- College of Sports and Health, Chengdu Sport University, Chengdu, China
Skeletal muscle wasting disorders, such as sarcopenia and cachexia, pose a significant clinical challenge. The gut-muscle axis, a bidirectional signaling network, is now understood to be a critical regulator of muscle homeostasis, with the gut microbiota functioning as a key metabolic organ. Physical activity is a cornerstone intervention, exerting benefits by directly stimulating muscle and by favorably modulating the composition and metabolic output of the gut microbiota. This review synthesizes the molecular mechanisms of muscle wasting and the pathways of the gut-muscle axis, with a specific focus on microbial metabolites like short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). We analyze how different exercise modalities modulate this system and critically evaluate evidence from human trials. By identifying key research gaps, this review argues for a paradigm shift toward integrated, personalized interventions that combine targeted exercise with nutritional and microbial strategies to more effectively combat muscle wasting disorders.
1 Introduction
Muscle wasting disorders, encompassing both sarcopenia and cachexia, are progressive and debilitating syndromes that lead to the involuntary loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength (Carlier et al., 2015; Brogi et al., 2024). Sarcopenia, first defined by Rosenberg in 1989, is characterized as a geriatric syndrome marked by a progressive decline in muscle mass, strength, and physical performance, often exacerbated by aging (Wang et al., 2025; Dohertya, 2010; Cederholm et al., 2011). Its prevalence is alarmingly high, affecting 5–13% of adults aged 60–70 and rising to 11–50% in those over 80 (Wang et al., 2025; von Haehling et al., 2010; Shafiee et al., 2017), with this wide range reflecting differences in diagnostic criteria and the specific populations studied. The clinical implications are severe, including an increased risk of falls, fractures, mobility challenges, and a diminished quality of life (Wang et al., 2025; Costa et al., 2008). In contrast, cachexia is a more severe wasting syndrome associated with chronic, systemic diseases such as cancer (Mortellaro et al., 2024), heart failure (Maeda et al., 2024), AIDS (Li Y-. H. et al., 2022), and chronic kidney disease (Rahbar Saadat et al., 2025), and is marked by significant loss of both fat and fat-free mass, along with intense systemic inflammation (Wang et al., 2025; Biolo et al., 2014; Kotler, 2000).
Skeletal muscle homeostasis is governed by a delicate balance between anabolic and catabolic signaling pathways (Liu and Tang, 2022; McCarthy and Murach, 2019). While traditional therapeutic approaches have focused on nutritional support and exercise, emerging evidence points to a multi-organ communication network as a critical therapeutic target (Wang et al., 2025, 2021; Monda et al., 2017; Afzaal et al., 2022). Within this network, the human gut microbiota—a complex ecosystem of trillions of microorganisms—is now recognized as a vital player in host health, functioning as a “metabolic organ” that modulates immune responses and produces beneficial metabolites from indigestible carbohydrates (Monda et al., 2017; Afzaal et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2024).
The reciprocal influence between the gut microbiota and skeletal muscle, termed the “gut-muscle axis” or, more specifically, the “gut microbes-muscle axis,” has been substantiated by a growing body of evidence, highlighting its potential role in the pathogenesis of muscle wasting disorders (Li G. et al., 2022; Chae and Lee, 2023; He et al., 2025; Chew et al., 2023). This review therefore synthesizes the intricate mechanisms of this axis, focusing specifically on how physical activity serves as a potent, non-pharmacological modulator of the gut microbiota to prevent and treat sarcopenia and cachexia. In doing so, we frame these components as an integrated signaling network—the gut-muscle axis—whereby physical activity serves as a primary modulator.
2 Molecular pathogenesis of muscle wasting: a foundation for intervention
2.1 The anabolic-catabolic imbalance
Muscle atrophy is a pathological state defined by a reduction in muscle fiber size and overall muscle mass, which occurs when protein degradation outpaces protein synthesis (Fanzani et al., 2012). This imbalance is regulated by an intricate network of anabolic and catabolic signaling pathways (Liu and Tang, 2022).
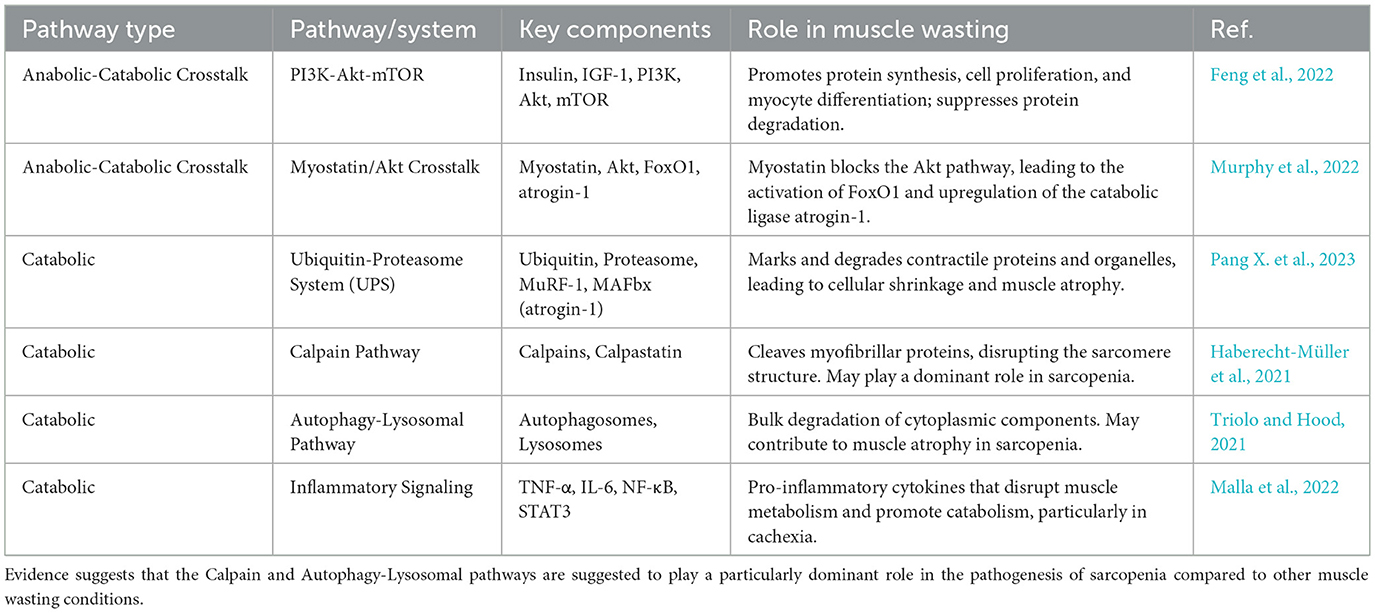
Catabolic signaling is primarily driven by proteolytic systems that dismantle muscle proteins (Chapela et al., 2023). The most prominent of these is the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), which tags proteins with ubiquitin for targeted removal by the proteasome (Pang X. et al., 2023). In muscle atrophy, muscle-specific E3-ubiquitin ligases such as MuRF-1 and MAFbx (atrogin-1) are transcriptionally upregulated, marking contractile proteins for degradation (Bowen et al., 2015; Peris-Moreno et al., 2021). Other major proteolytic pathways include the calpain pathway and the autophagy-lysosomal pathway, which also contribute to the loss of muscle mass (Bowen et al., 2015; Triolo and Hood, 2021). A potent catabolic factor is myostatin, a member of the TGFβ family that acts as a negative regulator of muscle growth (Bonaldo and Sandri, 2013). Myostatin-induced atrophy is mediated by its capacity to block the key anabolic IGF-1-PI3K-Akt pathway and activate the transcription factor FoxO1, thereby increasing the expression of atrogin-1 (Bonaldo and Sandri, 2013; Permpoon et al., 2025; Xu et al., 2023). This direct antagonism between myostatin and the IGF-1/Akt pathway is a crucial mechanistic aspect of atrophy, as a catabolic signal actively suppresses an anabolic one, creating a powerful feedback loop that accelerates muscle loss (Huang et al., 2022a).
In contrast, muscle anabolism is driven by growth factors and hormones such as Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) and insulin (Fanzani et al., 2012; Lowe, 2024). The central pathway for protein synthesis is the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway, which promotes myocyte proliferation, differentiation, and protein synthesis while simultaneously suppressing protein degradation (Wang et al., 2025; Lowe, 2024; Chen et al., 2025). Low circulating levels of IGF-1 have been associated with sarcopenia and other chronic diseases, highlighting the central role of this anabolic pathway in maintaining muscle mass (Fanzani et al., 2012; Nyul-Toth et al., 2025). The activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway is a critical step that promotes protein synthesis and reduces protein degradation, serving as a primary target for therapeutic interventions (Fanzani et al., 2012; He Y. et al., 2021; Verma et al., 2023) (Table 1).
