- 1Biological Sciences Division, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, WA, United States
- 2Department of Biological Systems Engineering, Washington State University, Richland, WA, United States
- 3Energy and Environment Directorate, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, WA, United States
- 4Agile BioFoundry, U.S. Department of Energy, Emeryville, CA, United States
Fungi are vital to the bioeconomy, serving as key producers of food, beverages, biofuels, and medicines, while also acting as essential resource recyclers in ecosystem management. For nearly a century, oleaginous yeast and filamentous fungi have been explored for their proficiency in oleochemicals production and carbon storage. Lipogenesis is one of the most well-studied fungal processes, with substantial progress having been made through reductionist biochemical approaches; however, the physiology and metabolism of fungal systems operating under different conditions arise from the functions of thousands of proteins, for which very little is known outside of model yeast. In this review, we discuss how proteomics provides a valuable analytical approach to contextualize lipogenesis within a complex biological system, where lipid accumulation is fundamentally governed by changes in proteins of multiple pathways. In the past two decades, proteomics has been applied to study stress response to nutrient limitations, metabolism of various carbon and nitrogen sources, the lipid droplet hub of carbon storage, protein post-translational modifications and signaling pathways, as well as oleochemical biosynthesis, thereby advancing our understanding of the oleaginous phenotype. Over 40 studies are reviewed herein to evaluate the impact, critically assess the utility, and propose future applications of proteomics. In the coming years, large systems-level proteomics studies will lay a foundation for marrying modeling and metabolic engineering strategies to optimize oleochemicals production in oleaginous fungi.
1 Introduction
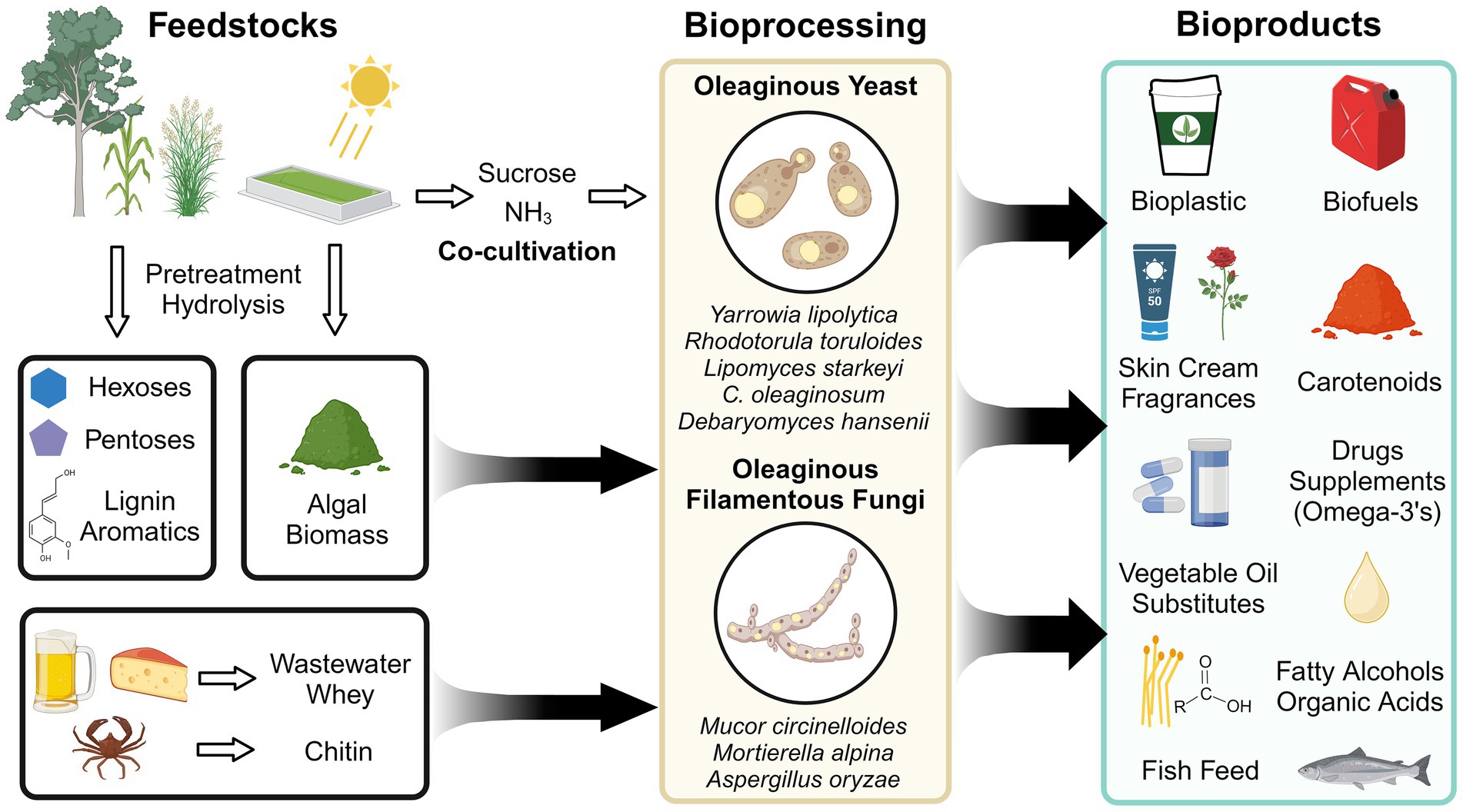
Ubiquitous in nature, fungi have evolved diverse metabolic capabilities for survival in a spectrum of niches. Certain fungi including single-celled yeast and multicellular filamentous fungi have developed a strategy to store surplus carbon as neutral lipids (triacylglyerides and sterols) in the face of competition or nutrient limitation (Mason-Jones et al., 2021). Strains capable of producing ≥ 20% of their cell dry weight as lipids are termed “oleaginous” and have been studied for three-quarters of a century (Lundin, 1950; Kessell, 1968; Gill et al., 1977; Botham and Ratledge, 1979; Higashiyama et al., 1999; Song et al., 2001). Oleaginous fungi have garnered sustained interest because of their potential as secure sources of oleochemicals (i.e., chemicals derived from natural oils) for biofuels, bioplastics, surfactants, and drug delivery vehicles (Figure 1) (Abeln and Chuck, 2021; Alhattab et al., 2024). With overfishing depleting marine ecosystems and accelerated deforestation due to land-intensive vegetable oil production, oleaginous fungi also offer cheaper and less land-intensive alternatives for fish feed, palm oil, and cocoa butter (Blomqvist et al., 2018; Tramontin et al., 2019; Abeln and Chuck, 2021; Brunel et al., 2022, 2024; Zhang X. Y. et al., 2022; Sigtryggsson et al., 2023).
To develop economically viable bioprocesses using oleaginous fungi, the value of the product, productivity at commercially-relevant scales (g/L/day product), and feedstock cost must be considered (Banerjee and Singh, 2024). Additional factors that should be considered include product yield (g product / g carbon source), land usage (tons product / hectare of land harvested for a carbon source), and energy and water inputs (Banerjee and Singh, 2024; Collett et al., 2014; Davis et al., 2022; Bhatt et al., 2022; Sartaj et al., 2023; Chopra et al., 2020). Several bioprocesses target low-cost feedstocks to provide carbon (and other nutrients) for bioproducts synthesis by oleaginous fungi (Figure 1). Emerging strategies include using algal biomass, plastic wastes, and even carbon/nitrogen-capturing co-cultures to supply resources (Younes et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2023; Mihreteab et al., 2021; Yen et al., 2015; Cheirsilp et al., 2012; Pomraning et al., 2024). However, the single largest feedstock is lignocellulosic biomass derived from bioenergy crops and agricultural/forestry industry residues (Bioenergy Technologies Office, 2024). Lignocellulose is primarily composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. Cellulose and hemicellulose are polysaccharides containing glucose, xylose, arabinose, and other monomers, while lignin is a complex heterogeneous polymer containing interlinked phenolics (Vanholme et al., 2010). Many oleaginous fungi natively utilize the major constituents of lignocellulose and are resistant to inhibitors from pretreatment steps that depolymerize lignocellulose (e.g., acetic acid, furan, furfural, and vanillin), making them poised for valorization strategies (Spagnuolo et al., 2019; Hassane et al., 2024).
Though hundreds of strains of oleaginous fungi from various phyla have been identified and studied for their lipid-producing capabilities (Ayadi et al., 2018; Abeln and Chuck, 2021; Zhang X. Y. et al., 2022), only a selection have sequenced genomes and even fewer have an accompanying set of genetic engineering tools. For yeasts, these include certain strains of the ascomycetes Yarrowia lipolytica (Abdel-Mawgoud et al., 2018), Lipomyces starkeyi (Zhang L. et al., 2022; Czajka et al., 2024), Debaryomyces hansenii (Yaguchi et al., 2017a; Strucko et al., 2021), and Candida tropicalis (Craft et al., 2003; Zhang et al., 2020) as well as the basidiomycetes Rhodotorula toruloides (Yu and Shi, 2023), Rhodotorula glutinis (Pi et al., 2018), and Cutaneotrichosporon oleaginosum (Bracharz et al., 2017; Stellner et al., 2023; Shaigani et al., 2023). For filamentous fungi, the mucoromycetes Mucor circinelloides (Nagy et al., 2017; Fazili et al., 2022b) and Mortierella alpina (Hao et al., 2016; Sakamoto et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2023) have been investigated for production of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) (Zhang X. Y. et al., 2022). Nitrogen limitation is the most popular strategy to induce lipid accumulation, though phosphate, sulfate, or iron limitation can also be used (with combinatorial effects observed by limiting multiple nutrients) (Granger et al., 1993; Wu et al., 2010, 2011; Nambou et al., 2014; Dzurendova et al., 2021; Wierzchowska et al., 2021). The earliest systems-level analyses of oleaginous Y. lipolytica grown in nitrogen-rich vs. limited conditions were conducted using transcriptomics (Morin et al., 2011; Poorinmohammad and Kerkhoven, 2021). However, these studies showed no significant changes in the transcriptional profiles of fatty acid biosynthesis genes in response to nitrogen limitation. This suggests that lipogenesis may primarily be regulated at the post-transcriptional level, leading to alterations in protein profiles that ultimately drive differences in lipogenesis and lipid storage mechanisms between oleaginous and non-oleaginous fungi.
Proteins are the major functional units in biological systems, and these functions ultimately give rise to phenotypes. Thus, studying proteins is key to understanding the unique characteristics of oleaginous fungi, and how they regulate lipid production in different environmental conditions. Biochemical tools for characterizing individual fungal proteins and genetically manipulating fungal strains have significantly advanced our understanding of enzyme function and central carbon metabolism (i.e., glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway or PPP, TCA cycle, and transhydrogenase cycle). However, these reductionist approaches fall short of capturing physiological snapshots of a biological system’s response to environmental conditions. In the past two decades, advances in mass spectrometry-based proteomics have enabled systems-level studies of proteins in oleaginous fungi. Unlike transcriptomics, which examines RNA expression, proteomics directly measures protein expression, offering a more precise view of cellular activity. As of writing, more than 40 publications have harnessed proteomics to investigate the physiologies of oleaginous fungi according to Pubmed and Web of Science™ (Dec, 2024). This body of work encompasses studies involving stress response to nutrient limitation, utilization of different carbon sources, the lipid droplet composition, secreted proteins (the secretome), protein modifications, comparisons among fungi, and integration with other omics approaches such as transcriptomics (transcriptional regulation), lipidomics (lipid profiles), and metabolomics (metabolites analysis) (Figure 2).
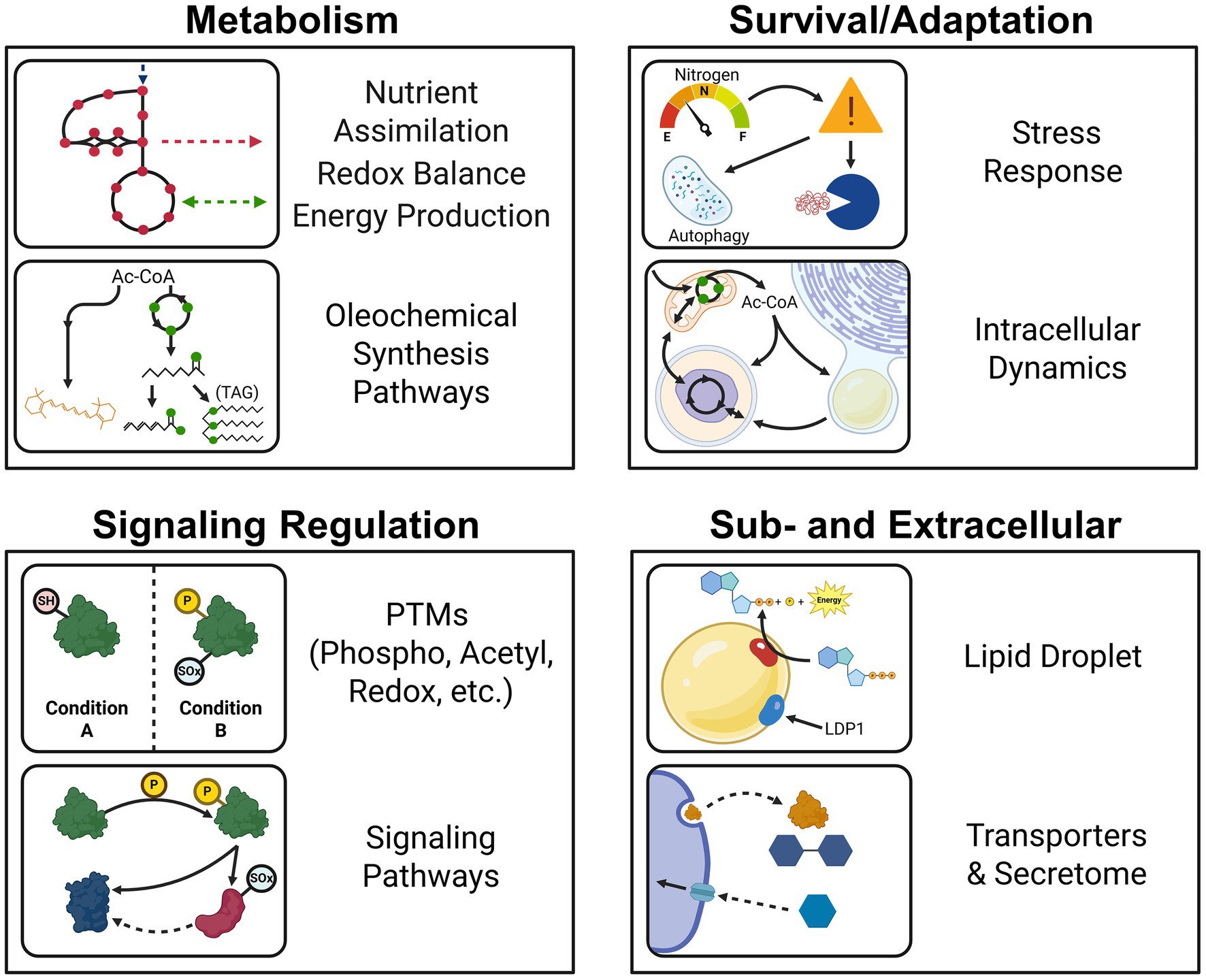
Figure 2. Summary of proteomics applications in studying the physiologies and metabolisms of oleaginous fungi.
In this review, we provide a critical summary of proteomics studies in oleaginous fungi and highlight the role of proteomics in advancing our understanding of the oleaginous yeast phenotype. First, we provide an overview of the prevailing theory that explains in part how carbon flux is regulated and re-routed for lipid production in oleaginous fungi. Then, we summarize the overall proteomics workflow, and approaches that have been used to study oleaginous yeast and filamentous fungi. The core of our review focuses on proteomics insights into the unique physiology, metabolism, and stress responses mechanisms of these microorganisms (Figure 2). Lastly, we address challenges, offer recommendations, and identify unexplored opportunities to bolster proteomics applications for developing hyperlipogenic fungi.
2 Lipid accumulation in oleaginous fungi
The mechanisms of lipid accumulation in oleaginous fungi and their environmental and metabolic triggers have been extensively reviewed (Beopoulos et al., 2011; Adrio, 2017; Spagnuolo et al., 2019; Abeln and Chuck, 2021; Zhang X. Y. et al., 2022). The current model for oleaginocity implicates triacylglycerides (TAGs) as sinks for carbon that would have otherwise been used for cell growth and division (Figure 3). When a key nutrient is limiting, flux through anabolic growth-promoting processes is generally downregulated, thereby severely perturbing cellular energy homeostasis and resulting in inhibition of key enzymes such as isocitrate dehydrogenase (ICDH) (Evans and Ratledge, 1985a,b). Nitrogen limitation leads to a decrease in cellular AMP levels, which is exacerbated by (though not entirely due to) the activity of the nitrogen scavenger and regulator AMP deaminase (Evans and Ratledge, 1985a,b). As an allosteric positive regulator of ICDH, a decrease in AMP leads to excretion of citrate from the mitochondria. ATP citrate lyase (ACL) then converts citrate into acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate, fueling lipid biosynthesis (Ratledge and Wynn, 2002).
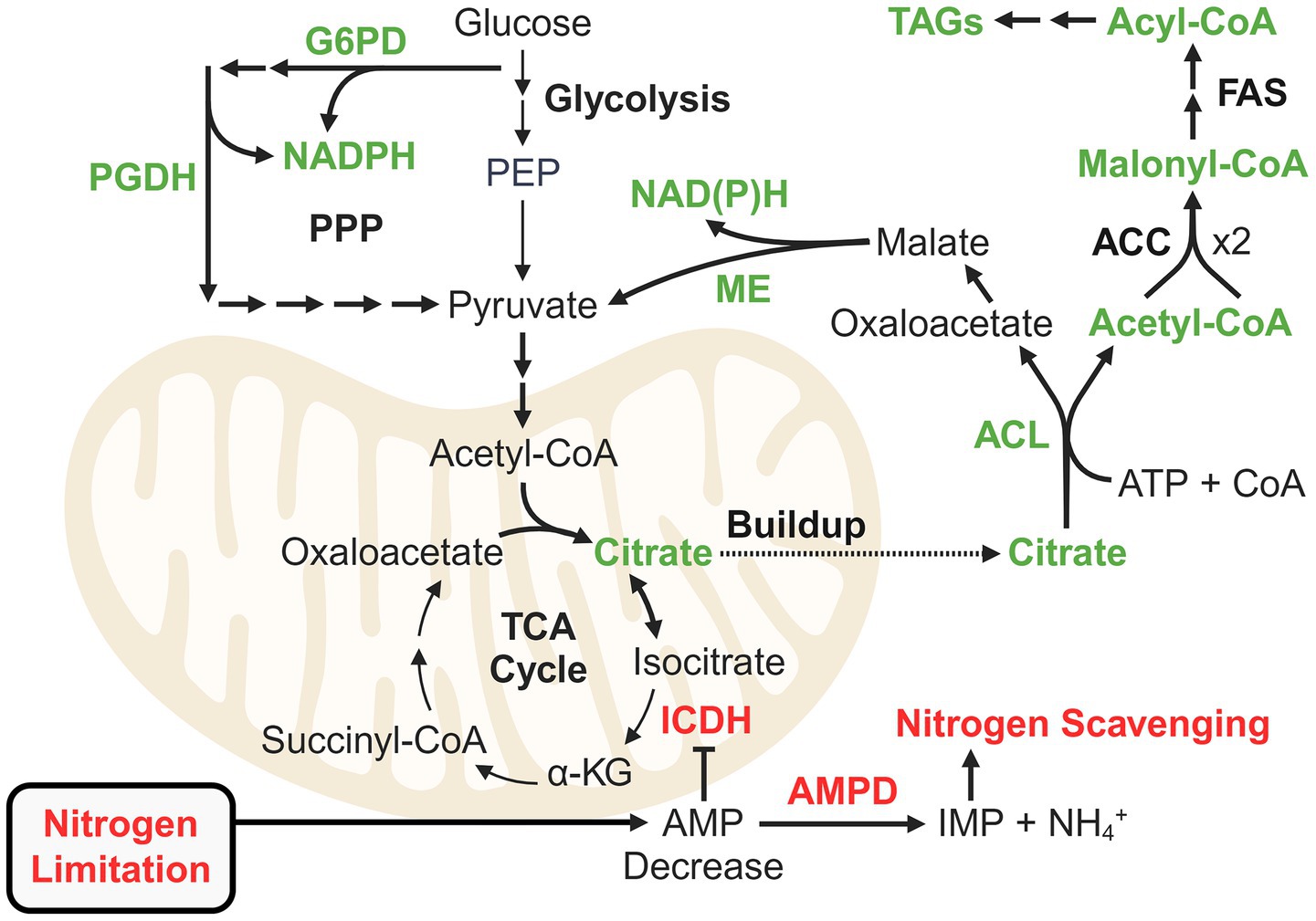
Figure 3. Theory of carbon re-routing for lipid accumulation in oleaginous fungi as a stress response to nutrient limitation. Green represents enzymes important for routing carbon flux to fatty acid biosynthesis. Red represents the regulatory mechanism linked to nitrogen recycling that leads to inhibition of isocitrate dehydrogenase and mitochondrial citrate buildup. Proteomics studies have elucidated additional pathways and reactions for supplying NADPH and acetyl-CoA for fatty acid biosynthesis. ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; ACL: ATP citrate lyase; AMPD: AMP deaminase; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; G6PD (GND1): Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; ICDH: Isocitrate dehydrogenase; ME: Malic enzyme; PGDH (ZWF1): 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase; PPP: Pentose phosphate pathway.
