- 1College of Life Sciences, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun, China
- 2Engineering Research Center of Bioreactor and Pharmaceutical Development, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun, China
As an acute and highly contagious enteric disease of swine, porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) has caused high piglet mortality and significant economic losses. Commercialized vaccines provide only partial cross-protection against the novel, highly virulent PEDV strains. Developing new vaccines against highly virulent PEDV strains would help protect the pig industry from the serious challenges posed by novel, highly virulent PEDV infections. Natural compounds and chemical and biochemical source-targeted drugs designed to act on specific proteins, enzymes, or mechanisms can complement each other’s advantages when used in combination, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of drug-based prevention in the control of highly virulent PEDV. Drugs targeting Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) can aid vaccines to compensate for interferon (IFN) secretory deficiencies to protect pigs from highly virulent PEDV infection. This review summarizes recent progress in the development of vaccines against highly virulent PEDV, natural compounds, and chemical and biochemical source-targeted drugs that have been explored in cell and pig models with clearly defined mechanisms. It also aims to provide comprehensive strategies for the prevention and control of highly virulent PEDV infections in pigs.
1 Introduction
As an acute and highly contagious enteric disease of pigs, porcine epidemic diarrhea (PED) can result in dehydration, vomiting, diarrhea, and severe enteritis. Its lethality is particularly high in suckling pigs (Stadler et al., 2015). Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV), a causative agent belonging to the genus Alphacoronavirus in the family Coronaviridae, is an enveloped, positive, single-stranded RNA virus (Karte et al., 2020). The PEDV genome is approximately 28 kb and contains at least seven open reading frames (ORFs), which encode two large polyprotein precursors (pp1a and pp1ab); the spike (S), membrane (M), and envelope (E) structural proteins; and nucleocapsid (N) proteins, as well as an accessory protein, ORF3 (Zhuang et al., 2025). The virus genotype includes G1 (classical G1a and recombinant G1b) and G2 (local epidemic G2a and global epidemic G2b) (Jang et al., 2023).
The highly pathogenic (HP)-G2b PEDV caused a pandemic that severely impacted pig-producing nations in America and Asia during 2013–2014 and also threatened the global pig industry (Park et al., 2007; Puranaveja et al., 2009; Lee et al., 2024). Most PEDV strains isolated from Vietnam belonged to the genotypes G1 and G2 and had very high genetic similarity with strains isolated from China and Thailand (Nguyen et al., 2023). The virus was first recognized in Europe in the 1970s and caused high piglet mortality and significant economic losses in Germany, France, Belgium, Ukraine, Austria, Portugal, and the Netherlands in 2014 (Dastjerdi et al., 2015; Grasland et al., 2015; Mesquita et al., 2015; Stadler et al., 2015; Steinrigl et al., 2015; Theuns et al., 2015; Dortmans et al., 2018). It was reported that the prevalence of PEDV-positive piglets during the first week on Spanish farms ranged from 3.7 to 12.9% in 2014 (Mesonero-Escuredo et al., 2018; Vidal et al., 2019). A recent investigation of 106 Spanish pig farms between 2017 and 2019 showed that the detected PEDV rate was 38.7% (Monteagudo et al., 2022). The investigation showed that PED can rapidly spread in PEDV-negative herds and cause 100% morbidity and 30 to 90% mortality in piglets (Jang et al., 2023). PEDV can also cause a 12.6% reduction in the farrowing rate and result in a 5.7% failure-to-breed rate, a 1.3% abortion rate, and 2.0% mummified fetuses, negatively affecting the reproductive performance of mature sows (Weng et al., 2016).
To fight the novel highly virulent PEDV infection, this review summarizes recent progress in the development of vaccines against highly virulent PEDV, natural compounds, and chemical and biochemical source-targeted drugs that have been explored in cell and pig models with clearly defined mechanisms. It also aims to provide comprehensive strategies for the prevention and control of highly virulent PEDV infections in pigs.
2 Progress and strategies in vaccines against highly virulent PEDV
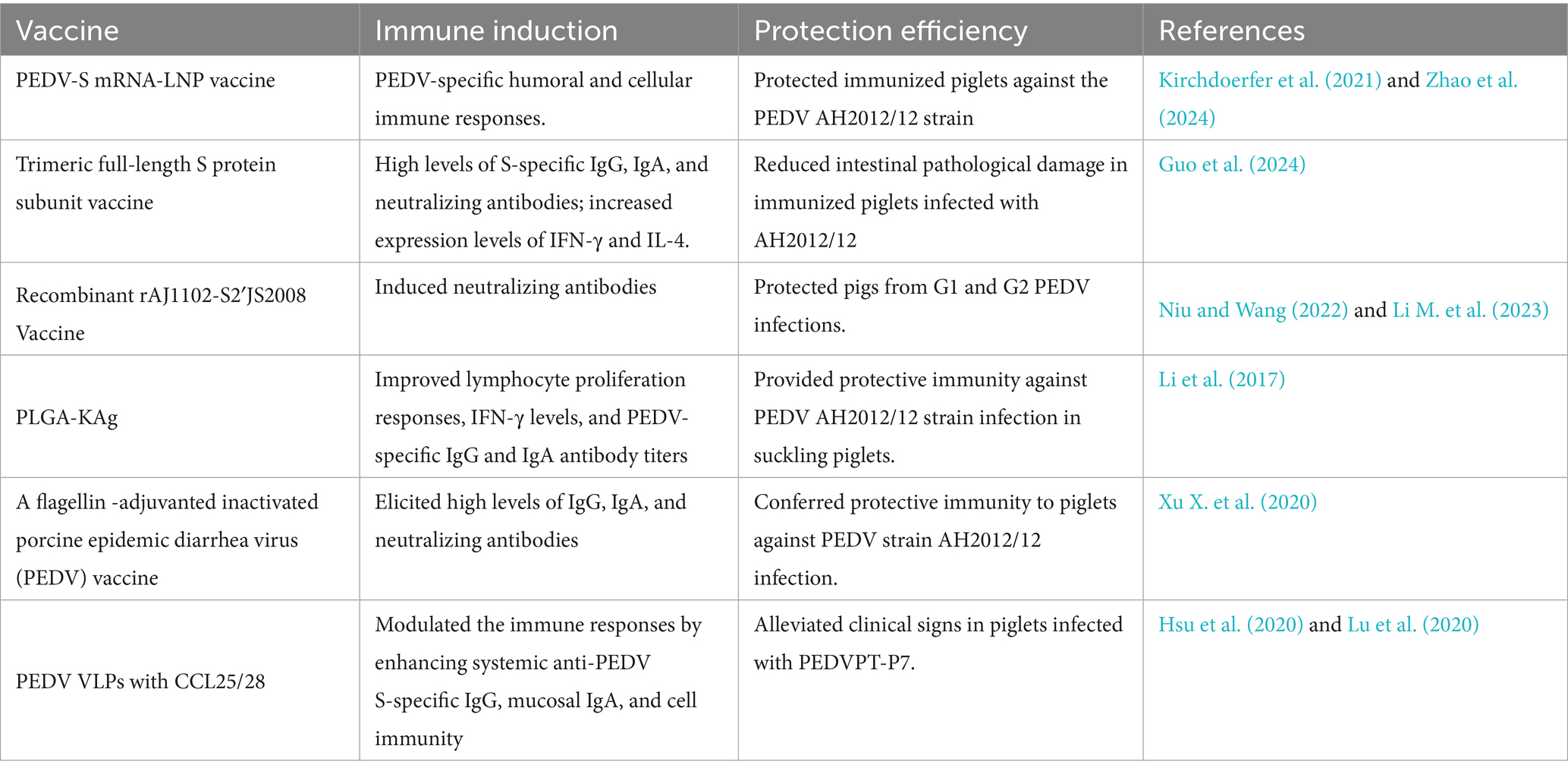
Viral entry, attachment, induction of neutralizing antibodies, and membrane fusion are mediated by the S1and S2 domains of the PEDV S glycoprotein. The CO-26 K-equivalent (COE) and N-terminal domain (NTD) in the S1 region are crucial neutralizing epitopes and potential co-receptor binding sites for the vaccine development of PEDV (Kirchdoerfer et al., 2021). Lipid nanoparticle (LNP)-encapsulated mRNA (mRNA-LNP) vaccines encoding a PEDV multiepitope chimeric spike (Sm) protein (PEDV-S mRNA-LNP) have been demonstrated to activate CD4 + and CD8 + T cells and induce PEDV-specific IgG and IgA in the serum and colostrum of S-mRNA-immunized sows, which could be transferred to suckling neonatal piglets, providing protection against AH2012/12 infection (Kirchdoerfer et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2024).