2.2 Differentiating sarcopenia and cachexia
Although both are muscle wasting disorders, sarcopenia and cachexia have distinct underlying mechanisms and clinical presentations (Wang et al., 2025; Rausch et al., 2021). This distinction is critical for tailoring effective therapeutic strategies. Sarcopenia is a muscle disease often associated with aging, and is primarily characterized by a progressive loss of muscle mass and strength without significant fat loss (Wang et al., 2025; Najm et al., 2024). While the UPS is involved, existing evidence is inconsistent, suggesting that other proteolytic pathways, particularly the calpain and autophagy pathways, may play a more dominant role in sarcopenia pathogenesis (Pang X. et al., 2023; Bowen et al., 2015). Sarcopenia is often associated with mild, or even undetectable, systemic inflammation, in contrast to the intense inflammatory state of cachexia (Wang et al., 2025; Jimenez-Gutierrez et al., 2022). This lower inflammatory burden may make sarcopenia more responsive to certain non-pharmacological interventions (Ispoglou et al., 2023; Clerton, 2025).
Cachexia, a more severe, involuntary wasting syndrome, is typically linked to chronic diseases such as cancer, heart failure, and AIDS (Wang et al., 2025; Rausch et al., 2021). It is characterized by significant loss of both fat and fat-free mass, and is marked by an intense inflammatory response driven by pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6 (Timmanpyati et al., 2024; He M. et al., 2021). The activation of these cytokines directly disrupts muscle metabolism and leads to the upregulation of catabolic pathways (Wang et al., 2025; He M. et al., 2021). While some signaling pathways like myostatin, NF-κB, and STAT3 are shared between the conditions, the more robust and systemic inflammatory response in cachexia necessitates more aggressive interventions (Wang et al., 2025; Ahmad et al., 2022; Malla et al., 2022; Cao et al., 2021). The distinct inflammatory profiles and primary proteolytic pathways of sarcopenia and cachexia imply that while the gut-muscle axis is relevant to both, the specific therapeutic modulation required may differ (Malla et al., 2022; Nardone et al., 2021). For example, while targeting the gut microbiota to reduce low-grade inflammation could benefit sarcopenia, a more robust anti-inflammatory strategy via the gut-muscle axis might be necessary to counteract the intense inflammatory state of cachexia (Nardone et al., 2021). This highlights the need for a personalized approach to modulating the gut-muscle axis for muscle wasting (Figure 1).
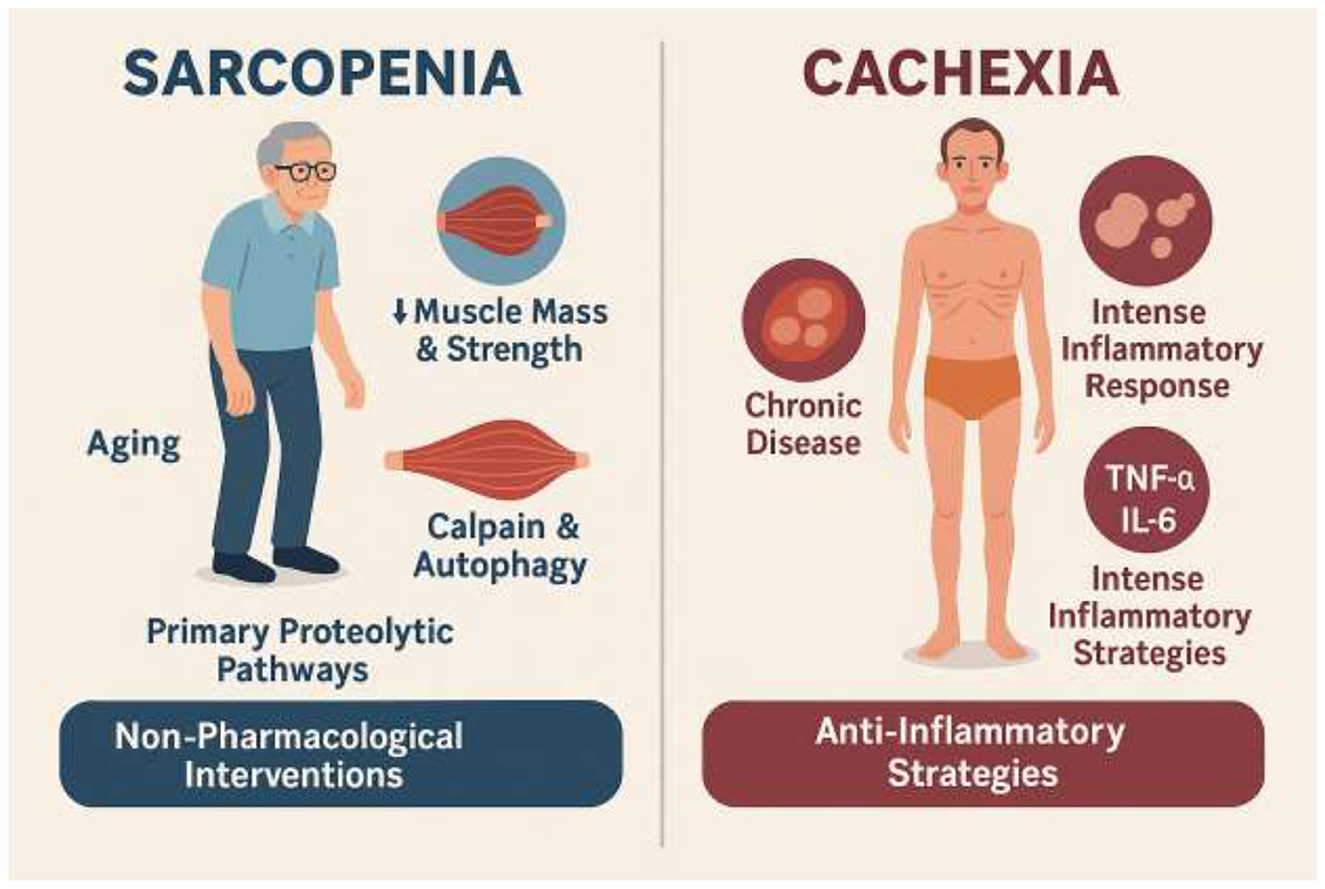
Figure 1. Comparative overview of sarcopenia and cachexia. Sarcopenia is an aging-associated muscle disease characterized by progressive loss of muscle mass and strength with minimal fat loss. Its pathogenesis involves calpain and autophagy pathways, with inconsistent UPS involvement, and is typically accompanied by low-grade inflammation. These features make it more responsive to non-pharmacological interventions such as exercise and nutrition. Cachexia, in contrast, is a severe wasting syndrome linked to chronic diseases (e.g., cancer, heart failure, AIDS), characterized by loss of both fat and fat-free mass, and driven by intense systemic inflammation mediated by TNF-α and IL-6. It activates proteolytic pathways including UPS, NF-κB, STAT3, and myostatin, requiring aggressive anti-inflammatory and multimodal therapeutic strategies.