Fatty acid biosynthesis requires substantial NADPH, which, in oleaginous fungi like Rhodosporidium toruloides and Mucor circinelloides, is often supplied by malic enzyme (ME) (Ratledge, 2014). However, in species such as Y. lipolytica and L. starkeyi, ME does not produce NADPH, implicating alternative pathways (Tang et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2013). The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) is a well-studied source of NADPH, but other pathways such as the pyruvate-isocitrate-α-ketoglutarate cycle (involving NADP+-dependent ICDH) and the GABA shunt also play roles (Ratledge, 2014; Liu et al., 2019; Henriques et al., 2021). Moreover, it is clear that there are organism and condition-specific nuances regarding NADPH (and acetyl-CoA) generation. Such nuances have been revealed in recent proteomics studies, and insights beyond the hackneyed role of PPP (unless relevant to xylose utilization) will be explored for oleaginous yeast and filamentous fungi.
3 Proteomics approaches to study oleaginous fungi
A major goal of proteomics is to identify and understand proteins as a function of a biological system’s response to environmental stimuli (Li X. et al., 2021). Mass spectrometry (MS) is currently the premier platform for analyzing complex mixtures of proteins/peptides (Aebersold and Goodlett, 2001; Aebersold and Mann, 2003; Cox and Mann, 2011; Shuken, 2023). There are two general proteomics strategies: the bottom-up approach in which proteins are enzymatically digested into peptides prior to liquid chromatography (LC) MS analysis (LC–MS), and the top-down approach in which intact proteins are analyzed directly (Dupree et al., 2020). In both cases, peptides/proteins are separated by LC, followed by electrospray ionization (or matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization, MALDI) to enter MS. Currently, the top-down approach has not been applied to oleaginous fungi and will not be discussed. For bottom-up proteomics studies of oleaginous fungi, data-dependent acquisition (DDA) is commonly used to collect MS spectra, which contain mass-to-charge (m/z) ratios at particular retention times (Li X. et al., 2021). A selection of peptides at a particular time are subjected to fragmentation (MS2 or tandem MS/MS) for confident identification of peptide sequences through proteome database searching. Additional details regarding proteomics methodologies are reviewed elsewhere (Jiang et al., 2024).
The bottom-up approach can be used to study the cellular proteome and the secretome containing extracellular proteins. To study intracellular proteins, fungi are first lysed via chemical (e.g., HCl), enzymatic (e.g., Zymolyase), and/or mechanical (e.g., bead-beating) means (Zhao et al., 2024). For filamentous fungi in particular, homogenization has often been employed for cell lysis due to their thick chitinous cell walls (Ling et al., 2015; Tang et al., 2016). Following lysis, proteins are solubilized and denatured by a variety of methods tailored to downstream sample processing steps (Awad and Brueck, 2020). One common approach involves using high concentrations of denaturing agents such as urea followed by dilution and digestion. For oleaginous fungi in particular, effort has been invested in solubilizing hydrophobic proteins and removing excess lipids using detergents (e.g., SDS and Triton X-100) and chloroform/methanol precipitation (Liu et al., 2009; Martinez-Moya et al., 2011; Kim et al., 2021). Compared to the intracellular proteome, proteins in the secretome are dilute and must be concentrated prior to sample processing using molecular weight cut-off filters or precipitation (Wei et al., 2013; Onésime et al., 2022). As with older cellular proteomics studies, some secretomics approaches employ SDS-PAGE for separation and in-gel digestion to acquire peptides for MS (Athenstaedt et al., 2006; Wei et al., 2013; Ciesielska et al., 2014).
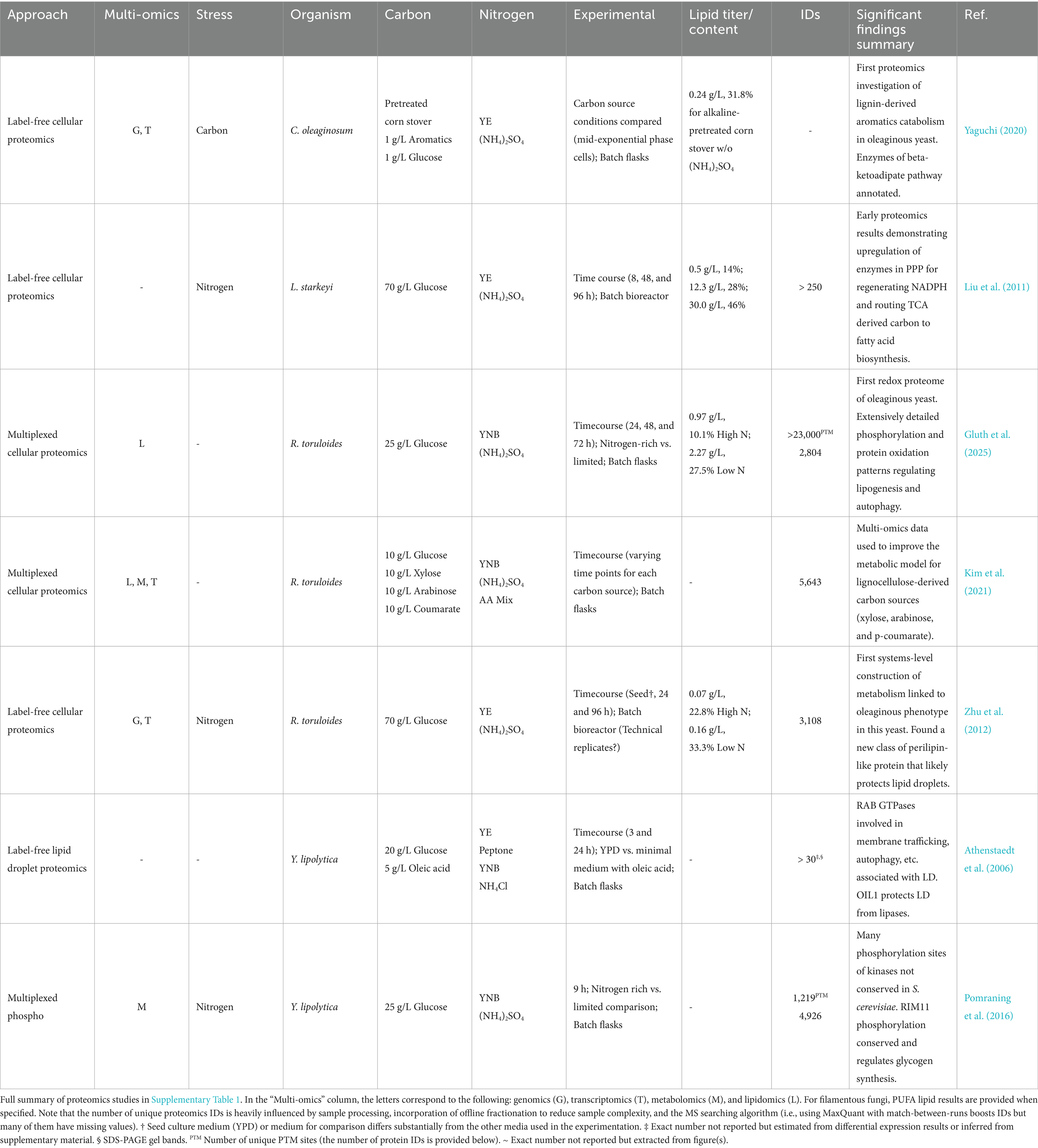
Proteomics strategies are further categorized according to quantification methodology (Figure 4). Label-free proteomics refers to workflows without peptide labeling. Relative quantification is achieved by comparing peptide spectrum matches (PSMs) from MS2 or extracted ion chromatography peak areas using MS1 intensity for a given protein across different conditions. Though relatively straightforward, label-free proteomics suffers from the missing data problem—peptides detected in one sample may not be detected in the other samples (Webb-Robertson et al., 2015). Multiplexed quantitative proteomics typically refers to workflows in which peptides are labeled with isobaric mass tags such as iTRAQ or TMT (Figure 4) (Pappireddi et al., 2019; Li J. et al., 2021). Labeling strategies such as stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) (Ong et al., 2002) and stable-isotope dimethyl labeling (Hsu et al., 2003) also technically facilitate multiplexing, but few have applied these methods to oleaginous fungi (Tables 1, 2 and Supplementary Table 1).
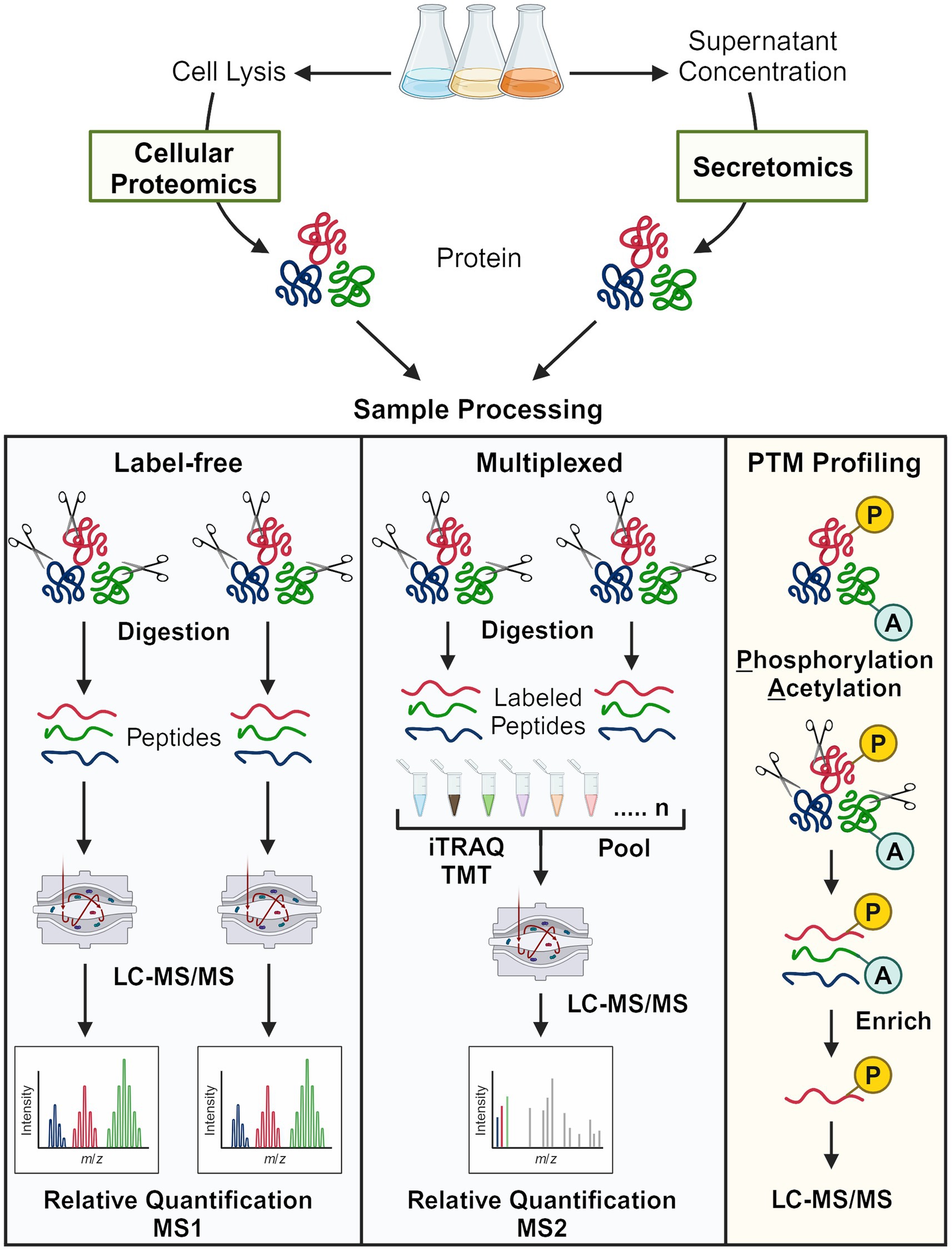
Figure 4. Overview of bottom-up proteomics approaches used to study oleaginous fungi. The two major quantification methods, label-free and peptide tagging (multiplexed), are shown. For PTM profiling, the selectivity of the enrichment method determines the major type of modified peptide that is enriched (generally one type). Note that many secretomics, lipid droplet proteomics, and early proteomics approaches employed SDS-PAGE and in-gel digestion prior to mass spectrometry analysis.
Protein function is not solely attributed to abundance; rather, post-translational modifications (PTMs), protein–protein interactions, and subcellular localization also have important regulatory implications. PTMs such as phosphorylation and acetylation are labile and sub-stoichiometric, thus requiring additional sample processing considerations (e.g., phosphatase inhibitors) to avoid artifacts and enrich low-abundance PTMs. Enrichment strategies mainly include immunoprecipitation by PTM-specific antibodies (e.g., acetylation) and affinity capture techniques based on the chemical properties of PTMs (e.g., phosphorylation) (James Sanford and Bustamante Smolka, 2022). Though not summarized in Figure 4, proteins that localize to the lipid droplet are particularly interesting because of their structural and regulatory roles in TAG/sterol storage, lipid metabolism, and energy homeostasis (Athenstaedt, 2019). As with PTMs, additional steps are required to study protein localization and include, for instance, ultracentrifugation in the presence of high concentration salts or density gradients of sucrose or sorbitol (Athenstaedt et al., 2006; Zhu et al., 2015; Yu et al., 2017; Bhutada et al., 2018). All the methods summarized thus far have been applied to study oleaginous fungi; this proteomics anthology and the resulting physiological insights are reviewed hereafter.
4 Proteomics insights for oleaginous yeast
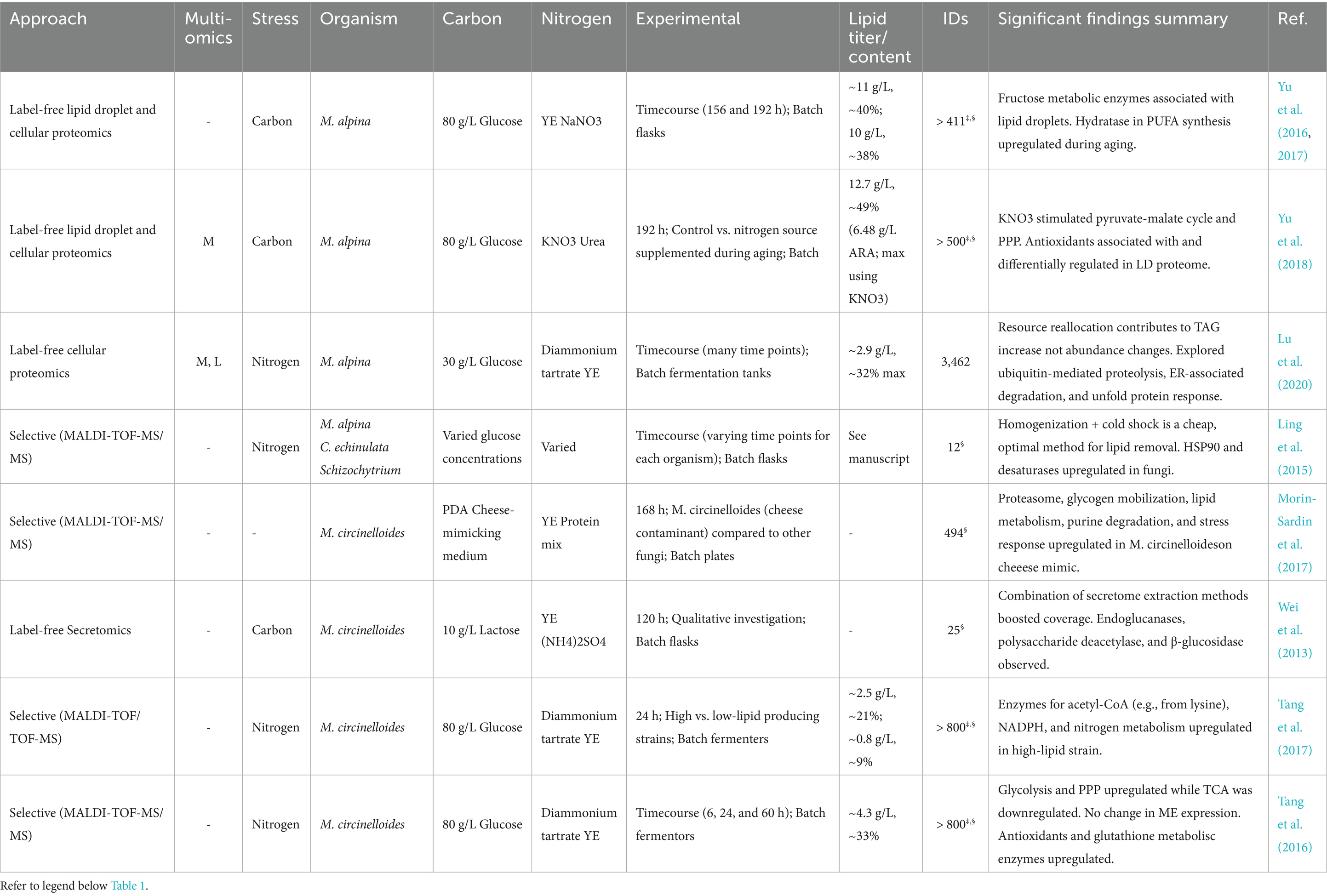
Proteomics enables us to decipher the expressed metabolism of oleaginous yeasts in response to environmental stimuli. Characterizing an organism’s expressed metabolism under different conditions reveals key enzymes and pathways that coordinate central metabolites for biosynthesis of lipids and other bioproducts, energy production, and redox balance. The proteomes of oleaginous yeast, especially Y. lipolytica and R. toruloides, have been studied more extensively than filamentous fungi and are reviewed hereafter (Table 1 and Supplementary Table 1, which includes all oleaginous yeast proteomics studies). Results from other biotechnologically-relevant oleaginous yeasts like Lipomyces starkeyi and Cutaneotrichosporon oleaginosum (formerly Cryptococcus curvatus and Trichosporon oleaginosus) are reviewed in the final portion of this section.
4.1 Yarrowia lipolytica
Yarrowia lipolytica is a model bio-oil producing ascomycete yeast, for which a number of strains have been isolated and engineered. Few of the wildtype strains are considered oleaginous with much of the genetic engineering conducted on strain W29 (a.k.a. CLIB89 and ATCC 20460) (Abeln and Chuck, 2021; Salvador López et al., 2022), for example, to confer non-native assimilation of monosaccharides (xylose, galactose, etc.) and disaccharides (fructose, cellobiose, etc.) (Guo et al., 2015; Lazar et al., 2015; Ledesma-Amaro et al., 2016; Hapeta et al., 2017). Y. lipolytica can utilize hydrophobic substrates (e.g., oleic acid) for growth, ex novo lipid synthesis, and bioproduct synthesis (e.g., citric acid), hence its species nomenclature (Madzak, 2021). It accomplishes this task by producing a complex extracellular bioemulsifier called liposan, which is comprised of proteins, exopolysaccharides, lipids, and other metabolites (Onésime et al., 2022). Proteomics investigations of Y. lipolytica, its derivatives, and other oleaginous strains have been conducted using various nutrient sources and stress conditions (Table 2 and Supplementary Table 1). These proteomic results played key roles in enhancing the understanding of the oleaginous phenotype and are detailed in the following subsections.
