- Department of Nutrition, Sanya Central Hospital (The Third People's Hospital of Hainan Province), Sanya, China
Objective: This study endeavors to elucidate how Bifidobacteria supplementation affects metabolic parameters among overweight or obese populations.
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis were carried out leveraging PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science. Merely randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included.
Results: 21 RCTs were encompassed for our final analysis. Bifidobacteria supplementation was effective in weight management for overweight or obese patients. The experimental group receiving Bifidobacteria exhibited a marked decrease in weight (WMD: −0.607 kg; 95% CI: −0.910, −0.303, I2 = 11.9%) and BMI (WMD: −0.214 kg/m2; 95% CI: −0.259, −0.169, I2 = 4.1%) in contrast to the control, although the significant effect was not noted on WC. Moreover, while Bifidobacteria supplementation led to no marked drop in FBG or HbA1c, it improved the insulin (SMD: -0.268; 95% CI: −0.470, −0.066, I2 = 5.4%). However, there were no evident variations in TC, TG, HDL-C, or LDL-C across groups.
Conclusion: Our study findings confirmed that Bifidobacteria contributes to a slight reduction in weight and BMI among the overweight or obese populations, making it a potential adjunctive approach for weight management. Furthermore, it may help regulate insulin levels, though its impact on hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia remains limited.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO. Registration No. CRD42025635324.
1 Introduction
As the global obesity epidemic continues to intensify, overweight and obesity have become significant public health concerns worldwide (GBD 2021 Adult BMI Collaborators, 2025). Obesity not only diminishes an individual’s quality of life but is also strongly associated with various chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), certain cancers, and a range of metabolic disorders (Blüher, 2019). Consequently, identifying effective interventions for the prevention and treatment of obesity has become increasingly critical.
In recent, growing attention has been directed towards the relationship between the gut microbiota and obesity (Asadi et al., 2022). The gut microbiota, an intricate ecosystem involving trillions of microorganisms, is crucial in host metabolism, immunity, as well as disease susceptibility (Geng et al., 2022). Among these microorganisms, Bifidobacteria, an important component of the gut microbiota, has garnered particular attention due to its potential health benefits (Sarita et al., 2024). Bifidobacteria are Gram-positive, anaerobic probiotics known to exert multiple positive effects on host health, including improving gut barrier function, modulating immune responses, and influencing energy metabolism (Amabebe et al., 2020). Multiple studies have demonstrated that the abundance of Bifidobacterium in the gut of obese individuals is generally lower than that in healthy populations (Leite et al., 2024; Gong et al., 2022). This dysbiosis may be associated with high-fat diets, metabolic disturbances, and chronic inflammation (Hills et al., 2019). Experimental evidence indicates that reduced Bifidobacterium abundance, accompanied by fat accumulation and inflammation, can be ameliorated by supplementation with specific Bifidobacterium strains, leading to attenuated weight gain and reduced fat deposition in obese mice (Zha et al., 2024). Furthermore, Da Silva et al. (2020) found that the proportion of Bifidobacterium in the gut microbiota of obese children was significantly lower than that of healthy counterparts. Some studies have suggested that the abundance of Bifidobacterium may be restored following bariatric surgery or dietary interventions (Seganfredo et al., 2017). The potential mechanisms may involve metabolic regulation mediated by short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). For example, acetate and propionate can activate G-protein-coupled receptors (GPR41/GPR43), thereby suppressing lipogenesis and promoting energy utilization (Yun et al., 2024). Butyrate may stimulate the secretion of GLP-1 and PYY, reducing appetite through hormonal regulation (Horiuchi et al., 2020). In addition, SCFAs can enhance AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity, thereby facilitating fatty acid β-oxidation and promoting fat catabolism. Bifidobacterium may also influence bile acid metabolism by activating farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and TGR5, thereby improving glucose and lipid metabolism (Joyce and Gahan, 2016). Although studies have suggested that Bifidobacteria may be closely linked to weight management and glucose and lipid metabolic homeostasis in the population with excess weight or obesity, related findings show discrepancies, and a systematic evaluation and quantitative analysis are lacking. For instance, Bai et al. (2024) proved that the short-chain Bifidobacterium BBr60 markedly lowered weight, body mass index (BMI), and FBG, and modulated lipid profiles safely and effectively. In contrast, Sudha et al. (2019) found no significant changes in blood lipids or blood glucose levels. Additionally, some studies have indicated that yogurt containing Bifidobacteria does not produce significant changes in weight or BMI in overweight or obese populations.
However, the evidence remains inconsistent. Some trials have demonstrated beneficial effects of Bifidobacteria supplementation on weight, glucose, and lipid metabolism, while other studies report negligible or no benefits. To date, no comprehensive quantitative synthesis has been performed to resolve these discrepancies. Therefore, this study seeks to unveil the effects of Bifidobacteria supplementation on metabolic parameters within individuals with excess weight or obesity based on randomized controlled trials (RCTs) via systematic review and meta-analysis.
2 Methods
2.1 Registration and PRISMA statement
This review complied with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and was prospectively registered in PROSPERO (Registration No. CRD42025635324) (Page et al., 2021).
2.2 Literature search
2.2.1 Data sources and search scope
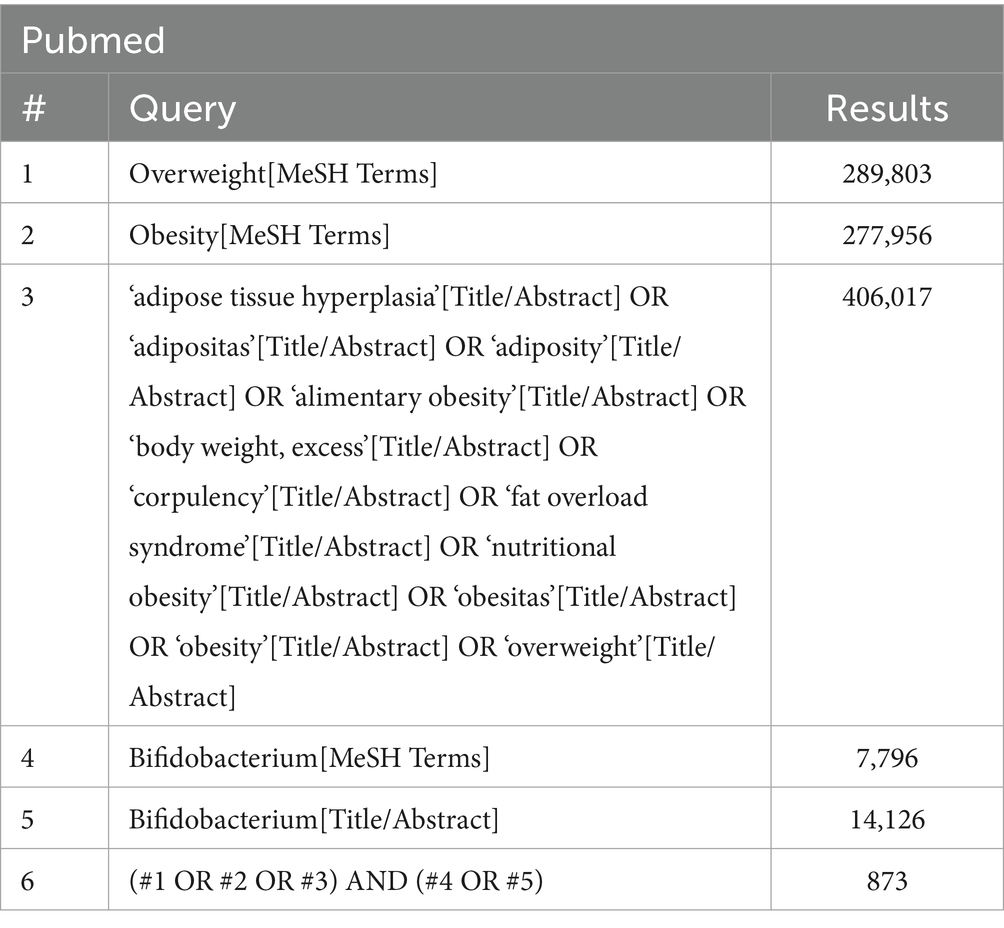
A comprehensive literature search was performed in four online databases (PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science) to identify RCTs. The search covered the period from database inception to December 3, 2024. Keywords such as “Bifidobacterium,” “obesity,” and “overweight” were used as both subject terms and free words in the search. The search strategy is presented in Table 1. The references of prior systematic reviews were also checked for eligible RCTs.
2.2.2 Eligibility criteria
Inclusion criteria: (1) Adults (≥18) diagnosed by a physician with overweight (BMI 25–29.9 kg/m2) or obesity (BMI 30–34.9 kg/m2); (2) Explicit use of Bifidobacterium as an intervention; (3) A control group receiving either a placebo or another type of intervention not involving Bifidobacterium, with all other conditions equivalent to the experimental group, ensuring comparability (e.g., routine care or blank control); (4) Outcome measures including anthropometric measurements, blood glucose, or lipid laboratory result; (5) Randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Exclusion criteria: (1) Duplicates, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses; (2) Literature reviews, case reports, non-English publications, animal studies, letters to the editor, and narrative reviews; (3) Full texts were inaccessible, data could not be extracted, or the studies were ineligible.
2.2.3 Literature screening and data extraction
Two researchers independently filtered the literature, collected related data, and assessed study quality. EndNote was utilized during the screening process. The extracted data encompassed bibliographic information (authors, publication year, country), study characteristics (sample size, bacterial strains, study outcomes), and participant characteristics (age, BMI). Data extraction was conducted utilizing Excel. Dissents were addressed via discussion or consultation with a third researcher.
2.2.4 Outcome measures
The primary outcomes assessed in this meta-analysis were: weight, BMI, as well as waist circumference (WC). Secondary outcomes encompassed fasting blood glucose (FBG), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), insulin, total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C).
2.3 Risk of bias assessment
The risk of bias was rated independently by two reviewers. Dissents were addressed after discussion or judgment of a third party. Concerning quality assessment, both reviewers used the NIH RCT Quality Assessment Tool for study quality evaluation. There were 14 items, each assessed as “Yes” or “No” based on the study’s design and implementation standards (NIH, n.d.). In case of discrepancies during the evaluation, a third researcher was consulted to ensure fairness and consistency. Studies were rated for potential bias via a scoring scale, with three distinct categories: high risk (0–5, poor), moderate risk (6–10, fair), and low risk (11–14, good).