3 The gut-muscle axis: a bidirectional signaling network
3.1 Microbial metabolites as key mediators
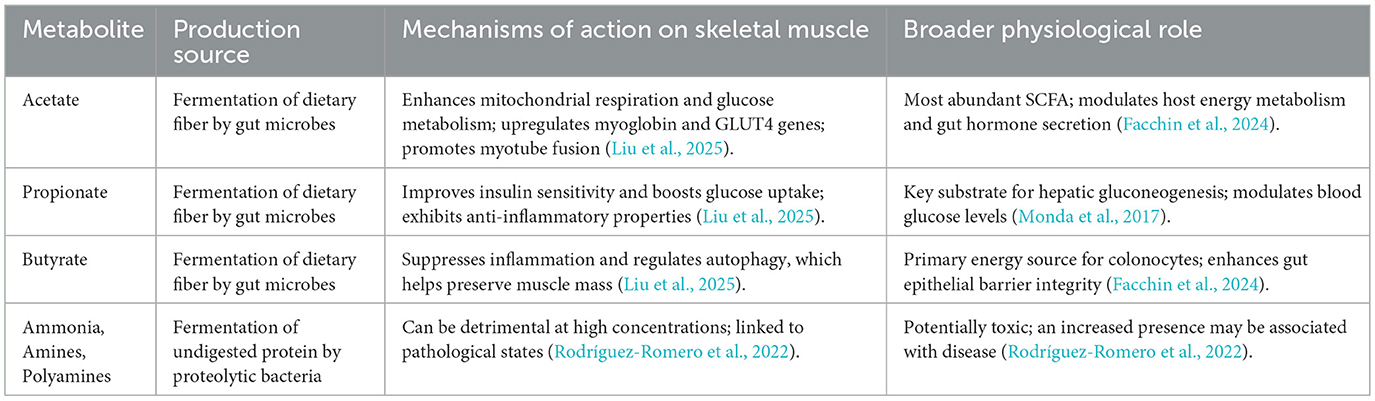
The gut microbiota is a complex metabolic organ that transforms indigestible dietary components into a diverse array of metabolites that influence host health (Monda et al., 2017; Zhang, 2022). Among the most critical are short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)—primarily acetate, propionate, and butyrate—produced through the anaerobic fermentation of dietary fibers (Facchin et al., 2024; Ashaolu et al., 2021). These metabolites are absorbed from the gut lumen and enter systemic circulation to modulate host metabolic responses, including those in skeletal muscle (Frampton et al., 2020; Lefevre and Bindels, 2022).
A closer examination of the individual SCFAs reveals distinct roles. In the human colon, these are typically found in a molar ratio of approximately 60:20:20 for acetate, propionate, and butyrate, respectively (Morrison and Preston, 2016).
Acetate, as the most abundant SCFA, plays a crucial role in host energy balance. It serves as a substrate for lipid synthesis and can enhance mitochondrial function and glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle, while also upregulating key genes like myoglobin and GLUT4 (Liu et al., 2025; Swalsingh et al., 2022). Furthermore, acetate can mitigate the negative effects of gut microbiota depletion on muscle development (Liu et al., 2025; Yang et al., 2024).
Propionate is primarily absorbed and utilized by the liver, where it acts as a critical substrate for hepatic gluconeogenesis. This function helps regulate blood glucose levels, which in turn improves insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues like skeletal muscle (Monda et al., 2017; Pang R. et al., 2023).
Although less abundant, butyrate is often highlighted for its pivotal role in gut health and systemic anti-inflammatory effects. It is the primary energy source for colonocytes, enhancing the integrity of the intestinal epithelial barrier (Facchin et al., 2024; Salvi and Cowles, 2021). Importantly for muscle health, butyrate has been shown to support muscle mass preservation by suppressing inflammation and regulating autophagy, a key catabolic pathway in muscle wasting (Liu et al., 2025). This detailed understanding of the individual functions of SCFAs provides a rationale for personalized dietary and microbial interventions designed to modulate specific SCFA production for different clinical outcomes (Rauf and Khalil, 2022).
Beyond SCFAs, the gut microbiota is a critical regulator of host amino acid metabolism, which directly impacts muscle health. Gut microbes can synthesize essential amino acids and modulate the levels of circulating amino acids that serve as building blocks for muscle protein. For example, specific amino acids such as glutamine and leucine have been shown to activate the anabolic Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and upregulate the expression of myogenic factors like MyoD and myogenin, thereby promoting muscle regeneration (He et al., 2025). Furthermore, microbial metabolism of tryptophan into compounds like indolepropionic acid can exert local and systemic antioxidant effects, potentially protecting muscle from oxidative damage (Owe-Larsson et al., 2025; Jiang et al., 2022).
Secondary bile acids and vitamins, both heavily influenced by microbial activity, also act as key signaling molecules in the axis. Microbes convert primary bile acids from the liver into secondary bile acids, which can activate receptors in muscle tissue, such as TGR5, to influence energy metabolism and muscle growth (Zhao et al., 2025; Ferrell and Chiang, 2021). Similarly, the gut microbiota synthesizes essential vitamins, including B vitamins and vitamin K. These vitamins are crucial cofactors in energy metabolism and can protect muscle from damage; for instance, vitamin K has been shown to downregulate atrophy-related proteins during inflammatory states (He et al., 2025). This highlights a complex system where microbial processing of both host- and diet-derived compounds creates a pool of bioactive molecules that regulate muscle function.
However, the gut microbiota also metabolizes undigested protein. The catabolism of indigestible protein can lead to the production of potentially detrimental metabolites such as ammonia, amines, polyamines, and branched-chain fatty acids (Rodríguez-Romero et al., 2022; Torres et al., 2023; Duncan et al., 2021). This creates a paradox: while dietary protein is essential for muscle anabolism, an excess of undigested protein reaching the large intestine can promote the growth of proteolytic bacteria, which produce these potentially toxic metabolites (Ashkar and Wu, 2023; Prokopidis et al., 2021). This underscores the need for a holistic, balanced nutritional approach that includes sufficient dietary fiber to promote saccharolytic fermentation over proteolytic fermentation, rather than a single-macronutrient focus on protein alone (Table 2).
3.2 The intestinal barrier as a critical mediator
Beyond the production of metabolites, the structural and functional integrity of the intestine itself is a cornerstone of the gut-muscle axis. The intestinal epithelium forms a critical barrier that regulates the absorption of nutrients essential for muscle protein synthesis while simultaneously preventing the translocation of pro-inflammatory microbial components, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), into systemic circulation (Vancamelbeke and Vermeire, 2017). A compromised or “leaky” gut barrier allows for endotoxemia, which can trigger a state of low-grade systemic inflammation. This inflammation directly contributes to muscle wasting by activating catabolic signaling pathways (e.g., NF-κB) in skeletal muscle and promoting anabolic resistance. Therefore, a healthy intestinal barrier is essential for maintaining muscle homeostasis, acting as a gatekeeper that translates gut health into systemic metabolic and inflammatory balance.
3.3 Bidirectional signaling via hormones, cytokines, and extracellular vesicles
The gut-muscle axis is maintained by a complex, bidirectional flow of information mediated by hormones, cytokines, and extracellular vesicles (EVs). Gut microbes stimulate intestinal enteroendocrine cells to secrete hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and ghrelin, which enter circulation and influence muscle glucose uptake and anabolism. In the reverse direction, exercising muscle releases signaling molecules known as myokines (e.g., IL-6, IGF-1), which can travel back to the gut and modulate microbial composition and intestinal function (He et al., 2025; Leeuwendaal et al., 2021; Everard and Cani, 2014). This bidirectional hormonal and cytokine crosstalk ensures that the metabolic state of the muscle is communicated to the gut and vice-versa.
More recently, extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from gut microbes have been identified as novel mediators in this axis. These lipid-bilayer vesicles can transport a wide array of bioactive cargo—including nucleic acids, proteins, and metabolites—from the gut lumen into systemic circulation, eventually reaching peripheral tissues like skeletal muscle. It has been demonstrated that microbial EVs can directly influence insulin signaling and glucose uptake in muscle cells (He et al., 2025; Sun et al., 2023; Kumar et al., 2024; Wu et al., 2024). EVs thus represent a direct transport mechanism, allowing microbial components to exert functional effects on muscle physiology far from the gut itself.
4 Physical activity as a therapeutic modulator of the gut-muscle axis
4.1 Exercise-induced changes in gut microbiota composition and diversity
As a key behavioral input, physical activity does not act on muscle in isolation; instead, it serves as a powerful regulator of the entire gut-muscle axis. Physical activity is a powerful environmental factor that can reshape the gut microbiota. Numerous studies have shown that exercise enhances microbial diversity and enriches the microflora with beneficial species (Lapauw et al., 2024; Dziewiecka et al., 2022; Campaniello et al., 2022). Athletes and active individuals generally exhibit greater microbial biodiversity and a higher abundance of SCFA-producing bacteria, such as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, than their sedentary counterparts (Dziewiecka et al., 2022; Sohail et al., 2019). Longitudinal studies have further confirmed that a transition from a sedentary to an active lifestyle can reduce disease-related bacteria and increase health-associated taxa (Boytar et al., 2023; Lelonek et al., 2025). This positive modulation of the gut microbiota, which includes improved barrier function and reduced systemic inflammation, is a key mechanism by which exercise promotes overall health and mitigates disease (Monda et al., 2017; Dmytriv et al., 2024).
