. This action enables SARS-CoV-2 to evade immune clearance, facilitating viral survival and replication within host cells and enhancing its pathogenicity (Miao et al., 2021). These studies suggest that autophagy acts as a double-edged sword in viral infection, either contributing to the antiviral response or possibly being exploited by the virus to evade the immune response and promote its replication.
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are RNA molecules that do not encode functional proteins or peptides (Matsui and Corey, 2017). However, ncRNAs are involved in numerous cellular activities, such as gene activation and silencing, RNA splicing, modification and editing, protein translation, and binding to chromatin modification complexes (Kim et al., 2025; Margvelani et al., 2025). They also play a role in the transcription of enhancer RNA, contributing to the dynamic regulation of gene expression and cellular functions (Liu Z. et al., 2023; Mattick et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024). The regulatory role of ncRNAs in viral infections is highly diverse. They can not only regulate viral protein expression by interacting with viral RNA or the host’s transcriptional machinery, but also modulate antiviral immunity by influencing the production and activity of interferons and other cytokines (Chen et al., 2023; Liu X. et al., 2023). In recent years, an accumulating body of evidence suggests that ncRNAs play a significant regulatory role in autophagy induced upon viral infection (Beermann et al., 2016). For instance, following adenovirus infection, IGFBPrP1 expression increases. This upregulation of IGFBPrP1 in turn boosts the expression of lncRNA NEAT1, which subsequently enhances autophagy in mouse hepatic stellate cells by modulating the miR-29b/Atg9a axis (Kong et al., 2019). Additionally, the expression of miR-193b-3p is markedly upregulated in patients with chronic hepatitis B after HBV infection. This miRNA enhances the Akt/MDM2/p53 signaling pathway by targeting IGF-1R, thereby promoting cell autophagy and enhancing the post-transcriptional activity of HBV (Deng et al., 2025). Moreover, circular RNA also plays a crucial role in regulating autophagy induced upon viral infection. circ-Vav3 can sponge gga-miR-375 to activate the CIP2A/AKT axis, thereby suppressing autophagy induced by avian leukosis virus subgroup J (ALV-J) infection (Chen et al., 2025). These findings have shed light on the complex interactions between viruses and host cellular processes, revealing potential targets for therapeutic intervention. This article reviews the regulatory effects and mechanisms of ncRNAs on autophagy induced upon viral infection. A deeper understanding of the relevant processes and mechanisms will contribute to the development of antiviral drugs and further basic research.
2 Regulatory network of autophagy and the mechanism of ncRNAs action
Autophagy is a highly intricate cellular process essential for maintaining homeostasis and responding to various stressors. It is tightly regulated by multiple vital signaling pathways and protein complexes (Figure 1).
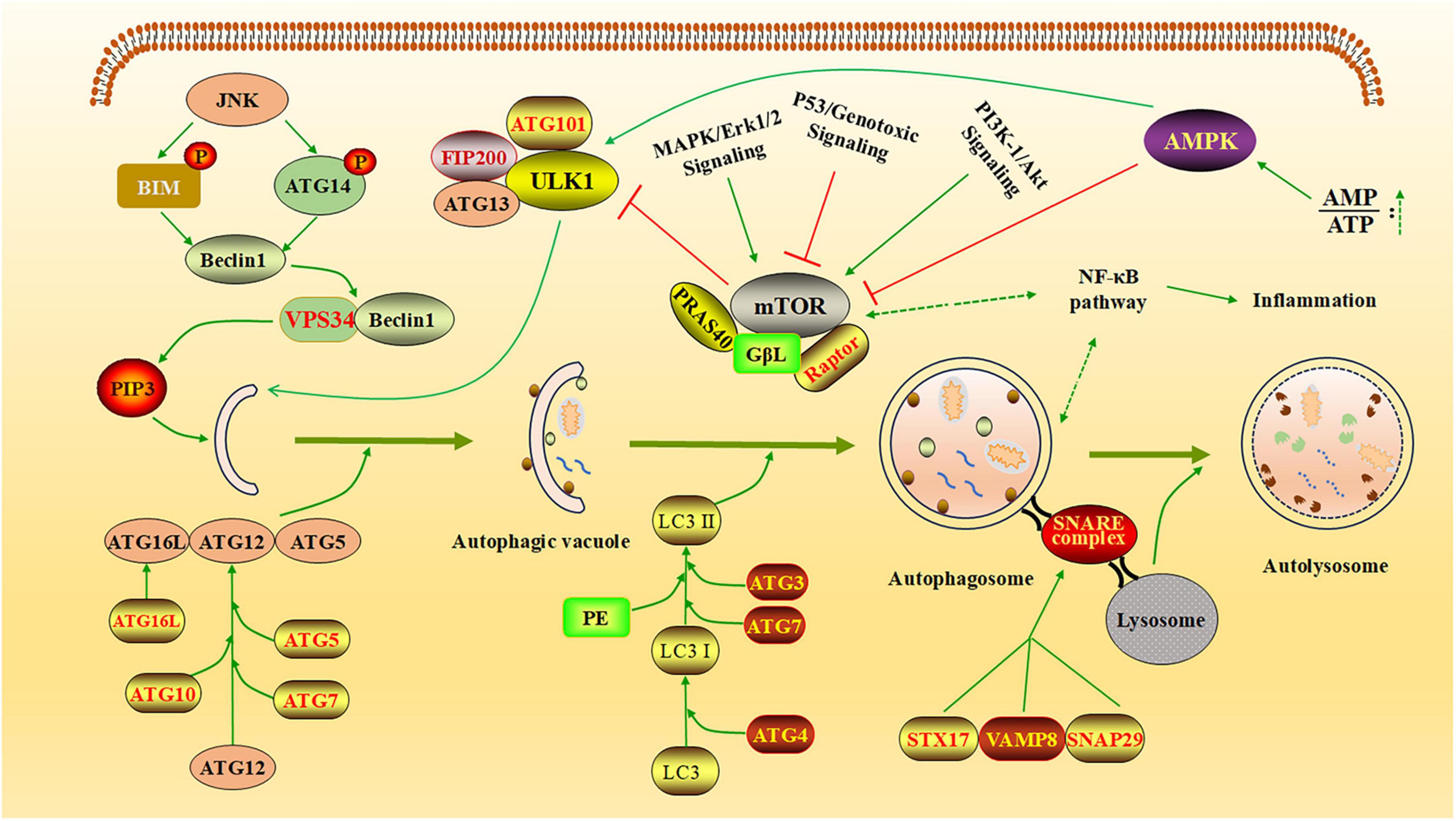
Figure 1. The regulatory network of autophagy. The diagram illustrates how autophagy is regulated by several key cellular pathways and protein complexes. AMPK inhibits the formation of the mTOR complex, thereby reducing mTOR’s suppressive effect on the ULK1 complex and promoting the generation of autophagic vesicles (Khandia et al., 2019). JNK kinase phosphorylates BCL-2 and BIM, leading to the release of Beclin-1. Free Beclin-1 activates VPS34 and binds to it, forming a complex that facilitates the production of PI3P, which promotes the elongation of autophagic vesicles. The autophagy process is further supported by two essential coupling mechanisms: the Atg12-Atg5-Atg16L system and the LC3/ATG8-PE conjugation system (Chen et al., 2023). These systems play critical roles in tagging specific proteins for autophagic degradation and actively participating in autophagosome formation. Additionally, STX17 binds to SNAP29 and VAMP8 to form the SNARE complex, which translocate to the autophagosome membrane, enabling the fusion of lysosomes with autophagosomes and the formation of autolysosomes (Liang et al., 2021). Created with BioRender.com and Microsoft PowerPoint 2019.
