- 1College of Pharmacy and Life Sciences, Jiujiang University, Jiujiang, China
- 2Institute of Medicinal Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China
Cyanobacterial blooms have become a worldwide problem. Chemical algicides play important role in controlling cyanobacterial blooms in spite of their potential secondary pollution to aquatic environments. The algicidal microorganisms and their metabolites are potential substitutes for non-selective chemical algicides because of their environmentally friendly characteristics. In this paper, an actinomycete strain, designated as LMJ-114, capable of eliminating cyanobacteria, was isolated from a soil sample collected from Lushan Mountains of China. Strain LMJ-114, belonging to Streptomyces, showed the highest similarity to Streptomyces jiujiangensis JXJ 0074T based on the 16S rRNA gene sequences. This strain showed algicidal activities on both Microcystis and filamentous cyanobacteria. The extracellular water-soluble substances exhibited strong algicidal activity on Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-905. The algicidal components from strain LMJ-114 could induce M. aeruginosa to produce massive reactive oxygen species (ROS), and seriously affected its antioxidant system. Lipid peroxidation, therefore, occurred seriously in cells of M. aeruginosa, which resulted in 91.6–525.2% higher of malondialdehyde (MDA), and disintegration of gelatinous sheaths, and subsequent sunk cell surface and perforation of the cells. The treatments of both culture broth supernatant and mycelia of strain LMJ-114 significantly affected the contents of retinoic acids (RAs) and microcystins (MCs), and 4 days later, RAs eliminated completely, and 7 days later, microcystin RR (MC-RR) decreased by 96.7 and 87.9%, respectively, and microcystin LR (MC-LR) contents decreased by 89.9 and 81.0%, respectively. L-valine was one of the algicidal compounds in the culture broth supernatant of strain LMJ-114. Strain LMJ-114 and its extracellular metabolites showed potential application in controlling cyanobacterial blooms.
Highlights
• Cyanobacterial blooms are persistent environmental problems.
• An algicidal Streptomyces strain LMJ-114 was isolated from soil sample.
• LMJ-114 resulted in abundant ROS, and serious lipid-peroxidation in M. aeruginosa cells.
• LMJ-114 greatly reduced MCs and RAs in M. aeruginosa culture.
1 Introduction
Cyanobacterial blooms have been one of the prominent environmental concerns worldwide (Chen et al., 2011; de Figueiredo et al., 2004), especially in China (Guo, 2007; Wu et al., 2011). One of the most detrimental effects of cyanobacterial blooms is the production of large quantities of cyanotoxins. These toxins pose serious threats to the environment and human health (Azevedo et al., 2002). It is also a major reason for huge economic losses especially in aquaculture and fishing industries (Mizuno et al., 2008). An unforgettable tragedy caused by exposure to cyanotoxins occurred in 1996 in Caruaru, Brazil, during which 116 people became ill and 52 died of toxic hepatitis (Azevedo et al., 2002).
Cyanobacterial blooms are generally favored by high temperature and eutrophication (Matthijs et al., 2012). As such, cyanobacteria form the dominant phytoplankton during summer months (Contardo-Jara et al., 2008). Soaring agricultural and industrial activities without proper water management (de Figueiredo et al., 2004) and high input of nutrient-enriched pollutants into the aquatic environment are the major reasons for increasing eutrophication (de Figueiredo et al., 2004; Contardo-Jara et al., 2008), which further result in frequent breakouts of cyanobacterial blooms (de Figueiredo et al., 2004; Žegura et al., 2011). In tropical climates, blooms can occur throughout the year (Dejenie et al., 2009). Meanwhile, human activities have also accelerated the process of global warming (Davis et al., 2009; Paerl et al., 2008), which in turn promotes the growth of toxic cyanobacteria (Guo, 2007; Davis et al., 2009), leading to blooms with higher cyanotoxins content (Davis et al., 2009).
Another consequence of cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic water is the presence of retinoic acids (RAs) and other analogues of retinoids. Various kinds of deformities can be generated in animals when their embryos are exposed to exogenous RAs (Gardiner et al., 2003). Cyanobacterial blooms in Taihu Lake have been found to produce high concentrations of RAs. 22 of 24 Cyanophyta present produce RAs and 4-oxo-RAs, the highest producer being Microcystis flos-aquae and Microcystis aeruginosa (Wu et al., 2012). These findings further reveal the serious detriment of cyanobacterial blooms. It is therefore urgently required to study effective means of eliminating the harmful cyanobacteria and their toxic metabolites from the water environments.
Many methods, such as biomanipulation, physical and chemical agents, have been employed to control cyanobacterial blooms. But all these methods have their drawbacks. For instances, the physical methods are usually expensive (Matthijs et al., 2012) and are applicable only in small impoundments such as pond and water reservoirs (Wu et al., 2011; Matthijs et al., 2012); chemical agents cause secondary pollution (Yan et al., 2011) though hydrogen peroxide can selectively kill the cyanobacteria without major impacts on other organisms in small lake (Matthijs et al., 2012), while application of biomanipulation in a large water ecosystem is difficult (Liu, 2010). Microbes and their metabolites show great potential in controlling cyanobacterial blooms. Algae-lysing microbes include virus, bacteria, actinomycetes and fungi (Sigee et al., 1999), and their main action modes are: (1) lysing the cyanobacterial cell after invading them (direct cyanobacterial cells inhibition), e.g., Saprospira sp. SS98-5 (Furusawa et al., 2003); (2) secreting bioactive compounds that lyse algae (indirect cyanobacterial cells inhibition), e.g., Streptomyces eurocidicus JXJ-0089 (Zhang et al., 2016b), and S. jiujiangensis JXJ 0074T (Zhang et al., 2015, 2016a); (3) inducing production of self-cell lytic compounds when co-culturing with cyanobacteria, e.g., Brevibacillus (Ozaki et al., 2008).
In this study, the screening of algicidal activities and characterization of an algicidal Streptomyces sp., LMJ-114 is reported. The lytic properties of the strain and its metabolites, including the efficiency and algicidal range, the effects on M. aeruginosa physiology, and one of the algicidal compounds were also reported.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Cyanobacteria culture
The cyanobacteria used in this study were all obtained from Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and cultured in HGZ medium (Zhang et al., 2015) under an illumination of 35 μmol photon/m2/s on a 12 h light–dark cycle at 25 °C. M. aeruginosa FACHB-905 lawn was prepared as described below: 100 mL of algal culture (2–4 × 107 CFU/mL) was mixed with 150–200 mL HGZ agar medium (cooling down to about 44 °C before mixing), and the mixture was poured into petri dishes and cultured at the condition described above. The algal lawns can be used for algicidal test after it become bright green.
2.2 Isolation and identification of algicidal strain LMJ-114
Actinomycete strains, isolated from soil samples collected from the Lushan Mountains of China by a serial dilution technique on ISP2 medium (yeast extract-malt extract agar) (Shirling and Gottlieb, 1966). The colonies growing on the ISP2 medium were placed on the algal lawns to test for the algicidal activity. The vanish of the bright green around the colony indicated that the strain has the algicidal activity. The morphological characteristics of algicidal actinomycete were observed by using a scanning electron microscopy (VEGA\\TESCNA) after the strain being cultured on ISP2 medium at 28 °C for 3–7 days. Extraction of genomic DNA was extracted using Rapid Bacterial Genomic DNA Isolation Kit (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China) according to the instructions of the manufacturer. The 16S rRNA gene sequence was amplified using universal bacterial primers 27F (5’-AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG-3′) and 1492R (5’-TACGYTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′).
2.3 Algicidal activity of strain LMJ-114 and its different metabolites
Algicidal strain was cultured using ISP2 liquid medium (No agar) on a shaker at 28 °C and 120 r/min for 6 days. The culture broth was centrifuged at 4527 × g for 10 min with the supernatant and the mycelial precipitate being collected, respectively. The supernatant was then treated by reduced pressure distillation at 50 °C, and the resultant solid material was fully extracted using ethyl acetate and deionized water successively to obtain the extracellular fat- and water-soluble metabolites of strain LMJ-114. The mycelial precipitate was firstly immersed in a mixture of ethyl acetate-methyl alcohol-deionized water (1:1:1, vol/vol/vol) at 50 °C to release its intracellular metabolites into the mixture. Then the soaking extract solution was treated as described above to obtain the intracellular fat- and water-soluble metabolites of strain LMJ-114. Algicidal assay was performed using the culture broth supernatant, fat- and water-soluble extracts of intracellular and extracellular metabolites and mycelia of the strain with the experimental set-up described below: 2 mL of culture broth supernatant (filtered through 0.45 μm membrane filter), 10 mg each of fat- and water-soluble extracellular and intracellular metabolites, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 g of mycelia, were added into separate 100 mL of M. aeruginosa FACHB-905 culture (1 × 107 CFU/mL). Nothing was added into 100 mL of M. aeruginosa FACHB-905 culture (1 × 107 CFU/mL) for the control group. They were incubated for 3 days and the algicidal activities were determined by the removal rates of the chlorophyll a (chl-a) content. The chl-a contents were measured using hot-ethanol extract method (Chen et al., 2006) as following steps: (i) the algae cultures were sampled and the samples were centrifuged at 4527 × g for 10 min; (ii) the resultant algal cells precipitates were stored at −20 °C for 24 h, and then mixed with 5 mL hot-ethanol of 90% (85 °C) and heated using water bath of 85 °C for 1 min, and kept in dark place at room temperature for 4–6 h to extract the chl-a; (iii) the mixtures were centrifuged at 4527 × g for 10 min, and the absorbances (E665 and E750) of the resultant supernatants were measured at 665 and 750 nm, respectively, using ethanol of 90% ethanol as the reference for zero adjustment; (iv) the absorbances (A665 and A750) of the samples were measured at 665 and 750 nm once again, respectively, after being treated with hydrochloric acid solution (1 M; 70 μL for 3 mL supernatant) for 1 min. Chl-a contents were calculated by the formula: Chl-a content (mg/L) = 27.9 × Ve × (E665 − E750 − A665 + A750)/Vs, where, Ve and Vs represent the volumes (mL) of ethanol used to extract chl-a and algae culture samples collected, respectively.