Whole-virus vaccines in traditional PEDV vaccines include inactivated and attenuated vaccines. In contrast to traditional PEDV vaccines, subunit vaccines can provide safety, without viral nucleic acids, the redesigned antigens and multiple antigens combination with the adjuvant addition in immunity efficacy elevation (Du et al., 2016). A complete subunit vaccine production system would greatly facilitate a quick response to emergency epidemics (Li Z. et al., 2020). The study showed that the full-length S protein subunit vaccine could effectively induce high levels of S-specific IgG, IgA, and neutralizing antibodies in pigs infected with AH2012/12. It also increased the proliferation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and increased interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and interleukin-4 (IL-4) expression levels in peripheral blood to reduce diarrheal index scores, fecal viral loads, and intestinal pathological damage in immunized piglets (Guo et al., 2024).
The addition of trypsin is crucial but also increases the complexity of vaccine production and cost in the propagation of PEDV. It has been reported that PEDV trypsin independence is associated with the S2′ site and Y976/977 of the PEDV spike (S) protein (Li M. et al., 2023). Li M et al. used AJ1102 and the trypsin-independent genotype 1 (G1) PEDV strain JS2008 to generate a recombinant PEDV carrying a chimeric S protein and successfully constructed the trypsin-independent PEDV strain rAJ1102-S2′JS2008 (Li M. et al., 2023). It was able to effectively replicate in the absence of trypsin and could induce neutralizing antibodies against AJ1102 and JS2008, providing protection to pigs against G1 and G2 PEDV infections (Niu and Wang, 2022; Li M. et al., 2023).
Immunizing sows with PEDV vaccines between 20 and 30 days will provide substantial passive immunity to their newborn piglets, especially mucosal immunity, which is essential for the sows (Lin et al., 2016). As a particle-mediated delivery system for vaccines, biodegradable and biocompatible poly (D, L-lactide-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles (NPs) can protect the entrapped vaccine from protease-mediated degradation at mucosal surfaces and stimulate the underlying mucosal immune cells to provide protection for sows infected with AH2012/12 (Binjawadagi et al., 2014a; Binjawadagi et al., 2014b). PLGA nanoparticle-entrapped PEDV killed vaccine antigens (KAg) (PLGA-KAg) have been shown to improve PEDV-specific IgG and IgA antibody titers, induce lymphocyte proliferation responses, and increase IFN-γ levels in pregnant sows and their suckling piglets (Li et al., 2017).
As a potential adjuvant, flagellin can induce Th1 and Th2 mixed-cell responses (Li et al., 2018). Flagellin can be used in combination with inactivated or killed PEDV vaccines to elevate mucosal and systemic IgG and IgA levels, thereby protecting piglets from PEDV AH2012/12 infection (Xu X. et al., 2020).
For the highly virulent PEDV G2 strains, traditional vaccines can only provide partial cross-protection (Wang et al., 2016). Commercialized vaccines, including recombinant PEDV S protein, an inactivated whole-virus vaccine based on a non-S INDEL PEDV strain, and a subunit vaccine using HEK-293 T cell-expressed PEDV S1 proteins, have been used to control virulent G2 viruses in the United States (Makadiya et al., 2016). However, commercialized vaccines cannot provide consistency in stimulating solid lactogenic immunity to protect suckling piglets from G2 virus infection (Crawford et al., 2016). Virus-like particles (VLPs) can improve immunogenicity, drain freely into lymph nodes, and be efficiently taken up by antigen-presenting cells to promote CD4 + T helper cell and CD8 + cytotoxic T cell responses (Dudziak et al., 2007; Mohsen et al., 2017). As characterized nanoparticles of conformational epitopes, VLPs can induce the subsequent humoral immunity by interacting with B cells (Manolova et al., 2008; Hsueh et al., 2020). In the development of safe, effective, and economical vaccines against enteric viral diseases, VLP vaccines represent an important strategy by stimulating cellular, mucosal, and humoral immunity. In the current study, PEDV VLPs of CCL25/28 were demonstrated to protect pigs from PEDVPT-P7infection by increasing systemic anti-PEDV S-specific IgG, mucosal IgA, and cellular immunity (Leidenberger et al., 2017; Hsu et al., 2020; Lu et al., 2020).
mRNA-LNP vaccines, the full-length S protein subunit, the trypsin-independent genotype 1 (G1) PEDV JS2008 strain, PLGA nanoparticle-entrapped PEDV killed vaccines, flagellin, and PEDV VLPs of CCL25/28 have shown different immune regulation efficiencies in enhancing systemic anti-PEDV S-specific IgG, mucosal IgA, and cell immunity to protect pigs from highly virulent PEDV infection (Table 1). To continue exploring vaccines, it is indispensable to prevent and control PED infections caused by different novel highly virulent PEDV strains in pigs.