Among these, the mTOR, AMPK, PI3K/Akt, and NF-κB pathways play pivotal roles in modulating autophagy activity, often responding to changes in cellular energy status, nutrient availability, and external stress signals (Alharbi et al., 2021; Park et al., 2023). The mTOR pathway acts as a central regulator of cell metabolism, suppressing autophagy initiation in response to nutrient sufficiency, such as high amino acid levels, to prioritize growth and biosynthesis (Panwar et al., 2023). The AMPK pathway functions as an energy sensor, activating autophagy under conditions of low energy (e.g., reduced ATP levels) to restore energy homeostasis and maintain cellular balance (Garcia and Shaw, 2017). The PI3K/Akt pathway indirectly inhibits autophagy by upregulating mTOR activity, promoting cell survival and metabolism in response to external signals, such as growth factors or insulin (Liu et al., 2020). The NF-κB pathway regulates autophagy through the transcriptional control of autophagy-related genes, particularly during conditions of external stress, such as inflammation or oxidative stress, to balance cell survival and stress responses (Zhong et al., 2024). These pathways work together to fine-tune autophagy activity, ensuring dynamic regulation in response to cellular and environmental changes. The process of autophagy involves a coordinated series of steps regulated by distinct protein complexes. The ULK1 complex initiates autophagy by integrating upstream signals and triggering the formation of autophagosomes (Kishi-Itakura et al., 2014). This is followed by phagophore nucleation, which is mediated by the VPS34 complex, a core component of the class III PI3K machinery. Autophagosome elongation and closure depend on the ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L1 complex, which facilitates membrane expansion (Lystad et al., 2019). Additionally, LC3 (microtubule-associated protein light chain 3), a widely recognized marker of autophagosomes, plays a crucial role in cargo sequestration by binding to membranes and autophagic receptors. Among these receptors, p62 (also known as SQSTM1) is particularly important for selective autophagy, as it recognizes and delivers ubiquitinated cargo to autophagosomes for degradation (Li et al., 2024). Therefore, influencing these cellular pathways and key proteins related to autophagy can regulate the autophagy process in host cells.
Non-coding RNAs are involved in regulating autophagy through various molecular pathways and essential protein complexes, thereby influencing the autophagic process. For example, miRNAs can regulate autophagy by influencing specific signaling pathways, such as the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, or by targeting key proteins like LC3 (Gong et al., 2018). lncRNAs can interact with other biological macromolecules (DNA, RNA, and proteins) to regulate autophagy and cellular functions at multiple levels (Zhang et al., 2019; Statello et al., 2021). In addition, lncRNAs can also act as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) and indirectly affect the autophagy process by binding to miRNAs (Yang L. et al., 2017; Cao Z. et al., 2022). For example, the overexpression of lncRNA PTENP1 results in a significant increase in PTEN, which regulates autophagy through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Simultaneously, PTENP1 can competitively bind to miRNA-17, miRNA-19b, and miRNA-20a, thereby promoting the expression of ULK1 and ATG7, and consequently facilitating cellular autophagy (Jung et al., 2010; Chen et al., 2015). Moreover, lncRNA APF promotes the expression of ATG7 by competitively binding to miR-188-3p, thereby facilitating cellular autophagy (Wang et al., 2015). Through a review of the published literature, we found that ncRNAs play a dual role in regulating autophagy during viral infections, functioning in both positive and negative modes of modulation. This, in turn, influences viral replication and the host’s cellular immune response.
3 The role of ncRNAs in promoting autophagy
Several studies have shown that miRNAs promote cell autophagy caused by HBV infection (Li et al., 2011; Lazar et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2014). For example, miR-99 family members can promote HBV self-replication by directly targeting the 3′UTR of IGF-1R, Akt, and mTOR mRNA, leading to ULK1 dephosphorylation to induce autophagy through the mTOR/ULK1 pathway (Figure 2; Lin et al., 2017).