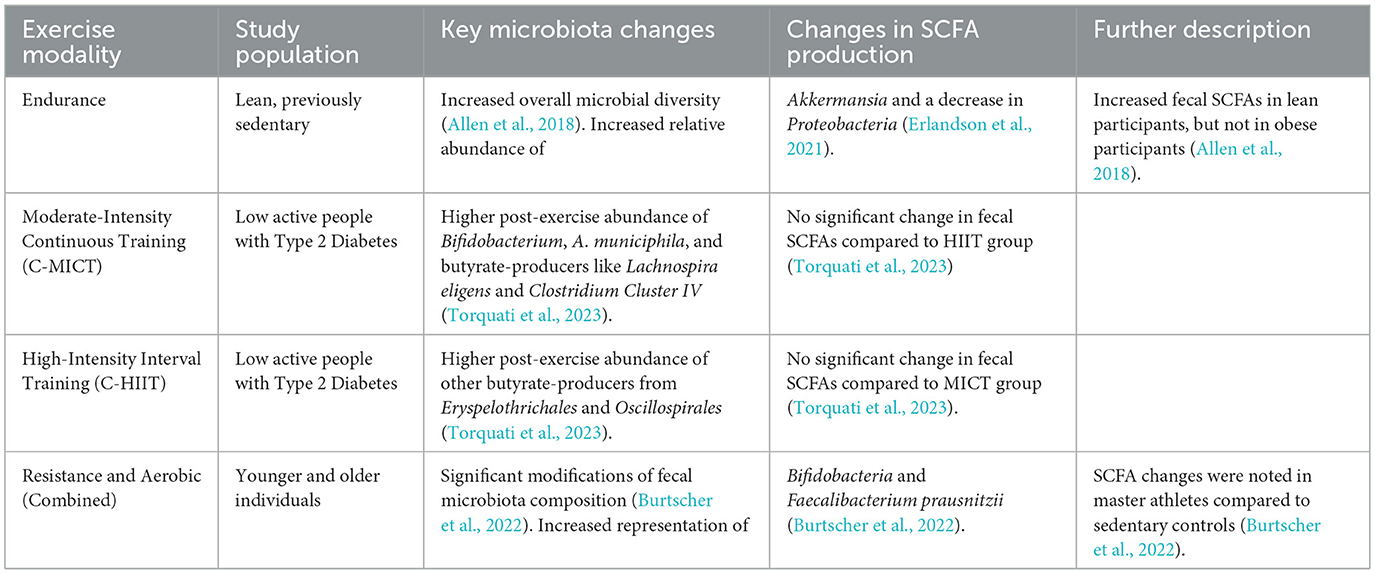
However, the effects of exercise on the gut microbiota are not universal; they are contingent on several variables, including the type and intensity of exercise, as well as the host's health status (Bonomini-Gnutzmann et al., 2022; Cataldi et al., 2022). For example, a six-week endurance exercise intervention increased fecal SCFAs in lean but not obese participants (Allen et al., 2018). This suggests that obesity-related dysbiosis or inflammation may blunt the gut's metabolic response to exercise. A separate study on individuals with type 2 diabetes found that different exercise intensities increased the abundance of distinct butyrate-producing species (Torquati et al., 2023). Moderate-intensity continuous training (MICT) led to a higher relative abundance of Lachnospira eligens (Torquati et al., 2023) and Clostridium Cluster IV (Torquati et al., 2023), while high-intensity interval training (HIIT) promoted other butyrate-producers from Eryspelothrichales and Oscillospirales (Torquati et al., 2023). This finding is significant because it indicates that different exercise prescriptions can specifically target and modulate distinct microbial communities and their functions (Figure 2 and Table 3).
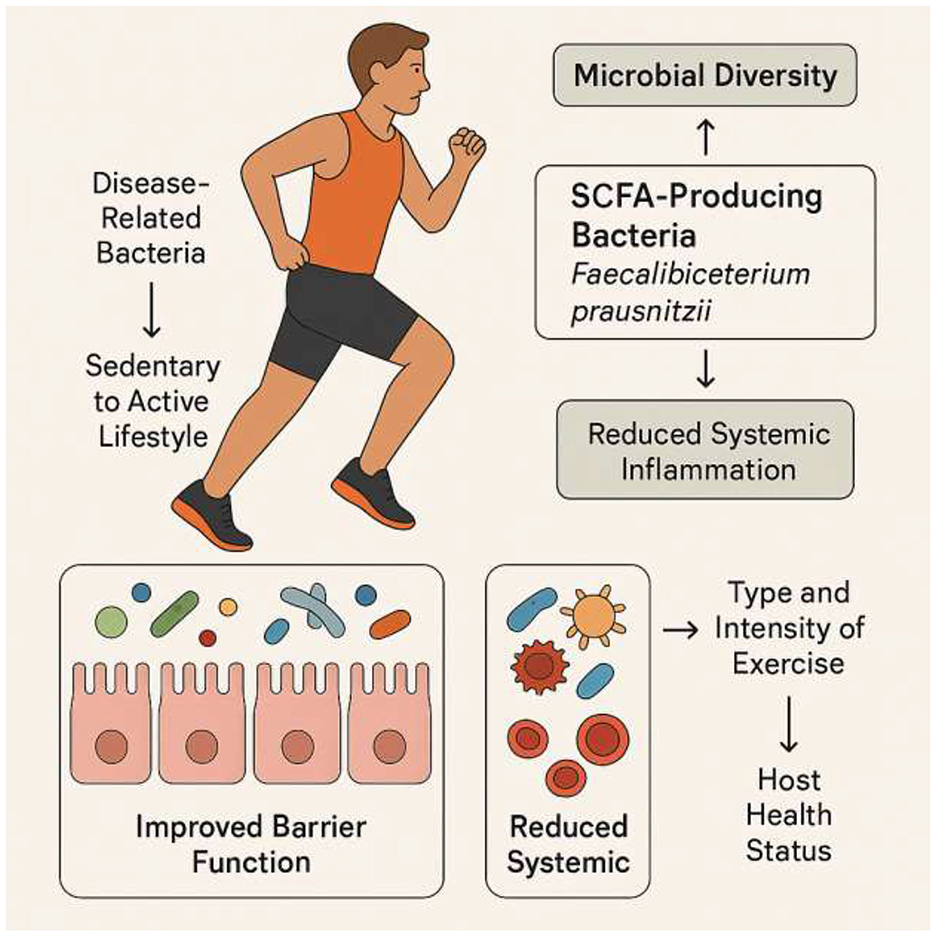
Figure 2. Exercise-mediated modulation of gut microbiota. Transitioning from a sedentary to an active lifestyle enhances microbial diversity and increases the abundance of SCFA-producing bacteria such as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. These changes improve gut barrier function and reduce systemic inflammation, contributing to overall health. The effects of exercise vary with type, intensity, and host health status: moderate-intensity continuous training (MICT) enriches species like Lachnospira eligens and Clostridium Cluster IV, whereas high-intensity interval training (HIIT) promotes other butyrate-producing taxa from Erysipelotrichales and Oscillospirales. Obesity and metabolic diseases may blunt these beneficial responses, highlighting the importance of personalized exercise prescriptions.
4.2 The differential impact of exercise modalities on muscle and gut homeostasis
Different forms of physical activity elicit distinct physiological adaptations in muscle, and mounting evidence suggests a similar specificity in their effects on the gut microbiome.
• Resistance Training (RT): This modality is a potent stimulus for increasing muscle mass and strength, primarily through muscle hypertrophy and neural adaptations (McLeod et al., 2024; Alix-Fages et al., 2022). RT prescription variables like volume (number of sets) and load are key determinants of its effectiveness (McLeod et al., 2024).
While RT's influence on gut microbiota is a developing area of research, emerging evidence suggests its effects are distinct from that of endurance training. Unlike the consistent increases in microbial diversity seen with aerobic exercise, RT appears to exert a more targeted influence on microbiota composition (Wegierska et al., 2022; Varghese et al., 2024; Polo-Ferrero et al., 2025; Zhong et al., 2022; Cullen et al., 2024). Recent studies have demonstrated that structured RT can increase the abundance of beneficial, SCFA-producing genera such as Roseburia and Faecalibacterium, particularly in individuals who show significant strength gains (Meiners et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024). Furthermore, some research indicates RT may improve gut barrier integrity by increasing the metabolic capacity of the microbiome to produce mucin and decreasing serum zonulin, a marker associated with intestinal permeability (Di Vincenzo et al., 2024; Dmytriv et al., 2024). These findings suggest that RT's primary impact may be on modulating specific microbial functions related to gut health and anti-inflammatory pathways, rather than broad changes in diversity.