2.4 Statistical analysis
Data analysis was enabled by Stata MP 15. Continuous data were shown in standardized mean difference (SMD) or mean difference (MD). An SMD of < 0.2 indicates a negligible difference between groups, whereas a value ranging from 0.2 to 0.49 suggests a small difference. A value between 0.5 and 0.79 represents a moderate difference, and a value ≥ 0.8 denotes a substantial difference across groups. For dichotomous data, the risk ratio (RR) and its 95% confidence interval (CI) were computed. Heterogeneity was detected via the I2 statistic and the Q-test. When the I2 value exceeded 50% and the p < 0.05, a random-effects model was applied; otherwise, a fixed-effects model was used. The robustness of our results was rated through sensitivity analyses. For meta-analyses involving over 10 studies, possible publication bias was examined utilizing funnel plots and Egger’s test. In cases of bias, the effect on the results was evaluated through the trim-and-fill approach.
3 Results
3.1 Literature search results
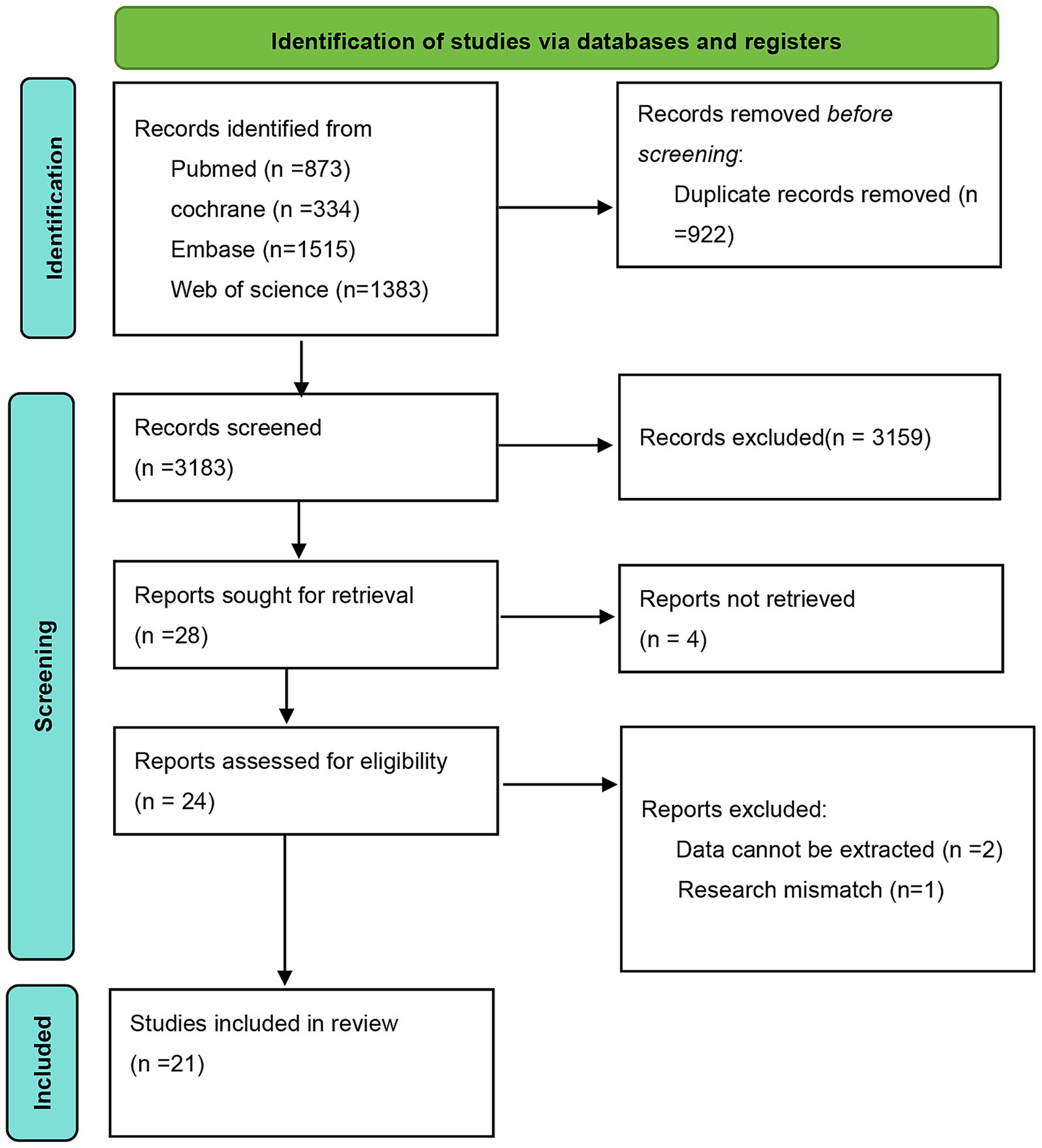
Based on the predefined search strategy, a preliminary search of the databases identified 4,105 articles. After screening titles and abstracts, 922 duplicate entries were excluded, resulting in 3,159 articles being discarded. The remaining 28 articles were subjected to full-text review. Four articles were excluded owing to unavailable full texts, two owing to the inability to extract data, and one due to failure to meet the inclusion criteria. Ultimately, 21 eligible RCTs were included, as shown in Figure 1.
3.2 Study characteristics
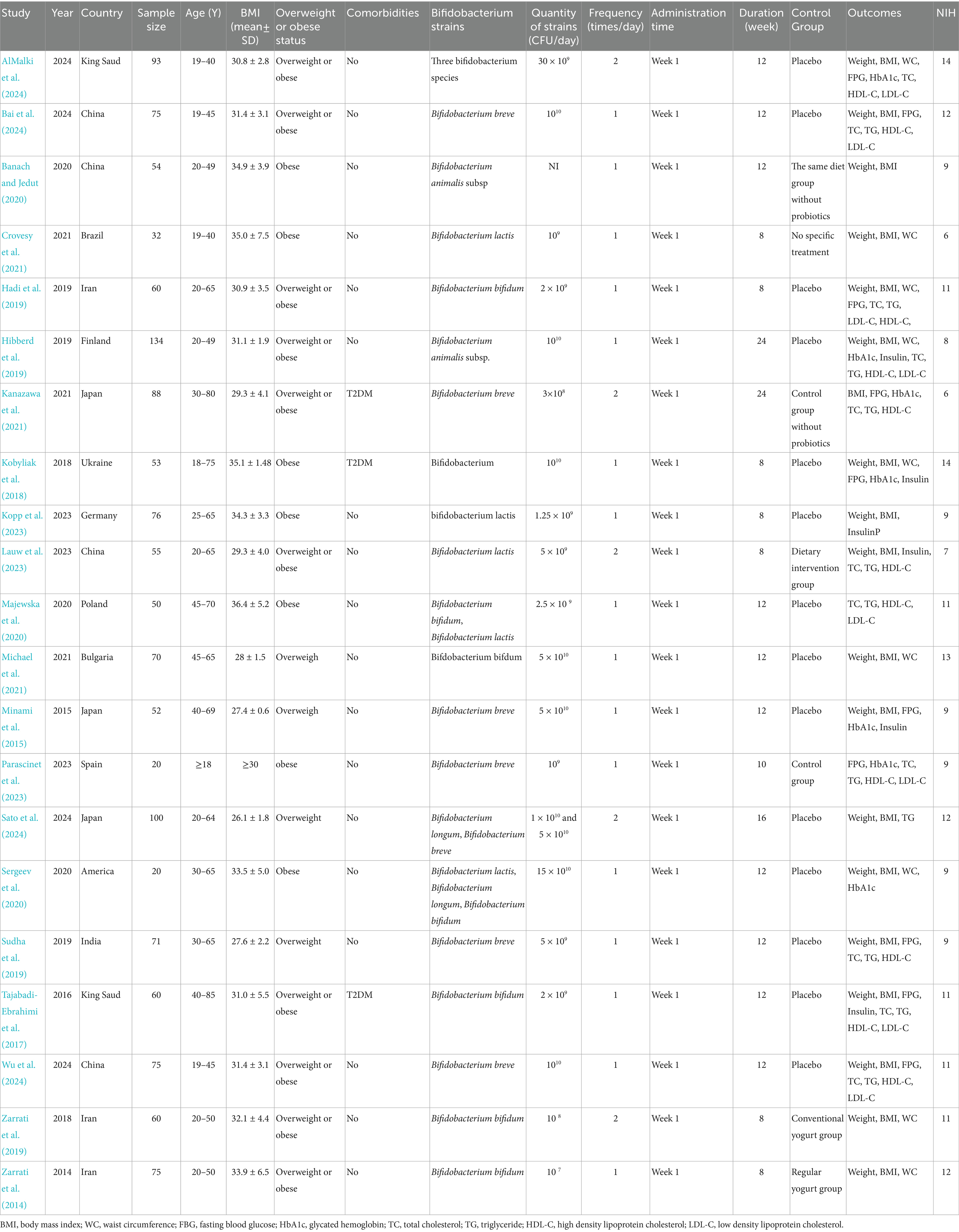
The baseline characteristics of the 21 included RCTs are summarized in Table 2. Of these, 13 (Bai et al., 2024; Sudha et al., 2019; AlMalki et al., 2024; Banach and Jedut, 2020; Hadi et al., 2019; Kanazawa et al., 2021; Lauw et al., 2023; Minami et al., 2015; Sato et al., 2024; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2024; Zarrati et al., 2019; Zarrati et al., 2014) were conducted in Asian countries, 6 (Hibberd et al., 2019; Kobyliak et al., 2018; Kopp et al., 2023; Majewska et al., 2020; Michael et al., 2021; Parascinet et al., 2023) in European countries, and 2 (Crovesy et al., 2021; Sergeev et al., 2020) in the United States and Brazil, respectively. The studies were published between 2014 and 2024 and collectively enrolled 1,392 participants. All studies used BMI as the indicator for overweight or obesity. According to the World Health Organization’s classification (WHO, 2024), overweight was defined as a BMI between 25 and 29.9 kg/m2, while obesity was confirmed by a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or higher. 8 studies (Bai et al., 2024; Sudha et al., 2019; Kanazawa et al., 2021; Minami et al., 2015; Wu et al., 2024; Zarrati et al., 2019; Zarrati et al., 2014; Parascinet et al., 2023) reported the use of Bifidobacterium breve, three studies (Hadi et al., 2019; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi et al., 2017; Michael et al., 2021) used Bifidobacterium longum, five studies (Sato et al., 2024; Kobyliak et al., 2018; Majewska et al., 2020; Sergeev et al., 2020; AlMalki et al., 2024) used a mixed Bifidobacterium species, two studies (Banach and Jedut, 2020; Hibberd et al., 2019) used Bifidobacterium animalis, and three studies (Lauw et al., 2023; Kopp et al., 2023; Crovesy et al., 2021) used Bifidobacterium lactis. The NIH quality assessment indicated that 11 studies (Bai et al., 2024; AlMalki et al., 2024; Sato et al., 2024; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2024; Zarrati et al., 2019; Zarrati et al., 2014; Kobyliak et al., 2018; Majewska et al., 2020; Michael et al., 2021; Crovesy et al., 2021) had low risk of bias, while 10 studies (Sudha et al., 2019; Banach and Jedut, 2020; Kanazawa et al., 2021; Lauw et al., 2023; Minami et al., 2015; Hibberd et al., 2019; Kopp et al., 2023; Parascinet et al., 2023; Crovesy et al., 2021; Sergeev et al., 2020) exhibited moderate risk of bias, as detailed in Supplementary Table 1.