3 Progress and strategies in drugs targeting highly virulent PEDV
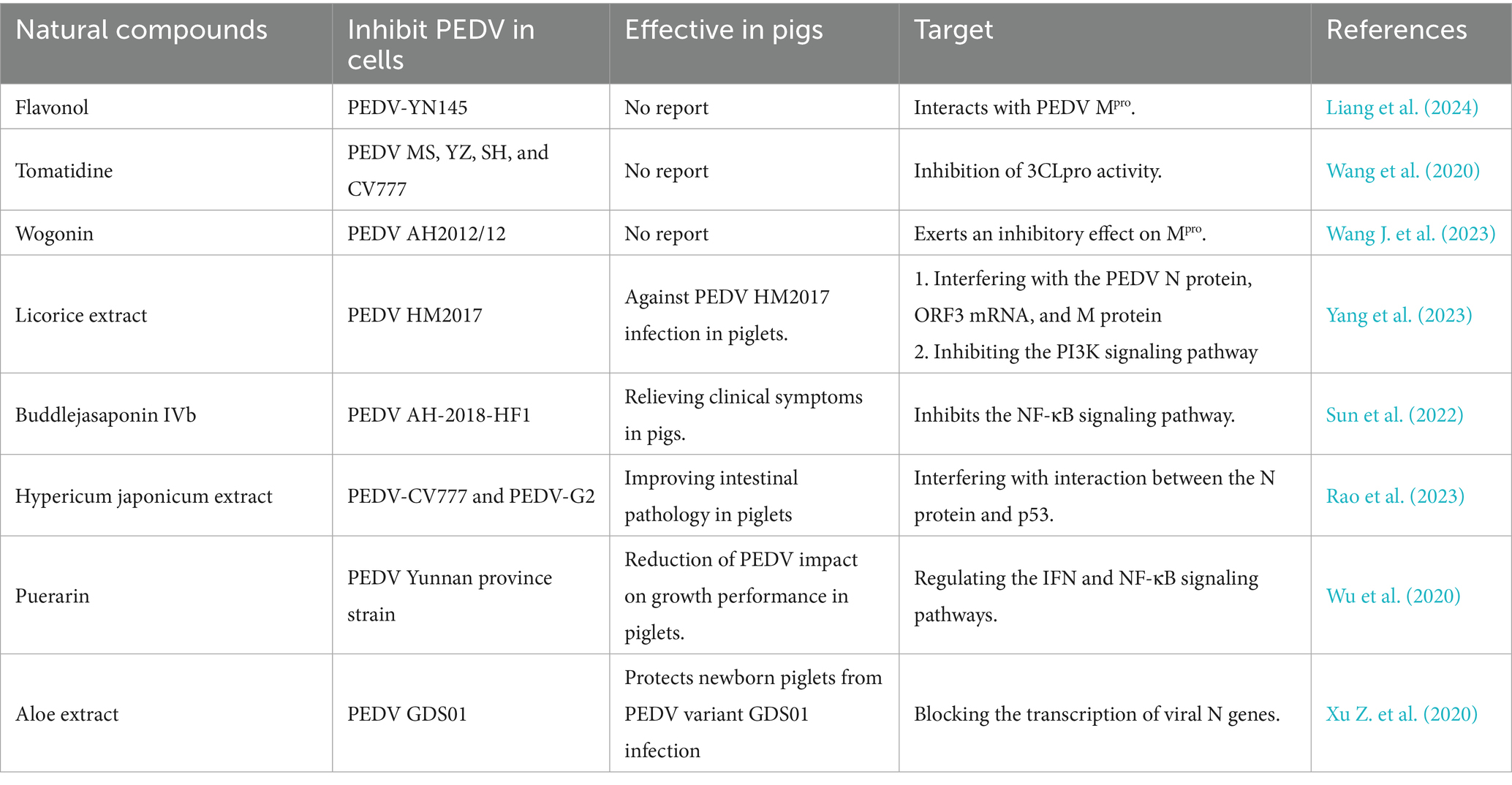
Maternal antibodies from colostrum and milk are important to protect piglets from PEDV infection (Leidenberger et al., 2017). PEDV mutation could decrease the full protection of the vaccines (Li S. et al., 2020). Therefore, it is necessary to update vaccines based on prevalent PEDV strains and explore new strategies (Yang et al., 2023). Antiviral natural compounds from plant extracts and Chinese herbal medicines have been increasingly demonstrated in recent years. In view of rich sources, unique chemical structures, and diverse activities of natural compounds in the development of new anti-highly virulent PEDV drugs, natural compounds will compensate for the vaccine deficiency in against PEDV prevalent strains (Russo et al., 2020; Gong et al., 2023). Recently, the anti-highly virulent PEDV of natural products target drugs have become a hot spot because of its lower side effects, cheaper investment and avoidable risk in developing resistance (Behzadi et al., 2023; Liang et al., 2024). Many natural compounds have also been reported to be effective in inhibiting highly virulent PEDV (Sun et al., 2022). Drugs including flavonol, tomatidine, and wogonin have been reported to affect highly virulent PEDV by interacting with the Mpro or 3CLpro proteins of PEDV in vitro (Wang et al., 2020; Wang J. et al., 2023; Liang et al., 2024) (Table 2). These compounds can be good candidate drugs against highly virulent PEDV in cells or pigs, pending further demonstration in in vivo studies. Based on their effects on highly virulent PEDV in vitro and vivo, licorice extract, buddlejasaponin IVb, hypericum japonicum extract, puerarin, and aloe extract have been shown to inhibit highly virulent PEDV by interfering with the N protein, ORF3 mRNA, and M protein; inhibiting the PI3K and NF-κB signaling pathways; and blocking the transcription of viral N genes (Wu et al., 2020; Xu Z. et al., 2020; Su et al., 2021; Sun et al., 2022; Rao et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2023). These drugs could reduce the replication of highly virulent PEDV and also alleviate clinical symptoms in pigs. They hold promising clinical value for future exploration of their effects against highly virulent PEDV both in vitro and in vivo.
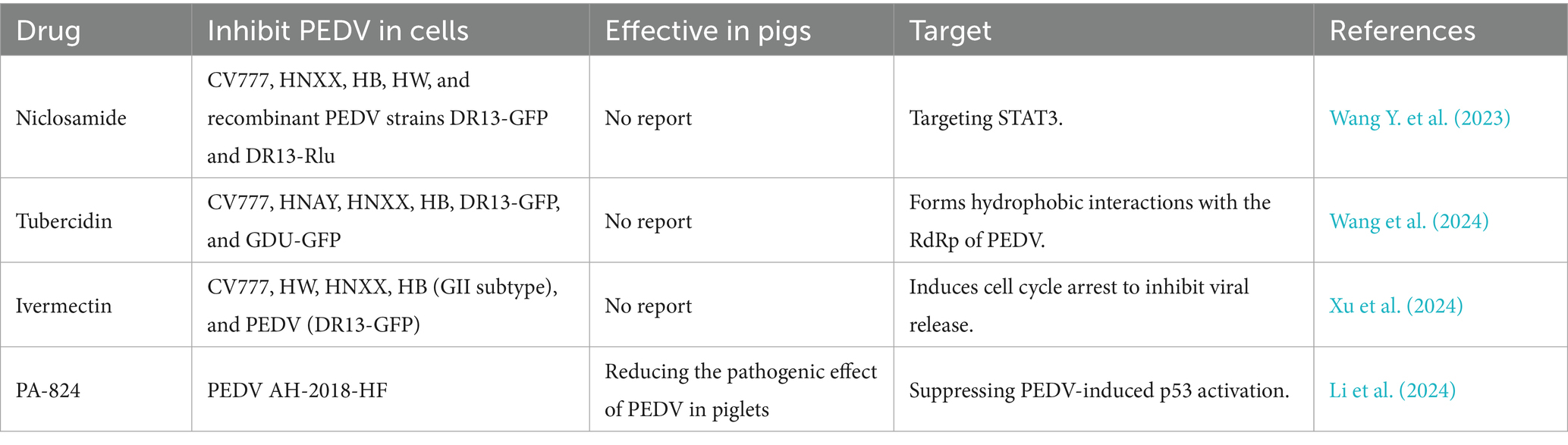
There are chemical drugs targeting highly virulent PEDV, including niclosamide, tubercidin, and ivermectin, that can inhibit the proliferation of highly virulent PEDV in vitro by targeting the specific viral mechanisms (Wang Y. et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2024) (Table 3). Considering the evasive strategies of PEDV, it is important to regulate the proliferation of highly virulent PEDV by targeting the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) (Wang Y. et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2024). Although these targeted drugs have only been tested in vitro, they still offer extraordinary therapy strategies for the prevention of highly virulent PEDV. Among these drugs, PA-824 has been demonstrated to inhibit the proliferation of highly virulent PEDV and alleviate diarrhea symptoms in pigs caused by PEDV AH-2018-HF infection by suppressing PEDV-induced p53 activation in vitro and in vivo (Li et al., 2024). Especially, the specially target drugs tested in pigs will be priority in synergistic therapy and increase anti-highly virulent PEDV efficiency.