2.4 Effect of metabolites of LMJ-114 on the morphology of Microcystis aeruginosa
After being treated with the culture broth supernatant of strain LMJ-114 (culture broth supernatant of strain LMJ-114 was abbreviated to CBSL) for 2 days, M. aeruginosa FACHB-905 was centrifuged at 2800 × g for 10 min at 4 °C, and the resultant cell precipitate was treated with 0.1 M phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.0) containing 2.5% glutaraldehyde for 1 h at 4 °C. After removing PBS, the algal cells were dehydrated for 4 min by successively using 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, and 100% ethanol, and dried on clean coverslip and coated with gold for scanning electron microscopy (VEGA\\TESCNA) analysis.
2.5 Antioxidant system assays of Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-905
Three percent (vol/vol) of CBSL (replaced with 3 mL HGZ medium for control group) were added into M. aeruginosa FACHB-905 culture (2.0 × 107 CFU/mL), and cultured under the condition described above. Then the cultures were sampled every 12 h, and the samples were centrifuged at 4527 × g for 20 min at 4 °C. The algae cell precipitates were homogenized using an ultrasonic cell pulverizer (JY92-2DN; Xinzhi Co., Ningbo, China) at 200 W for 5 min (ultrasonic time, 2 s; rest time, 8 s) under ice bath cooling. Then, the homogenates were centrifuged at 12,000 g for 10 min at 4 °C. The resultant supernatants were used to detect the lipid-peroxidation, enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant of M. aeruginosa.
The activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD; EC 1.15.1.1), catalase (CAT; EC 1.11.1.6) and peroxidase (POD; EC 1.11.1.7) were measured according to the method described by Chen and Wang (2006). For measuring the SOD activity, the reaction mixture contained 1.9 mL PBS solution (50 mmol/L, pH7.8, containing 100 μmol/L EDTA), 0.3 mL methionine solution (220 mmol/L), 0.3 mL nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) solution (1.25 mmol/L), 0.3 mL riboflavin solution (33 μmol/L), and 0.2 mL cell-free extract (replaced with 0.2 mL PBS for both negative control and positive control). Both treatment and positive control were exposed to an illumination of 70 μmol photon/m2/s for 20 min at 25 °C, and the negative control was kept wrapped in aluminum foil to prevent any photochemical reaction of NBT. And then the absorbances of treatment and positive control were measured at 560 nm after adjusting zero using negative control. One unit (U) of SOD activity is defined as the amount of enzyme required to inhibit 50% of photochemical reactions of NBT. The specific activity of SOD (SODSA) was calculated according the following formula: SODSA (U/mg) = VE × (AP − AT) / (0.5 × AP × VS × 0.2 × CP), where VE and VS were volumes (mL) of the cell free extracts and algal samples collected, respectively; and AP and AT were the absorbances of the positive controls and treatments, respectively; CP (mg/mL) was the protein content of the cell free extract. The protein contents in the cell free extracts were determined by using method of Coomassie brilliant blue G-250, in which bovine serum albumin was used as the standard protein.
For measuring CAT activity, the reaction was done in a total volume of 3 mL, containing 1.8 mL PBS solution (50 mmol/L, pH 7.0), 1.0 mL H2O2 (0.1 mol/L) and 0.2 mL cell-free extract. The absorbance decreases of the mixtures in 5 min were measured at 240 nm. One unit (U) of CAT activity is defined as the decrease in absorbance at 240 nm by 0.01 in 1 min. The specific activity of CAT (CATSA) was calculated according the following formula: CATSA (U/mg) = (DA × VE) / (0.2 × VS × 5 × 0.01 × CP), where DA, VE (mL), VS (mL), and CP (mg/mL) were the decrease values of the absorbance, total volume of the cell free extracts, volume of the algal samples collected, and protein content of the cell free extract. The protein contents were measured as described above.
The reaction mixture for POD assay contained 1.0 mL PBS solution (50 mmol/L, pH7.0), 1.0 mL guaiacol (16 mmol/L), 1.0 mL H2O2 (0.1 mol/L), and 1.0 mL cell-free extract. The absorbance increases of the reaction mixtures in 5 min were measured at 470 nm. One unit (U) of POD activity is defined as the increase in absorbance at 470 nm by 0.01 in 1 min. The specific activity of POD (PODSA) was calculated according the following formula: PODSA (U/mg) = (IA × VE) / (1 × VS × 5 × 0.01 × CP), where IA, VE (mL), VS (mL), and CP (mg/mL) were the increase values of the absorbance, total volume of the cell free extracts, volume of the algal samples collected, and protein content of the cell free extract. The protein contents were measured as described above.
The assay for ascorbic acid (AsA) content was based on the formation of the red complex between 2,2′-bipyridine and ferrous ion (reduced from ferric ion by AsA in acid solution) (Chen and Wang, 2006). 0.3 mL each of cell-free extract, NaH2PO4 (150 mmol/L, pH7.4) and H2O were mixed, followed by addition of 0.6 mL trichloroacetic acid (TCA, 600 mmol/L), 0.6 mL H3PO4 (4.49 mol/L), 0.6 mL 2,2′-bipyridine (250 mmol/L) and 0.3 mL FeCl3 (185 mmol/L) after 30 s. The reaction mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 60 min and the absorbance was measured at 525 nm. The AsA content of the cell-free extract was calculated according AsA standard graph: CAsA (μmol/mL) = (A525−0.001)/1.4409, where A525 was the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 525 nm. AsA standard graph was drawn as described above using different concentrations of AsA.
The content of reduced glutathione (GSH) was determined by measuring the formation rate of 5-thio-2-nitrobenzoic acid (TNB) from 5,5′-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB) (Anderson, 1985). The reaction mixture includes 0.25 mL cell-free extract, 2.6 mL NaH2PO4 (150 mmol/L, pH 7.7), and 0.15 mL DTNB (6 mmol/L). After incubation at 30 °C for 5 min, the absorbance of the solutions was measured at 412 nm. The GSH content of the cell-free extract was calculated according GSH standard graph: CGSH (μmol/mL) = (A412−0.0003)/1.3212, where A412 was the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 412 nm. GSH standard graph was drawn as described above using different concentrations of GSH.
Lipid peroxidation was determined by measuring the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) according to the method described by Chen and Wang (2006). 2 mL cell-free extract and 2 mL thiobarbituric acid reagent (0.5% in 10% TCA) were mixed and heated for 20 min at 100 °C. The mixture was cooled and centrifuged at 4527 × g for 20 min at 4 °C. The absorbances of the supernatants were measured at 450 nm, 532 nm and 600 nm, respectively. MDA content was calculated by the following formula: CMDA (μmol/L) = 6.45 (A532 − A600) − 0.56 × A450, Where A450, A532, and A600 represents the absorbances of the supernatants at 450 nm, 532 nm and 600 nm, respectively.
2.6 Algicidal range of CBSL
Three milliliters of CBSL were added into the following cyanobacteria strains of 100 mL, and cultured for 3 days as described above. Then the chl-a contents of these cyanobacteria were measured as described above. M. aeruginosa FACHB-905, Microcystis wesenbergii FACHB-1112, Microcystis viridis FACHB-1284, Aphanizomenon flos-aquae FACHB-1171, Oscillatoria planctonica FACHB-708, and Anabaena flos-aquae FACHB-1092 were involved in this study. In control groups, 3 mL HGZ medium replaced 3 mL CBSL in the above cyanobacterial cultures.