3.3 Primary outcomes
3.3.1 Effects of Bifidobacterium on weight management
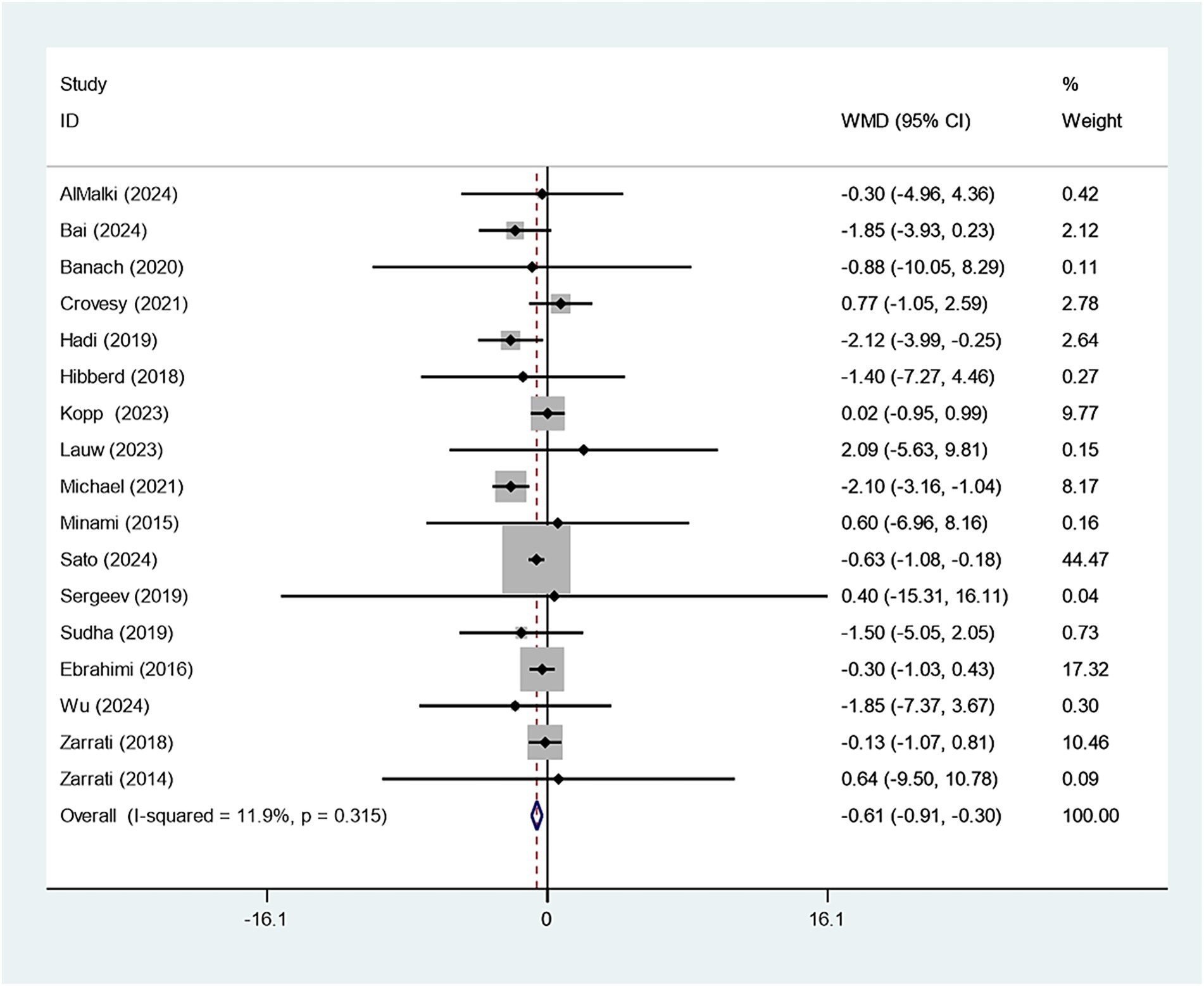
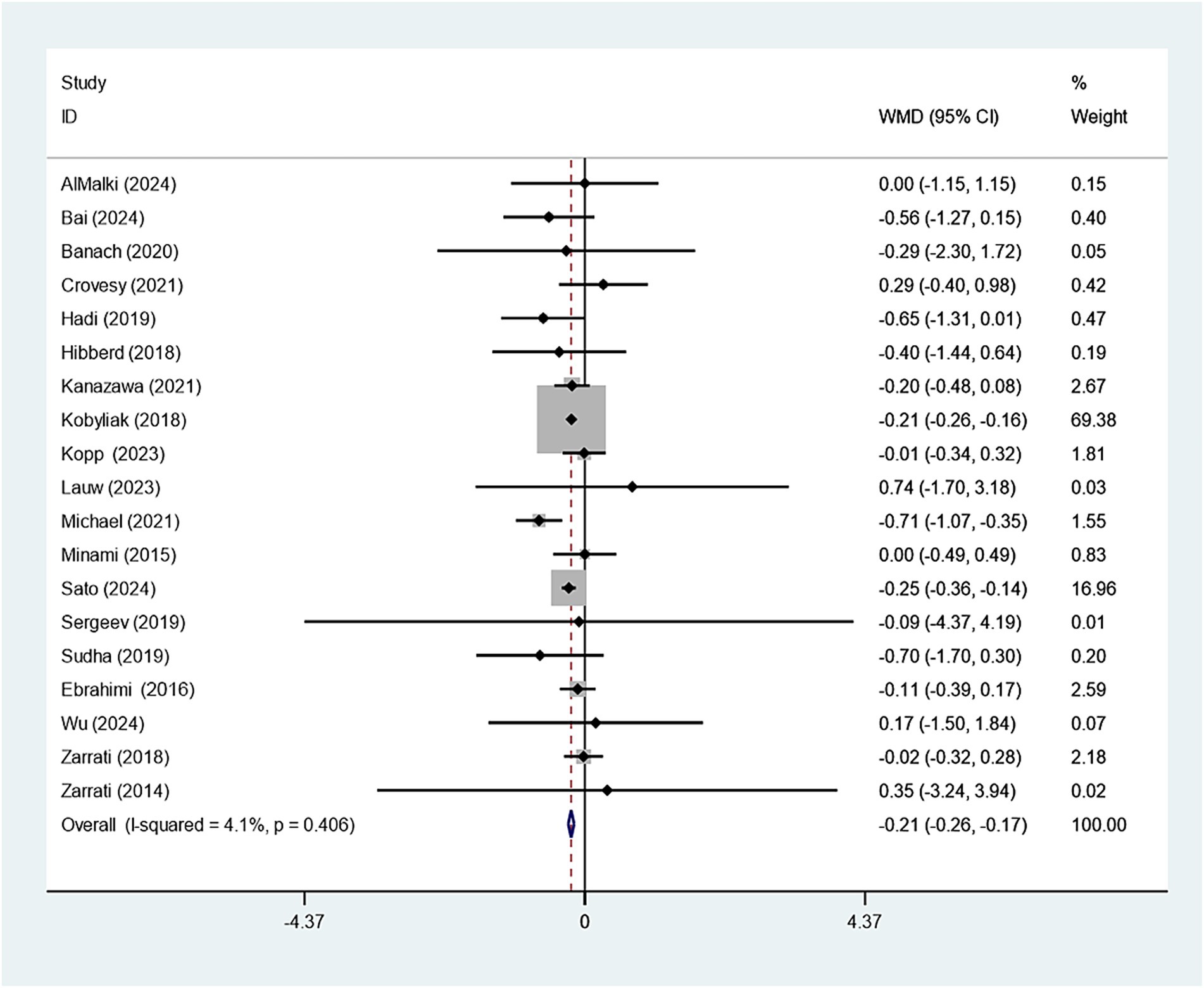
Eighteen studies reported on the relationship between Bifidobacterium supplementation and weight change. Sensitivity analysis demonstrated that the study conducted by Kobyliak had a considerable impact on the overall findings, as illustrated in Supplementary Figure 1. Upon exclusion of this study, the experimental group receiving Bifidobacterium supplementation showed a significantly greater reduction in body weight compared to the control group (WMD: −0.607 kg; 95% CI: −0.910,–0.303; I2 = 11.9%), as shown in Figure 2. Funnel plot symmetry and the Egger test (p = 0.804) suggested no significant publication bias, as presented in Supplementary Figure 2.