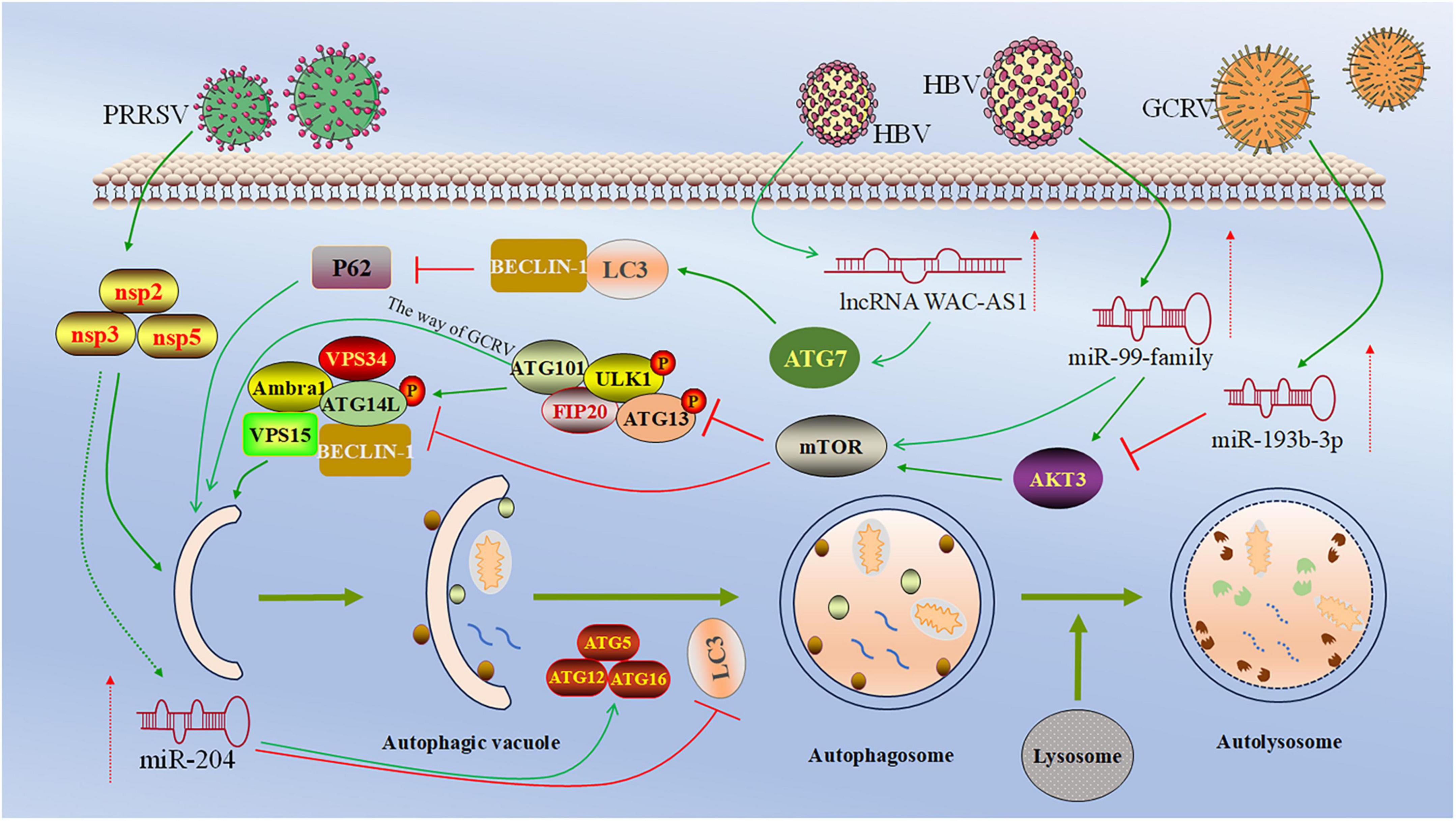
Figure 2. Regulatory roles and mechanism of ncRNA in viral infection-induced autophagy. This figure depicts the regulation of ncRNA in viral infection-induced autophagy. miR-99 family members target 3′-UTR of the mRNAs of IGF-1R, Akt, and mTOR, followed by the dephosphorylation of ULK1, leading to the initiation of autophagosome formation (Lin et al., 2017). miR-193b-3p targets the 3′-UTR of Akt3, inhibiting the expression of Akt3 and promoting autophagy in CIK cells (Yu et al., 2024a). miR-204 directly targets the 3′-UTR of LC3B and suppresses its expression, thereby inhibiting autophagy in PAMs cells (Yao et al., 2023). lncRNA WAC-AS1 enhances autophagy by targeting ATG7, enhancing LC3 and Beclin-1 expression and reducing p62 (Cao M. et al., 2022). Created with BioRender.com and Microsoft PowerPoint 2019.
Another study has shown that HBV core protein (HBc) and HBV X protein (HBx) upregulate the expression of miR-146a-5p through NF-κB in HBV-infected hepatocytes. This miRNA promotes HBV replication by targeting the Xiap-mediated MDM2/p53 axis, thereby inducing cell autophagy (Fu et al., 2019). In addition, Wang et al. (2019) found that the interaction between HBx and c-myc can inhibit the expression of miR-192-3p, and this miRNA can inhibit Xiap expression by targeting the 3′-UTR of Xiap, thereby affecting NF-κB. Therefore, HBV infection can promote autophagy and enhance HBV replication through the miR-192-3p/Xiap/NF-κB axis (Wang et al., 2019). It is worth noting that lncRNA also plays an essential role in HepG2.2.15 cells infected with HBV. For example, lncRNA WAC-as1 promotes autophagy of HepG2.2.15 cells by targeting ATG7 or enhancing the expression of miR-192-5p, thereby promoting HBV replication in vitro (Cao M. et al., 2022; Table 1). In conclusion, it is evident that ncRNAs play a role in inducing and promoting autophagy during HBV infection, and autophagy, in turn, encourages the replication of HBV both in vivo and in vitro.