2.7 Effect of strain LMJ-114 on the contents of microcystins and RAs
Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-905 produces high contents of microcystins (MCs) (Zhang et al., 2016b) and RAs (Wu et al., 2012), and therefore it was used in this study. The RAs and MCs contents were detected after 4 and 7 days of cultivation, respectively. M. aeruginosa FACHB-905 culture (2 × 107 CFU/mL, 100 mL) were treated with 2 mL of CBSL and 2 g mycelial cake (0.23 g dry weight) of strain LMJ-114. The cultures were centrifuged at 4527 × g for 20 min at 4 °C. Both the supernatants and sediments were collected for analysis of MCs and RAs.
MCs in the supernatants were extracted using solid-phase extraction (SPE) columns (Bakerbond™ spe 7020-06, Octadecyl C18 Disposable Extraction Columns; J. T. Baker, United States) as described below: the SPE columns were pretreated with 5 mL methanol in 0.1% (v/v) trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), 5 mL 100% methanol and 10 mL water; and then the supernatants were loaded into the SPE columns, the toxins were eluted with 8 mL methanol in 0.1% (v/v) TFA after the SPE columns being washed by 5 mL of 5, 10 and 20% methanol successively. The eluent was evaporated to dryness, and redissolved in 1.0 mL deionized water for analysis by HPLC. The sediment was mixed with 30 mL of methanol/water (75:25, vol/vol), and homogenized in an ice bath, and centrifuged at 4527 × g for 20 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was collected, while the residue was retreated as described above. The supernatants obtained were combined and evaporated to dryness. The dry residues were redissolved in 20 mL of deionized water, and the extracted intracellular toxins were purified by the method described above and analyzed by HPLC. MC-RR and MC-LR were analyzed using Agilent 1,200 LC with an Agilent LC C18 column (Eclipse XDB-C18, 5 μm, 4.6 × 150 mm). The mobile phase in channel A was water containing 0.05% (v/v) TFA and the mobile phase in channel B was acetonitrile containing 0.05% (v/v) TFA. Elution was performed with 10–60% B linear gradient for 20 min at a flow rate of 1 mL/min. The absorbance was monitored at 240 nm with sample injection volumes of 20 μL.
RAs were quantified according to Wu et al. (2010, 2012) with some modifications. The Oasis HLB cartridge (6 mL, 200 mg, Waters) was pretreated with 6 mL ethyl acetate, 6 mL methanol, and 12 mL ultrapure water, at a flow rate of 7 mL/min before the supernatant was loaded. The cartridge was then dried and followed by elution of the analytes with 7 mL ethyl acetate (containing 0.5% acetic acid) and 3 mL acetone. The extracted eluent was evaporated to dryness at 27 °C and the dry residues redissolved in 0.4 mL methylene chloride and 4 mL hexane. The solutions obtained were purified in a silica cartridge (6 mL, 500 mg, Waters; pretreated with 8 mL of hexane). After the cartridge was washed with 2 mL of hexane-methylene chloride (1:1, vol/vol), elution was done with 10 mL of hexane-methylene chloride-isopropanol-acetic acid (87:10:1:2, vol/vol/vol/vol). The extract was evaporated to dryness under the condition described above and redissolved in 0.25 mL methanol. The samples were filtered through 0.22 μm filter membrane before analyzing by HPLC. The sediments were mixed with 30 mL acetone and homogenized in an ice bath, followed by centrifugation at 4527 × g for 20 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was collected and the residue was treated again as described above. The combined supernatants were purified as the methods described above before analyzing by HPLC. The chromatographic mobile phases were water containing 0.5% (vol/vol) acetic acid in channel A and methanol containing 0.5% (vol/vol) acetic acid in channel B. The elution was done for 17 min with a flow rate of 1 mL/min in the mobile phase ratio of 14:86 (channel A: channel B, vol/vol). The absorbance was monitored at 353 nm with sample injection volumes of 50 μL.
2.8 Purification and elucidation of algicidal compounds
Water-soluble extracellular metabolites were purified repeatedly by column chromatography of Sephadex™ LH-20 (GE healthcare) and C18 (YMC*GEL, ODS-AQ-HG) using deionized water/methanol (1:1; vol/vol) and deionized water/methanol (1:0 → 0:1; vol/vol) as the elution solvents, respectively. The algicidal activities of the fractions were assayed by filter paper method using M. aeruginosa lawn (Zhang et al., 2016b). The algicidal compound was elucidated from the data of 13C NMR and 1H NMR (in D2O) obtained on a Bruker DRX-500 MHz instrument with tetramethylsilane (TMS) as the internal standard.
2.9 Toxicity of culture broth of LMJ-114 on aquatic organisms
The toxicity of strain LMJ-114 and its metabolites on aquatic organisms were studied by using Carassius auratus var. pengzesis (weighing approximately 25 g) and Viviparus chinensis (~2.87 g). One percent (vol/vol) culture broth of strain LMJ-114 was added into a fish tank (volumes maintained at 100 L for 50 fish, and 20 L for 120 viviparids). The energetic fish with few scales shed were selected for this test. The viviparids were collected from the pond in the wild field. The water and culture broth in the fishpond were replaced every 24 h. Fifty grams of rice and 20 grams of fresh vegetable leaves were supplied for fish and viviparids of a fish tank, respectively. The growth and mortalities of the test aquatic organisms were calculated 7 days later. No culture broth of strain LMJ-114 was added into the controls. These tests were carried out at 20 °C under laboratory conditions.
2.10 Data analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS19.0 software. The mean value and standard deviation (SD) of three replicates were calculated, and the graph was plotted using the mean value. All error bars indicate the SD of three replicates. Comparisons of the activities of SOD, CAT, and POD, and the contents of chl-a, RAs, AsA, GSH, MDA, MC-RR, and MC-LR between treatments and controls were performed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s pairwise comparisons. Significance was set at p values of 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Isolation and characterization of algicidal strain LMJ-114
Strain LMJ-114 exhibited strong algicidal activity on M. aeruginosa FACHB-905 lawn, and it showed an inhibition zone diameter of about 3.6 cm against its colony diameter of 0.7 cm after 3 days of incubation (Supplementary Figure S1).
Strain LMJ-114 developed well-branched substrate and aerial mycelia on ISP2 medium. At maturity, the aerial mycelia formed straight or spiral spore chains, and the spores were offwhite in color and ellipsoid in shape (Supplementary Figure S2). Its 16S rRNA gene sequence (1,446 bp; GenBank accession number: PV915256) showed the highest similarity to that of Streptomyces jiujiangensis 0074T (99.51%), and they also formed a distinct clade on neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree with 100% of bootstrap value (Figure 1). Therefore, strain LMJ-114 belonged to the genus of Streptomyces.
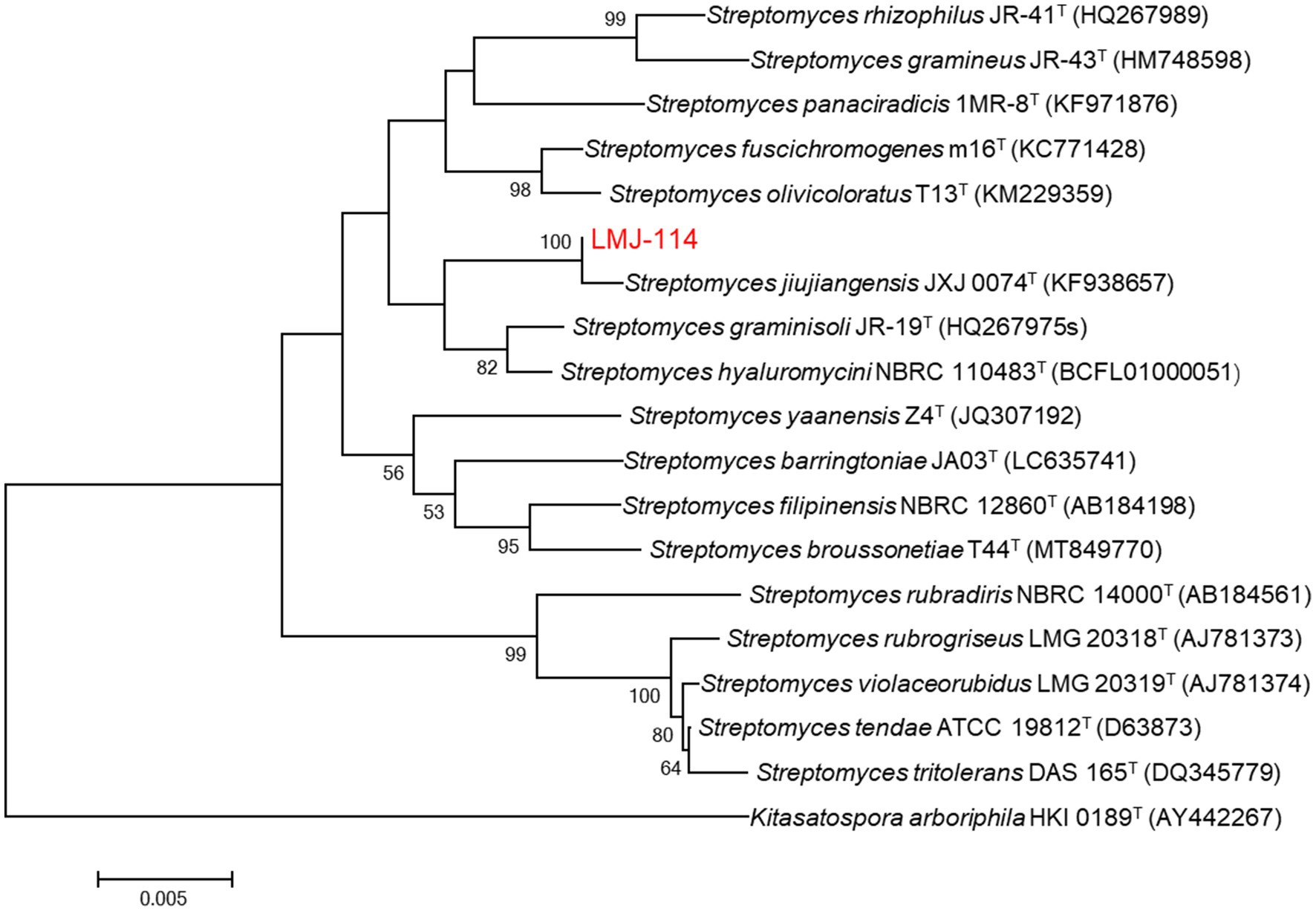
Figure 1. Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences of strain LMJ-114 and its closest relative species of the genus Streptomyces. Bootstrap values (≥50%) based on 1,000 replications are shown at the branching points. Bar, 0.005 changes per nucleotide position.