4.1.1 The lipid droplet proteome
The earliest proteomics study of Y. lipolytica strain W29 was conducted in 2006 by Athenstaedt et al., who characterized its lipid droplet proteomes using either glucose or oleic acid as the carbon source (Athenstaedt et al., 2006). The authors isolated lipid particles and identified 21 proteins, involved in fatty acid activation, lipid and sterol metabolism, and transport processes (Athenstaedt et al., 2006). The low number of protein identifications was due to the study being performed at the early stage of proteomics. Interestingly, several Rab GTPases were only observed in the oleic acid condition; these enzymes are involved in trafficking membrane proteins and lipids. They may help facilitate lipid droplet interactions with other organelles (e.g., endosomes and lysosomes) and recruit proteins to a burgeoning lipid droplet (Liu et al., 2007; Bouchez et al., 2015). The authors also observed a protein without a homolog in S. cerevisiae—Bhutada et al. keenly noted this and found that deleting this protein (termed OIL1) eliminated the oleaginous phenotype (Bhutada et al., 2018). They concluded that OIL1 functioned similarly to perilipins found in higher eukaryotes and protects the lipid droplet from lipase activity.
4.1.2 Molecular mechanisms of nitrogen limitation response
To investigate regulatory mechanisms governing nitrogen limitation-induced lipid accumulation, Pomraning et al. (2016) performed a multi-omics analysis of the metabolome, proteome, and phosphoproteome in Y. lipolytica under nitrogen-replete and limited conditions. Global proteomics showed an upregulation of proteins associated with proteolysis and downregulation of proteins in β-oxidation, amino acid metabolism, and translation after 9 h of nitrogen limitation. Given those results, they tested if inhibiting translation using cycloheximide would result in lipid accumulation and observed lipid droplet growth as a consequence, though to a lesser extent than nitrogen limitation (Pomraning et al., 2016). In agreement with earlier transcriptomics work (Morin et al., 2011), they did not observe differential expression of ATP-citrate lyase (ACL) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) at the protein level, suggesting post-translational regulation of lipogenesis. Using phosphoproteomics, Pomraning et al. identified 599 proteins that were significantly enriched in tyrosine and serine/threonine kinase activity, with 80 and 53 phosphopeptides showing an increase or decrease, respectively, under nitrogen limitation (Pomraning et al., 2016). For example, they observed increased phosphorylation levels of ACL and ACC during nitrogen limitation. ACC is negatively regulated by AMP kinase (AMPK or SNF1 in yeast) by phosphorylation (Shi et al., 2014), which has been used to engineer constitutively active ACC (Qiao et al., 2015). Unless the observed sites are different from those regulated by SNF1, the increase in ACC phosphorylation seems counterintuitive—highlighting a challenge with using proteomics for discovery when so much relies on assumptions regarding homology of conserved sequences.
In. S. cerevisiae, response to the quantity and quality of nitrogen sources is regulated by nitrogen catabolite repression, which may be partially conserved in Y. lipolytica (Mazurie et al., 2005; Lavoie et al., 2009; Pomraning et al., 2017). When high-quality nitrogen like amino acids or ammonium is available, GATA-type transcription factors GLN3 and GAT1 are phosphorylated and remain bound to URE2 in the cytosol. Under poor nitrogen conditions, they localize to the nucleus and activate nitrogen utilization genes. Pomraning et al. did not report changes in phosphorylation for GLN3, GAT1, GCN4, TOR1, or GATA-type transcriptional repressors GZF3 and DAL80, which may be due to phosphoproteomic coverage limitations, the low abundance of phosphorylated proteins, or the selected time points for analysis (Pomraning et al., 2016). However, they did observe changes in protein abundances for predicted GATA family transcription factors (e.g., upregulation of GLN3 during nitrogen limitation). They also keenly demonstrated how proteomics can be used to identify DNA motifs that associate transcription factors with up- and downregulated proteins. Genes with a G[AC]TAAGC and [GA]TGAGTCA motifs were enriched for amino acid biosynthesis. The latter may be bound by Gcn4p, which activates expression of genes in response to amino acid starvation (Pomraning et al., 2016). Interestingly, genes with the [GA]TGAGTCA motif tended to be downregulated, suggesting the importance of autophagy for scavenging amino acids and nitrogen and/or regulatory responses to ammonium starvation that are unique to Y. lipolytica.
4.1.3 Growth rate and lipid accumulation
Disentangling growth-dependent proteome changes during nutrient-limitation from those consequential to lipid accumulation remains a challenge. To explore the relationship between growth rate and lipid accumulation, Poorinmohammad et al. (2022) used chemostat Y. lipolytica cultures at different dilution rates and performed comparative proteomic analysis. They found that lower growth rates often lead to higher lipid yields and observed upregulation of fatty acid synthase (FAS), ACL, and ACC in low growth rate vs. high growth rate conditions. Using a linear modeling approach and comparisons to a non-lipid accumulating strain, they were able to tease out some enzymes that regulate lipid accumulation independent to some extent of growth rate. Outside of PPP, which had been detailed before proteomics studies (Wasylenko et al., 2015), they identified the role of NADPH-producing enzymes formate dehydrogenase (FDH) and isocitrate dehydrogenase (ICDH) in driving lipid biosynthesis. Additionally, downregulation of ER-plasma membrane tethering proteins and upregulation of ER stress proteins (specific targets not provided) suggested the involvement of unfolded protein response (UPR) activation in lipid accumulation. Upregulation of chaperone-mediated autophagy proteins highlighted a possible connection between ER stress, UPR, and selective autophagy in regulating lipid metabolism. Interestingly, they proposed an additional link to oxidative stress according to superoxide dismutase upregulation that may be explained by mitophagy during nitrogen limitation (Venditti and Di Meo, 2020). Lastly, Poorinmohammad et al. observed downregulation of high osmolarity glycerol response 1 (HOG1), a mitogen-activated protein kinase known for its role in osmotic stress, which likely plays a role in lipid homeostasis (Herrero-de-Dios et al., 2020; Poorinmohammad et al., 2022). They knocked out HOG1 which resulted in a 20% increase in lipid production, demonstrating the power of proteomics analysis when paired with chemostat growth studies and metabolic engineering (Poorinmohammad et al., 2022).
4.1.4 Impacts of low-cost carbon sources: plastics and lignocellulosic biomass
Hydrophobic substrate utilization by Y. lipolytica has translated to growing research interest in hybrid processes to upcycle plastic wastes, few of which focus on testing yeast in general (Gluth et al., 2022). Walker et al. (2023) studied proteome changes resulting from cultivation on hydrocarbon-rich oil (C11–C28 alkanes and alkenes) generated from catalytic decomposition of polyethylene. To grow on this toxic substrate, the yeast allocated a substantial portion of its proteome towards expression of alkane-degrading enzymes including cytochrome P450 oxidases, alcohol/aldehyde dehydrogenases, alcohol oxidases, fatty acid ligases, and β-oxidation enzymes. They also noted significant upregulation of an oxysterol-binding protein that may play a role in intracellular hydrocarbon transport (Fukuda, 2023).
In another study, lignocellulosic substrate from hydrolysis of switchgrass was used to compare the proteomes of Y. lipolytica strain W29 to the isolate strain YB420, which unlike the former is capable of growth and lipid production using xylose (Walker et al., 2021). Strain W29 encodes the genes for xylose utilization (xylose reductase, xylitol dehydrogenase, and xylulokinase) (Rodriguez et al., 2016); however, they appear to be “silent,” whereas YB420 upregulated xylitol dehydrogenase, xylulokinase, and PPP enzymes providing NADPH for further xylose assimilation and lipid biosynthesis. As a potential result of redox imbalances, W29 secreted xylitol and degraded lipids as a carbon and energy source in stationary phase.
4.1.5 Thiamine deficiency
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP, the active form of vitamin B1) is a coenzyme required for pyruvate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activity. Y. lipolytica cannot natively synthesize thiamine and its absence leads to a downregulation of proteins in lipid biosynthesis and energy metabolism (particularly ATP synthase) (Walker et al., 2020). Using genomics, the authors identified the missing thiamine biosynthesis protein 13 (THI13) gene and engineered a strain capable of de novo thiamine biosynthesis, which yielded a significant although moderate increase in lipogenesis (~4% vs. ~1% lipid accumulation for the parental strain) in the absence of supplemented thiamine during nitrogen limitation. It follows that all studies using Y. lipolytica listed in Supplementary Table 1 include a source of vitamins—a cost that may not be required for other oleaginous yeast (Nutrition Reviews, 1958).
4.2 Rhodotorula toruloides
Rhodotorula toruloides (formerly Rhodosporidium toruloides) is a model oleaginous basidiomycete yeast with an expansive catalog of studies probing its lipid-accumulating, carotenoid-producing phenotype. Popular oleaginous strains for this yeast include NP11 (haploid derived ultimately from CGMCC 2.1389) (Li et al., 2007; Zhu et al., 2012) and IFO0880 (now NBRC 0880) (Coradetti et al., 2018), both of which naturally utilize xylose for growth and lipid accumulation compared to prominent oleaginous Y. lipolytica strains.
4.2.1 Setting the stage for multi-omics investigations of oleaginicity
In an early seminal multi-omics study, Zhu et al. sequenced the genome of R. toruloides and performed comparative transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of cells cultured under nitrogen-limited conditions (Zhu et al., 2012). They detailed lipid metabolism (including a novel FAS) and repression of TOR1, a negative regulator of autophagy, in R. toruloides under nitrogen-limiting conditions. Consequently, they observed suppression of protein biosynthesis machinery alongside an activation of autophagy-related proteins such as vacuolar proteases and ATPases. Lipid synthesis-related proteins, including key enzymes in fatty acid biosynthesis (ACL1, ACC1, FAS1/2), were elevated when comparing YPD seed cultures to those grown in minimal medium with limited nitrogen. Upon close inspection of their results, abundance changes between the 24 h and 96 h time points in nitrogen-limited minimal medium were in fact minimal (< 2 fold) or insignificant for many enzymes involved in fatty acid synthesis. There were several enzymes in other pathways (e.g., the PPP with GND1 downregulated and ZWF1 upregulated) that were, nevertheless, differentially expressed.
Importantly, their work shows how proteomics provides information about protein expression in organelles, and how said changes in expression may affect their corresponding processes. Zhu et al. noted that a perilipin-like protein (LDP1) was highly expressed during lipid production, suggesting its involvement in lipid droplet stability and formation (Zhu et al., 2012). In a follow-up study, the authors characterized this yeast’s lipid droplet proteome confirming the localization of LDP1, which was indeed upregulated during nitrogen and, separately, phosphate limitation (Zhu et al., 2015). They also observed several metabolic enzymes including GND1 and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase that were localized to the lipid droplet yet not directly involved in lipid metabolism. Additionally, the study found an oxylipin-producing enzyme PpoA, which is involved in hormone-like signaling that may be linked to lipid homeostasis and signaling.
4.2.2 Lipid accumulation induced by phosphate limitation
Some waste streams (e.g., those from food processing, distilleries, and anaerobic digestors) are rich in nitrogenous compounds, necessitating other strategies to induce lipid accumulation. This justified Wang et al.’s novel proteomics investigations of phosphate (inorganic phosphorus source, Pi) limitation (Wang et al., 2018, 2023a). In their first study (Wang et al., 2018), they found that Pi limitation activates the PHO pathway (phosphate homeostasis signaling), which triggers upregulation of Pi transporters, ribosome degradation, and RNA recycling to reclaim phosphate. In addition to key proteins involved in fatty acid biosynthesis, such as ACC1, upregulation of phosphatidate phosphatase and downregulation of DAG kinase routed carbon to lipid accumulation while limiting phospholipid production. Degradation of nucleotides appears to further connect phosphate limitation to lipid accumulation and was demonstrated by upregulation of phosphatases. Pi limitation leads to reduced AMP levels, shifting TCA cycle flux toward citrate accumulation (Figure 5A).
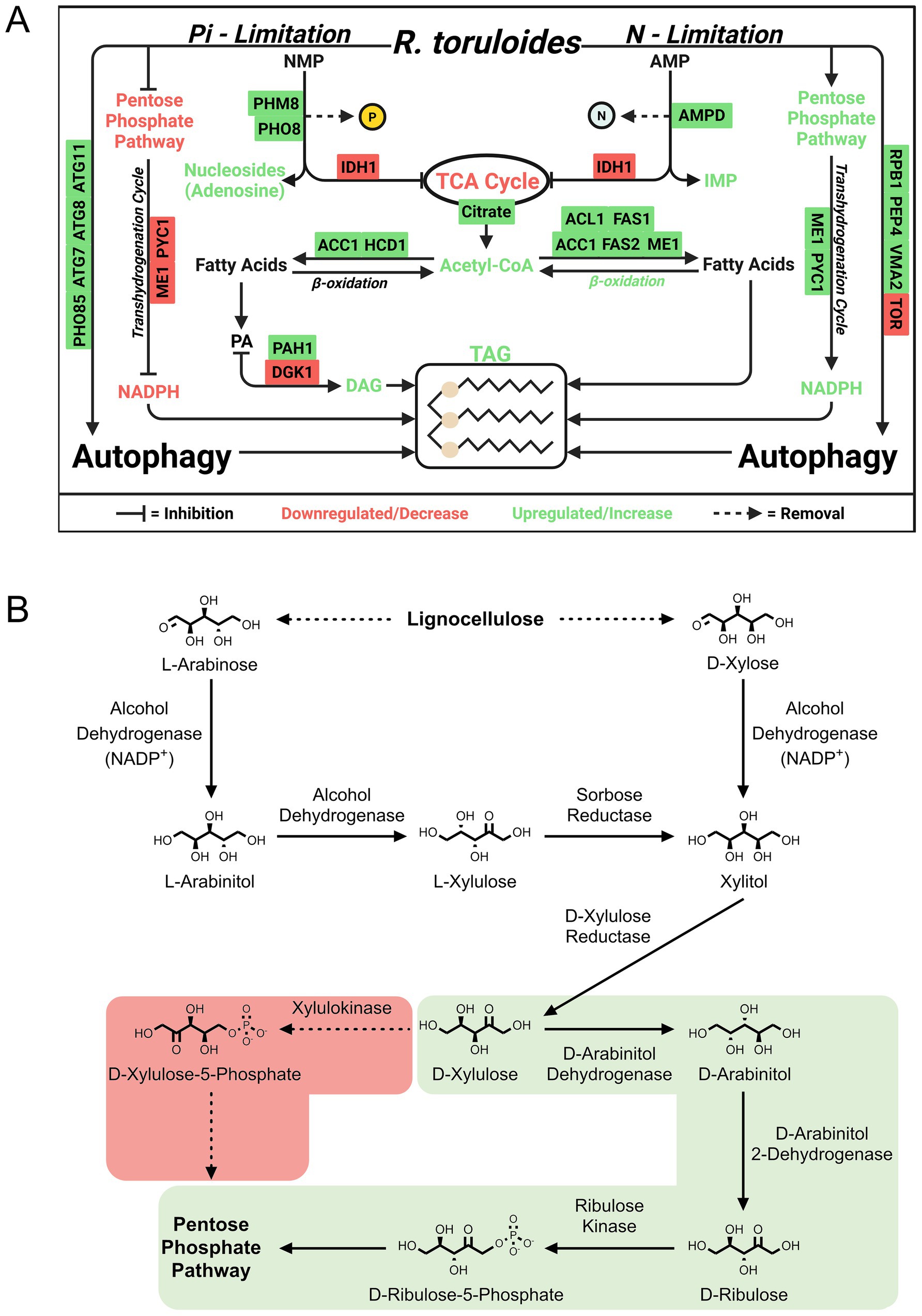
Figure 5. Examples of discoveries in Rhodotorula toruloides using proteomics. (A) Phosphate-limited regulation of lipid accumulation and stress response according to Wang et al. (2018, 2023a). (B) Xylose and arabinose metabolism as annotated by Kim et al. (2021). The light green shading indicates the correct pathway containing the intermediate D-arabinitol. ACC1, Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1; ACL1, ATP citrate lyase 1; AGK1, Acylglycerol kinase 1; AMPD, AMP deaminase; ATG7, Autophagy-related protein 7; ATG8, Autophagy-related protein 8; ATG11, Autophagy-related protein 11; FAS1, Fatty acid synthase subunit beta; FAS2, Fatty acid synthase subunit alpha; HCD1, Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase 1; ME1, Malic enzyme 1; PAH1, Phosphatidate phosphatase 1; PEP4, Proteinase A (vacuolar aspartyl protease); PHM8, Pyrimidine 5′-nucleotidase; PHO8, Vacuolar alkaline phosphatase; PHO85, Cyclin-dependent kinase; PYC1, Pyruvate carboxylase 1; RPB1, RNA polymerase II largest subunit; TOR, Target of rapamycin kinase; VMA2, Vacuolar H+-ATPase subunit B.
In a follow-up study (Wang et al., 2023a), the same group addressed the impacts of Pi limitation on the phosphoproteome, raising important regulatory considerations involving autophagy—rather than the PHO pathway directly. Phosphoregulation of autophagy-related proteins (ATG) is controlled by upstream regulators including TORC1, a nutrient-sensing negative regulator of autophagy and positive regulator of ribosome biogenesis, and SNF1, a positive regulator of autophagy. Because ATG9, an important regulator of autophagosome formation, was upregulated in protein abundance, the authors used RNA interference to silence its expression, which led to a ~ 50% decrease in lipid accumulation. Unfortunately, many of these proteins including TOR1 and ATG9 were not observed in either the global proteome (protein abundances) or phosphoproteome (PTM abundances) results, limiting conclusions that can be drawn about significant changes in protein phosphorylation that are independent of changes in protein abundances.
4.2.3 Metabolic network analysis for lignocellulose-relevant carbon sources
To explore lignocellulosic carbon utilization, which includes appreciable quantities of glucose, xylose, and p-coumaric acid, Kim et al. reconstructed the metabolic network of R. toruloides using transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics data (Kim et al., 2021). Importantly, they employed RB-TDNA sequencing to build a library of mutants to test fitness on these carbon sources. Consistent with a previous report that D-arabinitol was among the main fermentation byproducts from xylose in R. toruloides (Jagtap and Rao, 2018), their findings reveal that R. toruloides employs an alternative xylose utilization pathway in which D-xylulose is converted to D-arabinitol by a reductase and/or arabinitol dehydrogenase and subsequently converted to D-ribulose by a D-arabinitol 2-dehydrogenase (Figure 5B). D-ribulose is converted to D-ribulose-5-phosphate by D-ribulose kinase, which had significant fitness defects in the tested pentose sugar and alcohol media conditions.
A recent study by Alīna et al. used genome-scale metabolic modeling to explore metabolic trade-offs in R. toruloides related to lipid production using different carbon sources (glucose, xylose, and acetate) (Reķēna et al., 2023). They identified a key metabolic route for acetyl-CoA generation via ACL and the phosphoketolase pathway, which produces acetyl-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. This pathway provides an engineering opportunity for carbon-efficient production of acetyl-CoA by bypassing CO2 generation from the pyruvate dehydrogenase step of glycolysis/TCA cycle (Hellgren et al., 2020).
4.2.4 Xylose utilization and oxidative stress
Xylose utilization has been studied quite often in R. toruloides using proteomics. Tiukova et al. (2019) compared glucose vs. xylose-grown cells and observed upregulation of enzymes for xylose assimilation, such as xylitol dehydrogenase and several NADPH-dependent xylose reductases, as expected (Figure 5B). They also highlighted proteins involved in glutathione metabolism, oxidative stress response, and autophagy that were upregulated during nitrogen limitation in both conditions but also for the specific glucose vs. xylose comparison. The study revealed that peroxisomal β-oxidation was more pronounced in cells grown on xylose. Though not explicitly conjectured in their work, it is possible that H2O2 levels as a result of upregulated β-oxidation and competition between antioxidants and xylose reductase for NADPH partially explain those results.