The expression of miR-155-5p is decreased after HPV infection in cervical cancer cell lines. This miRNA inhibits the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and enhances autophagy by targeting PDK1 expression (Wang et al., 2018). In addition, Enterovirus 71 (EV71) infection in Hep2 and Vero cells decreased the expression of miR-30a, which could enhance EV71 replication by targeting the 3′-UTR of Beclin-1 (a key autophagy-promoting gene) to induce autophagy (Fu et al., 2015). lncRNAs can affect autophagy induced upon influenza infection. For example, Chi et al. (2024) found that PESP, a small protein encoded by the lncRNA PCBP1-AS1, causes the upregulation of ATG7 expression by targeting the enhancement of ATG7 promoter activity, which promotes autophagy and leads to enhanced replication of IAV.
Non-coding RNAs can also enhance autophagy during animal virus infection. When porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) infected 3D4/21 cells, miR-30a-5p enhanced PCV2 virus-induced autophagy and promoted PCV2 replication by targeting the 14-3-3 gene, a regulator of autophagy that also promotes G2 phase cell cycle arrest (Wang et al., 2017). miRNAs can affect autophagy induced by white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) through different targets. For example, the expression of miR-71 is upregulated after WSSV infection, which promotes host autophagy by targeting the host calcification-associated peptide-1 (CAP-1) gene. Furthermore, host autophagy enhances the expression of miR-71. This eventually leads to improved WSSV replication (He et al., 2017). Similarly, miR-13b promotes autophagy caused by WSSV infection by targeting the host knickkopf gene, thereby facilitating the replication of WSSV. In addition, Jia et al. (2021) demonstrated that lja-miR-145 promoted red spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus (RGNNV)-induced autophagy in LJB cells and enhanced virus replication by acting on LC3B-II/I and p62 proteins. In addition, the expression of miR-193b-3p was increased in CIK cells infected with grass carp reovirus (GCRV). This miRNA targets the 3′-UTR of Akt3 (a key regulator of autophagy), inhibiting the expression of Akt3 and promoting autophagy in CIK cells and inhibiting the replication of the virus (Yu et al., 2024a).
Recent studies have demonstrated that siRNAs can modulate virus-induced autophagy by targeting and silencing specific proteins. Following infection with duck enteritis virus (DEV), siRNA can regulate autophagy by targeting AMPK or TSC2, thereby affecting the AMPK-TSC2-MTOR signaling pathway. In this process, autophagy can promote the replication of the DEV virus (Yin et al., 2017). When porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) infects Vero cells, siRNA effectively downregulates the expression of TAK1, thereby affecting the AMPK/c-Jun pathway, promoting autophagy in Vero cells, and enhancing the replication of PEDV (Wang et al., 2022).
In both human and animal viral infections, ncRNAs play a role in enhancing autophagy within host cells. Our analysis reveals that ncRNAs can target host genes to promote autophagy, which, in turn, influences viral replication. It is worth noting that different ncRNAs can regulate autophagy induced upon the same virus. As mentioned above, miR-99 family, miR-146a-5p, miR-192-3p, and lncRNA WAC-as1 can all regulate HBV-induced autophagy. However, it remains uncertain whether these ncRNAs have synergistic effects that merit further exploration.
4 The role of non-coding RNAs in inhibiting autophagy
Non-coding RNAs can also act as negative regulators of autophagy. For example, miR-141 downregulated the expression level of Sirt1 after HBV infection in hepatocytes. This miRNA can directly target the 3′-UTR of Sirt1, thereby reducing the expression level of Sirt1 and inhibiting autophagy in hepatocytes. In turn, miR-141 can reduce the expression of HBV-DNA, HBsAg, and HBeAg, thereby reducing HBV replication, and may be developed into an RNA-based drug for HBV therapy (Yang Y. et al., 2017). In addition, Pu et al. (2017) demonstrated that miR-146a inhibited autophagy in dengue virus (DENV)-infected A549 and THP-1 cells by targeting TRAF6, resulting in decreased IFN-β expression. Through the regulation of autophagy, DENV2-induced TNF-α and IL-6 proinflammatory cytokine synthesis was enhanced. It also inhibited the excessive inflammation in host cells, thereby alleviating the immune damage caused by DENV2 infection (Pu et al., 2017). Additionally, FIP200 is a protein required for autophagosome formation by interacting with ULK1. HPV infection of cervical cancer cells can induce the upregulation of miR-224-3p. This miRNA can directly target the 3′-UTR of FIP200, thereby inhibiting FIP200 expression and subsequently suppressing autophagy in cervical cancer cells (Fang et al., 2016). Alternatively, the expression of miR-136 was upregulated in respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)-infected BEAS-2B cells. This miRNA inhibited cell autophagy by targeting the Sirt1 signaling pathway. Urolithin A can inhibit miR-136, thereby indirectly promoting cell autophagy and playing an antiviral role (Wang et al., 2024). Furthermore, silencing SNX5 or SNX32 proteins by siRNA has been shown to inhibit autophagy induced upon a variety of viruses, including Zika virus (ZIKV) (Liu et al., 2018), West Nile virus (WNV) (Kobayashi et al., 2014), chikungunya virus (CHIKV) (Joubert et al., 2012), poliovirus (Jackson et al., 2005), Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) (Alirezaei et al., 2012), and IAV (Gannagé et al., 2009).