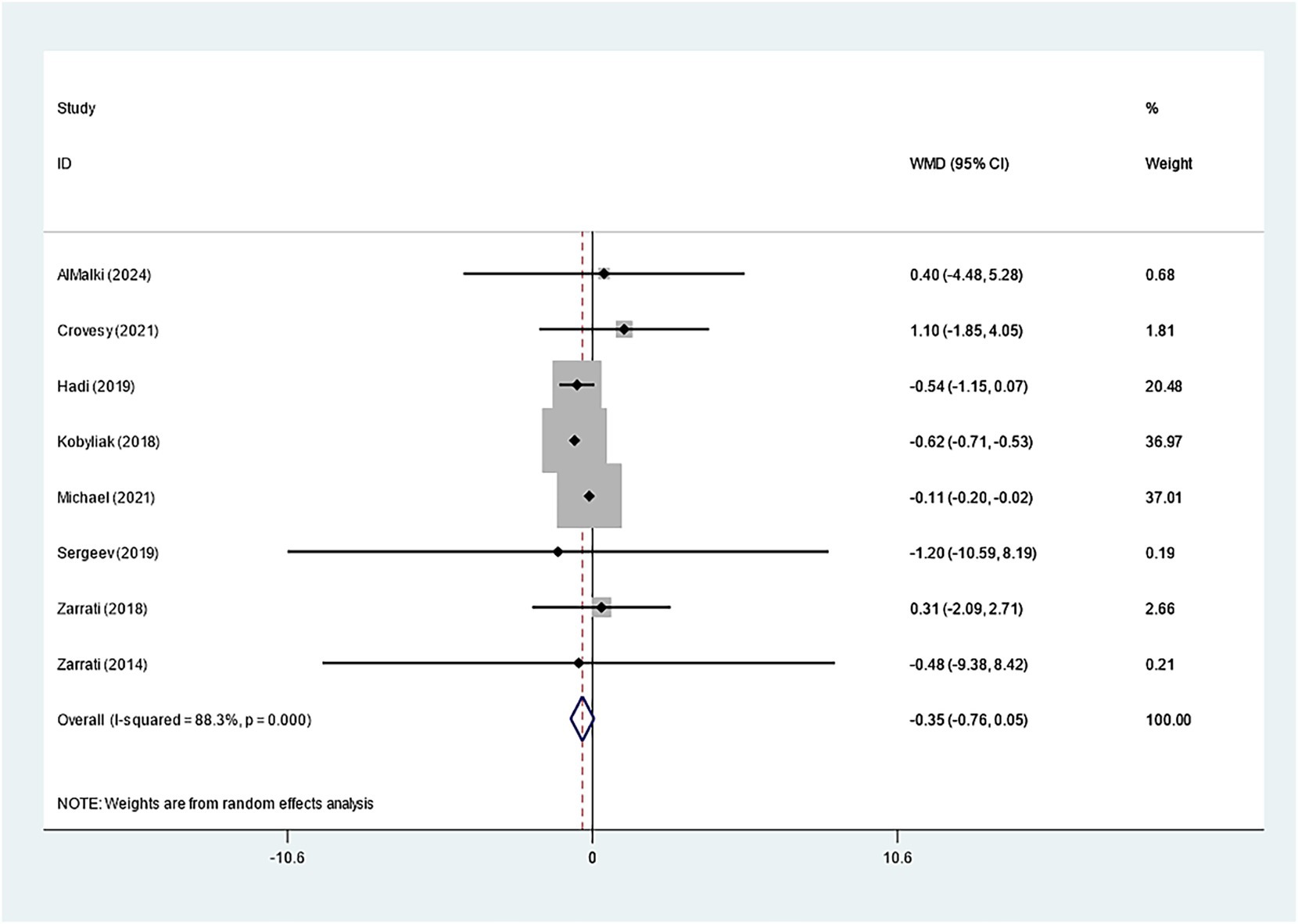
19 studies explored how Bifidobacterium supplementation influences BMI. Our meta-analysis demonstrated a notably larger BMI decline in the experimental group relative to the control (WMD: −0.214 kg/m2; 95% CI: −0.259, −0.169, I2 = 4.1%) (Figure 3). Eight studies examined the impact of Bifidobacterium on WC, but the difference across groups was insignificant (WMD: −0.353 cm; 95% CI: −0.759, −0.053, I2 = 88.3%) (Figure 4). Sensitivity analyses for BMI and WC indicated robust results, as shown in Supplementary Figures 3, 4. Both the funnel plot and Egger’s test (p = 0.867) demonstrated no discernible publication bias (Supplementary Figure 5).
3.4 Secondary outcomes
3.4.1 Effects of Bifidobacterium on glycemic control
Ten studies evaluated how Bifidobacterium supplementation influences FBG within the cohort with excess weight or obesity. Bifidobacterium did not markedly affect FBG (SMD: -0.143; 95% CI: −0.302, −0.016, I2 = 