Pinheiro et al. (2020) further investigated the role of oxidative stress on R. toruloides’ xylose metabolism and its role in enhancing lipid and carotenoid production. Oxidative stress, induced by H2O2 and indicated by a resulting upregulation of catalase, led to a marked increase in lipid content due in part to downregulation of fatty acid β-oxidation. They also reported that D-arabinitol was among the main fermentation byproducts, which agrees with an earlier study and raises questions regarding redox cofactor homeostasis because some sugar alcohols may be secreted to regenerate NAD(P)+ (Jagtap and Rao, 2018). Additionally, autophagy pathways and reduced amino acid biosynthesis under nitrogen depletion further enhance lipid accumulation, showing a tight coupling between oxidative stress responses and metabolic shifts during xylose fermentation.
Xylose is the primary constituent from dilute acid hydrolysis of lignocelluse. This and other pretreatment methods release additional compounds like vanillin, an aldehyde constituent of lignin, that are inhibitory and implicated in oxidative stress response in fungi (Kim et al., 2014; Nguyen et al., 2014). Qi et al. (2014) screened mutant strains with enhanced tolerance to sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate and, in a following study, used proteomics to compare the wild-type strain to one of the mutants (Qi et al., 2017). Gene ontology enrichment analysis highlighted distinctions in differential expression of stress response and antioxidant proteins, though the identities of these proteins were not published. Enzymes involved in DNA repair, spliceosome assembly, acetate utilization (e.g., dehydrogenases), and MAPK signaling were upregulated in the mutants. MAPK-related proteins STE20 and SSK2 were highly expressed, perhaps to maintain cell integrity under high-osmolarity hydrolysate cultivation and efficient oxidative phosphorylation by mitigating oxidative stress (Fuchs and Mylonakis, 2009) caused by hydrolysate-derived inhibitors. Interestingly, these proteins are upstream regulators of HOG1 in S. cerevisiae (Raitt et al., 2000)—as discussed above, knocking-out HOG1 in Y. lipolytica increases lipid production (Poorinmohammad et al., 2022). Intriguingly, its role in stress-induced regulation of lipid homeostasis may ultimately be conserved even in unrelated yeast.
Industrially-relevant oleaginous yeast must rapidly assimilate both hexose and pentose sugars derived from low-cost lignocellusic substrates. R. toruloides not only grows slower on xylose than glucose but also exhibits a diauxic shift when switching between these sugars (Wiebe et al., 2012). Coradetti et al. (2023) used proteomics to study diauxic sugar utilization including transport and regulation of carbon catabolite repression, which will help unveil targets to engineer glucose and xylose co-utilizing strains. In their previous study of RB-TDNA mutants discussed above (Coradetti et al., 2018; Kim et al., 2021), mutations in a zinc binuclear cluster transcription factor (RTO4_12978, or PNT1) greatly decreased fitness on pentose sugars. Proteomic analysis of PNT1 overexpression and deletion mutants grown on xylose confirmed the role of PNT1 in regulating xylose assimilation, but also raised some confounding questions regarding PPP regulation (Coradetti et al., 2023). Interestingly, PNT1 overexpression decreases the relative abundance of xylulose phosphoketolase, which breaks down xylulose 5-phosphate to produce acetyl phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. It appears that xylose assimilation regulates how carbon flows through the non-oxidative portion of the PPP—bypassing pyruvate dehydrogenase and the TCA to directly produce acetyl-CoA for fatty acid synthesis or dihydroxyacetone phosphate and other PPP anabolic precursors for phospholipids and nucleosides. Their exemplary work demonstrates how regulons can be deduced from proteomics and strain engineering data, providing unexplored targets for optimizing pentose utilization.
4.3 Other yeasts of biotechnological value
4.3.1 Sophorolipid synthesis
Sophorolipids are glycolipid biosurfactants with antimicrobial properties, making them valuable for acne treatments, eco-friendly cleaning solutions, and other food and health applications (Cho et al., 2022). The oleaginous yeast Starmerella bombicola, isolated from bumblebees, secretes sophorolipids and is a star candidate for metabolic engineering (Roelants et al., 2024). Ciesielska et al. performed two proteomics investigations of sophorolipid synthesis in S. bombicola (Ciesielska et al., 2013, 2014). In the first, they used an auxotrophic strain to perform SILAC-based characterization of exponentially growing cells vs. those producing sophorolipids in stationary phase (Ciesielska et al., 2013). In the first step of sophorolipid biosynthesis, fatty acids are hydroxylated by a membrane-bound cytochrome P450 monooxygenase (Cyp52M1) (Van Bogaert et al., 2009), which was only identified in the stationary growth phase. The authors noted that a heme-binding protein DAP1 was upregulated and may enhance Cyp52M1 activity through stabilization. Other enzymes involved in sophorolipid synthesis like UDP-glucosyltransferases were upregulated (see Figure 6 for full metabolic pathway Roelants et al., 2024). In the stationary phase, oxidative stress defense enzymes and vacuolar proteins were upregulated, while proteins involved in translation were downregulated. In their second secretomics study, Ciesielska et al. (2014) identified an esterase required for the lactonization of secreted sophorolipids and knocked out this enzyme for functional validation, providing another example of how proteomics insights can direct metabolic engineering.
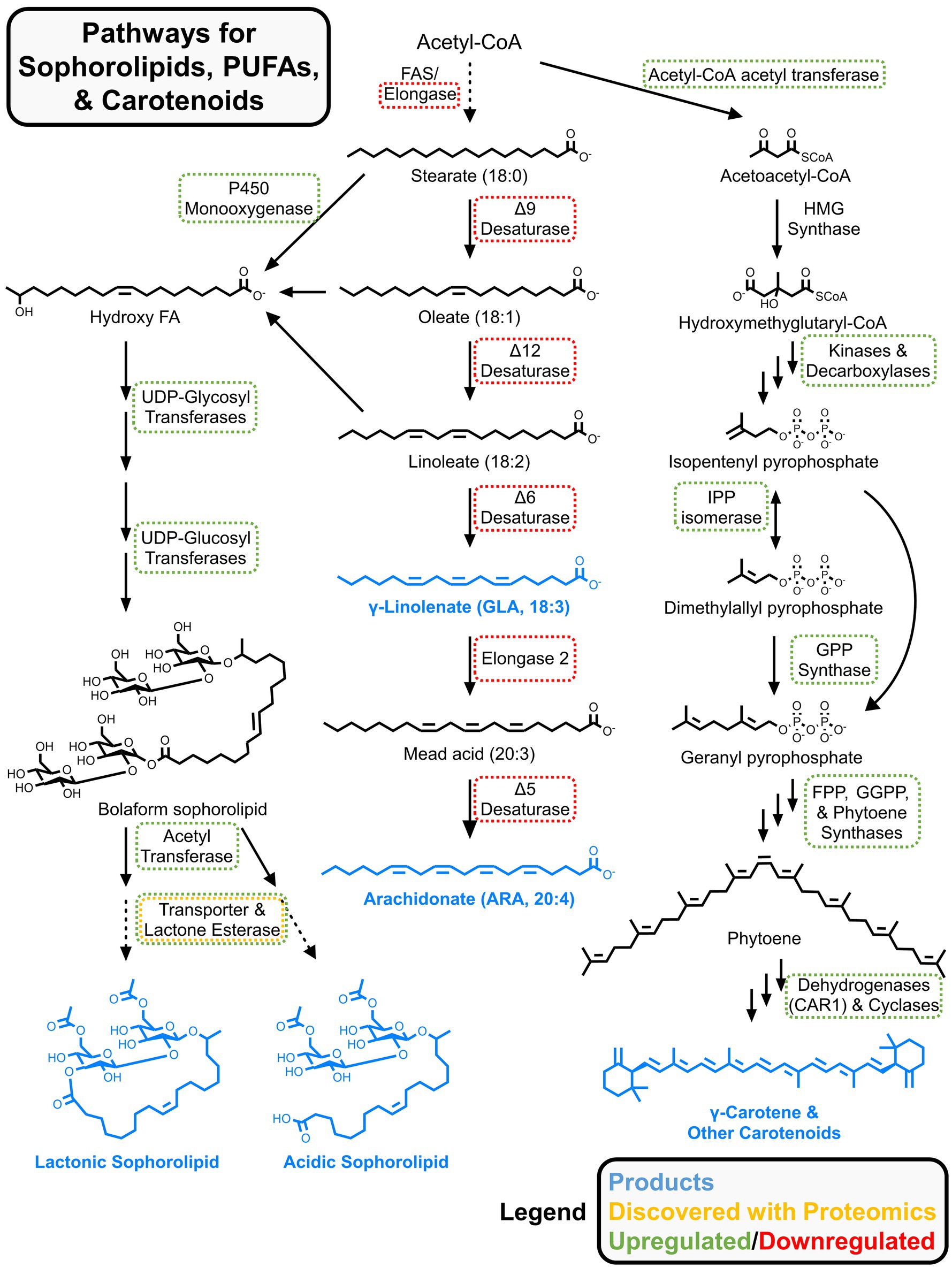
Figure 6. Metabolic pathways for sophorolipids, carotenoids, and omega-3/6 fatty acids. Proteomics results from multiple studies are summarized. Up/downregulated refers to relative changes to protein abundances for nutrient limited vs. rich conditions. Generalized abundance changes were pulled from references in subsection 4.3 (for sophorolipids and carotenoids) and section 5 (for omega-3/6 fatty acids).
4.3.2 Carotenoid synthesis
The Rhodotorula genus includes several carotogenic oleaginous yeast with the characteristic red color, including R. toruloides. The mevalonate pathway is used to produce carotenoids from acetyl-CoA. The first step involves acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase to produce acetoacetyl-CoA, which, together with acetyl-CoA, is condensed to form hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) by the corresponding synthase (Kot et al., 2016; Ochoa-Viñals et al., 2024). Then, HMG-CoA is transformed to mevalonic acid by a specific reductase. Several steps involving a kinase, decarboxylase, isomerase, prenyl transferase, phytoene synthase and desaturase, and cyclases ultimately produce a mix of carotenoids. These include carotenes (α-, β-, and γ-isomers), torulene, and torularhodin (Figure 6).
Although most proteomics studies of oleaginous yeast focus on nitrogen availability, oxygen availability also affects lipid accumulation and carotenoid synthesis (Calvey et al., 2016; Mosqueda-Martínez et al., 2024; Thumkasem et al., 2024). Fakankun et al. employed proteomics to investigate the effects of dual nitrogen and oxygen limitation on lipogenesis and carotenoid production in R. diobovata (Fakankun et al., 2021). Samples were analyzed for the late exponential and early stationary phase at which point carotenoid concentrations began to increase. During early stationary phase, upregulation of malic enzyme and PPP enzymes was observed, but an expected increase in lipid biosynthesis was not, indicating a redirection of reducing equivalents away from fatty acid synthesis. Key enzymes in the mevalonate pathway and carotenoid synthesis including acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase (also known as thiolase), phosphomevalonate kinase, and phytoene dehydrogenase were upregulated suggesting that acetyl-CoA flux was preferentially directed toward carotenoid biosynthesis. Nevertheless, other studies have shown the importance of oxygen availability for carotenoid production (Wang and Yu, 2009; Thumkasem et al., 2024).
Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous (teleomorph of Phaffia rhodozyma) is another oleaginous yeast (Flores-Cotera et al., 2001; Chávez-Cabrera et al., 2010) of biotechnological intrigue for its production of astaxanthin, an antioxidant carotenoid (Martinez-Moya et al., 2011). Martinez-Moya et al. (2015) conducted a proteomic and metabolomic analysis of how this yeast regulates astaxanthin synthesis according to carbon source (glucose or succinate). When succinate is supplied, carotenogenesis is induced during the exponential phase, whereas for glucose it is induced during the stationary phase—demonstrating dependence on not only resource availability over time (e.g., nitrogen) but also carbon source. Their metabolomics results largely follow expectations for carbon source entry points into primary metabolism (glycolysis/PPP for glucose and TCA cycle for succinate). Unfortunately, considerations about how exactly NADPH would be regenerated using succinate (e.g., NADP+ dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase) were not discussed despite its requirement for carotenoid synthesis. Because succinate is transformed into fumarate by succinate dehydrogenase (upregulated in succinate condition; Complex II of the electron transport chain), they propose that respiratory ROS formation is a mechanism by which carotenogenesis is regulated. Though the antioxidant enzyme expression levels do not fully align with this conclusion (e.g., downregulation of peroxiredoxin, TSA2), astaxanthin synthase and cytochrome P450 reductase were significantly upregulated on succinate. This is in addition to phosphoglucomutase, which is involved in trehalose formation and often associated with stress response (Weeks et al., 2006).
4.3.3 Additional important chassis for TAG accumulation
Though most proteomics studies have been conducted on Y. lipolytica and R. toruloides, these are not the only promising lipogenic chassis for metabolic engineering. L. starkeyi and Cutaneotrichosporon oleaginosum (formerly Crytococcus curvatus and Trichosporon oleaginosus) are considered top lipid producers, with both naturally utilizing and in some cases co-utilizing (Gong et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2014; Yu et al., 2014) a variety of biomass-derived carbon sources. Studies using these two yeasts are reviewed in this subsection.
Liu et al. (2011) performed the first timecourse proteomics investigations of oleaginous yeast, including one in which L. starkeyi was cultivated in nitrogen-rich vs. deficient media with a high concentration of glucose (Table 2). Many of the primary metabolic processes (e.g., alternative nitrogen source utilization and protein, amino acid, and nucleic acid turnover) discussed in the previous subsections exhibited changes. Increased lipid production was linked to upregulation of key TCA and transhydrogenase cycle enzymes, including citrate synthase (CIT1) to buildup citrate and route carbon towards fatty acid biosynthesis. Acetyl-CoA carboxylases ACC1 (cytosolic) and HFA1 (mitochondrial) were also upregulated in the late culture stage. Additionally, the drastic upregulation of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (GND2) provides early support for the PPP’s role in supplying NADPH for fatty acid biosynthesis. With this and their earlier study (Liu et al., 2009)—as well as other endeavoring to study protein expression in unconventional microorganisms--it’s evident that having a sequenced and well-annotated genome is crucial for maximizing proteomics’ potential.
Two proteomics research areas related to carbon efficient bioconversion of biomass hydrolysates that have largely been shirked were studied by the Blenner and Brueck labs using C. oleaginosum: lignin-derived aromatics utilization (Yaguchi et al., 2017b; Yaguchi, 2020) and carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZy) for transport and metabolism of mono-, and importantly, disaccharides (Fuchs et al., 2021). Yaguchi harnessed multi-omics and biochemical assays to elucidate catabolic pathways for monoaromatics including phenol, resorcinol, p-hydroxybenzoate, ferulate, and p-coumarate, as well as the yeast’s growth on an alkaline-pretreated corn stover rich in lignin, aromatics, and acetate (Yaguchi, 2020). Yaguchi annotated several transporters, stress response proteins, and metabolic enzymes such as dioxygenases, which perform the ring-cleaving step of aromatics degradation. Fuchs et al. performed a comprehensive proteomics analysis of secreted, cell wall-associated, and cytoplasmatic proteins to uncover enzymes (based on EC, enzyme classes) that cleave and transport dissaccharides (Fuchs et al., 2021). These include various glycoside hydrolases (GH) found in different CAZy database (sub)families; however, it’s unclear if the CAZy database (Levasseur et al., 2013) was specifically used to search their results. Nonetheless, compared to a glucose control, significant differences in the cell-bound and secreted fractions were observed for α-galactosidase, β-galactosidase, β-glucosidase, β-mannosidase and α-amylase as expected under carbon catabolite derepression.
5 Proteomics insights for filamentous fungi
Though fewer compared to studies of oleaginous yeast, proteomics investigations of oleaginous filamentous fungi have revealed important insights regarding stress response and metabolic regulation during nutrient limitation. Mucor circinelloides and Mortierella alpina have been used in these studies due to their ability to produce omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids (Zhang X. et al., 2022). In addition to accumulating TAGs in media with high C: N ratios, M. circinelloides has been primarily investigated for native synthesis of β-carotene and significant quantities of γ-linolenic acid (GLA; ω-6 C18:3) (Fazili et al., 2022b; Wang et al., 2022). It has also been engineered to produce the skin and neurological health-promoting antioxidant astaxanthin from β-carotene (Papp et al., 2006; Hameed et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2021; Adıgüzel and Ülger, 2024). Moreover, M. circinelloides secretes cellulases and hemicellulases to improve carbon utilization from pretreated lignocellulose and potentially reduce the cost of enzymatic saccharification (Wei et al., 2013; Al Mousa et al., 2022a,b).
Mortierella alpina is popular for its ability to produce arachidonic acid (ARA; ω-6 C20:4), and some strains even produce eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; ω-6 20:5) among other economically attractive, bioactive PUFAs (Yamada et al., 1987; Shimiziu et al., 1988; Singh and Ward, 1997; Takeno et al., 2005; Kikukawa et al., 2018; Chang et al., 2022). It is generally regarded as safe with FDA approval for use of its ARA-rich oil in infant formulation (Ratledge et al., 2010; Ryan et al., 2010). For these reasons, proteomics investigations of oleaginous filamentous fungi have focused exclusively on these particular species (Table 2). Overall, these studies highlight the intricate role of autophagy and alterations to central carbon metabolism that are crucial for understanding lipid accumulation.
5.1 Mucor circinelloides
5.1.1 γ-linolenic acid production
The oleaginous M. circinelloides strain WJ11 was isolated and sequenced by Tang et al. Under nitrogen limitation, this strain accumulates ≥ 36% of its CDW as lipids with a ~ 13% GLA content (Tang et al., 2015a, 2015b). GLA is produced via multiple desaturation reactions: stearic acid (C18:0) is converted to oleic acid (C18:1) by Δ9-desaturase and further desaturated to linoleic acid (C18:2) by Δ12-desaturase and, finally, to GLA by Δ6-desaturase (Figure 6) (Zhang Y. et al., 2017). Two proteomics studies were conducted on M. circinelloides WJ11 (Table 1): a time-course experiment in which cultures were sampled at 6 h (exponential phase), 24 h (rapid lipid production phase), and 60 h (stationary phase) (Tang et al., 2016) as well as an experiment comparing M. circinelloides WJ11 to strain CBS 277.49, a low lipid but high carotenoid-producing strain (Tang et al., 2017). In both studies, a modified K & R growth medium (Kendrick and Ratledge, 1992) was used, which contained 80 g/L glucose, 2 g/L diammonium tartrate, 1.5 g/L yeast extract (~80:1 C: N ratio), and other defined nutrients.
In the timecourse experiment, nitrogen limitation generally led to downregulation of the TCA cycle and amino acid biosynthesis (Tang et al., 2016); however, S-adenosylmethionine synthase, which participates in methionine degradation, was upregulated and may provide resources for glutathione synthesis. In a later study using genome-scale metabolic modeling and data integration, methionine degradation was highlighted and recapitulates the importance of sulfur amino acid metabolism during nitrogen-limited stress response (Vongsangnak et al., 2018). In further support of the role of antioxidants during nitrogen limitation, S-formylglutathione hydrolase was upregulated and hydrolyzes S-formylglutathione to restore glutathione that had condensed with formaldehyde. Amino acid degradation, demethylation reactions, and tetrahydrofolate (THF)-dependent pathways can generate formaldehyde (Weimer et al., 1993; Degrassi et al., 1999; Pham et al., 2023). Interestingly, they observed upregulation of the antioxidants peroxiredoxin and glutathione peroxidase, which detoxify peroxides (Pócsi et al., 2004). Strengthening the link between antioxidants and the oleaginous phenotype, peroxiredoxin and catalase were upregulated in strain WJ11 compared to strain CBS 499.25 during nitrogen limitation (Tang et al., 2017). A thiazole biosynthetic enzyme involved in thiamine metabolism (also upregulated in WJ11 compared to CBS 499.25), a 14–3-3 family protein that promotes cell survival by negatively regulating apoptosis, and heat shock proteins for regulating proper protein folding were all upregulated (Tang et al., 2016). These present interesting yet unexplored targets for engineering improved stress response.