• Endurance Training (ET): Classically performed at a low load for a long duration, ET enhances cardiorespiratory fitness, promotes mitochondrial biogenesis, and increases capillary density (Hughes et al., 2018; Mølmen et al., 2025). These adaptations improve the muscle's ability to utilize oxygen and delay fatigue (Hughes et al., 2018). As a potent modulator of the gut microbiome, endurance training is a potent modulator of the gut microbiome, consistently shown to enhance microbial diversity and metabolic function (Clauss et al., 2021). Mechanistically, ET can increase gut motility and blood flow, creating a favorable environment for the proliferation of SCFA-producing bacteria (Hawley et al., 2025). These microbial shifts are directly linked to higher circulating levels of butyrate, which confers systemic anti-inflammatory benefits and serves as an energy source for colonocytes. This enhancement of SCFA production is a cornerstone of how endurance exercise translates into improved metabolic health and supports the gut-muscle axis (Martín et al., 2023; Singh et al., 2022).
The combination of RT's direct hypertrophy benefits and ET's systemic metabolic and microbial benefits suggests that concurrent training might be the most effective strategy. Resistance training directly stimulates protein synthesis and combats muscle atrophy (Gedara and Othalawa, 2023), while endurance training improves mitochondrial function and cardiorespiratory fitness (Hughes et al., 2018). Endurance training has also been shown to modulate the gut microbiota and SCFA production (Sohail et al., 2019; Huang et al., 2022b). A combined approach could leverage both the direct mechanical stimulus of RT and the systemic, metabolic, and microbial benefits of ET. The ongoing DEMGUTS study (NCT06545123) is a prime example of a clinical trial designed to test this very hypothesis, directly comparing the effects of aerobic, resistance, and concurrent exercise on gut microbiota and physical outcomes in older adults with sarcopenia (Merelim et al., 2025).
A critical clinical consideration is the reversibility of exercise-induced benefits. The positive effects of exercise on muscle strength, endurance, and gut microbiota composition are largely reversed when training ceases (Bonomini-Gnutzmann et al., 2022; Allen et al., 2018). This underscores a fundamental principle: exercise must be a sustained, lifelong intervention to combat the progressive nature of sarcopenia and chronic disease-related muscle wasting (Chen, 2024). This shifts the clinical focus from short-term programs to promoting long-term behavioral change and adherence.
5 Clinical and translational perspectives
5.1 Evidence from human studies and research challenges
Observational studies in elderly populations have consistently shown significant differences in the gut microbiota between individuals with and without sarcopenia (Lapauw et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2021). Sarcopenic patients have been found to have lower microbial alpha-diversity (richness and diversity) compared to those with preserved muscle status (Lapauw et al., 2024). The microbial composition of sarcopenic individuals also clusters differently, with specific genera, including Blautia, Lachnospiraceae, and Subdoligranulum (Liu et al., 2021), identified as having potential diagnostic value for the disease (Zhou et al., 2023). Metabolomics analysis further links sarcopenia to significant alterations in 172 metabolites and pathways, including butanoate metabolism, which is a key SCFA pathway (Zhou et al., 2023). However, the field faces significant challenges that hinder direct translation of these findings into clinical practice. The heterogeneity of study designs, exercise prescriptions, and reporting methods complicates a direct meta-analysis of the data (Lapauw et al., 2024). Many studies are cross-sectional, which makes it impossible to establish causality—it is unclear if dysbiosis causes muscle wasting or vice versa (Lapauw et al., 2024). Furthermore, there is no universally accepted “sarcopenia-specific GM signature,” and findings are often conflicting (Lapauw et al., 2024).
5.2 Future directions and personalized medicine
Overcoming the aforementioned challenges is crucial for translating scientific findings into clinical practice. The progression of research in this field is a key narrative, marked by a shift from broad observational studies to targeted, hypothesis-driven longitudinal clinical trials. There is an urgent need for uniformly designed trials with large sample sizes, standardized exercise prescriptions, and clear, defined core outcome sets (Lapauw et al., 2024).
Due to the multifactorial nature of muscle wasting, the most promising therapeutic strategies will likely be multi-modal, combining exercise with targeted nutritional support and microbial modulation (Das et al., 2024). The ultimate goal is to move toward a personalized precision medicine paradigm. The future trajectory of the field will involve leveraging emerging technologies like multi-omics (genomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics) (Mohr et al., 2024) and artificial intelligence to enable the dynamic monitoring and real-time modulation of microbial activity and its impact on muscle health (Wang et al., 2023). This integrated approach will allow clinicians to design individualized exercise and nutritional prescriptions based on a patient's unique biological profile to optimize health outcomes.
6 Conclusion
Skeletal muscle wasting disorders are complex conditions driven by an imbalance of catabolic and anabolic signaling. A growing body of evidence has established the existence of a bidirectional gut-muscle axis, where the gut microbiota, through the production of key metabolites like SCFAs, plays a direct and profound role in regulating muscle health, metabolism, and inflammation. Physical activity is a powerful, non-pharmacological modulator of this axis, influencing microbial composition, diversity, and metabolic output in a manner dependent on the exercise modality, intensity, and host factors. While the field has progressed significantly from observational studies to interventional trials, key challenges remain, including a lack of standardized research and the heterogeneity of findings. The future of therapeutic intervention for sarcopenia and cachexia lies in a shift toward personalized, multi-modal strategies that leverage the principles of the gut-muscle axis. By integrating exercise, nutrition, and microbial modulation with advanced technologies like multi-omics and artificial intelligence, the scientific community can move closer to developing truly effective, individualized therapies to preserve muscle function and enhance the quality of life for millions of individuals affected by these debilitating disorders.
Author contributions
YX: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Afzaal, M., Saeed, F., Shah, Y. A., Hussain, M., Rabail, R., Socol, C. T., et al. (2022). Human gut microbiota in health and disease: unveiling the relationship. Front. Microbiol. 13:999001. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.999001
Ahmad, S. S., Ahmad, K., Shaikh, S., You, H. J., Lee, E-. Y., Ali, S., et al. (2022). Molecular mechanisms and current treatment options for cancer cachexia. Cancers. 14:2107. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092107
Alix-Fages, C., Del Vecchio, A., Baz-Valle, E., Santos-Concejero, J., and Balsalobre-Fernández, C. (2022). The role of the neural stimulus in regulating skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 122, 1111–1128. doi: 10.1007/s00421-022-04906-6
Allen, J. M., Mailing, L. J., Niemiro, G. M., Moore, R., Cook, M. D., White, B. A., et al. (2018). Exercise alters gut microbiota composition and function in lean and obese humans. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 50, 747–757. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000001495
Ashaolu, T. J., Ashaolu, J. O., and Adeyeye, S. A. (2021). Fermentation of prebiotics by human colonic microbiota in vitro and short-chain fatty acids production: a critical review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 130, 677–687. doi: 10.1111/jam.14843
Ashkar, F., and Wu, J. (2023). Effects of food factors and processing on protein digestibility and gut microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71, 8685–8698. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c00442
Biolo, G., Cederholm, T., and Muscaritoli, M. (2014). Muscle contractile and metabolic dysfunction is a common feature of sarcopenia of aging and chronic diseases: from sarcopenic obesity to cachexia. Clin. Nutr. 33, 737–48. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2014.03.007
Bonaldo, P., and Sandri, M. (2013). Cellular and molecular mechanisms of muscle atrophy. Dis. Model. Mech. 6, 25–39. doi: 10.1242/dmm.010389
Bonomini-Gnutzmann, R., Plaza-Diaz, J., Jorquera-Aguilera, C., Rodriguez-Rodriguez, A., and Rodriguez-Rodriguez, F. (2022). Effect of intensity and duration of exercise on gut microbiota in humans: a systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 19:9518. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19159518
Bowen, T. S., Schuler, G., and Adams, V. (2015). Skeletal muscle wasting in cachexia and sarcopenia: molecular pathophysiology and impact of exercise training. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 6, 197–207. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12043
Boytar, A. N., Skinner, T. L., Wallen, R. E., Jenkins, D. G., and Dekker Nitert, M. (2023). The effect of exercise prescription on the human gut microbiota and comparison between clinical and apparently healthy populations: a systematic review. Nutrients. 15:1534. doi: 10.3390/nu15061534
Brogi, E., Umbrello, M., Lassola, S., and Forfori, F. (2024). “Acute skeletal muscle wasting during critical illness,” in Nutrition, Metabolism and Kidney Support: A Critical Care Approach (Berlin: Springer), 3–16.