0.0%) (Figure 5). Our sensitivity analysis indicated robustness. Egger’s test (p = 0.215) and the funnel plot demonstrated no publication bias, as depicted in Supplementary Figures 6, 7.
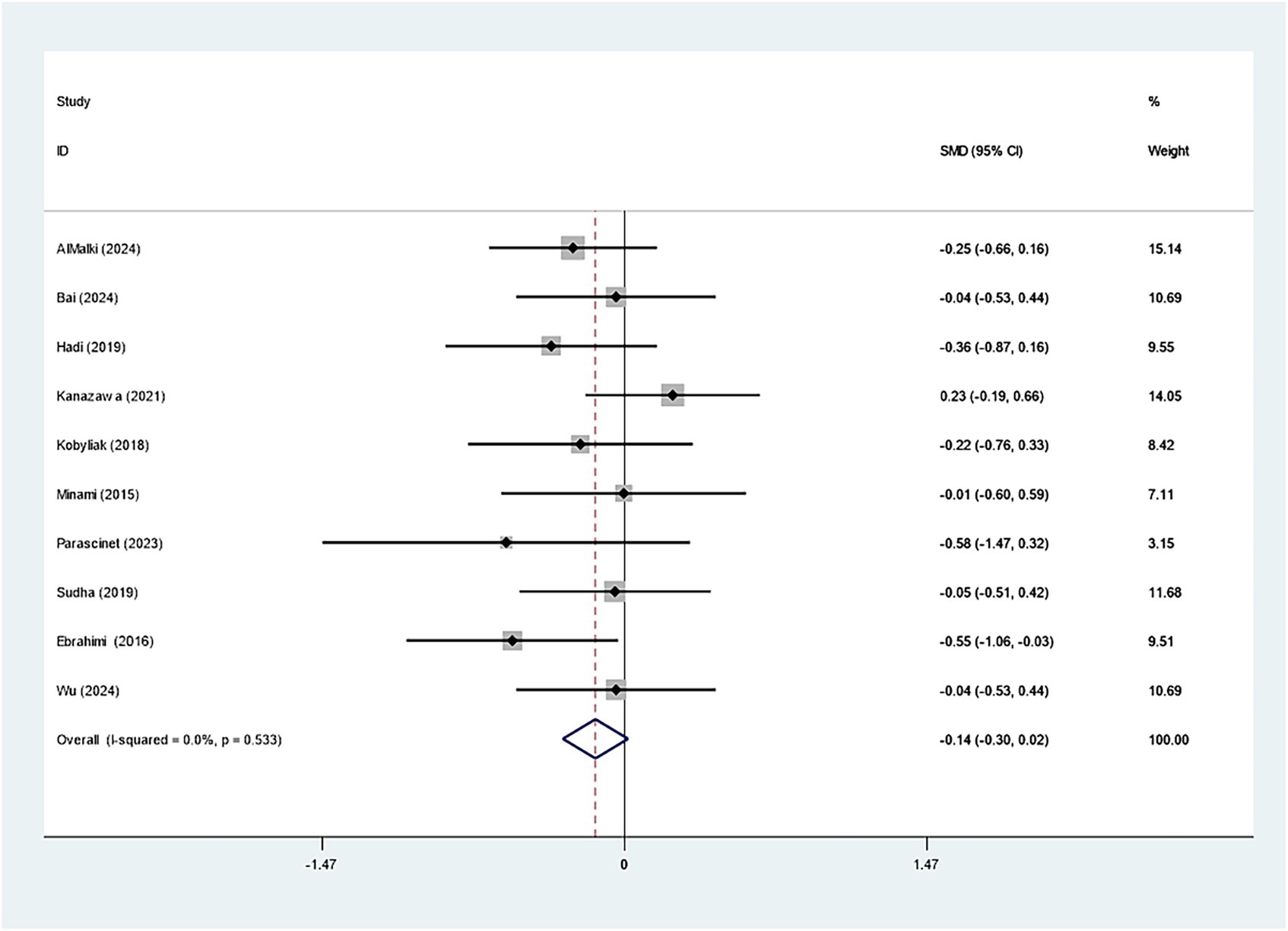
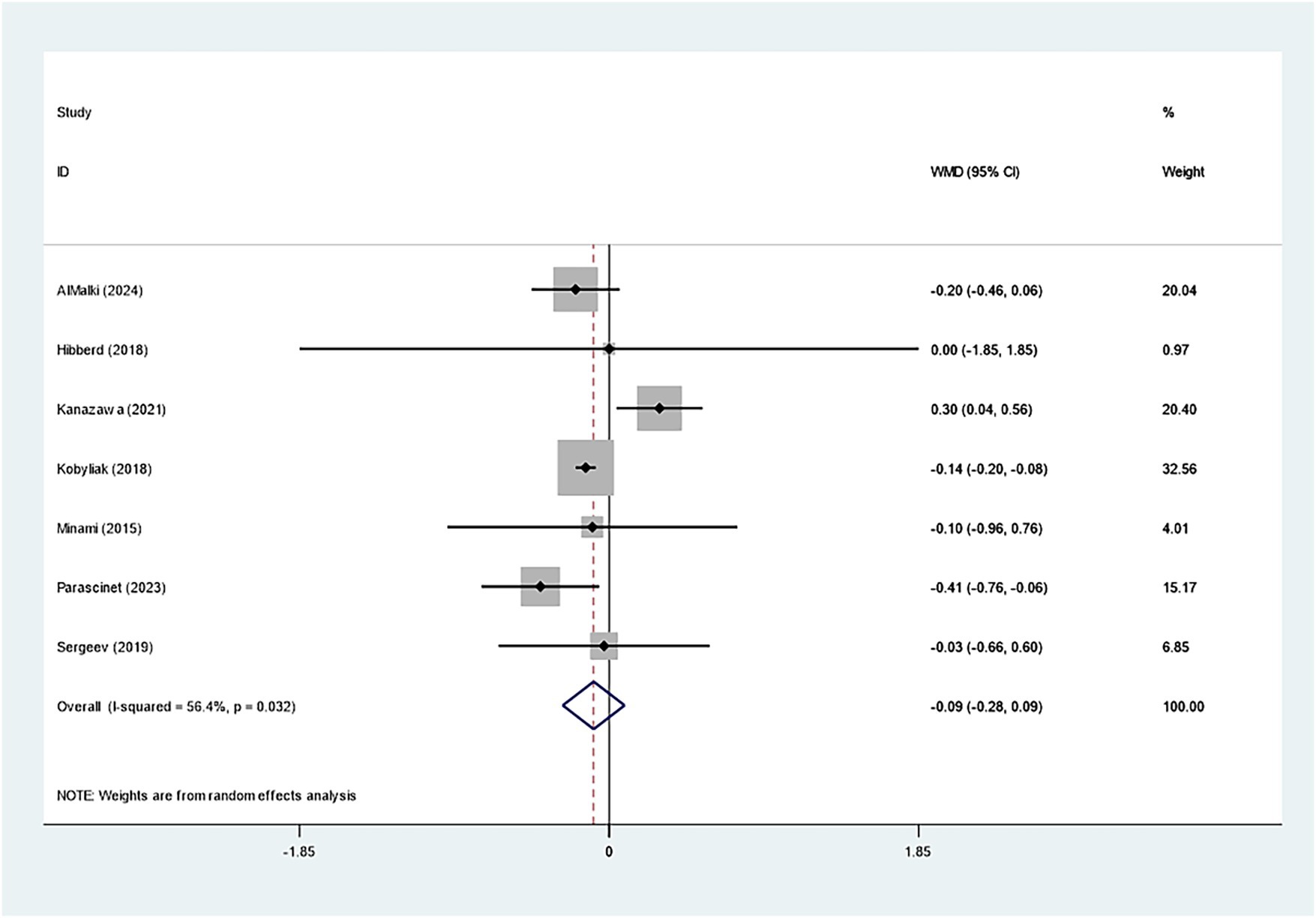
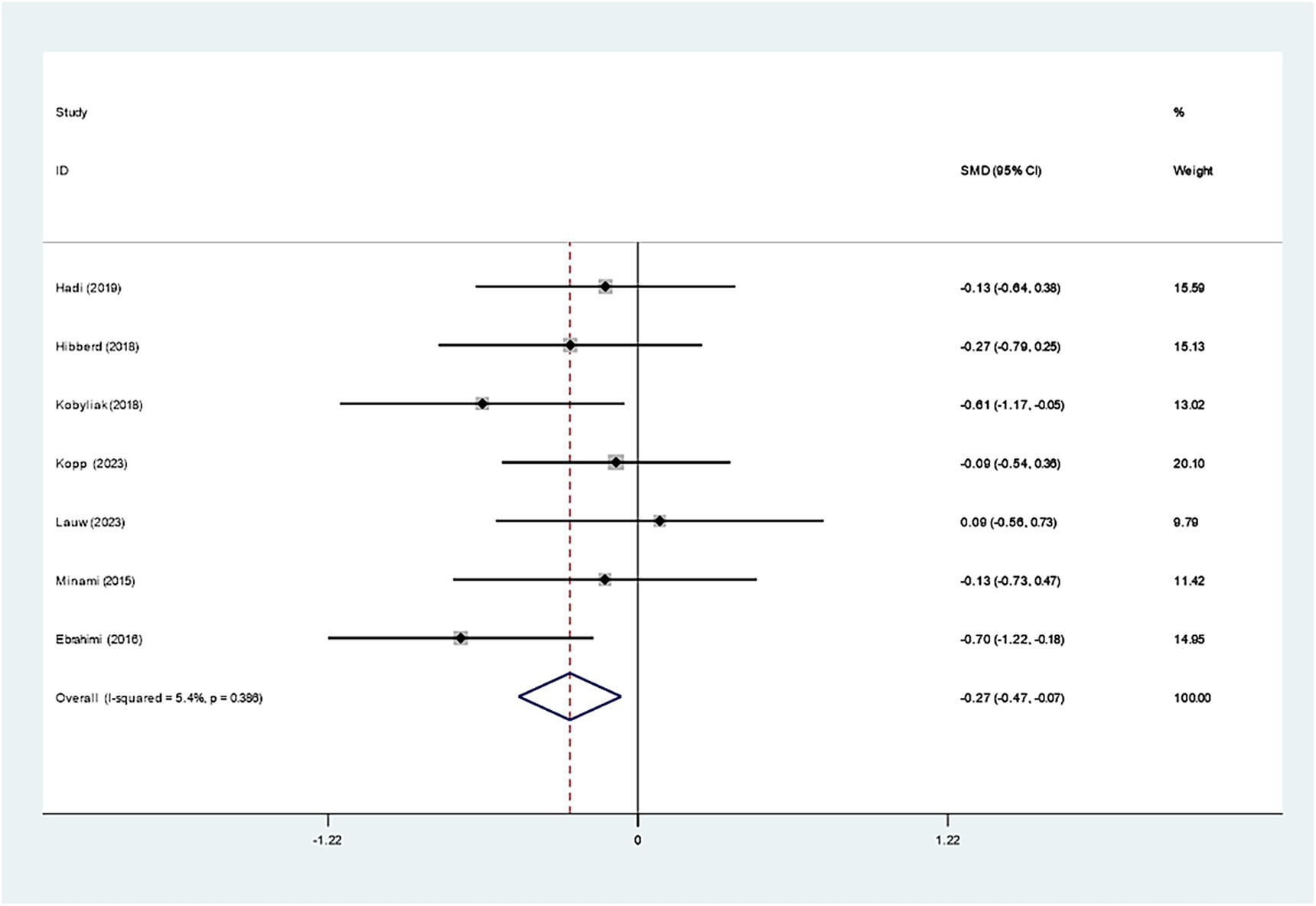
Seven studies investigated the effect of Bifidobacterium on HbA1c, demonstrating insignificant variations across groups (WMD: −0.093%; 95% CI: −0.277, −0.091, I2 = 56.4%) (Figure 6). However, regarding insulin levels, seven studies reported a notable decrease in insulin levels in the Bifidobacterium supplementation cohort (SMD: −0.268; 95% CI: −0.470, −0.066, I2 = 5.4%) (Figure 7). These findings were robust after sensitivity analysis, as presented in Supplementary Figures 8, 9.
3.4.2 Effects of Bifidobacterium on lipid metabolism
To unravel how Bifidobacterium impacts lipid metabolism, our study incorporated studies evaluating TC, TG, HDL-C, and LDL-C. The effects on lipid levels were insignificant.