During animal virus infections, accumulating evidence has shown that miRNAs can suppress viral replication by inhibiting cellular autophagy. For example, when porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) infects porcine alveolar macrophages (PAMs), miR-204 inhibits autophagy in PAMs cells. It reduces the level of PRRSV replication by directly targeting the 3′-UTR of LC3B and inhibiting its expression (Yao et al., 2023). Additionally, miR-192 and miR-731 target the 3′-UTR of LjULK1 in the ULK-VAPs-Atg13 pathway, altering the distribution of LC3 and the expression of autophagy-related proteins, thereby reducing the level of autophagy induced by RGNNV and inhibiting RGNNV proliferation (Pan et al., 2024). In another study, when RGNNV infects LJB cells, lja-miR-183 inhibits autophagy in LJB cells induced by RGNNV by targeting LC3B-II/I and p62, thereby reducing the replication levels of RGNNV (Jia et al., 2021). In bovine viruses, miR-2904 inhibits MDBK cell autophagy by targeting the 3′-UTR region of autophagy-related gene 13 (ATG13) mRNA during the infection of bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV). Overexpression of miR-2904 inhibits the replication of BVDV (Yang et al., 2022). In addition, avian reovirus (ARV) infection in DF-1 cells enhances the expression of gga-miR-30c-5p. This miRNA negatively regulates the expression of autophagy-related gene 5 (ATG5) by targeting its 3′-UTR, thereby inhibiting virus-induced autophagy in DF-1 cells. This inhibition of autophagy simultaneously suppresses ARV replication and syncytium formation, exerting an antiviral effect (Zhou et al., 2022). It is worth noting that ncRNAs can also promote viral replication by negatively regulating autophagy. For example, deptor, a protein containing the DEP domain that interacts with mTOR, downregulating deptor can inhibit cellular autophagy (Kim et al., 2011; Catena and Fanciulli, 2017). miR-193b-5p negatively regulates the expression of deptor mRNA by targeting the 3′-UTR of deptor. It reduces the level of autophagy in CIK cells and promotes the replication of GCRV virus (Yu et al., 2024b).
Above all, miRNAs play a critical role in the negative regulation of autophagy. These ncRNAs inhibit cellular autophagy by targeting key regulatory proteins or protein complexes, such as LC3B and ULK-VAPs-Atg13. Based on the above review, we speculate that targeted intervention of ncRNAs can affect autophagy induced by viral infection, thereby achieving antiviral effects and host cell protection.
5 Summary and prospects
In this study, we comprehensively reviewed the roles of ncRNAs in autophagy induced upon viral infections. It was demonstrated that ncRNAs play a key regulatory role in regulating cellular autophagy during viral infections. ncRNAs can promote or inhibit virus-induced autophagy by influencing crucial signaling pathways, such as IGF-1/PI3K/Akt/mTOR and AMPK/Erk/mTOR/ULK1, or by targeting key regulatory proteins, such as ATG5, Beclin-1, and LC3B. Therefore, ncRNAs-mediated post-transcriptional regulation may shed new light on the interplay between viral infection and host autophagy and may provide potential targets for drug development.
In addition, we found that ncRNAs affect autophagy as well as viral replication. For example, ncRNAs such as the miR-99 family, miR-146a-5p, and miR-192-3p promote autophagy induced by HBV, and also enhance HBV replication and expression. It is worth noting that the same ncRNA can exert distinct effects on autophagy regulation during viral infections. For instance, miR-146a promotes autophagy in HBV infection by targeting the Xiap-mediated MDM2/p53 axis, thereby facilitating viral replication. Conversely, during DENV infection, miR-146a inhibits autophagy by targeting TRAF6, thereby suppressing viral replication and reducing the production of proinflammatory cytokines. With a deeper understanding of ncRNAs’ function and mechanism, we can design specific drugs to modulate ncRNAs expression, thereby intervening in the autophagy process, affecting viral replication, and protecting host cells.
The regulatory network of ncRNAs is complex, involving a variety of molecules and signaling pathways. Understanding how these networks work in coordination across different cell types and physiological states is also an important direction for future research. Although we have some understanding of the role of ncRNAs in virus-induced autophagy, many mysteries remain. Future research should thoroughly investigate the interaction mechanisms between viral and host ncRNAs, elucidating how viruses precisely regulate host autophagy to facilitate their own replication and spread. Meanwhile, advanced techniques should be employed to investigate the dynamic regulatory roles of ncRNAs across different stages of autophagy. It is also crucial to focus on how ncRNAs influence viral drug resistance and develop novel antiviral therapies. Additionally, validating the potential of ncRNAs as biomarkers and therapeutic targets, as well as studying their specific functions in diverse cells and tissues, is of great importance. These research directions will enhance our understanding of ncRNAs in virus-related autophagy and drive the development of antiviral treatment strategies.
Author contributions
MY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft. HY: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. YZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32260908) and Guizhou Science and Technology Plan Project (QKHJC-ZK [2023]-Key057).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alharbi, Y. M., Bima, A. I., and Elsamanoudy, A. Z. (2021). An overview of the perspective of cellular autophagy: Mechanism, regulation, and the role of autophagy dysregulation in the pathogenesis of diseases. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 9, 47–54. doi: 10.4103/jmau.Jmau_33_20
Alirezaei, M., Flynn, C. T., Wood, M. R., and Whitton, J. L. (2012). Pancreatic acinar cell-specific autophagy disruption reduces coxsackievirus replication and pathogenesis in vivo. Cell Host Microbe 11, 298–305. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.01.014
Beermann, J., Piccoli, M. T., Viereck, J., and Thum, T. (2016). Non-coding RNAs in development and disease: Background, mechanisms, and therapeutic approaches. Physiol. Rev. 96, 1297–1325. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00041.2015