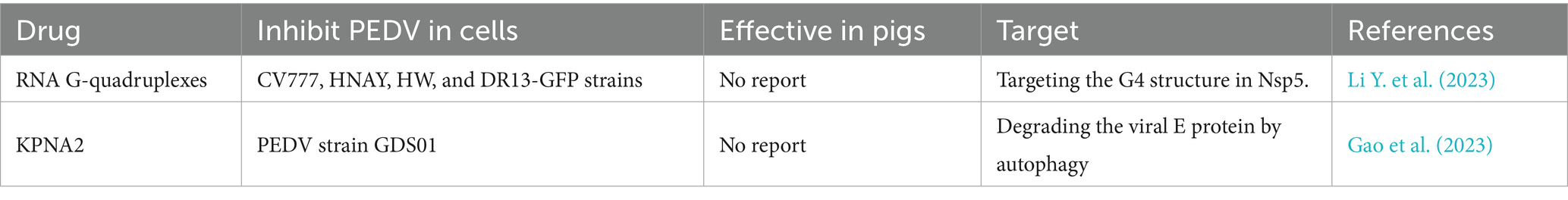
Biochemical source drugs, including RNA G-quadruplexes and Karyopherin α2 (KPNA2), have shown substantial inhibition of highly virulent PEDV replication by targeting the G4 structure in Nsp5 and the E protein, respectively, in vitro (Gao et al., 2023; Li Y. et al., 2023). The highly virulent PEDV genome and structural proteins (S, E, M, and N) (Table 4) are crucial determinants of the molecular epidemiological characteristics of PEDV (Karte et al., 2020; Jang et al., 2023; Zhuang et al., 2025). It is necessary to further explore and test biochemical source drugs in vivo, as they may provide new options to face emerging challenges from PEDV variant strains. As an important direction for future studies, there is a real demand in veterinary clinics to explore and screen high-efficiency, low-toxicity, and low-residue drugs with targeted therapy against highly virulent PEDV (Behzadi et al., 2023). Natural compounds and chemical and biochemical source-targeted drugs can complement each other’s advantages through drug combination, thereby promoting the efficacy of drug-based prevention and control of highly virulent PEDV.
4 Progress and strategies in drugs targeting toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3)
Inducing antiviral innate immune and inflammatory responses is an important precondition for repelling viral infections (Yang and Shu, 2020). Studies have shown that the production of type I or type III IFNs could be inhibited by highly virulent PEDV N proteins, such as nsp1, PLP2, nsp5, nsp15, and nsp16 (Deng et al., 2019; Shi et al., 2019). This inhibition benefits highly virulent PEDV by enabling immune evasion through suppression of IFN production pathways and disruption of transcription factor activation involved in IFN induction (Cao et al., 2015a; Guo et al., 2016; Li S. et al., 2020). Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) can specifically recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) by activating IFN- and interleukin-1 (IL-1)-mediated proinflammatory responses in animals (Rai, 2020). As a member of the virus-perceiving PRRs, Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) can initiate downstream signal transduction, upregulate the IFN-α/β expression, and induce antiviral protein (AVP) synthesis activity by recognizing viral double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) (Unterholzner et al., 2010; Matsumoto et al., 2011). Within the TLR family, TLR3 is the only receptor that induces IFN-β production through the Toll/IL-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β (TRIF) pathway (Yang and Shu, 2020). The TRIF-dependent nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and IFN regulatory factor 3/7 (IRF3/7) pathways are regulated by TLR3 (Matsumoto et al., 2011). When TLR3 is activated by viral dsRNA, TRIF could elicit a cascade of reactions by triggering tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3) and TRAF6 (Fang et al., 2013; Bugge et al., 2017) (Figure 1).
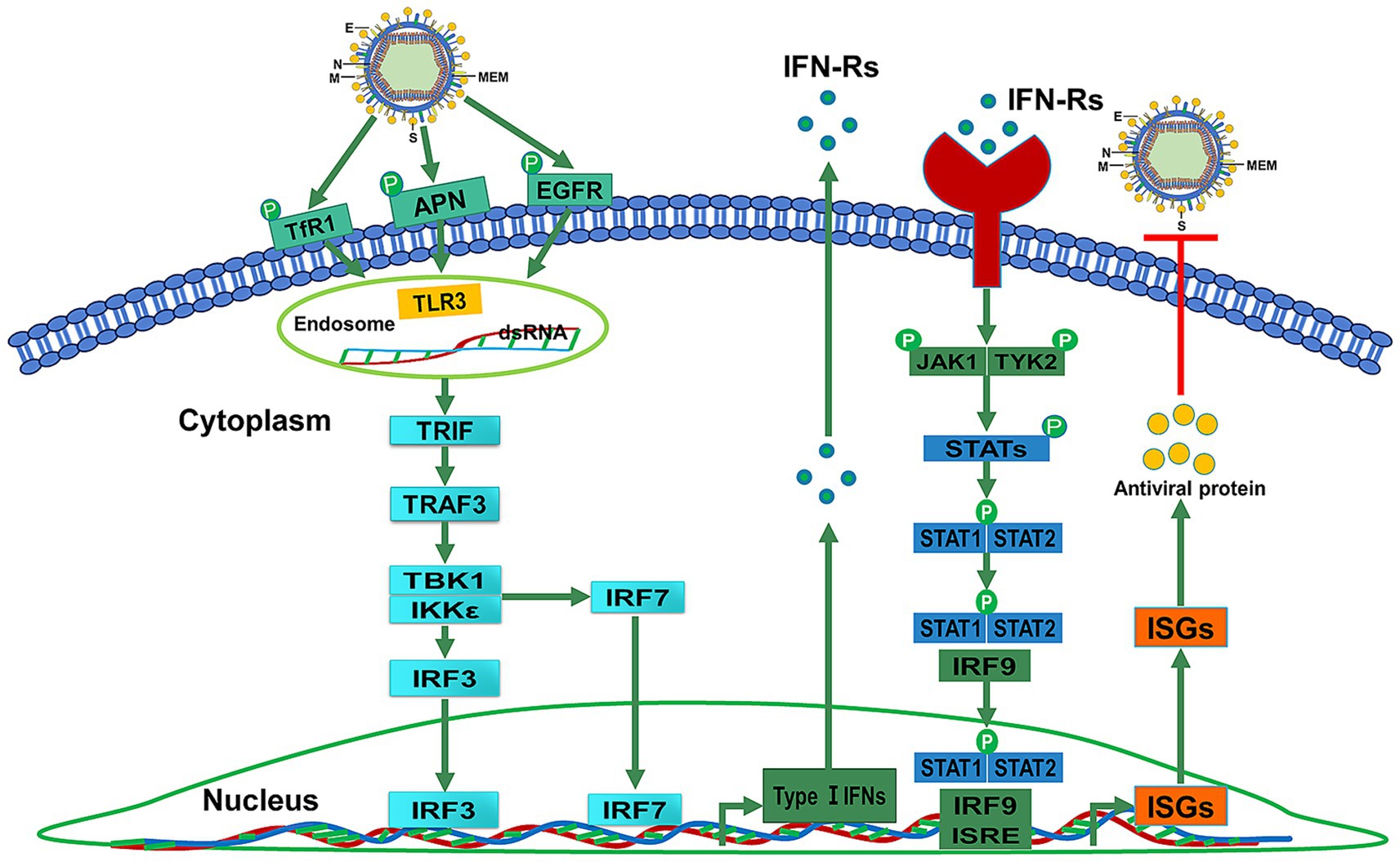
Figure 1. TLR3 upregulates IFN-α/β expression and induces AVP synthesis activity by recognizing dsRNA. The TLR3-mediated signaling pathway includes the TRIF-dependent NF-κB and IRF3/7 pathways. TRIF interacts with TRAF3 to elicit a cascade of reactions to induce the production of IFNs-1.