3.2 Algicidal efficiency of strain LMJ-114 and its different metabolites
The pH value of culture broth of strain LMJ-114 was about 7.0. And the pH value of algal culture was not affected by the addition of the culture broth of strain LMJ-114 in this study, which indicated that strain LMJ-114 produced algicidal metabolites. Chl-a content of the control increased initially from 1.63 mg/L to 2.31 mg/L after 3 days of cultivation. Both CBSL and extracellular water-soluble substances exhibited strong algicidal activity (Figure 2A), and the chl-a contents treated with both CBSL and extracellular water-soluble substances were only 0.14–0.141 mg/L, decreased by 94% than that of the control (p < 0.01). However, the chl-a contents treated with extracellular fat-soluble substances and intracellular components were similar to that of the control (p > 0.05), indicating that these components had no obvious algicidal activity on M. aeruginosa FACHB-905. The mycelia of strain LMJ-114 also showed strong algicidal activity on M. aeruginosa FACHB-905 with a dose effect (Figure 2B). The chl-a content in group treated with 0.5 g of mycelia were 1.37 mg/L, which was 40.7% lower than that of the control (p < 0.01); while the chl-a content in group treated with 2 g of mycelia were only 0.154 mg/L, 93.3% lower than that of the control (p < 0.01).
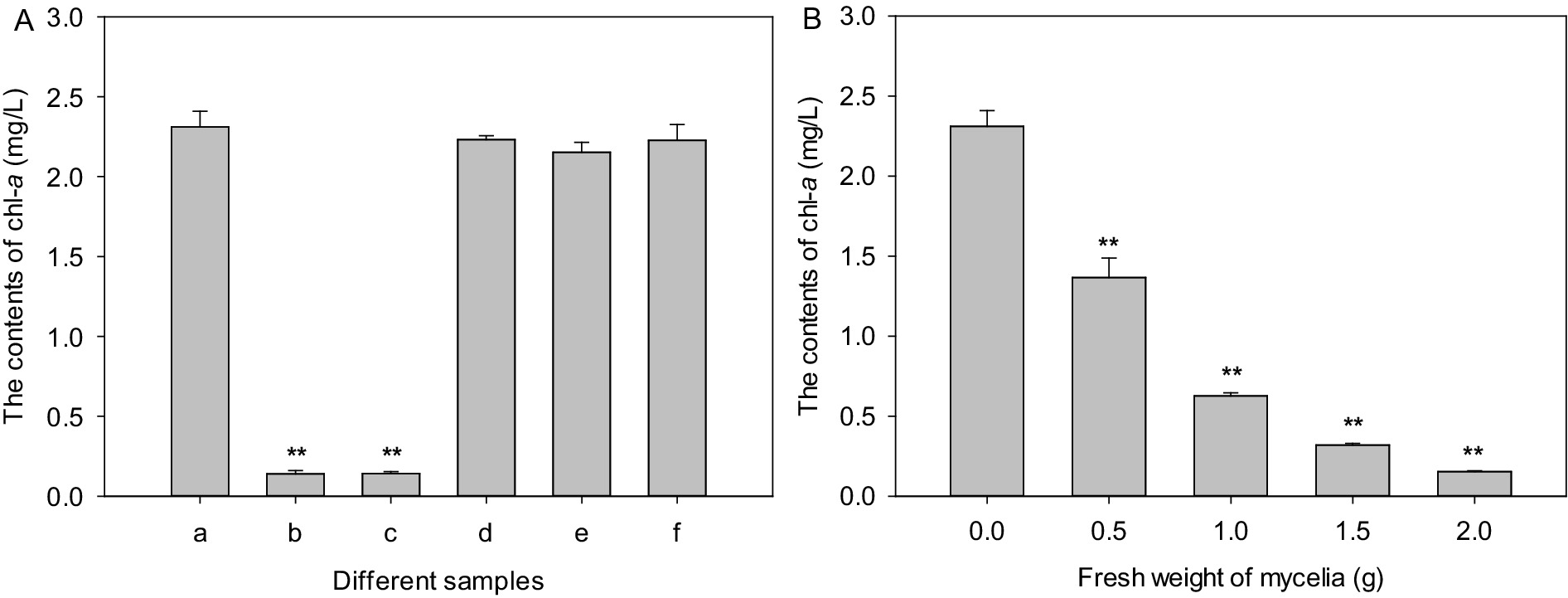
Figure 2. The algicidal activities of metabolites and mycelia of strain LMJ-114. (A) treated with different metabolites, (B) treated with mycelia. (a) Control, (b) culture broth supernatant, (c) water-soluble extracellular metabolites, (d) fat-soluble extracellular metabolites, (e) water-soluble intracellular metabolites, (f) fat-soluble intracellular metabolites. Error bars indicate standard deviations for the three replicates. Comparisons between control and different treatments were performed using ANOVA. Significant differences are shown by asterisks: **, p < 0.01.
3.3 Morphological damage of cyanobacteria by CBSL
The cellular surfaces of M. aeruginosa FACHB-905 of the control group were intact and covered with gelatinous sheaths. However, the gelatinous sheaths of the algae cells treated with CBSL tended to be disintegrated, and its cell surfaces were sunken and perforated (Figure 3), indicating that the metabolites of strain LMJ-114 can damage the surface morphological structure of algal cells.
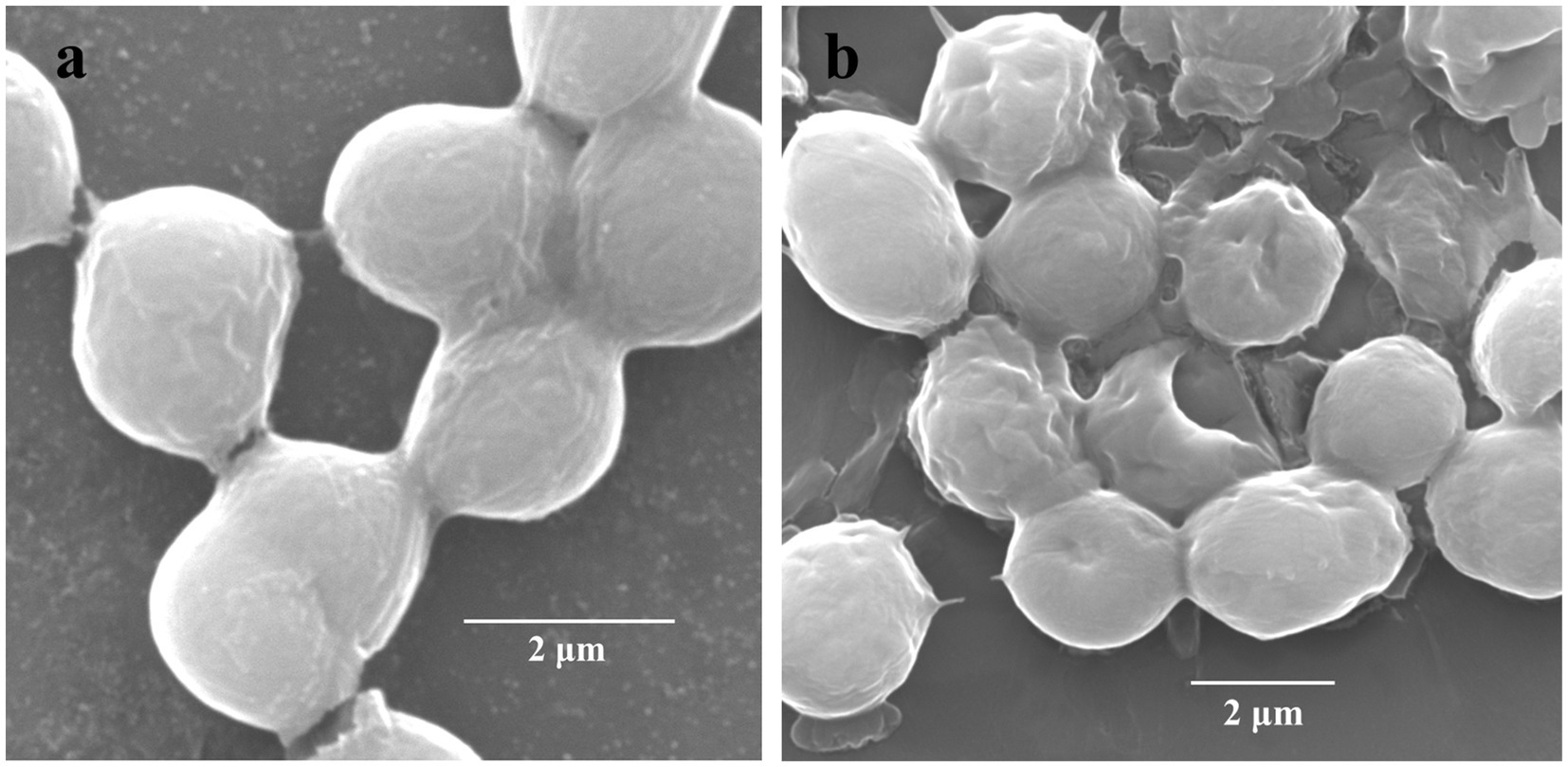

Figure 3. Scanning electron micrographs of M. aeruginosa FACHB-905 cells. (a,b) Represent algal cells of the control and the treatment of CBSL, respectively.