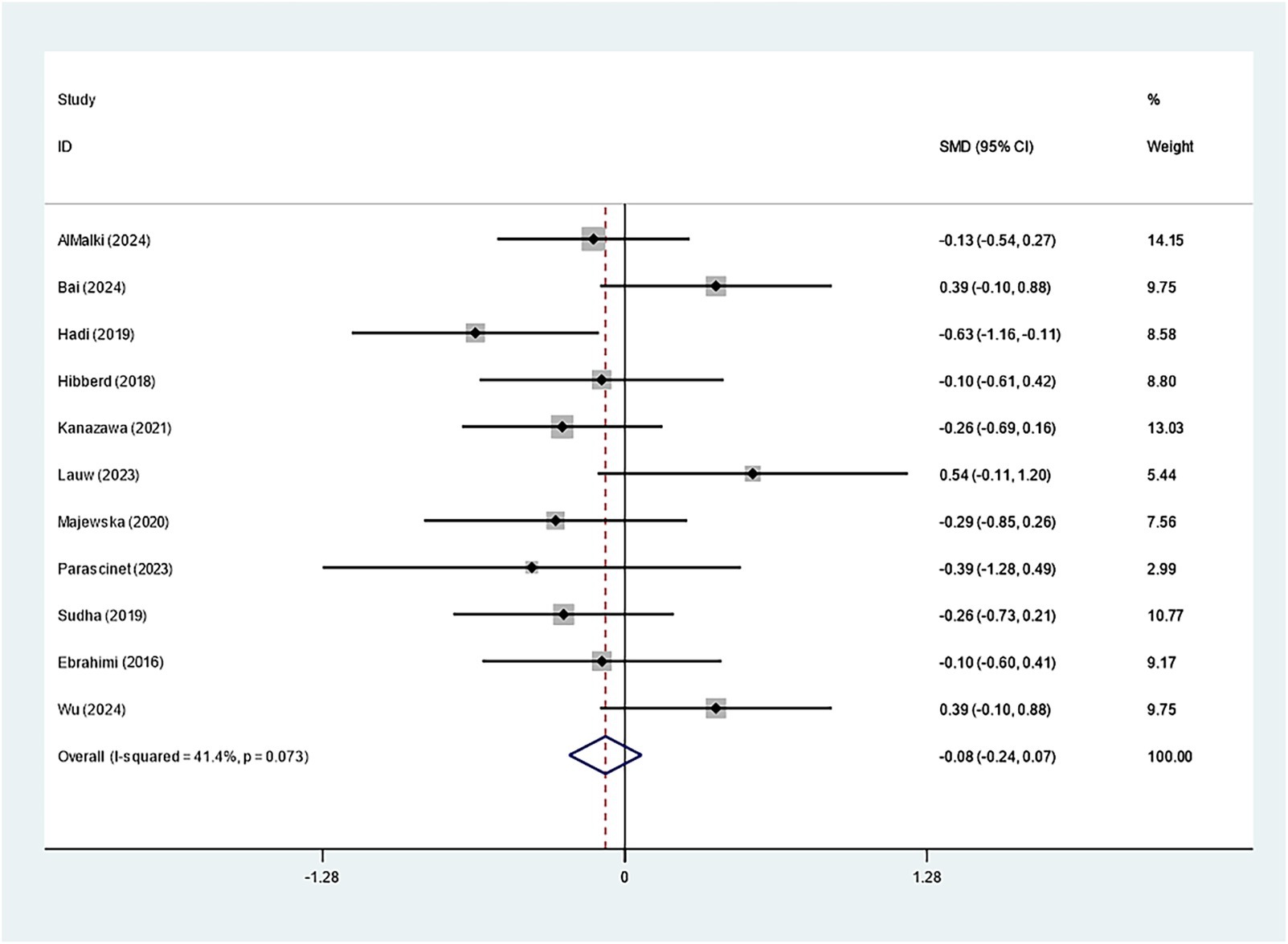
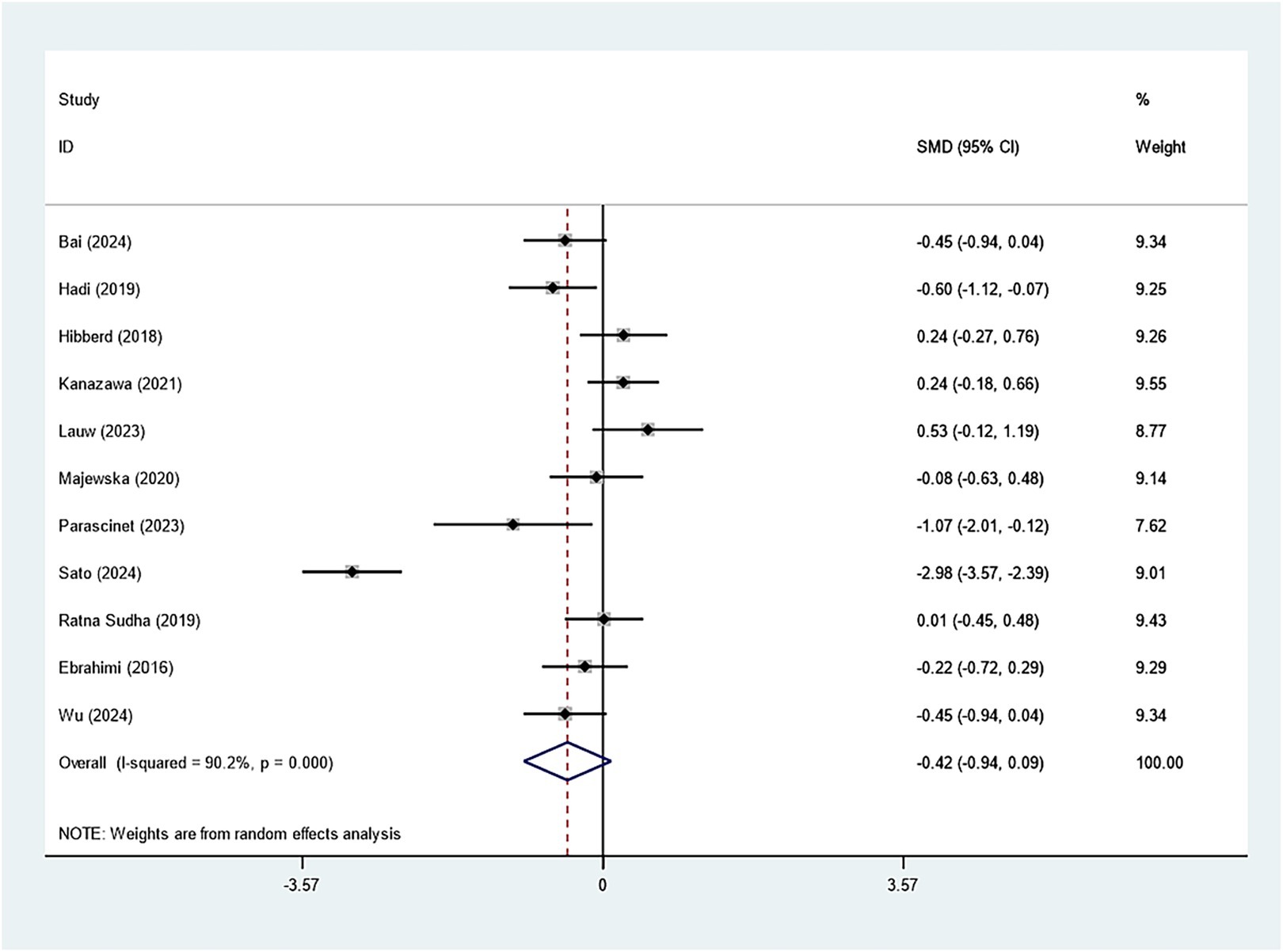
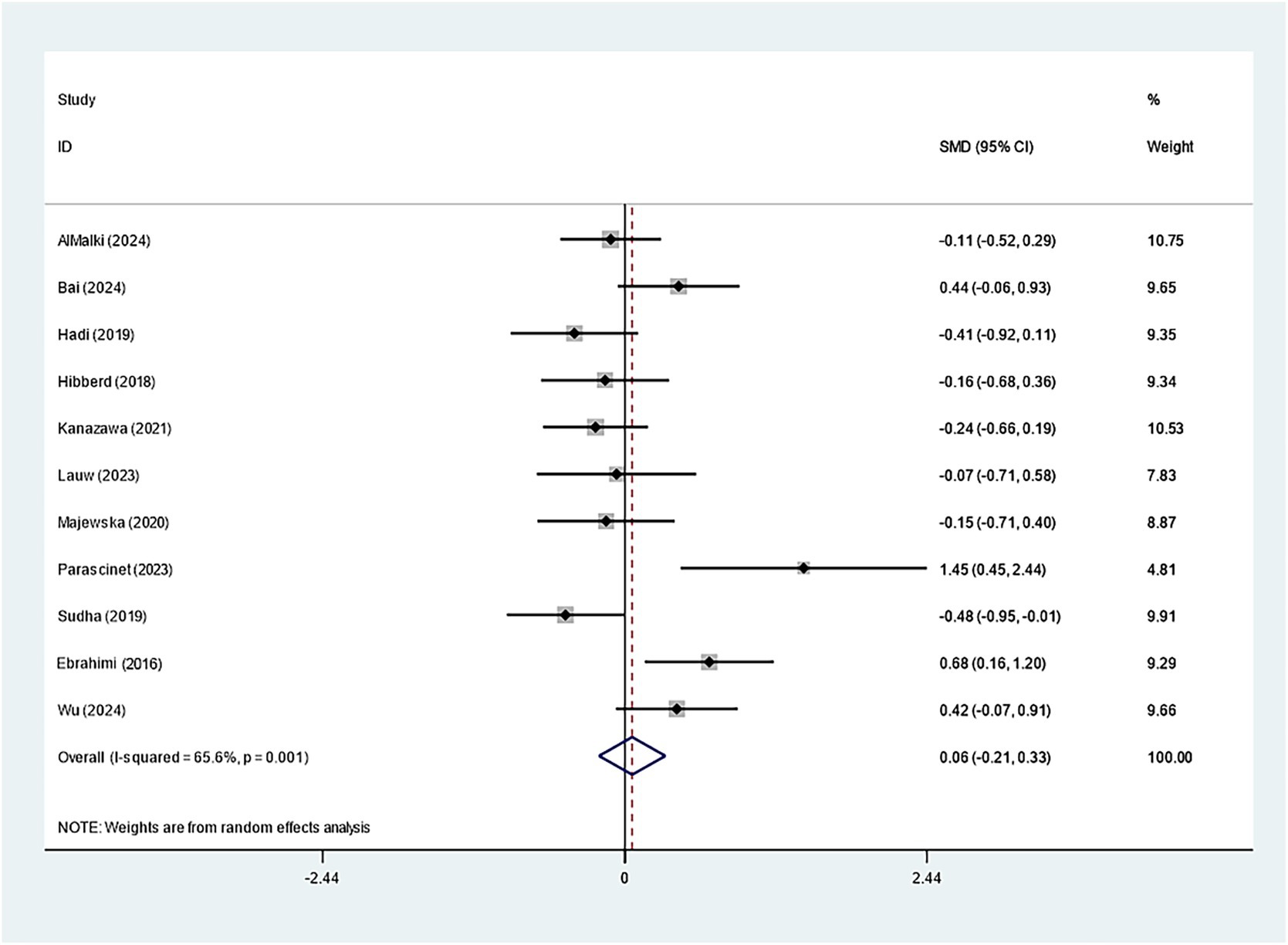
Specifically, eleven studies regarding TC, TG, and HDL-C suggested insignificant effects of Bifidobacterium supplementation (TC: SMD: -0.082; 95% CI: −0.235, 0.071, I2 = 41.4%; TG: SMD: -0.423; 95% CI: −0.939, 0.094, I2 = 90.2%; HDL-C: SMD: 0.060; 95% CI: −0.209, 0.328, I2 = 65.6%) (Figures 8–10). The robustness of the foregoing results was proved by utilizing sensitivity analysis. Publication bias did not exist in funnel plots and Egger’s test (Supplementary Figures 10–15).
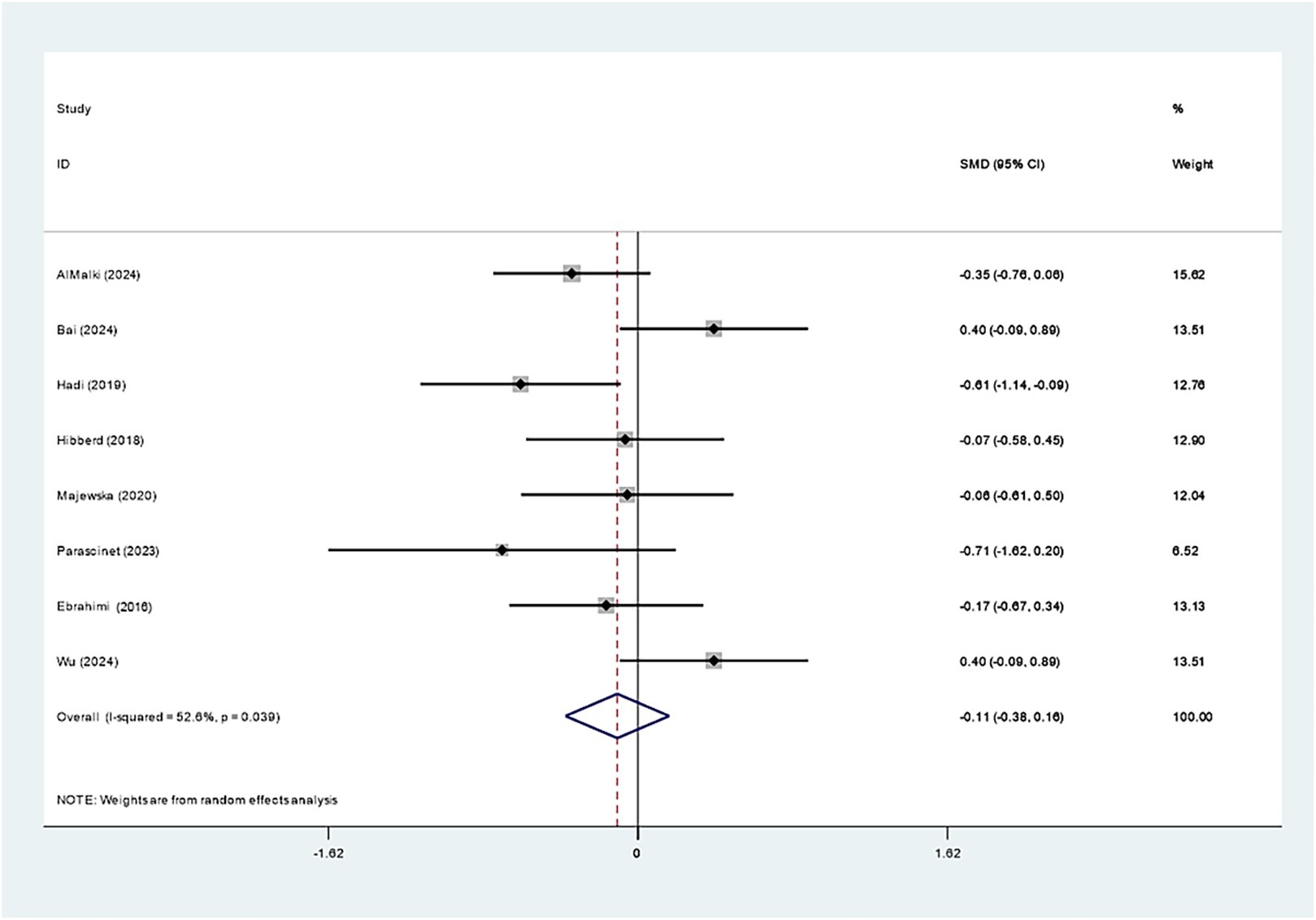
Eight studies examined the impact of Bifidobacterium on LDL-C and revealed no evident effect (SMD: -0.108; 95% CI: −0.379, 0.162, I2 = 52.6%) (Figure 11). Sequential exclusion of individual studies in sensitivity analyses did not markedly affect the results, as presented in Supplementary Figure 16.