TLR3 localizes to endosomes and the cell surface in macrophages and mast cells (MCs) but is restricted to endosomes in myeloid dendritic cells (DCs) (Matsumoto et al., 2003; Matsumoto et al., 2011; Agier et al., 2016). Type I IFNs (α and β) are associated with viral clearance and can be produced by DCs (Matsumoto et al., 2003). TLR3 can drive antigen-presenting DCs to induce IFN production (Soto et al., 2020). TLR3 also promotes IRF3, type I and II IFN receptor, and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) I expression in MCs to enhance the cellular antiviral response (Soto et al., 2020; Witczak et al., 2020). Viral infection leads to TLR3 expression upregulation in DCs of mice and humans. Virus dsRNA is recognized by the TLR3 ectodomain (ECD) (Negishi et al., 2008; Abe et al., 2012). The TIR domain of TLR3 can recruit TRIF (Chattopadhyay and Sen, 2014). It can stimulate the phosphorylation of IRF3, which leads to the production of type I IFNs (Takeda and Akira, 2004). A study demonstrated that TLR3 positively contributes to NF-kB activation in response to PEDV infection (Cao et al., 2015b). TLR3 activates NF-κB signaling through TRIF-dependent conscription of two cascades. It is most noteworthy pathway of TLR3 signaling that can provoke TNF, IL-1, CCL2, CXCL8, endothelial adhesion molecules, and type I IFNs to against viruses (Komal et al., 2021). The TLR3 agonist can upregulate the expression of IFN-α/β and induce AVP synthesis activity by recognizing virus dsRNA to activate TLR3 downstream signal transduction (Unterholzner et al., 2010; Matsumoto et al., 2011).
Novel TLR3 agonists include RGC100, Poly-IC, and ARNAX. As a novel TLR3 agonist, RGC100 can target endosomal TLR3 and activate murine myeloid DCs to promote proinflammatory cytokine secretion in a dose-dependent manner (Naumann et al., 2013). Considering its immunological properties, RGC100 may represent a promising candidate for prevention and therapy vaccination strategies against PEDV. As a synthetic dsRNA analog, polycytidylic acid (PolyI:C) can be recognized by RIG-I/MDA-5 and TLR3 receptors to activate transcription factors that are responsible for the expression of type I IFNs and inflammatory cytokines/chemokines (Kanmani and Kim, 2019). Poly-IC12U is an altered form of poly IC. It reduces poly IC-associated toxicity and regulates IFN expression by activating the TLR3 receptor (Martins et al., 2015). As a synthetically derived form of poly-IC, Poly-ICLC can induce strong Th1 cytokine responses, including IL-6, IL-12, TNF-α, IFN-γ, and type 1 IFNs (Komal et al., 2021). ARNAX is a synthetic DNA–dsRNA hybrid compound and can activate MDA5 (Komal et al., 2021). ARNAX cannot activate the TLR3 pathway.
Different from ARNAX, poly-IC can activate both TLR3 and MDA5 (Shime et al., 2017). In addition, the inflammatory status of macrophages and DCs can also be changed by poly-IC and RGC100 (Longhi et al., 2009; Gupta et al., 2016; Takeda et al., 2018). Therefore, TLR3 agonists, poly-IC and RGC100, ought to be considered as adjuvants for highly virulent PEDV vaccination.
5 Conclusion
As an acute and highly contagious enteric disease of swine, highly virulent PEDV causes high piglet mortality and significant economic losses. However, commercialized vaccines can only provide partial cross-protection against novel highly virulent PEDV strains. The development of new vaccines against highly virulent PEDV including mRNA-LNP, subunit, trypsin-independent, nanoparticle-entrapped killed PEDV, and virus-like particle (VLP) vaccines will help protect the swine industry from the serious challenges posed by highly virulent PEDV infection. Natural compounds and chemical and biochemical source-targeted drugs can enhance the effectiveness of drug-based prevention in controlling highly virulent PEDV. As adjuvants, TLR3 agonists can aid vaccines to compensate for IFN secretory deficiencies to protect pigs from highly virulent PEDV infection. Researchers working on the vaccines and drugs mentioned in this review need more time to complete in-depth studies on vaccines and targeted drugs against highly virulent porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Continued focus on the ongoing research of these vaccines and drugs will provide valuable scientific information for their application in PEDV control and prevention, once sufficient evidence supports effective strategies for managing the disease.
Author contributions
QW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. SL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. HC: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. XL: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. XW: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. QM: Formal analysis, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. HD: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The key research and development program of Jilin Province, China (Grant: 20230202083NC) provided financial support for preparation of the article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan Item, China, for supporting this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abe, Y., Fujii, K., Nagata, N., Takeuchi, O., Akira, S., Oshiumi, H., et al. (2012). The toll-like receptor 3-mediated antiviral response is important for protection against poliovirus infection in poliovirus receptor transgenic mice. J. Virol. 86, 185–194. doi: 10.1128/jvi.05245-11
Agier, J., Żelechowska, P., Kozłowska, E., and Brzezińska-Błaszczyk, E. (2016). Expression of surface and intracellular toll-like receptors by mature mast cells. Cent Eur J Immunol 4, 333–338. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2016.65131
Behzadi, A., Imani, S., Deravi, N., Mohammad Taheri, Z., Mohammadian, F., Moraveji, Z., et al. (2023). Antiviral potential of Melissa officinalis L.: a literature review. Nutr. Metab. Insights 16:11786388221146683. doi: 10.1177/11786388221146683
Binjawadagi, B., Dwivedi, V., Manickam, C., Ouyang, K., Torrelles, J. B., and Renukaradhya, G. J. (2014a). An innovative approach to induce cross-protective immunity against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in the lungs of pigs through adjuvanted nanotechnology-based vaccination. Int. J. Nanomedicine 9, 1519–1535. doi: 10.2147/ijn.S59924
Binjawadagi, B., Dwivedi, V., Manickam, C., Ouyang, K., Wu, Y., Lee, L. J., et al. (2014b). Adjuvanted poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid nanoparticle-entrapped inactivated porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus vaccine elicits cross-protective immune response in pigs. Int. J. Nanomedicine 9, 679–694. doi: 10.2147/ijn.S56127
Bugge, M., Bergstrom, B., Eide, O. K., Solli, H., Kjønstad, I. F., Stenvik, J., et al. (2017). Surface toll-like receptor 3 expression in metastatic intestinal epithelial cells induces inflammatory cytokine production and promotes invasiveness. J. Biol. Chem. 292, 15408–15425. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.784090
Cao, L., Ge, X., Gao, Y., Herrler, G., Ren, Y., Ren, X., et al. (2015a). Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus inhibits dsRNA-induced interferon-β production in porcine intestinal epithelial cells by blockade of the RIG-I-mediated pathway. Virol. J. 12:127. doi: 10.1186/s12985-015-0345-x
Cao, L., Ge, X., Gao, Y., Ren, Y., Ren, X., and Li, G. (2015b). Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection induces NF-κB activation through the TLR2, TLR3 and TLR9 pathways in porcine intestinal epithelial cells. J. Gen. Virol. 96, 1757–1767. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.000133
Chattopadhyay, S., and Sen, G. C. (2014). dsRNA-activation of TLR3 and RLR signaling: gene induction-dependent and independent effects. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 34, 427–436. doi: 10.1089/jir.2014.0034