Concurrently, pyruvate kinase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, fructose bisphosphate aldolase, and enolase were upregulated in the timecourse experiment of WJ11; these enzymes function at the intersection of the PPP, glycolysis, and lipid synthesis. For instance, enzymes in the PPP were upregulated to generate NADPH—a relationship that had been established prior to proteomics(Zhao et al., 2015; Masi et al., 2021). Nevertheless, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase was upregulated compared to the lower lipid-producing strain CBS 477.25, reinforcing the role of PPP for the oleaginocity (Tang et al., 2017). The expression of ME did not change in both the timecourse experiment and comparative proteomics study (Tang et al., 2016, 2017); however, M. circinelloides contains several isoforms of ME with only one being NADP+-dependent (Song et al., 2001). Because the full set of proteomics data was not published and this enzyme was not listed in the table of presented results, it is unclear which isoform they are referring to (Tang et al., 2016). Moreover, studies of ME overexpression in different strains are conflicting (Zhang et al., 2007; Rodríguez-Frómeta et al., 2013; Fazili et al., 2022a). Two additional insights related to acetyl-CoA flux were gleaned from the comparative proteomics study. Firstly, aldehyde can be produced from pyruvate and converted to acetate by aldehyde dehydrogenase, thereby providing an alternative source of acetyl-CoA: this enzyme was upregulated in WJ11 compared to CBS 277.49. Secondly, degradation of branched-chain amino acids (e.g., leucine) and lysine provides acetyl-CoA: enzymes that degrade these amino acids were upregulated in WJ11 (Tang et al., 2017). As yet another example of proteomics results directing subsequent metabolic engineering studies, Tang et al. overexpressed glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and β-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase in CBS 277.49 leading to as much as a 47 and 73% increase in lipid content, respectively (Tang et al., 2020).
5.2 Mortierella alpina
5.2.1 Arachidonic acid production
In contrast to the conditions used for lipid production in M. circinelloides, ARA production using M. alpina is often conducted via a multistage aging process, during which biomass is first generated in a nutrient-replete environment, followed by a transition (or even transfer of mycelia) to a carbon-deficient environment (Ji et al., 2014). Jin et al. optimized a fed-batch strategy using strain ME-1 to yield as much as 19.8 g/L ARA (Jin et al., 2008). Overall, this process is characterized by long cultivation periods, and proteomics sampling was conducted at extended (~200 h) time points (Table 1). Three similar studies by Yu et al. harnessed this strategy to produce appreciable quantities of ARA (~ 6 g/L) via batch cultivation of strain R807 on 80 g/L glucose, 3 g/L NaNO3, and 10 g/L yeast extract (~20:1 C: N ratio), and other nutrients (Yu et al., 2016, 2017, 2018). In their first study, label-free proteomics was used to study the change of cellular proteins during aging of M. alpina for ARA accumulation, revealing a total of 171 significant proteins that are enriched in ROS response (Yu et al., 2016). Next, the same group quantified changes in the lipid droplet proteome of M. alpina during aging, identifying significant changes in 62 out of the 400 lipid droplet-associated proteins (Yu et al., 2017). In a more recent study, a similar analysis of the lipid droplet proteome, as well as the cellular proteome, was performed to study the impact of two nitrogen sources (KNO3 and urea) on ARA production (Yu et al., 2018).
Comparing a nutrient-rich time point to a later time point during carbon starvation, their proteomics results showed a characteristic shift towards autophagy: enzymes involved in amino acid degradation were upregulated in concert with a minor increase in several amino acids suggesting protein turnover (Yu et al., 2016). An uncharacterized autophagy-related protein and Rab GTPases were observed in the lipid droplet proteome underlining the role of lipid droplet in lipid and protein trafficking (Martin and Parton, 2008; Welte, 2015). As expected, carbohydrate catabolic pathways and fatty acid biosynthesis (e.g., ACC) were also generally suppressed while the PPP exhibited insignificant changes in this study (Yu et al., 2016). Interestingly, a relative increase in PPP and fatty acid biosynthesis enzymes was found when KNO3 was supplemented during aging, which may contribute to the slight though significant increase in ARA (Yu et al., 2018).
During carbon starvation, lipids from the lipid droplets can be mobilized via β-oxidation to provide ATP and acetyl-CoA for TCA cycle anaplerosis (Enkler and Spang, 2024). Accordingly, Yu et al. (2017) observed aggregates of enlarged mitochondria and shrunken lipid droplets, correlating with upregulation of some β-oxidation enzymes (e.g., acetyl-coA synthetase). During aging, two enzymes involved in fructose, sucrose, mannose, and fucose metabolism were upregulated and localized to lipid droplets, supporting an autophagic or energy balancing role of lipid droplets in antioxidant ascorbate metabolism, cell wall remodeling, or recycling amino/nucleotide sugars, glycoproteins, and/or sucrose stores that accumulated during growth (Yu et al., 2017, 2018). Interestingly, one of these enzymes is GDP-keto-6-deoxymannose 3,5-epimerase/4-reductase that uses either NADH or NADPH (Ren et al., 2010). In the cellular proteome, the abundances and measured enzymatic activities for NADP+-dependent ME decreased while ICDH increased, suggesting a repressed transhydrogenase cycle and activity of an alternative cytoplasmic NADPH-generating shuttle to supply reducing power for fatty acid biosynthesis and antioxidant defense (Tang et al., 2021). Though a thorough explanation is absent, it’s curious that glutathione metabolism was significantly downregulated according to KEGG pathway analysis, and that they noted a drastic increase in ROS during aging according to an assay using a fluorogenic probe (Yu et al., 2017).
5.2.2 Nitrogen limitation-induced resource reallocation
Lu et al. investigated the response of M. alpina to nitrogen limitation using an integrated lipidomics, metabolomics, and proteomics approach (Lu et al., 2020). They cultured M. alpina strain ATCC 32222 under nitrogen limitation with a medium containing 30.0 g/L glucose, 2.0 g/L diammonium tartrate, and 1.5 g/L yeast extract (~30 C: N ratio) and observed a drop in ARA and TAG accumulation. Enzymes and the corresponding glycolytic metabolites were downregulated during nitrogen limitation, whereas TCA cycle enzymes were generally downregulated with a concomitant accumulation of citrate. ME was downregulated while ACL and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase were upregulated, providing a route from citrate to phosphoenolpyruvate to feed gluconeogenesis. Though they do not explicitly report the expression levels of FAS1/2 nor ACC, they conclude that TAG accumulation was a consequence of resource reallocation, rather than an upregulation of fatty acid biosynthesis enzymes. This is a reasonable conclusion given that succinate increased up to the 144 h time point, paralleling an increase in succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase and glutamate decarboxylase of the GABA shunt, which provides a TCA cycle entry point for autophagy-derived carbon. According to their lipidomics and proteomics results, an increase in TAGs may be additionally explained by upregulation of phospholipases C and D, which convert phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine into precursor DAGs.
The relative quantities of proteins, peptides, amino acids, and a plethora of other nitrogenous compounds decreased during nitrogen limitation (Lu et al., 2020). This is corroborated by an increase in ubiquitin-proteasome system components, including 26S proteasome subunits and ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1 during the early stages of nitrogen deprivation. The importance of autophagic processes are further highlighted by an increase in autophagy-related proteins, vacuolar components, and peroxisomal enzymes—including a catalase that detoxifies H2O2 generated as a byproduct of β-oxidation, which was upregulated during nitrogen limitation. Autophagic processes are negatively regulated by TOR (Wang et al., 2023b) in nutrient-rich environments: in their results, a homolog of mammalian TOR decreased in abundance over time. A regulatory link between autophagy and lipid metabolism has been established but little is known in oleaginous filamentous fungi (Singh et al., 2009). Excitingly, in a follow-up study, they harnessed their proteomics insights to delve into autophagy-regulated lipid metabolism: they showed that overexpression of autophagy-related gene 8 (ATG8) increased fatty acid biosynthesis by ~10% (Lu et al., 2022).
6 Cross-species patterns in proteomic signatures of lipogenesis
Across species like Yarrowia lipolytica, Rhodotorula toruloides, and Mucor circinelloides, differential expression of key lipid biosynthesis enzymes—ATP citrate lyase (ACL), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), and/or fatty acid synthase (FAS)—is a common signature under nutrient limitation (Zhu et al., 2012; Pomraning et al., 2016; Tang et al., 2017). Lipid droplet-associated proteins, such as the perilipin-like proteins OIL1 in Y. lipolytica (Bhutada et al., 2018) and LDP1 in R. toruloides (Zhu et al., 2015), are consistently upregulated, suggesting a conserved role in regulating lipid droplets and storage lipids. Differential expression of autophagy-related proteins, including ATG8 and ATG9 which are discussed in studies of R. toruloides (Wang et al., 2023a) and Mortierella alpina (Lu et al., 2020), also suggests resource recycling as a universal stress response to nutrient limitation. In addition, some components of autophagy-regulated lipid metabolism are conserved (Wang et al., 2023b), including the AMP deaminase-isocitrate dehydrogenase (ICDH)-citrate axis that reroutes carbon to lipid biosynthesis under nitrogen limitation. Phosphoregulation of ACL and ACC is another shared feature, though specific phosphorylation sites may differ (Pomraning et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2023a).
The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) is a major source of NADPH across fungi. There are additional species-specific sources like NADP+-dependent ICDH in Y. lipolytica and malic enzyme in R. toruloides and M. circinelloides (Ratledge, 2014). Of course, differing NADPH requirements and regeneration reactions may explain differences in protein expression for the corresponding pathways in central carbon metabolism. However, this is difficult to evaluate without a detailed phyloproteomics investigation or, preferably, direct comparisons within sample sets analyzed using the same proteomics workflow. In addition to fatty acid synthesis, NADPH is required for antioxidant defense against pro-oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide. This and other reactive oxygen species are readily generated during respiration, as a byproduct of purine and amino acid scavenging, as well as β-oxidation (Sibirny, 2016; Picazo and Molin, 2021; Mattila et al., 2022). Though the number and types of antioxidant proteins differ among fungi (Mattila et al., 2022), a link between starvation stress response and redox systems was pronounced for many of the studies reviewed herein. In a recent publication, a multi-PTM proteomics and lipidomics approach was used to reveal that nitrogen limitation in R. toruloides drives widespread changes in protein thiol oxidation and phosphorylation for stress response signaling, metabolic pathways, and autophagy (Gluth et al., 2025).
7 Discussion
MS-based proteomics can quantify thousands of proteins (and modifications to them) in parallel, thereby revealing key cellular pathways that culminate in a specific phenotype. In this review, we demonstrate the power of proteomics for characterizing molecular events that drive oleochemical production in oleaginous fungi. Applications of proteomics in oleaginous fungi in the last decade has pointed to the role of multiple pathways/processes governing oleaginicity including signaling pathways (TOR, AMPK, MAPK, etc.), redox balance (including antioxidant defense), autophagy, nitrogen metabolism (especially pertaining to branched chain amino acids, asparagine and the urea cycle, and purine degradation), transport, cellular trafficking, and energy homeostasis. Comparative proteomics has also identified proteins that can be used as engineering targets to improve lipid content. In addition, subcellular proteomics of lipid droplets has revealed this organelle’s multifaceted role in energy and redox homeostasis as well as stress response (Jarc and Petan, 2019)—even identifying the associated proteins that regulate access to its carbon stores (Zhu et al., 2015; Bhutada et al., 2018).
Even though this review is comprehensive, we were challenged by the fact that oleaginocity is generally strain-dependent (Salvador López et al., 2022), may involve nuances that are not completely conserved or well-annotated, is not represented solely by storage lipids (TAGs) as the primary oleochemical product, and is not always the focus of proteomics investigations. There are studies of oleaginous fungi that were not included here because (1) “oleaginous” was not explicitly mentioned in the study (Martinez-Moya et al., 2020), (2) conditions conducive to lipid production were not studied or oleochemicals were not the focus (Morín et al., 2007; Mansour et al., 2009; Swennen et al., 2010; Navarro et al., 2013; Celińska et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2015; Zhang H. et al., 2017; da Silva et al., 2020; Sekova et al., 2021; Li X. et al., 2022), and/or (3) it is unclear if the strain in question is indeed oleaginous. For instance, some strains of Aspergillus and Geotrichum species are oleaginous, yet their proteomes have not been investigated for lipogenic conditions (Thammarongtham et al., 2018; Grygier et al., 2019; Srinivasan et al., 2022; Kamilari et al., 2023; Hassane et al., 2024). Another example is the yeast Debaryomyces hansenii, which has been studied for its halophilic behavior and could potentially reduce the demand for fresh water during lipid production (Yaguchi et al., 2017a; Navarrete et al., 2022).
The proteomics field is still progressing along with the appropriate and relevant applications. Proteomics data sharing is of great importance for cross-study comparisons and is gradually improving (Shome et al., 2024); however, some of the studies reviewed herein do not have accompanying (or well-annotated and organized) datasets, which severely mars the interpretation of results and stymies a phyloproteomics investigation of carbon storage evolution in fungi. Moreover, some do not explicitly include details for their bioinformatics approaches or erroneously compare intensity values among different proteins despite not using an approach for absolute quantification (Ankney et al., 2018). This raises an intriguing opportunity, though: targeted proteomics, in which libraries of peptide standards are used for absolute quantification of proteins, has also not been applied to oleaginous fungi. Overall, integrating proteomics data into genome-scale metabolic models (GEMs) will be essential for predictive design, and future work should prioritize absolute quantification to support accurate kinetic modeling. Quantitative proteomics can refine enzyme-constrained models and improve flux balance predictions (Tang et al., 2017; Kim et al., 2021). Furthermore, incorporating absolute enzyme quantities with metabolomics data would provide valuable inputs to construct highly accurate metabolic models and engineer optimal lipid production (Yunus and Lee, 2022). Artificial Intelligence / Machine Learning (AI/ML) can analyze large proteomic datasets to predict protein functions, interactions, and regulatory networks (Li F. et al., 2022; Smith et al., 2022). For oleaginous fungi, AI/ML could identify novel lipid biosynthesis regulators by integrating proteomics with transcriptomics and metabolomics (Ballard et al., 2024).
Several newer proteomics strategies have yet to be explored in oleaginous fungi but could significantly improve the scalability needed for large-scale studies and the resolution required for investigations that, for example, aim to characterize how different populations of yeast cells respond to the microenvironments which are present even in well-mixed bioreactors (Boswell et al., 2003). Regarding the former, data-independent acquisition (DIA) is an emerging technique for label-free quantification and has yet to be applied for proteomics investigations of oleaginous fungi, even though cost savings could be realized by avoiding expensive mass tags and the throughput of modern LC–MS/MS systems has been rapidly improving. Single-cell proteomics is another emerging frontier in systems biology that will enable dissection of cell-to-cell heterogeneity in lipid accumulation (Shuken, 2023), particularly relevant for filamentous fungi, where hyphal differentiation may lead to varied lipogenic capacities within a culture. This approach could uncover cell-specific proteomic signatures in Y. lipolytica or R. toruloides under nutrient limitation, identifying subpopulations optimized for lipid accumulation. For example, single-cell proteomics could elucidate why certain cells within a culture exhibit higher TAG storage. Techniques such as SCoPE-MS and NanoPOTS offer new possibilities for such investigations (Budnik et al., 2018; Zhu et al., 2018; Martin et al., 2021).
Looking forward, the burgeoning application of proteomics in synthetic biology is rife with opportunity. Frequently, the rationale for single-cell oil production is tied to the valorization of low-cost organic wastes, especially lignocellulosic feedstocks. However, there are surprisingly few proteomics studies of the fungal oleaginous phenotype using these complex substrates and scaled-up cultivations (> 5 L). Thus, one direction for future studies would be the analysis of dynamic carbon utilization under bioprocessing-relevant scenarios with engineered vs. wildtype strains. There are currently no metaproteomics studies of oleaginous fungi co-cultured with carbon- and/or nitrogen-fixing microorganisms (algae, cyanobacteria, azitobacter, etc.) (Bohutskyi et al., 2024). Additionally, the few quantitative proteomics investigations of PTMs have focused exclusively on phosphorylation, even though methylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, and cysteine oxidation (redox proteomics) also regulate protein function, proteasomal processing, signaling pathways, and transcriptional programs (Tripodi et al., 2015; Šoštarić and van Noort, 2021). For instance, the OIL1 protein of Y. lipolytica protects the lipid droplet from being accessed by lipases—it is ubiquitinated (Bhutada et al., 2018), raising the question of how much oleaginocity is regulated by the PTMome vs. changes to enzyme abundances. Indeed, this conclusion was reached in a recent publication that describes a novel proteomics approach for profiling multiple types of PTMs (Table 2), specifically protein cysteine oxidation and phosphorylation (Gluth et al., 2025). Protein structure confers function; thus, with sophisticated algorithms to link PTM dynamics to protein structural changes at the proteome level, one can envision substantial improvements to metabolic modeling approaches (i.e., more accurate predictions of kcat values) (Li F. et al., 2022; Smith et al., 2022).
Finally, we recommend integrating multi-omics approaches into the field of oleochemicals production and encourage multi-institutional collaborations to actualize this goal in the near future. It is imperative that we understand how genetic/metabolic engineering affects biological systems as a whole—especially during the multi-phase, stress-induced fermentations that are applied for oleochemicals production. Employing automated workflows (Gluth et al., 2024, 2025) to screen various engineered and wildtype strains over time and in different conditions will provide a wealth of phenotypic data (i.e., growth, lipid production, etc.) that can be paired with proteomics (including PTMs), transcriptomics, metabolomics, and lipidomics data. Together, these data will facilitate the training of AI/ML models to help us connect phenotypes with the underlying molecular mechanisms. This data can then be leveraged to guide genetic/metabolic engineering strategies for targeted phenotypes (i.e., lipid overproduction). The era defined by integrative multi-omics modeling approaches to direct unintuitive metabolic engineering ventures is upon us.
Author contributions
AG: Data curation, Visualization, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JBT: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JJC: Writing – review & editing, Visualization. SD: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. W-JQ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. BY: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. TZ: Project administration, Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Resources, Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors thank the Predictive Phenomics Initiative (PPI) at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) for funding. A portion of the research was performed on a project award from the Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory, a DOE Office of Science User Facility sponsored by the Biological and Environmental Research program under Contract No. DE-AC05-76RL01830. AG was supported by the PNNL-Washington State University (WSU) Distinguished Graduate Research Program (DGRP) Fellowship. The research described in this paper is part of the Predictive Phenomics Initiative at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory and conducted under the Laboratory Directed Research and Development Program.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Zhangyang Xu (PNNL) for helpful discussions. Portions of the Figures 1–5 were created with Biorender.com.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1637123/full#supplementary-material
References
Abdel-Mawgoud, A. M., Markham, K. A., Palmer, C. M., Liu, N., Stephanopoulos, G., and Alper, H. S. (2018). Metabolic engineering in the host Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab. Eng. 50, 192–208. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2018.07.016
Abeln, F., and Chuck, C. J. (2021). The history, state of the art and future prospects for oleaginous yeast research. Microb. Cell Factories 20:221. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01712-1
Adıgüzel, E., and Ülger, T. G. (2024). A marine-derived antioxidant astaxanthin as a potential neuroprotective and neurotherapeutic agent: a review of its efficacy on neurodegenerative conditions. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 977:176706. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176706
Adrio, J. L. (2017). Oleaginous yeasts: promising platforms for the production of oleochemicals and biofuels. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 114, 1915–1920. doi: 10.1002/bit.26337
Aebersold, R., and Goodlett, D. R. (2001). Mass spectrometry in proteomics. Chem. Rev. 101, 269–296. doi: 10.1021/cr990076h
Aebersold, R., and Mann, M. (2003). Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature 422, 198–207. doi: 10.1038/nature01511
Al Mousa, A. A., Abo-Dahab, N. F., Hassane, A. M. A., Gomaa, A. E.-R. F., Aljuriss, J. A., and Dahmash, N. D. (2022a). Harnessing Mucor spp. for Xylanase production: statistical optimization in submerged fermentation using agro-industrial wastes. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022:3816010. doi: 10.1155/2022/3816010
Al Mousa, A. A., Hassane, A. M. A., Gomaa, A. E.-R. F., Aljuriss, J. A., Dahmash, N. D., and Abo-Dahab, N. F. (2022b). Response-surface statistical optimization of submerged fermentation for pectinase and cellulase production by Mucor circinelloides and M. hiemalis. Fermentation 8:205. doi: 10.3390/fermentation8050205
Alhattab, M., Moorthy, L. S., Patel, D., Franco, C. M. M., and Puri, M. (2024). Oleaginous microbial lipids’ potential in the prevention and treatment of neurological disorders. Mar. Drugs 22:80. doi: 10.3390/md22020080
Ankney, J. A., Muneer, A., and Chen, X. (2018). Relative and absolute quantitation in mass spectrometry–based proteomics. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 11, 49–77. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-061516-045357
Athenstaedt, K. (2019). “Nonpolar lipids in yeast: synthesis, storage, and degradation” in Biogenesis of fatty acids, lipids and membranes. ed. O. Geiger (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 363–373.