4 Discussion
This meta-analysis assessed the impact of Bifidobacterium supplementation on individuals with overweight or obesity. Our study on 21 RCTs proved that Bifidobacterium supplementation is effective in managing weight of the overweight or obese patients. The Bifidobacterium cohort had a prominent decline in weight and BMI, though no significant effect on WC was observed. Furthermore, supplementation with Bifidobacterium did not notably lower FBG or HbA1c but was linked to improved insulin levels. In contrast, marked differences were not found across the two groups with regard to TC, TG, HDL-C, and LDL-C. Therefore, Bifidobacterium supplementation is beneficial for overweight or obese individuals, potentially aiding in weight control and improving insulin secretion.
Probiotics, including Bifidobacterium, have been shown to help manage overweight and obesity (Geng et al., 2022). Our findings prove that Bifidobacterium supplementation lowers the weight and BMI of the population with excess weight or obesity, which aligns with previous research results (Sadeghi et al., 2024). Bifidobacterium may promote the production of SCFAs, such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate, in the gut. These SCFAs can activate the AMPK pathway in the liver, muscle, and adipose tissues. AMPK phosphorylates acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), thereby inhibiting fatty acid synthesis, while simultaneously activating carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1 (CPT-1), which facilitates the mitochondrial uptake and oxidation of fatty acids, enhancing lipid catabolism (Yun et al., 2024). In overweight or obese individuals, sustained supplementation with Bifidobacterium may reduce excessive lipid absorption. Furthermore, SCFAs can activate free fatty acid receptors (FFAR2/3) on intestinal epithelial cells, stimulating the secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and peptide YY (PYY), which suppress the release of the appetite-stimulating hormone ghrelin (Horiuchi et al., 2020). This leads to reduced food intake and subsequent caloric restriction, thereby contributing to a natural decline in BMI. Individuals with obesity often exhibit lower levels of SCFAs produced by gut microbiota; supplementation with probiotics such as Bifidobacterium can enhance SCFA production, increase satiety, and promote weight reduction. López-Moreno et al. (2020) noted marked weight and BMI drops in a cohort receiving probiotics containing Bifidobacterium in contrast to a placebo cohort. Nevertheless, this meta-analysis found no significant reduction in WC among overweight or obese individuals receiving Bifidobacterium supplementation. Ejtahed et al. (2019) demonstrated that probiotic intervention over 2–24 weeks was effective in reducing WC in overweight or obese subjects, which may be attributed to the relatively shorter intervention period (less than 12 weeks) in the present study. Additionally, there exist gender differences in probiotic effects on weight management among the overweight or obese population, with some studies noting a reduction in WC only in women (Cao et al., 2024). This may also explain the insignificant effect on WC in our findings.
Our study demonstrated that supplementation with Bifidobacterium significantly reduced insulin levels in overweight or obese individuals. This effect may be attributed to the capacity of Bifidobacterium to reshape the composition and function of the gut microbiota. In such populations, its metabolic byproducts, particularly SCFAs, may activate the gut-metabolism axis, enhance insulin signaling, reduce adipose tissue accumulation, improve insulin sensitivity, and ultimately lower the risk of obesity-related diseases (Guney-Coskun and Basaranoglu, 2024). Teo et al. (2024) also proved that probiotics containing Bifidobacterium were more effective in improving insulin levels. Although the present study supports the beneficial role of Bifidobacterium in modulating insulin levels, the differences in the results are relatively small. Further randomized controlled trials and prospective cohort studies are warranted to elucidate the role of Bifidobacterium in mitigating insulin resistance among obese populations. Furthermore, this meta-analysis found no significant changes in FBG or HbA1c levels. Barengolts et al. (2019) also reported no changes in HbA1c, FBG, or fasting insulin following consumption of Bifidobacterium-containing probiotic yogurt in the obese cohort with T2DM in comparison to traditional yogurt. This may be because Bifidobacterium’s effect on postprandial blood glucose is more prominent. Therefore, additional research is necessitated to verify the efficacy of Bifidobacterium supplementation in managing blood glucose levels in overweight or obese individuals.
This study found no significant effect of Bifidobacterium on lipid metabolism in the experimental group, suggesting that Bifidobacterium may primarily exert its effects through energy metabolism rather than lipid redistribution. Dong et al.’s meta-analysis (Dong et al., 2019) also reported insignificant disparities in TC, TG, or HDL between the intervention group (which used probiotic foods and Bifidobacterium-containing supplements) and the control group in individuals with metabolic syndrome. Additionally, other studies (Ruscica et al., 2019) have indicated that Bifidobacterium longum evidently reduces serum TC and LDL-C in the hyperlipidemic population by influencing gut microbiota composition and fecal metabolic products. This discrepancy possibly arises from differences in the specific strains of Bifidobacterium in this study, as the lipid-lowering effects of different Bifidobacterium strains may vary. Although our study showed no significant effect on these lipid parameters, interest in the role of Bifidobacterium in lipid metabolism remains strong in the academic community. High-quality RCTs are necessitated to better elucidate the efficacy of Bifidobacterium in lipid metabolism.
This study has two limitations. First, heterogeneity in the studies on Bifidobacterium may confound the results due to differences in ethnicity, sex, strain types, and dosages. Second, the lack of standardization in the units of measurement for blood glucose and lipids may introduce measurement errors. However, efforts were made in this study to minimize such effects through standardization.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, this study suggests that supplementation with Bifidobacterium exerts a moderate positive effect on lowering the weight and BMI of overweight or obese people, indicating that Bifidobacterium may serve as an adjunct in weight management for these individuals. Additionally, our findings demonstrate a beneficial role of Bifidobacterium in regulating insulin levels in overweight or obese patients, though its effects on improving hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia were limited. Future studies should focus on high-quality clinical trials that consider individual factors such as gender, fat distribution, and strain specificity. Specific Bifidobacterium strains may have superior effects, and more research is necessitated to verify the role of Bifidobacterium in managing weight, providing valuable insights into its potential applications.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JH: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HC: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1633434/full#supplementary-material
References
AlMalki, S. M., Alfawaz, H. A., Binmoammar, T. A., AlBahlei, S. F., Al Bakr, L. M., Alzahrani, A. M., et al. (2024). Effects of probiotics on selected anthropometrics and biochemical measures in overweight or obese Saudi subjects: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised clinical trial. Public Health Nutr. 27:e225. doi: 10.1017/S1368980024002003
Amabebe, E., Robert, F. O., Agbalalah, T., and Orubu, E. S. F. (2020). Microbial dysbiosis-induced obesity: role of gut microbiota in homoeostasis of energy metabolism. Br. J. Nutr. 123, 1127–1137. doi: 10.1017/S0007114520000380
Asadi, A., Shadab Mehr, N., Mohamadi, M. H., Shokri, F., Heidary, M., Sadeghifard, N., et al. (2022). Obesity and gut-microbiota-brain axis: a narrative review. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 36:e24420. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24420
Bai, Z., Wu, Y., Gao, D., Dong, Y., Pan, Y., and Gu, S. (2024). Gut microbiome and metabolome alterations in overweight or obese adult population after weight-loss Bifidobacterium breve BBr60 intervention: a randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25:10871. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010871
Banach, K. G., and Jedut, P. (2020). The effect of probiotic yogurt containing Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5 and Bifidobacterium lactis BB-12 on selected anthropometric parameters in obese individuals on an energy-restricted diet: a randomized, controlled trial. Appl. Sci. 10:5830. doi: 10.3390/app10175830
Barengolts, E., Smith, E. D., Reutrakul, S., Tonucci, L., and Anothaisintawee, T. (2019). The effect of probiotic yogurt on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes or obesity: a Meta-analysis of nine randomized controlled trials. Nutrients 11:671. doi: 10.3390/nu11030671
Blüher, M. (2019). Obesity: global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 15, 288–298. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0176-8
Cao, N., Zhao, F., Kwok, L. Y., Wang, H., and Sun, Z. (2024). Impact of probiotics on weight loss, glucose and lipid metabolism in overweight or obese women: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 9:100810. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100810
Crovesy, L., El-Bacha, T., and Rosado, E. L. (2021). Modulation of the gut microbiota by probiotics and symbiotics is associated with changes in serum metabolite profile related to a decrease in inflammation and overall benefits to metabolic health: a double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial in women with obesity. Food Funct. 12, 2161–2170. doi: 10.1039/d0fo02748k
Da Silva, C. C., Monteil, M. A., and Davis, E. M. (2020). Overweight and obesity in children are associated with an abundance of Firmicutes and reduction of Bifidobacterium in their gastrointestinal microbiota. Child. Obes. 16, 204–210. doi: 10.1089/chi.2019.0280
Dong, Y., Xu, M., Chen, L., and Bhochhibhoya, A. (2019). Probiotic foods and supplements interventions for metabolic syndromes: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of recent clinical trials. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 74, 224–241. doi: 10.1159/000499028
Ejtahed, H. S., Angoorani, P., Soroush, A. R., Atlasi, R., Hasani-Ranjbar, S., Mortazavian, A. M., et al. (2019). Probiotics supplementation for the obesity management; a systematic review of animal studies and clinical trials. J. Funct. Foods 52, 228–242. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.10.039