Cao, Z., Guan, L., Yu, R., and Chen, J. (2022). Identifying autophagy-related lncRNAs and potential ceRNA networks in NAFLD. Front. Genet. 13:931928. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.931928
Cao, M., Yuan, D., Jiang, H., Zhou, G., Chen, C., and Han, G. (2022). Long non-coding RNA WAC antisense RNA 1 mediates hepatitis B virus replication in vitro by reinforcing miR-192-5p/ATG7-induced autophagy. Eur. J. Histochem. 66:3438. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2022.3438
Catena, V., and Fanciulli, M. (2017). Deptor: Not only a mTOR inhibitor. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 36:12. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0484-y
Chang, N. C. (2020). Autophagy and stem cells: Self-eating for self-renewal. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 8:138. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00138
Chen, C. L., Tseng, Y. W., Wu, J. C., Chen, G. Y., Lin, K. C., Hwang, S. M., et al. (2015). Suppression of hepatocellular carcinoma by baculovirus-mediated expression of long non-coding RNA PTENP1 and MicroRNA regulation. Biomaterials 44, 71–81. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.12.023
Chen, L., Xu, H., Liu, R., Yao, Z., Xie, Q., and Zhang, X. (2025). Circular RNA Vav3 mediated ALV-J inhibition of autophagy by modulating the gga-miR-375/CIP2A axis and activating AKT. Poult. Sci. 104:104923. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104923
Chen, T., Tu, S., Ding, L., Jin, M., Chen, H., and Zhou, H. (2023). The role of autophagy in viral infections. J. Biomed. Sci. 30:5. doi: 10.1186/s12929-023-00899-2
Chi, X., Huang, G., Wang, L., Zhang, X., Liu, J., Yin, Z., et al. (2024). A small protein encoded by PCBP1-AS1 is identified as a key regulator of influenza virus replication via enhancing autophagy. PLoS Pathog. 20:e1012461. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012461
Choi, Y., Bowman, J. W., and Jung, J. U. (2018). Autophagy during viral infection - a double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 16, 341–354. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0003-6
Deng, Y., Zheng, J., Li, F., Zou, H., Tian, S., Zhao, Z., et al. (2025). Hepatocyte-enriched miRNA-193b-3p promotes hepatitis B virus replication by dual activation of viral core promoter activity and autophagy induction by targeting IGF-1R. J. Med. Virol. 97:e70330. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70330
Fang, W., Shu, S., Yongmei, L., Endong, Z., Lirong, Y., and Bei, S. (2016). miR-224-3p inhibits autophagy in cervical cancer cells by targeting FIP200. Sci. Rep. 6:33229. doi: 10.1038/srep33229
Fu, L., Fu, X., Mo, J., Li, X., Li, R., and Peng, S. (2019). miR-146a-5p enhances hepatitis B virus replication through autophagy to promote aggravation of chronic hepatitis B. IUBMB Life 71, 1336–1346. doi: 10.1002/iub.2044
Fu, Y., Xu, W., Chen, D., Feng, C., Zhang, L., Wang, X., et al. (2015). Enterovirus 71 induces autophagy by regulating has-miR-30a expression to promote viral replication. Antiviral Res. 124, 43–53. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.09.016
Füllgrabe, J., Ghislat, G., Cho, D. H., and Rubinsztein, D. C. (2016). Transcriptional regulation of mammalian autophagy at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 129, 3059–3066. doi: 10.1242/jcs.188920
Gannagé, M., Dormann, D., Albrecht, R., Dengjel, J., Torossi, T., Rämer, P. C., et al. (2009). Matrix protein 2 of influenza A virus blocks autophagosome fusion with lysosomes. Cell Host Microbe 6, 367–380. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2009.09.005
Garcia, D., and Shaw, R. J. (2017). AMPK: Mechanisms of cellular energy sensing and restoration of metabolic balance. Mol. Cell 66, 789–800. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.05.032
Ghafouri-Fard, S., Shoorei, H., Mohaqiq, M., Majidpoor, J., Moosavi, M. A., and Taheri, M. (2022). Exploring the role of non-coding RNAs in autophagy. Autophagy 18, 949–970. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1883881
Gómez-Virgilio, L., Silva-Lucero, M. D., Flores-Morelos, D. S., Gallardo-Nieto, J., Lopez-Toledo, G., Abarca-Fernandez, A. M., et al. (2022). Autophagy: A key regulator of homeostasis and disease: An overview of molecular mechanisms and modulators. Cells 11:2262. doi: 10.3390/cells11152262
Gong, G., Yin, J., Yang, X., Zhang, X. H., Zhang, Y., and Wan, W. H. (2018). [Long non-coding RNA act as regulators of autophagy in disease treatment]. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 40, 827–831. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.10273
He, Y., Sun, Y., and Zhang, X. (2017). Noncoding miRNAs bridge virus infection and host autophagy in shrimp in vivo. FASEB J. 31, 2854–2868. doi: 10.1096/fj.201601141RR
Jackson, W. T., Giddings, T. H. Jr., Taylor, M. P., Mulinyawe, S., Rabinovitch, M., Kopito, R. R., et al. (2005). Subversion of cellular autophagosomal machinery by RNA viruses. PLoS Biol. 3:e156. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030156
Jia, P., Pan, H., Cui, K., Jia, K., and Yi, M. (2021). MicroRNA expression profiling of sea perch brain cells reveals the roles of microRNAs in autophagy induced by RGNNV infection. J. Fish Dis. 44, 1305–1314. doi: 10.1111/jfd.13389
Joubert, P. E., Werneke, S. W., de la Calle, C., Guivel-Benhassine, F., Giodini, A., Peduto, L., et al. (2012). Chikungunya virus-induced autophagy delays caspase-dependent cell death. J. Exp. Med. 209, 1029–1047. doi: 10.1084/jem.20110996
Jung, C. H., Ro, S. H., Cao, J., Otto, N. M., and Kim, D. H. (2010). mTOR regulation of autophagy. FEBS Lett. 584, 1287–1295. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.01.017
Khandia, R., Dadar, M., Munjal, A., Dhama, K., Karthik, K., Tiwari, R., et al. (2019). A comprehensive review of autophagy and its various roles in infectious, non-infectious, and lifestyle diseases: Current knowledge and prospects for disease prevention, novel drug design, and therapy. Cells 8:674. doi: 10.3390/cells8070674
Kim, H. J., Lee, S., and Jung, J. U. (2010). When autophagy meets viruses: A double-edged sword with functions in defense and offense. Semin. Immunopathol. 32, 323–341. doi: 10.1007/s00281-010-0226-8
Kim, H., Lee, Y. Y., and Kim, V. N. (2025). The biogenesis and regulation of animal microRNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 26, 276–296. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00805-0