Burtscher, J., Ticinesi, A., Millet, G. P., Burtscher, M., and Strasser, B. (2022). Exercise-microbiota interactions in aging-related sarcopenia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 13, 775–780. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12942
Campaniello, D., Corbo, M. R., Sinigaglia, M., Speranza, B., Racioppo, A., Altieri, C., et al. (2022). How diet and physical activity modulate gut microbiota: evidence, and perspectives. Nutrients. 14:2456. doi: 10.3390/nu14122456
Cao, Z., Scott, A. M., Hoogenraad, N. J., and Osellame, L. D. (2021). Mediators and clinical treatment for cancer cachexia: a systematic review. JCSM Rapid Commun. 4, 166–186. doi: 10.1002/rco2.30
Carlier, P. G., Hogrel, J-.Y., and Azzabou, N. (2015). Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle Wasting, Paris, France, 4-6 December 2015. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 6, 398–509. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12087
Cataldi, S., Bonavolontà, V., Poli, L., Clemente, F. M., De Candia, M., Carvutto, R., et al. (2022). The relationship between physical activity, physical exercise, and human gut microbiota in healthy and unhealthy subjects: a systematic review. Biology. 11:479. doi: 10.3390/biology11030479
Cederholm, T. E., Bauer, J. M., Boirie, Y., Schneider, S. M., Sieber, C. C., Rolland, Y., et al. (2011). Toward a definition of sarcopenia. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 27, 341–353. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2011.04.001
Chae, S., and Lee, S. (2023). Integrative insights into the gut-muscle axis: unraveling its role in sarcopenia pathogenesis and therapeutic approaches. Curr. Topics Lactic Acid Bact. Probiot. 9, 45–57. doi: 10.35732/ctlabp.2023.9.2.45
Chapela, S. P., Simancas-Racines, D., Montalvan, M., Frias-Toral, E., Simancas-Racines, A., Muscogiuri, G., et al. (2023). Signals for muscular protein turnover and insulin resistance in critically ill patients: a narrative review. Nutrients. 15:1071. doi: 10.3390/nu15051071
Chen, L-. K. (2024). Sarcopenia in the era of precision health: toward personalized interventions for healthy longevity. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 87, 980–987. doi: 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000001164
Chen, P., Jia, F., Wang, M., and Yang, S. (2025). Analysis of the mechanism of skeletal muscle atrophy from the pathway of decreased protein synthesis. Front. Physiol. 16:1533394. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1533394
Chew, W., Lim, Y. P., Lim, W. S., Chambers, E. S., Frost, G., Wong, S. H., et al. (2023). Gut-muscle crosstalk. A perspective on influence of microbes on muscle function. Front. Med. 9:2022. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1065365
Clauss, M., Gérard, P., Mosca, A., and Leclerc, M. (2021). Interplay between exercise and gut microbiome in the context of human health and performance. Front Nutr. 8:637010. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.637010
Clerton, M. G. (2025). Review of Interventions to Manage Sarcopenia. Vilnius: Vilniaus universitetas.
Costa, L., Badia, X., Chow, E., Lipton, A., and Wardley, A. (2008). Impact of skeletal complications on patients' quality of life, mobility, and functional independence. Support. Care Cancer. 16, 879–889. doi: 10.1007/s00520-008-0418-0
Cullen, J. M. A., Shahzad, S., Kanaley, J. A., Ericsson, A. C., and Dhillon, J. (2024). The effects of 6 wk of resistance training on the gut microbiome and cardiometabolic health in young adults with overweight and obesity. J. Appl. Physiol. 136, 349–361. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00350.2023
Das, S., Preethi, B., Kushwaha, S., and Shrivastava, R. (2024). Therapeutic Strategies to Modulate Gut Microbial Health: Approaches for Sarcopenia Management.
Di Vincenzo, F., Del Gaudio, A., Petito, V., Lopetuso, L. R., and Scaldaferri, F. (2024). Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, and systemic inflammation: a narrative review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 19, 275–293. doi: 10.1007/s11739-023-03374-w
Dmytriv, T. R., Storey, K. B., and Lushchak, V. I. (2024). Intestinal barrier permeability: the influence of gut microbiota, nutrition, and exercise. Front. Physiol. 15:1380713. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1380713
Dohertya, M. J. B. T. J. (2010). Sarcopenia: prevalence, mechanisms, and functional consequences. Body Compos. Aging. 37:94. doi: 10.1159/000319997
Duncan, S. H., Iyer, A., and Russell, W. R. (2021). Impact of protein on the composition and metabolism of the human gut microbiota and health. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 80, 173–185. doi: 10.1017/S0029665120008022
Dziewiecka, H., Buttar, H. S., Kasperska, A., Ostapiuk–Karolczuk, J., Domagalska, M., Cichoń, J, et al. (2022). Physical activity induced alterations of gut microbiota in humans: a systematic review. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 14:122. doi: 10.1186/s13102-022-00513-2
Erlandson, K. M., Liu, J., Johnson, R., Dillon, S., Jankowski, C. M., Kroehl, M., et al. (2021). An exercise intervention alters stool microbiota and metabolites among older, sedentary adults. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 8:20499361211027067. doi: 10.1177/20499361211027067
Everard, A., and Cani, P. D. (2014). Gut microbiota and GLP-1. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 15, 189–196. doi: 10.1007/s11154-014-9288-6
Facchin, S., Bertin, L., Bonazzi, E., Lorenzon, G., De Barba, C., Barberio, B., et al. (2024). Short-chain fatty acids and human health: from metabolic pathways to current therapeutic implications. Life. 14:559. doi: 10.3390/life14050559
Fanzani, A., Conraads, V. M., Penna, F., and Martinet, W. (2012). Molecular and cellular mechanisms of skeletal muscle atrophy: an update. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 3, 163–179. doi: 10.1007/s13539-012-0074-6
Feng, L., Li, B., Xi, Y, Cai, M., and Tian, Z. (2022). Aerobic exercise and resistance exercise alleviate skeletal muscle atrophy through IGF-1/IGF-1R-PI3K/Akt pathway in mice with myocardial infarction. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 322, C164–C176. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00344.2021
Ferrell, J. M., and Chiang, J. Y. L. (2021). Bile acid receptors and signaling crosstalk in the liver, gut and brain. Liver Res. 5, 105–118. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2021.07.002
Frampton, J., Murphy, K. G., Frost, G., and Chambers, E. S. (2020). Short-chain fatty acids as potential regulators of skeletal muscle metabolism and function. Nat. Metab. 2, 840–848. doi: 10.1038/s42255-020-0188-7
Gedara, O., and Othalawa, S. (2023). Long Term Adaptations and Mechanisms of Different Protocols of “Concurernt” Training in Recreationally Trained Male Adults.