Crawford, K., Lager, K. M., Kulshreshtha, V., Miller, L. C., and Faaberg, K. S. (2016). Status of vaccines for porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in the United States and Canada. Virus Res. 226, 108–116. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.08.005
Dastjerdi, A., Carr, J., Ellis, R. J., Steinbach, F., and Williamson, S. (2015). Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus among farmed pigs, Ukraine. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 21, 2235–2237. doi: 10.3201/eid2112.150272
Deng, X., van Geelen, A., Buckley, A. C., O'Brien, A., Pillatzki, A., Lager, K. M., et al. (2019). Coronavirus endoribonuclease activity in porcine epidemic diarrhea virus suppresses type I and type III interferon responses. J. Virol. 93:e02000–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02000-18
Dortmans, J., Li, W., van der Wolf, P. J., Buter, G. J., Franssen, P. J. M., van Schaik, G., et al. (2018). Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) introduction into a naive Dutch pig population in 2014. Vet. Microbiol. 221, 13–18. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.05.014
Du, L., Tai, W., Zhou, Y., and Jiang, S. (2016). Vaccines for the prevention against the threat of MERS-CoV. Expert Rev. Vaccines 15, 1123–1134. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2016.1167603
Dudziak, D., Kamphorst, A. O., Heidkamp, G. F., Buchholz, V. R., Trumpfheller, C., Yamazaki, S., et al. (2007). Differential antigen processing by dendritic cell subsets in vivo. Science 315, 107–111. doi: 10.1126/science.1136080
Fang, F., Ooka, K., Sun, X., Shah, R., Bhattacharyya, S., Wei, J., et al. (2013). A synthetic TLR3 ligand mitigates profibrotic fibroblast responses by inducing autocrine IFN signaling. J. Immunol. 191, 2956–2966. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300376
Gao, Q., Weng, Z., Feng, Y., Gong, T., Zheng, X., Zhang, G., et al. (2023). KPNA2 suppresses porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication by targeting and degrading virus envelope protein through selective autophagy. J. Virol. 97:e0011523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00115-23
Gong, M., Xia, X., Chen, D., Ren, Y., Liu, Y., Xiang, H., et al. (2023). Antiviral activity of chrysin and naringenin against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection. Front Vet Sci 10:1278997. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1278997
Grasland, B., Bigault, L., Bernard, C., Quenault, H., Toulouse, O., Fablet, C., et al. (2015). Complete genome sequence of a porcine epidemic diarrhea s gene indel strain isolated in France in december 2014. Genome Announc. 3:e00535–15. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00535-15
Guo, L., Luo, X., Li, R., Xu, Y., Zhang, J., Ge, J., et al. (2016). Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection inhibits interferon signaling by targeted degradation of STAT1. J. Virol. 90, 8281–8292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01091-16
Guo, W., Wang, C., Song, X., Xu, H., Zhao, S., Gu, J., et al. (2024). Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a trimeric full-length S protein subunit vaccine for porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Vaccine 42, 828–839. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.01.020
Gupta, S. K., Yadav, P. K., Tiwari, A. K., Gandham, R. K., and Sahoo, A. P. (2016). Poly (I:C) enhances the anti-tumor activity of canine parvovirus NS1 protein by inducing a potent anti-tumor immune response. Tumour Biol. 37, 12089–12102. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5093-z
Hsu, C. W., Chang, M. H., Chang, H. W., Wu, T. Y., and Chang, Y. C. (2020). Parenterally administered porcine epidemic diarrhea virus-like particle-based vaccine formulated with CCL25/28 chemokines induces systemic and mucosal immune Protectivity in pigs. Viruses 12:1122. doi: 10.3390/v12101122
Hsueh, F. C., Chang, Y. C., Kao, C. F., Hsu, C. W., and Chang, H. W. (2020). Intramuscular immunization with chemokine-Adjuvanted inactive porcine epidemic diarrhea virus induces substantial protection in pigs. Vaccines (Basel) 8:102. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8010102
Jang, G., Lee, D., Shin, S., Lim, J., Won, H., Eo, Y., et al. (2023). Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: an update overview of virus epidemiology, vaccines, and control strategies in South Korea. J. Vet. Sci. 24:e58. doi: 10.4142/jvs.23090
Kanmani, P., and Kim, H. (2019). Immunobiotic strains modulate toll-like receptor 3 agonist induced innate antiviral immune response in human intestinal epithelial cells by modulating IFN regulatory factor 3 and NF-κB signaling. Front. Immunol. 10:1536. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01536
Karte, C., Platje, N., Bullermann, J., Beer, M., Höper, D., and Blome, S. (2020). Re-emergence of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in a piglet-producing farm in northwestern Germany in 2019. BMC Vet. Res. 16:329. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02548-4
Kirchdoerfer, R. N., Bhandari, M., Martini, O., Sewall, L. M., Bangaru, S., Yoon, K. J., et al. (2021). Structure and immune recognition of the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus spike protein. Structure 29, 385–392.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2020.12.003
Komal, A., Noreen, M., and El-Kott, A. F. (2021). TLR3 agonists: RGC100, ARNAX, and poly-IC: a comparative review. Immunol. Res. 69, 312–322. doi: 10.1007/s12026-021-09203-6
Lee, D., Kim, S., Gim, Y., and Lee, C. (2024). Genotypic characterization of novel S-DEL variants of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus identified in South Korea. Arch. Virol. 169:158. doi: 10.1007/s00705-024-06088-2
Leidenberger, S., Schröder, C., Zani, L., Auste, A., Pinette, M., Ambagala, A., et al. (2017). Virulence of current German PEDV strains in suckling pigs and investigation of protective effects of maternally derived antibodies. Sci. Rep. 7:10825. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11160-w
Li, B., Du, L., Yu, Z., Sun, B., Xu, X., Fan, B., et al. (2017). Poly (d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticle-entrapped vaccine induces a protective immune response against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection in piglets. Vaccine 35, 7010–7017. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.10.054
Li, L., Li, H., Qiu, Y., Li, J., Zhou, Y., Lv, M., et al. (2024). PA-824 inhibits porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection in vivo and in vitro by inhibiting p53 activation. J. Virol. 98:e0041323. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00413-23
Li, Z., Ma, Z., Li, Y., Gao, S., and Xiao, S. (2020). Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: molecular mechanisms of attenuation and vaccines. Microb. Pathog. 149:104553. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104553
Li, Q., Peng, O., Wu, T., Xu, Z., Huang, L., Zhang, Y., et al. (2018). PED subunit vaccine based on COE domain replacement of flagellin domain D3 improved specific humoral and mucosal immunity in mice. Vaccine 36, 1381–1388. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.01.086
Li, S., Yang, J., Zhu, Z., and Zheng, H. (2020). Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and the host innate immune response. Pathogens 9:367. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9050367
Li, M., Zhang, Y., Fang, Y., Xiao, S., Fang, P., and Fang, L. (2023). Construction and immunogenicity of a trypsin-independent porcine epidemic diarrhea virus variant. Front. Immunol. 14:1165606. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1165606
Li, Y., Zhu, Y., Wang, Y., Feng, Y., Li, D., Li, S., et al. (2023). Characterization of RNA G-quadruplexes in porcine epidemic diarrhea virus genome and the antiviral activity of G-quadruplex ligands. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 231:123282. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123282