3.4 Effects on the antioxidant system of Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-905
Metabolites from strain LMJ-114 severely affected the function of cyanobacterial antioxidant system. The activities of SOD, POD and CAT in groups treated with CBSL gradually increased initially from 31.3, 5.2, and 10.9 U/mg protein to their maximum values (33.9, 20.1 and 33.1 U/mg protein, respectively) at 24, 36 and 36 h, respectively, which were 15.6, 686.0, and 209.8% higher than those of the control groups (Figure 4A) (p < 0.01). And then their activities decreased quickly to 16.4, 1.8 and 18.9 U/mg protein, respectively, which were 37.3 and 24.2% lower and 85.7% higher than those of the control groups (Figure 4A) (p < 0.01), respectively. The contents of GSH, AsA, and MDA were also seriously influenced by CBSL (Figure 4B). The contents of GSH and AsA in test group treated with CBSL increased initially from 0.129 and 0.252 μmol/mg protein to 0.444 and 0.451 μmol/mg protein at 36 h, respectively, which were 83.5 and 146.0% higher than those of the controls (p < 0.01), respectively; and then decreased to 0.094 and 0.190 μmol/mg protein at 72 h, which was 46.8% lower and 21.6% higher than those of the controls (Figure 4B) (p < 0.01, p < 0.05), respectively. The MDA contents of the cell free extract of the controls were between 0.099–0.120 μmol/L during the test time. However, the MDA contents in the cell free extract of the test groups treated with CBSL increased initially from 0.120 μmol/L to 0.621 μmol/L at 24 h, 525.2% higher than that of the control (Figure 4B) (p < 0.01). Then the MDA contents of treatment decreased quickly to 0.224–0.234 μmol/L, which were still 98.9–252.2% higher than those of the controls (Figure 4B) (p < 0.01).
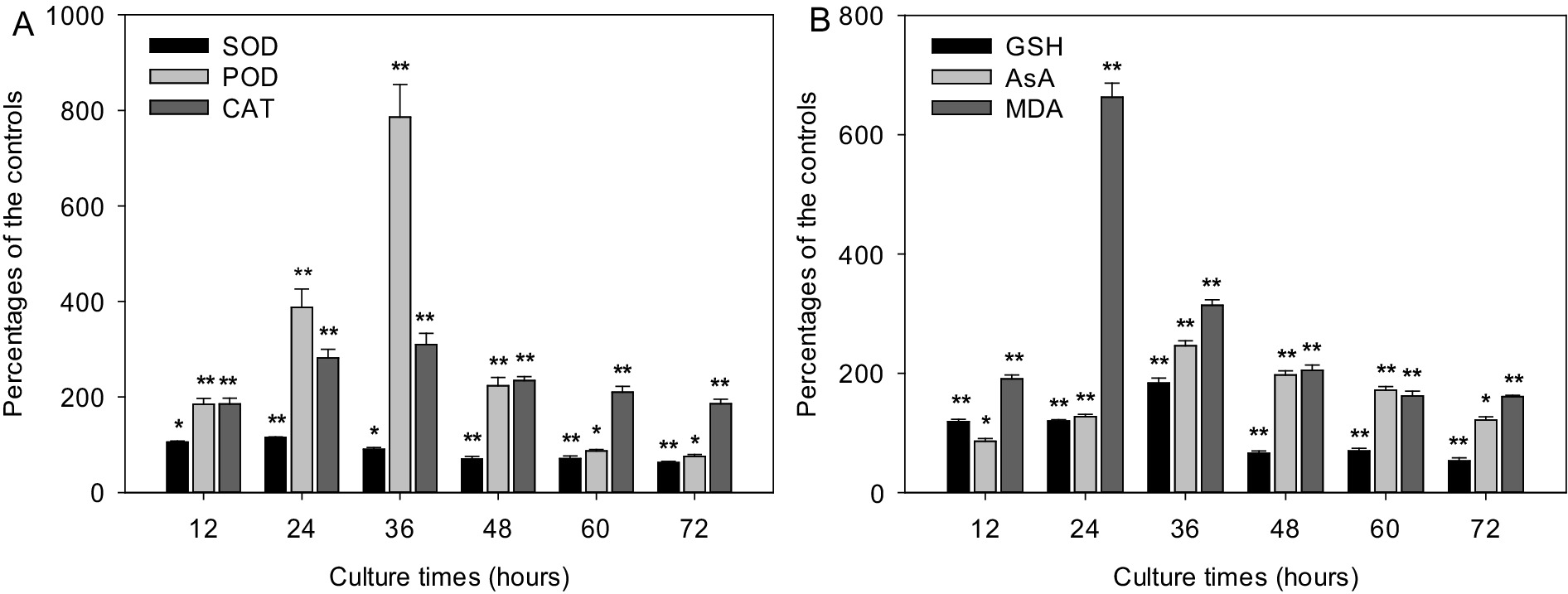
Figure 4. Effects of metabolites from strain LMJ-114 on the antioxidant system of M. aeruginosa FACHB-905. (A) antioxidant enzymes, (B) non-enzymatic antioxidants and MDA. Error bars indicate standard deviations for the three replicates. Comparisons between controls and treatments at different times were performed using ANOVA. Significant differences are shown by asterisks: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.
3.5 Effect of strain LMJ-114 on MCs and RAs contents
The extracellular and intracellular MC-RR contents of the control increased initially from 20.9 and 14.7 μg/L to 94.1 and 52.0 μg/L after 7 days of culture (Figure 5A), respectively. However, the extracellular MC-RR contents of the test groups treated with mycelia and CBSL decreased initially from 20.9 μg/L to 4.9 and 17.6 μg/L 7 days later, respectively, which were 94.8 and 81.3% lower than that of the control (p < 0.01) (Figure 5A), respectively. And the intracellular MC-RR of the extracts treated with mycelia and CBSL were not detected (Figure 5A). After 7 days of culture, the extracellular and intracellular MC-LR contents of the control decreased and increased initially from 1301.7 and 1101.3 μg/L to 824.9 and 2224.2 μg/L, respectively. The extracellular MC-LR contents of the test groups treated with mycelia and CBSL were 261.0 and 468.6 μg/L 7 days later, which were 68.4 and 43.2% lower than that of the control (p < 0.01) (Figure 5B), respectively. And the intracellular MC-LR contents of the test groups treated with mycelia and CBSL were 47.7 and 112.2 μg/L 7 days later, which were 97.9 and 95.0% lower than that of the control (p < 0.01) (Figure 5B), respectively. After 4 days of culture, the extracellular and intracellular RAs contents of the control were 999.4 and 1292.4 ng/L, respectively. However, RAs could not be detected in the test groups treated with both mycelia and CBSL.