Athenstaedt, K., Jolivet, P., Boulard, C., Zivy, M., Negroni, L., Nicaud, J.-M., et al. (2006). Lipid particle composition of the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica depends on the carbon source. Proteomics 6, 1450–1459. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200500339
Awad, D., and Brueck, T. (2020). Optimization of protein isolation by proteomic qualification from Cutaneotrichosporon oleaginosus. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 412, 449–462. doi: 10.1007/s00216-019-02254-7
Ayadi, I., Belghith, H., Gargouri, A., and Guerfali, M. (2018). Screening of new oleaginous yeasts for single cell oil production, hydrolytic potential exploitation and agro-industrial by-products valorization. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 119, 104–114. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2018.07.012
Ballard, J. L., Wang, Z., Li, W., Shen, L., and Long, Q. (2024). Deep learning-based approaches for multi-omics data integration and analysis. BioData Min. 17:38. doi: 10.1186/s13040-024-00391-z
Banerjee, S., and Singh, V. (2024). Economic and environmental bottlenecks in the industrial-scale production of lipid-derived biofuels from oleaginous yeasts: a review of the current trends and future prospects. GCB Bioenergy 16:e13173. doi: 10.1111/gcbb.13173
Beopoulos, A., Nicaud, J.-M., and Gaillardin, C. (2011). An overview of lipid metabolism in yeasts and its impact on biotechnological processes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 90, 1193–1206. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3212-8
Bhatt, A. H., Zhang, Y., Davis, R., Heath, G., and Ravi, V. (2022). Biorefinery upgrading of herbaceous biomass to renewable hydrocarbon fuels, part 2: air pollutant emissions and permitting implications. J. Clean. Prod. 362:132409. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132409
Bhutada, G., Kavšček, M., Hofer, F., Gogg-Fassolter, G., Schweiger, M., Darnhofer, B., et al. (2018). Characterization of a lipid droplet protein from Yarrowia lipolytica that is required for its oleaginous phenotype. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1863, 1193–1205. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.07.010
Bioenergy Technologies Office. (2024). 2023 billion-ton report: An assessment of U.S. renewable carbon resources. United States. Available online at: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/2335461 (Accessed December 1, 2024).
Blomqvist, J., Pickova, J., Tilami, S. K., Sampels, S., Mikkelsen, N., Brandenburg, J., et al. (2018). Oleaginous yeast as a component in fish feed. Sci. Rep. 8:15945. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34232-x
Bohutskyi, P., Pomraning, K. R., Jenkins, J. P., Kim, Y.-M., Poirier, B. C., Betenbaugh, M. J., et al. (2024). Mixed and membrane-separated culturing of synthetic cyanobacteria-yeast consortia reveals metabolic cross-talk mimicking natural cyanolichens. Sci. Rep. 14:25303. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74743-4
Boswell, C. D., Nienow, A. W., Gill, N. K., Kocharunchitt, S., and Hewitt, C. J. (2003). The impact of fluid mechanical stress on Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells during continuous cultivation in an agitated, aerated bioreactor; its implication for mixing in the brewing process and aerobic fermentations. Food Bioprod. Process. 81, 23–32. doi: 10.1205/096030803765208634
Botham, P. A., and Ratledge, C. (1979). A biochemical explanation for lipid accumulation in Candida 107 and other oleaginous Micro-organisms. Microbiology 114, 361–375. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-361
Bouchez, I., Pouteaux, M., Canonge, M., Genet, M., Chardot, T., Guillot, A., et al. (2015). Regulation of lipid droplet dynamics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae depends on the Rab7-like Ypt7p, HOPS complex and V1-ATPase. Biol. Open 4, 764–775. doi: 10.1242/bio.20148615
Bracharz, F., Beukhout, T., Mehlmer, N., and Brück, T. (2017). Opportunities and challenges in the development of Cutaneotrichosporon oleaginosus ATCC 20509 as a new cell factory for custom tailored microbial oils. Microb. Cell Factories 16:791. doi: 10.1186/s12934-017-0791-9
Brunel, M., Burkina, V., Pickova, J., Sampels, S., and Moazzami, A. A. (2022). Oleaginous yeast Rhodotorula toruloides biomass effect on the metabolism of Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus). Front. Mol. Biosci. 9:931946. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.931946
Brunel, M., Burkina, V., Sampels, S., Dahlberg, A. K., Passoth, V., and Pickova, J. (2024). Biomass of the oleaginous yeast Rhodotorula toruloides as feed ingredient in the diet of Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus): impact on quality; safety and sensory outcome. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. Anim. Sci. 73, 1–13. doi: 10.1080/09064702.2024.2322145
Budnik, B., Levy, E., Harmange, G., and Slavov, N. (2018). SCoPE-MS: mass spectrometry of single mammalian cells quantifies proteome heterogeneity during cell differentiation. Genome Biol. 19:161. doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1547-5
Calvey, C. H., Su, Y.-K., Willis, L. B., McGee, M., and Jeffries, T. W. (2016). Nitrogen limitation, oxygen limitation, and lipid accumulation in Lipomyces starkeyi. Bioresour. Technol. 200, 780–788. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.10.104
Celińska, E., Olkowicz, M., and Grajek, W. (2015). L-phenylalanine catabolism and 2-phenylethanol synthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica—mapping molecular identities through whole-proteome quantitative mass spectrometry analysis. FEMS Yeast Res. 15:fov041. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/fov041
Chang, L., Lu, H., Chen, H., Tang, X., Zhao, J., Zhang, H., et al. (2022). Lipid metabolism research in oleaginous fungus Mortierella alpina: current progress and future prospects. Biotechnol. Adv. 54:107794. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107794
Chávez-Cabrera, C., Flores-Bustamante, Z. R., Marsch, R., Montes, M. d. C., Sánchez, S., Cancino-Díaz, J. C., et al. (2010). ATP-citrate lyase activity and carotenoid production in batch cultures of Phaffia rhodozyma under nitrogen-limited and nonlimited conditions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 85, 1953–1960. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2271-6
Cheirsilp, B., Kitcha, S., and Torpee, S. (2012). Co-culture of an oleaginous yeast Rhodotorula glutinis and a microalga Chlorella vulgaris for biomass and lipid production using pure and crude glycerol as a sole carbon source. Ann. Microbiol. 62, 987–993. doi: 10.1007/s13213-011-0338-y
Cho, W. Y., Ng, J. F., Yap, W. H., and Goh, B. H. (2022). Sophorolipids—bio-based antimicrobial formulating agents for applications in food and health. Molecules 27:5556. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175556
Chopra, J., Tiwari, B. R., Dubey, B. K., and Sen, R. (2020). Environmental impact analysis of oleaginous yeast based biodiesel and bio-crude production by life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 271:122349. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122349
Ciesielska, K., Li, B., Groeneboer, S., Van Bogaert, I., Lin, Y.-C., Soetaert, W., et al. (2013). SILAC-based proteome analysis of Starmerella bombicola Sophorolipid production. J. Proteome Res. 12, 4376–4392. doi: 10.1021/pr400392a
Ciesielska, K., Van Bogaert, I. N., Chevineau, S., Li, B., Groeneboer, S., Soetaert, W., et al. (2014). Exoproteome analysis of Starmerella bombicola results in the discovery of an esterase required for lactonization of sophorolipids. J. Proteome 98, 159–174. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.12.026
Collett, J. R., Meyer, P. A., and Jones, S. B. (2014). Preliminary economics for hydrocarbon fuel production from cellulosic sugars. Richland, WA: U.S. Department of Energy. PNNL-23374.
Coradetti, S. T., Adamczyk, P. A., Liu, D., Gao, Y., Otoupal, P. B., Geiselman, G. M., et al. (2023). Engineering transcriptional regulation of pentose metabolism in Rhodosporidium toruloides for improved conversion of xylose to bioproducts. Microb. Cell Factories 22:144. doi: 10.1186/s12934-023-02148-5
Coradetti, S. T., Pinel, D., Geiselman, G. M., Ito, M., Mondo, S. J., Reilly, M. C., et al. (2018). Functional genomics of lipid metabolism in the oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides. eLife 7:e32110. doi: 10.7554/eLife.32110
Cox, J., and Mann, M. (2011). Quantitative, high-resolution proteomics for data-driven systems biology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 80, 273–299. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-061308-093216
Craft, D. L., Madduri, K. M., Eshoo, M., and Wilson, C. R. (2003). Identification and characterization of the CYP52 family of Candida tropicalis ATCC 20336, important for the conversion of fatty acids and alkanes to α,ω-dicarboxylic acids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69, 5983–5991. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.10.5983-5991.2003
Czajka, J. J., Han, Y., Kim, J., Mondo, S. J., Hofstad, B. A., Robles, A., et al. (2024). Genome-scale model development and genomic sequencing of the oleaginous clade Lipomyces. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 12:1356551. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1356551
da Silva, L. V., Coelho, M. A. Z., da Silva, M. R. S., and Amaral, P. F. F. (2020). Investigation of mitochondrial protein expression profiles of Yarrowia lipolytica in response to citric acid production. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 43, 1703–1715. doi: 10.1007/s00449-020-02363-z
Davis, R., Bhatt, A. H., Zhang, Y., Tan, E. C. D., Ravi, V., and Heath, G. (2022). Biorefinery upgrading of herbaceous biomass to renewable hydrocarbon fuels, part 1: process modeling and mass balance analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 362:132439. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132439
Degrassi, G., Uotila, L., Klima, R., and Venturi, V. (1999). Purification and properties of an esterase from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and identification of the encoding gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65, 3470–3472. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.8.3470-3472.1999
Dupree, E. J., Jayathirtha, M., Yorkey, H., Mihasan, M., Petre, B. A., and Darie, C. C. (2020). A critical review of bottom-up proteomics: the good, the bad, and the future of this field. Proteomes 8:14. doi: 10.3390/proteomes8030014
Dzurendova, S., Zimmermann, B., Kohler, A., Reitzel, K., Nielsen, U. G., Dupuy--Galet, B. X., et al. (2021). Calcium affects polyphosphate and lipid accumulation in Mucoromycota fungi. J. Fungi 7:300. doi: 10.3390/jof7040300
Enkler, L., and Spang, A. (2024). Functional interplay of lipid droplets and mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 598, 1235–1251. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14809
Evans, C. T., and Ratledge, C. (1985a). Possible regulatory roles of ATP:citrate lyase, malic enzyme, and AMP deaminase in lipid accumulation by Rhodosporidium toruloides CBS 14. Can. J. Microbiol. 31, 1000–1005. doi: 10.1139/m85-189
Evans, C. T., and Ratledge, C. (1985b). The physiological significance of citric acid in the control of metabolism in lipid-accumulating yeasts. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 3, 349–376. doi: 10.1080/02648725.1985.10647818
Fakankun, I., Spicer, V., and Levin, D. B. (2021). Proteomic analyses of the oleaginous and carotenogenic yeast Rhodotorula diobovata across growth phases under nitrogen- and oxygen-limited conditions. J. Biotechnol. 332, 11–19. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2021.03.016
Fazili, A. B. A., Shah, A. M., Albeshr, M. F., Naz, T., Dar, M. A., Yang, W., et al. (2022a). Overexpression of the mitochondrial malic enzyme genes (malC and malD) improved the lipid accumulation in Mucor circinelloides WJ11. Front. Microbiol. 13:919364. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.919364
Fazili, A. B. A., Shah, A. M., Zan, X., Naz, T., Nosheen, S., Nazir, Y., et al. (2022b). Mucor circinelloides: a model organism for oleaginous fungi and its potential applications in bioactive lipid production. Microb. Cell Factories 21:29. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01758-9
Flores-Cotera, L. B., Martín, R., and Sánchez, S. (2001). Citrate, a possible precursor of astaxanthin in Phaffia rhodozyma: influence of varying levels of ammonium, phosphate and citrate in a chemically defined medium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 55, 341–347. doi: 10.1007/s002530000498
Fuchs, T., Melcher, F., Rerop, Z. S., Lorenzen, J., Shaigani, P., Awad, D., et al. (2021). Identifying carbohydrate-active enzymes of Cutaneotrichosporon oleaginosus using systems biology. Microb. Cell Factories 20:205. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01692-2
Fuchs, B. B., and Mylonakis, E. (2009). Our paths might cross: the role of the fungal Cell Wall integrity pathway in stress response and cross talk with other stress response pathways. Eukaryot. Cell 8, 1616–1625. doi: 10.1128/EC.00193-09
Fukuda, R. (2023). Utilization of n-alkane and roles of lipid transfer proteins in Yarrowia lipolytica. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 39:97. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03541-3
Gill, C. O., Hall, M. J., and Ratledge, C. (1977). Lipid accumulation in an oleaginous yeast (Candida 107) growing on glucose in single-stage continuous culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 33, 231–239. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.231-239.1977
Gluth, A., Czajka, J. J., Li, X., Bloodsworth, K. J., Eder, J. G., Kyle, J. E., et al. (2025). Nitrogen limitation causes a seismic shift in redox state and phosphorylation of proteins implicated in carbon flux and lipidome remodeling in Rhodotorula toruloides. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 18:80. doi: 10.1186/s13068-025-02657-y
Gluth, A., Li, X., Gritsenko, M. A., Gaffrey, M. J., Kim, D. N., Lalli, P. M., et al. (2024). Integrative multi-PTM proteomics reveals dynamic global, redox, phosphorylation, and acetylation regulation in cytokine-treated pancreatic Beta cells. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 23:100881. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2024.100881
Gluth, A., Xu, Z., Fifield, L. S., and Yang, B. (2022). Advancing biological processing for valorization of plastic wastes. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 170:112966. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2022.112966
Gong, Z., Wang, Q., Shen, H., Hu, C., Jin, G., and Zhao, Z. K. (2012). Co-fermentation of cellobiose and xylose by Lipomyces starkeyi for lipid production. Bioresour. Technol. 117, 20–24. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.04.063
Granger, L. M., Perlot, P., Goma, G., and Pareilleux, A. (1993). Effect of various nutrient limitations on fatty acid production by Rhodotorula glutinis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 38, 784–789. doi: 10.1007/BF00167145
Grygier, A., Myszka, K., Szwengiel, A., Stuper-Szablewska, K., Pawlicka-Kaczorowska, J., Chwatko, G., et al. (2019). Production of bioactive compounds by food associated Galactomyces geotrichum 38, as determined by proteome analysis. Nutrients 11:471. doi: 10.3390/nu11020471
Guo, Z., Duquesne, S., Bozonnet, S., Cioci, G., Nicaud, J.-M., Marty, A., et al. (2015). Development of cellobiose-degrading ability in Yarrowia lipolytica strain by overexpression of endogenous genes. Biotechnol. Biofuels 8:109. doi: 10.1186/s13068-015-0289-9
Hameed, A., Hussain, S. A., Yang, J., Ijaz, M. U., Liu, Q., Suleria, H. A. R., et al. (2017). Antioxidants potential of the filamentous Fungi (Mucor circinelloides). Nutrients 9:1101. doi: 10.3390/nu9101101
Hao, G., Chen, H., Gu, Z., Zhang, H., Chen, W., and Chen, Y. Q. (2016). Metabolic engineering of Mortierella alpina for enhanced arachidonic acid production through the NADPH-supplying strategy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 82, 3280–3288. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00572-16
Hapeta, P., Rakicka, M., Dulermo, R., Gamboa-Meléndez, H., Cruz-Le Coq, A.-M., Nicaud, J.-M., et al. (2017). Transforming sugars into fat - lipid biosynthesis using different sugars in Yarrowia lipolytica: lipid biosynthesis using different sugars in Yarrowia lipolytica. Yeast 34, 293–304. doi: 10.1002/yea.3232
Hassane, A. M. A., Eldiehy, K. S. H., Saha, D., Mohamed, H., Mosa, M. A., Abouelela, M. E., et al. (2024). Oleaginous fungi: a promising source of biofuels and nutraceuticals with enhanced lipid production strategies. Arch. Microbiol. 206:338. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04054-9
Hellgren, J., Godina, A., Nielsen, J., and Siewers, V. (2020). Promiscuous phosphoketolase and metabolic rewiring enables novel non-oxidative glycolysis in yeast for high-yield production of acetyl-CoA derived products. Metab. Eng. 62, 150–160. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2020.09.003
Henriques, D., Minebois, R., Mendoza, S. N., Macías, L. G., Pérez-Torrado, R., Barrio, E., et al. (2021). A multiphase multiobjective dynamic genome-scale model shows different redox balancing among yeast species of the Saccharomyces genus in fermentation. mSystems 6:e00260-21. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00260-21
Herrero-de-Dios, C., Román, E., Pla, J., and Alonso-Monge, R. (2020). Hog1 controls lipids homeostasis upon osmotic stress in Candida albicans. J. Fungi 6:355. doi: 10.3390/jof6040355
Higashiyama, K., Sugimoto, T., Yonezawa, T., Fujikawa, S., and Asami, K. (1999). Dielectric analysis for estimation of oil content in the mycelia of Mortierella alpina. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 65, 537–541. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19991205)65:5<537::AID-BIT6>3.0.CO;2-O
Hsu, J.-L., Huang, S.-Y., Chow, N.-H., and Chen, S.-H. (2003). Stable-isotope dimethyl labeling for quantitative proteomics. Anal. Chem. 75, 6843–6852. doi: 10.1021/ac0348625
Jagtap, S. S., and Rao, C. V. (2018). Production of D-arabitol from D-xylose by the oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides IFO0880. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 102, 143–151. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8581-1
James Sanford, E., and Bustamante Smolka, M. (2022). A field guide to the proteomics of post-translational modifications in DNA repair. Proteomics 22:e2200064. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202200064
Jarc, E., and Petan, T. (2019). Lipid droplets and the management of cellular stress. Yale J. Biol. Med. 92, 435–452.