Liang, J., Xu, W., Gou, F., Qin, L., Yang, H., Xiao, J., et al. (2024). Antiviral activity of flavonol against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Virology 597:110128. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2024.110128
Lin, H., Chen, L., Gao, L., Yuan, X., Ma, Z., and Fan, H. (2016). Epidemic strain YC2014 of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus could provide piglets against homologous challenge. Virol. J. 13:68. doi: 10.1186/s12985-016-0529-z
Longhi, M. P., Trumpfheller, C., Idoyaga, J., Caskey, M., Matos, I., Kluger, C., et al. (2009). Dendritic cells require a systemic type I interferon response to mature and induce CD4+ Th1 immunity with poly IC as adjuvant. J. Exp. Med. 206, 1589–1602. doi: 10.1084/jem.20090247
Lu, Y., Clark-Deener, S., Gillam, F., Heffron, C. L., Tian, D., Sooryanarain, H., et al. (2020). Virus-like particle vaccine with B-cell epitope from porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) incorporated into hepatitis B virus core capsid provides clinical alleviation against PEDV in neonatal piglets through lactogenic immunity. Vaccine 38, 5212–5218. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.06.009
Makadiya, N., Brownlie, R., van den Hurk, J., Berube, N., Allan, B., Gerdts, V., et al. (2016). S1 domain of the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus spike protein as a vaccine antigen. Virol. J. 13:57. doi: 10.1186/s12985-016-0512-8
Manolova, V., Flace, A., Bauer, M., Schwarz, K., Saudan, P., and Bachmann, M. F. (2008). Nanoparticles target distinct dendritic cell populations according to their size. Eur. J. Immunol. 38, 1404–1413. doi: 10.1002/eji.200737984
Martins, K. A., Bavari, S., and Salazar, A. M. (2015). Vaccine adjuvant uses of poly-IC and derivatives. Expert Rev. Vaccines 14, 447–459. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2015.966085
Matsumoto, M., Funami, K., Tanabe, M., Oshiumi, H., Shingai, M., Seto, Y., et al. (2003). Subcellular localization of toll-like receptor 3 in human dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 171, 3154–3162. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.6.3154
Matsumoto, M., Oshiumi, H., and Seya, T. (2011). Antiviral responses induced by the TLR3 pathway. Rev. Med. Virol. 21, 67–77. doi: 10.1002/rmv.680
Mesonero-Escuredo, S., Strutzberg-Minder, K., Casanovas, C., and Segalés, J. (2018). Viral and bacterial investigations on the aetiology of recurrent pig neonatal diarrhoea cases in Spain. Porcine Health Manag 4:5. doi: 10.1186/s40813-018-0083-8
Mesquita, J. R., Hakze-van der Honing, R., Almeida, A., Lourenço, M., van der Poel, W. H., and Nascimento, M. S. (2015). Outbreak of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in Portugal, 2015. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 62, 586–588. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12409
Mohsen, M. O., Gomes, A. C., Cabral-Miranda, G., Krueger, C. C., Leoratti, F. M., Stein, J. V., et al. (2017). Delivering adjuvants and antigens in separate nanoparticles eliminates the need of physical linkage for effective vaccination. J. Control. Release 251, 92–100. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.02.031
Monteagudo, L. V., Benito, A. A., Lázaro-Gaspar, S., Arnal, J. L., Martin-Jurado, D., Menjon, R., et al. (2022). Occurrence of rotavirus a genotypes and other enteric pathogens in diarrheic suckling piglets from Spanish swine farms. Animals (Basel) 12:251. doi: 10.3390/ani12030251
Naumann, K., Wehner, R., Schwarze, A., Petzold, C., Schmitz, M., and Rohayem, J. (2013). Activation of dendritic cells by the novel toll-like receptor 3 agonist RGC100. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013:283649. doi: 10.1155/2013/283649
Negishi, H., Osawa, T., Ogami, K., Ouyang, X., Sakaguchi, S., Koshiba, R., et al. (2008). A critical link between toll-like receptor 3 and type II interferon signaling pathways in antiviral innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 20446–20451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810372105
Nguyen, N. H., Huynh, T. M., Nguyen, H. D., Lai, D. C., and Nguyen, M. N. (2023). Epidemiological and genetic characterization of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam, from 2015 to 2017. Arch. Virol. 168:152. doi: 10.1007/s00705-023-05779-6
Niu, X., and Wang, Q. (2022). Prevention and control of porcine epidemic diarrhea: the development of recombination-resistant live attenuated vaccines. Viruses 14:1317. doi: 10.3390/v14061317
Park, S. J., Moon, H. J., Yang, J. S., Lee, C. S., Song, D. S., Kang, B. K., et al. (2007). Sequence analysis of the partial spike glycoprotein gene of porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses isolated in Korea. Virus Genes 35, 321–332. doi: 10.1007/s11262-007-0096-x
Puranaveja, S., Poolperm, P., Lertwatcharasarakul, P., Kesdaengsakonwut, S., Boonsoongnern, A., Urairong, K., et al. (2009). Chinese-like strain of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, Thailand. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 15, 1112–1115. doi: 10.3201/eid1507.081256
Rai, R. C. (2020). Host inflammatory responses to intracellular invaders: review study. Life Sci. 240:117084. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117084
Rao, H., Su, W., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Li, T., Li, J., et al. (2023). Hypericum japonicum extract inhibited porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in vitro and in vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 14:1112610. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1112610
Russo, M., Moccia, S., Spagnuolo, C., Tedesco, I., and Russo, G. L. (2020). Roles of flavonoids against coronavirus infection. Chem. Biol. Interact. 328:109211. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109211
Shi, P., Su, Y., Li, R., Liang, Z., Dong, S., and Huang, J. (2019). PEDV nsp16 negatively regulates innate immunity to promote viral proliferation. Virus Res. 265, 57–66. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2019.03.005
Shime, H., Maruyama, A., Yoshida, S., Takeda, Y., Matsumoto, M., and Seya, T. (2017). Toll-like receptor 2 ligand and interferon-γ suppress anti-tumor T cell responses by enhancing the immunosuppressive activity of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Onco Targets Ther 7:e1373231. doi: 10.1080/2162402x.2017.1373231
Soto, J. A., Gálvez, N. M. S., Andrade, C. A., Pacheco, G. A., Bohmwald, K., Berrios, R. V., et al. (2020). The role of dendritic cells during infections caused by highly prevalent viruses. Front. Immunol. 11:1513. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01513
Stadler, J., Zoels, S., Fux, R., Hanke, D., Pohlmann, A., Blome, S., et al. (2015). Emergence of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in southern Germany. BMC Vet. Res. 11:142. doi: 10.1186/s12917-015-0454-1
Steinrigl, A., Fernández, S. R., Stoiber, F., Pikalo, J., Sattler, T., and Schmoll, F. (2015). First detection, clinical presentation and phylogenetic characterization of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in Austria. BMC Vet. Res. 11:310. doi: 10.1186/s12917-015-0624-1
Su, M., Shi, D., Xing, X., Qi, S., Yang, D., Zhang, J., et al. (2021). Coronavirus porcine epidemic diarrhea virus Nucleocapsid protein interacts with p53 to induce cell cycle arrest in S-phase and promotes viral replication. J. Virol. 95:e0018721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00187-21
Sun, P., Wang, M., Li, J., Qiu, Y., Li, H., Lv, M., et al. (2022). Inhibitory effect of Buddlejasaponin IVb on porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in vivo and in vitro. Vet. Microbiol. 272:109516. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2022.109516
Takeda, K., and Akira, S. (2004). TLR signaling pathways. Semin. Immunol. 16, 3–9. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2003.10.003