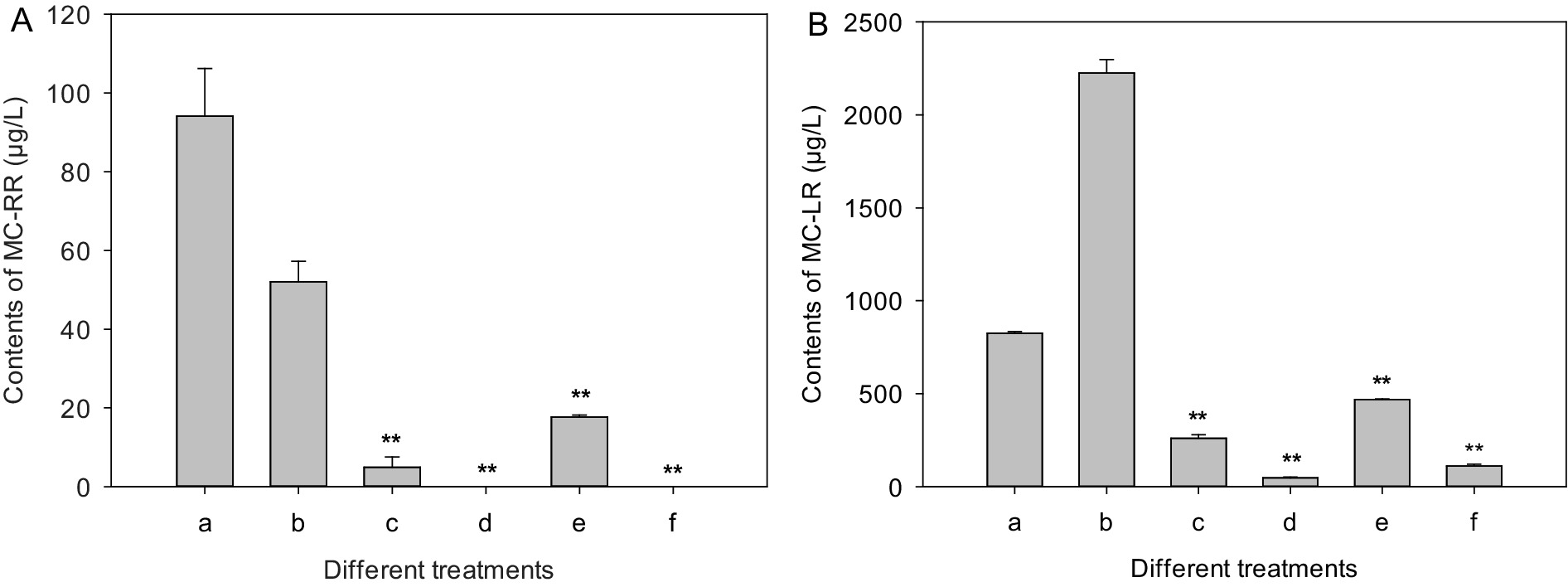
Figure 5. Influences of treatments of CBSL and mycelia on MC-RR and MC-LR contents of M. aeruginosa. (A) MC-RR, (B) MC-LR. (a) Extracellular MCs of the controls, (b) intracellular MCs of the controls, (c) extracellular MCs treated with mycelia, (d) intracellular MCs treated with mycelia, (e) extracellular MCs treated with CBSL, (f) intracellular MCs treated with CBSL. Error bars indicate standard deviations for the three replicates. Comparisons between controls and treatments were performed using ANOVA. Significant differences are shown by asterisks: **, p < 0.01.
3.6 Algicidal compound from strain LMJ-114
The algicidal assays using different components isolated from the fermentation broth of strain LMJ-114 indicated that its metabolites comprised many algicidal compounds. And a white powder with strong algicidal activity on M. aeruginosa FACHB-905 lawn was purified. The algicidal compound showed no absorbance at 254 nm or 365 nm wavelength, but was stained by ninhydrin indicating that it is an amino-group containing compound. S. jiujiangensis JXJ 0074T produces algicidal L-valine (Zhang et al., 2016a). Therefore, we detected both the algicidal compound isolated from LMJ-114 and the L-valine using thin layer chromatography of silica gel plate, and these two compounds had the same Rf values and ninhydrin staining (Supplementary Figure S3). The spectra of 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and DEPT (distortionless enhancement by polarization transfer) (in D2O) showed this compound has one carbonyl (δC 175.0), two methines (δC 61.1, δH 3.47; 29.8, δH 2.14), and two methyls (δC 18.7, δH 0.91; δC 17.3, δH 0. 85) (Supplementary Figure S4). These spectra data were similar to L-valine (Pretsch et al., 2000; Zhang et al., 2016a). Based on these data above, the algicidal compound from LMJ-114 was identified as L-valine.
3.7 Algicidal range of CBSL
After 3 days of culture, the chl-a contents of M. aeruginosa FACHB-905, M. wesenbergii FACHB-1112, M. viridis FACHB-1284, Aphanizomenon flos-aquae FACHB-1171, Oscillatoria planctonica FACHB-708, and Anabaena flos-aquae FACHB-1092 were 3.82, 3.21, 3.62, 2.37, 4.95, and 3.92 mg/L for the controls, respectively. However, after treated with CBSL, the chl-a contents of six cyanobacterial strains were 0.402–0.621 mg/L, which were 83.0–88.8% lower than these of the controls (p < 0.01) (Figure 6).
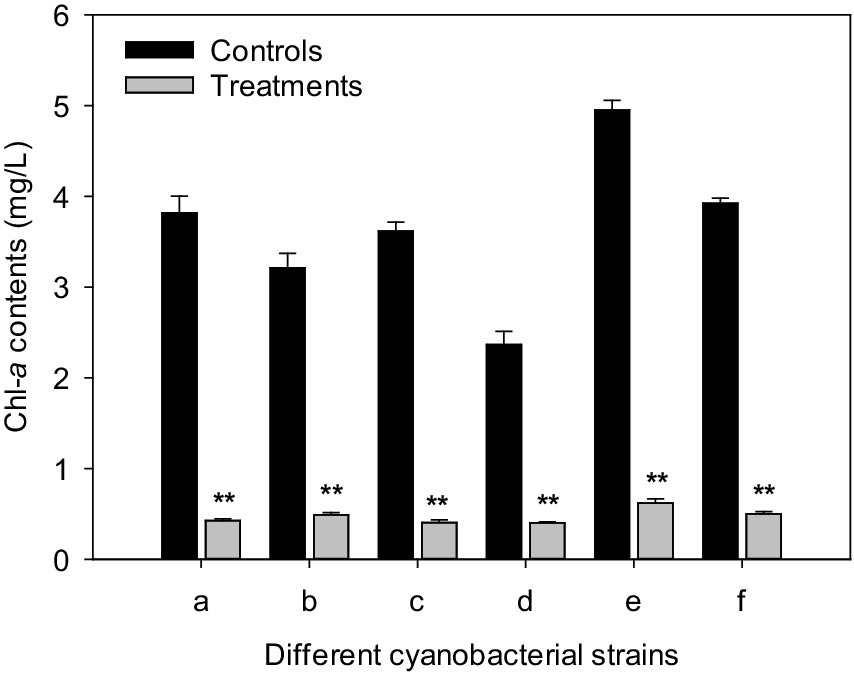
Figure 6. Influences of CBSL on six cyanobacterial strains. (a) M. aeruginosa FACHB-905, (b) M. wesenbergii FACHB-1112, (c) M. viridis FACHB-1284, (d) Aphanizomenon flos-aquae FACHB-1171, (e) Oscillatoria planctonica FACHB-708, (f) Anabaena flos-aquae FACHB-1092. Error bars indicate standard deviations for the three replicates. Comparisons between controls and treatments were performed using ANOVA. Significant differences are shown by asterisks: **, p < 0.01.
3.8 The toxicity on aquatic organisms
All fish grew well and no fish died for both control group and test group during the test period, indicating that culture broth of strain LMJ-114 was not toxic to fish. Meanwhile, twenty viviparids died in control group, which accounted for 5.56% of 360 viviparids. And nineteen viviparids died in treatment group, which accounted for 5.28% of 360 viviparids, similar to that of the control group (p > 0.05). Therefore, culture broth of strain LMJ-114 was also not toxic to mollusk viviparid.
4 Discussion
Strain LMJ-114, a member of Streptomyces, showed strong algicidal activity on both unicellular Microcystis, such as M. aeruginosa FACHB-905, M. wesenbergii FACHB-1112, and M. viridis FACHB-1284, and filamentous cyanobacteria, such as Aphanizomenon flos-aquae FACHB-1171, Oscillatoria planctonica FACHB-708, and Anabaena flos-aquae FACHB-1092 (Figure 6). Its metabolites resulted in abundant ROS, and serious lipid-peroxidation in M. aeruginosa cells. L-valine is one of its algicidal compounds.