Haberecht-Müller, S., Krüger, E., and Fielitz, J. (2021). Out of control: the role of the ubiquitin proteasome system in skeletal muscle during inflammation. Biomolecules. 11:1327. doi: 10.3390/biom11091327
Hawley, J. A., Forster, S. C., and Giles, E. M. (2025). Exercise, the gut microbiome and gastrointestinal diseases: therapeutic impact and molecular mechanisms. Gastroenterology. 169, 48–62. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.01.224
He, M., Luo, Y., Chen, L., Zeng, M., Liao, Q., Zhang, W., et al. (2021). Shashen maidong decoction: the effect of TNF-α and IL-6 on lung cancer cachexia based on cancer toxicity theory. Am. J. Transl. Res. 13:6752. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-813922-6.00024-2
He, Y., Hu, H., Liang, X., Liang, J., Li, F., Zhou, X., et al. (2025). Gut microbes-muscle axis in muscle function and meat quality. Science China Life Sciences. doi: 10.1007/s11427-024-2885-4
He, Y., Sun, M. M., Zhang, G. G., Yang, J., Chen, K. S., Xu, W. W., et al. (2021). Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 6:425. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00828-5
Huang, L., Li, M., Deng, C., Qiu, J., Wang, K., Chang, M., et al. (2022a). Potential therapeutic strategies for skeletal muscle atrophy. Antioxidants. 12:44. doi: 10.3390/antiox12010044
Huang, L., Li, T., Zhou, M., Deng, M., Zhang, L., Yi, L., et al. (2022b). Hypoxia improves endurance performance by enhancing short chain fatty acids production via gut microbiota remodeling. Front. Microbiol. 12:820691. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.820691
Hughes, D. C., Ellefsen, S., and Baar, K. (2018). Adaptations to endurance and strength training. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 8:a029769. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a029769
Ispoglou, T., Wilson, O., McCullough, D., Aldrich, L., Ferentinos, P., Lyall, G., et al. (2023). A narrative review of non-pharmacological strategies for managing sarcopenia in older adults with cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Biology. 12:892. doi: 10.3390/biology12070892
Jiang, H., Chen, C., and Gao, J. (2022). Extensive summary of the important roles of indole propionic acid, a gut microbial metabolite in host health and disease. Nutrients 15:151 doi: 10.3390/nu15010151
Jimenez-Gutierrez, G. E., Martínez-Gómez, L. E., Martínez-Armenta, C., Pineda, C., Martínez-Nava, G. A., Lopez-Reyes, A., et al. (2022). Molecular mechanisms of inflammation in sarcopenia: diagnosis and therapeutic update. Cells. 11:2359. doi: 10.3390/cells11152359
Kotler, D. P. (2000). Cachexia. Ann. Intern. Med. 133, 622–34. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-133-8-200010170-00015
Kumar, M. A., Baba, S. K., Sadida, H. Q., Marzooqi, S. A., Jerobin, J., Altemani, F. H., et al. (2024). Extracellular vesicles as tools and targets in therapy for diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 9:27. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01735-1
Lapauw, L., Rutten, A., Dupont, J., Amini, N., Vercauteren, L., Derrien, M., et al. (2024). Associations between gut microbiota and sarcopenia or its defining parameters in older adults: a systematic review. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 15, 2190–2207. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13569
Leeuwendaal, N. K., Cryan, J. F., and Schellekens, H. (2021). Gut peptides and the microbiome: focus on ghrelin. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 28, 243–252. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000616
Lefevre, C., and Bindels, L. B. (2022). Role of the gut microbiome in skeletal muscle physiology and pathophysiology. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 20, 422–432. doi: 10.1007/s11914-022-00752-9
Lelonek, E., Krajewski, P. K., and Szepietowski, J. C. (2025). Gut microbiome correlations in hidradenitis suppurativa patients. J. Clin. Med. 14:5074. doi: 10.3390/jcm14145074
Li, G., Jin, B., and Fan, Z. (2022). Mechanisms Involved in Gut Microbiota Regulation of Skeletal Muscle. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022:2151191. doi: 10.1155/2022/2151191
Li, Y-. H., Cheng, P-. F., Tsai, P-. C., Wang, Y-. J., and Chen, H-. Z. (2022). Nursing experience of an AIDS female patient facing terminal cancer cachexia and death. Tzu Chi Nurs. J. 21, 45–52
Liu, C., Cheung, W. H., Li, J., Chow, S. K. H., Yu, J., Wong, S. H., et al. (2021). Understanding the gut microbiota and sarcopenia: a systematic review. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 12, 1393–407. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12784
Liu, C-. F., and Tang, W. W. (2022). Gut microbiota in sarcopenia and heart failure. J. Cardiovasc. Aging. 2:35. doi: 10.20517/jca.2022.07
Liu, X., Xu, M., Wang, H., and Zhu, L. (2025). Role and mechanism of short-chain fatty acids in skeletal muscle homeostasis and exercise performance. Nutrients. 17:1463. doi: 10.3390/nu17091463
Lowe, W. L. (2024). “Biological actions of the insulin-like growth factors,” in Insulin-Like Growth Factors (Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press), 49–85.
Maeda, D., Fujimoto, Y., Nakade, T., Abe, T., Ishihara, S., Jujo, K., et al. (2024). Frailty, sarcopenia, cachexia, and malnutrition in heart failure. Korean Circ. J. 54, 363–381. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2024.0089
Malla, J., Zahra, A., Venugopal, S., Selvamani, T. Y., Shoukrie, S. I., Selvaraj, R., et al. (2022). What role do inflammatory cytokines play in cancer cachexia? Cureus. 14:e26798. doi: 10.7759/cureus.26798
Martín, R., Rios-Covian, D., Huillet, E., Auger, S., Khazaal, S., Bermúdez-Humarán, L. G., et al. (2023). Faecalibacterium: a bacterial genus with promising human health applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 47:fuad039. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuad039
McCarthy, J. J., and Murach, K. A. (2019). “Anabolic and catabolic signaling pathways that regulate skeletal muscle mass,” in Nutrition and Enhanced Sports Performance (Cambridge, MA: Academic Press). 275–290.
McLeod, J. C., Currier, B. S., Lowisz, C. V., and Phillips, S. M. (2024). The influence of resistance exercise training prescription variables on skeletal muscle mass, strength, and physical function in healthy adults: an umbrella review. J Sport Health Sci. 13, 47–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2023.06.005
Meiners, F., Kreikemeyer, B., Newels, P., Zude, I., Walter, M., Hartmann, A., et al. (2024). Strawberry dietary intervention influences diversity and increases abundances of SCFA-producing bacteria in healthy elderly people. Microbiol. Spect. 13:e01913-24. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01913-24
Merelim, A. S., Zacca, R., Moreira-Gonçalves, D., Costa, P. P., and Baptista, L. C. (2025). Distinct exercise modalities on GUT microbiome in sarcopenic older adults: study protocol of a pilot randomized controlled trial. Front. Med. 12:1504786. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1504786
Mohr, A. E., Ortega-Santos, C. P., Whisner, C. M., Klein-Seetharaman, J., and Jasbi, P. (2024). Navigating challenges and opportunities in multi-omics integration for personalized healthcare. Biomedicines. 12:1496. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071496
Mølmen, K. S., Almquist, N. W., and Skattebo, Ø. (2025). Effects of exercise training on mitochondrial and capillary growth in human skeletal muscle: a systematic review and meta-regression. Sports Med. 55, 115–144. doi: 10.1007/s40279-024-02120-2
Monda, V., Villano, I., Messina, A., Valenzano, A., Esposito, T., Moscatelli, F., et al. (2017). Exercise modifies the gut microbiota with positive health effects. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017:3831972. doi: 10.1155/2017/3831972
Morrison, D. J., and Preston, T. (2016). Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut microbes. 7, 189–200. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2015.1134082
Mortellaro, S., Triggiani, S., Mascaretti, F., Galloni, M., Garrone, O., Carrafiello, G., et al. (2024). Quantitative and qualitative radiological assessment of sarcopenia and cachexia in cancer patients: a systematic review. J. Pers. Med. 14:243. doi: 10.3390/jpm14030243
Murphy, B. T., Mackrill, J. J., and O'Halloran, K. D. (2022). Impact of cancer cachexia on respiratory muscle function and the therapeutic potential of exercise. J. Physiol. 600, 4979–5004. doi: 10.1113/JP283569
Najm, A., Niculescu, A-. G., Grumezescu, A. M., and Beuran, M. (2024). Emerging therapeutic strategies in sarcopenia: an updated review on pathogenesis and treatment advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25:4300. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084300
Nardone, O. M., de Sire, R., Petito, V., Testa, A., Villani, G., Scaldaferri, F., et al. (2021). Inflammatory bowel diseases and sarcopenia: the role of inflammation and gut microbiota in the development of muscle failure. Front. Immunol. 12:694217. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.694217
Nyul-Toth, A., Shanmugarama, S., Patai, R., Gulej, R., Faakye, J., Nagy, D., et al. (2025). “Endothelial IGF-1R deficiency disrupts microvascular homeostasis, impairing skeletal muscle perfusion and endurance: implications for age-related sarcopenia,” in GeroScience (Cham: Springer), 1–18.