GBD 2021 Adult BMI Collaborators (2025). Global, regional, and national prevalence of adult overweight and obesity, 1990-2021, with forecasts to 2050: a forecasting study for the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet 405, 813–838. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(25)00355-1
Geng, J., Ni, Q., Sun, W., Li, L., and Feng, X. (2022). The links between gut microbiota and obesity and obesity related diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 147:112678. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112678
Gong, H., Gao, H., Ren, Q., and He, J. (2022). The abundance of bifidobacterium in relation to visceral obesity and serum uric acid. Sci. Rep. 12:13073. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17417-3
Guney-Coskun, M., and Basaranoglu, M. (2024). Interplay of gut microbiota, glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists, and nutrition: new frontiers in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 30, 4682–4688. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i43.4682
Hadi, A., Sepandi, M., Marx, W., Moradi, S., and Parastouei, K. (2019). Clinical and psychological responses to synbiotic supplementation in obese or overweight adults: a randomized clinical trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 47:102216. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2019.102216
Hibberd, A. A., Yde, C. C., Ziegler, M. L., Honoré, A. H., Saarinen, M. T., Lahtinen, S., et al. (2019). Probiotic or synbiotic alters the gut microbiota and metabolism in a randomised controlled trial of weight management in overweight adults. Benef Microbes. 10, 121–135. doi: 10.3920/BM2018.0028
Hills, R. D. Jr., Pontefract, B. A., Mishcon, H. R., Black, C. A., Sutton, S. C., and Theberge, C. R. (2019). Gut microbiome: profound implications for diet and disease. Nutrients 11. doi: 10.3390/nu11071613
Horiuchi, H., Kamikado, K., Aoki, R., Suganuma, N., Nishijima, T., Nakatani, A., et al. (2020). Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis GCL2505 modulates host energy metabolism via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43. Sci. Rep. 10:4158. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60984-6
Joyce, S. A., and Gahan, C. G. (2016). Bile acid modifications at the microbe-host Interface: potential for nutraceutical and pharmaceutical interventions in host health. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 7, 313–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-041715-033159
Kanazawa, A., Aida, M., Yoshida, Y., Kaga, H., Katahira, T., Suzuki, L., et al. (2021). Effects of Synbiotic supplementation on chronic inflammation and the gut microbiota in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled study. Nutrients 13:558. doi: 10.3390/nu13020558
Kobyliak, N., Falalyeyeva, T., Mykhalchyshyn, G., Kyriienko, D., and Komissarenko, I. (2018). Effect of alive probiotic on insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes patients: randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 12, 617–624. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2018.04.015
Kopp, L., Schweinlin, A., Tingö, L., Hutchinson, A. N., Feit, V., Jähnichen, T., et al. (2023). Potential modulation of inflammation and physical function by combined probiotics, Omega-3 supplementation and vitamin D supplementation in overweight/obese patients with chronic low-grade inflammation: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:8567. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108567
Lauw, S., Kei, N., Chan, P. L., Yau, T. K., Ma, K. L., Szeto, C. Y. Y., et al. (2023). Effects of Synbiotic supplementation on metabolic syndrome traits and gut microbial profile among overweight and obese Hong Kong Chinese individuals: a randomized trial. Nutrients 15:4248. doi: 10.3390/nu15194248
Leite, G., Barlow, G. M., Rashid, M., Hosseini, A., Cohrs, D., Parodi, G., et al. (2024). Characterization of the small bowel microbiome reveals different profiles in human subjects who are overweight or have obesity. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 119, 1141–1153. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002790
López-Moreno, A., Suárez, A., Avanzi, C., Monteoliva-Sánchez, M., and Aguilera, M. (2020). Probiotic strains and intervention Total doses for modulating obesity-related microbiota Dysbiosis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Nutrients 12:1921. doi: 10.3390/nu12071921
Majewska, K., Kręgielska-Narożna, M., Jakubowski, H., Szulińska, M., and Bogdański, P. (2020). The multispecies probiotic effectively reduces homocysteine concentration in obese women: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. J. Clin. Med. 9:998. doi: 10.3390/jcm9040998
Michael, D. R., Davies, T. S., Jack, A. A., Masetti, G., Marchesi, J. R., Wang, D., et al. (2021). Daily supplementation with the Lab4P probiotic consortium induces significant weight loss in overweight adults. Sci. Rep. 11:5. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78285-3
Minami, J., Kondo, S., Yanagisawa, N., Odamaki, T., Xiao, J. Z., Abe, F., et al. (2015). Oral administration of Bifidobacterium breve B-3 modifies metabolic functions in adults with obese tendencies in a randomised controlled trial. J Nutr Sci. 4:e17. doi: 10.1017/jns.2015.5
NIH. National Institutes of Health. Available online at: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71. doi: 10.1186/s13643-021-01626-4
Parascinet, O., Mas, S., Hang, T., Llavero, C., Lorenzo, Ó., and Ruiz-Tovar, J. (2023). A pilot study: the reduction in fecal acetate in obese patients after probiotic administration and percutaneous electrical neurostimulation. Nutrients 15:1067. doi: 10.3390/nu15051067
Ruscica, M., Pavanello, C., Gandini, S., Macchi, C., Botta, M., Dall'Orto, D., et al. (2019). Nutraceutical approach for the management of cardiovascular risk—a combination containing the probiotic Bifidobacterium longum BB536 and red yeast rice extract: results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutr. J. 18:13. doi: 10.1186/s12937-019-0438-2
Sadeghi, A., Daroudi, R., Davari, M., Gharib-Naseri, Z., Jafarzadeh, J., and Tajvar, M. (2024). Efficacy of probiotics in overweight and obesity control: an umbrella review and subgroup Meta-analysis. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 16, 2316–2328. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10363-8
Sarita, B., Samadhan, D., Hassan, M. Z., and Kovaleva, E. G. (2024). A comprehensive review of probiotics and human health-current prospective and applications. Front. Microbiol. 15:1487641. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1487641
Sato, S., Arai, S., Kato, K., Yoshida, K., Iwabuchi, N., Sagami, T., et al. (2024). Effects of Bifidobacterium longum BB536 and Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 on body composition in Normal and overweight adults in randomized placebo-controlled study. Nutrients 16:815. doi: 10.3390/nu16060815
Seganfredo, F. B., Blume, C. A., Moehlecke, M., Giongo, A., Casagrande, D. S., Spolidoro, J. V. N., et al. (2017). Weight-loss interventions and gut microbiota changes in overweight and obese patients: a systematic review. Obes. Rev. 18, 832–851. doi: 10.1111/obr.12541
Sergeev, I. N., Aljutaily, T., Walton, G., and Huarte, E. (2020). Effects of Synbiotic supplement on human gut microbiota, body composition and weight loss in obesity. Nutrients 12:222. doi: 10.3390/nu12010222
Sudha, M. R., Ahire, J. J., Jayanthi, N., Tripathi, A., and Nanal, S. (2019). Effect of multi-strain probiotic (UB0316) in weight management in overweight/obese adults: a 12-week double blind, randomised, placebo-controlled study. Benef Microbes. 10, 855–866. doi: 10.3920/BM2019.0052
Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M., Sharifi, N., Farrokhian, A., Raygan, F., Karamali, F., Razzaghi, R., et al. (2017). A randomized controlled clinical trial investigating the effect of Synbiotic administration on markers of insulin metabolism and lipid profiles in overweight type 2 diabetic patients with coronary heart disease. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 125, 21–27. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-105441
Teo, Y. Q. J., Chong, B., Soong, R. Y., Yong, C. L., Chew, N. W., and Chew, H. S. J. (2024). Effects of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics on anthropometric, cardiometabolic and inflammatory markers: an umbrella review of meta-analyses. Clin. Nutr. 43, 1563–1583. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2024.05.019
WHO (2024). Obesity and overweight 2024. Obesity. Available online at: https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity
Wu, Y., Gao, D., Pan, Y., Dong, Y., Bai, Z., and Gu, S. (2024). Modulation of serum metabolic profiles by Bifidobacterium breve BBr60 in obesity: a randomized controlled trial. Foods 13:3655. doi: 10.3390/foods13223655
Yun, S. W., Shin, Y. J., Ma, X., and Kim, D. H. (2024). Lactobacillus plantarum and Bifidobacterium longum alleviate high-fat diet-induced obesity and depression/cognitive impairment-like behavior in mice by upregulating AMPK activation and downregulating Adipogenesis and gut Dysbiosis. Nutrients 16:3810. doi: 10.3390/nu16223810
Zarrati, M., Raji Lahiji, M., Salehi, E., Yazdani, B., Razmpoosh, E., Shokouhi Shoormasti, R., et al. (2019). Effects of probiotic yogurt on serum Omentin-1, Adropin, and Nesfatin-1 concentrations in overweight and obese participants under low-calorie diet. Probiot. Antimicrob Prot. 11, 1202–1209. doi: 10.1007/s12602-018-9470-3
Zarrati, M., Salehi, E., Nourijelyani, K., Mofid, V., Zadeh, M. J., Najafi, F., et al. (2014). Effects of probiotic yogurt on fat distribution and gene expression of proinflammatory factors in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in overweight and obese people with or without weight-loss diet. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 33, 417–425. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2013.874937
Keywords: Bifidobacteria , overweight or obesity, weight, blood glucose, blood lipids
Citation: Huang J and Cheng H (2025) Effects of Bifidobacterium on metabolic parameters in overweight or obesity adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Microbiol. 16:1633434. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1633434
Edited by:
Malgorzata Ziarno, Warsaw University of Life Sciences, PolandReviewed by:
Francesco Pizza, ASL Napoli 2 Nord, ItalyChang Hong, Baotou Medical College, China
So Youn An, Wonkwang University, Republic of Korea
Copyright © 2025 Huang and Cheng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Junmei Huang, aHVhbmdqbTY3ODNAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Junmei Huang
Junmei Huang Hao Cheng
Hao Cheng