S. jiujiangensis JXJ 0074T showed the highest similarity to strain LMJ-114. However, the supernatant of its culture broth has strong algicidal activity mainly on Microcystis such as M. aeruginosa FACHB-905, M. aeruginosa FACHB-1203, M. wesenbergii FACHB-1112, M. viridis FACHB-1284 and M. flosaquae FACHB-1285, and weak or no activity on filamentous cyanobacteria, such as Oscillatoria planctonica FACHB-708, Anabaena flosaquae FACHB-1092, Nostoc punctiforme FACHB-252 and Oscillatoria tennuis FACHB-247 (Zhang B. et al., 2014). Strain JXJ 0074T produced algicidal compounds L-valine and 2′-deoxyguanosine. The former showed algicidal activity mainly on Microcystis (Zhang et al., 2016a), and the latter showed low to moderate algicidal activity on Microcystis and filamentous cyanobacteria at 10 μg/mL (Zhang et al., 2015). Therefore, strain LMJ-114 can probably produce other unknown algicidal compounds that different from these produced by S. jiujiangensis JXJ 0074T. Furthermore, different media were used in the fermentations of S. jiujiangensis JXJ 0074T (Zhang B. et al., 2014) and LMJ-114, which was probably another reason that the metabolites from the two strains showed different algicidal activity on filamentous cyanobacteria. More study should be performed to illustrate this question.
The formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is accelerated under stress conditions (Noctor and Foyer, 1998). ROS, including ·OH, O2−, H2O2, and 1O2, can initiate free radical reactions in biological cell, which causes significant damages to organism. Chain reactions are one of the most significant characteristics of radical reactions. O2− is the most active reactive oxygen except ·OH. SOD can terminate O2− initiating chain reaction by converting it into O2 and H2O2. Algicidal compounds from Streptomyces can result in a large amount of O2− (more 240% higher than that of the control) in cyanobacterial cells (Zhang et al., 2015, 2016a, 2016b). And upon exposure to CBSL, the cyanobacterial SOD activity only increased to 115.6% of the control after 24 h of culture, and then decreased quickly to only 62.7% of the control after 72 h of culture (Figure 4A). As a result, most of the O2− induced by CBSL cannot be terminated by SOD. Lipid-peroxidation is a typical radical chain reaction which can be easily initiated on the biological membrane as there are plenty of oxygen and polyunsaturated fatty acids. Therefore, the residual O2− can initiate a large amount of lipid-peroxidation, which was probably the main reason that MDA contents were far higher than these of the controls during the test (Figure 4B).
H2O2 can be decomposed into nontoxic H2O and O2 by CAT and POD. Two important antioxidative compounds AsA and GSH serve as substrates for POD (Noctor and Foyer, 1998), and also help in H2O2 detoxification (Mehlhorn et al., 1996). Upon exposure to CBSL, the cyanobacterial CAT and POD activities and the contents of GSH and AsA increased quickly to 309.8 and 786.0%, 183.5 and 246.0% of the controls (Figure 4), respectively, indicating that H2O2 probably can be decomposed into nontoxic H2O and O2 quickly. Therefore, H2O2 induced by CBSL or from O2− probably contributed lesser to MDA production in cyanobacterial cell.
MCs pose a serious threat to human and environmental health, and are one of the most significant problems brought by Microcystis water blooms. Moreover, the cyanobacteria can release massive toxins under the stresses of algicides, which aggravates water-quality problems (Griffiths and Saker, 2003; Ross et al., 2006). Previously studies also found that exposure to algicidal compounds from Streptomyces, such as 2′-deoxyadenosine (Zhang et al., 2015), L-valine (Zhang et al., 2016a) tryptamine, and tryptoline (Zhang et al., 2016b), would stimulate Microcystis to produce and release more MC-LR within a certain period of cultivation time. These MCs are chemically stable and biological degradation plays an important role in detoxification of the MCs in natural water environments (Dawson, 1998). Many microorganisms can degrade cyanobacterial toxins, such as Sphingomonas, Arthrobacter, Bacillus (Ling et al., 2024), Lactobacillus plantarum IS-10506 and IS-20506, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and LC-705, Bifidobacterium lactis 420 and Bb12, Bifidobacterium longum 46 (Nybom et al., 2007a; Nybom et al., 2007b; Nybom et al., 2008), Burkholderia (Lemes et al., 2008), Poterioochromonas (Ou et al., 2005), Paucibacter toxinivorans (Rapala et al., 2005) and Sphingosinicella microcystinivorans (Maruyama et al., 2006). Moreover, MCs could be degraded effectively by mixed bacterial populations (Babica et al., 2005; Bourne et al., 2006; Edward et al., 2008). In our test, the contents of MC-RR and MC-LR decreased by 86.7 and 81.0% for treatment of CBSL, and by 96.3 and 89.9% for treatment of mycelia (Figure 5). Therefore, the additions of both CBSL and mycelia can significantly promote the degradations of MCs (p < 0.01). Microcystis has many nonculturable attached bacteria, such as Lactobacillus, Sphingomonas, and Bifidobacterium etc. (Xiao et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024). These nonculturable attached bacteria were probably involved in the degradations of MCs in this study.
RAs, strong animal teratogens (Bryant and Gardiner, 1992), are usually known as endogenous metabolites of vitamin A in vertebrate animals. However, Wu et al. (2012) found that RAs can be produced by most of the cyanobacteria. This finding would make people reconsider hazards of cyanobacterial blooms. The exogenous RAs from cyanobacteria are probably one of the main reasons of deformed animals in eutrophic water. Drinking water contaminated by the exogenous RAs may cause the deformity of human embryo. Therefore, how to remove the exogenous RAs in water environments in time should be emphasized when we control the cyanobacterial blooms. In this study, RAs were not detected by HPLC after M. aeruginosa FACHB-905 culture being treated with both CBSL and mycelia, indicating that RAs were effectively removed by strain LMJ-114 and its metabolites.
5 Conclusion
Streptomyces LMJ-114 showed good algicidal activity on both Microcystis and filamentous cyanobacteria. Its metabolites influenced M. aeruginosa antioxidant system significantly, and resulted in the formation of abundant ROS, and a resultant serious lipid-peroxidation radical chain reaction, and subsequent a sunken and perforated cell surface. L-valine is one of its algicidal compounds. Application of strain LMJ-114 and its metabolites in M. aeruginosa culture greatly reduced MCs and RAs. Strain LMJ-114 and its metabolites showed good potential application in controlling cyanobacterial blooms.
Data availability statement
The 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain LMJ-114 has been deposited in GenBank under accession number PV915256 and is available via the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/). Additional data are provided in the published article and its supplementary materials, or can be obtained from the authors upon request.
Author contributions
MD: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. QX: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. HS: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. JY: Writing – review & editing. QG: Writing – original draft. YZ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. BZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1669970/full#supplementary-material
References
Anderson, M. E. (1985). Determination of glutatione and glutathione disulfide in biological samples. Methods Enzymol. 113, 548–555. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(85)13073-9
Azevedo, S. M., Carmichael, W. W., Jochimsen, E. M., Rinehart, K. L., Lau, S., Shaw, G. R., et al. (2002). Human intoxication by microcystins during renal dialysis treatment in Caruaru-Brazil. Toxicology 181, 441–446. doi: 10.1016/S0300-483X(02)00491-2
Babica, P., Bláha, L., and Maršálek, B. (2005). Removal of microcystins by phototrophic biofilms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 12, 369–374. doi: 10.1065/espr2005.05.259
Bourne, D. G., Blakeley, R. L., Riddles, P., and Jones, G. J. (2006). Biodegradation of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin LR in natural water and biologically active slow sand filters. Water Res. 40, 1294–1302. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.01.022
Bryant, S. V., and Gardiner, D. M. (1992). Retinoic acid, local cell-cell interactions, and pattern formation in vertebrate limbs. Dev. Biol. 152, 1–25. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90152-7
Chen, Y. W., Chen, K. N., and Hu, Y. H. (2006). Discussion on possible error for phytoplankton chlorophyll-a concentration analysis using hot-ethanol extraction method. J. Lake Sci. 5, 550–552. doi: 10.18307/2006.0519
Chen, W. M., Sheu, F. S., and Sheu, S. Y. (2011). Novel L-amino acid oxidase with algicidal activity against toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa synthesized by a bacterium Aquimarina sp. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 49, 372–379. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2011.06.016
Chen, J. X., and Wang, X. F. (2006). Plant physiology experiment guidance, 2nd ed. Guangzhou, China: South China University of Technology Press, 68–77.