Owe-Larsson, M., Drobek, D., Iwaniak, P., Kloc, R., Urbanska, E. M., Chwil, M., et al. (2025). Microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolite indole-3-propionic acid-emerging role in neuroprotection. Molecules. 30:3628. doi: 10.3390/molecules30173628
Pang, R., Xiao, X., Mao, T., Yu, J., Huang, L., Xu, W., et al. (2023). The molecular mechanism of propionate-regulating gluconeogenesis in bovine hepatocytes. Anim. Biosci. 36:1693. doi: 10.5713/ab.23.0061
Pang, X., Zhang, P., Chen, X., and Liu, W. (2023). Ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in skeletal muscle atrophy. Front. Physiol. 14:1289537. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1289537
Peris-Moreno, D., Cussonneau, L., Combaret, L., Polge, C., and Taillandier, D. (2021). Ubiquitin ligases at the heart of skeletal muscle atrophy control. Molecules. 26:407. doi: 10.3390/molecules26020407
Permpoon, U., Moon, J., and Kim, C. Y. (2025). Nam T-g. glucocorticoid-mediated skeletal muscle atrophy: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26:7616. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157616
Polo-Ferrero, L., Navarro-López, V., Fuentes, M., Lacal, J., Cancelas-Felgueras, M. D., Santos-Blázquez, N., et al. (2025). Effect of resistance training on older adults with sarcopenic obesity: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of blood biomarkers, functionality, and body composition. Nurs. Rep. 15:89. doi: 10.3390/nursrep15030089
Prokopidis, K., Chambers, E., Ni Lochlainn, M., and Witard, O. C. (2021). Mechanisms linking the gut-muscle axis with muscle protein metabolism and anabolic resistance: implications for older adults at risk of sarcopenia. Front. Physiol. 12:770455. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.770455
Rahbar Saadat, Y., Abbasi, A., Hejazian, S. S., Hekmatshoar, Y., Ardalan, M., Farnood, F., et al. (2025). Combating chronic kidney disease-associated cachexia: a literature review of recent therapeutic approaches. BMC Nephrol. 26:133. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04057-8
Rauf, A., and Khalil, A. A. (2022). Rahman U-u-, Khalid A, Naz S, Shariati MA, et al. Recent advances in the therapeutic application of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs): an updated review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 62, 6034–6054. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1895064
Rausch, V., Sala, V., Penna, F., Porporato, P. E., and Ghigo, A. (2021). Understanding the common mechanisms of heart and skeletal muscle wasting in cancer cachexia. Oncogenesis. 10:1. doi: 10.1038/s41389-020-00288-6
Rodríguez-Romero, J. J., Durán-Castañeda, A. C., Cárdenas-Castro, A. P., Sánchez-Burgos, J. A., Zamora-Gasga, V. M., Sáyago-Ayerdi, S. G., et al. (2022). What we know about protein gut metabolites: Implications and insights for human health and diseases. Food Chem X. 13:100195. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2021.100195
Salvi, P. S., and Cowles, R. A. (2021). Butyrate and the intestinal epithelium: modulation of proliferation and inflammation in homeostasis and disease. Cells. 10:1775. doi: 10.3390/cells10071775
Shafiee, G., Keshtkar, A., Soltani, A., Ahadi, Z., Larijani, B., Heshmat, R., et al. (2017). Prevalence of sarcopenia in the world: a systematic review and meta-analysis of general population studies. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 16:21. doi: 10.1186/s40200-017-0302-x
Singh, V., Lee, G., Son, H., Koh, H., Kim, E. S., Unno, T., et al. (2022). Butyrate producers, “The Sentinel of Gut”: Their intestinal significance with and beyond butyrate, and prospective use as microbial therapeutics. Front. Microbiol. 13:1103836. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1103836
Sohail, M. U., Yassine, H. M., Sohail, A., and Thani, A. A. A. (2019). Impact of physical exercise on gut microbiome, inflammation, and the pathobiology of metabolic disorders. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 15, 35–48. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2019.15.35
Sun, B., Sawant, H., Borthakur, A., and Bihl, J. C. (2023). Emerging therapeutic role of gut microbial extracellular vesicles in neurological disorders. Front. Neurosci. 17:1241418. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1241418
Swalsingh, G., Pani, P., and Bal, N. C. (2022). Structural functionality of skeletal muscle mitochondria and its correlation with metabolic diseases. Clin. Sci. 136, 1851–1871. doi: 10.1042/CS20220636
Timmanpyati, S., Canday, E., Samant, B., Gorey, V., Thakur, S. C., Suryanarayana, V. P., et al. (2024). Nutritional M anagement in Cancer Cachexia. J. Nutr. Res. 12:75. doi: 10.55289/jnutres/v12i2.43
Torquati, L., Gajanand, T., Cox, E. R., Willis, C. R. G., Zaugg, J., Keating, S. E., et al. (2023). Effects of exercise intensity on gut microbiome composition and function in people with type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 23, 530–541. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2022.2035436
Torres, N., Tobón-Cornejo, S., Velazquez-Villegas, L. A., Noriega, L. G., Alemán-Escondrillas, G., Tovar, A. R., et al. (2023). Amino acid catabolism: an overlooked area of metabolism. Nutrients. 15:3378. doi: 10.3390/nu15153378
Triolo, M., and Hood, D. A. (2021). Manifestations of age on autophagy, mitophagy and lysosomes in skeletal muscle. Cells. 10:1054. doi: 10.3390/cells10051054
Vancamelbeke, M., and Vermeire, S. (2017). The intestinal barrier: a fundamental role in health and disease. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 11, 821–834. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2017.1343143
Varghese, S., Rao, S., Khattak, A., Zamir, F., and Chaari, A. (2024). Physical exercise and the gut microbiome: a bidirectional relationship influencing health and performance. Nutrients. 16:3663. doi: 10.3390/nu16213663
Verma, K., Jaiswal, R., Paliwal, S., Dwivedi, J., and Sharma, S. (2023). An insight into PI3k/Akt pathway and associated protein–protein interactions in metabolic syndrome: a recent update. J. Cell. Biochem. 124, 923–942. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30433
von Haehling, S., Morley, J. E., and Anker, S. D. (2010). An overview of sarcopenia: facts and numbers on prevalence and clinical impact. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 1, 129–133. doi: 10.1007/s13539-010-0014-2
Wang, C., He, T., Zhou, H., Zhang, Z., and Lee, C. (2023). Artificial intelligence enhanced sensors-enabling technologies to next-generation healthcare and biomedical platform. Bioelectron. Med. 9:17. doi: 10.1186/s42234-023-00118-1
Wang, F., So, K-. F., Xiao, J., and Wang, H. (2021). Organ-organ communication: the liver's perspective. Theranostics 11:3317. doi: 10.7150/thno.55795
Wang, T., Zhou, D., and Hong, Z. (2025). Sarcopenia and cachexia: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. MedComm (2020). 6:e70030. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70030
Wegierska, A. E., Charitos, I. A., Topi, S., Potenza, M. A., Montagnani, M., Santacroce, L., et al. (2022). The connection between physical exercise and gut microbiota: implications for competitive sports athletes. Sports Med. 52, 2355–2369. doi: 10.1007/s40279-022-01696-x
Wu, Q., Kan, J., Fu, C., Liu, X., Cui, Z., Wang, S., et al. (2024). Insights into the unique roles of extracellular vesicles for gut health modulation: Mechanisms, challenges, and perspectives. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 7:100301. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2024.100301
Xu, X., Talifu, Z., Zhang, C-. J., Gao, F., Ke, H., Pan, Y-. Z., et al. (2023). Mechanism of skeletal muscle atrophy after spinal cord injury: a narrative review. Front. Nutr. 10:1099143. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1099143
Yang, G., Zhang, J., Liu, Y., Sun, J., Ge, L., Lu, L., et al. (2024). Acetate alleviates gut microbiota Depletion-Induced retardation of skeletal muscle growth and development in young mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25:5129. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105129
Zhang, L., Li, H., Song, Z., Liu, Y., and Zhang, X. (2024). Dietary strategies to improve exercise performance by modulating the gut microbiota. Foods. 13:1680. doi: 10.3390/foods13111680
Zhang, P. (2022). Influence of foods and nutrition on the gut microbiome and implications for intestinal health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:9588. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179588
Zhao, M., Zhao, J., Yang, H., Ouyang, Z., Lv, C., Geng, Z., et al. (2025). The bile acid-gut microbiota axis: A central hub for physiological regulation and a novel therapeutic target for metabolic diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 188:118182. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118182
Zhong, F., Xu, Y., Lai, H. Y., Yang, M., Cheng, L., Liu, X., et al. (2022). Effects of combined aerobic and resistance training on gut microbiota and cardiovascular risk factors in physically active elderly women: a randomized controlled trial. Front. Physiol. 13:1004863. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1004863
Zhou, J., Liu, J., Lin, Q., Shi, L., Zeng, Z., Guan, L., et al. (2023). Characteristics of the gut microbiome and metabolic profile in elderly patients with sarcopenia. Front. Pharmacol. 14:1279448. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1279448
Keywords: skeletal muscle wasting, sarcopenia, cachexia, gut-muscle axis, gut microbiota, physical activity, short-chain fatty acids
Citation: Xu Y and He B (2025) The gut-muscle axis: a comprehensive review of the interplay between physical activity and gut microbiota in the prevention and treatment of muscle wasting disorders. Front. Microbiol. 16:1695448. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1695448
Received: 29 August 2025; Accepted: 03 October 2025;
Published: 30 October 2025.
Edited by:
Lorenzo Nissen, University of Bologna, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Xu and He. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Benxiang He, YmVueGlhbmdoZTIwMjRAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Yan Xu
Yan Xu Benxiang He
Benxiang He