Kim, J., Kundu, M., Viollet, B., and Guan, K. L. (2011). AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat. Cell Biol. 13, 132–141. doi: 10.1038/ncb2152
Kishi-Itakura, C., Koyama-Honda, I., Itakura, E., and Mizushima, N. (2014). Ultrastructural analysis of autophagosome organization using mammalian autophagy-deficient cells. J. Cell Sci. 127, 4089–4102. doi: 10.1242/jcs.156034
Kobayashi, S., Orba, Y., Yamaguchi, H., Takahashi, K., Sasaki, M., Hasebe, R., et al. (2014). Autophagy inhibits viral genome replication and gene expression stages in West Nile virus infection. Virus Res. 191, 83–91. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.07.016
Kong, Y., Huang, T., Zhang, H., Zhang, Q., Ren, J., Guo, X., et al. (2019). The lncRNA NEAT1/miR-29b/Atg9a axis regulates IGFBPrP1-induced autophagy and activation of mouse hepatic stellate cells. Life Sci. 237:116902. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116902
Lazar, C., Uta, M., and Branza-Nichita, N. (2014). Modulation of the unfolded protein response by the human hepatitis B virus. Front. Microbiol. 5:433. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00433
Lee, M. S. (2018). Overview of the Minireviews on Autophagy. Mol. Cells 41, 1–2. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2018.0400
Levine, B., and Kroemer, G. (2009). Autophagy in aging, disease and death: The true identity of a cell death impostor. Cell Death Differ. 16, 1–2. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2008.139
Levine, B., and Kroemer, G. (2019). Biological functions of autophagy genes: A disease perspective. Cell 176, 11–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.048
Li, J., Liu, Y., Wang, Z., Liu, K., Wang, Y., Liu, J., et al. (2011). Subversion of cellular autophagy machinery by hepatitis B virus for viral envelopment. J. Virol. 85, 6319–6333. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02627-10
Li, Z., Chen, B., Wu, Y., Jin, F., Xia, Y., and Liu, X. (2010). Genetic and epigenetic silencing of the beclin 1 gene in sporadic breast tumors. BMC Cancer 10:98. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-98
Li, Z., Zhong, H., Lv, S., Huang, Y., Pei, S., Wei, Y., et al. (2024). Selective autophagy receptor p62/SQSTM1 inhibits TBK1-IRF7 innate immune pathway in triploid hybrid fish. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 153:109805. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109805
Liang, S., Wu, Y. S., Li, D. Y., Tang, J. X., and Liu, H. F. (2021). Autophagy in viral infection and pathogenesis. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 9:766142. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.766142
Lin, Y., Deng, W., Pang, J., Kemper, T., Hu, J., Yin, J., et al. (2017). The microRNA-99 family modulates hepatitis B virus replication by promoting IGF-1R/PI3K/Akt/mTOR/ULK1 signaling-induced autophagy. Cell Microbiol. 19:9. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12709
Liu, B., Fang, M., Hu, Y., Huang, B., Li, N., Chang, C., et al. (2014). Hepatitis B virus X protein inhibits autophagic degradation by impairing lysosomal maturation. Autophagy 10, 416–430. doi: 10.4161/auto.27286
Liu, R., Chen, Y., Liu, G., Li, C., Song, Y., Cao, Z., et al. (2020). PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers. Cell Death Dis. 11:797. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02998-6
Liu, Z., Gao, L., Cheng, L., Lv, G., Sun, B., Wang, G., et al. (2023). The roles of N6-methyladenosine and its target regulatory noncoding RNAs in tumors: Classification, mechanisms, and potential therapeutic implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 55, 487–501. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-00944-y
Liu, X., Xiong, W., Ye, M., Lu, T., Yuan, K., Chang, S., et al. (2023). Non-coding RNAs expression in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Pathogenesis, clinical significance, and therapeutic targets. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 8:441. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01669-0
Liu, Y., Gordesky-Gold, B., Leney-Greene, M., Weinbren, N. L., Tudor, M., and Cherry, S. (2018). Inflammation-induced, STING-dependent autophagy restricts zika virus infection in the drosophila brain. Cell Host Microbe 24:57–68.e53. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2018.05.022
Lystad, A. H., Carlsson, S. R., and Simonsen, A. (2019). Toward the function of mammalian ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L1 complex in autophagy and related processes. Autophagy 15, 1485–1486. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1618100
Margvelani, G., Maquera, K. A. A., Welden, J. R., Rodgers, D. W., and Stamm, S. (2025). Translation of circular RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 53:gkae1167. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1167
Matsui, M., and Corey, D. R. (2017). Non-coding RNAs as drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 16, 167–179. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.117
Mattick, J. S., Amaral, P. P., Carninci, P., Carpenter, S., Chang, H. Y., Chen, L. L., et al. (2023). Long non-coding RNAs: Definitions, functions, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 24, 430–447. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00566-8
Miao, G., Zhao, H., Li, Y., Ji, M., Chen, Y., Shi, Y., et al. (2021). ORF3a of the COVID-19 virus SARS-CoV-2 blocks HOPS complex-mediated assembly of the SNARE complex required for autolysosome formation. Dev. Cell 56:427–442.e425. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.12.010
Pan, H., Zhang, W., Qin, Z., Jia, K., Jia, P., and Yi, M. (2024). MiR-192 and miR-731 synergically inhibit RGNNV infection by targeting ULK1-mediated autophagy in sea perch (Lateolabrax japonicus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 282:136748. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.136748
Panwar, V., Singh, A., Bhatt, M., Tonk, R. K., Azizov, S., Raza, A. S., et al. (2023). Multifaceted role of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling pathway in human health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 8:375. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01608-z
Park, J. M., Lee, D. H., and Kim, D. H. (2023). Redefining the role of AMPK in autophagy and the energy stress response. Nat. Commun. 14:2994. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38401-z