Takeda, Y., Takaki, H., Fukui-Miyazaki, A., Yoshida, S., Matsumoto, M., and Seya, T. (2018). Vaccine adjuvant ARNAX promotes mucosal IgA production in influenza HA vaccination. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 506, 1019–1025. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.10.166
Theuns, S., Conceição-Neto, N., Christiaens, I., Zeller, M., Desmarets, L. M., Roukaerts, I. D., et al. (2015). Complete genome sequence of a porcine epidemic diarrhea virus from a novel outbreak in Belgium, January 2015. Genome Announc. 3:e00506–15. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00506-15
Unterholzner, L., Keating, S. E., Baran, M., Horan, K. A., Jensen, S. B., Sharma, S., et al. (2010). IFI16 is an innate immune sensor for intracellular DNA. Nat. Immunol. 11, 997–1004. doi: 10.1038/ni.1932
Vidal, A., Martín-Valls, G. E., Tello, M., Mateu, E., Martín, M., and Darwich, L. (2019). Prevalence of enteric pathogens in diarrheic and non-diarrheic samples from pig farms with neonatal diarrhea in the north east of Spain. Vet. Microbiol. 237:108419. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.108419
Wang, P., Bai, J., Liu, X., Wang, M., Wang, X., and Jiang, P. (2020). Tomatidine inhibits porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication by targeting 3CL protease. Vet. Res. 51:136. doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00865-y
Wang, X., Chen, J., Shi, D., Shi, H., Zhang, X., Yuan, J., et al. (2016). Immunogenicity and antigenic relationships among spike proteins of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus subtypes G1 and G2. Arch. Virol. 161, 537–547. doi: 10.1007/s00705-015-2694-6
Wang, Y., Huang, H., Li, D., Zhao, C., Li, S., Qin, P., et al. (2023). Identification of niclosamide as a novel antiviral agent against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection by targeting viral internalization. Virol. Sin. 38, 296–308. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2023.01.008
Wang, J., Zeng, X., Yin, D., Yin, L., Shen, X., Xu, F., et al. (2023). In silico and in vitro evaluation of antiviral activity of wogonin against main protease of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 13:1123650. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1123650
Wang, T., Zheng, G., Chen, Z., Wang, Y., Zhao, C., Li, Y., et al. (2024). Drug repurposing screens identify tubercidin as a potent antiviral agent against porcine nidovirus infections. Virus Res. 339:199275. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199275
Weng, L., Weersink, A., Poljak, Z., de Lange, K., and von Massow, M. (2016). An economic evaluation of intervention strategies for porcine epidemic diarrhea (PED). Prev. Vet. Med. 134, 58–68. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2016.09.018
Witczak, P., Brzezińska-Błaszczyk, E., and Agier, J. (2020). The response of tissue mast cells to TLR3 ligand poly(I:C) treatment. J Immunol Res 2020, 1–13. doi: 10.1155/2020/2140694
Wu, M., Zhang, Q., Yi, D., Wu, T., Chen, H., Guo, S., et al. (2020). Quantitative proteomic analysis reveals antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects of Puerarin in piglets infected with porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Front. Immunol. 11:169. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00169
Xu, X., Du, L., Fan, B., Sun, B., Zhou, J., Guo, R., et al. (2020). A flagellin-adjuvanted inactivated porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) vaccine provides enhanced immune protection against PEDV challenge in piglets. Arch. Virol. 165, 1299–1309. doi: 10.1007/s00705-020-04567-w
Xu, X., Gao, S., Zuo, Q., Gong, J., Song, X., Liu, Y., et al. (2024). Enhanced in vitro antiviral activity of Ivermectin-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus via improved intracellular delivery. Pharmaceutics 16:601. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16050601
Xu, Z., Liu, Y., Peng, P., Liu, Y., Huang, M., Ma, Y., et al. (2020). Aloe extract inhibits porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in vitro and in vivo. Vet. Microbiol. 249:108849. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2020.108849
Yang, S., Huang, X., Li, S., Wang, C., Jansen, C. A., Savelkoul, H. F. J., et al. (2023). Linoleic acid: a natural feed compound against porcine epidemic diarrhea disease. J. Virol. 97:e0170023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01700-23
Yang, Q., and Shu, H. B. (2020). Deciphering the pathways to antiviral innate immunity and inflammation. Adv. Immunol. 145, 1–36. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2019.11.001
Zhao, Y., Fan, B., Song, X., Gao, J., Guo, R., Yi, C., et al. (2024). PEDV-spike-protein-expressing mRNA vaccine protects piglets against PEDV challenge. MBio 15:e0295823. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02958-23
Zhuang, L., Zhao, Y., Shen, J., Sun, L., Hao, P., Yang, J., et al. (2025). Advances in porcine epidemic diarrhea virus research: genome, epidemiology, vaccines, and detection methods. Discov Nano 20:48. doi: 10.1186/s11671-025-04220-y
Glossary
AVP - Antiviral protein
COE - CO-26 K-equivalent
DCs - Dendritic cells
dsRNA - Double-stranded RNA
ECD - Ectodomain
HP - Highly pathogenic
IKK - Nuclear factor-kappab (ikappab) kinase
IRF3/7 - IFN-regulatory factor 3/7
ISGs - IFN-stimulated genes
ISRE - IFN-stimulated response element
KAg - Killed vaccine antigens
KPNA2 - Karyopherin α 2
LNP - Lipid nanoparticle
MCs - Mast cells
MDA-5 - Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5
MHC - Major histocompatibility complex
mRNA-LNP - LNP-encapsulated mRNA
N protein - PEDV nucleocapsid (N) protein
NF-κB - Nuclear transcription factor-κB
NPs - Nanoparticles
NTD - N-terminal domain
NTPase - Nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase
ORFs - Open reading frames
PAMPs - Pathogen-associated molecular patterns
PED - Porcine epidemic diarrhea
PEDV - Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus
PEDV-S mRNA-LNP vaccine - mRNA-LNP vaccines encoding a PEDV multiepitope Sm protein
PI3K - Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
PKB/AKT - PI3K /protein kinase B
PLGA - Poly (D, L -lactide-co-glycolide)
PLGA-KAg - PLGA nanoparticle–entrapped PEDV KAG
PLP2 - Papain-like protease 2
PolyI:C - Polycytidylic acid
PRRs - Pattern-recognition receptors
RdRp - RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
RIG-I - Retinoic acid-inducible gene 1
STAT3 - Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
Sm - Chimeric spike protein
STAT - Signal transducer and activator of transcription
TIR - Toll/IL-1 receptor
TLRs - Toll-like receptors
TLR3 - Toll-like receptor 3
TRAF3 - Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor 3
TRIF - TIR domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β;
VLPs - Virus-like particles
Keywords: porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, anti-virus, vaccine, drug, toll-like receptors 3
Citation: Wang Q, Liu S, Chen H, Liu X, Zhang H, Wang X, Meng Q and Dong H (2025) Research progress and strategies for vaccines and targeted drugs against highly virulent porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Front. Microbiol. 16:1666167. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1666167
Edited by:
Shengwei Ji, Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine, JapanReviewed by:
Nadeem Shabir, Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology, IndiaJaveed Ahmad, University of Nebraska Medical Center, United States
Fusheng Si, Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Liu, Chen, Liu, Zhang, Wang, Meng and Dong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hao Dong, ZG9uZ2hhb0BqbGF1LmVkdS5jbg==; Qingfeng Meng, bXFmYm95QDE2My5jb20=
 Qiuxuan Wang
Qiuxuan Wang Songrui Liu1
Songrui Liu1 Hongrui Chen
Hongrui Chen Xuanyi Liu
Xuanyi Liu Hanjia Zhang
Hanjia Zhang Qingfeng Meng
Qingfeng Meng Hao Dong
Hao Dong