Ji, X.-J., Ren, L.-J., Nie, Z.-K., Huang, H., and Ouyang, P.-K. (2014). Fungal arachidonic acid-rich oil: research, development and industrialization. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 34, 197–214. doi: 10.3109/07388551.2013.778229
Jiang, Y., Rex, D. A. B., Schuster, D., Neely, B. A., Rosano, G. L., Volkmar, N., et al. (2024). Comprehensive overview of bottom-up proteomics using mass spectrometry. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 4, 338–417. doi: 10.1021/acsmeasuresciau.3c00068
Jin, M.-J., Huang, H., Xiao, A.-H., Zhang, K., Liu, X., Li, S., et al. (2008). A novel two-step fermentation process for improved arachidonic acid production by Mortierella alpina. Biotechnol. Lett. 30, 1087–1091. doi: 10.1007/s10529-008-9661-1
Kamilari, E., Stanton, C., Reen, F. J., and Ross, R. P. (2023). Uncovering the biotechnological importance of Geotrichum candidum. Foods 12:1124. doi: 10.3390/foods12061124
Kendrick, A., and Ratledge, C. (1992). Desaturation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in Mucor circinelloides and the involvement of a novel membrane-bound malic enzyme. Eur. J. Biochem. 209, 667–673. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17334.x
Kessell, R. H. J. (1968). Fatty acids of Rhodotorula gracilis: fat production in submerged culture and the particular effect of pH value. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 31, 220–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1968.tb00361.x
Kikukawa, H., Sakuradani, E., Ando, A., Shimizu, S., and Ogawa, J. (2018). Arachidonic acid production by the oleaginous fungus Mortierella alpina 1S-4: a review. J. Adv. Res. 11, 15–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2018.02.003
Kim, J., Coradetti, S. T., Kim, Y.-M., Gao, Y., Yaegashi, J., Zucker, J. D., et al. (2021). Multi-omics driven metabolic network reconstruction and analysis of Lignocellulosic carbon utilization in Rhodosporidium toruloides. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8:612832. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.612832
Kim, J. H., Lee, H.-O., Cho, Y.-J., Kim, J., Chun, J., Choi, J., et al. (2014). A vanillin derivative causes mitochondrial dysfunction and triggers oxidative stress in Cryptococcus neoformans. PLoS One 9:e89122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089122
Kot, A. M., Błażejak, S., Kurcz, A., Gientka, I., and Kieliszek, M. (2016). Rhodotorula glutinis—potential source of lipids, carotenoids, and enzymes for use in industries. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 100, 6103–6117. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7611-8
Lavoie, H., Hogues, H., and Whiteway, M. (2009). Rearrangements of the transcriptional regulatory networks of metabolic pathways in fungi. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 12, 655–663. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2009.09.015
Lazar, Z., Gamboa-Meléndez, H., Le Coq, A. M. C., Neuvéglise, C., and Nicaud, J. M. (2015). Awakening the endogenous Leloir pathway for efficient galactose utilization by Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol. Biofuels 8:185. doi: 10.1186/s13068-015-0370-4
Ledesma-Amaro, R., Lazar, Z., Rakicka, M., Guo, Z., Fouchard, F., Coq, A.-M. C.-L., et al. (2016). Metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica to produce chemicals and fuels from xylose. Metab. Eng. 38, 115–124. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2016.07.001
Levasseur, A., Drula, E., Lombard, V., Coutinho, P. M., and Henrissat, B. (2013). Expansion of the enzymatic repertoire of the CAZy database to integrate auxiliary redox enzymes. Biotechnol. Biofuels 6:41. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-6-41
Li, X., An, Q., Qu, S., Ren, J.-N., Fan, G., Zhang, L.-L., et al. (2022). Differential proteomic analysis of citrus flavor (+)-valencene biotransformation to (+)-nootkatone by Yarrowia lipolytica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 220, 1031–1048. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.08.020
Li, J., Cai, Z., Bomgarden, R. D., Pike, I., Kuhn, K., Rogers, J. C., et al. (2021). TMTpro-18plex: the expanded and complete set of TMTpro reagents for sample multiplexing. J. Proteome Res. 20, 2964–2972. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.1c00168
Li, X., Xu, Z., Gluth, A., Qian, W.-J., and Yang, B. (2021). “Proteomic approaches for advancing the understanding and application of oleaginous Bacteria for bioconversion of lignin to lipids” in Lignin utilization strategies: From processing to applications. eds. C. G. Yoo and A. Ragauskas (Washington, DC: American Chemical Society), 61–96.
Li, F., Yuan, L., Lu, H., Li, G., Chen, Y., Engqvist, M. K. M., et al. (2022). Deep learning-based kcat prediction enables improved enzyme-constrained model reconstruction. Nat. Catal. 5, 662–672. doi: 10.1038/s41929-022-00798-z
Li, Y., Zhao, Z., and Bai, F. (2007). High-density cultivation of oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides Y4 in fed-batch culture. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 41, 312–317. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2007.02.008
Ling, X., Guo, J., Zheng, C., Ye, C., Lu, Y., Pan, X., et al. (2015). Simple, effective protein extraction method and proteomics analysis from polyunsaturated fatty acids-producing micro-organisms. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 38, 2331–2341. doi: 10.1007/s00449-015-1467-7
Liu, P., Bartz, R., Zehmer, J. K., Ying, Y., Zhu, M., Serrero, G., et al. (2007). Rab-regulated interaction of early endosomes with lipid droplets. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1773, 784–793. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.02.004
Liu, H., Marsafari, M., Deng, L., and Xu, P. (2019). Understanding lipogenesis by dynamically profiling transcriptional activity of lipogenic promoters in Yarrowia lipolytica. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 103, 3167–3179. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09664-8
Liu, H., Zhao, X., Wang, F., Jiang, X., Zhang, S., Ye, M., et al. (2011). The proteome analysis of oleaginous yeast Lipomyces starkeyi. FEMS Yeast Res. 11, 42–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2010.00687.x
Liu, H., Zhao, X., Wang, F., Li, Y., Jiang, X., Ye, M., et al. (2009). Comparative proteomic analysis of Rhodosporidium toruloides during lipid accumulation. Yeast 26, 553–566. doi: 10.1002/yea.1706
Lu, H., Chen, H., Tang, X., Yang, Q., Zhang, H., Chen, Y. Q., et al. (2020). Time-resolved multi-omics analysis reveals the role of nutrient stress-induced resource reallocation for TAG accumulation in oleaginous fungus Mortierella alpina. Biotechnol. Biofuels 13:116. doi: 10.1186/s13068-020-01757-1
Lu, H., Chen, H., Tang, X., Yang, Q., Zhang, H., Chen, Y. Q., et al. (2022). Autophagy improves ARA-rich TAG accumulation in Mortierella alpina by regulating resource allocation. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e01300–e01321. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01300-21
Lundin, H. (1950). Fat synthesis by micro-organisms and its possible applications in industry. J. Inst. Brew. 56, 17–28. doi: 10.1002/j.2050-0416.1950.tb01516.x
Madzak, C. (2021). Yarrowia lipolytica strains and their biotechnological applications: how natural biodiversity and metabolic engineering could contribute to cell factories improvement. J. Fungi 7:548. doi: 10.3390/jof7070548
Mansour, S., Bailly, J., Delettre, J., and Bonnarme, P. (2009). A proteomic and transcriptomic view of amino acids catabolism in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Proteomics 9, 4714–4725. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200900161
Martin, S., and Parton, R. G. (2008). “Characterization of Rab18, a lipid droplet–associated small GTPase” in Methods in enzymology. eds. W. E. Balch, C. J. Der, and A. Hall, vol. 438 (London: Academic Press), 109–129.
Martin, K., Zhang, T., Lin, T.-T., Habowski, A. N., Zhao, R., Tsai, C.-F., et al. (2021). Facile one-pot Nanoproteomics for label-free proteome profiling of 50–1000 mammalian cells. J. Proteome Res. 20, 4452–4461. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.1c00403
Martinez-Moya, P., Campusano, S., Córdova, P., Paradela, A., Sepulveda, D., Alcaíno, J., et al. (2020). Convergence between regulation of carbon utilization and catabolic repression in Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. mSphere 5:e00065. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00065-20
Martinez-Moya, P., Niehaus, K., Alcaíno, J., Baeza, M., and Cifuentes, V. (2015). Proteomic and metabolomic analysis of the carotenogenic yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous using different carbon sources. BMC Genomics 16:289. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1484-6
Martinez-Moya, P., Watt, S. A., Niehaus, K., Alcaíno, J., Baeza, M., and Cifuentes, V. (2011). Proteomic analysis of the carotenogenic yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. BMC Microbiol. 11:131. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-131
Masi, A., Mach, R. L., and Mach-Aigner, A. R. (2021). The pentose phosphate pathway in industrially relevant fungi: crucial insights for bioprocessing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 105, 4017–4031. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11314-x
Mason-Jones, K., Robinson, S. L., Veen, G. F., Manzoni, S., and van der Putten, W. H. (2021). Microbial storage and its implications for soil ecology. ISME J. 16, 617–629. doi: 10.1038/s41396-021-01110-w
Mattila, H., Österman-Udd, J., Mali, T., and Lundell, T. (2022). Basidiomycota Fungi and ROS: genomic perspective on key enzymes involved in generation and mitigation of reactive oxygen species. Front. Fungal Biol. 3:837605. doi: 10.3389/ffunb.2022.837605
Mazurie, A., Bottani, S., and Vergassola, M. (2005). An evolutionary and functional assessment of regulatory network motifs. Genome Biol. 6:R35. doi: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-4-r35
Mihreteab, M., Stubblefield, B. A., and Gilbert, E. S. (2021). Enhancing polypropylene bioconversion and lipogenesis by Yarrowia lipolytica using a chemical/biological hybrid process. J. Biotechnol. 332, 94–102. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2021.03.015
Morin, N., Cescut, J., Beopoulos, A., Lelandais, G., Berre, V. L., Uribelarrea, J.-L., et al. (2011). Transcriptomic analyses during the transition from biomass production to lipid accumulation in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. PLoS One 6:e27966. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027966
Morín, M., Monteoliva, L., Insenser, M., Gil, C., and Domínguez, Á. (2007). Proteomic analysis reveals metabolic changes during yeast to hypha transition in Yarrowia lipolytica. J. Mass Spectrom. 42, 1453–1462. doi: 10.1002/jms.1284
Morin-Sardin, S., Jany, J.-L., Artigaud, S., Pichereau, V., Bernay, B., Coton, E., et al. (2017). Proteomic analysis of the adaptative response of “Mucor” spp. to cheese environment. J. Proteomics 154, 30–39. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.12.001
Mosqueda-Martínez, E., Chiquete-Félix, N., Castañeda-Tamez, P., Ricardez-García, C., Gutiérrez-Aguilar, M., Uribe-Carvajal, S., et al. (2024). In Rhodotorula mucilaginosa, active oxidative metabolism increases carotenoids to inactivate excess reactive oxygen species. Front. Fungal Biol. 5:1378590. doi: 10.3389/ffunb.2024.1378590
Nagy, G., Szebenyi, C., Csernetics, Á., Vaz, A. G., Tóth, E. J., Vágvölgyi, C., et al. (2017). Development of a plasmid free CRISPR-Cas9 system for the genetic modification of Mucor circinelloides. Sci. Rep. 7:16800. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17118-2
Nambou, K., Zhao, C., Wei, L., Chen, J., Imanaka, T., and Hua, Q. (2014). Designing of a “cheap to run” fermentation platform for an enhanced production of single cell oil from Yarrowia lipolytica DSM3286 as a potential feedstock for biodiesel. Bioresour. Technol. 173, 324–333. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.096
Navarrete, C., Sánchez, B. J., Savickas, S., and Martínez, J. L. (2022). DebaryOmics: an integrative –omics study to understand the halophilic behaviour of Debaryomyces hansenii. Microb. Biotechnol. 15, 1133–1151. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13954
Navarro, E., Peñaranda, A., Hansberg, W., Torres-Martínez, S., and Garre, V. (2013). A white collar 1-like protein mediates opposite regulatory functions in Mucor circinelloides. Fungal Genet. Biol. 52, 42–52. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2012.12.003
Nguyen, T. T. M., Iwaki, A., Ohya, Y., and Izawa, S. (2014). Vanillin causes the activation of Yap1 and mitochondrial fragmentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 117, 33–38. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.06.008
Nutrition Reviews (1958). Vitamins from Rhodotorula yeast. Nutr. Rev. 16, 147–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1958.tb00725.x
Ochoa-Viñals, N., Alonso-Estrada, D., Pacios-Michelena, S., García-Cruz, A., Ramos-González, R., Faife-Pérez, E., et al. (2024). Current advances in carotenoid production by Rhodotorula sp. Fermentation 10:190. doi: 10.3390/fermentation10040190
Onésime, D., Vidal, L., Thomas, S., Henry, C., Martin, V., André, G., et al. (2022). A unique, newly discovered four-member protein family involved in extracellular fatty acid binding in Yarrowia lipolytica. Microb. Cell Factories 21:200. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01925-y
Ong, S.-E., Blagoev, B., Kratchmarova, I., Kristensen, D. B., Steen, H., Pandey, A., et al. (2002). Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture, SILAC, as a simple and accurate approach to expression proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 1, 376–386. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M200025-MCP200
Papp, T., Velayos, A., Bartók, T., Eslava, A. P., Vágvölgyi, C., and Iturriaga, E. A. (2006). Heterologous expression of astaxanthin biosynthesis genes in Mucor circinelloides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 69, 526–531. doi: 10.1007/s00253-005-0026-6
Pappireddi, N., Martin, L., and Wühr, M. (2019). A review on quantitative multiplexed proteomics. Chembiochem 20, 1210–1224. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201800650
Pham, V. N., Bruemmer, K. J., Toh, J. D. W., Ge, E. J., Tenney, L., Ward, C. C., et al. (2023). Formaldehyde regulates S-adenosylmethionine biosynthesis and one-carbon metabolism. Science 382:eabp9201. doi: 10.1126/science.abp9201
Pi, H.-W., Anandharaj, M., Kao, Y.-Y., Lin, Y.-J., Chang, J.-J., and Li, W.-H. (2018). Engineering the oleaginous red yeast Rhodotorula glutinis for simultaneous β-carotene and cellulase production. Sci. Rep. 8:10850. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29194-z
Picazo, C., and Molin, M. (2021). Impact of hydrogen peroxide on protein synthesis in yeast. Antioxidants 10:952. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060952
Pinheiro, M. J., Bonturi, N., Belouah, I., Miranda, E. A., and Lahtvee, P.-J. (2020). Xylose metabolism and the effect of oxidative stress on lipid and carotenoid production in Rhodotorula toruloides: insights for future biorefinery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8:1008. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.01008
Pócsi, I., Prade, R. A., and Penninckx, M. J. (2004). “Glutathione, altruistic metabolite in Fungi” in Advances in microbial physiology. ed. R. K. Poole, vol. 49 (London, UK: Academic Press), 1–76.
Pomraning, K. R., Bredeweg, E. L., and Baker, S. E. (2017). Regulation of nitrogen metabolism by GATA zinc finger transcription factors in Yarrowia lipolytica. mSphere 2:e00038-17. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00038-17
Pomraning, K. R., Deng, S., Duong, R. D., Czajka, J. J., and Bohutskyi, P. (2024). Identification of Yarrowia lipolytica as a platform for designed consortia that incorporate in situ nitrogen fixation to enable ammonia-free bioconversion. Front. Ind. Microbiol. 2:1473316. doi: 10.3389/finmi.2024.1473316
Pomraning, K. R., Kim, Y.-M., Nicora, C. D., Chu, R. K., Bredeweg, E. L., Purvine, S. O., et al. (2016). Multi-omics analysis reveals regulators of the response to nitrogen limitation in Yarrowia lipolytica. BMC Genomics 17:138. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2471-2
Poorinmohammad, N., Fu, J., Wabeke, B., and Kerkhoven, E. J. (2022). Validated growth rate-dependent regulation of lipid metabolism in Yarrowia lipolytica. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:8517. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158517
Poorinmohammad, N., and Kerkhoven, E. J. (2021). Systems-level approaches for understanding and engineering of the oleaginous cell factory Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 118, 3640–3654. doi: 10.1002/bit.27859
Qi, F., Kitahara, Y., Wang, Z., Zhao, X., Du, W., and Liu, D. (2014). Novel mutant strains of Rhodosporidium toruloides by plasma mutagenesis approach and their tolerance for inhibitors in lignocellulosic hydrolyzate. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 89, 735–742. doi: 10.1002/jctb.4180
Qi, F., Zhao, X., Kitahara, Y., Li, T., Ou, X., Du, W., et al. (2017). Integrative transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of the mutant lignocellulosic hydrolyzate-tolerant Rhodosporidium toruloides. Eng. Life Sci. 17, 249–261. doi: 10.1002/elsc.201500143
Qiao, K., Imam Abidi, S. H., Liu, H., Zhang, H., Chakraborty, S., Watson, N., et al. (2015). Engineering lipid overproduction in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab. Eng. 29, 56–65. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2015.02.005
Raitt, D. C., Posas, F., and Saito, H. (2000). Yeast Cdc42 GTPase and Ste20 PAK-like kinase regulate Sho1-dependent activation of the Hog1 MAPK pathway. EMBO J. 19, 4623–4631. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.17.4623
Ratledge, C. (2014). The role of malic enzyme as the provider of NADPH in oleaginous microorganisms: a reappraisal and unsolved problems. Biotechnol. Lett. 36, 1557–1568. doi: 10.1007/s10529-014-1532-3
Ratledge, C., Streekstra, H., Cohen, Z., and Fichtali, J. (2010). “9 - Downstream Processing, Extraction, and Purification of Single Cell Oils” in Single Cell Oils. eds. Z. Cohen and C. Ratledge. Second ed (Champaign, IL: AOCS Press), 179–197.
Ratledge, C., and Wynn, J. P. (2002). “The biochemistry and molecular biology of lipid accumulation in oleaginous microorganisms” in Advances in applied microbiology. eds. A. I. Laskin, J. W. Bennett, and G. M. Gadd (San Diego, CA: Academic Press), 1–52.
Reķēna, A., Pinheiro, M. J., Bonturi, N., Belouah, I., Tammekivi, E., Herodes, K., et al. (2023). Genome-scale metabolic modeling reveals metabolic trade-offs associated with lipid production in Rhodotorula toruloides. PLoS Comput. Biol. 19:e1011009. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011009
Ren, Y., Perepelov, A. V., Wang, H., Zhang, H., Knirel, Y. A., Wang, L., et al. (2010). Biochemical characterization of GDP-l-fucose de novo synthesis pathway in fungus Mortierella alpina. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 391, 1663–1669. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.12.116
Rodriguez, G. M., Hussain, M. S., Gambill, L., Gao, D., Yaguchi, A., and Blenner, M. (2016). Engineering xylose utilization in Yarrowia lipolytica by understanding its cryptic xylose pathway. Biotechnol. Biofuels 9:149. doi: 10.1186/s13068-016-0562-6
Rodríguez-Frómeta, R. A., Gutiérrez, A., Torres-Martínez, S., and Garre, V. (2013). Malic enzyme activity is not the only bottleneck for lipid accumulation in the oleaginous fungus Mucor circinelloides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97, 3063–3072. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4432-2
Roelants, S. L. K. W., Bovijn, S., Bytyqi, E., de Fooz, N., Luyten, G., Castelein, M., et al. (2024). Bubbling insights: unveiling the true sophorolipid biosynthetic pathway by Starmerella bombicola. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 17:113. doi: 10.1186/s13068-024-02557-7
Ryan, A. S., Zeller, S., and Nelson, E. B. (2010). “15 - safety evaluation of single cell oils and the regulatory requirements for use as food ingredients” in Single Cell Oils. eds. Z. Cohen and C. Ratledge. Second ed (Champaign, IL: AOCS Press), 317–350.