Contardo-Jara, V., Pflugmacher, S., and Wiegand, C. (2008). Multi-xenobiotic- resistance a possible explanation for the insensitivity of bivalves towards cyanobacterial toxins. Toxicon 52, 936–943. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2008.09.005
Davis, T. W., Berry, D. L., Boyer, G. L., and Gobler, C. J. (2009). The effects of temperature and nutrients on the growth a dynamics of toxic and non-toxic strains of Microcystis during cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 8, 715–725. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2009.02.004
Dawson, R. M. (1998). The toxicology of microcystins. Toxicon 36, 953–962. doi: 10.1016/S0041-0101(97)00102-5
de Figueiredo, D. R., Azeiteiro, U. M., Esteves, S. M., Gonçalves, F. J., and Pereira, M. J. (2004). Microcystin-producing blooms—a serious global public health issue. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 59, 151–163. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2004.04.006
Dejenie, T., Asmelash, T., Rousseaux, S., Gebregiorgis, T., Gebrekidan, A., Teferi, M., et al. (2009). Impact of the fish Garra on the ecology of reservoirs and the occurrence of Microcystis blooms in semi-arid tropical highlands: an experimental assessment using enclosures. Freshw. Biol. 54, 1605–1615. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2427.2009.02209.x
Edward, C., Graham, D., Fowler, N., and Lawton, L. A. (2008). Biodegradation of microcystins and nodularin in freshwaters. Chemosphere 73, 1315–1321. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.07.015
Furusawa, G., Yoshikawa, T., Yasuda, A., and Sakata, T. (2003). Algicidal activity and gliding motility of Saprospira sp. SS98-5. Can. J. Microbiol. 49, 92–100. doi: 10.1139/w03-017
Gardiner, D., Ndayibagira, A., Grun, F., and Blumberg, B. (2003). Deformed frogs and environmental retinoids. Pure Appl. Chem. 75, 2263–2273. doi: 10.1351/pac200375112263
Griffiths, D. J., and Saker, M. L. (2003). The Palm Island mystery disease 20 years on: a review of research on the cyanotoxin cylindrospermopsin. Environ. Toxicol. 18, 78–93. doi: 10.1002/tox.10103
Guo, L. (2007). Doing battle with the green monster of Taihu Lake. Science 317:1166. doi: 10.1126/science.317.5842.1166
Lemes, G. A., Kersanach, R., Pinto Lda, S., Dellagostin, O. A., Yunes, J. S., and Matthiensen, A. (2008). Biodegradation of microcystins by aquatic Burkholderia sp. from a south Brazilian coastal lagoon. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 69, 358–365. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.03.013
Ling, L., Ruan, Y., Xu, C., Liu, D., Shi, B., Yang, Y., et al. (2024). Analysis of factors affecting microbial degradation of cyanobacterial toxins based on theoretical calculations. Environ. Geochem. Health 46:430. doi: 10.1007/s10653-024-02192-z
Liu, E. S. (2010). Analysis on biomanipulation, non-traditional biomanipulation and discussion of the countermeasures of biomanipulation application in water. J. Lake Sci. 22, 307–314. doi: 10.18307/2010.0301
Maruyama, T., Park, H. D., Ozawa, K., Tanaka, Y., Sumino, T., Hamana, K., et al. (2006). Sphingosinicella microcystinivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a microcystin-degrading bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 85–89. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.63789-0
Matthijs, H. C., Visser, P. M., Reeze, B., Meeuse, J., Slot, P. C., Wijn, G., et al. (2012). Selective suppression of harmful cyanobacteria in an entire lake with hydrogen peroxide. Water Res. 46, 1460–1472. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.016
Mehlhorn, H., Lelandais, M., Korth, H. G., and Foyer, C. H. (1996). Ascorbate is the natural substrate for plant peroxidases. FEBS Lett. 378, 203–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01448-9
Mizuno, C. S., Schrader, K. K., and Rimando, A. M. (2008). Algicidal activity of stilbene analogues. J. Agric. Food Chem. 56, 9140–9145. doi: 10.1021/jf801988p
Noctor, G., and Foyer, C. H. (1998). Ascorbate and glutathione: keeping active oxygen under control. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 49, 249–279. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.49.1.249
Nybom, S. M., Collado, M. C., Surono, I. S., Salminen, S. J., and Meriluoto, J. A. (2008). Effect of glucose in removal of microcystin-LR by viable commercial probiotic strains and strains isolated from Dadih fermented Milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 56, 3714–3720. doi: 10.1021/jf071835x
Nybom, S. M., Salminen, S. J., and Meriluoto, J. A. (2007a). Removal of microcystin-LR by strains of metabolically active probiotic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 270, 27–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00644.x
Nybom, S. M., Salminen, S. J., and Meriluoto, J. A. (2007b). Specific strains of probiotic bacteria are efficient in removal of several different cyanobacterial toxins from solution. Toxicon 52, 214–220. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2008.04.169
Ou, D., Song, L., Gan, N., and Chen, W. (2005). Effects of microcystins on and toxin degradation by Poterioochromonas sp. Environ. Toxicol. 20, 373–380. doi: 10.1002/tox.20114
Ozaki, K., Ohta, A., Iwata, C., Horikawa, A., Tsuji, K., Ito, E., et al. (2008). Lysis of cyanobacteria with volatile organic compounds. Chemosphere 71, 1531–1538. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.11.052
Paerl, H. W., and Huisman, J. (2008). Climate-blooms like it hot. Science 320, 57–58. doi: 10.1126/science.1155398
Pretsch, E., Bühlmann, P., and Affolter, C. (2000). Structure determination of organic compounds table of spectral data. Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer-Verlag, 148.
Rapala, J., Berg, K. A., Lyra, C., Niemi, R. M., Manz, W., Suomalainen, S., et al. (2005). Paucibacter toxinivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a bacterium that degrades cyclic cyanobacterial hepatotoxins microcystins and nodularin. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55, 1563–1568. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.63599-0
Ross, C., Santiago-Vázquez, L., and Paul, V. (2006). Toxin release in response to oxidative stress and programmed cell death in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat. Toxicol. 78, 66–73. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.02.007
Shirling, E. B., and Gottlieb, D. (1966). Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 16, 313–340. doi: 10.1099/00207713-16-3-313
Sigee, D. C., Glenn, R., Andrews, M. J., Bellinger, E. G., Butler, R. D., Epton, H. A. S., et al. (1999). Biological control of cyanobacteria: principles and possibilities. Hydrobiologia 395, 161–172. doi: 10.1023/A:1017097502124
Wang, X., Xiao, Y., Deng, Y., Sang, X., Deng, Q., Wang, L., et al. (2024). Sphingomonas lacusdianchii sp. nov., an attached bacterium inhibited by metabolites from its symbiotic cyanobacterium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 108:309. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13081-x
Wu, X., Hu, J., Jia, A., Peng, H., Wu, S., and Dong, Z. (2010). Determination and occurrence of retinoic acids and their 4-oxo metabolites in Liaodong Bay, China, and its adjacent rivers. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 29, 2491–2497. doi: 10.1002/etc.322
Wu, X., Jiang, J., Wan, Y., Giesy, J. P., and Hu, J. (2012). Cyanobacteria blooms produce teratogenic retinoic acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 109, 9477–9482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1200062109
Wu, X. G., Joyce, E. M., and Mason, T. J. (2011). The effects of ultrasound on cyanobacteria. Harmful Algae 10, 738–743. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2011.06.005
Xiao, Y., Du, M., Deng, Y., Deng, Q., Wang, X., Yang, Y., et al. (2024). Modulation of growth, microcystin production, and algal-bacterial interactions of the bloom-forming algae Microcystis aeruginosa by a novel bacterium recovered from its phycosphere. Front. Microbiol. 15:1295696. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1295696
Yan, R., Wu, Y., Ji, H., Fang, Y., Kerr, P. G., and Yang, L. (2011). The decoction of Radix astragali inhibits the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 74, 1006–1010. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.01.014
Žegura, B., Štraser, A., and Filipič, M. (2011). Genotoxicity and potential carcinogenicity of cyanobacterial toxins-a review. Mutat. Res. 727, 16–41. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2011.01.002
Zhang, B., Chen, W., Li, H., Yang, J., Zha, D., Duan, Y., et al. (2016a). L-valine, an antialgal amino acid from Streptomyces jiujiangensis JXJ 0074T. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 100, 4627–4636. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-7150-8
Zhang, B., Chen, W., Li, H., Zhou, E., Hu, W., Duan, Y., et al. (2015). An antialgal compound produced by Streptomyces jiujiangensis JXJ 0074T. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 5, 7673–7683. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6584-3
Zhang, B., Cheng, J., Li, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Li, H., et al. (2014). Streptomyces jiujiangensis sp. nov., isolated from soil in South China. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 105, 763–770. doi: 10.1007/s10482-014-0132-5
Keywords: cyanobacterial blooms, Microcystis aeruginosa, Streptomyces, algicidal activity, microcystins, retinoic acids
Citation: Du M, Xie Q, Shi H, Yang J, Guo Q, Zhang Y and Zhang B (2025) Algicidal activity of Streptomyces sp. LMJ-114 against Microcystis aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 16:1669970. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1669970
Edited by:
Jin-Ho Yun, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB), Republic of KoreaReviewed by:
Thuy Nguyen, New Mexico State University, United StatesPatrick Thomas, Montana State University System, United States
Copyright © 2025 Du, Xie, Shi, Yang, Guo, Zhang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongqiu Shi, NDQ2MDgwNjI2QHFxLmNvbQ==; Yuqin Zhang, emh5dXFpbkAxMjYuY29t; Binghuo Zhang, YmluZ2h1b3poQDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Mijia Du1†
Mijia Du1† Yuqin Zhang
Yuqin Zhang Binghuo Zhang
Binghuo Zhang