Pu, J., Wu, S., Xie, H., Li, Y., Yang, Z., Wu, X., et al. (2017). miR-146a Inhibits dengue-virus-induced autophagy by targeting TRAF6. Arch. Virol. 162, 3645–3659. doi: 10.1007/s00705-017-3516-9
Statello, L., Guo, C. J., Chen, L. L., and Huarte, M. (2021). Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 22, 96–118. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-00315-9
Tang, H., Sebti, S., Titone, R., Zhou, Y., Isidoro, C., Ross, T. S., et al. (2015). Decreased BECN1 mRNA expression in human breast cancer is associated with estrogen receptor-negative subtypes and poor prognosis. EBioMedicine 2, 255–263. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.01.008
Ueno, T., and Komatsu, M. (2017). Autophagy in the liver: Functions in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 14, 170–184. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.185
Wang, F., Shan, S., Huo, Y., Xie, Z., Fang, Y., Qi, Z., et al. (2018). MiR-155-5p inhibits PDK1 and promotes autophagy via the mTOR pathway in cervical cancer. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 99, 91–99. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.04.005
Wang, H., Xie, H., Xu, W., and Li, M. (2024). [Urolithin A alleviates respiratory syncytial virus-induced lung infection in neonatal mice by activating miR-136-mediated Sirt1 signaling]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 44, 1370–1381. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.07.17
Wang, J., Chen, J., Liu, Y., Zeng, X., Wei, M., Wu, S., et al. (2019). Hepatitis B virus induces autophagy to promote its replication by the axis of miR-192-3p-XIAP through NF kappa B signaling. Hepatology 69, 974–992. doi: 10.1002/hep.30248
Wang, J., Kan, X., Li, X., Sun, J., and Xu, X. (2022). Porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus (PEDV) infection activates AMPK and JNK through TAK1 to induce autophagy and enhance virus replication. Virulence 13, 1697–1712. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2127192
Wang, K., Liu, C. Y., Zhou, L. Y., Wang, J. X., Wang, M., Zhao, B., et al. (2015). APF lncRNA regulates autophagy and myocardial infarction by targeting miR-188-3p. Nat. Commun. 6:6779. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7779
Wang, X., Xu, X., Wang, W., Yu, Z., Wen, L., He, K., et al. (2017). MicroRNA-30a-5p promotes replication of porcine circovirus type 2 through enhancing autophagy by targeting 14-3-3. Arch. Virol. 162, 2643–2654. doi: 10.1007/s00705-017-3400-7
Wu, J., Zhu, Y., Cong, Q., and Xu, Q. (2023). Non-coding RNAs: Role of miRNAs and lncRNAs in the regulation of autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma (Review). Oncol. Rep. 49:113. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8550
Yang, L., Wang, H., Shen, Q., Feng, L., and Jin, H. (2017). Long non-coding RNAs involved in autophagy regulation. Cell Death Dis. 8:e3073. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.464
Yang, Y., Liu, Y., Xue, J., Yang, Z., Shi, Y., Shi, Y., et al. (2017). MicroRNA-141 targets Sirt1 and inhibits autophagy to reduce HBV replication. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 41, 310–322. doi: 10.1159/000456162
Yang, N., Hu, N., Zhang, J., Yi, J., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., et al. (2022). bta-miR-2904 inhibits bovine viral diarrhea virus replication by targeting viral-infection-induced autophagy via ATG13. Arch. Virol. 168:11. doi: 10.1007/s00705-022-05630-4
Yao, Y., Li, S., Zhu, Y., Xu, Y., Hao, S., Guo, S., et al. (2023). miR-204 suppresses porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) replication via inhibiting LC3B-mediated autophagy. Virol. Sin. 38, 690–698. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2023.07.004
Yin, H., Zhao, L., Li, S., Xu, L., Wang, Y., and Chen, H. (2017). Impaired cellular energy metabolism contributes to duck-enteritis-virus-induced autophagy via the AMPK-TSC2-MTOR signaling pathway. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 7:423. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00423
Yu, H., Chen, Z., Liu, Y., Shen, Y., Gui, L., Qiu, J., et al. (2024a). Deep sequencing identified miR-193b-3p as a positive regulator of autophagy targeting Akt3 in Ctenopharyngodon idella CIK cells during GCRV infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 149:109586. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109586
Yu, H., Chen, Z., Yu, Q., Shen, Y., Gui, L., Xu, X., et al. (2024b). miR-193b-5p promotes GCRV replication by inhibiting autophagy via targeting deptor in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 147:109453. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109453
Zhang, G., Lan, Y., Xie, A., Shi, J., Zhao, H., Xu, L., et al. (2019). Comprehensive analysis of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-chromatin interactions reveals lncRNA functions dependent on binding diverse regulatory elements. J. Biol. Chem. 294, 15613–15622. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008732
Zhang, Y., Zhan, L., Jiang, X., and Tang, X. (2024). Comprehensive review for non-coding RNAs: From mechanisms to therapeutic applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 224:116218. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116218
Zhong, S., Zhou, Q., Yang, J., Zhang, Z., Zhang, X., Liu, J., et al. (2024). Relationship between the cGAS-STING and NF-κB pathways-role in neurotoxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 175:116698. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116698
Zhou, H., Hu, Z., and Castro-Gonzalez, S. (2023). Bidirectional interplay between SARS-CoV-2 and autophagy. mBio 14:e0102023. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01020-23
Keywords: non-coding RNAs, autophagy, viral infection, regulatory mechanism, virology
Citation: Yu M, Yi Y, Yang H and Zhang Y (2025) Unveiling the impact of non-coding RNAs on virus-induced cellular autophagy: roles and research advances. Front. Microbiol. 16:1632425. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1632425
Received: 21 May 2025; Accepted: 21 July 2025;
Published: 06 August 2025.
Edited by:
Glenn Randall, The University of Chicago, United StatesReviewed by:
Seungmin “Sam” Hwang, Broad Institute, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Yu, Yi, Yang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yi Zhang, emhhbmd5aXptdUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Ming Yu1,2†
Ming Yu1,2† Honglin Yang
Honglin Yang Yi Zhang
Yi Zhang