Sakamoto, T., Sakuradani, E., Okuda, T., Kikukawa, H., Ando, A., Kishino, S., et al. (2017). Metabolic engineering of oleaginous fungus Mortierella alpina for high production of oleic and linoleic acids. Bioresour. Technol. 245, 1610–1615. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.089
Salvador López, J. M., Vandeputte, M., and Van Bogaert, I. N. A. (2022). Oleaginous yeasts: time to rethink the definition? Yeast 39, 553–606. doi: 10.1002/yea.3827
Sartaj, K., Prasad, R., Matsakas, L., and Patel, A. (2023). Transforming recalcitrant wastes into biodiesel by oleaginous yeast: an insight into the metabolic pathways and multi-omics landscape. Chem. Eng. J. 474:145625. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.145625
Sekova, V. Y., Kovalyov, L. I., Kovalyova, M. A., Gessler, N. N., Danilova, M. A., Isakova, E. P., et al. (2021). Proteomics readjustment of the Yarrowia lipolytica yeast in response to increased temperature and alkaline stress. Microorganisms 9:2619. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9122619
Shaigani, P., Fuchs, T., Graban, P., Prem, S., Haack, M., Masri, M., et al. (2023). Mastering targeted genome engineering of GC-rich oleaginous yeast for tailored plant oil alternatives for the food and chemical sector. Microb. Cell Factories 22:25. doi: 10.1186/s12934-023-02033-1
Shi, S., Chen, Y., Siewers, V., and Nielsen, J. (2014). Improving production of Malonyl coenzyme A-derived metabolites by abolishing Snf1-dependent regulation of Acc1. MBio 5, e01130–e01114. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01130-14
Shimiziu, S., Kawashima, H., Shinmen, Y., Akimoto, K., and Yamada, H. (1988). Production of eicosapentaenoic acid by Mortierella fungi. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 65, 1455–1459. doi: 10.1007/BF02898307
Shome, M., MacKenzie, T. M. G., Subbareddy, S. R., and Snyder, M. P. (2024). The importance, challenges, and possible solutions for sharing proteomics data while safeguarding individuals’ privacy. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 23:100731. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2024.100731
Shuken, S. R. (2023). An introduction to mass spectrometry-based proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 22, 2151–2171. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.2c00838
Sibirny, A. A. (2016). Yeast peroxisomes: structure, functions and biotechnological opportunities. FEMS Yeast Res. 16:fow038. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/fow038
Sigtryggsson, C., Karlsson Potter, H., Passoth, V., and Hansson, P.-A. (2023). From straw to salmon: a technical design and energy balance for production of yeast oil for fish feed from wheat straw. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 16:140. doi: 10.1186/s13068-023-02392-2
Singh, R., Kaushik, S., Wang, Y., Xiang, Y., Novak, I., Komatsu, M., et al. (2009). Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature 458, 1131–1135. doi: 10.1038/nature07976
Singh, A., and Ward, O. P. (1997). Production of high yields of arachidonic acid in a fed-batch system by Mortierella alpina ATCC 32222. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 48, 1–5. doi: 10.1007/s002530051005
Smith, K., Rhoads, N., and Chandrasekaran, S. (2022). Protocol for CAROM: a machine learning tool to predict post-translational regulation from metabolic signatures. STAR Protoc. 3:101799. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2022.101799
Song, Y., Wynn, J. P., Li, Y., Grantham, D., and Ratledge, C. (2001). A pre-genetic study of the isoforms of malic enzyme associated with lipid accumulation in Mucor circinelloides. Microbiology 147, 1507–1515. doi: 10.1099/00221287-147-6-1507
Šoštarić, N., and van Noort, V. (2021). Molecular dynamics shows complex interplay and long-range effects of post-translational modifications in yeast protein interactions. PLoS Comput. Biol. 17:e1008988. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008988
Spagnuolo, M., Yaguchi, A., and Blenner, M. (2019). Oleaginous yeast for biofuel and oleochemical production. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 57, 73–81. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2019.02.011
Srinivasan, N., Thangavelu, K., and Uthandi, S. (2022). Lovastatin production by an oleaginous fungus, aspergillus terreus KPR12 using sago processing wastewater (SWW). Microb. Cell Factories 21:22. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01751-2
Stellner, N. I., Rerop, Z. S., Mehlmer, N., Masri, M., Ringel, M., and Brück, T. B. (2023). Expanding the genetic toolbox for Cutaneotrichosporon oleaginosus employing newly identified promoters and a novel antibiotic resistance marker. BMC Biotechnol. 23:40. doi: 10.1186/s12896-023-00812-7
Strucko, T., Andersen, N. L., Mahler, M. R., Martínez, J. L., and Mortensen, U. H. (2021). A CRISPR/Cas9 method facilitates efficient oligo-mediated gene editing in Debaryomyces hansenii. Synth. Biol. 6:ysab031. doi: 10.1093/synbio/ysab031
Swennen, D., Henry, C., and Beckerich, J.-M. (2010). Folding proteome of Yarrowia lipolytica targeting with uracil Permease mutants. J. Proteome Res. 9, 6169–6179. doi: 10.1021/pr100340p
Takeno, S., Sakuradani, E., Tomi, A., Inohara-Ochiai, M., Kawashima, H., and Shimizu, S. (2005). Transformation of oil-producing fungus, Mortierella alpina 1S-4, using Zeocin, and application to arachidonic acid production. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 100, 617–622. doi: 10.1263/jbb.100.617
Tang, X., Chen, H., Chen, Y. Q., Chen, W., Garre, V., Song, Y., et al. (2015a). Comparison of biochemical activities between high and low lipid-producing strains of Mucor circinelloides: An explanation for the high Oleaginicity of strain WJ11. PLoS One 10:e0128396. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128396
Tang, X., Chen, H., Gu, Z., Zhang, H., Chen, Y. Q., Song, Y., et al. (2017). Comparative proteome analysis between high lipid-producing strain Mucor circinelloides WJ11 and low lipid-producing strain CBS 277.49. J. Agric. Food Chem. 65, 5074–5082. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00935
Tang, X., Chen, H., Gu, Z., Zhang, H., Chen, Y. Q., Song, Y., et al. (2020). Role of g6pdh and leuB on lipid accumulation in Mucor circinelloides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68, 4245–4251. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b08155
Tang, X., Sun, X., Wang, X., Zhang, H., Chen, Y. Q., Zhao, J., et al. (2021). Characterization of NAD+/NADP+-specific Isocitrate dehydrogenases from oleaginous fungus Mortierella alpina involved in lipid accumulation. Front. Nutr. 8:746342. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.746342
Tang, X., Zan, X., Zhao, L., Chen, H., Chen, Y. Q., Chen, W., et al. (2016). Proteomics analysis of high lipid-producing strain Mucor circinelloides WJ11: an explanation for the mechanism of lipid accumulation at the proteomic level. Microb. Cell Factories 15:35. doi: 10.1186/s12934-016-0428-4
Tang, W., Zhang, S., Tan, H., and Zhao, Z. K. (2010). Molecular cloning and characterization of a malic enzyme gene from the oleaginous yeast Lipomyces starkeyi. Mol. Biotechnol. 45, 121–128. doi: 10.1007/s12033-010-9255-8
Tang, X., Zhao, L., Chen, H., Chen, Y. Q., Chen, W., Song, Y., et al. (2015b). Complete genome sequence of a high lipid-producing strain of Mucor circinelloides WJ11 and comparative genome analysis with a low lipid-producing strain CBS 277.49. PLoS One 10:e0137543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137543
Thammarongtham, C., Nookaew, I., Vorapreeda, T., Srisuk, T., Land, M. L., Jeennor, S., et al. (2018). Genome characterization of oleaginous aspergillus oryzae BCC7051: a potential fungal-based platform for lipid production. Curr. Microbiol. 75, 57–70. doi: 10.1007/s00284-017-1350-7
Thumkasem, N., On-mee, T., Kongsinkaew, C., Chittapun, S., Pornpukdeewattana, S., Ketudat-Cairns, M., et al. (2024). Enhanced high β-carotene yeast cell production by Rhodotorula paludigena CM33 and in vitro digestibility in aquatic animals. Sci. Rep. 14:9188. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59809-7
Tiukova, I. A., Brandenburg, J., Blomqvist, J., Sampels, S., Mikkelsen, N., Skaugen, M., et al. (2019). Proteome analysis of xylose metabolism in Rhodotorula toruloides during lipid production. Biotechnol. Biofuels 12:137. doi: 10.1186/s13068-019-1478-8
Tramontin, L. R. R., Kildegaard, K. R., Sudarsan, S., and Borodina, I. (2019). Enhancement of Astaxanthin biosynthesis in oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica via microalgal pathway. Microorganisms 7:472. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7100472
Tripodi, F., Nicastro, R., Reghellin, V., and Coccetti, P. (2015). Post-translational modifications on yeast carbon metabolism: regulatory mechanisms beyond transcriptional control. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1850, 620–627. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.12.010
Van Bogaert, I. N. A., Demey, M., Develter, D., Soetaert, W., and Vandamme, E. J. (2009). Importance of the cytochrome P450 monooxygenase CYP52 family for the sophorolipid-producing yeast Candida bombicola. FEMS Yeast Res. 9, 87–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2008.00454.x
Vanholme, R., Demedts, B., Morreel, K., Ralph, J., and Boerjan, W. (2010). Lignin biosynthesis and structure. Plant Physiol. 153, 895–905. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.155119
Venditti, P., and Di Meo, S. (2020). The role of reactive oxygen species in the life cycle of the mitochondrion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21:2173. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062173
Vongsangnak, W., Kingkaw, A., Yang, J., Song, Y., and Laoteng, K. (2018). Dissecting metabolic behavior of lipid over-producing strain of Mucor circinelloides through genome-scale metabolic network and multi-level data integration. Gene 670, 87–97. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.05.085
Walker, C., Dien, B., Giannone, R. J., Slininger, P., Thompson, S. R., and Trinh, C. T. (2021). Exploring proteomes of robust Yarrowia lipolytica isolates cultivated in biomass hydrolysate reveals key processes impacting mixed sugar utilization, lipid accumulation, and degradation. mSystems 6:e00443-21. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00443-21
Walker, C., Mortensen, M., Poudel, B., Cotter, C., Myers, R., Okekeogbu, I. O., et al. (2023). Proteomes reveal metabolic capabilities of Yarrowia lipolytica for biological upcycling of polyethylene into high-value chemicals. mSystems 8:e00741-23. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00741-23
Walker, C., Ryu, S., Giannone, R. J., Garcia, S., and Trinh, C. T. (2020). Understanding and eliminating the detrimental effect of thiamine deficiency on the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 86:e02299-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02299-19
Wang, Y., Liu, F., Liu, H., Zhang, Y., Jiao, X., Ye, M., et al. (2023a). Regulation of autophagy and lipid accumulation under phosphate limitation in Rhodotorula toruloides. Front. Microbiol. 13:1046114. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1046114
Wang, X., Yang, J., Mohamed, H., Shah, A. M., Li, S., Pang, S., et al. (2022). Simultaneous overexpression of ∆6-, ∆12- and ∆9-desaturases enhanced the production of γ-linolenic acid in Mucor circinelloides WJ11. Front. Microbiol. 13:1078157. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1078157
Wang, W., and Yu, L. (2009). Effects of oxygen supply on growth and carotenoids accumulation by Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. Z. Naturforsch. C 64, 853–858. doi: 10.1515/znc-2009-11-1216
Wang, Y., Zhang, S., Zhu, Z., Shen, H., Lin, X., Jin, X., et al. (2018). Systems analysis of phosphate-limitation-induced lipid accumulation by the oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides. Biotechnol. Biofuels 11:148. doi: 10.1186/s13068-018-1134-8
Wang, Y., Zheng, X., Li, G., and Wang, X. (2023b). TORC1 signaling in Fungi: from yeasts to filamentous Fungi. Microorganisms 11:218. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010218
Wasylenko, T. M., Ahn, W. S., and Stephanopoulos, G. (2015). The oxidative pentose phosphate pathway is the primary source of NADPH for lipid overproduction from glucose in Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab. Eng. 30, 27–39. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2015.02.007
Webb-Robertson, B.-J. M., Wiberg, H. K., Matzke, M. M., Brown, J. N., Wang, J., McDermott, J. E., et al. (2015). Review, evaluation, and discussion of the challenges of missing value imputation for mass spectrometry-based label-free global proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 14, 1993–2001. doi: 10.1021/pr501138h
Weeks, M. E., Sinclair, J., Butt, A., Chung, Y.-L., Worthington, J. L., Wilkinson, C. R. M., et al. (2006). A parallel proteomic and metabolomic analysis of the hydrogen peroxide- and Sty1p-dependent stress response in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Proteomics 6, 2772–2796. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200500741
Wei, H., Wang, W., Yarbrough, J. M., Baker, J. O., Laurens, L., Wychen, S. V., et al. (2013). Genomic, proteomic, and biochemical analyses of oleaginous Mucor circinelloides: evaluating its capability in utilizing cellulolytic substrates for lipid production. PLoS One 8:e71068. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071068
Weimer, E. P., Rao, E., and Brendel, M. (1993). Molecular structure and genetic regulation of SFA, a gene responsible for resistance to formaldehyde in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and characterization of its protein product. Mol. Gen. Genet. MGG 237, 351–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00279438
Welte, M. A. (2015). Expanding roles for lipid droplets. Curr. Biol. 25, R470–R481. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.04.004
Wiebe, M. G., Koivuranta, K., Penttilä, M., and Ruohonen, L. (2012). Lipid production in batch and fed-batch cultures of Rhodosporidium toruloides from 5 and 6 carbon carbohydrates. BMC Biotechnol. 12:26. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-12-26
Wierzchowska, K., Zieniuk, B., Nowak, D., and Fabiszewska, A. (2021). Phosphorus and nitrogen limitation as a part of the strategy to stimulate microbial lipid biosynthesis. Appl. Sci. 11:11819. doi: 10.3390/app112411819
Wu, S., Hu, C., Jin, G., Zhao, X., and Zhao, Z. K. (2010). Phosphate-limitation mediated lipid production by Rhodosporidium toruloides. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 6124–6129. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.111
Wu, S., Zhao, X., Shen, H., Wang, Q., and Zhao, Z. K. (2011). Microbial lipid production by Rhodosporidium toruloides under sulfate-limited conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 1803–1807. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.033
Yaguchi, A. (2020) Development of Cutaneotrichosporon oleaginosus to convert lignin-derived Phenolics to Oleochemicals. Available online at: https://tigerprints.clemson.edu/all_dissertations/2755 (Accessed February 7, 2021).
Yaguchi, A., Rives, D., and Blenner, M. (2017a). New kids on the block: emerging oleaginous yeast of biotechnological importance. AIMS Microbiol. 3, 227–247. doi: 10.3934/microbiol.2017.2.227
Yaguchi, A., Robinson, A., Mihealsick, E., and Blenner, M. (2017b). Metabolism of aromatics by Trichosporon oleaginosus while remaining oleaginous. Microb. Cell Factories 16:206. doi: 10.1186/s12934-017-0820-8
Yamada, H., Shimizu, S., and Shinmen, Y. (1987). Production of arachidonic acid by Mortierella elongata 1S-5. Agric. Biol. Chem. 51, 785–790. doi: 10.1080/00021369.1987.10868119
Yang, L.-B., Dai, X.-M., Zheng, Z.-Y., Zhu, L., Zhan, X.-B., and Lin, C.-C. (2015). Proteomic analysis of Erythritol-producing Yarrowia lipolytica from glycerol in response to osmotic pressure. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 25, 1056–1069. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1412.12026
Yang, X., Jin, G., Gong, Z., Shen, H., Song, Y., Bai, F., et al. (2014). Simultaneous utilization of glucose and mannose from spent yeast cell mass for lipid production by Lipomyces starkeyi. Bioresour. Technol. 158, 383–387. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.02.121
Yen, H.-W., Chen, P.-W., and Chen, L.-J. (2015). The synergistic effects for the co-cultivation of oleaginous yeast-Rhodotorula glutinis and microalgae-Scenedesmus obliquus on the biomass and total lipids accumulation. Bioresour. Technol. 184, 148–152. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.113
Younes, S., Bracharz, F., Awad, D., Qoura, F., Mehlmer, N., and Brueck, T. (2020). Microbial lipid production by oleaginous yeasts grown on Scenedesmus obtusiusculus microalgae biomass hydrolysate. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 43, 1629–1638. doi: 10.1007/s00449-020-02354-0
Yu, Y., Li, T., Wu, N., Jiang, L., Ji, X., and Huang, H. (2017). The role of lipid droplets in Mortierella alpina aging revealed by integrative subcellular and whole-cell proteome analysis. Sci. Rep. 7:43896. doi: 10.1038/srep43896
Yu, Y., Li, T., Wu, N., Ren, L., Jiang, L., Ji, X., et al. (2016). Mechanism of arachidonic acid accumulation during aging in Mortierella alpina: a large-scale label-free comparative proteomics study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 64, 9124–9134. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b03284
Yu, Y., and Shi, S. (2023). Development and perspective of Rhodotorula toruloides as an efficient cell factory. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71, 1802–1819. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c07361
Yu, Y., Zhang, L., Li, T., Wu, N., Jiang, L., Ji, X., et al. (2018). How nitrogen sources influence Mortierella alpina aging: from the lipid droplet proteome to the whole-cell proteome and metabolome. J. Proteome 179, 140–149. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2018.03.014
Yu, X., Zheng, Y., Xiong, X., and Chen, S. (2014). Co-utilization of glucose, xylose and cellobiose by the oleaginous yeast Cryptococcus curvatus. Biomass Bioenergy 71, 340–349. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2014.09.023
Yunus, I. S., and Lee, T. S. (2022). Applications of targeted proteomics in metabolic engineering: advances and opportunities. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 75:102709. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2022.102709
Zhang, Y., Adams, I. P., and Ratledge, C. (2007). Malic enzyme: the controlling activity for lipid production? Overexpression of malic enzyme in Mucor circinelloides leads to a 2.5-fold increase in lipid accumulation. Microbiology 153, 2013–2025. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2006/002683-0
Zhang, H., Chen, L., Sun, Y., Zhao, L., Zheng, X., Yang, Q., et al. (2017). Investigating proteome and transcriptome defense response of apples induced by Yarrowia lipolytica. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 30, 301–311. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-09-16-0189-R
Zhang, L., Lee, J. T. E., Ok, Y. S., Dai, Y., and Tong, Y. W. (2022). Enhancing microbial lipids yield for biodiesel production by oleaginous yeast Lipomyces starkeyi fermentation: a review. Bioresour. Technol. 344:126294. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126294
Zhang, X. Y., Li, B., Huang, B.-C., Wang, F.-B., Zhang, Y.-Q., Zhao, S.-G., et al. (2022). Production, biosynthesis, and commercial applications of fatty acids from oleaginous Fungi. Front. Nutr. 9:873657. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.873657
Zhang, Y., Luan, X., Zhang, H., Garre, V., Song, Y., and Ratledge, C. (2017). Improved γ-linolenic acid production in Mucor circinelloides by homologous overexpressing of delta-12 and delta-6 desaturases. Microb. Cell Factories 16:113. doi: 10.1186/s12934-017-0723-8
Zhang, H., Wan, W., Cui, Q., and Song, X. (2023). Modular metabolic engineering of Mortierella alpina by the 2A peptide platform to improve arachidonic acid production. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71, 12519–12527. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c03016
Zhang, H., Zhang, L., Chen, H., Chen, Y. Q., Ratledge, C., Song, Y., et al. (2013). Regulatory properties of malic enzyme in the oleaginous yeast, Yarrowia lipolytica, and its non-involvement in lipid accumulation. Biotechnol. Lett. 35, 2091–2098. doi: 10.1007/s10529-013-1302-7
Zhang, L., Zhang, H., Liu, Y., Zhou, J., Shen, W., Liu, L., et al. (2020). A CRISPR–Cas9 system for multiple genome editing and pathway assembly in Candida tropicalis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 117, 531–542. doi: 10.1002/bit.27207
Zhao, Y., Han, Z., Zhu, X., Chen, B., Zhou, L., Liu, X., et al. (2024). Yeast proteins: proteomics, extraction, modification, functional characterization, and structure: a review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72, 18774–18793. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c04821
Zhao, L., Tang, X., Luan, X., Chen, H., Chen, Y. Q., Chen, W., et al. (2015). Role of pentose phosphate pathway in lipid accumulation of oleaginous fungus Mucor circinelloides. RSC Adv. 5, 97658–97664. doi: 10.1039/C5RA20364C
Zhou, X., Cao, Q., Orfila, C., Zhao, J., and Zhang, L. (2021). Systematic review and Meta-analysis on the effects of Astaxanthin on human skin ageing. Nutrients 13:2917. doi: 10.3390/nu13092917
Zhou, X., Wu, B., Qian, X., Xu, L., Xu, A., Zhou, J., et al. (2023). Valorization of PE plastic waste into lipid cells through tandem catalytic pyrolysis and biological conversion. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 11:111016. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.111016
Zhu, Z., Ding, Y., Gong, Z., Yang, L., Zhang, S., Zhang, C., et al. (2015). Dynamics of the lipid droplet proteome of the oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides. Eukaryot. Cell 14, 252–264. doi: 10.1128/EC.00141-14
Zhu, Y., Piehowski, P. D., Zhao, R., Chen, J., Shen, Y., Moore, R. J., et al. (2018). Nanodroplet processing platform for deep and quantitative proteome profiling of 10–100 mammalian cells. Nat. Commun. 9:882. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03367-w
Keywords: proteomics, oleaginous, yeast, fungi, bioproducts, oleochemicals, lipid production, stress response
Citation: Gluth A, Trejo JB, Czaijka JJ, Deng S, Qian W-J, Yang B and Zhang T (2025) Proteomic insights into the physiology and metabolism of oleaginous yeasts and filamentous fungi. Front. Microbiol. 16:1637123. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1637123
Edited by:
Yun-Peng Chao, Feng Chia University, TaiwanReviewed by:
Thanh Ta, Feng Chia University, TaiwanNaghmeh Poorinmohammad, McGill University, Canada
Copyright © 2025 Gluth, Trejo, Czaijka, Deng, Qian, Yang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bin Yang, YmluLnlhbmdAd3N1LmVkdQ==; Tong Zhang, dG9uZy56aGFuZ0Bwbm5sLmdvdg==
 Austin Gluth
Austin Gluth Jesse B. Trejo
Jesse B. Trejo Jeffrey J. Czaijka
Jeffrey J. Czaijka Shuang Deng
Shuang Deng Wei-Jun Qian
Wei-Jun Qian Bin Yang
Bin Yang Tong Zhang
Tong Zhang